EP2411990B1 - Trennschalter zur galvanischen gleichstromunterbrechung - Google Patents
Trennschalter zur galvanischen gleichstromunterbrechung Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2411990B1 EP2411990B1 EP10708895A EP10708895A EP2411990B1 EP 2411990 B1 EP2411990 B1 EP 2411990B1 EP 10708895 A EP10708895 A EP 10708895A EP 10708895 A EP10708895 A EP 10708895A EP 2411990 B1 EP2411990 B1 EP 2411990B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- semiconductor
- switch
- arc
- electronics
- current
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 93
- 238000004146 energy storage Methods 0.000 claims description 18
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 14
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 12
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008033 biological extinction Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003628 erosive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010891 electric arc Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H33/00—High-tension or heavy-current switches with arc-extinguishing or arc-preventing means
- H01H33/02—Details
- H01H33/59—Circuit arrangements not adapted to a particular application of the switch and not otherwise provided for, e.g. for ensuring operation of the switch at a predetermined point in the ac cycle
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H9/00—Details of switching devices, not covered by groups H01H1/00 - H01H7/00
- H01H9/54—Circuit arrangements not adapted to a particular application of the switching device and for which no provision exists elsewhere
- H01H9/541—Contacts shunted by semiconductor devices
- H01H9/542—Contacts shunted by static switch means
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H9/00—Details of switching devices, not covered by groups H01H1/00 - H01H7/00
- H01H9/54—Circuit arrangements not adapted to a particular application of the switching device and for which no provision exists elsewhere
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H9/00—Details of switching devices, not covered by groups H01H1/00 - H01H7/00
- H01H9/54—Circuit arrangements not adapted to a particular application of the switching device and for which no provision exists elsewhere
- H01H9/541—Contacts shunted by semiconductor devices
- H01H9/542—Contacts shunted by static switch means
- H01H2009/544—Contacts shunted by static switch means the static switching means being an insulated gate bipolar transistor, e.g. IGBT, Darlington configuration of FET and bipolar transistor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H9/00—Details of switching devices, not covered by groups H01H1/00 - H01H7/00
- H01H9/54—Circuit arrangements not adapted to a particular application of the switching device and for which no provision exists elsewhere
- H01H9/541—Contacts shunted by semiconductor devices
- H01H9/542—Contacts shunted by static switch means
- H01H2009/546—Contacts shunted by static switch means the static switching means being triggered by the voltage over the mechanical switch contacts
Definitions
- the invention relates to a separation device for DC interruption between a DC power source and an electrical input, with a current-carrying mechanical switching contact and a semiconductor electronics connected in parallel, according to the preamble of claim 1.
- a separation device for example from DE 10 2005 040 432 A1 known.
- a DC power source is understood to mean, in particular, a photovoltaic generator (solar system) and an electrical device is understood in particular to be an inverter.
- a mechanical switch switching contact
- a galvanic isolation of the electrical device (inverter) from the DC power source (photovoltaic system) is made.
- the disadvantage is that such mechanical switching contacts are worn very quickly due to the arcing occurring at the contact opening or an additional effort is required to enclose and cool the arc, which is usually done by a corresponding mechanical switch with a Löschkammem.
- a load breaker electrical connector which has the manner of a hybrid switch a semiconductor switching element in the form of, for example, a thyristor in the housing of the inverter and main and auxiliary contacts, which are connected to photovoltaic modules.
- the leading in a Aussteckvorgang main contact is connected in parallel to the trailing and connected to the semiconductor switching element in series auxiliary contact. In this case, the semiconductor switching element is driven to avoid arcing or arc extinction by this periodically switched on and off.
- the invention is based on the object, a particularly suitable separation device for DC interruption between a DC power source, in particular a photovoltaic generator, and an electrical device, in particular an inverter to specify.
- the circuit breaker suitably comprises a mechanical switching contact suitable for a short-time arc, i. is designed for an arc duration of less than 1 ms, preferably less than or equal to 500 ⁇ s.
- the mechanical switching contact (switch or separating element) is connected in parallel with semiconductor electronics which comprise a first semiconductor switch, preferably an IGBT, and a second semiconductor switch, preferably a MOSFET.
- the semiconductor electronics of the circuit breaker according to the invention has no additional energy source and is therefore with a closed mechanical switch current blocking, d. H. high impedance and therefore virtually without current and voltage. Since no current flows through the semiconductor electronics when the mechanical switching contacts are closed and therefore, in particular, no voltage drop occurs across the or each semiconductor switch, the semiconductor circuit also generates no power losses when the mechanical switch is closed. Rather, the semiconductor electronics obtains the energy required for their operation from the separator, d. H. from the circuit breaker system itself. For this purpose, the energy of the resulting when opening the mechanical switch arc is used and used.
- a control input of the semiconductor electronics or of the semiconductor switch is connected in such a way with the mechanical switching contacts, that at opening switch, the arc voltage across the switch or via its switch contacts and the semiconductor electronics parallel thereto as a result of the electric arc semiconductor electronics, d. H. Low impedance and thus energized switches.
- the arc current starts to commute from the mechanical switch to the semiconductor electronics.
- the corresponding arc voltage or the arc current in this case charges an energy store in the form of preferably a capacitor, which discharges in a targeted manner, generating a control voltage for arc-free switching off of the semiconductor electronics.
- the predetermined period of time or time constant and thus the charging time of the energy storage or capacitor determines the arc duration.
- a timer is started during which the semiconductor electronics are controlled to block the current in an arc-free manner.
- the duration of the timer is set to a safe extinguishing and reliable cooling of the arc or -plasmas.
- the invention is based on the consideration that for a touch-safe and reliable DC interruption designed as a pure two-terminal hybrid separation device can be used when a semiconductor electronics can be used without its own auxiliary power source.
- This in turn, can be achieved by the fact that the arc energy generated when opening one of the electronics connected in parallel with the electronic switch is used to operate the electronics.
- the electronics could have an energy storage, the at least one Tei! stores the arc energy, which is then available to the electronics for a certain period of operation, which should be designed to reliably extinguish the arc.
- the charging time of the energy storage and thus the arc duration is preferably set to less than 1 ms, advantageously to less than or equal to 0.5 ms.
- this period of time is short enough to reliably prevent unwanted contact erosion of the switching contacts of the mechanical switch.
- this period of time is long enough to ensure the self-supply of the semiconductor electronics for the subsequent time period determined by the timer, within which the triggering of the electronics from the low-impedance Commutation state in the high-impedance shutdown state (initial state) takes place. After expiry of the timer, it is ensured that the extinguished arc can not occur again even with high-impedance switched electronics. As a result, reliable isolation and DC interruption have already been achieved.
- a further mechanical circuit breaker is suitably provided, which is connected in series with the parallel circuit of the mechanical switch and the semiconductor electronics.
- the semiconductor electronics in addition to the preferably designed as an IGBT power or semiconductor switch comprises another power or semiconductor switch, which is preferably designed as a MOSFET (metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor).
- MOSFET metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor
- the almost powerless controllable and good blocking behavior with high blocking voltage IGBT is suitably connected in series with the further semiconductor switch (MOSFET) in the manner of a cascode arrangement.
- the semiconductor switches thus form a commutation path parallel to the main current path formed by the mechanical switch, to which the arc current increasingly commutates with opening of the mechanical switch and as a result of the control of the or each semiconductor switch.
- the falling during the commutation of the hybrid circuit breaker and thus on the semiconductor electronics arc voltage is between about 15V and 30V.
- the first semiconductor switch is controlled such that between the two semiconductor switches - that is, almost at a Kaskodenmittenabgriff - sufficient for charging the energy storage voltage in the amount of, for example, 12V (DC) can be tapped.
- This voltage is used to charge the energy storage and its stored energy, in turn, to drive the semiconductor switches within the semiconductor electronics to turn off the two turn on the semiconductor switch again completely, d. H. to control current blocking.
- the main path is then galvanically opened and the commutation path parallel thereto has a high impedance, with the consequence that the high DC voltage (permanently) generated by the DC power source is present at, for example, greater than 1000 V (DC) at the hybrid disconnector. Therefore, it must be ensured via the timing element that not only the arc extinguishes, but also the resulting plasma has cooled.
- the advantages achieved by the invention are, in particular, that no external power source or additional auxiliary power for supplying the electronics is required by the use of an autoclave hybrid separation device, the semiconductor electronics, the energy for its own power supply from the arc resulting from the opening of the mechanical switch.
- the semiconductor electronics is preferably designed as a second pole and high resistance with the mechanical switch closed, so that virtually no power losses occur in normal load operation of the hybrid separator according to the invention.
- the separating device according to the invention is preferably also provided for DC interruption in the DC voltage range up to 1500V (DC).
- this self-sufficient, hybrid disconnecting device is therefore particularly suitable for reliable and touch-proof galvanic DC interruption both between a photovoltaic system and one of its associated inverters and in connection with, for example, a fuel cell system or an accumulator (battery).
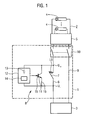
- Fig. 1 schematically shows a separator 1, which is connected in the embodiment between a photovoltaic generator 2 and an inverter 3.
- the photovoltaic generator 2 comprises a number of solar modules 4, which are guided parallel to each other to a common generator junction box 5, which serves as a kind of energy collection point.
- the separating device 1 comprises a switching contact 7, also referred to below as a mechanical switch, and semiconductor electronics 8 connected in parallel therewith.
- the mechanical switch 7 and the semiconductor electronics 8 form a self-sufficient hybrid disconnecting switch.
- the negative pole representing return line 9 of the separation device 1 - and thus the overall system - can be connected in a manner not shown another hybrid circuit breaker 7, 8.
- Both in the plus pole representing the lead line (Hauptfpad) 6 and in the return line 9 can mechanically coupled switch contacts another mechanical separation element 10 for a complete galvanic isolation or DC interruption between the photovoltaic generator 2 and the inverter 3 may be arranged.
- the semiconductor electronics 8 essentially comprises a semiconductor switch 11, which is connected in parallel to the mechanical switch 7, and a drive circuit 12 with an energy store 13 and with a timer 14.
- the drive circuit 12 is preferably connected via a resistor or a resistor row R (FIG. Fig. 2 ), connected to the main current path 6.
- the gate of an IGBT preferably used as a semiconductor switch 11 forms the control input 15 of the semiconductor circuit 8. This control input 15 is guided via the drive circuit 12 to the main current path 6.
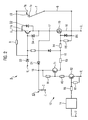
- Fig. 2 shows a comparatively detailed circuit diagram of the mechanical switch 7 in parallel with the electronics 8 of the self-sufficient hybrid disconnector. Visible, the first semiconductor switch (IGBT) 11 a in a cascode arrangement with a second semiconductor switch 11 b connected in series in the form of a MOSFET.
- the cascode arrangement with the two semiconductor switches 11a, 11b thus forms analogously to Fig. 1 the Komrmut istspfad 16 parallel to the mechanical switch 7 and thus to the main current path 6.
- the first semiconductor switch 11a between the DC power source 2 and the hybrid circuit breaker 7.8 is guided to the main current path 6.
- the potential U + is always greater than the potential U - on the opposite side of the switch, at which the second semiconductor switch (MOSFET) 11 b is guided to the main circuit 6.
- the positive potential U + is 0V when the mechanical switch 7 is closed.
- the first semiconductor switch (IGBT) 11 a is connected to a freewheeling diode D2.
- a first Zener diode D3 is the anode side to the potential U - and the cathode side to the gate (control input 15) of the first semiconductor switch (IGBT) 11a connected.
- Another Zener diode D4 is the cathode side again with the Gate (control input 15) and the anode side connected to the emitter of the first semiconductor switch (IGBT) 11 a.
- a diode D1 is connected on the anode side, which is connected on the cathode side via a serving as an energy storage capacitor 13 C against the potential U.
- a plurality of capacitors C form the energy storage 13.
- Via an anode-side voltage tap 18 between the diode D1 and the energy store 13 or the capacitor C is connected to ohmic resistors R1 and R2 transistor T1 via further resistors R3 and R4 with the again guided to the control input 15 of the semiconductor electronics 8 gate of the second semiconductor switch (MOSFET) 15 connected.
- Another Zener diode D5 with parallel resistor R5 is the cathode side to the gate and the anode side connected to the emitter of the second semiconductor switch (MOSFET) 11 b.
- the transistor T1 On the base side, the transistor T1 is driven via a transistor T2, which in turn is connected to the base side via a resistor R6 with the example executed as Monoflopp timer 14. Base-emitter side, the transistor T2 is also connected to a further resistor R7.
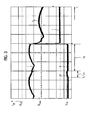
- Fig. 3 shows in a current and voltage time diagram, the course of the switch voltage U and the switch current I of the hybrid circuit breaker 7, 8 temporally before a contact opening of the mechanical switch 7 at time t K and during the period t LB of an arc LB above the switch 7 and whose switch contacts 7a, 7b ( Fig. 2 ) As well as during a particular, predetermined or set period of time t of the timer 14.
- ZG closed mechanical switch 7 of the main current path 6 is low, while the parallel commutation path 16 of the hybrid circuit breaker 7, 8 has a high impedance and therefore current-off.
- the one in the left half of the figure Fig. 3 illustrated current waveform represents the current flowing exclusively through the mechanical switch 7 current I to Time t K of the contact opening of the switch contacts 7a and 7b.
- the opening of the mechanical switch 7 already took place at an unspecified time before the time t K of the contact opening.
- the in the lower left half of the figure Fig. 3 illustrated switch voltage U is in time before the contact opening time t K practically 0V and increases with the opening of the switch contacts 7a, 7b of the mechanical switch 7 at time t K abruptly to a value characteristic of an arc LB with a typical arc voltage U LB, for example 20V to 30V on.
- the positive potential U + thus goes against this arc voltage U LB ⁇ 30V when the mechanical switch 7 opens.
- the arc current I between the main current path 6-that is to say via the mechanical switch 7 -and the commutation path 16-that is, the semiconductor electronics 8, are practically divided.
- the energy store 13 is charged.
- the time t LB is set such that, on the one hand, sufficient energy is available for reliably triggering the semiconductor electronics 8, in particular for switching them off during a period t ZG following the time duration t LB representing the arc duration.
- the time t LB is sufficiently short, so that an undesirable contact erosion or wear of the switch 7 and the switch contacts 7a, 7b is avoided.
- the resistance R via the resistor R (FIG. Fig. 2 ), the first semiconductor switch (IGBT) 11a at least as far controlled that a sufficient charging voltage and a sufficient arc or charging current for the capacitors C and thus for the energy storage 13 is available.
- this is done with the corresponding circuit of the first semiconductor switch (IGBT) 11 a
- U Ab 12 V (DC)
- the tap voltage U Ab serves to supply the drive circuit 12 of the electronics 8, which is essentially formed by the transistors T1 and T2 and the timer 14 and the energy store 13.
- the diode D1 connected to the cascode tap 17 and the cathode side to the capacitor C prevents the return flow of the diode D1 Charging current from the capacitors C and the commutation path 16 in the direction of the potential U - .
- the charge capacitance and thus the storage energy contained in the capacitor C is dimensioned such that the semiconductor electronics 8 carries the switch current I for a time period t ZG predetermined by the timer 14.
- the dimensioning of this period of time t ZG and thus the definition of the timer 14 depends essentially on the application-specific or typical time periods for a complete extinction of the arc LB and after a sufficient cooling of the case formed plasma.
- the essential proviso here is that after the shutdown of the electronics 8 with then turn high-impedance commutation 16 and consequently current-blocking semiconductor electronics 8 on the still open mechanical switch 7 or via its switch contacts 7a, 7b no re-arc LB can arise.
- the positive potential U + thus goes against this operating voltage U B ⁇ 1000V when the commutation path 16 due to the blocking of the semiconductor switch 11 high impedance and thus the electronics 8 is again current blocking.
- the main current path 6 is galvanically opened at the same time as the high-resistance commutation path 16, an arc-free DC interruption between the DC power source 2 and the electrical device 3 is already established.
- the connection between the DC power source 2 and the inverter 3 exemplified as the electrical equipment is already reliably disconnected.
- the mechanical separating element 10 of the separating device 1 can then additionally be opened in a load-free and arc-free manner.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Driving Mechanisms And Operating Circuits Of Arc-Extinguishing High-Tension Switches (AREA)
- Arc-Extinguishing Devices That Are Switches (AREA)
- Keying Circuit Devices (AREA)
- Inverter Devices (AREA)
- Emergency Protection Circuit Devices (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PL10708895T PL2411990T3 (pl) | 2009-03-25 | 2010-02-02 | Odłącznik do galwanicznego przerywania prądu stałego |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE202009004198U DE202009004198U1 (de) | 2009-03-25 | 2009-03-25 | Trennschalter zur galvanischen Gleichstromunterbrechung |
| PCT/EP2010/000607 WO2010108565A1 (de) | 2009-03-25 | 2010-02-02 | Trennschalter zur galvanischen gleichstromunterbrechung |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2411990A1 EP2411990A1 (de) | 2012-02-01 |
| EP2411990B1 true EP2411990B1 (de) | 2013-01-23 |
Family
ID=42244204
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP10708895A Active EP2411990B1 (de) | 2009-03-25 | 2010-02-02 | Trennschalter zur galvanischen gleichstromunterbrechung |
Country Status (19)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8742828B2 (ru) |
| EP (1) | EP2411990B1 (ru) |
| JP (1) | JP5469236B2 (ru) |
| KR (1) | KR101420831B1 (ru) |
| CN (1) | CN102349124B (ru) |
| AU (1) | AU2010227893B2 (ru) |
| BR (1) | BRPI1012338A2 (ru) |
| CA (1) | CA2752895C (ru) |
| DE (1) | DE202009004198U1 (ru) |
| ES (1) | ES2401777T3 (ru) |
| HR (1) | HRP20130321T1 (ru) |
| IL (1) | IL213866A (ru) |
| PL (1) | PL2411990T3 (ru) |
| PT (1) | PT2411990E (ru) |
| RU (1) | RU2482565C2 (ru) |
| SG (1) | SG174124A1 (ru) |
| TN (1) | TN2011000306A1 (ru) |
| WO (1) | WO2010108565A1 (ru) |
| ZA (1) | ZA201103651B (ru) |
Families Citing this family (56)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT510512B1 (de) | 2010-09-30 | 2015-08-15 | Fronius Int Gmbh | Wechselrichter |
| AT510502B1 (de) * | 2010-09-30 | 2015-08-15 | Fronius Int Gmbh | Wechselrichter und verfahren zur trennung von photovoltaikmodulen von einem wechselrichter |
| DE102011016056A1 (de) * | 2011-04-05 | 2012-10-11 | Volkswagen Aktiengesellschaft | Hybrides Schaltelement, Schaltungsanordnung und Verfahren zur Steuerung eines hybriden Schaltelements einer Schaltungsanordnung |
| DE102011078034A1 (de) * | 2011-06-24 | 2012-12-27 | Siemens Ag | Schaltvorrichtung |
| FR2977738B1 (fr) * | 2011-07-04 | 2015-01-16 | Mersen France Sb Sas | Systeme d'interruption de courant continu apte a ouvrir une ligne de courant continu a comportement inductif |
| DE102011109920B4 (de) * | 2011-08-10 | 2021-10-07 | Ellenberger & Poensgen Gmbh | Mechatronisches Mehrfachstecksystem |
| DE102011053524B4 (de) * | 2011-09-12 | 2015-05-28 | Sma Solar Technology Ag | Sicherheitseinrichtung für eine Photovoltaikanlage und Verfahren zum Betreiben einer Sicherheitseinrichtung für eine Photovoltaikanlage |
| WO2013091689A1 (de) * | 2011-12-21 | 2013-06-27 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Trennvorrichtung zur gleichstromunterbrechung zwischen einem photovoltaikgenerator und einer elektrischen einrichtung sowie photovoltaikanlage mit einer derartigen trennvorrichtung |
| EP2810289B1 (de) * | 2012-03-09 | 2016-05-04 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren zum zuschalten eines gleichspannungsnetzabschnitts mittels eines gleichspannungsschalters |
| DE102012008614A1 (de) * | 2012-04-27 | 2013-10-31 | Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V. | Elektrischer Steckverbinder zum sicheren Trennen von elektrischen Strömen unter elektrischer Gleichspannung in Stromnetzen mit bidirektionalem Stromfluss |
| DE102012106505A1 (de) | 2012-07-18 | 2014-01-23 | Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V. | Freischalteinrichtung für einen eine Gleichspannung erzeugenden Photovoltaik-Strang |
| DE202012007257U1 (de) | 2012-07-26 | 2013-10-28 | Ellenberger & Poensgen Gmbh | Vorrichtung zum sicheren Schalten einer Photovoltaikanlage |
| EP2701255B1 (en) | 2012-08-23 | 2016-05-04 | General Electric Technology GmbH | Circuit interruption device |
| EP2701254B1 (en) | 2012-08-23 | 2020-04-08 | General Electric Technology GmbH | Circuit interruption device |
| DE102012024728A1 (de) * | 2012-12-18 | 2014-07-03 | Ellenberger & Poensgen Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Überwachung einer elektrischen Anlage auf einen Rückstrom |
| US20140217832A1 (en) * | 2013-02-06 | 2014-08-07 | Astec International Limited | Disconnect switches in dc power systems |
| GB2510871B (en) | 2013-02-15 | 2016-03-09 | Control Tech Ltd | Electrical protection device and method |
| US9054530B2 (en) | 2013-04-25 | 2015-06-09 | General Atomics | Pulsed interrupter and method of operation |
| DE102013110240B4 (de) | 2013-09-17 | 2017-09-07 | Sma Solar Technology Ag | Schaltungsanordnung für einen Photovoltaikwechselrichter zur Ausschaltentlastung mit Kurzschlussschaltern und Verwendungen der Schaltungsanordnung |
| DE102013114259A1 (de) | 2013-12-17 | 2015-06-18 | Eaton Electrical Ip Gmbh & Co. Kg | Schaltvorrichtung zum Führen und Trennen von elektrischen Strömen |
| CN104409256B (zh) | 2014-03-07 | 2016-08-17 | 广州市金矢电子有限公司 | 电流反馈式电子灭弧装置 |
| DE102014008706A1 (de) * | 2014-06-18 | 2015-12-24 | Ellenberger & Poensgen Gmbh | Trennschalter zur Gleichstromunterbrechung |
| JP6299507B2 (ja) * | 2014-07-29 | 2018-03-28 | オムロン株式会社 | 太陽光発電システムの保護装置および太陽光発電システムの保護方法 |
| WO2016047209A1 (ja) | 2014-09-26 | 2016-03-31 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 直流遮断器 |
| ES2738553T3 (es) | 2014-10-24 | 2020-01-23 | Ellenberger & Poensgen | Disyuntor para la interrupción galvánica de la corriente continua |
| US10014680B2 (en) * | 2014-12-09 | 2018-07-03 | Electronic Systems Protection, Inc. | Overvoltage notching of electricity delivered to an electrical load |
| EP3038226B1 (en) * | 2014-12-26 | 2022-08-03 | Fico Triad, S.A. | System and method for supplying electric power |
| CN104637723B (zh) * | 2015-02-06 | 2018-12-28 | 孙毅彪 | 无电弧型智能桥式高压断路器 |
| CN104616926B (zh) * | 2015-02-06 | 2018-06-26 | 孙毅彪 | 无电弧型串联智能桥式高压断路器 |
| DE102015001945A1 (de) | 2015-02-16 | 2016-08-18 | Ellenberger & Poensgen Gmbh | Schutzschalter und Verfahren zu dessen Betrieb |
| DE102015212802A1 (de) * | 2015-07-08 | 2017-01-12 | Ellenberger & Poensgen Gmbh | Trennvorrichtung zur Gleichstromunterbrechung |
| DE102015011990A1 (de) | 2015-09-14 | 2017-03-16 | Christian Sodtke | Automatisch auslösende und wieder einschaltende elektrische Freischalteinrichtung |
| CN105304413B (zh) * | 2015-11-06 | 2017-11-21 | 沈红 | 消除直流器件触头电弧的方法及其装置和应用 |
| DE102016204400A1 (de) * | 2016-03-17 | 2017-09-21 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Gleichspannungsschalter |
| DE102016106415A1 (de) * | 2016-04-07 | 2017-10-12 | Eaton Electrical Ip Gmbh & Co. Kg | Schaltvorrichtung zum Führen und Trennen von elektrischen Strömen |
| WO2018046653A1 (de) | 2016-09-12 | 2018-03-15 | Phoenix Contact Gmbh & Co. Kg | Photovoltaik-anlage, gleichstrom-hybrid-schalteinrichtung, verwendung und verfahren zum an- und abschalten eines photovoltaik-strangs |
| DE102016123283A1 (de) | 2016-12-01 | 2018-06-07 | Innofas Gmbh | Vorrichtung zum Trennen eines Bordnetzes von einer Energiequelle |
| EP3330992B1 (en) * | 2016-12-05 | 2019-11-20 | ABB Schweiz AG | Electrical dc switching system |
| BR112019014882B1 (pt) | 2017-02-10 | 2022-03-03 | Abb Schweiz Ag | Montagem de forno para um processo de produção de metal |
| DE102017204044A1 (de) | 2017-02-14 | 2018-08-16 | Ellenberger & Poensgen Gmbh | Verfahren und Spannungsvervielfacher zur Wandlung einer Eingangsspannung sowie Trennschaltung |
| FR3067165A1 (fr) * | 2017-05-30 | 2018-12-07 | Leach International Europe | Systeme d'hybridation pour courant continu haute tension |
| DE102017122218A1 (de) * | 2017-09-26 | 2019-03-28 | Eaton Industries (Austria) Gmbh | Niederspannungs-Schutzschaltgerät |
| DE102017127886A1 (de) * | 2017-11-24 | 2019-05-29 | Eaton Electrical Ip Gmbh & Co. Kg | Schaltvorrichtung zum Führen und Trennen von elektrischen Strömen und Schaltgerät mit einer derartigen Schaltvorrichtung |
| US10629391B2 (en) | 2017-12-21 | 2020-04-21 | Eaton Intelligent Power Limited | Fusible safety disconnect in solid state circuit breakers and combination motor starters |
| DE102018203636B3 (de) | 2018-03-09 | 2019-07-04 | Ellenberger & Poensgen Gmbh | Trennvorrichtung zur Gleichstromunterbrechung eines Strompfads, und Bordnetz eines Kraftfahrzeugs |
| US11127552B2 (en) | 2019-04-05 | 2021-09-21 | Eaton Intelligent Power Limited | Hybrid switch assembly and circuit interrupter including the same |
| DE102019213604A1 (de) * | 2019-09-06 | 2021-03-11 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Schutzschaltgerät, Schutzschaltsystem und Verfahren |
| CN111029184B (zh) * | 2019-12-16 | 2022-03-08 | 广东瑞德智能科技股份有限公司 | 一种开关装置及具有该开关装置的烘烤装置、家用电器 |
| DE102020208401A1 (de) | 2020-07-03 | 2022-01-05 | Robert Bosch Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung | Verfahren zur Absicherung insbesondere sicherheitsrelevanter Verbraucher in einem Kraftfahrzeug |
| FR3116391B1 (fr) * | 2020-11-18 | 2022-12-16 | Hager Electro Sas | Appareillage de protection à coupure électronique |
| DE102020216409B4 (de) * | 2020-12-21 | 2022-08-25 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Schutzschaltgerät und Verfahren |
| DE102021113589A1 (de) | 2021-05-26 | 2022-12-01 | Lisa Dräxlmaier GmbH | Elektronischer stromverteiler |
| US20240047151A1 (en) * | 2022-08-02 | 2024-02-08 | Rockwell Automation Technologies, Inc. | Hybrid circuit breaker system with integrated galvanic isolating switch |
| CN115967346B (zh) * | 2023-01-13 | 2024-04-09 | 合肥仙湖半导体科技有限公司 | 一种太阳能电池组件可脱离接线盒及其电路 |
| DE102023203234B3 (de) | 2023-04-06 | 2024-03-28 | Ellenberger & Poensgen Gmbh | Verfahren zum Betrieb eines Hybridschalters sowie ein entsprechender Hybridschalter |
| DE102023203236B3 (de) | 2023-04-06 | 2024-05-23 | Ellenberger & Poensgen Gmbh | Ansteuerschaltung für einen Hybridschalter und Hybridschalter |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS519246A (ja) * | 1974-07-15 | 1976-01-24 | Tokyo Shibaura Electric Co | Chokuryushadansochi |
| JPS5293808A (en) | 1976-02-02 | 1977-08-06 | Hitachi Ltd | Steam turbine controller |
| DE4317965A1 (de) * | 1993-05-28 | 1994-12-01 | Siemens Ag | Hybrider Leistungsschalter |
| JP3441813B2 (ja) * | 1994-10-05 | 2003-09-02 | アルプス電気株式会社 | 機械式スイッチの接点間アークの消去装置 |
| WO2002071429A1 (de) * | 2001-03-01 | 2002-09-12 | Tyco Electronics Amp Gmbh | Elektrische schaltung zur vermeidung eines lichtbogens über einem elektrischen kontakt |
| KR100434153B1 (ko) * | 2002-04-12 | 2004-06-04 | 엘지산전 주식회사 | 하이브리드 직류 전자 접촉기 |
| DE10225259B3 (de) | 2002-06-07 | 2004-01-22 | Sma Regelsysteme Gmbh | Elektrischer Steckverbinder |
| DE102005040432A1 (de) | 2005-08-25 | 2007-03-01 | Rwth Aachen | Strombegrenzender Schalter |
| ITTO20060539A1 (it) * | 2006-07-20 | 2008-01-21 | Ansaldo Ricerche S P A | Interruttore ibrido |
| DE202008010312U1 (de) | 2008-07-31 | 2008-10-02 | Phoenix Solar Ag | Photovoltaische Anlage und Generatoranschlusskasten in einer photovoltaischen Anlage |
| US7646178B1 (en) * | 2009-05-08 | 2010-01-12 | Fradella Richard B | Broad-speed-range generator |
-
2009
- 2009-03-25 DE DE202009004198U patent/DE202009004198U1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2010
- 2010-02-02 EP EP10708895A patent/EP2411990B1/de active Active
- 2010-02-02 RU RU2011134639/07A patent/RU2482565C2/ru not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2010-02-02 PL PL10708895T patent/PL2411990T3/pl unknown
- 2010-02-02 CN CN201080011647.4A patent/CN102349124B/zh active Active
- 2010-02-02 WO PCT/EP2010/000607 patent/WO2010108565A1/de active Application Filing
- 2010-02-02 CA CA2752895A patent/CA2752895C/en active Active
- 2010-02-02 PT PT107088957T patent/PT2411990E/pt unknown
- 2010-02-02 KR KR1020117025219A patent/KR101420831B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2010-02-02 SG SG2011054871A patent/SG174124A1/en unknown
- 2010-02-02 ES ES10708895T patent/ES2401777T3/es active Active
- 2010-02-02 BR BRPI1012338A patent/BRPI1012338A2/pt not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2010-02-02 AU AU2010227893A patent/AU2010227893B2/en active Active
- 2010-02-02 JP JP2012501149A patent/JP5469236B2/ja active Active
-
2011
- 2011-05-19 ZA ZA2011/03651A patent/ZA201103651B/en unknown
- 2011-06-16 TN TN2011000306A patent/TN2011000306A1/fr unknown
- 2011-06-30 IL IL213866A patent/IL213866A/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2011-09-22 US US13/240,505 patent/US8742828B2/en active Active
-
2013
- 2013-04-10 HR HRP20130321AT patent/HRP20130321T1/hr unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE202009004198U1 (de) | 2010-08-12 |
| HRP20130321T1 (en) | 2013-05-31 |
| CA2752895A1 (en) | 2010-09-30 |
| EP2411990A1 (de) | 2012-02-01 |
| JP5469236B2 (ja) | 2014-04-16 |
| BRPI1012338A2 (pt) | 2016-03-29 |
| ZA201103651B (en) | 2012-01-25 |
| CN102349124B (zh) | 2015-01-07 |
| SG174124A1 (en) | 2011-10-28 |
| WO2010108565A1 (de) | 2010-09-30 |
| PL2411990T3 (pl) | 2013-06-28 |
| KR20110129979A (ko) | 2011-12-02 |
| RU2011134639A (ru) | 2013-04-27 |
| RU2482565C2 (ru) | 2013-05-20 |
| CN102349124A (zh) | 2012-02-08 |
| US8742828B2 (en) | 2014-06-03 |
| PT2411990E (pt) | 2013-03-18 |
| IL213866A (en) | 2013-04-30 |
| JP2012521620A (ja) | 2012-09-13 |
| US20120007657A1 (en) | 2012-01-12 |
| TN2011000306A1 (en) | 2012-12-17 |
| ES2401777T3 (es) | 2013-04-24 |
| IL213866A0 (en) | 2011-07-31 |
| CA2752895C (en) | 2017-05-16 |
| AU2010227893A1 (en) | 2011-07-28 |
| AU2010227893B2 (en) | 2015-02-12 |
| KR101420831B1 (ko) | 2014-07-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2411990B1 (de) | Trennschalter zur galvanischen gleichstromunterbrechung | |
| EP3855465B1 (de) | Trennschalter zur gleichstromunterbrechung | |
| EP3320553B1 (de) | Trennvorrichtung zur gleichstromunterbrechung | |
| DE102011109920B4 (de) | Mechatronisches Mehrfachstecksystem | |
| EP3072143B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum schalten eines gleichstroms | |
| EP2483984B1 (de) | Freilaufkreis | |
| DE3717491A1 (de) | Elektronischer leistungstrennschalter | |
| DE19719919A1 (de) | Anordnung zum Schutz von elektrischen Einrichtungen | |
| EP3210226B1 (de) | Trennschalter zur galvanischen gleichstromunterbrechung | |
| EP3403271B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum schalten eines gleichstroms in einem pol eines gleichspannungsnetzes | |
| DE102012008614A1 (de) | Elektrischer Steckverbinder zum sicheren Trennen von elektrischen Strömen unter elektrischer Gleichspannung in Stromnetzen mit bidirektionalem Stromfluss | |
| DE2024785B2 (de) | Einrichtung zum Abschalten von Gleichstrom-Hochspannungsleitungen | |
| DE102013017091A1 (de) | Energiespeichereinrichtung für einen Kraftwagen | |
| EP2511956B1 (de) | Drei-Schalter Überspannungsschutz für eine Photovoltaikanlage | |
| DE102018203636B3 (de) | Trennvorrichtung zur Gleichstromunterbrechung eines Strompfads, und Bordnetz eines Kraftfahrzeugs | |
| DE102012200679A1 (de) | Schaltungsanordnung zur Reduktion der Stromstärke in einer Hochspannungs-Gleichstrom-Übertragungsleitung, Hochspannungs-Gleichstrom-Übertragungsanlage und Verfahren zum Reduzieren der Stromstärke eines elektrischen Stromes | |
| WO2013091689A1 (de) | Trennvorrichtung zur gleichstromunterbrechung zwischen einem photovoltaikgenerator und einer elektrischen einrichtung sowie photovoltaikanlage mit einer derartigen trennvorrichtung | |
| DE10256121A1 (de) | Umschaltbarer Gleichstromwandler für ein Netz mit zwei Spannungen und ein Netz mit zwei Spannungen, das mit einem derartigen Wandler ausgestattet ist | |
| DE3317942A1 (de) | Schaltungsanordnung | |
| DE3442932A1 (de) | Verfahren zum schutz von ladegeraeten, schaltschraenken oder verbrauchern in photovoltaischen energieversorgungsanlagen gegen direkten blitzschlag oder dergleichen |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20110530 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 595356 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20130215 Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: E. BLUM AND CO. AG PATENT- UND MARKENANWAELTE , CH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PT Ref legal event code: SC4A Free format text: AVAILABILITY OF NATIONAL TRANSLATION Effective date: 20130308 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502010002205 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130321 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HR Ref legal event code: TUEP Ref document number: P20130321 Country of ref document: HR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2401777 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20130424 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HR Ref legal event code: T1PR Ref document number: P20130321 Country of ref document: HR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GR Ref legal event code: EP Ref document number: 20130400693 Country of ref document: GR Effective date: 20130517 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PL Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130423 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130423 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130523 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130123 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130123 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130123 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130123 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130228 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130123 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130123 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130123 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130123 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HU Ref legal event code: AG4A Ref document number: E017496 Country of ref document: HU |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130123 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20131024 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130202 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502010002205 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20131024 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130123 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130123 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130202 Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130123 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HR Ref legal event code: ODRP Ref document number: P20130321 Country of ref document: HR Payment date: 20160127 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Payment date: 20160127 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Payment date: 20170120 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: HU Payment date: 20170119 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: CZ Payment date: 20170126 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: PT Payment date: 20170123 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20170201 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20170217 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HR Ref legal event code: PBON Ref document number: P20130321 Country of ref document: HR Effective date: 20170202 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170202 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180203 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180802 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180202 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180202 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180202 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180202 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Payment date: 20240219 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20240220 Year of fee payment: 15 Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20240319 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20240216 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20240228 Year of fee payment: 15 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20240301 Year of fee payment: 15 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20240222 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20240221 Year of fee payment: 15 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20240222 Year of fee payment: 15 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20240219 Year of fee payment: 15 |