EP2095174B1 - Verbesserte unifokal-brillenlinse - Google Patents
Verbesserte unifokal-brillenlinse Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2095174B1 EP2095174B1 EP06850358A EP06850358A EP2095174B1 EP 2095174 B1 EP2095174 B1 EP 2095174B1 EP 06850358 A EP06850358 A EP 06850358A EP 06850358 A EP06850358 A EP 06850358A EP 2095174 B1 EP2095174 B1 EP 2095174B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- lens
- zone
- zones
- height
- effective power
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000004438 eyesight Effects 0.000 title claims description 37
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 claims description 16
- 208000001491 myopia Diseases 0.000 claims description 12
- 230000000750 progressive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000004305 hyperopia Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 201000006318 hyperopia Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000004379 myopia Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 201000009310 astigmatism Diseases 0.000 description 6
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000004256 retinal image Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001373 regressive effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 206010020675 Hypermetropia Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 206010047513 Vision blurred Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003754 machining Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 2
- JHQVCQDWGSXTFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-prop-2-enoxycarbonyloxyethoxy)ethyl prop-2-enyl carbonate Chemical compound C=CCOC(=O)OCCOCCOC(=O)OCC=C JHQVCQDWGSXTFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000004308 accommodation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005266 casting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006386 neutralization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008447 perception Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000001747 pupil Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 208000014733 refractive error Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000009877 rendering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002123 temporal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012876 topography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004304 visual acuity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004382 visual function Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B3/00—Simple or compound lenses
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02C—SPECTACLES; SUNGLASSES OR GOGGLES INSOFAR AS THEY HAVE THE SAME FEATURES AS SPECTACLES; CONTACT LENSES
- G02C7/00—Optical parts
- G02C7/02—Lenses; Lens systems ; Methods of designing lenses
Definitions
- the invention relates to an improved single vision spectacle lens.
- Single vision lenses are prescribed when the patient is either farsighted or nearsighted and have the same focal power throughout (top to bottom).
- Vision correction for myopia (nearsightedness) and hypermetropia (farsightedness) can be accomplished using spectacle lenses having appropriate spherical curves on the anterior (outer or front surface) and posterior (inner or back surface on the eye side) surfaces. Astigmatism can also be corrected when using toroidal or spherocylindrical surfaces.
- the retinal images of near objects are too small in size to provide adequate visual comfort or contrast sensitivity especially at low or controlled illumination conditions, for example when reading a menu in a restaurant, or threading a needle indoors.
- the size of the focused retinal image is usually expressed in the form of angular magnification or paraxial magnification, in which magnification is defined as the ratio of the retinal image size formed by a particular lens to the image size formed by an emmetropic eye, i.e., an eye requiring no refractive correction.
- M is the lens magnification
- t is the lens thickness
- n is the refractive index of the lens material
- F 1 is the curvature of the front surface of the lens
- d is the distance from the back vertex, or distance from the point of intersection on the lens of the principal axis, to the entrance pupil of the eye
- F v is the back vertex power, or the reciprocal of the distance, in air, from the back surface of the lens to the secondary focal point.
- Equation 1 shows that image magnification is higher for plus powers and increases with plus power of a lens.
- SM is the spectacle magnification, defined as the ratio of retinal image size when wearing a lens of power D to the image size in an emmetropic eye; D 1 is the base curve; D is the power of the lens in diopters.
- Single vision lenses in particular myopes who wear minus power single vision lenses may desire to enhance image magnification for near objects.
- single vision lens wearers require single vision lenses of a particular power in order to avoid image blur, they can not be provided a higher level of image magnification without causing them to have blurry vision.
- non-presbyopic wearers of all types of vision correction including users of single vision spectacle lenses or contact lenses experience reduced contrast sensitivity and visual comfort when viewing near objects, since near vision tasks typically require finer resolution and ability to function in low or controlled illumination environments, e.g., indoors at night.
- WO 02/084382 discloses multifocal ophthalmic lenses, such as progressive addition lenses in which unwanted lens astigmatism is reduced compared to prior art.
- WO 2005/091054 discloses a method for increasing the magnification of a lens without changing the dioptric power.
- the object of the present invention is to provide an improved single vision lens whereby image magnification is provided for near objects without causing a blurry vision.
- an improved single lens comprising:
- an "improved single lens” is a substantially single vision lens having at least the same focal power on the main part of the lens.
- the main part of the lens corresponds to at least 75% of the surface of the lens.
- the topography of the lens curvature may be designed to follow the path of natural gaze while viewing near objects.
- the maximum difference of effective power of the lower part of the lens and the effective power of the upper part of the lens is equal or less to 0.3 Diopter.
- front and back surfaces are aligned to each other such that the effective power of the whole lens is constant.
- front and back lower zones comprise each an intermediate zone and a bottom zone where the curvature of both front and back zones follows a top to down increasing curvature gradient; a preferred gradient is a linear gradient.
- the gradient in surface curvature is less or equal to 3 Diopters.
- the bottom zones are zones of constant focal power.
- the height h 1 of top zone, the height h 2 of intermediate zone, the height h 3 of bottom zone of the front surface are respectively equal to the height h 1 of top zone, the height h 2 of intermediate zone, the height h 3 of bottom zone of the back surface.
- h 1 is comprised between 50 to 70% of the total height h of the lens
- h 2 is comprised between 5 to 20% of the total height h of the lens
- h 3 is comprised between 20 to 40% of the total height of the lens.
- the front and back surfaces are progressive surfaces comprising each a top far vision zone, an intermediate vision zone and a bottom near vision zone, the surfaces being adjusted so that the resulting lens power is held to a nominal value.
- the front and back progressive surfaces each comprise a steep curvature zone being disposed along a central meridian so as the steepening curvature profile matches the charge in gaze direction as the eyes move from a distant target to a near target.
- the lens is spherical or toric or aspheric.
- the lens is a minus lens for nearsightedness correction, with negative effective power.
- the lens is a plano lens with 0 Diopter effective power.
- the lens is a plus lens for farsightedness correction with positive effective power.
- a Diopter power value is constant when its variation on a surface is equal or less to 0.1 Diopter.
- a height value is equal to another when the difference between the heights is equal or less to 1 mm.
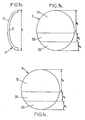
- Figures 1a to c are schematic views of an improved single lens according to the present invention.
- the wordings "top” or “up”, “bottom” or “down” indicate positions in the lens when wearing the lens with an horizontal gaze, consequently indicating the height of a zone means the maximum distance between two vertical points of said zone when the lens is wear likewise.
- the lens 1 of figure 1 is an improved single vision lens following an embodiment of the present invention.
- the lens 1 comprises a front surface 2 and a back surface 3.
- Figure 1a shows a schematic side view of the lens 1
- figure 1b shows a schematic front view of the front surface 2 of lens 1
- figure 1c shows a schematic front view of the back surface 3 of lens 1.
- the front surface 2 comprises three top to bottom successive zones 21, 22, 23 where 21 and 23 are zones of constant curvature and curvature of bottom zone 23 is higher than curvature of top zone 21 and where the curvature of intermediate zone 22 is continuously increasing from the curvature value of top zone 21 at the interface between zones 21 and 22 to the curvature value of bottom zone 23 at the interface between zones 22 and 23.
- the back surface 3 comprises three top to bottom successive zones 31, 32, 33 where 31 and 33 are zones of constant curvature and curvature of bottom zone 33 is higher than curvature of top zone 31 and where the curvature of intermediate zone 32 is continuously increasing from the curvature value of top zone 31 at the interface between zones 31 and 32 to the curvature value of bottom zone 33 at the interface between zones 32 and 33.
- the height h 1 of top zone 21 of the front surface 2 is the same as the height h 1 of the top zone 31 of back surface 3.
- the height h 2 of intermediate zone 22 of the front surface 2 is the same as the height h 2 of intermediate zone 32 of back surface 3.
- the height h 3 of bottom zone 23 of the front surface 2 is the same as the height h 3 of bottom zone. 33 of back surface 3.
- h 60 mm
- h 1 35 mm
- h 2 7 mm
- h 3 18 mm.
- front surface 2 and back surface 3 are aligned to each other, such that the effective power of the lens as measured by ray tracing analysis is constant everywhere.
- Example 1 is an improved single vision lens which has an overall spherical power of -2.0 Diopters, with both surfaces having curvatures that vary across the optical surface, as shown in Figures 1b and 1c .
- the two surfaces of the lens are aligned to each other, such that the effective power of the lens as measured by ray tracing analysis is -2.0 Diopters everywhere.
- Example 2 is an improved single vision lens which has an overall power of 0.0 Diopter (plano). It is known that even emmetropic persons who do not vision correction may need image magnification in order to comfortably read fine print or perform tasks that require fine resolution at near distances.
- the improved plano single vision lens depicted in example 2 is made up by combining to progressive addition surfaces, one with progressive addition power (front surface) and the other with regressive power (back surface).
- the power profile of these two surfaces may be adjusted so that the change in spherical power of the resulting lens is held to a value below a nominal limit. For example, it is possible to use a progressive addition surface with a 2.00 Diopters add power and a regressive surface with a 2.00 Diopters power to create the single improved vision lens of example 2.
- the front surface curvature ranges from 2.00 Diopters to 4.00 Diopters, with the relatively steep zone being disposed along a central meridian, so that the steepening curvature profile matches the change in gaze direction as the eye moves from a distant target to a near target.
- the increase in magnification (per cent increase in SM) for such a lens (made of a material of refractive index 1.50) is going from the zone where the curvature of the front surface is 2.00 Diopters to the zone where the curvature is 4.00 Diopters is 0.5%, ignoring the slight increase in vertex distance.
- the impact of base curve steepening on spectacle magnification is more pronounced when the single vision lens provides a correction. For example, for a plus 4.00 Diopters improved single lens, the front curve might be 6.00 Diopters and the back curve 2.00 Diopters. If the near vision zone is steepened by 2.00 Diopters, then the increase in SM is from 1.068 to 1.088, i.e. from 6.8% to 8.8%, or 30%.
- Example 3 is an improved single vision lens constructed by joining two progressive addition surfaces, the front surface with a 3.50 Diopters base curve and a 2.00 Diopters add power zone and the back being a 5.00 Diopters base curve with a 2.00 Diopters regressive power.
- the near vision zone of this lens provides a spherical correction of -1.50 Diopters, with a front curve of 5.00 Diopters.
- image magnification is enhanced or image minification is reduced in all types of single vision lenses (plus, plano or minus) by increasing the front curve of the lens on that portion of the lens surface that is used for viewing near objects.
- This approach of providing a gradient (or an abrupt) increase in lens curvature at the lower portion of the optic, or that portion of the optic that is used for viewing near objects will lead to enhanced visual comfort and better resolution (e.g., contrast sensitivity) while reading, or performing other tasks that require fine resolution.
- the increase in spectacle lens magnification may also be achieved by providing a small amount of add power (increased sphere power) at the lower portion of the optic, or the near vision zone.
- the magnitude of this increase in spherical correction should be limited so that the resulting defocus or image blurring is not noticeable, or is indeed below the level of perception.
- an add power 0.10-0.50 Diopter, and preferably of 0.10-0.30 Diopter does not cause a change in visual acuity, but provides a small increase in spectacle lens magnification.
- an add power of 0.15 Diopter with a front curve of 5.00 Diopters in a plano lens provides an SM of 1.012 or a per cent SM of 1.2 approximately
- an add power of 0.30 Diopter provides an SM of 1.014
- the lens material has an index of 1.50.
- Table 1 shows the values of SM for a range of single vision lenses. It is assumed that the material has a refractive index of 1.50, the edge thickness of plus lenses is 1.0 mm and center thickness of plano and minus lenses is 2.00 mm. Lens thickness were recomputed for the new front curves in Table 1 which shows the changes in SM with lens power and front curvature. Table 1.
- Example Front curve, Diopcer Back curve, Diopter Spherical Power, Diopter Thickness mm@OC SM, Prior Art Near Curve Diopter Add Power, Diopter SM invention A 7.50 2.50 - 5.00 5.87 1.114 9.50 0 1.126 B 5.00 4.00 1.00 1.95 1.022 7.75 0 1.026 C 6.00 6.00 0.00 2.00 1.008 9.00 0 1.012 D 4.00 5.00 - 1.00 2.00 0.991 7.00 0 0.995 E 2.00 7.00 - 5.00 2.00 0.933 4.50 0 0.936 F 5.00 0.00 2.00 1.007 7.75 0.15 1.013 G 7.00 4.00 + 3.00 3.95 1.067 8.00 0.15 1.072 H 4.00 4.00 0.00 2.00 1.005 7.00 0.30 1.014 I 2.00 5.00 - 3.00 2.00 0.959 4.75 0.30 0.967
- the "spherical power" corresponds to resulting effective power of the main part of the lens.
- Thintickness @ OC is the thickness of the lens measured at the optical center of the lens.
- Near curve is the maximum curvature of the front surface lower zone with top to bottom increasing curvature, used for lenses according to the present invention.
- the curvature of the back surfaces of Examples A to E, according to the invention is designed so that the effective power of the whole lens is constant.
- the curvature of the back surfaces of Examples F and G, according to the invention is designed so that the effective power of the main part of the lens is constant and the maximum difference of the effective power of the lower part of the lens and the effective power of the upper part of the lens is 0.15 Diopter.
- the curvature of the back surfaces of Examples H and I, according to the invention is designed so that the effective power of the main part of the lens is constant and the maximum difference of the effective power of the lower part of the lens and the effective power of the upper part of the lens is 0.30 Diopter.
- Table 1 makes possible to compare the spectacle magnification SM of prior art lenses with lenses according to the present invention.
- Table 2 shows the difference in per cent SM values for each of the examples in Table 1 and the increase in Per Cent SM by changing front curvatures of single vision lenses and providing them with moderate values of add power.
- Table 2 shows the difference in per cent SM values for each of the examples in Table 1 and the increase in Per Cent SM by changing front curvatures of single vision lenses and providing them with moderate values of add power.
- Example SM, Prior Art SM invention Diff (% SM) A 1.114 1.126 1.2 B 1.022 1.026 0.4 C 1.008 1.012 0.4 D 0.991 0.995 0.4 E 0.933 0.936 0.3 F 1.007 1.013 0.6 G 1.067 1.072 0.5 H 1.005 1.014 0.9 I 0.959 0.967 0.8
- Maintaining the add power to a value less than or equal to 0.30 Diopter will ensure that the unwanted astigmatism that develops as a consequence of providing the add power will be less or equal to 0.25 Diopter, and may be pushed outward where it can not interfere with direct gaze in any eye position.
- the steepening of the front curve (without providing an add power) will also introduce surface astigmatism on the front surface. The effect of this surface astigmatism will be apparent in causing image distortion, unless it is compensated by providing a complementary curve on the back surface.
- a high quality design of the overall lens may be derived by performing a simultaneous optimization of both surfaces using an algorithm that compute retinal image distortion by performing ray tracing analysis through multiple points of the lens optic, with the lens positioned in an "as worn" position.
- a method for defining a lens by optimizing the optical characteristics of the lens is disclosed in patent document US 6,318,859 to T. Baudart et al. which is enclosed by reference, where optical characteristics are calculated during optimization using a ray tracing program, under wearing conditions. Said method is suitable to perform a simultaneous optimization of both surfaces according to the present invention.
- Still another suitable method is disclosed in patent application PCT/IB2006/003220.
- This concept may be applied to both spherical and toric single vision lenses.
- the value of the spectacle lens magnification is preferably computed in every meridian, since the power (effective power or spherocylindrical power) will be different at each meridian.
- the increase in SM between state of the art designs and designs disclosed in this invention will be proportionately the same as the front curve is altered or when moderate add power is provided.
- the surfaces of the single vision optic may be further enhanced by rendering them aspheric.
- Advantages of using aspheric surfaces include a wider field of view, and reduced thickness of plus lenses.
- the fabrication of these novel single vision lenses requires the use of state of the art lens machining or molding technology.
- the steepening of the front curve of the increase in spherical power is preferably provided at the inferior portion of the optic.
- the optic design is relatively insensitive to the precise orientation of the central meridian of the altered zone. Therefore, it may be possible to cover all possible values of the axis of the prescribed cylinder with two possible orientations of the altered zones, such as inferior nasal and inferior temporal.
- the front curve will have a highly complex, non symmetric form, and is preferably provided by molding or casting a blank against an optical tool embodying this geometry, or using a free form machining process. Every spectacle lens material may be used in the frame of the present invention such as non limiting materials known under commercial references « ORMA » « PC » « MR8 » « MR7 » « 1.74 Colour
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Ophthalmology & Optometry (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Eyeglasses (AREA)
Claims (12)
- Linse für eine Brille bestehend aus einer im Wesentlichen Einstärkenlinse, welche wenigstens die gleiche Brechkraft an dem Hauptteil der Linse aufweist, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass sie umfasst:- eine kontinuierliche Änderung der Linsenkrümmung nach unten gehend;- eine vordere (2) und eine hintere (3) Oberfläche;- einen oberen Teil, dessen vordere und hintere Oberfläche oberste Bereiche (21, 31) der vorderen (2) und hinteren (3) Oberfläche sind, welcher wenigstens die Hälfte der jeweiligen vorderen (2) und hinteren (3) Oberfläche abdeckt, und wobei die zwei obersten Bereiche (21, 31) derart zueinander ausgerichtet sind, dass die effektive Brechkraft des oberen Teils der Linse konstant ist;- einen unteren Teil, welcher zum Betrachten naher Objekte verwendet wird, dessen vordere und hintere Oberfläche untere Bereiche (22 und 23, 32 und 33) der vorderen (2) und hinteren (3) Oberfläche sind, wobei die vorderen und hinteren unteren Bereiche jeweils einen Oberflächenbereich (22, 32) umfassen, wobei eine von oben nach unten zunehmende Krümmung jedes Oberflächenbereichs (22, 32) vorgesehen ist und wobei die zwei vorderen und hinteren unteren Bereiche (22 und 23, 32 und 33) derart zueinander ausgerichtet sind, dass die maximale Differenz der effektiven Brechkraft des unteren Teils der Linse und die effektive Brechkraft des oberen Teils der Linse zwischen 0 und 0,5 Dioptrien liegt.
- Linse nach Anspruch 1, wobei die maximale Differenz der effektiven Brechkraft des unteren Teils der Linse und die effektive Brechkraft des oberen Teils der Linse gleich oder kleiner als 0,3 Dioptrien ist.
- Linse nach Anspruch 1, wobei die vordere (2) und hintere (3) Oberfläche derart zueinander ausgerichtet sind, dass die effektive Brechkraft der gesamten Linse konstant ist.
- Linse nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, wobei die vorderen und hinteren unteren Bereiche jeweils einen Zwischenbereich (22, 32) und einen untersten Bereich (23, 33) umfassen, wobei die Krümmung sowohl des vorderen (22) als auch hinteren (32) Bereichs einem von oben nach unten zunehmenden Krümmungsgradienten folgt.
- Linse nach Anspruch 3 oder 4, wobei die untersten Bereiche (23, 33) Bereiche mit konstanter Brechkraft sind.
- Linse nach einem der Ansprüche 4 oder 5, wobei die Höhe h1 des obersten Bereichs (21), die Höhe h2 des Zwischenbereichs (22), die Höhe h3 des untersten Bereichs (23) der vorderen Oberfläche (2) jeweils gleich sind zu der Höhe h1 des obersten Bereichs (31), der Höhe h2 des Zwischenbereichs (32), der Höhe h3 des untersten Bereichs (33) der hinteren Oberfläche (3).
- Linse nach Anspruch 6, wobei h1 zwischen 50 bis 70% der gesamten Höhe h der Linse liegt, h2 zwischen 5 bis 20% der gesamten Höhe h der Linse liegt, h3 zwischen 20 bis 40% der gesamten Höhe h der Linse liegt.
- Linse nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, wobei die vordere (2) und hintere (3) Oberfläche Gleitsichtflächen sind, welche jeweils einen obersten Weitsichtbereich, einen Zwischensichtbereich und einen untersten Kurzsichtbereich aufweisen.
- Linse nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, wobei die Linse sphärisch oder torisch oder asphärisch ist.
- Linse nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, wobei die Linse eine Minuslinse zur Kurzsichtigkeitskorrektur mit negativer effektiver Brechkraft ist.
- Linse nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 9, wobei die Linse eine Planlinse mit einer effektiven Brechkraft von 0 Dioptrien ist.
- Linse nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 9, wobei die Linse eine Pluslinse zur Weitsichtigkeitskorrektur mit positiver effektiver Brechkraft ist.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2006/062563 WO2008079150A1 (en) | 2006-12-22 | 2006-12-22 | Improved single vision spectacle lens |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2095174A1 EP2095174A1 (de) | 2009-09-02 |
| EP2095174B1 true EP2095174B1 (de) | 2012-10-31 |
Family
ID=38441917
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP06850358A Active EP2095174B1 (de) | 2006-12-22 | 2006-12-22 | Verbesserte unifokal-brillenlinse |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8092012B2 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP2095174B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP2010513985A (de) |
| KR (1) | KR101359721B1 (de) |
| ES (1) | ES2395394T3 (de) |
| WO (1) | WO2008079150A1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108351531B (zh) * | 2015-11-13 | 2021-04-30 | 依视路国际公司 | 畸变管理得到改善的镜片 |
| EP3547013A1 (de) | 2018-03-30 | 2019-10-02 | Essilor International (Compagnie Generale D'optique) | Verfahren zur bestimmung eines einstärkenbrillenglases |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2753805B1 (fr) * | 1996-09-20 | 1998-11-13 | Essilor Int | Jeu de lentilles ophtalmiques multifocales progressives |
| JP4036921B2 (ja) * | 1997-06-10 | 2008-01-23 | ペンタックス株式会社 | 眼鏡レンズ |
| US6089710A (en) * | 1998-07-20 | 2000-07-18 | Oracle Lens Manufacturing Corporation | Single-vision ophthalmic lens series |
| US6199984B1 (en) * | 1999-03-17 | 2001-03-13 | Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc. | Progressive addition lenses with varying power profiles |
| DE19960826A1 (de) * | 1999-12-16 | 2001-07-05 | Rodenstock Optik G | Einstärken-Brillenglas mit Vollkorrektion |
| FR2820515B1 (fr) * | 2001-02-02 | 2003-05-16 | Essilor Int | Lentille ophtalmique multifocale progressive a variation de puissance rapide |
| US6709105B2 (en) * | 2001-04-10 | 2004-03-23 | Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc. | Progressive addition lenses |
| JP2004309589A (ja) | 2003-04-02 | 2004-11-04 | Seiko Epson Corp | 累進多焦点レンズ及びその設計方法 |
| JP3101681U (ja) * | 2003-04-30 | 2004-06-17 | ぐんじ 武田 | 特殊防眩サングラスレンズ |
| US7275822B2 (en) | 2004-03-18 | 2007-10-02 | Essilor International (Compagnie Generale D'optique) | Progressive addition lenses with adjusted image magnification |
| US7229173B2 (en) * | 2004-08-25 | 2007-06-12 | Essilor International (Compagnie Generale D'optique) S.A. | Short corridor progressive addition lenses with reduced unwanted astigmatism |
| JP4166768B2 (ja) * | 2005-03-25 | 2008-10-15 | オプティカル ベンチャーズ,インコーポレイテッド | サングラス用レンズおよびその製法並びにその製造装置 |
-
2006
- 2006-12-22 EP EP06850358A patent/EP2095174B1/de active Active
- 2006-12-22 KR KR1020097015321A patent/KR101359721B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2006-12-22 JP JP2009542749A patent/JP2010513985A/ja active Pending
- 2006-12-22 ES ES06850358T patent/ES2395394T3/es active Active
- 2006-12-22 WO PCT/US2006/062563 patent/WO2008079150A1/en active Application Filing
- 2006-12-22 US US12/520,607 patent/US8092012B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR101359721B1 (ko) | 2014-02-05 |
| US20100060852A1 (en) | 2010-03-11 |
| ES2395394T3 (es) | 2013-02-12 |
| US8092012B2 (en) | 2012-01-10 |
| WO2008079150A1 (en) | 2008-07-03 |
| EP2095174A1 (de) | 2009-09-02 |
| KR20090092843A (ko) | 2009-09-01 |
| JP2010513985A (ja) | 2010-04-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1216432B1 (de) | Progressive linse | |
| EP2404212B1 (de) | Brille für ein kurzsichtiges kind | |
| CA2375162C (en) | Progressive lens | |
| US8042940B2 (en) | Opthalmic lenses having reduced base out prism | |
| US20060092375A1 (en) | Multifocal lenses for pre-presbyopic individuals | |
| US20130070199A1 (en) | Multifocal lens having a progressive optical power region and a discontinuity | |
| EP2778749B1 (de) | Presbyopie-Linse mit Pupillengrößenkorrektur auf Grundlage des Brechungsfehlergrads | |
| US8807746B2 (en) | Spectacle lens, spectacles, and method for manufacturing spectacle lens | |
| JP2007241276A (ja) | 累進焦点眼鏡レンズの決定方法 | |
| WO2007069006A1 (en) | Method for determination of an ophtalmic lens | |
| US20050110945A1 (en) | Progressive spectacle lens having two aspherical progressive surfaces | |
| US7048376B2 (en) | Progressive addition power lens | |
| US8757799B2 (en) | Progressive multifocal ophthalmic lens | |
| EP2095174B1 (de) | Verbesserte unifokal-brillenlinse | |
| JPH07294859A (ja) | 累進多焦点レンズ | |
| US6776487B2 (en) | Progressive spectacle lens having only a small change of binocular properties during a movement of glance | |
| JP2010513985A5 (de) | ||
| JP3226108B2 (ja) | 累進焦点レンズの製造方法 | |
| AU772399B2 (en) | Progressive lens | |
| AU771955B2 (en) | Progressive lens | |
| JPH04338918A (ja) | 累進多焦点レンズ | |
| WO2023006579A1 (en) | Spectacle lens design, method of determining a spectacle lens design, method of manufacturing a spectacle lens, computer program, computer readable storage medium, data processing system and data set stored on a computer-readable storage medium | |
| JPH08211340A (ja) | 累進多焦点レンズ及び眼鏡 | |
| JPH04338920A (ja) | 累進多焦点レンズ | |
| JPH04338919A (ja) | 累進多焦点レンズ |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20090618 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: THE OTHER INVENTORS HAVE AGREED TO WAIVE THEIR ENT Inventor name: MERRITT, JIM Inventor name: WOOLEY, BEN Inventor name: GUPTA, AMITAVA Inventor name: SASTRY, SHYAMY |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20090924 |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 582311 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20121115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602006032854 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2395394 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20130212 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 582311 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: VDEP Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130228 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130228 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130131 Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20121231 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20130801 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20121222 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20121231 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20121231 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602006032854 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130801 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20121222 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20061222 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20151222 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20151222 |
|
| PGRI | Patent reinstated in contracting state [announced from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Effective date: 20170710 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 602006032854 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: ESSILOR INTERNATIONAL, FR Free format text: FORMER OWNER: ESSILOR INTERNATIONAL COMPAGNIE GENERALE D'OPTIQUE, CHARENTON, FR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: PC2A Owner name: ESSILOR INTERNATIONAL Effective date: 20180521 Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: PC2A Effective date: 20180521 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: 732E Free format text: REGISTERED BETWEEN 20180517 AND 20180523 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: TP Owner name: ESSILOR INTERNATIONAL, FR Effective date: 20180601 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230525 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20231227 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20231220 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20231227 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20240102 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20231229 Year of fee payment: 18 |