EP1749331B1 - Antenne de radiotelephonie mobile a element de formation de faisceau - Google Patents
Antenne de radiotelephonie mobile a element de formation de faisceau Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1749331B1 EP1749331B1 EP05745719A EP05745719A EP1749331B1 EP 1749331 B1 EP1749331 B1 EP 1749331B1 EP 05745719 A EP05745719 A EP 05745719A EP 05745719 A EP05745719 A EP 05745719A EP 1749331 B1 EP1749331 B1 EP 1749331B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- plane
- reflector
- operating
- antenna
- section
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Not-in-force
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01Q—ANTENNAS, i.e. RADIO AERIALS
- H01Q1/00—Details of, or arrangements associated with, antennas
- H01Q1/12—Supports; Mounting means
- H01Q1/22—Supports; Mounting means by structural association with other equipment or articles
- H01Q1/24—Supports; Mounting means by structural association with other equipment or articles with receiving set
- H01Q1/241—Supports; Mounting means by structural association with other equipment or articles with receiving set used in mobile communications, e.g. GSM
- H01Q1/246—Supports; Mounting means by structural association with other equipment or articles with receiving set used in mobile communications, e.g. GSM specially adapted for base stations
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01Q—ANTENNAS, i.e. RADIO AERIALS
- H01Q21/00—Antenna arrays or systems
- H01Q21/24—Combinations of antenna units polarised in different directions for transmitting or receiving circularly and elliptically polarised waves or waves linearly polarised in any direction
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01Q—ANTENNAS, i.e. RADIO AERIALS
- H01Q5/00—Arrangements for simultaneous operation of antennas on two or more different wavebands, e.g. dual-band or multi-band arrangements
- H01Q5/40—Imbricated or interleaved structures; Combined or electromagnetically coupled arrangements, e.g. comprising two or more non-connected fed radiating elements
- H01Q5/42—Imbricated or interleaved structures; Combined or electromagnetically coupled arrangements, e.g. comprising two or more non-connected fed radiating elements using two or more imbricated arrays
Definitions
- Antennas in particular in the form of stationary mobile radio antennas are well known.
- an antenna array with a plurality of vertically stacked primary radiator modules which radiate and receive in a position, for example, with vertical orientation.
- the individual radiating element can consist of dipole radiators or dipole radiator arrangements.
- antennas in particular in the form of antenna arrays, which can transmit and / or receive in two mutually orthogonal polarization planes are also known.
- dual polarized antennas are for example from DE 198 60 121 A1 known.
- the two mutually perpendicular polarization planes are rotated at a 45 ° angle relative to the horizontal (or vertical). This is also common spoken of a so-called X-polarization or orientation of the radiator elements.
- dipole radiators are again preferably used, for example, cross-shaped dipole radiators or dipole squares.
- vector dipoles come into consideration, as they basically from the DE 198 60 121 A1 are known.
- These dipole structures are a dual-polarized radiator arrangement which is constructed in the electrical manner in the manner of a crossed dipole and is more closely approximated in terms of construction to a quadratic structure.
- Beam-shaping elements for influencing the radiation pattern are basically, for example, from US 5,629,713 A known. It is a horizontally polarized antenna which symmetrically to the central longitudinal axis on each left and right on a horizontally oriented dipole radiator so-called parasitic radiator shows, which are also designed dipolstrahlerä Inc, namely with a central support column, of the parasitic in a horizontal plane to the left and right Stand aside dipole halves. These dipole halves or dipole arms extend from their middle fastening and holding point obliquely downwards in the direction of the reflector plane, in such a way that an angle of 90 ° is formed between the two reflector halves.
- pure decoupling elements are also known in the prior art which are not beamforming, in particular taking into account a far-field diagram, but merely decoupling between serve two perpendicular polarizations.
- decoupling elements for decoupling between two polarizations in the case of a dual-polarized antenna are known, for example, from US Pat WO 01/04991 A1 or the WO 98/01923 A1 known.
- a generic radiator arrangement for the use of patch antennas is for example also from WO 98/36472 A1 to be known as known. Described is an antenna with horizontally and vertically aligned patch elements, which in each case in the horizontal direction outside relative to the reflector plane in the radiator direction elevating path sections are assigned. In one embodiment, these web portions may also be provided with opposite outwardly extending wing members having a length in the vertical direction, corresponding to the length of the webs carrying them and rising from the reflector. In a further embodiment dual polarized patch radiators are shown, which are aligned in the polarization plane at a + 45 ° or -45 ° angle to the horizontal or vertical.
- an object of the present invention to provide an improved antenna, in particular in the form of a dual-polarized, stationary antenna for a base station for the mobile radio area, which is equipped with a device for performing a beam shaping.
- an improved antenna in particular in the form of a dual-polarized, stationary antenna for a base station for the mobile radio area, which is equipped with a device for performing a beam shaping.
- it should be possible according to the invention to be able to make an improved shaping of far-field diagrams for such antennas.
- the invention can be used in a radiator arrangement which radiates in two polarization planes.
- the invention has advantages especially in a dual polarized antenna.
- the invention is not limited to a single-band antenna, but can also be implemented and implemented in a dual-band or generally a multi-band antenna.
- the present invention is also characterized by the fact that the desired improvement explained by comparatively simple and inexpensive measures can be realized. Furthermore, the measures that effect the improvement can be used selectively and, above all, assigned to individual radiators or radiator elements.
- the measures according to the invention can be used and used not only in dual-polarized antennas with dipole radiators but, for example, also in patch antennas. In principle, there are no restrictions on certain emitter shapes.
- the solution according to the invention is characterized inter alia by the fact that at least four passive electrically conductive Elements are provided which are at least indirectly galvanically connected to the electrically conductive reflector or capacitively coupled.
- the inventively provided at least four passive electrically conductive elements which are additionally provided for at least one radiator or a radiator arrangement, are divided into at least two parts and each comprise a support portion, which preferably emanates from the reflector and electrically connected thereto or capacitively coupled and preferably at least indirectly mechanically connected to the reflector.
- a so-called active portion is then provided, which is preferably arranged in a direction parallel to the reflector plane.
- this effective portion may be arranged at least in an angular range of less than ⁇ 20 °, preferably less than ⁇ 10 ° deviating from the orientation of the reflector plane, ie extend at an angle to the reflector plane.
- this effective section has a length of preferably 0.2 ⁇ to 1.0 inclusive ⁇ , where ⁇ corresponds to the wavelength in the frequency range or frequency band to be transmitted, preferably the average wavelength of the frequency range to be transmitted.
- the active plane itself can be arranged above or below the radiator plane of the active radiator to be influenced. A restriction is not specified here. However, the length of the support portion which is greater than the distance of the active portion of the passive electrically conductive element to the reflector, do not exceed a maximum value corresponding to twice the aforementioned wavelength.
- the at least four beam-shaping elements are designed in such a way that the at least two pairs of support sections run apart from the plane of the reflector in the plane of action and the effective sections adjoining the upper end of the support section converge again.
- the material thickness or the transverse dimensions should be transverse to the direction of extension of the electrically conductive additionally provided Strahlformerides less than 0.1 of the operating wavelength, preferably the average operating wavelength of the element to be influenced.
- This may be a rod-shaped or cross-shaped decoupling structure, which is arranged between two dual-polarized radiators, in order to improve or to effect a decoupling between the two polarizations in the case of a dual-polarized antenna.
- the aim of the present invention is not to ensure a decoupling element for improving the decoupling between two dual-polarized radiation planes. Rather, the aim of the present invention is to modify and shape the radiation pattern as desired, especially in far-field viewing. Therefore, it is also provided according to the invention that the active portion of the electrically conductive beam-forming element according to the invention extends at least substantially or approximately in the above-mentioned preferably parallel to the reflector plane extending working plane in the polarization direction of the element to be influenced. Again, deviations of preferably less than 20%, in particular less than 10%, can also bring about the desired inventive success.
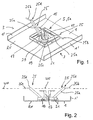
- the antenna according to FIGS. 1 and 2 comprises a reflector arrangement or a reflector 1, which is conductive.
- a radiator arrangement 5 is preferably provided in the middle region, which in the example shown consists of a single radiator 5a.
- the single radiator 5a is in this example formed from a simple polarized dipole radiator which radiates in a plane perpendicular to the plane of the reflector 1 (ie, sends and / or receives).
- the reflector 1 is designed substantially flat at least in the area of the radiator arrangement 5.
- reflector webs or wall sections 1 'projecting transversely to the reflector plane and extending in the beam direction are provided on the longitudinal side regions 3. These need not necessarily be arranged on the outer lateral end of the reflector 1, but may also be provided lying further inside.
- additional webs or outer side boundary sections may be arranged, as for example from the Vorveröttingungen WO 99/62138 A1 of the US 5,710,569 A or the EP 0 916 169 B1 is known.
- the illustrated antenna arrangement is usually set up so that the reflector 1 extends lying in a vertical plane, while the mentioned in the side region arranged webs 1 'also extend in the vertical direction.
- the linearly polarized radiator or the linearly polarized radiator arrangement could also be oriented differently, for example in such a way that the plane of polarization does not lie in a horizontal plane but deviates from it in another plane, for example in the vertical direction.
- the radiator arrangement would then be aligned rotated by 90 ° with the Abstrahlformungselement still to be explained below, so that the dipole radiator then parallel to the laterally provided webs 1 'extends.
- the radiator 5 is constructed essentially in a known manner and comprises two dipole halves 15, which is held in the form of a balancing 17 via a dipole support device.
- the radiator arrangement is arranged in a field 19 on the reflector 1, which is designed at least approximately square in plan view and has a circumferential ridge or a circumferential wall 21.
- a passive electrically conductive element 25 is now provided, which is also referred to below as a beam-shaping element 25.
- this beam-shaping element 25 is at least approximately divided into two sections, namely a support section 25a and a so-called active section 25b.
- the support portion 25a which is like the active portion 25b electrically conductive or provided with an electrically conductive surface or partially with an electrically conductive surface, also contributes to the overall effect, the effect is therefore not triggered alone on the so-called active portion 25b ,
- the support section 25a is preferably arranged directly electrically galvanically on the reflector 1 and connected to this electrically and preferably mechanically.
- the connection can also be capacitive, so that the support portion 25a and in particular its base 25c is capacitively coupled to the reflector 1.
- the mechanical and / or electrical-galvanic or electrically capacitive connection or coupling can but with the reflector 1 also indirectly take place by a corresponding connection via additional intermediate element or with the base of the balancing 17 is made.
- a conductive ring structure 29 is provided on the reflector 1 and at the base of the symmetrization 17 on which the foot portion of the support portion 25a is mechanically and electrically connected (or in the case of capacitive coupling capacitively coupled here with the interposition of an insulator or dielectric is).
- the so-called active section 25b adjoins the upper end of the support section 25a at a so-called transition region or transition point 25d, which preferably lies in a working plane WE.
- This active plane WE is preferably aligned parallel to the plane of the reflector 1, i. are arranged at least parallel to that reflector portion in the region of the radiator or the radiator-forming element.
- the active section 25b or its essential or predominant parts need not necessarily be aligned exactly parallel to the respective reflector section or reflector 1. Deviations from the relevant section of the reflector of preferably less than ⁇ 20 °, in particular less than ⁇ 10 ° still lead to the desired effects.
- the length of the support section from the lower foot 25c to the level of the active plane ie in particular to the transition region 25d longer than the distance between the reflector plane RE and the active plane WE.
- the support portion 25a should be greater than the distance of the active plane WE to the reflector plane RE at least in the area
- the length of the carrier should preferably not exceed twice the wavelength (2 ⁇ ) of the associated operating center wavelength of the emitter array 5, this wavelength being at the lower or upper end of the frequency band to be considered, preferably corresponding to the wavelength lying in the middle frequency band.
- the length of the effective section 25b in the direction of the active plane WE should preferably correspond to 0.2 ⁇ to and including ⁇ 1.0 ⁇ , based on the operating wavelength (in particular the mean operating wavelength of a frequency band to be transmitted).
- the plane of action itself may be both below, above and at the level of the active radiating element, i. the dipole halves 15 are.
- the active plane (in particular in the region of the effective section 25b) should be at a distance of preferably 0.2 ⁇ to 1.5 ⁇ inclusive, where ⁇ again corresponds to the wavelength of the frequency band to be transmitted, preferably the central wavelength of the frequency band to be transmitted.
- the active section 25b is arranged co-polar, that is to say it is aligned in the direction of the plane of polarization.
- the polarization plane PE remains perpendicular to the reflector 1, with the dipole halves 15 lying in this plane of polarization PE and .alpha there in the preferred embodiment ultimately also the support portion 25a and the effective portion 25b of the beam-shaping elements 25 come to rest.
- two beam-shaping elements 25 are provided for the only dipole radiator provided, which extend symmetrically to a plane perpendicular to the reflector 1 and perpendicular to the polarization plane PE and through the center of the radiator arrangement 5.
- radiator assembly 5 which in this embodiment, however, consists of two individual dipole radiators 5a and 5b, which are designed in the manner of a dipole cross.
- the two dipole radiators oriented perpendicular to one another are preferably arranged rotated at an angle of + 45 ° with respect to the horizontal or vertical plane, so that this radiator arrangement comprises two polarization planes PE that are perpendicular to each other in + 45 ° and -45 °.
- one beam-shaping element 25 is now provided for each dipole half, i. two beam shaping elements according to the invention for each polarization plane PE.
- the associated support sections 25a are preferably each again in one of the respective polarization planes of the associated dipole arrangement.
- the at the top At the end of the respective support section 25a subsequent active section 25b is aligned to the plane of polarization, in which the associated support section 25a is arranged to extend in a plane perpendicular to polarization, ie aligned parallel to the other polarization plane.
- the length and size ratios are comparable to the embodiment of Figure 1 and 2.
- the arrangement may also be such that the support portion 25a is not necessarily in each associated polarization plane PE, but between its base and its transition region to the associated active portion 25b and from this Level out or is arranged at an angle at right angles to the polarization plane. Deviations of less than ⁇ 20 °, in particular less than ⁇ 10 ° are possible.
- the effective portions 25b each extend parallel to an associated polarization plane PE (with lateral distance to the polarization plane of the associated radiator), whereby deviations of less than ⁇ 20 °, in particular less than ⁇ 10 ° with respect to the polarization plane are possible , Deviations of the active plane WE or the orientation of the active sections 25b in relation to the same may also occur in the same area Move reflector plane, so this deviation is less than ⁇ 20 °, in particular ⁇ 10 °, should be.
- FIG. 4 differs from that according to FIG. 3 in that a square compact radiator is used as the cross-shaped polarized radiator arrangement 5.
- This is a radiator arrangement, as in principle from the DE 198 60 121 A1 is known.
- the outer corners of the conductive structure can be open (as in the DE 198 60 121 A1 has been described) or by means of an insulator or dielectric or electrically closed. Reference is here made to known solutions. Also in this case the polarization planes are oriented at an angle of + 45 ° and -45 °, respectively, with respect to a horizontal or vertical.
- the electrically cross-shaped dipole radiator structure according to FIG. 4 is a radiator arrangement, which is sometimes referred to as a vector radiator or a cross-vector radiator or radiator arrangement.
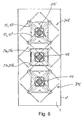
- a dual-band antenna array in particular for a stationary mobile radio antenna, may comprise a conventional radiator arrangement with radiators 115 for a higher frequency band and radiator arrangements 215 for transmission in a lower frequency band.
- the radiator arrangement 215 for transmission in the lower frequency band consists in each case of two pairs of dipoles 215 'and 215 "arranged parallel to one another and arranged in such a way that a dipole square is formed Emitter provided in the higher frequency band whose dipole radiator elements lie on a plane closer to the reflector plane RE than the dipole elements 215 'and 215 "of the radiator elements radiating in the higher frequency band
- the radiator arrangement 215 is provided for transmission and / or reception in the lower frequency band (this may preferably be a frequency band, which is operated, for example, at half the frequency with respect to the frequency in the higher frequency band, but a limitation on this is not absolutely necessary.)
- Both the internal radiators 115 and the external radiators 215 are so arranged and aligned so that both radiator types radiate in two mutually perpendicular planes of polarization, which are aligned in the embodiment shown at an angle of + 45 ° and -45 ° relative to a horizontal or vertical plane.
- an additional radiator arrangement 115 is then arranged between the centers of the two radiator arrangements 215 on the reflector 1 (in particular when transmitting in a frequency band twice as high as the low frequency band, the beam sequence and thus the radiator spacing are between the radiators for the higher frequency band only half as large as for the lower frequency band). If, for the central emitter array 115, that is to say for the emitter array 115 respectively situated between two emitter array 215 provided for the low frequency range, those beam shaping elements 25 are used, as described in the exemplary embodiment according to FIG. 4, a structure results according to the example according to FIG. 5.
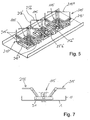
- the beam-shaping elements 25 are shaped with the respective support section 25a and the adjoining effective section 25b in this exemplary embodiment in such a way that the respective support section 25a has a part of the support or the symmetrization 17 corresponding dipole arrangement for radiating in the lower frequency band radiator assembly 115 and then the support portion 25a subsequent effective portion 25b of a respective associated dipole half 215 'of an adjacent radiator assembly 215, that is preferably aligned parallel thereto.
- the support portion 25'a substantially in the same length, the same orientation and slope parallel to the one part of the support portion or the symmetrization 17 'and the further support portion 25 "a in corresponding, in plan view offset by 90 ° orientation and otherwise the same pitch and similar or comparable length as the associated part of the support section or the symmetrization 17 "of the radiator 215 arranged and positioned, ie also at the same distance from the vertical side edge 1 'of the reflector 1 or in the same side distance from one of the middle perpendicular to the reflector plane extending vertical plane etc.
- the effective portions 25b are arranged in a plane of action WE parallel to the reflector, in which also come the dipole elements 215 'provided for the lower frequency band dipole radiator 215 to lie.
- the length of the effective portions 25b corresponds approximately to the length of the respective dipole half for the lower frequency band or deviates by less than 40%, in particular less than 30%, less than 20% or even less than 10% thereof.
- the arrangement of the effective sections in Relation to the reflector comparable to the arrangement of the dipole halves of the adjacent radiators for transmission in the low frequency band.
- the effective sections are arranged above the reflector so that, for example, the dipole half 215 "starts and ends at approximately the same distance from the adjacent side boundary in 1 'of the reflector, in which also the corresponding parallel dipole half 215" of the radiator element for the higher frequency band also starts or ends.
- the same relative position in the transverse direction of the reflector is arranged correspondingly for the respective second active section 25b 'perpendicular thereto, like the parallel dipole half 215' of an adjacent radiator for the lower frequency band.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Aerials With Secondary Devices (AREA)
- Variable-Direction Aerials And Aerial Arrays (AREA)
- Input Circuits Of Receivers And Coupling Of Receivers And Audio Equipment (AREA)
- Details Of Aerials (AREA)
Claims (14)
- Antenne présentant les éléments suivants :- un réflecteur (1),- un agencement de rayonnement qui comprend au moins un élément rayonneur (115, 215) pour un fonctionnement dans deux plans de polarisation (PE),- au moins quatre éléments passifs électriquement conducteurs qui sont connectés au moins indirectement au réflecteur (1) par voie électrique-galvanique ou qui y sont couplés par voie électrique-capacitive,caractérisée par les autres éléments suivants :- les éléments passifs électriquement conducteurs sont constitués par des éléments de formation de rayon (25),- lesdits au moins quatre éléments de formation de rayon prévus (25) sont classés en au moins deux tronçons que sont un tronçon de support (25a) et un tronçon d'action (25b) qui se raccorde au tronçon de support (25a) au niveau de sa zone plus éloignée du réflecteur (1),- le tronçon d'action (25b) se trouve dans un plan d'action (WE) qui, au moins dans la zone de l'élément de formation de rayon (25) et/ou de l'élément rayonneur à influencer par celui-ci (15, 115, 215), s'étend parallèlement au réflecteur (1) ou s'en écarte de moins de ± 20°,- la longueur du tronçon d'action (25b) est de 0,2 λ, à 1,0 λ,- le tronçon d'action (25b) ou le plan d'action (WE) dans la zone du tronçon d'action (25b) présente une distance vis-à-vis du réflecteur, qui est supérieure ou égale à 0,2 λ et inférieure ou égale à 1,5 λ,- la longueur du tronçon de support (25a) est inférieure au double de la longueur d'onde 2 λ, lambda (λ) étant une longueur d'onde de la bande de fréquence à transmettre,- le tronçon d'action (25b) est orienté parallèlement au plan de polarisation associé (PE) de l'élément rayonneur (115, 215) à influencer par celui-ci ou s'en écarte de moins de ± 20°,- la longueur du tronçon de support (25a) est supérieure à la distance du tronçon d'action (25b) vis-à-vis du réflecteur (1), et- lesdits au moins quatre tronçons de support prévus (25a) munis des tronçons d'action associés (25b) sont ainsi agencés que deux tronçons de support respectifs (25a) divergent à partir du plan du réflecteur (1) en direction du plan d'action (WE), et les tronçons d'action (25b) qui se raccordent à l'extrémité supérieure des tronçons de support (25a) convergent en se retrouvant dans un plan d'action commun (WE).
- Antenne selon la revendication 1, caractérisée en ce que l'épaisseur de matériau ou la dimension en section transversale du tronçon de support (25a) et/ou du tronçon d'action (25b) est inférieure à 0,1 λ, lambda étant la longueur d'onde de la bande de fréquence à transmettre.
- Antenne selon la revendication 1 ou 2, caractérisée en ce que le tronçon de support (25a) se trouve au moins sensiblement dans un plan de polarisation (PE) de l'agencement de rayonnement.
- Antenne selon l'une des revendications 1 à 3, caractérisée en ce que le point de base (25c) du tronçon de support (25a) ainsi que sa zone de transition ou son point de transition (25d) éloigné(e) du réflecteur (1) et à laquelle/auquel commence le tronçon d'action (25b) se trouvent au moins approximativement dans un plan de polarisation (PE) de l'élément rayonneur (15, 115, 215).
- Antenne selon l'une des revendications 1 à 4, caractérisée en ce qu'il est prévu au moins deux éléments de formation de rayon (25) par polarisation.
- Antenne selon l'une des revendications 1 à 5, caractérisée en ce qu'au moins un tronçon d'action (25b) s'étend parallèlement à l'un des deux plans de polarisation (PE) perpendiculaires l'un à l'autre, et au moins un autre tronçon d'action (25b) s'étend parallèlement à l'autre plan de polarisation (PE).
- Antenne selon l'une des revendications 1 à 6, caractérisée en ce que le tronçon de support (25a) appartenant à un élément de formation de rayon (25) est parallèle à l'un des deux plans de polarisation (PE) perpendiculaires l'un à l'autre, et en ce que le tronçon d'action (25b) retenu par ce tronçon de support (25a) s'étend parallèlement à l'autre plan de polarisation (PE) perpendiculaire à celui-ci.
- Antenne selon l'une des revendications 1 à 7, caractérisée en ce que le tronçon d'action (25b) est orienté à angle droit ou au moins approximativement à angle droit par rapport au tronçon de support (25a) qui le porte.
- Antenne selon l'une des revendications 1 à 8, caractérisée en ce qu'en vue de dessus sur une antenne à bande double ou à bandes multiples, des parties au moins des tronçons d'action (25b) sont agencées de manière à se trouver au moins approximativement à la même distance latérale de la délimitation latérale (1') du réflecteur (1) que les moitiés de dipôle parallèles associées (215', 215") d'éléments rayonneurs voisins (215) destinés à la transmission dans une bande de fréquence plus basse.
- Antenne selon l'une des revendications 1 à 9, caractérisée en ce que les tronçons d'action (25b, 25b', 25b") sont agencés parallèlement aux moitiés de dipôle (215', 215") d'éléments rayonneurs voisins (215) qui sont prévus pour la transmission dans une bande de fréquence plus basse.
- Antenne selon la revendication 9 ou 10, caractérisée en ce que les tronçons d'action (25b) se trouvent dans un plan d'action (WE) qui correspond au plan de rayonnement des éléments rayonneurs (215) qui rayonnent dans une bande de fréquence plus basse.
- Antenne selon l'une des revendications 1 à 11, caractérisée en ce que le tronçon d'action (25b) est orienté de façon copolaire par rapport à l'élément rayonneur respectif (215) à influencer.
- Antenne selon l'une des revendications 1 à 12, caractérisée en ce que l'antenne est une antenne stationnaire de radiotéléphonie mobile.
- Antenne selon l'une des revendications 1 à 13, caractérisée en ce que les tronçons de support (25'a, 25"a) et/ou les tronçons d'action (25b, 25b', 25b") sont agencés à la même distance d'un plan vertical qui s'étend au centre par rapport au réflecteur (1) et perpendiculairement au plan de réflecteur.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102004025904A DE102004025904B4 (de) | 2004-05-27 | 2004-05-27 | Antenne |
| PCT/EP2005/005456 WO2005119835A1 (fr) | 2004-05-27 | 2005-05-19 | Antenne de radiotelephonie mobile a element de formation de faisceau |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1749331A1 EP1749331A1 (fr) | 2007-02-07 |
| EP1749331B1 true EP1749331B1 (fr) | 2008-01-30 |
Family
ID=34969022
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP05745719A Not-in-force EP1749331B1 (fr) | 2004-05-27 | 2005-05-19 | Antenne de radiotelephonie mobile a element de formation de faisceau |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7075498B2 (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP1749331B1 (fr) |
| CN (1) | CN1702913B (fr) |
| AT (1) | ATE385348T1 (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE102004025904B4 (fr) |
| ES (1) | ES2300022T3 (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO2005119835A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7868843B2 (en) * | 2004-08-31 | 2011-01-11 | Fractus, S.A. | Slim multi-band antenna array for cellular base stations |
| US7701409B2 (en) | 2005-06-29 | 2010-04-20 | Cushcraft Corporation | System and method for providing antenna radiation pattern control |
| US7180469B2 (en) * | 2005-06-29 | 2007-02-20 | Cushcraft Corporation | System and method for providing antenna radiation pattern control |
| TWM284087U (en) * | 2005-08-26 | 2005-12-21 | Aonvision Technology Corp | Broadband planar dipole antenna |
| WO2007042938A2 (fr) * | 2005-10-14 | 2007-04-19 | Fractus, Sa | Batterie d'antennes minces triple bande pour stations de base cellulaires |
| KR100883408B1 (ko) * | 2006-09-11 | 2009-03-03 | 주식회사 케이엠더블유 | 이동통신 기지국용 이중대역 이중편파 안테나 |
| CN101425626B (zh) * | 2007-10-30 | 2013-10-16 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | 宽频带环状双极化辐射单元及线阵天线 |
| EP2073309B1 (fr) * | 2007-12-21 | 2015-02-25 | Alcatel Lucent | Élément de rayonnement à double polarisation pour antennes de station de base cellulaire |
| EP2346114B1 (fr) * | 2008-09-22 | 2016-01-27 | KMW Inc. | Antenne bifréquence à double polarisation pour station de base de communication mobile |
| CN101964447B (zh) * | 2010-10-14 | 2013-01-16 | 西北工业大学 | 垂直极化宽带偶极子天线 |
| CN102299398B (zh) * | 2011-05-20 | 2013-12-25 | 广东通宇通讯股份有限公司 | 一种双频双极化天线 |
| WO2013140408A1 (fr) * | 2012-03-19 | 2013-09-26 | Galtronics Corporation Ltd. | Antenne à entrées multiples et sorties multiples et élément rayonnant dipôle à large bande de ladite antenne |
| WO2014174510A1 (fr) * | 2013-04-22 | 2014-10-30 | Galtronics Corporation Ltd. | Antenne multibandes et plan de sol à fentes destiné à cette dernière |
| KR101574495B1 (ko) * | 2013-08-13 | 2015-12-04 | 주식회사 에이스테크놀로지 | 광대역 기지국 안테나 방사체 |
| CN203813033U (zh) * | 2013-12-23 | 2014-09-03 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种多频阵列天线 |
| CN104600439B (zh) * | 2014-12-31 | 2018-03-13 | 广东通宇通讯股份有限公司 | 多频双极化天线 |
| US11611143B2 (en) | 2020-03-24 | 2023-03-21 | Commscope Technologies Llc | Base station antenna with high performance active antenna system (AAS) integrated therein |
| MX2022011871A (es) | 2020-03-24 | 2022-12-06 | Commscope Technologies Llc | Antenas de estación base con un módulo de antena activa y dispositivos y métodos relacionados. |
| AU2021242222A1 (en) * | 2020-03-24 | 2022-11-17 | Outdoor Wireless Networks LLC | Radiating elements having angled feed stalks and base station antennas including same |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB982155A (en) * | 1962-08-21 | 1965-02-03 | Marconi Co Ltd | Improvements in or relating to aerial systems |
| KR0185962B1 (ko) * | 1995-03-03 | 1999-05-15 | 구관영 | 안테나 측면 복사에너지를 최소화한 안테나 |
| US5629713A (en) * | 1995-05-17 | 1997-05-13 | Allen Telecom Group, Inc. | Horizontally polarized antenna array having extended E-plane beam width and method for accomplishing beam width extension |
| DE19627015C2 (de) * | 1996-07-04 | 2000-07-13 | Kathrein Werke Kg | Antennenfeld |
| SE508537C2 (sv) | 1997-02-14 | 1998-10-12 | Ericsson Telefon Ab L M | Dubbelpolariserad antenn för mottagning och sändning av elektromagnetiska signaler |
| DE19722742C2 (de) | 1997-05-30 | 2002-07-18 | Kathrein Werke Kg | Dualpolarisierte Antennenanordnung |
| FR2766626B1 (fr) | 1997-07-28 | 1999-10-01 | Alsthom Cge Alcatel | Systeme d'antennes directionnelles a polarisation croisee |
| DE19823750A1 (de) * | 1998-05-27 | 1999-12-09 | Kathrein Werke Kg | Antennenarray mit mehreren vertikal übereinander angeordneten Primärstrahler-Modulen |
| DE19823749C2 (de) | 1998-05-27 | 2002-07-11 | Kathrein Werke Kg | Dualpolarisierte Mehrbereichsantenne |
| DE19860121A1 (de) * | 1998-12-23 | 2000-07-13 | Kathrein Werke Kg | Dualpolarisierter Dipolstrahler |
| DE19931907C2 (de) | 1999-07-08 | 2001-08-09 | Kathrein Werke Kg | Antenne |
| EP1334537B1 (fr) * | 2000-11-17 | 2007-03-21 | EMS Technologies, Inc. | Carte d'isolement de radiofrequences |
| DE10064129B4 (de) * | 2000-12-21 | 2006-04-20 | Kathrein-Werke Kg | Antenne, insbesondere Mobilfunkantenne |
-
2004
- 2004-05-27 DE DE102004025904A patent/DE102004025904B4/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-08-19 US US10/921,292 patent/US7075498B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-09-07 CN CN200410076812.0A patent/CN1702913B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2005
- 2005-05-19 WO PCT/EP2005/005456 patent/WO2005119835A1/fr active IP Right Grant
- 2005-05-19 EP EP05745719A patent/EP1749331B1/fr not_active Not-in-force
- 2005-05-19 ES ES05745719T patent/ES2300022T3/es active Active
- 2005-05-19 AT AT05745719T patent/ATE385348T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2005-05-19 DE DE502005002729T patent/DE502005002729D1/de active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN1702913A (zh) | 2005-11-30 |
| CN1702913B (zh) | 2010-12-01 |
| ES2300022T3 (es) | 2008-06-01 |
| US20050264463A1 (en) | 2005-12-01 |
| ATE385348T1 (de) | 2008-02-15 |
| DE102004025904A1 (de) | 2005-12-22 |
| DE102004025904B4 (de) | 2007-04-05 |
| DE502005002729D1 (de) | 2008-03-20 |
| EP1749331A1 (fr) | 2007-02-07 |
| US7075498B2 (en) | 2006-07-11 |
| WO2005119835A1 (fr) | 2005-12-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1749331B1 (fr) | Antenne de radiotelephonie mobile a element de formation de faisceau | |
| EP1470615B1 (fr) | Ensemble antenne rayonnante a double polarisation | |
| DE10064129B4 (de) | Antenne, insbesondere Mobilfunkantenne | |
| EP0848862B1 (fr) | Reseau d'antennes | |
| EP2929589B1 (fr) | Antenne omnidirectionnelle à double polarité | |
| DE69901026T2 (de) | Doppelbandantenne | |
| EP0916169B1 (fr) | Systeme d'antenne | |
| DE19829714B4 (de) | Antenne mit dualer Polarisation | |
| EP3025395B1 (fr) | Réseau d'antennes à large bande | |
| WO2006058658A1 (fr) | Antenne radio mobile a double bande | |
| DE10012809A1 (de) | Dualpolarisierte Dipolantenne | |
| EP3306742A1 (fr) | Antenne radio mobile | |
| EP1964205A1 (fr) | Antenne a double polarisation avec maillons longitudinaux ou transversaux | |
| DE102007060083A1 (de) | Mehrspalten-Multiband-Antennen-Array | |
| WO2016050336A1 (fr) | Système d'émetteur multi-bandes | |
| EP1525642B1 (fr) | Reseau d'antennes bidimensionnel | |
| EP3756235A1 (fr) | Dispositif d'antennes à multiples bandes pour des applications de communications mobiles | |
| DE202004008770U1 (de) | Dualpolarisierte Antenne | |
| EP1056155A2 (fr) | Antenne pour mobile en particulier pour véhicule comprenant au moins une polarisation circulaire et une polarisation linéaire, de préférence verticale | |
| DE202004013971U1 (de) | Antenne, insbesondere Mobilfunkantenne |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20060921 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20070221 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20080130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 502005002729 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20080320 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2300022 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080530 |
|
| NLV1 | Nl: lapsed or annulled due to failure to fulfill the requirements of art. 29p and 29m of the patents act | ||
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080630 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FD4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: KATHREIN-WERKE K.G. Effective date: 20080531 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080531 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20081031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080430 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080519 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090531 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080519 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080731 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080501 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20160523 Year of fee payment: 12 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20160523 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20170522 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20170522 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20170519 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170519 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20180703 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 502005002729 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: FLACH BAUER STAHL PATENTANWAELTE PARTNERSCHAFT, DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170520 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 502005002729 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 502005002729 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: FLACH BAUER STAHL PATENTANWAELTE PARTNERSCHAFT, DE Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 502005002729 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: KATHREIN SE, DE Free format text: FORMER OWNER: KATHREIN-WERKE KG, 83022 ROSENHEIM, DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180531 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20181201 |