EP1636485B1 - Injector for fuel injection systems of internal combustion engines, especially direct injection diesel engines - Google Patents
Injector for fuel injection systems of internal combustion engines, especially direct injection diesel engines Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1636485B1 EP1636485B1 EP04726421A EP04726421A EP1636485B1 EP 1636485 B1 EP1636485 B1 EP 1636485B1 EP 04726421 A EP04726421 A EP 04726421A EP 04726421 A EP04726421 A EP 04726421A EP 1636485 B1 EP1636485 B1 EP 1636485B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- nozzle
- nozzle needle
- intensifier piston
- injector
- space
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 title claims description 26
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 title claims description 12
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 title claims description 12
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 title claims description 4
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02M—SUPPLYING COMBUSTION ENGINES IN GENERAL WITH COMBUSTIBLE MIXTURES OR CONSTITUENTS THEREOF
- F02M51/00—Fuel-injection apparatus characterised by being operated electrically
- F02M51/06—Injectors peculiar thereto with means directly operating the valve needle
- F02M51/0603—Injectors peculiar thereto with means directly operating the valve needle using piezoelectric or magnetostrictive operating means
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02M—SUPPLYING COMBUSTION ENGINES IN GENERAL WITH COMBUSTIBLE MIXTURES OR CONSTITUENTS THEREOF
- F02M2200/00—Details of fuel-injection apparatus, not otherwise provided for
- F02M2200/21—Fuel-injection apparatus with piezoelectric or magnetostrictive elements
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02M—SUPPLYING COMBUSTION ENGINES IN GENERAL WITH COMBUSTIBLE MIXTURES OR CONSTITUENTS THEREOF
- F02M2200/00—Details of fuel-injection apparatus, not otherwise provided for
- F02M2200/70—Linkage between actuator and actuated element, e.g. between piezoelectric actuator and needle valve or pump plunger
- F02M2200/703—Linkage between actuator and actuated element, e.g. between piezoelectric actuator and needle valve or pump plunger hydraulic
- F02M2200/704—Linkage between actuator and actuated element, e.g. between piezoelectric actuator and needle valve or pump plunger hydraulic with actuator and actuated element moving in different directions, e.g. in opposite directions
Definitions
- the invention relates to an injector according to the preamble of claim 1.
- An injector for fuel injection systems with a directly controlled nozzle needle and with a pulling actuator for opening the nozzle needle is made EP 1174 615 A2 known.
- the nozzle needle is designed with a nozzle needle piston, which is guided in a sleeve-shaped booster piston.
- the sleeve-shaped booster piston includes a control chamber to which the nozzle needle piston is exposed.
- To open the nozzle needle of the booster piston performs a pulling movement, so that increases the volume of the control chamber, whereby the force acting in the opening direction of the nozzle needle opening force exceeds the force acting in the control chamber on the nozzle needle piston closing force. This lifts the nozzle needle off the nozzle needle seat and injects fuel.
- the injector has a nozzle needle piston with two piston sections, wherein one piston section is exposed to the high pressure of the fuel supply line and the other piston section is separated from the high pressure hydraulic chamber as a control chamber. On the separated from the high pressure control chamber and the associated with the piezoelectric actuator booster piston acts. If the pressure is increased by actuating the piezo actuator and the booster piston in the control chamber, this acts on the opening direction acting piston surface of the nozzle needle piston and the nozzle needle is lifted from the nozzle needle seat, so that fuel is injected.
- An injector for fuel injection systems with a directly controlled nozzle needle and with a pushing actuator for opening the nozzle needle is still off DE 43 060 73 C1 known.
- the nozzle needle is surrounded by a nozzle needle pressure chamber which is connected to a fuel supply.
- a translation device with a booster piston and a nozzle needle piston is arranged in a piston-in-piston system.
- the nozzle needle piston here also has a piston surface which acts in the opening direction of the nozzle needle and is exposed to the hydraulic chamber. If the pressure is increased by actuating the actuator and the booster piston in the hydraulic chamber, this acts on the piston surface of the nozzle needle piston acting in the opening direction and the nozzle needle is lifted off the nozzle needle seat, so that fuel is injected.
- Another injector with a directly controlled nozzle needle is also off DE 195 19 191 C2 known.
- the subject matter of this document sitting piezoelectric actuator and booster piston at the upper end of the injector body and the power transmission to the arranged at the lower end of the injector nozzle needle via a long plunger.
- the plunger is in hydraulic communication with the fuel inlet.
- Piezo actuator and booster piston are separated from the fuel inlet.
- An incorporated into the injector pressure channel leads to the nozzle exit.
- an annular space surrounding the plunger in the lower region is provided, from which a fuel return duct emerges.
- the fuel return passage is hydraulically connected to an interior of the booster piston extending above the ram.
- a trained under the booster piston control chamber is fed by the fuel inlet via a plunger surrounding the injector body leakage gap.
- JP 11 200 981 A known injector for fuel injection systems with a directly controlled nozzle needle booster piston and nozzle needle are arranged spatially separated from each other.
- a significant advantage of the invention lies in the direct control of the nozzle needle by the piezoelectric actuator.
- the speed of the nozzle needle movement can be adjusted via the voltage curve of the piezo actuator.
- For a dosage of particularly small pre-injection amounts and a partial stroke can be specified.
- Another advantage of the injector according to the invention is also to be seen in the fact that this manages without a fuel return.
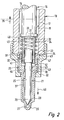
- the recess 11 denotes a cylindrical injector body with a continuous, on the predominant part of its longitudinal extent cylindrical recess 11. At its upper end, the recess 11 first has a conically tapered portion 12, which in a right angle bent, finally outwardly opening section 13, the fourteenth passes.
- a likewise cylindrical piezoactuator 16 of relatively large longitudinal extension is arranged, whose diameter is smaller than the inner diameter of the recess section 15. This results in an annular space 17 between the outer wall of the piezoactuator 16 and the inner wall of the injector body 10
- the conical section 12 of the axial recess 11 is used for one.
- fluid-permeable spacers can be provided in the annular space 17 at certain axial distances as required (not shown).
- the upper, angled portion 13, 14 of the recess 11 acts as a cable bushing for the power supply of the piezoelectric actuator 16th
- a fuel supply 18 e.g. High-pressure connection of a common rail system, provided, which is connected via a pressure channel 19 with the annular space 17 in hydraulic communication.
- a nozzle body 20 connects, which receives a nozzle needle 21.
- the nozzle body 20 is attached by means of a union nut (clamping nut) 22 on the injector body 10, such that it comes with a rear end face 23 sealingly abutting a lower end face 24 of the injector body 10.
- the nozzle body 20 has an upwardly open, multi-stepped interior 25, which forms a bottom opening into two nozzle outlet holes 26, 27 conical valve seat 28.
- the valve seat 28 cooperates with a conical end section 29 of the nozzle needle 21 functioning as a closing body.
- the nozzle needle 21 has a portion 30 of larger diameter, which is fitted into a cylindrical interior 31 of a sleeve-shaped, downwardly open booster piston 32.
- the upper end of the booster piston .32 forms a collar 33.
- a in the annular space 17 - in this case the booster piston 32 surrounding - arranged on the one hand on the end face 23 of the nozzle body 20, on the other hand on the collar 33 of the booster piston 32 supporting the compression coil spring 34 holds the booster piston 32nd with the piezoelectric actuator 16 at the front in contact.
- a nozzle needle 21 concentrically surrounding cylindrical pressure chamber 37 is formed, which via holes 38, 39 in the nozzle body 20 and between the nozzle body 20 and the clamping nut 22 formed annular space 40 is hydraulically connected to the annular space 17 of the injector body 10.
- the interior 25 of the nozzle body 20 at the top has a stepped diameter extension 41, in which the booster piston 32 is guided so that a in the extended interior part 41st formed below the booster piston 32 control chamber 42 via a leakage gap 43 (see in particular Fig. 2 ) is in hydraulic communication with the annular space 17 of the injector body 10.
- a section 44 of the nozzle body interior 25 with a comparatively small diameter serves to guide the nozzle needle 21 within the nozzle body 20.
- this section 44 is designed so that a leakage gap 45th (see, in particular Fig. 2 ).
- the control chamber 42 is thus hydraulically connected via the second leakage gap 45 with the cylindrical space 37, which in turn - via the recesses 38 to 40 - from the annular space 17 of the injector 10 is pressurized high.
- a special feature is further that the above the nozzle needle 21 extending interior 31 of the booster piston 32 is also hydraulically connected to the high pressure-loaded annular space 17 of the injector body 10, via a lateral bore 46 in the booster piston 32nd
- a (second) helical compression spring 48 is arranged, which exerts on the nozzle needle 21 in the closing direction (arrow 49) directed force.
- the (second) compression spring 48 so the nozzle needle 21 is kept closed during the pauses between the injections and at rest of the vehicle.
- Fig. 1 and 2 the closed position of the nozzle needle 21 is shown. In the open position, however, the injection process takes place, whereby from the cylindrical pressure chamber 37 fuel passes through the outlet holes 26, 27 in the (not shown) cylinder combustion chamber of the internal combustion engine.
- the trained at the lower end of the booster piston 32 control chamber 42 is used for hydraulic length compensation and as a hydraulic translator for the expansion movement of the piezoelectric actuator 16th
- the injector described above operates as follows. During the pauses between the individual injection processes, the piezoelectric actuator 16 is de-energized. Now, if the piezoelectric actuator 16 is electrically driven, it expands and moves the booster piston 32 against the force of the two compression springs 34, 48 down (in the direction of arrow 49). In this case, the volume of the control chamber 42 is reduced, and the pressure in the control chamber 42 increases. As a result, an opening force (in the direction of arrow 35) is exerted on the nozzle needle 21. As soon as the opening force exceeds the closing pressure forces and the force of the compression spring 48, the nozzle opens by the nozzle needle 21 assumes the (upper) position shown in the drawing and thus the outlet holes 26, 27 releases. By translating by means of the booster piston 32, the nozzle needle 21 can perform a maximum stroke, which is significantly greater than the expansion stroke of the electrically controlled piezoelectric actuator 16th
- the longest possible activation duration is determined by the leakage (43, 45, 47) from the control chamber 42.
- the nozzle needle 21 moves downward (in the direction of arrow 49) until it closes the outlet bores 26, 27 with the lateral surface of its conical tip 29.
- the electrical control of the piezoelectric actuator 16 is interrupted.
- the piezoelectric actuator 16 then contracts, and the pressure in the control chamber 42 drops below the rail pressure.
- the nozzle needle 21 undergoes the necessary closing forces and closes.
- the compression spring 34 prevents this, that the piezoelectric actuator 16 separates from the booster piston 32. Piezo actuator 16 and booster piston 32 thus remain constantly in the (off Fig. 1 and 2 apparent) non-positive abutment position to each other.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Fuel-Injection Apparatus (AREA)
Description
Die Erfindung bezieht sich auf einen Injektor nach dem Oberbegriff des Anspruchs 1.The invention relates to an injector according to the preamble of claim 1.
Ein Injektor für Kraftstoff-Einspritzsysteme mit einer direkt angesteuerten Düsennadel und mit einem ziehenden Aktor zum Öffnen der Düsennadel gemäß den Merkmalen des Oberbegriffs des Anspruchs 1 ist aus
Ein weiterer Injektor für Kraftstoff-Einspritzsysteme mit einer direkt angesteuerten Düsennadel und mit einem drückenden Aktor zum Öffnen der Düsennadel ist aus
Ein Injektor für Kraftstoff-Einspritzsysteme mit einer direkt angesteuerten Düsennadel und mit einem drückenden Aktor zum Öffnen der Düsennadel ist weiterhin aus
Ein weiterer Injektor mit einer direkt angesteuerten Düsennadel ist auch aus
Bei einem aus
Ausgehend von dem im Vorstehenden geschilderten Stand der Technik ist es Aufgabe der vorliegenden Erfindung, einen auch für Common-Rail-Systeme geeigneten Injektor zu schaffen, der vergleichsweise einfach im Aufbau ist, mit einem Minimum an Einzelteilen auskommt und effizient arbeitet.Based on the above-described prior art, it is an object of the present invention to provide a suitable also for common rail systems injector, which is relatively simple in construction, manages with a minimum of individual parts and works efficiently.
Erfindungsgemäß wird die Aufgabe bei einem Injektor der eingangs bezeichneten Art durch die Merkmale des Anspruchs 1 gelöst.According to the invention the object is achieved in an injector of the type described by the features of claim 1.
Vorteilhafte Ausgestaltungen des Grundgedankens der Erfindung enthalten die Ansprüche 2 - 4.Advantageous embodiments of the basic concept of the invention include claims 2-4.
Ein wesentlicher Vorteil der Erfindung liegt in der direkten Steuerung der Düsennadel durch den Piezoaktor. Die Geschwindigkeit der Düsennadelbewegung kann über den Spannungsverlauf des Piezoaktors eingestellt werden. Für eine Dosierung von besonders kleinen Voreinspritzmengen kann auch ein Teilhub vorgegeben werden. Ein weiterer Vorteil des erfindungsgemäßen Injektors ist auch darin zu sehen, dass dieser ohne einen Kraftstoff-Rücklauf auskommt.A significant advantage of the invention lies in the direct control of the nozzle needle by the piezoelectric actuator. The speed of the nozzle needle movement can be adjusted via the voltage curve of the piezo actuator. For a dosage of particularly small pre-injection amounts and a partial stroke can be specified. Another advantage of the injector according to the invention is also to be seen in the fact that this manages without a fuel return.
Die Erfindung ist anhand eines Ausführungsbeispiels in der Zeichnung veranschaulicht und im Folgenden detailliert beschrieben. Es zeigt jeweils schematisch:
- Fig. 1
- eine Ausführungsform eines direktgesteuerten Common-Rail-Injektors mit Piezoaktor, im vertikalen Längsschnitt, und
- Fig. 2
- einen unteren Teilbereich des Injektors nach
Fig. 1 , in gegenüberFig. 1 vergrößerter Darstellung.
- Fig. 1
- an embodiment of a direct-controlled common rail injector with piezoelectric actuator, in vertical longitudinal section, and
- Fig. 2
- a lower portion of the injector after
Fig. 1 , in oppositeFig. 1 enlarged view.
Es bezeichnet 10 einen zylindrischen Injektorkörper mit einer durchgehenden, auf dem überwiegenden Teil ihrer Längserstreckung zylindrischen Ausnehmung 11. An ihrem oberen Ende besitzt die Ausnehmung 11 zunächst einen sich konisch verjüngenden Abschnitt 12, der in einen rechtwinklig abgebogenen, schließlich nach außen mündenden Abschnitt 13, 14 übergeht. In dem mit 15 bezifferten zylindrischen Abschnitt der Ausnehmung 11 ist ein ebenfalls zylindrischer Piezoaktor 16 vergleichsweise großer Längserstreckung angeordnet, dessen Durchmesser kleiner ist als der Innendurchmesser des Ausnehmungsabschnitts 15. Hierdurch ergibt sich zwischen der Außenwand des Piezoaktors 16 und der Innenwandung des Injektorkörpers 10 ein Ringraum 17. Zur hierzu erforderlichen Zentrierung des Piezoaktors 16 innerhalb des Injektorkörpers 10 dient zum einen der konische Abschnitt 12 der axialen Ausnehmung 11. Zum anderen können bei Bedarf in dem Ringraum 17 in bestimmten axialen Abständen voneinander fluiddurchlässige Distanzscheiben vorgesehen sein (nicht gezeigt).It denotes a cylindrical injector body with a continuous, on the predominant part of its longitudinal extent
Der obere, abgewinkelte Abschnitt 13, 14 der Ausnehmung 11 fungiert als Kabeldurchführung für die Stromversorgung des Piezoaktors 16.The upper,
Am oberen Ende des Injektorkörpers 10 ist eine Kraftstoffzuführung 18, z.B. Hochdruckanschluss eines Common-Rail-Systems, vorgesehen, die über einen Druckkanal 19 mit dem Ringraum 17 in hydraulischer Verbindung steht.At the upper end of the
An das untere Ende des Injektorkörpers 10 und koaxial zu diesem schließt sich ein Düsenkörper 20 an, der eine Düsennadel 21 aufnimmt. Der Düsenkörper 20 ist mittels einer Überwurfmutter (Spannmutter) 22 an dem Injektorkörper 10 befestigt, derart, dass er mit einer rückseitigen Stirnfläche 23 an einer unteren Stirnfläche 24 des Injektorkörpers 10 dichtend zur Anlage kommt.At the lower end of the
Zur Aufnahme der Düsennadel 21 besitzt der Düsenkörper 20 einen nach oben hin offenen, mehrfach abgestuften Innenraum 25, der unten einen in zwei Düsen-Austrittsbohrungen 26, 27 ausmündenden konischen Ventilsitz 28 bildet. Der Ventilsitz 28 wirkt mit einem als Schließkörper fungierenden konischen Endabschnitt 29 der Düsennadel 21 zusammen.To accommodate the
An ihrem oberen Ende besitzt die Düsennadel 21 einen Abschnitt 30 größeren Durchmessers, der in einen zylindrischen Innenraum 31 eines hülsenförmigen, nach unten offenen Übersetzerkolbens 32 eingepasst ist. Den oberen Abschluss des Übersetzerkolbens .32 bildet ein Bund 33. Eine in dem Ringraum 17 - hierbei den Übersetzerkolben 32 umschließend - angeordnete, sich einerseits an der Stirnfläche 23 des Düsenkörpers 20, andererseits am Bund 33 des Übersetzerkolbens 32 abstützende Schraubendruckfeder 34 hält den Übersetzerkolben 32 mit dem Piezoaktor 16 stirnseitig in Anlage. Durch den von der Druckfeder 34 über den Übersetzerkolben 32 auf den Piezoaktor 16 in Pfeilrichtung 35 wirkenden Druck wird der Piezoaktor 16 an seiner Oberseite 36 gegen den Injektorkörper 10 abgedichtet, und der elektrische Anschluss (nicht gezeigt) kann somit durch die abgewinkelten Bohrungen 13, 14 aus dem Injektorkörper 10 herausgeführt werden.At its upper end, the
Wie die Zeichnung des Weiteren zeigt, ist im unteren Teil des Düsenkörpers 20 - als Bestandteil des Düsenkörper-Innenraumes 25 - ein die Düsennadel 21 konzentrisch umgebender zylindrischer Druckraum 37 ausgebildet, der über Bohrungen 38, 39 im Düsenkörper 20 und einen zwischen dem Düsenkörper 20 und der Spannmutter 22 ausgebildeten Ringraum 40 mit dem Ringraum 17 des Injektorkörpers 10 hydraulisch verbunden ist.As the drawing further shows, in the lower part of the nozzle body 20 - as part of the nozzle body interior 25 - a
Eine weitere Besonderheit besteht darin, dass der Innenraum 25 des Düsenkörpers 20 oben eine abgestufte Durchmessererweiterung 41 aufweist, in der der Übersetzerkolben 32 so geführt ist, dass ein in dem erweiterten Innenraumteil 41 unterhalb des Übersetzerkolbens 32 ausgebildeter Steuerraum 42 über einen Leckspalt 43 (siehe insbesondere
Eine Besonderheit liegt des Weiteren darin, dass der sich oberhalb der Düsennadel 21 erstreckende Innenraum 31 des Übersetzerkolbens 32 ebenfalls mit dem hochdruckbeaufschlagten Ringraum 17 des Injektorkörpers 10 hydraulisch verbunden ist, und zwar über eine seitliche Bohrung 46 im Übersetzerkolben 32.A special feature is further that the above the
Der obere (verdickte) Abschnitt 30 der Düsennadel 21 ist nun so im Übersetzerkolben 32 geführt, dass sich ein (weiterer) Leckspalt 47 (siehe
Eine weitere Besonderheit besteht darin, dass in dem Innenraum 31 des Übersetzerkolbens 32 eine (zweite) Schraubendruckfeder 48 angeordnet ist, die auf die Düsennadel 21 eine in Schließrichtung (Pfeil 49) gerichtete Kraft ausübt. Durch die (zweite) Druckfeder 48 wird also die Düsennadel 21 während der Pausen zwischen den Einspritzvorgängen und bei stillstand des Fahrzeugs geschlossen gehalten. In
Der am unteren Ende des Übersetzerkolbens 32 ausgebildete Steuerraum 42 dient zum hydraulischen Längenausgleich und als hydraulischer Übersetzer für die Dehnungsbewegung des Piezoaktors 16.The trained at the lower end of the
Der Transport des Kraftstoffs vom Injektorkörper 10 bis zu den Düsenaustrittsbohrungen erfolgt über die (vergleichsweise kurze) Ausnehmung 38 (oder mehrere derartige Ausnehmungen) durch den Düsenkörper 20, die den Injektorkörper 10 mit dem Ringraum 40 zwischen Spannmutter 22 und Düsenkörper 20 verbindet. Von dem Ringraum 40 aus wird der Kraftstoff durch die weitere (vergleichsweise kurze) Bohrung 39 (oder mehrere derartige Bohrungen) zu den Düsen-Austrittsbohrungen 26, 27 geleitet.The transport of the fuel from the
Der im Vorstehenden beschriebene Injektor arbeitet wie folgt. Während der Pausen zwischen den einzelnen Einspritzvorgängen ist der Piezoaktor 16 unbestromt. Wird nun der Piezoaktor 16 elektrisch angesteuert, so dehnt er sich aus und bewegt den Übersetzerkolben 32 gegen die Kraft der beiden Druckfedern 34, 48 nach unten (in Pfeilrichtung 49). Hierbei wird das Volumen des Steuerraumes 42 verkleinert, und der Druck im Steuerraum 42 steigt. Dadurch wird auf die Düsennadel 21 eine öffnende Kraft (in Pfeilrichtung 35) ausgeübt. Sobald die öffnende Kraft die schließenden Druckkräfte und die Kraft der Druckfeder 48 übersteigt, öffnet die Düse, indem die Düsennadel 21 die aus der Zeichnung ersichtliche (obere) Stellung einnimmt und damit die Austrittsbohrungen 26, 27 freigibt. Durch die Wegübersetzung mittels des Übersetzerkolbens 32 kann die Düsennadel 21 einen maximalen Hub ausführen, der deutlich größer ist als der Dehnungshub des elektrisch angesteuerten Piezoaktors 16.The injector described above operates as follows. During the pauses between the individual injection processes, the
Sobald die Düsennadel 21 den Hubbereich der Sitzdrosselung verlassen hat (siehe
Die längstmögliche Ansteuerdauer wird durch die Leckage (43, 45, 47) aus dem Steuerraum 42 bestimmt.The longest possible activation duration is determined by the leakage (43, 45, 47) from the
Sinkt der Druck im Steuerraum 42 auf den Raildruck ab, so führt die Düsennadel 21 eine Bewegung nach unten (in Pfeilrichtung 49) aus bis sie mit der Mantelfläche ihrer konischen Spitze 29 die Austrittsbohrungen 26, 27 verschließt. Zum Schließen der Düsennadel 21 wird die elektrische Ansteuerung des Piezoaktors 16 unterbrochen. Der Piezoaktor 16 zieht sich daraufhin zusammen, und der Druck im Steuerraum 42 sinkt unter den Raildruck. Dadurch erfährt die Düsennadel 21 die erforderlichen schließenden Kräfte und schließt.If the pressure in the
Die Druckfeder 34 verhindert hierbei, dass sich der Piezoaktor 16 vom Übersetzerkolben 32 trennt. Piezoaktor 16 und Übersetzerkolben 32 bleiben also ständig in der (aus
Claims (4)
- Injector for fuel injection systems of internal combustion engines, in particular of direct-injection diesel engines, with a piezoactuator which is arranged in an injector body (10) and which via first spring means (34) is held in bearing contact, on the one hand, with the injector body (10) and, on the other hand, with a sleeve-like intensifier piston (32), with a nozzle body (20) which is connected to the injector body (10) and has at least one nozzle outlet orifice (26, 27) and in which a stepped nozzle needle (21) is guided axially displaceably, with second spring means (48) which are arranged within the intensifier piston (32) and which, together with the fuel pressure acting on the nozzle needle (21) on the rear side, hold the nozzle needle (21) in the closing position, and with a control space (42) which is formed at the nozzle needle-side end of the intensifier piston (32) and which is connected via at least one leakage gap (43, 45, 47) to a fuel feed (18) which is under high pressure, the nozzle needle (21) being acted upon in the opening direction (35) by the fuel located in the control space (42), the intensifier piston (32) actuated by the piezoactuator (16) being spatially assigned directly to the nozzle needle (21), in such a way that the nozzle needle (21) is fitted with a rear region (30), which has a larger diameter than a nozzle outlet-side region of the nozzle needle (21), in an inner space (31) of the intensifier piston (32), an annular space (17) being provided, which is directly connected hydraulically to the fuel feed (18) which is under high pressure, which annular space extends into the region of the intensifier piston (32) axially adjacent to the piezoactuator (16), the inner space (31) of the intensifier piston (32) being connected hydraulically to the annular space (17) and consequently to the fuel feed (18), the nozzle body (20) being fastened to the injector body (10) by means of a union nut (22), and the piezoactuator (16) being centred in an axial cylindrical recess (15) of the injector body (10) in such a way as to give rise to the annular space (17) between the outer wall of the piezoactuator (16) and the inner wall of the cylindrical recess (15) of the injector body (10), characterized in that the intensifier piston (32) is guided in the nozzle body (20), thereby forming a leakage gap (43), in such a way that a hydraulic connection is made between the annular space (17) which is under high pressure and the control space (42), and in that, between the outer wall of the nozzle body (20) and the inner wall of the union nut (22), a cylindrical gap (40) is formed, which is connected hydraulically via recesses (38, 39) incorporated into the nozzle body (20), on the one hand, to the annular space (17) and, on the other hand, to a cylindrical pressure space (37) concentrically surrounding the nozzle needle (21) in the nozzle outlet-side region of the nozzle body (20).
- Injector according to Claim 1, characterized in that, in that region of the annular space (17) which is assigned to the intensifier piston (32), a compression spring (34) is arranged which concentrically surrounds the intensifier piston (32) and which is supported on the piezoactuator side against a collar (33) of the intensifier piston (32) and on the nozzle-outlet side against a rear end face (23) of the nozzle body (20), in such a way that the piezoactuator (16) and intensifier piston (32) are held non-positively in bearing contact.
- Injector according to Claim 1, characterized in that the nozzle needle (21) is guided in the inner space (31) of the intensifier piston (32), thereby forming a cylindrical leakage gap (47), in such a way that a hydraulic connection is made between the inner space (31), under high pressure, of the intensifier piston (32) and the control space (42).
- Injector according to one or more of the preceding claims, characterized in that in the nozzle body (20), on the rear side of the cylindrical pressure space (37), a portion (44) is formed, in which the nozzle needle (21) is guided, thereby forming a leakage gap (45), in such a way that a hydraulic connection is made between the cylindrical pressure space (37) which is under high pressure and the control space (42).
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE10326259A DE10326259A1 (en) | 2003-06-11 | 2003-06-11 | Injector for fuel injection systems of internal combustion engines, in particular direct injection diesel engines |
| PCT/DE2004/000738 WO2004111434A1 (en) | 2003-06-11 | 2004-04-08 | Injector for fuel injection systems of internal combustion engines, especially direct injection diesel engines |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1636485A1 EP1636485A1 (en) | 2006-03-22 |
| EP1636485B1 true EP1636485B1 (en) | 2009-01-14 |
Family
ID=33494946
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP04726421A Expired - Lifetime EP1636485B1 (en) | 2003-06-11 | 2004-04-08 | Injector for fuel injection systems of internal combustion engines, especially direct injection diesel engines |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7431220B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1636485B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2006510850A (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20060021357A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN100432420C (en) |
| DE (2) | DE10326259A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2004111434A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (31)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10346242B4 (en) * | 2003-10-06 | 2012-04-12 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Injector body for a common rail injector |
| DE102004004006A1 (en) * | 2004-01-27 | 2005-08-11 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Integrated hydraulic intensifier for fuel injectors on high-pressure accumulator injection systems |
| DE102005015997A1 (en) * | 2004-12-23 | 2006-07-13 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Fuel injector with direct control of the injection valve member |
| DE102005007543A1 (en) * | 2005-02-18 | 2006-08-24 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Fuel injector with direct needle control for an internal combustion engine |
| DE102005012929A1 (en) * | 2005-03-21 | 2006-09-28 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Fuel injector with direct control of the injection valve member and variable ratio |
| DE102005015735A1 (en) * | 2005-04-06 | 2006-10-12 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Fuel injector |
| DE102005015731A1 (en) * | 2005-04-06 | 2006-10-12 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Fuel injector with piezo actuator |
| DE102006006889A1 (en) | 2006-02-15 | 2007-08-23 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Fuel injector |
| ATE511014T1 (en) * | 2006-03-20 | 2011-06-15 | Delphi Tech Holding Sarl | DAMPING ARRANGEMENT FOR AN INJECTION VALVE |
| EP1837515A1 (en) | 2006-03-20 | 2007-09-26 | Delphi Technologies, Inc. | Damping arrangement for a fuel injector |
| DE102006018032A1 (en) | 2006-04-19 | 2007-10-31 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | actuator module |
| DE102006036780A1 (en) * | 2006-08-07 | 2008-02-21 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Fuel injector with direct needle control and servo valve support |
| DE102007004380A1 (en) | 2007-01-29 | 2008-07-31 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Injector with piezoelectric actuator |
| DE102007044361A1 (en) * | 2007-09-17 | 2009-03-19 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Control valve for a fuel injector |
| FR2922406A1 (en) * | 2007-10-12 | 2009-04-17 | Commissariat Energie Atomique | LIQUID CHARGE INJECTION DEVICE FOR MIXING / CONVERTING WITHIN A DARD PLASMA OR A GASEOUS FLOW |
| DE102008003851A1 (en) | 2008-01-10 | 2009-07-16 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Fuel injector |
| DE102008003838A1 (en) * | 2008-01-10 | 2009-07-16 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Piezoelectric actuator and piezoelectric injector and a method for producing a piezoelectric actuator |
| DE102008002438A1 (en) | 2008-06-16 | 2009-12-17 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Injector for injection of fuel into combustion chamber of internal combustion engine, has actuator connected with control piston |
| CN101649796B (en) * | 2008-08-16 | 2013-08-07 | 柳州福尔曼汽车电子有限公司 | Zero-backpressure electronically-controlled diesel injector driven by magnetostrictive component |
| CN101649797B (en) * | 2008-08-16 | 2013-05-29 | 柳州福尔曼汽车电子有限公司 | Zero-backpressure electronically-controlled diesel injector driven by magnetostrictive component |
| DE102008041645A1 (en) | 2008-08-28 | 2010-03-04 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Actuator module for fuel injection valve, particularly injector for air-compression, auto-ignition internal combustion engine, has piezoelectric actuator and transition piece connected with actuator |
| DE102008044164A1 (en) | 2008-11-28 | 2010-06-02 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Actuator module for fuel injection valve, particularly injector for fuel injection system, has actuator, where adapter is fixed to actuator, and centering element has bolt-shaped centering extension |
| US8201543B2 (en) * | 2009-05-14 | 2012-06-19 | Cummins Intellectual Properties, Inc. | Piezoelectric direct acting fuel injector with hydraulic link |
| DE102009054682A1 (en) | 2009-12-15 | 2011-06-16 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Injection valve i.e. injector, for fuel injection system in e.g. air-compressing, self-ignited internal combustion engine of motor vehicle, has valve element whose joining section is partially inserted into actuator head |
| DE102010063219B4 (en) | 2010-12-16 | 2018-05-24 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Piezoelectric actuator module and fuel injection valve |
| US9284930B2 (en) * | 2011-06-03 | 2016-03-15 | Michael R. Harwood | High pressure piezoelectric fuel injector |
| DE102012005319A1 (en) * | 2012-03-19 | 2013-09-19 | L'orange Gmbh | Injector assembly for fuel injector of motor vehicle, has actuating element that generates pressure in fluid, which is increased with respect to system high pressure, where injector assembly is formed to be effective against pressure force |
| DE102012209616A1 (en) | 2012-06-08 | 2013-12-12 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Arrangement with a piezoelectric actuator and a controller, and method for driving a piezoelectric actuator |
| CN103244321B (en) * | 2013-04-28 | 2015-03-11 | 哈尔滨工程大学 | Dual-fuel dual-piezoelectric control type injector |
| CN103244322B (en) * | 2013-04-28 | 2015-03-11 | 哈尔滨工程大学 | Dual-fuel electromagnetic and piezoelectric control type injector |
| DE102014211334B3 (en) * | 2014-06-13 | 2015-08-27 | Continental Automotive Gmbh | Method for characterizing a hydraulic coupling element of a piezo injector |
Family Cites Families (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4022166A (en) * | 1975-04-03 | 1977-05-10 | Teledyne Industries, Inc. | Piezoelectric fuel injector valve |
| DE2931874C2 (en) * | 1979-08-06 | 1983-08-04 | Audi Nsu Auto Union Ag, 7107 Neckarsulm | Electrically operated valve |
| DE3518945A1 (en) * | 1985-05-25 | 1986-11-27 | Robert Bosch Gmbh, 7000 Stuttgart | Fuel injection nozzle for internal combustion engines |
| DE4306073C1 (en) * | 1993-02-26 | 1994-06-01 | Siemens Ag | Metering system for dosing of fluids with injection valve for IC engine - has piston acting on closing unit, and spring with actuator acting on large dia. piston moving in cylinder |
| US5482213A (en) | 1993-05-31 | 1996-01-09 | Aisin Seiki Kabushiki Kaisha | Fuel injection valve operated by expansion and contraction of piezoelectric element |
| JP3814935B2 (en) * | 1997-04-18 | 2006-08-30 | 日産自動車株式会社 | Engine fuel injection valve |
| US5947380A (en) * | 1997-11-03 | 1999-09-07 | Caterpillar Inc. | Fuel injector utilizing flat-seat poppet valves |
| JP3922780B2 (en) * | 1998-01-08 | 2007-05-30 | 株式会社日本自動車部品総合研究所 | Fuel injection valve and driving method thereof |
| JP2000161175A (en) | 1998-11-26 | 2000-06-13 | Hitachi Ltd | Injector and fuel injection system |
| DE19946840A1 (en) * | 1999-09-30 | 2001-05-03 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | Valve for controlling liquids |
| US20020053611A1 (en) * | 2000-06-29 | 2002-05-09 | Friedrich Boecking | High-pressure injector with reduced leakage |
| DE60126380T2 (en) | 2000-07-18 | 2007-11-15 | Delphi Technologies, Inc., Troy | Fuel injection valve |
| JP2002202022A (en) * | 2000-10-30 | 2002-07-19 | Denso Corp | Valve driving device and fuel injection valve |
| US6766965B2 (en) * | 2001-08-31 | 2004-07-27 | Siemens Automotive Corporation | Twin tube hydraulic compensator for a fuel injector |
| DE10151688A1 (en) | 2001-10-19 | 2003-04-30 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | Valve for controlling liquids |
| DE10326046A1 (en) * | 2003-06-10 | 2004-12-30 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Injection nozzle for internal combustion engines |
| DE102005004738A1 (en) * | 2005-02-02 | 2006-08-10 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Fuel injector with direct needle control for an internal combustion engine |
| DE102005012929A1 (en) * | 2005-03-21 | 2006-09-28 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Fuel injector with direct control of the injection valve member and variable ratio |
-
2003
- 2003-06-11 DE DE10326259A patent/DE10326259A1/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2004
- 2004-04-08 DE DE502004008875T patent/DE502004008875D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2004-04-08 JP JP2005518248A patent/JP2006510850A/en active Pending
- 2004-04-08 WO PCT/DE2004/000738 patent/WO2004111434A1/en active Application Filing
- 2004-04-08 EP EP04726421A patent/EP1636485B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2004-04-08 US US10/559,710 patent/US7431220B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-04-08 CN CNB2004800163770A patent/CN100432420C/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-04-08 KR KR1020057023685A patent/KR20060021357A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1636485A1 (en) | 2006-03-22 |
| WO2004111434A1 (en) | 2004-12-23 |
| CN1806116A (en) | 2006-07-19 |
| CN100432420C (en) | 2008-11-12 |
| KR20060021357A (en) | 2006-03-07 |
| JP2006510850A (en) | 2006-03-30 |
| US20060255184A1 (en) | 2006-11-16 |
| US7431220B2 (en) | 2008-10-07 |
| DE502004008875D1 (en) | 2009-03-05 |
| DE10326259A1 (en) | 2005-01-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1636485B1 (en) | Injector for fuel injection systems of internal combustion engines, especially direct injection diesel engines | |
| DE10336327B4 (en) | Injector for fuel injection systems of internal combustion engines, in particular direct injection diesel engines | |
| EP1733139B1 (en) | Common rail injector | |
| DE2742466A1 (en) | PUMP NOZZLE FOR AIR-COMPRESSING INJECTION COMBUSTION MACHINES | |
| EP0686763A1 (en) | Fuel injection valve for internal combustion engines | |
| DE19519191A1 (en) | Injector | |
| EP1554488B1 (en) | Pressure-boosted fuel injection device comprising an internal control line | |
| WO2002084106A1 (en) | Valve for controlling liquids | |
| EP0657643A2 (en) | Fuel injection device for internal combustion engines | |
| DE10221384A1 (en) | Fuel injection device for an internal combustion engine | |
| DE4332124A1 (en) | Fuel injection nozzle for internal combustion engines | |
| EP1558843B1 (en) | Fuel injection system for internal combustion engines | |
| DE102008035087B4 (en) | Injector | |
| EP1682769B1 (en) | Fuel injector with a multipart, directly controlled injection valve element | |
| EP1703119B1 (en) | Fuel injection nozzle | |
| DE10141679A1 (en) | Fuel injection device for an internal combustion engine | |
| WO2001038724A1 (en) | Fuel injection valve for internal combustion engines | |
| DE19936667A1 (en) | Common rail injector | |
| DE102006029392A1 (en) | injector | |
| EP0685645B1 (en) | Injection valve for a fuel injection system of an internal combustion engine, particularly of a diesel engine | |
| EP1908953B1 (en) | Fuel injection device | |
| DE102006050164A1 (en) | Fuel injector for internal combustion engine, has piezo-actuator actuating force-balance formed servo valve under in connection of hydraulic combiner, where injector is actuated by piezo-actuator, which controls servo valve | |
| EP1210512B1 (en) | Injector | |
| EP2136067A1 (en) | Fuel injector | |
| DE102005008973A1 (en) | Injection jet for internal combustion engine has two coupling pistons with control surfaces |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20060111 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB IT |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): DE FR GB IT |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20060413 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB IT |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 502004008875 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20090305 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20091015 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20170619 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20170420 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20170623 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20180403 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 502004008875 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20181101 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180408 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180430 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20190408 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190408 |