EP1528186B1 - Panel for modular housing construction in particular of ventilating and air conditioning plants - Google Patents
Panel for modular housing construction in particular of ventilating and air conditioning plants Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1528186B1 EP1528186B1 EP04023654A EP04023654A EP1528186B1 EP 1528186 B1 EP1528186 B1 EP 1528186B1 EP 04023654 A EP04023654 A EP 04023654A EP 04023654 A EP04023654 A EP 04023654A EP 1528186 B1 EP1528186 B1 EP 1528186B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- panel element
- metal profiles
- element according
- insulating material
- panel
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 12
- 238000004378 air conditioning Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 7
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 50
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 28
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 claims abstract 2
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000011490 mineral wool Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000003063 flame retardant Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000009423 ventilation Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 229920002943 EPDM rubber Polymers 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229920001971 elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910001369 Brass Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000032683 aging Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000010951 brass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005266 casting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007596 consolidation process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005336 cracking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013016 damping Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000806 elastomer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003365 glass fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000020169 heat generation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 1
- -1 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920005749 polyurethane resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000002940 repellent Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000005871 repellent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04C—STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS; BUILDING MATERIALS
- E04C2/00—Building elements of relatively thin form for the construction of parts of buildings, e.g. sheet materials, slabs, or panels
- E04C2/02—Building elements of relatively thin form for the construction of parts of buildings, e.g. sheet materials, slabs, or panels characterised by specified materials
- E04C2/26—Building elements of relatively thin form for the construction of parts of buildings, e.g. sheet materials, slabs, or panels characterised by specified materials composed of materials covered by two or more of groups E04C2/04, E04C2/08, E04C2/10 or of materials covered by one of these groups with a material not specified in one of the groups
- E04C2/284—Building elements of relatively thin form for the construction of parts of buildings, e.g. sheet materials, slabs, or panels characterised by specified materials composed of materials covered by two or more of groups E04C2/04, E04C2/08, E04C2/10 or of materials covered by one of these groups with a material not specified in one of the groups at least one of the materials being insulating
- E04C2/292—Building elements of relatively thin form for the construction of parts of buildings, e.g. sheet materials, slabs, or panels characterised by specified materials composed of materials covered by two or more of groups E04C2/04, E04C2/08, E04C2/10 or of materials covered by one of these groups with a material not specified in one of the groups at least one of the materials being insulating composed of insulating material and sheet metal
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04H—BUILDINGS OR LIKE STRUCTURES FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSES; SWIMMING OR SPLASH BATHS OR POOLS; MASTS; FENCING; TENTS OR CANOPIES, IN GENERAL
- E04H5/00—Buildings or groups of buildings for industrial or agricultural purposes
- E04H5/10—Buildings forming part of cooling plants
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a plate member for modular construction of housings, preferably of ventilation and air conditioning systems, with two spaced and substantially parallel side walls with interposed insulation and with a perpendicular to the side walls extending around the plate member end face, said End face in the cross-sectional view has two spaced apart metal profiles, between which insulating material is arranged.
- a plate element is from each of the publications DE-A-3 244 743 . US-A 1 697 189 and FR-A-2 604 739 known.
- the modular design with panel elements in ventilation and air conditioning systems is already known.
- the prior art discloses numerous variants for the realization of such plate elements.
- the DE 30 42 109 discloses a plate member having an insulating core, on whose end faces in each case an end profile of U-shaped cross-section is arranged.
- a disadvantage of these plate elements is the high heat transfer in the region of the end profiles.
- the FR 2 604 739 describes a facade panel with two parallel metal plates, between which an insulating core of mineral wool is arranged. To connect the plate elements on the front side Verank fürselemertt, 8 'are provided of an elastomer, so that a gap between the individual facade panels remains.
- the US 1,697,189 shows an insulating plate member having two mutually parallel side walls, between which insulating material is arranged.
- the DE 32 44 743 A1 discloses a rolling wall for cooling and insulating containers, with no thermal bridges from the inside to the outside of the roll wall.
- insulating material is penetrated by sockets, which are provided for connection to adjacent plate elements and / or for connection to corner profiles.
- the standard EN 1886 under point 7 describes a classification of RLT (room air-technical) devices in classes, the devices in the classes T1 and T2 are substantially completely thermally decoupled from the warm to the cold side. Due to the end face according to the invention, these standard values can be made possible with a simple construction. Due to the spaced metal profiles, a favorable thermal decoupling can be realized.
- RLT room air-technical
- a preferred embodiment of the invention provides that the insulating material is formed substantially cuboid and that the metal profiles embrace the insulating material on its narrow side. This allows the greatest possible distance between the metal profiles, whereby the heat transfer is additionally reduced. By the Enveloping the metal profiles on the narrow side also requires less material to minimize the naturally good heat-conducting metal surfaces.
- a special embodiment of the invention provides that the metal profiles surround the edge of the insulating material with a substantially U-shaped edge. This design ensures a good hold of the insulating material, which remains firmly anchored between the metal profiles even with large thermal fluctuations. It is advantageously provided that the metal profiles are at least partially double-walled, whereby additional stability of the profile end frame is achieved.
- the metal profiles have mutually parallel sections between which an insulating gap remains.
- the parallel sections a higher strength and a better torsional rigidity of the profile end frame is achieved, the trapped air gap acts as an insulator layer, thereby improving the thermal decoupling.
- the metal profiles have grooves for receiving a seal.
- double-circumferential seals can be inserted into the grooves provided, which give the RLT housing the required degree of tightness in Unterwie in the overpressure.
- the seal is an EPDM seal. This rubber seal is characterized i.a. by flame retardancy and largely withstands large temperature fluctuations.
- the metal profiles are each connected to one side wall.
- an increased strength of the plate element is achieved.
- the metal profiles are preferably integrally formed from the U-shaped edge to the flat surfaces, these can be easily connected to the side walls, with a stable double-walled construction is achieved.
- conventional mechanical fastening means preferably rivet nuts, are provided. Of course, other methods, such as spot welding, can be used.
- the side walls are at least partially rolled with the metal profiles, whereby an additional strength of the construction is made possible. By rotting, a vertical slippage of the side wall with respect to the metal profiles can be prevented.
- the insulating material is heat and fire retardant material, preferably PU resin.
- Polyurethane resin products are characterized i.a. good fire resistance, good phonic absorption and good resistance to cracking.
- the sockets, which are provided for connecting the plate element with other plate elements in a modular composite, for example, are designed as Eing manmuttern with usual metric thread which are provided for receiving corresponding metric screws.
- the insulating material between the side walls is fire-retardant and temperature-insulating material, preferably mineral wool.
- the insulation with rock wool causes a favorable insulation against heat, cold and noise.
- a standard product is used which is nonflammable, water repellent and resistant to aging.
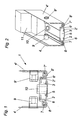
- Fig. 1 shows a cross-sectional view of the end face of a plate member 1.
- the front side has two spaced-apart metal profiles 2, 2 ', between which insulating material 3 is arranged. There is no metallic connection between the Metal profiles 2, 2 ', which would lead to an undesirable thermal coupling of a side wall 4 to the parallel opposite side wall 4'.
- the metal profiles 2, 2 ' embrace the essentially cuboidal insulating material 3 on its narrow side, the metal profiles 2, 2' embracing the edge of the insulating material 3 with a substantially U-shaped edge.
- the insulating material 3 is for example PU resin, which is poured in the manufacture in liquid form between the metal profiles 2, 2 '. To prevent leakage of the liquid resin, a piping 5 is provided. This plastic cover is removed after the curing of the insulating material 3 again.
- the metal profiles 2, 2 ' are at least partially double-walled, resulting in improved stability.
- the metal profiles 2, 2 ' include an insulating gap 6, 6', which causes an improved thermal decoupling.
- the metal profiles 2, 2 'grooves 7, 7' which are provided for receiving seals 8, 8 '.
- the metal profiles 2, 2 ' are each connected to a side wall 4, 4'. By this connection, a favorable strength of the plate element 1 is achieved.
- a further increase in strength is achieved by the rotting of the side walls 4, 4 'with the metal profiles 2, 2', wherein the side walls 4, 4 'at least partially in the grooves 7, 7' of the metal profiles 2, 2 'engage.
- sockets 10 are provided, which pass through the insulating material 3. These bushes 10 are used in the casting process of the insulating material 3 and serve to accommodate matching screws that are screwed, for example, from corresponding corner profiles 14 in the end face of the plate elements 1.
- Fig. 1 drawn socket 10 is provided only by way of example for a plurality of interspersing sockets 10, which are arranged at regular intervals on the front side of the plate elements 1.
- Fig. 2 shows a three-dimensional representation of the in Fig. 1
- the spaced metal profiles 2, 2 ' enclose the narrow side of the insulating material 3 with a substantially U-shaped edge.
- the metal profiles 2, 2 ' have at least partially mutually parallel sections, between which an insulating gap 6, 6' remains.
- the metal profiles have channel-shaped sections 7, 7 ', which are provided for receiving circumferentially extending seals 8, 8'.
- insulation 11 between the side walls 4, 4 'rock wool is provided, for example, the next the insulation has good fire and noise-reducing properties.
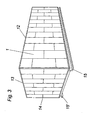
- Fig. 3 shows an RLT housing with plate elements 1 different standard sizes. Inside, the inclusion of ventilation and air conditioning systems is provided, which cause not only strong heat generation but also considerable noise emissions.
- the plate elements 1 according to the invention are provided, which are characterized by a frameless construction for a substantially thermally decoupled system.
- the individual plate elements 1 are connected to each other with the front side.
- the plate elements 1 are screwed, for example, with longitudinal bars 12 and transverse bars 13, at the corners vertical corner profiles 14 are provided which also have a thermally decoupled system as the plate elements 1.
- the housing can rest, for example, on U-shaped profile rails 15, 15 ', which is mounted vibration-damped by vibration-damping pads.
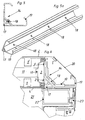
- Fig. 4 shows a schematically illustrated another embodiment of an RLT housing.
- the thermally separated plate elements 1 here have a standardized unit size.
- a corner profile 14 is provided, which has a substantially C-shaped section 19 made of metal, preferably made of steel, and a triangular corner strip 17 made of plastic, preferably polypropylene.
- plastic corner strip 17 can also be realized on the edge side thermal decoupling.
- the construction of the doors 16 is also thermally decoupled from the inside to the outside.
- the Fig. 4a shows a front view of the in Fig. 4 illustrated housing.
- the Fig. 4b shows a sectional view along the axis AA Fig. 4a with a detail C, on which in the Figure 6 will be discussed in more detail.
- Fig. 5 shows a schematic front view of a corner profile 14 with the C-shaped portion 19 made of metal and the triangular corner molding 17 made of plastic.
- the C-shaped portion 19 is connectable at its central part with the corner strip 17, preferably screwed to the screw 18 shown by way of example.
- Fig. 5a shows the corner profile 14 in a perspective view with corner strip 17 and metallic part 19, which are connected by screws 18.
- Fig. 6 shows detail C. Fig. 4b in an enlarged view.
- the corner profile 14 is provided, which has a substantially C-shaped portion 19 made of metal, preferably made of steel, and a triangular, corner strip 17 made of plastic.
- a cover strip 20 serves to cover the C-shaped section.
- the C-shaped portion 19 is connectable at its central part with the corner bar 17, for example by the screws 18. It is advantageous that the C-shaped portion 19 of the corner profile 14 of the inner metal profiles 2, 2 'of the plate elements 1, preferably through the corner bar 17, is spaced. This ensures that there is no metallic and therefore good heat-conducting connection of the inner metal profile 2 to the opposite metal profile 2 'and thus to the outer side wall 4'.
- a door 16 is exemplified, which is also thermally decoupled from the housing interior 21 to the outside.
- a plastic profile 22 is arranged with a rectangular cross-section. This plastic profile 22 may be glass fiber reinforced, for example.
- a door seal 24 is used for thermal decoupling, preferably an EPDM seal, which effects a thermal separation from the interior 21 of the housing to the outside.
- the present invention is not limited to the exemplary embodiments shown in the figures, nor should they be limited by them.
- other materials than mineral wool and PU resin can be used as insulation and as insulating material.
- the plastic corner strip in addition to the triangular shape shown in the figures, another geometry, such as a polygonal have.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Building Environments (AREA)
- Air Filters, Heat-Exchange Apparatuses, And Housings Of Air-Conditioning Units (AREA)
- Cooling Or The Like Of Electrical Apparatus (AREA)
- Thermal Insulation (AREA)
- Duct Arrangements (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Die vorliegende Erfindung betrifft ein Plattenelement zum modularen Aufbau von Gehäusen, vorzugsweise von Lüftungs- und Klimaanlagen, mit zwei beabstandeten und im Wesentlichen parallel zueinander verlaufenden Seitenwänden mit dazwischen angeordneter Isolierung und mit einer im rechten Winkel zu den Seitenwänden um das Plattenelement verlaufenden Stirnfläche, wobei die Stirnfläche in der Querschnittansicht zwei voneinander beabstandete Metallprofile aufweist, zwischen denen Isoliermaterial angeordnet ist. Ein solches plattenelement ist aus jeder einzelnen der Druckschriften
Der modulare Aufbau mit Plattenelementen im Lüftungs- und Klimaanlagenbau ist bereits bekannt. Der Stand der Technik offenbart zahlreiche Varianten zur Realisierung derartiger Plattenelemente. Die
Die
Die
Die
Aufgabe der vorliegenden Erfindung ist es daher, ein Plattenelement zu schaffen, weiches obigen Nachteil nicht aufweist und die an den Außenbereich abgegebene Wärmemenge reduziert.It is therefore an object of the present invention to provide a plate member which does not have the above disadvantage and reduces the amount of heat discharged to the outside.
Dies wird erfindungsgemäß dadurch erreicht, dass das Isoliermaterial von Buchsen durchsetzt ist, die zur Verbindung mit benachbarten Plattenelementen und/oder zur Verbindung mit Eckprofilen vorgesehen sind.This is inventively achieved in that the insulating material is penetrated by sockets, which are provided for connection to adjacent plate elements and / or for connection to corner profiles.
Um den steigenden Anforderungen an Klimageräten gerecht zu werden, müssen technische Parameter wie Wärmedurchgangskoeffizient oder Wärmebrückenfaktor des Klimagehäuses entsprechende Werte aufweisen. Die Norm EN 1886 unter Punkt 7 beschreibt eine Einteilung von RLT (Raumluft-technischen) Geräten in Klassen, wobei die Geräte in den Klassen T1 bzw. T2 im Wesentlichen vollständig von der warmen zur kalten Seite hin thermisch entkoppelt sind. Durch die erfindungsgemäße Stirnfläche können diese Normwerte mit einfacher Konstruktion ermöglicht werden. Durch die beabstandeten Metallprofile kann eine günstige thermische Entkopplung realisiert werden.In order to meet the increasing demands on air conditioners, technical parameters such as heat transfer coefficient or thermal bridge factor of the air conditioning housing must have corresponding values. The standard EN 1886 under
Eine bevorzugte Ausführungsform der Erfindung sieht vor, dass das Isoliermaterial im Wesentlichen quaderförmig ausgebildet ist und dass die Metallprofile das Isoliermaterial an dessen Schmalseite umgreifen. Damit wird ein möglichst großer Abstand zwischen den Metallprofilen ermöglicht, wodurch der Wärmeübergang zusätzlich reduziert wird. Durch das Umgreifen der Metallprofile an der Schmalseite wird zudem weniger Material benötigt, um die naturgemäß gut wärmeleitenden Metallflächen zu minimieren.A preferred embodiment of the invention provides that the insulating material is formed substantially cuboid and that the metal profiles embrace the insulating material on its narrow side. This allows the greatest possible distance between the metal profiles, whereby the heat transfer is additionally reduced. By the Enveloping the metal profiles on the narrow side also requires less material to minimize the naturally good heat-conducting metal surfaces.
Eine spezielle Ausführungsform der Erfindung sieht vor, dass die Metallprofile den Rand des Isoliermaterials mit einem im Wesentlichen U-förmigen Rand umgreifen. Durch diese Gestaltungsform wird ein guter Halt des Isoliermaterials gewährleistet, welches selbst bei großen thermischen Schwankungen fix zwischen den Metallprofilen verankert bleibt. Vorteilhaft ist vorgesehen, dass die Metallprofile zumindest teilweise doppelwandig ausgeführt sind, wodurch eine zusätzliche Stabilität des Profilstirnrahmens erzielt wird.A special embodiment of the invention provides that the metal profiles surround the edge of the insulating material with a substantially U-shaped edge. This design ensures a good hold of the insulating material, which remains firmly anchored between the metal profiles even with large thermal fluctuations. It is advantageously provided that the metal profiles are at least partially double-walled, whereby additional stability of the profile end frame is achieved.
Vorteilhaft ist weiters vorgesehen, dass die Metallprofile parallel zueinander verlaufende Abschnitte aufweisen, zwischen denen ein isolierender Spalt verbleibt. Durch die parallel verlaufenden Abschnitte wird eine höhere Festigkeit und eine bessere Verwindungssteifigkeit des Profilstirnrahmens erzielt, der eingeschlossene Luftspalt wirkt als Isolatorschicht und verbessert dadurch die thermische Entkopplung.Advantageously, it is further provided that the metal profiles have mutually parallel sections between which an insulating gap remains. By the parallel sections, a higher strength and a better torsional rigidity of the profile end frame is achieved, the trapped air gap acts as an insulator layer, thereby improving the thermal decoupling.
Günstigerweise ist vorgesehen, dass die Metallprofile zur Aufnahme einer Dichtung Rinnen aufweisen. Vorzugsweise können doppelt umlaufende Dichtungen in die vorgesehenen Rinnen eingelegt werden, die dem RLT-Gehäuse den erforderlichen Dichtheitsgrad im Unterwie im Überdruckbereich verleihen. Vorteilhaft ist vorgesehen, dass die Dichtung eine EPDM-Dichtung ist. Diese Kautschuk-Dichtung zeichnet sich u.a. durch Schwerentflammbarkeit aus und widersteht weitgehend auch großen Temperaturschwankungen.It is advantageously provided that the metal profiles have grooves for receiving a seal. Preferably, double-circumferential seals can be inserted into the grooves provided, which give the RLT housing the required degree of tightness in Unterwie in the overpressure. It is advantageously provided that the seal is an EPDM seal. This rubber seal is characterized i.a. by flame retardancy and largely withstands large temperature fluctuations.
Besonders günstig ist es, wenn die Metallprofile mit jeweils einer Seitenwand verbunden sind. Durch diese Maßnahme wird eine erhöhte Festigkeit des Plattenelementes erreicht. Da die Metallprofile bevorzugt vom U-förmigen Rand bis zu den ebenen Flächen einstückig ausgebildet sind, können diese auf einfache Art mit den Seitenwänden verbunden werden, wobei eine stabile doppelwandige Konstruktion erzielt wird. Zum Verbinden der Metallprofile mit den Seitenwänden werden übliche mechanische Befestigungsmittel, vorzugsweise Einnietmuttern, vorgesehen. Selbstverständlich können auch andere Methoden, wie z.B. Punktschweißen, angewendet werden. Vorteilhaft ist vorgesehen, dass die Seitenwände mit den Metallprofilen zumindest teilweise verrollt werden, wodurch eine zusätzliche Festigkeit der Konstruktion ermöglicht wird. Durch das Verrotten kann auch ein vertikales Verrutschen der Seitenwand in Bezug auf die Metallprofile verhindert werden.It is particularly favorable if the metal profiles are each connected to one side wall. By this measure, an increased strength of the plate element is achieved. Since the metal profiles are preferably integrally formed from the U-shaped edge to the flat surfaces, these can be easily connected to the side walls, with a stable double-walled construction is achieved. For connecting the metal profiles to the side walls, conventional mechanical fastening means, preferably rivet nuts, are provided. Of course, other methods, such as spot welding, can be used. It is advantageously provided that the side walls are at least partially rolled with the metal profiles, whereby an additional strength of the construction is made possible. By rotting, a vertical slippage of the side wall with respect to the metal profiles can be prevented.
Eine bevorzugte Ausführungsform der Erfindung sieht vor, dass das Isoliermaterial hitze- und feuerhemmendes Material, vorzugsweise PU-Harz, ist. Polyurethanharz-Produkte zeichnen sich u.a. durch gute Feuerbeständigkeit, gute phonische Absorption und gute Widerstandsfähigkeit gegen Rissebildung aus. Vorteilhaft ist vorgesehen, dass die Buchsen, die zum Verbinden des Plattenelementes mit anderen Plattenelementen im modularen Verbund vorgesehen sind, beispielsweise als Eingießmuttern mit üblichem metrischem Gewinde ausgeführt sind die für die Aufnahme von korrespondierenden metrischen Schrauben vorgesehen sind.A preferred embodiment of the invention provides that the insulating material is heat and fire retardant material, preferably PU resin. Polyurethane resin products are characterized i.a. good fire resistance, good phonic absorption and good resistance to cracking. It is advantageously provided that the sockets, which are provided for connecting the plate element with other plate elements in a modular composite, for example, are designed as Eingießmuttern with usual metric thread which are provided for receiving corresponding metric screws.
Schließlich ist vorgesehen, dass das Isoliermaterial zwischen den Seitenwänden feuerhemmendes und temperaturdämmendes Material, vorzugsweise Mineralwolle, ist. Die Isolierung mit Steinwolle bewirkt eine günstige Dämmung gegen Hitze, Kälte und Lärm. Darüber hinaus wird ein Standardprodukt verwendet, welches nicht brennbar, wasserabweisend und alterungsbeständig ist.Finally, it is provided that the insulating material between the side walls is fire-retardant and temperature-insulating material, preferably mineral wool. The insulation with rock wool causes a favorable insulation against heat, cold and noise. In addition, a standard product is used which is nonflammable, water repellent and resistant to aging.
Weitere Einzelheiten und Vorteile der vorliegenden Erfindung werden anhand der Figurenbeschreibung unter Bezugnahme auf die Zeichnungen im Folgenden näher erläutert. Darin zeigt:
- Fig. 1
- einen schematischen Querschnitt durch die Stirnfläche eines Ausführungsbeispiels eines Plattenelementes,
- Fig. 2
- eine schematische perspektivische Darstellung eines Ausschnittes des Plattenelementes aus
Fig. 1 , - Fig. 3
- ein zusammengebautes Gehäuse mit Plattenelementen verschiedener Standardgrößen,
- Fig. 4, 4a und 4b
- ein weiteres Ausführungsbeispiel eines zusammengebauten Gehäuses sowie verschiedene Ansichten desselben und
- Fig. 5 und 5a
- eine schematische Seitenansicht eines Eckprofils sowie eine perspektivische Darstellung desselben,
- Fig. 6
- eine vergrößerte Darstellung des Details C aus
Fig. 4b .
- Fig. 1
- a schematic cross-section through the end face of an embodiment of a plate element,
- Fig. 2
- a schematic perspective view of a section of the plate element from
Fig. 1 . - Fig. 3
- an assembled housing with plate elements of different standard sizes,
- Fig. 4, 4a and 4b
- a further embodiment of an assembled housing and various views thereof and
- Fig. 5 and 5a
- a schematic side view of a corner profile and a perspective view of the same,
- Fig. 6
- an enlarged view of the detail C from
Fig. 4b ,
Die Metallprofile 2, 2' sind zumindest teilweise doppelwandig ausgeführt, was zu einer verbesserten Stabilität führt. Neben diesen parallel zueinander verlaufenden Abschnitten schließen die Metallprofile 2, 2' einen isolierenden Spalt 6, 6' ein, der eine verbesserte thermische Entkopplung bewirkt. In weiterer Folge weisen die Metallprofile 2, 2' Rinnen 7, 7' auf, die zur Aufnahme von Dichtungen 8, 8' vorgesehen sind. Die Metallprofile 2, 2' sind mit jeweils einer Seitenwand 4, 4' verbunden. Durch diese Verbindung wird eine günstige Festigkeit des Plattenelementes 1 erzielt. Als Verbindungsmittel werden seitliche Einnietmuttern 9, 9' verwendet, die der Konstruktion den erforderlichen Halt verleihen. Eine weitere Festigkeitssteigerung wird durch das Verrotten der Seitenwände 4, 4' mit den Metallprofilen 2, 2' erreicht, wobei die Seitenwände 4, 4' zumindest teilweise in die Rinnen 7, 7' der Metallprofile 2, 2' eingreifen. Zum Verbinden des Plattenelementes 1 mit den Stirnflächen anderer Plattenelemente 1 sind Buchsen 10 vorgesehen, die das Isoliermaterial 3 durchsetzen. Diese Buchsen 10 werden beim Gussvorgang des Isoliermaterials 3 eingesetzt und dienen zur Aufnahme passender Schrauben, die beispielsweise von entsprechenden Eckprofilen 14 aus in die Stirnseite der Plattenelemente 1 eingeschraubt werden. Die in
Es versteht sich von selbst, dass die vorliegende Erfindung nicht auf die in den Figuren dargestellten Ausführungsbeispiele beschränkt ist, noch durch diese eingeschränkt werden soll. Als Isolierung und als Isoliermaterial können selbstverständlich auch andere Materialien als Mineralwolle und PU-Harz eingesetzt werden. Auch die Eckleiste aus Kunststoff kann neben der in den Figuren dargestellten dreieckigen Form eine andere Geometrie, beispielsweise eine polygonale, aufweisen.It goes without saying that the present invention is not limited to the exemplary embodiments shown in the figures, nor should they be limited by them. Of course, other materials than mineral wool and PU resin can be used as insulation and as insulating material. Also, the plastic corner strip, in addition to the triangular shape shown in the figures, another geometry, such as a polygonal have.
Claims (16)
- A panel element (1) for the modular construction of housings, in particular of ventilation and air-conditioning installations, comprising two spaced side walls (4, 4') which extend substantially parallel to each other with insulation (11) arranged therebetween and with an end face extending at a right angle to the side walls (4, 4') around the panel element (1), wherein the end face in a cross-sectional view has two metal profiles (2, 2') which are spaced from each other and between which insulating material (3) is arranged, characterised in that the insulating material (3) is interspersed with bushings (10) which are provided for connection to adjacent panel elements (1) and/or for connection to corner profiles (14).
- A panel element according to claim 1, characterised in that the insulating material (3) is of a substantially block-shaped configuration.
- A panel element according to claim 1 or 2, characterised in that the metal profiles (2, 2') encompass the insulating material (3) at the narrow side thereof.
- A panel element according to one of claims 1 to 3, characterised in that the metal profiles (2, 2') encompass the edge of the insulating material (3) with a substantially U-shaped edge.
- A panel element according to one of claims 1 to 4, characterised in that the metal profiles (2, 2') are at least partially of a double-wall structure.
- A panel element according to one of claims 1 to 5, characterised in that the metal profiles (2, 2') have portions which extend parallel to each other and between which there remains an insulating gap (6).
- A panel element according to one of claims 1 to 6, characterised in that the metal profiles (2, 2') have channels (7, 7') for receiving a seal (8).
- A panel element according to claim 7, characterised in that the seal (8) is an EPDM seal.
- A panel element according to one of claims 1 to 8, characterised in that the metal profiles (2, 2') are each connected to a respective side wall (4,4').
- A panel element according to claim 9, characterised in that mechanical fixing means (9, 9'), preferably riveting nuts, are provided for connecting the metal profiles (2, 2') to the side walls (4, 4').
- A panel element according to claim 9, characterised in that the side walls (4, 4') are at least partially rolled with the metal profiles (2, 2').
- A panel element according to one of claims 1 to 11, characterised in that the insulating material (2) is heat- and fire-retardant material, preferably PU resin.
- A panel element according to one of claims 1 to 12, characterised in that the insulation (11) between the side walls (4, 4') is fire-retardant and temperature-insulating material, preferably mineral wool.
- An arrangement of at least two panel elements according to one of claims 1 to 13, characterised in that there is provided a corner profile (14) for connection of the panel elements (1) at the edge side, the corner profile having a substantially C-shaped portion (19) of metal, preferably steel, and a - preferably triangular - corner bar (17) of plastic material.
- An arrangement according to claim 14, characterised in that the C-shaped portion (19) can be connected, preferably screwed, at the central part thereof to the corner bar (17).
- An arrangement according to claim 14 or 15, characterised in that the C-shaped portion (19) of the corner profile (14) is spaced from the inwardly disposed metal profiles (2, 2') of the plate elements (1), preferably by the corner bar (17).
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT17142003 | 2003-10-29 | ||
| AT0171403A AT413408B (en) | 2003-10-29 | 2003-10-29 | PANEL ELEMENT FOR MODULAR CONSTRUCTION OF HOUSING, PREFERABLY VENTILATION AND AIR CONDITIONING |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1528186A1 EP1528186A1 (en) | 2005-05-04 |
| EP1528186B1 true EP1528186B1 (en) | 2008-05-21 |
Family
ID=34397361
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP04023654A Expired - Lifetime EP1528186B1 (en) | 2003-10-29 | 2004-10-05 | Panel for modular housing construction in particular of ventilating and air conditioning plants |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1528186B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN100398933C (en) |
| AT (2) | AT413408B (en) |
| DE (1) | DE502004007211D1 (en) |
| TW (1) | TW200523483A (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106766077B (en) * | 2017-03-21 | 2022-06-07 | 博纳环境设备(太仓)有限公司 | Combined air conditioning unit frame and upright post thereof |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US1697189A (en) * | 1927-06-13 | 1929-01-01 | Kirk & Blum Mfg Company | Heat-insulating structural element |
| DE3042109C2 (en) | 1980-11-07 | 1983-08-11 | Aeolos Holding AG, St.Gallen | Plate element for the construction of insulating chambers and housings for ventilation and air conditioning systems |
| DE3244743A1 (en) * | 1982-12-03 | 1984-06-07 | Karosserie- und Fahrzeugbau Werner Brandt, 4923 Extertal | Roller wall for cooling and insulating containers |
| FR2604739A1 (en) * | 1986-10-07 | 1988-04-08 | Cegedur | Insulating panel |
-
2003
- 2003-10-29 AT AT0171403A patent/AT413408B/en not_active IP Right Cessation
-
2004
- 2004-10-05 DE DE502004007211T patent/DE502004007211D1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-10-05 AT AT04023654T patent/ATE396314T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2004-10-05 TW TW093130057A patent/TW200523483A/en unknown
- 2004-10-05 EP EP04023654A patent/EP1528186B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2004-10-29 CN CNB2004100901733A patent/CN100398933C/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| AT413408B (en) | 2006-02-15 |
| TW200523483A (en) | 2005-07-16 |
| ATA17142003A (en) | 2005-07-15 |
| EP1528186A1 (en) | 2005-05-04 |
| TWI319057B (en) | 2010-01-01 |
| CN100398933C (en) | 2008-07-02 |
| DE502004007211D1 (en) | 2008-07-03 |
| ATE396314T1 (en) | 2008-06-15 |
| CN1619233A (en) | 2005-05-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1024243B1 (en) | Fireproof connection with isolating web | |
| EP3155187A1 (en) | Thermally insulating spacer profile | |
| EP1369359A1 (en) | Container | |
| EP0117308B1 (en) | Plastic hollow profile reinforced by a metallic profile and frame | |
| DE69013864T2 (en) | Heat insulating and fire retardant wall panel. | |
| DE3438861A1 (en) | Interlocking profile for manufacturing window frames, door frames, facade constructions and the like | |
| EP1528186B1 (en) | Panel for modular housing construction in particular of ventilating and air conditioning plants | |
| EP0775789A1 (en) | Building element of glass made of a multipane composite unit with an edge protection proceeding | |
| EP0124807B1 (en) | Cabin | |
| EP0279820B1 (en) | Prefabricated panels for the construction of insulating chambers | |
| DE29880053U1 (en) | Profile system for the production of windows or doors | |
| EP2573307A1 (en) | Multi-section profile frame system for doors, gates, conservatories and windows | |
| DE102008063482A1 (en) | Housing for ventilation and air conditioning units, has multiple edge profiles and connecting elements interconnected with sandwich panels with metal between two cover plates | |
| EP0430921A1 (en) | Wall made of box-like panels | |
| EP1681430A2 (en) | Composite profile for frames of wall elements, doors and windows | |
| EP2803804A2 (en) | Door | |
| AT522638B1 (en) | profile | |
| EP1152194B1 (en) | Corner connection for an air conditioning housing frame | |
| DE29712751U1 (en) | Frame construction | |
| EP1004739B1 (en) | Insulating disposition for aluminium section members | |
| DE102004010936A1 (en) | Stratified storage with a housing and insulation | |
| DE19627121C2 (en) | Composite profile | |
| DE19654048C2 (en) | Double-walled container with an inner wall and an outer wall made of a thermally highly conductive material, in particular for refrigerators and heating cabinets | |
| DE2718839A1 (en) | Fireproof duct for air conditioning system - has lightweight non-rigid panels reinforced by duct suspension units | |
| DE102010032947A1 (en) | Attachment construction for timber mullion / transom elements with improved thermal insulation properties |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL HR LT LV MK |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20050811 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20071122 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 502004007211 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20080703 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080521 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080901 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080521 |
|
| NLV1 | Nl: lapsed or annulled due to failure to fulfill the requirements of art. 29p and 29m of the patents act | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080521 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080521 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FD4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080521 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080521 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081021 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080521 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080821 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080521 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080521 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20090224 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: EUROCLIMA APPARATEBAU GMBH Effective date: 20081031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080821 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080521 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20081031 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20081005 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20090630 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090501 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080521 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20081031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20081031 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20081031 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20081031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20081005 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20091014 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20081005 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081122 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080521 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080521 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080822 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20101005 |