EP1524089A2 - Verfahren zum Erzeugen einer speziellen Oberfläche, wie Palladium-ähnliche Verkleidung, auf Betonplatten - Google Patents
Verfahren zum Erzeugen einer speziellen Oberfläche, wie Palladium-ähnliche Verkleidung, auf Betonplatten Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1524089A2 EP1524089A2 EP04077842A EP04077842A EP1524089A2 EP 1524089 A2 EP1524089 A2 EP 1524089A2 EP 04077842 A EP04077842 A EP 04077842A EP 04077842 A EP04077842 A EP 04077842A EP 1524089 A2 EP1524089 A2 EP 1524089A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- abrasive
- procedure
- panels
- parts
- panel
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B28—WORKING CEMENT, CLAY, OR STONE
- B28D—WORKING STONE OR STONE-LIKE MATERIALS
- B28D1/00—Working stone or stone-like materials, e.g. brick, concrete or glass, not provided for elsewhere; Machines, devices, tools therefor
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B24—GRINDING; POLISHING
- B24B—MACHINES, DEVICES, OR PROCESSES FOR GRINDING OR POLISHING; DRESSING OR CONDITIONING OF ABRADING SURFACES; FEEDING OF GRINDING, POLISHING, OR LAPPING AGENTS
- B24B7/00—Machines or devices designed for grinding plane surfaces on work, including polishing plane glass surfaces; Accessories therefor
- B24B7/20—Machines or devices designed for grinding plane surfaces on work, including polishing plane glass surfaces; Accessories therefor characterised by a special design with respect to properties of the material of non-metallic articles to be ground
- B24B7/22—Machines or devices designed for grinding plane surfaces on work, including polishing plane glass surfaces; Accessories therefor characterised by a special design with respect to properties of the material of non-metallic articles to be ground for grinding inorganic material, e.g. stone, ceramics, porcelain
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B28—WORKING CEMENT, CLAY, OR STONE
- B28B—SHAPING CLAY OR OTHER CERAMIC COMPOSITIONS; SHAPING SLAG; SHAPING MIXTURES CONTAINING CEMENTITIOUS MATERIAL, e.g. PLASTER
- B28B11/00—Apparatus or processes for treating or working the shaped or preshaped articles
- B28B11/08—Apparatus or processes for treating or working the shaped or preshaped articles for reshaping the surface, e.g. smoothing, roughening, corrugating, making screw-threads
- B28B11/0818—Apparatus or processes for treating or working the shaped or preshaped articles for reshaping the surface, e.g. smoothing, roughening, corrugating, making screw-threads for roughening, profiling, corrugating
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B28—WORKING CEMENT, CLAY, OR STONE
- B28B—SHAPING CLAY OR OTHER CERAMIC COMPOSITIONS; SHAPING SLAG; SHAPING MIXTURES CONTAINING CEMENTITIOUS MATERIAL, e.g. PLASTER
- B28B11/00—Apparatus or processes for treating or working the shaped or preshaped articles
- B28B11/08—Apparatus or processes for treating or working the shaped or preshaped articles for reshaping the surface, e.g. smoothing, roughening, corrugating, making screw-threads
- B28B11/0845—Apparatus or processes for treating or working the shaped or preshaped articles for reshaping the surface, e.g. smoothing, roughening, corrugating, making screw-threads for smoothing
Definitions
- This invention has as its object a special procedure which makes it possible to obtain on a surface of a so-called palladium or travertine type carried out on at least one surface of a relative prefabricated panel made of vibrated reinforced concrete or pre-compressed reinforced concrete, a flat surface which is yet opportunely variously discontinuous so as to obtain substantial functional, aesthetic, and usage advantages as compared to well-known similar solutions.
- This procedure can basically be used in the construction sector for various purposes; it was however designed, created and developed for a special application, specifically, to obtain a new special surface conformation of the covering of one of the surfaces of well-known prefabricated concrete panels, referred to as fillers, and used for some time to form the perimeter walls of industrial, commercial and civil buildings.
- the concrete panels of the type referred to above have rough surfaces all of the same color as the concrete used. Therefore, for applications which require a certain aesthetic aspect, especially surfaces which are visible, usually those walls on the outside of the relative building are plastered with colored plasters or painted.
- the realization has been provided for in the manufacturing phase of the covering of at least one surface, in particular usually the one which in application will be on the outside of the building, of a layer formed of an opportune cement mortar mixed with stones and/or pieces of stone of various type, granulometry and color as well as often being opportunely colored.
- this covering layer will be practically the same as that used for elements called palladium or travertine type.
- a well-known procedural phase the surface of the covering carried out as referred to above is ground with known tools and methods, obtaining the same appearance as well as the same characteristics of the so-called palladium or flooring which are performed in the same way.
- a second procedural phase which is also well-known, to the cement mortar used to form the layering cover there is added an opportune substance called a retardant, which delays setting and through this in the form used to produce the entire cement panel there forms a thin layer which will be located on the outer surface of the previous layer of normal cement mortar (without retardant) mixed as usual with stone grit, which forms the covering of the relative concrete panel.
- the aforementioned thin layer of cement mortar with retardant will not yet be hardened, so that by striking the surface of the covering with high pressure jets of water, part of the non-hardened cement mortar will be removed.
- the result will be an irregular surface formed of a number of flat surfaces of various shapes and sizes generated by the corresponding surfaces washed by the stone elements (pebbles, stone chips, etc.) which are in the covering layer and a true network of canals between the edges of said elements.
- the palladium-type solution is aesthetically questionable in that, depending on the type and size of grain used, it recalls the appearance of the tops of tables, counters and other objects of the past which are no longer fashionable. Furthermore, since the surface is normally smooth or even shiny, it provokes, especially if the observer is in certain positions, objectionable and not always pleasing reflection effects.
- the grit which is used is mostly obtained from stones which are broken or crushed in special crushers, the single pieces which make it up have irregular polyhedral shapes with various sharp sides and various acute edges which, after the washing operation, protrude from the grooves between them.
- the purpose of this invention is to overcome the aforementioned problems and defects, which is achieved with the new procedure by means of which, on the surface of prefabricated concrete panels of various types and especially cement filler panels used in the construction sector mainly to form outer perimeter walls of industrial, commercial and civil buildings, there is carried out in a traditional and known way an opportune covering referred to as palladium or travertine type, which is first ground with suitable grinders and then brushed with suitable abrasive brushes, thus obtaining a special surface conformation which not only eliminates the problems and defects of the known and traditional coverings but also provides substantial and new advantageous characteristics.
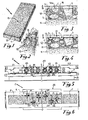
- Said concrete panel 1 will be composed of a basic body 11 of an essentially parallelepiped form, the two largest faces of which, of a considerable size and parallel to each other, respectively define the external face, that is, the one which in usage conditions will be the exterior of the building and the opposing interior face. At least one of these larger faces, normally the one on the outside of the building, will be covered with an opportune covering layer 12, which will be obtained by proceeding as follows. First, one casts on the bottom of the form used to produce panel 1 a substantial layer consisting of an opportune mixture of cement mortar and stone grit, and then one proceeds with the formation of panel 1 by further pouring normal cement mortar so as to form its basic body 11.
- Said basic body 1 will be executed in manners and with techniques which are known, that is, by pouring normal cement mortar into an opportune form.
- suitable reinforcing means normally rod iron grids welded into squares
- suitable block of insutalting material normally expanded polystyrene
- Said grit can therefore be composed of a variety of elements, both of natural origin such as whole or crushed pebbles or various rock chips, as well as of artificial origin such as pieces of glass, gres, ceramic, etc.
- the particles that make up said grit may be of a very different shape and granulometry, or also roughly similar, and they may be of different, similar or even the same colors.
- the cement mortar used to bind the aforementioned particles of said grit may be left in their natural state, thus presenting the characteristic gray color, or they may be opportunely colored with suitable pigments of either a natural or synthetic base.
- the concrete panel 1 complete as described above with the relative covering layer 12 is opportunely left to cure completely or at least opportunely partially before proceeding with the subsequent treatment operations established by the procedure described herein.
- Curing may take place naturally, in which case a substantial period of immobility will be necessary, or it can be artificially forced in a known manner through the use of steam so as to substantially reduce the aforementioned period of immobility.
- the obtained concrete panel 1 is practically completely identical to normal equivalent concrete panels upon the surface of which a palladium type covering is performed and obviously the resulting surface will be quite smooth, but overall quite raw. Therefore, if one were to proceed in the normal way of completion the entire piece with just simple grinding, there would be nothing new.
- the elements which make up the grit may consist of pebbles and/or chips of various types of stone materials (rocks) such as granite, marble, etc.
- the pebbles are indicted by the letter C and the chips with the letter S.
- the abrasives bristles of said abrasive brushes are able to remove from the surface indicated by line B essentially the material which makes up the cement mortar M which is among the elements of grit (C and S) because it has a consistency and hardness which is considerably less than the hardness or consistency of the substances which form the aforementioned elements (pebbles C and stone chips S) which make up the grit.
- the abrasive bristles of said abrasive brushes along with the described action, by striking the surface of the cement mortar M which is between the various elements C and S of the grit, cause upon it at the same time a compacting action which greatly reduces, and in fact practically eliminates, even the slightest porosity which may have remained in it.
- the surface obtained by means of the described treatment presents the noteworthy characteristic of almost totally keeping various pollutants, dust from incombustibles or other materials, water from atmospheric humidity condensation and/or acid rain which in conjunction with the aforementioned dusts and pollutants generates aggressive solutions, from building up and attaching to it, thus forming in certain parts of it areas with dark spots or smudges which appear to be dirty and which, as is known, in normal surfaces not treated with the procedure contained herein turn out not to be cleanable, not even through washing with various surface active substances, nor even with solvents.
- the resulting special surface conformation makes it possible to achieve various and appreciable aesthetic effects which are not obtainable with normal surfaces obtained with known procedures and systems in the covering of concrete panels equivalent to those considered by this invention.
- the described solution can be advantageously used for various other applications such as covering floor tiles or paving tiles which can be used for covering buildings of any kind.
- machine 2 is composed basically of a base 21 the purpose of which is to support the conveyor belt N which runs in the direction shown by the arrows in a working structure 20 whose ends it protrudes from with opportune free sections for the purpose of forming respectively a loading zone Z1 and an unloading zone Z2.
- said working structure 20 there is an appropriate number of working units and specifically a first group of working units U1 composed of grinders 22 and a second group of working units U2 composed of abrasive brushes 23 which, for example purposes, mainly only for illustrative clarity, are represented as being composed of a ring of bristles 24 which spread out radially from a central cylindrical support25.
- Both the abrasive grinders 22 and the abrasive brushes will be connected and set in rotation by respective electrical motors E and the respective resulting groups will be connected to respective supports 26 which in turn are supported on the relative guides 4 which are placed transversally as well as at right angles to the conveyor belt N.
- Opportune devices which are in themselves known for simplicity and clarity are not illustrated in the figures referred to are provided for the activation of each grinder/motor or brush/motor group to move alternately transversally to the conveyor belt N below so as to move the single abrasive grinders 22 and the single abrasive brushes 23 along the entire section included between the two side edges of it (N).
- the panels P to be treated are loaded onto the free section of the conveyor belt N which protrudes beyond the working structure 20 thus forming the so-called loading zone 20.
- the conveyor belt N being in movement (as shown in figure 5 by the arrows) sends the concrete panels P towards the working structure 20.
- Each panel P will then pass progressively first under the abrasive grinders 22 of the first working group U 1 where it will undergo a progressing grinding treatment consisting in the removal of a thin layer of coating (the layer which in figures 3 and 4 is between lines A and B).
- the panel thus ground then moves under the abrasive brushes 23 of the second working group U2 where it undergoes the final brushing treatment required by the procedure for the invention described herein. After this treatment, the panel, which is completely finished and therefore has the surface of its covering conformed as described in detail above, will continue onto the free section of the conveyor belt N which forms the unloading zone Z2 from which it will be removed.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Mining & Mineral Resources (AREA)
- Aftertreatments Of Artificial And Natural Stones (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| ITPN20030074 ITPN20030074A1 (it) | 2003-10-17 | 2003-10-17 | Procedimento per generare una particolare conformazione |
| ITPN20030074 | 2003-10-17 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1524089A2 true EP1524089A2 (de) | 2005-04-20 |
| EP1524089A3 EP1524089A3 (de) | 2006-04-26 |
Family
ID=34362438
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP04077842A Withdrawn EP1524089A3 (de) | 2003-10-17 | 2004-10-15 | Verfahren zum Erzeugen einer speziellen Oberfläche, wie Palladium-ähnliche Verkleidung, auf Betonplatten |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1524089A3 (de) |
| IT (1) | ITPN20030074A1 (de) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2007014809A1 (en) * | 2005-08-01 | 2007-02-08 | Luca Toncelli | Method for manufacturing articles in the form of sheets consisting of a conglomerate stone material and a binder and resultant sheet |
| KR100722505B1 (ko) | 2005-08-24 | 2007-05-29 | 조용구 | 타일 상감장치 |
| CN109333206A (zh) * | 2018-09-30 | 2019-02-15 | 清远戈兰迪高分子材料有限公司 | 一种石英石麻面板材的加工方法 |
| EP3723998A1 (de) * | 2017-12-15 | 2020-10-21 | Flooring Industries Limited, SARL | Abdeckelement, verfahren zum dekorieren eines abdeckelementes und maschine zum dekorieren eines abdeckelementes |
| DE102019113084A1 (de) * | 2019-05-17 | 2020-11-19 | Schindler GmbH | Verfahren zur Oberflächenbearbeitung einer Gesteins- und/oder Betonoberfläche |
| KR102347254B1 (ko) * | 2021-08-23 | 2022-01-03 | 윤찬호 | 입체감을 위한 석재 표면 처리 방법 |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3202025A (en) * | 1959-09-28 | 1965-08-24 | Wood Conversion Co | Tool for producing fissures in mineral felt |
| FR2144974A5 (de) * | 1971-07-05 | 1973-02-16 | Marquier Dalles | |
| DE19715937C1 (de) * | 1997-04-16 | 1998-11-05 | Fraunhofer Ges Forschung | Verfahren zur Herstellung rutschfester Fußbodenbeläge |
| ITRM20010330A1 (it) * | 2001-06-11 | 2002-12-11 | Venix S R L | Metodo per la fabbricazione di mattonelle, in particolare per pavimenti detti alla veneziana e simili. |
-
2003
- 2003-10-17 IT ITPN20030074 patent/ITPN20030074A1/it unknown
-
2004
- 2004-10-15 EP EP04077842A patent/EP1524089A3/de not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2007014809A1 (en) * | 2005-08-01 | 2007-02-08 | Luca Toncelli | Method for manufacturing articles in the form of sheets consisting of a conglomerate stone material and a binder and resultant sheet |
| KR100722505B1 (ko) | 2005-08-24 | 2007-05-29 | 조용구 | 타일 상감장치 |
| EP3723998A1 (de) * | 2017-12-15 | 2020-10-21 | Flooring Industries Limited, SARL | Abdeckelement, verfahren zum dekorieren eines abdeckelementes und maschine zum dekorieren eines abdeckelementes |
| CN109333206A (zh) * | 2018-09-30 | 2019-02-15 | 清远戈兰迪高分子材料有限公司 | 一种石英石麻面板材的加工方法 |
| CN109333206B (zh) * | 2018-09-30 | 2022-05-27 | 清远戈兰迪高分子材料有限公司 | 一种石英石麻面板材的加工方法 |
| DE102019113084A1 (de) * | 2019-05-17 | 2020-11-19 | Schindler GmbH | Verfahren zur Oberflächenbearbeitung einer Gesteins- und/oder Betonoberfläche |
| KR102347254B1 (ko) * | 2021-08-23 | 2022-01-03 | 윤찬호 | 입체감을 위한 석재 표면 처리 방법 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1524089A3 (de) | 2006-04-26 |
| ITPN20030074A1 (it) | 2005-04-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20240011291A1 (en) | Decorative concrete with uniform surface and method of forming the same | |
| US8079775B2 (en) | Non-slick surface-seeded aggregate concrete and method of forming | |
| US9114664B2 (en) | Concrete mosaic and method of forming the same | |
| US7591967B2 (en) | Method for the aesthetic surface treatment of a monolithic concrete floor and product of the method | |
| US8936411B1 (en) | Architectural concrete | |
| JPH01200910A (ja) | 天然石コンクリートブロツク及びその製造方法 | |
| US20240167270A1 (en) | Lightweight blocks with stone-like appearance and method of manufacture | |
| CN110230380B (zh) | 一种浇捣一体磨石地坪的施工方法 | |
| US20070248411A1 (en) | Concrete template and method of use | |
| US7607859B2 (en) | Surface seeded fine aggregate concrete simulating quarried stone | |
| EP1524089A2 (de) | Verfahren zum Erzeugen einer speziellen Oberfläche, wie Palladium-ähnliche Verkleidung, auf Betonplatten | |
| RU2145928C1 (ru) | Способ мозаичной или декоративной облицовки поверхности плиточным материалом из природного камня | |
| CN109293319A (zh) | 一种水磨石墙及其制备方法 | |
| JP2794468B2 (ja) | コンクリート系擬石製品の表面仕上げ法 | |
| WO2001036762A1 (en) | Terrazzo flooring system | |
| JP3636712B1 (ja) | 人造石材およびその製造方法 | |
| CN115354825A (zh) | 一种干磨密封固化混凝土地面施工方法 | |
| KR20100035204A (ko) | 건축물의 건식 갈기용 바닥마감재의 시공방법 | |
| RU2240235C1 (ru) | Способ декоративной обработки изделий | |
| US20240082978A1 (en) | Methods and systems for finishing plaster layers applied to block products | |
| CN219773444U (zh) | 一种方便清洁的仿石皮纹砖 | |
| EP4242183A1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung einer dekorativen bodenfliese sowie durch dieses verfahren hergestellte dekorative bodenfliese | |
| GB2432170A (en) | Decorative building block | |
| KR19990078705A (ko) | 합성 석재 및 그 응용자재 | |
| Zhadanovsky et al. | Processing of exterior light concrete wall panels |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL HR LT LV MK |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL HR LT LV MK |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: 8566 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 20061027 |