EP1069224B1 - Felting needle - Google Patents
Felting needle Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1069224B1 EP1069224B1 EP00109536A EP00109536A EP1069224B1 EP 1069224 B1 EP1069224 B1 EP 1069224B1 EP 00109536 A EP00109536 A EP 00109536A EP 00109536 A EP00109536 A EP 00109536A EP 1069224 B1 EP1069224 B1 EP 1069224B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- transition
- needle
- felting needle
- working part
- region
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H18/00—Needling machines
- D04H18/02—Needling machines with needles
Definitions
- the invention relates to a needle having the features of the preamble of patent claim 1 or claim 2.
- Deposits form after a certain period of the machine for producing the felt.
- the deposits can clog the needles to such an extent that the needles are no longer able to penetrate through the holes of the stripper plate.
- These deposits cause needle breaks and production losses.
- the air flow between the needles is adversely affected, with the result that the deposits accelerate even more.
- the production must be interrupted. Needle cleaning often results in needle breakage.
- the material is solidified.
- the material is relatively loose and voluminous. Penetrating the needle with its shank portion or its intermediate portion in the material, it produces holes with shaft diameter or the diameter of the intermediate portion, which is greater than the diameter of the working part. This results in a poor surface quality of the felt.
- Felt needles are known with a long straight shaft, which is angled at its upper end for clamping in a needle board.
- the shank tapers at its other end to a reduced cross section and is further provided with hooks.
- This Section forms a working part that serves to matt the fiber fleece.
- a device for needling a mineral fiber fleece is known.
- the felting needles held on a needle board extend parallel to each other away from the needle board through corresponding openings of a stripper plate. Between this and a bed plate, which also has openings for the felting needles, a gap is formed through which the nonwoven fabric is guided.
- the felting needles have a cylindrical, upwardly angled and relatively thick shaft, of which a portion is held in the needle board. Between the clamping part and the toothed working part, a transition region is formed whose length is barely larger than the diameter of the shaft region.
- Deposits can form on the cylindrical shaft.
- a forked needle which has a unge leopardten workspace. This connects via a conical intermediate region to a cylindrical shaft.
- the working part is smooth on its outside and provided only at its free end with a mouth-like fork.
- a more or less steep transition region may be provided in the form of a cone.
- Forked needles are used to structure consolidated webs in a sequential process. They tend because of the smooth ungebergten edges of the working part little to dissolve fibers from the fiber structure and take.
- Felting needles with a serrated working part tend to accumulate fibers pulled out of the fiber structure on their shafts.
- the shaft extends during needling of the fibers partially in the working space between stripper plate and bed plate.
- the extracted fibers form deposits in the form of fiber rings which slide from the relatively thin working part over the short transition region to the cylindrical shaft region between the needle board and the stripper plate. They are widened and tightened. If these deposits exceed a tolerable level, the piercing of the needles into the fleece is hindered because the needle board can no longer be brought close enough to the stripper plate. Therefore, depending on the nonwoven material used, cleaning actions are required from time to time. Due to the large number of needles held on a needle board, such cleaning is cumbersome and time consuming.
- the needle according to the invention is characterized in that a relatively slender transition part or transition region is formed between the toothed working part and the untoothed clamping part, which has at least one region in which the diameter gradually reduces from the shaft diameter to the diameter of the working part.
- the length of this area which may also be divided into several subregions as needed, is at least twice as long as the length of the toothed working part.
- the length of the transition region with conventional needle board thicknesses or thicknesses is greater than the respective thickness of the needle board.
- the transition part preferably occupies the entire space between the needle board and the respective working part. The result is a slim transition, which results in less deposits forming on the needle.
- the precipitation rings made of fibers expand only slowly, which results in less adhesion to the transition area.
- the cleaning of the respective needles by the long transition part is easier.
- Flush rings sitting on the needles and fiber accumulations between the needles are easier to wipe or remove from the needle.
- the working part of the needle can be made slimmer than conventional needles.
- the transition is preferably longer 11, better still 20 mm.
- the needle according to the invention can replace felting needles with single, double or triple diameter reduction. This reduces the variety of types to be provided by the needle manufacturer.
- shank area which passes between the stripper plate and bed plate during needling, has a smaller diameter compared to conventional needles.
- the openings produced by the shaft region in the felt produced in the diameter are smaller.
- the surface quality of the felt improves.
- the transition part is preferably formed conically in a continuous part.
- the cone can be a straight circle truncated cone. This means that a generating line of this area is a straight line.
- the cone may also be formed by a non-straight cone. A generatrix of the transition part is then arcuate.
- the working part and the clamping part are preferably arranged coaxially relative to one another. If necessary, however, it can also deviate from this become.
- the working part has a constant diameter and also connects preferably without diameter change smoothly to the transition part.
- the transition part occupies the entire space between the needle board and the working part.
- the total length of the transition part may be smaller than twice the working part length due to the needle dimensions.
- the needle consists of three areas: working part, transition part and shaft part, which sits completely in the needle board.
- transition part is longer than the thickness of the needle board provided for attachment of the needles. Regardless of the overall length of the transition piece, in one embodiment of the needle, the transition piece begins immediately on the needle board.
- FIG. 1 illustrates a device 1 for needling a nonwoven fabric.
- a needle board 2 which is driven, for example. Via an eccentric and performs a reciprocating motion in a direction illustrated by an arrow 3 direction.
- the needle board 2 has openings 4 for holding and supporting needles 5.
- the needles 5 extend at a distance and parallel to each other from the needle board 2 away. They protrude through wiper openings 6, which are formed in a stripper plate 7. This is arranged at some distance from a bed plate 8 and defines with this a gap 9, are guided by the loose and disordered fibers in a direction indicated in Figure 1 by an arrow 11 direction. In the course of these fibers are solidified by the up and down movement of the needles 5 to form a nonwoven.
- openings 12 are provided, wherein in each case an opening 12 of the bed plate 8 is aligned with an opening 6 of the stripper plate 7.
- the needles 5 are constructed to match each other. They each have a clamping part 14 held in the needle board 2 and a working part 16 provided with barbs or hooks 15. Between the Einspannteil 14 and the working part 16, a transition part 17 is arranged. The transition part 17 extends from the chucking part 14 to the working part 16, starting in the immediate vicinity of the needle board 2.
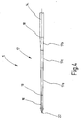
- FIG. 2 shows a needle 5 for the purpose of illustrating the proportions.
- the diameter decreases from the larger value to be measured at the transition point 18 to a lower value to be measured at a transition point 19 at which the working part 16 begins.
- the transition piece 17 is arranged coaxially to a longitudinal axis 21 of the needle 5 and forms a total of a contiguous area for the adjustment of the diameter.
- the clamping part 14 and the working part 16 are arranged coaxially with the longitudinal axis 21. Along the longitudinal axis 21, the diameter of the transition part 17 decreases steadily and linearly.
- the between the transition points 18, 19 to be measured length of the transition part 17 is at least twice as large as the length of the working part 16, ie the distance of the transition point 19 formed by a free end of the needle 5 tip 22. This makes the transition part is very slim and long. He has no steps or heels.
- the device 1 operates as follows:
- FIG. 3 illustrates a somewhat modified embodiment of the needle 5.
- the region formed by the transition part 17 is divided into two subregions 17a, 17b, in which the diameter of the needle 5 is reduced from the shaft diameter to the working part diameter.
- the partial area 17a adjoins the transition point 19, while the partial area 17b adjoins the transition point 18.
- a cylindrical intermediate section 17c is formed between the sections 17a, 17b.
- the transition part 17 begins immediately after the needle board 2, ie that the transition point 18 is aligned with the underside of the needle board 2.
- the portions 17a, 17b, in which the taper of the needle 5 takes place, taken together have a length which is equal to or greater than twice the length of the working part 16, ie the distance between the transition point 19 and the top 22nd
- the portions 17a, 17b are each on the mantle of a narrow cone, i. the diameter decreases in these partial regions 17a, 17b towards the tip 22.
- the diameter reduction is linear in the embodiment of FIG. 4 for the portion 17a, not for the portion 17b.
- the trained cone is thus curvilinearly limited.
- Such a cone may also be formed instead of the cone in the portion 17a or in the embodiment of Figure 2 instead of the straight slender truncated cone in the transition part 17.
- a transition part 17 is provided between clamping part 14 and working part 16, which is designed as a long slender truncated cone.
- the length of this transition part 17 is at least twice as long as the working part. This results in a very slim transition region, which has little tendency to pull fibers from the fleece and collect. If fiber deposits nevertheless form, these are easy to remove.
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft eine Nadel mit den Merkmalen des Oberbegriffs des Patentanspruchs 1 oder des Patentanspruchs 2.The invention relates to a needle having the features of the preamble of
Bei der Filzherstellung werden lose und ungeordnet übereinander liegenden Fasern durch eine Maschine zwischen einer vielfach gelochten Abstreiferplatte und einer ebenfalls gelochten Bettplatte geführt. Dieses Fasergemisch wird wiederholt mit einer größeren Anzahl spezieller Nadeln (Filznadeln) durchstochen. Die Filznadeln bewirken dabei eine Bindung der Faser untereinander, so dass die Bahn nach und nach verdichtet und letztlich ein fester Filz hergestellt wird. Als Fasern kommen außer Naturfasern und Kunstfasern auch Recyclingfasern zum Einsatz, die in der Regel jedoch eine verstärkte Tendenz haben, sich an den Nadeln festzusetzen und Ablagerungen zu bilden.In felt production, loosely and randomly superimposed fibers are fed through a machine between a multiple perforated stripper plate and a likewise perforated bed plate. This fiber mixture is repeatedly pierced with a larger number of special needles (felting needles). The felting needles effect thereby bonding the fiber together, so that the web is gradually compressed and ultimately a solid felt is produced. Apart from natural fibers and synthetic fibers, recycled fibers are also used as fibers, but as a rule they have an increased tendency to attach to the needles and form deposits.
Ablagerungen bilden sich nach einer gewissen Laufzeit der Maschine zum Herstellen des Filzes. Die Ablagerungen können die Nadeln in einem solchen Maß zusetzen, dass die Nadeln nicht länger in der Lage sind, durch die Löcher der Abstreiferplatte durchzudringen. Diese Ablagerungen verursachen Nadelbrüche und Produktionsausfälle. Sobald der Ablagerungsprozess beginnt, wird die Luftströmung zwischen den Nadeln negativ beeinflusst, mit dem Ergebnis, dass sich die Ablagerungen noch beschleunigen. Zur Nadelreinigung muss die Produktion unterbrochen werden. Bei der Nadelreinigung kommt es häufig zum Nadelbruch.Deposits form after a certain period of the machine for producing the felt. The deposits can clog the needles to such an extent that the needles are no longer able to penetrate through the holes of the stripper plate. These deposits cause needle breaks and production losses. Once the deposition process begins, the air flow between the needles is adversely affected, with the result that the deposits accelerate even more. To clean the needle, the production must be interrupted. Needle cleaning often results in needle breakage.
Beim Nadelprozess wird das Material verfestigt. Zu Anfang, d.h. beim Vornadeln, ist das Material relativ locker und voluminös. Dringt die Nadel mit ihrem Schaftabschnitt oder ihrem Zwischenbereich in das Material ein, erzeugt sie Löcher mit Schaftdurchmesser oder dem Durchmesser des Zwischenabschnitts, der größer ist als der Durchmesser des Arbeitsteils. Dies ergibt eine schlechte Oberflächenqualität des Filzes.During the needle process, the material is solidified. At the beginning, i. When pre-needling, the material is relatively loose and voluminous. Penetrating the needle with its shank portion or its intermediate portion in the material, it produces holes with shaft diameter or the diameter of the intermediate portion, which is greater than the diameter of the working part. This results in a poor surface quality of the felt.
Aus der
Der Übergang zwischen dem Arbeitsteil und dem übrigen, als Einspannteil dienenden Schaft ist relativ steil.The transition between the working part and the rest, serving as Einspannteil shaft is relatively steep.
Aus der
Auf dem zylindrischen Schaft können sich Ablagerungen bilden.Deposits can form on the cylindrical shaft.
Aus der
Gabelnadeln werden verwendet, um verfestigte Vliese in einem Folgeprozess zu strukturieren. Sie neigen wegen der glatten ungezahnten Flanken des Arbeitsteils wenig dazu, Fasern aus dem Faserverband herauszulösen und mitzunehmen.Forked needles are used to structure consolidated webs in a sequential process. They tend because of the smooth ungezahnten edges of the working part little to dissolve fibers from the fiber structure and take.
Aus der
Filznadeln mit gezahntem Arbeitsteil neigen dazu, aus dem Faserverband herausgezogene Fasern auf ihrem Schaft anzusammeln. Der Schaft reicht beim Vernadeln der Fasern teilweise in den Arbeitsraum zwischen Abstreiferplatte und Bettplatte. Die herausgezogenen Fasern bilden Ablagerungen in Form von Faserringen, welche sich vom relativ dünnen Arbeitsteil über den kurzen Übergangsbereich auf den zylindrischen Schaftbereich zwischen dem Nadelbrett und der Abstreifplatte schieben. Dabei werden sie aufgeweitet und festgezogen. Übersteigen diese Ablagerungen ein tolerierbares Maß, wird das Einstechen der Nadeln in das Vlies behindert, weil das Nadelbrett nicht mehr nahe genug an die Abstreifplatte herangeführt werden kann. Es sind deshalb je nach verwendetem Vliesmaterial von Zeit zu Zeit Reinigungsaktionen erforderlich. Aufgrund der großen Zahl der an einen Nadelbrett gehaltenen Nadeln ist eine solche Reinigung mühsam und zeitaufwendig.Felting needles with a serrated working part tend to accumulate fibers pulled out of the fiber structure on their shafts. The shaft extends during needling of the fibers partially in the working space between stripper plate and bed plate. The extracted fibers form deposits in the form of fiber rings which slide from the relatively thin working part over the short transition region to the cylindrical shaft region between the needle board and the stripper plate. They are widened and tightened. If these deposits exceed a tolerable level, the piercing of the needles into the fleece is hindered because the needle board can no longer be brought close enough to the stripper plate. Therefore, depending on the nonwoven material used, cleaning actions are required from time to time. Due to the large number of needles held on a needle board, such cleaning is cumbersome and time consuming.
Davon ausgehend ist es Aufgabe der Erfindung, die Reinigung der Nadeln zu erleichtern und/oder die Neigung der Nadeln zum Akkumulieren von Fasern zu vermindern.On this basis, it is an object of the invention to facilitate the cleaning of the needles and / or to reduce the tendency of the needles to accumulate fibers.
Diese Aufgabe wird mit Nadeln nach Anspruch 1 gelöst.This object is achieved with needles according to
Die erfindungsgemäße Nadel zeichnet sich dadurch aus, dass zwischen dem gezahnten Arbeitsteil und dem ungezahnten Einspannteil ein relativ schlanker Übergangsteil bzw. Übergangsbereich ausgebildet ist, der zumindest einen Bereich aufweist, in dem sich der Durchmesser von dem Schaftdurchmesser auf den Durchmesser des Arbeitsteils allmählich verringert. Die Länge dieses Bereichs, der bedarfsweise auch in mehrere Teilbereiche aufgeteilt sein kann, ist insgesamt mindestens zweimal so lang wie die Länge des gezahnten Arbeitsteils. Somit ist die Länge des Übergangsbereichs bei üblichen Nadelbrettstärken oder - dicken größer als die betreffende Dicke des Nadelbretts. Außerdem nimmt der Übergangsteil vorzugsweise den gesamten Raum zwischen dem Nadelbrett und dem jeweiligen Arbeitsteil ein. Es ergibt sich ein schlanker Übergang, der dazu führt, dass sich an der Nadel weniger Ablagerungen bilden. In vielen werden die aus Fasern bestehenden Ablagerungsringe nur langsam aufgeweitet, was dazu führt, dass sie an dem Übergangsbereich nicht so stark haften. Wenn sich jedoch Ablagerungen bilden, ist die Reinigung der betreffenden Nadeln durch den langen Übergangsteil leichter. Auf den Nadeln sitzende Flusringe und zwischen den Nadeln befindliche Faseransammlungen können leichter von der Nadel abgestreift oder entfernt werden.The needle according to the invention is characterized in that a relatively slender transition part or transition region is formed between the toothed working part and the untoothed clamping part, which has at least one region in which the diameter gradually reduces from the shaft diameter to the diameter of the working part. The length of this area, which may also be divided into several subregions as needed, is at least twice as long as the length of the toothed working part. Thus, the length of the transition region with conventional needle board thicknesses or thicknesses is greater than the respective thickness of the needle board. In addition, the transition part preferably occupies the entire space between the needle board and the respective working part. The result is a slim transition, which results in less deposits forming on the needle. In many, the precipitation rings made of fibers expand only slowly, which results in less adhesion to the transition area. However, when deposits form, the cleaning of the respective needles by the long transition part is easier. Flush rings sitting on the needles and fiber accumulations between the needles are easier to wipe or remove from the needle.
Infolge des allmählichen Übergangs des großen Schaftdurchmessers des Einspannteils zu dem kleinen Durchmesser des Arbeitsteils, sind die Brucheigenschaften und die Flexibilität der Nadeln verbessert. Es werden Spannungskonzentrationen im Übergangsbereich vermieden.Due to the gradual transition of the large shaft diameter of the clamping part to the small diameter of the working part, the breaking properties and the flexibility are the needles improved. Stress concentrations in the transition region are avoided.
Daraus ergibt sich auch, dass der Arbeitsteil der Nadel schlanker ausgebildet werden kann als bei herkömmlichen Nadeln. Der Übergang ist vorzugsweise länger 11, besser noch 20 mm.It also follows that the working part of the needle can be made slimmer than conventional needles. The transition is preferably longer 11, better still 20 mm.
Es hat sich weiterhin als vorteilhaft herausgestellt, dass viele Typen vorhandener Nadeln durch die erfindungsgemäße Nadel ersetzt werden können. Die erfindungsgemäße Nadel kann Filznadeln mit einfacher, doppelter oder dreifacher Durchmesserreduzierung ersetzen. Damit sinkt die von dem Nadelhersteller bereitzustellende Typenvielfalt.It has also been found to be advantageous that many types of existing needles can be replaced by the needle according to the invention. The needle according to the invention can replace felting needles with single, double or triple diameter reduction. This reduces the variety of types to be provided by the needle manufacturer.
Ein weiterer Vorteil ist, dass der Schaftbereich, der beim Vernadeln in den Arbeitsbereich zwischen Abstreiferplatte und Bettplatte gelangt, einen geringeren Durchmesser im Vergleich zu herkömmlichen Nadeln aufweist. Dadurch werden die durch den Schaftbereich erzeugten Öffnungen im hergestellten Filz im Durchmesser kleiner. Somit verbessert sich die Oberflächenqualität des Filzes.Another advantage is that the shank area, which passes between the stripper plate and bed plate during needling, has a smaller diameter compared to conventional needles. As a result, the openings produced by the shaft region in the felt produced in the diameter are smaller. Thus, the surface quality of the felt improves.
Der Übergangsteil ist vorzugsweise konisch in einem durchgehenden Teil ausgebildet. Der Konus kann ein gerader Kreiskegelstumpf sein. Dies bedeutet, dass eine Mantellinie dieses Bereichs eine Gerade ist. Alternativ kann der Konus auch durch einen nichtgeraden Kegel gebildet sein. Eine Mantellinie des Übergangsteils ist dann bogenförmig.The transition part is preferably formed conically in a continuous part. The cone can be a straight circle truncated cone. This means that a generating line of this area is a straight line. Alternatively, the cone may also be formed by a non-straight cone. A generatrix of the transition part is then arcuate.
Bei der erfindungsgemäßen Nadel sind der Arbeitsteil und der Einspannteil zueinander vorzugsweise koaxial angeordnet. Bedarfsweise kann davon jedoch auch abgewichen werden. Außerdem wird bevorzugt, dass der Arbeitsteil einen konstanten Durchmesser aufweist und sich ebenfalls vorzugsweise ohne Durchmesseränderung glatt an den Übergangsteil anschließt.In the case of the needle according to the invention, the working part and the clamping part are preferably arranged coaxially relative to one another. If necessary, however, it can also deviate from this become. In addition, it is preferred that the working part has a constant diameter and also connects preferably without diameter change smoothly to the transition part.
Gemäß Anspruch 2 nimmt der Übergangsteil den gesamten Raum zwischen dem Nadelbrett und dem Arbeitsteil ein. Die Gesamtlänge des Übergangsteils kann aufgrund der Nadelabmessungen kleiner als das Doppelte der Arbeitsteillänge sein. In diesem Fall besteht die Nadel aus drei Bereichen: Arbeitsteil, Übergangsteil und Schaftteil, der vollständig in dem Nadelbrett sitzt.According to
Dabei ist es vorteilhaft, wenn der Übergangsteil länger ist als die Dicke des zur Befestigung der Nadeln vorgesehenen Nadelbretts. Ungeachtet der Gesamtlänge des Übergangsteils beginnt der Übergangsteil bei einer Ausführungsform der Nadel unmittelbar an dem Nadelbrett.It is advantageous if the transition part is longer than the thickness of the needle board provided for attachment of the needles. Regardless of the overall length of the transition piece, in one embodiment of the needle, the transition piece begins immediately on the needle board.
Weitere Einzelheiten vorteilhafter Ausführungsformen der Erfindung sind Gegenstand der Beschreibung, der Zeichnung oder von Unteransprüchen.Further details of advantageous embodiments of the invention are the subject of the description, the drawings or subclaims.
In der Zeichnung sind Ausführungsbeispiele der Erfindung veranschaulicht. Es zeigen:
- Fig. 1 eine Vorrichtung zum Nadeln eines Filzes, in schematisierter längs geschnittener Darstellung,
- Fig. 2 eine Nadel der Vorrichtung nach Figur 1, in einer schematisierten Seitenansicht,
- Fig. 3 eine abgewandelte Ausführungsform der Nadeln nach Figur 1,
- Fig. 4 eine weiter abgewandelte Ausführungsform einer
Nadel nach Figur 1, in Seitenansicht, und - Fig. 5 die Nadel nach Fig. 4 in einer ausschnittsweisen Seitenansicht, in einem anderen Maßstab.
- 1 is a device for needling a felt, in a schematic longitudinal sectional view,
- 2 shows a needle of the device according to FIG. 1, in a schematic side view,
- 3 shows a modified embodiment of the needles according to FIG. 1,
- Fig. 4 shows a further modified embodiment of a needle according to Figure 1, in side view, and
- Fig. 5, the needle of Fig. 4 in a fragmentary side view, in a different scale.
In Figur 1 ist eine Vorrichtung 1 zum Nadeln eines Faservlieses veranschaulicht. Zu der Vorrichtung 1 gehört ein Nadelbrett 2, das bspw. über einen Exzenter angetrieben ist und eine hin- und hergehende Bewegung in einer durch einen Pfeil 3 veranschaulichten Richtung ausführt. Das Nadelbrett 2 weist Öffnungen 4 zur Halterung und Lagerung von Nadeln 5 auf. Die Nadeln 5 erstrecken sich im Abstand und parallel zueinander von dem Nadelbrett 2 weg. Sie ragen durch Abstreiföffnungen 6, die in einer Abstreifplatte 7 ausgebildet sind. Diese ist in einigem Abstand zu einer Bettplatte 8 angeordnet und legt mit dieser einen Zwischenraum 9 fest, durch den lose und ungeordnet liegende Fasern in einer in Figur 1 durch einen Pfeil 11 bezeichneten Richtung geführt werden. Im weiteren Verlauf werden diese Fasern durch die Auf- und Abbewegung der Nadeln 5 zu einem Vlies verfestigt.FIG. 1 illustrates a
In der Bettplatte 8 sind Öffnungen 12 vorgesehen, wobei jeweils eine Öffnung 12 der Bettplatte 8 mit einer Öffnung 6 der Abstreifplatte 7 fluchtet.In the
Die Nadeln 5 sind miteinander übereinstimmend aufgebaut. Sie weisen jeweils einen in dem Nadelbrett 2 gehaltenen Einspannteil 14 sowie einen mit Widerhaken oder Haken 15 versehenen Arbeitsteil 16 auf. Zwischen dem Einspannteil 14 und dem Arbeitsteil 16 ist ein Übergangsteil 17 angeordnet. Der Übergangsteil 17 erstreckt sich von dem Einspannteil 14 bis zu dem Arbeitsteil 16, wobei er in unmittelbarer Nachbarschaft von dem Nadelbrett 2 beginnt.The
In Figur 2 ist eine Nadel 5 zur Veranschaulichung der Proportionen dargestellt. Der Einspannteil 14, der zylindrisch ausgebildet ist, geht an einer Übergangsstelle 18 in den Übergangsteil 17 über, der die Form eines schlanken Konus aufweist. In dem Übergangsteil 17 verringert sich der Durchmesser von dem größeren, bei der Übergangsstelle 18 zu messenden Wert auf einen geringeren Wert, der bei einer Übergangsstelle 19 zu messen ist, bei der der Arbeitsteil 16 beginnt. Der Übergangsteil 17 ist koaxial zu einer Längsachse 21 der Nadel 5 angeordnet und bildet insgesamt einen zusammenhängenden Bereich für die Anpassung des Durchmessers. Ebenso sind der Einspannteil 14 und der Arbeitsteil 16 koaxial zu der Längsachse 21 angeordnet. Entlang der Längsachse 21 vermindert sich der Durchmesser des Übergangsteils 17 stetig und linear. Die zwischen den Übergangsstellen 18, 19 zu messende Länge des Übergangsteils 17 ist mindesten zweimal so groß wie die Länge des Arbeitsteils 16, d.h. des Abstandes der Übergangsstelle 19 von einer an dem freien Ende der Nadel 5 ausgebildeten Spitze 22. Dadurch wird der Übergangsteil sehr schlank und lang. Er weist keinerlei Stufen oder Absätze auf.FIG. 2 shows a
Die Vorrichtung 1 arbeitet wie folgt:The
In Betrieb werden lose Fasern durch den Zwischenraum 9 geführt. Das Nadelbrett 2 wird dabei in schneller Folge derart in Richtung des Pfeils 3 hin- und hergehend bewegt, dass die Nadeln 5 den Zwischenraum 9 periodisch freigeben und durchstechen. Die Haken 15 der Arbeitsteile 16 verfestigen dabei die einzelnen Fasern zu einem Vlies. Bei diesem Vorgang besteht insbesondere für die ersten noch mit unverfestigten Fasern in Berührung kommenden Nadeln die Gefahr, dass einzelne Faserfilamente mitgenommen und durch die Abstreiföffnungen 6 gezogen werden und sich an der Nadel 5 ablagern. Bei den erfindungsgemäßen Nadeln 5 wird dieser Tendenz durch die lange und schlanke Ausbildung der Übergangsteile 17 entgegengewirkt. Die Nadeln 5 ziehen wenigstens bei einigen Vliesmaterialien und insbesondere bei Recyclingfasern weniger Fasern durch die Abstreiföffnungen 6. Es sammelt sich dadurch, wenn überhaupt, dann weniger Flus zwischen dem Nadelbrett 2 und der Abstreifplatte 7. Sollten sich dennoch Faseransammlungen an den Nadeln 5 zwischen dem Nadelbrett 2 und der Abstreifplatte 7 bilden, können diese von den schlanken Übergangsbereichen 17 relativ leicht abgestreift werden. Dies gilt insbesondere, wenn die Übergangsstelle 18, anders als in Figur 1 dargestellt, unmittelbar an der Unterseite des Nadelbretts 2 liegt.In operation, loose fibers are passed through the
In Figur 3 ist eine etwas abgewandelte Ausführungsform der Nadel 5 veranschaulicht. Der von dem Übergangsteil 17 gebildete Bereich ist in zwei Teilbereiche 17a, 17b aufgeteilt, in denen sich der Durchmesser der Nadel 5 vom Schaftdurchmesser auf den Arbeitsteildurchmesser vermindert. Der Teilbereich 17a grenzt dabei an die Übergangsstelle 19, während der Teilbereich 17b an die Übergangsstelle 18 grenzt. Zwischen den Teilbereichen 17a, 17b ist ein zylindrischer Zwischenabschnitt 17c ausgebildet. Für diese Ausführungsform gilt, dass auch hier vorteilhafterweise der Übergangsteil 17 unmittelbar im Anschluss an das Nadelbrett 2 beginnt, d.h. dass die Übergangsstelle 18 mit der Unterseite des Nadelbretts 2 fluchtet. Die Teilbereiche 17a, 17b, in denen die Verjüngung der Nadel 5 stattfindet, haben zusammengenommen eine Länge, die gleich oder größer ist als das Doppelte der Länge des Arbeitsteils 16, d.h. des Abstands zwischen der Übergangsstelle 19 und der Spitze 22.FIG. 3 illustrates a somewhat modified embodiment of the
Letzeres gilt entsprechend für die in Figur 4 und Figur 5 veranschaulichte Ausführungsform der Nadel 5. Die vorstehende Beschreibung gilt entsprechend, jedoch mit einer Ausnahme. Die Teilbereiche 17a, 17b liegen jeweils auf dem Mantel eines schmalen Kegels, d.h. der Durchmesser nimmt in diesen Teilbereichen 17a, 17b auf die Spitze 22 hin ab. Die Durchmesserreduzierung ist bei der Ausführungsform nach Fig. 4 für den Teilbereich 17a linear, nicht für den Teilbereich 17b. Dies gilt bei der Ausführungsform nach Figur 4 für den Teilbereich 17a, nicht jedoch für den Teilbereich 17b. In diesem nimmt der Durchmesser zur Spitze hin ausgehend von der Übergangsstelle 18 zunächst stärker und dann weniger stark ab. Der ausgebildete Konus ist somit krummlinig begrenzt. Ein solcher Konus kann auch anstelle des Konus im Teilbereich 17a oder bei der Ausführungsform nach Figur 2 anstelle des geraden schlanken Kegelstumpfs in dem Übergangsteil 17 ausgebildet sein.The latter applies correspondingly to the embodiment of the
Bei einer Filznadel 5 ist zwischen Einspannteil 14 und Arbeitsteil 16 ein Übergangsteil 17 vorgesehen, der als langer schlanker Kegelstumpf ausgebildet ist. Die Länge dieses Übergangsteils 17 ist mindestens zweimal so lang wie das Arbeitsteil. Es ergibt sich dadurch ein sehr schlanker Übergangsbereich, der wenig dazu neigt, Fasern aus dem Vlies zu ziehen und aufzusammeln. Sollten sich dennoch Faserablagerungen bilden, sind diese leicht zu entfernen.In a
- 11
- Vorrichtungcontraption
- 22
- Nadelbrettneedle board
- 33
- Pfeilarrow
- 44
- Öffnungenopenings
- 55
- Nadelnneedles
- 66
- Abstreiföffnungenstripping openings
- 77
- Abstreifplattestripper
- 88th
- Bettplattebedplate
- 99
- Zwischenraumgap
- 1111
- Pfeilarrow
- 1212
- Öffnungenopenings
- 1414
- Einspannteilchucking
- 1515
- Hakenhook
- 1616
- Arbeitsteilworking part
- 1717
- ÜbergangsteilTransitional part
- 17a17a
- Teilbereichsubregion
- 17b17b
- Teilbereichsubregion
- 17c17c
- Zwischenabschnittintermediate section
- 1818
- ÜbergangsstelleCheckpoint
- 1919
- ÜbergangsstelleCheckpoint
- 2121
- Längsachselongitudinal axis
- 2222
- Spitzetop
Claims (12)
- Felting needle (5) for fastening to a needle bed (2),
with an elongated needle body, on which a clamping part (14) and a working part (16) provided with hooks (15) along its longitudinal extension are configured, wherein the clamping part (14) has a larger diameter than the working part (16),
with a transition part (17) configured between the working part (16) and the clamping part (14) with a region (17, 17a, 17b) configured therein, in which the diameter decreases from the diameter of the clamping part (14) to the diameter of the working part (16),
characterised in that
the region (17, 17a, 17b) has a length overall, which is equal to or larger than double the length of the working part (16). - Felting needle according to Claim 1, characterised in that the region (17, 17a, 17b) extends from the clamping part (14), the length of which is determined by the thickness of the needle bed, to the working part (16).
- Felting needle according to Claim 1, characterised in that the transition region (17) is larger than 11 mm.
- Felting needle according to Claim 3, characterised in that the transition region is larger than 20 mm.
- Felting needle according to Claim 1, 2 or 3, characterised in that the region (17, 17a, 17b) is conical.
- Felting needle according to Claim 1, 2 or 3, characterised in that the region (17) is divided into at least two conical sub-regions (17a, 17b).
- Felting needle according to Claim 5 or 6, characterised in that the conical regions (17) or sub-regions (17a, 17b) are straight, truncated circular cones.
- Felting needle according to Claim 5 or 6, characterised in that the conical region (17) or the sub-regions (17a, 17b) are truncated circular cones with curved surface lines.
- Felting needle according to Claim 1, 2 or 3, characterised in that the working part (16) and the clamping part (14) are arranged coaxially to one,another.
- Felting needle according to Claim 1, 2 or 3, characterised in that the working part (16) has a constant diameter.
- Felting needle according to Claim 1, 2 or 3, characterised in that the clamping part (14) has a constant diameter.
- Felting needle according to Claim 1, 2 or 3, characterised in that the clamping part (14) and the transition part (17) have a circular cross-section.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/352,369 US6233797B1 (en) | 1999-07-13 | 1999-07-13 | Felt needle |
| US352369 | 1999-07-13 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1069224A1 EP1069224A1 (en) | 2001-01-17 |
| EP1069224B1 true EP1069224B1 (en) | 2007-06-27 |
Family
ID=23384854
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP00109536A Expired - Lifetime EP1069224B1 (en) | 1999-07-13 | 2000-05-04 | Felting needle |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6233797B1 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1069224B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP3566187B2 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE50014437D1 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2288815T3 (en) |
Families Citing this family (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB0402131D0 (en) * | 2004-01-30 | 2004-03-03 | Isis Innovation | Delivery method |
| DE102004037716B4 (en) * | 2004-08-04 | 2009-04-02 | Groz-Beckert Kg | Post-treatment needle for textile fabrics |
| FR2885621B1 (en) * | 2005-05-16 | 2007-08-10 | Duflot Ind Sa | NEEDLE WITHOUT BAR FOR NEEDLE ROLLER, USE THEREOF AND COMPLEX NEEDLE AND PERFORATED PRODUCT OBTAINED |
| US20070044696A1 (en) * | 2005-08-31 | 2007-03-01 | Chih-Po Yang | Needle for stereographic embroidery |
| DE502005007017D1 (en) * | 2005-12-27 | 2009-05-14 | Groz Beckert Kg | felting needle |
| ES2446521T3 (en) * | 2007-02-02 | 2014-03-10 | Groz-Beckert Kg | Procedure and device for equipping needle tables for felt machines |
| ES2366169T3 (en) * | 2009-02-12 | 2011-10-17 | Groz-Beckert Kg | NEEDLE FOR A TEXTILE MACHINE. |
| US8251262B2 (en) * | 2009-08-12 | 2012-08-28 | Timothy Peckels | Volume metered pour spout |
| WO2013053022A1 (en) | 2011-10-12 | 2013-04-18 | The University Of Queensland | Delivery device |
| CN103938369A (en) * | 2014-04-11 | 2014-07-23 | 吴江龙升纺织有限公司 | Fiber web reinforcing device |
| CA2975275C (en) | 2015-02-02 | 2023-08-29 | Vaxxas Pty Limited | Microprojection array applicator and method |
| WO2017045031A1 (en) | 2015-09-18 | 2017-03-23 | Vaxxas Pty Limited | Microprojection arrays with microprojections having large surface area profiles |
| EP4306803A3 (en) | 2017-03-31 | 2024-04-10 | Vaxxas Pty Limited | Device and method for coating surfaces |
| US11175128B2 (en) | 2017-06-13 | 2021-11-16 | Vaxxas Pty Limited | Quality control of substrate coatings |
| AU2018309562A1 (en) | 2017-08-04 | 2020-02-20 | Vaxxas Pty Limited | Compact high mechanical energy storage and low trigger force actuator for the delivery of microprojection array patches (MAP) |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE536394A (en) * | 1954-03-10 | 1900-01-01 | ||
| NL110401C (en) | 1954-03-10 | |||
| US2883585A (en) * | 1954-06-15 | 1959-04-21 | Westinghouse Electric Corp | Circuit breaker |
| DE1265426B (en) * | 1964-04-15 | 1968-04-04 | J J Marx Fa | Needle board for needle felting machines and process for its assembly with needles |
| US3347192A (en) * | 1965-05-24 | 1967-10-17 | Union Special Machine Co | Sewing machine needle |
| US3464097A (en) | 1967-06-01 | 1969-09-02 | Singer Co | Felting needle |
| US3542632A (en) * | 1969-02-28 | 1970-11-24 | Standard Oil Co | Fibrillated fabrics and a process for the preparation thereof |
| US3877120A (en) * | 1970-02-20 | 1975-04-15 | Toray Industries | Needle board |
| US3727276A (en) * | 1971-04-06 | 1973-04-17 | E Foster | Felting needle |
| US3753412A (en) * | 1971-12-02 | 1973-08-21 | Torrington Co | Selectively hardened needles |
| US3844004A (en) | 1973-09-20 | 1974-10-29 | E Foster | Felting needle |
| US4131978A (en) | 1977-11-09 | 1979-01-02 | The Singer Company | Felting needle |
-
1999
- 1999-07-13 US US09/352,369 patent/US6233797B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2000
- 2000-05-04 ES ES00109536T patent/ES2288815T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-05-04 EP EP00109536A patent/EP1069224B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-05-04 DE DE50014437T patent/DE50014437D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-07-11 JP JP2000210172A patent/JP3566187B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| None * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ES2288815T3 (en) | 2008-02-01 |
| EP1069224A1 (en) | 2001-01-17 |
| JP3566187B2 (en) | 2004-09-15 |
| US6233797B1 (en) | 2001-05-22 |
| JP2001040567A (en) | 2001-02-13 |
| DE50014437D1 (en) | 2007-08-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1069224B1 (en) | Felting needle | |
| DE10232148B4 (en) | Process for the liquid-permeable perforation of a fleece | |
| AT394401B (en) | DEVICE ON NEEDLE MACHINES FOR THE PRODUCTION OF NEEDLE FELT COVERS OD. DGL. | |
| EP1806444B1 (en) | Felt needle | |
| EP2395143A1 (en) | Needle board for a needle machine | |
| EP1871937B1 (en) | Device for patterning and consolidating a web of endless fabric with an exchangeable patterning sleeve | |
| DE1560701C3 (en) | Device for the production of a non-woven fiber material | |
| DE19640750B4 (en) | Device for needling a fleece | |
| AT501434B1 (en) | VLIESZUFÜHRVORRICHTUNG | |
| EP3061855B1 (en) | Roller card and method for fixing at least one fibre web | |
| DE19819733A1 (en) | Device for needling a fleece | |
| EP2918710A1 (en) | Card clothing wire and method for the preparation of staple fibre non-woven fabrics | |
| DE19713350C2 (en) | Device for needling a pre-consolidated fleece | |
| WO2008110134A1 (en) | Device for the compaction of stable fibers or a non-woven material comprised of filaments | |
| EP1191135B1 (en) | Aprons for doubleapron-drafting machine | |
| AT404144B (en) | DEVICE FOR NEEDLING A FIBER FIBER | |
| AT406391B (en) | Apparatus for the needling of a nonwoven | |
| AT407059B (en) | DEVICE FOR NEEDING A FLEECE | |
| AT404143B (en) | Apparatus for needling the surface of a nonwoven | |
| EP0924329B1 (en) | Device and process for needling nonwoven fabrics to produce an insulation mat | |
| CH696072A5 (en) | Apparatus for solidifying a recoverable woven fabric. | |
| AT405303B (en) | Apparatus for the needling of a pre-consolidated nonwoven web | |
| AT406781B (en) | Apparatus for the needling of a preconsolidated nonwoven | |
| AT390971B (en) | DEVICE FOR NEEDING A FIBER MINERAL FIBER | |
| AT405535B (en) | Apparatus for the needling of a nonwoven |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): DE ES FR GB IT |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20010618 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: DE ES FR GB IT |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20040819 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE ES FR GB IT |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 50014437 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20070809 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20070920 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2288815 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20080328 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20120522 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20120525 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20130504 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130504 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20140606 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130505 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20190313 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20190531 Year of fee payment: 20 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20190527 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R071 Ref document number: 50014437 Country of ref document: DE |