EP0959190B1 - Wärmedämmelement - Google Patents
Wärmedämmelement Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0959190B1 EP0959190B1 EP99108797A EP99108797A EP0959190B1 EP 0959190 B1 EP0959190 B1 EP 0959190B1 EP 99108797 A EP99108797 A EP 99108797A EP 99108797 A EP99108797 A EP 99108797A EP 0959190 B1 EP0959190 B1 EP 0959190B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- cover layers
- heat insulation
- insulation element
- core panel
- element according
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 title claims 11
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract 3
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 claims abstract 2
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 claims abstract 2
- 239000004793 Polystyrene Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 1
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000005011 phenolic resin Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 229920002223 polystyrene Polymers 0.000 claims 1
- 239000008259 solid foam Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 abstract 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 abstract 1
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04B—GENERAL BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS; WALLS, e.g. PARTITIONS; ROOFS; FLOORS; CEILINGS; INSULATION OR OTHER PROTECTION OF BUILDINGS
- E04B1/00—Constructions in general; Structures which are not restricted either to walls, e.g. partitions, or floors or ceilings or roofs
- E04B1/62—Insulation or other protection; Elements or use of specified material therefor
- E04B1/74—Heat, sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection; Other building methods affording favourable thermal or acoustical conditions, e.g. accumulating of heat within walls
- E04B1/76—Heat, sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection; Other building methods affording favourable thermal or acoustical conditions, e.g. accumulating of heat within walls specifically with respect to heat only
- E04B1/78—Heat insulating elements
- E04B1/80—Heat insulating elements slab-shaped
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04C—STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS; BUILDING MATERIALS
- E04C2/00—Building elements of relatively thin form for the construction of parts of buildings, e.g. sheet materials, slabs, or panels
- E04C2/02—Building elements of relatively thin form for the construction of parts of buildings, e.g. sheet materials, slabs, or panels characterised by specified materials
- E04C2/26—Building elements of relatively thin form for the construction of parts of buildings, e.g. sheet materials, slabs, or panels characterised by specified materials composed of materials covered by two or more of groups E04C2/04, E04C2/08, E04C2/10 or of materials covered by one of these groups with a material not specified in one of the groups
- E04C2/284—Building elements of relatively thin form for the construction of parts of buildings, e.g. sheet materials, slabs, or panels characterised by specified materials composed of materials covered by two or more of groups E04C2/04, E04C2/08, E04C2/10 or of materials covered by one of these groups with a material not specified in one of the groups at least one of the materials being insulating
- E04C2/296—Building elements of relatively thin form for the construction of parts of buildings, e.g. sheet materials, slabs, or panels characterised by specified materials composed of materials covered by two or more of groups E04C2/04, E04C2/08, E04C2/10 or of materials covered by one of these groups with a material not specified in one of the groups at least one of the materials being insulating composed of insulating material and non-metallic or unspecified sheet-material
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04B—GENERAL BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS; WALLS, e.g. PARTITIONS; ROOFS; FLOORS; CEILINGS; INSULATION OR OTHER PROTECTION OF BUILDINGS
- E04B1/00—Constructions in general; Structures which are not restricted either to walls, e.g. partitions, or floors or ceilings or roofs
- E04B1/62—Insulation or other protection; Elements or use of specified material therefor
- E04B1/74—Heat, sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection; Other building methods affording favourable thermal or acoustical conditions, e.g. accumulating of heat within walls
- E04B1/76—Heat, sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection; Other building methods affording favourable thermal or acoustical conditions, e.g. accumulating of heat within walls specifically with respect to heat only
- E04B2001/7683—Fibrous blankets or panels characterised by the orientation of the fibres
Definitions
- the invention relates to a thermal insulation element for the insulation of Flat roofs and sloping roofs.
- thermal insulation elements are laid on flat roofs and flat-roofed roofs.
- the material thicknesses of the thermal insulation elements installed on flat roofs and flat-roofed roofs have steadily increased as a result of legal requirements. These specifications serve to save heating energy.
- the current level of required thermal insulation is defined by a heat transfer coefficient k D ⁇ 0.30 W / m 2 K.
- predominantly mineral wool insulating materials are installed on flat or flat roofed roofs. These mineral wool insulating materials are applied essentially to load-bearing roof shells, which consist mostly of profile sheets for cost reasons.
- the insulating materials must have sufficient bending tensile strength so that they can bridge the clear widths between the upper chords of the profile sheets or are sufficiently stable when projecting over a top chord.
- the mineral wool insulating materials have densities of more than 120 kg / m 3 , with an average of about 145 kg / m 3 is achieved.
- the basis weight is thus more than 18.9 kg / m 2 .
- the use of large-sized elements with dimensions of 2 mx 1.2 m thus leads to a weight of more than 45 kg per element. Due to their weight, such elements lead to considerable loads on the craftsmen carrying out the laying.
- the invention has for its object to provide a sufficiently stable, especially resistant to heat insulation element for the insulation of flat roofs and flat-inclined roofs, which due to a low density even with large-sized elements in a simple manner manageable and meets the non-combustibility requirements.
- thermal insulation element which consists of a core plate with two large surfaces and disposed on the large surfaces cover layers of mineral wool fibers, the core plate consists of a deviating from the material of the outer layers material whose density is lower than the density of each Cover layer and wherein the cover layers are pressure-resistant in the direction of the surface normals of the large surfaces.
- Such a trained thermal insulation element has the advantage that through the Use of a relatively lightweight core plate in conjunction with two pressure-resistant and fire-resistant cover layers elements with relatively low Weight can be created, which can therefore be handled in a simple manner are so that it can be dispensed with the laying of multiple layers.
- the thermal insulation element according to the invention is therefore suitable for a Covering a flat roof or a flat-inclined roof with sufficiently large elements requiring fast flashing, i. in short Periods allows, so that the requirements in terms of Bridging the upper straps is met.
- the core plate consists of a hard foam, such as expanded or extruded polystyrene, polyurethane or phenolic resin foam. These materials have a bulk density between 10 and 30 kg / m 3 , preferably between 15 and 20 kg / m 3 .
- An 8 cm thick core plate with the dimensions 2 mx 1.2 m and a density of 30 kg / m 3 then weighs 5.76 kg and is easily handled even with applied cover layers, the cover layers the necessary compressive strength and fire resistance of the Provide thermal insulation element.
- the cover layers are preferably non-positively connected to the core plate connected, wherein the bonding of the cover layers with the core plate as has proved advantageous.
- cover layers comprise fibers which predominantly perpendicular to the large surfaces of the core plate are aligned.
- the core plate made of hard foam prevents the Plates above the cavity between the top straps of the profile sheets during Passing or other burdens are punched.
- the inventive Arrangement of the fibers in the outer layers leads to a higher Compressive strength or allows for a given compressive strength, the density to lower the mineral wool insulation boards as topcoats, resulting in significant cost reductions in the production of appropriate Heat insulation elements can be realized.
- the Cover layers at least 2 cm, preferably 3 cm thick, so that a effective protection against a fire attack from above - flying fire and Radiant heat - as in a fire attack is achieved from below.
- So formed cover layers can both an immediate Ignition as well as incineration prevented or significantly delayed become.
- thermal decoupling of the outer layers made of mineral wool fibers from the core plate of hard foam which thermally conditional irreversible change of the expanded foam Polystyrene significantly reduced or prevented.
- the cover layers are slightly laterally over the core plate out. It has proven to be advantageous in practice, the supernatant of Form layers in a range between 2 and 5 mm. Especially in combination with the large surfaces right-angled arrangement of the fibers of the outer layers gives the advantage since the supernatant of the cover layers is relatively compressible, a joint density Laying the thermal insulation elements to allow.
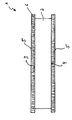
- the drawing shows a thermal insulation element 1 for the insulation of Flat roofs and sloping roofs.
- the thermal insulation element 1 consists of a core plate 2, which has two large surfaces 3 and 4. The large surfaces 3 and 4 are parallel to each other.
- the Topcoats 5 consist of mineral wool insulating panels made of individual fibers are produced in a known manner. The fibers are in the drawing indicated by the reference numeral 6 and extend in the substantially at right angles to the large surfaces 3, 4 of the core plate 2.
- the core plate 2 is made of a hard foam, such as expanded or extruded polystyrene, polyurethane or Phenolic foam.
- the large surfaces 3, 4 of the core plate 2 are with the Cover layers 5 glued.
- cover layers 5 slightly laterally over the Protect core plate 2, wherein the parallel aligned fibers a Flexibility of the cover layers 5 parallel to the large surfaces 3, 4 of Core plate 2 allow, whereas the cover layers 5 parallel to Surface normals of the surfaces 3, 4 have a high compressive strength.
- a heat-insulating element 1 described above may consist, for example, of a polystyrene rigid foam plate as the core plate 2 with a material thickness of 8 cm and a bulk density of 20 kg / m 3 .
- a material thickness of 8 cm and a bulk density of 20 kg / m 3 On this core plate 2, two cover layers of 3 cm thickness of mineral wool insulation boards are applied, which have a bulk density of 150 kg / m 3 .
- the cover layers 5 are adhesively bonded to the core plate 2 with a weight of 1 kg / m 2 .
- Such a thermal insulation element 1 has a basis weight of 11.6 kg / m 2 .
- Compared to a conventional mineral wool insulation board with a standard basis weight of 20.6 kg / m 2 there is a 43% weight reduction, which means a substantial handling simplification.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Acoustics & Sound (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Cable Accessories (AREA)
- Thermistors And Varistors (AREA)
- Devices For Indicating Variable Information By Combining Individual Elements (AREA)
- Building Environments (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
Description
Claims (9)
- Wärmedämmelement für die Dämmung von Flachdächern und flachgeneigten Dächern, bestehend aus einer Kernplatte (2) mit zwei großen Oberflächen (4, 5), und auf den großen Oberflächen (4, 5) angeordneten Deckschichten (5) aus Mineralwollefasern,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Kernplatte (2) aus einem von dem Material der Deckschichten (5) abweichenden Material besteht, dessen Rohdichte geringer ist, als die Rohdichte jeder Deckschicht (5) und dass die Deckschichten (5) in Richtung der Flächennormalen der großen Oberflächen (3, 4) druckfest sind. - Wärmedämmelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Kernplatte (2) aus einem Hartschaum, wie beispielsweise expandiertem oder extrudiertem Polystyrol, Polyurethan oder Phenolharzschaum besteht. - Wärmedämmelement nach Anspruch 2,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Kernplatte (2) eine Rohdichte zwischen 10 und 30 kg/m3, vorzugsweise zwischen 15 und 20 kg/m3 aufweist. - Wärmedämmelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Deckschichten (5) kraftschlüssig mit der Kernplatte (2) verbunden, insbesondere verklebt sind. - Wärmedämmelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Deckschichten (5) Fasern (6) aufweisen, die überwiegend rechtwinklig zu den großen Oberflächen (3, 4) der Kernplatte (2) ausgerichtet sind. - Wärmedämmelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Deckschichten (5) zumindest 2 cm, vorzugsweise 3 cm dick sind. - Wärmedämmelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Deckschichten (5) seitlich geringfügig über die Kernplatte (2) hervorstehen. - Wärmedämmelement nach Anspruch 7,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Deckschichten (5) zumindest in ihrem Randbereich parallel zu den großen Oberflächen (3, 4) flexibel sind. - Wärmedämmelement nach Anspruch 7,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Deckschichten (5) 2 bis 5 mm über den Rand der Kernplatte (2) überstehen.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE29808924U DE29808924U1 (de) | 1998-05-16 | 1998-05-16 | Wärmedämmelement |
| DE29808924U | 1998-05-16 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0959190A2 EP0959190A2 (de) | 1999-11-24 |
| EP0959190A3 EP0959190A3 (de) | 2000-02-23 |
| EP0959190B1 true EP0959190B1 (de) | 2005-09-07 |
Family
ID=8057304
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP99108797A Expired - Lifetime EP0959190B1 (de) | 1998-05-16 | 1999-05-03 | Wärmedämmelement |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0959190B1 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE304091T1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE29808924U1 (de) |
| DK (1) | DK0959190T3 (de) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10104737A1 (de) * | 2001-02-02 | 2002-09-12 | Rommersbach Carmen | Bauplatte |
| WO2002099220A1 (de) † | 2001-06-02 | 2002-12-12 | Deutsche Rockwool Mineralwoll Gmbh & Co. Ohg | Dachkonstruktion in flacher und/oder flach geneigter ausgestaltung sowie dämmstoffelement hierfür |
| DE10261988B4 (de) * | 2002-07-19 | 2007-01-25 | Deutsche Rockwool Mineralwoll Gmbh + Co Ohg | Dämmschicht aus Mineralfasern |
| EP2136010A1 (de) * | 2008-06-17 | 2009-12-23 | Rockwool International A/S | Gebäudesystem für eine Gebäudekonstruktion |
| EP2941512A4 (de) * | 2012-12-31 | 2016-09-21 | Rockwool Int | Starre isolierplatte |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE755178A (fr) * | 1969-09-04 | 1971-02-01 | Weinsheim Gmbh Chem Werke | Element de couverture prefabrique pour toitures plates |
| DK3693D0 (da) * | 1993-01-14 | 1993-01-14 | Rockwool Int | A method of producing a mineral fiber-insulating web, a plant for producing a mineral fiber web, and a mineral fiber-insulated plate |
| BE1009158A6 (nl) * | 1995-02-24 | 1996-12-03 | Cospi Naamloze Vennootschap | Verbindingselement voor isolerende panelen. |
| NL1002686C2 (nl) * | 1996-03-22 | 1997-09-23 | Isobouw Systems Bv | Samenstel voor het vormen van een dak alsmede dakelement voor een dergelijk samenstel. |
-
1998
- 1998-05-16 DE DE29808924U patent/DE29808924U1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1999
- 1999-05-03 EP EP99108797A patent/EP0959190B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1999-05-03 DK DK99108797T patent/DK0959190T3/da active
- 1999-05-03 AT AT99108797T patent/ATE304091T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1999-05-03 DE DE59912514T patent/DE59912514D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0959190A2 (de) | 1999-11-24 |
| DK0959190T3 (da) | 2006-01-16 |
| DE29808924U1 (de) | 1998-09-03 |
| DE59912514D1 (de) | 2005-10-13 |
| EP0959190A3 (de) | 2000-02-23 |
| ATE304091T1 (de) | 2005-09-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE2135007B2 (de) | Konstruktionselement | |
| EP0692423B1 (de) | Schalldämmende Fussbodenplatte für Fahrzeuge mit mindestens einer Sperrholzplatte | |
| DE10344755A1 (de) | Verwindungssichere Fussbodenplatte mit Oberflächenschicht und damit hergestellter Boden | |
| EP0959190B1 (de) | Wärmedämmelement | |
| DE202010001675U1 (de) | Bodendämmplattensystem | |
| DE102015015633A1 (de) | Paneelsystem für die Erstellung von Räumen | |
| EP1707349A2 (de) | Thermisch isolierendes Panel | |
| DE69609981T2 (de) | Paneele | |
| EP0947638B1 (de) | Dämmplatte zur Verwendung an Aussenfassaden von Häusern | |
| DE8532239U1 (de) | Anorganische Mehrschicht-Leichtbauplatte | |
| DE2700416C3 (de) | Mehrschichtiges Verbundtragwerk | |
| DE3900397A1 (de) | Halteeinrichtung zum befestigen von fassadenplatten | |
| DE3540455A1 (de) | Anorganische mehrschicht-leichtbauplatte | |
| DE202022101604U1 (de) | Inlay für Metalltüren | |
| DE19860993C2 (de) | Dämmstoffelement | |
| DE3203314A1 (de) | Dachkonstruktion | |
| EP2166166B1 (de) | Dämmelement und Verwendung eines Dämmelements | |
| DE3804311A1 (de) | Grossflaechige platte aus keramik, steinzeug, naturstein und/oder kunststein | |
| DE7513144U (de) | Mehrschichtenverbundplatte | |
| EP0936063A2 (de) | Wärmedämmendes Verbundbauelement | |
| DE20304627U1 (de) | Trockenbauwand | |
| DE202018004628U1 (de) | Verbundplatte und Bauwerk mit mindestens einer Verbundplatte | |
| DE2927315A1 (de) | Stegplatte aus kunststoffmaterial | |
| DE8809427U1 (de) | Flächenbauteil zur Erstellung von Boden-, Wand- oder Deckenflächen, insbesondere auf Schiffen | |
| DE9420217U1 (de) | Plattenförmiges, mit einer Matrix aus Beton ausgebildetes Bauelement |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Free format text: 7E 04B 7/22 A, 7E 04D 13/16 B, 7E 04B 1/80 B, 7E 04B 7/20 B |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20000818 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: DEUTSCHE ROCKWOOL MINERALWOLL GMBH & CO. OHG |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20030514 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20050907 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59912514 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20051013 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: HEPP, WENGER & RYFFEL AG |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20051207 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20051218 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20060207 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20060302 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20060503 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20060531 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20060608 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20060503 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20050907 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 59912514 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: STENGER WATZKE RING INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY, DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 59912514 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: STENGER WATZKE RING INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY, DE Effective date: 20140801 Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 59912514 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: ROCKWOOL INTERNATIONAL A/S, DK Free format text: FORMER OWNER: DEUTSCHE ROCKWOOL MINERALWOLL GMBH + CO OHG, 45966 GLADBECK, DE Effective date: 20140801 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: 732E Free format text: REGISTERED BETWEEN 20150122 AND 20150128 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: SD Effective date: 20150424 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PUE Owner name: ROCKWOOL INTERNATIONAL A/S, DK Free format text: FORMER OWNER: DEUTSCHE ROCKWOOL MINERALWOLL GMBH AND CO. OHG, DE |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20150428 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20160510 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20160511 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: FI Payment date: 20160509 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20160511 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20160425 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: DK Payment date: 20160510 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20160426 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 59912514 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20161201 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: EUG Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: EBP Effective date: 20170531 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20170601 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170503 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170531 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170504 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170531 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20180131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170601 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: PD Owner name: ROCKWOOL INTERNATIONAL A/S; DK Free format text: DETAILS ASSIGNMENT: CHANGE OF OWNER(S), AFFECTATION / CESSION; FORMER OWNER NAME: DEUTSCHE ROCKWOOL MINERALWOLL GMBH & CO. OHG Effective date: 20141216 Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20170531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170531 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Payment date: 20180529 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170531 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20180529 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: PE20 Expiry date: 20190502 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MK9A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 20190503 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 20190502 |