EP0592007B1 - Dispositif de commutation - Google Patents
Dispositif de commutation Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0592007B1 EP0592007B1 EP19930116449 EP93116449A EP0592007B1 EP 0592007 B1 EP0592007 B1 EP 0592007B1 EP 19930116449 EP19930116449 EP 19930116449 EP 93116449 A EP93116449 A EP 93116449A EP 0592007 B1 EP0592007 B1 EP 0592007B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- switch
- contact
- separating element
- separating
- lever
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 17
- 210000000629 knee joint Anatomy 0.000 description 13
- 210000002414 leg Anatomy 0.000 description 7
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001934 delay Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007257 malfunction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010791 quenching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000171 quenching effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001960 triggered effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H9/00—Details of switching devices, not covered by groups H01H1/00 - H01H7/00
- H01H9/30—Means for extinguishing or preventing arc between current-carrying parts
- H01H9/32—Insulating body insertable between contacts
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H1/00—Contacts
- H01H1/58—Electric connections to or between contacts; Terminals
- H01H1/5833—Electric connections to or between contacts; Terminals comprising an articulating, sliding or rolling contact between movable contact and terminal
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H71/00—Details of the protective switches or relays covered by groups H01H73/00 - H01H83/00
- H01H71/10—Operating or release mechanisms
- H01H71/50—Manual reset mechanisms which may be also used for manual release
- H01H71/52—Manual reset mechanisms which may be also used for manual release actuated by lever
- H01H71/528—Manual reset mechanisms which may be also used for manual release actuated by lever comprising a toggle or collapsible link between handle and contact arm, e.g. sear pin mechanism
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H89/00—Combinations of two or more different basic types of electric switches, relays, selectors and emergency protective devices, not covered by any single one of the other main groups of this subclass
- H01H89/06—Combination of a manual reset circuit with a contactor, i.e. the same circuit controlled by both a protective and a remote control device
- H01H89/08—Combination of a manual reset circuit with a contactor, i.e. the same circuit controlled by both a protective and a remote control device with both devices using the same contact pair
Definitions
- the invention relates to a switching device according to the preamble of claim 1.
- Switching devices of this type are used to automatically interrupt an electrical circuit when a certain current is exceeded, for example in the event of a short circuit, or when a fault current occurs in the electrical system.
- Such a switching device is known from EP-A-0 350 828, in which a movable contact in the switched-on position is held in pressure contact with a fixed contact by means of a dead center spring.
- a circular sector-shaped separating lever is provided at the free end with a cylindrically curved partition, the center of curvature of which coincides with the pivot axis of the separating lever.
- the separating lever is mechanically coupled to a trigger, for example an electromechanical and / or thermoelectric trigger, and is pivoted in the event of a trigger such that the partition pushes in the space between the two contacts and pushes the movable contact away from the fixed contact.
- the movable contact is hereby moved beyond the dead center position of the associated spring, so that it is pivoted further away from the fixed contact under spring action.
- the partition moves further in the circumferential direction and shields the fixed contact from the movable contact.
- the switch-off arc formed between the two contacts must therefore make a relatively long detour around the free end of the partition, so that its electrical resistance increases rapidly, and the arc finally enters a quenching chamber and is quenched.
- a disadvantage of this construction is that the partition wall has to overcome a high frictional resistance when entering the space between the two contacts, which is increased considerably by the contact pressure. This delays the switch-off process and can easily lead to malfunctions.
- Switching devices are described in FR-A-2 563 939 and EP-A-0 244 276, which also work with a partition for extending and extinguishing the arc.
- these devices not only the separation lever, but also the movable contact actuated by a trigger, and the switching functions are coordinated so that the movable contact is released from the fixed contact before the partition enters the space between the contacts. In this way, an unimpeded entry of the partition into the space is made possible.
- the switch-off process is also delayed in these devices, since the partition only takes effect after a certain delay time.
- these devices have a relatively complex structure with a large number of components, so that there is an increased susceptibility to failure and higher manufacturing costs.
- a switching device according to the preamble of claim 1 is known.
- a pressure member in the form of a projection is arranged on the pivoting separating element carrying the dividing wall, which rests on one of the contacts in the switched-on position and maintains the contact pressure, while it releases the contact pressure when the separating element moves into the switched-off position before the Partition between the contacts occurs.
- the contacts in this known switching device extend perpendicular to the direction of movement of the partition.
- the pressure element is provided with run-on and run-off bevels which, when reaching and leaving the switch-on position, cause the movement of one contact relative to the other. When switching off there is therefore initially a certain frictional resistance between the pressure element and the contact in contact with it.
- the object of the invention is to provide a switching device according to the preamble of claim 1, in which the switch-off process is accelerated.
- one of the two contacts runs at an angle to the direction of movement of the partition, and the pressure element bears against this inclined contact in the switched-on position.
- a pivot bearing for the movable contact is preferably formed by an electrically conductive joint element which is in pressure contact with the movable contact and via which the current is supplied to the movable contact. It is therefore not necessary to attach flexible wires or cables to the movable contact, which would hinder the opening movement and also because of the frequently changing ones mechanical stress could break or come loose.
- the movable contact and the joint element are pressed together elastically, so that good electrical contact is ensured. However, since this elastic pressure is exerted directly at the location of the pivot bearing, the movable contact can still move freely between the open position and the closed position.
- the release lever is actuated in the event of a trigger by a switching lever which is biased towards the switch-off position with a relatively high spring force and remains mechanically blocked in the switch-on position until it is triggered.
- the separating lever is movable independently of the switching lever and is elastically biased relative to the switching lever in the direction of the switch-on position. This results in the possibility of having another trigger controlled by a remote control act directly on the separating lever. In the case of remote shutdown, the isolating lever is then pivoted into the off position against the relatively low spring force, while the shift lever remains in the ready-to-release state.
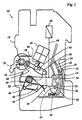
- the switching device 10 shown in FIG. 1 has a housing 12 which can be snapped onto a terminal strip of a distribution box or the like in the usual way.
- a fixed contact 14 is arranged in the housing 12 and is electrically connected to a first connection terminal (not shown) of the switching device.
- a leaf spring-like movable contact 16 protrudes through a window 18 of an inner housing wall 20 and is in pressure contact with the fixed contact 14.
- a pivot bearing for the movable contact 14 is formed by a pin 22 fixed to the housing and an electrically conductive joint element 24, which presses the contact 14 elastically against the pin 22.
- the conductive joint element 24 is connected in a manner not shown via the coil of an overcurrent release 26 to a further terminal, not shown, of the switching device 10.
- a separating lever 28 is pivotable about an axis 30 fixed to the housing and carries at the free end a cylindrically curved partition wall 32 which is arranged concentrically to the axis 30 and is located between the inner housing wall 20 and the fixed contact 14.
- a projection 34 is formed on the separating lever 28, which, in the position of the separating lever 28 shown in FIG. 1, bears against the movable contact 16 and serves as a pressure element for generating the contact pressure between the movable contact 16 and the fixed contact 14.
- a spring 36 is arranged on the movable contact 16 in the vicinity of the pivot bearing 22, 24, which ensures sufficient contact pressure between the movable contact 16 and the conductive joint element 24.
- the spring 36 tends to pivot the movable contact 16 counterclockwise so that it somewhat reduces the contact pressure between the contacts 14 and 16. In the position shown in FIG. 1, however, the force exerted by the pressure member 34 prevails, which acts in the sense of an increase in the contact pressure.
- a shift lever 38 is mounted on the axis 30 and is connected to an extension 42 of the separating lever 28 via a tension spring 40.
- the separating lever 28 is thereby biased clockwise so that the projection 34 presses the movable contact 16 against the fixed contact 14.
- the contact pressure between the contacts 14, 16 is thus largely determined by the force of the tension spring 40.
- the shift lever 38 is biased counterclockwise by a relatively strong leg spring 44 which acts on a driver 46, but is fixed in the position shown in FIG. 1 by a toggle lever 48 in the extended position.
- a first joint member 50 of the knee joint lever 48 is pivotally attached at one end to a manual actuation lever 52 and bears with its opposite end against a stop 54 of the second joint member 56 of the knee joint lever.
- a relatively weak tension spring not specified, the Knee joint lever 48 held in the extended position.
- a spring 58 tends to pivot the manual control lever 52 clockwise. In the state shown in FIG. 1, however, the force of the spring 58 is overcome by the force of the leg spring 44, which acts on the manual actuation lever via the shift lever 38 and the knee joint lever 48.
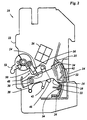
- the overcurrent release 26 triggers a safety shutdown.
- a plunger 60 of the overcurrent release 26 extends and strikes the knee joint lever 48, so that the knee joint lever is broken through.
- the strong leg spring 44 Under the action of the strong leg spring 44, the knee joint lever buckles, and the shift lever 38 is pivoted into the position shown in FIG. 2, taking the separating lever 28 with it through the driver 46.
- the projection 34 is released from the movable contact 16, so that the contact pressure between the contacts 14, 16 is released and the spring 36 lifts the movable contact 16 from the fixed contact 14.
- the partition 32 moves freely into the space between the contacts 14 and 16 so that it shields them from each other.
- the partition wall 32 pushes further between the contacts 14, 16, so that the arc formed between the contacts is forced through the partition wall 32 into a spark channel 62 formed between the inner housing wall 20 and an outer housing wall and finally extinguished becomes.
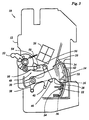
- the circuit closed by the contacts 14, 16 can also be interrupted independently of the action of the overcurrent release 26.
- the manual operating lever 52 is rotated into the position shown in FIG. 3, so that a tension is exerted on the switching lever 38 via the extended knee joint lever 48 and this is pivoted counterclockwise.
- the separating lever 28 is carried along with this pivoting movement of the switching lever 38, so that its partition 32 separates the movable contact 16 from the fixed contact 14.
- the pivoting movements of the switching lever 38 and the separating lever 28 into the switched-off position are supported by the leg spring 44 as soon as the manual operating lever 52 with the knee joint lever 48 articulated thereon has exceeded the dead center position.
- the manual actuation lever 52 When the overcurrent is switched off with the aid of the overcurrent release 26, the manual actuation lever 52 is pivoted by the spring 58 into the switch-off position shown in FIG. 3 as soon as the knee joint lever 48 has broken through and the force of the leg spring 44 is no longer via the switch lever 38 and the knee joint lever on the manual actuation lever works. If the manual actuation lever 52 is pivoted back from the position shown in FIG. 3 to the position shown in FIG. 1 after an overcurrent switch-off or after a manual switch-off, the extended knee joint lever 48 presses the switch lever 38 against the force of the leg spring 44 into that shown in FIG Position back until the knee joint lever exceeds the dead center and the manual operating lever 52 engages under the action of the leg spring in the switch-on position shown in FIG. 1. When the switching lever 38 pivots into the switch-on position shown in FIG. 1, the separating lever 28 is carried along by the action of the tension spring 40.
- an electromagnetic remote release 64 is arranged in the housing 12 and acts directly on the separating lever 28 via a pull rod 66.
- the remote release 64 is connected via cables and connecting terminals, not shown, to an on / off switch, also not shown, which can be arranged outside the housing 12 at a relatively great distance from the switching device 10.
- the on / off switch is turned to the off position, the solenoid of the remote release 64 is energized and the disconnect lever 28 is pulled into the off position by the pull rod 66 so that the contacts 14 and 16 are separated from each other.
- the shift lever 38 does not take part in the pivoting movement into the off position.
- the remote release 64 only needs to overcome the low force of the tension spring 40.
- the excitation current in the remote release 64 drops, the isolating lever 28 returns under the action of the tension spring 40 back to the switch-on position shown in FIG. 1.
Landscapes
- Mechanisms For Operating Contacts (AREA)
Claims (7)
- Dispositif de commutation comprenant deux contacts électriques (14, 16), qui sont appliqués l'un contre l'autre dans la position en circuit, comprenant un élément séparateur pivotant (28) sur lequel est disposée une paroi de séparation isolante (32) s'étendant dans le sens de pivotement, de sorte qu'en cas de passage de l'élément séparateur en position hors circuit elle s'insère entre les deux contacts (14, 16) et les écarte l'un de l'autre, et comprenant un organe de pression (34) présentant la forme d'une saillie qui est disposée contre l'élément séparateur (28) radialement à l'intérieur de la paroi de séparation (32) et qui, lorsque l'élément séparateur est en position en circuit, exerce une pression sur l'un des contacts (16) et maintient la pression de contact entre les contacts (14, 16) et, lors du passage en position hors circuit, supprime la pression de contact avant que la paroi de séparation (32) ne passe entre les contacts (14, 16), caractérisé en ce que l'élément séparateur (28) est conçu sous la forme d'un levier à l'extrémité libre duquel est disposée la paroi de séparation (32), et en ce que celui (16) des deux contacts (14, 16) sur lequel l'organe de pression (34) exerce une pression comporte une portion inclinée par rapport au trajet de déplacement de la paroi de séparation (32), l'organe de pression (34) prenant appui sur la portion inclinée dans la position en circuit.
- Dispositif de commutation selon la revendication 1, caractérisé en ce que l'un des contacts (16) est monté pivotant en un point d'articulation (22, 24), et en ce que la mise en contact électrique de ce contact s'effectue à l'aide d'un élément d'articulation conducteur d'électricité (24) qui exerce une pression sur le contact au point d'articulation.
- Dispositif de commutation selon la revendication 2, caractérisé en ce qu'un ressort (36), qui maintient le contact (16) en contact avec l'élément d'articulation (24), exerce sur le contact (16) un couple de rotation qui est inférieur au couple de rotation exercé par l'organe de pression (34) en position en circuit et qui s'y oppose.
- Dispositif de commutation selon l'une des revendications précédentes, caractérisé en ce que l'élément séparateur (28) est soumis à une précontrainte élastique vers la position hors circuit et peut être bloqué dans la position en circuit, et en ce que le blocage peut être supprimé par un mécanisme de déclenchement (26, 48, 52).
- Dispositif de commutation selon la revendication 4, caractérisé en ce que le mécanisme de déclenchement comporte un levier à genouillère (48) qui, en position d'extension, maintient l'élément séparateur (28) dans la position en circuit.
- Dispositif de commutation selon la revendication 4 ou 5, caractérisé en ce qu'un ressort (44) exerçant sur l'élément séparateur (28) une précontrainte vers la position hors circuit et le mécanisme de déclenchement (26, 48, 52) agissent sur un levier de commutation (38) qui comporte un moyen d'entraînement (46) sollicitant l'élément séparateur (28) vers la position hors circuit et qui, en outre, est relié à l'élément séparateur par un ressort (40) qui plaque l'élément séparateur contre le moyen d'entraînement (46).
- Dispositif de commutation selon la revendication 6, caractérisé par un élément télécommandé à actionnement électrique (64) qui permet d'amener l'élément séparateur (28) dans la position hors circuit indépendamment du levier de commutation (38).
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19924234065 DE4234065C1 (de) | 1992-10-09 | 1992-10-09 | Schaltgerät |
| DE4234065 | 1992-10-09 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0592007A1 EP0592007A1 (fr) | 1994-04-13 |
| EP0592007B1 true EP0592007B1 (fr) | 1997-03-26 |
Family
ID=6470074
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19930116449 Expired - Lifetime EP0592007B1 (fr) | 1992-10-09 | 1993-10-11 | Dispositif de commutation |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0592007B1 (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE4234065C1 (fr) |
| DK (1) | DK0592007T3 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19726402B4 (de) * | 1997-06-21 | 2009-03-05 | Marquardt Gmbh | Elektrischer Schalter |
| DE19735521A1 (de) * | 1997-08-16 | 1999-02-18 | Kloeckner Moeller Gmbh | Lichtbogenlöscheinrichtung für einen kurzschlußstrombegrenzenden Niederspannungsschalter |
| EP1803137B1 (fr) * | 2004-10-08 | 2012-12-05 | ABB France | Dispositif de protection contre les surtensions pourvu de moyens de cisaillement d'arc et procede correspondant |
| FR2892849B1 (fr) * | 2005-10-28 | 2013-12-20 | Hager Electro Sas | Mecanisme a serrure pour appareil electrique |
| CN107731594B (zh) * | 2017-11-27 | 2020-04-17 | 国隆电气有限公司 | 一种无间隙电涌保护器的后备保护器 |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2829860A1 (de) * | 1978-07-07 | 1980-01-17 | Hartmann & Braun Ag | Elektrischer schalter mit einander gegenueberliegenden schaltkontakten |
| FR2563939B1 (fr) * | 1984-05-03 | 1988-03-18 | Telemecanique Electrique | Dispositif interrupteur a ecran de coupure d'arc |
| DE3770516D1 (de) * | 1986-04-04 | 1991-07-11 | Telemecanique Electrique | Elektrischer schalter fuer schutzgeraet, wie schutzschalter. |
| DE3823790A1 (de) * | 1988-07-14 | 1990-01-18 | Asea Brown Boveri | Elektrisches installationsgeraet mit kontakttrennwand |
-
1992
- 1992-10-09 DE DE19924234065 patent/DE4234065C1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
1993
- 1993-10-11 DE DE59305943T patent/DE59305943D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1993-10-11 EP EP19930116449 patent/EP0592007B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1993-10-11 DK DK93116449T patent/DK0592007T3/da active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE59305943D1 (de) | 1997-04-30 |
| DE4234065C1 (de) | 1993-12-02 |
| DK0592007T3 (da) | 1997-10-06 |
| EP0592007A1 (fr) | 1994-04-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3248204B1 (fr) | Disjoncteur de protection | |
| EP0466287B1 (fr) | Disjoncteur avec un dispositif d'encliquetage indépendant du contact mobile | |
| EP0592007B1 (fr) | Dispositif de commutation | |
| DE69008144T2 (de) | Selbstcoordinierendes schaltschutzgerät für elektrische apparate. | |
| EP0352679B1 (fr) | Appareillage interrupteur électrique | |
| DE2616554C2 (de) | Elektrischer Installationsschalter, insbesondere Leitungsschutzschalter mit Fehlerstromschutzeinrichtung | |
| EP2097917B1 (fr) | Dispositif de commutation doté d'une poignée | |
| DE2115034B2 (de) | Schutzschalter mit ueberstrom-, kurzschluss- und fehlerstromschutz | |
| DE69014741T2 (de) | Betätigungsmechanismus für elektrischen Schalter. | |
| DE2343908C2 (de) | Stromunterbrecher mit Überstrom- und Hilfs-Auslösung | |
| DE1286188B (de) | Installationsselbstschalter mit Hilfskontakt | |
| DE102008016575B4 (de) | Voll-Schutzschalter und motorsteuerbarer Vollschutzschalter | |
| EP0091040A2 (fr) | Disjoncteur de protection à courant excessif | |
| EP0271669B1 (fr) | Mécanisme pour un disjoncteur à courant de défaut à la terre combiné avec un disjoncteur de ligne | |
| EP0070248A2 (fr) | Sectionneur | |
| EP0043020A1 (fr) | Appareillage d'installation électrique, notamment disjoncteur automatique | |
| EP0014871B1 (fr) | Disjoncteur de courant de fuite couplé à un interrupteur de circuit | |
| DE69833637T2 (de) | Selektiver Auslöser für Leistungsschalter | |
| DE102011079593B4 (de) | Elektromechanisches Schutzschaltgerät | |
| EP0371419A2 (fr) | Disjoncteur électrique | |
| EP2680293B1 (fr) | Mécanisme de déclenchement | |
| EP0599800B1 (fr) | Disjoncteur de ligne | |
| EP1488438B1 (fr) | Disjoncteur avec interruption bipolaire | |
| DE4339425A1 (de) | Schaltschloß für einen Fehlerstromschutzschalter | |
| EP0158241B1 (fr) | Interrupteur électrique |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): DE DK FR GB IT SE |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: KREMSER, JARO Inventor name: BEBAR, BRANE Inventor name: STREHAR, MATIJA Inventor name: KOPRIVSEK, MITJA Inventor name: DOLINSEK, MIRAN |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19941010 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19950731 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE DK FR GB IT SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59305943 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19970430 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 19970627 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20000926 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20000928 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20001019 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Payment date: 20001025 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20001030 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20011011 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20011011 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20011012 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20011011 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 93116449.5 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: EBP |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020628 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020702 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20051011 |