EP0436718A1 - Verfahren zum erzchargieren bei der schmelzreduktion - Google Patents
Verfahren zum erzchargieren bei der schmelzreduktion Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0436718A1 EP0436718A1 EP88907777A EP88907777A EP0436718A1 EP 0436718 A1 EP0436718 A1 EP 0436718A1 EP 88907777 A EP88907777 A EP 88907777A EP 88907777 A EP88907777 A EP 88907777A EP 0436718 A1 EP0436718 A1 EP 0436718A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- furnace
- ores
- charging
- coal
- chute
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21B—MANUFACTURE OF IRON OR STEEL
- C21B13/00—Making spongy iron or liquid steel, by direct processes
- C21B13/0006—Making spongy iron or liquid steel, by direct processes obtaining iron or steel in a molten state
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21C—PROCESSING OF PIG-IRON, e.g. REFINING, MANUFACTURE OF WROUGHT-IRON OR STEEL; TREATMENT IN MOLTEN STATE OF FERROUS ALLOYS
- C21C5/00—Manufacture of carbon-steel, e.g. plain mild steel, medium carbon steel or cast steel or stainless steel
- C21C5/005—Manufacture of stainless steel
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21C—PROCESSING OF PIG-IRON, e.g. REFINING, MANUFACTURE OF WROUGHT-IRON OR STEEL; TREATMENT IN MOLTEN STATE OF FERROUS ALLOYS
- C21C5/00—Manufacture of carbon-steel, e.g. plain mild steel, medium carbon steel or cast steel or stainless steel
- C21C5/28—Manufacture of steel in the converter
- C21C5/30—Regulating or controlling the blowing
- C21C5/35—Blowing from above and through the bath
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22B—PRODUCTION AND REFINING OF METALS; PRETREATMENT OF RAW MATERIALS
- C22B34/00—Obtaining refractory metals
- C22B34/30—Obtaining chromium, molybdenum or tungsten
- C22B34/32—Obtaining chromium
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22B—PRODUCTION AND REFINING OF METALS; PRETREATMENT OF RAW MATERIALS
- C22B5/00—General methods of reducing to metals
- C22B5/02—Dry methods smelting of sulfides or formation of mattes
- C22B5/10—Dry methods smelting of sulfides or formation of mattes by solid carbonaceous reducing agents
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F27—FURNACES; KILNS; OVENS; RETORTS
- F27D—DETAILS OR ACCESSORIES OF FURNACES, KILNS, OVENS OR RETORTS, IN SO FAR AS THEY ARE OF KINDS OCCURRING IN MORE THAN ONE KIND OF FURNACE
- F27D3/00—Charging; Discharging; Manipulation of charge
- F27D3/0025—Charging or loading melting furnaces with material in the solid state
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F27—FURNACES; KILNS; OVENS; RETORTS
- F27D—DETAILS OR ACCESSORIES OF FURNACES, KILNS, OVENS OR RETORTS, IN SO FAR AS THEY ARE OF KINDS OCCURRING IN MORE THAN ONE KIND OF FURNACE
- F27D3/00—Charging; Discharging; Manipulation of charge
- F27D3/10—Charging directly from hoppers or shoots
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F27—FURNACES; KILNS; OVENS; RETORTS
- F27B—FURNACES, KILNS, OVENS OR RETORTS IN GENERAL; OPEN SINTERING OR LIKE APPARATUS
- F27B3/00—Hearth-type furnaces, e.g. of reverberatory type; Electric arc furnaces ; Tank furnaces
- F27B3/08—Hearth-type furnaces, e.g. of reverberatory type; Electric arc furnaces ; Tank furnaces heated electrically, with or without any other source of heat
- F27B3/085—Arc furnaces
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F27—FURNACES; KILNS; OVENS; RETORTS
- F27D—DETAILS OR ACCESSORIES OF FURNACES, KILNS, OVENS OR RETORTS, IN SO FAR AS THEY ARE OF KINDS OCCURRING IN MORE THAN ONE KIND OF FURNACE
- F27D3/00—Charging; Discharging; Manipulation of charge
- F27D3/16—Introducing a fluid jet or current into the charge
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F27—FURNACES; KILNS; OVENS; RETORTS
- F27D—DETAILS OR ACCESSORIES OF FURNACES, KILNS, OVENS OR RETORTS, IN SO FAR AS THEY ARE OF KINDS OCCURRING IN MORE THAN ONE KIND OF FURNACE
- F27D99/00—Subject matter not provided for in other groups of this subclass
- F27D99/0073—Seals
- F27D99/0075—Gas curtain seals
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F27—FURNACES; KILNS; OVENS; RETORTS
- F27M—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO ASPECTS OF THE CHARGES OR FURNACES, KILNS, OVENS OR RETORTS
- F27M2001/00—Composition, conformation or state of the charge
- F27M2001/16—Particulate material, e.g. comminuted scrap
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a method of charging powder Cr ore raw materials, iron ores and coal in a smelthing reduction thereof.
- High Cr steel as stainless steel has been conventionally produced from ferrochromium as raw material.
- a so-called smelting reduction method has been recently remarked, which directly obtains high Cr molten metal from Cr ores.
- Cr ores, coal and so on are charged into a reduction furnace of a converter type for reducing Cr so as to directly produce high Cr molten metal therefrom.
- Cr raw ores are very fine in grain diameters, and ordinarily around 90% contain those having grain diameters of not more than 1 mm. Therefore, when powder Cr raw ores are charged into the reduction furance from its top part onto the bath, they are lost up to 30% by upflowing gas.
- the present invention is to provide a method of charging ores, carbonaceous material as checking their flying losses in the smelting reduction method of Cr ores, iron ores and so on.
- powder Cr raw ores, or iron ores and coal are charged into the furnace through a charging chute extending nearly a furnace mouth of the smelting furnace of the converter type or connected to the furnace body thereof, so that the flying losses of the ores and coal are checked.
- the powder Cr raw ores, the iron ores and the coal are charged into the furnace while the gas is jetted toward the outside of the charging chute, thereby to enable to charge the raw materials as checking effectively the flying losses.
- Figs.1 to 5 concern the smelting reduction of Cr ores
- Figs.6 to 8 concern the smelting reduction of iron ores
- 1 is a furnace body, 6, 6′ chutes.
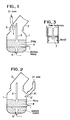
- Fig.1 shows one embodiment of the invention in the smelting reduction of Cr ore, where the reference numeral 1 is the furnace body, and 2 is an exhausting hood provided at a top part of the furnace body.
- the gases are blown from a top blowing lance 3, a side blowing tuyere 4 and a bottom blowing tuyere 5 for carrying out the smelting reduction.
- the powder Cr raw ores are supplied by the chute 6 extending through the exhaust hood 2 to nearly the furnace mouth.
- the charging chute 6 is determined at a height of its lower end so that it does not contact the furnace body when the furnace is tilted.
- Fig.2 shows that the powder Cr and raw ores are charged via a chute 6′ connected to the upper part of the furnace body 1, and also in this case the same effect could be obtained.
- the charging chute 6′ may be seperated at a part 61 on the way, and when the furnace body is tilted, this part 61 is seperated.
- the powder Cr raw ores may be charged into the furnace, thereby to enable to exactly avoid the flying losses of the raw materials.
- the gas is jetted from the nozzle provided in the circumferential direction within the chute toward the outside of the chute, the powder Cr ores are guided in the gas jetting direction and the ore flying is exactly avoided.
- the jet gas also serves as a purge gas for preventing invasion of CO and CO2 of the furnace into the chute.
- Fig.6 shows a further embodiment of the invention in the smelting reduction of the iron ores, where the iron ores and the coal are charged into the furnace from the chute 6.
- Other structures are the same as illustrated in Fig.1.
- Fig.7 shows that the iron ores and the coal are charged via the chute 6′ connected to the top part of the furnace body 1, and the structure is the same as illustrated in Fig.2.
- the iron ores and the coal may be charged into the furnace, thereby to enable to exactly check the flying losses of the raw materials.
- the smelting reduction was carried out as charging the powder Cr raw ores into the smelting reduction furnace (capacity: 5 ton) of the converter type by the method as shown in Fig.1.
- the dispersion in grain diameters of the charged Cr raw ores are as follows. +1mm +0.5mm +0.25mm +0.149mm -0.149mm 1.7% 3.8% 20.1% 42.9% 31.5%
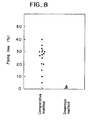
- Fig.4 shows the flying losses of Cr raw ores at the above charging in comparison with the case (comparative method) not using the charging chute, from which it is seen that the flying losses of Cr raw ores were considerably decreased by the present invention method.
- Fig.5 investigates Cr reducing rate (Cr increasing rate in the molten metal) when grain Cr raw ores were charged as they were, and the pelletized Cr raw ores were charged, from which it is seen that the former is shorter to pre-heat the ores, and is faster to reduce Cr than the latter.
- the smelting reduction was carried out as charging the Cr iron ores and the coal into the smelting reduction furnace (capacity: 5 ton) of the converter type by the method as shown in Fig. 6.
- the comparative method did not use the charging chute as shown in Fig. 6, and practised the smelting reduction while charging the raw materials.
- the producing conditions are as follows.
- Fig.8 shows the flying losses of the coal in comparison with the case not using the chute (the comparative method), from which it is seen that the flying losses of the coal was decreased considerably by the present invention method.
- the present invention is useful to charging of raw materials or the coal as the carbonaceous materials in the smelting reduction of the Cr ores or the iron ores.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacture Of Iron (AREA)
- Carbon Steel Or Casting Steel Manufacturing (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP22525387 | 1987-09-10 | ||
| JP225253/87 | 1987-09-10 | ||
| JP63020472A JPH01165743A (ja) | 1987-09-10 | 1988-01-29 | 鉱石の溶融還元における原料装入方法 |
| JP20472/88 | 1988-01-29 | ||
| PCT/JP1988/000911 WO1989002477A1 (fr) | 1987-09-10 | 1988-09-09 | Procede de chargement de minerais pendant une etape de reduction en fusion |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0436718A4 EP0436718A4 (de) | 1989-12-28 |
| EP0436718A1 true EP0436718A1 (de) | 1991-07-17 |
| EP0436718B1 EP0436718B1 (de) | 1994-07-06 |
Family
ID=27283057
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP88907777A Expired - Lifetime EP0436718B1 (de) | 1987-09-10 | 1988-09-09 | Verfahren zum erzchargieren bei der schmelzreduktion |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0436718B1 (de) |
| AU (1) | AU620344B2 (de) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7341080B2 (en) * | 2003-07-04 | 2008-03-11 | Voest-Alpine Industrieanlagenbau Gmbh & Co. | Method for loading pourable material and device for carrying out said method |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2784037A (en) * | 1954-08-18 | 1957-03-05 | Rexroth Alfred | Apparatus for shooting material into cupolas |
| US3169055A (en) * | 1961-10-12 | 1965-02-09 | Stora Kopparbergs Bergslags Ab | Process for producing pig iron in rotary furnace |
| US3462263A (en) * | 1965-08-11 | 1969-08-19 | John H Walsh | Reduction of iron ore |
| ZA827820B (en) * | 1981-10-30 | 1983-08-31 | British Steel Corp | Production of steel |
| US4541866A (en) * | 1984-01-26 | 1985-09-17 | Westinghouse Electric Corp. | Hot injection ladle metallurgy |
-
1988
- 1988-09-09 EP EP88907777A patent/EP0436718B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1988-09-09 AU AU23055/88A patent/AU620344B2/en not_active Ceased
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7341080B2 (en) * | 2003-07-04 | 2008-03-11 | Voest-Alpine Industrieanlagenbau Gmbh & Co. | Method for loading pourable material and device for carrying out said method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0436718B1 (de) | 1994-07-06 |
| AU620344B2 (en) | 1992-02-20 |
| EP0436718A4 (de) | 1989-12-28 |
| AU2305588A (en) | 1989-04-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6689182B2 (en) | Method and device for producing molten iron | |
| EP0308925B1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Einschmelzen und Reduzieren von Eisenerzen | |
| US6503289B2 (en) | Process for manufacturing molten metal iron | |
| JP2006528732A (ja) | スラグの利用プロセス | |
| KR890008330A (ko) | 금속산화물의 용융환원을 수반하는 금속제조장치 | |
| CN103627836B (zh) | 一种炼钢装置及方法 | |
| EP0328677A1 (de) | Ofen und verfahren zur reduktion eines chromvorproduktes durch schmelzen | |
| JPS58123809A (ja) | 酸化物を含有する細粒鉱石の還元方法とその装置 | |
| US4935054A (en) | Method of charging chromium ores in a smelting reduction | |
| EP0436718B1 (de) | Verfahren zum erzchargieren bei der schmelzreduktion | |
| RU2051180C1 (ru) | Способ получения стали в жидкой ванне | |
| JPH06240338A (ja) | 溶鋼の脱硫方法 | |
| US6477195B2 (en) | Process for melting sponge iron and electric-arc furnace for carrying out the process | |
| JPS58141345A (ja) | 有価金属の回収方法 | |
| JPH10500455A (ja) | 電気アーク炉で鋼を製造する方法とそのための電気アーク炉 | |
| JP2018003075A (ja) | 酸化鉄含有鉄原料の還元・溶解方法 | |
| KR102231653B1 (ko) | 고로용 장입물의 장입장치 및 그 장입방법 | |
| JPS57198205A (en) | Production of molten metal from powder and granular ore | |
| JP3752051B2 (ja) | スクラップ溶解方法及びスクラップ溶解用ランス | |
| JP2546018B2 (ja) | 予備還元された鉄鉱石の溶融還元炉内への供給方法 | |
| JPH07216430A (ja) | 溶鋼製造法および溶融金属精錬用上吹きランス | |
| EP4656742A1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von geschmolzenem eisen | |
| KR20240169325A (ko) | 용강의 제조 방법 및 용강 | |
| EP1380656A1 (de) | Direktschmelzanlage sowie Verfahren | |
| JP4686873B2 (ja) | 溶銑の脱燐方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19890125 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE DE FR GB IT NL SE |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19920320 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE DE FR GB IT NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 108212 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19940715 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3850578 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19940811 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| EAL | Se: european patent in force in sweden |
Ref document number: 88907777.2 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19970901 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19970909 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19970912 Year of fee payment: 10 Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19970912 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19970918 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19970929 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19971104 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980909 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980909 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980910 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980930 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: NKK CORP. Effective date: 19980930 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19990401 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19980909 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 88907777.2 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19990531 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 19990401 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19990701 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20050909 |