EP0128126A2 - Queraufhängung mit wechselnden Eigenschaften für Schienenfahrzeuge - Google Patents
Queraufhängung mit wechselnden Eigenschaften für Schienenfahrzeuge Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0128126A2 EP0128126A2 EP84830133A EP84830133A EP0128126A2 EP 0128126 A2 EP0128126 A2 EP 0128126A2 EP 84830133 A EP84830133 A EP 84830133A EP 84830133 A EP84830133 A EP 84830133A EP 0128126 A2 EP0128126 A2 EP 0128126A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- springs
- transverse
- bogie
- suspension
- spring
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 28
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 2
- 241000009298 Trigla lyra Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000006096 absorbing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000033228 biological regulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000013016 damping Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004146 energy storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000750 progressive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035939 shock Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61F—RAIL VEHICLE SUSPENSIONS, e.g. UNDERFRAMES, BOGIES OR ARRANGEMENTS OF WHEEL AXLES; RAIL VEHICLES FOR USE ON TRACKS OF DIFFERENT WIDTH; PREVENTING DERAILING OF RAIL VEHICLES; WHEEL GUARDS, OBSTRUCTION REMOVERS OR THE LIKE FOR RAIL VEHICLES
- B61F5/00—Constructional details of bogies; Connections between bogies and vehicle underframes; Arrangements or devices for adjusting or allowing self-adjustment of wheel axles or bogies when rounding curves
- B61F5/02—Arrangements permitting limited transverse relative movements between vehicle underframe or bolster and bogie; Connections between underframes and bogies
- B61F5/04—Bolster supports or mountings
- B61F5/10—Bolster supports or mountings incorporating fluid springs
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61F—RAIL VEHICLE SUSPENSIONS, e.g. UNDERFRAMES, BOGIES OR ARRANGEMENTS OF WHEEL AXLES; RAIL VEHICLES FOR USE ON TRACKS OF DIFFERENT WIDTH; PREVENTING DERAILING OF RAIL VEHICLES; WHEEL GUARDS, OBSTRUCTION REMOVERS OR THE LIKE FOR RAIL VEHICLES
- B61F5/00—Constructional details of bogies; Connections between bogies and vehicle underframes; Arrangements or devices for adjusting or allowing self-adjustment of wheel axles or bogies when rounding curves
- B61F5/02—Arrangements permitting limited transverse relative movements between vehicle underframe or bolster and bogie; Connections between underframes and bogies
- B61F5/14—Side bearings
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a transverse suspension for railway vehicles including a body and bogies articulated to the body about a substantially vertical axis with the possible interposition of a pivoted cross member and in which resilient vertical and transverse suspension means are interposed between each bogie and the body or pivoted cross member.
- the function of the transverse suspension means is to separate the transverse movements, due to vibrational effects, of the body from those of the bogies.
- the objects which are achieved by this are two-fold: first of all a reduction in the reactions which the keeping of the vehicle on the track causes between the wheels and the rails, and in the second place an improvement in the dynamic behaviour of the body, particularly as regards comfort during travel of the vehicle.
- the conformation of the transverse suspension means according to the known art is essentially of two types.
- the first widely used until recent times, is based on the pendulous suspension of the body on the bogie by means of vertical or inclined connecting rods and hence uses the force of gravity.
- the second mainly used in railway vehicles of more recent manufacture, uses the transverse resilience of vertical suspension means normally constituted by helical springs or pneumatic springs.
- the object of the present invention is to avoid this disadvantage by entrusting the containing and transmission of transverse forces between the body and the bogie to a resilient system the load-yield characteristic of which can be displaced substantially parallel to itself in response to an external command, the characteristic frequency of the connection between the body and the bogie thus being kept constant.
- the present invention provides a suspension for railway vehicles of the type defined at the beginning, characterised in that the transverse suspension means include at least one pair of pneumatic or hydro-pneumatic springs which are separate and distinct from the vertical suspension means, disposed substantially horizontally and reacting between the body or the pivoted cross member and the opposite sides of the bogie, and automatic control means for progressively increasing the forces transmitted by the or each spring which is compressed by the action of the transverse forces transmitted between the body or the pivoted cross member and the bogie, on increase of these forces, by means of an increase in the pressure of the fluid contained in t'he spring.
- the transverse suspension means include at least one pair of pneumatic or hydro-pneumatic springs which are separate and distinct from the vertical suspension means, disposed substantially horizontally and reacting between the body or the pivoted cross member and the opposite sides of the bogie, and automatic control means for progressively increasing the forces transmitted by the or each spring which is compressed by the action of the transverse forces transmitted between the body or the pivoted cross member and the bogie, on increase of these forces
- the two springs of the transverse suspension have identical characteristics. and, by working in counter-parallel, give rise to a force-diaplacement characteristic which has its zero point in the middle of the vehicle.
- the automatic control means to advantage comprise a circuit including valve means controlled by the transverse relative movements between the body or the pivoted cross member and the bogie.
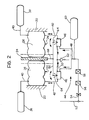
- the chassis of the body of a railway vehicle is generally indicated 10 and below the middle part thereof is fixed a kingpin 12 inserted in an orientable bush 14 carried by a pivoted cross member 16 on which the chassis 10 of the body bears by means of shoes or bearing rollers 18.
- the chassis of one of the bogies of the vehicle is generally indicated 20 and is connected in known manner to the pivot cross member 16.
- a secondary suspension system including a pair of vertical suspension helical springs 22 with which respective telescopic shock absorbers 23 are associated,and a pair of transverse suspension springs 24.
- the two springs 24 are of the opposing, horizontal-axis, hydro-pneumatic or pneumatic type with force-displacement characteristics which are variable in dependence on the pressure of the fluid within them.
- each spring 24 is constituted by an air-tight flexible casing 26 having end covers 28, 30 the first of which is rigidly fixed at 32 to the chassis 20.
- the covers 30 of the two springs 24 bear against a central appendage 34 of the pivoted cross member 16 and are each supported by two connecting rods, only one of which, indicated 36,is shown in Figure 1, disposed at 90° to each other with respective axes perpendicular to the axes of the springs 24 themselves.
- the casings 26 of the two springs 24 are each connected to a respective auxiliary compressed air reservoir 38 by piper 40 in order to allow the regulation of the force-displacement and shock-absorbing characteristics.
- the casings 26 are also connected by respective . 42 to pneumatic control cricuit generally indrcate 44 in tigure 2.
- the circuit 44 includes a pair of three-way selector valves 46 each of which is connected bl one side to the pipe 42 of one of the springs 24 and on the other side to a respective supply duct 48 and to an exhaust duct 50.
- the supply ducts 48 are in their turn connected to the main pneumatic duct 52 of the vehicle through a cock 54, a supply valve 56 and a pressure reducer 58 and to a compressed air supply reservoir 60.
- the exhaust duct 50 is connected to the atmosphere through a calibrated relief valve 62.
- the two valves 46 are operated by means of two linkage levers generally indicated 64 and are movable simultaneously from a central position in which the two springs 24 are both in communication with the exhaust duct 50.
- the valve 46 associated with the left hand spring 24 keeps communication between this spring and the exhaust duct 50 open while the valve 46 associated with the right hand spring 24 is disposed initially in a first position in which the right hand spring 24 is isolated both from the supply duct 48 and from the exhaust duct 50 and subsequently in a second position in which communication between this spring and the supply duct 48 is open while communication with the exhaust duct 50 is closed.
- valve 46 The operation of the valve 46 is effected automatically for example by means of a transmission 66 connected to a control member 68 fixed to the appendage 34 of the pivoted cross member 16.
- the two levers 64 are maintained in their central position whereby the two springs 24 are supplied at a given constant pressure (for example, 2 kg/cm2) and thus have identical characteristics, working in counter-parallel.
- the lateral loads are thus opposed by the normal deformation of the two springs 24 and the springs 22.
- one of the two springs 24 (that is,the compressed spring) is connected, after a first movement into the position of complete isolation from the supply duct 48 and exhaust duct 50, to the supply duct 48.
- the other spring 24 remains connected to the exhaust duct 50.
- connection between the body 10 and the bogie does not include the use of a pivoted cross member 16, that is, both the case in which the body 10 is pendulously suspended from the chassis 20 of the bogie and the case in which the springs 22 are interposed directly between the body and the bogie, without the pivoted cross member.
- the conformation and the number of the pneum tic springs 20 could differ from those of the example.
- the pneumatic springs 24 could conveniently be replaced by hydro-pneumatic spr - ngs and the operation of the valves 46 could be effected by various devices arranged to achieve the conditions described above.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Vehicle Body Suspensions (AREA)
- Vibration Prevention Devices (AREA)
- Springs (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT67605/83A IT1159021B (it) | 1983-06-01 | 1983-06-01 | Sospensione trasversale a caratteristica variabile per veicoli ferroviari |
| IT6760583 | 1983-06-01 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0128126A2 true EP0128126A2 (de) | 1984-12-12 |
| EP0128126A3 EP0128126A3 (de) | 1987-02-25 |
Family
ID=11303806
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP84830133A Withdrawn EP0128126A3 (de) | 1983-06-01 | 1984-04-30 | Queraufhängung mit wechselnden Eigenschaften für Schienenfahrzeuge |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0128126A3 (de) |
| JP (1) | JPS608154A (de) |
| AU (1) | AU2729384A (de) |
| BR (1) | BR8402639A (de) |
| IT (1) | IT1159021B (de) |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1992020559A1 (en) * | 1991-05-21 | 1992-11-26 | Brel Limited | Apparatus for controlling lateral movement of vehicle bodies |
| US5222440A (en) * | 1988-10-13 | 1993-06-29 | Sig Schweizerisch Industrie-Gesellschaft | Tilt compensator for high-speed vehicles, in particular rail vehicles |
| FR2689476A1 (fr) * | 1992-04-01 | 1993-10-08 | Faiveley Transport | Suspension transversale pour véhicule ferroviaire. |
| FR2689475A1 (fr) * | 1992-04-01 | 1993-10-08 | Faiveley Transport | Suspension transversale pour véhicule ferroviaire. |
| US5255611A (en) * | 1988-10-13 | 1993-10-26 | Sig Schweizerische Industrie-Gesellschaft | Tilt compensator for high-speed vehicles, in particular rail vehicles |
| EP0592388A1 (de) * | 1992-10-08 | 1994-04-13 | SGP Verkehrstechnik Gesellschaft m.b.H. | Anordnung zur Regelung des Druckniveaus bei einer Querfederung zwischen Drehgestell und Wagenkasten für Schienenfahrzeuge |
| EP0592387A1 (de) * | 1992-10-08 | 1994-04-13 | SGP Verkehrstechnik Gesellschaft m.b.H. | Anordnung zur Regelung einer Querfederung zwischen Drehgestell und Wagenkasten eines Schienenfahrzeuges |
| EP0592950A1 (de) * | 1992-10-14 | 1994-04-20 | ABB HENSCHEL WAGGON UNION GmbH | Laufwerk für Schienenfahrzeuge |
| EP0615890A1 (de) * | 1993-03-19 | 1994-09-21 | FIAT FERROVIARIA S.p.A. | Aktive seitliche Neigungsaufhängung für Schienenfahrzeuge |
| DE19608179A1 (de) * | 1996-03-04 | 1997-09-11 | Deutsche Waggonbau Ag | Abstützung von Schienenfahrzeugen mittels Luftfedersysteme |
| DE19647998A1 (de) * | 1996-11-20 | 1998-05-28 | Duewag Ag | Luftfeder für Schienenfahrzeuge |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH075076B2 (ja) * | 1987-07-22 | 1995-01-25 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 鉄道車両 |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2954746A (en) * | 1956-01-10 | 1960-10-04 | Chesapeake & Ohio Railway | Radially guided, single axle, above center of gravity suspension for articulated trains |
| DE1605083C3 (de) * | 1967-12-15 | 1976-01-08 | Knorr-Bremse Gmbh, 8000 Muenchen | Luftfederung für Fahrzeuge, insbesondere Schienenfahrzeuge |
| CH514455A (de) * | 1970-06-17 | 1971-10-31 | Schweizerische Lokomotiv | Schienenfahrzeug |
| DE2040922A1 (de) * | 1970-08-18 | 1972-02-24 | Mak Maschb Gmbh | Querfederung des Aufbaus von Schienenfahrzeugen |
| US3826202A (en) * | 1973-03-12 | 1974-07-30 | Budd Co | Pneumatically sprung railway car truck |
-
1983
- 1983-06-01 IT IT67605/83A patent/IT1159021B/it active
-
1984
- 1984-04-26 AU AU27293/84A patent/AU2729384A/en not_active Abandoned
- 1984-04-30 EP EP84830133A patent/EP0128126A3/de not_active Withdrawn
- 1984-05-31 BR BR8402639A patent/BR8402639A/pt unknown
- 1984-06-01 JP JP59111081A patent/JPS608154A/ja active Pending
Cited By (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5222440A (en) * | 1988-10-13 | 1993-06-29 | Sig Schweizerisch Industrie-Gesellschaft | Tilt compensator for high-speed vehicles, in particular rail vehicles |
| US5255611A (en) * | 1988-10-13 | 1993-10-26 | Sig Schweizerische Industrie-Gesellschaft | Tilt compensator for high-speed vehicles, in particular rail vehicles |
| WO1992020559A1 (en) * | 1991-05-21 | 1992-11-26 | Brel Limited | Apparatus for controlling lateral movement of vehicle bodies |
| FR2689476A1 (fr) * | 1992-04-01 | 1993-10-08 | Faiveley Transport | Suspension transversale pour véhicule ferroviaire. |
| FR2689475A1 (fr) * | 1992-04-01 | 1993-10-08 | Faiveley Transport | Suspension transversale pour véhicule ferroviaire. |
| EP0592387A1 (de) * | 1992-10-08 | 1994-04-13 | SGP Verkehrstechnik Gesellschaft m.b.H. | Anordnung zur Regelung einer Querfederung zwischen Drehgestell und Wagenkasten eines Schienenfahrzeuges |
| EP0592388A1 (de) * | 1992-10-08 | 1994-04-13 | SGP Verkehrstechnik Gesellschaft m.b.H. | Anordnung zur Regelung des Druckniveaus bei einer Querfederung zwischen Drehgestell und Wagenkasten für Schienenfahrzeuge |
| AT402387B (de) * | 1992-10-08 | 1997-04-25 | Sgp Verkehrstechnik | Anordnung zur regelung des druckniveaus der querfederung zwischen drehgestell und wagenkasten für ein schienenfahrzeug |
| AT408975B (de) * | 1992-10-08 | 2002-04-25 | Siemens Sgp Verkehrstech Gmbh | Anordnung zur regelung einer querfederung zwischen drehgestell und wagenkasten eines schienenfahrzeuges |
| EP0592950A1 (de) * | 1992-10-14 | 1994-04-20 | ABB HENSCHEL WAGGON UNION GmbH | Laufwerk für Schienenfahrzeuge |
| EP0615890A1 (de) * | 1993-03-19 | 1994-09-21 | FIAT FERROVIARIA S.p.A. | Aktive seitliche Neigungsaufhängung für Schienenfahrzeuge |
| US5454329A (en) * | 1993-03-19 | 1995-10-03 | Fiat Ferroviaria Spa | Anticentrifugal active lateral suspension for railway vehicles |
| DE19608179A1 (de) * | 1996-03-04 | 1997-09-11 | Deutsche Waggonbau Ag | Abstützung von Schienenfahrzeugen mittels Luftfedersysteme |
| DE19647998A1 (de) * | 1996-11-20 | 1998-05-28 | Duewag Ag | Luftfeder für Schienenfahrzeuge |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| IT1159021B (it) | 1987-02-25 |
| JPS608154A (ja) | 1985-01-17 |
| IT8367605A0 (it) | 1983-06-01 |
| AU2729384A (en) | 1984-12-06 |
| BR8402639A (pt) | 1985-04-30 |
| EP0128126A3 (de) | 1987-02-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0128126A2 (de) | Queraufhängung mit wechselnden Eigenschaften für Schienenfahrzeuge | |
| US4488495A (en) | Soft primar suspension system for a railway car | |
| US4641586A (en) | Magnetic suspension railway | |
| US4448131A (en) | Suspension system for rail vehicles | |
| KR101730491B1 (ko) | 차체 지지 장치 및 철도 차량 | |
| CA1148029A (en) | Bolsterless bogie with air-spring suspension for rail vehicles | |
| US3868911A (en) | Railway car suspension motion control system | |
| US4735149A (en) | Railway vehicle suspension | |
| US5943962A (en) | Device for counteracting transverse forces acting on a rail vehicle | |
| CA2264128C (en) | Running gear for a rail vehicle | |
| US3970009A (en) | Fluid railroad passenger car suspension | |
| US3913495A (en) | Railway car bogie suspension system | |
| US4841873A (en) | Railway locomotive and stabilized self steering truck therefor | |
| EP0547010A1 (de) | Mehrzweck-Eisenbahndrehgestell | |
| US3059591A (en) | Suspension railway | |
| EP0189382A2 (de) | Hochgeschwindigkeits-Eisenbahnfahrzeug mit neigbarem Oberbau | |
| US2594734A (en) | Railway truck | |
| CA1055784A (en) | Vehicle suspension system with rubber springs and friction damping | |
| US2217034A (en) | Suspension system for vehicles | |
| US2954746A (en) | Radially guided, single axle, above center of gravity suspension for articulated trains | |
| US5170716A (en) | Device for applying a force to the underframe of a railway vehicle, for the inclination of the underframe or the transverse stabilization of the vehicle | |
| US2740360A (en) | Railway passenger car truck | |
| US3001484A (en) | Monorail car | |
| US3845724A (en) | Railway car centrifugal force stabilizing device | |
| US3010411A (en) | Suspension systems of tire-mounted bogie trucks with lateral guide means |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19870324 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19881028 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 19900425 |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: SANTANERA, ORESTE |