WO2024106136A1 - プログラム及び情報処理装置 - Google Patents
プログラム及び情報処理装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2024106136A1 WO2024106136A1 PCT/JP2023/037981 JP2023037981W WO2024106136A1 WO 2024106136 A1 WO2024106136 A1 WO 2024106136A1 JP 2023037981 W JP2023037981 W JP 2023037981W WO 2024106136 A1 WO2024106136 A1 WO 2024106136A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- time
- enemy object
- player
- control means
- battle
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A63—SPORTS; GAMES; AMUSEMENTS
- A63F—CARD, BOARD, OR ROULETTE GAMES; INDOOR GAMES USING SMALL MOVING PLAYING BODIES; VIDEO GAMES; GAMES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- A63F13/00—Video games, i.e. games using an electronically generated display having two or more dimensions
- A63F13/60—Generating or modifying game content before or while executing the game program, e.g. authoring tools specially adapted for game development or game-integrated level editor
- A63F13/65—Generating or modifying game content before or while executing the game program, e.g. authoring tools specially adapted for game development or game-integrated level editor automatically by game devices or servers from real world data, e.g. measurement in live racing competition
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A63—SPORTS; GAMES; AMUSEMENTS
- A63F—CARD, BOARD, OR ROULETTE GAMES; INDOOR GAMES USING SMALL MOVING PLAYING BODIES; VIDEO GAMES; GAMES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- A63F13/00—Video games, i.e. games using an electronically generated display having two or more dimensions
- A63F13/20—Input arrangements for video game devices
- A63F13/21—Input arrangements for video game devices characterised by their sensors, purposes or types
- A63F13/216—Input arrangements for video game devices characterised by their sensors, purposes or types using geographical information, e.g. location of the game device or player using GPS
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A63—SPORTS; GAMES; AMUSEMENTS
- A63F—CARD, BOARD, OR ROULETTE GAMES; INDOOR GAMES USING SMALL MOVING PLAYING BODIES; VIDEO GAMES; GAMES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- A63F13/00—Video games, i.e. games using an electronically generated display having two or more dimensions
- A63F13/30—Interconnection arrangements between game servers and game devices; Interconnection arrangements between game devices; Interconnection arrangements between game servers
- A63F13/35—Details of game servers
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A63—SPORTS; GAMES; AMUSEMENTS
- A63F—CARD, BOARD, OR ROULETTE GAMES; INDOOR GAMES USING SMALL MOVING PLAYING BODIES; VIDEO GAMES; GAMES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- A63F13/00—Video games, i.e. games using an electronically generated display having two or more dimensions
- A63F13/40—Processing input control signals of video game devices, e.g. signals generated by the player or derived from the environment
- A63F13/44—Processing input control signals of video game devices, e.g. signals generated by the player or derived from the environment involving timing of operations, e.g. performing an action within a time slot
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A63—SPORTS; GAMES; AMUSEMENTS
- A63F—CARD, BOARD, OR ROULETTE GAMES; INDOOR GAMES USING SMALL MOVING PLAYING BODIES; VIDEO GAMES; GAMES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- A63F13/00—Video games, i.e. games using an electronically generated display having two or more dimensions
- A63F13/45—Controlling the progress of the video game
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A63—SPORTS; GAMES; AMUSEMENTS
- A63F—CARD, BOARD, OR ROULETTE GAMES; INDOOR GAMES USING SMALL MOVING PLAYING BODIES; VIDEO GAMES; GAMES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- A63F13/00—Video games, i.e. games using an electronically generated display having two or more dimensions
- A63F13/45—Controlling the progress of the video game
- A63F13/48—Starting a game, e.g. activating a game device or waiting for other players to join a multiplayer session
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A63—SPORTS; GAMES; AMUSEMENTS
- A63F—CARD, BOARD, OR ROULETTE GAMES; INDOOR GAMES USING SMALL MOVING PLAYING BODIES; VIDEO GAMES; GAMES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- A63F13/00—Video games, i.e. games using an electronically generated display having two or more dimensions
- A63F13/55—Controlling game characters or game objects based on the game progress
- A63F13/57—Simulating properties, behaviour or motion of objects in the game world, e.g. computing tyre load in a car race game
- A63F13/577—Simulating properties, behaviour or motion of objects in the game world, e.g. computing tyre load in a car race game using determination of contact between game characters or objects, e.g. to avoid collision between virtual racing cars
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A63—SPORTS; GAMES; AMUSEMENTS
- A63F—CARD, BOARD, OR ROULETTE GAMES; INDOOR GAMES USING SMALL MOVING PLAYING BODIES; VIDEO GAMES; GAMES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- A63F13/00—Video games, i.e. games using an electronically generated display having two or more dimensions
- A63F13/80—Special adaptations for executing a specific game genre or game mode
- A63F13/822—Strategy games; Role-playing games
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A63—SPORTS; GAMES; AMUSEMENTS
- A63F—CARD, BOARD, OR ROULETTE GAMES; INDOOR GAMES USING SMALL MOVING PLAYING BODIES; VIDEO GAMES; GAMES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- A63F13/00—Video games, i.e. games using an electronically generated display having two or more dimensions
- A63F13/80—Special adaptations for executing a specific game genre or game mode
- A63F13/847—Cooperative playing, e.g. requiring coordinated actions from several players to achieve a common goal
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a program and an information processing device.
- Location-based games have been known in which a player object (e.g., a player character) is moved in a virtual world based on the player's position in the real world.
- a player object e.g., a player character
- Patent Document 1 discloses a technology that allows each player to battle a common enemy object (raid boss).
- the present invention was made in consideration of these problems, and its purpose is to provide a program and information processing device that can motivate players in areas with a small number of players to play location-based games.
- the program according to the first aspect of the present invention is a program that executes a fighting game against an enemy object that each player can fight at the time when the enemy object appears, and causes a computer to function as an acquisition means that acquires the current position of each player, and a control means that executes the fighting game against the enemy object on condition that the current position of the player has reached a fighting range with the enemy object, and the control means expands the fighting range if the number of times the fighting game has been executed at a predetermined point in time is less than a predetermined number of times.
- the predetermined time is when a unit time has elapsed
- the control means expands the possible battle range each time the unit time elapses if the number of times per unit time is less than the predetermined number of times.
- the predetermined time is the time when the appearance time of the enemy object becomes less than a certain time.
- control means extends the appearance time when the battle range is expanded.
- a fifth aspect of the present invention is a program for executing a fighting game against an enemy object that can be fought by each player during the appearance time of the enemy object, and causes a computer to function as an acquisition means for acquiring the current position of each player, and a control means for executing a fighting game against the enemy object on condition that the current position of the player has reached a fighting range with the enemy object, and the control means extends the appearance time of the enemy object if the number of times the fighting game has been executed at a predetermined point in time is less than a predetermined number of times.
- the predetermined time is a time when a unit time has elapsed
- the control means extends the appearance time of the enemy object each time a unit time has elapsed if the number of times per unit time is less than the predetermined number of times.
- the predetermined time is the time when the appearance time of the enemy object becomes less than a certain time.
- the present invention can provide players in areas with a small number of players with an incentive to play location-based games.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an example of the overall configuration of a game system according to a first embodiment.
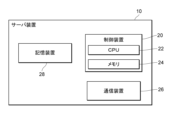
- 2 is a diagram illustrating an example of a hardware configuration of a server device illustrated in FIG. 1 .
- FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating an example of a hardware configuration of a smartphone as the terminal device illustrated in FIG. 1 .
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing an example of a functional configuration of a server device.
- 11 is a flowchart showing an example of a processing flow in which a player plays a battle game against a raid boss monster in the game system according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an example of a game screen according to the first embodiment.
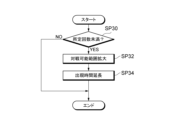
- 13 is a flowchart showing an example of a process flow for expanding a battle available range and extending an appearance time in the game system according to the first embodiment. 13 is a flowchart showing an example of a process flow for expanding a battle available range and extending an appearance time in a game system according to a second embodiment.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an example of the overall configuration of a game system 1 according to the first embodiment.
- the game system 1 includes a server device 10 and one or more terminal devices 12.
- the server device 10 and the terminal devices 12 are connected to each other so as to be able to communicate with each other via a communication network NT such as the Internet, a telephone line, or an intranet.
- a communication network NT such as the Internet, a telephone line, or an intranet.
- the server device 10 is an information processing device that provides the game execution results obtained by executing the game program 14, or the game program 14 itself, to players of each terminal device 12 via the communication network NT.
- Each terminal device 12 is a portable communication terminal device that can be operated and carried by each player. Examples of each terminal device 12 include a smartphone, mobile phone, tablet, and laptop computer. Each terminal device 12 is an information processing device that provides a game to a player by transmitting operation information of the player to the server device 10 and outputting the execution result of the game program 14 received from the server device 10, or by executing the game program 14 based on the operation information of the player. Note that the game program 14 may be executed by the terminal device 12 and the server device 10 in cooperation.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating an example of a hardware configuration of the server device 10 illustrated in FIG.
- the server device 10 includes a control device 20, a communication device 26, and a storage device 28.
- the control device 20 is mainly configured with a CPU (Central Processing Unit) 22 and a memory 24.
- CPU Central Processing Unit
- the CPU 22 executes a predetermined program stored in the memory 24 or the storage device 28, etc., to function as various functional means. Details of these functional means will be described later.
- the communication device 26 is configured with a communication interface for communicating with an external device.
- the communication device 26 transmits and receives various information to and from the terminal device 12, for example.
- the storage device 28 is composed of a hard disk or the like. This storage device 28 stores various programs and information necessary for executing processes in the control device 20, including the game program 14, as well as information on the results of processing.
- the server device 10 can be realized using an information processing device such as a dedicated or general-purpose server computer.
- the server device 10 may be composed of a single information processing device, or may be composed of multiple information processing devices distributed over the communication network NT.
- FIG. 2 shows only a portion of the main hardware configuration of the server device 10, and the server device 10 may be equipped with other configurations that are generally equipped in servers.
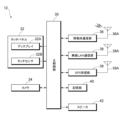
- FIG. 3 is a diagram showing an example of the hardware configuration of a smartphone as the terminal device 12 shown in FIG. 1.
- the terminal device 12 includes a main control unit 30, a touch panel 32, an acceleration sensor 33, an angular velocity sensor 34, a mobile communication unit 36, a wireless LAN communication unit 38, a GPS receiving unit 39, a memory unit 40, and a speaker 42.
- the main control unit 30 is configured to include a CPU, memory, etc.
- the main control unit 30 is connected to a touch panel 32 as a display input device, an acceleration sensor 33, an angular velocity sensor 34, a mobile communication unit 36, a wireless LAN communication unit 38, a GPS receiving unit 39, a memory unit 40, and a speaker 42.
- the main control unit 30 has the function of controlling these connection destinations.
- the touch panel 32 has both display and input functions, and is composed of a display 32A that performs the display function, and a touch sensor 32B that performs the input function.
- the display 32A is capable of displaying game images including operation input images such as button images, cross key images, and joystick images.
- the touch sensor 32B is capable of detecting the player's input position relative to the game image.
- the acceleration sensor 33 is capable of measuring the acceleration of the terminal device 12, in other words, the player. Specifically, the acceleration sensor 33 can detect the movement and vibrations of the player.
- the angular velocity sensor 34 is capable of measuring the orientation and inclination of the terminal device 12.
- the mobile communication unit 36 has the function of connecting to a mobile communication network via the antenna 36A and communicating with other communication devices connected to the mobile communication network.
- the wireless LAN communication unit 38 has the function of connecting to the communication network NT via the antenna 38A and communicating with other devices such as the server device 10 connected to the communication network NT.
- the GPS receiver 39 has the function of receiving radio waves from GPS satellites via the antenna 39A and acquiring location information indicating the player's current location.
- This location information is, for example, latitude and longitude.
- the storage unit 40 stores various programs and data, including all or part of the game program 14.
- the speaker 42 has the function of outputting game sounds, etc.
- the game according to the first embodiment is a position information game in which the position and movement of the player in the real world are reflected in the game content.
- a player object arranged in a game field also moves.
- This player object is one or more characters that the player can use in the game.
- the player gives instructions to the player object by performing an input operation or the like on the touch panel 32.
- the player object may be a robot, a car, an airplane, a ship, or the like other than a character.
- the game according to the first embodiment also has a field mode and an event mode.
- Field mode is a mode in which the player object moves around the game field.
- the player can instruct the player object to equip (put on or take off) equipment items that the player owns, and to use (consume) consumable items that the player owns.
- Equipment items include, for example, weapons, armor, accessories, etc.
- Consumable items include, for example, tools that restore the player object's hit points, tools that restore the player object's status abnormalities (paralysis, confusion, etc.), tools that strengthen equipment items, etc.
- the event mode is a mode in which an event that occurs in response to the player's movement in the real world, i.e., the player object's movement in the game field, is executed.
- This event is, for example, a battle game against an enemy object.
- the enemy object include normal monsters, boss monsters, raid boss monsters, etc.
- a battle game against a normal monster is executed on the condition that the normal monster appears around the player object in the game field.
- the normal monster appears randomly according to each area of the game field.
- a player can execute a battle game against the normal monster by designating (e.g., touching) the normal monster that has appeared in the game field.
- the battle game against the boss monster is executed on the condition that the player's current position has reached the destination of the quest.
- the battle game against the raid boss monster is executed on the condition that the player's current position reaches the vicinity of the spawn point of the raid boss monster (battle possible range).
- This battle game against the raid boss monster is, for example, a common event in which all players can participate, and is a game in which the players cooperate with each other to defeat the raid boss monster.
- each player fights against a common (same) raid boss monster and cooperates with each other to gradually reduce the hit points of the raid boss monster and defeat the raid boss monster.
- the player instructs the player object to attack, use skills, defend, use (consume) items, etc.
- a reward is given to the player.
- Defeating a monster means, for example, reducing the monster's hit points to 0 or less.
- the reward is, for example, experience points that allow the player object to grow (level up), currency that can be used in the game (for example, medals or coins), dropped items (for example, equipment items or consumable items), etc.
- the monster has high abilities or appears infrequently, a large amount of experience points, currency, etc. is given as a reward.
- the game according to the first embodiment has multiple types of quests, each with a different name (title).
- Each quest can be selected by the player on a quest menu screen or the like. The player can clear the quest by defeating the boss monster encountered at the quest's destination (goal point).
- These quests include normal quests and limited-time quests.
- a normal quest is a quest in which the next quest becomes playable (unlocked) when the player clears one of the selectable quests. This next quest is set to a higher difficulty level than the first quest, and the monsters and boss monsters have higher abilities.
- a limited-time quest is a quest in which the selectable quests change depending on the time of day or period.
- the location where the raid boss monster appears and the destination of each quest are set at a location in the real world.
- locations include commercial facilities, public facilities, and tourist spots. These locations are associated with virtual locations in the game field, and the virtual locations can be the locations where the raid boss monster or boss monster appears.
- a player who is performing a quest can fight against normal monsters and raid boss monsters that appear in the game field on the way (on the travel route) to the destination of the quest.
- a player can cooperate with another player to battle the raid boss monster by reaching (moving) close to the spawn point of the raid boss monster (battle range).
- the player can fight a boss monster corresponding to a quest in the game field by moving to the vicinity (for example, within a 20 m radius) of the point where the destination of the quest is set.
- the destination (goal point) of each quest may be set by the player or the game operator.
- the game according to the first embodiment allows the use of game currency.
- This game currency includes paid currency and free currency.
- Paid currency is paid content that can be acquired by purchasing (paying) money, prepaid cards, credit cards, electronic money, crypto assets, etc.
- paid currency include paid items, paid coins, and paid points.
- paid item can be purchased for 100 yen.
- free currency is free content that can be acquired by playing the game. Examples of free currency include non-paid items, non-paid coins, and non-paid points.
- game execution include the player logging in to the game, clearing a quest for the first time, and completing a mission. Free currency can be consumed in various games without distinction from paid currency.
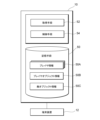
- FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing an example of the functional configuration of the server device 10. As shown in FIG. 4
- the server device 10 has, as its functional configuration, a storage means 50, an acquisition means 52, and a control means 54.
- the storage means 50 is realized by one or more storage devices 28.
- the functional means other than the storage means 50 are realized by the control device 20 executing the game program 14 stored in the storage device 28 or the like. Note that all or part of these functional configurations may be provided in the terminal device 12.
- the storage means 50 is a functional means for storing player information 50A, player object information 50B, enemy object information 50C, etc.
- the player information 50A is stored for each player in association with the player ID of the player.
- the player information 50A includes, for example, the player's name, character information, owned item information, and quest progress information.
- the available character information includes ability information associated with the character ID of each player object available to the player.
- the ability information includes ability values and skill information.
- the ability values include, for example, level, hit points, attack power, defense power, etc.
- the skill information includes skill IDs of skills that have been acquired (and are available for use). Examples of such skills include magic that recovers hit points and a special skill that attacks with a fire attribute.
- the owned item information includes the item IDs and the number of items (equipment items and consumable items) owned by the player.
- the player object information 50B is stored for each player object in association with the character ID of the player object.
- the player object information 50B includes, for example, the name and image of the player object, the required experience points for each level, ability information for each level, equippable items, and the like.
- Experience required includes the total experience needed to reach each level.
- the ability information includes acquired skills at each level, hit points, attack power, defense power, and the like.
- the equippable item includes the item ID of the equippable equipment item.
- the enemy object information 50C is stored for each enemy object in association with the object ID of the enemy object.
- the enemy object includes a raid boss monster.
- the enemy object information 50C includes a name, an image, appearance information, a battle range, battle information, ability information, reward information, and the like.
- the appearance information includes the available time and the available range.
- the available time is the time period during which the player can fight the enemy object (raid boss monster).
- the available time includes the appearance start date and time and the appearance time.
- the appearance start date and time includes the date and time when the enemy object starts to appear in the game field corresponding to the real world and the appearance time. For example, the appearance start date and time of a certain raid boss monster is 5:00 PM every Monday. Also, for example, the appearance time of a certain raid boss monster is 2 hours.
- the available time for a certain raid boss monster is 5:00 PM to 7:00 PM every Monday.
- This appearance time decreases from the timing when the appearance start date and time is reached.
- this appearance time may be updated (increased or decreased) by the control means 54.
- the available range includes the range (area) in which the enemy object can fight in the game field corresponding to the real world.
- the available range includes, for example, the occurrence point of the raid boss monster indicated by the latitude and longitude in the real world, and the radius of a circular area having the occurrence point as the center point. The initial value of this radius is, for example, 20 m.
- this battle range may be indicated by the spawn point of the raid boss monster in the game field and a circular area having the spawn point as its center.
- the battle information includes the number of battles in which a battle game with an enemy object was played, the date and time when each battle game was played, and the player ID of the player who played the battle game with the enemy object (raid boss monster). Examples of the number of battles include the total number (cumulative number) of battle games played by one or more players, the number of battle games played per unit time, etc.
- the ability information includes ability values (level, hit points, attack power, defense power, etc.) and skill information. For example, the hit points of a raid boss monster decrease (approaching 0) each time a battle game is played by one or more players.
- the reward information includes experience points, currency amount, and dropped item information.
- the dropped item information includes the item ID of the dropped item and a drop rate. The drop rate is the probability that a dropped item will be given to the player as a reward.
- the acquisition means 52 is a functional means for acquiring the current position of each player.
- the acquisition means 52 acquires position information (latitude and longitude) in the real world received by the GPS receiving unit 39 via the terminal device 12.
- the acquisition means 52 may also acquire the position of the player object in the game field (for example, coordinates on the game field).
- the control means 54 is a functional means for controlling the entire game.
- the control means 54 executes a battle game against an enemy object (raid boss monster) that each player can commonly battle during a battle-available time for the enemy object.
- the control means 54 also executes a battle game against the enemy object on the condition that the player's current position has reached a battle-available range for the enemy object.
- the control means 54 refers to the appearance information in the enemy object information 50C, and permits the execution of a battle game against the enemy object if the player's position information is within the battle-available range of the appearance information during a battle-available time for the enemy object (e.g., a raid boss monster).
- the control means 54 executes the battle game when an instruction (battle instruction) to execute a battle game against the enemy object is given by the player.
- control means 54 expands the battle possible range when the number of times the battle game has been played at a predetermined time point is less than a predetermined number.
- This predetermined time point is, for example, the time when a unit time has elapsed. Examples of this unit time include 10 minutes, 30 minutes, and 1 hour.
- the unit time may be a value obtained by dividing the appearance time of the enemy object by a predetermined number (for example, 2 or 5).
- the control means 54 expands the battle possible range each time a unit time elapses when the number of battles per unit time is less than a predetermined number.
- the control means 54 refers to the battle information in the enemy object information 50C each time a unit time (for example, 30 minutes) elapses from the appearance start date and time of the raid boss monster, and obtains the number of battles with the raid boss monster per unit time.
- the control means 54 expands the battle possible range included in the appearance information of the raid boss monster by a predetermined area when the obtained number of battles is less than a predetermined number (for example, 5 times). Examples of this predetermined area include increasing the radius of a circular area centered on the spawn point of a raid boss monster by 50 m, or by 100 m. Note that the predetermined number of times may be gradually increased or decreased each time a unit of time elapses.
- the specified point in time may also be the point in time when the appearance time of the enemy object becomes less than a certain time. Examples of this specified time include 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 30 minutes, etc.
- the control means 54 refers to the battle information in the enemy object information 50C to obtain the number of battles (total number) with the raid boss monster. Next, when the obtained number of battles is less than a certain number (e.g., 15 times), the control means 54 expands the battle possible range included in the appearance information of the raid boss monster by a certain area.
- the specified time may be a value obtained by dividing the appearance time of the enemy object by a certain number (e.g., 2 or 5). This specified point in time may occur multiple times during the appearance time of the enemy object.
- control means 54 extends the appearance time of the enemy object (raid boss monster) when expanding the battle range. In addition, the control means 54 extends the appearance time of the enemy object when the number of times the battle game has been played at a given point in time is less than a predetermined number of times. For example, the control means 54 extends the appearance time of the raid boss monster in the appearance information of the enemy object information 50C by 30 minutes when the number of times the battle game has been played is less than a predetermined number of times.
- control means 54 extends the appearance time of the enemy object each time a unit of time elapses if the number of times per unit of time is less than a predetermined number of times.
- the control means 54 refers to the battle information in the enemy object information 50C each time a unit of time (e.g., 30 minutes) elapses from the date and time when the raid boss monster started appearing, and obtains the number of battles with the raid boss monster per unit of time.
- a predetermined number of times e.g., 5 times
- the control means 54 extends the appearance time of the raid boss monster in the appearance information by 10 minutes.
- ⁇ Match processing flow> 5 is a flow chart showing an example of a process flow in which a player plays a battle game against a raid boss monster in the game system 1 according to the first embodiment.
- the process of the following steps is started, for example, when the appearance start date and time of a certain raid boss monster arrives.
- the order and contents of the following steps can be changed as appropriate.
- Step SP10 The control means 54 refers to the appearance information of the enemy object information 50C and judges whether the appearance time of a certain raid boss monster is longer than 0 (0 seconds). If the judgment is affirmative, the process proceeds to step SP12. On the other hand, if the judgment is negative, the process ends the series of processes shown in FIG. 5.
- Step SP12 The acquiring means 52 acquires the player's current position (latitude and longitude), and the process proceeds to step SP14.
- Step SP14 Based on the current position of the player acquired in step SP12, the control means 54 updates the game screen displayed on the touch panel 32. That is, the control means 54 moves the player object to a position (coordinates) on the game field that corresponds to the current position of the player.
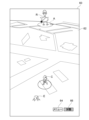
- FIG. 6 shows an example of a game screen 60 according to the first embodiment.
- the game screen 60 is provided with a game field 62 , a menu button 64 , and a battle button 66 .
- the game field 62 is represented to resemble, for example, the scenery around the player's current position in the real world.
- a player object P, a normal monster E, and a raid boss monster R are depicted in the game field 62.
- the player object P is displayed based on the player object information 50B of the player.
- the normal monster E and the raid boss monster R are displayed based on the enemy object information 50C.
- a battle possible range A is set with the appearance point of the raid boss monster R as the center.
- the menu button 64 is a button for issuing instructions to display various menus for equipping (attaching) equipment items and using consumable items.
- the battle button 66 is a button for instructing execution of a battle game against a raid boss monster R. This battle button 66 can be pressed when the player object P reaches the inside of the battle range A.
- step SP16 processing proceeds to step SP16.
- Step SP16 The control means 54 determines whether or not the player's current position obtained in step SP12 is within the battle range of a certain raid boss monster. If the determination is affirmative, the process proceeds to step SP18. On the other hand, if the determination is negative, the process proceeds to step SP10.
- Step SP18 The control means 54 permits the execution of a battle game against a certain raid boss monster. Specifically, the control means 54 enables the pressing of a battle button. Next, the control means 54 determines whether or not the execution of a battle game against a certain raid boss monster has been requested by the player. For example, the control means 54 determines whether or not the battle button has been pressed by the player. Then, if the determination is affirmative, the process proceeds to step SP20. On the other hand, if the determination is negative, the process proceeds to step SP10.
- Step SP20 The control means 54 executes a battle game between a player object associated with the player and a certain raid boss monster.
- the control means 54 updates various information in the enemy object information 50C corresponding to the certain raid boss monster through this battle game. For example, the control means 54 increments (+1) the number of battles included in the battle information of the certain raid boss monster. Also, the control means 54 decreases the hit points included in the ability information of the certain raid boss monster. Then, the process proceeds to step SP22.
- Step SP22 The control means 54 determines whether or not a certain raid boss monster has been defeated. For example, the control means 54 determines whether or not the hit points of a certain raid boss monster have become 0 or less. If the determination is affirmative, the process proceeds to step SP24. On the other hand, if the determination is negative, the process proceeds to step SP10.
- Step SP24 The control means 54 refers to the battle information in the enemy object information 50C and awards a reward to each player who has played a battle game against a certain raid boss monster. Then, the process ends with the series of processes shown in FIG.
- ⁇ Expansion/extension process flow> 7 is a flow chart showing an example of the process flow for expanding the battle range and extending the appearance time in the game system 1 according to the first embodiment.
- the process of the following steps is started, for example, at a predetermined time point (e.g., when a unit time has elapsed) within the battle time of a certain raid boss monster.
- a predetermined time point e.g., when a unit time has elapsed
- the order and contents of the following steps can be changed as appropriate.
- Step SP30 The control means 54 refers to the battle information in the enemy object information 50C and determines whether or not the number of battles with a certain raid boss monster is less than a predetermined number (e.g., 5 times). If the determination is affirmative, the process proceeds to step SP32. On the other hand, if the determination is negative, the process ends the series of processes shown in FIG. 7.
- a predetermined number e.g. 5 times
- Step SP32 The control means 54 expands the battle range of a certain raid boss monster by a predetermined area. For example, the control means 54 increases the radius of the circular area in the battle range of the enemy object information 50C by 100 m. Then, the processing proceeds to the processing of step SP34.
- Step SP34 The control means 54 extends the appearance time of a certain raid boss monster. For example, the control means 54 extends (increases) the appearance time of the raid boss monster in the appearance information of the enemy object information 50C by 30 minutes. Then, the process ends the series of processes shown in FIG. 7.
- a program for executing a fighting game against an enemy object that can be fought by each player at the time when the enemy object appears, and causes a computer to function as an acquisition means 52 for acquiring the current position of each player, and a control means 54 for executing a fighting game against the enemy object on condition that the current position of the player has reached a fighting range with the enemy object, and the control means 54 expands the fighting range if the number of times the fighting game has been executed at a predetermined point in time is less than a predetermined number of times.
- the battle range is expanded when the number of times a battle game with an enemy object has been played is low, making it easier to defeat the enemy object, and thus providing players who play in areas with a low number of players with an incentive to play location-based games.
- the predetermined time is the time when a unit time has elapsed
- the control means 54 expands the range of possible battles each time a unit time elapses if the number of battles per unit time is less than the predetermined number of times.
- the battle range expands with each passing unit of time, making it easier to defeat enemy objects, and thus providing players in areas with a small number of players with an incentive to play location-based games.
- the predetermined time is the time when the appearance time of the enemy object becomes less than a certain time.
- the battle range can be expanded, making it easier to defeat the enemy object, and thus providing players in areas with a small number of players with an incentive to play location-based games.
- control means 54 extends the appearance time when expanding the battle range.
- This configuration expands the range in which battles can take place and extends the time that enemy objects appear, making it easier to defeat the enemy objects, and thus providing players in areas with a small number of players with an incentive to play location-based games.
- the program executes a fighting game against an enemy object that can be fought by each player during the appearance time of the enemy object, and causes the computer to function as acquisition means 52 for acquiring the current position of each player, and control means 54 for executing the fighting game against the enemy object on the condition that the current position of the player has reached a fighting range with the enemy object, and the control means 54 extends the appearance time of the enemy object if the number of times the fighting game has been executed at a predetermined point in time is less than a predetermined number of times.
- the predetermined time is the time when a unit time has elapsed
- the control means 54 extends the appearance time of the enemy object each time a unit time has elapsed if the number of times per unit time is less than the predetermined number of times.
- the appearance time of the enemy object can be extended every time a unit of time elapses, making it easier to defeat the enemy object, and thus providing players in areas with a small number of players with an incentive to play the location-based game.
- the predetermined time is the time when the appearance time of the enemy object becomes less than a certain time.
- the appearance time of an enemy object falls below a certain time, the appearance time can be extended, making it easier to defeat the enemy object, and thus providing players in areas with a small number of players with an incentive to play location-based games.
- the second embodiment differs from the first embodiment in that the control means 54 expands the battle range and extends the appearance time of the enemy object in accordance with a predetermined parameter of the enemy object.
- the configuration and functions of the game system 1 according to the second embodiment which are not described below, are similar to the configuration and functions of the game system 1 according to the first embodiment.
- the control means 54 expands the battle range when a predetermined parameter of the enemy object is equal to or greater than a predetermined value at a predetermined time.
- the predetermined parameter is a parameter that indicates that the battle game (defeat) is progressing when the value is low.
- the predetermined parameter is a parameter that indicates that the defeat of the enemy object is imminent when the value is low.
- the predetermined parameter is the hit points (stamina) of the enemy object.
- the control means 54 expands the battle range when the hit points of the enemy object are equal to or greater than a predetermined value each time a unit of time elapses.
- control means 54 refers to the ability information of the enemy object information 50C and acquires the hit points of the raid boss monster each time a unit of time (e.g., 50 minutes) elapses from the appearance start date and time of the raid boss monster.
- the control means 54 expands the battle range included in the appearance information of the raid boss monster by a predetermined area when the acquired hit points are equal to or greater than a predetermined value (e.g., 10,000).
- a predetermined value e.g. 10,000
- An example of this predetermined area is to increase the radius of a circular area centered on the spawn point of the raid boss monster by 50 m, or by 100 m.
- the predetermined parameter may be gradually increased or decreased with each unit of time.
- control means 54 extends the appearance time of the enemy object (raid boss monster) when expanding the battle range. In addition, the control means 54 extends the appearance time of the enemy object when a predetermined parameter of the enemy object is equal to or greater than a predetermined value at a predetermined time. In addition, the control means 54 extends the appearance time of the enemy object each time a unit of time elapses when a predetermined parameter of the enemy object is equal to or greater than a predetermined value. For example, the control means 54 extends the appearance time of the raid boss monster in the appearance information of the enemy object information 50C by 30 minutes when a predetermined parameter of the enemy object is equal to or greater than a predetermined value.
- ⁇ Expansion/extension processing> 8 is a flow chart showing an example of the process flow for expanding the battle range and extending the appearance time in the game system 1 according to the second embodiment.
- the process of the following steps is started, for example, at a predetermined point in time during the battle time of a certain raid boss monster (for example, when the appearance time of a certain raid boss monster falls below a certain time).
- the order and content of the following steps can be changed as appropriate.
- Step SP40 The control means 54 refers to the ability information in the enemy object information 50C and judges whether or not the hit points of a certain raid boss monster are equal to or greater than a predetermined value (e.g., 10,000). If the judgment is affirmative, the process proceeds to step SP42. On the other hand, if the judgment is negative, the process ends the series of steps shown in FIG. 8.
- a predetermined value e.g. 10,000
- Steps SP42 to SP44 The processing in steps SP42 to SP44 is the same as the processing in steps SP32 to SP34 described above, and therefore the description thereof will be omitted. Then, the processing ends with the series of processing shown in FIG.
- a program for executing a fighting game against an enemy object that can be fought by each player at the time when the enemy object appears, and causes a computer to function as an acquisition means 52 for acquiring the current position of each player, and a control means 54 for executing a fighting game against the enemy object on the condition that the current position of the player has reached a fighting range with the enemy object, and the control means 54 expands the fighting range when a predetermined parameter of the enemy object is equal to or greater than a predetermined value at a predetermined time point.
- the battle range is expanded when the enemy object has many predetermined parameters, making it easier to defeat the enemy object, and thus providing players in areas with a small number of players with an incentive to play location-based games.
- the predetermined time is the time when a unit time has elapsed
- the control means 54 expands the battle range each time a unit time elapses if the enemy object's predetermined parameter is equal to or greater than a predetermined value.
- the battle range expands with each passing unit of time, making it easier to defeat enemy objects, and thus providing players in areas with a small number of players with an incentive to play location-based games.
- the predetermined time is the time when the appearance time of the enemy object becomes less than a certain time.
- the battle range can be expanded, making it easier to defeat the enemy object, and thus providing players in areas with a small number of players with an incentive to play location-based games.
- control means 54 extends the appearance time of the enemy object when expanding the battle range.
- This configuration expands the range in which battles can take place and extends the time that enemy objects appear, making it easier to defeat the enemy objects, thereby providing players in areas with a small number of players with an incentive to play location-based games.
- a program executes a fighting game against an enemy object that can be fought by all players during the appearance time of the enemy object, and causes a computer to function as acquisition means 52 for acquiring the current position of each player, and control means 54 for executing a fighting game against the enemy object on the condition that the current position of the player has reached a battle range with the enemy object, and the control means 54 extends the appearance time of the enemy object if a predetermined parameter of the enemy object is equal to or greater than a predetermined value at a predetermined time point.
- the predetermined time point is the point at which a unit time has elapsed
- the control means 54 extends the appearance time of the enemy object each time a unit time elapses if the predetermined parameter of the enemy object is equal to or greater than a predetermined value.
- the appearance time of the enemy object can be extended every time a unit of time elapses, making it easier to defeat the enemy object, and thus providing players in areas with a small number of players with an incentive to play the location-based game.
- the predetermined time is the time when the appearance time of the enemy object becomes less than a certain time.
- the appearance time of an enemy object falls below a certain time, the appearance time can be extended, making it easier to defeat the enemy object, and thus providing players in areas with a small number of players with an incentive to play the location-based game.
- the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment. In other words, even if a person skilled in the art appropriately modifies the above-described embodiment, the same will be included in the scope of the present invention as long as the features of the present invention are included.
- the elements of the above-described embodiment and the modified examples described below can be combined to the extent technically possible, and the combination of these elements will be included in the scope of the present invention as long as the features of the present invention are included.
- the control means 54 expands the battle range of the raid boss monster or extends its appearance time if the number of times the battle game has been played at a given point in time is less than a predetermined number, but this predetermined number may be changed for each raid boss monster.
- the predetermined number may be increased or decreased depending on at least one of the ability values (level, hit points, attack power, defense power, etc.) of the raid boss monster.
- control means 54 expands the battle range of the raid boss monster or extends the appearance time when a predetermined parameter of an enemy object is equal to or greater than a predetermined value at a predetermined time, but this predetermined parameter may be changed for each raid boss monster.
- the predetermined value may be increased or decreased depending on at least one of the ability values (level, hit points, attack power, defense power, etc.) of the raid boss monster.
- control means 54 may expand the battleable range of the raid boss monster or extend the appearance time of the raid boss monster if the amount by which the raid boss monster's specified parameter has decreased per unit time is less than a specified value.
- control means 54 may expand the battleable range of the raid boss monster or extend the appearance time of the raid boss monster if the amount by which the raid boss monster's hit points have decreased per 10 minutes is less than 1000.
- the predetermined parameter is a hit point, but it may be an amount of energy, a defensive power, or the like.
- the predetermined parameter may be a parameter that indicates that the battle game (subjugation) is progressing when its value is large.
- the predetermined parameter may be the number of weak points of the enemy object discovered by each player.
- the control means 54 expands the battle possible range when the predetermined parameter of the enemy object (the number of weak points discovered) is less than a predetermined value at a predetermined time point.
- the enemy objects are mainly monsters, but they may also be characters, robots, cars, airplanes, ships, etc.
- Server device computer, information processing device
- Terminal device computer, information processing device
- Storage means storage means
- Acquisition means Control means
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Processing Or Creating Images (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US19/209,157 US20250295999A1 (en) | 2022-11-17 | 2025-05-15 | Recording medium and information processing device that execute gaming based on position information in real world |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022184068A JP7661959B2 (ja) | 2022-11-17 | 2022-11-17 | プログラム及び情報処理装置 |
| JP2022-184068 | 2022-11-17 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US19/209,157 Continuation US20250295999A1 (en) | 2022-11-17 | 2025-05-15 | Recording medium and information processing device that execute gaming based on position information in real world |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2024106136A1 true WO2024106136A1 (ja) | 2024-05-23 |
Family
ID=91084201
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2023/037981 Ceased WO2024106136A1 (ja) | 2022-11-17 | 2023-10-20 | プログラム及び情報処理装置 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20250295999A1 (enExample) |
| JP (2) | JP7661959B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2024106136A1 (enExample) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017170109A (ja) * | 2016-11-17 | 2017-09-28 | 株式会社セガゲームス | 情報処理装置 |
| JP2017170121A (ja) * | 2017-01-27 | 2017-09-28 | 株式会社セガゲームス | 情報処理装置、端末装置及びプログラム |
| JP2021115310A (ja) * | 2020-01-28 | 2021-08-10 | 株式会社ポケモン | ゲームプログラム、ゲーム方法、およびゲームサーバ |
| JP2021166671A (ja) * | 2020-04-13 | 2021-10-21 | 株式会社カプコン | ゲームプログラム、ゲームシステム、及びコンピュータ |
| JP2022164891A (ja) * | 2021-02-22 | 2022-10-27 | 株式会社セガ | プログラム及び情報処理装置 |
-
2022
- 2022-11-17 JP JP2022184068A patent/JP7661959B2/ja active Active
-
2023
- 2023-10-20 WO PCT/JP2023/037981 patent/WO2024106136A1/ja not_active Ceased
-
2025
- 2025-04-01 JP JP2025060556A patent/JP2025096326A/ja active Pending
- 2025-05-15 US US19/209,157 patent/US20250295999A1/en active Pending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017170109A (ja) * | 2016-11-17 | 2017-09-28 | 株式会社セガゲームス | 情報処理装置 |
| JP2017170121A (ja) * | 2017-01-27 | 2017-09-28 | 株式会社セガゲームス | 情報処理装置、端末装置及びプログラム |
| JP2021115310A (ja) * | 2020-01-28 | 2021-08-10 | 株式会社ポケモン | ゲームプログラム、ゲーム方法、およびゲームサーバ |
| JP2021166671A (ja) * | 2020-04-13 | 2021-10-21 | 株式会社カプコン | ゲームプログラム、ゲームシステム、及びコンピュータ |
| JP2022164891A (ja) * | 2021-02-22 | 2022-10-27 | 株式会社セガ | プログラム及び情報処理装置 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| ANONYMOUS: "[Pokemon GO] The range of circles that can participate in raid battles should be wider! Isn't it a bit too narrow?", 25 June 2017 (2017-06-25), XP093171784, Retrieved from the Internet <URL:https://pokemongo-soku.com/kyoryoku/reido/post-44817/> * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20250295999A1 (en) | 2025-09-25 |
| JP7661959B2 (ja) | 2025-04-15 |
| JP2025096326A (ja) | 2025-06-26 |
| JP2024073069A (ja) | 2024-05-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7711668B2 (ja) | プログラム及び情報処理装置 | |
| JP7057930B2 (ja) | ユーザの位置情報に基づきコンピュータがゲームを進行させる方法およびシステムならびに当該方法をコンピュータに実行させるプログラム | |
| JP7509301B2 (ja) | プログラム及び情報処理装置 | |
| JP7011383B2 (ja) | ユーザの位置情報に基づきコンピュータがゲームを進行させる方法およびシステムならびに当該方法をコンピュータに実行させるプログラム | |
| JP7559494B2 (ja) | プログラム及び情報処理装置 | |
| JP2018064708A (ja) | ユーザの位置情報に基づきコンピュータがゲームを進行させる方法およびシステムならびに当該方法をコンピュータに実行させるプログラム | |
| JP7404422B2 (ja) | ユーザの位置情報に基づきコンピュータがゲームを進行させる方法およびシステムならびに当該方法をコンピュータに実行させるプログラム | |
| WO2018074464A1 (ja) | ユーザの位置情報に基づきコンピュータがゲームを進行させる方法およびシステムならびに当該方法をコンピュータに実行させるプログラム | |
| US20250010177A1 (en) | Recording medium and information processing device | |
| JP2018064711A (ja) | ユーザの位置情報に基づきコンピュータがゲームを進行させる方法およびシステムならびに当該方法をコンピュータに実行させるプログラム | |
| JP7661959B2 (ja) | プログラム及び情報処理装置 | |
| JP7658356B2 (ja) | プログラム及び情報処理装置 | |
| JP7514138B2 (ja) | コンピュータシステム、ゲームシステム及びプログラム | |
| JP6795114B1 (ja) | プログラム及び情報処理装置 | |
| JP2018064710A (ja) | ユーザの位置情報に基づきコンピュータがゲームを進行させる方法およびシステムならびに当該方法をコンピュータに実行させるプログラム | |
| JP7024836B1 (ja) | プログラム及び情報処理装置 | |
| WO2021166863A1 (ja) | プログラム及び情報処理装置 | |
| JP7341277B2 (ja) | ユーザの位置情報に基づきコンピュータがゲームを進行させる方法およびシステムならびに当該方法をコンピュータに実行させるプログラム | |
| JP2021023533A (ja) | ゲームプログラムおよびゲームシステム | |
| JP7738232B2 (ja) | プログラム、情報処理方法および情報処理装置 | |
| JP2018064712A (ja) | ユーザの位置情報に基づきコンピュータがゲームを進行させる方法およびシステムならびに当該方法をコンピュータに実行させるプログラム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 23891292 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 23891292 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |