WO2023112779A1 - 診療支援システム、診療支援装置及びプログラム - Google Patents
診療支援システム、診療支援装置及びプログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2023112779A1 WO2023112779A1 PCT/JP2022/044959 JP2022044959W WO2023112779A1 WO 2023112779 A1 WO2023112779 A1 WO 2023112779A1 JP 2022044959 W JP2022044959 W JP 2022044959W WO 2023112779 A1 WO2023112779 A1 WO 2023112779A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- information
- measured value
- drug
- medication
- average
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H20/00—ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans, e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance
- G16H20/10—ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans, e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance relating to drugs or medications, e.g. for ensuring correct administration to patients
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the cardiovascular system, e.g. pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow
- A61B5/021—Measuring pressure in heart or blood vessels
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the cardiovascular system, e.g. pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow
- A61B5/024—Measuring pulse rate or heart rate
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H10/00—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of patient-related medical or healthcare data
- G16H10/60—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of patient-related medical or healthcare data for patient-specific data, e.g. for electronic patient records
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H15/00—ICT specially adapted for medical reports, e.g. generation or transmission thereof
Definitions
- the present invention belongs to a healthcare-related technical field, and relates to a medical support system, a medical support device, and a program.
- medication information including the type and amount of medicine, blood pressure measurement information of the patient, and medication information indicating the medication status of the patient are acquired, respectively, and these information are comprehensively associated in chronological order. Also disclosed is a medication assistance device that displays medication treatment results.
- a doctor can determine the effect of a drug by comprehensively associating information on the drug prescribed to the patient with the patient's drug compliance status and the blood pressure measurement value, and adopt an appropriate treatment policy. can be done.
- the present invention relates to a system related to medical support, and aims to provide technology that enables medical staff to reliably and easily confirm the effects of medication.
- a measured value acquiring means for acquiring a measured value related to patient's biological information
- Medication information acquiring means for acquiring medication information including information on a first prescription start date, which is the earliest date on which the medication was prescribed according to at least one prescription content, with respect to the medication prescribed to the patient
- Average measured value calculation means for calculating an average measured value, which is an average value of the measured values of the patient for each predetermined period
- It is a medical care support system.
- the "predetermined period” is not particularly limited as long as it is a valid period for confirming drug efficacy, but can be, for example, one week or more.
- the “output means” may be a display device such as a liquid crystal display, or a printing device such as a printer.
- the average value of the biological information for each predetermined period after the day when the prescription was started (or changed. The same applies hereinafter), and the biological information for each predetermined period before the reference date Average values can be compared. That is, by checking the drug effect confirmation support image, the medical staff can compare the average values obtained by smoothing out the daily variations in the measured values of the biological information within the prescribed period of time from the start of the prescription. can be easily and reliably confirmed.
- the measured value acquiring means further acquires information related to the time period and/or place where the biological information was measured
- the average measured value calculating means calculates the average measured value for each time zone and/or place where the biological information was measured
- the measured value transition information in the drug efficacy confirmation support image may indicate changes in the average measured value for each time period and/or place where the biological information was measured.
- the "time zone” can be divided into divisions such as morning, noon, evening, and night.
- the "information related to the time period” may be time data indicating date and time, for example, and the time period may be specified within the range to which the time belongs.
- the “place” here can be classified as a range that can affect the measured value of biological information, such as home (household), examination room, or the like.
- the "location information” may be, for example, GPS positioning information, and the "location” may be specified by the positioning information.
- the medical support system further includes target achievement determination means for determining whether or not a preset improvement target for the biological information of the patient is achieved for each average measured value
- the measurement value transition information in the drug efficacy confirmation support image may indicate information as to whether or not the improvement target is achieved for each average measurement value.
- the "improvement target value” may be something like a general so-called normal value, or a value that is determined each time according to the individual patient's situation, prescription, etc. good. Furthermore, it may be an absolute value that targets the measured value of biological information itself, or a relative value that is a target increase/decrease value based on the measured value at a certain point in time. Also, the 'information indicating whether or not it has been achieved' can be, for example, a text message, a color, a symbol (mark), a line segment on a graph indicating a target value, or the like. With such a configuration, the medical staff can easily confirm whether or not the improvement target value is achieved, and it becomes possible to judge the drug efficacy more quickly.
- the medical support system further includes change amount calculation means for calculating an amount of increase or decrease in the average measured value in one predetermined period from the average measured value in the predetermined period immediately before the average measured value,
- the measured value transition information in the drug efficacy confirmation support image may indicate the increase/decrease change amount for each average measured value in such a manner that increase/decrease can be visually recognized.
- whether the amount of change is increased or decreased can be indicated by, for example, text messages, colors, symbols (marks), and the like.
- the medical staff can easily confirm the amount of change in the average measured value, and it becomes possible to judge the drug efficacy more quickly.
- the medical care support system further includes reliability determination means for determining whether the average measured value has a predetermined reliability, and the measured value transition information in the drug efficacy confirmation support image is the The presence or absence of the reliability may be indicated so as to be discriminable for each average measured value. Further, the reliability determination means may determine whether or not the reliability is present based on whether or not the number of measurements of the biological information within the predetermined period satisfies a predetermined standard.
- the presence or absence of reliability can be indicated by text messages, colors, symbols (marks), etc. It should be noted that whether or not the number of times of measurement satisfies a predetermined criterion may be determined for each time zone or place. With such a configuration, it is possible to recognize when the reliability of the average measurement value is low (due to a small number of measurements, etc.), so medical professionals can make decisions on the premise that reliability is low. It becomes possible to do
- the measured value acquisition means acquires information about the abnormality together with the measured value
- the average measured value calculating means calculates an average value of the measured values within the predetermined period excluding the measured values when the abnormality occurs
- the reliability determination means may determine whether or not the predetermined criteria are satisfied by excluding the measurement of the biological information when the abnormality occurs from the number of measurements.
- abnormalities during measurement of biological information can include, for example, body movements and arrhythmias that affect measurement.
- body movements and arrhythmias that affect measurement.
- the medication information includes information on the name of the prescribed drug and the amount of the prescribed drug
- the drug efficacy confirmation support image may indicate drug-related information including the medication information in addition to the measured value transition information.
- the drug-related information is the other prescription content. It also shows information on the name of the drug and the amount of the drug during the period when the drug was prescribed,
- the medication information includes information on a second prescription start date, which is the earliest date on which the drug was prescribed with the other prescription content,
- a sign indicating the second prescription start date is displayed on the drug efficacy confirmation support image, good too.
- the start date of the second prescription may be a date before the start date of the first prescription chronologically, or may be a date after the start date of the first prescription.
- the medical care support system further comprises medication-related information acquisition means for acquiring medication information relating to the patient's medication status and/or side effect information relating to side effects caused by the patient taking the medication. cage,
- the drug-related information in the drug efficacy confirmation support image may also indicate the medication information and/or the side effect information.
- the medication information can be, for example, the presence or absence of medication, the compliance rate, etc.
- the side effect information can include the type and frequency of side effects.
- medication information and side effect information can be obtained subjectively from the patient through questions and answers with a so-called chatbot as a function of the application of a portable information processing terminal such as a smartphone used by the patient. be able to.
- the means for acquiring information is not limited to such a mode, and may be of any type.
- a container in which a patient stores a drug is provided with a sensor that detects the taking out of the drug, and the medication information is acquired from the information (amount of the drug taken out, date and time) acquired by the sensor. There may be.
- the medication information may be obtained from the sales history.
- the measured value transition information can include a graphical representation of the transition of the average measured value of the biological information. According to such a configuration, it becomes possible to more intuitively grasp the transition of the average measured value, and it is possible to contribute to medical efficacy judgment of the medical staff.
- the measured values of the biological information include a blood pressure value and a pulse rate
- the graph display may coaxially display an average value of the blood pressure value and the pulse rate measured in the same predetermined period.
- the present invention includes the measured value acquisition means, the medication information acquisition means, the average measured value calculation means, and the drug efficacy confirmation support image generation means, and at least It can also be regarded as a medical support device that constitutes a part.
- the present invention can also be regarded as a program for causing a computer to function as such a medical assistance device, and a computer-readable recording medium that non-temporarily records such a program.
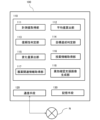
- FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing the configuration of a medical support system according to an embodiment.
- FIG. 2 is a flow chart schematically showing the flow of telemedicine performed in the embodiment.
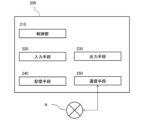
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram of the functional configuration of the server device according to the embodiment.
- FIG. 4 is a block diagram illustrating the functional configuration of the doctor-side terminal according to the embodiment;
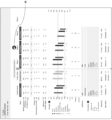
- FIG. 5 is a first diagram for explaining an example of a screen output on the doctor's terminal.
- FIG. 6 is a second diagram for explaining an example of a screen output on the doctor's terminal.
- FIG. 7 is a third diagram for explaining an example of a screen output on the doctor's terminal.
- FIG. 8 is a block diagram illustrating the functional configuration of the patient terminal according to the embodiment;
- FIG. 8 is a block diagram illustrating the functional configuration of the patient terminal according to the embodiment;
- FIG. 9A is a first diagram showing an example of a screen during execution of the automatic medical inquiry program according to the embodiment.
- FIG. 9B is a second diagram showing an example of a screen during execution of the automatic medical inquiry program according to the embodiment.
- FIG. 10 is a diagram showing the flow of information transfer and processing performed within the medical assistance system according to the embodiment.
- FIG. 11 is a first diagram showing an example of a screen output on the doctor-side terminal according to the modification.
- FIG. 12 is a second diagram showing an example of a screen output on the doctor-side terminal according to the modification.
- FIG. 13 is a diagram showing an outline of another aspect of the medical support system.
- FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing the configuration of a medical support system 1 according to this embodiment.
- the medical support system 1 includes a server device 100, a doctor-side terminal 200 used by a doctor, a patient-side terminal 300 used by a patient P, and a sphygmomanometer 400. Each of these components is Through the communication network N, they can communicate with each other.
- the medical support system 1 is a system related to telemedicine, and transmits the measured values of biological information such as the blood pressure value measured by the patient at home to the server device 100 via the communication network N, to assist physicians in treating patients by processing and providing them to healthcare professionals.
- FIG. 2 is a flow chart schematically showing the flow of telemedicine performed in this embodiment. Telemedicine performed in this embodiment will be specifically described below with reference to FIG. That is, a patient who has been diagnosed with hypertension begins medication according to a doctor's prescription, and continuously measures his or her blood pressure at home.
- the medical support system 1 collects the measured values, and after a predetermined period of time (here, one week later), the average value of the measured values within the predetermined period (hereinafter also referred to as the average measured value) is set in advance. It is determined whether or not the target value is achieved (hereinafter, the fact that the average measured value has achieved the target value is also expressed as “controlled”).
- the average measured value has achieved the target value means, for example, that the (average) blood pressure value is less than a predetermined threshold value. Then, if the average measured value is controlled, the administration of the same drug is continued, and after a predetermined period (here, one week) has passed, it is determined whether the average measured value of blood pressure is controlled. Judgment is made.
- the patient's medication status will be checked to see if the patient is taking the medicine as prescribed.
- the physician confirms changes in the average measured value for each predetermined period, which is used together with the information on the medication status to determine the treatment policy. It should be noted that the dosing information may be checked periodically regardless of the success or failure of the control of the average measured value.
- the doctor confirms the changes in the average measured value, and if it is determined that the medication has a certain effect, the doctor will continue to administer the same drug (wait-and-see). In that case, after a predetermined period of time (here, one week) has passed, it is determined whether or not the average blood pressure value is controlled.
- the doctor will consider the possibility of other diseases and implement additional examinations and treatment (including prescription changes) considering other diseases. to decide. In that case, after a predetermined period of time (here, one week) has passed, it is determined whether or not the average blood pressure value is controlled.
- the prescription will be changed. In that case, after a predetermined period of time (here, one week) has passed, it is determined whether or not the average blood pressure value is controlled.
- Telemedicine for hypertensive patients is performed by repeating the flow described above.
- the medical care support system 1 according to the present embodiment supports performing such a flow and reduces the burden on doctors (medical workers). Each configuration of the system will be described in detail below.
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing the functional configuration of the server device 100. As shown in FIG.
- the server device 100 is composed of a general server computer, and as shown in FIG.
- the control unit 110 is means for controlling the server apparatus 100, and is configured by processors such as a CPU (Central Processing Unit) and a DSP (Digital Signal Processor).
- the control unit 110 includes, as functional modules related to biological information management, a measured value acquisition unit 111, an average value calculation unit 112, a reliability determination unit 113, a target achievement determination unit 114, a change amount calculation unit 115, and a medication information acquisition unit. 116 , a medication-related information acquisition unit 117 , and a drug efficacy confirmation support image generation unit 118 .
- processors such as a CPU (Central Processing Unit) and a DSP (Digital Signal Processor).
- the control unit 110 includes, as functional modules related to biological information management, a measured value acquisition unit 111, an average value calculation unit 112, a reliability determination unit 113, a target achievement determination unit 114, a change amount calculation unit 115, and a medication information acquisition unit. 116 , a medication-related information acquisition unit 117 , and a drug efficacy
- the communication means 120 is communication means for connecting the server device 100 to the communication network N, and includes, for example, a communication interface board and a wireless communication circuit for wireless communication.
- the storage means 130 includes main storage such as ROM (Read Only Memory) and RAM (Random Access Memory), and auxiliary storage such as EPROM, HDD (Hard Disk Drive) or SSD (Solid State Device), and removable media. and a storage unit.
- the auxiliary storage stores an operating system (OS), various programs, and the like. By loading the stored program into the working area of the main storage unit and executing it, and by controlling each component through the execution of the program, each functional unit that achieves a predetermined purpose can be realized. .
- OS operating system
- the measured value acquisition unit 111 acquires, via the communication network N, biological information measured values (eg, systolic blood pressure value, diastolic blood pressure value, pulse rate, etc.) measured by the patient P with the sphygmomanometer 400, and stores them. Store in means 130 .
- the information acquired by the measured value acquiring unit 111 includes not only the measured value of biological information, but also information related to the time zone in which the measurement was performed (for example, time data), and information related to the location where the measurement was performed. information (e.g. home, examination room, etc.), information related to abnormalities during measurement that adversely affect the reliability of measurements (e.g., presence of body movement exceeding the allowable range, irregular pulse waves, etc.), also get
- the average value calculation unit 112 calculates an average measured value, which is the average value of the acquired measured values within a predetermined period. If there are a plurality of time zones and locations in which biometric information is measured, the average measurement value is calculated for each of the time zones and locations. Moreover, when an abnormality during measurement as described above is included, the average value may be calculated by excluding the measured values when the abnormality occurs. The calculated average value is stored in the storage means 130 .
- the reliability determination unit 113 determines whether the calculated average measurement value has a certain degree of reliability. Specifically, for example, the presence or absence of reliability may be determined based on whether or not the number of blood pressure measurements (and/or measurement occasions) within a predetermined period has reached a certain number. Further, when an abnormality during measurement as described above is included, it is possible not to count the measurement when the abnormality occurs in the number of measurements.
- the goal achievement determination unit 114 determines whether the improvement goal set in advance for each individual patient P is achieved for each calculated average measurement value. Specifically, determination may be made based on whether or not the average measured value deviates from a predetermined upper (lower) threshold as the improvement target value. The result of the determination indicates whether or not the blood pressure value of the patient P is being controlled.
- the improvement target value may be stored in advance in the storage means 130, for example.
- the change amount calculation unit 115 compares the average measured value in a predetermined period (for example, one week) with the average measured value in the predetermined period immediately before that, and calculates the amount of increase or decrease from the average measured value immediately before that. calculate.
- the value calculated here is stored in the storage means 130 .
- the medication information acquisition unit 116 acquires medication information related to the name of the drug prescribed to the patient P, the amount of each drug, and the prescription start date for the prescription content.
- the medication information may be stored in the storage unit 130 including the past history, and the medication information may be obtained by reading the information from the storage unit 130 .
- medication information may be obtained from a doctor-side terminal 200, which will be described later, an electronic medical record management system (not shown), or the like, via communication means.
- the medication-related information acquisition unit 117 also obtains, for example, via the patient-side terminal 300 as will be described later, medication information related to whether or not the patient is taking medication and the medication compliance rate (frequency of medication), and information related to the content and frequency of side effects when taking medication. Acquire medication-related information, including side effect information.
- the acquisition timing of the medication-related information can be, for example, when the goal achievement determination unit 114 determines that the improvement goal has not been achieved. However, without being limited to this, the medication-related information may be acquired periodically.
- the drug efficacy confirmation support image generation unit 118 generates measurement value transition information, medication information, and medication-related information (hereinafter referred to as medication information and medication-related information collectively referred to as drug-related information) is generated. Specifically, the functions of the measured value acquisition unit 111, the average value calculation unit 112, the reliability determination unit 113, the target achievement determination unit 114, the variation calculation unit 115, the medication information acquisition unit 116, and the medication-related information acquisition unit 117 Based on the data output from the unit and stored in the storage means 130, display contents related to the measurement value transition information and the drug-related information are specified.
- the measured value transition information includes information on the reliability of the average measured value, success or failure in achieving the improvement target, amount of change from the previous average measured value, etc. for each displayed average measured value. as shown.
- the generated drug efficacy confirmation support image is transmitted to the doctor side terminal 200 via the communication network N. FIG. Details of the drug efficacy confirmation support image will be described later.
- FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing the functional configuration of the doctor-side terminal 200.
- the doctor side terminal 200 is a general computer, for example, a fixed installation type personal computer, a portable notebook type personal computer or a tablet type terminal, etc.
- a communication means 250 is provided.
- the control unit 210 is means for controlling the doctor-side terminal 200, and is composed of, for example, a CPU.
- the input means 220 is means for receiving information input from the outside, such as a keyboard, mouse, touch panel, camera, and microphone.
- the output means 230 includes a liquid crystal display, a speaker, and the like.
- the storage unit 240 includes a main storage unit, an auxiliary storage unit, etc., similar to the server device, and stores an operating system (OS), various programs, and various other data acquired via the communication network N.
- the communication means 250 includes, for example, a communication interface board and a wireless communication circuit for wireless communication.
- the doctor's terminal may be able to access the electronic medical record management system.
- the patient's electronic medical record data stored in the electronic medical record management system may be read out and transmitted to the server device 100, or may be transmitted from the server device 100.
- the information may be linked with electronic medical record data.
- the doctor-side terminal 200 acquires the drug efficacy confirmation support image from the server device 100 via the communication network N, and outputs this information to the output means 230 .
- 5 to 7 show examples of screens displayed by the output means 230 of the doctor-side terminal 200.
- FIG. FIG. 5 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of a drug efficacy confirmation support image for one of the patients P who is in charge of the doctor who is the administrator of the terminal.
- the drug efficacy confirmation support image shows information on patient attributes such as patient name, sex, age, etc. It is an image that can be seen.
- FIG. 6 is an enlarged view showing the portion of the measured value transition information Tr
- FIG. 7 is an enlarged view showing the portion of the medicine-related information Me.
- the systolic blood pressure (SYS ), diastolic blood pressure (DIA), and heart rate (Pulse) (Weekly avg home BP & Pulse) are displayed in chronological order. More specifically, average home blood pressure values (blood pressure values measured at home) for each week of SYS and DIA are displayed for each time period of am (after waking up) and pm (before going to bed). .
- the prescription change date is used as a reference, and the next day is used as the starting date to divide the predetermined period (that is, the prescription change date is included in the period one week before). After the prescription is changed, it is often the next day, not the day of the prescription change, that the content of the medication actually changes.
- the measured value transition information Tr includes the amount of change compared to the value of the previous week (Change from the previous week) and the preset target values (in this example, SYS is 130 mmHg and DIA is 80 mmHg). A value indicating the deviation (difference from the target) is also shown.
- the average value of the previous week and the difference from the target value are respectively attached with "+" and "-" symbols next to the numerical value, but instead of or in addition to this, The color of the characters may be changed (red for increase, green for decrease, etc.). Symbols such as arrows can also be used.
- information (Controlled, Uncontrolled) indicating whether the target value was achieved (whether the average measured value was below the target value in this embodiment) is displayed for each average measured value in each period.
- the success or failure of the achievement of the target value may be indicated by changing the frame color, etc., instead of displaying by characters.
- the measured value transition information Tr when it is determined that the average measured value does not have a predetermined reliability, it is displayed so that it can be identified. Specifically, "Insufficient data" is displayed in the column indicating whether or not the target value has been achieved, indicating that the amount of data is insufficient.
- the information on the average measured value is not only written numerically, but also shown in FIGS. It is also displayed as a graphical representation. Furthermore, in the same graph, in addition to am and pm time zone data, if there is measurement data for nighttime blood pressure (BP Nocturnal) and blood pressure measured in the examination room (BP Office), that graph is also displayed. It has become so. Also, the pulse rate is displayed coaxially with the blood pressure. If the reliability of the average measured value does not meet a predetermined standard, the graph is displayed with hatching, so that it can be understood at a glance that the data is unreliable.
- BP Nocturnal nighttime blood pressure
- BP Office blood pressure measured in the examination room
- the drug-related information Me of this embodiment includes the types of drugs that the patient P has taken in that week, the actual frequency of drug taking display), symptoms and frequencies of complained side effects, etc. are displayed together with the measured value transition information Tr in chronological order.
- information (Prescription) indicating prescription contents such as drug brand, dosage form, and dose.
- the doctor can easily and accurately grasp the effect of the prescribed drug by referring to the screen on which the measured value transition information Tr and the drug-related information Me can be listed, and can determine which drug to treat the patient P. It is possible to quickly determine whether such a treatment policy should be adopted.
- FIG. 8 is a block diagram showing the functional configuration of the patient terminal 300.
- the patient-side terminal 300 is, for example, a smartphone, a tablet terminal, a portable information processing terminal such as a wristwatch-type wearable terminal, or the like, and includes a control unit 310, an input means 320, an output means 330, a storage means 340, and a communication means 350.
- a control unit 310 for example, a smartphone, a tablet terminal, a portable information processing terminal such as a wristwatch-type wearable terminal, or the like.
- the control unit 310 is means for controlling the patient-side terminal 300, and is composed of, for example, a CPU.
- the input means 320 can adopt a touch panel display integrated with the output means 330 or the like.
- the storage unit 340 includes a main storage unit, an auxiliary storage unit, etc., like other terminals, and stores an operating system (OS), various programs, and various other data acquired via the communication network N. be.
- the communication means 250 includes, for example, a wireless communication circuit for wireless communication.
- the control unit 310 includes an automatic medical inquiry execution unit 311 as a functional module related to medication-related information management.
- the automatic medical inquiry executing unit 311 receives an automatic medical inquiry trigger signal transmitted from the server device 100, for example, and executes an application for automatically inquiring about the frequency of taking medication and the presence or absence of side effects and their types.
- the automatic medical inquiry application can adopt a form such as a chatbot, for example, and may be stored in advance in the storage means 340 of the patient-side terminal 300, or an ASP (Application Service Provider) in the server device 100. It may be provided in the form.
- FIG. 9 shows an example of a screen when the automatic medical inquiry program is executed.
- FIG. 9A shows an inquiry screen about taking medication
- FIG. 9B shows an inquiry screen about side effects.
- the answer given by the patient P to the automatic medical inquiry as described above is transmitted from the communication means 350 to the server device 100 via the communication network N.
- necessary information input by the patient P is transmitted to the server device 100 .
- the patient terminal 300 receives, from the server device 100, behavior evaluation information including information relating to the evaluation of the effort according to the result of the effort for treatment of the patient P, and outputs the content to the output means 330. output.
- the sphygmomanometer 400 is used by the patient P for daily blood pressure measurement, and may be of any type. For example, it may be a general stationary type, a portable type in which a portable cuff is wrapped around the upper arm, or a wearable type that is worn on the patient's wrist. good too. Blood pressure is measured by the oscillometric method by operation of the patient P (or at preset timing or time intervals in the case of wearable type), and the blood pressure data is wirelessly transmitted to the patient side terminal 300 by wireless communication, for example.
- a short-range wireless data communication standard such as Bluetooth (registered trademark) or infrared communication can be adopted.
- the sphygmomanometer 400 may be one without communication means, in which case the patient P manually inputs the measurement data (including the blood pressure value, pulse rate, and measurement date and time) to the patient-side terminal 300. , the information may be sent to the server device 100 .
- the patient-side terminal 300 may have the function of the sphygmomanometer 400 as well.
- the wearable terminal can serve as the sphygmomanometer 400 if the blood pressure measurement function is provided in the wearable terminal.
- the stationary sphygmomanometer 400 may have a function as an information processing terminal and may also serve as the patient terminal 300 .
- the measurement method of the sphygmomanometer 400 is a method of measuring each beat of the heartbeat, or a trigger measurement method of estimating blood pressure fluctuations from the pulse wave propagation time and using the fluctuations as a trigger to measure the blood pressure in spots. good too.
- FIG. 10 is a diagram showing the flow of information transfer and processing performed within the medical assistance system 1.
- measurement data obtained by the patient P measuring his own blood pressure with the sphygmomanometer 400 is input to the patient terminal 300 (S101).
- the measurement data is sent from the patient terminal 300 to the server device 100 each time or collectively for a predetermined period (for example, one week) (S102).
- the received measurement data is stored in the storage means 130, and based on the measurement data, it is confirmed whether or not the blood pressure of the patient P is being controlled by comparing with a predetermined target value.
- different target values are set for systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure, and whether the average values of systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure for each predetermined period have achieved their corresponding target values is determined. Then, if the blood pressure is not under control (that is, if either the systolic blood pressure or the diastolic blood pressure exceeds the target value), an inquiry about the frequency of medication administration, etc. is made to the patient-side terminal 300 (S104). ).
- the medication information is transmitted to the server device 100 (S105).
- a drug efficacy confirmation support image is generated that includes information on changes in the blood pressure value and information on the medication frequency of the patient P (S106).
- the doctor transmits the request information for the drug efficacy confirmation support image to the server device 100 via the doctor-side terminal 200 (S107).
- the server device 100 that has received the request provides the drug effect confirmation support image to the doctor side terminal 200 (S108), and the drug effect confirmation support image is displayed on the output means 230 of the doctor side terminal 200 (S109).
- the drug efficacy confirmation support image may be transmitted to the doctor-side terminal 200 and stored in the storage means 240 of the doctor-side terminal 200, or may be provided in the form of an ASP, and the image data may be stored. It may be prohibited.
- the content of the drug efficacy confirmation support image is as described above.
- the prescription start date (change date) is used as a reference, and the drug efficacy confirmation support image showing the transition of the average measured value for the predetermined period before and after is displayed. Therefore, it is possible to easily and reliably determine whether or not there is an effect of changing the prescription without being confused with daily fluctuations in the blood pressure value.
- the most recent prescription change date (December 21) is used as a reference, and an example of a drug efficacy confirmation support image in the case where no other prescription change date exists within the display period within 4 weeks after that is shown. However, there may be other prescription change dates within the display period.
- this modified example an example of a drug efficacy confirmation support image in such a case will be described.
- FIG. 11 and 12 are explanatory diagrams showing an example of a drug efficacy confirmation support image according to this modified example.
- the prescription change was performed on December 21, and measurement value change information and drug-related information until January 10 of the following year are shown.
- this modified example an example in which the prescription was changed on December 31st will also be described.
- FIG. 11 at the top of the column indicating the week to which December 31 belongs (the second week from the prescription change date of December 21), new prescription contents for the week
- a prescription start date mark M indicating that the prescription of has been started (prescription has been changed) is displayed.
- the date of the actual prescription start date may be displayed.
- the doctor can grasp that there is a prescription start date for other prescription content within the period displayed in the drug efficacy confirmation support image.
- FIG. 12 shows an example of a drug efficacy confirmation support image showing measured value transition information with December 31 as the reference date.
- the reference date is set to December 31, and the predetermined period for calculating the average measured value is reset and recalculated.
- ) shows an example of a drug efficacy confirmation support image.
- December 31 was included in the second week, so in the redrawn drug efficacy confirmation support image shown in FIG. and the first half of Week 3, and the new Week 2 will include the latter half of the previous 3 weeks.
- the average measured value for the first week is displayed as "Controlled". That is, it can be confirmed that the prescription was changed further on December 31, and the improvement target was achieved as an effect of this prescription change.
- the reference date may be displayed by sliding it to the left for about two weeks.
- the means of obtaining medication information is not limited to the automatic interview program using a chatbot.
- a sensor for detecting the taking out of the drug is provided in the container for the drug taken by the patient P, and the taking information is obtained based on the information regarding the taking out of the drug detected by the sensor (medication frequency, dose, etc.). It doesn't matter if there is.
- medication information may be obtained from the information on the sold medicines, the information on the timing of sales, and the like.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Medical Treatment And Welfare Office Work (AREA)
- Measuring And Recording Apparatus For Diagnosis (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202280053073.XA CN117795609A (zh) | 2021-12-15 | 2022-12-06 | 诊疗辅助系统、诊疗辅助装置以及程序 |
| DE112022005939.7T DE112022005939T5 (de) | 2021-12-15 | 2022-12-06 | System zur medizinischen versorgungsunterstützung, vorrichtung zur medizinischen versorgungsunterstützung und programm |
| US18/442,711 US20240194314A1 (en) | 2021-12-15 | 2024-02-15 | Medical care assistance system, medical care assistance device, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021203296A JP7760906B2 (ja) | 2021-12-15 | 2021-12-15 | 診療支援システム、診療支援装置及びプログラム |
| JP2021-203296 | 2021-12-15 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US18/442,711 Continuation US20240194314A1 (en) | 2021-12-15 | 2024-02-15 | Medical care assistance system, medical care assistance device, and program |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2023112779A1 true WO2023112779A1 (ja) | 2023-06-22 |
Family
ID=86774615
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2022/044959 Ceased WO2023112779A1 (ja) | 2021-12-15 | 2022-12-06 | 診療支援システム、診療支援装置及びプログラム |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20240194314A1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP7760906B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN117795609A (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE112022005939T5 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2023112779A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN117672449A (zh) * | 2023-12-04 | 2024-03-08 | 启康保(北京)健康科技有限公司 | 一种基于物联网的药品管理系统 |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2025044225A (ja) * | 2023-09-19 | 2025-04-01 | ソフトバンクグループ株式会社 | システム |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013196185A (ja) * | 2012-03-16 | 2013-09-30 | Omron Healthcare Co Ltd | 生体情報表示方法、生体情報表示画像データ作成装置およびそのためのプログラム |
| US20150265217A1 (en) * | 2014-03-24 | 2015-09-24 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Confidence indicator for physiological measurements using a wearable sensor platform |
| JP2016066138A (ja) * | 2014-09-24 | 2016-04-28 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 診療支援装置、診療支援装置の作動方法および作動プログラム、並びに診療支援システム |
| JP2016182248A (ja) * | 2015-03-26 | 2016-10-20 | テルモ株式会社 | 情報管理装置、情報管理方法及び情報管理プログラム |
| JP2017038844A (ja) * | 2015-08-21 | 2017-02-23 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | 診療支援装置、診療支援方法、診療支援プログラム、生体情報測定装置 |
| JP2018151993A (ja) * | 2017-03-14 | 2018-09-27 | オムロン株式会社 | 投薬支援装置、方法及びプログラム |
| JP2019207536A (ja) * | 2018-05-29 | 2019-12-05 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | 投薬管理装置、投薬管理方法及び投薬管理プログラム |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3668843B2 (ja) * | 2001-08-27 | 2005-07-06 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | 電子血圧計および血圧測定データ処理システム |
| US11837334B2 (en) * | 2019-08-29 | 2023-12-05 | Shrpro, Llc | Whole-life, medication management, and ordering display system |
| US11901083B1 (en) * | 2021-11-30 | 2024-02-13 | Vignet Incorporated | Using genetic and phenotypic data sets for drug discovery clinical trials |
-
2021
- 2021-12-15 JP JP2021203296A patent/JP7760906B2/ja active Active
-
2022
- 2022-12-06 DE DE112022005939.7T patent/DE112022005939T5/de active Pending
- 2022-12-06 CN CN202280053073.XA patent/CN117795609A/zh active Pending
- 2022-12-06 WO PCT/JP2022/044959 patent/WO2023112779A1/ja not_active Ceased
-
2024
- 2024-02-15 US US18/442,711 patent/US20240194314A1/en active Pending
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013196185A (ja) * | 2012-03-16 | 2013-09-30 | Omron Healthcare Co Ltd | 生体情報表示方法、生体情報表示画像データ作成装置およびそのためのプログラム |
| US20150265217A1 (en) * | 2014-03-24 | 2015-09-24 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Confidence indicator for physiological measurements using a wearable sensor platform |
| JP2016066138A (ja) * | 2014-09-24 | 2016-04-28 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 診療支援装置、診療支援装置の作動方法および作動プログラム、並びに診療支援システム |
| JP2016182248A (ja) * | 2015-03-26 | 2016-10-20 | テルモ株式会社 | 情報管理装置、情報管理方法及び情報管理プログラム |
| JP2017038844A (ja) * | 2015-08-21 | 2017-02-23 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | 診療支援装置、診療支援方法、診療支援プログラム、生体情報測定装置 |
| JP2018151993A (ja) * | 2017-03-14 | 2018-09-27 | オムロン株式会社 | 投薬支援装置、方法及びプログラム |
| JP2019207536A (ja) * | 2018-05-29 | 2019-12-05 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | 投薬管理装置、投薬管理方法及び投薬管理プログラム |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN117672449A (zh) * | 2023-12-04 | 2024-03-08 | 启康保(北京)健康科技有限公司 | 一种基于物联网的药品管理系统 |
| CN117672449B (zh) * | 2023-12-04 | 2024-05-17 | 启康保(北京)健康科技有限公司 | 一种基于物联网的药品管理系统 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN117795609A (zh) | 2024-03-29 |
| DE112022005939T5 (de) | 2024-10-24 |
| US20240194314A1 (en) | 2024-06-13 |
| JP7760906B2 (ja) | 2025-10-28 |
| JP2023088513A (ja) | 2023-06-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7124453B2 (ja) | 投薬管理装置、投薬管理方法及び投薬管理プログラム | |
| US20110105979A1 (en) | Patient treatment and monitoring systems and methods | |
| CN110402465B (zh) | 给药辅助装置、方法以及记录介质 | |
| EP3207474A1 (en) | Monitoring information providing device and method | |
| US20240194314A1 (en) | Medical care assistance system, medical care assistance device, and program | |
| Weinfeld et al. | Home blood pressure monitoring | |
| US20210118539A1 (en) | Medication management device, medication management method, and non-transitory computer-readable storage medium storing medication management program | |
| WO2018168803A1 (ja) | 投薬支援装置、方法およびプログラム | |
| WO2018235652A1 (ja) | 健康管理装置、健康管理方法、および健康管理プログラム | |
| CN113544791B (zh) | 服药情况管理装置、方法以及记录有程序的计算机可读记录介质 | |
| US20100280395A1 (en) | System and Method for Hypertension Management | |
| JP7707655B2 (ja) | 生体情報処理システム、生体情報処理装置、生体情報処理方法及びプログラム | |
| US20240274293A1 (en) | Medical care assistance system, medical care assistance device, and recording medium | |
| US20240185982A1 (en) | Medical care assistance system, medical care assistance device, and recording medium | |
| US20240180438A1 (en) | Medical care assistance system, medical care assistance device, and recording medium | |
| WO2023282234A1 (ja) | 診療支援システム、診療支援装置、診療支援方法及びプログラム | |
| JP7555755B2 (ja) | 医用情報処理装置、医用情報処理システム及び医用情報処理プログラム | |
| JP2025069586A (ja) | 情報処理装置及びプログラム | |
| Kateryna et al. | PROSPECTS OF MOBILE APPLICATIONS FOR MONITORING AND PREVENTION OF HEART DISEASES | |
| JP2024011287A (ja) | 健康管理支援装置、健康管理支援システム、健康管理支援方法、およびプログラム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 22905496 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 202417004022 Country of ref document: IN |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 202280053073.X Country of ref document: CN |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 112022005939 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 22905496 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |