WO2022259293A1 - 空気調和システム - Google Patents
空気調和システム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2022259293A1 WO2022259293A1 PCT/JP2021/021525 JP2021021525W WO2022259293A1 WO 2022259293 A1 WO2022259293 A1 WO 2022259293A1 JP 2021021525 W JP2021021525 W JP 2021021525W WO 2022259293 A1 WO2022259293 A1 WO 2022259293A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- person
- sensor
- image
- target area
- air
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000004378 air conditioning Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 51
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 40
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 55
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000007726 management method Methods 0.000 description 27
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 10
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 10
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000013500 data storage Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000002776 aggregation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004220 aggregation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000012447 hatching Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/50—Control or safety arrangements characterised by user interfaces or communication
- F24F11/52—Indication arrangements, e.g. displays
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/62—Control or safety arrangements characterised by the type of control or by internal processing, e.g. using fuzzy logic, adaptive control or estimation of values
- F24F11/63—Electronic processing
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F2120/00—Control inputs relating to users or occupants
- F24F2120/10—Occupancy
- F24F2120/12—Position of occupants
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to air conditioning systems.
- Patent Literature 1 considers a facility capable of ventilating a large indoor space.
- the air conditioning system of the present disclosure solves the above problems, and aims to automatically control the environment of a target area to a state preferred by people present in the target area.
- the air conditioning system of the present disclosure includes an air conditioner that air-conditions a target area, a control device that controls the air conditioner, an operation device that allows a person to operate setting information related to control of the control device, and a person existing in the target area. together with position information, and a second sensor that detects the state of the air at a specific position in the target area, and the control device detects the detection data of the first sensor, the detection data of the second sensor, and , based on the operation information of the operating device, learns the good environment information about the good environment preferred by the person existing in the target area.
- the environment of the target area can be automatically controlled to a state preferred by people present in the target area.
- FIG. 4 is a flow chart showing the flow of processing within the air conditioning system 100 when learning a favorable environment corresponding to a person's attributes. 4 is a flow chart showing the flow of processing within a control system for reproducing a favorable environment corresponding to a person's attributes in the air conditioning system 100.
- FIG. 7 is a display screen diagram showing an example of a management screen displayed on an image display unit 71 of the display device 7.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of an air conditioning system 100 according to an embodiment.
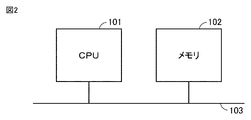
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing the hardware configuration of control device 10 in air conditioning system 100. As shown in FIG. The configuration of the air conditioning system 100 will be described below with reference to FIGS. 1 and 2.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of an air conditioning system 100 according to an embodiment.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing the hardware configuration of control device 10 in air conditioning system 100. As shown in FIG. The configuration of the air conditioning system 100 will be described below with reference to FIGS. 1 and 2.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of an air conditioning system 100 according to an embodiment.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing the hardware configuration of control device 10 in air conditioning system 100. As shown in FIG. The configuration of the air conditioning system 100 will be described below with reference to FIGS. 1 and 2.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of an air conditioning system 100 according to an embodiment.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing the hardware configuration
- the air conditioning system 100 includes an air conditioner 2, a display device 7, an air quality sensor 8, a human sensor 9, and a control device 10.
- Control device 10 includes control instruction unit 1 , detection data totalization unit 3 , management data creation unit 4 , learning unit 5 , map data creation unit 6 , and floor data storage unit 50 .
- the air conditioner 2 includes an indoor unit and an outdoor unit, and measures the state of air such as air and humidity (hereinafter referred to as air quality or air quality).
- the air conditioner 2 also has a ventilating function to ventilate between the indoor and outdoor spaces by taking in and exhausting air between the indoor unit and the outdoor unit.
- the air conditioner 2 has a plurality of indoor units in the target area and one or a plurality of outdoor units outdoors.
- the plurality of indoor units are installed at appropriate intervals in the target area.
- the number of indoor units installed in the target area increases as the volume or area of the target area increases.
- the installation interval and the number of indoor units increase or decrease depending on the layout of the indoor space in the target area.
- the control device 10 includes a CPU (Central Processing Unit) 101 connected by a bus 103, a memory 102 such as ROM (Read Only Memory) and RAM (Random Access Memory), and input/output ports.
- a system controller composed of a microprocessor including
- FIG. 1 and 2 in control device 10, floor data storage unit 50 is configured by memory 102.
- FIG. The control instruction unit 1, the detection data totalization unit 3, the management data creation unit 4, the learning unit 5, and the map data creation unit 6 are implemented by software programs executed by the CPU 101.
- FIG. Part or all of the control instruction unit 1, the detected data aggregation unit 3, the management data creation unit 4, the learning unit 5, the map data creation unit 6, and the floor data storage unit 50 are configured by hardware circuits. good too.
- display device 7 is a touch panel type display device in which an image display unit 71, which is an image display device made of a liquid crystal display, and an operation unit 72, which is a position input device such as a touch pad, are combined.
- the image display section 71 has a function of displaying an image
- the operation section 72 has a function of receiving an operation of touching the surface of the image display section 71 by a person and detecting the operation.
- the operation unit 72 detects the operation and sends a detection signal to the control instruction unit 1 . send.
- the floor data storage unit 50 stores floor data, which is two-dimensional coordinate data indicating the layout based on the architectural data, for the floor that is the target area.
- the map data creation unit 6 reads floor data from the floor data storage unit 50 and creates map data of the floor that is the target area. Based on the created map data, the map data creation unit 6 sends image data for displaying a map image of the floor, which is the target area, to the display device 7 .
- the control device 10 Based on the image data created by the map data creation unit 6 , the control device 10 displays the map image of the floor, which is the target area, on the image display unit 71 of the display device 7 .
- the air quality sensor 8 includes a plurality of temperature sensors and a plurality of humidity sensors installed at appropriate intervals in a plurality of locations within the target area, and a temperature sensor and a humidity sensor installed outdoors outside the target area. It is a sensor that detects the state of Detection data obtained by a plurality of sensors in the air quality sensor 8 are sent to the detection data summarizing section 3 .
- the human sensor 9 is provided in the target area and is configured by a receiving device that receives radio waves transmitted from a radio wave transmitter 90 possessed by a person present in the target area.
- a radio wave transmitter 90 a portable terminal device that transmits radio waves, such as a smart phone or a beacon terminal, is used.
- the human sensor 9 receives radio waves emitted from a radio wave transmitter 90 possessed by a person present in the target area, and based on information contained in the received radio waves, detects the positional information of the person having the radio wave transmitter 90 and the radio wave transmission. Attribute information of the person who owns the machine 90 is detected. Detected data obtained by detection by the human sensor 9 is sent to the detected data totalizing section 3 and the control instructing section 1 .
- the owner of the radio wave transmitter 90 may be identified by the identification number such as the terminal number of the radio wave transmitter 90, for example.
- the profile of a person who may exist in the target area is registered in advance in the memory 102 together with the identification number of the radio wave transmitter 90, and based on the registered information, the person sensor 9 can identify the person from the radio wave received.
- the human sensor 9 may detect attributes such as the name and sex of the owner of the radio wave transmitter 90 .
- the detection data aggregation unit 3 aggregates the detection data of the air quality sensor 8 and the detection data of the human sensor 9.
- the detection data totaling unit 3 for example, associates the detection data of the air quality sensor 8 with the detection data of the air quality sensor 8 and totals them.
- the target area Create management data for managing air conditioning control Based on the created management data, the management data creation unit 4 adds a human image, which is an image showing a person detected by the human sensor 9, to the map image displayed on the image display unit 71, and the air quality sensor 8. Image data used for displaying an air condition image showing the condition of the air such as the temperature detected in is also created.
- the management data created by the management data creating unit 4 by associating the coordinates of the map image in the map data with the position information included in the detection data of the person sensor 9, the person detected by the person sensor 9 is displayed on the map image. It is specified at which position of .
- the management data creation unit 4 stores in advance where each of the plurality of sensors in the target area of the air quality sensor 8 exists in the map image in the map data, and from the plurality of sensors in the air quality sensor 8 It recognizes which position of the map image the sent detection data corresponds to.
- the coordinates of the map image in the map data and the position information included in the detection data of the air quality sensor 8 are associated with each other, so that the air quality detected by the air quality sensor 8 is It is specified where the state exists in the map image.
- the management data creation unit 4 is used to display a human image, which is an image showing a person detected by the human sensor 9, and an air condition image showing the condition of the air, such as temperature, detected by the air quality sensor 8.
- the image data is sent to the image display section 71 of the display device 7 .
- the image display section 71 displays a management screen displaying the person image and the air condition image on the map image.
- the learning unit 5 acquires the management data created by the management data creation unit 4 and the operation information of the operation unit 72 .
- the learning unit 5 learns the favorable environment regarding the air condition that the person prefers, detected by the human sensor 9, based on the acquired management data and operation information.
- the learning unit 5 uses learning data in which human attributes, outdoor temperature, indoor temperature, and temperature setting operation content are associated with each other based on the acquired management data and operation information, A trained model is generated that infers a good environment for a person's preferred temperature setting from the attributes of the person, the outdoor temperature, the indoor temperature, and the details of the temperature setting operation. In this way, the learning unit 5 generates and stores a learned model for each person's attribute.
- control instruction unit 1 Based on the detection data sent from the human sensor 9, the control instruction unit 1 detects that a person exists in the target area. Based on the learned model, a good environment with an air condition corresponding to the detected attribute of the person is inferred, based on the inference result, an instruction to control the air conditioner 2 is sent to the air conditioner 2, to control.
- control instruction unit 1 When the control instruction unit 1 recognizes that a person has been detected by the human sensor 9 in a state where such a learned model has been generated, the control instruction unit 1 uses the learned model generated by the learning unit 5 to 1 infers a favorable environment with respect to the air condition corresponding to the attributes of the person detected by the person sensor 9 . Then, the control instruction unit 1 determines the control contents of the air conditioner 2 for realizing the inferred good environment, and sends a control instruction to the air conditioner 2, such as outputting a control signal for temperature setting.
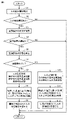
- FIG. 3 is a flow chart showing the flow of processing within the air conditioning system 100 when learning a favorable environment corresponding to a person's attributes.
- FIG. 3 illustrates an example of learning a favorable environment based on the temperature of a target area as an example of learning a favorable environment corresponding to a person's attribute in the air conditioning system 100.
- the CPU 101 of the control device 10 executes the following processing.
- step S1 based on the data detected by the human sensor 9, the human detection information is confirmed.
- step S2 it is determined whether or not there is human detection information based on the confirmation result of the human detection information in step S1. If it is determined in step S2 that there is no human detection information, the process returns. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S2 that there is human detection information, it is determined whether the air conditioner 2 is in operation based on the detection signal sent from the operation section 72 to the control instruction section 1. .
- step S4 If it is determined in step S4 that the air conditioner 2 is not in operation, return. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S4 that the air conditioner 2 is in operation, the state of the air conditioning operation is confirmed based on the detection signal sent from the operation section 72 to the control instruction section 1 in step S5.
- step S6 it is determined whether or not there has been an adjustment operation, such as an operation to adjust the set temperature, among the air conditioning operations. If it is determined in step S6 that an adjustment operation has been performed, in step S7, the attribute of the person who performed the adjustment operation is specified based on the detection information of the person confirmed in step S2. Furthermore, in step S7, the outdoor temperature when the adjustment operation is performed and the indoor temperature when the adjustment operation is performed are confirmed based on the detection data of the air quality sensor 8. FIG. Further, in step S7, the content of the operation such as the set value of the outdoor temperature adjusted when the adjustment operation is performed is confirmed based on the operation information of the operation unit 72. FIG.
- step S8 the environment based on the temperature confirmed in step S7 is determined as a favorable environment corresponding to the person whose attribute was specified in step S7.
- step S9 the temperature-based environment judged to be a good environment in step S8 is learned as a good environment corresponding to the person whose attributes are specified in step S7, and the process returns.
- step S9 for example, environmental information specified by the correlation between the outdoor temperature, indoor temperature, and operation content confirmed in step S7 is learned as a favorable environment corresponding to the person whose attributes are specified.
- a learned model is generated that infers a good environment for the temperature setting that the person prefers, from the outdoor temperature, the indoor temperature, and the details of the temperature setting operation corresponding to the person's attributes.
- step S10 the attribute of the person who performed the adjustment operation is specified based on the detection information of the person confirmed in step S2. Furthermore, in step S10, the outdoor temperature at the time step S10 is executed and the indoor temperature at the time step S10 is executed are checked based on the data detected by the air quality sensor 8.
- step S11 the environment based on the temperature confirmed in step S10 is determined to be a good environment for the person whose attribute was specified in step S10.
- step S12 the temperature-based environment judged to be a good environment in step S11 is learned as a good environment corresponding to the person whose attributes are specified in step S10, and the process returns.
- step S12 for example, the environmental information specified by the correlation between the outdoor temperature and the indoor temperature confirmed in step S10 is learned as a favorable environment corresponding to the person whose attributes are specified. As a result, a trained model is generated that is used for inferring a good environment for the temperature setting that the person prefers, from the outdoor temperature and the indoor temperature, corresponding to the person's attributes.
- Steps S7 to S9 are processing for learning a favorable environment for a person whose attributes are specified when he or she operates the air conditioning. This is because the reason why a person operates the air conditioning is that the person is likely to operate the air conditioning in order to make the surrounding environment favorable.
- steps S10 to S12 are processing for learning a favorable environment for a person whose attribute has been specified when he or she does not operate the air conditioning. This is because the reason why a person does not operate the air conditioning is that the percentage of people who perceive the surrounding environment to be a favorable environment is considered to be high.
- steps S7 to S9 if a plurality of people perform operations within a certain period of time, the average value of the operation details within the certain period of time may be learned as a favorable environment for the plurality of persons.
- the detected person performs the adjustment operation of the air conditioner 2, based on the attribute of the detected person, the detected indoor temperature, the detected outdoor temperature, and the details of the operation, , the attributes of the person, the outdoor temperature, the indoor temperature, and the details of the operation, the favorable environment that the person prefers is learned. Further, when the detected person adjusts the air conditioner 2, based on the detected person's attribute, the detected indoor temperature, and the detected outdoor temperature, the person's attribute, the outdoor temperature, Then, the favorable environment that the person prefers is learned from the room temperature. Through such learning, the environment of the target area can be automatically controlled to a state preferred by the person present in the target area.
- steps S1 to S5 have the functions of the detection data totalization unit 3 and the management data creation unit 4.
- steps S6 to S12 have the function of the learning section 5.
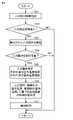
- FIG. 4 is a flow chart showing the flow of processing within the control system that reproduces a favorable environment corresponding to human attributes in the air conditioning system 100 .
- step S21 based on the data detected by the human sensor 9, the human detection information is confirmed.
- step S22 it is determined whether or not there is human detection information based on the confirmation result of the human detection information in step S21. If it is determined in step S22 that there is no human detection information, the process returns. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S22 that there is human detection information, the attributes of the person detected by the human sensor 9 are confirmed based on the data detected by the human sensor 9 in step S23.
- step S24 it is determined whether or not a person's attribute can be determined based on the confirmation result of the person's attribute in step S23. If it is determined in step S24 that the attribute of the person cannot be determined, the process returns. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S24 that the attribute of the person can be determined, the attribute of the person who performed the adjustment operation is specified in step S25 based on the detection information of the person determined to be identifiable in step S24. do. Furthermore, in step S25, the outdoor temperature at the time step S25 is executed and the indoor temperature at the time step S25 is executed are checked based on the detection data of the air quality sensor 8.
- step S26 a good environment corresponding to the attributes of the person detected by the human sensor 9 is inferred based on the learned model obtained by the learning in steps S9 and S12, and the inferred good environment Based on, the control content of the air conditioner 2 is determined.
- step S26 the attribute of the person identified in step S25, the room temperature confirmed in step S25, and the , from the outdoor temperature confirmed in step S25, a favorable environment with a set temperature corresponding to the specified attribute of the person is inferred, and the set temperature as the control content of the air conditioner 2 is determined based on the inference result.
- step S27 a control signal instructing the control content determined in step S26 is sent to the air conditioner 2, and the process returns.
- the air conditioner 2 is controlled to automatically adjust the air condition of the target area so as to create a favorable environment corresponding to the attribute of the person detected by the human sensor 9 .
- steps S21 to S27 a favorable environment with set temperatures corresponding to the attributes of a plurality of people is inferred. An inference is made, an average value of the set temperatures as an inference result is obtained, and the air conditioner 2 is controlled based on the average value.
- the attributes of the detected person when a person whose attributes can be identified in the target area is detected, the attributes of the detected person, A favorable environment preferred by the person is inferred from the detected indoor temperature and the detected outdoor temperature based on the detected attributes of the person, and an air conditioner is provided so as to create a favorable environment according to the result of the inference. 2 is controlled, the environment of the target area can be automatically controlled to a state preferred by the person present in the target area.
- FIG. 5 is a display screen diagram showing an example of a management screen displayed on the image display section 71 of the display device 7. As shown in FIG.
- the image display unit 71 displays the target area image 30 as a map image showing the actual indoor layout of the target area.
- a desk image 31 a private room image 32, an indoor unit image 33, an operation device image 34, a human image 35, a human presence area image 36, an air condition image 37 indicated by diagonal lines, and an air condition level index image. 41 is displayed.
- the desk image 31 is an image showing a desk arranged in the target area.
- the private room image 32 is an image showing private rooms separated by walls or the like in the target area.
- the indoor unit image 33 is an image showing the indoor unit of the air conditioner 2 .
- the operation device image 34 is an image showing the operation unit 72, which is the operation device.
- the operation device image 34 is basically not displayed, and when a person performs a touch operation on any of the indoor unit images 33, the operation device image 34 appears and is displayed in a display mode surrounding the touch-operated indoor unit image 33. be.
- the air conditioning system 100 can adjust the control details for each indoor unit.
- a display device 7 having an image display section 71 and an operation section 72 is attached to a predetermined position such as a wall within the target area.
- a person in the target area performs a touch operation to select one of the indoor unit images 33 displayed on the image display unit 71, thereby performing actual temperature control of the indoor unit corresponding to the selected indoor unit image 33. It is possible to adjust the control contents.
- the operation unit 72 detects the operation, and the operation unit 72 sends a detection signal to the control instruction unit 1 .
- the human image 35 is an image showing a person existing in the target area, and is displayed in the target area image 30 at a position corresponding to the position of the radio wave transmitter 90 detected by the human sensor 9 . Therefore, when a person moves, the position of the person image 35 moves according to the movement.
- a person presence area image 36 indicating an area where a person exists is displayed.
- an air condition image 37 is displayed as hatched in the drawing.
- the air condition image 37 is an image that indicates the level of the air condition, such as the height of the temperature, by color. In the drawing, for example, areas where the temperature is relatively high are indicated by oblique lines. Portions with different types of hatching indicate portions with different levels of air conditions as an example, and portions with different levels of air conditions are indicated in different colors in the actual image.
- the air condition level index image 41 is displayed at a position that does not interfere with the main image display, such as the edge of the target area image 30 .
- the air condition level index image 41 clearly shows the relationship between the color of the air condition image 37 and the height of the level of the air condition by means of a level gauge-like image. displayed as an indicator of the relationship between the height of the level of By displaying the air condition level index image 41, the height of the level of the air condition image 37 displayed in the target area image 30 can be easily confirmed.
- Modification (1) Part of the configuration of the control device 10 may exist on a cloud server.
- the management data creation unit 4 and the learning unit 5 may exist on a cloud server.
- the control device 10 may include a control section that controls the control instruction section 1, the detected data totalization section 3, the management data creation section 4, the learning section 5, and the map data creation section 6 in an integrated manner. .
- the radio wave transmitter 90 may be capable of detecting position information within the target area and transmitting it by radio waves, or simply transmitting the presence within the air conditioning target area by radio waves. good too. If the radio wave transmitter 90 can detect the positional information in the target area and transmit it by radio waves, the control device 10 specifies the positional information of the person based on the positional information transmitted by the radio wave transmitter 90. You should do it. Further, if the radio wave transmitter 90 can simply transmit the existence of the air conditioning target area by radio waves, the control device 10 specifies the position information based on the radio waves transmitted by the radio wave transmitter 90. Processing should be executed.
- Bluetooth (registered trademark) communication such as BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) (registered trademark) may be used.
- Communication between the radio wave transmitter 90 and the human sensor 9 may use a communication method other than Bluetooth communication. In other words, any communication method may be used for communication between the radio wave transmitter 90 and the human sensor 9 as long as the radio wave from the radio wave transmitter 90 can be received within the harmonization target area.
- control instruction unit 1 may infer a favorable environment of the air condition corresponding to the detected attribute of the person based on the learned model created by the learning unit 5. .
- control instruction section 1 may not have such a function of inference, and a separately provided inference section may have a function of such inference.
- the floor data storage unit 50 is included in the control device 10 .
- the present invention is not limited to this, and the floor data storage unit 50 may be provided in a storage device provided separately from the control device 10 instead of being included in the control device 10 .
- Examples of learning a good environment based on the temperature of the target area include temperature, humidity, wind direction, and air volume, or a combination of any two, or a combination of three You may make it learn the favorable environment which added.
- the map data creation unit 6 creates map data.
- the map data creation section 6 may not be provided, and the management data creation section 4 may have the function of creating map data as well.
- the present disclosure relates to an air conditioning system 100.
- the air-conditioning system 100 includes an air-conditioning device 2 that air-conditions a target area, a control device 10 that controls the air-conditioning device 2, and an operation unit 72 that is an operation device that allows a person to operate setting information related to control of the control device 10. , a human sensor 9 that is a first sensor that detects a person present in the target area along with position information, and an air quality sensor 8 that is a second sensor that detects the air condition at a specific position in the target area.
- the device 10 exists in the target area based on the detection data of the human sensor 9 that is the first sensor, the detection data of the air quality sensor 8 that is the second sensor, and the operation information of the operation unit 72 that is the operation device. Good environmental information about good environments that people like is learned (steps S7 to S12 in FIG. 3).
- control device 10 detects the detection data of the human sensor 9 as the first sensor, the detection data of the air quality sensor 8 as the second sensor, and the operation of the operation unit 72 as the operation device.
- the environment of the target area can be automatically controlled to a state preferred by the person present in the target area by learning the good environment information about the good environment preferred by the person present in the target area based on the information.
- the control device 10 determines setting information necessary for realizing a favorable environment based on the learned favorable environment information. is determined, and the air conditioner is controlled based on the determined setting information (steps S21 to S27 in FIG. 4).
- the control device 10 when the human sensor 9, which is the first sensor, detects a person existing in the target area, the control device 10 performs settings necessary for realizing a favorable environment based on the learned favorable environment information. By determining the information and controlling the air conditioner 2 based on the determined setting information, it is possible to automatically control the environment of the target area to a state preferred by the person present in the target area.
- the human sensor 9, which is the first sensor further detects the attribute of the detected person, and the control device 10 learns favorable environment information for each human attribute, and the human sensor 9, which is the first sensor, is the object
- the human sensor 9, which is the first sensor is the object
- setting information corresponding to each attribute of the person is determined based on the learned favorable environment information, and the air conditioner 2 is controlled based on the determined setting information (see FIG. 3). Steps S7 to S12).
- the control device 10 learns good environment information for each person's attribute, and when the human sensor 9, which is the first sensor, detects a person in the target area, based on the learned good environment information, By determining the setting information necessary to reproduce a good environment for each attribute of the person, and controlling the air conditioner based on the determined setting information, the environment of the target area is reproduced in the target area for each attribute of the person. It can be automatically controlled to the state that the user prefers.
- the control device 10 detects the plurality of persons in the target area based on the environment-friendly information learned corresponding to the attributes of each of the plurality of persons. , determines setting information necessary to realize an average good environment, and controls the air conditioner 2 based on the determined setting information (a modification of steps S21 to S27 in FIG. 4).
- the control device 10 can detect a plurality of people based on the environment-friendly information learned corresponding to the attributes of each of the plurality of people. Based on the determined setting information, the air conditioner 2 is controlled so that more people prefer the environment of the target area. It can be automatically controlled according to the state.
- the human sensor 9 which is the first sensor, receives radio waves transmitted from a radio wave transmitter 90 as a transmitting device possessed by a person present in the target area, and detects the position of the person based on the received radio waves. to detect
- the human sensor 9 which is the first sensor, receives radio waves transmitted from the radio wave transmitter 90 as a transmitting device possessed by a person present in the target area, and based on the received radio waves, Since the position is detected, the position of the person can be detected more accurately.
- the control device 10 further includes an image display unit 71, which is an image display device, and the control device 10 displays coordinate data preset with respect to the target area, the human body, which is the first sensor, in the image display unit 71, which is the image display device.
- the control device 10 displays coordinate data preset with respect to the target area, the human body, which is the first sensor, in the image display unit 71, which is the image display device.
- a person image 35 which is the first image indicating the position of the detected person, is displayed on the map of the target area, and the state of the air.
- the operating device image 34 which is the third image corresponding to the operating device, are displayed (FIG. 5).
- control device 10 causes the image display unit 71, which is an image display device, to display the human image 35, which is the first image indicating the position of the detected person, and the second image, which indicates the state of the air, on the map of the target area.
- the image display unit 71 which is an image display device
- the human image 35 which is the first image indicating the position of the detected person
- the second image which indicates the state of the air
- the control device 10 causes the image display unit 71, which is an image display device, to display the human image 35, which is the first image indicating the position of the detected person, and the second image, which indicates the state of the air, on the map of the target area.
- control device 10 is configured so that the setting information can be changed based on the operation of the operation device image 34, which is the third image displayed on the image display unit 71 (FIG. 5).
- control device 10 can change the setting information based on the operation of the operation device image 34, which is the third image displayed on the image display unit 71, which is an image display device. It is possible to easily change the setting information of the air conditioner 2 .
- control device 10 moves the position of the human image 35, which is the first image, on the map based on the detection data of the human sensor 9, which is the first sensor (Fig. 5).
- control device 10 moves the position of the human image 35, which is the first image, on the map based on the detection data of the human sensor 9, which is the first sensor. can be easily verified.
- control device 10 displays the air condition in a color-visible image in the second image showing the air condition based on the detection data of the air quality sensor 8, which is the second sensor (Fig. 5 ).
- control device 10 displays the state of the air in a visually recognizable image in color in the second image showing the state of the air based on the data detected by the air quality sensor 8, which is the second sensor. , the air condition can be easily checked visually.
- the setting information can be changed by a person's touch operation of the operating device image 34, which is the third image, on the image display unit 71, which is an image display device (FIG. 5).
- the operation device image 34 which is the third image, on the image display unit 71, which is an image display device, is touch-operated by a person, whereby the setting information can be changed, thereby controlling the air conditioner 2. It is possible to facilitate the operation for
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fuzzy Systems (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Air Conditioning Control Device (AREA)
Abstract
空気調和システム(100)が、対象領域の空調をする空調装置(2)と、空調装置(2)を制御する制御装置(10)と、制御装置(10)の制御に関する設定情報を人が操作可能な操作装置(72)と、対象領域に存在する人を位置情報とともに検出する第1センサ(9)と、対象領域での特定位置における空気の状態を検出する第2センサ(8)とを備える。制御装置(10)は、第1センサ(9)の検出データ、第2センサ(8)の検出データ、および、操作装置(72)の操作情報に基づいて、対象領域に存在する人が好む好環境に関する好環境情報を学習する。
Description
本開示は、空気調和システムに関する。
ビルの内部空間などの大型室内空間においては、温度および湿度などの空気の状態を利用者にとって快適なものとする必要がある。例えば、特許文献1においては、大型室内空間に適した換気をすることができる設備が考えられている。
室内空間における空気の質を、室内空間を利用する人にとって快適なものとするためには、室内空間における人の存在位置を検出したり、室内空間における空気の状態を検出したりするなど、室内空間の状態を把握し、室内空間における空気の状態を調節する必要がある。
しかし、従来の空気調和システムでは、空気調和をする対象領域における空気の状態を把握することが可能であったが、対象領域に存在する人が、気がついたときに、その都度、自らの感覚に基づいて対象領域の空気の状態を手動で調節する操作を行っているのが実情であった。このように従来の空気調和システムでは、対象領域における空気の状態のような環境を、対象領域に存在する人が好む状態に自動的に制御する技術が確立できていないという課題があった。
本開示の空気調和システムは、上記課題を解決するものであり、対象領域の環境を、対象領域に存在する人が好む状態に自動的に制御することができるようにすることを目的とする。
本開示の空気調和システムは、対象領域の空調をする空調装置と、空調装置を制御する制御装置と、制御装置の制御に関する設定情報を人が操作可能な操作装置と、対象領域に存在する人を位置情報とともに検出する第1センサと、対象領域での特定位置における空気の状態を検出する第2センサとを備え、制御装置は、第1センサの検出データ、第2センサの検出データ、および、操作装置の操作情報に基づいて、対象領域に存在する人が好む好環境に関する好環境情報を学習する。
本開示の空気調和システムによれば、対象領域の環境を、対象領域に存在する人が好む状態に自動的に制御することができる。
以下、本開示の実施の形態について、図面を参照しながら詳細に説明する。以下では、実施の形態について各種の技術を説明するが、実施の形態で説明された各種の技術を適宜組み合わせることは出願当初から予定されている。なお、図中同一又は相当部分には同一符号を付してその説明は繰返さない。
図1は、実施の形態による空気調和システム100の構成を示すブロック図である。図2は、空気調和システム100における制御装置10のハードウェア構成を表わす図である。以下においては、図1および図2を用いて、空気調和システム100の構成を説明する。
図1に示すように、空気調和システム100は、空調装置2、表示装置7、空質センサ8、人センサ9、および、制御装置10を含む。制御装置10は、制御指示部1、検出データ集計部3、管理データ作成部4、学習部5、マップデータ作成部6、および、フロアデータ記憶部50を含む。
空調装置2は、室内機と室外機とを備え、空調装置2の室内機が設置された室内空間である空気調和の対象領域内での空気および湿度などの空気の状態(以下、空気の質または空質ともいう)を調整する機能を有する。空調装置2は、さらに、室内機と室外機との間で空気の吸気および排気をすることにより室内と屋外との間で換気をする喚起機能も有する。
空調装置2は、対象領域に複数の室内機を備え、屋外に1つ又は複数の室外機を備える。複数の室内機は、対象領域において、適宜間隔を空けて設置されている。対象領域に設置される複数の室内機は、対象領域の容積または面積が増加するにしたがって、設置する台数が増加する。また、室内機は、対象領域における室内空間のレイアウトにより、設置間隔および設置台数が増減する。
図2に示すように、制御装置10は、バス103によって接続されたCPU(Central Processing Unit)101と、ROM(Read Only Memory)およびRAM(Random Access Memory)のようなメモリ102と、入出力ポートとを含むマイクロプロセッサにより構成されるシステムコントローラである。
図1および図2を参照して、制御装置10において、フロアデータ記憶部50は、メモリ102により構成される。制御指示部1、検出データ集計部3、管理データ作成部4、学習部5、および、マップデータ作成部6は、CPU101が実行するソフトウェアプログラムにより実現される。なお、制御指示部1、検出データ集計部3、管理データ作成部4、学習部5、マップデータ作成部6、および、フロアデータ記憶部50は、一部またはすべてがハードウェア回路により構成されてもよい。
図1を参照して、表示装置7は、液晶表示器よりなる画像表示装置である画像表示部71と、タッチパッドのような位置入力装置よりなる操作部72とを組み合わせたタッチパネル式の表示装置である。表示装置7は、画像表示部71が、画像を表示する機能を有し、操作部72が、人による画像表示部71の表面をタッチする操作を受け付けてその操作を検出する機能を有する。操作部72は、画像表示部71に表示された操作装置を示す画像である操作装置画像に対して、人がタッチ操作をした場合に、その操作を検出し、検出信号を制御指示部1に送る。
フロアデータ記憶部50は、対象領域となるフロアについて、建築データに基づくレイアウトを示す2次元の座標データであるフロアデータを記憶している。マップデータ作成部6は、フロアデータ記憶部50からフロアデータを読出し、対象領域となるフロアのマップデータを作成する。マップデータ作成部6は、作成したマップデータに基づいて、対象領域となるフロアのマップ画像を表示するための画像データを表示装置7に送る。
制御装置10では、マップデータ作成部6で作成された画像データに基づき、表示装置7において、対象領域となるフロアのマップ画像を画像表示部71に表示する。
空質センサ8は、対象領域内の複数箇所に適宜間隔を空けて設置された複数の温度センサおよび複数の湿度センサと、対象領域外である屋外に設置された温度センサおよび湿度センサを含む空気の状態を検出するセンサである。空質センサ8における複数のセンサにより得られた検出データは、検出データ集計部3に送られる。
人センサ9は、対象領域に設けられ、対象領域内に存在する人が所持する電波発信機90から発信される電波を受信する受信装置により構成される。電波発信機90は、例えばスマートフォン、および、ビーコンの端末機等の電波を発信する携帯式の端末装置が用いられる。
人センサ9は、対象領域に存在する人が所持する電波発信機90から発信される電波を受信し、受信した電波が含む情報に基づいて、電波発信機90を有する人の位置情報と電波発信機90を所有する人の属性の情報とを検出する。人センサ9の検出により得られた検出データは、検出データ集計部3および制御指示部1に送られる。
電波発信機90を所有する人の属性は、例えば、電波発信機90の端末機番号等の識別番号により電波発信機90の所有者が識別されればよい。なお、対象領域内に存在する可能性がある人のプロフィールを電波発信機90の識別番号とともに予めメモリ102に登録しておき、その登録情報に基づいて、人センサ9が受信した電波から特定された電波発信機90の識別番号に基づいて、電波発信機90の所有者の氏名および性別等の属性を人センサ9が検出できるようにしてもよい。
検出データ集計部3では、空質センサ8の検出データおよび人センサ9の検出データを集計する。検出データ集計部3は、たとえば、空質センサ8の検出データと、空質センサ8の検出データとを関連付けて集計する。
管理データ作成部4では、検出データ集計部3で集計された空質センサ8の検出データおよび人センサ9の検出データと、マップデータ作成部6で作成されたマップデータとに基づいて、対象領域の空調制御を管理するための管理データを作成する。管理データ作成部4では、作成した管理データに基づいて、画像表示部71に表示されるマップ画像中に、人センサ9で検出された人を示す画像である人画像、および、空質センサ8で検出された温度などの空気の状態を示す空気状態画像を表示するために用いる画像データも作成する。
管理データ作成部4で作成される管理データでは、マップデータにおけるマップ画像の座標と、人センサ9の検出データに含まれる位置情報とを対応付けることにより、人センサ9により検出された人がマップ画像のどの位置に存在するかが特定される。
管理データ作成部4では、空質センサ8における対象領域内の複数のセンサのそれぞれがマップデータにおけるマップ画像のどの位置に存在するかを予め記憶しており、空質センサ8における複数のセンサから送られてくる検出データがマップ画像のどの位置のデータであるかを認識する。管理データ作成部4で作成される管理データでは、マップデータにおけるマップ画像の座標と、空質センサ8の検出データに含まれる位置情報とを対応付けることにより、空質センサ8により検出された空気の状態がマップ画像のどの位置に存在するかが特定される。
管理データ作成部4は、人センサ9で検出された人を示す画像である人画像、および、空質センサ8で検出された温度などの空気の状態を示す空気状態画像を表示するために用いる画像データを表示装置7の画像表示部71に送る。表示装置7では、管理データ作成部4から送られた画像データに基づき、画像表示部71において、マップ画像上に人画像および空気状態画像を表示する管理画面が表示される。
学習部5は、管理データ作成部4で作成された管理データと、操作部72の操作情報とを取得する。学習部5では、取得した管理データ、および、操作情報に基づいて、人センサ9で検出された人が好む空気状態に関する好環境を学習する。一例として、学習部5は、取得した管理データ、および、操作情報に基づいて、人の属性、室外温度、室内温度、および、温度設定の操作内容が相互に関連付けられた学習用データを用い、人の属性、室外温度、室内温度、および、温度設定の操作内容から、その人が好む温度設定に関する好環境を推論する学習済モデルを生成する。このように、学習部5では、人の属性別に学習済モデルを生成し、記憶する。
制御指示部1では、人センサ9から送られた検出データに基づいて、人が対象領域内に存在することが検出され、予め定められた制御条件が成立した場合に、学習部5により作成された学習済モデルに基づいて、検出された人の属性に対応する空気状態の好環境を推論し、その推論結果に基づいて、空調装置2を制御する指示を空調装置2に送り、空調装置2を制御する。
このような学習済モデルが生成された状態において、人センサ9で人が検出されたことを制御指示部1が認識した場合は、学習部5で生成した学習済みモデルを用いて、制御指示部1が人センサ9で検出された人の属性に対応する空気状態に関する好環境を推論する。そして、制御指示部1は、推論した好環境を実現するための空調装置2の制御内容を決定し、空調装置2に、温度設定の制御信号を出力するなど、制御指示を送る。
[空気調和システム100での人の属性に対応する好環境を学習する流れ]
次に、空気調和システム100での人の属性に対応する好環境を学習する流れを説明する。図3は、空気調和システム100において人の属性に対応する好環境を学習する場合のシステム内での処理の流れを示すフローチャートである。
次に、空気調和システム100での人の属性に対応する好環境を学習する流れを説明する。図3は、空気調和システム100において人の属性に対応する好環境を学習する場合のシステム内での処理の流れを示すフローチャートである。
図3では、空気調和システム100において人の属性に対応する好環境を学習する一例として、対象領域の温度に基づく好環境を学習する例を説明する。制御装置10のCPU101は、以下のような処理を実行する。
ステップS1においては、人センサ9による検出データに基づいて、人の検出情報を確認する。ステップS2においては、ステップS1での人の検出情報の確認結果に基づいて、人の検出情報があるか否かを判断する。ステップS2で人の検出情報がないと判断された場合は、リターンする。一方、ステップS2で人の検出情報があると判断された場合は、操作部72から制御指示部1に送られた検出信号に基づいて、空調装置2が運転中であるか否かを判断する。
ステップS4で空調装置2が運転中ではないと判断された場合は、リターンする。一方、ステップS4で空調装置2が運転中であると判断された場合は、ステップS5において、操作部72から制御指示部1に送られた検出信号に基づき空調操作の状態を確認する。
ステップS6においては、空調操作のうち、設定温度を調整する操作のような調整操作があったか否かを判断する。ステップS6で調整操作があったと判断された場合は、ステップS7において、ステップS2で確認された人の検出情報に基づいて、調整操作をした人の属性を特定する。さらに、ステップS7においては、調整操作がされたときの室外温度と、調整操作がされたときの室内温度とを、空質センサ8の検出データに基づいて確認する。さらに、ステップS7においては、調整操作がされたときの調整された室外温度の設定値などの操作内容を、操作部72の操作情報に基づいて確認する。
ステップS8においてはステップS7で確認した温度に基づく環境を、ステップS7で属性が特定された人に対応する好環境と判断する。ステップS9においては、ステップS8で好環境と判断された温度に基づく環境を、ステップS7で属性が特定された人に対応する好環境として学習し、リターンする。ステップS9では、例えば、ステップS7で確認した室外温度、室内温度、および、操作内容の相関関係により特定される環境情報を、属性が特定された人に対応する好環境として学習する。これにより、人の属性に対応して、室外温度、室内温度、および、温度設定の操作内容から、その人が好む温度設定に関する好環境を推論する学習済モデルが生成される。
また、ステップS6で調整操作がなかったと判断された場合は、ステップS10において、ステップS2で確認された人の検出情報に基づいて、調整操作をした人の属性を特定する。さらに、ステップS10においては、ステップS10が実行される時点での室外温度と、ステップS10が実行される時点での室内温度とを、空質センサ8の検出データに基づいて確認する。
ステップS11においてはステップS10で確認した温度に基づく環境を、ステップS10で属性が特定された人に対応する好環境と判断する。ステップS12においては、ステップS11で好環境と判断された温度に基づく環境を、ステップS10で属性が特定された人に対応する好環境として学習し、リターンする。ステップS12では、例えば、ステップS10で確認した室外温度、および、室内温度の相関関係により特定される環境情報を、属性が特定された人に対応する好環境として学習する。これにより、人の属性に対応して、室外温度、および、室内温度から、その人が好む温度設定に関する好環境を推論するために用いる学習済モデルが生成される。
ステップS7~S9は、属性が特定された人が空調操作をした場合における当該人の好環境を学習する処理である。人が空調操作をするということは、その人が周囲の環境を好環境とするために空調操作をする割合が高いと考えられるからである。一方、ステップS10~S12は、属性が特定された人が空調操作を特にしなかった場合における当該人の好環境を学習する処理である。人が空調操作をしないということは、その人が周囲の環境を好環境と感じている割合が高いと考えられるからである。なお、ステップS7~S9において、一定期間内に複数の人が操作をした場合には、一定時間内における操作内容の平均値を、複数の人の好環境として学習するようにすればよい。
以上に説明したように、検出された人が空調装置2の調整操作をした場合には、検出された人の属性、検出された室内温度、検出された室外温度、および、操作内容に基づいて、人の属性、室外温度、室内温度、および、操作内容から、その人が好む好環境が学習される。また、検出された人が空調装置2の調整操作をした場合には、検出された人の属性、検出された室内温度、および、検出された室外温度に基づいて、人の属性、室外温度、および、室内温度から、その人が好む好環境が学習される。このような学習がされることにより、対象領域の環境を、対象領域に存在する人が好む状態に自動的に制御することができるようになる。
図3のフローチャートでは、ステップS1~S5が検出データ集計部3および管理データ作成部4の機能を有する。図3のフローチャートでは、ステップS6~S12が学習部5の機能を有する。
[空気調和システム100での人の属性に対応する好環境を再現する制御の流れ]
次に、制御装置10が図3で説明したような学習をした後、その学習結果に基づいて、空気調和システム100での人の属性に対応する好環境を再現する制御の流れを説明する。図4は、空気調和システム100において人の属性に対応する好環境を再現する制御のシステム内での処理の流れを示すフローチャートである。
次に、制御装置10が図3で説明したような学習をした後、その学習結果に基づいて、空気調和システム100での人の属性に対応する好環境を再現する制御の流れを説明する。図4は、空気調和システム100において人の属性に対応する好環境を再現する制御のシステム内での処理の流れを示すフローチャートである。
図4では、制御装置10が図3で説明したような学習をした後、空気調和システム100において人の属性に対応する好環境を再現することにより実現する制御の一例として、対象領域の温度に基づく好環境を再現することにより実現する例を説明する。制御装置10のCPU101は、以下のような処理を実行する。
ステップS21においては、人センサ9による検出データに基づいて、人の検出情報を確認する。ステップS22においては、ステップS21での人の検出情報の確認結果に基づいて、人の検出情報があるか否かを判断する。ステップS22で人の検出情報がないと判断された場合は、リターンする。一方、ステップS22で人の検出情報があると判断された場合は、ステップS23において、人センサ9で検出された人の属性を、人センサ9による検出データに基づいて確認する。
ステップS24においては、ステップS23での人の属性の確認結果に基づいて、人の属性を判別可能であるか否かを判断する。ステップS24で人の属性を判別可能でないと判断された場合は、リターンする。一方、ステップS24で人の属性を判別可能であると判断された場合は、ステップS25において、ステップS24で判別可能と判断された人の検出情報に基づいて、調整操作をした人の属性を特定する。さらに、ステップS25においては、ステップS25が実行される時点での室外温度と、ステップS25が実行される時点での室内温度とを、空質センサ8の検出データに基づいて確認する。
ステップS26においては、前述のステップS9およびS12のような学習により得られた学習済モデルに基づいて、人センサ9で検出された人の属性に対応する好環境を推論し、推論された好環境に基づいて、空調装置2の制御内容を決定する。
具体的に、ステップS26においては、前述のステップS9およびS12のような学習により得られた学習済モデルに基づいて、ステップS25で特定された人の属性、ステップS25で確認された室内温度、および、ステップS25で確認された室外温度から、特定された人の属性に対応する設定温度の好環境を推論し、その推論結果に基づいて、空調装置2の制御内容としての設定温度を決定する。ステップS27においては、ステップS26で決定された制御内容を指令する制御指示をする制御信号を空調装置2に送り、リターンする。これにより、空調装置2は、人センサ9で検出された人の属性に対応する好環境となるように、自動的に対象領域の空気状態を調整する動作をするように制御される。
なお、ステップS21~S27において、複数の人を対象として、人の属性に対応する設定温度の好環境を推論し、空調装置2を制御する場合には、複数人分の設定温度の好環境を推論し、推論結果となる設定温度の平均値を求め、その平均値に基づいて空調装置2を制御すればよい。
以上に説明したように、前述のような学習済モデルが生成された後、対象領域で属性を特定できる人が検出された場合には、学習済モデルに基づいて、検出された人の属性、検出された室内温度、および、検出された室外温度から、検出された人の属性に基づいて、その人が好む好環境が推論され、その推論結果に応じた好環境となるように、空調装置2が制御されるので、対象領域の環境を、対象領域に存在する人が好む状態に自動的に制御することができる。
図4のフローチャートでは、ステップS21~S27が制御指示部1の機能を有する。
[画像表示部71で表示される管理画面例]
次に、表示装置7の画像表示部71で表示される管理画面の一例を説明する。図5は、表示装置7の画像表示部71で表示される管理画面の一例を示す表示画面図である。
[画像表示部71で表示される管理画面例]
次に、表示装置7の画像表示部71で表示される管理画面の一例を説明する。図5は、表示装置7の画像表示部71で表示される管理画面の一例を示す表示画面図である。
図5を参照して、画像表示部71においては、対象領域画像30が、実際の対象領域の室内レイアウトを示すマップ画像として表示される。対象領域画像30においては、デスク画像31,個室画像32、室内機画像33、操作装置画像34、人画像35、人存在領域画像36、斜線で示す空気状態画像37、および、空気状態レベル指標画像41が表示される。
デスク画像31は、対象領域に配置されたデスクを示す画像である。個室画像32は、対象領域において壁などにより区切られた個室を示す画像である。室内機画像33は、空調装置2の室内機を示す画像である。
操作装置画像34は、操作装置である操作部72を示す画像である。操作装置画像34は、基本的には表示されておらず、人がいずれかの室内機画像33をタッチ操作すると、タッチ操作をした室内機画像33の周りを囲む表示態様で出現して表示される。
空気調和システム100は、室内機ごとに制御内容を調整することが可能である。画像表示部71および操作部72を備えた表示装置7は、対象領域内の壁などの予め定められた位置に取り付けられている。
対象領域にいる人は、画像表示部71に表示されたいずれかの室内機画像33を選択するタッチ操作をすることにより、選択した室内機画像33に対応する実際の室内機の温度制御などの制御内容を調整することが可能である。
操作装置画像34は、人がタッチ操作をすることに応じて、その操作を操作部72が検出し、検出信号を操作部72が制御指示部1に送る。
人画像35は、対象領域に存在する人を示す像であり、対象領域画像30において、人センサ9が検出した電波発信機90の位置に対応する位置に表示される。したがって、人が移動する場合は、その移動に応じて、人画像35の位置が移動する。人画像35の周囲には、人が存在する領域を示す人存在領域画像36が表示される。このような人画像35および人存在領域画像36が表示されることにより、人がどの位置にいるかを容易に確認することができる。
対象領域画像30のすべての領域においては、図中に斜線で示すような空気状態画像37が表示される。空気状態画像37は、例えば温度の高さなどの空気状態のレベルを色により示す画像である。図中においては、例えば温度が比較的に高い領域が斜線で示されている。斜線の種類が異なる部分は、空気状態のレベルが違う部分を一例として示しており、空気状態のレベルが違う部分は、実際の画像においては異なる色で示される。
空気状態レベル指標画像41は、対象領域画像30における端部等のように、主な画像表示の邪魔にならないような位置に表示される。空気状態レベル指標画像41は、レベルゲージ状の画像により、空気状態画像37の色と、空気状態のレベルの高さとの関係を明確に示すものであり、空気状態画像37の色と、空気状態のレベルの高さとの関係の指標として表示される。空気状態レベル指標画像41が表示されることにより、対象領域画像30に表示された空気状態画像37のレベルの高さを容易に確認することができる。
[変形例]
(1)制御装置10の構成の一部は、クラウドサーバ上に存在するものであってもよい。例えば、管理データ作成部4および学習部5は、クラウドサーバ上に存在するものであってもよい。
(1)制御装置10の構成の一部は、クラウドサーバ上に存在するものであってもよい。例えば、管理データ作成部4および学習部5は、クラウドサーバ上に存在するものであってもよい。
(2)制御装置10においては、制御指示部1、検出データ集計部3、管理データ作成部4、学習部5、および、マップデータ作成部6を統括的に制御する制御部を備えてもよい。
(3)電波発信機90は、対象領域内での位置情報を検出して電波で発信できるものであってもよく、単に気調和対象領域内に存在することを電波で発信できるものであってもよい。電波発信機90が対象領域内での位置情報を検出して電波で発信できるものである場合は、制御装置10において、電波発信機90が発信した位置情報に基づいて、人の位置情報を特定するようにすればよい。また、電波発信機90が単に気調和対象領域内に存在することを電波で発信できるものである場合は、制御装置10において、電波発信機90が発信した電波に基づいて、位置情報を特定する処理を実行すればよい。
(4)電波発信機90と、人センサ9との間の通信は、例えば、BLE〔Bluetooth Low Energy〕(登録商標)のようなブルートゥース(登録商標)通信を用いればよい。また、電波発信機90と、人センサ9との間の通信は、ブルートゥース通信以外の通信方式での通信を用いてもよい。つまり、電波発信機90と、人センサ9との間の通信は、単に調和対象領域内において電波発信機90の電波を受信できる通信方式であればどのような通信方式を用いてもよい。
(5)前述の実施の形態では、制御指示部1が、学習部5により作成された学習済モデルに基づいて、検出された人の属性に対応する空気状態の好環境を推論してもよい。また、これに限らず、制御指示部1がこのような推論をする機能を有さず、別に設けられた推論部がこのような推論をする機能を有するようにしてもよい。
(6)前述の実施の形態では、フロアデータ記憶部50が制御装置10に含まれている例を示した。しかし、これに限らず、フロアデータ記憶部50が制御装置10に含まれず、制御装置10とは別に設けられた記憶装置に設けられてもよい。
(7)前述の実施の形態では、空気調和システム100での人の属性に対応する好環境を学習する流れの説明において、対象領域の温度に基づく好環境を学習する例を説明した。しかし、これに限らず、人の属性に対応する好環境を学習する例としては、温度に湿度も加えた好環境を学習するようにしてもよい。この場合に、空質センサ8としては、湿度を検出するセンサも設ける必要がある。
(8)対象領域の温度に基づく好環境を学習する例としては、温度に、湿度と、風向と、風量とのうちのいずれか1つ、または、いずれか2つの組合せ、または、3つの組合せを加えた好環境を学習するようにしてもよい。
(9)前述の実施の形態では、制御装置10において、マップデータ作成部6がマップデータを作成する例を示した。しかし、これに限らず、制御装置10において、マップデータ作成部6を設けず、管理データ作成部4がマップデータも作成する機能を有するようにしてもよい。
[実施の形態のまとめ]
以上説明した実施の形態について、再び図面を参照して説明する。
以上説明した実施の形態について、再び図面を参照して説明する。
本開示は、空気調和システム100に関する。空気調和システム100は、対象領域の空調をする空調装置2と、空調装置2を制御する制御装置10と、制御装置10の制御に関する設定情報を人が操作可能な操作装置である操作部72と、対象領域に存在する人を位置情報とともに検出する第1センサである人センサ9と、対象領域での特定位置における空気の状態を検出する第2センサである空質センサ8とを備え、制御装置10は、第1センサである人センサ9の検出データ、第2センサである空質センサ8の検出データ、および、操作装置である操作部72の操作情報に基づいて、対象領域に存在する人が好む好環境に関する好環境情報を学習する(図3のステップS7~S12)。
このように、制御装置10は、制御装置10が、第1センサである人センサ9の検出データ、第2センサである空質センサ8の検出データ、および、操作装置である操作部72の操作情報に基づいて、対象領域に存在する人が好む好環境に関する好環境情報を学習することにより、対象領域の環境を、対象領域に存在する人が好む状態に自動的に制御することができる。
好ましくは、制御装置10は、第1センサである人センサ9が対象領域に存在する人を検出した場合に、学習した好環境情報に基づいて、好環境を実現するために必要となる設定情報を決定し、決定した設定情報に基づいて、空調装置を制御する(図4のステップS21~S27)。
このように、第1センサである人センサ9が対象領域に存在する人を検出した場合に、制御装置10が、学習した好環境情報に基づいて、好環境を実現するために必要となる設定情報を決定し、決定した設定情報に基づいて、空調装置2を制御することにより、対象領域の環境を、対象領域に存在する人が好む状態に自動的に制御することができる。
好ましくは、第1センサである人センサ9は、検出された人の属性をさらに検出し、制御装置10は、人の属性別に好環境情報を学習し、第1センサである人センサ9が対象領域内に人を検出した場合に、学習した好環境情報に基づいて、当該人の属性別に対応した設定情報を決定し、決定した設定情報に基づいて、空調装置2を制御する(図3のステップS7~S12)。
このように、制御装置10が、人の属性別に好環境情報を学習し、第1センサである人センサ9が対象領域内に人を検出した場合に、学習した好環境情報に基づいて、人の属性別に好環境を再現するために必要となる設定情報を決定し、決定した設定情報に基づいて、空調装置を制御することにより、人の属性別に、対象領域の環境を、対象領域に存在する人が好む状態に自動的に制御することができる。
好ましくは、制御装置10は、第1センサである人センサ9が対象領域内に複数の人を検出した場合に、複数の人の各々の属性に対応して学習された好環境情報に基づいて、平均的な好環境を実現するために必要となる設定情報を決定し、決定した設定情報に基づいて、空調装置2を制御する(図4のステップS21~S27の変形例)。
このように、制御装置10が、第1センサである人センサ9が対象領域内に複数の人を検出した場合に、複数の人の各々の属性に対応して学習された好環境情報に基づいて、平均的な好環境を実現するために必要となる設定情報を決定し、決定した設定情報に基づいて、空調装置2を制御することにより、対象領域の環境を、より多くの人が好む状態に自動的に制御することができる。
好ましくは、第1センサである人センサ9は、対象領域に存在する人が所持する発信装置としての電波発信機90から発信される電波を受信し、受信した電波に基づいて、当該人の位置を検出する。
このように、第1センサである人センサ9が、対象領域に存在する人が所持する発信装置としての電波発信機90から発信される電波を受信し、受信した電波に基づいて、当該人の位置を検出するので、より正確に人の位置を検出することができる。
好ましくは、画像表示装置である画像表示部71をさらに備え、制御装置10は、画像表示装置である画像表示部71において、対象領域に対して予め設定された座標データ、第1センサである人センサ9の検出データ、および、第2センサである空質センサ8の検出データに基づき、対象領域のマップ上に、検出された人の位置を示す第1画像である人画像35、空気の状態を示す第2画像、および、操作装置に対応する第3画像である操作装置画像34を表示する(図5)。
このように、制御装置10が、画像表示装置である画像表示部71において、対象領域のマップ上に、検出された人の位置を示す第1画像である人画像35、空気の状態を示す第2画像、および、操作装置に対応する第3画像である操作装置画像34を表示することにより、対象領域における人、および、空気の状態を容易に確認することができる。
好ましくは、制御装置10は、画像表示装置である画像表示部71に表示された第3画像である操作装置画像34の操作に基づいて、設定情報を変更可能に構成される(図5)。
このように、制御装置10が、画像表示装置である画像表示部71に表示された第3画像である操作装置画像34の操作に基づいて、設定情報を変更可能であることにより、対象領域における空調装置2の設定情報の変更を容易に実行することができる。
好ましくは、制御装置10は、第1センサである人センサ9の検出データに基づいて、マップ上における第1画像である人画像35の位置を移動する(図5)。
このように、制御装置10が、第1センサである人センサ9の検出データに基づいて、マップ上における第1画像である人画像35の位置を移動することにより、人が現在どの位置にいるかを容易に確認することができる。
好ましくは、制御装置10は、第2センサである空質センサ8の検出データに基づいて、空気の状態を示す第2画像において、空気の状態を色により視認可能な画像で表示する(図5)。
このように、制御装置10が、第2センサである空質センサ8の検出データに基づいて、空気の状態を示す第2画像において、空気の状態を色により視認可能な画像で表示することにより、空気の状態を視覚的に容易に確認することができる。
好ましくは、画像表示装置である画像表示部71において第3画像である操作装置画像34が、人によりタッチ操作されることにより、設定情報の変更が可能である(図5)。
このように、画像表示装置である画像表示部71において第3画像である操作装置画像34が、人によりタッチ操作されることにより、設定情報の変更が可能であることにより、空調装置2を制御するための操作を容易化することができる。
今回開示された実施の形態は、すべての点で例示であって制限的なものではないと考えられるべきである。本開示の範囲は、上記した実施の形態の説明ではなくて請求の範囲によって示され、請求の範囲と均等の意味及び範囲内でのすべての変更が含まれることが意図される。
100 空気調和システム、2 空調装置、10 制御装置、72 操作部、9 人センサ、8 空質センサ、7 表示装置、71 画像表示部。
Claims (10)
- 対象領域の空調をする空調装置と、
前記空調装置を制御する制御装置と、
前記制御装置の制御に関する設定情報を人が操作可能な操作装置と、
前記対象領域に存在する人を位置情報とともに検出する第1センサと、
前記対象領域での特定位置における空気の状態を検出する第2センサとを備え、
前記制御装置は、前記第1センサの検出データ、前記第2センサの検出データ、および、前記操作装置の操作情報に基づいて、前記対象領域に存在する人が好む好環境に関する好環境情報を学習する、空気調和システム。 - 前記制御装置は、前記第1センサが前記対象領域に存在する人を検出した場合に、学習した前記好環境情報に基づいて、前記好環境を実現するために必要となる前記設定情報を決定し、決定した前記設定情報に基づいて、前記空調装置を制御する、請求項1に記載の空気調和システム。
- 前記第1センサは、検出された人の属性をさらに検出し、
前記制御装置は、
人の属性別に前記好環境情報を学習し、
前記第1センサが前記対象領域内に人を検出した場合に、学習した前記好環境情報に基づいて、当該人の属性別に対応した前記設定情報を決定し、決定した前記設定情報に基づいて、前記空調装置を制御する、請求項2に記載の空気調和システム。 - 前記制御装置は、前記第1センサが前記対象領域内に複数の人を検出した場合に、前記複数の人の各々の属性に対応して学習された前記好環境情報に基づいて、平均的な前記好環境を実現するために必要となる前記設定情報を決定し、決定した前記設定情報に基づいて、前記空調装置を制御する、請求項3に記載の空気調和システム。
- 前記第1センサは、前記対象領域に存在する人が所持する発信装置から発信される電波を受信し、受信した電波に基づいて、当該人の位置を検出する、請求項1~4のいずれか1項に記載の空気調和システム。
- 画像表示装置をさらに備え、
前記制御装置は、前記画像表示装置において、前記対象領域に対して予め設定された座標データ、前記第1センサの検出データ、および、前記第2センサの検出データに基づき、前記対象領域のマップ上に、検出された人の位置を示す第1画像、前記空気の状態を示す第2画像、および、前記操作装置に対応する第3画像を表示する、請求項1~5のいずれか1項に記載の空気調和システム。 - 前記制御装置は、前記画像表示装置に表示された前記第3画像の操作に基づいて、前記設定情報を変更可能に構成される、請求項6に記載の空気調和システム。
- 前記制御装置は、前記第1センサの検出データに基づいて、前記マップ上における前記第1画像の位置を移動する、請求項6または請求項7に記載の空気調和システム。
- 前記制御装置は、前記第2センサの検出データに基づいて、前記第2画像において、前記空気の状態を色により視認可能な画像で表示する、請求項6~8のいずれか1項に記載の空気調和システム。
- 前記画像表示装置において前記第3画像がタッチ操作されることにより、前記設定情報の変更が可能である、請求項6~9のいずれか1項に記載の空気調和システム。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/021525 WO2022259293A1 (ja) | 2021-06-07 | 2021-06-07 | 空気調和システム |
| JP2023527137A JPWO2022259293A1 (ja) | 2021-06-07 | 2021-06-07 |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/021525 WO2022259293A1 (ja) | 2021-06-07 | 2021-06-07 | 空気調和システム |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2022259293A1 true WO2022259293A1 (ja) | 2022-12-15 |
Family
ID=84424965
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/021525 WO2022259293A1 (ja) | 2021-06-07 | 2021-06-07 | 空気調和システム |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JPWO2022259293A1 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2022259293A1 (ja) |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017098589A1 (ja) * | 2015-12-08 | 2017-06-15 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 空気調和システム |
| WO2019021675A1 (ja) * | 2017-07-25 | 2019-01-31 | 三菱重工サーマルシステムズ株式会社 | 空調制御装置、空調システム、空調制御方法、及びプログラム |
| JP2019082312A (ja) * | 2017-10-30 | 2019-05-30 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 空調制御装置 |
| JP2019207050A (ja) * | 2018-05-28 | 2019-12-05 | 株式会社大林組 | 環境条件制御装置、環境条件制御方法及び環境条件制御システム |
-
2021
- 2021-06-07 WO PCT/JP2021/021525 patent/WO2022259293A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2021-06-07 JP JP2023527137A patent/JPWO2022259293A1/ja active Pending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017098589A1 (ja) * | 2015-12-08 | 2017-06-15 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 空気調和システム |
| WO2019021675A1 (ja) * | 2017-07-25 | 2019-01-31 | 三菱重工サーマルシステムズ株式会社 | 空調制御装置、空調システム、空調制御方法、及びプログラム |
| JP2019082312A (ja) * | 2017-10-30 | 2019-05-30 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 空調制御装置 |
| JP2019207050A (ja) * | 2018-05-28 | 2019-12-05 | 株式会社大林組 | 環境条件制御装置、環境条件制御方法及び環境条件制御システム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2022259293A1 (ja) | 2022-12-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN108489040B (zh) | 立式空调器及其控制方法、以及计算机可读存储介质 | |
| CN110910503B (zh) | 一种空调环境的仿真方法及装置 | |
| WO2012023297A1 (ja) | 空調制御装置、空調制御方法及びプログラム | |
| US10365004B2 (en) | Control method and communication device | |
| JPWO2012101762A1 (ja) | 制御装置、空調システム、制御方法及びプログラム | |
| WO2008066093A1 (fr) | Système de représentation d'informations dépendant d'une position, contrôleur de représentation d'informations dépendant d'une position et procédé de représentation d'informations dépendant d'une position | |
| US10054328B2 (en) | Operational conditioning based on environmental components | |
| CN203810634U (zh) | 室内舒适性状态获取装置、空调器和移动终端 | |
| WO2016157675A1 (ja) | 制御システム、制御方法及び制御プログラム | |
| JP2012172910A (ja) | 室内環境調整用機器の操作システム | |
| KR102206461B1 (ko) | 공기조화기 시스템 및 그 동작방법 | |
| WO2022259293A1 (ja) | 空気調和システム | |
| CN113467267A (zh) | 一种智能家居系统的控制方法及智能家居系统 | |
| JP6972371B2 (ja) | 空気調和システム | |
| JP2019207206A (ja) | 検出装置、見守りシステムおよび空調システム | |
| JP2014070865A (ja) | 空調管理システム | |
| JP7004837B2 (ja) | 空気調和システム | |
| JP7523561B2 (ja) | 空気調和機、空気調和システム、および制御方法 | |
| WO2024150407A1 (ja) | 空調システム及び空調システムの制御方法 | |
| WO2023135750A1 (ja) | 遠隔操作装置および空気調和システム | |
| JP2019050055A (ja) | 制御システム及びプログラム | |
| JP7286125B1 (ja) | 機器制御サーバ | |
| TWM545943U (zh) | 遙控器整合平台 | |
| US20230006858A1 (en) | Time-dependent progressive disclosure of information | |
| JP4899978B2 (ja) | 空調制御システムおよびサーバ |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 21944974 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2023527137 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 21944974 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |