WO2019223267A1 - 一种会话处理方法及装置、计算机存储介质 - Google Patents
一种会话处理方法及装置、计算机存储介质 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2019223267A1 WO2019223267A1 PCT/CN2018/116549 CN2018116549W WO2019223267A1 WO 2019223267 A1 WO2019223267 A1 WO 2019223267A1 CN 2018116549 W CN2018116549 W CN 2018116549W WO 2019223267 A1 WO2019223267 A1 WO 2019223267A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- base station
- data
- core network
- sequence number
- network element
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/16—Performing reselection for specific purposes
- H04W36/18—Performing reselection for specific purposes for allowing seamless reselection, e.g. soft reselection
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/0005—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off
- H04W36/0011—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off for data sessions of end-to-end connection
- H04W36/0027—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off for data sessions of end-to-end connection for a plurality of data sessions of end-to-end connections, e.g. multi-call or multi-bearer end-to-end data connections
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/0005—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off
- H04W36/0055—Transmission or use of information for re-establishing the radio link
- H04W36/0069—Transmission or use of information for re-establishing the radio link in case of dual connectivity, e.g. decoupled uplink/downlink
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/02—Buffering or recovering information during reselection ; Modification of the traffic flow during hand-off
- H04W36/023—Buffering or recovering information during reselection
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/02—Buffering or recovering information during reselection ; Modification of the traffic flow during hand-off
- H04W36/026—Multicasting of data during hand-off
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/08—Reselecting an access point
- H04W36/083—Reselecting an access point wherein at least one of the access points is a moving node
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/16—Performing reselection for specific purposes
- H04W36/18—Performing reselection for specific purposes for allowing seamless reselection, e.g. soft reselection
- H04W36/185—Performing reselection for specific purposes for allowing seamless reselection, e.g. soft reselection using make before break
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/24—Reselection being triggered by specific parameters
- H04W36/26—Reselection being triggered by specific parameters by agreed or negotiated communication parameters
- H04W36/28—Reselection being triggered by specific parameters by agreed or negotiated communication parameters involving a plurality of connections, e.g. multi-call or multi-bearer connections
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/34—Reselection control
- H04W36/38—Reselection control by fixed network equipment
- H04W36/385—Reselection control by fixed network equipment of the core network
Definitions
- the present application relates to the field of wireless communication technologies, and in particular, to a method and device for session processing, and a computer storage medium.
- FIG. 2 (a) is a N2 interface-based handover preparation process
- FIG. 2 (b) is an N2 interface-based handover execution process.
- the main cause of the short-term data transmission is that the terminal is always in a single-pass (Single Radio) state.
- the old session must be disconnected The session on the source base station side) and the delay and interruption caused by the single-pass handover on the air interface side cannot be avoided.
- Embodiments of the present application provide a session processing method and device, and a computer storage medium.
- the path performs data copy-type transmission on the data packet, and / or performs first-level transmission on the data packet.
- the first-priority transmission refers to a data stream corresponding to a specified set of quality of service (QoS, Quality). of Service) parameters;
- the first type of handover process includes: before the air interface data radio bearer is handed over from the first base station to the second base station, the second core network element completes the establishment of the first path with the first base station and communicates with the first base station. Establishment of a second path between the second base stations; after the handover of the air interface data radio bearer from the first base station to the second base station is completed, the second core network element releases the A first path between a base station.
- a control unit configured to perform a first-type transmission and / or a first-type handover process on a PDU session and / or a data flow in the PDU session, wherein the first-type transmission includes: multiple paths are passed between the network side and the terminal side Performing a data copy transmission on the data packet, and / or transmitting a first priority to the data packet, where the first priority transmission refers to a transmitted data stream corresponding to a specified set of QoS parameters;
- the first type of handover process includes: before the air interface data radio bearer is handed over from the first base station to the second base station, the second core network element completes the establishment of the first path with the first base station and communicates with the first base station. Establishment of a second path between the second base stations; after the handover of the air interface data radio bearer from the first base station to the second base station is completed, the second core network element releases the A first path between a base station.
- the computer storage medium provided in the embodiment of the present application stores computer-executable instructions, and the computer-executable instructions implement the foregoing session processing method when executed by a processor.
- a first-type transmission and / or a first-type switching process is performed on a PDU session and / or a data flow in the PDU session, where the first-type transmission includes: a network side and a terminal side Performing data copy-type transmission on data packets through multiple paths, and / or transmitting data packets of a first priority, where the first priority transmission refers to a data stream corresponding to a specified set of QoS parameters;
- the first type of handover process includes: before the air interface data radio bearer is handed over from the first base station to the second base station, the second core network element completes the establishment of the first path with the first base station and communicates with the first base station.
- the terminal is in single-pass mode or dual-pass mode, and its interruption time is limited to the air interface switchover process or the air interface switchover process is completely uninterrupted, avoiding the core network side link on the data plane ( (Also known as a tunnel) due to the extra delay and interruption caused by the establishment or modification, thereby achieving a fast handover capability across base stations.
- the terminal is in single-pass mode or dual-pass mode, and its interruption time is limited to the air interface switchover process or the air interface switchover process is completely uninterrupted, avoiding the core network side link on the data plane (Also known as a tunnel) due to the extra delay and interruption caused by the establishment or modification, thereby achieving a fast handover capability across base stations.
- FIG. 1 is a flowchart of a handover based on an Xn interface
- FIG. 2 (a) is a flowchart of preparation for handover based on an N2 interface
- FIG. 2 (b) is a flowchart of a handover execution based on an N2 interface
- FIG. 3 is a schematic flowchart of a session processing method according to an embodiment of the present application.
- FIG. 4 (a) is a first schematic diagram of a network architecture for a cross-base station handover according to an embodiment of the present application
- FIG. 4 (b) is a second schematic diagram of a network architecture for a cross-base station handover according to an embodiment of the present application.
- FIG. 5 is a schematic flowchart of a fast handover implemented based on an N2 interface without changing a core network in a terminal single-pass or dual-pass mode according to an embodiment of the present application;
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart of a fast handover implemented based on an Xn interface without changing the core network in a terminal single-pass or dual-pass mode according to an embodiment of the present application;
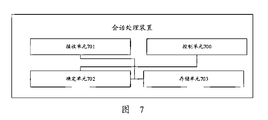
- FIG. 7 is a schematic structural composition diagram of a session processing apparatus according to an embodiment of the present application.
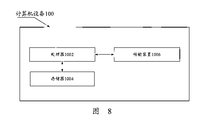
- FIG. 8 is a schematic structural composition diagram of a computer device according to an embodiment of the present application.
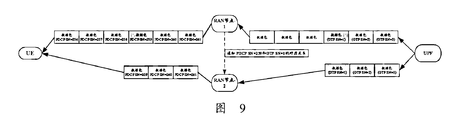
- FIG. 9 is a first schematic diagram of reordering data packets according to an embodiment of the present application.
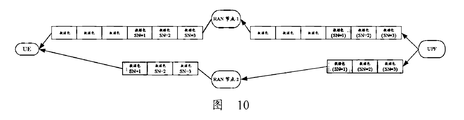
- FIG. 10 is a second schematic diagram of reordering data packets according to an embodiment of the present application.
- FIG. 3 is a schematic flowchart of a session processing method according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 3, the session processing method includes the following steps:
- Step 301 Perform a first type transmission and / or a first type switching process on a PDU session and / or a data flow in the PDU session, where the first type transmission includes: the network side and the terminal side pair the data through multiple paths.
- the data packet is transmitted in a data replication type, and / or the data packet is transmitted with a first priority, where the first priority transmission refers to a data stream transmitted corresponding to a specified set of QoS parameters; wherein the first
- the type of handover process includes: before the air interface data radio bearer is handed over from the first base station to the second base station, the second core network element completes the establishment of the first path with the first base station and establishes a first path with the second base station. The establishment of a second path between the two; after the handover of the air interface data radio bearer from the first base station to the second base station is completed, the second core network element releases the first A path.
- the first core network element receives a session establishment or modification request message, and the session establishment or modification request message carries identification information of the PDU session and / or data flow identification information and / or slice selection assistance information SNSSAI And / or DNN information, based on the information in the session establishment or modification request message, determining whether to perform a first-type transmission and / or a first-type switching process on the PDU session and / or the data stream in the PDU session. Further, the first core network element determines whether to respond to the PDU session and / or the data flow in the PDU session based on the SNSSAI and / or DNN and / or the first policy in the session establishment or modification request message. Performing the first type of transmission and / or the first type of handover process;
- the first policy includes at least a set of correspondence between S-NSSAI and / or DNN and the first indication information and / or policy and charging control (PCC, Policy Control and Charging) policy information, and the first policy An indication information is used to indicate whether the first type of transmission and / or the first type of handover process is performed.
- PCC Policy Control and Charging
- the session establishment or modification request message includes two PDU session identification information and / or data flow identification information;
- the first core network element determines, based on the two PDU session identification information and / or data flow identification information, that all or part of the data flows in the two PDU sessions perform the first type of transmission and / or all data flows.
- the first type of switching process is described.
- the terminal initiates two session establishment or update requests, and the first session identification is carried in the first session establishment or modification request message, and the first session identification is carried in the second session establishment or modification request message.
- the second session identifier; and / or, carrying the first data flow identifier in the first session establishment or modification request message, and carrying the first data flow identifier and the second data flow identifier in the second session establishment or modification request message are examples of the first session establishment or modification request message.
- the PDU session identifier and / or data flow identifier carry first information, and the first information is used to instruct to perform a first type of transmission and / or a first type of handover process.
- the first core network element refers to a session management function (SMF, Session Management Function)
- the second core network element refers to a user plane function (UPF, User Plane Function)
- the third core network element It refers to receiving core access and mobility management (AMF).
- the first base station refers to the source base station of the serving terminal, and the second base station refers to the target base station of the serving terminal.
- a first type of handover process is introduced.
- the first type of handover is also referred to as fast handover.
- Quick switching can be applied in the following two scenarios:
- Scenario 1 In the terminal's single-pass or dual-pass mode, the core network does not change rapidly based on the N2 interface.
- the first core network element receives the session establishment or modification request message sent by the third core network element.
- the handover request message carries identification information of the PDU session and / or data flow identification information
- the session establishment or modification request message carries identification information of the PDU session and / or data flow identification information
- the identification information of the PDU session includes identification information of the PDU session on the first base station side and / or identification information of at least one second PDU session, the at least one second PDU session and the PDU on the first base station side
- the conversation has a first association relationship.
- Scenario 2 In the terminal single-pass or dual-pass mode, the core network does not change rapidly based on the Xn interface.
- the first core network element receives a session establishment sent by the first base station and / or the second base station.
- a modification request message where the handover request message carries identification information and / or data flow identification information of a PDU session, and the session establishment or modification request message carries identification information and / or data flow identification information of a PDU session;
- the identification information of the PDU session includes identification information of the PDU session on the first base station side and / or identification information of at least one second PDU session, the at least one second PDU session and the PDU on the first base station side
- the conversation has a first association relationship.
- the process of performing the air interface handover by the first base station and the second base station includes: the first base station sends a handover request message to the second base station; the second base station sends a handover reply to the first base station Message; the first base station and the second base station complete the air interface handover at the terminal side;
- the first core network element After the second base station sends a handover reply message to the first base station, the first core network element receives the session establishment or modification request message sent by the second base station; and / or,
- the first core network element receives the session establishment or modification request message sent by the first base station.
- the first type of transmission is also referred to as low-latency and / or high-reliability transmission.
- the low-latency and / or high-reliability transmission refers to multiple paths for a specific data packet on the network side and the UE side. Performing data duplication transmission and / or performing high priority transmission on a transmission queue of related data packets.
- the high priority transmission refers to a corresponding data stream corresponding to a specified set of QoS parameters.
- a process of handing over the air interface data radio bearer from the first base station to the second base station includes:
- Dual-pass mode of a terminal When an air interface data radio bearer is established between the terminal and the first base station, the air interface data radio bearer is simultaneously established with the second base station, and then the first base station side is released Air interface data wireless bearer.
- the release of the first path between the second core network element and the first base station includes: the terminal sending to the first core network element the release of the first base station side A request message for a PDU session, so that the first core network element triggers the second core network element to release the PDU session at the first base station side; or the first core network element triggers the second The core network element releases the PDU session on the first base station side.
- the release of the first path between the network element of the second core network and the first base station includes: the second base station sends a path switching request message to the network element of the third core network; The third core network element sends a session modification request message to the first core network element, so that the first core network element triggers the second core network element to release the PDU session on the first base station side. .
- the PDU session identification information and / or data flow identification information is used to indicate whether to perform the first type of handover.
- the air interface data radio bearer (air interface DRB) is transmitted from the source base station (base station 1) to Before the target base station (base station 2) completes the handover, the core network side (5GC) has completed the data plane UPF link establishment with base station 1 and base station 2, and sent downlink data streams to base station 1 and base station 2 at the same time.
- the solid line is the data plane
- the dashed arrow is the data transmission direction (uplink, downlink, or uplink and downlink).
- the terminal is in single pass mode throughout, and its interruption time is limited to the air interface handover process, which avoids the extra delay caused by the core network side data link establishment / modification. Break.
- the terminal is in dual-pass mode.
- the "build first and then cut” solution is adopted, that is, the air interface data radio bearer on the base station 2 side is established first.
- the air interface data radio bearer is switched from base station 1 to base station 2. This process of air interface switching is completely without interruption delay, and it also avoids extra delay and interruption caused by core network side data link establishment / modification.
- a first policy (also referred to as a "fast handover" policy) is introduced, and the first core network element determines whether the PDU session and the PDU session are based on the identification information of the PDU session and the first policy.
- the data stream in the PDU session is subjected to a first type of transmission and / or a first type of switching process.
- the first policy includes at least a set of correspondence between S-NSSAI and / or DNN and first indication information and / or PCC policy information, where the first indication information is used to indicate whether to perform the first type of transmission. And / or the first type of switching process.
- the first strategy is shown in Table 1:
- the first core network element determines the first instruction information corresponding to the S-NSSAI and / or DNN based on the SNSSAI and / or DNN in the session establishment or modification request message and the first policy. Determining whether to perform a first type of transmission and / or a first type of handover process on the PDU session and / or the data flow in the PDU session based on the first indication information.
- the first core network element stores the correspondence between the PDU session identification information and / or data flow identification information and whether to perform the first type of transmission and / or the first type of switching process, and subsequently
- the first core network element ie, SMF
- the first core network element receives the handover request, based on the locally stored PDU session identification information and / or data flow identification information and whether to perform the first type
- a correspondence between transmission and / or a first type of switching process to determine whether to perform a first type of transmission and / or a first type of switching process on a PDU session and / or a data flow in the PDU session.
- the first core network element notifies the base station of the PDU session and / or the data flow in the PDU session for the first type of transmission and / or the first type of handover process.
- the base station performs processing on the air interface for the data packets corresponding to the session and / or data flow, such as optimizing the retransmission mechanism and timer time adjustment.
- the base station does not perform data forwarding processing on the session and / or data stream.
- the first policy is configured in at least one of the following network elements: a subscription information database (UDM), a policy control network element (PCF), and the first core network element.
- the first policy may be configured in the UDM and / or PCF on the network side based on the user granularity, or may be statically configured in the SMF.
- the SMF decides whether to Quickly switch the current PDU session and / or some of its data streams.
- the first core network element determines whether the PDU session is based on the information in the session establishment or modification request message and / or the first policy and / or the QoS parameters of the data flow in the PDU session. And / or the data stream in the PDU session performs a first type of transmission and / or a first type of handover process.
- the basis for the SMF to decide whether to perform the first type of handover may consider the QoS parameters of the data flow, such as preferentially performing fast handover for some specific 5QI valued data flows.
- the association relationship between the PDU session ID and the fast handover policy is stored locally.
- the PDU session ID can determine whether to perform fast handover.
- the first path on the first base station side and the second path on the second base station side are assigned the same IP address, and the first base station The PDU session on the side and the PDU session on the second base station side correspond to the same data flow and QoS policy.
- the second core network element For data transmission, during the first type of handover, the second core network element completes the establishment of the first path with the first base station and the second path with the second base station. After the path is established, the same data is sent to the first base station and the second base station simultaneously in the downlink direction, and / or the same data sent by the first base station and the second base station is received in the uplink direction; In one example, the first path and the second path belong to the same PDU session. After the second base station receives downlink data sent by the second core network element through the second path, before the air interface data radio bearer is handed over from the first base station to the second base station, or Before the air interface data radio bearer is established on the second base station side, the downlink data is buffered or discarded.
- the second base station After the air interface data radio bearer is handed over from the first base station to the second base station or after the air interface data radio bearer on the second base station side is established, the second base station starts sending downlink data to the terminal; Wherein, if the second base station buffers downlink data from the network element of the second core network, the buffered downlink data from the network element of the second core network is also sent to the terminal.
- the replication type transmission refers to: transmitting the same data on two different paths.
- the transmitting the same data on two different paths includes: on the core network side, the same second core network element transmits the same data on two different paths; or, two different paths The second core network element transmits the same data on two different paths; on the access network side, two different data bearers of the same base station transmit the same data; or, two different base stations transmit the same data Two different data bearers transmit the same data.
- the IP addresses of the different paths are different or the same, and the data flows and QoS policies of the different paths are different or the same.
- data bearers refer to connections and / or links
- different data bearers refer to different connections and / or links on the user plane.
- the second core network element sends the same downlink data packet to the first base station and the second base station simultaneously.
- the data flow identifiers of data transmitted on different paths are the same. Or, the data flow identifiers of the data transmitted on different paths are different.
- how to ensure that the same downlink data is received in an orderly manner on the terminal side or that the uplink data is received in an orderly manner on the network element side of the second core network may be implemented in the following ways:
- the second core network element adds a first sequence number to the same downlink data packet sent by the first base station and the second base station at the same time; wherein for downlink data transmission, the first base station will The correspondence between the first sequence number of one layer in the core network protocol of the downlink data packet and the second sequence number of one layer in the air interface protocol is notified to the second base station, and the second base station receives the data packet from the second base station. Parsing to obtain the first sequence number of a layer in the core network protocol, and based on the correspondence between the first sequence number and the second sequence number, the second sequence corresponding to the first sequence number The number is sent to the terminal, and the terminal reorders the data packets based on the second sequence number;
- the second base station calculates The second sequence number corresponding to the first sequence number in the data packet.
- the second base station receives the correspondence relationship and During the period of downlink data packets, some data packets were transmitted at the first base station, resulting in that the GTP-U layer SN value of the data packet received by the second base station is different from the GTP-U layer SN value in the corresponding relationship)
- the second base station needs to derive the correspondence between the SN value of the GTP-U layer of the data packet and the SN of the air interface protocol layer by itself.
- the correspondence relationship is transparently transmitted by the first base station to the second base station through a core network element, or the correspondence relationship is transmitted to the second base station by the first base station through a direct interface between the base stations.
- the second base station is described.
- the corresponding relationship may be added to a container of a handover request (handover required) message in the handover preparation phase shown in FIG. 6, or may be added in the handover preparation phase shown in FIG. 5.
- a new parameter is added to a handover request message to indicate the corresponding relationship.
- the terminal simultaneously adds a second sequence number to the same uplink data packet sent by the first base station and the second base station; wherein, for uplink data transmission, the first base station adds the air interface protocol of the uplink data packet to the air interface protocol of the uplink data packet.
- the correspondence between the second sequence number of a layer and the first sequence number of a layer in the core network protocol is notified to the second base station, and the second base station obtains the air interface protocol from the received data packet.
- a second sequence number of one of the layers, and sending the first sequence number corresponding to the second sequence number to the second core network network based on the correspondence between the second sequence number and the first sequence number Element, the second core network element reorders the data packets based on the first sequence number.
- the second base station calculates The first sequence number corresponding to the second sequence number in the data packet.
- the second base station needs to derive the air interface layer of the data packet by itself The corresponding relationship between the SN value and the SN of the GTP-U layer.
- the correspondence relationship is transparently transmitted by the first base station to the second base station through a core network element, or the correspondence relationship is transmitted to the second base station by the first base station through a direct interface between the base stations.
- the second base station is described.
- the corresponding relationship may be added to a container of a handover request (handover required) message in the handover preparation phase shown in FIG. 6, or may be added in the handover preparation phase shown in FIG. 5.
- a new parameter is added to a handover request message to indicate the corresponding relationship.
- one layer of the air interface protocol includes a PDCP layer and / or a Service Data Adaptation Protocol (SDAP) layer
- one layer of the core network protocol includes a GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP). )Floor.
- GTP GPRS Tunneling Protocol
- the first base station notifies the second base station of the correspondence between the first sequence number and the second sequence number through the Xn interface; or, the first base station notifies the first sequence number through the N2 interface.
- the correspondence between the sequence number and the second sequence number is sent to the core network, and the core network sends the correspondence between the first sequence number and the second sequence number to the second base station; or The first base station notifies the second base station of the correspondence between the first sequence number and the second sequence number through an air interface message.
- the first base station parses the data packet to obtain the first sequence number, and performs a second sequence number on a layer in the air interface protocol to the data packet. Reordering to determine the correspondence between the first sequence number and the second sequence number of the data packet.
- the second core network element adds the first sequence number to the same downlink data packet sent by the first base station and the second base station at the same time; wherein for downlink data transmission, the first base station and / Or after the second base station receives the downlink data packet, the first sequence number in the downlink data packet is passed to the terminal, so that the terminal parses and obtains the first serial number from the downlink data packet.
- the terminal adds a first sequence to the same uplink data packet sent by the first base station and the second base station at the same time Number; wherein for uplink data transmission, after the first base station and / or the second base station receive an uplink data packet, the first sequence number in the uplink data packet is passed to the second core Network element, so that the second core network element parses the first sequence number from the uplink data packet, and reorders the uplink data packet based on the first sequence number.
- the first sequence number in the data packet is included in a protocol layer above the PDCP layer, the SDAP layer, or the GTP layer.
- FIG. 5 is a schematic flowchart of a fast handover based on an N2 interface that is not changed in a core network in a terminal single-pass or dual-pass mode according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 5, the process includes the following steps:
- Step 501 The source base station sends a handover request message to the AMF / MME.
- the handover request message carries the PDU session ID and the target base station ID. Further, the PDU session ID carried in the handover request message is the same as the PDU session ID on the source base station side; or, the handover request message carries a PDU session ID that is different from the PDU session ID on the source base station side, but it needs to specify Association relationship of the PDU session ID (that is, the current session ID).
- Step 502 The AMF / MME sends a session modification request message to the SMF / PGW-C.
- the session modification request message carries a PDU session ID and a target base station ID.
- Step 503 Update the session between the UPF / PGW-U and the SMF / PGW-C to complete the preparation of the session resources on the target base station side.
- Session 1 of the source base station and session 2 of the target base station can Run the same flow and enforce the same QoS policy. or,
- Step 504 The SMF / PGW-C sends a session establishment request message to the target base station.
- the session establishment request carries a PDU session ID and a Flow list.
- Step 505 The target base station sends a session establishment request reply message to the SMF / PGW-C.
- the session establishment request reply message carries the accepted / rejected PDU session ID and Flow list.
- Step 506 Perform session update between the SMF / PGW-C and UPF / PGW-U, and perform session update according to the reply from the target base station side.
- Step 507 The SMF / PGW-C sends a session update request reply message to the AMF / MME.
- Step 508 The AMF / MME sends a handover command to the source base station.
- Step 509 The UPF / PGW-U transmits downlink data to the source base station and the target base station simultaneously.
- the UPF / PGW-U After the UPF / PGW-U completes step 505, it can directly start transmitting data to the source base station and the target base station.
- the two base stations can replicate the same data transmission (can be performed in parallel with step 508).
- Step 510 The target base station buffers or discards the downlink data before establishing the air interface data radio bearer.
- the data packet may be buffered or discarded until the DRB is established after the handover is completed in step 511.
- Step 511 The source base station triggers a handover procedure.
- Step 512 The UE sends a handover completion notification message to the target base station.
- Step 513 The target base station side air interface data radio bearer establishment is completed, and the downlink data is sent to the UE.
- the target base station After the target base station receives the handover completion notification message or after the target base station has established the air interface data radio bearer, it starts to send downlink data to the UE, and if it has previously buffered the downlink data from the UPF, it also sends it to the UE.
- Step 514 The target base station sends a handover completion notification message to the SMF / PGW-C.
- Step 515 Perform session update between the SMF / PGW-C and the UPF / PGW-U (optional).
- Step 516a The UE sends a session request message to the source base station side to the SMF / PGW-C.
- Step 516b The SMF / PGW-C side triggers the release of the session on the source base station side.
- releasing the session on the source base station side may be implemented by step 516a and / or step 516b.
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart of a fast handover implemented based on an Xn interface without changing the core network in a terminal single-pass or dual-pass mode according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 6, the process includes the following steps:
- Step 601 An air interface handover process is performed between the source base station and the target base station.
- the source base station sends a handover request message to the target base station; the target base station sends a handover reply message to the source base station; and the UE performs an air interface handover between the source base station and the target base station.
- Step 602 The core network side performs a session establishment process on the target base station side.
- This step includes:
- the target base station sends a session establishment / modification request message to the SMF / PGW-C.
- the session establishment / modification request message carries the first indication information and the ID of the PDU session to be established.
- the first indication information is used for whether the PDU session corresponding to the PDU session ID needs to be quickly switched.
- the source base station sends a session establishment / modification request message (that is, a handover request message) to the SMF / PGW-C.
- the session establishment / modification request message carries the first indication information, the PDU session ID to be established, and the target base station ID.
- the first indication information is used for whether the PDU session corresponding to the PDU session ID needs to be quickly switched.
- a session establishment / update is performed between the SMF / PGW-C and the UPF / PGW-U, and the UPF / PGW-U establishes a link with the target base station side.
- the SMF / PGW-C sends a session establishment / modification request message to the target base station.
- 602d needs to be executed to complete the establishment of the link between the UPF / PGW-U and the target base station side.
- the session establishment process on the core network side is performed in parallel with the air interface handover process on the access network side.
- the target base station or source base station sends a session establishment / update request Core Network.
- Session 1 of the source base station and session 2 of the target base station can Run the same flow and enforce the same QoS policy. or,
- Step 603 The target base station buffers or discards the received downlink data before the air interface handover is completed or the target base station establishes the air interface data radio bearer, and after the air interface handover is completed or the target base station establishes the air interface data radio bearer, the downlink data is transmitted. Send to UE.
- the target base station After receiving the downlink data, the target base station has not yet established a DRB connection with the UE, so it can buffer or discard the data packets. Until step 604 completes the handover and establishes the DRB, it starts to send downlink data to the UE. The downlink data is also sent to the UE.
- Step 604 The UE sends a handover completion message to the target base station.
- Step 605 The target base station sends a path switching request message to the AMF / MME.
- Step 606 The AMF / MME sends a session modification request message to the SMF / PGW-C.
- Step 607 The SMF / PGW-C triggers the UPF / PGW-U to perform a session update, and deletes the PDU session on the source base station side.
- the air interface is suitable for switching between single-pass or dual-pass mode.
- the added SN is analyzed at the RAN base station side, and then the duplicate data packets are reordered by the SN at the PDCP layer. Specifically, the data packet between the UPF and the base station is added with an SN in the existing protocol layer, which can be a GTP-U data packet.
- the source base station receives the first duplicate data packet
- the source base station sends
- the target base station sends the first duplicate data packet in the PDCP layer.
- the SN (referred to as PDCP SN) and the GTP-U SN (referred to as GTP SN).
- the SN value of the PDCP of the duplicate data packet is the same as the SN value of the PDCP currently used by the source base station, and the SN value sent subsequently will remain synchronized, as shown in FIG. 9.
- RAN node-1 notifies RAN node-2 about the correspondence relationship between PDCP SN and GTP SN of duplicate data packets in the following three ways:
- Node-1 informs Node-2 via the Xn interface
- Node-1 sends it to the core network through the N2 interface and sends it to Node-2;
- Node-1 informs Node-2 through an air interface message (such as RRC Connection Reconfig).
- an air interface message such as RRC Connection Reconfig
- the added SN is transparently transmitted to the UE at the RAN base station side, and the added SN may be included on the GTP-U protocol layer.
- the SN is directly transparently transmitted to the UE, and the UE analyzes the SN of the packet at this layer to complete the reordering of the packet.
- the UE sends duplicate data for the same reason Packets are parsed by UPF, as shown in Figure 10.
- FIG. 7 is a schematic structural composition diagram of a session processing apparatus according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 7, the session processing apparatus includes:
- the control unit 700 is configured to perform a first-type transmission and / or a first-type handover process on a PDU session and / or a data flow in the PDU session, where the first-type transmission includes: The path performs data copy-type transmission on the data packet, and / or transmits a first priority transmission to the data packet, where the first priority transmission refers to a transmitted data stream corresponding to a specified set of QoS parameters;
- the first type of handover process includes: before the air interface data radio bearer is handed over from the first base station to the second base station, the second core network element completes the establishment of the first path with the first base station and communicates with the first base station. Establishment of a second path between the second base stations; after the handover of the air interface data radio bearer from the first base station to the second base station is completed, the second core network element releases the A first path between a base station.
- the process of handover of the air interface data radio bearer from the first base station to the second base station includes:
- the terminal When the terminal establishes an air interface data radio bearer with the first base station, the terminal directly switches the air interface data radio bearer from the first base station to the second base station; or,
- the terminal When the terminal establishes an air interface data radio bearer with the first base station, it simultaneously establishes an air interface data radio bearer with the second base station, and then releases the air interface data radio bearer on the side of the first base station.
- the apparatus further includes: a receiving unit 701; after the third core network element receives the handover request sent by the first base station, the receiving unit 701 receives the A session establishment or modification request message, where the handover request message carries identification information and / or data flow identification information of a PDU session, and the session establishment or modification request message carries identification information and / or data flow identification information of a PDU session; ,
- the identification information of the PDU session includes identification information of the PDU session on the first base station side and / or identification information of at least one second PDU session, the at least one second PDU session and the PDU on the first base station side
- the conversation has a first association relationship.
- the releasing of the first path between the second core network element and the first base station includes:
- the terminal sends a request message to the first core network element to release the PDU session on the first base station side, so that the first core network element triggers the second core network element to release the first base station side.
- PDU session ; or,
- the first core network element triggers the second core network element to release the PDU session on the first base station side.
- the apparatus further includes: a receiving unit 701; in a process in which the first base station and the second base station perform air interface handover, the receiving unit 701 receives the first base station and / or The session establishment or modification request message sent by the second base station, the handover request message carries identification information of the PDU session and / or data flow identification information, and the session establishment or modification request message carries identification information of the PDU session and / or Data flow identification information;
- the identification information of the PDU session includes identification information of the PDU session on the first base station side and / or identification information of at least one second PDU session, the at least one second PDU session and the PDU on the first base station side
- the conversation has a first association relationship.
- the process of performing the air interface handover by the first base station and the second base station includes: the first base station sends a handover request message to the second base station; and the second base station sends the first base station to the first base station.
- the base station sends a handover reply message; the first base station and the second base station complete the air interface handover at the terminal side;
- the receiving unit 701 receives a session establishment or modification request message sent by the second base station; and / or,
- the receiving unit 701 receives a session establishment or modification request message sent by the first base station.
- the releasing of the first path between the second core network element and the first base station includes:
- the second base station sends a path switching request message to a third core network element; the third core network element sends a session modification request message to the first core network element, so that the first core network element Triggering the second core network element to release the PDU session on the first base station side.
- the PDU session identification information and / or data flow identification information is used to indicate whether to perform the first type of handover.
- the device further includes:
- the receiving unit 701 is configured to receive a session establishment or modification request message, where the session establishment or modification request message carries identification information of a PDU session and / or data flow identification information and / or slice selection assistance information SNSSAI and / or DNN information;
- a determining unit 702 is configured to determine, based on information in the session establishment or modification request message, whether to perform a first-type transmission and / or a first-type switching process on the PDU session and / or a data stream in the PDU session.
- the determining unit 702 is configured to determine whether the PDU session and / or the PDU session are based on the SNSSAI and / or DNN and / or the first policy in the session establishment or modification request message.
- the first policy includes at least a set of correspondence between S-NSSAI and / or DNN and first indication information and / or PCC policy information, and the first indication information is used to indicate whether to perform the first type of transmission. And / or the first type of switching process.
- the session establishment or modification request message includes two PDU session identification information and / or data flow identification information;
- the first core network element determines, based on the two PDU session identification information and / or data flow identification information, that all or part of the data flows in the two PDU sessions perform the first type of transmission and / or all data flows.
- the first type of switching process is described.
- the terminal initiates two session establishment or update requests, carrying a first session identifier in a first session establishment or modification request message, and carrying a first session identifier in a second session establishment or modification request message. And the second session identifier; and / or, carrying the first data flow identifier in the first session establishment or modification request message, and carrying the first data flow identifier and the second data flow identifier in the second session establishment or modification request message .
- the PDU session identifier and / or the data flow identifier carry first information, and the first information is used to instruct execution of a first type of transmission and / or a first type of handover procedure.
- the device further includes:
- a storage unit 703 configured to store a correspondence between identification information and / or data flow identification information of the PDU session and whether to perform the first-type transmission and / or the first-type switching process;
- the determining unit 702 is further configured to, after the receiving unit receives the switching request, based on the locally stored PDU session identification information and / or data flow identification information and whether to perform the first type of transmission and / or the first The corresponding relationship of the class switching process to determine whether to perform a first type transmission and / or a first type switching process on a PDU session and / or a data flow in the PDU session.
- the first core network element notifies the base station of the PDU session and / or the data flow in the PDU session for the first type of transmission and / or the first type of handover process.
- the first policy is configured in at least one of the following network elements: a subscription information database UDM, a policy control network element PCF, and the first core network element.
- the determining unit 702 is further configured to determine whether to determine whether to base on information in the session establishment or modification request message and / or a first policy and / or QoS parameters of a data flow in the PDU session. Performing a first-type transmission and / or a first-type switching process on the PDU session and / or the data flow in the PDU session.
- the first path on the first base station side and the second path on the second base station side are assigned the same IP address, and the first base station side
- the PDU session and the PDU session on the second base station side correspond to the same data flow and QoS policy.
- different IP addresses are allocated to the first path on the first base station side and the second path on the second base station side, and the first base station side
- the PDU session and the PDU session on the second base station side correspond to the same data flow and QoS policy.
- the second core network element After the second core network element completes the establishment of the first path with the first base station and the establishment of the second path with the second base station, it simultaneously sends the first base station in the downlink direction. Sending the same data with the second base station, and / or receiving the same data sent by the first base station and the second base station in an uplink direction;
- the downlink data is buffered or discarded.
- the first path and the second path belong to the same PDU session.
- the replication type transmission refers to transmitting the same data on two different paths.
- the transmitting the same data on two different paths includes:
- the same second core network element transmits the same data on two different paths; or, two different second core network elements transmit the same data on two different paths ;
- two different data bearers of the same base station transmit the same data; or two different data bearers of two different base stations transmit the same data.
- the IP addresses of the different paths are different or the same, and the data flows and QoS policies of the different paths are different or the same.
- data bearers refer to paths and / or links
- different data bearers refer to different paths and / or links on the user plane.
- the same second core network element transmits the same data on two different paths on the core network side, it is carried by two different data of two different base stations on the access network side. To transmit the same data, then:
- the second core network element sends the same downlink data packet to the first base station and the second base station at the same time.
- the data flow identifiers of data transmitted on different paths are the same. Or, the data flow identifiers of the data transmitted on different paths are different.
- the second core network element adds a first sequence number to the same downlink data packet sent by the first base station and the second base station at the same time;
- the first base station For downlink data transmission, the first base station notifies the second base station of a correspondence between a first sequence number of a layer in a core network protocol of a downlink data packet and a second sequence number of a layer in an air interface protocol, Parsing, by the second base station, the first sequence number of a layer in the core network protocol from the received data packet, and based on the correspondence between the first sequence number and the second sequence number, Sending the second sequence number corresponding to the first sequence number to a terminal, and the terminal reorders the data packet based on the second sequence number;
- the second base station is based on the correspondence The relationship calculates a second sequence number corresponding to the first sequence number in the data packet.
- the corresponding relationship is transparently transmitted by the first base station to the second base station through a core network element, or the corresponding relationship is transmitted by the first base station through a direct interface between the base stations. To the second base station.
- a second sequence number is added to the same uplink data packet sent by the terminal to the first base station and the second base station at the same time;
- the first base station For uplink data transmission, the first base station notifies the second base station of a correspondence between a second sequential number of a layer in an air interface protocol of an uplink data packet and a first sequential number of a layer in a core network protocol, The second base station parses the received data packet to obtain a second sequence number of a layer in the air interface protocol, and based on the correspondence between the second sequence number and the first sequence number, The first sequence number corresponding to the second sequence number is sent to a second core network element, and the second core network element reorders the data packet based on the first sequence number.
- the second base station is based on the correspondence The relationship calculates a first sequence number corresponding to a second sequence number in the data packet.
- the corresponding relationship is transparently transmitted by the first base station to the second base station through a core network element, or the corresponding relationship is transmitted by the first base station through a direct interface between the base stations. To the second base station.
- one layer in the air interface protocol includes a PDCP layer and / or an SDAP layer
- one layer in the core network protocol includes a GTP layer
- the first base station notifies the second base station of the correspondence between the first sequence number and the second sequence number through an Xn interface; or,
- the first base station sends the correspondence between the first sequence number and the second sequence number to the core network through the N2 interface, and the core network sends the first sequence number and the second sequence number to the core network. Sending the corresponding relationship to the second base station; or
- the first base station notifies the second base station of the correspondence between the first sequence number and the second sequence number through an air interface message.
- the first base station after receiving the downlink data packet, parses the data packet to obtain the first sequence number, and uses the second sequence number of a layer in the air interface protocol to identify the first sequence number.
- the data packets are reordered to determine a correspondence between the first sequence number and the second sequence number of the data packet.
- the second core network element adds a first sequence number to the same downlink data packet sent by the first base station and the second base station at the same time;
- the first sequence number in the downlink data packet is passed to the terminal, so that the terminal starts from The downlink data packet is parsed to obtain the first sequence number, and the downlink data packet is reordered based on the first sequence number.
- the terminal adds a first sequence number to the same uplink data packet sent by the first base station and the second base station at the same time;
- the first sequence number in the uplink data packet is passed to the second core network element, Therefore, the second core network element parses the first sequence number from the uplink data packet, and reorders the uplink data packet based on the first sequence number.
- the first sequence number in the data packet is included in a protocol layer above the PDCP layer, the SDAP layer, or the GTP layer.
- the air interface data radio bearer corresponding to the data stream redundantly transmitted by the user plane of the core network is not transmitted for other data streams.
- the second base station After the handover of the air interface data radio bearer is completed by the first base station to the second base station or after the establishment of the air interface data radio bearer on the second base station side, the second base station starts Sending downlink data to the terminal; if the second base station buffers downlink data from the network element of the second core network, sending the buffered downlink data from the network element of the second core network to the network Mentioned terminal.
- the implementation functions of the units in the session processing apparatus shown in FIG. 7 can be understood by referring to the related description of the foregoing session processing method.
- the functions of the units in the session processing device shown in FIG. 7 may be implemented by a program running on a processor, or may be implemented by a specific logic circuit.
- the session processing device if the session processing device is implemented in the form of a software functional module and sold or used as an independent product, it may also be stored in a computer-readable storage medium.
- the computer software product is stored in a storage medium and includes several instructions for A computer device (which may be a personal computer, a server, or a network device) is caused to execute all or part of the methods described in the embodiments of the present application.
- the foregoing storage medium includes: a U disk, a mobile hard disk, a read-only memory (ROM, Read Only Memory), a magnetic disk, or an optical disk, and other media that can store program codes.
- ROM Read Only Memory
- magnetic disk or an optical disk, and other media that can store program codes.
- an embodiment of the present application further provides a computer storage medium in which computer-executable instructions are stored.
- the computer-executable instructions are executed by a processor, the foregoing session processing method in the embodiment of the present application is implemented.
- FIG. 8 is a schematic structural composition diagram of a computer device according to an embodiment of the present application.
- the computer device may be an access network device or a core network device.
- the computer device 100 may include one or more (only one shown in the figure) a processor 1002 (the processor 1002 may include but is not limited to a microprocessor (MCU, Micro Controller Unit) or a programmable logic device. (FPGA, Field Programmable Gate Array, etc.), a memory 1004 for storing data, and a transmission device 1006 for a communication function.
- MCU Microprocessor
- FPGA Field Programmable Gate Array
- FIG. 8 is only schematic, and it does not limit the structure of the electronic device.
- the computer device 100 may also include more or fewer components than those shown in FIG. 8, or have a different configuration from that shown in FIG. 8.
- the memory 1004 may be used to store software programs and modules of application software, such as program instructions / modules corresponding to the methods in the embodiments of the present application.
- the processor 1002 executes various functional applications by running the software programs and modules stored in the memory 1004. As well as data processing, the method described above is implemented.
- the memory 1004 may include a high-speed random access memory, and may further include a non-volatile memory, such as one or more magnetic storage devices, a flash memory, or other non-volatile solid-state memory.
- the memory 1004 may further include memory remotely set with respect to the processor 1002, and these remote memories may be connected to the computer device 100 through a network. Examples of the above network include, but are not limited to, the Internet, an intranet, a local area network, a mobile communication network, and combinations thereof.
- the transmission device 1006 is used for receiving or transmitting data via a network.
- a specific example of the network described above may include a wireless network provided by a communication provider of the computer device 100.
- the transmission device 1006 includes a network adapter (NIC, Network Interface Controller), which can be connected to other network devices through a base station so as to communicate with the Internet.
- the transmission device 1006 may be a radio frequency (RF, Radio Frequency) module, which is used to communicate with the Internet in a wireless manner.
- RF Radio Frequency
- the disclosed method and smart device may be implemented in other ways.
- the device embodiments described above are only schematic.
- the division of the units is only a logical function division.
- there may be another division manner such as multiple units or components may be combined, or Can be integrated into another system, or some features can be ignored or not implemented.
- the displayed or discussed components are coupled, or directly coupled, or communicated with each other through some interfaces.
- the indirect coupling or communications of the device or unit may be electrical, mechanical, or other forms. of.
- the units described above as separate components may or may not be physically separated, and the components displayed as units may or may not be physical units, which may be located in one place or distributed across multiple network units; Some or all of the units may be selected according to actual needs to achieve the objective of the solution of this embodiment.
- each functional unit in each embodiment of the present application may be integrated into a second processing unit, or each unit may be separately used as a unit, or two or more units may be integrated into a unit;
- the above integrated unit may be implemented in the form of hardware, or in the form of hardware plus software functional units.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Priority Applications (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP18920018.1A EP3761703B1 (en) | 2018-05-21 | 2018-11-20 | Session processing method and device, computer storage medium |
| JP2020557227A JP2021525015A (ja) | 2018-05-21 | 2018-11-20 | セッション処理方法、装置及びコンピュータ記憶媒体 |
| CN201880067822.8A CN111247833A (zh) | 2018-05-21 | 2018-11-20 | 一种会话处理方法及装置、计算机存储介质 |
| AU2018424780A AU2018424780A1 (en) | 2018-05-21 | 2018-11-20 | Session processing method and device, computer storage medium |
| KR1020207030374A KR20210010851A (ko) | 2018-05-21 | 2018-11-20 | 세션 처리 방법, 장치 및 컴퓨터 기억 매체 |
| TW108116511A TW202005435A (zh) | 2018-05-21 | 2019-05-14 | 一種會話處理方法及裝置、電腦存儲媒介 |
| US17/031,882 US11627508B2 (en) | 2018-05-21 | 2020-09-24 | Session processing method and device, computer storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (8)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201810491348.3 | 2018-05-21 | ||
| CN201810491348 | 2018-05-21 | ||
| CN201810621962.7 | 2018-06-15 | ||
| CN201810621962 | 2018-06-15 | ||
| CN201810664945 | 2018-06-25 | ||
| CN201810664945.1 | 2018-06-25 | ||
| CN201810924672.X | 2018-08-14 | ||
| CN201810924672 | 2018-08-14 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US17/031,882 Continuation US11627508B2 (en) | 2018-05-21 | 2020-09-24 | Session processing method and device, computer storage medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2019223267A1 true WO2019223267A1 (zh) | 2019-11-28 |
Family
ID=68615666
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2018/116549 Ceased WO2019223267A1 (zh) | 2018-05-21 | 2018-11-20 | 一种会话处理方法及装置、计算机存储介质 |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11627508B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP3761703B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP2021525015A (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR20210010851A (enExample) |
| CN (2) | CN111757405B (enExample) |
| AU (1) | AU2018424780A1 (enExample) |
| TW (1) | TW202005435A (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2019223267A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11627508B2 (en) | 2018-05-21 | 2023-04-11 | Guangdong Oppo Mobile Telecommunications Corp., Ltd. | Session processing method and device, computer storage medium |
| EP4224796A4 (en) * | 2020-10-22 | 2023-10-25 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | COMMUNICATION METHOD AND DEVICE |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110636568B (zh) | 2018-06-25 | 2021-07-09 | 华为技术有限公司 | 通信方法和通信装置 |
| US11903065B2 (en) * | 2018-12-20 | 2024-02-13 | Sony Group Corporation | Telecommunications apparatus and methods |
| CN111586769B (zh) * | 2019-02-15 | 2021-10-15 | 华为技术有限公司 | 无线通信系统中的切换方法、装置及系统 |
| CN113825181B (zh) * | 2020-06-18 | 2023-08-15 | 中国移动通信有限公司研究院 | 切片管理方法、装置、接入网设备及核心网设备 |
| CN111953618B (zh) * | 2020-08-21 | 2022-07-19 | 锐捷网络股份有限公司 | 一种多级并行交换架构下的解乱序方法、装置及系统 |
| USD1030718S1 (en) | 2020-11-11 | 2024-06-11 | Apple Inc. | Case |
| USD1035275S1 (en) | 2021-10-22 | 2024-07-16 | Apple Inc. | Case |
| TWI822066B (zh) * | 2022-01-11 | 2023-11-11 | 啟碁科技股份有限公司 | 通訊設備及其自適應服務品質設置方法 |
| CN118235517A (zh) * | 2022-01-27 | 2024-06-21 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | 无线通信方法、远端ue以及网元 |
| CN114599066B (zh) * | 2022-01-29 | 2024-06-11 | 北京全路通信信号研究设计院集团有限公司 | 一种基于无线网络的无线闭塞中心切换方法及系统 |
| CN120958874A (zh) * | 2023-04-25 | 2025-11-14 | 深圳Tcl新技术有限公司 | 网络切换增强方法、网络系统及网络节点 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102387557A (zh) * | 2010-08-30 | 2012-03-21 | 华为技术有限公司 | 反向单一无线语音呼叫连续性的处理方法、设备及系统 |
| CN105450367A (zh) * | 2014-09-01 | 2016-03-30 | 电信科学技术研究院 | 一种进行数据传输的方法和设备 |
| WO2016140757A1 (en) * | 2015-03-04 | 2016-09-09 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Dual link handover |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080095114A1 (en) * | 2006-10-21 | 2008-04-24 | Toshiba America Research, Inc. | Key Caching, QoS and Multicast Extensions to Media-Independent Pre-Authentication |
| EP2835925B1 (en) * | 2013-08-09 | 2018-08-08 | Panasonic Intellectual Property Corporation of America | Efficient Status Reporting for UEs in dual connectivity during mobility |
| CN104822169B (zh) * | 2014-01-30 | 2019-01-25 | 上海诺基亚贝尔股份有限公司 | 用于为用户设备的切换提供服务的方法、基站和双连接系统 |
| CN104935414B (zh) * | 2014-03-21 | 2019-05-24 | 上海诺基亚贝尔股份有限公司 | 一种在双连接系统中传输信息的方法和装置 |
| US10772021B2 (en) * | 2014-12-05 | 2020-09-08 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Low latency and/or enhanced component carrier discovery for services and handover |
| KR20180038716A (ko) * | 2016-10-07 | 2018-04-17 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 단말의 시그널링 메시지를 Network Function 간 전달하는 방안 |
| GB2555445B (en) * | 2016-10-28 | 2020-07-15 | Canon Kk | Multi-copy data transmission with rate adaptation |
| CN111757405B (zh) | 2018-05-21 | 2021-11-16 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | 一种会话处理方法及装置 |
-
2018
- 2018-11-20 CN CN202010500023.4A patent/CN111757405B/zh active Active
- 2018-11-20 KR KR1020207030374A patent/KR20210010851A/ko not_active Withdrawn
- 2018-11-20 CN CN201880067822.8A patent/CN111247833A/zh active Pending
- 2018-11-20 JP JP2020557227A patent/JP2021525015A/ja not_active Withdrawn
- 2018-11-20 EP EP18920018.1A patent/EP3761703B1/en active Active
- 2018-11-20 AU AU2018424780A patent/AU2018424780A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2018-11-20 WO PCT/CN2018/116549 patent/WO2019223267A1/zh not_active Ceased
-
2019
- 2019-05-14 TW TW108116511A patent/TW202005435A/zh unknown
-
2020
- 2020-09-24 US US17/031,882 patent/US11627508B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102387557A (zh) * | 2010-08-30 | 2012-03-21 | 华为技术有限公司 | 反向单一无线语音呼叫连续性的处理方法、设备及系统 |
| CN105450367A (zh) * | 2014-09-01 | 2016-03-30 | 电信科学技术研究院 | 一种进行数据传输的方法和设备 |
| WO2016140757A1 (en) * | 2015-03-04 | 2016-09-09 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Dual link handover |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| SAMSUNG: "End marker handling in HO and DC", 3GPP TSG-RAN WG3 #99BIS MEETING, R3-181886, vol. RAN WG3, 6 April 2018 (2018-04-06), Sanya, China, pages 1 - 5, XP051416790 * |
| See also references of EP3761703A4 * |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11627508B2 (en) | 2018-05-21 | 2023-04-11 | Guangdong Oppo Mobile Telecommunications Corp., Ltd. | Session processing method and device, computer storage medium |
| EP4224796A4 (en) * | 2020-10-22 | 2023-10-25 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | COMMUNICATION METHOD AND DEVICE |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2021525015A (ja) | 2021-09-16 |
| EP3761703B1 (en) | 2023-06-28 |
| CN111757405A (zh) | 2020-10-09 |
| TW202005435A (zh) | 2020-01-16 |
| EP3761703A1 (en) | 2021-01-06 |
| CN111757405B (zh) | 2021-11-16 |
| AU2018424780A1 (en) | 2020-11-19 |
| KR20210010851A (ko) | 2021-01-28 |
| EP3761703A4 (en) | 2021-05-05 |
| US20210014756A1 (en) | 2021-01-14 |
| US11627508B2 (en) | 2023-04-11 |
| CN111247833A (zh) | 2020-06-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN111757405B (zh) | 一种会话处理方法及装置 | |
| US11818603B2 (en) | Packet duplication | |
| CN112740824B (zh) | 恢复请求随后释放和重定向 | |
| CN108738086B (zh) | 一种用户面重选的方法及装置 | |
| CN110519807B (zh) | 一种通信方法及装置 | |
| CN113630827B (zh) | 支持切换的方法及对应的基站和网络节点 | |
| CN112020873B (zh) | 用于发送和接收数据包流的方法和相关设备 | |
| CN109246747B (zh) | 前向接口的建立方法、ue接入方法、ue切换方法及装置 | |
| WO2015184889A1 (zh) | 一种用户设备切换基站的方法及基站、用户设备 | |
| WO2015100733A1 (zh) | 一种用户设备切换方法及基站 | |
| WO2020146991A1 (zh) | 一种数据流处理方法、设备及存储介质 | |
| WO2018103675A1 (zh) | 数据流重映射方法及装置和用户设备、ran设备 | |
| CN115707053A (zh) | 一种网络切换方法、装置及网络设备 | |
| WO2024000110A1 (zh) | 一种小区切换方法及装置、终端设备、网络设备 | |
| CN111757397A (zh) | 一种进行数据前转的方法及设备 | |
| WO2020258018A1 (zh) | 一种数据包处理方法、设备及存储介质 | |
| WO2020163999A1 (zh) | 无线通信的方法和设备 | |
| CN101193440A (zh) | 在切换过程中确定分组数据转发方式的方法、系统及装置 | |
| CN101175313B (zh) | 分组交换域业务的通信方法、系统及设备 | |
| CN115696385A (zh) | 用户面安全策略配置方法及相关设备 | |
| CN113507733A (zh) | 一种基于mec的用户切换方法、服务器和存储介质 | |
| CN102282808B (zh) | 一种数据的传输方法、相关设备和通信系统 | |
| WO2022089660A1 (zh) | 切换方法、终端和网络侧设备 | |
| CN100527709C (zh) | 移动通信分组切换过程中监控临时块流无线资源的方法 | |
| CN118804145A (zh) | 上行数据压缩方法及基站 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 18920018 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2018920018 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20200928 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2020557227 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2018424780 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20181120 Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |