WO2017192013A1 - 팥을 포함하는 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 조성물 - Google Patents
팥을 포함하는 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 조성물 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017192013A1 WO2017192013A1 PCT/KR2017/004701 KR2017004701W WO2017192013A1 WO 2017192013 A1 WO2017192013 A1 WO 2017192013A1 KR 2017004701 W KR2017004701 W KR 2017004701W WO 2017192013 A1 WO2017192013 A1 WO 2017192013A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- muscle
- extract
- exercise performance
- improving
- red bean
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A23—FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS; TREATMENT THEREOF, NOT COVERED BY OTHER CLASSES
- A23L—FOODS, FOODSTUFFS, OR NON-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES, NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES A21D OR A23B-A23J; THEIR PREPARATION OR TREATMENT, e.g. COOKING, MODIFICATION OF NUTRITIVE QUALITIES, PHYSICAL TREATMENT; PRESERVATION OF FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS, IN GENERAL
- A23L33/00—Modifying nutritive qualities of foods; Dietetic products; Preparation or treatment thereof
- A23L33/10—Modifying nutritive qualities of foods; Dietetic products; Preparation or treatment thereof using additives
- A23L33/105—Plant extracts, their artificial duplicates or their derivatives
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K36/00—Medicinal preparations of undetermined constitution containing material from algae, lichens, fungi or plants, or derivatives thereof, e.g. traditional herbal medicines
- A61K36/18—Magnoliophyta (angiosperms)
- A61K36/185—Magnoliopsida (dicotyledons)
- A61K36/48—Fabaceae or Leguminosae (Pea or Legume family); Caesalpiniaceae; Mimosaceae; Papilionaceae
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/18—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition
- A61K8/96—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing materials, or derivatives thereof of undetermined constitution
- A61K8/97—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing materials, or derivatives thereof of undetermined constitution from algae, fungi, lichens or plants; from derivatives thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61Q—SPECIFIC USE OF COSMETICS OR SIMILAR TOILETRY PREPARATIONS
- A61Q19/00—Preparations for care of the skin
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a composition for improving muscle function or improving exercise performance, which contains red beans extract, red beans derived protein and red beans derived peptide as active ingredients.
- Muscle atrophy is caused by a gradual decrease in muscle mass and refers to muscle weakness and degeneration (Cell, 119 (7): 907-910, 2004). Muscular atrophy is promoted by inactivity, oxidative stress or chronic inflammation and impairs muscle function and motor capacity (Clinical Nutrition, 26 (5): 524-534, 2007).
- muscle mass which is maintained by the balance of muscle protein synthesis and degradation. Muscular dystrophy occurs when proteolysis occurs more than synthesis (The International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 37 (10): 1985-1996, 2005).
- Muscle size is controlled by intracellular signaling pathways that induce anabolism or catabolism in the muscle, and when there are more signaling reactions that induce synthesis than muscle protein degradation Muscle protein synthesis is increased, which is manifested as an increase in muscle size (hypertrophy) or muscle fiber number (hyperplasia) (The Korea Journal of Sports Science, 20 (3): 1551-1561, 2011).
- Muscle hypertrophy inducers induce protein synthesis by phosphorylating downstream proteins from the stimulation of the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K) / Akt pathway in muscle cells.
- PI3K phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase
- mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin
- Akt phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase
- muscle cells can be regulated by various muscle regulatory factors.
- MyoD promotes the process of myoblast myotube through the induction of myogenin expression. Muscle fibers formed through this process are bundled to form muscles finally (Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 70: 4117-4130, 2013).
- Vigna one of the representative beans angularis is a perennial herb that belongs to the Vigna spp. of the Fabaceae family and is the second most important legume crop after beans.
- Red beans are rich in vitamin B1, and when mixed with rice to make rice, it is known that it provides vitamins that are not enough for rice and is effective in recovering from fatigue as well as in various diseases.
- Saponin in red beans, along with fiber, helps to make bowel movements, cleanses the intestines by detoxifying, promotes bowel movements, and is also used to improve kidney disease or hangover (Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology, 42 (6): 693 -698, 2010).
- red beans are antioxidant (Journal of Food Lipids 11 (4): 278-286, 2004), antidiabetic (Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 68 (12): 24212426, 2004), antibacterial (Phytotherapy Research 20 (2) : 162164, 2006) Whitening (International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12 (10): 7048-7058, 2011) has been reported, but there is no report on the effects related to muscle function improvement.
- the present inventors have tried to develop a therapeutic agent for diseases related to muscle function deterioration such as muscle atrophy derived from plant extracts.
- extracts of red beans or legumes have been shown to express proteins related to muscle protein synthesis and muscle mass in muscle cells. Since the level of phosphorylation can be increased, the red bean or red bean extract of the present invention has been completed by confirming that it can be used as an active ingredient for preventing and treating muscle diseases or improving muscle function.
- the present inventors have completed the present invention by confirming that there is an activity to improve muscle function or exercise performance in red beans as a result of searching for natural materials which have an activity of improving muscle function or improving exercise performance and can be safely applied.
- the object of the present invention is red beans ( Vigna Angularis ) comprising the extract as an active ingredient, to provide a composition for treating muscle diseases or improving exercise performance.
- Still another object of the present invention is to provide a composition for treating muscle diseases or improving exercise performance, comprising red bean-derived protein or peptide as an active ingredient.
- Still another object of the present invention is to provide a composition for improving muscle function, which comprises red bean extract as an active ingredient.
- Still another object of the present invention is to provide a composition for improving muscle function, comprising a red bean-derived protein or peptide as an active ingredient.
- the present invention is a red bean ( Vigna Provided is a pharmaceutical composition for treating muscle diseases or improving athletic performance, comprising angularis extract as an active ingredient.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition for treating muscle diseases or improving exercise performance, comprising a red bean-derived protein or peptide as an active ingredient.
- the present invention provides a composition for improving muscle function, comprising an extract of red beans ( Vigna angularis ) as an active ingredient.
- the present invention provides a composition for improving muscle function, comprising a red bean-derived protein or peptide as an active ingredient.
- the present invention provides a composition for preventing and treating muscle diseases, improving muscle function, or improving athletic performance, comprising red bean extract, red bean derived protein or red bean derived peptide as an active ingredient.
- the red bean extract of the present invention promotes the mRNA transcription level and protein activity of factors involved in muscle function, muscle mass control or differentiation of muscle cells in muscle cells, thereby enabling improvement of muscle function or exercise performance due to muscle mass increase, It may exhibit an effect of preventing, treating or improving such as a decrease in exercise performance, muscle function, and muscle loss caused by various diseases.
- the red bean extract, red bean-derived protein and red bean-derived peptide of the present invention can be effectively used for medicines or foods as there is no side effect in the body as a natural substance.
- Figure 1 shows the results of measuring the activity of mTOR according to the treatment of red bean ethanol extract in L6 muscle cells.
- Figure 2 shows the results of measuring the protein expression of p-p70S6K and p-4EBP1 mRNA translation-related biomarkers according to the treatment of red bean ethanol extract in L6 muscle cells.
- Figure 3 shows the results of measuring the mRNA expression levels of muscle protein degradation promoting biomarkers MuRF-1 and atrogin-1 according to the treatment of red bean ethanol extract in L6 muscle cells.
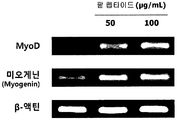
- Figure 4 shows the results of measuring the mRNA expression levels of muscle differentiation biomarkers MyoD and myogenin according to the treatment of red bean ethanol extract in L6 muscle cells.
- Figure 5 shows the results of measuring the activity of mTOR according to the treatment of hot water extract of red beans in L6 muscle cells.
- Figure 6 shows the results of measuring the expression level of mTOR in the L6 muscle cells, the red bean subcritical extract treatment.
- Figure 7 shows the results of measuring the expression level of mTOR according to the red bean peptide treatment by red bean protein and enzyme reaction in L6 muscle cells.
- Figure 8 shows the results of measuring the protein expression of p-p70S6K and p-4EBP1 mRNA translation-related biomarkers according to the red bean peptide treatment in L6 muscle cells.
- Figure 9 shows the results of measuring the mRNA expression of muscle differentiation biomarkers MyoD and myoenin according to the red bean peptide treatment in L6 muscle cells.
- Figure 10 shows the results of measuring the activity of mTOR according to the treatment of black bean ethanol extract in L6 muscle cells
- Figure 11 shows the results of measuring the activity of PGC-1 ⁇ according to the treatment of red bean ethanol extract in COS-7 kidney cells.
- Figure 13 shows the results of measuring the activity of PGC-1 ⁇ according to the treatment of red beans peptides by red beans protein and enzyme reaction in L6 muscle cells.
- Figure 15 shows the results of measuring the activity of PGC-1 ⁇ according to the treatment of black bean ethanol extract in COS-7 kidney cells.
- Figure 16 shows the results of measuring muscle strength according to the treatment of red bean ethanol extract in muscle atrophy induced rats.
- Figure 17 shows the results of measuring endurance according to the treatment of red bean ethanol in muscle atrophy induced rats (a: exercise time, b: movement distance).
- Figure 18 shows the result of measuring the weight of the proximal bone muscle according to the treatment of red bean ethanol extract in muscle atrophy induced rats.
- the present invention red beans ( Vigna Provided is a pharmaceutical composition for treating muscle diseases or improving athletic performance, comprising angularis extract as an active ingredient.
- Vigna angularis is a red bean ( V. angularis WFWight) and black bean ( V. angularis ) belonging to the Vigna spp. of the Fabaceae. var. angularis) or other seeds of the plant are dried and may be used alone or in combination.
- 'red bean extract' means an extract obtained by extracting the red bean.
- the preparation method of the red bean extract may be obtained by extracting the red bean from the red bean with one or more solvents selected from the group consisting of water, an organic solvent of C 1 to C 6 , a subcritical fluid and a supercritical fluid. More specifically, the solvent is alcohol having 1 to 6 carbon atoms (aceco), acetone (acetone), ether (ether), benzene (benzene), chloroform (chloroform), ethyl acetate (ethyl acetate), methylene chloride (methylene chloride) It may be at least one selected from the group consisting of hexane, cyclohexane and petroleum ether.
- the extract is preferably prepared by a manufacturing method comprising the following steps, but is not limited thereto:
- step 3 drying the filtered extract of step 2) under reduced pressure.
- the red beans of step 1) can be used without limitation, such as those grown or commercially available.
- the extraction method of the red bean extract conventional methods in the art, such as filtration, hot water extraction, dipping extraction, reflux cooling extraction, ultrasonic extraction, ultrahigh pressure extraction and subcritical extraction, can be used.
- the extraction method when performing the ultra-high pressure extraction, it is preferable to extract at a pressure of 100 to 500 Mpa.
- the decompression concentration in step 3) preferably uses a vacuum decompression concentrator or a vacuum rotary evaporator, but is not limited thereto.
- the drying is preferably reduced pressure drying, vacuum drying, boiling drying, spray drying or freeze drying, but is not limited thereto.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition for treating muscle diseases or improving exercise performance, comprising a red bean-derived protein or peptide as an active ingredient.
- 'red bean-derived protein' may be obtained by a method consisting of the following steps i) to v):
- step ii) removing the hexane extract extracted in step i) and adding water to the foil and leaving it at pH 7.0 to 10.0;
- step iv) leaving the supernatant obtained in step iii) again at a pH of 2.0 to 6.0;
- step iv) centrifuging the solution left in step iv) to obtain precipitated precipitate as red beans derived protein.
- 'peptide-derived peptide' refers to a protein obtained by treating proteolytic enzymes on red beans protein isolated from red beans.
- adzuki bean-derived peptides can be obtained by a method consisting of the following steps i) to vii):
- step ii) removing the hexane extract extracted in step i) and adding water to the foil and leaving it at pH 7.0 to 10.0;
- step iv) leaving the supernatant obtained in step iii) again at a pH of 2.0 to 6.0;
- step iv) centrifuging the solution left in step iv) to obtain precipitated precipitate as red beans derived protein
- step v) adding a hydrolase to the red bean-derived protein obtained in step v) and performing an enzymatic reaction, followed by filtration to remove the precipitate;
- step vii) lyophilizing the filtrate from which the precipitate is removed in step vi) to obtain a peptide.
- the 'hydrolase' refers to alcalase, flavorzyme, neutrase, protamex and protease-NP (Protease-NP). It may be any one or more proteolytic enzyme selected from the group consisting of.
- Muscle disease herein is preferably a disease reported in the art as a muscle disease due to muscle function decline, muscle wasting or muscle degeneration.
- the muscle wasting or degeneration is caused by genetic factors, acquired factors, aging, etc., muscle wasting is characterized by a gradual loss of muscle mass, weakening and degeneration of muscle, especially skeletal or veterinary and cardiac muscle.
- Examples of related diseases include atony, muscular atrophy, muscular dystrophy, muscle degeneration, myasthenia gravis, cachexia and sarcopenia.
- the composition of the present invention has an effect of increasing muscle mass, the muscle does not limit its kind.
- 'muscle' refers to tendons, muscles, and tendons
- 'muscle function' or 'muscle function' means an ability to exert a force by contraction of muscles, and the muscles overcome the resistance.
- Muscle strength capable of exerting maximum resilience
- Muscle endurance the ability to indicate how long or how many times a muscle can repeat contraction and relaxation at a given weight
- quickness which is the ability to exert a strong force in a short time.
- the muscle function is proportional to muscle mass, and the term 'muscle function improvement' means improving muscle function in a more positive direction.
- the 'exercise performance ability' is a fast, strong, accurate, long, skillfully when the physical movements seen in daily life or sports are divided into running, running, throwing, swimming, etc.
- the exercise performance is defined as factors such as muscle strength, agility and endurance.
- the term 'improving athletic performance' refers to improving or improving athletic performance.
- composition of the present invention is a pharmaceutical composition for improving exercise performance, it can be used for the prevention or treatment of diseases caused by the degradation of exercise ability.
- diseases related thereto include degenerative diseases, mitochondrial disorders, endurance, impairment, lethargy, muscle discard and depression.
- the composition of the present invention has an effect of improving exercise performance, and does not limit the form and type of exercise.
- the pharmaceutical composition for improving muscle function of the present invention can be used for the prevention or treatment of muscle diseases caused by muscle wastage or degeneration.
- Muscle depletion and degeneration occur due to genetic factors, acquired factors, aging, etc., muscle depletion is characterized by a gradual loss of muscle mass, weakening and degeneration of muscles, especially skeletal or veterinary and cardiac muscles.
- Examples of related diseases include atony, muscular atrophy, muscular dystrophy, muscle degeneration, myasthenia gravis, cachexia and sarcopenia.
- the composition of the present invention has an effect of increasing muscle mass, the muscle does not limit its kind.
- the pharmaceutical composition for improving exercise performance of the present invention can be used for the prevention or treatment of diseases caused by exercise capacity decline.
- diseases include mitochondrial disorders, endurance, impairment, lethargy, muscle abandonment and depression.
- the composition of the present invention has an effect of improving exercise performance, and does not limit the form and type of exercise.
- the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention may further comprise a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
- Pharmaceutically acceptable carriers may further include, for example, carriers for oral administration or carriers for parenteral administration.
- Carriers for oral administration may include lactose, starch, cellulose derivatives, magnesium stearate, stearic acid and the like.
- Carriers for parenteral administration may also include water, suitable oils, saline, aqueous glucose, glycols, and the like.
- stabilizers and preservatives may be further included. Suitable stabilizers include antioxidants such as sodium hydrogen sulfite, sodium sulfite or ascorbic acid.
- Suitable preservatives include benzalkonium chloride, methyl- or propyl-paraben and chlorobutanol.
- Other pharmaceutically acceptable carriers may be referred to those described in the following documents (Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences, 19th ed., Mack Publishing Company, Easton, PA, 1995).
- composition of the present invention can be administered to any mammal, including humans.
- parenteral administration methods include, but are not limited to, intravenous, intramuscular, intraarterial, intramedullary, intradural, intracardiac, transdermal, subcutaneous, intraperitoneal , Intranasal, intestinal, topical, sublingual or rectal administration.
- the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention may be formulated into a preparation for oral or parenteral administration according to the route of administration as described above.
- one or more buffers e.g. saline or PBS
- antioxidants e.g. saline or PBS
- bacteriostatic agents e.g. EDTA or glutathione
- fillers e.g., extenders, binders, adjuvants (e.g. aluminum hydroxide) Side)
- suspending agents e.g. aluminum hydroxide
- Solid form preparations for oral administration include tablets, pills, powders, granules, solutions, gels, syrups, slurries, suspensions, or capsules, and the like may include at least one excipient in the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention.
- starch including corn starch, wheat starch, rice starch, potato starch, etc.
- calcium carbonate sucrose, lactose, dextrose, sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol, erythritol maltitol
- It can be prepared by mixing cellulose, methyl cellulose, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and hydroxypropylmethyl-cellulose or gelatin.
- tablets or dragees can be obtained by combining the active ingredients with solid excipients and then grinding them and adding suitable auxiliaries and then processing them into granule mixtures.
- Liquid preparations for oral use include suspensions, solutions, emulsions, or syrups, and may include various excipients, such as wetting agents, sweeteners, fragrances, or preservatives, in addition to water or liquid paraffin, which are commonly used simple diluents. .
- crosslinked polyvinylpyrrolidone, agar, alginic acid or sodium alginate may be added as a disintegrant, and may further include an anticoagulant, a lubricant, a humectant, a perfume, an emulsifier, a preservative, and the like. .
- compositions of the present invention may be formulated according to methods known in the art in the form of injections, transdermal and nasal inhalants with suitable parenteral carriers.
- suitable parenteral carriers include, but are not limited to, solvents or dispersion media comprising water, ethanol, polyols (e.g., glycerol, propylene glycol and liquid polyethylene glycols, etc.), mixtures thereof and / or vegetable oils Can be.
- suitable carriers include Hanks' solution, Ringer's solution, phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing triethanol amine or sterile water for injection, 10% ethanol, 40% propylene glycol and 5% dextrose Etc. can be used.
- PBS phosphate buffered saline
- various antibacterial and antifungal agents such as parabens, chlorobutanol, phenol, sorbic acid, thimerosal, and the like may be further included.
- the injection may in most cases further comprise an isotonic agent such as sugar or sodium chloride.
- transdermal administrations In the case of transdermal administrations, ointments, creams, lotions, gels, external preparations, pasta preparations, linen preparations, air rolls and the like are included.
- 'transdermal administration' means that the pharmaceutical composition is locally administered to the skin so that an effective amount of the active ingredient contained in the pharmaceutical composition is delivered into the skin.
- the compounds used according to the invention may be pressurized packs or by means of suitable propellants, for example dichlorofluoromethane, trichlorofluoromethane, dichlorotetrafluoroethane, carbon dioxide or other suitable gas. It can be delivered conveniently from the nebulizer in the form of an aerosol spray. In the case of a pressurized aerosol, the dosage unit can be determined by providing a valve to deliver a metered amount.
- gelatin capsules and cartridges for use in inhalers or blowers can be formulated to contain a mixture of the compound and a suitable powder base such as lactose or starch. Formulations for parenteral administration are described in Remington's Pharmaceutical Science, 15th Edition, 1975. Mack Publishing Company, Easton, Pennsylvania 18042, Chapter 87: Blaug, Seymour, a prescription generally known in all pharmaceutical chemistries.
- the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention may provide a desirable muscle function improving effect or exercise performance enhancing effect when the red bean extract, red bean protein or red bean peptide is contained in an effective amount.
- the "effective amount” refers to an amount that exhibits a higher response than the negative control, and preferably refers to an amount sufficient to improve muscle function or improve exercise performance.
- red bean extract, red bean protein or red bean peptide may be included in an amount of 0.01 to 99.99%, and the remaining amount may be occupied by a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
- the effective amount of the red bean extract, red bean protein or red bean peptide included in the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention will vary depending on the form in which the composition is commercialized.
- the total effective amount of the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention may be administered to a patient in a single dose and may be administered by a fractionated treatment protocol which is administered in multiple doses for a long time.
- the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention may vary the content of the active ingredient depending on the extent of the disease. When administered parenterally, it is preferably administered in an amount of 0.01 to 50 mg, more preferably 0.1 to 30 mg per kg of body weight per day, based on the red bean extract, red bean protein or red bean peptide, and red bean when orally administered.
- red bean protein or red bean peptide On the basis of extract, red bean protein or red bean peptide, it can be administered in one or several times so as to be administered in an amount of preferably 0.01 to 100 mg, more preferably 0.01 to 10 mg per kg of body weight per day.
- the dose of the adzuki bean extract, the adzuki protein or the adzuki bean peptide is considered in consideration of various factors such as the age, weight, health condition, sex, severity of the disease, diet and excretion rate, as well as the route of administration and frequency of treatment of the pharmaceutical composition. Since effective dosages for these are determined, those of ordinary skill in the art should consider the effective use of red bean extract, red bean protein or red bean peptides for specific purposes to improve muscle function or enhance motor performance. Will determine the quantity.
- the pharmaceutical composition according to the present invention is not particularly limited to its formulation, route of administration and method of administration as long as the effect of the present invention is shown.
- composition of the present invention may be used alone or in combination with methods using surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy or biological response modifiers.
- the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention may also be provided in a formulation of an external preparation comprising red bean extract, red bean protein or red bean peptide as an active ingredient.
- the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention is used as an external preparation for skin, it is additionally used for fatty substances, organic solvents, solubilizers, thickening and gelling agents, emollients, antioxidants, suspending agents, stabilizers, foaming agents, fragrances, interfaces.
- Skin such as active agents, water, ionic emulsifiers, nonionic emulsifiers, fillers, metal ion sequestrants, chelating agents, preservatives, vitamins, blockers, wetting agents, essential oils, dyes, pigments, hydrophilic active agents, lipophilic active agents or lipid vesicles It may contain adjuvants commonly used in the field of dermatology, such as any other ingredients commonly used in external preparations. The ingredients may also be introduced in amounts generally used in the field of dermatology.
- the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention when provided as an external preparation for skin, it may be a formulation such as, but not limited to, an ointment, a patch, a gel, a cream, or a spray.
- the present invention provides a food composition for improving muscle function or improving exercise performance.
- the food composition of the present invention is a food composition for improving muscle function
- it may be used for the prevention or improvement of diseases reported in the art as muscle diseases due to muscle function deterioration, muscle wasting or muscle degeneration.
- the muscle wasting or degeneration is caused by genetic factors, acquired factors, aging, etc., muscle wasting is characterized by a gradual loss of muscle mass, weakening and degeneration of muscle, especially skeletal or veterinary and cardiac muscle.
- related diseases include atony, muscular atrophy, muscular dystrophy, muscle degeneration, myasthenia gravis, cachexia and sarcopenia.
- the composition of the present invention has an effect of increasing muscle mass, the muscle does not limit its kind.
- the muscle function is proportional to muscle mass, and the term 'muscle function improvement' means improving muscle function in a more positive direction.
- the food composition of the present invention is a food composition for improving athletic performance
- it may be used for the prevention or treatment of diseases caused by the deterioration of athletic performance.
- diseases related thereto include degenerative diseases, mitochondrial disorders, endurance, impairment, lethargy, muscle discard and depression.
- the composition of the present invention has an effect of improving exercise performance, and does not limit the form and type of exercise.
- the food composition of the present invention includes all forms such as functional food, nutritional supplement, health food, food additives and feed, and includes animals such as humans or livestock. It is for eating. Food compositions of this type can be prepared in various forms according to conventional methods known in the art.
- Food compositions of this type can be prepared in various forms according to conventional methods known in the art.
- General foods include, but are not limited to, beverages (including alcoholic beverages), fruits and processed foods (e.g. canned fruit, canned foods, jams, marmalade, etc.), fish, meat and processed foods (e.g. hams, sausages) Cornbread, etc.), breads and noodles (e.g. udon, soba noodles, ramen, spagate, macaroni, etc.), fruit juices, various drinks, cookies, malts, dairy products (e.g.
- red bean extract and red bean peptide may be prepared by adding the red bean extract and red bean peptide.
- a nutritional supplement is not limited thereto, it can be prepared by adding a red bean extract, red bean protein or red bean peptide to capsules, tablets, pills and the like.
- a health functional food but not limited to, for example, the red bean extract itself in the form of tea, juice and drinks can be consumed by liquefying, granulated, encapsulated and powdered to drink (healthy drink) Can be.
- red bean extract in the form of food additives, it can be prepared in powder or concentrate form.
- the red bean extract, red bean protein or red bean peptide can be prepared in the form of a composition by mixing with known active ingredients known to improve muscle function or exercise performance.
- the health beverage composition may contain various flavors or natural carbohydrates as additional components, as in general beverages.
- the above-mentioned natural carbohydrates include monosaccharides such as glucose and fructose; Disaccharides such as maltose and sucrose; Polysaccharides such as dextrin, cyclodextrin; Sugar alcohols such as xylitol, sorbitol, and erythritol.
- Sweeteners include natural sweeteners such as taumartin, stevia extract; Synthetic sweeteners such as saccharin and aspartame;
- the proportion of the natural carbohydrate is generally about 0.01 to 0.04 g, preferably about 0.02 to 0.03 g per 100 mL of the composition of the present invention.
- Red bean extract, red bean protein or red bean peptide may be contained as an active ingredient in the food composition for improving muscle function or exercise performance, the amount of which is particularly effective in achieving an action for improving muscle function or exercise performance. Although not limited, it is preferably 0.01 to 100% by weight based on the total weight of the composition.
- the food composition of the present invention may be prepared by mixing with the red bean extract and other active ingredients known to be effective in the composition for improving muscle function or exercise performance.
- the health food of the present invention is various nutrients, vitamins, electrolytes, flavors, coloring agents, pectic acid, salts of pectic acid, alginic acid, salts of alginic acid, organic acids, protective colloidal thickeners, pH regulators, stabilizers, preservatives, Glycerin, alcohol or carbonation agent, and the like.
- the health food of the present invention may contain a flesh for preparing natural fruit juice, fruit juice beverage, or vegetable beverage. These components can be used independently or in combination. The proportion of such additives is not critical but is generally selected in the range of 0.01 to 0.1 parts by weight per 100 parts by weight of the composition of the present invention.
- Dried Red Beans Vigna After angularis WFWight was ground with a mixer, 100 g of the ground red bean powder was immersed in 1 L of 100% methanol and left at room temperature for 24 hours. The obtained extract was filtered under Whatman No. 2 filter paper under reduced pressure, and the filtered extract was concentrated with a vacuum rotary concentrator to obtain a red bean methanol extract from which the solvent component was removed.
- the dried red bean ( V. angularis WFWight) was ground with a mixer, and then 100 g of the ground red bean powder was immersed in 1 L of 100%, 70%, 50% or 30% ethanol, and allowed to stand at room temperature for 24 hours. The process of obtaining was repeated three times.
- the resulting extract was filtered under reduced pressure with Whatman No. 2 filter paper, and the filtered extract was concentrated with a vacuum rotary concentrator to obtain a red bean ethanol extract from which the solvent component was removed.
- the dried red bean ( V. angularis WFWight) was pulverized with a mixer, and 100 g of the ground red bean powder was immersed in 1 L of 100% ethyl acetate, and left at room temperature for 24 hours. .
- the resulting extract was filtered under reduced pressure with Whatman No. 2 filter paper, and the filtered extract was concentrated with a vacuum rotary concentrator to obtain a red bean ethyl acetate extract from which the solvent component was removed.
- the dried red bean ( V. angularis WFWight) was pulverized with a mixer, and then 100 g of the ground red bean powder was immersed in 1 L of 100% hexane and left at room temperature for 24 hours.
- the resulting extract was filtered under reduced pressure with Whatman No. 2 filter paper, and the filtered extract was concentrated with a vacuum rotary concentrator to obtain a red bean hexane extract from which the solvent component was removed.
- the dried red beans ( V. angularis WFWight) was ground with a mixer, and then 100 g of the ground red beans powder was put in 1 L of water and stirred at 80 ° C. for 2 hours to obtain an extract.
- the resulting extract was filtered under reduced pressure with Whatman No. 2 filter paper, and the filtered extract was concentrated with a vacuum rotary concentrator to obtain a red bean hot water extract from which the solvent component was removed.
- the dried red beans ( V. angularis WFWight) were crushed with a mixer, and then 76 mL of 18% ethanol was put in a polyethylene pack and sealed, and the ultra-high pressure extractor (Frescal MFP-7000; Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Tokyo, Japan) was Extracted using.
- the ultrahigh pressure extraction conditions the extraction pressure was set to 320 MPa and the extraction time was set to 5 minutes.
- the extracted sample was filtered using Whatman No. 2 filter paper, and the filtered extract was concentrated with a vacuum rotary concentrator to remove the solvent component, thereby obtaining a red bean ultra high pressure extract.
- the dried red beans ( V. angularis WFWight) were ground with a mixer, and then 50 g of the ground red beans were placed in a subcritical water reactor (Biovan, Gyeonggi, Korea) with 1 L water and sealed. After sealing, the temperature of the reactor was raised to 200 ° C., and when the temperature of the reactor reached 200 ° C., the temperature was maintained for 20 minutes and extracted. After 20 minutes, the extract was transferred to a storage tank to which cooling water was supplied and rapidly cooled to 30 ° C., followed by centrifugation at 3,600 rpm for 30 minutes to separate the floating residue, and only the supernatant was taken. Red beans subcritical extract was obtained by removing all the solvent using a lyophilizer (ilShin Lab Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea).
- Proteolytic enzyme 1% alkalase (Novozymes, Bagsvaerd, Denmark) was added to the red bean protein obtained in Example ⁇ 2-1> and subjected to enzymatic reaction for 50 to 6 hours. After 6 hours, the enzyme was inactivated for 90 to 20 minutes and the precipitate was removed by filtration through Whatman 2 filter paper. The filtered liquid was removed by using a lyophilizer (ilShin Lab Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea) to remove all the water to obtain adzuki beans peptides by the alkalase treatment.
- a lyophilizer ilShin Lab Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea
- Flavorzyme-treated red bean peptides were obtained by treating flavozyme instead of alkalase in the same manner as in Example ⁇ 2-2>.
- Example ⁇ 2-2> instead of the alkalase was treated with procamex (Novozymes) to obtain a red bean peptide by the protamex treatment.
- procamex Novozymes
- Protease-NP Bioland, Asan, Korea
- alkalase Asan, Korea
- Dried Black Bean ( V. angularis) var. angularis) was pulverized with a mixer, and then 100 g of crushed black bean powder was immersed in 1 L of 100%, 70%, 50%, or 30% ethanol, and allowed to stand at room temperature for 24 hours. Repeated.
- the obtained extract was filtered under reduced pressure with Whatman No. 2 filter paper, and the filtered extract was concentrated with a vacuum rotary concentrator to obtain a black bean ethanol extract from which the solvent component was removed.
- the extract obtained was filtered under reduced pressure with Whatman No. 2 filter paper, and the filtered extract was concentrated with a vacuum rotary concentrator to obtain a black bean hexane extract from which the solvent component was removed.
- Dried Black Bean ( V. angularis) var. angularis) was ground with a mixer, and then 100 g of the ground black bean powder was put in 1 L of water and stirred at 80 ° C. for 2 hours to obtain an extract.
- the obtained extract was filtered under reduced pressure with Whatman No. 2 filter paper, and the filtered extract was concentrated with a vacuum rotary concentrator to obtain a black bean hot water extract from which the solvent component was removed.
- Dried Black Bean ( V. angularis) var. Angularis) was pulverized with a mixer, and 76 mL of 18% ethanol was put in a polyethylene pack, sealed, and extracted using an ultrahigh pressure extractor (Frescal MFP-7000; Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Tokyo, Japan).
- an ultrahigh pressure extractor Frscal MFP-7000; Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Tokyo, Japan.
- the extraction pressure was set to 320 MPa and the extraction time was set to 5 minutes.
- the extracted sample was filtered with Whatman No. 2 filter paper, and the filtered extract was concentrated with a vacuum rotary concentrator to remove the solvent component to obtain a black bean ultra high pressure extract.
- Dried Black Bean ( V. angularis) var. angularis) was pulverized, and then 1 kg of the pulverized black bean sample was placed in 1 L hexane and extracted with stirring at room temperature for 4 hours. After removing the hexane extract, water was added to the remaining gourd and left to stand at pH 9, 25 for 30 minutes. The supernatant was collected by centrifugation at 6,000 rpm for 30 minutes, and the supernatant was left to stand again for 30 minutes under the conditions of pH 4.5 and 25. The precipitated protein was obtained by centrifugation at 6,000 rpm for 30 minutes, and the precipitated protein was dissolved in water and neutralized to remove all water using a lyophilizer (ilShin Lab Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea). Black bean protein was obtained.
- Proteolytic enzyme 1% alkalase (Novozymes, Bagsvaerd, Denmark) was added to the black bean protein obtained in Example ⁇ 4-1> and subjected to enzymatic reaction for 50 to 6 hours. After 6 hours, the enzyme was inactivated for 90 to 20 minutes and the precipitate was removed by filtration through Whatman 2 filter paper. The filtered liquid was removed by using a lyophilizer (ilShin Lab Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea) to remove all the water to obtain a black bean peptide by alkalase treatment.
- a lyophilizer ilShin Lab Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea
- Example ⁇ 4-2> the treatment of flavorzyme (Novozymes) instead of alkalase to obtain a black bean peptide by the flavorzyme treatment.
- procamex Novozymes
- Protease-NP Bioland, Chaonan, Korea
- alkalase instead of alkalase was treated in the same manner as in Example ⁇ 4-2> to obtain black bean peptides by protease-NP treatment.
- mTOR protein when phosphorylated and activated, can induce activation of proteins involved in muscle protein synthesis and muscle mass increase in PI3K / Akt signaling pathways in muscle cells.
- mTOR Sandwich ELISA kit Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA, USA
- Myoblasts, L6 cells (ATCC; Manassas, VA, USA) were plated in 6-well plates with Dulbecco's modified Eagle's media (DMEM; Hyclone) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA). Incubated for 24 hours after inoculation to 1 ⁇ 10 5 cell / mL. After incubation, the medium in the wells was removed, exchanged with DMEM (Hyclone) containing 2% horse serum (HS; Hyclone), and further cultured for 6 days to differentiate L6 cells into myotubes.
- DMEM Dulbecco's modified Eagle's media
- FBS Hyclone
- FBS fetal bovine serum
- HS horse serum
- the red bean ethanol extract prepared in 100% ethanol in Example ⁇ 1-2> was treated to the cells at a concentration of 40 ⁇ g / mL and incubated for 12 hours. After incubation, the cells were lysed by treating with a cell lysis buffer. The protein in the cell lysate obtained was quantified by the Bradford (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, CA, USA) method, and then quantitated at a concentration of 1 mg / mL for the cells in the microwell to which the anti-mTOR antibody was attached. Seafood was aliquoted at 50 ⁇ L and incubated at 37 ° C. for 2 hours.
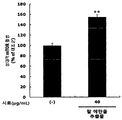
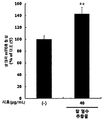
- the activity of mTOR in L6 muscle cells was significantly increased ( ** p ⁇ 0.01) by treatment of red bean ethanol extract.
- the red bean ethanol extract of the present invention has an excellent ability to increase muscle production in muscle cells.
- L6 cells (ATCC), myoblasts, were inoculated to 2 ⁇ 10 5 cells / mL in 6-well plates with DMEM containing 10% FBS (Hyclone). When the cell density reached about 80-85%, the medium in the wells was removed and exchanged with DMEM (Hyclone) containing 2% HS (Hyclone) to differentiate L6 cells into myotubes. After 6 days, the red bean ethanol extract prepared in 100% ethanol in Example ⁇ 1-2> was replaced with DMEM (Hyclone) dissolved in a concentration of 25, 50 or 40 ⁇ g / mL and incubated for 24 hours. At this time, the group treated with 0.01% DMSO instead of the sample was used as a control.
- NP-40 buffer solution EPIS-Biotech, Daejeon, Korea
- protease inhibitor cocktail Sigma-Aldrich St. Louis, MO, USA.
- the obtained cell lysate was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 minutes to obtain a supernatant. Protein concentration in the supernatant was quantitated by Bradford, and then the protein of the concentration was heated for 5 minutes and developed on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel to separate the intracellular protein by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis.
- the isolated protein was transferred to nitrocellulose membrane.
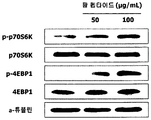
- anti-p-p70S6K antibody, anti-t-p70S6K antibody, anti-p-4EBP1 antibody, anti-t-4EBP1 antibody, or anti- ⁇ -tubulin antibody were each treated with 2.5% bovine serum albumin ( BSA) was diluted 1: 1000 and reacted with the protein delivered to the nitrocellulose membrane as a primary antibody at room temperature for 20 hours.
- BSA bovine serum albumin
- nitrocellulose membrane was washed three times for 10 minutes using (Tris-buffer Saline Tween20 (TBST) .Then, HRP conjugated secondary antibody (Bethyl Laboratories, Inc., Montgomery, TA, USA) was diluted to 2.5% BSA (bioWORLD) to 1: 5000 and reacted with nitrocellulose membrane at room temperature for 2 hours, and washed three times with TBST for 10 minutes. Protein bands were developed using ECL western blot detection reagents (Amersham, Tokyo, Japan), and the protein bands were identified using G; BOX EF imaging system (Syngene, Cambridge, UK). Shown in
- L6 cells (ATCC), myoblasts, were incubated with 2% 10 5 cells / mL in 6-well plates with DMEM (Hyclone) containing 10% FBS (Hyclone). When the cell density reached about 80-85%, the medium in the wells was removed and exchanged for DMEM (Hyclone) containing 2% HS (Hyclone) to differentiate L6 cells into myotubes. Once every two days, the cells were replaced with fresh medium for a total of six days of differentiation.
- the red bean ethanol extract prepared in 100% ethanol in Example ⁇ 1-2> was dissolved in DMEM medium containing 50 ng / mL of TNF- ⁇ at a concentration of 20 or 40 ⁇ g / mL, and then Treated. After 6 hours, total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent (Takara, Osaka, Japan). Total RNA isolated was quantified using NanoDrop 1000; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, Mass., USA.
- RNA 16 ⁇ L RNA was quantified, mixed with Reverse Transcriptase Premix (ELPIS-Biotech), and subjected to a PCR machine (Gene Amp PCR System 2700; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) at 42 ° C 55 minutes, 70 CDNA was synthesized under conditions of 15 minutes.
- PCR samples were prepared by mixing 4 ⁇ L of cDNA in the synthesized cDNA, forward and reverse primer pairs (Bioneer, Deajeon, Korea), and PCR premix (ELPIS-Biotech) of the sequence shown in Table 1 below. PCR was performed by repeating 30 seconds at 30 ° C., 1 minute at 60 ° C., and 1 minute at 72 ° C. for 30 times.
- the cDNA amplified by the PCR result was separated by electrophoresis with 1.5% agarose gel, and cDNA bands were identified using a G; BOX EF imaging system (Syngene). The results are shown in FIG.
- Primer sequences used for PCR in the present invention Amplification gene Sequence name SEQ ID NO: order direction Atrogin-1 Atrogin_F SEQ ID NO: 1 5'-GTCCAGAGAGTCGGCAAGTC-3 ' Forward direction Atrogin_R SEQ ID NO: 2 5'-GTCGGTGATCGTGAGACCTT-3 ' Reverse MuRF-1 MuRF_F SEQ ID NO: 3 5'-TCTACTCGGCCACAGGCGCT-3 ' Forward direction MuRF_R SEQ ID NO: 4 5'-CTTGACAGCTCCCGCCGCAA-3 ' Reverse ⁇ -Actin Actin_F SEQ ID NO: 5 5'-CTGTGTGGATTGGTGGCTCTAT-3 ' Forward direction Actin_R SEQ ID NO: 6 5'-GTGTAAAACGCAGCTCAGTAACA3 ' Reverse
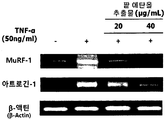
- the red bean ethanol extract of the present invention has an excellent ability to inhibit muscle protein degradation in muscle cells.
- L6 cells (ATCC), myoblasts, were incubated with 2% 10 5 cells / mL in 6-well plates with DMEM (Hyclone) containing 10% FBS (Hyclone).
- DMEM Hexaene
- FBS Hexaene
- the red bean ethanol extract prepared with 100% ethanol in Example ⁇ 1-2> in DMEM (Hyclone) containing 2% HS was 25
- the cells were treated to induce differentiation into myotubes.
- the group treated with 0.01% DMSO instead of the sample was used as a control.
- the sequence of the primer (Bioneer) used for PCR is as shown in the following [Table 2].
- the cDNA amplified by the PCR result was separated by electrophoresis with 1.5% agarose gel, and cDNA bands were identified using G; BOX EF imaging system (Syngene). The results are shown in FIG.
- Primer sequences used for PCR in the present invention Amplification gene Sequence name SEQ ID NO: order direction Myod Myod_f SEQ ID NO: 7 5'-GGATGGTGCCCCTGGGTCCT-3 ' Forward direction Myod_r SEQ ID NO: 8 5'-TGGCCTTCGCTGTGAGTCGC-3 ' Reverse Myogenin Myogenin_f SEQ ID NO: 9 5'-TGGGCTGCCACAAGCCAGAC-3 ' Forward direction Myogenin_r SEQ ID NO: 10 5'-CAGCCCAGCCACTGGCATCA-3 ' Reverse ⁇ -Actin Actin_F SEQ ID NO: 5 5'-CTGTGTGGATTGGTGGCTCTAT-3 ' Forward direction Actin_R SEQ ID NO: 6 5'-GTGTAAAACGCAGCTCAGTAACA3 ' Reverse
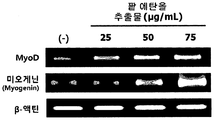
- the red bean ethanol extract of the present invention has an excellent ability to promote muscle differentiation in muscle cells.
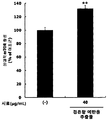
- the activity of mTOR was significantly increased ( ** p ⁇ 0.01) in L6 muscle cells by treatment of hot water extract. This means that the red bean hydrothermal extract of the present invention has an excellent ability to increase muscle production in muscle cells.
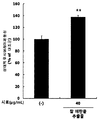
- the activity of mTOR in L6 muscle cells was significantly increased ( ** p ⁇ 0.01) by the treatment of red bean subcritical extract. This means that the red bean subcritical extract of the present invention has an excellent ability to increase muscle production in muscle cells.
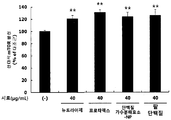
- the activity of mTOR in L6 muscle cells was significantly increased ( ** p ⁇ 0.01) by treatment of red bean protein and red bean peptide.
- the red bean protein and red bean peptide of the present invention have an excellent ability to increase muscle production in muscle cells.
- the red bean peptide of the present invention promotes the mRNA transcription process for muscle protein synthesis in muscle cells.
- Example 4 The same method experiment as in Experimental Example 4 was conducted. Instead of the red bean ethanol extract, the red bean peptide prepared in Example ⁇ 2-5> was dissolved at a concentration of 50 or 100 ⁇ g / mL, and then treated to cells to induce root canal cell differentiation. At this time, the group treated with 0.01% DMSO instead of the sample was used as a control. The results are shown in FIG.
- PGC-1 ⁇ activity was performed by luciferase assay to evaluate the exercise performance of the red bean ethanol extract.
- COS7 monkey kidney cells (ATCC) were incubated in 24-well plates at 1.5 ⁇ 10 5 cells / well, followed by pGL3-PGC-1 ⁇ -Luc plasmid (Addgene, Cambridge, Calif.) Using lipofectors (Aptabio, Yongin, Korea). MA, USA) were transfected into the cells. After 4 hours transfection, cells were stabilized for 24 hours. Then, red bean ethanol extract prepared in 100% ethanol in Example ⁇ 1-2> was dissolved in DMEM at a concentration of 40 ⁇ g / mL, and then treated with cells for 24 hours. After the last 24 hours, cells were lysed by lysing with NP-40 buffer (ELPIS-Biotech), and luciferase activity in the cell lysate was measured. The results are shown in FIG.
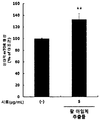
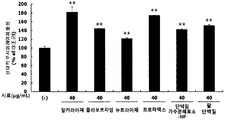
- red bean ethanol extract was found to significantly increase the activity of PGC-1 ⁇ , a major factor involved in exercise performance ( ** p ⁇ 0.01). Therefore, it was confirmed that red bean ethanol extract enhances exercise performance.
- the experiment was conducted in the same manner as in Experimental Example 4.
- the red bean ethanol extract prepared in 100% ethanol in Example 1-2 was dissolved at a concentration of 25, 50, 40 ⁇ g / mL, and then treated with cells to induce myotube differentiation. At this time, the group treated with 0.01% DMSO instead of the sample was used as a control.
- PCR was performed using the following specific primer (Bioneer) at RT-PCR. The results are shown in FIG.
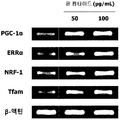
- Primer sequences used for PCR in the present invention Amplification gene Sequence name SEQ ID NO: order direction PGC-1 ⁇ PGC_F SEQ ID NO: 11 5'-ATGTGTCGCCTTCTTGCTCT-3 ' Forward direction PGC_R SEQ ID NO: 12 5'-ATCTACTGCCTGGGGACCTT-3 ' Reverse ERR ⁇ ERR_F SEQ ID NO: 13 5'-AAGGGGATGGAGACCACAGT-3 ' Forward direction ERR_R SEQ ID NO: 14 5'-TGAGGTGGGAGCTGATAGGG-3 ' Reverse NRF-1 NRF_F SEQ ID NO: 15 5'-TGGACCCAAGCATTACGGAC-3 ' Forward direction NRF_R SEQ ID NO: 16 5'-GGTCATTTCACCGCCCTGTA-3 ' Reverse Tfam Tfam_F SEQ ID NO: 17 5'-GCTTCCAGGAGGCTAAGGAT-3 ' Forward direction Tfam_R SEQ ID NO: 18 5'-CCCAATCCCAATGACA
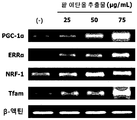
- the red bean ethanol extract of the present invention has an excellent ability to increase the expression of mitochondrial biosynthesis related genes that are deeply related to exercise performance.
- red bean protein and red bean peptide significantly increased the activity of PGC-1 ⁇ , which is a major factor involved in exercise performance ( ** p ⁇ 0.01). Therefore, it was confirmed that red bean protein and red bean peptide enhance exercise performance.
- the red bean peptide prepared in Example ⁇ 2-5> was treated with 50 or 100 ⁇ g / mL in the same manner as in Experimental Example 4 to evaluate the mitochondrial biosynthesis promoting activity of the red bean peptide. The results are shown in FIG.
- red bean peptide of the present invention has an excellent ability to increase the expression of mitochondrial biosynthesis related genes that are deeply related to exercise performance.
- black ethanol extract was found to significantly increase the activity of PGC-1 ⁇ , a major factor involved in exercise performance ( ** p ⁇ 0.01). Therefore, it was confirmed that black bean ethanol extract enhances exercise performance.
- mice Seven weeks old male rats (C57BL / 6N; Young Bio) were purchased as experimental animals. All animals were raised at Yonsei Laboratory Animal Reaserch Center (YLARC, Seoul, Korea), and the environment was maintained at 23 ⁇ 2 and 55 ⁇ 10% relative humidity. Before starting the experiment, a total of 20 rats were randomly divided into normal group, muscular atrophy group, red bean 300 administration group, and red bean 600 administration group so as to be 5 birds per group. After adaptation for one week, anesthesia was induced by intraperitoneal injection of 325 mg / kg tribromoethanol (Sigma-aldrich).
- the right hindlimb gastrocnemius muscle and right foot of the rats in the muscle atrophy group and the adzuki bean group were used as a stapler seam using a skin stapler (Unidus, Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea). He was injured, prevented the right hind limb from moving and maintained this state for a week. A week later, the staple cores fixed in the calf muscles and the sole of the foot were removed, and the red bean ethanol extract prepared in 50% ethanol in Example ⁇ 1-2> was again orally administered at a concentration of 300 mg / kg or 600 mg / kg for one week. Dosing led to recovery. At this time, the normal group and the muscular atrophy group were orally administered with saline instead of the sample.
- the performance performance of experimental animals was evaluated using a treadmill device (LE8710MTS; Panlab, Barcelona, Spain). Starting at the first 8 m / min, the speed was increased by 1 m / min every minute. The rat was set to give 0.2 mA of electricity when it touched the shock grid, and the experiment was stopped and time and distance were measured when the rat was no longer running after receiving the electric shock for 10 seconds.
- the animals were intraperitoneally injected with 325 mg / kg tribromomethanol (Sigma-aldrich) and anesthesia was sacrificed through cardiac blood. After confirming that the heartbeat stopped, the injured tibialis anterior muscles were extracted from the right hind limb and weighed.
- the red bean ethanol extract of the present invention has an excellent effect of increasing the weight of muscles reduced due to muscular atrophy.
- the preparation examples of the foodstuffs and medicines for improving muscle function or enhancing exercise performance containing the red bean according to the present invention as an active ingredient, but the present invention is not intended to limit the present invention.
- the red bean ethanol extract with excellent muscle function improving effect or exercise performance enhancing effect was prepared according to the conventional method according to the conventional methods according to the composition and the composition ratio as follows.
- the red powder extract, red bean peptide, black bean extract or black bean peptide of 50 mg, crystalline cellulose was mixed with 2 g of Examples 1 to 4, and filled in an airtight cloth according to a conventional powder preparation method to prepare a powder.
- Tablets were prepared by mixing the red bean extract, red bean peptide, black bean extract or black bean peptide of 50 mg, crystalline cellulose 400 mg, and magnesium stearate 5 mg of Examples 1 to 4 and then tableting according to a conventional tablet preparation method.
- the resulting solution is filtered and obtained in a sterilized 2 L container, sealed and sterilized and stored in refrigerated and then used in the manufacture of a healthy beverage composition.
- Chewing gum was prepared by the method.
- Candy was prepared by combining 60 wt% of sugar, 39.8 wt% of starch syrup, and 0.1 wt% of fragrance, and 0.1 wt% of the red bean extract, red bean peptide, black bean extract, or black bean peptide of Examples 1 to 4.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Natural Medicines & Medicinal Plants (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Botany (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Alternative & Traditional Medicine (AREA)
- Nutrition Science (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Birds (AREA)
- Dermatology (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Plant Substances (AREA)
- Coloring Foods And Improving Nutritive Qualities (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
Abstract
본 발명에 따른 팥은 근육의 기능, 근육량 증대 또는 근육세포의 분화에 관여하는 유전자의 mRNA 또는 단백질 발현 및 활성을 촉진시키는 효과를 통해서, 근육량의 증대, 근 기능 또는 운동수해능력의 향상을 가능하게 하고, 각종 질병에 의하여 유발되는 운동수행능력 저하, 근육의 기능 저하, 근육의 손실 등을 예방, 치료 또는 개선할 수 있으며, 천연물질로서 체내 부작용이 없어 의약품 또는 식품 등에 효과적으로 사용될 수 있다.
Description
본 출원은 2016년 05월 02일 출원된 대한민국 특허출원 제10-2016-0054290호; 및 2017년 05월 02일 출원된 대한민국 특허출원 제10-2017-0056162호를 우선권으로 주장하고, 상기 명세서 전체는 본 출원의 참고문헌이다.
본 발명은 팥 추출물, 팥 유래 단백질 및 팥 유래 펩타이드를 유효성분으로 함유하는 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 조성물에 관한 것이다.
근위축(Muscle atrophy)이란 근육량의 점진적 감소에 의하여 발생하는 것으로, 근육의 약화 및 퇴행을 일컫는다(Cell, 119(7): 907-910, 2004). 근위축은 비활동, 산화적 스트레스 또는 만성 염증 등에 의해 촉진되며 근육 기능과 운동 능력을 약화시킨다(Clinical Nutrition, 26(5): 524-534, 2007).
이와 관련되어, 근육 기능을 결정짓는 가장 중요한 요소는 근육량이며, 이는 근육 단백질 합성과 분해의 균형에 의해 유지된다. 근위축증은 단백질 분해가 합성보다 더 일어날 때 발생한다(The International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 37(10): 1985-1996, 2005).
근육 크기는 근육 내에서 일어나는 동화작용(anabolism)이나 이화작용(catabolism)을 유도하는 세포 내 신호전달 과정(signaling pathways)에 의해 조절되며 근육 단백질의 분해보다 합성을 유도하는 신호전달 반응이 많이 일어날 경우 근육 단백질 합성이 증가 되는데, 이는 근육 단백질 증가에 따른 근육 크기 증가(hypertrophy, 근비대)나 근섬유 수 증가(hyperplasia)로 나타난다(The Korea Journal of Sports Science, 20(3): 1551-1561, 2011).
근비대 유도 인자들은 근 세포 내에서 phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway의 자극을 기점으로 다운스트림 단백질(downstream proteins)을 인산화 시킴으로써 단백질 합성을 유도한다. 이 중 PI3K/Akt 신호전달에 의한 mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)의 활성은 세포 내에서 다양한 성장 신호를 통합하는 주요 성장 신호전달 기전으로 인정되고 있다. mTOR의 활성화는 두 개의 다운스트림 타겟(downstream targets)인 4E-binding protein (4EBP1)과 phosphorylated 70-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase (p70S6K)를 활성화시킴으로써 근 단백질 합성을 유도하여 근육량 증가에 기여할 수 있다(The Korea Journal of Sports Science, 20(3): 1551-1561, 2011; The International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 43(9): 1267-1276, 2011).
이와는 반대로, 전사 인자(transcription factor)인 forhead box (FoxO)가 세포질에서 핵 내로 이동하면 단백질 분해에 관여하는 E3 유비퀴틴 리가아제 인자인 아트로긴-1(atrogin-1)과 MuRF-1의 발현을 증가시킨다(Disease Models & Mechanisms, 6: 25-39, 2013). 이들의 발현량이 증가하면 근육 내의 단백질 분해가 촉진되어 근육량이 줄어들게 된다. 따라서 mTOR의 활성 촉진과 atrogin-1과 MuRF-1 발현 억제는 근육 단백질의 양을 증가시켜 근육량을 증가시키게 된다.
이 외에도, 근육세포의 분화와 근육 형성은 다양한 근육 조절 인자(muscle regulatory factors)에 의해 조절될 수 있다. 그 중, MyoD는 myogenin의 발현 유도를 통해 근원세포(myoblast)가 근관세포(myotube)되는 과정을 촉진시킨다. 이와 같은 과정을 통해 형성된 근섬유는 다발을 이루어 최종적으로 근육을 형성하게 된다(Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 70: 4117-4130, 2013).
대표적인 두류 중 하나인 팥(Vigna
angularis)은 쌍떡잎식물 콩과(Fabaceae)의 동부속(Vigna spp.)에 속하는 한해살이풀로 콩 다음으로 중요한 두류작물이다. 팥은 비타민 B1이 풍부하여 쌀과 혼합하여 밥을 만들면, 쌀밥에 부족하기 쉬운 비타민을 공급하여 주며 각기병뿐만 아니라 피로회복에도 효과가 있음이 알려져 있다. 팥에 함유된 사포닌은 섬유질과 함께 변통을 돕는 효과가 있고 독을 풀고 배변을 촉진하여 장을 깨끗이 해주며, 신장병 또는 숙취 개선에도 이용된다(Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology, 42(6): 693-698, 2010). 또한, 팥은 항산화(Journal of Food Lipids 11(4): 278-286, 2004), 항당뇨 (Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 68(12): 24212426, 2004), 항균(Phytotherapy Research 20(2): 162164, 2006) 미백(International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12(10): 7048-7058, 2011)등의 활성이 보고 되어있으나, 근육 기능 개선과 관련된 효능에 관하여는 보고된 바 없다.
이에, 본 발명자들은 식물 추출물 유래의 근위축과 같은 근육 기능 저하와 관련된 질병의 치료제를 개발하고자 노력한 결과, 팥 또는 콩과 식물의 추출물이 근육 세포에서 근단백질 합성 및 근육량 증가와 관련된 단백질의 발현 및 인산화 수준을 증가시킬 수 있으므로, 본 발명의 팥 또는 팥 추출물은 근육 질환 예방 및 치료용, 또는 근 기능 개선용 조성물의 유효성분으로 사용할 수 있음을 확인함으로써, 본 발명을 완성하였다.
이에 본 발명자들은 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상 활성을 가지며 안전하게 적용될 수 있는 천연물질을 탐색한 결과, 팥에서 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상 활성이 있음을 확인하여 본 발명을 완성하였다.
따라서, 본 발명의 목적은 팥(Vigna
angularis)의 추출물을 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 조성물을 제공하는 것이다.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은, 팥 유래 단백질 또는 펩타이드를 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 조성물을 제공하는 것이다.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은, 팥 추출물을 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근기능 개선용 조성물을 제공하는 것이다.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은, 팥 유래 단백질 또는 펩타이드를 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근기능 개선용 조성물을 제공하는 것이다.
상기 과제를 해결하기 위한 수단으로서, 본 발명은 팥(Vigna
angularis)의 추출물을 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물을 제공한다.
또한, 본 발명은 팥 유래 단백질 또는 펩타이드를 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물을 제공한다.
상기 과제를 해결하기 위한 또 다른 수단으로서, 본 발명은 팥(Vigna
angularis)의 추출물을 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근기능 개선용 조성물을 제공한다.
또한, 본 발명은 팥 유래 단백질 또는 펩타이드를 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근기능 개선용 조성물을 제공한다.
따라서 본 발명은 팥 추출물, 팥 유래 단백질 또는 팥 유래 펩타이드를 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근육 질환 예방 및 치료용, 근 기능 개선용, 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 조성물을 제공한다.
본 발명의 팥 추출물은 근육 세포에서 근육 기능, 근육량 조절 또는 근육 세포의 분화에 관여하는 인자들의 mRNA 전사 수준 및 단백질 활성을 촉진시켜 근육량 증대로 인한 근 기능 또는 운동수행능력의 향상을 가능하게 하고, 각종 질병에 의하여 유발되는 운동수행능력의 저하, 근기능 저하, 근육 손실 등의 예방, 치료 또는 개선 효과를 나타낼 수 있다. 또한, 본 발명의 팥 추출물, 팥 유래 단백질 및 팥 유래 펩타이드는 천연물질로서 체내 부작용이 없으므로 의약품 또는 식품 등에 효과적으로 사용될 수 있다.
도 1은 L6 근육세포에서, 팥 에탄올 추출물 처리에 따른 mTOR의 활성을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
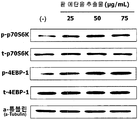
도 2는 L6 근육세포에서, 팥 에탄올 추출물 처리에 따른 mRNA translation 관련 생체지표 p-p70S6K와 p-4EBP1의 단백질 발현량을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 3은 L6 근육세포에서, 팥 에탄올 추출물 처리에 따른 근 단백질 분해 촉진 생체지표 MuRF-1 및 atrogin-1의 mRNA 발현량을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 4는 L6 근육세포에서, 팥 에탄올 추출물 처리에 따른 근육 분화 생체지표 MyoD와 myogenin의 mRNA 발현량을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 5는 L6 근육세포에서, 팥 열수 추출물 처리에 따른 mTOR의 활성을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 6은 L6 근육세포에서, 팥 아임계 추출물 처리에 따른 mTOR의 발현 수준을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 7은 L6 근육세포에서, 팥 단백질 및 효소 반응에 의한 팥 펩타이드 처리에 따른 mTOR의 발현 수준을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 8은 L6 근육세포에서, 팥 펩타이드 처리에 따른 mRNA translation 관련 생체지표 p-p70S6K와 p-4EBP1의 단백질 발현량을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 9는 L6 근육세포에서, 팥 펩타이드 처리에 따른 근육 분화 생체지표 MyoD와 myoenin의 mRNA 발현량을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 10은 L6 근육세포에서, 검은팥 에탄올 추출물 처리에 따른 mTOR의 활성을 측정한 결과를 보여준다
도 11은 COS-7 신장세포에서, 팥 에탄올 추출물 처리에 따른 PGC-1α의 활성을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 12는 L6 근육세포에서, 팥 에탄올 추출물 처리에 따른 미토콘드리아 생합성 생체지표 PGC-1α, ERRα, NRF-1, Tfam의 mRNA 발현량을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 13은 L6 근육세포에서, 팥 단백질 및 효소 반응에 의한 팥 펩타이드 처리에 따른 PGC-1α의 활성을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 14는 L6 근육세포에서, 팥 펩타이드 처리에 따른 미토콘드리아 생합성 생체지표 PGC-1α, ERRα, NRF-1, Tfam의 mRNA 발현량을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 15는 COS-7 신장세포에서, 검은팥 에탄올 추출물 처리에 따른 PGC-1α의 활성을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 16은 근위축 유도 쥐에서, 팥 에탄올 추출물 처리에 따른 근력을 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
도 17은 근위축 유도 쥐에서, 팥 에탄올 추출물 처리에 따른 지구력을 측정한 결과를 보여준다(a: 운동시간, b: 운동거리).
도 18은 근위축 유도 쥐에서, 팥 에탄올 추출물 처리에 따른 전경골근의 무게를 측정한 결과를 보여준다.
이하, 본 발명의 구성을 구체적으로 설명한다.
본 발명은 팥(Vigna
angularis)의 추출물을 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물을 제공한다.
본 명세서에서 '팥(Vigna
angularis)'은 쌍떡잎식물 콩과(Fabaceae)의 동부속(Vigna spp.)에 속하는 팥(V.
angularis W.F.Wight), 검은팥(V.
angularis
var. angularis) 또는 그 이외의 식물들의 씨앗을 건조한 것이며, 이들을 단독으로 사용하여도 좋고, 혼합하여 사용하여도 좋다.
본 명세서에서 ‘팥 추출물’은 팥을 추출하여 수득한 추출물을 의미한다. 팥 추출물의 제조방법은 팥으로부터 물, C1 내지 C6의 유기용매, 아임계 유체 및 초임계 유체로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 하나 이상의 용매로 팥을 추출하여 수득할 수 있다. 보다 구체적으로, 상기 용매는 탄소수 1 내지 6의 알코올(alcohol), 아세톤(acetone), 에테르(ether), 벤젠(benzene), 클로로포름(chloroform), 에틸아세테이트(ethyl acetate), 메틸렌 클로라이드(methylene chloride), 헥산(hexane), 시클로헥산(cyclohexane) 및 석유에테르(petroleum ether)로 이루어진 군 중에서 선택되는 하나 이상일 수 있다.
보다 구체적으로, 상기 추출물은 하기의 단계들을 포함하는 제조방법에 의해 제조되는 것이 바람직하나 이에 한정되지 않는다:
1) 팥에 추출용매를 가하여 추출하는 단계;
2) 단계 1)의 추출물을 여과하는 단계; 및
3) 단계 2)의 여과한 추출물을 감압 농축한 후 건조하는 단계.
상기 방법에 있어서, 단계 1)의 팥은 재배한 것 또는 시판되는 것 등 제한 없이 사용할 수 있다.
상기 방법에 있어서, 팥 추출물의 추출 방법으로는 여과법, 열수 추출, 침지 추출, 환류냉각 추출, 초음파추출, 초고압 추출 및 아임계 추출 등 당업계의 통상적인 방법을 이용할 수 있다. 추출 방법과 관련하여, 상기 초고압 추출을 수행하는 경우 100 내지 500 Mpa의 압력으로 추출하는 것이 바람직하다.
상기 방법에 있어서, 단계 3)의 감압농축은 진공감압농축기 또는 진공회전증발기를 이용하는 것이 바람직하나 이에 한정하지 않는다. 또한, 건조는 감압건조, 진공건조, 비등건조, 분무건조 또는 동결건조하는 것이 바람직하나 이에 한정하지 않는다.
또한, 본 발명은 팥 유래 단백질 또는 펩타이드를 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물을 제공한다.
본 명세서에서, '팥 유래 단백질'은 하기 i) 내지 v) 단계로 이루어진 방법으로 수득할 수 있다:
i) 건조된 팥을 분쇄하고 헥산을 용매로 추출하는 단계;
ii) 상기 단계 i)에서 추출한 헥산 추출물을 제거하고, 박에 물을 가하여 pH 7.0 내지 10.0 조건에서 방치하는 단계;
iii) 상기 단계 ii)에서 방치한 용액을 원심분리하여 상등액을 수득하는 단계;
iv) 상기 단계 iii)에서 수득한 상층액을 다시 pH 2.0 내지 6.0 조건에서 방치하는 단계; 및
v) 상기 단계 iv)에서 방치한 용액을 다시 원심분리하여 침전한 침전체를 팥 유래 단백질로 수득하는 단계.
본 명세서에서, '팥 유래 펩타이드'는 팥으로부터 분리한 팥 단백질에 단백질 가수분해효소를 처리하여 수득한 것을 의미한다. 구체적으로, 팥 유래 펩타이드는 하기 i) 내지 vii) 단계로 이루어진 방법으로 수득할 수 있다:
i) 건조된 팥을 분쇄하고 헥산을 용매로 추출하는 단계;
ii) 상기 단계 i)에서 추출한 헥산 추출물을 제거하고, 박에 물을 가하여 pH 7.0 내지 10.0 조건에서 방치하는 단계;
iii) 상기 단계 ii)에서 방치한 용액을 원심분리하여 상등액을 수득하는 단계;
iv) 상기 단계 iii)에서 수득한 상층액을 다시 pH 2.0 내지 6.0 조건에서 방치하는 단계;
v) 상기 단계 iv)에서 방치한 용액을 다시 원심분리하여 침전한 침전체를 팥 유래 단백질로 수득하는 단계;
vi) 상기 단계 v)에서 수득한 팥 유래 단백질에 가수분해효소를 가하고 효소 반응한 후, 여과하여 침전물을 제거하는 단계; 및
vii) 상기 단계 vi)에서 침전물이 제거된 여과액을 동결건조하여 펩타이드를 수득하는 단계.
본 명세서에서, 상기 '가수분해효소'는 알카라아제(Alcalase), 플라보르자임(Flavourzyme), 뉴트라아제(Neutrase), 프로타멕스(Protamex) 및 단백질가수분해효소-NP (Protease-NP)로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 어느 하나 이상의 단백질 가수분해효소일 수 있다.
본 명세서에서 근육 질환은 근기능 저하, 근육 소모 또는 근육 퇴화로 인한 근육 질환으로 당업계에 보고된 질병인 것이 바람직하다. 상기 근육 소모 또는 퇴화는 유전적 요인, 후천적 요인, 노화 등을 원인으로 발생하며, 근육 소모는 근육량의 점진적 손실, 근육, 특히 골격근 또는 수의근 및 심장근육의 약화 및 퇴행을 특징으로 한다. 이와 관련된 질환의 예로는 긴장감퇴증(atony), 근위축증(muscular atrophy), 근이영양증(muscular dystrophy), 근육 퇴화, 근무력증, 악액질(cachexia) 및 근육감소증(sarcopenia) 등을 들 수 있다. 본 발명의 조성물은 근육량 증대 효과가 있으며, 근육은 그 종류를 제한하지 않는다.
본 명세서에서,'근'은 심줄, 근육, 건을 포괄적으로 지칭하고, '근 기능' 또는 '근육 기능'은 근육의 수축에 의해 힘을 발휘할 수 있는 능력을 의미하며, 근육이 저항을 이겨내기 위하여 최대한의 수축력을 발휘할 수 있는 근력; 근육이 주어진 중량에 얼마나 오랫동안 또는 얼마나 여러 번 수축과 이완을 반복할 수 있는지 나타내는 능력인 근 지구력; 및 단시간 내에 강한 힘을 발휘하는 능력인 순발력을 포함한다. 상기 근 기능은 근육량에 비례하며, 용어 '근 기능 개선'은 근 기능을 보다 긍정적인 방향으로 향상시키는 것을 의미한다.
본 명세서에서, '운동수행능력'은 일상생활이나 스포츠에서 볼 수 있는 신체동작을 외형적으로 달리기, 뛰기, 던지기, 헤엄치기 등으로 구분할 때, 상기 동작을 빠르게, 강하게, 정확하게, 오래, 능숙하게 할 수 있는 정도를 나타내는 것으로, 운동수행능력은 근력, 민첩성 및 지구력 등의 인자로 규정된다. 용어'운동수행능력 향상'은 운동수행능력을 개선하거나 향상시키는 것을 말한다.
본 발명의 조성물이 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물인 경우, 운동능력의 퇴화로 인한 질환의 예방 또는 치료에 사용될 수 있다. 이와 관련된 질환의 예로는 퇴행성 질환, 미토콘드리아 이상 질환, 지구력 저하증, 순발력 저하증, 무기력증, 근육 폐기 및 우울증 등을 들 수 있다. 본 발명의 조성물은 운동수행능력 향상 효과가 있으며, 운동의 형태 및 종류를 제한하지 않는다.
본 발명의 근 기능 개선용 약학적 조성물인 경우, 근육 소모 또는 퇴화로 인한 근육 질환의 예방 또는 치료에 사용될 수 있다. 근육 소모 및 퇴화는 유전적 요인, 후천적 요인, 노화 등을 원인으로 발생하며, 근육 소모는 근육량의 점진적 손실, 근육, 특히 골격근 또는 수의근 및 심장근육의 약화 및 퇴행을 특징으로 한다. 이와 관련된 질환의 예로는 긴장감퇴증(atony), 근위축증(muscular atrophy), 근이영양증(muscular dystrophy), 근육 퇴화, 근무력증, 악액질(cachexia) 및 근육감소증(sarcopenia) 등을 들 수 있다. 본 발명의 조성물은 근육량 증대 효과가 있으며, 근육은 그 종류를 제한하지 않는다.
본 발명의 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물인 경우, 운동능력 퇴화로 인한 질환의 예방 또는 치료에 사용될 수 있다. 이와 관련된 질환의 예로는 미토콘드리아 이상 질환, 지구력 저하증, 순발력 저하증, 무기력증, 근육 폐기 및 우울증 등을 들 수 있다. 본 발명의 조성물은 운동수행능력 향상 효과가 있으며, 운동의 형태 및 종류를 제한하지 않는다.
본 발명의 약학적 조성물은 약학적으로 허용 가능한 담체를 더 포함할 수 있다. 약학적으로 허용되는 담체로는 예컨대, 경구 투여용 담체 또는 비경구 투여용 담체를 추가로 포함할 수 있다. 경구 투여용 담체는 락토스, 전분, 셀룰로스 유도체, 마그네슘 스테아레이트, 스테아르산 등을 포함할 수 있다. 또한 비경구 투여용 담체는 물, 적합한 오일, 식염수, 수성 글루코스 및 글리콜 등을 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 안정화제 및 보존제를 추가로 포함할 수 있다. 적합한 안정화제로는 아황산수소나트륨, 아황산나트륨 또는 아스코르브산과 같은 항산화제가 있다. 적합한 보존제로는 벤즈알코늄 클로라이드, 메틸- 또는 프로필-파라벤 및 클로로부탄올이 있다. 그 밖의 약학적으로 허용되는 담체로는 다음의 문헌에 기재되어 있는 것을 참고로 할 수 있다(Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences, 19th ed., Mack Publishing Company, Easton, PA, 1995).
본 발명의 약학적 조성물은 인간을 비롯한 포유동물에 어떠한 방법으로도 투여할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 경구 또는 비경구로 투여할 수 있으며, 비경구적인 투여방법으로는 이에 제한되는 것은 아니나, 정맥내, 근육내, 동맥내, 골수내, 경막내, 심장내, 경피, 피하, 복강내, 비강내, 장관, 국소, 설하 또는 직장내 투여일 수 있다.
본 발명의 약학적 조성물은 상술한 바와 같은 투여 경로에 따라 경구 투여용 또는 비경구 투여용 제제로 제형화 할 수 있다. 제형화할 경우에는 하나 이상의 완충제(예를 들어, 식염수 또는 PBS), 항산화제, 정균제, 킬레이트화제(예를 들어, EDTA 또는 글루타치온), 충진제, 증량제, 결합제, 아쥬반트(예를 들어, 알루미늄 하이드록사이드), 현탁제, 농후제 습윤제, 붕해제 또는 계면활성제, 희석제 또는 부형제를 사용하여 조제될 수 있다.
경구투여를 위한 고형제제에는 정제, 환제, 산제, 과립제, 액제, 겔제, 시럽제, 슬러리제, 현탁액 또는 캡슐제 등이 포함되며, 이러한 고형제제는 본 발명의 약학적 조성물에 적어도 하나 이상의 부형제 예를 들면, 전분(옥수수 전분, 밀 전분, 쌀 전분, 감자 전분 등 포함), 칼슘카보네이트(calcium carbonate), 수크로스(sucrose), 락토오스(lactose), 덱스트로오스, 솔비톨, 만니톨, 자일리톨, 에리스리톨 말티톨, 셀룰로즈, 메틸 셀룰로즈, 나트륨 카르복시메틸셀룰로오즈 및 하이드록시프로필메틸-셀룰로즈 또는 젤라틴 등을 섞어 조제될 수 있다. 예컨대, 활성성분을 고체 부형제와 배합한 다음 이를 분쇄하고 적합한 보조제를 첨가한 후 과립 혼합물로 가공함으로써 정제 또는 당의정제를 수득할 수 있다.
단순한 부형제 이외에 마그네슘 스티레이트 탈크 같은 윤활제들도 사용된다. 경구를 위한 액상 제제로는 현탁제, 내용액제, 유제 또는 시럽제 등이 해당되는데 흔히 사용되는 단순 희석제인 물 또는 리퀴드 파라핀 이외에 여러 가지 부형제, 예를 들면 습윤제, 감미제, 방향제 또는 보존제 등이 포함될 수 있다. 또한, 경우에 따라 가교결합 폴리비닐피롤리돈, 한천, 알긴산 또는 나트륨 알기네이트 등을 붕해제로 첨가할 수 있으며, 항응집제, 윤활제, 습윤제, 향료, 유화제 및 방부제 등을 추가로 포함할 수 있다.
비경구적으로 투여하는 경우 본 발명의 약학적 조성물은 적합한 비경구용 담체와 함께 주사제, 경피 투여제 및 비강 흡입제의 형태로 당 업계에 공지된 방법에 따라 제형화될 수 있다. 상기 주사제의 경우에는 반드시 멸균되어야 하며 박테리아 및 진균과 같은 미생물의 오염으로부터 보호되어야 한다. 주사제의 경우 적합한 담체의 예로는 이에 한정되지는 않으나, 물, 에탄올, 폴리올(예를 들어, 글리세롤, 프로필렌 글리콜 및 액체 폴리에틸렌 글리콜 등), 이들의 혼합물 및/또는 식물유를 포함하는 용매 또는 분산매질일 수 있다. 보다 바람직하게는, 적합한 담체로는 행크스 용액, 링거 용액, 트리에탄올 아민이 함유된 phosphate buffered saline (PBS) 또는 주사용 멸균수, 10% 에탄올, 40% 프로필렌 글리콜 및 5% 덱스트로즈와 같은 등장 용액 등을 사용할 수 있다. 상기 주사제를 미생물 오염으로부터 보호하기 위해서는 파라벤, 클로로부탄올, 페놀, 소르빈산, 티메로살 등과 같은 다양한 항균제 및 항진균제를 추가로 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 상기 주사제는 대부분의 경우 당 또는 나트륨 클로라이드와 같은 등장화제를 추가로 포함할 수 있다.
경피 투여제의 경우 연고제, 크림제, 로션제, 겔제, 외용액제, 파스타제, 리니멘트제, 에어롤제 등의 형태가 포함된다. 상기에서 '경피 투여'는 약학적 조성물을 국소적으로 피부에 투여하여 약학적 조성물에 함유된 유효한 양의 활성성분이 피부 내로 전달되는 것을 의미한다.
흡입 투여제의 경우, 본 발명에 따라 사용되는 화합물은 적합한 추진제, 예를 들면, 디클로로플루오로메탄, 트리클로로플루오로메탄, 디클로로테트라플루오로에탄, 이산화탄소 또는 다른 적합한 기체를 사용하여, 가압 팩 또는 연무기로부터 에어로졸 스프레이 형태로 편리하게 전달 할 수 있다. 가압 에어로졸의 경우, 투약 단위는 계량된 양을 전달하는 밸브를 제공하여 결정할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 흡입기 또는 취입기에 사용되는 젤라틴 캡슐 및 카트리지는 화합물, 및 락토즈 또는 전분과 같은 적합한 분말 기제의 분말 혼합물을 함유하도록 제형화할 수 있다. 비경구 투여용 제형은 모든 제약 화학에 일반적으로 공지된 처방서인 문헌(Remington's Pharmaceutical Science, 15th Edition, 1975. Mack Publishing Company, Easton, Pennsylvania 18042, Chapter 87: Blaug, Seymour)에 기재되어 있다.
본 발명의 약학적 조성물은 팥 추출물, 팥 단백질 또는 팥 펩타이드를 유효량으로 포함할 때 바람직한 근 기능 개선 효과 또는 운동수행능력 증강 효과를 제공할 수 있다. 본 명세서에서, '유효량'이라 함은 음성 대조군에 비해 그 이상의 반응을 나타내는 양을 말하며 바람직하게는 근 기능을 향상시키거나 운동수행능력을 향상하기에 충분한 양을 말한다. 본 발명의 약학적 조성물에 팥 추출물, 팥 단백질 또는 팥 펩타이드가 0.01 내지 99.99% 포함될 수 있으며, 잔량은 약학적으로 허용 가능한 담체가 차지할 수 있다. 본 발명의 약학적 조성물에 포함되는 팥 추출물, 팥 단백질 또는 팥 펩타이드의 유효량은 조성물이 제품화되는 형태 등에 따라 달라질 것이다.
본 발명의 약학적 조성물의 총 유효량은 단일 투여량(single dose)으로 환자에게 투여될 수 있으며, 다중 투여량(multiple dose)으로 장기간 투여되는 분할 치료 방법(fractionated treatment protocol)에 의해 투여될 수 있다. 본 발명의 약학적 조성물은 질환의 정도에 따라 유효성분의 함량을 달리할 수 있다. 비경구 투여시는 상기 팥 추출물, 팥 단백질 또는 팥 펩타이드를 기준으로 하루에 체중 1 kg당 바람직하게 0.01 내지 50 mg, 더 바람직하게는 0.1 내지 30 mg의 양으로 투여되도록, 그리고 경구 투여시는 팥 추출물, 팥 단백질 또는 팥 펩타이드를 기준으로 하루에 체중 1 kg당 바람직하게 0.01 내지 100 mg, 더 바람직하게는 0.01 내지 10 mg의 양으로 투여되도록 1 내지 수회에 나누어 투여할 수 있다. 그러나 상기 팥 추출물, 팥 단백질 또는 팥 펩타이드의 용량은 약학적 조성물의 투여 경로 및 치료 횟수뿐만 아니라 환자의 연령, 체중, 건강 상태, 성별, 질환의 중증도, 식이 및 배설율 등 다양한 요인들을 고려하여 환자에 대한 유효 투여량이 결정되는 것이므로, 이러한 점을 고려할 때 당 분야의 통상적인 지식을 가진 자라면 팥 추출물, 팥 단백질 또는 팥 펩타이드를 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 증강을 위한 특정한 용도에 따른 적절한 유효 투여량을 결정할 수 있을 것이다. 본 발명에 따른 약학적 조성물은 본 발명의 효과를 보이는 한 그 제형, 투여 경로 및 투여 방법에 특별히 제한되지 아니한다.
본 발명의 약학적 조성물은 단독으로, 또는 수술, 방사선 치료, 호르몬 치료, 화학 치료 또는 생물학적 반응조절제를 사용하는 방법들과 병용하여 사용할 수 있다.
본 발명의 약학적 조성물은 또한 팥 추출물, 팥 단백질 또는 팥 펩타이드를 유효성분으로 포함하는 외용제의 제형으로 제공할 수 있다.
본 발명의 약학적 조성물을 피부외용제로 사용하는 경우, 추가로 지방 물질, 유기 용매, 용해제, 농축제 및 겔화제, 연화제, 항산화제, 현탁화제, 안정화제, 발포제(foaming agent), 방향제, 계면활성제, 물, 이온형 유화제, 비이온형 유화제, 충전제, 금속이온봉쇄제, 킬레이트화제, 보존제, 비타민, 차단제, 습윤화제, 필수 오일, 염료, 안료, 친수성 활성제, 친유성 활성제 또는 지질 소낭 등 피부 외용제에 통상적으로 사용되는 임의의 다른 성분과 같은 피부 과학 분야에서 통상적으로 사용되는 보조제를 함유할 수 있다. 또한 상기 성분들은 피부 과학 분야에서 일반적으로 사용되는 양으로 도입될 수 있다.
본 발명의 약학적 조성물이 피부 외용제로 제공될 경우, 이에 제한되는 것은 아니나, 연고, 패취, 겔, 크림 또는 분무제 등의 제형일 수 있다.
또한, 본 발명의 근기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 식품 조성물을 제공한다.
본 발명의 식품 조성물이 근 기능 개선용 식품 조성물인 경우, 근기능 저하, 근육 소모 또는 근육 퇴화로 인한 근육 질환으로 당업계에 보고된 질병의 예방 또는 개선에 사용될 수 있다. 상기 근육 소모 또는 퇴화는 유전적 요인, 후천적 요인, 노화 등을 원인으로 발생하며, 근육 소모는 근육량의 점진적 손실, 근육, 특히 골격근 또는 수의근 및 심장근육의 약화 및 퇴행을 특징으로 한다. 이와 관련된 질환의 예로는 긴장감퇴증(atony), 근위축증(muscular atrophy), 근이영양증(muscular dystrophy), 근육 퇴화, 근무력증, 악액질(cachexia) 및 근육감소증(sarcopenia) 등을 들 수 있다. 본 발명의 조성물은 근육량 증대 효과가 있으며, 근육은 그 종류를 제한하지 않는다. 상기 근 기능은 근육량에 비례하며, 용어 '근 기능 개선'은 근 기능을 보다 긍정적인 방향으로 향상시키는 것을 의미한다.
본 발명의 식품 조성물이 운동수행능력 향상용 식품 조성물인 경우, 운동능력의 퇴화로 인한 질환의 예방 또는 치료에 사용될 수 있다. 이와 관련된 질환의 예로는 퇴행성 질환, 미토콘드리아 이상 질환, 지구력 저하증, 순발력 저하증, 무기력증, 근육 폐기 및 우울증 등을 들 수 있다. 본 발명의 조성물은 운동수행능력 향상 효과가 있으며, 운동의 형태 및 종류를 제한하지 않는다.
본 발명의 식품 조성물은 기능성 식품(functional food), 영양 보조제(nutritional supplement), 건강식품(health food), 식품 첨가제(food additives) 및 사료 등의 모든 형태를 포함하며, 인간 또는 가축을 비롯한 동물을 취식대상으로 한다. 상기 유형의 식품 조성물은 당 업계에 공지된 통상적인 방법에 따라 다양한 형태로 제조할 수 있다.
상기 유형의 식품 조성물은 당업계에 공지된 통상적인 방법에 따라 다양한 형태로 제조할 수 있다. 일반 식품으로는 이에 한정되지 않지만 음료(알콜성 음료 포함), 과실 및 그의 가공식품(예: 과일통조림, 병조림, 잼, 마아말레이드 등), 어류, 육류 및 그 가공식품(예: 햄, 소시지 콘비이프 등), 빵류 및 면류(예: 우동, 메밀국수, 라면, 스파게이트, 마카로니 등), 과즙, 각종 드링크, 쿠키, 엿, 유제품(예: 버터, 치이즈 등), 식용식물 유지, 마아가린, 식물성 단백질, 레토르트 식품, 냉동식품, 각종 조미료(예: 된장, 간장, 소스 등) 등에 상기 팥 추출물 및 팥 펩타이드를 첨가하여 제조할 수 있다. 또한, 영양보조제로는 이에 한정되지 않지만 캡슐, 타블렛, 환 등에 팥 추출물, 팥 단백질 또는 팥 펩타이드를 첨가하여 제조할 수 있다. 또한, 건강기능식품으로는 이에 한정되지 않지만 예를 들면, 상기 팥 추출물 자체를 차, 쥬스 및 드링크의 형태로 제조하여 음용(건강음료)할 수 있도록 액상화, 과립화, 캡슐화 및 분말화하여 섭취할 수 있다. 또한, 상기 팥 추출물, 팥 단백질 또는 팥 펩타이드를 을 식품 첨가제의 형태로 사용하기 위해서는 분말 또는 농축액 형태로 제조하여 사용할 수 있다. 또한, 상기 팥 추출물, 팥 단백질 또는 팥 펩타이드와 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상 효과가 있다고 알려진 공지의 활성 성분과 함께 혼합하여 조성물의 형태로 제조할 수 있다.
본 발명의 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 조성물이 건강음료 조성물로 이용되는 경우, 상기 건강음료 조성물은 통상의 음료와 같이 여러 가지 향미제 또는 천연 탄수화물 등을 추가 성분으로 함유할 수 있다. 상술한 천연 탄수화물은 포도당, 과당과 같은 모노사카라이드; 말토스, 슈크로스와 같은 디사카라이드; 덱스트린, 사이클로덱스트린과 같은 폴리사카라이드; 자일리톨, 소르비톨, 에리트리톨 등의 당알콜일 수 있다. 감미제는 타우마틴, 스테비아 추출물과 같은 천연 감미제; 사카린, 아스파르탐과 같은 합성 감미제 등을 사용할 수 있다. 상기 천연 탄수화물의 비율은 본 발명의 조성물 100 mL 당 일반적으로 약 0.01 ~ 0.04 g, 바람직하게는 약 0.02 ~ 0.03 g 이다.
팥 추출물, 팥 단백질 또는 팥 펩타이드를 는 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 식품 조성물의 유효성분으로 함유될 수 있는데, 그 양은 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 작용을 달성하기에 유효한 양으로 특별히 한정되는 것은 아니나, 전체 조성물 총 중량에 대하여 0.01 내지 100 중량%인 것이 바람직하다. 본 발명의 식품 조성물은 팥 추출물과 함께 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 조성물에 효과가 있는 것으로 알려진 다른 활성 성분과 함께 혼합하여 제조될 수 있다.
상기 외에 본 발명의 건강식품은 여러 가지 영양제, 비타민, 전해질, 풍미제, 착색제, 펙트산, 펙트산의 염, 알긴산, 알긴산의 염, 유기산, 보호성 콜로이드 증점제, pH 조절제, 안정화제, 방부제, 글리세린, 알코올 또는 탄산화제 등을 함유할 수 있다. 그 밖에 본 발명의 건강식품은 천연 과일주스, 과일주스 음료, 또는 야채 음료의 제조를 위한 과육을 함유할 수 있다. 이러한 성분은 독립적으로 또는 혼합하여 사용할 수 있다. 이러한 첨가제의 비율은 크게 중요하진 않지만 본 발명의 조성물 100 중량부당 0.01 ~ 0.1 중량부의 범위에서 선택되는 것이 일반적이다.
이하 본 발명을 실시예, 실험예 및 제조예를 통하여 보다 상세하게 설명한다.
단, 하기 실시예, 실험예 및 제조예는 본 발명을 예시하는 것일 뿐, 본 발명의 내용이 하기 실시예, 실험예 및 제조예에 한정되는 것은 아니다.
[실시예 1] 팥 추출물의 제조
<1-1> 팥의 메탄올 추출물 제조
건조된 팥(Vigna
angularis W.F.Wight)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 팥 분말 100 g을 100% 메탄올 1 L에 침지하여 24 시간 동안 상온에 방치한 후 추출액을 수득하는 과정을 3회 반복하였다. 수득한 추출액을 와트만(Whatman) 2번 여과지로 감압 여과하고, 여과된 추출액을 진공 회전 농축기로 농축하여 용매 성분을 제거한 팥 메탄올 추출물을 수득하였다.
<1-2> 팥의 에탄올 추출물 제조
건조된 팥(V.
angularis W.F.Wight)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 팥 분말 100 g을 100%, 70%, 50% 또는 30% 에탄올 1 L에 침지하여 24 시간 동안 상온에 방치한 후 추출액을 수득하는 과정을 3회 반복하였다. 수득한 추출액을 와트만 2번 여과지로 감압 여과하고, 여과된 추출액을 진공 회전 농축기로 농축하여 용매 성분을 제거한 팥 에탄올 추출물을 수득하였다.
<1-3> 팥의 에틸아세테이트 추출물 제조
건조된 팥(V.
angularis W.F.Wight)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 팥 분말 100 g을 100% 에틸아세테이트 1 L에 침지하여 24 시간 동안 상온에 방치한 후 추출액을 수득하는 과정을 3회 반복하였다. 수득한 추출액을 와트만 2번 여과지로 감압 여과하고, 여과된 추출액을 진공 회전 농축기로 농축하여 용매 성분을 제거한 팥 에틸아세테이트 추출물을 수득하였다.
<1-4> 팥의 헥산 추출물 제조
건조된 팥(V.
angularis W.F.Wight)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 팥 분말 100 g을 100% 헥산 1 L에 침지하여 24 시간 동안 상온에 방치한 후 추출액을 수득하는 과정을 3회 반복하였다. 수득한 추출액을 와트만 2번 여과지로 감압 여과하고, 여과된 추출액을 진공 회전 농축기로 농축하여 용매 성분을 제거한 팥 헥산 추출물을 수득하였다.
<1-5> 팥의 열수 추출물 제조
건조된 팥(V.
angularis W.F.Wight)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 팥 분말 100 g을 물 1 L에 넣고 80℃에서 2 시간 교반하여 추출액을 수득하였다. 수득한 추출액을 와트만 2번 여과지로 감압 여과하고, 여과된 추출액을 진공 회전 농축기로 농축하여 용매 성분을 제거한 팥 열수 추출물을 수득하였다.
<1-6> 팥 초고압 추출물의 제조
건조된 팥(V.
angularis W.F.Wight)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 18% 에탄올 76 mL을 폴리에틸렌(polyethylene) 팩에 넣고 밀봉한 후 초고압 추출장치(Frescal MFP-7000; Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Tokyo, Japan)를 이용하여 추출하였다. 초고압 추출 조건으로서 추출압력을 320 MPa, 추출시간은 5 분으로 설정하였다. 추출된 시료는 와트만 2번 여과지로 여과하고, 여과된 추출액을 진공 회전 농축기로 농축하여 용매성분을 제거함으로써 팥 초고압 추출물을 얻었다.
<1-7> 팥 아임계 추출물의 제조
건조된 팥(V.
angularis W.F.Wight)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 팥 50 g을 1 L 물과 함께 아임계 추출장치(Biovan, Gyeonggi, Korea)의 아임계수 반응기에 넣고 밀폐하였다. 밀폐 후, 반응기의 온도를 200℃까지 상승시켰으며, 반응기의 온도가 200℃에 도달하면 상기 온도를 20 분간 유지하여 추출을 하였다. 20 분 후, 추출물을 냉각수가 공급되는 저장탱크로 이송하여 30℃까지 급속 냉각시킨 후, 부유 잔사를 분리하기 위해 3,600 rpm으로 30분 동안 원심분리하여 상등액만 취하였다. 동결건조기(ilShin Lab Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea)를 이용하여 용매를 전부 제거함으로써 팥 아임계 추출물을 얻었다.
[실시예 2] 팥 유래 단백질 및 펩타이드의 분리
<2-1> 팥 유래 단백질의 분리
건조된 팥(V.
angularis W.F.Wight)을 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 팥 시료 1 kg을 1 L 헥산에 넣고 상온에서 4시간 교반하면서 추출하였다. 헥산 추출물을 제거한 뒤, 남은 박에 물을 넣고 pH 9, 25에서 30분간 방치하였다. 6,000 rpm에서 30 분간 원심분리하여 상등액 취하고, 상등액을 pH 4.5, 25의 조건에서 30 분간 다시 방치하였다. 6,000 rpm에서 30분간 원심분리하여 침전된 단백질을 수득하였으며, 침전된 단백질을 물에 녹이고 중성화과정을 거쳐 동결건조기(ilShin Lab Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea)를 이용하여 물을 전부 제거함으로써 분리한 팥 단백질을 수득하였다.
<2-2> 알카라아제(Alcalase) 처리에 따른 팥 펩타이드 제조
실시예 <2-1>에서 수득한 팥 단백질에 단백질 분해효소인 1% 알카라아제 (Novozymes, Bagsvaerd, Denmark)를 가하고 50에서 6시간 동안 효소반응을 시켰다. 6 시간 후에, 90에서 20 분간 효소를 불활성화시키고 와트만 2번 여과지로 여과하여 침전물을 제거하였다. 여과된 액체를 동결건조기(ilShin Lab Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea)를 이용하여 물을 전부 제거함으로써 알카라아제 처리에 의한 팥 펩타이드를 수득하였다.
<2-3> 플라보르자임(Flavourzyme) 처리에 따른 팥 펩타이드 제조
상기 실시예 <2-2>에서와 동일한 방법으로 알카라아제 대신 플라보르자임 (Novozymes)을 처리하여 플라보르지임 처리에 의한 팥 펩타이드를 수득하였다.
<2-4> 뉴트라제(Neutrase) 처리에 따른 팥 펩타이드 제조
상기 실시예 <2-2>에서와 동일한 방법으로 알카라아제 대신 뉴트라제 (Novozymes)을 처리하여 뉴트라제 처리에 의한 팥 펩타이드를 수득하였다.
<2-5> 프로타멕스(Protamex) 처리에 따른 팥 펩타이드 제조
상기 실시예 <2-2>에서와 동일한 방법으로 알카라아제 대신 프로타멕스 (Novozymes)를 처리하여 프로타멕스 처리에 의한 팥 펩타이드를 수득하였다.
<2-6> 프로테아제-NP(Protease-NP) 처리에 따른 팥 펩타이드 제조
상기 실시예 <2-2>에서와 동일한 방법으로 알카라아제 대신 프로테아제-NP (Bioland, Asan, Korea)를 처리하여 프로테아제-NP 처리에 의한 팥 펩타이드를 수득하였다.
[실시예 3] 검은팥 추출물의 제조
<3-1> 검은팥의 메탄올 추출물 제조
건조된 검은팥(V.
angularis
var. angularis)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 검은팥 분말 100 g을 100% 메탄올 1 L에 침지하여 24 시간 동안 상온에 방치한 후 추출액을 수득하는 과정을 3회 반복하였다. 수득한 추출액을 와트만(Whatman) 2번 여과지로 감압 여과하고, 여과된 추출액을 진공 회전 농축기로 농축하여 용매 성분을 제거한 검은팥 메탄올 추출물을 수득하였다.
<3-2> 검은팥의 에탄올 추출물 제조
건조된 검은팥(V.
angularis
var. angularis)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 검은팥 분말 100 g을 100%, 70%, 50% 또는 30% 에탄올 1 L에 침지하여 24 시간 동안 상온에 방치한 후 추출액을 수득하는 과정을 3회 반복하였다. 수득한 추출액을 와트만 2번 여과지로 감압 여과하고, 여과된 추출액을 진공 회전 농축기로 농축하여 용매 성분을 제거한 검은팥 에탄올 추출물을 수득하였다.
<3-3> 검은팥의 에틸아세테이트 추출물 제조
건조된 검은팥(V.
angularis
var. angularis)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 검은팥 분말 100 g을 100% 에틸아세테이트 1 L에 침지하여 24 시간 동안 상온에 방치한 후 추출액을 수득하는 과정을 3회 반복하였다. 수득한 추출액을 와트만 2번 여과지로 감압 여과하고, 여과된 추출액을 진공 회전 농축기로 농축하여 용매 성분을 제거한 검은팥 에틸아세테이트 추출물을 수득하였다.
<3-4> 검은팥의 헥산 추출물 제조
건조된 검은팥(V.
angularis
var. angularis)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 검은팥 분말 100 g을 100% 헥산 1 L에 침지하여 24 시간 동안 상온에 방치한 후 추출액을 수득하는 과정을 3회 반복하였다. 수득한 추출액을 와트만 2번 여과지로 감압 여과하고, 여과된 추출액을 진공 회전 농축기로 농축하여 용매 성분을 제거한 검은팥 헥산 추출물을 수득하였다.
<3-5> 검은팥의 열수 추출물 제조
건조된 검은팥(V.
angularis
var. angularis)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 검은팥 분말 100 g을 물 1 L에 넣고 80℃에서 2 시간 교반하여 추출액을 수득하였다. 수득한 추출액을 와트만 2번 여과지로 감압 여과하고, 여과된 추출액을 진공 회전 농축기로 농축하여 용매 성분을 제거한 검은팥 열수 추출물을 수득하였다.
<3-6> 검은팥 초고압 추출물의 제조
건조된 검은팥(V.
angularis
var. angularis)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 18% 에탄올 76 mL을 폴리에틸렌(polyethylene) 팩에 넣고 밀봉한 후 초고압 추출장치(Frescal MFP-7000; Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Tokyo, Japan)를 이용하여 추출하였다. 초고압 추출 조건으로서 추출압력을 320 MPa, 추출시간은 5 분으로 설정하였다. 추출된 시료는 와트만 2번 여과지로 여과하고, 여과된 추출액을 진공 회전 농축기로 농축하여 용매성분을 제거함으로써 검은팥 초고압 추출물을 얻었다.
<3-7> 검은팥 아임계 추출물의 제조
건조된 검은팥(V.
angularis
var. angularis)을 믹서로 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 검은팥 50 g을 1 L 물과 함께 아임계 추출장치(Biovan, Gyeonggi, Korea)의 아임계수 반응기에 넣고 밀폐하였다. 밀폐 후, 반응기의 온도를 200℃까지 상승시켰으며, 반응기의 온도가 200℃에 도달하면 상기 온도를 20 분간 유지하여 추출을 하였다. 20 분 후, 추출물을 냉각수가 공급되는 저장탱크로 이송하여 30℃까지 급속 냉각시킨 후, 부유 잔사를 분리하기 위해 3,600 rpm으로 30분 동안 원심분리하여 상등액만 취하였다. 동결건조기(ilShin Lab Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea)를 이용하여 용매를 전부 제거함으로써 검은팥 아임계 추출물을 얻었다.
[실시예 4] 검은팥 유래 단백질 및 펩타이드의 분리
<4-1> 검은팥 유래 단백질의 분리
건조된 검은팥(V.
angularis
var. angularis)을 분쇄한 다음, 분쇄한 검은팥 시료 1 kg을 1 L 헥산에 넣고 상온에서 4시간 교반하면서 추출하였다. 헥산 추출물을 제거한 뒤, 남은 박에 물을 넣고 pH 9, 25에서 30분간 방치하였다. 6,000 rpm에서 30 분간 원심분리하여 상등액 취하고, 상등액을 pH 4.5, 25의 조건에서 30 분간 다시 방치하였다. 6,000 rpm에서 30분간 원심분리하여 침전된 단백질을 수득하였으며, 침전된 단백질을 물에 녹이고 중성화과정을 거쳐 동결건조기(ilShin Lab Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea)를 이용하여 물을 전부 제거함으로써 분리한 검은팥 단백질을 수득하였다.
<4-2> 알카라아제(Alcalase) 처리에 따른 검은팥 펩타이드 제조
실시예 <4-1>에서 수득한 검은팥 단백질에 단백질 분해효소인 1% 알카라아제 (Novozymes, Bagsvaerd, Denmark)를 가하고 50에서 6시간 동안 효소반응을 시켰다. 6 시간 후에, 90에서 20 분간 효소를 불활성화시키고 와트만 2번 여과지로 여과하여 침전물을 제거하였다. 여과된 액체를 동결건조기(ilShin Lab Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea)를 이용하여 물을 전부 제거함으로써 알카라아제 처리에 의한 검은팥 펩타이드를 수득하였다.
<4-3> 플라보르자임(Flavourzyme) 처리에 따른 검은팥 펩타이드 제조
상기 실시예 <4-2>에서와 동일한 방법으로 알카라아제 대신 플라보르자임 (Novozymes)을 처리하여 플라보르지임 처리에 의한 검은팥 펩타이드를 수득하였다.
<4-4> 뉴트라제(Neutrase) 처리에 따른 검은팥 펩타이드 제조
상기 실시예 <4-2>에서와 동일한 방법으로 알카라아제 대신 뉴트라제 (Novozymes)을 처리하여 뉴트라제 처리에 의한 검은팥 펩타이드를 수득하였다.
<4-5> 프로타멕스(Protamex) 처리에 따른 검은팥 펩타이드 제조
상기 실시예 <4-2>에서와 동일한 방법으로 알카라아제 대신 프로타멕스 (Novozymes)를 처리하여 프로타멕스 처리에 의한 검은팥 펩타이드를 수득하였다.
<4-6> 프로테아제-NP(Protease-NP) 처리에 따른 검은팥 펩타이드 제조
상기 실시예 <4-2>에서와 동일한 방법으로 알카라아제 대신 프로테아제-NP (Bioland, Chaonan, Korea)를 처리하여 프로테아제-NP 처리에 의한 검은팥 펩타이드를 수득하였다.
[실험예 1] 팥 에탄올 추출물의 근육 생성 활성 확인
mTOR 단백질은 인산화되어 활성화되었을 때, 근 세포 내의 PI3K/Akt 신호전달경로에서 근단백질 합성 및 근육량 증가에 관여하는 단백질의 활성화를 유도할 수 있음이 알려져 있다. 이에, 팥 에탄올 추출물의 근육 생성 유도 활성을 확인하기 위해, mTOR Sandwich ELISA kit (Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA, USA)를 이용하여 mTOR의 활성을 확인하였다.
근육모세포주인 L6 세포(ATCC; Manassas, VA, USA)를 10% 우태아혈청(FBS; Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA)이 함유된 Dulbecco's modified Eagle's media (DMEM; Hyclone)와 함께 6-웰 플레이트에 1 × 105 cell/mL이 되도록 접종 후 24 시간 동안 배양하였다. 배양 후, 웰에 있는 배지를 제거하고 2% 말 혈청(HS; Hyclone)이 함유된 DMEM (Hyclone)로 교환하여 6일간 추가 배양하여 L6 세포를 근관세포(myotube)로 분화시켰다. 그런 다음, 상기 실시예 <1-2>에서 100% 에탄올로 제조한 팥 에탄올 추출물을 40 μg/mL의 농도로 세포에 처리하고 12 시간 동안 배양하였다. 배양 후, 세포 용해 완충용액(cell lysis buffer)를 처리하여 세포를 용해시켰다. 수득한 세포 용해물 내 단백질을 브래드포드(Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, CA, USA) 법으로 정량한 다음, 1 ㎎/mL 농도로 정량하여 항-mTOR 항체가 부착된 마이크로웰에 세포 용해물을 50 μL씩 분주하여 37℃에서 2 시간 동안 배양하였다. 배양 후, 세척 완충용액(Washing buffer)으로 총 4회 씻은 후, 확인용 항체(detection antibody)를 처리하고 37 에서 1시간 배양했으며, 다시 세척 완충용액으로 총 4회 씻은 후, 겨자무 과산화효소(horseradish peroxidase, HRP)가 접합된 2차 항체를 넣고 37 에서 30 분동안 배양하였다. 마지막으로 세척 완충용액으로 총 4회 씻은 후, TMB 기질을 각 웰에 넣고 37 에서 10 분 동안 배양하고 정지 완충용액(stop solution)을 가하여 TBM의 반응을 멈추었다. 2 분 뒤, 450 nm의 파장으로 흡광도를 측정하여 팥 에탄올 추출물을 처리한 근관 세포 내 mTOR 수준을 측정하였다. 그 결과를 도 1에 나타내었다.
그 결과, 도 1에 나타난 바와 같이 팥 에탄올 추출물의 처리에 의해 L6 근육세포에서 mTOR의 활성이 유의적(**p < 0.01)으로 증가한 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 에탄올 추출물이 근육세포 내에서 근육 생성을 증가시키는 능력이 우수하다는 것을 의미한다.
[
실험예
2] 팥 에탄올 추출물의
근단백질
합성 관여 인자의
mRNA
전사수준 확인
근육모세포주인 L6 세포(ATCC)를 10% FBS (Hyclone)가 함유된 DMEM와 함께 6-웰 플레이트에 2 × 105 cell/mL이 되도록 접종 후 배양하였다. 세포 밀도가 약 80 내지 85%가 되었을 때, 웰에 있는 배지를 제거하고 2% HS (Hyclone)가 함유된 DMEM (Hyclone)로 교환하여 L6 세포를 근관세포(myotube)로 분화시켰다. 6일 후, 상기 실시예 <1-2>에서 100% 에탄올로 제조한 팥 에탄올 추출물을 25, 50 또는 40 μg/mL의 농도로 녹인 DMEM (Hyclone)으로 배지를 교환하고 24 시간 동안 배양하였다. 이때, 시료 대신 0.01% DMSO를 처리한 군을 대조군으로 하였다. 24 시간 후, 세포를 수득하여 단백질 가수분해효소 억제제 칵테일(Sigma-Aldrich St. Louis, MO, USA)이 포함된 NP-40 완충용액(ELPIS-Biotech, Daejeon, Korea)으로 용해시켜 세포 용해물을 수득하였다. 수득한 세포 용해물은 13,000 rpm으로 10 분간 원심분리하여 상등액을 취하였다. 상등액 내 단백질 농도를 브래드포드로 정량한 다음, 일정 농도의 단백질을 5 분간 가열하고 10% SDS-PAGE gel에 전개하여 SDS-PAGE 전기영동으로 세포 내 단백질을 분리하였다. 분리된 단백질은 니트로셀룰로스 막으로 전달하였다. 그런 다음, 항-p-p70S6K 항체, 항-t-p70S6K 항체, 항-p-4EBP1 항체, 항-t-4EBP1 항체 또는 항-α-tubulin 항체(Cell Signaling Technology)를 각각 2.5% 소 혈청 알부민(BSA)에 1:1000 비율로 희석하여 1차 항체로서 니트로셀룰로스 막에 전달된 단백질과 20시간 동안 상온에서 반응시켰다. 1차 항체를 반응시킨 다음, (Tris-buffer Saline Tween20 (TBST)를 이용하여 니트로셀룰로스 막을 10 분간 3 회 세척하였다. 그런 다음, 1차 항체를 인지하는 HRP가 접합된 2차 항체(Bethyl Laboratories, Inc., Montgomery, TA, USA)를 2.5% BSA (bioWORLD)에 1:5000이 되도록 희석하여 니트로셀룰로스 막과 2시간 동안 상온에서 반응시켰으며, TBST를 이용하여 10분씩 3회에 걸쳐 세척하였다. 단백질 밴드는 ECL 웨스턴블럿 검출 시약(Amersham, Tokyo, Japan)을 사용하여 발색하였으며, G;BOX EF 이미징 시스템 (Syngene, Cambridge, UK)을 이용하여 발색된 단백질 밴드를 확인하였다. 그 결과를 도 2에 나타내었다.
그 결과, 도 2에서 나타난 바와 같이, 팥 에탄올 추출물을 처리함에 따라 L6 근육세포에서 mRNA 전사 과정을 통해 근단백질 합성에 관여하는 p-p70S6K 및 p-4EBP1의 단백질 발현 수준이 증가한 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 에탄올 추출물이 근육세포 내에서 근단백질 합성을 위한 관련 인자의 mRNA 번역 과정을 촉진시키는 것을 의미한다.
[실험예 3] 팥 에탄올 추출물의 근 단백질 분해 억제 활성 확인
근육모세포주인 L6 세포(ATCC)를 10% FBS (Hyclone)함유 DMEM (Hyclone)와 함께 6-웰 플레이트에 2 × 105 cell/mL이 되도록 접종 후 배양하였다. 세포 밀도가 약 80 내지 85%가 되었을 때, 웰에 있는 배지를 제거하고 2% HS (Hyclone)가 함유된 DMEM (Hyclone)으로 교환하여 L6 세포를 근관세포(myotube)로 분화시켰다. 2일에 한 번씩 새로운 배지로 교체하여 총 6일 동안 분화를 진행하였다. 분화 후, 50 ng/mL의 TNF-α가 함유된 DMEM 배지에 상기 실시예 <1-2>에서 100% 에탄올로 제조한 팥 에탄올 추출물을 20 또는 40 μg/mL의 농도로 녹인 후, 세포에 처리하였다. 6시간 후, TRIzol시약(Takara, Osaka, Japan)을 사용하여 총 RNA를 분리하였다. 분리한 총 RNA는 나노드랍(NanoDrop 1000; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA)을 이용하여 정량하였다. 16 μL RNA를 정량하여, 역전사효소 프리믹스(Reverse Transcriptase Premix, ELPIS-Biotech)와 혼합하여 PCR 기계(Gene Amp PCR System 2700; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA)를 이용하여 42℃ 55분, 70℃ 15분의 조건에서 cDNA로 합성하였다. 합성된 cDNA 중 4 μL의 cDNA, 하기 [표 1]에 기재된 서열의 정방향 및 역방향 프라이머쌍(Bioneer, Deajeon, Korea), 및 PCR 프리믹스(ELPIS-Biotech)를 혼합하여 PCR 시료를 제조한 뒤, 95℃에서 30초, 60℃에서 1분, 72℃에서 1분을 30번 반복하여 PCR을 수행하였다.
PCR 결과 증폭된 cDNA를 1.5% 아가로즈 젤로 전기영동으로 분리하였으며, G;BOX EF 영상화 시스템(Syngene)을 이용하여 cDNA 밴드를 확인하였다. 그 결과를 도 3에 나타내었다.
| 증폭유전자 | 서열명 | 서열번호 | 서열 | 방향 |
| Atrogin-1 | Atrogin_F | 서열번호 1 | 5'-GTCCAGAGAGTCGGCAAGTC-3' | 정방향 |
| Atrogin_R | 서열번호 2 | 5'-GTCGGTGATCGTGAGACCTT-3' | 역방향 | |
| MuRF-1 | MuRF_F | 서열번호 3 | 5'-TCTACTCGGCCACAGGCGCT-3' | 정방향 |
| MuRF_R | 서열번호 4 | 5'-CTTGACAGCTCCCGCCGCAA-3' | 역방향 | |
| β-Actin | Actin_F | 서열번호 5 | 5'-CTGTGTGGATTGGTGGCTCTAT-3' | 정방향 |
| Actin_R | 서열번호 6 | 5'-GTGTAAAACGCAGCTCAGTAACA3' | 역방향 |
그 결과, 도 3에 나타낸 바와 같이 팥 에탄올 추출물을 처리함에 따라 L6 근육세포에서 atrogin-1 및 MuRF-1의 mRNA 발현이 감소함을 알 수 있었다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 에탄올 추출물이 근육세포 내에서 근 단백질 분해를 억제하는 능력이 우수하다는 것을 의미한다.
[실험예 4] 팥 에탄올 추출물의 근육 분화 촉진 활성 확인
근육모세포주인 L6 세포(ATCC)를 10% FBS (Hyclone)함유 DMEM (Hyclone)와 함께 6-웰 플레이트에 2 × 105 cell/mL이 되도록 접종 후 배양하였다. 세포 밀도가 약 80 내지 85%가 되었을 때, 웰에 있는 배지를 제거하고 2% HS가 함유된 DMEM (Hyclone)에 상기 실시예 <1-2>에서 100% 에탄올로 제조한 팥 에탄올 추출물을 25, 50 또는 40 μg/mL의 농도로 녹인 후, 세포에 처리하여 근관세포로 분화를 유도하였다. 이 때, 시료 대신 0.01% DMSO를 처리한 군을 대조군으로 사용하였다. 이 과정을 2 일간 3회 반복, 총 6일 동안 진행하여 분화시킨 후, TRIzol시약(Takara)을 사용하여 총 RNA를 분리하였다. 분리한 RNA는 상기 [실험예 3]과 동일한 방법으로 cDNA 합성 및 PCR을 수행하여 MyoD 및 myogenin의 mRNA 전사 수준을 확인하였다. PCR을 위해 사용한 프라이머(Bioneer)의 서열은 하기 [표 2]에 나타난 바와 같다. PCR 결과 증폭된 cDNA를 1.5% 아가로즈 젤로 전기영동으로 분리하였으며, G;BOX EF 영상화 시스템(Syngene)을 이용하여 cDNA 밴드를 확인하였다. 그 결과를 도 4에 나타내었다.
| 증폭유전자 | 서열명 | 서열번호 | 서열 | 방향 |
| MyoD | MyoD_F | 서열번호 7 | 5'-GGATGGTGCCCCTGGGTCCT-3' | 정방향 |
| MyoD_R | 서열번호 8 | 5'-TGGCCTTCGCTGTGAGTCGC-3' | 역방향 | |
| Myogenin | Myogenin_F | 서열번호 9 | 5'-TGGGCTGCCACAAGCCAGAC-3' | 정방향 |
| Myogenin_R | 서열번호 10 | 5'-CAGCCCAGCCACTGGCATCA-3' | 역방향 | |
| β-Actin | Actin_F | 서열번호 5 | 5'-CTGTGTGGATTGGTGGCTCTAT-3' | 정방향 |
| Actin_R | 서열번호 6 | 5'-GTGTAAAACGCAGCTCAGTAACA3' | 역방향 |
그 결과, 도 4에 나타낸 바와 같이 팥 에탄올 추출물을 처리함에 따라 L6 근육세포에서 MyoD 및 myogenin의 mRNA 발현이 증가함을 알 수 있었다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 에탄올 추출물이 근육세포 내에서 근육 분화를 촉진하는 능력이 우수하다는 것을 의미한다.
[실험예 5] 팥 열수 추출물의 근육생성 활성
상기 실험예 1에서와 동일한 방법으로 실시예 <1-5>에서 제조한 팥 열수 추출물을 40 μg/mL로 처리하여 mTOR 활성을 평가하였다. 그 결과를 도 5 나타내었다.
도 5 나타낸 바와 같이 팥 열수 추출물의 처리에 의해 L6 근육세포에서 mTOR의 활성이 유의적(**p < 0.01)으로 증가한 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 열수 추출물이 근육세포 내에서 근육 생성을 증가시키는 능력이 우수하다는 것을 의미한다.
[실험예 6] 팥 아임계 추출물의 근육생성 활성
상기 실험예 1에서와 동일한 방법으로 실시예 <1-7>에서 제조한 팥 아임계 추출물을 5 μg/mL로 처리하여 mTOR 활성을 평가하였다. 그 결과를 도 6에 나타내었다.
도 6에 나타낸 바와 같이 팥 아임계 추출물의 처리에 의해 L6 근육세포에서 mTOR의 활성이 유의적(**p < 0.01)으로 증가한 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 아임계 추출물이 근육세포 내에서 근육 생성을 증가시키는 능력이 우수하다는 것을 의미한다.
[실험예 7] 팥 단백질 및 펩타이드의 근육생성 활성
상기 실험예 1에서와 동일한 방법으로 실시예 <2-1>, <2-4> <2-5>, <2-6> 에서 제조한 팥 단백질과 팥 펩타이드를 40 μg/mL로 처리하여 mTOR 활성을 평가하였다. 그 결과를 도 7에 나타내었다.
그 결과, 도 7에 나타낸 바와 같이 팥 단백질과 팥 펩타이드의 처리에 의해 L6 근육세포에서 mTOR의 활성이 유의적(**p < 0.01)으로 증가한 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 단백질과 팥 펩타이드가 근육세포 내에서 근육 생성을 증가시키는 능력이 우수하다는 것을 의미한다.
[실험예 8] 팥 펩타이드의 mRNA 전사 촉진 활성
상기 실험예 2에서와 동일한 방법으로 실시예 <2-5>에서 제조한 팥 펩타이드를 50과 또는 100 μg/mL를 처리하여 mTOR 활성을 평가하였다. 그 결과를 도 8에 나타내었다.
그 결과, 도 8에 나타낸 바와 같이 팥 펩타이드를 처리함에 따라 L6 근육세포에서 mRNA 전사 과정을 통해 근단백질 합성에 관여하는 p-p70S6K 및 p-4EBP1의 단백질 발현양이 증가한 것을 확인할 수 있다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 펩타이드가 근육세포 내에서 근단백질 합성을 위한 mRNA 전사 과정을 촉진시키는 것을 의미한다.
[실험예 9] 팥 펩타이드의 근육 분화 촉진 활성
상기 실험예 4에서와 동일한 방법 실험을 진행하였다. 팥 에탄올 추출물 대신 상기 실시예 <2-5>에서 제조한 팥 펩타이드를 50 또는 100 μg/mL의 농도로 녹인 후, 세포에 처리하여 근관세포 분화를 유도하였다. 이 때, 시료 대신 0.01% DMSO를 처리한 군을 대조군으로 하였다. 그 결과를 도 9에 나타내었다.
그 결과, 도 9에 나타낸 바와 같이 팥 펩타이드를 처리함에 따라 L6 근육세포에서 MyoD 및 myogenin의 mRNA 발현이 증가함을 알 수 있었다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 펩타이드가 근육세포 내에서 근육 분화를 촉진하는 능력이 우수하다는 것을 의미한다.
[실험예 10] 검은팥 에탄올 추출물의 근육생성 활성
상기 실험예 1에서와 동일한 방법으로 실시예 <3-2>에서 100% 에탄올로 제조한 검은팥 에탄올 추출물을 40 μg/mL로 처리하여 mTOR 활성을 평가하였다. 그 결과를 도 10에 나타내었다.
도 10에 나타낸 바와 같이 검은팥 에탄올 추출물의 처리에 의해 L6 근육세포에서 mTOR의 활성이 유의적(**p < 0.01)으로 증가한 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 이는 본 발명의 검은팥 에탄올 추출물이 근육세포 내에서 근육 생성을 증가시키는 능력이 우수하다는 것을 의미한다.
[실험예 11] 팥 에탄올 추출물의 운동수행능력 향상 활성
팥 에탄올 추출물의 운동수행능력을 평가하기 위해 PGC-1α 활성을 루시퍼라제 분석으로 수행하였다. COS7 원숭이 신장세포(ATCC)를 1.5 μ 105 cells/well로 24-웰 플레이트에서 배양한 뒤, 리포펙터(Aptabio, Yongin, Korea)를 이용하여 pGL3-PGC-1α-Luc 플라스미드 (Addgene, Cambridge, MA, USA)를 세포에 형질주입 하였다. 4시간 형질주입 후, 세포를 24시간 동안 안정화시켰다. 그런 다음, 상기 실시예 <1-2>에서 100% 에탄올로 제조한 팥 에탄올 추출물을 40 μg/mL의 농도로 DMEM에 녹인 후, 세포에 24시간 처리하였다. 최종 24시간 후, NP-40 완충용액(ELPIS-Biotech)으로 용해시켜 세포 용해하였고, 세포 용해물 내 루시퍼라제 활성을 측정하였다. 그 결과를 도 11에 나타내었다.
그 결과, 도 11에 나타낸 바와 같이 팥 에탄올 추출물이 운동수행능력에 관여하는 주요인자인 PGC-1α의 활성을 유의적(**p < 0.01)으로 증가시킴을 알 수 있었다. 따라서 팥 에탄올 추출물은 운동수행능력을 증진시킴을 확인하였다.
[실험예 12] 팥 에탄올 추출물의 미토콘드리아 생합성 촉진 활성
상기 실험예 4에서와 동일한 방법으로 실험을 진행하였다. 상기 실시예 1-2에서 100% 에탄올로 제조한 팥 에탄올 추출물을 25, 50, 40 μg/mL의 농도로 녹인 후, 세포에 처리하여 myotube 분화를 유도하였다. 이 때, 시료 대신 0.01% DMSO를 처리한 군을 대조군으로 하였다. 또한 RT-PCR시 하기의 특정 프라이머(Bioneer)를 사용하여 PCR을 수행하였다. 그 결과를 도 12에 나타내었다.
| 증폭유전자 | 서열명 | 서열번호 | 서열 | 방향 |
| PGC-1α | PGC_F | 서열번호 11 | 5'-ATGTGTCGCCTTCTTGCTCT-3' | 정방향 |
| PGC_R | 서열번호 12 | 5'-ATCTACTGCCTGGGGACCTT-3' | 역방향 | |
| ERRα | ERR_F | 서열번호 13 | 5'-AAGGGGATGGAGACCACAGT-3' | 정방향 |
| ERR_R | 서열번호 14 | 5'-TGAGGTGGGAGCTGATAGGG-3' | 역방향 | |
| NRF-1 | NRF_F | 서열번호 15 | 5'-TGGACCCAAGCATTACGGAC-3' | 정방향 |
| NRF_R | 서열번호 16 | 5'-GGTCATTTCACCGCCCTGTA-3' | 역방향 | |
| Tfam | Tfam_F | 서열번호 17 | 5'-GCTTCCAGGAGGCTAAGGAT-3' | 정방향 |
| Tfam_R | 서열번호 18 | 5'-CCCAATCCCAATGACAACTC-3' | 역방향 | |
| β-Actin | Actin_F | 서열번호 5 | 5'-CTGTGTGGATTGGTGGCTCTAT-3' | 정방향 |
| Actin_R | 서열번호 6 | 5'-GTGTAAAACGCAGCTCAGTAACA3' | 역방향 |
그 결과, 도 12에 나타낸 바와 같이 팥 에탄올 추출물을 처리함에 따라 PGC-1α, ERRα, NRF-1, Tfam의 mRNA 발현이 증가한 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 에탄올 추출물이 운동수행능력에 깊은 연관성이 있는 미토콘드리아 생합성 관련 유전자 발현을 증가시키는 능력이 우수하다는 것을 의미한다.
[실험예 13] 팥 단백질 및 펩타이드의 운동수행능력 향상 활성
상기 실험예 11에서와 동일한 방법으로 실시예 <2-1>, <2-2>, <2-3>, <2-4>, <2-5> 및 <2-6>에서 제조한 팥 단백질 및 팥 펩타이드를 각각 40 μg/mL로 처리하여 PGC-1α 활성을 평가하였다. 그 결과를 도 13에 나타내었다.
그 결과, 도 13에 나타낸 바와 같이 팥 단백질 및 팥 펩타이드가 운동수행능력에 관여하는 주요인자인 PGC-1α의 활성을 유의적(**p < 0.01)으로 증가시킴을 알 수 있었다. 따라서 팥 단백질 및 팥 펩타이드는 운동수행능력을 증진시킴을 확인하였다.
[실험예 14] 팥 펩타이드의 미토콘드리아 생합성 촉진 활성
상기 실험예 4에서와 동일한 방법으로 실시예 <2-5>에서 제조한 팥 펩타이드를 50 또는 100 μg/mL로 처리하여 팥 펩타이드의 미토콘드리아 생합성 촉진 활성 활성을 평가하였다. 그 결과를 도 14에 나타내었다.
그 결과, 도 14에 나타낸 바와 같이 팥 펩타이드를 처리함에 따라 PGC-1α, ERRα, NRF-1, Tfam의 mRNA 발현이 증가한 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 펩타이드가 운동수행능력에 깊은 연관성이 있는 미토콘드리아 생합성 관련 유전자 발현을 증가시키는 능력이 우수하다는 것을 의미한다.
[실험예 15] 검은팥 에탄올 추출물의 운동수행능력 향상 활성
상기 실험예 11에서와 동일한 방법으로 실시예 <3-2>에서 100% 에탄올로 제조한 검은팥 에탄올 추출물을 40 μg/mL로 처리하여 PGC-1α 활성을 평가하였다. 그 결과를 도 15에 나타내었다.
그 결과, 도 15에 나타낸 바와 같이 검은팥 에탄올 추출물이 운동수행능력에 관여하는 주요인자인 PGC-1α의 활성을 유의적(**p < 0.01)으로 증가시킴을 알 수 있었다. 따라서 검은팥 에탄올 추출물은 운동수행능력을 증진시킴을 확인하였다.
[실험예 16] 팥 펩타이드의 근위축 억제 활성
<16-1> 동물의 사육 및 근위축 유도
실험동물로 생후 7주된 수컷쥐(C57BL/6N; Young Bio)를 구입하여 실험을 진행하였다. 모든 동물의 사육은 연세실험동물연구센터(Yonsei Laboratory Animal Reaserch Center; YLARC, Seoul, Korea)에서 진행되었으며, 사육실 환경은 온도 23 ± 2, 상대습도 55 ± 10%로 유지시켰다. 실험 시작 전, 총 20마리의 쥐를 무작위로 1군당 5마리가 되도록 정상군, 근위축군, 팥300 투여군, 팥600 투여군으로 나누었다. 1 주일간 적응시킨 후, 325 mg/kg의 트리브로모메탄올(tribromoethanol, Sigma-aldrich)을 복강 주사하여 마취를 유도하였다. 마취 후, 근위축군과 팥 투여군에 있는 쥐의 오른쪽 뒷다리(hindlimb) 장딴지근육(gastrocnemius muscle)과 오른쪽 발바닥을 피부 스테이플러(skin stapler)(Unidus, Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea)를 사용하여 스테이플러 심으로 근육을 손상시키고 오른쪽 뒷다리가 움직이지 못하게 하였으며 이 상태를 일주일 간 유지시켰다. 일주일 후, 장딴지근과 발바닥에 고정되어 있던 스테이플러 심을 제거하고 다시 일주일간 실시예 <1-2>에서 50% 에탄올로 제조한 팥 에탄올 추출물을 300 mg/kg 또는 600 mg/kg의 농도로 매일 경구투여하여 회복을 유도하였다. 이 때, 정상군과 근위축군은 시료 대신에 식염수로 경구투여를 실시하였다.
<16-2> 근력 측정
경구 투여 기간이 끝나고, 근력측정기(Chatillon force measurement system; Columbus Instrument, Columbus, OH, USA)를 이용하여 쥐의 근력을 측정하였다. 쥐가 근력측정기의 막내를 놓을 때까지 일정한 힘으로 쥐의 꼬리를 당겼으며, 한 마리당 총 5회 연속 테스트를 실시하였다.
그 결과, 도 16에 나타낸 바와 같이 정상군에 비해 근위축군에서 근력이 유의적(#p < 0.05)으로 감소하였으나 팥 에탄올 추출물을 처리함에 따라 근력이 유의적(*p < 0.05)으로 증가한 것을 확인하였다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 에탄올 추출물이 근위축으로 인해 감소한 근력을 증가시키는 효과가 우수하다는 것을 의미한다.
<16-3> 지구력 측정
트레드밀 기기(LE8710MTS; Panlab, Barcelona, Spain)를 이용하여 실험동물의 운동수행능력을 평가하였다. 최초 8 m/min의 속도로 시작하여, 1 분마다 1 m/min씩 속도를 높였다. 쥐가 shock grid에 닿았을 때 0.2 mA의 전기를 주도록 설정하였으며, 쥐가 전기충격을 10초간 받아도 더 이상 달리지 않는 시점에서 실험을 멈추고 시간과 거리를 측정하였다.
그 결과, 도 17에 나타낸 바와 같이 정상군에 비해 근위축군에서 운동거리 및 운동시간이 유의적(#p < 0.05)으로 감소하였으나 팥 에탄올 추출물을 처리함에 따라 운동거리 및 시간이 유의적(*p < 0.05)으로 증가한 것을 확인하였다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 에탄올 추출물이 근위축으로 인해 감소한 운동수행능력을 향상시키는 효과가 우수하다는 것을 의미한다.
<16-4> 근육 무게 측정
근력과 운동수행능력 측정이 끝난 후, 실험동물을 325 mg/kg의 트리브로모메탄올(Sigma-aldrich)을 복강 주사하여 마취 후 심채혈을 통해 희생을 하였다. 심장박동이 멈춘 것을 확인한 뒤, 오른쪽 뒷다리에서 손상을 입지 않은 전경골근(tibialis anterior muscle)을 적출하여 무게를 측정하였다.
그 결과, 도 18에 나타낸 바와 같이 정상군에 비해 상처를 입지 않은 근위축군의 전경골근의 무게가 운동시간이 유의적(#p < 0.05)으로 감소하였으나 팥 에탄올 추출물을 처리함에 무게가 유의적(*p < 0.05)으로 증가한 것을 확인하였다. 이는 본 발명의 팥 에탄올 추출물이 근위축으로 인해 감소한 근육의 무게를 증가시키는 효과가 우수하다는 것을 의미한다.
이하, 본 발명에 따른 상기 팥을 유효성분으로 함유하는 근기능 개선용 또는 운동수행능력 증강용 식품류 및 의약품의 제조예를 설명하나, 본 발명은 이를 한정하고자 함이 아닌 단지 구체적으로 설명하고자 함이다. 상기 근 기능 개선 효과 또는 운동수행능력 증강 효과가 우수한 팥 에탄올 추출물을 가지고 하기와 같은 조성성분 및 조성비에 따라 제조예 1 내지 2의 의약품 및 식품 조성물을 통상적인 방법에 따라서 제조하였다.
[제조예 1] 의약품
[제조예 1-1] 산제
상기 실시예 1 내지 4의 팥 추출물, 팥 펩타이드, 검은팥 추출물 또는 검은팥 펩타이드 50 mg, 결정셀룰로오즈 2 g을 혼합한 후 통상의 산제 제조방법에 따라서 기밀포에 충진하여 산제를 제조하였다.
[제조예 1-2] 정제
상기 실시예 1 내지 4의 팥 추출물, 팥 펩타이드, 검은팥 추출물 또는 검은팥 펩타이드 50 mg, 결정셀룰로오즈 400 mg, 스테아린산 마그네슘 5 mg을 혼합한 후 통상의 정제 제조방법에 따라서 타정하여 정제를 제조하였다.
[제조예 1-3] 캡슐제
상기 실시예 1 내지 4의 팥 추출물, 팥 펩타이드, 검은팥 추출물 또는 검은팥 펩타이드 30 mg, 유청단백질 100 mg, 결정셀룰로오즈 400 mg, 스테아린산 마그네슘 6 mg을 혼합한 후 통상의 캡슐제 제조방법에 따라서 젤라틴 캡슐에 충전하여 캡슐제를 제조하였다.
[제조예 2] 식품
[제조예 2-1] 건강식품의 제조
상기 실시예 1 내지 4의 팥 추출물, 팥 펩타이드, 검은팥 추출물 또는 검은팥 펩타이드 1000 mg, 비타민 A 아세테이트 70 μg, 비타민 E 1.0 mg, 비타민 B1 0.13 mg, 비타민 B2 0.15 mg, 비타민 B6 0.5 mg, 비타민 B12 0.2 μg, 비타민 C 10 mg, 비오틴 10 μg, 니코틴산아미드 1.7 mg, 엽산 50 μg, 판토텐산 칼슘 0.5 mg, 황산제1철 1.75 mg, 산화아연 0.82 mg, 탄산마그네슘 25.3 mg, 제1인산칼륨 15 mg, 제2인산칼슘 55 mg, 구연산칼륨 90 mg, 탄산칼슘 100 mg, 염화마그네슘 24.8 mg를 혼합하여 제조할 수 있으며, 그 배합비를 임의로 변형 실시하여도 무방하며, 통상의 건강식품 제조방법에 따라 상기의 성분을 혼합한 다음, 과립을 제조하고, 통상의 방법에 따라 건강식품 조성물 제조에 사용할 수 있다.
[제조예 2-2] 건강음료의 제조
상기 실시예 1 내지 4의 팥 추출물, 팥 펩타이드, 검은팥 추출물 또는 검은팥 펩타이드 1000 mg, 구연산 1000 mg, 올리고당 100 g, 매실농축액 2 g, 타우린 1 g에 정제수를 가하여 전체 900 mL 통상의 건강음료 제조방법에 따라 상기의 성분을 혼합한 다음, 약 1시간동안 85에서 교반 가열한 후, 만들어진 용액을 여과하여 멸균된 2 L용기에 취득하여 밀봉 멸균한 뒤 냉장 보관한 다음 건강음료 조성물 제조에 사용할 수 있다.
[제조예 2-3] 츄잉껌
껌 베이스 20 중량%, 설탕 76.9 중량%, 향료 1 중량% 및 물 2 중량% 와 상기 실시예 실시예 1 내지 4의 팥 추출물, 팥 펩타이드, 검은팥 추출물 또는 검은팥 펩타이드 0.1 중량%를 배합하여 통상의 방법으로 츄잉껌을 제조하였다.
[제조예 2-4] 캔디
설탕 60 중량%, 물엿 39.8 중량% 및 향료 0.1 중량%와 상기 실시예 1 내지 4의 팥 추출물, 팥 펩타이드, 검은팥 추출물 또는 검은팥 펩타이드 0.1 중량%를 배합하여 통상의 방법으로 캔디를 제조하였다.
[제조예 2-5] 비스켓
박력 1급 25.59 중량%, 중력 1급 22.22 중량%, 정백당 4.80 중량%, 식염 0.73 중량%, 포도당 0.78 중량%, 팜쇼트닝 11.78 중량%, 암모늄 1.54 중량%, 중조 0.17 중량%, 중아황산나트륨 0.16 중량%, 쌀가루 1.45 중량%, 비타민 B 0.0001 중량%, 밀크향 0.04 중량%, 물 20.6999 중량%, 전지분유 1.16 중량%, 대용분유 0.29 중량%, 제1인산칼슘 0.03 중량%, 살포염 0.29 중량% 및 분무유 7.27 중량%와 상기 실시예 1 내지 4의 팥 추출물, 팥 펩타이드, 검은팥 추출물 또는 검은팥 펩타이드 1.00 중량%를 배합하여 통상의 방법으로 비스켓을 제조하였다.
Claims (28)
- 팥(Vigna angularis)의 추출물을 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물.
- 제 1항에 있어서, 상기 추출물은 물, C1 내지 C6의 유기용매, 아임계 유체 및 초임계 유체로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 하나 이상의 용매로 팥을 추출하여 수득한 것을 특징으로 하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물.
- 팥 유래 단백질 또는 펩타이드를 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물.
- 제 3항에 있어서, 상기 팥 유래 단백질은 하기 i) 내지 v) 단계로 이루어진 방법으로 수득하고, 상기 팥 유래 펩타이드는 하기 i) 내지 vii) 단계로 이루어진 방법으로 수득하는 것을 특징으로 하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물:i) 건조된 팥을 분쇄하고 헥산을 용매로 추출하는 단계;ii) 상기 단계 i)에서 추출한 헥산 추출물을 제거하고, 박에 물을 가하여 pH 7.0 내지 10.0 조건에서 방치하는 단계;iii) 상기 단계 ii)에서 방치한 용액을 원심분리하여 상등액을 수득하는 단계;iv) 상기 단계 iii)에서 수득한 상층액을 다시 pH 2.0 내지 6.0 조건에서 방치하는 단계;v) 상기 단계 iv)에서 방치한 용액을 다시 원심분리하여 침전한 침전체를 팥 유래 단백질로 수득하는 단계;vi) 상기 단계 v)에서 수득한 팥 유래 단백질에 가수분해효소를 가하고 효소 반응한 후, 여과하여 침전물을 제거하는 단계; 및vii) 상기 단계 vi)에서 침전물이 제거된 여과액을 동결건조하여 펩타이드를 수득하는 단계.
- 제 4 항에 있어서, 상기 단계 vi)의 가수분해 효소는 알카라아제(Alcalase), 플라보르자임(Flavourzyme), 뉴트라아제(Neutrase), 프로타멕스(Protamex) 및 단백질가수분해효소-NP(Protease-NP)로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 어느 하나 이상의 단백질 가수분해효소로 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물.
- 제 1항 내지 제 5항 중 어느 한 항에 있어서, 상기 팥은 팥(V. angularis W.F.Wight) 및 검은팥(V. angularis var. angularis)으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 어느 하나 또는 둘 다인 것을 특징으로 하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물.
- 제 1항 내지 제 5항 중 어느 한 항에 있어서, 상기 근육 질환은 근기능 저하, 근육 소모 또는 근육 퇴화로 인한 근육 질환인 것을 특징으로 하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물.
- 제 7항에 있어서, 상기 근육 질환은 긴장감퇴증(atony), 근위축증(muscular atrophy), 근이영양증(muscular dystrophy), 근무력증, 악액질(cachexia) 및 근육감소증(sarcopenia)으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 어느 하나 이상인 것을 특징으로 하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물.
- 제 1항 내지 제 5항 중 어느 한 항에 있어서, 운동수행능력 향상은 퇴행성 질환, 미토콘드리아 이상 질환, 지구력 저하증, 순발력 저하증, 무기력증, 근육 폐기 및 우울증 등으로 이루어진 군에서 선택되는 하나 이상의 질병을 예방 또는 치료하는 것임을 특징으로 하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물.
- 팥(Vigna angularis)의 추출물을 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 식품 조성물.
- 제 10항에 있어서, 상기 추출물은 물, C1 내지 C4의 유기용매, 아임계 유체 및 초임계 유체로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 하나 이상의 용매로 팥을 추출하여 수득한 것을 특징으로 하는, 근기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 식품 조성물.
- 팥 유래 단백질 또는 펩타이드를 유효성분으로 포함하는, 근기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 식품 조성물.
- 제 12항에 있어서, 상기 팥 유래 단백질은 하기 i) 내지 v) 단계로 이루어진 방법으로 수득하고, 상기 팥 유래 펩타이드는 하기 i) 내지 vii) 단계로 이루어진 방법으로 수득하는 것을 특징으로 하는, 근기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 식품 조성물:i) 건조된 팥을 분쇄하고 헥산을 용매로 추출하는 단계;ii) 상기 단계 i)에서 추출한 헥산 추출물을 제거하고, 박에 물을 가하여 pH 7.0 내지 10.0 조건에서 방치하는 단계;iii) 상기 단계 ii)에서 방치한 용액을 원심분리하여 상등액을 수득하는 단계;iv) 상기 단계 iii)에서 수득한 상층액을 다시 pH 2.0 내지 6.0 조건에서 방치하는 단계;v) 상기 단계 iv)에서 방치한 용액을 다시 원심분리하여 침전한 침전체를 팥 유래 단백질로 수득하는 단계;vi) 상기 단계 v)에서 수득한 팥 유래 단백질에 가수분해효소를 가하고 효소 반응한 후, 여과하여 침전물을 제거하는 단계; 및vii) 상기 단계 vi)에서 침전물이 제거된 여과액을 동결건조하여 펩타이드를 수득하는 단계.
- 제 13 항에 있어서, 상기 단계 vi)의 가수분해 효소는 알카라아제(Alcalase), 플라보르자임(Flavourzyme), 뉴트라아제(Neutrase), 프로타멕스(Protamex) 및 단백질가수분해효소-NP(Protease-NP)로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 어느 하나 이상의 단백질 가수분해효소로 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는, 근기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 식품 조성물.
- 제 10항 내지 제 14항 중 어느 한 항에 있어서, 상기 팥은 팥(V. angularis W.F.Wight) 및 검은팥(V. angularis var. angularis)으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 어느 하나 또는 둘 다인 것을 특징으로 하는, 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 약학적 조성물.
- 제 10항 내지 제 14항 중 어느 한 항에 있어서, 상기 근육 질환은 근기능 저하, 근육 소모 또는 근육 퇴화로 인한 근육 질환인 것을 특징으로 하는, 근기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 식품 조성물.
- 제 16항에 있어서, 상기 근육 질환은 긴장감퇴증(atony), 근위축증(muscular atrophy), 근이영양증(muscular dystrophy), 근무력증, 악액질(cachexia) 및 근육감소증(sarcopenia)으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 어느 하나 이상인 것을 특징으로 하는, 근기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 식품 조성물.
- 제 10항 내지 제 14항 중 어느 한 항에 있어서, 운동수행능력 향상은 퇴행성 질환, 미토콘드리아 이상 질환, 지구력 저하증, 순발력 저하증, 무기력증, 근육 폐기 및 우울증 등으로 이루어진 군에서 선택되는 하나 이상의 질병을 예방 또는 치료하는 것임을 특징으로 하는, 근기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 식품 조성물.
- 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상을 위한, 팥(Vigna angularis) 추출물을 유효성분으로 포함하는 약학적 조성물의 용도.
- 근육 질환 치료 또는 운동수행능력 향상을 위한, 팥 유래 단백질 또는 펩타이드를 유효성분으로 포함하는 약학적 조성물의 용도.
- 근기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상을 위한, 팥 추출물을 유효성분으로 포함하는 식품 조성물의 용도.
- 근기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상을 위한, 팥 유래 단백질 또는 펩타이드를 유효성분으로 포함하는 식품 조성물의 용도.
- 팥(Vigna angularis) 추출물을 필요로 하는 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하는, 근육 질환 치료 방법.
- 팥 유래 단백질 또는 펩타이드를 필요로 하는 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하는, 근육 질환 치료 방법.
- 팥(Vigna angularis) 추출물을 필요로 하는 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하는, 운동수행능력 향상 방법.
- 팥 유래 단백질 또는 펩타이드를 필요로 하는 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하는, 운동수행능력 향상 방법.
- 팥(Vigna angularis) 추출물을 필요로 하는 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하는, 근기능 개선 방법.
- 팥 유래 단백질 또는 펩타이드를 필요로 하는 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하는, 근기능 개선 방법.
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/098,416 US10821153B2 (en) | 2016-05-02 | 2017-05-02 | Composition for improving muscular function or for enhancing exercise performance comprising vigna angularis var. angularis |
| EP17792915.5A EP3453398A4 (en) | 2016-05-02 | 2017-05-02 | COMPOSITION FOR IMPROVING MUSCLE FUNCTION OR IMPROVING TRAINING PERFORMANCE WITH VIGNA ANGULARIS VAR.ANGULARIS |
| CN201780041210.7A CN109475588A (zh) | 2016-05-02 | 2017-05-02 | 一种包含小豆栽培种的用于改善肌肉功能或用于增强运动能力的组合物 |
| JP2018558236A JP2019520319A (ja) | 2016-05-02 | 2017-05-02 | 小豆を含む筋機能改善又は運動遂行能力向上用組成物 |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR20160054290 | 2016-05-02 | ||
| KR10-2016-0054290 | 2016-05-02 | ||
| KR1020170056162A KR101882006B1 (ko) | 2016-05-02 | 2017-05-02 | 팥을 포함하는 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 조성물 |
| KR10-2017-0056162 | 2017-05-02 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017192013A1 true WO2017192013A1 (ko) | 2017-11-09 |
Family
ID=60203575
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/KR2017/004701 WO2017192013A1 (ko) | 2016-05-02 | 2017-05-02 | 팥을 포함하는 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 조성물 |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2017192013A1 (ko) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021526555A (ja) * | 2018-05-28 | 2021-10-07 | ニューツリー カンパニー リミテッドNewtree Co., Ltd. | ダルマギク抽出物を含む筋肉疾患の予防、改善又は治療用、又は筋機能改善用組成物 |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6193124A (ja) * | 1984-10-12 | 1986-05-12 | Horiuchi:Kk | 肩凝り解消食品 |
| KR20020044535A (ko) * | 2000-12-05 | 2002-06-15 | 가부시끼가이샤 엔도세이안 | 팥을 원료로 하는 건강 음료 및 그의 제조 방법 |
| KR20070117151A (ko) * | 2006-06-07 | 2007-12-12 | 허베이 이링 메디슨 리서치 인스티튜트 코오포레이션 리미티드 | 근육 퇴화 및 근무력증 치료를 위한 의약 조성물 및 그제조 방법 |
| US20080096243A1 (en) * | 2004-12-17 | 2008-04-24 | Solae, Llc | Soy Protein Isolate and Process for its Manufacture |
| JP2014091686A (ja) * | 2012-11-01 | 2014-05-19 | Imuraya Group Co Ltd | アズキ由来骨代謝調節剤 |
| KR20170002846A (ko) * | 2015-06-30 | 2017-01-09 | (주)아모레퍼시픽 | 콩잎 추출물을 유효성분으로 함유하는 근질환 억제 및 예방용 조성물 |
-
2017
- 2017-05-02 WO PCT/KR2017/004701 patent/WO2017192013A1/ko unknown
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6193124A (ja) * | 1984-10-12 | 1986-05-12 | Horiuchi:Kk | 肩凝り解消食品 |
| KR20020044535A (ko) * | 2000-12-05 | 2002-06-15 | 가부시끼가이샤 엔도세이안 | 팥을 원료로 하는 건강 음료 및 그의 제조 방법 |
| US20080096243A1 (en) * | 2004-12-17 | 2008-04-24 | Solae, Llc | Soy Protein Isolate and Process for its Manufacture |
| KR20070117151A (ko) * | 2006-06-07 | 2007-12-12 | 허베이 이링 메디슨 리서치 인스티튜트 코오포레이션 리미티드 | 근육 퇴화 및 근무력증 치료를 위한 의약 조성물 및 그제조 방법 |
| JP2014091686A (ja) * | 2012-11-01 | 2014-05-19 | Imuraya Group Co Ltd | アズキ由来骨代謝調節剤 |
| KR20170002846A (ko) * | 2015-06-30 | 2017-01-09 | (주)아모레퍼시픽 | 콩잎 추출물을 유효성분으로 함유하는 근질환 억제 및 예방용 조성물 |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| KIM, CHANG-HEE ET AL.: "Inhibitory Effect of Red Bean Extract on TNF-alpha-induced Muscle Atrophy in Skeletal Muscle Cells", JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY OF FOOD SCIENCE AND NUTRITION, vol. 10, October 2016 (2016-10-01), pages 491 - 492, XP009510167 * |
| See also references of EP3453398A4 * |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021526555A (ja) * | 2018-05-28 | 2021-10-07 | ニューツリー カンパニー リミテッドNewtree Co., Ltd. | ダルマギク抽出物を含む筋肉疾患の予防、改善又は治療用、又は筋機能改善用組成物 |
| JP7149548B2 (ja) | 2018-05-28 | 2022-10-07 | ニューツリー カンパニー リミテッド | ダルマギク抽出物を含む筋肉疾患の予防、改善又は治療用、又は筋機能改善用組成物 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2018124508A1 (ko) | 3,5-디카페오일퀴닉에시드 또는 국화 추출물을 함유하는 근육 질환 예방 및 치료용 또는 근 기능 개선용 조성물 | |
| WO2017030410A1 (ko) | 검정콩잎 추출물 및 이로부터 분리한 플라보놀배당체를 유효성분으로 함유하는 대사증후군의 예방 또는 치료용, 또는 항산화용 조성물 | |
| WO2012124888A2 (en) | Composition comprising the extract of herbal combination for preventing or treating diabetic peripheral neuropathy | |
| WO2020218720A1 (ko) | 익모초 추출물 또는 레오누린을 함유하는 근육 질환 예방 또는 치료용 또는 근 기능 개선용 조성물 | |
| WO2012067316A1 (ko) | 테로카판계 화합물 또는 이의 약학적으로 허용가능한 염을 유효성분으로 함유하는 대사성 질환 또는 이들의 합병증의 예방 또는 치료용, 또는 항산화용 조성물 | |
| WO2019231150A1 (ko) | 해국 추출물을 포함하는 근육 질환 예방, 개선 또는 치료용, 또는 근 기능 개선용 조성물 | |
| WO2018062820A1 (ko) | 피토에스트로겐을 유효성분으로 포함하는 탈모방지 및 모발 성장 촉진용 조성물 | |
| WO2010090498A2 (ko) | 이고들빼기 추출물, 이의 분획물 또는 이로부터 분리한 화합물을 유효성분으로 함유하는 간 기능 개선용 약학적 조성물 및 간 기능 개선용 건강기능 식품조성물 | |
| WO2019017677A9 (ko) | 시트랄을 유효성분으로 함유하는 근력강화, 근육증강, 근육분화, 근육재생 또는 근감소증 억제효과를 갖는 조성물 | |
| WO2018070705A1 (ko) | 디오스민 또는 이의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염을 유효성분으로 포함하는 근육 질환 예방 또는 치료용 조성물 | |
| WO2017192013A1 (ko) | 팥을 포함하는 근 기능 개선 또는 운동수행능력 향상용 조성물 | |
| WO2010041908A2 (ko) | 판두라틴 유도체 또는 보에센베르기아 판두라타 추출물의 신규한 용도 | |
| WO2020085826A1 (ko) | 육두구 추출물 또는 메이스리그난을 유효성분으로 함유하는 환경오염인자로부터 유도되는 피부자극 완화 및 피부보호용 조성물 | |
| WO2010143825A2 (en) | Anti-arthritic agent using cyathula officinalis | |
| WO2019045467A9 (ko) | 항산화 및 항고혈압 효과를 가지는 광어 연육 및 이의 제조방법 | |
| WO2016190689A2 (ko) | 근육 질환 예방, 개선 또는 치료용 또는 근 기능 개선용 조성물 | |
| WO2021206455A1 (ko) | 멜리사엽 분획 추출물 및 이를 포함하는 신규한 약학적 조성물 | |
| WO2015199516A1 (ko) | 키레놀 또는 희첨 추출물을 포함하는 근기능 개선용 또는 운동수행능력 증강용 조성물 | |
| WO2015046743A1 (ko) | 댕댕이나무 열매 추출물을 유효성분으로 포함하는 갑상선 질환의 예방 또는 치료용 약학적 조성물 | |
| WO2015111904A1 (ko) | 커큐미노이드계 화합물, 및 감초 추출물 또는 이의 분획물을 포함하는 인플루엔자 바이러스 감염의 예방 또는 치료용 조성물 | |
| WO2020139057A2 (ko) | 팔각회향 추출물 또는 시킴산을 함유하는 근육 질환 예방 및 치료용 또는 근 기능 개선용 조성물 | |
| WO2011122805A2 (en) | A composition comprising ajoene for preventing or treating a disease caused by overexpression of lxr-alpha | |
| WO2020246863A1 (ko) | 꾸지뽕나무를 유효성분으로 함유하는 근육 질환 개선, 치료 또는 예방용, 또는 근 기능 개선용 조성물 | |
| WO2019017676A2 (ko) | 에틸바닐린을 유효성분으로 함유하는 근력강화, 근육증강, 근육분화, 근육재생 또는 근감소증 억제효과를 갖는 조성물 | |
| WO2024090929A1 (ko) | 결명 새싹 및 메밀 새싹을 포함하는 지방 축적 억제용 조성물 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2018558236 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 17792915 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2017792915 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20181203 |