WO2017037009A1 - Verfahren zur herstellung von phosphorhaltigen cyanhydrinestern - Google Patents
Verfahren zur herstellung von phosphorhaltigen cyanhydrinestern Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017037009A1 WO2017037009A1 PCT/EP2016/070301 EP2016070301W WO2017037009A1 WO 2017037009 A1 WO2017037009 A1 WO 2017037009A1 EP 2016070301 W EP2016070301 W EP 2016070301W WO 2017037009 A1 WO2017037009 A1 WO 2017037009A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- formula
- mol
- total amount
- radical
- compound
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
- 0 C*P(*)(CC(*)C(*)(C#N)OC(*)=O)=* Chemical compound C*P(*)(CC(*)C(*)(C#N)OC(*)=O)=* 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F9/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 5 or 15 of the Periodic Table
- C07F9/02—Phosphorus compounds
- C07F9/28—Phosphorus compounds with one or more P—C bonds
- C07F9/30—Phosphinic acids [R2P(=O)(OH)]; Thiophosphinic acids ; [R2P(=X1)(X2H) (X1, X2 are each independently O, S or Se)]
- C07F9/32—Esters thereof
- C07F9/3205—Esters thereof the acid moiety containing a substituent or a structure which is considered as characteristic
- C07F9/3211—Esters of acyclic saturated acids which can have further substituents on alkyl
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N57/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic phosphorus compounds
- A01N57/10—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic phosphorus compounds having phosphorus-to-oxygen bonds or phosphorus-to-sulfur bonds
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N57/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic phosphorus compounds
- A01N57/18—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic phosphorus compounds having phosphorus-to-carbon bonds
Definitions
- the present invention relates primarily to a process for the preparation of certain phosphorus-containing cyanohydrin esters of the formula (I) defined below and their use for the preparation of glufosinate or of glufosinate salts. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a process for the preparation of glufosinate or of glufosinate salts.
- Phosphorus-containing cyanohydrin esters are valuable intermediates in various technical fields, in particular for the production of biologically active substances which can be used in the pharmaceutical or agrochemical sector.
- No. 4,168,963 describes various phosphorus-containing herbicidally active compounds, of which in particular phosphinothricin (2-amino-4- [hydroxy (methyl) phosphinoyl] butanoic acid; short name (“common name”): glufosinate, hereinafter glufosinate) or its salts are of commercial importance in the Field of agrochemistry (agricultural chemistry).
- Glufosinate Methods for the preparation of intermediates for the synthesis of such phosphorus-containing herbicidally active compounds, in particular glufosinate, are described, for example, in US Pat. Nos. 4,521,348, 4,529,207 and 6,359,162B1.
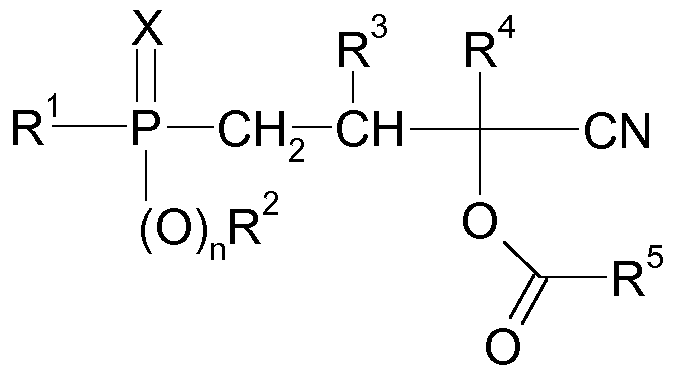
- the present invention relates to a process for preparing phosphorus-containing cyanohydrin esters of the formula (I)
- R 1 is (Ci-Ci 2) -alkyl, (Ci-C 2) -haloalkyl, (C 6 -Cio) aryl, (C 6 -Cio) haloaryl, (C 7 -Cio) aralkyl, (C 7- Cio) -haloalkyl, (C 4 -C 10) -cycloalkyl or (C 4 -C 10) -halocycloalkyl,
- R 2 is (Ci-Ci 2) -alkyl, (Ci-C 2) -haloalkyl, (C 6 -Cio) aryl, (C 6 -Cio) haloaryl, (C 7 -Cio) aralkyl, (C 7- Cio) -haloalkyl, (C 4 -C 10) -cycloalkyl or (C 4 -C 10) -halocycloalkyl, R 3 and R 4 are each independently of one another hydrogen, (C 1 -C 4 ) -alkyl, phenyl or benzyl,
- R 5 is (Ci-Ci 2) -alkyl, (Ci-C 2) -haloalkyl, (C 6 -Cio) aryl, (C 6 -Cio) haloaryl, (C 7 -Cio) aralkyl, (C 7- Cio) -haloalkyl, (C 4 -C 10) -cycloalkyl or (C 4 -C 10) -halocycloalkyl,
- X is oxygen or sulfur, and n is 0 or 1, in the presence of one or more radical-forming substances (IV) is reacted, with two separate metered streams (Dl) and (D2) are metered into the reactor, and these metered streams (Dl) and (D2) have the following composition:
- Dosing (Dl) contains one or more compounds of formula (II) and one or more radical-forming substances (IV), and
- Dosing stream (D2) contains one or more compounds of formula (III), and optionally one or more compounds of formula (II), and optionally one or more radical-forming substances (IV), wherein the reaction is carried out continuously.
- the process of the invention is carried out in a continuous mode (i.e., continuous process).
- a continuous process for the purposes of the present invention is to be understood as meaning that compounds (ie educts such as compounds of the formulas (II) and (III)) are introduced into the reactor (entry / feed) and, at the same time, but spatially separated therefrom, compounds (ie products such as compounds of formula (I)) are discharged from the reactor (discharge / discharge).
- Such continuous process management is of economic advantage as, for example, unproductive reactor times due to filling and emptying processes and prolonged Reaction times due to safety reasons, reactor-specific heat exchange performance as well as heating and cooling processes, such as occur in semi-batch process and batch process can be avoided or minimized.
- starting materials ie starting materials such as compounds of formula (II) and (III)
- reaction ie reaction of the starting materials
- products ie products such as compounds of formula (I)
- the phosphorus-containing Cyanhydrinester of formula (I) or the formulas defined below (Ia) or (Ib) in better yield and regularly obtained in higher purity.
- the metered streams (D1) and (D2) defined in the context of the present invention are metered from separate (i.e., spatially separated) containers into the reactor (i.e., the reaction vessel).
- the respective alkyl radicals of the radicals R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 and R 5 may each be straight-chain or branched-chain (branched) in the carbon skeleton.
- (C 1 -C 4 -alkyl) is the short notation for an alkyl radical having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, ie the radicals include methyl, ethyl, 1-propyl, 2-propyl, 1-butyl, 2-butyl, 2-methylpropyl or tert-butyl
- General alkyl radicals having a larger specified range of C atoms for example "(C 1 -C 6) -alkyl”, correspondingly also include straight-chain or branched alkyl radicals having a larger number of C atoms, ie, according to the example, also the alkyl radicals 5 and 6 carbon atoms.
- Halogen preferably refers to the group consisting of fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine.
- Haloalkyl, haloaryl, haloaralkyl and halocycloalkyl denote by identical or different halogen atoms, preferably from the group fluorine, chlorine and bromine, in particular from the group fluorine and chlorine, partially or completely substituted alkyl, aryl, aralkyl or cycloalkyl.
- perhaloalkyl such as CF 3 , CHF 2 , CH 2 F, CF 3 CF 2 , CH 2 FCHCl, CC 1 3 , CHCl 2 , CH 2 CH 2 Cl.
- Suitable compounds of the formula (II) are, inter alia, the following suitable and preferred: methanephosphonous acid mono (C 1 -C 6) -alkyl ester, methanephosphonous acid mono-dodecylester, methanephosphonous acid mono-phenylester; Ethane phosphonous acid mono (C 1 -C 6) alkyl ester, ethane phosphonoic acid mono dodecyl ester, ethane phosphonoic acid mono-phenyl ester; Propanephosphonous acid mono (C 1 -C 6) -alkyl ester, propanephosphonous acid mono-dodecylester, propanephosphonous mono-phenylester; Butane phosphonoic acid mono (C 1 -C 6) alkyl ester, butane phosphonoic acid mono-dodecyl ester, butane phosphonoic acid mono-phenyl ester; Phenylphosphonous acid mono (C 1 -C 6) -
- the preparation of the compounds of the formula (II) is known to the person skilled in the art and can be carried out by processes known from the literature (for example US 3,914,345, US 4,474,711, US 4,485,052, US 4,839,105, US 5,128,495).
- R 3 and R 4 are each independently hydrogen or methyl, and / or
- X is oxygen, and / or n is 1.
- the process according to the invention preferably relates to the preparation of phosphorus-containing cyanohydrin esters of the formula (Ia)
- R 1 is (Ci-C 6) -alkyl, (Ci-C 6) -haloalkyl, (C 6 -C 8) -aryl, (C 6 -C 8) haloaryl, (C 7 -Cio) aralkyl, ( C7-C10) - haloaralkyl, (C5-C8) -cycloalkyl or (C5-C8) -halocycloalkyl, and
- R 2 is (Ci-C 6) -alkyl, (Ci-C 6) -haloalkyl, (C 6 -C 8) -aryl, (C 6 -C 8) haloaryl, (C 7 -Cio) aralkyl, ( C7-C10) - haloalkyl, (C5-C8) -cycloalkyl or (C5-C8) -halocycloalkyl.
- preference is given to: means (C 1 -C 4 ) -alkyl or (C 1 -C 4 ) -haloalkyl, preferably methyl or ethyl,
- R 2 is (C 1 -C 6) -alkyl or (C 1 -C 6) -haloalkyl, preferably (C 3 -C 6) -alkyl, again preferably C 4 -alkyl or C 5 -alkyl.
- R 1 particularly preferably methyl
- R 2 particularly preferably (C 1 -C 6) -alkyl, again preferably (C 4 -C 5) -alkyl.
- the method according to the invention is further preferably at least a subset of the total amount of total compounds of the formula (II) or (IIa) used with the compound or compounds of formula (III) or (IIIa), and optionally additionally with one or more radical-forming Substances (IV), mixed, before the resulting metering stream (D2) is metered into the reactor.
- Dosing (Dl) contains one or more compounds of formula (II) and one or more radical-forming substances (IV), wherein dosing (Dl) 10 - 100 mol .-% of the total amount of the reaction in the total amount of radical-forming substances (IV ) contains.
- Dosing flow (Dl) 20 to 100 mol .-% of the total amount of the total amount of the radical-forming substances (IV) used in the reaction, preferably 25 to 100 mol%, preferably 30 to 100 mol%.
- a further preferred method according to the invention is characterized in that
- Dosing flow (Dl) 40 to 100 mol .-% of the total amount of the total amount of the radical-forming substances (IV) used in the reaction, preferably 50 to 100 mol%, preferably 60 to 100 mol .-%, more preferably 70 - 100 mol .-%, even more preferably 80 - 100 mol .-%, particularly preferably 90 - 100 mol .-%, particularly preferably 95 - 100 mol .-%.
- Dosing flow (Dl) 80-100% by weight, preferably 90-100% by weight, preferably 95-100% by weight, especially preferably 100% by weight of the total amount in the dosing streams (D1) and (D2) total used amount of compounds of formula (II).
- An alternative preferred embodiment of the process according to the invention is characterized in that metered flow (Dl) 10 to 90 wt .-%, preferably 20 to 80 wt .-%, more preferably 25 to 75 wt .-%, particularly preferably 30 to 70 wt. %, and more preferably 40-60 wt .-% of the total amount in the metered streams (Dl) and (D2) used in total amount of compounds of formula (II).
- metered flow (Dl) 10 to 90 wt .-% preferably 20 to 80 wt .-%, more preferably 25 to 75 wt .-%, particularly preferably 30 to 70 wt. %, and more preferably 40-60 wt .-% of the total amount in the metered streams (Dl) and (D2) used in total amount of compounds of formula (II).
- Dosing stream (D2) 80-100% by weight, preferably 90-100% by weight, preferably 95-100% by weight, especially preferably 100% by weight of the total amount in the metered streams (D1) and (D2) total amount of compounds of formula (III) contains.
- Dosing stream (Dl) 40-100 mol%, preferably 50-100 mol%, preferably 60-100 mol%, more preferably 70-100 mol%, particularly preferably 80-100 mol%, and particularly preferably 90-100 mol% of the total amount of the total amount of radical-forming substances (IV) used in the metered streams (D1) and (D2), and / or
- Dosing stream (D2) 0-60 mol%, preferably 0-50 mol%, preferably 0-40 mol%, more preferably 0-30 mol%, especially preferably 0-20 mol%, and particularly preferably 0-10 mol% of the total amount of the total amount of radical-forming substances (IV) used in the metered streams (D1) and (D2).
- the method according to the invention is characterized in that Dosing stream (Dl) 90-100 mol%, preferably 95-100 mol%, preferably 97-100 mol%, more preferably 98-100 mol% of the total amount in the dosing streams (D1) and ( D2) contains a total amount of radical-forming substances (IV), and metered flow (D2) 0-10 mol%, preferably 0-5 mol%, preferably 0-3 mol%, more preferably 0-2 mol .-% of the total amount in the metered streams (Dl) and (D2) used in total amount of the radical-forming substances (IV).
- Dosing stream (Dl) 90-100 mol%, preferably 95-100 mol%, preferably 97-100 mol%, more preferably 98-100 mol% of the total amount in the dosing streams (D1) and ( D2) contains a total amount of radical-forming substances (IV), and metered flow (D2) 0-10 mol%, preferably 0-5
- the process according to the invention is characterized in that the metered stream (D1) is 99-100 mol%, preferably 100 mol%, of the total amount of the radical-forming substances used in the metered streams (D1) and (D2) (IV) contains, and
- Dosing stream (D2) 0 - 1 mol .-%, preferably 0 mol .-% of the total amount in the metered streams (Dl) and (D2) used in total amount of the radical-forming substances (IV).
- a particularly preferred process according to the invention is characterized in that the total amount of compounds (II) and (IV) in the metering stream (D1) is 75 to 100% by weight, preferably 80 to 100% by weight, more preferably 85 to 100% by weight .-%, more preferably 90 to 100 wt .-%, each based on the total weight of the metered flow (Dl).
- the inventive method is preferably carried out in such a way that the metered streams (Dl) and (D2) are predominantly dosed simultaneously, preferably simultaneously in the reactor.
- the process according to the invention is preferably carried out under conditions in which radicals are formed.
- reaction of the compounds of the formula (II) and (III) or of the formula (IIa) and (IIIa) to give the compounds of the formula (I) or (Ia) in a process according to the invention is preferably carried out with the aid of a radical-forming source, for example using electromagnetic fields such as UV, gamma or X-rays, electric fields or electrochemical methods, or in the presence of one or more radical-forming substances.
- a radical-forming source for example using electromagnetic fields such as UV, gamma or X-rays, electric fields or electrochemical methods, or in the presence of one or more radical-forming substances.
- a preferred process according to the invention is characterized in that one, several or all radical-forming substances (IV) correspond to the formula (V)
- R 6 is independently hydrogen, (Ci-Cio) alkyl, preferably (Ci-C6) alkyl, preferably (Ci-C 4 ) alkyl
- R 7 is hydrogen or (Ci-Cio) alkyl, preferably hydrogen or (C 1 -C 6) -alkyl, preferably hydrogen or (C 1 -C 4 ) -alkyl
- R 6 is independently hydrogen, (Ci-Cio) alkyl, preferably (Ci-C6) alkyl, preferably (Ci-C 4 ) alkyl
- R 7 is hydrogen or (Ci-Cio) alkyl, preferably hydrogen or (C 1 -C 6) -alkyl, preferably hydrogen or (C 1 -C 4 ) -alkyl
- R 8 is methyl, ethyl, 2,2-dimethylpropyl or phenyl.
- Preferred free-radical-forming substances of the formula (V) are those in which R 6 independently of one another is (C 1 -C 10) -alkyl, preferably (C 1 -C 6 ) -alkyl, preferably (C 1 -C 4) -
- R 7 is hydrogen or (C 1 -C 10) -alkyl, preferably hydrogen or (C 1 -C 6) -alkyl, preferably hydrogen or (C 1 -C 4 ) -alkyl, and
- R 8 is methyl, ethyl, 2,2-dimethylpropyl or phenyl.
- the free-radical initiators (radical initiators) of the formula (V) are known per se and in some cases are commercially available.
- the radical formers of the formula (V) are preferably selected from the group consisting of tert-butyl peroxypivalate, tert-amyl peroxypivalate, tert-butyl peroxyneodecanoate, 1,1,3,3-
- Tetramethylbutyl peroxyneodecanoate Tetramethylbutyl peroxyneodecanoate, tert-butyl peroxy-2-ethylhexanoate, 1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl peroxy-2-ethylhexanoate, tert-amyl peroxyneodecanoate, cumyl peroxyneodecanoate, cumyl peroxyneoheptanoate, cumyl peroxypivalate, and mixtures thereof.
- the free-radical formers of the formula (V) are preferably selected from the group consisting of tert-butyl peroxyneodecanoate, 1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutylperoxyneodecanoate, tert-butylperoxy-2-ethylhexanoate, 1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutylperoxy-2- ethylhexanoate, cumylperoxyneodecanoate, and mixtures thereof, again particularly preferred are 1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutylperoxyneodecanoate, tert-butylperoxyneodecanoate and / or tert-butylperoxy-2-ethylhexanoate.
- the process according to the invention makes it possible to prepare the phosphorus-containing cyanohydrin esters of the formula (I) or (Ia) or the formula (Ib) defined below under mild reaction conditions and simpler process or plant-technical feasibility.
- the phosphorus-containing cyanohydrin esters of the formula (I), (Ia) or (Ib) can be obtained in terms of process technology more easily, in even better yields and in high purity.
- the process according to the invention is preferably carried out in such a manner that the reaction takes place at a temperature in the range from 40 to 120 ° C., preferably at a temperature in the range from 50 to 110 ° C., more preferably at a temperature in the range from 55 to 100 ° C, and more preferably at a temperature in the range of 60 to 95 ° C.
- a disproportionation of educts of the formula (II) or (IIa) is significantly reduced or largely avoided.
- the oligo- and polymerization of the compounds of the formula (III) or (IIIa) is significantly reduced or largely avoided.
- the cyanohydrin esters of the formula (III) or (IIIa) are preferably used in a purity of greater than or equal to 90% by weight, preferably greater than or equal to 92% by weight, more preferably greater than or equal to 95% by weight. , particularly preferably greater than or equal to 98 wt .-%.
- the phosphorus-containing cyanohydrin esters of the formula (I) or (Ia) or the formula (Ib) defined below can be used as starting materials for the synthesis of phosphorus-containing amino acids, such as For example, glufosinate be used (such a synthetic route will be described in more detail below).
- the process according to the invention is advantageous in that no high excesses of compounds of the formula (II) or (IIa) with respect to the total amount of compounds of the formula (III) or (IIIa) used are required to achieve the advantageous effects of the method according to the invention.
- the molar ratio of the total amount of the compound of the formula (II) or (IIa) used to the total amount of the compound of the formula (III) or (IIIa) used is preferably in the range from 8: 1 to 1: 1 , preferably in the range of 5: 1 to 2: 1.
- the molar ratio of the total amount of the compound of the formula (II) or (IIa) used to the total amount of the compound of the formula (III) or (IIIa) used is preferably in the range from 5: 1 to 5: 2 , more preferably in the range of 9: 2 to 5: 2.
- Dosing stream (Dl) contains 30-100 mol% of the total amount of the radical-forming substances (IV) used in the reaction, preferably 40-100 mol%, preferably 50-100 mol%, more preferably 60% 100 mol%, even more preferably 70-100 mol%, particularly preferably 80-100 mol%, particularly preferably 90-100 mol%, and most preferably 95-100 mol%, of the total amount of the compounds (II) and (IV) in the metering stream (D1) is 75 to 100% by weight, preferably 80 to 100% by weight, more preferably 85 to 100% by weight, particularly preferably 90 to 100% by weight.
- the molar ratio of the total amount of the compound of the formula (II) used to the total amount of the compound of the formula (III) used is in the range from 8: 1 to 1: 1, preferably Range from 5: 1 to 2: 1, and the reaction is carried out at a temperature in the range of 40 to 120 ° C, preferably at a temperature in the range of 50 to 110 ° C, more preferably at a temperature in the range of 55 to 100 ° C, and most preferably at a temperature in the range from 60 to 95 ° C.
- Dosing stream (Dl) 40-100 mol%, preferably 50-100 mol%, preferably 60-100 mol%, more preferably 70-100 mol%, particularly preferably 80-100 mol%, and particularly preferably 90-100 mol% of the total amount of the total amount of radical-forming substances (IV) used in the metered streams (D1) and (D2),
- Dosing stream (D2) 0-60 mol%, preferably 0-50 mol%, preferably 0-40 mol%, more preferably 0-30 mol%, especially preferably 0-20 mol%, and particularly preferably 0-10 mol% of the total amount of the total amount of radical-forming substances (IV) used in the metered streams (D1) and (D2), the total amount of the compounds (II) and (IV) in the metered stream (D1) 75 to 100 wt .-%, preferably 80 to 100 wt .-%, more preferably 85 to 100 wt .-%, particularly preferably 90 to 100 wt .-% in each case based on the total weight of the metered flow (Dl), the molar Ratio of the total amount of the compound of the formula (II) used to the total amount of the compound of the formula (III) used in the range of 8: 1 to 1: 1, preferably in the range of 5: 1 to 2: 1, wherein one, more or all radical-forming substances
- Particularly preferred embodiments of the process according to the invention for preparing the compounds of the formula (I) by reacting a compound of the formula (II) with the acrolein cyanohydrin ester of the formula (III), in particular for preparing the compounds of the formula (Ia) by reacting a compound of the formula ( IIa) with the acrolein cyanohydrin ester of the formula (IIIa), are characterized in that
- Particularly preferred embodiments of the method according to the invention for the preparation of the compounds of formula (I) by reacting a compound of formula (II) with the Acrolein cyanohydrin esters of the formula (III), in particular for the preparation of the compounds of the formula (Ia) by reacting a compound of the formula (IIa) with the acrolein cyanohydrin ester of the formula (IIIa), are characterized in that
- Dosing stream (D2) 0-30 mol%, particularly preferably 0-20 mol%, and particularly preferably 0-10 mol% of the total amount of the radical-forming amount used in the metered streams (D1) and (D2) Substances (IV), the total amount of the compounds (II) or (IIa) and (IV) in the metered stream (Dl) is 80 to 100 wt .-%, preferably 85 to 100 wt .-%, particularly preferably 90 to 100 % By weight, in each case based on the total weight of the metered flow (D1), of the molar ratio of the total amount of the compound of the formula (II) or (IIa) used to the total amount of the compound of the formula (III) or (IIIa) used.
- radical-forming substances (IV) correspond to formula (V) and are selected from the group consisting of tert-butyl peroxypivalate, tert-amyl peroxypivalate, tert-butyl peroxyneodecanoate, 1 , 1, 3,3-Tetramethylbutyl peroxyneodecanoate, tert-butyl peroxy-2-ethylhexanoate, 1, 1, 3, 3 -T etramethylbutylperoxy-2-ethylhexanoate, tert-amylperoxyneodecanoate, cumylperoxyneodecanoate, cumylperoxyneoheptanoate, cumyl peroxypivalate, and mixtures thereof, and the reaction is carried out at a temperature in the range of 50 to 110 ° C, preferably at a temperature in the range of 55 to 100 ° C, and more radical-forming substances (IV) correspond to formula (V) and mixtures thereof,
- Dosing (Dl) 70 - 100 mol .-%, particularly preferably 80 - 100 mol .-%, and particularly preferably 90 - 100 mol .-% of the total amount in the metered streams (Dl) and (D2) used in total amount of radical-forming Contains substances (IV),
- Dosing stream (D2) 0-30 mol%, particularly preferably 0-20 mol%, and particularly preferably 0-10 mol% of the total amount of the radical-forming amount used in the metered streams (D1) and (D2) Contains substances (IV),
- the total amount of the compounds (IIa) and (IV) in the metered stream (Dl) is 80 to 100 wt .-%, preferably 85 to 100 wt .-%, particularly preferably 90 to 100 wt .-%, in each case based on the total weight of the metered flow (D1), the molar ratio of the total amount of the compound of the formula (IIa) used to the total amount of the compound of
- Dosing stream (Dl) 90-100 mol%, preferably 95-100 mol%, preferably 97-100 mol%, more preferably 98-100 mol% of the total amount in the dosing streams (D1) and ( D2) contains a total amount of free-radical-forming substances (IV), metered flow (D2) 0-10 mol%, preferably 0-5 mol%, preferably 0-3 mol%, more preferably 0-2 mol.
- the total amount of the compounds (IIa) and (IV) in the metering (Dl) is 85 to 100 wt .-% , preferably 90 to 100 wt .-%, in each case based on the total weight of the metered flow (Dl), the molar ratio of the total amount of the compound of the formula (IIa) used to the total amount of the compound of the formula (IIIa) in the range of 5: 1 to 5: 2, wherein one, several or all radical-forming substances (IV) correspond to the formula (V) and are selected from the G consisting of tert-butyl peroxyneodecanoate, 1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl peroxyneodecanoate, tert-butyl peroxy-2-ethylhexanoate, 1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutylperoxy- 2-eth
- Particularly preferred embodiments of the process according to the invention for the preparation of the compounds of formula (Ia) by reacting a compound of formula (IIa) in which R 1 is methyl (and thus corresponds to the compound of formula (IIb) defined below) and R 2 (CI -C ⁇ ) - Alk l, with the Acroleincyanhydrinester of formula (IIIa), are characterized in that
- Dosing stream (Dl) 90-100 mol%, preferably 95-100 mol%, preferably 97-100 mol%, more preferably 98-100 mol% of the total amount in the dosing streams (D1) and ( D2) contains the total amount of radical-forming substances (IV) used,
- Dosing stream (D2) 0-10 mol%, preferably 0-5 mol%, preferably 0-3 mol%, more preferably 0-2 mol% of the total amount in the dosing streams (D1) and ( D2) contains a total amount of free-radical-forming substances (IV), the total amount of compounds (IIa) and (IV) in the dosing stream (Dl) is 85 to 100% by weight, preferably 90 to 100% by weight, based in each case on the total weight of the metered flow (D1), the molar ratio of the total amount of the compound of the formula (IIa) used to the total amount of the compound of the formula (IIIa) used in the range from 9: 2 to 5: 2, wherein one, several or all corresponding radical-forming substances (IV) of the formula (V) and are selected from the group consisting of tert-butyl peroxyneodecanoate, 1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutylperoxyneodecanoate, tert-buty
- Dosing stream (D2) contains 0-3 mol%, preferably 0-2 mol%, of the total amount of the total amount of radical-forming substances (IV) used in the metered streams (D1) and (D2), the total amount of compounds (IIa) and (IV) in the metered stream (Dl) is from 90 to 100% by weight, based on the total weight of the metered stream (D1), of the molar ratio of the total amount of compound of formula (IIa) used Total amount of the compound of the formula (IIIa) used is in the range from 9: 2 to 5: 2, where all radical-forming substances (IV) correspond to the formula (V) and are selected from the group consisting of 1,1,3,3- Tetramethylbutylperoxyneodecanoate, tert-butyl peroxyneodecanoate, tert-butylperoxy-2-ethylhexanoate and mixtures thereof, and the reaction is carried out at a temperature in the range of 60 to 95 ° C.
- the process of the invention can be carried out in an optional diluent.
- optional diluents it is possible in principle to use various organic solvents, preferably toluene, xylene, chlorobenzene, dichlorobenzene, dimethylformamide (DMF), dimethylacetamide, N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (II), or mixtures of these organic solvents.
- the process according to the invention is preferably carried out without such further optional solvents.
- reaction product of the formula (I), (Ia) or (Ib) may be advantageous to carry out the process according to the invention in previously formed reaction product of the formula (I), (Ia) or (Ib) as diluent.
- Glufosinate salts in the context of the present invention are preferably ammonium salts, phosphonium salts, sulfonium salts, alkali salts and alkaline earth salts of glufosinate.
- glufosinate particularly preferred within the scope of the present invention are glufosinate, glufosinate sodium and glufosinate ammonium.
- the present invention relates to the preparation of glufosinate o
- Glufosinat or glufosinate salts (preferably glufosinate-ammonium), characterized in that in this method, a compound of formula (Ib) is used
- R 2 has the meaning defined above according to the invention, preferably the meaning defined above as preferred, and particularly preferably the meaning defined above as particularly preferred meaning, and
- R 5 has the abovementioned meaning, and preferably methyl, and the preparation of the compound of formula (Ib) is carried out according to a method defined according to the invention.
- the present invention relates to the preparation of glufosinate and / or glufosinate salts or the like
- Glufosinate characterized by reacting a compound of formula (Ib), by the following step: reacting a compound of formula (IIb)
- R 2 is (C 1 -C 6) -alkyl, preferably (C 4 -C 5) -alkyl, and particularly preferably n-butyl or n-pentyl, with acrolein cyanohydrin O-acetate of the formula (IIIa)
- the present invention also relates to the use of a compound of the formula (I) or (Ib) prepared according to a method of the invention for producing glufosinate or glufosinate salts, in particular glufosinate, glufosinate sodium or glufosinate -Ammonium.
- the present invention further relates to a process for the preparation of glufosinate or of glufosinate salts, in particular of glufosinate, glufosinate sodium or glufosinate ammonium, comprising the following steps (a) and (b):
- step (B) Use of the compound of formula (I) or (Ib) prepared in step (a) for the production of glufosinate or of glufosinate salts, in particular of glufosinate, glufosinate sodium or glufosinate ammonium.
- MPE methanephosphonous acid mono-n-butyl ester
- a temperable, cylindrical glass reactor was charged with a portion of the required MPE to adequately cover the agitator and the reactor contents were brought to reaction temperature (typically 85 ° C).
- reaction temperature typically 85 ° C
- circulation / circulation circuit also the circulation circuit incl.
- the corresponding pump was filled with MPE.
- the mixing of the reactor contents was accomplished by a 6-blade disc stirrer in combination with four flow breakers. The reactor contents were always blanketed with nitrogen and operated without overpressure.
- starting materials El and E2 142.0 g of MPE (purity: 98% pure) were initially charged and heated to 85.degree. 5 min before starting the dosage of the starting materials El and E2, 1.0 mL (about 0.9 g) of the radical initiator tert-butylperneodecanoate (purity: 98% pure) was added. Subsequently, the following starting materials El and E2 were simultaneously metered into the reactor over a period of 4.0 hours: starting materials El was a mixture of MPE (102.1 g, purity: 98% pure) and tert-butyl perneodecanoate (3.0 g , Purity: 98%), starting material E2 consisted of 57.0 g of ACA (purity: 99% pure).
- the concentration of the radical initiator was thus 1.0 wt .-%, based on the total mixture.
- a mixture was prepared in the reactor, which was prepared according to the batchwise procedure according to Example 1 above.
- the reaction conditions and the apparatus parameters corresponded to those of Example 1.
- the metered streams (Dl) and (D2) were then metered separately into the reactor simultaneously.
- a temperable, cylindrical glass reactor was charged with a portion of the required MPE to adequately cover the agitator and the reactor contents were brought to reaction temperature (typically 85 ° C).
- reaction temperature typically 85 ° C
- circulation / circulation circuit also the circulation circuit incl.
- the corresponding pump was filled with MPE.
- the mixing of the reactor contents was accomplished by a 6-blade disc stirrer in combination with four flow breakers. The reactor contents were always blanketed with nitrogen and operated without overpressure.
- the pre-injected amount of tert-Butylperneodecanoat had dropped to ⁇ 10 "12 parts of the initial amount and thus without significant additional relevance for any subsequent tests (such as the ACM production in continuous driving).
- a mixture was prepared in the reactor, which was prepared according to the batchwise procedure according to the above Comparative Example la.
- the metered streams (Dl) and (D2) were metered separately into the reactor simultaneously.
- a mixture of ACA and radical starter tert-butylperneodecanoate at 15 ml / h was added to the reactor with metered flow (DI) MPE at 63 ml / h and with metered flow (D2);
- DI metered flow
- D2 metered flow
- the content of the radical initiator in the ACA was chosen (5.0% by weight) such that a content of 1.0% by weight of free-radical initiator was achieved in the overall mixture in the reactor.
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Dentistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Environmental Sciences (AREA)
- Plant Pathology (AREA)
- Pest Control & Pesticides (AREA)
- Agronomy & Crop Science (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| MX2018002729A MX2018002729A (es) | 2015-09-02 | 2016-08-29 | Proceso para la elaboracion de esteres de cianohidrina que contienen fosforo. |
| EP16757668.5A EP3344635B1 (de) | 2015-09-02 | 2016-08-29 | Verfahren zur herstellung von phosphorhaltigen cyanhydrinestern |
| US15/756,404 US10941167B2 (en) | 2015-09-02 | 2016-08-29 | Process for producing phosphorus-containing cyanohydrin esters |
| JP2018511191A JP2018526379A (ja) | 2015-09-02 | 2016-08-29 | リン含有シアノヒドリンエステルの製造方法 |
| KR1020187006004A KR20180048661A (ko) | 2015-09-02 | 2016-08-29 | 인 함유 시아노히드린 에스테르의 제조 방법 |
| CN201680050960.6A CN108026122B (zh) | 2015-09-02 | 2016-08-29 | 制备含磷氰醇酯的方法 |
| IL257375A IL257375A (en) | 2015-09-02 | 2018-02-06 | Method for producing cyanohydrin esters containing phosphorous |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP15183423 | 2015-09-02 | ||
| EP15183423.1 | 2015-09-02 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017037009A1 true WO2017037009A1 (de) | 2017-03-09 |
Family
ID=54062633
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/EP2016/070301 Ceased WO2017037009A1 (de) | 2015-09-02 | 2016-08-29 | Verfahren zur herstellung von phosphorhaltigen cyanhydrinestern |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10941167B2 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP3344635B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP2018526379A (de) |
| KR (1) | KR20180048661A (de) |
| CN (1) | CN108026122B (de) |
| IL (1) | IL257375A (de) |
| MX (1) | MX2018002729A (de) |
| TW (1) | TW201726693A (de) |
| WO (1) | WO2017037009A1 (de) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2019015909A1 (de) | 2017-07-21 | 2019-01-24 | Basf Se | Herstellung von glufosinat durch umsetzung von 3-[n-butoxy(methyl)phosphoryl]-1 -cyanopropylacetat zu einer mischung aus n-butyl(3-amino-3-cyanopropyl)-methylphosphinat und (3-amino-3-cyanopropyl)-methylphosphinsäure ammoniumsalz |
| WO2019121362A1 (de) | 2017-12-19 | 2019-06-27 | Basf Se | VERFAHREN ZUR HERSTELLUNG VON PHOSPHORHALTIGEN α-AMINONITRILEN |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113004325B (zh) * | 2021-03-15 | 2023-03-17 | 浙江新安化工集团股份有限公司 | 一种管式连续合成(3-乙酰氧-3-氰丙基)-甲基次膦酸烷基酯的方法 |
| CN116023409B (zh) * | 2023-01-13 | 2023-06-27 | 山东新和成氨基酸有限公司 | 一种草铵膦中间体的共催化制备方法 |
| CN116375765B (zh) * | 2023-06-07 | 2023-09-19 | 江苏七洲绿色科技研究院有限公司 | 一种3-(甲氧基(甲基)磷酰基)-1-氰基丙基乙酸酯的制备方法 |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4521348A (en) * | 1978-11-11 | 1985-06-04 | Hoechst Aktiengesellschaft | Phosphorus-containing cyanohydrine derivatives |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3914345A (en) | 1971-01-08 | 1975-10-21 | Hoechst Ag | Process for the manufacture of dialkyl-phosphinic acid esters |
| DE2717440C2 (de) | 1976-05-17 | 1984-04-05 | Hoechst Ag, 6230 Frankfurt | Unkrautbekämpfung mit [(3-Amino-3-carboxy)-propyl-1]-methylphosphinsäure-Derivaten |
| DE2918609A1 (de) | 1979-05-09 | 1980-11-20 | Hoechst Ag | Verfahren zur herstellung von cyanhydrinacylaten alpha , beta -ungesaettigter aldehyde |
| DE3146197A1 (de) | 1981-11-21 | 1983-05-26 | Hoechst Ag, 6230 Frankfurt | Verfahren zur herstellung von phosphonigsaeuremonoalkylestern |
| DE3146196A1 (de) | 1981-11-21 | 1983-05-26 | Hoechst Ag, 6230 Frankfurt | Verfahren zur herstellung phosphoniger saeuren |
| US4521349A (en) | 1983-01-20 | 1985-06-04 | A. R. Wilfley And Sons, Inc. | Fluid diffuser for gases and liquids |
| DE3319850C2 (de) * | 1983-06-01 | 1985-05-09 | Hoechst Ag, 6230 Frankfurt | Verfahren zur Herstellung von phosphorhaltigen Cyanhydrinderivaten |
| DE3402018A1 (de) | 1984-01-21 | 1985-07-25 | Hoechst Ag, 6230 Frankfurt | Verfahren zur herstellung alkanphosphoniger saeuren |
| DE3911230A1 (de) | 1989-04-07 | 1990-10-11 | Hoechst Ag | Verfahren zur herstellung von alkylphosphonigsaeurediestern und/oder dialkylphosphinigsaeureestern |
| DE19736125A1 (de) | 1997-08-20 | 1999-02-25 | Hoechst Schering Agrevo Gmbh | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Glufosinate und phosphorhaltige alpha-Aminonitrile als Zwischenprodukte |
| KR20180048894A (ko) * | 2015-09-02 | 2018-05-10 | 바이엘 크롭사이언스 악티엔게젤샤프트 | 인 함유 시아노하이드린 에스테르의 제조 방법 |
| MX2018002731A (es) * | 2015-09-02 | 2018-04-13 | Bayer Cropscience Ag | Proceso para la elaboracion de esteres de cianohidrina que contienen fosforo. |
| BR112018004247A2 (pt) * | 2015-09-02 | 2018-09-25 | Bayer Cropscience Aktiengesellschaft | método para produção de ésteres de cianidrina contendo fósforo. |
-
2016
- 2016-08-29 JP JP2018511191A patent/JP2018526379A/ja active Pending
- 2016-08-29 MX MX2018002729A patent/MX2018002729A/es unknown
- 2016-08-29 EP EP16757668.5A patent/EP3344635B1/de active Active
- 2016-08-29 CN CN201680050960.6A patent/CN108026122B/zh active Active
- 2016-08-29 KR KR1020187006004A patent/KR20180048661A/ko not_active Withdrawn
- 2016-08-29 US US15/756,404 patent/US10941167B2/en active Active
- 2016-08-29 WO PCT/EP2016/070301 patent/WO2017037009A1/de not_active Ceased
- 2016-08-31 TW TW105127968A patent/TW201726693A/zh unknown
-
2018
- 2018-02-06 IL IL257375A patent/IL257375A/en unknown
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4521348A (en) * | 1978-11-11 | 1985-06-04 | Hoechst Aktiengesellschaft | Phosphorus-containing cyanohydrine derivatives |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2019015909A1 (de) | 2017-07-21 | 2019-01-24 | Basf Se | Herstellung von glufosinat durch umsetzung von 3-[n-butoxy(methyl)phosphoryl]-1 -cyanopropylacetat zu einer mischung aus n-butyl(3-amino-3-cyanopropyl)-methylphosphinat und (3-amino-3-cyanopropyl)-methylphosphinsäure ammoniumsalz |
| US10822358B2 (en) | 2017-07-21 | 2020-11-03 | Basf Se | Process for preparing phosphorus-containing alpha-aminonitriles |
| WO2019121362A1 (de) | 2017-12-19 | 2019-06-27 | Basf Se | VERFAHREN ZUR HERSTELLUNG VON PHOSPHORHALTIGEN α-AMINONITRILEN |
| CN111479816A (zh) * | 2017-12-19 | 2020-07-31 | 巴斯夫欧洲公司 | 制备含磷α-氨基腈的方法 |
| US11220520B2 (en) | 2017-12-19 | 2022-01-11 | Basf Se | Method for preparing phosphorus-containing α-aminonitriles |
| CN111479816B (zh) * | 2017-12-19 | 2023-10-27 | 巴斯夫欧洲公司 | 制备含磷α-氨基腈的方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20180048661A (ko) | 2018-05-10 |
| TW201726693A (zh) | 2017-08-01 |
| MX2018002729A (es) | 2018-04-13 |
| US20180251481A1 (en) | 2018-09-06 |
| US10941167B2 (en) | 2021-03-09 |
| IL257375A (en) | 2018-04-30 |
| EP3344635B1 (de) | 2019-08-07 |
| CN108026122A (zh) | 2018-05-11 |
| EP3344635A1 (de) | 2018-07-11 |
| JP2018526379A (ja) | 2018-09-13 |
| CN108026122B (zh) | 2021-03-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3344636B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von phosphorhaltigen cyanhydrinestern | |
| EP3143030B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von phosphorhaltigen cyanhydrinen | |
| EP3344635B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von phosphorhaltigen cyanhydrinestern | |
| DE19923619C2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Dialkylphosphinsäuren und deren Salzen | |
| EP3344637B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von phosphorhaltigen cyanhydrinestern | |
| EP1034179B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von dialkylphosphinsäuren | |
| EP3344638B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von phosphorhaltigen cyanhydrinestern | |
| EP1217003B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Ethanbis(methylphosphinsäure) | |
| WO2019121362A1 (de) | VERFAHREN ZUR HERSTELLUNG VON PHOSPHORHALTIGEN α-AMINONITRILEN | |
| EP3356376B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von phosphinaten | |
| EP1061084B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Alkylphosphonsäuren | |
| EP3655413A1 (de) | Herstellung von glufosinat durch umsetzung von 3-[n-butoxy(methyl)phosphoryl]-1 -cyanopropylacetat zu einer mischung aus n-butyl(3-amino-3-cyanopropyl)-methylphosphinat und (3-amino-3-cyanopropyl)-methylphosphinsäure ammoniumsalz | |
| EP3392237B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von acroleincyanhydrinen | |
| EP2235028A1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von phosphonsäureanhydriden | |
| DE10003986A1 (de) | Kontinuierliche Verfahren zur ein- oder zweifachen C-Alkylierung von Malonsäurendiestern |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16757668 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 257375 Country of ref document: IL |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20187006004 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A Ref document number: 2018511191 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15756404 Country of ref document: US |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: MX/A/2018/002729 Country of ref document: MX |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to national code |
Ref country code: BR Ref legal event code: B01A Ref document number: 112018004226 Country of ref document: BR |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 112018004226 Country of ref document: BR Kind code of ref document: A2 Effective date: 20180302 |