WO2016117607A1 - アノテーション補助装置及びそのためのコンピュータプログラム - Google Patents
アノテーション補助装置及びそのためのコンピュータプログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2016117607A1 WO2016117607A1 PCT/JP2016/051577 JP2016051577W WO2016117607A1 WO 2016117607 A1 WO2016117607 A1 WO 2016117607A1 JP 2016051577 W JP2016051577 W JP 2016051577W WO 2016117607 A1 WO2016117607 A1 WO 2016117607A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- candidate
- annotation
- word
- text
- analysis
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F40/00—Handling natural language data
- G06F40/10—Text processing
- G06F40/166—Editing, e.g. inserting or deleting
- G06F40/169—Annotation, e.g. comment data or footnotes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F40/00—Handling natural language data
- G06F40/20—Natural language analysis
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F40/00—Handling natural language data
- G06F40/20—Natural language analysis
- G06F40/268—Morphological analysis
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F40/00—Handling natural language data
- G06F40/40—Processing or translation of natural language
- G06F40/53—Processing of non-Latin text
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/01—Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer
- G06F3/048—Interaction techniques based on graphical user interfaces [GUI]
- G06F3/0481—Interaction techniques based on graphical user interfaces [GUI] based on specific properties of the displayed interaction object or a metaphor-based environment, e.g. interaction with desktop elements like windows or icons, or assisted by a cursor's changing behaviour or appearance
- G06F3/0482—Interaction with lists of selectable items, e.g. menus
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F40/00—Handling natural language data
- G06F40/20—Natural language analysis
- G06F40/205—Parsing
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a natural language processing technique, and more particularly, to an annotation assisting device for efficiently performing annotation on an anaphoric relationship of an abbreviation, a pronoun, and other directives frequently appearing in a natural language sentence.
- the example sentence 30 shown in FIG. The example sentence 30 includes a first sentence and a second sentence.
- the second sentence includes an instruction word (pronoun) 42 “it”.
- the instruction word “it” indicates the expression 40 “Month history New Year date” in the first sentence.
- the process of specifying the word indicated by the instruction word is called “anaphoric analysis”.
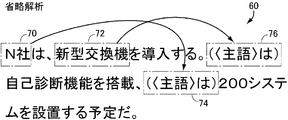
- the example sentence 60 of FIG. This example sentence 60 includes a first sentence and a second sentence. In the second sentence, the subject of the predicate “with self-diagnosis function” is omitted, but the word 72 “new switch” in the first sentence is omitted in the omitted part 76 of the subject.
- the subject of the predicate “scheduled to install 200 systems” is omitted.
- the word 70 “N company” in the first sentence is omitted.
- the process of detecting omission of a subject or the like and complementing it is called “omission analysis”.
- the anaphoric analysis and the omitted analysis are collectively referred to as “anaphoric / omitted analysis”.
- natural language processing is an indispensable technology for communicating with humans.
- automatic translation and question answering as important problems in natural language processing.
- the anaphora and omission analysis technique is an essential element technique in such automatic translation and question answering.
- the current technical level of anaphora and omission analysis has not yet reached a practical level although it depends on the language.
- Non-Patent Document 1 There is a technique described in Non-Patent Document 1 described later as a technique for creating learning data of an anaphoric / omitted analyzer.
- learning data is created as follows. That is, an operation is performed in which a human reads a text from the beginning and manually detects pronouns and omissions.
- the support by the machine is, for example, to enumerate expressions of pointing of the anaphoric relationship in advance.
- Non-Patent Document 2 discloses an anaphora / omission analysis algorithm that automatically performs anaphora / omission analysis in a certain procedure.
- the technique disclosed in this document uses information output by morphological analysis, syntax / dependency analysis (hereinafter simply referred to as “dependency analysis”), and an external resource tool such as a dictionary.
- the dictionary used here is a collection of characteristics that the object of the verb “eat” includes an expression corresponding to “food”, for example.
- the point of pronoun and the omission are omitted by referring to information obtained from the text.
- Non-Patent Document 2 in the case of Japanese anaphora analysis, the recall rate is 44%, the accuracy is 42%, and in the case of subject omission analysis, both the recall rate and accuracy are 35%.
- Abbreviations and pronouns are frequently used in documents found in daily life.
- In order to perform accurate resource language processing it is necessary to detect an abbreviated portion and to detect an abbreviated portion and a pronoun designation destination. For this purpose, it is necessary to obtain an accurate anaphoric / omitted analyzer.
- an anaphoric / omitted analyzer In order to perform accurate resource language processing, it is necessary to detect an abbreviated portion and to detect an abbreviated portion and a pronoun designation destination.
- in order to perform learning of such an anaphoric / omitted analyzer there is a problem that it takes much time to create learning data and is too expensive.
- the learning data is created by performing annotation on the text on the anaphoric relationship of the abbreviations and pronouns that appear in the sentence.
- human judgment must be reflected in the learning data.
- an object of the present invention is to provide an annotation assisting device that allows a human to easily construct annotation data for text and thereby reduce costs.
- the annotation assisting device assists in creating annotation data for anaphoric / abbreviated analysis of natural language text.
- the annotation assisting device includes a display device and an input device, and includes input / output means for receiving user input through interactive processing with a user, reading means for reading text data from a text archive to be annotated, and a reading means.
- Analysis means for performing morphological analysis and dependency analysis of the read text data and outputting a morpheme string to which information indicating the dependency structure is attached, and predicate search means for searching for a predicate in the morpheme string output by the analysis means And in the dependency relationship involving each of the predicates searched by the predicate search means, it is detected that a word that should be in a predetermined relationship with respect to the predicate is omitted or is a directive.
- Target identification means for identifying the position of the word as an annotation processing target, and the word identified by the target identification means For each of the positions, a candidate for the expression to be inserted at the position is estimated by using the relationship between the position and the surrounding morpheme sequence, and language knowledge prepared in advance, and the candidate estimation means
- Candidate storage means for storing the associated candidates in association with the word positions, and for each of the annotation processing targets, the candidates estimated by the candidate estimation means are read from the candidate storage means and displayed so that the user can select one of them
- Candidate display means for displaying on the apparatus, and interactive selection means for adding the selected candidate as an annotation to the position in response to a user instruction to select any of the candidates displayed by the candidate display means.
- the candidate estimating unit generates, for each of the word positions specified by the target specifying unit, a sentence that inquires about a word that should enter the position of the word using a word string around the position.
- a question sentence input means for giving the question sentence generated by the question sentence generation means as an input to a previously prepared question answering system, and an answer obtained from the question answering system for the question sentence given from the question sentence input means
- the candidate estimation means further specifies the position of the word and the position of the word for each of the word knowledge storage means for storing a plurality of language knowledge rules and the position of the word specified by the target specifying means.
- the linguistic knowledge rule to which the relevant expression is matched the expression to be inserted at the position of the word specified by the target specifying means in the expression is changed to the character string to be inserted at the position of the word.
- the candidate estimation means further includes an annotation search means for searching for a place where an annotation relating to omission or anaphoric relation is added in text included in an existing annotated text database prepared in advance, and an annotation search means For each of the locations retrieved by the above, a sentence is transformed according to a predetermined method for each annotation, and the modified storage section is stored in the candidate storage means as an annotation candidate for the retrieved location.
- the candidate estimation means further receives a morpheme sequence after analysis output from the analysis means as an input to another existing anaphoric / omitted analyzer and an anaphoric / abbreviated analysis result by the existing anaphoric / omitted analyzer.
- the anaphoric / abbreviated analysis result may be stored in a candidate storage unit.
- the computer program causes a computer to operate as an annotation assisting device that assists in creating annotation data for the analysis and omission analysis of natural language text.
- the computer program includes an input / output unit that accepts a user input through interactive processing with a user using a display device and an input device of the computer, and a reading unit that reads text data from a text archive to be annotated And a morpheme analysis and dependency analysis of the text data read by the reading unit to output a morpheme sequence to which information indicating the dependency structure is attached, and a predicate in the morpheme sequence output by the analysis unit.
- a word that should be in a predetermined relationship with the predicate is omitted or is an indicator.
- object identification means for identifying the position of the word as an object of annotation processing For each word position specified by the object specifying means, a candidate for estimating a candidate for expression to be inserted at the position using the relationship between the position and the surrounding morpheme sequence and language knowledge prepared in advance.
- An estimation unit a candidate storage unit that stores a candidate estimated by the candidate estimation unit in association with a word position, and a candidate estimated by the candidate estimation unit for each annotation processing target is read from the candidate storage unit, and the user Candidate display means for displaying either one of the candidates displayed on the display device so as to be selectable, and adding the selected candidate as an annotation in response to an instruction from the user to select one of the candidates displayed by the candidate display means Function as an interactive selection means.
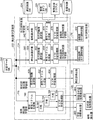
- FIG. 1 is an overall block diagram of a system for anaphora and omission analysis including a learning data generation assisting device according to an embodiment of the present invention. It is a figure for demonstrating schematic structure of the rule which comprises linguistic knowledge. It is a schematic diagram explaining schematic structure of question type DB. It is a schematic diagram which shows the outline of the annotation method using a question answering system. It is a block diagram of a learning data generation auxiliary device. It is a block diagram of the 1st candidate production
- FIG. 6 is a state transition diagram of a program for generating learning data by executing annotation on a text through interaction with a user.
- FIG. 3 is a detailed functional block diagram of a detector learning device 222.
- FIG. It is a figure which shows the external appearance of the computer which performs the program for producing
- FIG. 20 is a hardware block diagram of a computer whose appearance is shown in FIG. 19.
- work which attaches an annotation to a text in the learning data generation assistance apparatus which concerns on the 1st Embodiment of this invention is demonstrated.
- the annotation target text 90 is displayed on the screen of the display device.
- This text 90 consists of two sentences.
- the first sentence includes a predicate “introducing”, a word 100 “N company” that is the subject of the predicate, and a word 110 “new switch” that is the object of the predicate.
- the second sentence essentially consists of two sections. At the beginning of the first half of the sentence, there is a portion (omitted portion) 114 in which the subject “with self-diagnosis function” is omitted. There is an abbreviated portion 104 where the subject “200 system is scheduled to be installed” is omitted in the middle portion between the first half sentence and the latter half sentence.
- the omitted portion 104 or 114 is found. Thereafter, an expression to be supplemented for the omitted portion is searched and determined.
- the word 100 is an expression to be complemented.
- the word 110 is an expression to be complemented.
- the processing as shown in the lower part of FIG. 3 is performed for each omitted part.
- the word 110 “new switch” is found for the supplementary expression for the omitted portion 114 shown in the upper part of FIG. 3, and a plurality of words including the word 100 are found in the omitted portion 104.
- the learning data generation assisting device inserts a character string 130 consisting of the word “new type switch”, which is the same as the word 110, and the main case particle in the omitted part 114, and a so-called drop-down list is displayed on the right side. An icon “ ⁇ ” indicating the presence is displayed.
- a drop-down list 132 is displayed.
- two options YES, NO
- an option for manual input by a human "manual input"
- the user selects YES
- the character string 130 is added as an annotation to the omitted portion 114. If NO is selected, no annotation is added to the omitted portion 114.
- “Manual Input” is selected, an input dialog (not shown) is opened and annotations can be directly input.
- one of the candidates for example, the character string 134 including the same word as the word 100 and the case particle “c” is displayed, and an icon “ ⁇ ” indicating a drop-down list is displayed on the right side.
- an icon “ ⁇ ” indicating a drop-down list is displayed on the right side.
- a drop-down list including a plurality of candidate lists and “direct input” as options is displayed.
- the candidate word is added as an annotation for the omitted portion 104.
- the case where the direct input is selected is the same as the omitted portion 114.
- This anaphoric / abbreviated analysis system 150 detects abbreviations and anaphors for a large amount of text prepared in advance, and presents candidates for expressions (preceding antecedents) pointed to by a user to select them with a simple operation.
- the annotation data generation auxiliary system 160 that assists the user in generating the model learning data (annotation data) necessary for anaphora and omission analysis, and the learning generated by the user using the annotation data generation auxiliary system 160
- the abbreviation detector 166 detects abbreviations for any predicate in the text.
- the omission detector 166 includes a statistical model for detecting omissions where the subject, object, etc. in the text are omitted.
- the anaphoric detector 168 includes a statistical model for detecting an anaphor for indicating another word or the like with an arbitrary noun phrase (anaphor candidate) in the text as a classification target.
- the antecedent specifying unit 170 classifies a predicate having an abbreviation and a noun phrase that is an antecedent candidate in a text as a classification target, a noun in the text, and a noun in the text.
- a phrase pair (anaphoric and antecedent candidate) is classified, and a detector for specifying the antecedent pointed to by the anaphor is included.
- Each of these detectors has a separate statistical model.
- the omission detector 166, the anaphor detector 168, and the antecedent identifier 170 all use SVM (Support Vector Machine) as a statistical model.
- the anaphoric / abbreviated analysis system 150 further detects an abbreviation and an anaphor in the input text using the abbreviation detector 166, the anaphor detector 168, and the antecedent identifier 170, and identifies the antecedent pointed to by them. And an anaphoric / omitted analysis device 172 that outputs information attached thereto.
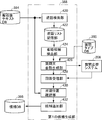
- the annotation data generation assisting system 160 is a text archive 192 using an input / output device 202 that performs interactive input / output with a user using a display device, a keyboard, a mouse, and the like, and various resources including language knowledge.
- a learning data generation assisting device 204 that generates learning data and outputs it to the learning data DB 162 by assisting the user with annotating work on a large amount of text stored in.
- the resources used by the learning data generation assisting device 204 include language knowledge in a format applicable to the existing small-scale learning data DB 190 storing learning data similar to the learning data DB 162 and text stored in the text archive 192.
- the language knowledge DB 194 stored in the form of a rule and the learning data generation assisting device 204 apply the language knowledge stored in the language knowledge DB 194 to text, the expression in the rule is rephrased to another expression,
- a paraphrase / category dictionary 196 storing a paraphrase rule and category used to replace a word in the rule with another word, and an abbreviated portion accompanying the pattern when the text has a specific pattern
- a pattern dictionary 198 for storing patterns prepared in advance.
- the annotation data generation assisting system 160 further includes a question answering system 206 that inquires about a word candidate indicated by the omitted portion when the learned data generation assisting device 204 finds an omitted portion in the text, and the learning data generation assisting device 204.
- a question type DB 200 that is referred to when creating a question for the question answering system 206 based on the text, and an anaphoric / omitted analysis executed by the learning data generation auxiliary device 204 by performing an anaphoric / omitted analysis on the text.
- an existing anaphoric / abbreviated analyzer 208 for presenting candidates such as omitted parts, anaphors, antecedents, etc. to the learning data generation assisting device 204 is included.
- the configuration of the existing small-scale learning data DB 190 may be in any format as long as it can specify omitted parts, anaphors, and antecedents in the text.
- the text stored in the text archive 192 is a simple text in the present embodiment, and it is assumed that morphological analysis and structure / dependency analysis have not been performed. However, the present invention is not limited to such an embodiment. A morphological analysis and / or a structure / dependency analysis performed by another system and the information to which such information is attached may be used.
- ⁇ Language knowledge DB 194> the rules of language knowledge stored in language knowledge DB 194 are roughly divided into four types. That is, causal relationship knowledge 290, implication relationship knowledge 292, event occurrence order relationship knowledge 294, and event occurrence invalidation relationship knowledge 296. Each knowledge may include a variable (hereinafter, represented by “X”, “Y”, etc.) that can be replaced by an arbitrary noun phrase or the like that plays a role of a wild card.
- the causal knowledge 290 is an ordered pair of an expression corresponding to the cause, for example, “X smokes tobacco” and an expression corresponding to the result, “X increases the possibility of lung cancer”.
- the expression corresponding to the cause is located first and the expression corresponding to the result is located later.
- the implication relation knowledge 292 indicates that the expression “X wrote Y” is implied by the expression “X is the author of Y”, for example, by an ordered pair of these two expressions. Here, it is assumed that an implied expression comes first and an implied expression comes later.
- the event occurrence order relationship knowledge 294 represents, for example, the normal order relationship of events that an event “X announces Y” can occur when an event “X discovers Y” occurs. This is expressed as an ordered pair. Here, it is assumed that expressions are arranged according to the order relation of events.
- the event occurrence invalidation relation knowledge 296 indicates that, for example, when an event of “prohibiting X” occurs, an occurrence of another event occurs due to the occurrence of an event such that an event “X cannot be disclosed” occurs.
- An ordered pair of expressions that are in a relationship that is invalidated. Here, it is assumed that an event that occurs is positioned first, and an event whose generation is invalidated by the event is positioned later.
- these knowledge can be applied to the text alone, but not only that.
- the latter half of one knowledge matches the first half of the other knowledge.
- knowledge can be chained and applied.
- “match” includes, for example, synonyms, paraphrases, implications, and the like.
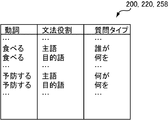
- question type DB 200 is used when learning data generation assisting device 204 obtains an antecedent candidate using question answering system 206.
- the question type DB 200 has a plurality of entries. For example, each entry asks what form a verb is asked to determine the grammatical role of the part omitted in the dependency relationship of the verb in an expression and the expression to be inserted into the omitted part.
- Information (question type) indicating whether a sentence should be generated. For example, for the verb “eating”, if the subject is omitted in an expression, if “who” is placed at the beginning of the sentence and the sentence is generated, the answer should be the subject of “eating” A representation is obtained from the question answering system.
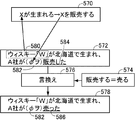
- the input text 320 includes two sentences.
- the first sentence is "Let's drink red wine for dinner”
- the second sentence is "Prevent heart disease”.
- the subject of the verb 332 “Prevent” is omitted at the beginning of the second sentence, and a tag indicating the omission is attached to the omitted portion 334.
- the word 330 “red wine” should be placed in this omitted part.
- the learning data generation assisting device 204 generates a question sentence 336 “what prevents heart disease” from these pieces of information.
- the end of the sentence is suitable for the question sentence, and is converted according to a rule prepared in advance.
- the conversion rule at the end of the sentence may be stored in advance in each entry of the question type DB 200.
- the question answering system 206 searches and extracts a word candidate group 342 suitable as an answer to the question sentence 336 from the database in the system.
- the question answering system 206 further transmits the word candidate group 342 obtained in this way to the learning data generation assisting device 204 so that each category 344, 346, and 348 includes one or more answer candidates for each category.
- the category 344 includes “red wine”, “sake”, and “beer”. The same applies to the other categories 346 and 348.
- the learning data generation assisting device 204 for example, of the word candidates obtained in this way, an expression that matches the word in the position before the omitted part 334 in the input text 320 (in this example, the word 330 “red wine”). Is selected, and the omitted portion 334 and the word 330 as a candidate for the destination are set as the target of the annotation 350.
- the above is the outline of the annotation addition work using the question answering system 206.
- an existing anaphora / omission analyzer 208 performs existing anaphora / omission analysis.
- the existing anaphoric / abbreviated analyzer 208 is used to present a candidate for an abbreviation, a candidate for an anaphor, and a candidate for an antecedent of the abbreviation and an anaphor.
- a human selects a correct candidate from these candidates. Therefore, the accuracy of the existing anaphoric / omitted analyzer 208 used here is not necessarily high.
- the learning data generation assisting device 204 performs a morphological analysis on each text included in the text archive 192 and outputs a morpheme analysis system 380 that outputs various grammatical sequences.
- a dependency relationship analysis system 382 that performs sentence structure and dependency analysis on the morpheme sequence output by the morpheme analysis system 380 and outputs a morpheme sequence to which structure / dependency information is attached, and a dependency relationship analysis system 382
- a post-analysis text DB 384 that stores the morpheme string output by, together with their grammatical information and structure / dependency relationships.
- the dependency relationship analysis system 382 attaches dependency information indicating at least which word is related to which word to each morpheme string.
- each element in the learning data generation auxiliary device 204 operates according to a user instruction via the input / output device 202 in the present embodiment. To do.
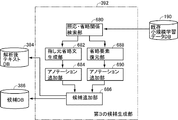
- the learning data generation assisting device 204 further detects an abbreviated portion in the analyzed text stored in the analyzed text DB 384 and uses the question type DB 200 and the question answering system 206 to indicate an annotated candidate group indicating the antecedent of each omitted portion.
- the omission is detected in the same manner as the first candidate generation unit 388, and the language knowledge DB 194 is detected for each omission.
- the second candidate generation unit 390 that generates an annotation candidate group related to the omitted part using the paraphrase / category dictionary 196 and the pattern dictionary 198, and the learning data stored in the existing small-scale learning data DB 190, Generate new learning data by changing some of the anaphoric relationships and omission relationships that exist
- the third candidate generation unit 392 that generates a new annotation candidate from the learning data and the existing anaphora / omission analyzer 208 are used to perform the anaphora / omission analysis on the text stored in the post-analysis text DB 384.
- a fourth candidate generation unit 394 that generates the result as an annotation candidate.
- the learning data generation assisting device 204 further selects the annotation candidate groups output from the first candidate generation unit 388, the second candidate generation unit 390, the third candidate generation unit 392, and the fourth candidate generation unit 394, respectively.
- the learning system 164 includes a question type DB 220 and a question answering system 226 similar to the question type DB 200 and the learning data generation auxiliary device 204 used in the annotation data generation auxiliary system 160, respectively, as will be described later.
- the selection restriction DB 224 describing the restrictions imposed on the antecedent selected is similar to the language knowledge DB 194 used in the annotation data generation auxiliary system 160.
- the first candidate generation unit 388 includes a predicate search unit 420 that searches for a predicate in each text data stored in the post-analysis text DB 384, and each predicate that the predicate search unit 420 outputs.
- a predicate list storage unit 422 that stores the list together with the appearance position of each predicate, and a portion that is omitted from the dependency relationship involving the predicate is detected among the predicates stored in the predicate list storage unit 422.
- the question sentence automatic generation unit 426 that generates and supplies the question answering system 206 as a question sentence, and the question sentence from the question sentence automatic generation unit 426
- the answer receiving unit 428 receives the candidate group from the question answering system 206 and outputs a combination of the question sentence and the answer candidate group, and receives a pair of the question sentence and the answer candidate group in which the answer receiving unit 428 appears.
- the appearance position confirmation unit 430 that is output as a pointing destination candidate for the omitted part and the omitted part that is output from the appearance position confirmation unit 430 and a candidate group that complements the omitted part are added to the candidate DB 386 as an annotation candidate.
- a candidate addition unit 432 A candidate addition unit 432.
- second candidate generation unit 390 includes predicate search unit 450, predicate list storage unit similar to predicate search unit 420, predicate list storage unit 422, and omission candidate detection unit 424 shown in FIG. 452, and abbreviation candidate detection unit 454, and among the abbreviation candidates detected by the abbreviation candidate detection unit 454, a search is performed for other predicates that appear before the predicate having the abbreviation candidate in the text.
- the target predicate search unit 456 that outputs each predicate and a predicate having a candidate for the omission as a pair, and for each predicate pair that the target predicate search unit 456 outputs, Whether there is language knowledge in the language knowledge DB 194 such that the predicate rephrased with an equivalent expression obtained by referring to the substitution / category dictionary 196 appears in the first sentence and the second sentence, respectively. Or It is determined whether or not the pattern of the expressed expression is in the pattern dictionary 198, and if there is, the language knowledge search unit 458 that outputs the language knowledge or pattern and the language knowledge or pattern output by the language knowledge search unit 458 are temporarily stored.
- Match language knowledge storage unit 460 and language knowledge or patterns stored in match language knowledge storage unit 460 are used, and expressions including each predicate of the predicate pair output by target predicate search unit 456 are included in those expressions.
- a candidate adding unit 462 is included that estimates the pointing destination of the omitted portion and stores the omitted portion and the pointing destination in the candidate DB 386 as annotation candidates.
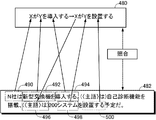
- language knowledge search unit 458 searches language knowledge 480 for a predicate pair appearing in text 482 (“install” in character string 494, “install” in character string 500). Shall be.
- Text 482 is the same sentence as example sentence 60 shown in FIG.
- the language knowledge 480 includes a first sentence “X introduces Y” and a second sentence “X installs Y”.
- the expression corresponding to the variable X of the first sentence is a character string 490 “N company is”.
- the expression corresponding to “Y” in the first sentence is a character string 492 “new switch” in the text 482.
- the expression “introducing” in the first sentence of the language knowledge 480 matches the character string 494 “introducing” in the text 482. From this relationship, it can be seen that the candidate indicated by the variable X is the word “N company” in the character string 490, and the candidate indicated by the variable Y is the word “new switch” in the character string 492.
- the second sentence “system” of the text 482 corresponds to the variable Y of the language knowledge 480, and therefore the character string 492 “new switch is” in the text 482 corresponds to the character string 498 “system” in the text 482. It turns out that it is a thing. In this way, the candidate for the destination of the omitted portion 496 is obtained by comparing the language knowledge 480 with the text.
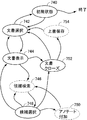
- the first language knowledge 520 has knowledge that “desertification proceeds ⁇ yellow sand increases” and the second language knowledge 522 has “yellow dust increases ⁇ asthma worsens”.
- the second sentence of the first language knowledge 520 matches the first sentence of the second language knowledge 522. Therefore, by linking these two knowledge, the third knowledge 524 that “desertification advances ⁇ yellow sand increases ⁇ asthma worsens” is obtained.
- the third knowledge 524 is compared with, for example, the text 526 shown in FIG.
- the omitted portion of the text 526 is estimated, and tags indicating the omitted portion 542, the omitted portion 548, and the like are added.
- Such comparison makes it possible to efficiently search for the point to be omitted by using the knowledge obtained by connecting two or more pieces of knowledge.
- the extent to which knowledge is linked is related to design matters. As the knowledge becomes longer, the maximum value of the number of points to be omitted that can be searched with one knowledge increases, but the number of texts to which the rules can be applied decreases. In this embodiment, it is assumed that up to two pieces of knowledge are connected. However, the present invention is not limited to such an embodiment. More knowledge may be concatenated and used to search for the abbreviation point. Alternatively, the maximum value of the number of connections may be changed depending on the type of sentence, or the user may specify the maximum value of the number of connections of knowledge.
- a pattern 612 is stored in the pattern dictionary 198 as shown in FIG.
- this pattern 612 when an expression 650 “X is”, an expression 652 “... do”, and an expression 654 “... do” appear in this order, the subject of the expression 654 is omitted at the head of the expression 654. It is assumed that a tag 656 indicating the location is attached and that the fingertip of the tag 656 is X.
- the third candidate generation unit 392 searches for an annotated anaphoric relationship and an abbreviated relationship from the existing small-scale learning data DB 190, and distinguishes and outputs the anaphoric / omitted relationship search unit 680. And for each of the noun phrase pairs constituting the anaphoric relation output by the anaphoric / abbreviated relation searching unit 680, the noun phrase (those located behind in the text) is automatically omitted.
- An abbreviated sentence generation unit 682 that generates a new text by generating a sentence, and among the sentences generated by the specified abbreviated sentence generation unit 682, an anaphoric relationship is annotated with the omitted part and the omitted part.
- An annotation adding unit 684 that adds a new omission relationship annotation candidate between the noun phrase and the text portion including the omission relationship output by the anaphora / omission relationship search unit 680 Among the omitted parts, the omitted element restoration unit 688 that generates a new sentence by restoring the pointed element as a pronoun in the omitted part based on the annotation, and the new part generated by the omitted element restoration unit 688 A new annotation generated by the annotation adding unit 684 and the annotation adding unit 690. The annotation adding unit 690 adds an annotation candidate including the pronoun pointing source and the pointing destination restored by the omitted element restoring unit 688. A candidate adding unit 686 for adding a sentence to the candidate DB 386 together with the annotation candidates.
- the third candidate generation unit 392 omits the pointing source, the omission is automatically performed according to a certain standard by the machine. For this reason, there is a case where a person cannot determine what the abbreviated part is pointed to. In such a case, the annotation is added to the learning data as a negative example.
- the candidate addition unit 686 adds these texts to the analyzed text DB 384, and adds annotation candidates. Is added to the candidate DB 386 in association with the text added to the post-analysis text DB 384.
- the fourth candidate generation unit 394 executes the anaphora / omission analysis by applying the existing anaphora / omission analyzer 208 to the analyzed text stored in the post-analysis text DB 384.
- An anaphoric / omission analysis execution unit 710 that obtains the result and adds it as an annotation to the analyzed text, and an analysis result storage that stores the annotated anaphoric / omission analysis result annotation output by the anaphoric / omission analysis execution unit 710
- a candidate adding unit 714 that adds an annotation included in the analysis result stored in the analysis result storage unit 712 to the candidate DB 386 as an annotation candidate for the text to be analyzed in the post-analysis text DB 384.
- the interactive annotation apparatus 396 shown in FIG. 8 is realized by a program that performs state transition as shown in FIG. Referring to FIG. 17, this program starts from a state (initial state) 740 in which initial processing is executed at the start of program execution and when a document is closed and the initial screen is displayed. In this state, it is possible to select either a process for selecting a document to be processed from the text archive or a process for terminating the execution of the program.
- the program state transitions to the document selection state 742.
- the document selection state 742 a document file selection dialog is displayed. Here, selection of a document file and cancellation of processing can be selected. If cancel processing is selected, the state returns to the initial state 740.
- the program transitions to a state (document display state) 744 that displays the contents of the document.
- a state (document display state) 744 that displays the contents of the document.
- processing for canceling the display of the document and returning to the document selection state 742 without reflecting the update, processing for closing the document reflecting the update, and learning data for anaphora / omission analysis are created.
- the annotation candidate is displayed after passing through the state (candidate search state) 746 for searching for an annotation candidate from the current processing position of the document toward the end of the document. Transition is made to a state of waiting for selection of an annotation candidate by the user (candidate selection standby state) 748.
- the candidate search state 746 the next position to which the annotation candidate is attached is searched. If there is only one annotation candidate attached to the searched position, the annotation candidate as shown in the lower part of FIG. A drop-down list for designating whether or not to approve is generated, and an icon “ ⁇ ” for displaying the drop-down list is displayed at the target location. When there are a plurality of annotation candidates, a drop-down list for displaying all of them is generated, and an icon for displaying the drop-down list is displayed at the target location. When the user moves the pointer to any of the lists when the drop-down list is displayed, the candidate and the expression on the document corresponding to the candidate are highlighted in the same color. By such processing, the user can easily understand the correspondence between the pointing source and the pointing destination. In this state, the annotation selection processing is interrupted and the state is changed to the document display state 744, the annotation selection performed so far is reflected in the document, the document is saved, and the document file is closed. Either of these can be selected.
- the program transits to the annotation addition state 750.
- the annotate addition state 750 the selected annotation is added to the designated place in the document according to the selection, and the document on the memory is updated so as to add information indicating that the other candidate is not selected.
- the program again moves to candidate search state 746 and transitions to candidate selection wait state 748 when the next candidate is found.
- the program transits to the document display state 744. If the current document is selected to reflect the annotation processing performed on the document, the program transitions to a document close state 752. In the document close state 752, the program overwrites and saves the updated document data loaded in the memory as a document file, closes the open document file, and does not save the document, and enters the document selection state 742. One of the transition processes can be selected. If it is selected not to save the document, the state transitions directly to the document selection state 742. When saving the document is selected, the state transits to a state (overwrite saving state) 754 in which the file on the memory is overwritten and saved on the storage medium as the document file, and when saving is completed, the state transits to the document selection state 742.
- a state overwrite saving state
- the device By executing this program, the device automatically searches for abbreviations and anaphors, and each time one of them is searched, an annotation candidate attached to that part is displayed. If there is one annotation candidate, the user may input whether to approve the annotation candidate. In some cases, annotation candidates may be entered manually. In any case, it is possible to annotate much more easily than when the user visually finds the deletion position or the anaphor, and further finds the pointing destination visually.
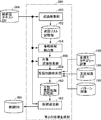
- the detector learning device 222 uses the selection restriction DB 224, the question type DB 220, and the question answering system 226 from the learning data stored in the learning data DB 162, and the omission detector 166, Learning of the anaphor detector 168 and the antecedent identifier 170 is performed separately. Further, the antecedent identifier 170 is further independently learned for the abbreviation antecedent identifier and the antecedent antecedent identifier.
- the detector learning device 222 includes an abbreviation detector learning unit 770, an anaphor detector learning unit 772, and an antecedent identifier learning unit 774 for this purpose.
- the omission detector 166 includes a subject omission detector 800, an object omission detector 802, and an indirect object omission detector 804. Since the abbreviated detector learning unit 770 performs learning of these three detectors individually, each of the omitted parts of the learning data stored in the learning data DB 162 includes the subject of the predicate (ga) and the direct object (W Class) or indirect object (second case), and classifying them to perform learning of the subject omission detector 800, the object omission detector 802, and the indirect object omission detector 804, respectively.
- the predicate ga
- W Class direct object
- second case indirect object
- a predicate is a verb, adjective, and a character string in the form of “noun +“ da ””.
- 1 is used when the predicate has omission, and 0 is used otherwise.
- the feature vector generated by the exceptional feature vector generation unit 780 includes the following elements. -Regarding the predicate of the omission detection target, 1 if the grammatical role of the detection target (for example, subject) is in a dependency relationship, 0 otherwise. -1 if the subject expression (noun phrase marked with "ha") appears in the same sentence as the predicate, 0 otherwise -1 if the omission detection target predicate appears in the first sentence of the target text, 0 otherwise -1 if the omission detection target predicate is after the beginning of the statement, 0 otherwise -Headwords and parts of speech of words that have a dependency relationship with the predicate to be omitted
- the anaphoric detector learning unit 772 uses the learning data stored in the learning data DB 162 to perform the SVM learning of the anaphoric detector 168, and is annotated as an anaphoric relationship origin (anaphoric).
- an SVM learning processing unit 834 for performing learning of SVMs constituting the anaphor detector 168 using the feature vector group generated by.
- the learning label is 1 if the noun phrase to be classified has an anaphoric destination in front of the text, and 0 otherwise.
- Elements of the feature vector for anaphoric detection learning include: ⁇ Part of speech, headword character string of anaphoric candidate, and case particle following the candidate ⁇ Part of speech, headword, and case particle following the subject of anaphoric candidate ⁇ Before anaphor candidate in text 1 if the noun phrase that appears at the position exactly matches the anaphor candidate as a character string, 0 otherwise -1 if the anaphora candidate partially matches in the text, 0 otherwise
- the antecedent identifier 170 includes an anaphoric antecedent identifier 900 and an abbreviation antecedent identifier 902. Therefore, the antecedent specifying device learning unit 774 has a configuration in which learning of the two specifying devices 900 and 902 is performed separately.
- the antecedent specifier learning unit 774 is an anaphoric antecedent specifier learning unit 840 that performs learning of the anaphoric antecedent specifier 900 and an abbreviation antecedent identifier 902 that is omitted.
- the antecedent antecedent identifier specifier learning unit 840 includes an anaphoric selector 850 that selects an expression annotated as an anaphoric relation indicator (anaphor) from the learning data stored in the learning data DB 162, and an anaphor An antecedent candidate selecting section 852 that selects an antecedent candidate composed of an annotated phrase that is actually annotated as an antecedent and an expression that may be another antecedent for the anaphor selected by the selecting section 850; Feature vector for generating a feature vector for learning the anaphor antecedent identifier 900 for each of the combinations of the anaphor selected by the verse selection unit 850 and the anaphor candidate selected by the antecedent candidate selection unit 852 To learn the SVM that constitutes the antecedent antecedent identifier 900 using the generation unit 854 and the feature vector generated by the feature vector generation unit 854 And a SVM learning processing unit 856.
- the abbreviation antecedent identifier learning unit 842 selects an expression (omitted) annotated as an abbreviation relationship from the learning data in the learning data DB 162, and the omission selected by the abbreviated selection unit 870.
- an antecedent candidate selecting unit 872 for selecting candidates that may become an antecedent in the learning data, an abbreviation selected by the abbreviation selecting unit 870, and an antecedent candidate selection For each combination with the antecedent candidate selected by the unit 872, a feature vector generation unit 874 for generating a feature vector, and a feature vector generated by the feature vector generation unit 874, and an abbreviation antecedent identifier And an SVM learning processing unit 876 that performs learning of the SVM that constitutes 902.
- the feature vector generation unit 874 is connected to the selection restriction DB 224, the question type DB 220, the question answering system 226, and the language knowledge DB 228, and uses information obtained from these when generating the feature vectors.
- the learning label is 1, if the abbreviation / antecedent candidate or the anaphoric / precedent candidate pair to be classified has an anaphoric / abbreviated relationship. Otherwise it is 0.
- the elements of the feature vector are as follows. -Part of speech candidate, headword character string, case particle following the candidate-1 if the antecedent candidate appears in the first sentence of the text, 0 otherwise -1 if the antecedent candidate is the first antecedent candidate mentioned in the sentence, 0 otherwise -1 if the antecedent candidate and anaphor are exactly the same string, 0 otherwise -1 if the antecedent candidate and the anaphor are partially the same string, 0 otherwise
- the question type DB 220 is used to generate a question sentence in which the part is an answer and give to the question answering system 226 that one of the answers is an antecedent candidate 1 if they match, 0 otherwise 1 if the predicate having an abbreviation or the predicate's predecessor predicate matches the predic
- the anaphora / omission analyzer 172 is connected to an omission detector 166, an anaphoric detector 168, and an antecedent identifier 170, and uses these to perform an anaphora / omission analysis and automatically
- a type DB 258, a question answering system 260, and a selection restriction DB 262 are included.
- the language knowledge DB 256 is a database storing language knowledge similar to the language knowledge DB 194 used in the anaphora / abbreviation analysis system 150 and the language knowledge DB 228 used in the learning system 164.
- the question type DB 258 has the same configuration as the question type DB 200 used in the annotation data generation auxiliary system 160 and the question type DB 220 used in the learning system 164, and the storage contents thereof are also the same.
- the question answering system 260 is a system having functions similar to the question answering system 206 used in the annotation data generation assisting system 160 and the question answering system 226 used in the learning system 164.
- the selection restriction DB 262 is the same as the selection restriction DB 224 used when generating a feature vector in the learning system 164.
- the DBs described as having the same configuration here may be the same as each other or different from each other.
- the anaphora / abbreviation analysis system 150 whose configuration has been described above operates as follows. The description will be divided into three phases: learning data creation, detector learning, and automatic annotation for input.
- the question answering system 206 is prepared in advance in the annotation data generation auxiliary system 160 and is made accessible from the learning data generation auxiliary device 204, or prepared so that a question sentence can be sent to an external question answering system. It is necessary to keep.
- the user activates learning data generation auxiliary device 204, designates text archive 192, and instructs the start of learning data generation.
- the morpheme analysis system 380 reads each text stored in the text archive 192, performs morpheme analysis, and gives a morpheme sequence with various grammatical information to the dependency relationship analysis system 382.
- the dependency relationship analysis system 382 performs grammatical structure analysis and dependency analysis for each sentence including a given morpheme sequence, and outputs the morpheme sequence to which the structure information and dependency information are attached to the text DB 384 after analysis. . In this way, each text stored in the text archive 192 is analyzed, and the analyzed text is accumulated in the analyzed text DB 384.
- the predicate search unit 420 of the first candidate generation unit 388 reads each post-analysis text stored in the post-analysis text DB 384, searches for the predicate, and writes it to the predicate list storage unit 422.
- the abbreviation candidate detection unit 424 has, for each predicate in the predicate list stored in the predicate list storage unit 422, any of the subject of the predicate, the object, the indirect object, etc. in the dependency relationship including the predicate. If it does not exist, that portion is detected as an omission candidate and given to the question sentence automatic generation unit 426.
- the question sentence automatic generation unit 426 generates a question sentence from a question sentence whose answer is a part of the omission candidate.
- the question sentence automatic generation unit 426 accesses the question type DB 200 using the predicate to be processed and the grammatical role (subject, object, etc.) of the omission candidate as keys, and reads out the question type.
- the question sentence automatic generation unit 426 further generates a question sentence such as the question sentence 336 shown in FIG. 7 by modifying the sentence including the omitted part using the read expression of the question type.
- the question sentence automatic generation unit 426 gives this question sentence to the question answering system 206 and the answer receiving unit 428.
- the answer receiving unit 428 waits until an answer to the question message is given from the question answering system 206.
- the question answering system 206 generates a plurality of answer candidates for each category for a given question sentence, and gives it to the answer receiving unit 428.
- the answer receiving unit 428 receives an answer from the question answering system 206
- the answer receiving unit 428 confirms to which question sentence the answer is sent from the question sentence automatic generating unit 426, and becomes an object to be processed by the appearance position confirmation unit 430. Give information and answer to identify the predicate.
- the appearance position confirmation unit 430 confirms the position of the abbreviated pointing destination candidate that appears before the predicate that is the processing target in the post-analysis text to be processed. Then, using these as candidates for omission of complementation, the predicates that are the processing targets and each of the candidates are combined and output to the candidate adding unit 432.
- the candidate addition unit 432 adds the candidate given from the appearance position confirmation unit 430 to the candidate DB 386.
- second candidate generation unit 390 operates as follows.
- the predicate search unit 450 searches each predicate in the analyzed text stored in the analyzed text DB 384 and accumulates it in the predicate list storage unit 452. Similar to the abbreviation candidate detection unit 424 shown in FIG. 8, the abbreviation candidate detection unit 454, for each predicate in the predicate list stored in the predicate list storage unit 452, in the dependency relationship including the predicate, the subject of the predicate, It is determined whether or not any of the object and the indirect object is present, and when it does not exist, that part is detected as an omission candidate.
- the omission candidate detection unit 454 gives information indicating the position of the detected omission candidate to the target predicate search unit 456.
- the target predicate search unit 456 searches for other predicates that appear before the predicate having the abbreviation candidate in the text among the abbreviation candidates detected by the abbreviation candidate detection unit 454.
- the predicate and the predicate having a candidate for the omission are paired and given to the language knowledge search unit 458.
- the linguistic knowledge search unit 458 For each predicate pair output by the target predicate search unit 456, the linguistic knowledge search unit 458 includes the first sentence in any of the linguistic knowledge in the linguistic knowledge DB 194 in which the predicate constituting the pair or the predicate rephrasing it is It is determined whether there is linguistic knowledge that appears in the second sentence, and if there is, linguistic knowledge is output. The linguistic knowledge search unit 458 also outputs an expression including the predicate pair given from the target predicate search unit 456, and if there is a match with the pattern stored in the pattern dictionary 198.
- the linguistic knowledge search unit 458 uses the paraphrase rules and categories stored in the paraphrase / category dictionary 196 when applying these linguistic knowledge and patterns to text, and paraphrases expressions in the rules to other expressions, Expand the scope of linguistic knowledge by replacing words in the rules with other words.
- the linguistic knowledge retrieved by the linguistic knowledge retrieval unit 458 is accumulated in the matching language knowledge storage unit 460 together with the predicate pair used in the retrieval of the linguistic knowledge.
- the candidate adding unit 462 collates the predicate pair stored in the matching language knowledge storage unit 460 with the matching language knowledge or pattern,
- the pointing candidate of the omission candidate is specified, and a pair of the omission candidate and each pointing destination candidate is added to the candidate DB 386 as an annotation candidate.
- the anaphoric / omitted relationship searching unit 680 of the third candidate generating unit 392 searches the existing small learning data DB 190 for the annotated anaphoric relationship and the omitted relationship, and a sentence including the anaphoric relationship. Is output to the source abbreviated sentence generation unit 682, and the sentence including the omission relation is output to the omitted element restoration unit 688.
- the ellipsis abbreviation generator 682 searches the text including the anaphoric relationship for a noun phrase pair that constitutes the anaphoric relationship, and for each of them, automatically identifies the locator located behind in the text within the noun phrase.
- a new omitted text is generated and given to the annotation adding unit 684.
- the annotation adding unit 684 creates a new line between the omitted part and the noun phrase in which the anaphoric relationship is annotated together with the omitted part of the sentence generated by the pointing source omitted sentence generating unit 682 in this way.
- Annotated annotation candidates are attached and output to the candidate adding unit 686.
- the candidate adding unit 686 generates new text by restoring the pointed element as a pronoun based on the annotation for the omitted part of the text including the omitted relationship output from the anaphoric / omitted relationship searching unit 680.
- the annotation adding unit 690 includes a new text generated by the omitted element restoring unit 688 and a pointing source composed of pronouns restored by the omitted element restoring unit 688 and a portion that was pointed to by the original annotation.
- a new anaphoric annotation candidate is added and output to the candidate addition unit 686.
- the candidate adding unit 686 adds the text output from the annotation adding unit 684 and the annotation adding unit 690 to the candidate DB 386 together with the annotation candidates added to them.
- the anaphora / omission analysis execution unit 710 of the fourth candidate generation unit 394 reads the text from the post-analysis text DB 384, and executes the anaphora / omission analysis by the existing anaphora / omission analyzer 208.
- the existing anaphora / omission analyzer 208 has a limit in its performance
- the anaphora / omission analysis is performed on the input text, and the annotated text is returned to the anaphora / omission analysis execution unit 710.
- the anaphora / omission analysis execution unit 710 accumulates the annotated analysis result in the analysis result storage unit 712.
- the candidate addition unit 714 adds the annotation included in the analysis result stored in the analysis result storage unit 712 to the candidate DB 386 as an annotation candidate.
- the text with the annotation candidates is finally accumulated in the candidate DB 386.
- the text accumulated in the candidate DB 386 includes abbreviation candidates and anaphoric candidates, and each abbreviation candidate and anaphoric candidate is added with one or more annotation candidates indicating their pointing destinations.
- the interactive annotation device 396 operates as follows for each of the abbreviation candidates and the anaphoric candidates for each of the candidates accumulated in the candidate DB 386 by interactive processing with the user using the input / output device 202.
- the interactive annotation apparatus 396 displays text 92 including annotation candidates on the screen.
- the interactive annotation apparatus 396 creates a drop-down menu for selecting an annotation candidate as follows for each of the omission candidate and the anaphoric candidate. That is, when there is only one point where the omission candidate is pointed, the same word as the word 110 that is the pointed candidate is displayed at the position of the omission candidate indicated by the character string 130 in FIG. An icon “ ⁇ ” indicating that there is a drop-down menu is displayed.
- an option YES / NO
- the selected annotation is confirmed as an annotation.
- the annotation is left indeterminate.
- direct input a dialog for directly specifying the destination of the omission candidate indicated by the character string 130 is displayed.
- a new annotation according to the user's specification is generated and becomes a final annotation.
- the annotation that is initially displayed but not selected by the user is used to generate a negative example when generating a feature vector during learning. Therefore, a flag indicating a negative example is attached to this annotation candidate.
- a drop-down list containing these multiple annotation candidates as options is generated.
- the top one of the annotation candidates or the annotation candidate with the highest score when scoring the annotation candidate in some form is displayed.
- an icon “ ⁇ ” indicating that there is a drop-down list is displayed.
- an option item for selecting to input directly is displayed in the drop-down list.
- the selected annotation candidate is confirmed as an annotation.
- the candidates that are not selected are used to generate a negative example when generating a feature vector during learning.
- the post-analysis text in which the annotation is confirmed is accumulated in the learning data DB 162.
- the learning data DB 162 is completed.
- detector learning device 222 operates as follows.
- the exceptional feature vector generation unit 780 of the omission detector learning unit 770 reads out learning data including omissions from the learning data that has been confirmed annotation stored in the learning data DB 162.
- the case feature vector generation unit 780 classifies each omitted part of the learning data when the predicate subject (ga case), direct object (wo case), or indirect object (second case).
- feature vector groups 782, 784 and 786 are generated and stored in a storage device (not shown).
- the exceptional feature vector generation unit 780 sets the learning label to 1 for the confirmed annotation and sets the learning label to 0 for the other annotations.
- the SVM learning processing unit 788 uses these feature vector groups 782, 784 and 786 to learn the SVMs included in the subject omission detector 800, the object omission detector 802, and the indirect object omission detector 804.
- the anaphoric candidate selection unit 830 of the anaphoric detector learning unit 772 reads the text including the anaphoric candidate from the learning data accumulated in the learning data DB 162, and adds an annotation as the anaphoric relationship origin (anaphoric). Selected words.
- the feature vector generation unit 832 generates the above-described feature vector for each of the anaphor candidates selected by the anaphor candidate selection unit 830. At this time, the feature vector generation unit 832 sets the learning label to 1 for the confirmed annotation and sets the learning label to 0 for the other annotations.
- the feature vectors generated by the feature vector generator 832 are stored in a storage device (not shown).
- the SVM learning processing unit 834 performs learning of the SVM constituting the anaphoric detector 168 using the feature vector group accumulated in this way.
- the antecedent classifier classifier learning unit 840 operates as follows.
- the anaphoric selector 850 of the antecedent antecedent specifier learning unit 840 selects, from the learning data stored in the learning data DB 162, an expression that is annotated as an anaphoric relationship indicator (anaphor), and precedes it. This is given to the word candidate selection unit 852.
- the antecedent candidate selection unit 852 displays both an annotated actual annotator and an expression (noun phrase) that may be another antecedent for the anaphor selected by the anaphor selector 850. Select an antecedent candidate to contain.
- the feature vector generation unit 854 performs learning of the antecedent antecedent specifier 900 for the combination of the anaphor selected by the anaphor selection unit 850 and each of the anaphor candidates selected by the antecedent candidate selection unit 852. Generate feature vectors of. At this time, the feature vector generation unit 854 sets the learning label as 1 and the other learning labels as 0 for the annotated expression as the pointing destination of the anaphor in the anaphoric relation.
- the SVM learning processing unit 856 learns the SVM that constitutes the antecedent antecedent specifier 900 using the feature vector generated by the feature vector generation unit 854.
- the abbreviation antecedent identifier learning unit 842 operates as follows.
- the abbreviation selection unit 870 of the abbreviation antecedent identifier learning unit 842 selects an expression (omitted) that has been annotated as an abbreviation relationship from the learning data in the learning data DB 162, and provides it to the antecedent candidate selection unit 872.
- the antecedent candidate selection unit 872 selects, in the learning data, candidates that may become an omitted antecedent, including an annotated expression as an antecedent for the omission selected by the abbreviation selection unit 870.
- the feature vector generation unit 874 generates a feature vector for each combination of the abbreviation selected by the abbreviation selection unit 870 and each of the antecedent candidates selected by the antecedent candidate selection unit 872 and stores it in a storage device (not shown). At this time, in the feature vector generated by the feature vector generation unit 874, the learning label is 1 if the omission / preceding candidate pair to be classified has an omission relationship, and 0 otherwise. Also, the feature vector generation unit 874 uses the selection restriction DB 224, the question type DB 220, the question answering system 226, and the language knowledge DB 228 as described above for generating the feature vector. The SVM learning processing unit 876 uses the feature vector generated by the feature vector generation unit 874 to learn the SVM that constitutes the abbreviation antecedent identifier 902.
- the subject omission detector 800, the object omission detector 802, the indirect object omission detector 804, the anaphor detector 168, and the antecedent identifier 170 included in the omission detector 166 are included. Learning of the antecedent antecedent identifier 900 and the abbreviation antecedent identifier 902 is completed.
- the anaphora / omission analysis for the input 250 by the anaphora / omission analyzer 252 and the automatic annotation of the result are executed as follows. This analysis is divided into an abbreviation analysis, an anaphoric analysis, an abbreviation, and an antecedent analysis for the anaphor.
- an omission detector 166 is used.
- an anaphor detector 168 is used.
- an antecedent identifier 170 is used.
- a morphological analysis and a structure / dependency analysis are performed on the input 250, and a morpheme sequence with the structure / dependency information is processed.
- a morpheme sequence in the omission analysis, feature vectors having the same configuration as those obtained when the subject omission omission detector 800, the object omission omission detector 802, and the indirect object omission omission detector 804 shown in FIG. Generated and fed to these detectors.
- an annotation as an abbreviation is attached to each portion of the input 250 indicating the highest score.
- a phrase that can be an anaphor candidate is selected from the noun phrase pairs included in the input 250, and each of the features has the same configuration as the feature vector generated by the feature vector generation unit 832 shown in FIG.
- a vector is generated from input 250.
- a score is obtained from the anaphor detector 168. Based on this score, it is determined whether or not it is an anaphor, and an annotation to that effect is attached.
- Prediction of antecedents by the antecedent antecedent identifier 900 is performed as follows. For each expression determined to be an anaphor by the anaphor detector 168, an expression that can be an antecedent is selected in the input 250, and a feature vector is generated in the same manner as the feature vector generation unit 854 in FIG. . Using this feature vector as an input to the antecedent antecedent identifier 900, the score of the antecedent antecedent identifier 900 is obtained, and the antecedent candidate that has the highest score with a score higher than the threshold Add an anaphoric annotation with the anaphor to be processed.
- a feature vector having the same configuration as that created by the feature vector generation unit 874 is used instead of the feature vector generated by the feature vector generation unit 854. Therefore, at this time, the selection restriction DB 224, the question type DB 220, the question answering system 226, and the language knowledge DB 228 are required.
- the present embodiment it is possible to easily generate learning data for learning a detector for anaphora and omission analysis from a text archive. For example, candidates for an anaphoric / abbreviated relationship are automatically searched, and the antecedent candidates are displayed as a list. The user may approve if there is one candidate displayed in the list and is correct, and select one of them if there are a plurality of candidates displayed in the list. As in the prior art, there is no need to visually search for an anaphoric / omission-related position, and then visually search for the indicated position and attach an anaphoric / omission-related annotation to both. If the correct pointer is not shown in the displayed list, the correct pointer can be designated manually.
- the question answering system 206 is assumed to be singular. However, the present invention is not limited to such an embodiment. If a plurality of question answering systems can be used, a plurality of question answering systems may be used. In this case, if each question answering system receives natural language texts as input, answer candidates can be obtained simply by sending the same question text to them.
- the learning data generation assisting device 204 can be realized by computer hardware and a computer program executed on the computer hardware.
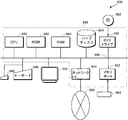
- FIG. 19 shows the external appearance of the computer system 930
- FIG. 20 shows the internal configuration of the computer system 930.
- the computer system 930 includes a computer 940 having a memory port 952 and a DVD (Digital Versatile Disc) drive 950, a keyboard 946, a mouse 948, and a monitor 942.
- a computer 940 having a memory port 952 and a DVD (Digital Versatile Disc) drive 950, a keyboard 946, a mouse 948, and a monitor 942.
- DVD Digital Versatile Disc
- the computer 940 includes a CPU (Central Processing Unit) 956, a bus 966 connected to the CPU 956, the memory port 952, and the DVD drive 950, and a boot program.
- a read-only memory (ROM) 958 for storing etc., a random access memory (RAM) 960 connected to the bus 966 for storing program instructions, system programs, work data and the like, and a hard disk 954 are included.
- the computer system 930 further includes a network interface (I / F) 944 that provides a connection to a network 968 that allows communication with other terminals.
- I / F network interface
- a computer program for causing the computer system 930 to function as each functional unit of the learning data generation assisting device 204 according to the above-described embodiment is stored in the DVD 962 or the removable memory 964 that is attached to the DVD drive 950 or the memory port 952. Further, it is transferred to the hard disk 954. Alternatively, the program may be transmitted to the computer 940 through the network 968 and stored in the hard disk 954. The program is loaded into the RAM 960 when executed. The program may be loaded directly from the DVD 962 into the RAM 960 from the removable memory 964 or via the network 968.
- This program includes an instruction sequence including a plurality of instructions for causing the computer 940 to function as each functional unit of the learning data generation auxiliary device 204 according to the above embodiment.
- Some of the basic functions necessary to cause computer 940 to perform this operation are an operating system or third party program that runs on computer 940 or various dynamically linkable programming toolkits or programs installed on computer 940. Provided by the library. Therefore, this program itself does not necessarily include all functions necessary for realizing the system and method of this embodiment.
- This program can be used as a system as described above by dynamically calling the appropriate program in the appropriate function or programming toolkit or program library at run time in a controlled manner to achieve the desired result. It is only necessary to include an instruction for realizing the function. Of course, all necessary functions may be provided only by the program.
- the present invention can be used in an industry that maintains learning data used for natural language processing, an apparatus therefor, and an industry that provides various services related to natural language processing using the learning data thus prepared. It is.
- Anaphoric / Omission Analysis System 160 Annotation Data Generation Auxiliary System 162 Learning Data DB 164 Learning system 166 Omission detector 168 Anaphoric detector 170 Antecedent identification device 172 Anaphoric / omission analysis device 190 Existing small learning data DB 192 Text Archive 194, 228, 256 Language Knowledge DB 196 Paraphrase / Category Dictionary 198 Pattern Dictionary 200, 220, 258 Question Type DB 202 I / O device 204 Learning data generation auxiliary device 206, 226, 260 Question answering system 222 Detector learning device 224, 262 Selection restriction DB 252 Anaphoric / abbreviated analyzer
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Audiology, Speech & Language Pathology (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Machine Translation (AREA)
- Document Processing Apparatus (AREA)
Abstract
Description
図3を参照して、本発明の第1の実施の形態に係る学習データ生成補助装置においてアノテーションをテキストに付する作業の概略を説明する。図3の上段を参照して、表示装置の画面に、アノテーション対象のテキスト90が表示される。このテキスト90は2つの文からなる。第1の文には、「導入する」という述部と、述部の主語である「N社」という単語100と、述部の目的語である「新型交換機」という単語110とが含まれる。第2の文は実質的には2つの節からなる。前半の文の先頭には「自己診断機能を搭載」の主語が省略されている箇所(省略箇所)114がある。前半の文と後半の文との中間箇所には、「200システムを設置する予定だ。」の主語が省略されている省略箇所104がある。
図4を参照して、最初に、本実施の形態に係る学習データ生成補助装置を使用する照応・省略解析システム150の全体構成について説明する。
アノテーションデータ生成補助システム160は、表示装置とキーボート及びマウス等を用いてユーザとの間で対話的な入出力を行う入出力装置202と、言語知識を含む様々な資源を用いて、テキストアーカイブ192に記憶された大量のテキストに対するユーザのアノテーション付与作業を補助することで、学習データを生成し学習データDB162に出力する学習データ生成補助装置204とを含む。
図5を参照して、言語知識DB194に記憶された言語知識の規則は、大きく分けて4種類ある。すなわち、因果関係知識290、含意関係知識292、事態生起順序関係知識294、及び事態生起無効化関係知識296である。各知識は、ワイルドカード的な役割を果たす、任意の名詞句等に置換可能な変数(以下では、「X」,「Y」等によって表わす)を含んでもよい。
図6を参照して、質問タイプDB200は、学習データ生成補助装置204が質問応答システム206を利用して先行詞の候補を入手するときに利用される。質問タイプDB200は、複数のエントリを持つ。各エントリは例えば、ある動詞について、ある表現内でのその動詞の係り受け関係において省略されている部分の文法役割と、省略部分に挿入されるべき表現を求める際に、どのような形で質問文を生成すればよいかを示す情報(質問タイプ)とを含む。例えば「食べる」という動詞について、ある表現内でその主語が省略されている場合には、「誰が」を文の先頭に配置して文を生成すれば、回答として「食べる」の主語になるべき表現が質問応答システムから得られる。
図7を参照して、質問応答システム206を利用して省略箇所の指す表現の候補を得るプロセスについて説明する。まず、入力テキスト320が2つの文を含むものとする。第1の文は「夕食に赤ワインを飲みましょう」という文であり、第2の文は「心臓病を防ぎます」であるものとする。第2の文の先頭には「防ぎます」という動詞332の主語が省略されており、この省略箇所334には省略を示すタグが付されているものとする。ここでは、この省略箇所には「赤ワイン」という単語330が入るべきである。
図8を参照して、既存照応・省略解析器208は、既存の、照応・省略解析を行うものである。ここでは、既存照応・省略解析器208は、省略箇所の候補、照応詞の候補、及び省略箇所及び照応詞の先行詞の候補を提示するために使用される。最終的には人間がこれら候補の中から正しい候補を選択する。したがって、ここで用いる既存照応・省略解析器208の精度は必ずしも高くなくてもよい。
図8を参照して、学習データ生成補助装置204は、テキストアーカイブ192に含まれる各テキストに対して形態素解析を行い、さまざまな文法情報が付された形態素列を出力する形態素解析システム380と、形態素解析システム380の出力する形態素列に対し、文の構造及び係り受け解析を行い、構造・係り受け情報が付された形態素列を出力する係り受け関係解析システム382と、係り受け関係解析システム382が出力する形態素列を、それらの文法情報及び構造・係り受け関係とともに記憶する解析後テキストDB384とを含む。ここでは、係り受け関係解析システム382は、少なくともどの単語がどの単語に係っているかを示す係り受け情報を各形態素列に付すものとする。なお、図8においては、図面を簡略にするために図示していないが、本実施の形態では、学習データ生成補助装置204内の各要素は、入出力装置202を介したユーザの指示により動作する。
図9を参照して、第1の候補生成部388は、解析後テキストDB384に記憶された各テキストデータのうちの述語を検索する述語検索部420と、述語検索部420が出力した各述語のリストを各述語の出現位置とともに記憶する述語リスト記憶部422と、述語リスト記憶部422に記憶された各述語のうち、当該述語が関与する係り受け関係のうちで省略されている箇所を検出し、省略候補として出力する省略候補検出部424と、省略候補検出部424に記憶された省略候補の各々に対して、質問タイプDB200を参照してその省略箇所を補完する単語を回答として求める質問文を生成し、質問応答システム206に質問文として与える質問文自動生成部426と、質問文自動生成部426から質問文を、その質問文に対する回答候補群を質問応答システム206から受信し、質問文とその回答候補群とを組み合わせて出力する回答受信部428と、回答受信部428が出現する質問文と回答候補群とのペアを受け、回答候補群に含まれる候補のうち、解析後テキストDB384に記憶された解析後テキスト文内の出現箇所を確認し、質問の対象となっている省略箇所より前の位置に出現するものを全て選択して省略箇所の指し先候補として出力する出現位置確認部430と、出現位置確認部430から出力される省略箇所とその省略箇所を補完する候補群とを組にしてアノテーション候補として候補DB386に追加する候補追加部432とを含む。
図10を参照して、第2の候補生成部390は、図9に示す述語検索部420、述語リスト記憶部422、及び省略候補検出部424とそれぞれ同様の述語検索部450、述語リスト記憶部452、及び省略候補検出部454と、省略候補検出部454により検出された省略候補のうち、テキスト内でその省略の候補を持つ述語よりも前に出現している他の述語を検索し、検索された各述語とその省略の候補を持つ述語とをペアにして出力する対象述語検索部456と、対象述語検索部456が出力する各述語ペアについて、それらペアを構成する述語、又はそれを言換え・カテゴリ辞書196を参照して得られた等価な表現で言換えた述語が、第1文と第2文とにぞれぞれ出現するような言語知識が言語知識DB194内にあるか、又はそうした表現のパターンがパターン辞書198にあるか否かを判定し、あればその言語知識又はパターンを出力する言語知識検索部458と、言語知識検索部458が出力する言語知識又はパターンを一時記憶する合致言語知識記憶部460と、合致言語知識記憶部460に記憶された言語知識又はパターンを用い、対象述語検索部456が出力した述語ペアの各述語を含む表現を用いて、それら表現に含まれる省略箇所の指し先を推定し、省略箇所と指し先とを組にしてアノテーション候補として候補DB386に記憶させる候補追加部462とを含む。
図15を参照して、第3の候補生成部392は、既存小規模学習データDB190の中からアノテーション済の照応関係及び省略関係を検索し、両者を区別して出力する照応・省略関係検索部680と、照応・省略関係検索部680の出力する照応関係を構成する名詞句対の各々について、その名詞句の内の指し元(テキスト内で後方に位置するもの)を自動的に省略した新たな文を生成して新たなテキストを生成する指し元省略文生成部682と、指し元省略文生成部682の生成した文のうち、省略された箇所と、省略された箇所とともに照応関係がアノテーションされていた名詞句との間に新たな省略関係のアノテーション候補を付すアノテーション追加部684と、照応・省略関係検索部680が出力する省略関係を含むテキスト部分のうち、省略箇所について、アノテーションに基づいて省略箇所に、その指し先の要素を代名詞として復元することで新たな文を生成する省略要素復元部688と、省略要素復元部688により生成された新たな文に、省略要素復元部688により復元された代名詞の指し元とその指し先とからなるアノテーション候補を追加するアノテーション追加部690と、アノテーション追加部684及びアノテーション追加部690により生成された新たな文をそのアノテーション候補とともに候補DB386に追加する候補追加部686とを含む。
図16を参照して、第4の候補生成部394は、解析後テキストDB384に記憶された解析後テキストに対して、既存照応・省略解析器208を適用することにより、照応・省略解析の実行結果を得て、解析後テキストにアノテーションとして追加する照応・省略解析実行部710と、照応・省略解析実行部710の出力する照応・省略解析結果のアノテーションが付されたテキストを記憶する解析結果記憶部712と、解析結果記憶部712に記憶された解析結果に含まれるアノテーションを、解析後テキストDB384で解析対象となったテキストに対するアノテーション候補として候補DB386に追加する候補追加部714とを含む。
図8に示す対話型アノテーション装置396は、図17に示すような状態遷移を行うプログラムにより実現される。図17を参照して、このプログラムは、プログラム実行開始時及び文書クローズ時等に初期処理を実行し、初期画面を表示した状態(初期状態)740から開始する。この状態では、テキストアーカイブから処理対象の文書を選択する処理と、プログラムの実行を終了する処理とのいずれかを選択できる。文書の選択が選ばれるとプログラムの状態は文書選択状態742に遷移する。文書選択状態742では、文書ファイルの選択ダイアログが表示される。ここでは文書ファイルの選択と、処理のキャンセルとを選ぶことができる。処理のキャンセルが選ばれると状態は初期状態740に戻る。文書選択状態742で文書が選択されるとプログラムは文書の内容を表示する状態(文書表示状態)744に遷移する。文書表示状態744では、文書の表示をキャンセルし、更新を反映せずに再度文書選択状態742に戻る処理と、更新を反映して文書をクローズする処理と、照応・省略解析の学習データを作成するために、アノテーション候補の選択を指示する処理とのいずれかを選択できる。アノテーション候補の選択が指示されると、文書の、現在処理中の位置から文書の末尾方向に向かって、アノテーション候補を検索する状態(候補検索状態)746を経由した後、アノテーション候補を表示してユーザによるアノテーション候補の選択を待つ状態(候補選択待機状態)748に遷移する。
再び図4を参照して、検出器学習装置222は、前述したとおり、学習データDB162に記憶された学習データから、選択制限DB224、質問タイプDB220及び質問応答システム226を用いて省略検出器166、照応詞検出器168、及び先行詞特定器170の学習をそれぞれ別々に行う。先行詞特定器170についてはさらに、省略箇所の先行詞用の特定器と、照応詞の先行詞用の特定器との学習を独立に行う。
本実施の形態では、省略検出器166は、主語省略検出器800、目的語省略検出器802,及び間接目的語省略検出器804を含む。省略検出器学習部770は、これら3つの検出器の学習を個別に行うため、学習データDB162に記憶された学習データの省略箇所の各々が、述語の主語(ガ格)、直接目的語(ヲ格)、又は間接目的語(二格)であるときに、それらを分類して、主語省略検出器800、目的語省略検出器802、及び間接目的語省略検出器804の学習をそれぞれ行うための素性ベクトル群782、784及び786を生成するための格別素性ベクトル生成部780と、これら素性ベクトル群782,784及び786を用いてそれぞれ主語省略検出器800、目的語省略検出器802、及び間接目的語省略検出器804を構成するSVMの学習を行うためのSVM学習処理部788とを含む。
・省略検出対象の述語に関して、検出対象の文法役割(例えば、主語)が係り受け関係にあるなら1,それ以外なら0
・主題となる表現(「は」でマークされた名詞句)が述語と同一文内に出現しているなら1,それ以外なら0
・省略検出対象の述語が対象テキストの1文目に出現しているなら1,それ以外なら0
・省略検出対象の述語が文の最初の後であるなら1,それ以外なら0
・省略検出対象の述語と係り受け関係にある語の見出し語、品詞
照応詞検出器学習部772は、学習データDB162に記憶された学習データから、照応詞検出器168のSVMの学習を行うために、照応関係の差し元(照応詞)としてアノテーションが付された単語を選択する照応詞候補選択部830と、照応詞候補選択部830により選択された照応詞の各々について、後述するような素性ベクトルを生成するための素性ベクトル生成部832と、素性ベクトル生成部832により生成された素性ベクトル群を用い、照応詞検出器168を構成するSVMの学習を行うためのSVM学習処理部834とを含む。
・照応詞候補の品詞、見出し語文字列、及びその候補に後続する格助詞
・照応詞候補の係り先の品詞、見出し語、その係り先に後続する格助詞
・テキスト中で照応詞候補より前の位置に出現する名詞句が文字列として照応詞候補と完全一致する場合に1,それ以外は0
・テキスト中で照応詞候補と部分一致する場合に1,それ以外は0
先行詞特定器170は、照応詞用先行詞特定器900と、省略用先行詞特定器902とを含む。そのため、先行詞特定器学習部774はこの2つの特定器900及び902の学習を別個に行う構成を有する。
・先行詞候補の品詞、見出し語文字列、その候補に後続する格助詞
・先行詞候補がテキストの1文目に出現するなら1,それ以外なら0
・先行詞候補が文内で最初に言及された先行詞候補なら1,それ以外なら0
・先行詞候補と照応詞が完全に同じ文字列なら1,それ以外なら0
・先行詞候補と照応詞が部分的に同じ文字列なら1,それ以外なら0
・選択制限DB224を用い、省略を持つ述語と先行詞となる名詞句の間で選択制限が満たされる場合には1,それ以外なら0
・省略を含む文、その省略の箇所について、質問タイプDB220を用いてその箇所が回答となるような質問文を生成し質問応答システム226に与えて得られた回答のいずれかが先行詞候補と一致すれば1,それ以外なら0
・省略を持つ述語、先行詞の係り先の述語が検出器学習装置222に登録されている因果関係知識に含まれる述語対と合致するなら1,それ以外なら0
図4を参照して、照応・省略解析装置172は、省略検出器166、照応詞検出器168及び先行詞特定器170に接続され、これらを用いて入力250に対する照応・省略解析をし、自動的にアノテーションを入力250に追加して出力254とするための照応・省略解析器252と、照応・省略解析器252が照応・省略解析をする際の素性ベクトル生成に使用する言語知識DB256、質問タイプDB258、質問応答システム260、及び選択制限DB262を含む。言語知識DB256は、照応・省略解析システム150で使用される言語知識DB194、学習システム164で使用される言語知識DB228と同様の言語知識を記憶したデータベースである。質問タイプDB258は、アノテーションデータ生成補助システム160で使用される質問タイプDB200及び学習システム164で使用される質問タイプDB220と同様の構成を持ち、その記憶内容も同様である。質問応答システム260は、アノテーションデータ生成補助システム160で使用される質問応答システム206及び学習システム164で使用される質問応答システム226と同様の機能を持つシステムである。選択制限DB262は、学習システム164における素性ベクトルの生成時に使用される選択制限DB224と同様のものである。なお、ここで同様の構成を持つと記載したDBは、互いに同一のものでもよいし、互いに異なるものでもよい。
以上に構成を述べた照応・省略解析システム150は以下のように動作する。学習データの作成、検出器の学習、及び入力に対する自動アノテーションの3つのフェーズに分けて説明する。
学習データの作成はアノテーションデータ生成補助システム160により行われる。この処理に先立ち、既存小規模学習データDB190、テキストアーカイブ192、言語知識DB194、言換え・カテゴリ辞書196、パターン辞書198、既存照応・省略解析器208、及び質問タイプDB200を準備しておく必要がある。また、質問応答システム206については、予めアノテーションデータ生成補助システム160内に準備し学習データ生成補助装置204からアクセス可能にしておくか、外部の質問応答システムに対して質問文を送れるよう準備しておく必要がある。
図18を参照して、検出器学習装置222は以下のように動作する。省略検出器学習部770の格別素性ベクトル生成部780は、学習データDB162に記憶されたアノテーション確定済の学習データのうち、省略を含む学習データを読出す。格別素性ベクトル生成部780は、学習データの省略箇所の各々が、述語の主語(ガ格)、直接目的語(ヲ格)、又は間接目的語(二格)であるときに、それらを分類して、それぞれ素性ベクトル群782、784及び786を生成し図示しない記憶装置に蓄積する。この際、格別素性ベクトル生成部780は、確定したアノテーションについては学習ラベルを1、それ以外のアノテーションについては学習ラベルを0とする。SVM学習処理部788は、これら素性ベクトル群782、784及び786を用いて、主語省略検出器800、目的語省略検出器802、及び間接目的語省略検出器804が有するSVMの学習を行う。
図4に戻り、照応・省略解析器252による入力250に対する照応・省略解析とその結果の自動アノテーションは以下のようにして実行される。なお、この解析は省略解析、照応解析、省略及び照応詞に対する先行詞解析に分割される。省略解析では省略検出器166が用いられる。照応解析では照応詞検出器168が用いられる。先行詞解析では先行詞特定器170が用いられる。
上記実施の形態に係る学習データ生成補助装置204は、コンピュータハードウェアと、そのコンピュータハードウェア上で実行されるコンピュータプログラムとにより実現できる。図19はこのコンピュータシステム930の外観を示し、図20はコンピュータシステム930の内部構成を示す。
160 アノテーションデータ生成補助システム
162 学習データDB
164 学習システム
166 省略検出器
168 照応詞検出器
170 先行詞特定器
172 照応・省略解析装置
190 既存小規模学習データDB
192 テキストアーカイブ
194,228,256 言語知識DB
196 言換え・カテゴリ辞書
198 パターン辞書
200,220,258 質問タイプDB
202 入出力装置
204 学習データ生成補助装置
206,226,260 質問応答システム
222 検出器学習装置
224,262 選択制限DB
252 照応・省略解析器
Claims (6)
- 自然言語文の照応・省略解析のためのアノテーションデータの作成を補助するアノテーション補助装置であって、
表示装置と入力装置とからなり、ユーザとの対話型処理によりユーザ入力を受け付ける入出力手段と、
アノテーションの対象となるテキストアーカイブからテキストデータを読み出す読出手段と、
前記読出手段が読み出したテキストデータの形態素解析及び係り受け解析を行って、係り受け構造を示す情報が付された形態素列を出力する解析手段と、
前記解析手段の出力する形態素列中の述語を検索する述語検索手段と、
前記述語検索手段が検索した述語の各々が関与する係り受け関係において、当該述語に対して所定の関係にあるべき単語が省略されていること、又は指示語となっていることを検出し、アノテーション処理の対象として当該単語の位置を特定するための対象特定手段と、
前記対象特定手段が特定した前記単語の位置の各々について、当該位置に挿入されるべき表現の候補を、当該位置と周囲の形態素列との関係、及び言語知識を用いて推定する候補推定手段と、
前記候補推定手段により推定された候補を前記単語の位置と関連付けて記憶する候補記憶手段と、
前記アノテーション処理の対象の各々について、前記候補推定手段が推定した候補を前記候補記憶手段から読出し、ユーザがいずれかを選択可能なように前記表示装置に表示する候補表示手段と、
前記候補表示手段により表示された候補のいずれかを選択するユーザの指示に応答して、選択された候補を前記位置にアノテーションとして付加する対話的選択手段とを含む、アノテーション補助装置。 - 前記候補推定手段は、
前記対象特定手段が特定した前記単語の位置の各々について、当該単語の位置に入るべき単語を問い合わせる文を、当該位置の周囲の単語列を用いて生成する質問文生成手段と、
前記質問文生成手段が生成した質問文を、予め準備された質問応答システムに入力として与える質問文入力手段と、
前記質問文入力手段から与えられた質問文に対して前記質問応答システムから得られる回答から、前記単語の位置に挿入されるべき単語の候補を当該単語の位置と関連付けて前記候補記憶手段に記憶させる手段とを含む、請求項1に記載のアノテーション補助装置。 - 前記候補推定手段は、さらに、
複数の言語知識規則を記憶する言語知識記憶手段と、
前記対象特定手段が特定した前記単語の位置の各々について、当該単語の位置と、当該単語の位置を特定する際に用いられた前記述語とを含む表現であって、前記言語知識記憶手段に記憶された言語知識のいずれかに適合する表現を特定する適合表現抽出手段と、
前記適合表現抽出手段により抽出された表現と、当該表現が適合した言語知識規則とを照合することにより、前記表現中の、前記対象特定手段が特定した前記単語の位置に挿入されるべき表現を、当該単語の位置に挿入されるべき文字列の候補として前記候補記憶手段に記憶させる手段とを含む、請求項2に記載のアノテーション補助装置。 - 前記候補推定手段はさらに、
予め準備された既存のアノテーション済テキストデータベースに含まれるテキスト中で、省略又は照応関係に関するアノテーションが付されている箇所を検索するアノテーション検索手段と、
前記アノテーション検索手段により検索された箇所の各々について、各アノテーションごとに予め定められた方式にしたがって文を変形し、当該変形箇所を前記検索された箇所に対するアノテーションの候補として前記候補記憶手段に記憶させる手段とを含む、請求項3に記載のアノテーション補助装置。 - 前記候補推定手段はさらに、
前記解析手段の出力する解析後の形態素列を、他の既存の照応・省略解析器への入力として与える手段と、
前記既存の照応・省略解析器による照応・省略解析結果を受け、当該照応・省略解析結果を、前記候補記憶手段に記憶させる手段とを含む、請求項2~請求項4のいずれかに記載のアノテーション補助装置。 - 自然言語文の照応・省略解析のためのアノテーションデータの作成を補助するアノテーション補助装置としてコンピュータを動作させるコンピュータプログラムであって、コンピュータを、
当該コンピュータの表示装置と入力装置とを用いたユーザとの対話型処理によりユーザ入力を受け付ける入出力手段と、
アノテーションの対象となるテキストアーカイブからテキストデータを読み出す読出手段と、
前記読出手段が読み出したテキストデータの形態素解析及び係り受け解析を行って、係り受け構造を示す情報が付された形態素列を出力する解析手段と、
前記解析手段の出力する形態素列中の述語を検索する述語検索手段と、
前記述語検索手段が検索した述語の各々が関与する係り受け関係において、当該述語に対して所定の関係にあるべき単語が省略されていること、又は指示語となっていることを検出し、アノテーション処理の対象として当該単語の位置を特定するための対象特定手段と、
前記対象特定手段が特定した前記単語の位置の各々について、当該位置に挿入されるべき表現の候補を、当該位置と周囲の形態素列との関係、及び言語知識を用いて推定する候補推定手段と、
前記候補推定手段により推定された候補を前記単語の位置と関連付けて記憶する候補記憶手段と、
前記アノテーション処理の対象の各々について、前記候補推定手段が推定した候補を前記候補記憶手段から読出し、ユーザがいずれかを選択可能なように前記表示装置に表示する候補表示手段と、
前記候補表示手段により表示された候補のいずれかを選択するユーザの指示に応答して、選択された候補を前記位置にアノテーションとして付加する対話的選択手段として機能させる、コンピュータプログラム。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/544,227 US10157171B2 (en) | 2015-01-23 | 2016-01-20 | Annotation assisting apparatus and computer program therefor |
| KR1020177017635A KR20170106308A (ko) | 2015-01-23 | 2016-01-20 | 어노테이션 보조 장치 및 그것을 위한 컴퓨터 프로그램 |
| CN201680006728.2A CN107209759B (zh) | 2015-01-23 | 2016-01-20 | 注解辅助装置及记录介质 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015-011491 | 2015-01-23 | ||
| JP2015011491A JP6074820B2 (ja) | 2015-01-23 | 2015-01-23 | アノテーション補助装置及びそのためのコンピュータプログラム |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2016117607A1 true WO2016117607A1 (ja) | 2016-07-28 |
Family
ID=56417145
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2016/051577 WO2016117607A1 (ja) | 2015-01-23 | 2016-01-20 | アノテーション補助装置及びそのためのコンピュータプログラム |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10157171B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6074820B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR20170106308A (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN107209759B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2016117607A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108319467A (zh) * | 2018-01-03 | 2018-07-24 | 武汉斗鱼网络科技有限公司 | 一种注释填充方法 |
Families Citing this family (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018131048A1 (en) * | 2017-01-11 | 2018-07-19 | Satyanarayana Krishnamurthy | System and method for natural language generation |
| US20180203856A1 (en) * | 2017-01-17 | 2018-07-19 | International Business Machines Corporation | Enhancing performance of structured lookups using set operations |
| CN106874467B (zh) * | 2017-02-15 | 2019-12-06 | 百度在线网络技术(北京)有限公司 | 用于提供搜索结果的方法和装置 |
| JP6888357B2 (ja) | 2017-03-22 | 2021-06-16 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | 情報表示装置、情報表示方法、及びプログラム |
| JP6957918B2 (ja) | 2017-03-22 | 2021-11-02 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | 情報表示装置、情報表示方法、及びプログラム |
| JP6911432B2 (ja) * | 2017-03-23 | 2021-07-28 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | 情報表示装置、情報表示装置の制御方法、及び情報表示装置の制御プログラム |
| JP7174717B2 (ja) * | 2017-10-20 | 2022-11-17 | グーグル エルエルシー | 臨床ドキュメンテーションで使用される患者-医師間会話からの詳細構造の取込み |
| US10860800B2 (en) * | 2017-10-30 | 2020-12-08 | Panasonic Intellectual Property Management Co., Ltd. | Information processing method, information processing apparatus, and program for solving a specific task using a model of a dialogue system |
| CN108664465B (zh) * | 2018-03-07 | 2023-06-27 | 珍岛信息技术(上海)股份有限公司 | 一种自动生成文本方法以及相关装置 |
| US10740541B2 (en) * | 2018-05-24 | 2020-08-11 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Fact validation in document editors |
| CN109446517B (zh) * | 2018-10-08 | 2022-07-05 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | 指代消解方法、电子装置及计算机可读存储介质 |
| JP7159778B2 (ja) * | 2018-10-16 | 2022-10-25 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | 発話生成装置、方法、及びプログラム |
| KR102220106B1 (ko) * | 2018-12-12 | 2021-02-24 | 주식회사 엘지유플러스 | 음성 인식된 문장의 보정 방법 |
| KR102194424B1 (ko) * | 2018-12-18 | 2020-12-23 | 주식회사 엘지유플러스 | 문장 복원 방법 및 장치 |
| JP7103264B2 (ja) * | 2019-02-20 | 2022-07-20 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | 生成装置、学習装置、生成方法及びプログラム |
| CN109933217B (zh) * | 2019-03-12 | 2020-05-01 | 北京字节跳动网络技术有限公司 | 用于推送语句的方法和装置 |
| US11409950B2 (en) * | 2019-05-08 | 2022-08-09 | International Business Machines Corporation | Annotating documents for processing by cognitive systems |
| JP7239863B2 (ja) | 2019-10-30 | 2023-03-15 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | 自己校正機能付きadコンバータ |
| JP7374756B2 (ja) * | 2019-12-20 | 2023-11-07 | キヤノン株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及びプログラム |
| WO2021210142A1 (ja) * | 2020-04-16 | 2021-10-21 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | データパターンの分類方法および分類システム |
| KR102383043B1 (ko) * | 2020-07-02 | 2022-04-05 | 주식회사 엔씨소프트 | 생략 복원 학습 방법과 인식 방법 및 이를 수행하기 위한 장치 |
| KR102417531B1 (ko) | 2020-07-08 | 2022-07-06 | 주식회사 메가젠임플란트 | 학습 데이터 생성장치 및 그 장치의 구동방법, 그리고 컴퓨터 판독가능 기록매체 |
| US11853702B2 (en) * | 2021-01-29 | 2023-12-26 | International Business Machines Corporation | Self-supervised semantic shift detection and alignment |
| US11977852B2 (en) * | 2022-01-12 | 2024-05-07 | Bank Of America Corporation | Anaphoric reference resolution using natural language processing and machine learning |
| JP7455338B2 (ja) | 2022-07-13 | 2024-03-26 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 情報処理方法、情報処理装置及びコンピュータプログラム |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004005648A (ja) * | 2002-05-10 | 2004-01-08 | Microsoft Corp | 自然言語理解システムに関するトレーニングデータの自動注釈付けのための方法およびユーザインターフェース |
Family Cites Families (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6442524B1 (en) * | 1999-01-29 | 2002-08-27 | Sony Corporation | Analyzing inflectional morphology in a spoken language translation system |
| US6925432B2 (en) * | 2000-10-11 | 2005-08-02 | Lucent Technologies Inc. | Method and apparatus using discriminative training in natural language call routing and document retrieval |
| US7475010B2 (en) * | 2003-09-03 | 2009-01-06 | Lingospot, Inc. | Adaptive and scalable method for resolving natural language ambiguities |
| CA2549769A1 (en) * | 2003-12-15 | 2005-06-30 | Laboratory For Language Technology Incorporated | System, method, and program for identifying the corresponding translation |
| US20050273314A1 (en) * | 2004-06-07 | 2005-12-08 | Simpleact Incorporated | Method for processing Chinese natural language sentence |
| JP3986531B2 (ja) * | 2005-09-21 | 2007-10-03 | 沖電気工業株式会社 | 形態素解析装置及び形態素解析プログラム |
| JP5010885B2 (ja) * | 2006-09-29 | 2012-08-29 | 株式会社ジャストシステム | 文書検索装置、文書検索方法および文書検索プログラム |
| US20080162117A1 (en) * | 2006-12-28 | 2008-07-03 | Srinivas Bangalore | Discriminative training of models for sequence classification |
| US8527262B2 (en) * | 2007-06-22 | 2013-09-03 | International Business Machines Corporation | Systems and methods for automatic semantic role labeling of high morphological text for natural language processing applications |
| CN101446943A (zh) * | 2008-12-10 | 2009-06-03 | 苏州大学 | 一种中文处理中基于语义角色信息的指代消解方法 |
| CN102193946A (zh) * | 2010-03-18 | 2011-09-21 | 株式会社理光 | 为媒体文件添加标签方法和使用该方法的系统 |
| JP5390463B2 (ja) * | 2010-04-27 | 2014-01-15 | インターナショナル・ビジネス・マシーンズ・コーポレーション | 不具合を示す述語表現を抽出するための不具合述語表現抽出装置、不具合述語表現抽出方法及び不具合述語表現抽出プログラム |
| US9575937B2 (en) * | 2010-08-24 | 2017-02-21 | Nec Corporation | Document analysis system, document analysis method, document analysis program and recording medium |
| EP2635965A4 (en) * | 2010-11-05 | 2016-08-10 | Rakuten Inc | SYSTEMS AND METHODS RELATING TO KEYWORD EXTRACTION |
| US8880391B2 (en) * | 2010-12-17 | 2014-11-04 | Rakuten, Inc. | Natural language processing apparatus, natural language processing method, natural language processing program, and computer-readable recording medium storing natural language processing program |
| JP5197774B2 (ja) * | 2011-01-18 | 2013-05-15 | 株式会社東芝 | 学習装置、判定装置、学習方法、判定方法、学習プログラム及び判定プログラム |
| US8868407B2 (en) * | 2011-07-06 | 2014-10-21 | Honda Motor Co., Ltd. | Language processor |
| CN104169909B (zh) * | 2012-06-25 | 2016-10-05 | 株式会社东芝 | 上下文解析装置及上下文解析方法 |
| JP2014067179A (ja) * | 2012-09-25 | 2014-04-17 | Toshiba Corp | 文書処理装置及び文書処理プログラム |
| WO2014132402A1 (ja) * | 2013-02-28 | 2014-09-04 | 株式会社東芝 | データ処理装置および物語モデル構築方法 |
| US9171542B2 (en) * | 2013-03-11 | 2015-10-27 | Nuance Communications, Inc. | Anaphora resolution using linguisitic cues, dialogue context, and general knowledge |
| CN104268132B (zh) * | 2014-09-11 | 2017-04-26 | 北京交通大学 | 机器翻译方法及系统 |
| CN105988990B (zh) * | 2015-02-26 | 2021-06-01 | 索尼公司 | 汉语零指代消解装置和方法、模型训练方法和存储介质 |
-
2015
- 2015-01-23 JP JP2015011491A patent/JP6074820B2/ja active Active
-
2016
- 2016-01-20 US US15/544,227 patent/US10157171B2/en active Active
- 2016-01-20 CN CN201680006728.2A patent/CN107209759B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2016-01-20 WO PCT/JP2016/051577 patent/WO2016117607A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2016-01-20 KR KR1020177017635A patent/KR20170106308A/ko unknown
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004005648A (ja) * | 2002-05-10 | 2004-01-08 | Microsoft Corp | 自然言語理解システムに関するトレーニングデータの自動注釈付けのための方法およびユーザインターフェース |
Non-Patent Citations (4)
| Title |
|---|
| KAZUSHI IKEDA ET AL.: "Estimation and Complementation Approach for the Analysis of the Omission of Postposition on Colloquial Style Sentences", IPSJ SIG NOTES HEISEI 22 NENDO [ CD-ROM, 15 December 2010 (2010-12-15), pages 1 - 8 * |
| SHINPEI KAWAGUCHI ET AL.: "Shoo Kaiseki ni Chishikigen o Riyo shita Kanren Shitsumongun ni Taisuru Shitsumon Oto", PROCEEDINGS OF THE 12TH ANNUAL MEETING OF THE ASSOCIATION FOR NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING, 13 March 2006 (2006-03-13), pages 927 - 930 * |
| TAKAFUMI SUZUKI ET AL.: "Daihyo·Hasei Kankei o Riyo shita Nihongo Kino Hyogen no Kaiseki Hoshiki no Hyoka", THE ASSOCIATION FOR NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING DAI 18 KAI NENJI TAIKAI HAPPYO RONBUNSHU TUTORIAL HONKAIGI [ CD-ROM, 13 March 2012 (2012-03-13), pages 598 - 601 * |
| YUJI MATSUMOTO: "Corpus Annotation and Annotation-Assistance Tools", JOURNAL OF JAPANESE SOCIETY FOR ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE, vol. 24, no. 5, 1 September 2009 (2009-09-01), pages 632 - 639 * |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108319467A (zh) * | 2018-01-03 | 2018-07-24 | 武汉斗鱼网络科技有限公司 | 一种注释填充方法 |
| CN108319467B (zh) * | 2018-01-03 | 2022-01-04 | 武汉斗鱼网络科技有限公司 | 一种注释填充方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2016136341A (ja) | 2016-07-28 |
| KR20170106308A (ko) | 2017-09-20 |
| US10157171B2 (en) | 2018-12-18 |
| US20180011830A1 (en) | 2018-01-11 |
| JP6074820B2 (ja) | 2017-02-08 |
| CN107209759B (zh) | 2020-09-18 |
| CN107209759A (zh) | 2017-09-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6074820B2 (ja) | アノテーション補助装置及びそのためのコンピュータプログラム | |
| JP3009215B2 (ja) | 自然語処理方法および自然語処理システム | |
| US10296584B2 (en) | Semantic textual analysis | |
| US8972240B2 (en) | User-modifiable word lattice display for editing documents and search queries | |
| US10496756B2 (en) | Sentence creation system | |
| JP2002215617A (ja) | 品詞タグ付けをする方法 | |
| JPS6091450A (ja) | テ−ブル型言語翻訳器 | |
| Borsje et al. | Semi-automatic financial events discovery based on lexico-semantic patterns | |
| US20180293215A1 (en) | Method and Computer Program for Sharing Memo between Electronic Documents | |
| JP2020190970A (ja) | 文書処理装置およびその方法、プログラム | |
| Quirchmayr et al. | Semi-automatic Software Feature-Relevant Information Extraction from Natural Language User Manuals: An Approach and Practical Experience at Roche Diagnostics GmbH | |
| Choi et al. | Syntactic and semantic information extraction from NPP procedures utilizing natural language processing integrated with rules | |
| JP2005228075A (ja) | 日常言語プログラム処理システム、その方法および修辞構造解析方法 | |
| Ahmed et al. | Studying and recommending information highlighting in Stack Overflow answers | |
| JP6976585B2 (ja) | 照応・省略解析装置及びコンピュータプログラム | |
| Bimson et al. | The lexical bridge: A methodology for bridging the semantic gaps between a natural language and an ontology | |
| Revanth et al. | Nl2sql: Natural language to sql query translator | |
| Syu et al. | Rule-based extraction of tuple-based service demand from natural language-based software requirement for automated service composition | |
| Vo et al. | VietSentiLex: A sentiment dictionary that considers the polarity of ambiguous sentiment words | |
| Patel et al. | Incorporating linguistic expertise using ilp for named entity recognition in data hungry indian languages | |
| JP2013206130A (ja) | 検索装置、検索方法およびプログラム | |
| JP4300056B2 (ja) | 概念表現生成方法、プログラム、記憶媒体及び概念表現生成装置 | |
| Xu et al. | A Pipeline-Based Multimodal Military Event Argument Extraction Framework | |
| KR102640887B1 (ko) | 다국어 웹사이트 콘텐츠를 생성하는 방법 및 전자 장치 | |
| Damaratskaya | Identification and Visualization of Legal Definitions and their Relations Based on European Regulatory Documents |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16740214 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20177017635 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15544227 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 16740214 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |