WO2015056657A1 - 複合アミン吸収液、co2又はh2s又はその双方の除去装置及び方法 - Google Patents
複合アミン吸収液、co2又はh2s又はその双方の除去装置及び方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015056657A1 WO2015056657A1 PCT/JP2014/077264 JP2014077264W WO2015056657A1 WO 2015056657 A1 WO2015056657 A1 WO 2015056657A1 JP 2014077264 W JP2014077264 W JP 2014077264W WO 2015056657 A1 WO2015056657 A1 WO 2015056657A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- compound
- amine
- amine compound
- group
- disulfide
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 *C1N(*)CCCC1 Chemical compound *C1N(*)CCCC1 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/14—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols by absorption
- B01D53/1456—Removing acid components
- B01D53/1462—Removing mixtures of hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/14—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols by absorption
- B01D53/1425—Regeneration of liquid absorbents
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/14—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols by absorption
- B01D53/1456—Removing acid components
- B01D53/1468—Removing hydrogen sulfide
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/14—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols by absorption
- B01D53/1456—Removing acid components
- B01D53/1475—Removing carbon dioxide
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/14—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols by absorption
- B01D53/1493—Selection of liquid materials for use as absorbents
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/14—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols by absorption
- B01D53/18—Absorbing units; Liquid distributors therefor
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2252/00—Absorbents, i.e. solvents and liquid materials for gas absorption
- B01D2252/20—Organic absorbents
- B01D2252/204—Amines
- B01D2252/20405—Monoamines
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2252/00—Absorbents, i.e. solvents and liquid materials for gas absorption
- B01D2252/20—Organic absorbents
- B01D2252/204—Amines
- B01D2252/2041—Diamines
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2252/00—Absorbents, i.e. solvents and liquid materials for gas absorption
- B01D2252/20—Organic absorbents
- B01D2252/204—Amines
- B01D2252/20421—Primary amines
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2252/00—Absorbents, i.e. solvents and liquid materials for gas absorption
- B01D2252/20—Organic absorbents
- B01D2252/204—Amines
- B01D2252/20426—Secondary amines
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2252/00—Absorbents, i.e. solvents and liquid materials for gas absorption
- B01D2252/20—Organic absorbents
- B01D2252/204—Amines
- B01D2252/20431—Tertiary amines
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2252/00—Absorbents, i.e. solvents and liquid materials for gas absorption
- B01D2252/20—Organic absorbents
- B01D2252/204—Amines
- B01D2252/20436—Cyclic amines
- B01D2252/20442—Cyclic amines containing a piperidine-ring
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2252/00—Absorbents, i.e. solvents and liquid materials for gas absorption
- B01D2252/20—Organic absorbents
- B01D2252/204—Amines
- B01D2252/20436—Cyclic amines
- B01D2252/20447—Cyclic amines containing a piperazine-ring
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2252/00—Absorbents, i.e. solvents and liquid materials for gas absorption
- B01D2252/20—Organic absorbents
- B01D2252/204—Amines
- B01D2252/20478—Alkanolamines
- B01D2252/20484—Alkanolamines with one hydroxyl group
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2252/00—Absorbents, i.e. solvents and liquid materials for gas absorption
- B01D2252/20—Organic absorbents
- B01D2252/204—Amines
- B01D2252/20478—Alkanolamines
- B01D2252/20489—Alkanolamines with two or more hydroxyl groups
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2252/00—Absorbents, i.e. solvents and liquid materials for gas absorption
- B01D2252/20—Organic absorbents
- B01D2252/205—Other organic compounds not covered by B01D2252/00 - B01D2252/20494
- B01D2252/2056—Sulfur compounds, e.g. Sulfolane, thiols
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2252/00—Absorbents, i.e. solvents and liquid materials for gas absorption
- B01D2252/50—Combinations of absorbents
- B01D2252/502—Combinations of absorbents having two or more functionalities in the same molecule other than alkanolamine
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2252/00—Absorbents, i.e. solvents and liquid materials for gas absorption
- B01D2252/50—Combinations of absorbents
- B01D2252/504—Mixtures of two or more absorbents
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2252/00—Absorbents, i.e. solvents and liquid materials for gas absorption
- B01D2252/60—Additives
- B01D2252/604—Stabilisers or agents inhibiting degradation
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2256/00—Main component in the product gas stream after treatment
- B01D2256/24—Hydrocarbons
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2258/00—Sources of waste gases
- B01D2258/02—Other waste gases
- B01D2258/0283—Flue gases
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02C—CAPTURE, STORAGE, SEQUESTRATION OR DISPOSAL OF GREENHOUSE GASES [GHG]
- Y02C20/00—Capture or disposal of greenhouse gases
- Y02C20/40—Capture or disposal of greenhouse gases of CO2
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a composite amine absorbing solution that absorbs CO 2 and / or H 2 S in a gas, or both, and an apparatus and method for removing CO 2 and / or H 2 S or both.
- the regeneration step consumes a large amount of heat energy, so it is necessary to make it an energy saving process as much as possible.
- Patent Document 3 In order to improve the performance of the CO 2 absorbent, there is a proposal of an absorbent that contributes to the improvement of the absorption performance (Patent Document 3).
- the CO 2 absorption liquid is important not only for its absorption performance but also for its release ability when regenerating the absorption liquid.
- many of the conventional CO 2 absorption liquids have been designed to improve the absorption performance and have good regeneration performance. There are few studies on this.
- an object of the present invention is to provide an apparatus and method for removing a composite amine absorbent, CO 2 and / or H 2 S, or both, which have not only absorption capacity but also regeneration capacity.
- the first invention of the present invention for solving the above-mentioned problems is an absorption liquid that absorbs CO 2 and / or H 2 S in gas, or both, and includes 1) at least one amine compound and 2) absorption.
- the composite amine absorbing liquid is characterized in that a disulfide compound which is an oxidative degradation inhibitor of the liquid is dissolved in water, and the disulfide compound is a compound represented by the following chemical formula (I).
- R 1 -SSR 2 (I)
- R 1 or R 2 is any one of an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, a hydroxyethyl group, a carboxyethyl group, a cyclohexyl group, and a dibutylthiocarbamoyl group.
- the composite amine absorbing liquid according to the first invention wherein the disulfide compound is added in an amount of 1 to 20% by weight based on the amine compound.
- the amine compound is at least one primary amine compound, or at least one secondary amine compound, or at least one tertiary amine compound, or a mixture thereof. It is in the composite amine absorption liquid characterized by these.
- a fourth invention provides a disulfide compound as the oxidative degradation inhibitor when the amine compound is at least one primary amine compound, or at least one secondary amine compound, or a mixture thereof in the third invention.
- a tertiary amine compound is contained, and the tertiary amine compound is a compound represented by the following chemical formula (II).
- R 3 is an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms
- R 4 is an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms or a hydroxyethyl group
- R 5 is an alkyl group having 2 to 4 carbon atoms.
- the disulfide compound and the tertiary amine compound are added in an amount of 1 to 20% by weight based on the primary amine compound, the secondary amine compound, or a mixture thereof.
- the composite amine absorbent is characterized in that.
- a disulfide compound is used as the oxidative degradation inhibitor.
- the composite amine absorbing liquid further comprises at least one piperidine compound, wherein the piperidine compound is a compound represented by the following chemical formula (III) (excluding piperidine).
- R 6 is H, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, a 2-aminoethyl group, or a 3-aminopropyl group
- R 7 is any one of H and an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms. .
- a seventh invention is characterized in that, in the sixth invention, the disulfide compound and the piperidine compound are added in an amount of 1 to 20% by weight based on the primary amine compound, the secondary amine compound or a mixture thereof. It is in the composite amine absorbing solution.
- the eighth invention is an absorbent that absorbs CO 2 or H 2 S or both in a gas, and 1) at least one primary amine compound, or at least one secondary amine compound, or a mixture thereof. And 2) an oxidative degradation inhibitor of the absorbing solution, dissolved in water, wherein the oxidative degradation inhibitor is a piperidine compound having the structure of the following chemical formula (III) and excluding piperidine: It is in the composite amine absorbent.
- R 6 is H, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, a 2-aminoethyl group, or a 3-aminopropyl group
- R 7 is any one of H and an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms. .
- a ninth invention is the composite amine according to the eighth invention, wherein the piperidine compound is added in an amount of 1 to 20% by weight to the primary amine compound, the secondary amine compound or a mixture thereof. In the absorbent.
- a tenth aspect of the invention is an absorption tower that removes CO 2 or H 2 S or both by bringing a gas containing CO 2 and / or H 2 S or both into contact with an absorbent, and CO 2 or H 2 S or a regenerator for reproducing a solution which has absorbed the both regenerator in a CO 2 or H 2 S or CO 2 removal or H 2 S or both reusing solution was regenerated to remove both of the absorption tower
- An eleventh aspect of the invention is an absorption tower for removing CO 2 or H 2 S or both by bringing a gas containing CO 2 or H 2 S or both into contact with an absorbing solution, and CO 2 or H 2 S or a regenerator for reproducing a solution which has absorbed the both regenerator in a CO 2 or H 2 S or CO 2 removal or H 2 S or both reusing solution was regenerated to remove both of the absorption tower a method, composite amine absorbent CO 2 or H 2 S or both, and removing CO 2 or H 2 S or both using any one invention of the first to ninth In the removal method.
- the oxidation reaction proceeds faster than the amine absorbing solution, the substance involved in the reaction is made a stable compound, and the amine absorbing solution is protected from oxidative degradation. Yes.
- the addition of the disulfide compound can suppress deterioration due to oxidation of the amine absorbing solution due to oxygen or the like in the gas.
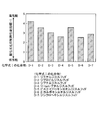
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a performance index of an oxidation degradation inhibitor of a disulfide compound.
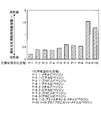
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a figure of merit of an oxidation degradation inhibitor of a piperidine compound.
- FIG. 3 is a diagram showing the results of a test example and a comparative example depending on whether or not a disulfide compound is added.
- FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the results of a test example and a comparative example depending on whether or not an oxidation inhibitor is added.
- FIG. 5 is a diagram showing the results of a test example and a comparative example depending on whether or not a piperidine compound is added.
- FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram illustrating the configuration of the CO 2 recovery device according to the third embodiment.
- the composite amine absorption liquid according to Example 1 of the present invention is an absorption liquid that absorbs CO 2 and / or H 2 S in gas, or both, and includes 1) at least one amine compound and 2) oxidation of the absorption liquid.
- a disulfide compound which is a deterioration inhibitor is dissolved in water, and the disulfide compound is a compound represented by the following chemical formula (I).
- R 1 or R 2 is any one of an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, a hydroxyethyl group, a carboxyethyl group, a cyclohexyl group, and a dibutylthiocarbamoyl group.
- the at least one amine compound of 1) is a known absorbing liquid that absorbs CO 2 or H 2 S, and is at least one primary amine compound, at least one secondary amine compound, or at least one tertiary amine. A compound, or a mixture thereof.
- the primary amine for example, monoethanolamine (MEA), 2-amino-1-propanol (2A1P), 2-amino-1-butanol (2A1B), 2-amino-3-methyl-1-butanol (AMB), 1-amino-2-propanol (1A2P), 1-amino-2-butanol (1A2B), 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) can be mentioned.
- MEA monoethanolamine
- 2-amino-1-propanol (2A1P
- AMB 2-amino-3-methyl-1-butanol
- 1-amino-2-propanol 1, 1-amino-2-butanol (1A2B)
- AMP 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol
- the secondary amine compound is preferably any one of a secondary monoamine and a secondary diamine, or a mixture thereof.
- secondary monoamines examples include 2-methylaminoethanol, 2-ethylaminoethanol, 2-n-propylaminoethanol, 2-n-butylaminoethanol, 2-n-pentylaminoethanol, 2-isopropylaminoethanol, 2
- a compound selected from at least one of -sec-butylaminoethanol and 2-isobutylaminoethanol can be exemplified, but the present invention is not limited thereto.
- Examples of secondary diamines include piperazine, 2-methylpiperazine, 2,3-dimethylpiperazine, 2,5-dimethylpiperazine, N, N′-dimethylethanediamine, N, N′-dimethylpropanediamine, N, Examples include compounds selected from at least one of N′-diethylethylenediamine, N, N′-diethylpropanediamine, N, N′-diisopropylethylenediamine, and N, N′-ditertiarybutylethanediamine. Is not limited to this.
- the tertiary amine compound is a compound represented by the following chemical formula (II).
- R 3 is an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms
- R 4 is an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms or a hydroxyethyl group
- R 5 is an alkyl group having 2 to 4 carbon atoms.
- tertiary amine compounds include N-methyldiethanolamine, N-ethyldiethanolamine, N-butyldiethanolamine, 2-dimethylaminoethanol, 2-diethylaminoethanol, 2-di-n-butylaminoethanol, N-ethyl-N- Examples include methylethanolamine, 3-dimethylamino-1-propanol, 2-dimethylamino-2-methyl-1-propanol, and 4-dimethylamino-1-butanol, but the present invention is not limited thereto. is not.
- the tertiary amine compound functions as an oxidative degradation inhibitor as described later, but can also be used as an absorbing solution.
- disulfide compound that is an oxidative degradation inhibitor examples include diethyl disulfide, dipropyl disulfide, dibutyl disulfide, di-tert-butyl disulfide, bis (2-hydroxyethyl) disulfide, 2-carboxyethyl disulfide, and dicyclohexyl disulfide.
- diethyl disulfide dipropyl disulfide
- dibutyl disulfide di-tert-butyl disulfide
- bis (2-hydroxyethyl) disulfide 2-carboxyethyl disulfide
- dicyclohexyl disulfide examples include diethyl disulfide, dipropyl disulfide, dibutyl disulfide, di-tert-butyl disulfide, bis (2-hydroxyethyl) disulfide, 2-carboxyethyl disulfide, and dicyclohexyl disul
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a performance index of an oxidation degradation inhibitor of a disulfide compound.
- the figure of merit of the oxidative degradation inhibitor refers to the difference between the radical reaction rate possessed by the amine absorbent and the radical reaction rate possessed by the oxidative degradation inhibitor. As shown in FIG.
- the disulfide compound advances the oxidation reaction faster than the amine absorption liquid, and the substance involved in the reaction is made a stable compound to protect the amine absorption liquid from oxidative deterioration.
- the addition of the disulfide compound can suppress deterioration due to oxidation of the amine absorbing solution due to oxygen or the like in the gas.
- the proportion of the disulfide compound added to the amine compound is preferably 1 to 20% by weight, more preferably 2 to 10% by weight.
- a tertiary amine compound is further added to the disulfide compound as an oxidative degradation inhibitor.
- the tertiary amine compound is a compound represented by the following chemical formula (II).
- R 3 is an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms
- R 4 is an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms or a hydroxyethyl group
- R 5 is an alkyl group having 2 to 4 carbon atoms.
- tertiary amine compounds include N-methyldiethanolamine, N-ethyldiethanolamine, N-butyldiethanolamine, 2-dimethylaminoethanol, 2-diethylaminoethanol, 2-di-n-butylaminoethanol, N-ethyl-N- Examples include methylethanolamine, 3-dimethylamino-1-propanol, 2-dimethylamino-2-methyl-1-propanol, and 4-dimethylamino-1-butanol, but the present invention is not limited thereto. is not.
- a disulfide compound and a tertiary amine compound are used as an oxidative degradation inhibitor, 1 to 20% by weight, more preferably 2 to 10% by weight, based on the primary amine compound, the secondary amine compound, or a mixture thereof. It is preferable to add it.
- the mixing ratio of the disulfide compound and the tertiary amine compound is preferably 70:30 to 30:70.
- At least one piperidine compound is further added to the disulfide compound.
- the piperidine compound is a compound represented by the following chemical formula (III) (excluding piperidine).
- R 6 is H, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, a 2-aminoethyl group, or a 3-aminopropyl group
- R 7 is any one of H and an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms.
- Examples of the piperidine compound represented by the chemical formula (III) include 1-methylpiperidine, 1-ethylpiperidine, 1-propylpiperidine, 1-butylpiperidine, 2-methylpiperidine, 2-ethylpiperidine, 2-propylpiperidine, Examples include 2-butylpiperidine, 1- (2-aminoethyl) -2-methylpiperidine, and 1- (3-aminopropyl) -2-methylpiperidine, but the present invention is not limited thereto. .
- a disulfide compound and a piperidine compound are used as an oxidation inhibitor, they are added in an amount of 1 to 20% by weight, more preferably 2 to 10% by weight, based on the primary amine compound, the secondary amine compound, or a mixture thereof. Preferably it is.
- the mixing ratio of the disulfide compound and the piperidine compound is preferably 70:30 to 30:70.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a performance index of an oxidation degradation inhibitor of a piperidine compound.
- a piperidine compound 1-methylpiperidine (P-1), 1-ethylpiperidine (P-2), 1-propylpiperidine (P-3), 1-butylpiperidine (P-4), 2-methyl Piperidine (P-5), 2-ethylpiperidine (P-6), 2-propylpiperidine (P-7), 2-butylpiperidine (P-8), 1- (2-aminoethyl) -2-methylpiperidine In (P-9) and 1- (3-aminopropyl) -2-methylpiperidine (P-10), an effect of suppressing oxidative degradation was confirmed. Therefore, the addition of the piperidine compound can suppress deterioration due to oxidation of the amine absorbing solution due to oxygen or the like in the gas.
- Test example Below, the test example which shows the effect of a present Example is demonstrated.
- Test Examples 1 and 2 In this test example, a secondary monoamine was used as the amine absorbent, and a piperazine compound was used as the secondary diamine to form a secondary amine composite absorbent. Next, by using dibutyl disulfide (D-3) and bis (2-hydroxyethyl) disulfide (D-5) in FIG. Test Example 1 and Test Example 2 (Trial-1, Trial-2) were used. For comparison, the case where the disulfide compound represented by the chemical formula (I) is not added is Comparative Example 1 (ratio-1), and the case where a tertiary amine compound (methyldiethanolamine (MDEA)) is added is Comparative Example 2 (ratio- 2).
- FIG. 3 is a diagram showing the results of a test example and a comparative example depending on whether or not a disulfide compound is added.
- the oxidation deterioration rate ratio means the ratio of the oxidation deterioration rate of the amine absorbent when the oxidation deterioration inhibitor is added to the oxidation deterioration rate of the amine absorbent when the oxidation deterioration inhibitor is not added.
- FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the results of test examples and comparative examples depending on whether or not an oxidation inhibitor is added.
- the composite amine absorbing liquid according to Example 2 according to the present invention is an absorbing liquid that absorbs CO 2 and / or H 2 S in gas, or both, and 1) at least one primary amine compound, or at least one 2 A secondary amine compound, or a mixture thereof, and 2) an oxidative degradation inhibitor of the absorbing solution, which are dissolved in water.
- the oxidative degradation inhibitor has the structure of the following chemical formula (III) and excludes piperidine It is a piperidine compound.
- R 6 is H, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, a 2-aminoethyl group, or a 3-aminopropyl group
- R 7 is any one of H and an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms.
- the piperidine compound is preferably added in an amount of 1 to 20% by weight, more preferably 2 to 10% by weight, based on the primary amine compound, the secondary amine compound or a mixture thereof.
- Test example Below, the test example which shows the effect of a present Example is demonstrated.
- FIG. 5 is a diagram showing the results of a test example and a comparative example depending on whether or not a piperidine compound is added.
- the process that can be employed in the method for removing CO 2 and / or H 2 S in the gas of the present invention is not particularly limited, but an example of a removal apparatus for removing CO 2 will be described with reference to FIG.
- the gas to be treated by the present invention such as coal gasification gas, syngas, coke oven gas, petroleum gas, natural gas, there may be mentioned a combustion exhaust gas or the like, but the invention is not limited to, CO 2 Any gas may be used as long as it contains an acidic gas such as H 2 S.
- FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram illustrating the configuration of the CO 2 recovery device according to the third embodiment.
- the CO 2 recovery device 12 according to the first embodiment cools an exhaust gas 14 containing CO 2 and O 2 discharged from an industrial combustion facility 13 such as a boiler or a gas turbine with cooling water 15.
- an industrial combustion facility 13 such as a boiler or a gas turbine with cooling water 15.
- an exhaust gas cooling device 16 which, CO 2 absorbing solution for absorbing the exhaust gas 14 and CO 2 containing the cooled CO 2 (hereinafter, also referred to as "absorbing solution”.) 17 and is contacted with by the CO 2 from the exhaust gas 14 and the CO 2 absorber 18 having a CO 2 recovery unit 18A to be removed, CO 2 absorbent having absorbed CO 2 (hereinafter, also referred to as "rich solvent”.) 19 to release CO 2 from the reproduction of CO 2 absorbing solution
- an absorption liquid regeneration tower 20 that performs the following operation.
- the absorbent regenerator 20 in reproducing the CO 2 absorbing liquid to remove CO 2 (hereinafter, also referred to as "lean solvent”.) 17 as a CO 2 absorbing solution in the CO 2 absorber 18 Reuse.
- reference numeral 13a is a flue
- 13b is a chimney
- 34 is steam condensed water.
- the CO 2 recovery device may be provided later in order to recover CO 2 from an existing exhaust gas source, or may be provided at the same time as a new exhaust gas source.
- the chimney 13b is provided with a door that can be opened and closed, and is closed when the CO 2 recovery device 12 is in operation. Although the exhaust gas source is running, when stopping the operation of the CO 2 recovering apparatus 12 is set to open.
- the exhaust gas 14 from the industrial combustion facility 13 such as a boiler or gas turbine containing CO 2 is pressurized by the exhaust gas blower 22, and then the exhaust gas cooling device. 16, where it is cooled by cooling water 15 and sent to a CO 2 absorption tower 18.
- the exhaust gas 14 is the CO 2 absorbing liquid 17 and countercurrent contact with an amine absorbent solution according to the present embodiment, CO 2 in the exhaust gas 14 is absorbed into the CO 2 absorbing solution 17 by a chemical reaction Is done.
- CO 2 flue gas after CO 2 is removed in the CO 2 recovery unit 18A, the cleaning water 21 circulating containing CO 2 absorbing liquid supplied from the nozzle at the water washing section 18B in the CO 2 absorber 18 and a gas-liquid contact with, CO 2 absorbing liquid 17 accompanying the CO 2 flue gas is recovered, then the exhaust gas 23 from which CO 2 has been removed is released out of the system.
- the rich solution is CO 2 absorbing liquid 19 that has absorbed CO 2, boosted by the rich solution pump 24, the rich-lean solution heat exchanger 25, which is reproduced in the absorbent regenerator 20 CO 2 absorbing solution 17 And is supplied to the absorption liquid regeneration tower 20.
- the rich solution 19 released to the inside from the upper part of the absorption liquid regeneration tower 20 generates an endothermic reaction with water vapor supplied from the bottom, and releases most of CO 2 .
- the CO 2 absorbent that has released a part or most of CO 2 in the absorbent regeneration tower 20 is called a semi-lean solution.
- This semi-lean solution becomes a CO 2 absorbent (lean solution) 17 from which almost all of the CO 2 has been removed by the time it reaches the bottom of the absorbent regeneration tower 20.
- a part of the lean solution 17 is superheated by the steam 27 in the regeneration superheater 26, and the steam is supplied into the absorbent regeneration tower 20.
- the CO 2 entrained gas 28 accompanied by the water vapor released from the rich solution 19 and the semi-lean solution is led out in the tower, the water vapor is condensed by the condenser 29, and the separation drum 30. Then, the water is separated and the CO 2 gas 40 is discharged out of the system, and is separately compressed and recovered by the compressor 41.
- the compressed / recovered CO 2 gas 42 passes through the separation drum 43 and is then injected into an oil field using an enhanced oil recovery (EOR) method or stored in an aquifer for warming. Measures are being taken.
- the reflux water 31 separated and refluxed from the CO 2 entrained gas 28 accompanied by water vapor by the separation drum 30 is supplied to the upper part of the absorption liquid regeneration tower 20 and the circulating wash water 21 side by the reflux water circulation pump 35.
- the regenerated CO 2 absorbing solution (lean solution) 17 is cooled by the rich solution 19 in the rich / lean solution heat exchanger 25, subsequently pressurized by the lean solution pump 32, and further by the lean solution cooler 33. After cooling, it is supplied into the CO 2 absorption tower 18.
- the outline is only described, and a part of the attached devices is omitted.
- the composite amine absorbing liquid of this embodiment as the amine absorbing liquid, deterioration due to oxidation of the amine absorbing liquid due to oxygen in the gas can be suppressed, and further deterioration of the absorbing liquid It is possible to reduce the absorption liquid loss due to the above.
Abstract
Description
R1-S-S-R2・・・(I)
ここで、R1又はR2は、炭素数1~4のアルキル基、ヒドロキシエチル基、カルボキシエチル基、シクロヘキシル基、ジブチルチオカルバモイル基のいずれかである。
R1-S-S-R2・・・(I)
ここで、R1又はR2は、炭素数1~4のアルキル基、ヒドロキシエチル基、カルボキシエチル基、シクロヘキシル基、ジブチルチオカルバモイル基のいずれかである。
ここで、酸化劣化抑制剤の性能指数とは、アミン吸収剤が有しているラジカル反応速度と、酸化劣化抑制剤が有しているラジカル反応速度との差をいう。
図1に示すように、ジエチルジスルフィド(D-1)、ジプロピルジスルフィド(D-2)、ジブチルジスルフィド(D-3)、ジ-tert-ブチルジスルフィド(D-4)、ビス(2-ヒドロキシエチル)ジスルフィド(D-5)、2-カルボキシエチルジスルフィド(D-6)、ジシクロヘキシルジスルフィド(D-7)においては、酸化劣化抑制効果が確認された。
ここで、3級アミン化合物は、下記化学式(II)で表される化合物である。
ジスルフィド化合物と3級アミン化合物との配合比率は70:30~30:70とするのが好ましい。
ジスルフィド化合物とピペリジン化合物との配合比率は70:30~30:70とするのが好ましい。
以下に、本実施例の効果を示す試験例について説明する。
本試験例では、アミン吸収液として、2級モノアミンを用い、2級ジアミンとしてピペラジン系化合物を用いて2級アミン系複合吸収剤とした。
次に、図1におけるジブチルジスルフィド(D-3)及びビス(2-ヒドロキシエチル)ジスルフィド(D-5)を用いて、2級複合アミン化合物に含有させてアミン吸収液酸化劣化速度比を求め、試験例1、試験例2(試-1、試-2)とした。
比較として、化学式(I)で表されるジスルフィド化合物を添加しない場合を比較例1(比-1)とし、3級アミン化合物(メチルジエタノールアミン(MDEA))を添加した場合を比較例2(比-2)とした。
ここで、酸化劣化速度比とは、酸化劣化抑制剤を添加しない場合のアミン吸収剤の酸化劣化速度に対する、酸化劣化抑制剤を添加した場合のアミン吸収剤の酸化劣化速度の比をいう。
これは、ジスルフィド化合物が、アミン吸収剤酸化の連鎖反応に関与する物質を安定な化合物に速く変換し、吸収剤の酸化を抑制する機能を有するためと考えられる。
本試験例では、アミン吸収液として、2級モノアミンを用い、2級ジアミンとしてピペラジン系化合物を用いて2級アミン系複合吸収剤とした。
比較として、化学式(I)で表されるジスルフィド化合物を添加しない場合を比較例1(比-1)とした。
また、図4に示すように、酸化抑制剤としてジスルフィド化合物とピペリジン化合物との添加(試-5)により、ガス中の酸素等によるアミン吸収液の酸化による劣化を抑制することができることが確認された。
特に、試験例3、4、及び5のように、アミン吸収剤酸化の連鎖反応において、ジスルフィド化合物と3級アミン化合物及びピペリジン化合物は、連鎖反応関与物質の安定化において、異なる機能を有するので、それらの相乗効果が発揮される。
以下に、本実施例の効果を示す試験例について説明する。
本試験例では、アミン吸収液として、2級モノアミンを用い、2級ジアミンとしてピペラジン系化合物を用いて2級アミン系複合吸収剤とした。
次に、図2における1-(3-アミノプロピル)-2-メチルピペリジン(P-10)を用いて、2級複合アミン化合物に含有させてアミン吸収液酸化劣化速度比を求め、試験例6)とした。
比較として、化学式(I)で表される1-(3-アミノプロピル)-2-メチルピペリジン(P-10)を添加しない場合を比較例1(比-1)とした。
図5は、ピペリジン化合物の添加の有無による試験例及び比較例の結果を示す図である。
CO2回収部18AでCO2が除去された後のCO2除去排ガスは、CO2吸収塔18内の水洗部18Bでノズルから供給されるCO2吸収液を含む循環する洗浄水21と気液接触して、CO2除去排ガスに同伴するCO2吸収液17が回収され、その後CO2が除去された排ガス23は系外に放出される。
また、CO2を吸収したCO2吸収液19であるリッチ溶液は、リッチ溶液ポンプ24により昇圧され、リッチ・リーン溶液熱交換器25において、吸収液再生塔20で再生されたCO2吸収液17であるリーン溶液により加熱され、吸収液再生塔20に供給される。
水蒸気を伴ったCO2同伴ガス28から分離ドラム30にて分離・還流された還流水31は還流水循環ポンプ35にて吸収液再生塔20の上部と循環洗浄水21側に各々供給される。
13 産業燃焼設備
14 排ガス
16 排ガス冷却装置
17 CO2吸収液(リーン溶液)
18 CO2吸収塔
19 CO2を吸収したCO2吸収液(リッチ溶液)
20 吸収液再生塔
21 洗浄水
Claims (11)
- ガス中のCO2又はH2S又はその双方を吸収する吸収液であって、
1)少なくとも一種のアミン化合物と、
2)吸収液の酸化劣化抑制剤であるジスルフィド化合物とを、
水に溶解してなり、
前記ジスルフィド化合物が、下記化学式(I)で表される化合物であることを特徴とする複合アミン吸収液。
R1-S-S-R2・・・(I)
ここで、R1又はR2は、炭素数1~4のアルキル基、ヒドロキシエチル基、カルボキシエチル基、シクロヘキシル基、ジブチルチオカルバモイル基のいずれかである。 - 請求項1において、
前記ジスルフィド化合物が、アミン化合物に対して1~20重量%添加してなることを特徴とする複合アミン吸収液。 - 請求項1において、
前記アミン化合物が、少なくとも一種の1級アミン化合物、又は少なくとも一種の2級アミン化合物、又は少なくとも一種の3級アミン化合物、又はそれらの混合物であることを特徴とする複合アミン吸収液。 - 請求項4において、
前記ジスルフィド化合物と3級アミン化合物とが、1級アミン化合物、又は2級アミン化合物、又はそれらの混合物に対して、1~20重量%添加してなることを特徴とする複合アミン吸収液。 - 請求項6において、
前記ジスルフィド化合物とピペリジン化合物とが、1級アミン化合物又は2級アミン化合物又はそれらの混合物に対して、1~20重量%添加してなることを特徴とする複合アミン吸収液。 - 請求項8において、
前記ピペリジン化合物が、1級アミン化合物又は2級アミン化合物又はそれらの混合物に対して、1~20重量%添加してなることを特徴とする複合アミン吸収液。 - CO2又はH2S又はその双方を含有するガスと吸収液とを接触させてCO2又はH2S又はその双方を除去する吸収塔と、CO2又はH2S又はその双方を吸収した溶液を再生する再生塔と、再生塔でCO2又はH2S又はその双方を除去して再生した溶液を吸収塔で再利用するCO2又はH2S又はその双方の除去装置であって、
請求項1乃至9のいずれか一つの複合アミン吸収液を用いてなることを特徴とするCO2又はH2S又はその双方の除去装置。 - CO2又はH2S又はその双方を含有するガスと吸収液とを接触させてCO2又はH2S又はその双方を除去する吸収塔と、CO2又はH2S又はその双方を吸収した溶液を再生する再生塔と、再生塔でCO2又はH2S又はその双方を除去して再生した溶液を吸収塔で再利用するCO2又はH2S又はその双方の除去方法であって、
請求項1乃至9のいずれか一つの複合アミン吸収液を用いてCO2又はH2S又はその双方を除去することを特徴とするCO2又はH2S又はその双方の除去方法。
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AU2014335384A AU2014335384B2 (en) | 2013-10-15 | 2014-10-10 | Composite amine absorption solution, and method and device for removing CO2 and/or H2S |
| CA2924300A CA2924300A1 (en) | 2013-10-15 | 2014-10-10 | Composite amine absorbent, and apparatus and method for removing co2 and/or h2s |
| US15/022,125 US20160220947A1 (en) | 2013-10-15 | 2014-10-10 | Composite amine absorbent, and apparatus and method for removing co2 and/or h2s |
| EP14853761.6A EP3034152A4 (en) | 2013-10-15 | 2014-10-10 | COMPOUND AMINE ABSORPTION SOLUTION AND PROCESS AND DEVICE FOR REMOVING CO2 AND / OR H2S |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013215064A JP5984776B2 (ja) | 2013-10-15 | 2013-10-15 | 複合アミン吸収液、co2又はh2s又はその双方の除去装置及び方法 |
| JP2013-215064 | 2013-10-15 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015056657A1 true WO2015056657A1 (ja) | 2015-04-23 |
Family
ID=52828101
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/077264 WO2015056657A1 (ja) | 2013-10-15 | 2014-10-10 | 複合アミン吸収液、co2又はh2s又はその双方の除去装置及び方法 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20160220947A1 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3034152A4 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5984776B2 (ja) |
| AU (1) | AU2014335384B2 (ja) |
| CA (1) | CA2924300A1 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2015056657A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017081100A1 (en) * | 2015-11-09 | 2017-05-18 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Process for removing mercaptans from a gas stream |
| US10710020B2 (en) * | 2017-06-30 | 2020-07-14 | Uop Llc | Processes for gas separation by solvent or absorbent |
| CN108854459B (zh) * | 2018-09-25 | 2022-03-15 | 天津工业大学 | 一种低能耗无水co2相变吸收剂及再生方法和应用 |
| JP7178911B2 (ja) | 2019-01-24 | 2022-11-28 | 三菱重工エンジニアリング株式会社 | 複合アミン吸収液、co2又はh2s又はその双方の除去装置及び方法 |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0751537A (ja) | 1993-06-30 | 1995-02-28 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Co2 含有ガス中のco2 を除去する方法 |
| JP2006136885A (ja) * | 2004-11-12 | 2006-06-01 | Inst Fr Petrole | 部分再生吸収剤溶液によるガス脱酸方法 |
| JP2008307519A (ja) | 2007-06-18 | 2008-12-25 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 吸収液、吸収液を用いたco2又はh2s除去装置及び方法 |
| JP2009529420A (ja) * | 2006-03-10 | 2009-08-20 | イエフペ | 加熱による分別再生を伴う、吸収溶液によりガスを脱酸する方法 |
| JP4634384B2 (ja) | 2005-04-04 | 2011-02-16 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 吸収液、co2又はh2s又はその双方の除去方法及び装置 |
| JP4690659B2 (ja) | 2004-03-15 | 2011-06-01 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | Co2回収装置 |
| JP2012516762A (ja) * | 2009-02-02 | 2012-07-26 | ビーエーエスエフ ソシエタス・ヨーロピア | 酸性ガスの除去のための環式アミン含有吸収剤 |
| JP2012143745A (ja) * | 2010-12-22 | 2012-08-02 | Toshiba Corp | 酸性ガス吸収剤、酸性ガス除去方法および酸性ガス除去装置 |
| JP2012245483A (ja) * | 2011-05-30 | 2012-12-13 | Toshiba Corp | 酸性ガス吸収剤、酸性ガス除去方法および酸性ガス除去装置 |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4020144A (en) * | 1975-05-02 | 1977-04-26 | Exxon Research And Engineering Company | Method for removal of gaseous sulfur and nitrogen compounds from gas streams |
| US4804485A (en) * | 1987-05-08 | 1989-02-14 | Pennwalt Corporation | Polyalkyleneoxyamine catalysts for dialkyl disulfides and/or polysulfides used in dissolving sulfur |
| US4959177A (en) * | 1987-10-09 | 1990-09-25 | Shell Oil Company | Reducing stress corrosion cracking in treating gases with alkanol amines |
| FR2933001B1 (fr) * | 2008-06-27 | 2010-08-20 | Inst Francais Du Petrole | Solution absorbante contenant un inhibiteur de degradation a fonction thiocarbonyle et methode pour limiter la degradation d'une solution absorbante |
| WO2012076378A1 (en) * | 2010-12-06 | 2012-06-14 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Process for removing mercaptans from a gas stream |
-
2013
- 2013-10-15 JP JP2013215064A patent/JP5984776B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2014
- 2014-10-10 US US15/022,125 patent/US20160220947A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2014-10-10 AU AU2014335384A patent/AU2014335384B2/en not_active Ceased
- 2014-10-10 WO PCT/JP2014/077264 patent/WO2015056657A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2014-10-10 CA CA2924300A patent/CA2924300A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2014-10-10 EP EP14853761.6A patent/EP3034152A4/en not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0751537A (ja) | 1993-06-30 | 1995-02-28 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Co2 含有ガス中のco2 を除去する方法 |
| JP4690659B2 (ja) | 2004-03-15 | 2011-06-01 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | Co2回収装置 |
| JP2006136885A (ja) * | 2004-11-12 | 2006-06-01 | Inst Fr Petrole | 部分再生吸収剤溶液によるガス脱酸方法 |
| JP4634384B2 (ja) | 2005-04-04 | 2011-02-16 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 吸収液、co2又はh2s又はその双方の除去方法及び装置 |
| JP2009529420A (ja) * | 2006-03-10 | 2009-08-20 | イエフペ | 加熱による分別再生を伴う、吸収溶液によりガスを脱酸する方法 |
| JP2008307519A (ja) | 2007-06-18 | 2008-12-25 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 吸収液、吸収液を用いたco2又はh2s除去装置及び方法 |
| JP2012516762A (ja) * | 2009-02-02 | 2012-07-26 | ビーエーエスエフ ソシエタス・ヨーロピア | 酸性ガスの除去のための環式アミン含有吸収剤 |
| JP2012143745A (ja) * | 2010-12-22 | 2012-08-02 | Toshiba Corp | 酸性ガス吸収剤、酸性ガス除去方法および酸性ガス除去装置 |
| JP2012245483A (ja) * | 2011-05-30 | 2012-12-13 | Toshiba Corp | 酸性ガス吸収剤、酸性ガス除去方法および酸性ガス除去装置 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP3034152A4 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20160220947A1 (en) | 2016-08-04 |
| JP2015077537A (ja) | 2015-04-23 |
| CA2924300A1 (en) | 2015-04-23 |
| AU2014335384B2 (en) | 2017-03-16 |
| EP3034152A1 (en) | 2016-06-22 |
| JP5984776B2 (ja) | 2016-09-06 |
| AU2014335384A1 (en) | 2016-04-07 |
| EP3034152A4 (en) | 2016-12-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6172884B2 (ja) | 3成分吸収液、co2又はh2s又はその双方の除去装置及び方法 | |
| JPWO2006107026A1 (ja) | 吸収液、co2又はh2s又はその双方の除去方法及び装置 | |
| JP2007325996A (ja) | 吸収液、co2又はh2s又はその双方の除去装置及び方法 | |
| JP2013086079A5 (ja) | ||
| WO2015056657A1 (ja) | 複合アミン吸収液、co2又はh2s又はその双方の除去装置及び方法 | |
| WO2018143192A1 (ja) | 複合アミン吸収液、co2又はh2s又はその双方の除去装置及び方法 | |
| WO2012073552A1 (ja) | Co2回収システム | |
| JP5986796B2 (ja) | 複合アミン吸収液、co2又はh2s又はその双方の除去装置及び方法 | |
| JP2013236987A5 (ja) | ||
| WO2017057179A1 (ja) | Co2、h2s又はそれら双方の吸収液並びにそれを用いた装置及び方法 | |
| JP7336245B2 (ja) | Co2、h2s又はそれら双方の吸収液並びにco2又はh2s又はその双方の除去装置及び方法 | |
| RU2780621C1 (ru) | Абсорбент со2 и/или h2s и устройство и способ для извлечения со2 и/или h2s | |
| AU2019423879B2 (en) | Composite amine absorption solution, and device and method both for removing CO2 or H2S or both of them | |
| WO2023027105A1 (ja) | 複合アミン吸収液、除去装置及び除去方法 | |
| WO2023209931A1 (ja) | 複合アミン吸収液、除去装置及び除去方法 | |
| AU2012327104B9 (en) | 3-component absorbent solution, and CO2 and/or H2S removal device and method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14853761 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2924300 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2014853761 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15022125 Country of ref document: US |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2014335384 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20141010 Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |