WO2014184996A1 - 農業用ハウスの設置評価装置、農業用ハウスの日照量調整装置、プログラム - Google Patents
農業用ハウスの設置評価装置、農業用ハウスの日照量調整装置、プログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014184996A1 WO2014184996A1 PCT/JP2014/001869 JP2014001869W WO2014184996A1 WO 2014184996 A1 WO2014184996 A1 WO 2014184996A1 JP 2014001869 W JP2014001869 W JP 2014001869W WO 2014184996 A1 WO2014184996 A1 WO 2014184996A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- sunshine
- agricultural house
- amount
- time
- planned
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01G—HORTICULTURE; CULTIVATION OF VEGETABLES, FLOWERS, RICE, FRUIT, VINES, HOPS OR SEAWEED; FORESTRY; WATERING
- A01G9/00—Cultivation in receptacles, forcing-frames or greenhouses; Edging for beds, lawn or the like
- A01G9/24—Devices or systems for heating, ventilating, regulating temperature, illuminating, or watering, in greenhouses, forcing-frames, or the like
- A01G9/243—Collecting solar energy
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01G—HORTICULTURE; CULTIVATION OF VEGETABLES, FLOWERS, RICE, FRUIT, VINES, HOPS OR SEAWEED; FORESTRY; WATERING
- A01G9/00—Cultivation in receptacles, forcing-frames or greenhouses; Edging for beds, lawn or the like
- A01G9/22—Shades or blinds for greenhouses, or the like
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01G—HORTICULTURE; CULTIVATION OF VEGETABLES, FLOWERS, RICE, FRUIT, VINES, HOPS OR SEAWEED; FORESTRY; WATERING
- A01G9/00—Cultivation in receptacles, forcing-frames or greenhouses; Edging for beds, lawn or the like
- A01G9/24—Devices or systems for heating, ventilating, regulating temperature, illuminating, or watering, in greenhouses, forcing-frames, or the like
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01J—MEASUREMENT OF INTENSITY, VELOCITY, SPECTRAL CONTENT, POLARISATION, PHASE OR PULSE CHARACTERISTICS OF INFRARED, VISIBLE OR ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT; COLORIMETRY; RADIATION PYROMETRY
- G01J1/00—Photometry, e.g. photographic exposure meter
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01W—METEOROLOGY
- G01W1/00—Meteorology
- G01W1/12—Sunshine duration recorders
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01J—MEASUREMENT OF INTENSITY, VELOCITY, SPECTRAL CONTENT, POLARISATION, PHASE OR PULSE CHARACTERISTICS OF INFRARED, VISIBLE OR ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT; COLORIMETRY; RADIATION PYROMETRY
- G01J1/00—Photometry, e.g. photographic exposure meter
- G01J1/42—Photometry, e.g. photographic exposure meter using electric radiation detectors
- G01J2001/4266—Photometry, e.g. photographic exposure meter using electric radiation detectors for measuring solar light
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A40/00—Adaptation technologies in agriculture, forestry, livestock or agroalimentary production
- Y02A40/10—Adaptation technologies in agriculture, forestry, livestock or agroalimentary production in agriculture
- Y02A40/25—Greenhouse technology, e.g. cooling systems therefor
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an installation evaluation device for an agricultural house that evaluates the amount of sunshine in a planned site where the agricultural house is installed, and an adjustment device for the amount of sunlight in an agricultural house that adjusts the amount of sunlight irradiated to a plant grown in the agricultural house.
- this invention relates to the program for implement
- Document 1 Japanese Patent Application Publication No. 2003-167065
- the shade obstacle adjacent to the site where the house is to be built forms the shade line for each hour that is formed for the target site, and the shade lines for one day are superimposed.
- a technique for obtaining a shadow integral value is described. Since the technique described in Document 1 is intended for residential construction, for example, the number of hours in which the shade line overlaps the winter solstice where the solar altitude is the lowest is obtained as the shade integral value.
- This invention aims at providing the installation evaluation apparatus of the agricultural house which can judge the suitability of the planned site which installs an agricultural house. Furthermore, the present invention provides a computer for adjusting the amount of sunshine for an agricultural house that adjusts the amount of sunlight applied to a plant grown in the agricultural house, and an installation evaluation device for an agricultural house or an amount of sunshine for an agricultural house. The purpose is to provide a program for realizing the above.
- An agricultural house installation evaluation apparatus includes an input device to which position information of a planned site where an agricultural house is installed is input, and sunshine at the planned site using the position information input to the input device. It is characterized by comprising a sunshine evaluation unit for obtaining a change in amount due to date and time by computer simulation, and a presentation device for visualizing and presenting a change in amount of sunshine due to the date and time obtained by the sunshine evaluation unit.
- the input device may form a shadow on the planned site and the size of the planned site and surrounding the planned site.
- the position and size of an obstacle is further input, and the sunshine evaluation unit obtains a change in the amount of sunshine in the planned location according to the date and time using the position and size of the obstacle in addition to the position information. Is preferred.
- an arrangement setting unit for determining candidates for arrangement and dimensions of the agricultural house from which a required amount of sunlight is obtained using a change in the amount of sunlight depending on the date and time obtained by the sunlight evaluation unit.
- the presenting device visualizes and presents candidates for arrangement and dimensions of the agricultural house determined by the arrangement setting unit.
- the arrangement setting unit obtains a sunshine amount suitable for the plant by using the type of plant grown in the agricultural house in addition to the change in the amount of sunshine according to the date and time. As described above, it is preferable to determine candidates for the arrangement and dimensions of the agricultural house.
- the input device is further input with the number of buildings of the agricultural house installed at the planned site, and the arrangement setting unit is provided with a plurality of the agricultural houses.
- the interval between the farmhouse ridges is automatically determined.
- the agricultural house installation evaluation device further includes a region extraction unit that extracts a region where the amount of sunshine satisfies a determination condition using a change in the amount of sunshine according to the date and time obtained by the sunshine evaluation unit, and the presentation device includes: Preferably, the region extracted by the region extraction unit is visualized and presented.
- the region extraction unit includes an integration unit that determines an integrated value of the amount of sunshine in a specified period at the planned site, and a sensor that monitors the environment of the agricultural house. It is preferable to include a determination unit that extracts a region that is a candidate for the installation location of the sensor with the determination condition being a reference range set for extracting the installation location of the sensor.
- the determination unit determines the reference range based on the amount of sunlight.
- the determination unit is configured to set the reference range to a range equal to or greater than a representative value obtained from the integrated value at the planned site in a season when the amount of sunshine is equal to or greater than a predetermined upper limit. It is preferable to determine to.
- the determination unit does not fall below the representative value obtained from the integrated value at the planned site, during the season when the amount of sunshine falls below a predetermined lower limit. It is preferable to set the range.
- the senor includes at least one selected from the group of a temperature sensor, a humidity sensor, and a soil moisture sensor.
- the region extraction unit includes an integration unit that calculates an integrated value of the amount of sunshine in a specified period at the planned site, and the integrated value is outside the agricultural house at the planned site. It is preferable to include a determination unit that extracts a candidate area for the installation location of the sensor on the basis of the determination condition that the reference range is set to extract the installation location of the sensor for monitoring the environment.
- the determination unit is configured to set the reference range to a range equal to or greater than a representative value obtained from the integrated value at the planned site in a season when the amount of sunshine is equal to or greater than a predetermined upper limit. It is preferable to determine to.
- the senor preferably includes an illuminance sensor or a solar radiation sensor.
- the sunshine amount adjustment device for an agricultural house includes an input device to which position information of a planned site where the agricultural house is installed is input, and sunshine at the planned site using the position information input to the input device.
- a sunshine evaluation unit that obtains a change due to date and time by computer simulation; and a control device that controls an operation of an environment adjustment device that adjusts a plant growth environment in the agricultural house, wherein the control device includes the sunshine evaluation.
- the control content is determined so that the amount of sunshine suitable for growing the plant is obtained.
- the input device can form a shadow on the planned site in the vicinity of the planned site size and the planned site, in addition to the location information of the planned site. Further, the position and size of the obstacle is input, and the sunlight evaluation unit uses the position and size of the obstacle in addition to the position information to determine the change of the amount of sunlight in the planned location according to the date and time. It is preferable.
- the environment adjusting device has a first position for dimming the external light irradiated on the plant, and a second position for not dimming the external light irradiated on the plant.
- a drive device for moving the curtain and the control device has a timing for moving the curtain to the first position and a timing for moving the curtain to the second position.
- the drive device is instructed.
- the curtain includes a roof curtain provided on the roof of the agricultural house, and the control device has a time from sunrise to sunset exceeding a predetermined reference time.
- the driving device is instructed to move the roof curtain to the first position at a certain time.
- the environmental adjusting device includes a first window provided on the east side wall of the agricultural house, and a second window provided on the west side wall of the agricultural house.
- a window, and an opening / closing device that drives the first window and the second window between an open position and a closed position, and the curtain is a first provided on the east side wall of the agricultural house.
- a second side curtain provided on the west side wall of the agricultural house.
- the control device instructs the opening / closing device to move the first window and the second window to an open position in summer, and Before the time and in a time zone in which the solar altitude is equal to or less than the first reference angle, the first side curtain is moved to the first position, and the second side curtain is moved to the second position. In the time zone in which the solar altitude is less than or equal to the second reference angle after the south-central time, the first side curtain is moved to the second position, and the second side is The driving device is instructed to move the curtain to the first position, and a time zone in which a solar altitude is between the first reference angle and the second reference angle is the first side curtain Move both the second side curtain and the first position It is preferable to instruct the drive apparatus.
- the control device instructs the opening / closing device to move the first window and the second window to a closed position in winter, and Prior to the time and in a time zone in which the solar altitude is equal to or less than the third reference angle, the first side curtain is moved to the second position, and the second side curtain is moved to the first position.
- the first side curtain is moved to the first position, and the second side is Preferably, the driving device is instructed to move the curtain to the second position.
- the program according to the present invention uses a computer to input position information of a planned site where an agricultural house is installed, and the date and time of the amount of sunshine in the planned site using the position information input to the input device.
- Another program includes a computer, an input device for inputting position information of a planned site where an agricultural house is installed, and the amount of sunlight at the planned site using the position information input to the input device.
- a sunshine evaluation unit that obtains changes due to date and time by computer simulation, and a control device that controls the operation of an environment adjustment device that adjusts the plant growth environment in the agricultural house, the control device comprising the sunshine evaluation unit Is used to function as an irradiance adjustment device for an agricultural house that determines the contents of control so that the sunshine amount suitable for growing the plant can be obtained using the change in the amount of sunshine according to the date and time obtained by the above.
- the present invention is not limited to a program, and may be a computer-readable storage medium storing the program.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating a first embodiment.
- 2A and 2B are diagrams illustrating an example of forming a shade by an obstacle in the first embodiment. It is a perspective view which shows the external appearance of the agricultural house used for Embodiment 1.
- FIG. It is a figure which shows the example of arrangement
- FIG. 5A and 5B are diagrams showing sunlight by a plurality of agricultural houses in Embodiment 1.
- FIG. FIG. 6 is a block diagram illustrating a second embodiment. 7A to 7C are diagrams illustrating an operation example of the second embodiment. 8A and 8B are diagrams illustrating an operation example of the second embodiment.
- FIG. 6 is a block diagram illustrating a third embodiment. 10 is a block diagram illustrating an example of use of Embodiment 3.
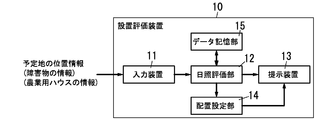
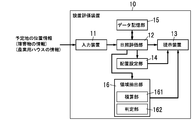
- an agricultural house installation evaluation device 10 As shown in FIGS. 1, 2A, and 2B, an agricultural house installation evaluation device 10 described below includes an input device 11, a sunshine evaluation unit 12, and a presentation device 13.
- the input device 11 receives position information of the planned site 22 where the agricultural house 20 is installed.
- the sunshine evaluation unit 12 obtains the change of the amount of sunshine in the planned location 22 according to the date and time by computer simulation using the position information input from the input device 11.
- the presentation device 13 visualizes and presents a change in the amount of sunlight depending on the date and time obtained by the sunlight evaluation unit 12.
- the input device 11 measures the size of the planned location 22, the location of the obstacle 40 that exists around the planned location 22 and may form a shadow 41 on the planned location 22, and It is desirable that further dimensions are entered.
- the sunshine evaluation unit 12 obtains the change of the amount of sunshine in the planned location 22 according to the date and time using the position and dimensions of the obstacle 40 in addition to the position information.
- the installation evaluation device 10 includes an arrangement setting unit 14 that determines candidates for the arrangement and dimensions of the agricultural house 20 from which the required amount of sunlight is obtained using changes in the amount of sunlight depending on the date and time obtained by the sunlight evaluation unit 12. desirable.
- the presentation device 13 visualizes and presents candidates for the arrangement and dimensions of the agricultural house determined by the arrangement setting unit 14.
- the arrangement setting unit 14 uses the types of plants grown in the agricultural house 20 in addition to changes in the amount of sunlight depending on the date and time, so that the arrangement of the agricultural house 20 can be obtained so that a suitable amount of sunlight can be obtained for this plant. It is desirable to define candidates for dimensions and dimensions.
- the input device 11 prefferably inputs the number of agricultural houses 20 installed in the planned site 22.
- the arrangement setting unit 14 automatically determines the interval between the agricultural houses 20.
- the installation evaluation apparatus 10 includes a region extraction unit 16 that extracts a region where the amount of sunshine satisfies the determination condition using the change in the amount of sunshine according to the date and time obtained by the sunshine evaluation unit 12.
- the presentation device 13 visualizes and presents the region extracted by the region extraction unit 16.
- the region extraction unit 16 includes an integration unit 161 and a determination unit 162.
- the integrating unit 161 obtains an integrated value of the amount of sunshine in the designated period at the planned location 22.
- the determination unit 162 uses the integrated value as a determination condition to extract the installation location of the sensor 55 that monitors the environment of the agricultural house 20 as a determination condition. To extract the region.
- the determination unit 162 determines the reference range based on the amount of sunlight. In this case, it is desirable that the determination unit 162 sets the reference range to a range equal to or greater than the representative value obtained from the integrated value at the planned location 22 in the season when the amount of sunshine is equal to or greater than the predetermined upper limit. On the other hand, it is desirable that the determination unit 162 sets the reference range to a range that does not fall below the representative value obtained from the integrated value at the planned location 22 in the season when the amount of sunshine is below a predetermined lower limit.
- the former season corresponds to the summer in the northern hemisphere, and the latter season corresponds to the winter in the northern hemisphere.
- the sensor 55 preferably includes at least one selected from the group of a temperature sensor, a humidity sensor, and a soil moisture sensor.
- the determination unit 162 uses the reference range set for extracting the installation location of the sensor 55 that monitors the external environment of the agricultural house 20 in the planned site 22 as a determination condition, Candidate areas may be extracted. In the case of providing a plurality of (for example, about 10) agricultural houses 20 in the planned site 22, this technique determines a place where one sensor 55 shared by the plurality of agricultural houses 20 is arranged. Used for
- the determination unit 162 sets the reference range to a range equal to or greater than the representative value obtained from the integrated value at the planned location 22 in the season when the amount of sunshine is equal to or greater than the predetermined upper limit.
- the sensor 55 preferably includes an illuminance sensor or a solar radiation sensor.
- an agricultural house sunshine amount adjusting device 30 described below includes an input device 31, a sunshine evaluation unit 32, and a control device 33.
- the position information of the planned site 22 where the agricultural house is installed is input to the input device 31.
- the sunshine evaluation unit 32 obtains a change in the amount of sunshine in the planned location 22 according to the date and time by computer simulation using the position information input from the input device 31.
- the control device 33 controls the operation of the environment adjusting device 50 that adjusts the plant growing environment in the agricultural house 20.
- the control apparatus 33 determines the control content so that the amount of sunlight suitable for plant growth can be obtained using the change in the amount of sunlight according to the date and time obtained by the sunlight evaluation unit 32.
- the input device 31 includes the size of the planned location 22, the location of the obstacle 40 that exists around the planned location 22 and may form a shadow 41 on the planned location 22, and Further dimensions are entered. It is desirable that the sunshine evaluation unit 32 obtains a change in the amount of sunshine at the planned location 22 according to the date and time using the position and dimensions of the obstacle 40 in addition to the position information.
- the environmental control device 50 is movable between a first position where the external light applied to the plant is dimmed and a second position where the external light applied to the plant is not dimmed. And a driving device 52 for moving the motor.
- the control device 33 instructs the drive device 52 of timing for moving the curtain 51 to the first position and timing for moving the curtain 51 to the second position.
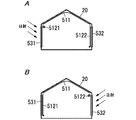
- the curtain 51 preferably includes a roof curtain 511 provided on the roof 21 of the agricultural house 20. It is desirable that the control device 33 instructs the drive device 52 to move the roof curtain 511 to the first position when the time from sunrise to sunset is equal to or greater than a predetermined reference time.
- the environmental control device 50 includes a first window 531 provided on the east side wall 23A of the agricultural house 20, a second window 532 provided on the west side wall 23B of the agricultural house 20, and a first window. And an opening / closing device 54 for driving the 531 and the second window 532 between the open position and the closed position.
- the curtain 51 preferably includes a first side curtain 5121 provided on the east side wall 23A of the agricultural house 20 and a second side curtain 5122 provided on the west side wall 23B of the agricultural house 20. .
- the control device 33 instructs the opening / closing device 54 to move the first window 531 and the second window 532 to the open position.
- the control device 33 instructs the drive device 52 to move the first side curtain 5121 and the second side curtain 5122 to the following positions according to the solar altitude. That is, it is desirable that the first side curtain 5121 is in the first position and the second side curtain 5122 is in the second position in the time zone before the solar time is below the first reference angle. Further, in the time zone after the solar time and the solar altitude being equal to or less than the second reference angle, the first side curtain 5121 is preferably in the second position, and the second side curtain 5122 is preferably in the first position. Further, in the time zone in which the solar altitude is between the first reference angle and the second reference angle, both the first side curtain 5121 and the second side curtain 5122 are preferably in the first position.
- the control device 33 instructs the opening / closing device 54 to move the first window 531 and the second window 532 to the closed position.
- the control device 33 instructs the drive device 52 to move the first side curtain 5121 and the second side curtain 5122 to the following positions according to the solar altitude. That is, it is desirable that the first side curtain 5121 is in the second position and the second side curtain 5122 is in the first position in the time zone before the solar time is below the third reference angle. In the time zone after the solar time and the solar altitude being equal to or less than the fourth reference angle, the first side curtain 5121 is preferably in the first position and the second side curtain 5122 is preferably in the second position.
- the program described below causes a computer to function as an installation evaluation device 10 for an agricultural house including an input device 11, a sunshine evaluation unit 12, and a presentation device 13.
- Another program described below causes a computer to function as an irradiance adjustment device 30 for an agricultural house including an input device 31, a sunshine evaluation unit 32, and a control device 33.
- the installation evaluation device 10 includes an input device 11, a sunshine evaluation unit 12, a presentation device 13, an arrangement setting unit 14, and a data storage unit 15.
- the installation evaluation apparatus 10 is realized by causing a general-purpose computer to execute a program.
- the installation evaluation device 10 may be a dedicated device.
- the program is provided through a telecommunication line such as the Internet or a computer-readable storage medium.
- the input device 11 and the presentation device 13 are integrally provided in the installation evaluation device 10, but the input device 11 and the presentation device 13 may be separated from other components.
- the input device 11 and the presentation device 13 may be terminal devices, and other computer devices connected to an electric communication line so that other components can communicate with the terminal device.
- the terminal device is selected from a notebook personal computer, a smartphone, a tablet terminal, or the like.
- the computer device is selected from a web server, a cloud computing system, and the like.
- the installation evaluation apparatus 10 is used for evaluating whether or not the amount of sunlight necessary for a plant grown using the agricultural house 20 can be secured in the planned site 22 where the agricultural house 20 (see FIGS. 2A and 2B) is installed. It is done. Therefore, information input to the input device 11 includes position information of the planned location 22.
- the input device 11 includes a display on which an input field for position information is displayed, and operation keys for inputting characters into the input field. The operation key is selected from, for example, a keyboard independent of the display, a touch panel overlaid on the display screen, or the like.
- Embodiment described below assumes soft vegetables, such as a spinach, Komatsuna, and a Mizuna.
- the agricultural house 20 for growing this kind of plant is required to suppress the temperature rise during the daytime in the summer, and to suppress the temperature drop at night in the wintertime.
- the location information of the planned land 22 is information necessary for estimating the sunshine on the surface of the soil where the plant is grown, and it is only necessary to know the relative position with the sun. Errors are acceptable. Therefore, the position information of the planned location 22 is specified by latitude and longitude with an accuracy of about 0.1 degree. The distance error in this case is about 10 km.
- the location information of the planned location 22 may be measured using a GPS (Global Positioning System) positioning device.
- GPS Global Positioning System
- a mobile terminal incorporating a GPS function such as a smartphone or a tablet terminal is used for the input device 11
- the GPS function built in the mobile terminal and the installation evaluation device 10 are linked to each other. It is possible to save the trouble of inputting position information.
- the installation evaluation apparatus 10 may use the latitude and longitude data acquired by specifying the position. .
- the user interface for inputting the position information to the input device 11 is not necessarily limited to the combination of the input field and the operation key, and various configurations are possible.
- the sunshine evaluation unit 12 obtains a change in the amount of sunshine at the planned location 22 according to the date and time by performing a computer simulation using the position information of the planned location 22 input to the input device 11. If the latitude and longitude of the planned location 22 and the date and time are known, the azimuth and elevation angle (altitude) of the sun can be obtained by performing simple interpolation calculations using known data relating these. In addition, since it is not necessary to obtain the sun's azimuth and altitude with high accuracy, the data relating the latitude and longitude, the date and time, the sun's azimuth and altitude may be of low accuracy, and the amount of data is relatively small. This data is stored in the data storage unit 15.
- the sunshine evaluation unit 12 calculates the azimuth and altitude of the sun according to the date and time using the position information input to the input device 11 and the data stored in the data storage unit 15. Since the agricultural house 20 is used for growing plants, it is necessary to evaluate the amount of sunlight during the period in which the plants are grown. Therefore, the sunshine evaluation unit 12 does not obtain the azimuth and altitude of the sun for a specific date and time, but for all the date and time in a predetermined period specified using the input device 11 or all the date and time for one year. It should be noted that it is practically sufficient to determine the azimuth and altitude of the sun at time intervals of about 10 minutes to 1 hour.
- the amount of sunlight (the amount of sunlight) for each date and time.
- the luminous flux per unit area emitted from the sun and reaching the earth is constant throughout the year.
- the luminous flux per unit area of the soil surface where plants are grown varies depending on the angle between the soil surface and the sun. Therefore, the amount of sunshine per unit time is greater in the summer than in the winter.
- the sunshine evaluation unit 12 Since the amount of sunshine necessary for the growth is known for the plant to be grown in the agricultural house 20, can the sunshine evaluation unit 12 obtain the necessary amount of sunshine (integrated value) for the plant at the planned site 22? Judge whether or not. It is desirable that the amount of sunlight necessary for the plant to be grown in the agricultural house 20 is stored in the data storage unit 15 in advance.
- At least one of the data relating the latitude and longitude, the date and time, the azimuth and the altitude of the sun, and the data relating the plant and the amount of sunlight is communicated not via the data storage unit 15 but via the electric communication line with the installation evaluation device 10. It may be stored in another computer device. That is, instead of the data storage unit 15, a computer server, a cloud computing system, or the like can be used.
- the sunlight evaluation unit 12 obtains the amount of sunlight at a predetermined time interval in a predetermined period (a period specified by the input device 11, for example, annual), the amount of sunlight necessary for the plant to be grown is obtained in the predetermined period. It is determined whether or not it is determined, and the determination result is output to the presentation device 13.
- a predetermined period a period specified by the input device 11, for example, annual
- the sunshine evaluation unit 12 may have a function of outputting a change in the amount of sunlight with the passage of time to the presentation device 13 without making a determination regarding the amount of sunlight. That is, regarding the planned site 22 where the agricultural house 20 is installed, the presentation device 13 may present the change in the amount of sunlight visualized. That is, the sunshine evaluation unit 12 presents data for presenting a change in the amount of sunshine obtained at a predetermined time interval as a moving image to the presentation device 13 and a change in the integrated value of the amount of sunshine in the period specified by the input device 11. At least one of data to be presented as a moving image to the device 13 is generated.
- the user makes a decision to install the agricultural house 20 based on the information presented on the presentation device 13. It becomes easy.
- the decision-making includes the contents relating to the specifications of the agricultural house 20 and the arrangement of the agricultural house 20.
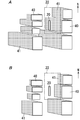
- the amount of sunlight in the planned site 22 where the agricultural house 20 is installed also varies depending on the shade 41. Therefore, when there is an obstacle 40 such as a building or a tree that may form a shadow 41 around the planned site 22, the sunshine evaluation unit 12 considers the shadow 41 formed by the obstacle 40. Estimate the amount of sunlight.
- the shadow 41 affects not only the obstacle 40 existing around the planned site 22 but also the topography around the planned site 22, except for the topography that tends to cause the shadow 41 such as mountains and valleys.
- the influence of the shade 41 due to the terrain may be omitted.
- 2A and 2B show a state in early spring
- FIG. 2A shows an example of a shadow 41 at 7:00
- FIG. 2B shows an example of a shadow 41 at 8:00.
- the input device 11 When considering the influence of the shade 41 due to the obstacle 40, the position (relative position with respect to the planned location 22) and dimensions of the obstacle 40 are input to the input device 11.
- the dimensions of the planned location 22 are also input from the input device 11.
- the input device 11 includes a display and operation keys.
- the display displays an input field for the position and size of the obstacle 40 and an input field for the size of the planned location 22, and the operation keys are used to input characters into the input field.
- the shade 41 formed by the obstacle 40 is obtained by simulation in consideration of the azimuth and altitude of the sun.
- the shape of the obstacle 40 is simplified to a rectangular parallelepiped.
- the entire miscellaneous forest is handled as one obstacle 40, and the entire miscellaneous forest is represented by one rectangular parallelepiped.
- the position of the obstacle 40 is represented by an azimuth and a distance with respect to the planned site 22, and the dimension of the obstacle 40 is represented by a height, a width, and a depth.
- the shape of the planned site 22 is simplified to a rectangular shape, and the size of the planned site 22 is expressed by the length of each side.
- the dimensions of the obstacle 40 can be obtained by actual measurement, but since a measurement device is required for actual measurement and time is required for measurement, it is not suitable for the purpose of simply evaluating the amount of sunlight in the planned location 22. Therefore, the size of the obstacle 40 is estimated using the photograph of the obstacle 40, or the size of the shadow 41 by the obstacle 40 is measured, and the size of the obstacle 40 is estimated from the azimuth and altitude of the sun at the measured date and time. It is desirable to do.
- the dimensions of the obstacle 40 thus easily determined are not highly accurate, but can be used as long as the amount of sunshine can be easily estimated. Further, the position of the obstacle 40 with respect to the planned site 22 can be easily obtained by using map data published on the Internet.
- the user can easily make a decision for installing the agricultural house 20 on the planned site 22.
- it is also possible to set an appropriate reference value for the amount of sunshine and automatically set the specifications and arrangement of the agricultural house 20 according to appropriate rules so that a sunshine amount equal to or greater than the reference value can be obtained.
- the amount of sunlight may be corrected based on past weather data at the planned location 22.
- the sunshine evaluation unit 12 determines whether or not to install the agricultural house 20 in the planned site 22 by obtaining a change in the amount of sunshine depending on the date and time.
- the amount of sunshine is uneven even in the planned site 22, it is necessary to consider the arrangement of the agricultural houses 20 in order to obtain an appropriate amount of sunshine.
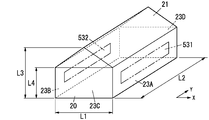
- the agricultural house 20 of the present embodiment has four side walls 23A to 23D (that is, the east side wall 23A, the west side wall 23B, A roof 21 having a south side wall 23C and a north side wall 23D) is formed in a shape in which a roof 21 having a triangular cross section that is formed by abutting two inclined planes is placed on the side walls 23A to 23D. That is, the roof 21 is formed in a shape like a gable roof.
- the shape of the roof 21 is an example, and may be, for example, a semicircular cross section.
- the direction connecting the end walls of the agricultural house 20 is referred to as a major axis direction
- the direction orthogonal to the major axis direction in a plane along the ground is referred to as a minor axis direction.
- An entrance door (not shown) is provided on the wife wall of the agricultural house 20.
- windows 53 are formed on the two side walls 23A and 23B, which are both ends in the minor axis direction of the agricultural house 20, respectively.
- one is called a first window 531 and the other is called a second window 532.
- the agricultural house 20 is arranged so that the major axis direction is along the north-south direction.
- the angle formed by the major axis direction and the north-south direction is relatively small (for example, within 30 degrees)
- the major axis direction does not necessarily coincide with the north-south direction.
- the major axis direction of the agricultural house 20 may be along the obstacle 40.
- the installation evaluation apparatus 10 includes the arrangement setting unit 14 that determines the arrangement and dimensions of the agricultural house 20 in the planned site 22.
- the arrangement setting unit 14 uses the change in the amount of sunshine according to the date and time obtained by the sunshine evaluation unit 12 to extract a region from which the required amount of sunshine is obtained from the planned location 22, and the farmhouse 20 that can be arranged in the region. Define dimensions and placement.
- the arrangement of the agricultural house 20 includes a major axis dimension, a minor axis dimension, and a major axis angle with respect to the north-south direction.
- the amount of sunshine used by the arrangement setting unit 14 can be appropriately determined by the user using the input device 11, but is determined according to the type of plant so that the amount of sunshine is suitable for the plant to be grown. Is desirable. Therefore, the arrangement setting unit 14 uses the types of plants grown in the agricultural house 20 to determine candidates for the arrangement and dimensions of the agricultural house 20 so that the amount of sunlight suitable for the plant can be obtained.
- the placement candidates and the size candidates of the agricultural house 20 determined by the placement setting unit 14 are presented in a state visualized by the presentation device 13.
- the input device 11 includes an input field for inputting the number of farmhouses 20 installed at the planned site 22.
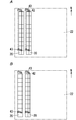
- the agricultural houses 20 are arranged at equal intervals along each side of the planned site 22, as shown in FIG. Further, the agricultural house 20 is arranged so that the marginal space 24 remains in the peripheral portion of the planned land 22, and the gap 25 is formed between the adjacent agricultural houses 20. Is placed.
- the X direction and the Y direction are defined according to the directions shown in FIG. In the illustrated example, the minor axis direction of the agricultural house 20 is defined as the X direction, and the major axis direction is defined as the Y direction.
- the number of buildings n1 in the X direction and the number of buildings n2 in the Y direction are designated.
- the input device 11 has respective input fields so that the dimensions in the X direction and the Y direction can be input with respect to the planned land 22, the marginal space 24, and the gap 25, respectively. That is, the input device 11 includes the dimensions W1 and W2 in the X direction and the Y direction of the planned land 22, the dimensions M11 and M12 in the X direction and the dimensions M21 and M22 in the Y direction, and the X of the gap 25. It is desirable to provide an input field for the dimensions D1 and D2 in the direction and the Y direction.
- the dimensions of the extra width 24 are determined by the four sides of the planned land 22. If the upward direction of the agricultural house 20 shown in FIG. 4 is northward, the dimension M11 corresponds to the west side, the dimension M12 corresponds to the east side, the dimension M21 corresponds to the north side, and the dimension M22 corresponds to the dimension of the marginal space 24 on the south side.
- the direction in this example is not intended to limit the present embodiment, but is a direction set for the sake of understanding.
- the upward direction of the agricultural house 20 is set to the east direction with respect to the north direction.
- the direction of the house 20 can be set as appropriate.
- the dimensions of the agricultural house 20 are also input to the input device 11 (see FIG. 3).
- the input device 11 includes an input field for inputting various dimensions and the number of farmhouses 20 as information on the farmhouse 20.
- the parameters given to the input device 11 must include the dimensions W1 and W2 of the planned site 22 and the dimensions L1 to L4 related to the specifications of the agricultural house 20.
- the parameters n1, n2 of the agricultural house 20 and the dimensions M11, M12, M21, M22, D1, D2 can be automatically calculated by giving some parameters. . Accordingly, some of the parameters input from the input device 11 can be omitted.
- the dimensions M11, M21 of the margin 24, and the dimensions D1, D2 of the gap 25 are automatically set. .
- D1 ⁇ W1 ⁇ (M11 + M12), respectively.
- D2 ⁇ W2 ⁇ (M21 + M22) ⁇ n2 ⁇ L2 ⁇ / (n2-1).
- the dimensions M11, M12, M21, and M22 of the margin 24 are unknown, and the dimensions (M11 + M12) and the dimensions (M21 + M22) are obtained directly from the relational expression.
- the sunshine evaluation unit 12 also evaluates the influence of the adjacent agricultural houses 20 on the amount of solar radiation.
- the amount of sunlight is corrected in consideration of the transmittance of the covering material used in the agricultural house 20.
- the transmittance of the covering material is, for example, 80%.
- the agricultural house 20 is provided with a roof curtain 511, a first side curtain 5121, and a second side curtain 5122 (see FIGS. 7A to 7C). These curtains 51 move between a first position where external light is dimmed and a second position where external light is not dimmed, and the curtains are collected at the second position to form a curtain pool.
- the light transmitted through the agricultural house 20 is attenuated by passing through the covering material of the agricultural house 20, and the soil surface is passed through the covering material of the adjacent agricultural house 20.
- 5A and 5B show a region 42 irradiated with light transmitted through the agricultural house 20 and a shade 43 formed by a curtain pool.
- the upward direction is set to the north direction.
- FIG. 5A and 5B show the state around autumn
- FIG. 5A shows the sunshine state at 10:00 am
- FIG. 5B shows the sunshine state at 11:00 am. Therefore, the sunshine evaluation unit 12 can obtain the change in the amount of sunshine according to the date and time by obtaining such a change in the amount of sunlight by computer simulation and presenting it to the user through the presentation device 13. Become.
- Embodiment 2 demonstrated the technique which determines arrangement
- the present embodiment includes a sunshine amount adjusting device 30 instead of the installation evaluation device 10.
- the sunshine amount adjusting device 30 includes an input device 31, a sunshine evaluation unit 32, and a control device 33.
- the sunshine amount adjusting device 30 is realized by causing a general-purpose computer to execute a program.
- the sunshine amount adjusting device 30 may be a dedicated device.
- the program is provided through a telecommunication line such as the Internet or a computer-readable storage medium.
- the input device 31 is provided integrally with the sunshine amount adjusting device 30, but the input device 31 may be separated from other components.
- the input device 31 may be a terminal device, and may be another computer device connected to a telecommunication line so that other components can communicate with the terminal device.
- the terminal device is selected from a notebook personal computer, a smartphone, a tablet terminal, or the like.
- the computer device is selected from a web server, a cloud computing system, and the like.
- the agricultural house 20 is provided with an environment adjusting device 50 for controlling the plant growing environment.
- the environmental control device 50 is also provided with a configuration for adjusting the ambient temperature and humidity of the plant, and a configuration for adjusting the amount of water irrigated to the plant.
- positioned in the interior space of the agricultural house 20 is used as a structure which adjusts the amount of sunlight.
- the first window 531 and the second window 532 described in Embodiment 1 are used as a configuration for adjusting the temperature and humidity around the plant.
- the agricultural house 20 is provided with other configurations as the environment adjusting device 50, but is not described in the present embodiment.
- the curtain 51 is formed so as to reduce external light by about 30 to 50%. Further, the curtain 51 moves between a first position where the external light applied to the plant is attenuated and a second position where the external light applied to the plant is not attenuated.
- the curtain 51 is moved by a driving device 52 having a motor.
- the curtain 51 includes a roof curtain 511 arranged along the roof 21, a first side curtain 5121 arranged along the first window 531, and a second curtain arranged along the second window 532.
- a side curtain 5122 is provided.
- the driving device 52 independently moves the roof curtain 511, the first side curtain 5121, and the second side curtain 5122 independently.
- the first window 531 and the second window 532 are individually opened and closed by the opening / closing device 54.
- the roof curtain 511 includes a form that moves along the gradient of the roof 21 and a form that moves along the long axis direction of the agricultural house 20, but this embodiment assumes the latter configuration. That is, the roof curtain 511 is provided with two roof curtains 511 arranged side by side in the longitudinal direction of the agricultural house 20. In this roof curtain 511, the position where the two roof curtains 511 are deployed is the first position, and the position where the two roof curtains 511 are drawn into both ends in the major axis direction of the agricultural house 20 is the second position. Position. Moreover, the 1st side curtain 5121 and the 2nd side curtain 5122 are roll-up types, Comprising: The position wound down is a 1st position, and the position wound up is a 2nd position.
- the operation of the driving device 52 and the opening / closing device 54 is controlled by the control device 33.
- the control device 33 instructs the drive device 52 of timing for moving the curtain 51 to the first position and timing for moving the curtain 51 to the second position.
- the roof curtain 511 is mainly used in summer to suppress an increase in the ambient temperature of the plant. Therefore, in order to drive the roof curtain 511, the control device 33 needs to recognize that it is summer.
- the control device 33 holds data in which the sunrise time and sunset time for each region divided as appropriate are associated with the date and time, and the date and time counted by a built-in clock (not shown) such as a real-time clock. Collate and grasp the sunrise time and sunset time. If the above-mentioned area is Japan, for example, it may be divided into about 8 areas.
- the time when the time from the sunrise time to the sunset time is equal to or greater than the reference time is determined as the summer.
- the reference time is, for example, 13 hours, but may be changed as appropriate according to the region.
- the control device 33 instructs the drive device 52 to move the roof curtain 511 to the first position in the time when summer is determined using the sunrise time and sunset time.
- the agricultural house 20 is arranged so that the major axis direction is the north-south direction or is inclined by a relatively small angle with respect to the north-south direction.
- the first window 531 is on the east side and the second window 532 is on the west side
- the first side curtain 5121 is located on the east side
- the second side curtain 5122 is located on the west side.
- the input device 31 has a configuration in which position information of the planned site 22 where the agricultural house 20 is installed is input. That is, the input device 31 includes a display on which an input field for position information is displayed, and operation keys for inputting characters into the input field.
- the operation key is selected from, for example, a keyboard independent of the display, a touch panel overlaid on the display screen, or the like.
- the GPS function built in the mobile terminal and the sunshine amount adjusting device 30 are linked to each other. It is possible to save the trouble of inputting information. Moreover, you may use the data of the latitude and longitude acquired by designating a position using the map data currently published on the internet with the sunshine amount adjustment apparatus 30.
- FIG. The technique for acquiring the position information of the planned location 22 is the same as that of the input device 11 described in the first embodiment.
- the sunshine evaluation unit 32 obtains a change in the amount of sunshine at the planned location 22 according to the date and time by performing a computer simulation using the position information of the planned location 22 input to the input device 31.
- the basic function of the sunshine evaluation unit 32 is the same as that of the sunshine evaluation unit 12 described in the first embodiment. That is, when there is an obstacle 40 (see FIGS. 2A and 2B), a shadow 41 due to the obstacle 40 is also considered. Moreover, since the light which permeate
- the input device 31 has the same function as the input device 11 of the first embodiment
- the sunshine evaluation unit 32 has the same function as the sunshine evaluation unit 12 of the first embodiment.
- the control device 33 uses the change in the amount of sunlight depending on the date and time obtained by the sunlight evaluation unit 32 to determine the control content so that the amount of sunlight suitable for plant growth can be obtained.
- the control device 33 controls the position of the curtain 51 so that the unevenness of the amount of sunlight due to the shade 43 caused by the roof curtain 511, the first side curtain 5121, and the second side curtain 5122 is reduced.
- summer and winter typical examples of the control by the control device 33 in summer and winter are shown.
- the time from sunrise time to sunset time may be used.
- the distinction between summer and winter can be performed using other information.
- a change in outside air temperature can also be used as information.
- the control device 33 gives instructions to the drive device 52 and the opening / closing device 54 so as to be in the following state. That is, the roof curtain 511 moves to the first position. Further, in a time zone before the solar time before the solar altitude is equal to or less than the first reference angle, as shown in FIG. 7A, the first side curtain 5121 is in the first position and the second side curtain 5122. Moves to the second position. As shown in FIG. 7C, the first side curtain 5121 is in the second position and the second side curtain 5122 is in the first position after the south-central time and when the solar altitude is equal to or less than the second reference angle. Move to position. As shown in FIG.
- the first side curtain 5121 and the second side curtain 5122 are both in the first position during the time period in which the solar altitude is between the first reference angle and the second reference angle. Move to. Further, in the summer, the first window 531 and the second window 532 move to the open position as shown in FIGS. 7A-7C.
- the first reference angle is set based on, for example, the solar altitude around 10 am
- the second reference angle is set based on, for example, the solar altitude around 3 pm. That is, the time zone in which the sunlight incident from the first window 531 is irradiated on the soil surface is reduced by moving the first side curtain 5121 to the first position. Further, the time zone in which the sunlight incident from the second window 532 is irradiated on the soil surface is dimmed by moving the second side curtain 5122 to the first position. In other time zones, the first side curtain 5121 and the second side curtain 5122 are moved to the second position. By moving the first side curtain 5121 and the second side curtain 5122 to the second position during the day, the ambient temperature of the plant is prevented from rising during the day.
- the control device 33 gives an instruction to the drive device 52 and the opening / closing device 54 so as to be in the following state. That is, the roof curtain 511 moves to the second position in principle.
- the first side curtain 5121 moves to the second position
- the second The side curtain 5122 moves to the first position.
- FIG. 8B as shown in FIG. 8B, the first side curtain 5121 moves to the first position and the second side curtain in the time zone in which the solar altitude is equal to or less than the fourth reference angle after the south-central time. 5122 moves to the second position.
- the first window 531 and the second window 532 move to the closed position as shown in FIGS. 8A and 8B.
- the third reference angle is set based on, for example, the solar altitude around 10 am
- the fourth reference angle is set based on, for example, the solar altitude around 3 pm. That is, in the time zone in which the sunlight incident from the first window 531 is irradiated on the soil surface, the first side curtain 5121 is moved to the second position to promote an increase in the ambient temperature of the plant. In addition, during the time period in which sunlight incident from the second window 532 is irradiated on the soil surface, the second side curtain 5122 is moved to the second position to promote an increase in the ambient temperature of the plant. In other time zones, the first side curtain 5121 and the second side curtain 5122 are appropriately moved to maintain the ambient temperature of the plant during the day at an appropriate temperature. Other configurations and operations are the same as those in the first embodiment.
- Embodiment 3 the time change of the amount of sunlight calculated
- FIG. 10 In order to control the environmental control apparatus 50 with higher accuracy, as shown in FIG. 10, a sensor 55 for monitoring the environment of the agricultural house 20 (plant growth environment) is provided, and information monitored by the sensor 55 is also included. It is desirable to use for control.
- Examples of the sensor 55 that monitors the environment of the agricultural house 20 include a temperature sensor, a humidity sensor, and a soil moisture sensor.
- the humidity sensor is a configuration that measures relative humidity. When a combined sensor is used for the temperature sensor and humidity sensor, the temperature and humidity can be measured simultaneously at one location, and the relative humidity can be accurately measured. There is.
- the soil moisture sensor is a sensor that monitors the moisture content of the soil. It is desirable to use at least one selected from these sensors 55 for the control of the environmental control device 50. Since the temperature, humidity, and moisture content of the soil have a correlation with the integrated value of the amount of sunshine, considering the installation location of the sensor 55 that monitors these environments based on the amount of sunshine, the environmental control device 50 Can be accurately controlled. If necessary, the sensor 55 may be a wind speed sensor, a CO 2 sensor that measures the carbon dioxide concentration, or the like.
- the environmental adjustment device 50 includes the curtain 51 (the roof curtain 511, the first side curtain 5121, the second side curtain 5122, etc.), the first window 531, the second window 532, and the like.
- the environment adjusting device 50 includes a device for watering, a device for generating mist, and the like. These environmental adjusting devices 50 contribute to the adjustment of temperature and humidity.
- the watering device is also controlled by the moisture content of the soil.
- the present embodiment proposes a technique for extracting a place suitable for arranging the sensor 55 based on the change in the amount of sunlight depending on the date and time obtained by the sunlight evaluation unit 12.
- the arrangement setting part 14 which determines the arrangement candidate and the dimension candidate of the agricultural house 20 using the change of the amount of sunlight by the date and time which the sunshine evaluation part 12 calculated
- the present embodiment includes a region extraction unit 16 that extracts a region where the amount of sunshine satisfies the determination condition using the change in the amount of sunshine according to the date and time obtained by the sunshine evaluation unit 12. Yes.
- the region extraction unit 16 extracts a region where the amount of sunlight satisfies the determination condition from the planned location 22.
- a technique for extracting a region that is a candidate for the installation location of the sensor 55 using the region extraction unit 16 will be described. Note that the region extracted by the region extraction unit 16 is visualized and presented by the presentation device 13.
- the area extracting unit 16 includes an integrating unit 161 that calculates an integrated value of the amount of sunshine in a designated period at the planned location 22. Specifically, the integration unit 161 divides the planned location 22 into a plurality of areas, and obtains an integrated value of the amount of sunlight for a specified period for each area.
- the designated period is a plurality of days such as one day or one week, and it is desirable to use one day as a unit.
- an average value for one day may be obtained from the integrated value of the specified period, in addition to using the integrated value of the entire period.
- the region extraction unit 16 includes a determination unit 162 that determines whether or not the integrated value of the sunshine amount is within a reference range in order to extract the installation location of the sensor 55 using the integrated value of the sunshine amount obtained by the integrating unit 161. ing. That is, the determination unit 162 uses, as a determination condition, the integrated value of the amount of sunshine is a reference range set for extracting the installation location of the sensor 55 that monitors the environment of the agricultural house 20. Then, the determination unit 162 extracts a region where the integrated value of the amount of sunlight satisfies the determination condition from a plurality of regions as a region that is a candidate for the installation location of the sensor 55. The region that is a candidate for the installation location of the sensor 55 extracted by the determination unit 162 is presented to the presentation device 13. The reference range is stored in advance in the data storage unit 15.
- the reference range it is desirable to change the reference range according to the season. This is because in the winter when the amount of daily sunshine is low, the morning temperature rises slowly, and in the evening the temperature drops quickly, and in the summer when the amount of daily irradiance is high, the morning temperature This is because the rise is fast and the temperature drop in the evening is slow.
- the determination unit 162 determines an upper limit value and a lower limit value for the amount of sunlight.
- the determination unit 162 determines that the season when the maximum value of the amount of sunshine at the planned location 22 is equal to or higher than the upper limit value is summer, and determines the season when the minimum value of the amount of sunshine at the planned location 22 is equal to or lower than the lower limit value.
- the condition for determining the summer season may be a season when the minimum value of the sunshine amount is equal to or greater than the upper limit value
- the condition for determining the winter season may be a season when the maximum value of the sunshine amount is equal to or less than the lower limit value.
- the determination unit 162 may determine the season by comparing the average value per unit time (for example, 30 minutes, 1 hour, etc.) obtained from the integrated value of the daily amount of sunlight with the upper limit value and the lower limit value. . Furthermore, it is possible not only to divide the season into two stages but also into three or more stages. In this case, not only the summer reference range and winter reference range, but also three or more types of reference ranges are stored in the data storage unit 15 in advance.
- the determination unit 162 sets the reference range to a range equal to or greater than the representative value obtained from the integrated value of the amount of sunlight at the planned location 22 in the season when the amount of sunlight is equal to or greater than the upper limit. On the other hand, the determination unit 162 sets the reference range to a range that does not fall below the representative value obtained from the integrated value of the amount of sunlight at the planned location 22 in the season when the amount of sunlight is equal to or lower than the lower limit.
- the representative value obtained from the integrated value of the sunshine amount may be selected from the average value, median value, mode value, etc. of the sunshine amount during the integrated period.
- the representative value may be a value calculated using an appropriate function in addition to the exemplified values.
- a candidate for a region where the sensor 55 is arranged becomes an unfavorable region in the planned site 22 as an environment for growing plants. Therefore, if the environmental control device 50 is controlled based on the environment monitored by the sensor 55 arranged in such a region, the environmental control device 50 in other regions can maintain a better environment for plant growth. It becomes possible.
- a candidate for a region where the sensor 55 is to be arranged is selected by comparing the integrated value of the amount of sunlight with a reference range.
- a reference range it is also possible to set a reference range so that a candidate for a region that is inappropriate as the location of the sensor 55 can be extracted. For example, a region where the integrated value of the amount of sunshine falls below the representative value in summer is a candidate for a region where the sensor 55 cannot be arranged, and a region where the integrated value of the amount of sunlight exceeds the representative value is arranged in winter. It is good also as a candidate of the area which cannot.
- the sensor 55 for monitoring the amount of sunshine needs to be arranged outside the agricultural house 20.
- the sensor 55 that monitors the external environment of the agricultural house 20 includes an illuminance sensor or a solar radiation sensor so that the amount of sunlight in the planned site 22 can be measured.
- the sensor 55 may include at least one type selected from the group of a temperature sensor and a humidity sensor.
- the installation location of the sensor 55 that monitors the external environment of the agricultural house 20 is within the set reference range, and the determination unit 162 extracts candidate areas. Is desirable. In other words, this type of sensor 55 is desirably arranged in a region where the integrated value of the amount of sunlight is the maximum regardless of the season. Therefore, it is desirable that the determination unit 162 sets the reference range to a range equal to or greater than the representative value obtained from the integrated value at the planned location 22 in the season when the amount of sunshine is equal to or greater than the predetermined upper limit value.
- Other configurations and operations of the present embodiment are the same as those of the first or second embodiment.
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Environmental Sciences (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Atmospheric Sciences (AREA)
- Ecology (AREA)
- Biodiversity & Conservation Biology (AREA)
- Sustainable Development (AREA)
- Sustainable Energy (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
- Greenhouses (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201480028088.6A CN105228441A (zh) | 2013-05-13 | 2014-03-31 | 温室用的安装评价装置、温室用的日照量调整装置和程序 |
| US14/787,512 US10506767B2 (en) | 2013-05-13 | 2014-03-31 | Installation evaluation apparatus for greenhouse, insolation regulation apparatus for greenhouse, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013-101056 | 2013-05-13 | ||
| JP2013101056 | 2013-05-13 | ||
| JP2013-252514 | 2013-12-05 | ||
| JP2013252514A JP6399426B2 (ja) | 2013-05-13 | 2013-12-05 | 農業用ハウスの設置評価装置、農業用ハウスの日照量調整装置、プログラム |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014184996A1 true WO2014184996A1 (ja) | 2014-11-20 |
Family
ID=51897990
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/001869 Ceased WO2014184996A1 (ja) | 2013-05-13 | 2014-03-31 | 農業用ハウスの設置評価装置、農業用ハウスの日照量調整装置、プログラム |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10506767B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6399426B2 (enExample) |
| CN (2) | CN107439273A (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2014184996A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015087496A1 (ja) * | 2013-12-12 | 2015-06-18 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 農業用ハウス |
| WO2018180239A1 (ja) * | 2017-03-27 | 2018-10-04 | ボッシュ株式会社 | 情報処理装置および情報処理方法 |
| JP2021126081A (ja) * | 2020-02-14 | 2021-09-02 | 国立研究開発法人農業・食品産業技術総合研究機構 | 環境制御装置、環境制御システム、及びプログラム |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101913398B1 (ko) * | 2017-02-24 | 2018-10-30 | 한국과학기술연구원 | 작물 결로 방지 시스템 |
| JP2019011969A (ja) * | 2017-06-29 | 2019-01-24 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 積算受光量推定方法、プログラム、積算受光量推定装置及び健康管理システム |
| KR102387391B1 (ko) * | 2019-12-02 | 2022-04-15 | 대한민국 | 온실 최적 치수 결정 방법 |
| US20230273344A1 (en) * | 2020-07-31 | 2023-08-31 | Mitsui Chemicals, Inc. | Insolation correction method, insolation correction device, recording medium, model, model generating method, and model providing method |
| JP7723488B2 (ja) * | 2021-03-15 | 2025-08-14 | Biprogy株式会社 | 土壌状態予測システム及び土壌状態予測プログラム |
| KR102689440B1 (ko) * | 2021-08-31 | 2024-07-30 | 주식회사 에이비씨랩스 | 딸기, 오이, 토마토의 생산성 향상을 위한 광레시피 기반의 광량 제어 시스템 및 방법 |
| JP2023131357A (ja) * | 2022-03-09 | 2023-09-22 | Biprogy株式会社 | 日射予測システム及び日射予測プログラム |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003167065A (ja) * | 2001-12-04 | 2003-06-13 | Asahi Kasei Corp | 日照シミュレーションシステム |
| JP2004201630A (ja) * | 2002-12-26 | 2004-07-22 | Esd:Kk | 温室内の環境制御方法および装置 |
| WO2011158363A1 (ja) * | 2010-06-17 | 2011-12-22 | 株式会社四国総合研究所 | 日射強度予測システムと太陽光発電出力予測システム |
Family Cites Families (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4462390A (en) * | 1981-10-16 | 1984-07-31 | Holdridge Robert B | Modular solar greenhouse with elevated overhead heat storage material and movable insulation barriers and method and system for solar heating of attached living space using thermostat-controlled air circulation for harvesting heat |
| US4569150A (en) * | 1983-10-31 | 1986-02-11 | Board Of Trustees Operating Michigan State University | Method and apparatus for optimization of growth of plants |
| US5818734A (en) * | 1996-06-12 | 1998-10-06 | Cornell Research Foundation, Inc. | Method for controlling greenhouse light |
| JP3871441B2 (ja) * | 1998-06-26 | 2007-01-24 | 旭化成ホームズ株式会社 | 住宅用日照シュミレーション装置 |
| JP2001265833A (ja) * | 2000-03-23 | 2001-09-28 | Misawa Homes Co Ltd | 日影シミュレーションシステム、日影のシミュレーション方法、および日影をシミュレーションする方法をコンピュータで実行させるプログラムを記憶した記憶媒体 |
| US20030126791A1 (en) * | 2000-05-03 | 2003-07-10 | Weder Donald E. | Low profile commercial greenhouse |
| JP2003242232A (ja) * | 2002-02-13 | 2003-08-29 | Sharp Corp | 周辺環境情報取得方法および装置、ならびに太陽光発電システムの発電量推定方法 |
| CA2543874A1 (en) * | 2003-10-31 | 2005-05-12 | Cornell Research Foundation, Inc. | Systems and methods for providing optimal light-co2 combinations for plant production |
| RU2448455C2 (ru) * | 2006-12-07 | 2012-04-27 | Конинклейке Филипс Электроникс Н.В. | Регулирующее устройство для теплицы |
| JP2009129686A (ja) * | 2007-11-22 | 2009-06-11 | Kiso Micro Kk | 太陽電池システム |
| JP4425983B1 (ja) | 2009-03-18 | 2010-03-03 | 株式会社パスコ | 日射量の評価方法および評価装置 |
| US20120035887A1 (en) * | 2010-08-03 | 2012-02-09 | Joseph Augenbraun | Shading analysis software |
| TWI453379B (zh) * | 2010-12-10 | 2014-09-21 | Inst Information Industry | Illumination sensing system, method and computer program products |
| US9078299B2 (en) * | 2011-04-14 | 2015-07-07 | Suntracker Technologies Ltd | Predictive daylight harvesting system |
| JP5769245B2 (ja) * | 2011-08-08 | 2015-08-26 | 東京瓦斯株式会社 | 日影シミュレーションシステム |
| CN202282962U (zh) * | 2011-09-30 | 2012-06-27 | 翁克伟 | 可调整透光系数的智能型遮光装置 |
| US8898954B2 (en) * | 2011-12-16 | 2014-12-02 | Hsi-Chin Wang | Combined greenhouse |
| CN203435457U (zh) * | 2013-08-20 | 2014-02-19 | 张竣淞 | 一种太阳能光伏农业大棚 |
-
2013
- 2013-12-05 JP JP2013252514A patent/JP6399426B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2014
- 2014-03-31 CN CN201710581630.6A patent/CN107439273A/zh not_active Withdrawn
- 2014-03-31 US US14/787,512 patent/US10506767B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2014-03-31 WO PCT/JP2014/001869 patent/WO2014184996A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2014-03-31 CN CN201480028088.6A patent/CN105228441A/zh active Pending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003167065A (ja) * | 2001-12-04 | 2003-06-13 | Asahi Kasei Corp | 日照シミュレーションシステム |
| JP2004201630A (ja) * | 2002-12-26 | 2004-07-22 | Esd:Kk | 温室内の環境制御方法および装置 |
| WO2011158363A1 (ja) * | 2010-06-17 | 2011-12-22 | 株式会社四国総合研究所 | 日射強度予測システムと太陽光発電出力予測システム |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015087496A1 (ja) * | 2013-12-12 | 2015-06-18 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 農業用ハウス |
| JPWO2015087496A1 (ja) * | 2013-12-12 | 2017-03-16 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 農業用ハウス |
| WO2018180239A1 (ja) * | 2017-03-27 | 2018-10-04 | ボッシュ株式会社 | 情報処理装置および情報処理方法 |
| JPWO2018180239A1 (ja) * | 2017-03-27 | 2019-12-12 | ボッシュ株式会社 | 情報処理装置および情報処理方法 |
| JP2021126081A (ja) * | 2020-02-14 | 2021-09-02 | 国立研究開発法人農業・食品産業技術総合研究機構 | 環境制御装置、環境制御システム、及びプログラム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN105228441A (zh) | 2016-01-06 |
| US10506767B2 (en) | 2019-12-17 |
| CN107439273A (zh) | 2017-12-08 |
| US20160066517A1 (en) | 2016-03-10 |
| JP6399426B2 (ja) | 2018-10-03 |
| JP2014240829A (ja) | 2014-12-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6399426B2 (ja) | 農業用ハウスの設置評価装置、農業用ハウスの日照量調整装置、プログラム | |
| Berry et al. | Tree canopy shade impacts on solar irradiance received by building walls and their surface temperature | |
| Koch-Nielsen | Stay cool: a design guide for the built environment in hot climates | |
| KR101933876B1 (ko) | 건물의 일조 특성 시뮬레이션 시스템 및 그 제어 방법 | |
| Bakhshoodeh et al. | Impact of ambient air temperature, orientation, and plant status on the thermal performance of green façades | |
| US20210080615A1 (en) | Method and system for predicting daily light integrals for crop growing | |
| CN113748886B (zh) | 温室幕布系统及温室 | |
| Qi et al. | Influence of university campus spatial morphology on outdoor thermal environment: A case study from Eastern China | |
| Eckmann et al. | Measuring and modeling microclimate impacts of Sequoiadendron giganteum | |
| Widiastuti et al. | Performance evaluation of vertical gardens | |
| JP5188535B2 (ja) | 取得日射エネルギー量表示装置 | |
| Abramczyk | Parametric building forms rationalizing the incident direct solar irradiation | |
| CN111708389B (zh) | 温室内环境数据生成方法 | |
| Misni | The effects of surrounding vegetation, building construction and human factors on the thermal performance of housing in a tropical environment | |
| KR20240022340A (ko) | 환경 상태 정보의 3d 시각화에 기초한 스마트팜 모니터링 및 관제 시스템 | |
| Babota | Increase energy efficiency and comfort in homes by incorporating passive solar design features | |
| JP4553750B2 (ja) | 取得日射エネルギー量表示装置 | |
| Kumakura et al. | Influence of residents’ behaviour on the thermal environment of a common garden path for detached houses in summer | |
| CN104360421A (zh) | 建筑日照时数测量仪 | |
| Harun et al. | Unveiling the Thermal Comfort Dynamics of Asymmetrical Buildings Configurations in Malaysia’s Public School Courtyard Design | |
| Udovicic | Retrofitting for a Biosolar Roof in Northeast Ohio using Modeling and Vegetative Field Studies | |
| Zonato | Modeling the Urban Boundary Layer in Complex Terrain | |
| Tosi | Green roofs and solar panels as a single assembly system in Austin, Texas | |
| Kumar | Significance of shadow and shading analysis in solar power projects | |
| KR20240058428A (ko) | 보온스크린이 설치된 온실 및 온실 시스템 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201480028088.6 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14797691 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14787512 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 14797691 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |