WO2011056983A1 - Zirconium-radiolabeled, cysteine engineered antibody conjugates - Google Patents
Zirconium-radiolabeled, cysteine engineered antibody conjugates Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2011056983A1 WO2011056983A1 PCT/US2010/055465 US2010055465W WO2011056983A1 WO 2011056983 A1 WO2011056983 A1 WO 2011056983A1 US 2010055465 W US2010055465 W US 2010055465W WO 2011056983 A1 WO2011056983 A1 WO 2011056983A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- antibody
- cysteine
- frac acc
- zirconium
- engineered antibody
- Prior art date
Links
- 235000018417 cysteine Nutrition 0.000 title claims abstract description 186
- XUJNEKJLAYXESH-UHFFFAOYSA-N cysteine Natural products SCC(N)C(O)=O XUJNEKJLAYXESH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title claims abstract description 179
- 229940127121 immunoconjugate Drugs 0.000 title abstract description 10
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 121
- -1 cysteine amino acids Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 99
- 235000001014 amino acid Nutrition 0.000 claims abstract description 65
- 229910052726 zirconium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 46
- QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zirconium Chemical compound [Zr] QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 38
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 34
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 32
- XUJNEKJLAYXESH-REOHCLBHSA-N L-Cysteine Chemical compound SC[C@H](N)C(O)=O XUJNEKJLAYXESH-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 claims description 223
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 claims description 117
- 229960000575 trastuzumab Drugs 0.000 claims description 95
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 claims description 93
- 235000018102 proteins Nutrition 0.000 claims description 90
- 239000000427 antigen Substances 0.000 claims description 82
- 108091007433 antigens Proteins 0.000 claims description 82
- 102000036639 antigens Human genes 0.000 claims description 82
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 claims description 79
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims description 65
- 101001012157 Homo sapiens Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 Proteins 0.000 claims description 62
- 229940024606 amino acid Drugs 0.000 claims description 62
- 102100030086 Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 Human genes 0.000 claims description 61
- 108090000765 processed proteins & peptides Proteins 0.000 claims description 55
- 241000282414 Homo sapiens Species 0.000 claims description 42
- 102000004196 processed proteins & peptides Human genes 0.000 claims description 38
- 102000005962 receptors Human genes 0.000 claims description 33
- 108020003175 receptors Proteins 0.000 claims description 33
- 108060003951 Immunoglobulin Proteins 0.000 claims description 21
- 102000018358 immunoglobulin Human genes 0.000 claims description 21
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 claims description 17
- 102100033423 GDNF family receptor alpha-1 Human genes 0.000 claims description 16
- 101000579425 Homo sapiens Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret Proteins 0.000 claims description 16
- 102100026711 Metalloreductase STEAP2 Human genes 0.000 claims description 16
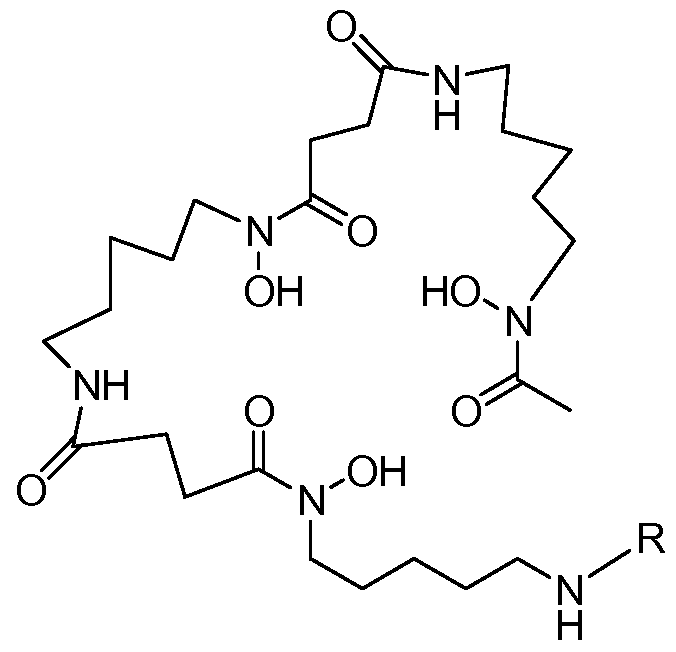
- UBQYURCVBFRUQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-benzoyl-Ferrioxamine B Chemical compound CC(=O)N(O)CCCCCNC(=O)CCC(=O)N(O)CCCCCNC(=O)CCC(=O)N(O)CCCCCN UBQYURCVBFRUQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 16
- 102100028286 Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret Human genes 0.000 claims description 16
- 125000000539 amino acid group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- 101000628535 Homo sapiens Metalloreductase STEAP2 Proteins 0.000 claims description 14
- 238000001727 in vivo Methods 0.000 claims description 14
- 238000002372 labelling Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 101000997961 Homo sapiens GDNF family receptor alpha-1 Proteins 0.000 claims description 12
- 102100034845 KiSS-1 receptor Human genes 0.000 claims description 12
- 102100022430 Melanocyte protein PMEL Human genes 0.000 claims description 12
- 102100032780 Semaphorin-5B Human genes 0.000 claims description 12
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 claims description 12
- 101000620359 Homo sapiens Melanocyte protein PMEL Proteins 0.000 claims description 10
- 101000654679 Homo sapiens Semaphorin-5B Proteins 0.000 claims description 10
- 101000713169 Homo sapiens Solute carrier family 52, riboflavin transporter, member 2 Proteins 0.000 claims description 10
- 102100032129 Lymphocyte antigen 6K Human genes 0.000 claims description 10
- 102100036862 Solute carrier family 52, riboflavin transporter, member 2 Human genes 0.000 claims description 10
- 102100029690 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13C Human genes 0.000 claims description 10
- 210000003719 b-lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 claims description 10
- 102100026159 Tomoregulin-1 Human genes 0.000 claims description 9
- 102100027203 B-cell antigen receptor complex-associated protein beta chain Human genes 0.000 claims description 8
- 101001091205 Homo sapiens KiSS-1 receptor Proteins 0.000 claims description 8
- 101001065550 Homo sapiens Lymphocyte antigen 6K Proteins 0.000 claims description 8
- 101000853730 Homo sapiens RING finger and transmembrane domain-containing protein 2 Proteins 0.000 claims description 8
- 102100035928 RING finger and transmembrane domain-containing protein 2 Human genes 0.000 claims description 8
- 102100039094 Tyrosinase Human genes 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 101000834937 Homo sapiens Tomoregulin-1 Proteins 0.000 claims description 7
- 102100025218 B-cell differentiation antigen CD72 Human genes 0.000 claims description 6
- 102100024220 CD180 antigen Human genes 0.000 claims description 6
- 108010001445 CD79 Antigens Proteins 0.000 claims description 6
- 102000000796 CD79 Antigens Human genes 0.000 claims description 6
- 108010023729 Complement 3d Receptors Proteins 0.000 claims description 6
- 102000011412 Complement 3d Receptors Human genes 0.000 claims description 6
- 102100031511 Fc receptor-like protein 2 Human genes 0.000 claims description 6
- 101000914491 Homo sapiens B-cell antigen receptor complex-associated protein beta chain Proteins 0.000 claims description 6
- 101000980829 Homo sapiens CD180 antigen Proteins 0.000 claims description 6
- 101001063456 Homo sapiens Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5 Proteins 0.000 claims description 6
- 101000825475 Homo sapiens Protein shisa-2 homolog Proteins 0.000 claims description 6
- 101000835745 Homo sapiens Teratocarcinoma-derived growth factor 1 Proteins 0.000 claims description 6
- 101000844504 Homo sapiens Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 4 Proteins 0.000 claims description 6
- 102100031036 Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5 Human genes 0.000 claims description 6
- 102100038210 Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d Human genes 0.000 claims description 6
- 102100032131 Lymphocyte antigen 6E Human genes 0.000 claims description 6
- 102100022938 Protein shisa-2 homolog Human genes 0.000 claims description 6
- 102100026404 Teratocarcinoma-derived growth factor 1 Human genes 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000004069 differentiation Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 150000007523 nucleic acids Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 102100038080 B-cell receptor CD22 Human genes 0.000 claims description 5
- 101000623901 Homo sapiens Mucin-16 Proteins 0.000 claims description 5
- 101000834948 Homo sapiens Tomoregulin-2 Proteins 0.000 claims description 5
- 108010054477 Immunoglobulin Fab Fragments Proteins 0.000 claims description 5
- 102000001706 Immunoglobulin Fab Fragments Human genes 0.000 claims description 5
- 102100023123 Mucin-16 Human genes 0.000 claims description 5
- 102100036735 Prostate stem cell antigen Human genes 0.000 claims description 5
- 102100038437 Sodium-dependent phosphate transport protein 2B Human genes 0.000 claims description 5
- 102100026160 Tomoregulin-2 Human genes 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 101710129514 B-cell differentiation antigen CD72 Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- 102100032312 Brevican core protein Human genes 0.000 claims description 4
- 102100032768 Complement receptor type 2 Human genes 0.000 claims description 4
- 101000846911 Homo sapiens Fc receptor-like protein 2 Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- 101000958332 Homo sapiens Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- 101001065568 Homo sapiens Lymphocyte antigen 6E Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- 101000829779 Homo sapiens Probable G-protein coupled receptor 19 Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- 101000606090 Homo sapiens Tyrosinase Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 claims description 4
- 108010076800 Kisspeptin-1 Receptors Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- 102000052922 Large Neutral Amino Acid-Transporter 1 Human genes 0.000 claims description 4
- 108010006444 Leucine-Rich Repeat Proteins Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- 108090000015 Mesothelin Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- 102000003735 Mesothelin Human genes 0.000 claims description 4
- 108091028043 Nucleic acid sequence Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- 102100037603 P2X purinoceptor 5 Human genes 0.000 claims description 4
- 102100023417 Probable G-protein coupled receptor 19 Human genes 0.000 claims description 4
- 108010029485 Protein Isoforms Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- 102000001708 Protein Isoforms Human genes 0.000 claims description 4
- 108091006232 SLC7A5 Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- 102100031228 Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 4 Human genes 0.000 claims description 4
- 101710178300 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13C Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- 108060008724 Tyrosinase Proteins 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000002299 complementary DNA Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 210000004901 leucine-rich repeat Anatomy 0.000 claims description 4
- 210000002307 prostate Anatomy 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000005945 translocation Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 102100020998 Aspartate beta-hydroxylase domain-containing protein 1 Human genes 0.000 claims description 3
- 108091008875 B cell receptors Proteins 0.000 claims description 3
- 108010046304 B-Cell Activation Factor Receptor Proteins 0.000 claims description 3
- 102100025473 Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 Human genes 0.000 claims description 3
- 101000783987 Homo sapiens Aspartate beta-hydroxylase domain-containing protein 1 Proteins 0.000 claims description 3
- 101000884305 Homo sapiens B-cell receptor CD22 Proteins 0.000 claims description 3
- 101000914326 Homo sapiens Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 Proteins 0.000 claims description 3
- 101000941929 Homo sapiens Complement receptor type 2 Proteins 0.000 claims description 3
- 101000604039 Homo sapiens Sodium-dependent phosphate transport protein 2B Proteins 0.000 claims description 3
- 101000716102 Homo sapiens T-cell surface glycoprotein CD4 Proteins 0.000 claims description 3
- 206010035226 Plasma cell myeloma Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 102100036011 T-cell surface glycoprotein CD4 Human genes 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000000536 complexating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000003102 growth factor Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 201000000050 myeloid neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 208000030507 AIDS Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000024704 B cell apoptotic process Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 102100027205 B-cell antigen receptor complex-associated protein alpha chain Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710166261 B-cell antigen receptor complex-associated protein beta chain Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000003844 B-cell-activation Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000007350 Bone Morphogenetic Proteins Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108010007726 Bone Morphogenetic Proteins Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 108010085074 Brevican Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 208000011691 Burkitt lymphomas Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 102100031658 C-X-C chemokine receptor type 5 Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108010008955 Chemokine CXCL13 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000006574 Chemokine CXCL13 Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 102100035294 Chemokine XC receptor 1 Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 101100004180 Chironomus tentans BR3 gene Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 102100026245 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF43 Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000002045 Endothelin Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108050009340 Endothelin Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 102100031517 Fc receptor-like protein 1 Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710120224 Fc receptor-like protein 1 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 102100031507 Fc receptor-like protein 5 Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108010014612 Follistatin Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000016970 Follistatin Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000003688 G-Protein-Coupled Receptors Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108090000045 G-Protein-Coupled Receptors Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 108090000722 Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor receptors Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 208000031886 HIV Infections Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 102100031546 HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DO beta chain Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000018713 Histocompatibility Antigens Class II Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108010027412 Histocompatibility Antigens Class II Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101000914489 Homo sapiens B-cell antigen receptor complex-associated protein alpha chain Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101000922405 Homo sapiens C-X-C chemokine receptor type 5 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101000804783 Homo sapiens Chemokine XC receptor 1 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101000692702 Homo sapiens E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF43 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101100119857 Homo sapiens FCRL2 gene Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101000846908 Homo sapiens Fc receptor-like protein 5 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101000866281 Homo sapiens HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DO beta chain Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101000576802 Homo sapiens Mesothelin Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101001024605 Homo sapiens Next to BRCA1 gene 1 protein Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101000883798 Homo sapiens Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX53 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101100425948 Homo sapiens TNFRSF13C gene Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 206010020853 Hypertonic bladder Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000004310 Ion Channels Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108090000862 Ion Channels Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000004086 Ligand-Gated Ion Channels Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108090000543 Ligand-Gated Ion Channels Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710160635 Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710157879 Lymphocyte antigen 6E Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710158212 Lymphocyte antigen 6K Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 206010025323 Lymphomas Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000018697 Membrane Proteins Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108010052285 Membrane Proteins Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 102100025096 Mesothelin Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710147242 Metalloreductase STEAP2 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101100182721 Mus musculus Ly6e gene Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101000623899 Mus musculus Mucin-13 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101100042271 Mus musculus Sema3b gene Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 102400000058 Neuregulin-1 Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108090000556 Neuregulin-1 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710189969 P2X purinoceptor 5 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 108010092528 Phosphate Transport Proteins Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000016462 Phosphate Transport Proteins Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000004160 Phosphoric Monoester Hydrolases Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108090000608 Phosphoric Monoester Hydrolases Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 102100033237 Pro-epidermal growth factor Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 102100038236 Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX53 Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 206010060862 Prostate cancer Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 208000000236 Prostatic Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 108010067787 Proteoglycans Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000016611 Proteoglycans Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108010080192 Purinergic Receptors Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000014400 SH2 domains Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108050003452 SH2 domains Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 108091058557 SILV Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 108091006576 SLC34A2 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710199399 Semaphorin-5B Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101100523267 Staphylococcus aureus qacC gene Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 210000001744 T-lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000003618 TRPM4 Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710098080 Teratocarcinoma-derived growth factor Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710175559 Tomoregulin-1 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940112869 bone morphogenetic protein Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000011712 cell development Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 101150107440 crl gene Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000007123 defense Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000007812 deficiency Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000003831 deregulation Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000009266 disease activity Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- ZUBDGKVDJUIMQQ-UBFCDGJISA-N endothelin-1 Chemical compound C([C@@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC=1C2=CC=CC=C2NC=1)C(O)=O)NC(=O)[C@H]1NC(=O)[C@H](CC=2C=CC=CC=2)NC(=O)[C@@H](CC=2C=CC(O)=CC=2)NC(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H]2CSSC[C@@H](C(N[C@H](CO)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(=O)N[C@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCSC)C(=O)N[C@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C(=O)N2)=O)NC(=O)[C@@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](N)CSSC1)C1=CNC=N1 ZUBDGKVDJUIMQQ-UBFCDGJISA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 208000032839 leukemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 210000004698 lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000036210 malignancy Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000005012 migration Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000013508 migration Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000004766 neurogenesis Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000007310 pathophysiology Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 208000035782 susceptibility to 1 Hirschsprung disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000005062 synaptic transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 201000000596 systemic lupus erythematosus Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 102000035160 transmembrane proteins Human genes 0.000 claims description 2
- 108091005703 transmembrane proteins Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101001136592 Homo sapiens Prostate stem cell antigen Proteins 0.000 claims 2
- 101150066838 12 gene Proteins 0.000 claims 1
- 101100118545 Holotrichia diomphalia EGF-like gene Proteins 0.000 claims 1
- DAWBXZHBYOYVLB-UHFFFAOYSA-J oxalate;zirconium(4+) Chemical compound [Zr+4].[O-]C(=O)C([O-])=O.[O-]C(=O)C([O-])=O DAWBXZHBYOYVLB-UHFFFAOYSA-J 0.000 claims 1
- 238000013413 tumor xenograft mouse model Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 108010021625 Immunoglobulin Fragments Proteins 0.000 abstract description 22
- 102000008394 Immunoglobulin Fragments Human genes 0.000 abstract description 22
- 150000001413 amino acids Chemical class 0.000 abstract description 19
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 abstract description 18
- 238000012216 screening Methods 0.000 abstract description 13
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 abstract description 7
- 230000027455 binding Effects 0.000 description 137
- 125000003396 thiol group Chemical class [H]S* 0.000 description 91
- 125000005647 linker group Chemical group 0.000 description 75
- 230000009257 reactivity Effects 0.000 description 66
- 108010090804 Streptavidin Proteins 0.000 description 60
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 59
- 239000000562 conjugate Substances 0.000 description 53
- YBJHBAHKTGYVGT-ZKWXMUAHSA-N (+)-Biotin Chemical compound N1C(=O)N[C@@H]2[C@H](CCCCC(=O)O)SC[C@@H]21 YBJHBAHKTGYVGT-ZKWXMUAHSA-N 0.000 description 48
- 230000021615 conjugation Effects 0.000 description 47
- KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Valine Chemical compound CC(C)C(N)C(O)=O KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 41
- DHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycine Chemical compound NCC(O)=O DHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 40
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 39
- 238000003556 assay Methods 0.000 description 33
- KDXKERNSBIXSRK-YFKPBYRVSA-N L-lysine Chemical compound NCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O KDXKERNSBIXSRK-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 32
- KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lysine Natural products NCCCCC(N)C(O)=O KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 32
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 32
- 229920001184 polypeptide Polymers 0.000 description 32
- ROHFNLRQFUQHCH-YFKPBYRVSA-N L-leucine Chemical compound CC(C)C[C@H](N)C(O)=O ROHFNLRQFUQHCH-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 30
- 201000011510 cancer Diseases 0.000 description 30
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 30
- 125000000151 cysteine group Chemical group N[C@@H](CS)C(=O)* 0.000 description 30
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 27
- 108010088751 Albumins Proteins 0.000 description 26
- 102000009027 Albumins Human genes 0.000 description 26
- 108020004414 DNA Proteins 0.000 description 26
- 108010001336 Horseradish Peroxidase Proteins 0.000 description 26
- 229960002685 biotin Drugs 0.000 description 25
- 239000011616 biotin Substances 0.000 description 25
- OUYCCCASQSFEME-QMMMGPOBSA-N L-tyrosine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 OUYCCCASQSFEME-QMMMGPOBSA-N 0.000 description 24
- 235000020958 biotin Nutrition 0.000 description 24
- 102000001301 EGF receptor Human genes 0.000 description 23
- ZDXPYRJPNDTMRX-VKHMYHEASA-N L-glutamine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCC(N)=O ZDXPYRJPNDTMRX-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 23
- 125000003275 alpha amino acid group Chemical group 0.000 description 23
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 23
- 238000002835 absorbance Methods 0.000 description 22
- 239000012634 fragment Substances 0.000 description 22
- 239000000543 intermediate Substances 0.000 description 20
- 238000002965 ELISA Methods 0.000 description 19
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N L-glutamic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCC(O)=O WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 19
- VHJLVAABSRFDPM-QWWZWVQMSA-N dithiothreitol Chemical compound SC[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CS VHJLVAABSRFDPM-QWWZWVQMSA-N 0.000 description 19
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 19
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 19
- CIVGYTYIDWRBQU-UFLZEWODSA-N 5-[(3as,4s,6ar)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanoic acid;pyrrole-2,5-dione Chemical compound O=C1NC(=O)C=C1.N1C(=O)N[C@@H]2[C@H](CCCCC(=O)O)SC[C@@H]21 CIVGYTYIDWRBQU-UFLZEWODSA-N 0.000 description 18
- 108060006698 EGF receptor Proteins 0.000 description 18
- CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N L-aspartic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC(O)=O CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 18
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 17
- 239000003446 ligand Substances 0.000 description 17
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 17
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 16
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 16
- DJQYYYCQOZMCRC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-aminopropane-1,3-dithiol Chemical group SCC(N)CS DJQYYYCQOZMCRC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- DCXYFEDJOCDNAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Asparagine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC(N)=O DCXYFEDJOCDNAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- DCXYFEDJOCDNAF-REOHCLBHSA-N L-asparagine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC(N)=O DCXYFEDJOCDNAF-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 15
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 description 15
- 230000014509 gene expression Effects 0.000 description 15
- 230000035772 mutation Effects 0.000 description 15
- 239000012070 reactive reagent Substances 0.000 description 15
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 description 15
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- 238000012879 PET imaging Methods 0.000 description 14
- 239000002202 Polyethylene glycol Substances 0.000 description 14
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 14
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 14
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 14
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 108091034117 Oligonucleotide Proteins 0.000 description 13
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical compound [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 13
- 125000004429 atom Chemical group 0.000 description 13
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 13
- 239000007850 fluorescent dye Substances 0.000 description 13
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 13
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 13
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 101000701051 Legionella pneumophila Zinc metalloproteinase Proteins 0.000 description 12
- 230000010056 antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity Effects 0.000 description 12
- 230000006287 biotinylation Effects 0.000 description 12
- 238000007413 biotinylation Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 12
- 230000000269 nucleophilic effect Effects 0.000 description 12
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 12
- 210000002966 serum Anatomy 0.000 description 12
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 12
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 11
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 11
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000013612 plasmid Substances 0.000 description 11
- 238000002415 sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 11
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetonitrile Chemical compound CC#N WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 241000283973 Oryctolagus cuniculus Species 0.000 description 10
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)=O MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- LOKCTEFSRHRXRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-I dipotassium trisodium dihydrogen phosphate hydrogen phosphate dichloride Chemical compound P(=O)(O)(O)[O-].[K+].P(=O)(O)([O-])[O-].[Na+].[Na+].[Cl-].[K+].[Cl-].[Na+] LOKCTEFSRHRXRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-I 0.000 description 10
- 239000000499 gel Substances 0.000 description 10
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 10
- 239000002953 phosphate buffered saline Substances 0.000 description 10
- 229920001223 polyethylene glycol Polymers 0.000 description 10
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 10
- WXTMDXOMEHJXQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC(O)=CC=C1O WXTMDXOMEHJXQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- PEEHTFAAVSWFBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Maleimide Chemical compound O=C1NC(=O)C=C1 PEEHTFAAVSWFBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) Chemical compound CCN(C(C)C)C(C)C JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 230000004071 biological effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- 239000000090 biomarker Substances 0.000 description 9
- 239000002738 chelating agent Substances 0.000 description 9
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 9
- 102000052116 epidermal growth factor receptor activity proteins Human genes 0.000 description 9
- 108700015053 epidermal growth factor receptor activity proteins Proteins 0.000 description 9
- 238000004949 mass spectrometry Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000012636 positron electron tomography Methods 0.000 description 9
- 238000000163 radioactive labelling Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 9
- NFGXHKASABOEEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methylethyl 11-methoxy-3,7,11-trimethyl-2,4-dodecadienoate Chemical compound COC(C)(C)CCCC(C)CC=CC(C)=CC(=O)OC(C)C NFGXHKASABOEEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 108091003079 Bovine Serum Albumin Proteins 0.000 description 8
- 241000588724 Escherichia coli Species 0.000 description 8
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 241000699666 Mus <mouse, genus> Species 0.000 description 8
- 241000699670 Mus sp. Species 0.000 description 8
- 229940098773 bovine serum albumin Drugs 0.000 description 8
- 210000000349 chromosome Anatomy 0.000 description 8
- 230000000875 corresponding effect Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000012636 effector Substances 0.000 description 8
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 8
- 125000000524 functional group Chemical group 0.000 description 8
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 8
- YOHYSYJDKVYCJI-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[3-[[6-[3-(trifluoromethyl)anilino]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]phenyl]cyclopropanecarboxamide Chemical compound FC(F)(F)C1=CC=CC(NC=2N=CN=C(NC=3C=C(NC(=O)C4CC4)C=CC=3)C=2)=C1 YOHYSYJDKVYCJI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 8
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 8
- 241000894007 species Species 0.000 description 8
- 239000011550 stock solution Substances 0.000 description 8
- QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-YPZZEJLDSA-N zirconium-89 Chemical compound [89Zr] QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-YPZZEJLDSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 102000000844 Cell Surface Receptors Human genes 0.000 description 7
- 108010001857 Cell Surface Receptors Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 7
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 108010087819 Fc receptors Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 102000009109 Fc receptors Human genes 0.000 description 7
- AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanesulfonic acid Chemical compound CS(O)(=O)=O AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 241001529936 Murinae Species 0.000 description 7
- 108700020796 Oncogene Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000007792 addition Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000001588 bifunctional effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229960000958 deferoxamine Drugs 0.000 description 7
- 229940088598 enzyme Drugs 0.000 description 7
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000000338 in vitro Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000003068 molecular probe Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000002703 mutagenesis Methods 0.000 description 7
- 231100000350 mutagenesis Toxicity 0.000 description 7
- 238000002264 polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis Methods 0.000 description 7
- DGVVWUTYPXICAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N β‐Mercaptoethanol Chemical compound OCCS DGVVWUTYPXICAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 101710132601 Capsid protein Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 101710094648 Coat protein Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 108010047041 Complementarity Determining Regions Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 239000004472 Lysine Substances 0.000 description 6
- 101710125418 Major capsid protein Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 101710141454 Nucleoprotein Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 101710083689 Probable capsid protein Proteins 0.000 description 6
- VMHLLURERBWHNL-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium acetate Chemical compound [Na+].CC([O-])=O VMHLLURERBWHNL-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 6
- 101710120037 Toxin CcdB Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 150000001408 amides Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 239000000611 antibody drug conjugate Substances 0.000 description 6
- 210000000988 bone and bone Anatomy 0.000 description 6
- 238000002866 fluorescence resonance energy transfer Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000002523 gelfiltration Methods 0.000 description 6
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 description 6
- 238000004895 liquid chromatography mass spectrometry Methods 0.000 description 6
- 210000003819 peripheral blood mononuclear cell Anatomy 0.000 description 6
- 238000002823 phage display Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000002600 positron emission tomography Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000000700 radioactive tracer Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000012552 review Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000002741 site-directed mutagenesis Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000001632 sodium acetate Substances 0.000 description 6
- 235000017281 sodium acetate Nutrition 0.000 description 6
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 6
- 102000002260 Alkaline Phosphatase Human genes 0.000 description 5
- 108020004774 Alkaline Phosphatase Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 206010006187 Breast cancer Diseases 0.000 description 5
- 208000026310 Breast neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 5
- 206010009944 Colon cancer Diseases 0.000 description 5
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- XTHFKEDIFFGKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethoxyethane Chemical compound COCCOC XTHFKEDIFFGKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 238000012286 ELISA Assay Methods 0.000 description 5
- 102100021181 Golgi phosphoprotein 3 Human genes 0.000 description 5
- 108091007491 NSP3 Papain-like protease domains Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 239000007983 Tris buffer Substances 0.000 description 5
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 125000003277 amino group Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- 239000011324 bead Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000012512 characterization method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 5
- 231100000433 cytotoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 5
- 230000001472 cytotoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000002330 electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000011068 loading method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000009206 nuclear medicine Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000003285 pharmacodynamic effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000001556 precipitation Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N trifluoroacetic acid Substances OC(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tris Chemical compound OCC(N)(CO)CO LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- ASOKPJOREAFHNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-Hydroxybenzotriazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2N(O)N=NC2=C1 ASOKPJOREAFHNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- VHYFNPMBLIVWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-Dimethylaminopyridine Chemical compound CN(C)C1=CC=NC=C1 VHYFNPMBLIVWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N Ascorbic acid Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1OC(=O)C(O)=C1O CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 241000699802 Cricetulus griseus Species 0.000 description 4
- QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dicylcohexylcarbodiimide Chemical compound C1CCCCC1N=C=NC1CCCCC1 QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- KCXVZYZYPLLWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N EDTA Chemical compound OC(=O)CN(CC(O)=O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O KCXVZYZYPLLWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 102100031968 Ephrin type-B receptor 2 Human genes 0.000 description 4
- FXHOOIRPVKKKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylacetamide Chemical compound CN(C)C(C)=O FXHOOIRPVKKKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910019142 PO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenol Natural products OC1=CC=CC=C1 ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229920003171 Poly (ethylene oxide) Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 241000700159 Rattus Species 0.000 description 4
- 102100029981 Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 101710100963 Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 Proteins 0.000 description 4
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 4
- JLCPHMBAVCMARE-UHFFFAOYSA-N [3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[5-(2-amino-6-oxo-1H-purin-9-yl)-3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[5-(2-amino-6-oxo-1H-purin-9-yl)-3-[[5-(2-amino-6-oxo-1H-purin-9-yl)-3-hydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(5-methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(5-methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(5-methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(5-methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methyl [5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-yl] hydrogen phosphate Polymers Cc1cn(C2CC(OP(O)(=O)OCC3OC(CC3OP(O)(=O)OCC3OC(CC3O)n3cnc4c3nc(N)[nH]c4=O)n3cnc4c3nc(N)[nH]c4=O)C(COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3CO)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3ccc(N)nc3=O)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3ccc(N)nc3=O)n3ccc(N)nc3=O)n3ccc(N)nc3=O)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3cc(C)c(=O)[nH]c3=O)n3cc(C)c(=O)[nH]c3=O)n3ccc(N)nc3=O)n3cc(C)c(=O)[nH]c3=O)n3cnc4c3nc(N)[nH]c4=O)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)O2)c(=O)[nH]c1=O JLCPHMBAVCMARE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229940049595 antibody-drug conjugate Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 230000006907 apoptotic process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000004422 calculation algorithm Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000013522 chelant Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000009920 chelation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000004440 column chromatography Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000010668 complexation reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000001086 cytosolic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000003745 diagnosis Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000539 dimer Substances 0.000 description 4
- 150000002019 disulfides Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 4
- GNBHRKFJIUUOQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluorescein Chemical compound O1C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2C21C1=CC=C(O)C=C1OC1=CC(O)=CC=C21 GNBHRKFJIUUOQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000004927 fusion Effects 0.000 description 4
- 108020001507 fusion proteins Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 102000037865 fusion proteins Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 229960005219 gentisic acid Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 230000036541 health Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000008241 heterogeneous mixture Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000004128 high performance liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000002998 immunogenetic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229940072221 immunoglobulins Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000011065 in-situ storage Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000011534 incubation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 4
- 125000005439 maleimidyl group Chemical group C1(C=CC(N1*)=O)=O 0.000 description 4
- 239000003550 marker Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000003094 microcapsule Substances 0.000 description 4
- 210000001672 ovary Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 239000000546 pharmaceutical excipient Substances 0.000 description 4
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K phosphate Chemical compound [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 4
- 239000010452 phosphate Substances 0.000 description 4
- 150000008300 phosphoramidites Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 description 4
- QELSKZZBTMNZEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylparaben Chemical compound CCCOC(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 QELSKZZBTMNZEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000009145 protein modification Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000011363 radioimmunotherapy Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- UMGDCJDMYOKAJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiourea Chemical compound NC(N)=S UMGDCJDMYOKAJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 4
- 241001515965 unidentified phage Species 0.000 description 4
- 239000013598 vector Substances 0.000 description 4
- BDNKZNFMNDZQMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-diisopropylcarbodiimide Chemical compound CC(C)N=C=NC(C)C BDNKZNFMNDZQMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 125000004042 4-aminobutyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])[H] 0.000 description 3
- 101100067974 Arabidopsis thaliana POP2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 3
- WVDDGKGOMKODPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzyl alcohol Chemical compound OCC1=CC=CC=C1 WVDDGKGOMKODPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 102000004506 Blood Proteins Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108010017384 Blood Proteins Proteins 0.000 description 3
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-K Citrate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CC(O)(CC([O-])=O)C([O-])=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 3
- 102100025698 Cytosolic carboxypeptidase 4 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- BWGNESOTFCXPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dihydrogen disulfide Chemical compound SS BWGNESOTFCXPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 101150029707 ERBB2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 3
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 102100027285 Fanconi anemia group B protein Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 241000724791 Filamentous phage Species 0.000 description 3
- GYHNNYVSQQEPJS-YPZZEJLDSA-N Gallium-68 Chemical compound [68Ga] GYHNNYVSQQEPJS-YPZZEJLDSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000004471 Glycine Substances 0.000 description 3
- 101000932590 Homo sapiens Cytosolic carboxypeptidase 4 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 101100118549 Homo sapiens EGFR gene Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 101001064462 Homo sapiens Ephrin type-B receptor 2 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 101001033003 Mus musculus Granzyme F Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 108010021466 Mutant Proteins Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 102000008300 Mutant Proteins Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108091005804 Peptidases Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 102000035195 Peptidases Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 101710100969 Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 102100029986 Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 101100123851 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) HER1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 108010071390 Serum Albumin Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 102000007562 Serum Albumin Human genes 0.000 description 3
- PZBFGYYEXUXCOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N TCEP Chemical compound OC(=O)CCP(CCC(O)=O)CCC(O)=O PZBFGYYEXUXCOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 125000002777 acetyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 3
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000008186 active pharmaceutical agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000010171 animal model Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001188 anti-phage Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000007900 aqueous suspension Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000001580 bacterial effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000006664 bond formation reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000004113 cell culture Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004663 cell proliferation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000015861 cell surface binding Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000007385 chemical modification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 210000004978 chinese hamster ovary cell Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 239000003593 chromogenic compound Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000007859 condensation product Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000001268 conjugating effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000003431 cross linking reagent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229940127089 cytotoxic agent Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 239000002254 cytotoxic agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000012217 deletion Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000037430 deletion Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000011033 desalting Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 230000029087 digestion Effects 0.000 description 3
- BGRWYRAHAFMIBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N diisopropylcarbodiimide Natural products CC(C)NC(=O)NC(C)C BGRWYRAHAFMIBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000975 dye Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000002255 enzymatic effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 235000019439 ethyl acetate Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 3
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 238000000855 fermentation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004151 fermentation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229940022353 herceptin Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 238000013537 high throughput screening Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000001802 infusion Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000001990 intravenous administration Methods 0.000 description 3
- XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-OIOBTWANSA-N iodane Chemical compound [124IH] XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-OIOBTWANSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000004811 liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 3
- 125000003588 lysine group Chemical group [H]N([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(N([H])[H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 3
- 238000002595 magnetic resonance imaging Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 3
- 210000004962 mammalian cell Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 230000001404 mediated effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 3
- HBAYEVATSBINBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[5-[acetyl(hydroxy)amino]pentyl]-n'-hydroxy-n'-[5-[[4-[hydroxy-[5-[(4-isothiocyanatophenyl)carbamothioylamino]pentyl]amino]-4-oxobutanoyl]amino]pentyl]butanediamide Chemical compound CC(=O)N(O)CCCCCNC(=O)CCC(=O)N(O)CCCCCNC(=O)CCC(=O)N(O)CCCCCNC(=S)NC1=CC=C(N=C=S)C=C1 HBAYEVATSBINBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 231100000252 nontoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 3
- 230000003000 nontoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 102000039446 nucleic acids Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108020004707 nucleic acids Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 230000036961 partial effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000008188 pellet Substances 0.000 description 3
- 102000013415 peroxidase activity proteins Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108040007629 peroxidase activity proteins Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920000036 polyvinylpyrrolidone Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 235000013855 polyvinylpyrrolidone Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 230000010076 replication Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 3
- PYWVYCXTNDRMGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N rhodamine B Chemical compound [Cl-].C=12C=CC(=[N+](CC)CC)C=C2OC2=CC(N(CC)CC)=CC=C2C=1C1=CC=CC=C1C(O)=O PYWVYCXTNDRMGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 102220206292 rs1057521851 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 239000007974 sodium acetate buffer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910000029 sodium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229940074404 sodium succinate Drugs 0.000 description 3
- ZDQYSKICYIVCPN-UHFFFAOYSA-L sodium succinate (anhydrous) Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C(=O)CCC([O-])=O ZDQYSKICYIVCPN-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 3
- 239000007790 solid phase Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000008362 succinate buffer Substances 0.000 description 3
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L succinate(2-) Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CCC([O-])=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 3
- 239000000375 suspending agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000004885 tandem mass spectrometry Methods 0.000 description 3
- 150000003573 thiols Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 230000001052 transient effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 210000004881 tumor cell Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 125000002987 valine group Chemical group [H]N([H])C([H])(C(*)=O)C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 3
- 230000003612 virological effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 150000003754 zirconium Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- PUPZLCDOIYMWBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N (+/-)-1,3-Butanediol Chemical compound CC(O)CCO PUPZLCDOIYMWBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VRDGQQTWSGDXCU-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) 2-iodoacetate Chemical compound ICC(=O)ON1C(=O)CCC1=O VRDGQQTWSGDXCU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GEYOCULIXLDCMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-phenylenediamine Chemical compound NC1=CC=CC=C1N GEYOCULIXLDCMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XQUPVDVFXZDTLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[4-[[4-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)phenyl]methyl]phenyl]pyrrole-2,5-dione Chemical compound O=C1C=CC(=O)N1C(C=C1)=CC=C1CC1=CC=C(N2C(C=CC2=O)=O)C=C1 XQUPVDVFXZDTLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Aminoethan-1-ol Chemical compound NCCO HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JKMHFZQWWAIEOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethanesulfonic acid Chemical compound OCC[NH+]1CCN(CCS([O-])(=O)=O)CC1 JKMHFZQWWAIEOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LSTRKXWIZZZYAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-bromoacetyl bromide Chemical compound BrCC(Br)=O LSTRKXWIZZZYAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PBVAJRFEEOIAGW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-[bis(2-carboxyethyl)phosphanyl]propanoic acid;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.OC(=O)CCP(CCC(O)=O)CCC(O)=O PBVAJRFEEOIAGW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acetate Chemical compound CC([O-])=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 108090000672 Annexin A5 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000004121 Annexin A5 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100027052 Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type-1B Human genes 0.000 description 2
- CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bromide Chemical compound [Br-] CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 241000283707 Capra Species 0.000 description 2
- 108020004705 Codon Proteins 0.000 description 2
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-QTVWNMPRSA-N D-mannopyranose Chemical compound OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-QTVWNMPRSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102100020743 Dipeptidase 1 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- AOJJSUZBOXZQNB-TZSSRYMLSA-N Doxorubicin Chemical compound O([C@H]1C[C@@](O)(CC=2C(O)=C3C(=O)C=4C=CC=C(C=4C(=O)C3=C(O)C=21)OC)C(=O)CO)[C@H]1C[C@H](N)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)O1 AOJJSUZBOXZQNB-TZSSRYMLSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241001524679 Escherichia virus M13 Species 0.000 description 2
- IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylene oxide Chemical compound C1CO1 IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 101150064015 FAS gene Proteins 0.000 description 2
- VTLYFUHAOXGGBS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fe3+ Chemical compound [Fe+3] VTLYFUHAOXGGBS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N Glucose Natural products OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000007821 HATU Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007995 HEPES buffer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 101000851181 Homo sapiens Epidermal growth factor receptor Proteins 0.000 description 2
- OAKJQQAXSVQMHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrazine Chemical compound NN OAKJQQAXSVQMHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 108010000817 Leuprolide Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 241000699660 Mus musculus Species 0.000 description 2
- 101100327295 Mus musculus Cd22 gene Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101100335081 Mus musculus Flt3 gene Proteins 0.000 description 2
- QPCDCPDFJACHGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-bis{2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl}glycine Chemical compound OC(=O)CN(CC(O)=O)CCN(CC(=O)O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O QPCDCPDFJACHGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NQTADLQHYWFPDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Hydroxysuccinimide Chemical compound ON1C(=O)CCC1=O NQTADLQHYWFPDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RHGKLRLOHDJJDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ndelta-carbamoyl-DL-ornithine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CCCNC(N)=O RHGKLRLOHDJJDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 206010029260 Neuroblastoma Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 108091005461 Nucleic proteins Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 208000008589 Obesity Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 102000004316 Oxidoreductases Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108090000854 Oxidoreductases Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 108010067902 Peptide Library Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 239000004793 Polystyrene Substances 0.000 description 2
- 101710193132 Pre-hexon-linking protein VIII Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 239000004365 Protease Substances 0.000 description 2
- 241000283984 Rodentia Species 0.000 description 2
- 108091006207 SLC-Transporter Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000037054 SLC-Transporter Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 239000000589 Siderophore Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229930006000 Sucrose Natural products 0.000 description 2
- CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N Sucrose Chemical compound O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Urea Natural products NC(N)=O XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000005789 Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010019530 Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors Proteins 0.000 description 2
- DPXJVFZANSGRMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetic acid;2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal;sodium Chemical compound [Na].CC(O)=O.OCC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C=O DPXJVFZANSGRMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000001042 affinity chromatography Methods 0.000 description 2
- 101150115889 al gene Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 150000001299 aldehydes Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000029936 alkylation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005804 alkylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000012080 ambient air Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001093 anti-cancer Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002494 anti-cea effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000259 anti-tumor effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000006708 antioxidants Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010323 ascorbic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000011668 ascorbic acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000005936 beta-Galactosidase Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010005774 beta-Galactosidase Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 238000001815 biotherapy Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910021538 borax Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000001720 carbohydrates Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 235000014633 carbohydrates Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 125000003178 carboxy group Chemical group [H]OC(*)=O 0.000 description 2
- 238000012219 cassette mutagenesis Methods 0.000 description 2
- YCIMNLLNPGFGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N catechol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1O YCIMNLLNPGFGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000030833 cell death Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000006037 cell lysis Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001413 cellular effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229960005395 cetuximab Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 238000003776 cleavage reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000024203 complement activation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000004540 complement-dependent cytotoxicity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000356 contaminant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910000365 copper sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- ARUVKPQLZAKDPS-UHFFFAOYSA-L copper(II) sulfate Chemical compound [Cu+2].[O-][S+2]([O-])([O-])[O-] ARUVKPQLZAKDPS-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 229910000366 copper(II) sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000004132 cross linking Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003405 delayed action preparation Substances 0.000 description 2
- FAMRKDQNMBBFBR-BQYQJAHWSA-N diethyl azodicarboxylate Substances CCOC(=O)\N=N\C(=O)OCC FAMRKDQNMBBFBR-BQYQJAHWSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HPNMFZURTQLUMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethylamine Chemical compound CCNCC HPNMFZURTQLUMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000002050 diffraction method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229960005156 digoxin Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000002228 disulfide group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 239000002552 dosage form Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004980 dosimetry Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003828 downregulation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000013604 expression vector Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000001943 fluorescence-activated cell sorting Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003117 fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001641 gel filtration chromatography Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008570 general process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000008103 glucose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000005179 haloacetyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 210000004408 hybridoma Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical class [H]* 0.000 description 2
- XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen iodide Chemical compound I XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NPZTUJOABDZTLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydroxybenzotriazole Substances O=C1C=CC=C2NNN=C12 NPZTUJOABDZTLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229960001001 ibritumomab tiuxetan Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 239000012216 imaging agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001900 immune effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010348 incorporation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000006698 induction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 208000015181 infectious disease Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000002458 infectious effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003834 intracellular effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- PGLTVOMIXTUURA-UHFFFAOYSA-N iodoacetamide Chemical compound NC(=O)CI PGLTVOMIXTUURA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000002540 isothiocyanates Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 210000000265 leukocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- RGLRXNKKBLIBQS-XNHQSDQCSA-N leuprolide acetate Chemical compound CC(O)=O.CCNC(=O)[C@@H]1CCCN1C(=O)[C@H](CCCNC(N)=N)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](CC=1C2=CC=CC=C2NC=1)NC(=O)[C@H](CC=1N=CNC=1)NC(=O)[C@H]1NC(=O)CC1)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 RGLRXNKKBLIBQS-XNHQSDQCSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 108020001756 ligand binding domains Proteins 0.000 description 2
- RLSSMJSEOOYNOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N m-cresol Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC(O)=C1 RLSSMJSEOOYNOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000002609 medium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002207 metabolite Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910021645 metal ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000004005 microsphere Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000010369 molecular cloning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229940125645 monoclonal antibody drug Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 210000001616 monocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- OWIUPIRUAQMTTK-UHFFFAOYSA-M n-aminocarbamate Chemical compound NNC([O-])=O OWIUPIRUAQMTTK-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 210000000822 natural killer cell Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 230000009826 neoplastic cell growth Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000000440 neutrophil Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000000346 nonvolatile oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000011580 nude mouse model Methods 0.000 description 2
- 235000020824 obesity Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N oleic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(O)=O ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 150000002894 organic compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 235000006408 oxalic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000007800 oxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000002923 oximes Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000007911 parenteral administration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001575 pathological effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000037361 pathway Effects 0.000 description 2
- AQIXEPGDORPWBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N pentan-3-ol Chemical compound CCC(O)CC AQIXEPGDORPWBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000001151 peptidyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 229920002223 polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000001267 polyvinylpyrrolidone Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002243 precursor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003755 preservative agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000005180 public health Effects 0.000 description 2
- CWZZGQMHJJMMPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyrrole-2,5-dione;zirconium Chemical compound [Zr].O=C1NC(=O)C=C1 CWZZGQMHJJMMPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000003156 radioimmunoprecipitation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012217 radiopharmaceutical Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229940121896 radiopharmaceutical Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 230000002799 radiopharmaceutical effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000035484 reaction time Effects 0.000 description 2
- 102000037983 regulatory factors Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108091008025 regulatory factors Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 125000006853 reporter group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- GHMLBKRAJCXXBS-UHFFFAOYSA-N resorcinol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC(O)=C1 GHMLBKRAJCXXBS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 206010039073 rheumatoid arthritis Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 2
- DFEYYRMXOJXZRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N sevoflurane Chemical compound FCOC(C(F)(F)F)C(F)(F)F DFEYYRMXOJXZRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229960002078 sevoflurane Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 230000011664 signaling Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000002603 single-photon emission computed tomography Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003998 size exclusion chromatography high performance liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 2
- 235000010339 sodium tetraborate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000012453 solvate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000010561 standard procedure Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007920 subcutaneous administration Methods 0.000 description 2
- KZNICNPSHKQLFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N succinimide Chemical group O=C1CCC(=O)N1 KZNICNPSHKQLFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000005720 sucrose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000000446 sulfanediyl group Chemical group *S* 0.000 description 2
- 238000002198 surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004083 survival effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013268 sustained release Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012730 sustained-release form Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003826 tablet Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 231100001274 therapeutic index Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 238000004809 thin layer chromatography Methods 0.000 description 2
- SRVJKTDHMYAMHA-WUXMJOGZSA-N thioacetazone Chemical compound CC(=O)NC1=CC=C(\C=N\NC(N)=S)C=C1 SRVJKTDHMYAMHA-WUXMJOGZSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003053 toxin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 231100000765 toxin Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 108700012359 toxins Proteins 0.000 description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-butenedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=CC(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000027257 transmembrane receptors Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108091008578 transmembrane receptors Proteins 0.000 description 2
- BSVBQGMMJUBVOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N trisodium borate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[O-]B([O-])[O-] BSVBQGMMJUBVOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000007306 turnover Effects 0.000 description 2
- OUYCCCASQSFEME-UHFFFAOYSA-N tyrosine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 OUYCCCASQSFEME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004474 valine Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003981 vehicle Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000003462 vein Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000001262 western blot Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000080 wetting agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- HDTRYLNUVZCQOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N α-D-glucopyranosyl-α-D-glucopyranoside Natural products OC1C(O)C(O)C(CO)OC1OC1C(O)C(O)C(O)C(CO)O1 HDTRYLNUVZCQOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JKHVDAUOODACDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) 3-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)propanoate Chemical compound O=C1CCC(=O)N1OC(=O)CCN1C(=O)C=CC1=O JKHVDAUOODACDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PVGATNRYUYNBHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) 4-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)butanoate Chemical compound O=C1CCC(=O)N1OC(=O)CCCN1C(=O)C=CC1=O PVGATNRYUYNBHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BQWBEDSJTMWJAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) 4-[(2-iodoacetyl)amino]benzoate Chemical compound C1=CC(NC(=O)CI)=CC=C1C(=O)ON1C(=O)CCC1=O BQWBEDSJTMWJAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PMJWDPGOWBRILU-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) 4-[4-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)phenyl]butanoate Chemical compound O=C1CCC(=O)N1OC(=O)CCCC(C=C1)=CC=C1N1C(=O)C=CC1=O PMJWDPGOWBRILU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VLARLSIGSPVYHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) 6-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)hexanoate Chemical compound O=C1CCC(=O)N1OC(=O)CCCCCN1C(=O)C=CC1=O VLARLSIGSPVYHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WCMOHMXWOOBVMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) 6-[3-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)propanoylamino]hexanoate Chemical compound O=C1CCC(=O)N1OC(=O)CCCCCNC(=O)CCN1C(=O)C=CC1=O WCMOHMXWOOBVMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IHVODYOQUSEYJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) 6-[[4-[(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)methyl]cyclohexanecarbonyl]amino]hexanoate Chemical compound O=C1CCC(=O)N1OC(=O)CCCCCNC(=O)C(CC1)CCC1CN1C(=O)C=CC1=O IHVODYOQUSEYJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LNAZSHAWQACDHT-XIYTZBAFSA-N (2r,3r,4s,5r,6s)-4,5-dimethoxy-2-(methoxymethyl)-3-[(2s,3r,4s,5r,6r)-3,4,5-trimethoxy-6-(methoxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-6-[(2r,3r,4s,5r,6r)-4,5,6-trimethoxy-2-(methoxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxyoxane Chemical compound CO[C@@H]1[C@@H](OC)[C@H](OC)[C@@H](COC)O[C@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](OC)[C@@H](OC)[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](OC)[C@H](OC)O[C@@H]2COC)OC)O[C@@H]1COC LNAZSHAWQACDHT-XIYTZBAFSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XMQUEQJCYRFIQS-YFKPBYRVSA-N (2s)-2-amino-5-ethoxy-5-oxopentanoic acid Chemical compound CCOC(=O)CC[C@H](N)C(O)=O XMQUEQJCYRFIQS-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LTDQGCFMTVHZKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N (4-bromophenyl)-(4,6-dimethoxy-3-methyl-1-benzofuran-2-yl)methanone Chemical compound O1C2=CC(OC)=CC(OC)=C2C(C)=C1C(=O)C1=CC=C(Br)C=C1 LTDQGCFMTVHZKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GHOKWGTUZJEAQD-ZETCQYMHSA-N (D)-(+)-Pantothenic acid Chemical compound OCC(C)(C)[C@@H](O)C(=O)NCCC(O)=O GHOKWGTUZJEAQD-ZETCQYMHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WRIDQFICGBMAFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N (E)-8-Octadecenoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCC(O)=O WRIDQFICGBMAFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-GSVOUGTGSA-N (R)-(-)-Propylene glycol Chemical compound C[C@@H](O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-GSVOUGTGSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003088 (fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- YYMCVDNIIFNDJK-XFQWXJFMSA-N (z)-1-(3-fluorophenyl)-n-[(z)-(3-fluorophenyl)methylideneamino]methanimine Chemical compound FC1=CC=CC(\C=N/N=C\C=2C=C(F)C=CC=2)=C1 YYMCVDNIIFNDJK-XFQWXJFMSA-N 0.000 description 1
- TZCPCKNHXULUIY-RGULYWFUSA-N 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoserine Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@H](COP(O)(=O)OC[C@H](N)C(O)=O)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC TZCPCKNHXULUIY-RGULYWFUSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LMDZBCPBFSXMTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide Substances CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C LMDZBCPBFSXMTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SGVWDRVQIYUSRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[2-[2-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)ethyldisulfanyl]ethyl]pyrrole-2,5-dione Chemical compound O=C1C=CC(=O)N1CCSSCCN1C(=O)C=CC1=O SGVWDRVQIYUSRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DIYPCWKHSODVAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[3-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)benzoyl]oxy-2,5-dioxopyrrolidine-3-sulfonic acid Chemical compound O=C1C(S(=O)(=O)O)CC(=O)N1OC(=O)C1=CC=CC(N2C(C=CC2=O)=O)=C1 DIYPCWKHSODVAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CULQNACJHGHAER-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[4-[(2-iodoacetyl)amino]benzoyl]oxy-2,5-dioxopyrrolidine-3-sulfonic acid Chemical compound O=C1C(S(=O)(=O)O)CC(=O)N1OC(=O)C1=CC=C(NC(=O)CI)C=C1 CULQNACJHGHAER-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IXPNQXFRVYWDDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methyl-2,4-dioxo-1,3-diazinane-5-carboximidamide Chemical compound CN1CC(C(N)=N)C(=O)NC1=O IXPNQXFRVYWDDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IIZPXYDJLKNOIY-JXPKJXOSSA-N 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@H](COP([O-])(=O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OC(=O)CCC\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCC IIZPXYDJLKNOIY-JXPKJXOSSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VOXZDWNPVJITMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 13-methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol Chemical compound OC1=CC=C2C3CCC(C)(C(CC4)O)C4C3CCC2=C1 VOXZDWNPVJITMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HRBGUGQWTMBDTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,4-tri(propan-2-yl)benzenesulfonyl chloride Chemical compound CC(C)C1=CC=C(S(Cl)(=O)=O)C(C(C)C)=C1C(C)C HRBGUGQWTMBDTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LDGWQMRUWMSZIU-LQDDAWAPSA-M 2,3-bis[(z)-octadec-9-enoxy]propyl-trimethylazanium;chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCCOCC(C[N+](C)(C)C)OCCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC LDGWQMRUWMSZIU-LQDDAWAPSA-M 0.000 description 1
- SNTWKPAKVQFCCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-dihydro-1h-triazole Chemical compound N1NC=CN1 SNTWKPAKVQFCCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KGLPWQKSKUVKMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione Chemical class C1=CC=C2C(=O)NNC(=O)C2=C1 KGLPWQKSKUVKMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LSYXXLMBRSSBGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,4,6-tris(hydroxymethyl)phenol Chemical compound OCC1=CC(CO)=C(O)C(CO)=C1 LSYXXLMBRSSBGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KUMMBDBTERQYCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-bis(hydroxymethyl)-4-methylphenol Chemical compound CC1=CC(CO)=C(O)C(CO)=C1 KUMMBDBTERQYCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QEVGZEDELICMKH-UHFFFAOYSA-L 2-(carboxylatomethoxy)acetate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)COCC([O-])=O QEVGZEDELICMKH-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- FALRKNHUBBKYCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(chloromethyl)pyridine-3-carbonitrile Chemical group ClCC1=NC=CC=C1C#N FALRKNHUBBKYCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FZDFGHZZPBUTGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[[2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]-3-(4-isothiocyanatophenyl)propyl]-[2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]propyl]amino]acetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CN(CC(O)=O)C(C)CN(CC(O)=O)CC(N(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O)CC1=CC=C(N=C=S)C=C1 FZDFGHZZPBUTGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QDGAVODICPCDMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-amino-3-[3-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phenyl]propanoic acid Chemical group OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CC=CC(N(CCCl)CCCl)=C1 QDGAVODICPCDMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JUIKUQOUMZUFQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-bromoacetamide Chemical compound NC(=O)CBr JUIKUQOUMZUFQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NEAQRZUHTPSBBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-7-nitro-4h-isoquinolin-1-one Chemical compound C1=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C2C(=O)N(O)C(C)(C)CC2=C1 NEAQRZUHTPSBBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003903 2-propenyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])=C([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- KGIGUEBEKRSTEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-vinylpyridine Chemical compound C=CC1=CC=CC=N1 KGIGUEBEKRSTEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LQJBNNIYVWPHFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 20:1omega9c fatty acid Natural products CCCCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O LQJBNNIYVWPHFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KIUMMUBSPKGMOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,3'-Dithiobis(6-nitrobenzoic acid) Chemical group C1=C([N+]([O-])=O)C(C(=O)O)=CC(SSC=2C=C(C(=CC=2)[N+]([O-])=O)C(O)=O)=C1 KIUMMUBSPKGMOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FPQQSJJWHUJYPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(dimethylamino)propyliminomethylidene-ethylazanium;chloride Chemical compound Cl.CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C FPQQSJJWHUJYPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HVCOBJNICQPDBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-[3-[3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl)oxyoxan-2-yl]oxydecanoyloxy]decanoic acid;hydrate Chemical compound O.OC1C(OC(CC(=O)OC(CCCCCCC)CC(O)=O)CCCCCCC)OC(C)C(O)C1OC1C(O)C(O)C(O)C(C)O1 HVCOBJNICQPDBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 3-carboxy-2,3-dihydroxypropanoate Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)C(O)C([O-])=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- SFYDWLYPIXHPML-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-nitro-1-(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)sulfonyl-1,2,4-triazole Chemical compound CC1=CC(C)=CC(C)=C1S(=O)(=O)N1N=C([N+]([O-])=O)N=C1 SFYDWLYPIXHPML-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UPMLOUAZCHDJJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4'-Diphenylmethane Diisocyanate Chemical compound C1=CC(N=C=O)=CC=C1CC1=CC=C(N=C=O)C=C1 UPMLOUAZCHDJJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NCPQROHLJFARLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)butanoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCCN1C(=O)C=CC1=O NCPQROHLJFARLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OBWSOTREAMFOCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(4-amino-3,5-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethylaniline;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.CC1=C(N)C(C)=CC(C=2C=C(C)C(N)=C(C)C=2)=C1 OBWSOTREAMFOCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XZKIHKMTEMTJQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-Nitrophenyl Phosphate Chemical compound OP(O)(=O)OC1=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1 XZKIHKMTEMTJQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QFVHZQCOUORWEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[(4-anilino-5-sulfonaphthalen-1-yl)diazenyl]-5-hydroxynaphthalene-2,7-disulfonic acid Chemical compound C=12C(O)=CC(S(O)(=O)=O)=CC2=CC(S(O)(=O)=O)=CC=1N=NC(C1=CC=CC(=C11)S(O)(=O)=O)=CC=C1NC1=CC=CC=C1 QFVHZQCOUORWEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZMRMMAOBSFSXLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[4-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)phenyl]butanehydrazide Chemical compound C1=CC(CCCC(=O)NN)=CC=C1N1C(=O)C=CC1=O ZMRMMAOBSFSXLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960000549 4-dimethylaminophenol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- DNXDWMHPTVQBIP-ZQIUZPCESA-N 5-[(3as,4s,6ar)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]-n-[6-[(2-iodoacetyl)amino]hexyl]pentanamide Chemical compound N1C(=O)N[C@@H]2[C@H](CCCCC(=O)NCCCCCCNC(=O)CI)SC[C@@H]21 DNXDWMHPTVQBIP-ZQIUZPCESA-N 0.000 description 1
- QLPHBNRMJLFRGO-YDHSSHFGSA-N 5-[(3as,4s,6ar)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]-n-[6-[3-(pyridin-2-yldisulfanyl)propanoylamino]hexyl]pentanamide Chemical compound C([C@H]1[C@H]2NC(=O)N[C@H]2CS1)CCCC(=O)NCCCCCCNC(=O)CCSSC1=CC=CC=N1 QLPHBNRMJLFRGO-YDHSSHFGSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NJYVEMPWNAYQQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-carboxyfluorescein Chemical compound C12=CC=C(O)C=C2OC2=CC(O)=CC=C2C21OC(=O)C1=CC(C(=O)O)=CC=C21 NJYVEMPWNAYQQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BZTDTCNHAFUJOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-carboxyfluorescein Chemical compound C12=CC=C(O)C=C2OC2=CC(O)=CC=C2C11OC(=O)C2=CC=C(C(=O)O)C=C21 BZTDTCNHAFUJOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102100031126 6-phosphogluconolactonase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010029731 6-phosphogluconolactonase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-(1-cyclopropylpyrazol-4-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl]-3-methyl-3,8-diazabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-2-one Chemical class C1(CC1)N1N=CC(=C1)C1=NNC2=C1N=C(N=C2)N1C2C(N(CC1CC2)C)=O HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QSBYPNXLFMSGKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-Heptadecensaeure Natural products CCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O QSBYPNXLFMSGKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 244000215068 Acacia senegal Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000006491 Acacia senegal Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920000936 Agarose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O Ammonium Chemical compound [NH4+] QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 1
- 102100021569 Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101000843904 Arabidopsis thaliana Bifunctional phosphatase IMPL2, chloroplastic Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000004475 Arginine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241000416162 Astragalus gummifer Species 0.000 description 1
- 208000023275 Autoimmune disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108090001008 Avidin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101710187595 B-cell receptor CD22 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100024222 B-lymphocyte antigen CD19 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102100022005 B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 238000011729 BALB/c nude mouse Methods 0.000 description 1
- 241000894006 Bacteria Species 0.000 description 1
- 108090000363 Bacterial Luciferases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000001733 Basic Amino Acid Transport Systems Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010015087 Basic Amino Acid Transport Systems Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010051728 Bone erosion Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000283690 Bos taurus Species 0.000 description 1
- 101710140080 Brevican core protein Proteins 0.000 description 1
- FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butyric acid Natural products CCCC(O)=O FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UGEVPPINYSCSQY-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCC(NCCCCCN(C(CCC(NCCCCCN(C(CCC(NCCCCCN(C(C)=O)O)=O)=O)O)=O)=O)O)=O Chemical compound CCC(NCCCCCN(C(CCC(NCCCCCN(C(CCC(NCCCCCN(C(C)=O)O)=O)=O)O)=O)=O)O)=O UGEVPPINYSCSQY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000017420 CD3 protein, epsilon/gamma/delta subunit Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108050005493 CD3 protein, epsilon/gamma/delta subunit Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101150013553 CD40 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010021064 CTLA-4 Antigen Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 229940045513 CTLA4 antagonist Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 101710205625 Capsid protein p24 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-NJFSPNSNSA-N Carbon-14 Chemical compound [14C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-NJFSPNSNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000003952 Caspase 3 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000397 Caspase 3 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010067225 Cell Adhesion Molecules Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000016289 Cell Adhesion Molecules Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 241000282693 Cercopithecidae Species 0.000 description 1
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M Chloride anion Chemical compound [Cl-] VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 208000030808 Clear cell renal carcinoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000001333 Colorectal Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229920002785 Croscarmellose sodium Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 102000036364 Cullin Ring E3 Ligases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102000004127 Cytokines Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000695 Cytokines Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100039498 Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102100037579 D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N D-Glucitol Natural products OC[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IGXWBGJHJZYPQS-SSDOTTSWSA-N D-Luciferin Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@H]1CSC(C=2SC3=CC=C(O)C=C3N=2)=N1 IGXWBGJHJZYPQS-SSDOTTSWSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N D-Mannitol Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DSLZVSRJTYRBFB-LLEIAEIESA-N D-glucaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O DSLZVSRJTYRBFB-LLEIAEIESA-N 0.000 description 1
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-JGWLITMVSA-N D-glucitol Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-JGWLITMVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-M D-gluconate Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C([O-])=O RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- AEMOLEFTQBMNLQ-AQKNRBDQSA-N D-glucopyranuronic acid Chemical compound OC1O[C@H](C(O)=O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O AEMOLEFTQBMNLQ-AQKNRBDQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000053602 DNA Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 239000003298 DNA probe Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001712 DNA sequencing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 102000016928 DNA-directed DNA polymerase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010014303 DNA-directed DNA polymerase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- CYCGRDQQIOGCKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dehydro-luciferin Natural products OC(=O)C1=CSC(C=2SC3=CC(O)=CC=C3N=2)=N1 CYCGRDQQIOGCKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004375 Dextrin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001353 Dextrin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N Dextrotartaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LTMHDMANZUZIPE-AMTYYWEZSA-N Digoxin Natural products O([C@H]1[C@H](C)O[C@H](O[C@@H]2C[C@@H]3[C@@](C)([C@@H]4[C@H]([C@]5(O)[C@](C)([C@H](O)C4)[C@H](C4=CC(=O)OC4)CC5)CC3)CC2)C[C@@H]1O)[C@H]1O[C@H](C)[C@@H](O[C@H]2O[C@@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C2)[C@@H](O)C1 LTMHDMANZUZIPE-AMTYYWEZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 101100285518 Drosophila melanogaster how gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 229910052693 Europium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 108010007457 Extracellular Signal-Regulated MAP Kinases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108050001049 Extracellular proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108090000331 Firefly luciferases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- BJGNCJDXODQBOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fivefly Luciferin Natural products OC(=O)C1CSC(C=2SC3=CC(O)=CC=C3N=2)=N1 BJGNCJDXODQBOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-M Formate Chemical compound [O-]C=O BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N Fumaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C\C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010015133 Galactose oxidase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000002464 Galactosidases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010093031 Galactosidases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010010803 Gelatin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010073178 Glucan 1,4-alpha-Glucosidase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100022624 Glucoamylase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 239000004366 Glucose oxidase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108010015776 Glucose oxidase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010018962 Glucosephosphate Dehydrogenase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- ZWZWYGMENQVNFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerophosphorylserin Natural products OC(=O)C(N)COP(O)(=O)OCC(O)CO ZWZWYGMENQVNFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229930186217 Glycolipid Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 102000003886 Glycoproteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000288 Glycoproteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000009465 Growth Factor Receptors Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010009202 Growth Factor Receptors Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 229920000084 Gum arabic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 102100031573 Hematopoietic progenitor cell antigen CD34 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102100028999 High mobility group protein HMGI-C Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101000971171 Homo sapiens Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000980825 Homo sapiens B-lymphocyte antigen CD19 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000897405 Homo sapiens B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000984546 Homo sapiens Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type-1B Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000731086 Homo sapiens Brevican core protein Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000932213 Homo sapiens Dipeptidase 1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000777663 Homo sapiens Hematopoietic progenitor cell antigen CD34 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000986379 Homo sapiens High mobility group protein HMGI-C Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101001044893 Homo sapiens Interleukin-20 receptor subunit alpha Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000628547 Homo sapiens Metalloreductase STEAP1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000738771 Homo sapiens Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase C Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000946843 Homo sapiens T-cell surface glycoprotein CD8 alpha chain Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000701044 Human gammaherpesvirus 4 Species 0.000 description 1
- 102100026120 IgG receptor FcRn large subunit p51 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101710177940 IgG receptor FcRn large subunit p51 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010009817 Immunoglobulin Constant Regions Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000009786 Immunoglobulin Constant Regions Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010067060 Immunoglobulin Variable Region Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000017727 Immunoglobulin Variable Region Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102100022420 Inactive rhomboid protein 1 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101710136320 Inactive rhomboid protein 1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010008212 Integrin alpha4beta1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100025390 Integrin beta-2 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102000008607 Integrin beta3 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010020950 Integrin beta3 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010064593 Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100037877 Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 238000012695 Interfacial polymerization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 108091029795 Intergenic region Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100022706 Interleukin-20 receptor subunit alpha Human genes 0.000 description 1
- WTDRDQBEARUVNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N L-Dopa Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CC=C(O)C(O)=C1 WTDRDQBEARUVNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-REOHCLBHSA-N L-alanine Chemical compound C[C@H](N)C(O)=O QNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-BYPYZUCNSA-P L-argininium(2+) Chemical compound NC(=[NH2+])NCCC[C@H]([NH3+])C(O)=O ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-BYPYZUCNSA-P 0.000 description 1
- RHGKLRLOHDJJDR-BYPYZUCNSA-N L-citrulline Chemical group NC(=O)NCCC[C@H]([NH3+])C([O-])=O RHGKLRLOHDJJDR-BYPYZUCNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-YFKPBYRVSA-N L-histidine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CN=CN1 HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FFEARJCKVFRZRR-BYPYZUCNSA-N L-methionine Chemical compound CSCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O FFEARJCKVFRZRR-BYPYZUCNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-BYPYZUCNSA-N L-valine Chemical compound CC(C)[C@H](N)C(O)=O KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-BYPYZUCNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Lactate Chemical compound CC(O)C([O-])=O JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 102100038609 Lactoperoxidase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010023244 Lactoperoxidase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010024612 Lipoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108060001084 Luciferase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- DDWFXDSYGUXRAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Luciferin Natural products CCc1c(C)c(CC2NC(=O)C(=C2C=C)C)[nH]c1Cc3[nH]c4C(=C5/NC(CC(=O)O)C(C)C5CC(=O)O)CC(=O)c4c3C DDWFXDSYGUXRAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000007433 Lymphatic Metastasis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108010064548 Lymphocyte Function-Associated Antigen-1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000008072 Lymphokines Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010074338 Lymphokines Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000004907 Macro-emulsion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108010026217 Malate Dehydrogenase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-L Malonate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CC([O-])=O OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 229930195725 Mannitol Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 102100026712 Metalloreductase STEAP1 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 206010027459 Metastases to lymph nodes Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102000016943 Muramidase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010014251 Muramidase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- APGLTERDKORUHK-LURJTMIESA-N N,N-dimethyl-L-Valine Chemical group CC(C)[C@H](N(C)C)C(O)=O APGLTERDKORUHK-LURJTMIESA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010062010 N-Acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine Amidase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- WHNWPMSKXPGLAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone Chemical compound C=CN1CCCC1=O WHNWPMSKXPGLAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BAQMYDQNMFBZNA-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-biotinyl-L-lysine Natural products N1C(=O)NC2C(CCCCC(=O)NCCCCC(N)C(O)=O)SCC21 BAQMYDQNMFBZNA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HDFGOPSGAURCEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-ethylmaleimide Chemical group CCN1C(=O)C=CC1=O HDFGOPSGAURCEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WTBIAPVQQBCLFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N N.N.N.CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O Chemical compound N.N.N.CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O WTBIAPVQQBCLFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910002651 NO3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- NHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitrate Chemical compound [O-][N+]([O-])=O NHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000020 Nitrocellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005642 Oleic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oleic acid Natural products CCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108020005187 Oligonucleotide Probes Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101710160107 Outer membrane protein A Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010061535 Ovarian neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108090000526 Papain Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241001504519 Papio ursinus Species 0.000 description 1
- 102000057297 Pepsin A Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000284 Pepsin A Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010081690 Pertussis Toxin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010057249 Phagocytosis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 101710177166 Phosphoprotein Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000276498 Pollachius virens Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001213 Polysorbate 20 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 241000288906 Primates Species 0.000 description 1
- 101710098940 Pro-epidermal growth factor Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101710120463 Prostate stem cell antigen Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101800004937 Protein C Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000017975 Protein C Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102000004022 Protein-Tyrosine Kinases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000412 Protein-Tyrosine Kinases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100501691 Rattus norvegicus Erbb2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100501698 Rattus norvegicus Erbb4 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000004278 Receptor Protein-Tyrosine Kinases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000873 Receptor Protein-Tyrosine Kinases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100037422 Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase C Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108020004511 Recombinant DNA Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 208000006265 Renal cell carcinoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010062104 Renal mass Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 201000000582 Retinoblastoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 101800001700 Saposin-D Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 229920005654 Sephadex Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000012507 Sephadex™ Substances 0.000 description 1
- MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Serine Natural products OCC(N)C(O)=O MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010029157 Sialic Acid Binding Ig-like Lectin 2 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101710149279 Small delta antigen Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241001137868 Streptomyces pilosus Species 0.000 description 1
- 238000000692 Student's t-test Methods 0.000 description 1
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sulfate Chemical compound [O-]S([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 102100034922 T-cell surface glycoprotein CD8 alpha chain Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 239000012317 TBTU Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002253 Tannate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- WDLRUFUQRNWCPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetraxetan Chemical compound OC(=O)CN1CCN(CC(O)=O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CC1 WDLRUFUQRNWCPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010000499 Thromboplastin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100030859 Tissue factor Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 229920001615 Tragacanth Polymers 0.000 description 1
- HDTRYLNUVZCQOY-WSWWMNSNSA-N Trehalose Natural products O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 HDTRYLNUVZCQOY-WSWWMNSNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102100022563 Tubulin polymerization-promoting protein Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108060008682 Tumor Necrosis Factor Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100040247 Tumor necrosis factor Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102100040245 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010051765 Type I Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptors Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010053613 Type IV hypersensitivity reaction Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229910052770 Uranium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 108010092464 Urate Oxidase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010046334 Urease Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000251539 Vertebrata <Metazoa> Species 0.000 description 1
- 102100033220 Xanthine oxidase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010093894 Xanthine oxidase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- BBTPHKWZMDGVTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N [N]CCCl Chemical compound [N]CCCl BBTPHKWZMDGVTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CLZISMQKJZCZDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N [benzotriazol-1-yloxy(dimethylamino)methylidene]-dimethylazanium Chemical compound C1=CC=C2N(OC(N(C)C)=[N+](C)C)N=NC2=C1 CLZISMQKJZCZDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000010489 acacia gum Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- VJHCJDRQFCCTHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetic acid 2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal Chemical compound CC(O)=O.OCC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C=O VJHCJDRQFCCTHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000023445 activated T cell autonomous cell death Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012190 activator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011149 active material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000010933 acylation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005917 acylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000000577 adipose tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000012382 advanced drug delivery Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001261 affinity purification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003570 air Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000004279 alanine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- HAXFWIACAGNFHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N aldrithiol Chemical compound C=1C=CC=NC=1SSC1=CC=CC=N1 HAXFWIACAGNFHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003545 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003282 alkyl amino group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002947 alkylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- HDTRYLNUVZCQOY-LIZSDCNHSA-N alpha,alpha-trehalose Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 HDTRYLNUVZCQOY-LIZSDCNHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000000540 analysis of variance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000033115 angiogenesis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001772 anti-angiogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940046836 anti-estrogen Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000001833 anti-estrogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009830 antibody antigen interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011230 antibody-based therapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009831 antigen interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000890 antigenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002246 antineoplastic agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003418 antiprogestin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001640 apoptogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N arginine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CCCNC(N)=N ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004391 aryl sulfonyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000732 arylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229940072107 ascorbate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229960005070 ascorbic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229960001230 asparagine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000009582 asparagine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000001363 autoimmune Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000376 autoradiography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229960000686 benzalkonium chloride Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940077388 benzenesulfonate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-M benzenesulfonate Chemical compound [O-]S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229960001950 benzethonium chloride Drugs 0.000 description 1
- UREZNYTWGJKWBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M benzethonium chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].C1=CC(C(C)(C)CC(C)(C)C)=CC=C1OCCOCC[N+](C)(C)CC1=CC=CC=C1 UREZNYTWGJKWBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 235000019445 benzyl alcohol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- CADWTSSKOVRVJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl(dimethyl)azanium;chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].C[NH+](C)CC1=CC=CC=C1 CADWTSSKOVRVJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000005266 beta plus decay Effects 0.000 description 1
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-FPRJBGLDSA-N beta-D-galactose Chemical compound OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-FPRJBGLDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N beta-D-glucose Chemical compound OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960000397 bevacizumab Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000010256 biochemical assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003115 biocidal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- BAQMYDQNMFBZNA-MNXVOIDGSA-N biocytin Chemical compound N1C(=O)N[C@@H]2[C@H](CCCCC(=O)NCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O)SC[C@@H]21 BAQMYDQNMFBZNA-MNXVOIDGSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000012925 biological evaluation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000031018 biological processes and functions Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000029918 bioluminescence Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005415 bioluminescence Methods 0.000 description 1
- 108091006004 biotinylated proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- HUTDDBSSHVOYJR-UHFFFAOYSA-H bis[(2-oxo-1,3,2$l^{5},4$l^{2}-dioxaphosphaplumbetan-2-yl)oxy]lead Chemical compound [Pb+2].[Pb+2].[Pb+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O HUTDDBSSHVOYJR-UHFFFAOYSA-H 0.000 description 1
- 238000004061 bleaching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000036760 body temperature Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007853 buffer solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- DQXBYHZEEUGOBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N but-3-enoic acid;ethene Chemical compound C=C.OC(=O)CC=C DQXBYHZEEUGOBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000019437 butane-1,3-diol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- SNCZNSNPXMPCGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N butanediamide Chemical compound NC(=O)CCC(N)=O SNCZNSNPXMPCGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl alcohol Substances CCCCO LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000484 butyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 210000004899 c-terminal region Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 102220366970 c.90A>C Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 239000002775 capsule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001718 carbodiimides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000001768 carboxy methyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001732 carboxylic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012876 carrier material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000423 cell based assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000024245 cell differentiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010261 cell growth Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012412 chemical coupling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001311 chemical methods and process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002512 chemotherapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940044683 chemotherapy drug Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940001468 citrate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229960002173 citrulline Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000013477 citrulline Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000003759 clinical diagnosis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005354 coacervation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000001072 colon Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012875 competitive assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004154 complement system Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000005289 controlled pore glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001276 controlling effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002596 correlated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229960005168 croscarmellose Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000001767 crosslinked sodium carboxy methyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012228 culture supernatant Substances 0.000 description 1
- HPXRVTGHNJAIIH-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexanol Chemical compound OC1CCCCC1 HPXRVTGHNJAIIH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000058 cyclopentadienyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC1)* 0.000 description 1
- 230000009089 cytolysis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000001151 cytotoxic T lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 231100000599 cytotoxic agent Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 238000002784 cytotoxicity assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 231100000263 cytotoxicity test Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000001295 dansyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(N(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])=C2C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C(C2=C1[H])S(*)(=O)=O 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005831 deiodination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004925 denaturation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000036425 denaturation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000412 dendrimer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000736 dendritic polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229940099217 desferal Drugs 0.000 description 1
- XMSHRLOQLUNKSN-UHFFFAOYSA-N destosyl pyrazolate Chemical compound CC1=NN(C)C(O)=C1C(=O)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1Cl XMSHRLOQLUNKSN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000001627 detrimental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000019425 dextrin Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 1
- LTMHDMANZUZIPE-PUGKRICDSA-N digoxin Chemical compound C1[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](C)O[C@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@@H](C)O[C@@H](O[C@@H]2[C@H](O[C@@H](O[C@@H]3C[C@@H]4[C@]([C@@H]5[C@H]([C@]6(CC[C@@H]([C@@]6(C)[C@H](O)C5)C=5COC(=O)C=5)O)CC4)(C)CC3)C[C@@H]2O)C)C[C@@H]1O LTMHDMANZUZIPE-PUGKRICDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LTMHDMANZUZIPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N digoxine Natural products C1C(O)C(O)C(C)OC1OC1C(C)OC(OC2C(OC(OC3CC4C(C5C(C6(CCC(C6(C)C(O)C5)C=5COC(=O)C=5)O)CC4)(C)CC3)CC2O)C)CC1O LTMHDMANZUZIPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MHUWZNTUIIFHAS-CLFAGFIQSA-N dioleoyl phosphatidic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(COP(O)(O)=O)OC(=O)CCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC MHUWZNTUIIFHAS-CLFAGFIQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000002016 disaccharides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- BJAJDJDODCWPNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N dotp Chemical compound O=C1N2CCOC2=NC2=C1SC=C2 BJAJDJDODCWPNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960004679 doxorubicin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000012377 drug delivery Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000132 electrospray ionisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- ZSWFCLXCOIISFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N endo-cyclopentadiene Natural products C1C=CC=C1 ZSWFCLXCOIISFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940116977 epidermal growth factor Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940011871 estrogen Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000262 estrogen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000328 estrogen antagonist Substances 0.000 description 1
- CCIVGXIOQKPBKL-UHFFFAOYSA-M ethanesulfonate Chemical compound CCS([O-])(=O)=O CCIVGXIOQKPBKL-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- FAMRKDQNMBBFBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl n-ethoxycarbonyliminocarbamate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)N=NC(=O)OCC FAMRKDQNMBBFBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005038 ethylene vinyl acetate Substances 0.000 description 1
- OGPBJKLSAFTDLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N europium atom Chemical compound [Eu] OGPBJKLSAFTDLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000029142 excretion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013401 experimental design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013613 expression plasmid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000003754 fetus Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229950003499 fibrin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000796 flavoring agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- UZCGKGPEKUCDTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluazinam Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C(Cl)C([N+]([O-])=O)=C1NC1=NC=C(C(F)(F)F)C=C1Cl UZCGKGPEKUCDTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MHMNJMPURVTYEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluorescein-5-isothiocyanate Chemical compound O1C(=O)C2=CC(N=C=S)=CC=C2C21C1=CC=C(O)C=C1OC1=CC(O)=CC=C21 MHMNJMPURVTYEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000013355 food flavoring agent Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000037406 food intake Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000003599 food sweetener Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000013467 fragmentation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006062 fragmentation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940050411 fumarate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 210000001035 gastrointestinal tract Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000008273 gelatin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000159 gelatin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000019322 gelatine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000011852 gelatine desserts Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000003168 generic drug Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010353 genetic engineering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940050410 gluconate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940116332 glucose oxidase Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019420 glucose oxidase Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940097042 glucuronate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229930195712 glutamate Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 229940049906 glutamate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229960002989 glutamic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- ZDXPYRJPNDTMRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N glutamine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CCC(N)=O ZDXPYRJPNDTMRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003630 glycyl group Chemical group [H]N([H])C([H])([H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 1
- 239000008187 granular material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000001963 growth medium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940093915 gynecological organic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000004820 halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000001475 halogen functional group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 201000010536 head and neck cancer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000014829 head and neck neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003958 hematopoietic stem cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 125000005549 heteroarylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005842 heteroatom Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000623 heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- ALBYIUDWACNRRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexanamide Chemical compound CCCCCC(N)=O ALBYIUDWACNRRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000013628 high molecular weight specie Substances 0.000 description 1
- HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N histidine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CN=CN1 HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940088597 hormone Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000005556 hormone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 102000051957 human ERBB2 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 238000009396 hybridization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000017 hydrogel Substances 0.000 description 1
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-M hydrogensulfate Chemical compound OS([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920001477 hydrophilic polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001600 hydrophobic polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920003063 hydroxymethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229940031574 hydroxymethyl cellulose Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 210000000987 immune system Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000003018 immunoassay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003312 immunocapture Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002163 immunogen Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940027941 immunoglobulin g Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000011532 immunohistochemical staining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001114 immunoprecipitation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001771 impaired effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011503 in vivo imaging Methods 0.000 description 1
- ADFCQWZHKCXPAJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N indofine Natural products C1=CC(O)=CC=C1C1CC2=CC=C(O)C=C2OC1 ADFCQWZHKCXPAJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004615 ingredient Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000013383 initial experiment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940102223 injectable solution Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940102213 injectable suspension Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000011081 inoculation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 210000000936 intestine Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000010189 intracellular transport Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007918 intramuscular administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007913 intrathecal administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 108091005979 iodinated proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 229910052740 iodine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005342 ion exchange Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012948 isocyanate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960000310 isoleucine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- AGPKZVBTJJNPAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N isoleucine Natural products CCC(C)C(N)C(O)=O AGPKZVBTJJNPAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000741 isoleucyl group Chemical group [H]N([H])C(C(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])C(=O)O* 0.000 description 1
- TWBYWOBDOCUKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-M isonicotinate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)C1=CC=NC=C1 TWBYWOBDOCUKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- QXJSBBXBKPUZAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N isooleic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QXJSBBXBKPUZAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000644 isotonic solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000155 isotopic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001948 isotopic labelling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000366 juvenile effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000002576 ketones Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 210000003734 kidney Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000012933 kinetic analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011005 laboratory method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940057428 lactoperoxidase Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 210000002429 large intestine Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 235000010445 lecithin Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000787 lecithin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940067606 lecithin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229960004338 leuprorelin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229960004502 levodopa Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000002502 liposome Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940087857 lupron Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000012931 lyophilized formulation Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008176 lyophilized powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006674 lysosomal degradation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003712 lysosome Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000001868 lysosomic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004325 lysozyme Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960000274 lysozyme Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000010335 lysozyme Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 210000002540 macrophage Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N maleic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C/C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000594 mannitol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010355 mannitol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000008774 maternal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 108010082117 matrigel Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010534 mechanism of action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229960004961 mechlorethamine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000004060 metabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229930182817 methionine Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 229920000609 methyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004292 methyl p-hydroxybenzoate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010270 methyl p-hydroxybenzoate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001923 methylcellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960002900 methylcellulose Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229960002216 methylparaben Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000004530 micro-emulsion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000813 microbial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 108010029942 microperoxidase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003607 modifier Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000302 molecular modelling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002772 monosaccharides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000011512 multiplexed immunoassay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 231100000219 mutagenic Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000003505 mutagenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- QAPPRYMOAGJPPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)-2-iodoacetamide Chemical compound ICC(=O)NN1C(=O)CCC1=O QAPPRYMOAGJPPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UPSFMJHZUCSEHU-JYGUBCOQSA-N n-[(2s,3r,4r,5s,6r)-2-[(2r,3s,4r,5r,6s)-5-acetamido-4-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-(4-methyl-2-oxochromen-7-yl)oxyoxan-3-yl]oxy-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]acetamide Chemical compound CC(=O)N[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](NC(C)=O)[C@H](OC=2C=C3OC(=O)C=C(C)C3=CC=2)O[C@@H]1CO UPSFMJHZUCSEHU-JYGUBCOQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002088 nanocapsule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002105 nanoparticle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000013642 negative control Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007857 nested PCR Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- GUCVJGMIXFAOAE-NJFSPNSNSA-N niobium-95 Chemical compound [95Nb] GUCVJGMIXFAOAE-NJFSPNSNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920001220 nitrocellulos Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002736 nonionic surfactant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000655 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011330 nucleic acid test Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002777 nucleoside Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003833 nucleoside derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002773 nucleotide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003729 nucleotide group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- GYCKQBWUSACYIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N o-hydroxybenzoic acid ethyl ester Natural products CCOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1O GYCKQBWUSACYIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940049964 oleate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000002751 oligonucleotide probe Substances 0.000 description 1
- 102000027450 oncoproteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108091008819 oncoproteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012634 optical imaging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000007524 organic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000005985 organic acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 125000002524 organometallic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000001590 oxidative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
- LXCFILQKKLGQFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N p-hydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester Natural products COC(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 LXCFILQKKLGQFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000636 p-nitrophenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(=C([H])C([H])=C1*)[N+]([O-])=O 0.000 description 1
- 229940014662 pantothenate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019161 pantothenic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011713 pantothenic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940055729 papain Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019834 papain Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000001717 pathogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035515 penetration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229960003330 pentetic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940111202 pepsin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000010412 perfusion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000001322 periplasm Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008782 phagocytosis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000144 pharmacologic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012071 phase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- NMHMNPHRMNGLLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N phloretic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 NMHMNPHRMNGLLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SXADIBFZNXBEGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N phosphoramidous acid Chemical group NP(O)O SXADIBFZNXBEGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000004962 physiological condition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000006187 pill Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000013600 plasmid vector Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001200 poly(ethylene-vinyl acetate) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000747 poly(lactic acid) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002338 polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000256 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010486 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000244 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010482 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920000053 polysorbate 80 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002451 polyvinyl alcohol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229940069328 povidone Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002028 premature Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003623 progesteronic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000750 progressive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001737 promoting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000644 propagated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- VVWRJUBEIPHGQF-MDZDMXLPSA-N propan-2-yl (ne)-n-propan-2-yloxycarbonyliminocarbamate Chemical compound CC(C)OC(=O)\N=N\C(=O)OC(C)C VVWRJUBEIPHGQF-MDZDMXLPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IVRIRQXJSNCSPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-2-yl carbonochloridate Chemical compound CC(C)OC(Cl)=O IVRIRQXJSNCSPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VVWRJUBEIPHGQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-2-yl n-propan-2-yloxycarbonyliminocarbamate Chemical compound CC(C)OC(=O)N=NC(=O)OC(C)C VVWRJUBEIPHGQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004405 propyl p-hydroxybenzoate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010232 propyl p-hydroxybenzoate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960003415 propylparaben Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019833 protease Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000019419 proteases Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000000159 protein binding assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229960000856 protein c Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000013636 protein dimer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001742 protein purification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000734 protein sequencing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940024999 proteolytic enzymes for treatment of wounds and ulcers Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000011002 quantification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000003254 radicals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000007420 radioactive assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000941 radioactive substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940051022 radioimmunoconjugate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000003439 radiotherapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052761 rare earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002910 rare earth metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000376 reactant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001525 receptor binding assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003259 recombinant expression Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010244 region-of-interest analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000022983 regulation of cell cycle Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000026267 regulation of growth Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010405 reoxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003252 repetitive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108091008146 restriction endonucleases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000004007 reversed phase HPLC Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 102220040503 rs576143888 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102200018250 rs61753233 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- CVHZOJJKTDOEJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N saccharin Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C2=C1 CVHZOJJKTDOEJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940081974 saccharin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019204 saccharin Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000901 saccharin and its Na,K and Ca salt Substances 0.000 description 1
- YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-M salicylate Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1C([O-])=O YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229960001860 salicylate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000013391 scatchard analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007017 scission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010187 selection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003958 selenols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004904 shortening Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001542 size-exclusion chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000000813 small intestine Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 235000010413 sodium alginate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000661 sodium alginate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940005550 sodium alginate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019812 sodium carboxymethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920001027 sodium carboxymethylcellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- MKNJJMHQBYVHRS-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;1-[11-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)undecanoyloxy]-2,5-dioxopyrrolidine-3-sulfonate Chemical compound [Na+].O=C1C(S(=O)(=O)[O-])CC(=O)N1OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCN1C(=O)C=CC1=O MKNJJMHQBYVHRS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- ULARYIUTHAWJMU-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;1-[4-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)butanoyloxy]-2,5-dioxopyrrolidine-3-sulfonate Chemical compound [Na+].O=C1C(S(=O)(=O)[O-])CC(=O)N1OC(=O)CCCN1C(=O)C=CC1=O ULARYIUTHAWJMU-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- VUFNRPJNRFOTGK-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;1-[4-[(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)methyl]cyclohexanecarbonyl]oxy-2,5-dioxopyrrolidine-3-sulfonate Chemical compound [Na+].O=C1C(S(=O)(=O)[O-])CC(=O)N1OC(=O)C1CCC(CN2C(C=CC2=O)=O)CC1 VUFNRPJNRFOTGK-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- MIDXXTLMKGZDPV-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;1-[6-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)hexanoyloxy]-2,5-dioxopyrrolidine-3-sulfonate Chemical compound [Na+].O=C1C(S(=O)(=O)[O-])CC(=O)N1OC(=O)CCCCCN1C(=O)C=CC1=O MIDXXTLMKGZDPV-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000000600 sorbitol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009870 specific binding Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009987 spinning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012453 sprague-dawley rat model Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006641 stabilisation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011105 stabilization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007619 statistical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- SFVFIFLLYFPGHH-UHFFFAOYSA-M stearalkonium chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC[N+](C)(C)CC1=CC=CC=C1 SFVFIFLLYFPGHH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 238000011146 sterile filtration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000547 structure data Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229940014800 succinic anhydride Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229960002317 succinimide Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000000346 sugar Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000008163 sugars Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000002653 sulfanylmethyl group Chemical group [H]SC([H])([H])[*] 0.000 description 1
- 125000001273 sulfonato group Chemical group [O-]S(*)(=O)=O 0.000 description 1
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- YBBRCQOCSYXUOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N sulfuryl dichloride Chemical compound ClS(Cl)(=O)=O YBBRCQOCSYXUOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003765 sweetening agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008409 synovial inflammation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001308 synthesis method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008685 targeting Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940095064 tartrate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- ABZLKHKQJHEPAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetramethylrhodamine Chemical compound C=12C=CC(N(C)C)=CC2=[O+]C2=CC(N(C)C)=CC=C2C=1C1=CC=CC=C1C([O-])=O ABZLKHKQJHEPAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MPLHNVLQVRSVEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N texas red Chemical compound [O-]S(=O)(=O)C1=CC(S(Cl)(=O)=O)=CC=C1C(C1=CC=2CCCN3CCCC(C=23)=C1O1)=C2C1=C(CCC1)C3=[N+]1CCCC3=C2 MPLHNVLQVRSVEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002560 therapeutic procedure Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002562 thickening agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000000101 thioether group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000003568 thioethers Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000025366 tissue development Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003325 tomography Methods 0.000 description 1
- PYHOFAHZHOBVGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N triazane Chemical compound NNN PYHOFAHZHOBVGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001493 tyrosinyl group Chemical group [H]OC1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])C([H])(N([H])[H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 1
- 238000002604 ultrasonography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003827 upregulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- JFALSRSLKYAFGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N uranium(0) Chemical compound [U] JFALSRSLKYAFGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000010200 validation analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004862 vasculogenesis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000005048 vimentin Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000002424 x-ray crystallography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052727 yttrium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-RNFDNDRNSA-N zirconium-95 Chemical compound [95Zr] QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-RNFDNDRNSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K51/00—Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo
- A61K51/02—Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo characterised by the carrier, i.e. characterised by the agent or material covalently linked or complexing the radioactive nucleus
- A61K51/04—Organic compounds
- A61K51/08—Peptides, e.g. proteins, carriers being peptides, polyamino acids, proteins
- A61K51/10—Antibodies or immunoglobulins; Fragments thereof, the carrier being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. a camelised human single domain antibody or the Fc fragment of an antibody
- A61K51/1093—Antibodies or immunoglobulins; Fragments thereof, the carrier being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. a camelised human single domain antibody or the Fc fragment of an antibody conjugates with carriers being antibodies
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K38/00—Medicinal preparations containing peptides
- A61K38/16—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
- A61K38/17—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from animals; from humans
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/395—Antibodies; Immunoglobulins; Immune serum, e.g. antilymphocytic serum
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/30—Macromolecular organic or inorganic compounds, e.g. inorganic polyphosphates
- A61K47/42—Proteins; Polypeptides; Degradation products thereof; Derivatives thereof, e.g. albumin, gelatin or zein
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K48/00—Medicinal preparations containing genetic material which is inserted into cells of the living body to treat genetic diseases; Gene therapy
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K49/00—Preparations for testing in vivo
- A61K49/06—Nuclear magnetic resonance [NMR] contrast preparations; Magnetic resonance imaging [MRI] contrast preparations
- A61K49/08—Nuclear magnetic resonance [NMR] contrast preparations; Magnetic resonance imaging [MRI] contrast preparations characterised by the carrier
- A61K49/10—Organic compounds
- A61K49/14—Peptides, e.g. proteins
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K49/00—Preparations for testing in vivo
- A61K49/06—Nuclear magnetic resonance [NMR] contrast preparations; Magnetic resonance imaging [MRI] contrast preparations
- A61K49/08—Nuclear magnetic resonance [NMR] contrast preparations; Magnetic resonance imaging [MRI] contrast preparations characterised by the carrier
- A61K49/10—Organic compounds
- A61K49/14—Peptides, e.g. proteins
- A61K49/16—Antibodies; Immunoglobulins; Fragments thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K51/00—Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo
- A61K51/02—Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo characterised by the carrier, i.e. characterised by the agent or material covalently linked or complexing the radioactive nucleus
- A61K51/04—Organic compounds
- A61K51/08—Peptides, e.g. proteins, carriers being peptides, polyamino acids, proteins
- A61K51/10—Antibodies or immunoglobulins; Fragments thereof, the carrier being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. a camelised human single domain antibody or the Fc fragment of an antibody
- A61K51/1027—Antibodies or immunoglobulins; Fragments thereof, the carrier being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. a camelised human single domain antibody or the Fc fragment of an antibody against receptors, cell-surface antigens or cell-surface determinants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K51/00—Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo
- A61K51/02—Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo characterised by the carrier, i.e. characterised by the agent or material covalently linked or complexing the radioactive nucleus
- A61K51/04—Organic compounds
- A61K51/08—Peptides, e.g. proteins, carriers being peptides, polyamino acids, proteins
- A61K51/10—Antibodies or immunoglobulins; Fragments thereof, the carrier being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. a camelised human single domain antibody or the Fc fragment of an antibody
- A61K51/1045—Antibodies or immunoglobulins; Fragments thereof, the carrier being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. a camelised human single domain antibody or the Fc fragment of an antibody against animal or human tumor cells or tumor cell determinants
- A61K51/1051—Antibodies or immunoglobulins; Fragments thereof, the carrier being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. a camelised human single domain antibody or the Fc fragment of an antibody against animal or human tumor cells or tumor cell determinants the tumor cell being from breast, e.g. the antibody being herceptin
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C259/00—Compounds containing carboxyl groups, an oxygen atom of a carboxyl group being replaced by a nitrogen atom, this nitrogen atom being further bound to an oxygen atom and not being part of nitro or nitroso groups
- C07C259/04—Compounds containing carboxyl groups, an oxygen atom of a carboxyl group being replaced by a nitrogen atom, this nitrogen atom being further bound to an oxygen atom and not being part of nitro or nitroso groups without replacement of the other oxygen atom of the carboxyl group, e.g. hydroxamic acids
- C07C259/06—Compounds containing carboxyl groups, an oxygen atom of a carboxyl group being replaced by a nitrogen atom, this nitrogen atom being further bound to an oxygen atom and not being part of nitro or nitroso groups without replacement of the other oxygen atom of the carboxyl group, e.g. hydroxamic acids having carbon atoms of hydroxamic groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C323/00—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups
- C07C323/50—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton
- C07C323/51—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton having the sulfur atoms of the thio groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton
- C07C323/60—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton having the sulfur atoms of the thio groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton with the carbon atom of at least one of the carboxyl groups bound to nitrogen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K14/00—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
- C07K14/435—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from animals; from humans
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K16/00—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K16/00—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies
- C07K16/18—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K16/00—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies
- C07K16/18—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans
- C07K16/28—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K16/00—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies
- C07K16/18—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans
- C07K16/32—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against translation products of oncogenes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K19/00—Hybrid peptides, i.e. peptides covalently bound to nucleic acids, or non-covalently bound protein-protein complexes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01K—ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; AVICULTURE; APICULTURE; PISCICULTURE; FISHING; REARING OR BREEDING ANIMALS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NEW BREEDS OF ANIMALS
- A01K2267/00—Animals characterised by purpose
- A01K2267/03—Animal model, e.g. for test or diseases
- A01K2267/0331—Animal model for proliferative diseases
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C2601/00—Systems containing only non-condensed rings
- C07C2601/12—Systems containing only non-condensed rings with a six-membered ring
- C07C2601/14—The ring being saturated
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/20—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by taxonomic origin
- C07K2317/21—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by taxonomic origin from primates, e.g. man
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/50—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by immunoglobulin fragments
- C07K2317/51—Complete heavy chain or Fd fragment, i.e. VH + CH1
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/50—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by immunoglobulin fragments
- C07K2317/52—Constant or Fc region; Isotype
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/50—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by immunoglobulin fragments
- C07K2317/55—Fab or Fab'
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/60—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by non-natural combinations of immunoglobulin fragments
- C07K2317/62—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by non-natural combinations of immunoglobulin fragments comprising only variable region components
- C07K2317/624—Disulfide-stabilized antibody (dsFv)
Definitions
- the invention relates generally to antibodies engineered with reactive cysteine residues and more specifically to antibodies with therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
- the cysteine engineered antibodies may be conjugated with chemotherapeutic drugs, toxins, affinity ligands such as biotin, and detection labels such as radioisotopes and fluorophores.
- the invention also relates to methods of using antibodies and antibody-drug conjugate compounds for in vitro, in situ, and in vivo diagnosis or treatment of mammalian cells, or associated pathological conditions.
- Immuno-positron emission tomography is a rapidly emerging method for tracking and quantifying monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) in vivo as it efficiently combines the high sensitivity of PET with the high specificity of mAbs.
- ImmunoPET aspires to be the clinical method of choice for non-invasive diagnosis providing "comprehensive immunohistochemical staining in vivo" (van Dongen GA, et al. "ImmunoPET: a navigator in monoclonal antibody development and applications" Oncologist
- PET Positron Emission Tomographic
- the isotopes are typically administered to a patient by injection of probe molecules that comprise a positron-emitting isotope, such as F-18, C-l 1, N-13, or 0-15, covalently attached to a molecule that is readily metabolized or localized in the body (e.g., glucose) or that chemically binds to receptor sites within the body.
- a positron-emitting isotope such as F-18, C-l 1, N-13, or 0-15
- covalently attached to a molecule that is readily metabolized or localized in the body e.g., glucose
- the isotope is administered to the patient as an ionic solution or by inhalation.
- Small immuno-PET imaging agents such as Fab antibody fragments (50 kDa) or diabodies, paired dimers of the covalently associated V H -V L region of Mab, 55 kDa (Shively et al (2007) J Nucl Med 48: 170- 2), may be particularly useful since they exhibit a short circulation half-life, high tissue permeability, and reach an optimal tumor to background ratio between two to four hours after
- Iodine 124 ( I) was coupled to antibody 3F9 and used to estimate the dosimetry for radioimmunotherapy of neuroblastoma (Larson SM, et al "PET scanning of iodine- 124-3 F9 as an approach to tumor dosimetry during treatment planning for radioimmunotherapy in a child with neuroblastoma" J Nucl Med 1992;33:2020-3). Later, as more sophisticated PET
- the complex decay scheme involves energetic positrons ( ⁇ + max. 1.5 and 2.1 MeV) which negatively affects the resolution of small animal microPET.
- a label such as a radioisotope, fluorescent dye, or drug moiety
- cytotoxic drugs have typically been conjugated to antibodies through the often-numerous lysine residues of an antibody, generating a heterogeneous antibody-drug conjugate mixture.
- the heterogeneous mixture typically contains a distribution of antibodies with from 0 to about 8, or more, attached drug moieties.
- Antibodies are large, complex and structurally diverse biomolecules, often with many reactive functional groups. Their reactivities with linker reagents and drug-linker
- Cysteine thiols are reactive at neutral pH, unlike most amines which are protonated and less nucleophilic near pH 7. Since free thiol (RSH, sulfhydryl) groups are relatively reactive, proteins with cysteine residues often exist in their oxidized form as disulfide-linked oligomers or have internally bridged disulfide groups. Extracellular proteins generally do not have free thiols (Garman, 1997, Non-Radioactive Labelling: A Practical Approach,
- the amount of free thiol in a protein may be estimated by the standard Ellman's assay.
- Immunoglobulin M is an example of a disulfide- linked pentamer
- immunoglobulin G is an example of a protein with internal disulfide bridges bonding the subunits together.
- DTT dithiothreitol
- selenol Singh et al (2002) Anal.
- Biochem. 304: 147-1566 is required to generate the reactive free thiol. This approach may result in loss of antibody tertiary structure and antigen binding specificity.
- Antibody cysteine thiol groups are generally more reactive, i.e. more nucleophilic, towards electrophilic conjugation reagents than antibody amine or hydroxyl groups.
- Cysteine residues have been introduced into proteins by genetic engineering techniques to form covalent attachments to ligands or to form new intramolecular disulfide bonds (Better et al (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269(13):9644-9650; Bernhard et al (1994) Bioconjugate Chem. 5: 126- 132; Greenwood et al (1994) Therapeutic Immunology 1 :247-255; Tu et al (1999) Proc. Natl. Acad.
- cysteine thiol groups by the mutation of various amino acid residues of a protein to cysteine amino acids is potentially problematic, particularly in the case of unpaired (free Cys) residues or those which are relatively accessible for reaction or oxidation.
- Site-specific conjugation is preferred over random amino modification as it enables chemical modification of a site away from the binding site, promoting complete retention of biological activity and allowing control over the possible number of prosthetic groups added.
- Cysteine-engineered antibodies have been designed as FAB antibody fragments (thioFab) and expressed as full-length, IgG monoclonal (thioMab) antibodies. See: US 7521541; Junutula JR et al. "Rapid identification of reactive cysteine residues for site-specific labeling of antibody-Fabs" J Immunol Methods 2008;332:41-52; Junutula JR et al. "Site-specific conjugation of a cytotoxic drug to an antibody improves the therapeutic index” (2008) Nat Biotechnol.
- ThioFab and ThioMab antibodies have been conjugated through linkers at the newly introduced cysteine thiols with thiol-reactive linker reagents and drug-linker reagents to prepare cysteine- engineered antibody drug conjugates (Thio ADC) with anti-cancer properties, including anti- MUC16 (US 2008/0311134), anti-CD22 (US 2008/0050310), anti-ROB04 (US)
- the compounds of the invention include cysteine engineered antibodies where one or more amino acids of a parent antibody are replaced with a free cysteine amino acid.
- a cysteine engineered antibody comprises one or more free cysteine amino acids having a thiol reactivity value in the range of 0.6 to l .O.
- a free cysteine amino acid is a cysteine residue which has been engineered into the parent antibody and is not part of a disulfide bridge.
- Cysteine engineered antibodies may be useful in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer and include antibodies specific for cell surface and transmembrane receptors, and tumor-associated antigens (TAA). Such antibodies may be used as naked antibodies
- Embodiments of the methods for preparing and screening a cysteine engineered antibody include where the parent antibody is an antibody fragment, such as hu4D5Fabv8.
- the parent antibody may also be a fusion protein comprising an albumin-binding peptide sequence (ABP).
- the parent antibody may also be a humanized antibody selected from huMAb4D5-l, huMAb4D5-2, huMAb4D5-3, huMAb4D5-4, huMAb4D5-5, huMAb4D5-6, huMAb4D5-7 and huMAb4D5-8 (trastuzumab).
- Cysteine engineered antibodies of the invention may be site-specifically and efficiently coupled with a thiol-reactive reagent.
- the thiol-reactive reagent may be a radioisotope reagent, multifunctional linker reagent, a capture label reagent, a fluorophore reagent, or a drug-linker intermediate.
- the cysteine engineered antibody may be labeled with a detectable label, immobilized on a solid phase support and/or conjugated with a drug moiety.
- Another aspect of the invention is a zirconium-labelled, cysteine-engineered antibody comprising a cysteine engineered antibody (Ab) conjugated through a free cysteine amino acid to a linker (L) and a zirconium complex (Z), having Formula I: where p is 1 to 4.
- Ab cysteine engineered antibody
- L linker
- Z zirconium complex
- Another aspect of the invention is a desferrioxamine-labelled, cysteine-engineered antibody comprising a cysteine engineered antibody (Ab) conjugated through a free cysteine amino acid to a linker (L) and a desferoxamine moiety (Df), having Formula II:
- p 1 to 4.
- Another aspect of the invention is a method of making a desferrioxamine-labelled, cysteine-engineered antibody comprising comprising a cysteine engineered antibody (Ab) conjugated through a free cysteine amino acid to a linker (L) and a desferoxamine moiety (Df), having Formula II:
- L-Df is selected from:
- p 1 to 4.
- R is selected from:
- cysteine-engineered antibody having one or more free cysteine amino acids, whereby the desferrioxamine-labelled, cysteine-engineered antibody is formed.
- Another aspect of the invention is a method of making a zirconium-labelled, cysteine- engineered antibody comprising a cysteine engineered antibody (Ab) conjugated through a free cysteine amino acid to a linker (L) and a zirconium complex (Z), having Formula I: where p is 1 to 4;
- the method comprising complexing a zirconium reagent with a desferrioxamine- labelled, cysteine-engineered antibody comprising a cysteine engineered antibody (Ab) conjugated through a free cysteine amino acid to a linker (L) and a desferoxamine moiety (Df), having Formula II:
- p 1 to 4.
- Another aspect of the invention is a method of imaging comprising:
- zirconium-labelled, cysteine-engineered antibody comprises a cysteine engineered antibody (Ab) having one or more free cysteine amino acids conjugated with one or more zirconium complex (Z) through a linker (L), and having Formula I:
- Another aspect of the invention includes diagnostic uses for the compounds and compositions disclosed herein. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
- Figure 1 A shows a three-dimensional representation of the hu4D5Fabv7 antibody fragment derived by X-ray crystal coordinates.
- the structure positions of the exemplary engineered Cys residues of the heavy and light chains are numbered (according to a sequential numbering system).
- Figure IB shows a sequential numbering scheme (top row), starting at the N-terminus in comparison with the Kabat numbering scheme (bottom row) for 4D5v7fabH. Kabat numbering insertions are noted by a,b,c.
- Figures 2 A and 2B show binding measurements with detection of absorbance at 450nm of hu4D5Fabv8 and hu4D5Fabv8 Cys mutant (ThioFab) phage variants: (A) non- biotinylated phage-hu4D5Fabv8 and (B) biotinylated phage-hu4D5Fabv8 (B) by the PHESELECTOR assay for interactions with BSA (open bar), HER2 (striped bar) or streptavidin (solid bar).
- FIG. 4A shows Fractional Surface Accessibility values of residues on wild type
- hu4D5Fabv8 Light chain sites are on the left side and heavy chain sites are on the right side.
- Figure 4B shows binding measurements with detection of absorbance at 450nm of
- Phage-hu4D5Fabv8 Cys variants were isolated and stored at 4 °C. Biotin conjugation was carried out either at day 2 or day 4 followed by PHESELECTOR analyses to monitor their interaction with Her2 and streptavidin as described in Example 2, and probe the stability of reactive thiol groups on engineered ThioFab variants.
- Figure 5 shows binding measurements with detection of absorbance at 450nm of biotin- maleimide conjugated-hu4D5Fabv8 (A121C) and non-biotinylated wild type hu4D5Fabv8 for binding to streptavidin and HER2. Each Fab was tested at 2 ng and 20 ng.
- Figure 6 shows ELISA analysis with detection of absorbance at 450nm of biotinylated ABP- hu4D5Fabv8 wild type (wt), and ABP-hu4D5Fabv8 cysteine mutants VI IOC and A121C for binding with rabbit albumin, streptavidin (SA), and HER2.
- Figure 7 shows ELISA analysis with detection of absorbance at 450nm of biotinylated ABP- hu4D5Fabv8 cysteine mutants (ThioFab variants): (left to right) single Cys variants ABP-V1 IOC, ABP-A121C, and double Cys variants ABP-V110C-A88C and ABP- VI 10C-A121C for binding with rabbit albumin, HER2 and streptavidin (SA), and probing with Fab-HRP or SA-HRP.
- ThioFab variants biotinylated ABP- hu4D5Fabv8 cysteine mutants
- Figure 8 shows binding of biotinylated ThioFab phage and an anti-phage HRP antibody to HER2 (top) and Streptavidin (bottom).
- Figure 13A shows a cartoon depiction of biotinylated antibody binding to immobilized HER2 with binding of HRP labeled secondary antibody for absorbance detection.
- Figure 13B shows binding measurements with detection of absorbance at 450nm of biotin- maleimide conjugated thio-trastuzumab variants and non-biotinylated wild type trastuzumab in binding to immobilized HER2. From left to right: VI IOC (single cys), A121C (single cys), VI 10C/A121C (double cys), and trastuzumab. Each thio IgG variant and trastuzumab was tested at 1, 10, and 100 ng.
- Figure 14A shows a cartoon depiction of biotinylated antibody binding to immobilized HER2 with binding of biotin to anti-IgG-HRP for absorbance detection.
- Figure 14B shows binding measurements with detection of absorbance at 450nm of biotin- maleimide conjugated-thio trastuzumab variants and non-biotinylated wild type trastuzumab in binding to immobilized streptavidin. From left to right: VI IOC (single cys), A121C (single cys), VI 10C/A121C (double cys), and trastuzumab. Each thio IgG variant and trastuzumab was tested at 1, 10, and 100 ng.
- Figure 15 shows the general process to prepare a cysteine engineered antibody (ThioMab) expressed from cell culture for conjugation.
- Figure 16 shows non-reducing (top) and reducing (bottom) denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis of 2H9 ThioMab Fc variants (left to right, lanes 1-9): A339C; S337C; S324C; A287C; V284C; V282C; V279C; V273C, and 2H9 wild type after purification on immobilized Protein A.
- the lane on the right is a size marker ladder, indicating the intact proteins are about 150 kDa, heavy chain fragments about 50 kDa, and light chain fragments about 25 kDa.
- Figure 17A shows non-reducing (left) and reducing (+DTT) (right) denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis of 2H9 ThioMab variants (left to right, lanes 1-4): L-V15C; S179C; S375C; S400C, after purification on immobilized Protein A.
- Figure 17B shows non-reducing (left) and reducing (+DTT) (right) denaturing
- Figure 18 shows western blot analysis of biotinylated Thio-IgG variants. 2H9 and 3A5
- ThioMab variants were analyzed on reduced denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, the proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membrane. The presence of antibody and conjugated biotin were probed with anti-IgG-HRP (top) and streptavidin-HRP (bottom), respectively. Lane 1 : 3A5 H-A121C. Lane 2: 3A5 L- VI IOC. Lane 3: 2H9 H-A121C. Lane 4: 2H9 L-V110C. Lane 5: 2H9 wild type.
- Figure 19 shows ELISA analysis for the binding of biotinylated 2H9 variants to streptavidin by probing with anti-IgG-HRP and measuring the absorbance at 450 nm of (top bar diagram).
- Bottom schematic diagram depicts the experimental design used in the ELISA analysis.
- Figure 20 shows bifunctional reagents for coupling chelator of 89 Zr desferoxamine B (Df, top) with proteins using amino reactive linkers, TFP-N-SucDf and Df-Bz-NCS (center) and thiol reactive linkers, Df-Chx-Mal, Df-Bac, and Df-lac (bottom).
- Figure 21 shows the preparation of Df-Chx-Mal, Df-Bac, Df-lac and conjugation to thio- trastuzumab via Cys residues incorporated into the heavy chain of Fab.
- Reaction conditions i. DIEA, DMF/H 2 0 (10: 1), RT, 0.5-1 h; ii. DIEA, DMF, 0°C, 4 h; iii. pH 7.5, RT, 1 h; iv. pH 9, RT, 5 h; v. pH 9, RT, 2 h.
- Figure 22 shows chelation of zirconium-89 oxalate with a desferrioxamine-labelled, cysteine- engineered antibody, such as variants of Df-linker-trastuzumab containing four linkers: N-Suc, Bz-SCN, Chx-maleimide (CHx-Mal), or acetyl (Ac).
- a desferrioxamine-labelled, cysteine- engineered antibody such as variants of Df-linker-trastuzumab containing four linkers: N-Suc, Bz-SCN, Chx-maleimide (CHx-Mal), or acetyl (Ac).
- Figure 23 shows mass spectrometry analysis of reduced antibodies showing separate signals from light and heavy chains.
- Figure 25 shows representative full-body images (maximum intensity projection) acquired 96 hours after the tail vein bolus injection of 100 ⁇ of Zr-Trasuzumab prepared using four different linkers (Bz-SCN, N-Suc, Chx-Mal, and Ac).
- Figure 26 shows In vivo uptake in selected tissues at 24, 96 and 144 h post injection as
- antibody herein is used in the broadest sense and specifically covers monoclonal antibodies, polyclonal antibodies, dimers, multimers, multispecific antibodies (e.g., bispecific antibodies), and antibody fragments, so long as they exhibit the desired biological activity (Miller et al (2003) Jour, of Immunology 170:4854-4861). Antibodies may be murine, human, humanized, chimeric, or derived from other species. An antibody is a protein generated by the immune system that is capable of recognizing and binding to a specific antigen. (Janeway, C, Travers, P., Walport, M., Shlomchik (2001) Immuno Biology, 5th Ed., Garland Publishing, New York).
- a target antigen generally has numerous binding sites, also called epitopes, recognized by CDRs on multiple antibodies. Each antibody that specifically binds to a different epitope has a different structure. Thus, one antigen may have more than one corresponding antibody.
- An antibody includes a full-length immunoglobulin molecule or an immunologically active portion of a full-length
- immunoglobulin molecule i.e., a molecule that contains an antigen binding site that immunospecifically binds an antigen of a target of interest or part thereof, such targets including but not limited to, cancer cell or cells that produce autoimmune antibodies associated with an autoimmune disease.
- the immunoglobulin disclosed herein can be of any type (e.g., IgG, IgE, IgM, IgD, and IgA), class (e.g., IgGl, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4, IgAl and
- immunoglobulins can be derived from any species. In one aspect, however, the immunoglobulin is of human, murine, or rabbit origin.
- Antibody fragments comprise a portion of a full length antibody, generally the antigen binding or variable region thereof.
- Examples of antibody fragments include Fab, Fab, and fragments thereof.
- Fab', F(ab') 2 , and Fv fragments diabodies; linear antibodies; minibodies (Olafsen et al (2004) Protein Eng. Design & Sel. 17(4):315-323), fragments produced by a Fab expression library, anti-idiotypic (anti-Id) antibodies, CDR (complementary determining region), and epitope- binding fragments of any of the above which immunospecifically bind to cancer cell antigens, viral antigens or microbial antigens, single-chain antibody molecules; and multispecific antibodies formed from antibody fragments.
- the term "monoclonal antibody” as used herein refers to an antibody obtained from a population of substantially homogeneous antibodies, i.e., the individual antibodies
- Monoclonal antibodies are highly specific, being directed against a single antigenic site. Furthermore, in contrast to polyclonal antibody preparations which include different antibodies directed against different determinants (epitopes), each monoclonal antibody is directed against a single determinant on the antigen. In addition to their specificity, the monoclonal antibodies are advantageous in that they may be synthesized uncontaminated by other antibodies.
- the modifier "monoclonal" indicates the character of the antibody as being obtained from a substantially homogeneous population of antibodies, and is not to be construed as requiring production of the antibody by any particular method.
- the monoclonal antibodies to be used in accordance with the present invention may be made by the hybridoma method first described by Kohler et al (1975) Nature 256:495, or may be made by recombinant DNA methods (see for example: US 4816567; US 5807715).
- the monoclonal antibodies may also be isolated from phage antibody libraries using the techniques described in Clackson et al (1991) Nature, 352:624-628; Marks et al (1991) J. Mol. Biol, 222:581-597; for example.
- the monoclonal antibodies herein specifically include "chimeric" antibodies in which a portion of the heavy and/or light chain is identical with or homologous to corresponding sequences in antibodies derived from a particular species or belonging to a particular antibody class or subclass, while the remainder of the chain(s) is identical with or homologous to corresponding sequences in antibodies derived from another species or belonging to another antibody class or subclass, as well as fragments of such antibodies, so long as they exhibit the desired biological activity (US 4816567; and Morrison et al (1984) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 81 :6851-6855).
- Chimeric antibodies of interest herein include "primatized" antibodies comprising variable domain antigen-binding sequences derived from a non-human primate (e.g., Old World Monkey, Ape etc) and human constant region sequences.
- an “intact antibody” herein is one comprising a VL and VH domains, as well as a light chain constant domain (CL) and heavy chain constant domains, CHI , CH2 and CH3.
- the constant domains may be native sequence constant domains (e.g., human native sequence constant domains) or amino acid sequence variant thereof.
- the intact antibody may have one or more "effector functions" which refer to those biological activities attributable to the Fc constant region (a native sequence Fc region or amino acid sequence variant Fc region) of an antibody. Examples of antibody effector functions include Clq binding;
- immunoglobulin antibodies can be assigned to different "classes.” There are five major classes of intact immunoglobulin antibodies: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM, and several of these may be further divided into “subclasses” (isotypes), e.g., IgGl , IgG2, IgG3, IgG4, IgA, and IgA2.
- the heavy-chain constant domains that correspond to the different classes of antibodies are called ⁇ , ⁇ , ⁇ , ⁇ , and ⁇ , respectively.
- the subunit structures and three-dimensional configurations of different classes of immunoglobulins are well known.
- Ig forms include hinge-modifications or hingeless forms (Roux et al (1998) J. Immunol. 161 :4083-4090; Lund et al (2000) Eur. J. Biochem. 267:7246-7256; US 2005/0048572; US 2004/0229310).
- An "ErbB receptor” is a receptor protein tyrosine kinase which belongs to the ErbB receptor family whose members are important mediators of cell growth, differentiation and survival.
- the ErbB receptor family includes four distinct members including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR, ErbBl, HER1), HER2 (ErbB2 or pl85neu), HER3 (ErbB3) and HER4 (ErbB4 or tyro2).
- a panel of anti-ErbB2 antibodies has been characterized using the human breast tumor cell line SKBR3 (Hudziak et al (1989) Mol. Cell. Biol. 9(3): 1165- 1172. Maximum inhibition was obtained with the antibody called 4D5 which inhibited cellular proliferation by 56%. Other antibodies in the panel reduced cellular proliferation to a lesser extent in this assay. The antibody 4D5 was further found to sensitize ErbB2- overexpressing breast tumor cell lines to the cytotoxic effects of TNF-a (US 5677171).
- the anti-ErbB2 antibodies discussed in Hudziak et al. are further characterized in Fendly et al
- the ErbB receptor will generally comprise an extracellular domain, which may bind an ErbB ligand; a lipophilic transmembrane domain; a conserved intracellular tyrosine kinase domain; and a carboxyl-terminal signaling domain harboring several tyrosine residues which can be phosphorylated.
- the ErbB receptor may be a "native sequence” ErbB receptor or an "amino acid sequence variant" thereof.
- the ErbB receptor is native sequence human ErbB receptor. Accordingly, a "member of the ErbB receptor family" is EGFR (ErbBl), ErbB2, ErbB3, ErbB4 or any other ErbB receptor currently known or to be identified in the future.
- ErbBl "epidermal growth factor receptor", “EGFR” and “HER1” are used interchangeably herein and refer to EGFR as disclosed, for example, in Carpenter et al (1987) Ann. Rev. Biochem., 56:881-914, including naturally occurring mutant forms thereof (e.g., a deletion mutant EGFR as in Humphrey et al (1990) Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA) 87:4207-4211).
- the term erbBl refers to the gene encoding the EGFR protein product. Antibodies against HER1 are described, for example, in Murthy et al (1987) Arch. Biochem.
- ERRP epidermal growth factor receptor
- EGF epidermal growth factor receptor
- ErbB2 and "HER2” are used interchangeably herein and refer to human HER2 protein described, for example, in Semba et al (1985) Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA) 82:6497-6501 and Yamamoto et al (1986) Nature, 319:230-234 (Genebank accession number X03363).
- the term “erbB2” refers to the gene encoding human ErbB2 and "neu” refers to the gene encoding rat pl85neu.
- Preferred ErbB2 is native sequence human ErbB2.
- ErbB3 and "HER3” refer to the receptor polypeptide as disclosed, for example, in U.S. Patent Nos. 5183884 and 5480968 as well as Kraus et al (1989) Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA) 86:9193-9197.
- Antibodies against ErbB3 are known in the art and are described, for example, in U.S. Patent Nos. 5183884, 5480968 and in WO 97/35885.
- ErbB4 and HER4 herein refer to the receptor polypeptide as disclosed, for example, in EP Pat Application No 599,274; Plowman et al (1993) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 1746-1750; and Plowman et al (1993) Nature 366:473-475, including isoforms thereof, e.g., as disclosed in WO 99/19488.
- Antibodies against HER4 are described, for example, in WO 02/18444.
- Antibodies to ErbB receptors are available commercially from a number of sources, including, for example, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., California, USA.
- amino acid sequence variant refers to polypeptides having amino acid sequences that differ to some extent from a native sequence polypeptide. Ordinarily, amino acid sequence variants will possess at least about 70% sequence identity with at least one receptor binding domain of a native ErbB ligand or with at least one ligand binding domain of a native ErbB receptor, and preferably, they will be at least about 80%, more preferably, at least about 90%> homologous by sequence with such receptor or ligand binding domains. The amino acid sequence variants possess substitutions, deletions, and/or insertions at certain positions within the amino acid sequence of the native amino acid sequence. Amino acids are designated by the conventional names, one-letter and three-letter codes.
- Sequence identity is defined as the percentage of residues in the amino acid sequence variant that are identical after aligning the sequences and introducing gaps, if necessary, to achieve the maximum percent sequence identity. Methods and computer programs for the alignment are well known in the art. One such computer program is "Align 2,” authored by Genentech, Inc., which was filed with user documentation in the United States Copyright Office, Washington, DC 20559, on December 10, 1991.
- Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and “ADCC” refer to a cell- mediated reaction in which nonspecific cytotoxic cells that express Fc receptors (FcRs) (e.g., Natural Killer (NK) cells, neutrophils, and macrophages) recognize bound antibody on a target cell and subsequently cause lysis of the target cell.
- FcRs Fc receptors
- FcR expression on hematopoietic cells in summarized is Table 3 on page 464 of Ravetch and Kinet, (1991) "Annu. Rev. Immunol.” 9:457-92.
- ADCC activity of a molecule of interest may be assessed in vitro, such as that described in US 5500362 and US 5821337.
- useful effector cells for such assays include peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and Natural Killer (NK) cells.
- PBMC peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- NK Natural Killer
- ADCC activity of the molecule of interest may be assessed in vivo, e.g., in a animal model such as that disclosed in Clynes et al (1998) PROC. NAT. ACAD. SCI. (USA) (USA) 95:652-656.
- Human effector cells are leukocytes which express one or more constant region receptors (FcRs) and perform effector functions. Preferably, the cells express at least FcyRIII and perform ADCC effector function. Examples of human leukocytes which mediate ADCC include peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), natural killer (NK) cells, monocytes, cytotoxic T cells and neutrophils; with PBMCs and NK cells being preferred.
- the effector cells may be isolated from a native source thereof, e.g., from blood or PBMCs as described herein.
- Fc receptor or “FcR” are used to describe a receptor that binds to the Fc constant region of an antibody.
- the preferred FcR is a native sequence human FcR.
- a preferred FcR is one which binds an IgG antibody (a gamma receptor) and includes receptors of the FcyRI, FcyRII, and Fey RIII subclasses, including allelic variants and alternatively spliced forms of these receptors.
- FcyRII receptors include FcyRIIA (anadvant), FcyRIIB (anadvant), and othersadvant.
- activating receptor and FcyRIIB (an “inhibiting receptor”), which have similar amino acid sequences that differ primarily in the cytoplasmic domains thereof.
- Activating receptor FcyRIIA contains an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (IT AM) in its cytoplasmic domain.
- Inhibiting receptor FcyRIIB contains an immunoreceptor tyrosine - based inhibition motif (ITIM) in its cytoplasmic domain.
- ITIM immunoreceptor tyrosine - based inhibition motif
- FcR neonatal receptor
- “Complement dependent cytotoxicity” or “CDC” refers to the ability of a molecule to lyse a target in the presence of complement.
- the complement activation pathway is initiated by the binding of the first component of the complement system (Clq) to a molecule (e.g., an antibody) complexed with a cognate antigen.
- a CDC assay e.g., as described in Gazzano-Santoro et al J. Immunol. Methods, 202: 163 (1996), may be performed.
- “Native antibodies” are usually heterotetrameric glycoproteins of about 150,000 daltons, composed of two identical light (L) chains and two identical heavy (H) chains. Each light chain is linked to a heavy chain by one covalent disulfide bond, while the number of disulfide linkages varies among the heavy chains of different immunoglobulin isotypes. Each heavy and light chain also has regularly spaced intrachain disulfide bridges. Each heavy chain has at one end a variable domain (V H ) followed by a number of constant domains. Each light chain has a variable domain at one end (V L ) and a constant domain at its other end. The constant domain of the light chain is aligned with the first constant domain of the heavy chain, and the light-chain variable domain is aligned with the variable domain of the heavy chain. Particular amino acid residues are believed to form an interface between the light chain and heavy chain variable domains.
- variable refers to the fact that certain portions of the variable domains differ extensively in sequence among antibodies and are used in the binding and specificity of each particular antibody for its particular antigen. However, the variability is not evenly distributed throughout the variable domains of antibodies. It is concentrated in three segments called hypervariable regions both in the light chain and the heavy chain variable domains. The more highly conserved portions of variable domains are called the framework regions (FRs).
- the variable domains of native heavy and light chains each comprise four FRs, largely adopting a ⁇ -sheet configuration, connected by three hypervariable regions, which form loops connecting, and in some cases forming part of, the ⁇ -sheet structure.
- the hypervariable regions in each chain are held together in close proximity by the FRs and, with the hypervariable regions from the other chain, contribute to the formation of the antigen- binding site of antibodies (see Kabat et al (1991) Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, 5th Ed. Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD).
- the constant domains are not involved directly in binding an antibody to an antigen, but exhibit various effector functions, such as participation of the antibody in antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC).
- hypervariable region when used herein refers to the amino acid residues of an antibody which are responsible for antigen-binding.
- the hypervariable region generally comprises amino acid residues from a "complementarity determining region" or "CDR" (e.g., residues 24-34 (LI), 50-56 (L2) and 89-97 (L3) in the light chain variable domain and 31-35 (HI), 50-65 (H2) and 95-102 (H3) in the heavy chain variable domain; Kabat et al supra) and/or those residues from a "hypervariable loop” (e.g., residues 26-32 (LI), 50-52 (L2) and 91-96 (L3) in the light chain variable domain and 26-32 (HI), 53-55 (H2) and 96-101 (H3) in the heavy chain variable domain; Chothia and Lesk (1987) J. Mol. Biol, 196:901-917).
- CDR complementarity determining region
- Framework Region or "FR” residues are those variable domain residues other than the hypervariable region residues as herein defined.
- Papain digestion of antibodies produces two identical antigen-binding fragments, called “Fab” fragments, each with a single antigen-binding site, and a residual "Fc” fragment, whose name reflects its ability to crystallize readily. Pepsin treatment yields an F(ab')2 fragment that has two antigen-binding sites and is still capable of cross-linking antigen.
- Fv is the minimum antibody fragment which contains a complete antigen- recognition and antigen-binding site. This region consists of a dimer of one heavy chain and one light chain variable domain in tight, non-covalent association. It is in this configuration that the three hypervariable regions of each variable domain interact to define an antigen- binding site on the surface of the V H -V L dimer. Collectively, the six hypervariable regions confer antigen-binding specificity to the antibody. However, even a single variable domain (or half of an Fv comprising only three hypervariable regions specific for an antigen) has the ability to recognize and bind antigen, although at a lower affinity than the entire binding site.
- the Fab fragment also contains the constant domain of the light chain and the first constant domain (CHI) of the heavy chain.
- Fab' fragments differ from Fab fragments by the addition of a few residues at the carboxy terminus of the heavy chain CHI domain including one or more cysteines from the antibody hinge region.
- Fab'-SH is the designation herein for Fab' in which the cysteine residue(s) of the constant domains bear at least one free thiol group.
- F(ab')2 antibody fragments originally were produced as pairs of Fab' fragments which have hinge cysteines between them. Other chemical couplings of antibody fragments are also known.
- the "light chains" of antibodies from any vertebrate species can be assigned to one of two clearly distinct types, called kappa ( ⁇ ) and lambda ( ⁇ ), based on the amino acid sequences of their constant domains.
- Single-chain Fv or “scFv” antibody fragments comprise the VH and VL domains of antibody, wherein these domains are present in a single polypeptide chain.
- the Fv polypeptide further comprises a polypeptide linker between the VH and VL domains which enables the scFv to form the desired structure for antigen binding.
- diabodies refers to small antibody fragments with two antigen-binding sites, which fragments comprise a variable heavy domain (VH) connected to a variable light domain (VL) in the same polypeptide chain (VH - VL).
- VH variable heavy domain
- VL variable light domain
- Diabodies are described more fully in, for example, EP 404,097; WO 93/11 161 ; and
- “Humanized” forms of non-human (e.g., rodent) antibodies are chimeric antibodies that contain minimal sequence derived from non-human immunoglobulin. Humanization is a method to transfer the murine antigen binding information to a non-immunogenic human antibody acceptor, and has resulted in many therapeutically useful drugs. The method of humanization generally begins by transferring all six murine complementarity determining regions (CDRs) onto a human antibody framework (Jones et al, (1986) Nature 321 :522-525). These CDR-grafted antibodies generally do not retain their original affinity for antigen binding, and in fact, affinity is often severely impaired. Besides the CDRs, select non-human antibody framework residues must also be incorporated to maintain proper CDR
- humanized antibodies are human immunoglobulins (recipient antibody) in which residues from a hypervariable region of the recipient are replaced by residues from a hypervariable region of a non-human species (donor antibody) such as mouse, rat, rabbit or nonhuman primate having the desired specificity, affinity, and capacity.
- donor antibody such as mouse, rat, rabbit or nonhuman primate having the desired specificity, affinity, and capacity.
- framework region (FR) residues of the human immunoglobulin are replaced by corresponding non-human residues.
- humanized antibodies may comprise residues that are not found in the recipient antibody or in the donor antibody. These modifications are made to further refine antibody performance.
- the humanized antibody will comprise substantially all of at least one, and typically two, variable domains, in which all or substantially all of the hypervariable loops correspond to those of a non-human immunoglobulin and all or substantially all of the FRs are those of a human immunoglobulin sequence.
- the humanized antibody optionally also will comprise at least a portion of an immunoglobulin constant region (Fc), typically that of a human immunoglobulin.
- Fc immunoglobulin constant region
- a “free cysteine amino acid” refers to a cysteine amino acid residue which has been engineered into a parent antibody, has a thiol functional group (-SH), and is not paired as an intramolecular or intermolecular disulfide bridge.
- thiol reactivity value is a quantitative characterization of the reactivity of free cysteine amino acids.
- the thiol reactivity value is the percentage of a free cysteine amino acid in a cysteine engineered antibody which reacts with a thiol-reactive reagent, and converted to a maximum value of 1.
- a free cysteine amino acid on a cysteine engineered antibody which reacts in 100% yield with a thiol-reactive reagent, such as a biotin-maleimide reagent, to form a biotin-labelled antibody has a thiol reactivity value of 1.0.
- Another cysteine amino acid engineered into the same or different parent antibody which reacts in 80% yield with a thiol-reactive reagent has a thiol reactivity value of 0.8.
- Another cysteine amino acid engineered into the same or different parent antibody which fails totally to react with a thiol-reactive reagent has a thiol reactivity value of 0.
- Determination of the thiol reactivity value of a particular cysteine may be conducted by ELISA assay, mass spectroscopy, liquid chromatography, autoradiography, or other quantitative analytical tests.
- a “parent antibody” is an antibody comprising an amino acid sequence from which one or more amino acid residues are replaced by one or more cysteine residues.
- the parent antibody may comprise a native or wild type sequence.
- the parent antibody may have preexisting amino acid sequence modifications (such as additions, deletions and/or substitutions) relative to other native, wild type, or modified forms of an antibody.
- a parent antibody may be directed against a target antigen of interest, e.g. a biologically important polypeptide.
- Antibodies directed against nonpolypeptide antigens are also contemplated.
- Exemplary parent antibodies include antibodies having affinity and selectivity for cell surface and transmembrane receptors and tumor-associated antigens (TAA).
- TAA tumor-associated antigens
- exemplary parent antibodies include those selected from, and without limitation, anti-estrogen receptor antibody, anti-progesterone receptor antibody, anti-p53 antibody, anti-HER-2/neu antibody, anti-EGFR antibody, anti-cathepsin D antibody, anti- Bcl-2 antibody, anti-E-cadherin antibody, anti-CA125 antibody, anti-CA15-3 antibody, anti- CA19-9 antibody, anti-c-erbB-2 antibody, anti-P-glycoprotein antibody, anti-CEA antibody, anti-retinoblastoma protein antibody, anti-ras oncoprotein antibody, anti-Lewis X antibody, anti-Ki-67 antibody, anti-PCNA antibody, anti-CD3 antibody, anti-CD4 antibody, anti-CD5 antibody, anti-CD7 antibody, anti-CD8 antibody, anti-CD9/p24 antibody, anti-CD 10 antibody, anti-CDl lc antibody, anti-CD 13 antibody, anti-CD 14 antibody, anti-CD 15 antibody, anti-CD 19 antibody, anti-CD20 antibody, anti
- an “isolated” antibody is one which has been identified and separated and/or recovered from a component of its natural environment. Contaminant components of its natural environment are materials which would interfere with diagnostic or therapeutic uses for the antibody, and may include enzymes, hormones, and other proteinaceous or
- the antibody will be purified (1) to greater than 95% by weight of antibody as determined by the Lowry method, and most preferably more than 99% by weight, (2) to a degree sufficient to obtain at least 15 residues of N-terminal or internal amino acid sequence by use of a spinning cup sequenator, or (3) to homogeneity by SDS-PAGE under reducing or nonreducing conditions using Coomassie blue or, preferably, silver stain.
- Isolated antibody includes the antibody in situ within recombinant cells since at least one component of the antibody's natural environment will not be present. Ordinarily, however, isolated antibody will be prepared by at least one purification step.
- an antibody "which binds" a molecular target or an antigen of interest is one capable of binding that antigen with sufficient affinity such that the antibody is useful in targeting a cell expressing the antigen.
- the antibody is one which binds ErbB2
- it will usually preferentially bind ErbB2 as opposed to other ErbB receptors, and may be one which does not significantly cross-react with other proteins such as EGFR, ErbB3 or ErbB4.
- the extent of binding of the antibody to these non-ErbB2 proteins e.g., cell surface binding to endogenous receptor
- FACS fluorescence activated cell sorting
- RIA radioimmunoprecipitation
- CD proteins and their ligands such as, but not limited to: (i) CD3, CD4, CD8, CD19, CD20, CD22, CD34, CD40, CD79a (CD79a), and CD79p (CD79b); (ii) members of the ErbB receptor family such as the EGF receptor, HER2, HER3 or HER4 receptor; (iii) cell adhesion molecules such as LFA-1, Macl, pl50,95, VLA-4, ICAM-1, VCAM and ⁇ / ⁇ 3 integrin, including either alpha or beta subunits thereof (e.g.
- anti-CD 1 la, anti-CD 18 or anti-CD 1 lb antibodies growth factors such as VEGF; IgE; blood group antigens; flk2/flt3 receptor; obesity (OB) receptor; mpl receptor; CTLA-4; protein C, BR3, c-met, tissue factor, ⁇ 7 etc; and (v) cell surface and transmembrane tumor-associated antigens (TAA).
- growth factors such as VEGF; IgE; blood group antigens; flk2/flt3 receptor; obesity (OB) receptor; mpl receptor; CTLA-4; protein C, BR3, c-met, tissue factor, ⁇ 7 etc; and TAA).
- the term “monoclonal antibody 4D5" refers to an antibody that has antigen binding residues of, or derived from, the murine 4D5 antibody (ATCC CRL 10463).
- the monoclonal antibody 4D5 may be murine
- monoclonal antibody 4D5 or a variant thereof, such as a humanized 4D5.
- exemplary humanized 4D5 antibodies include huMAb4D5-l, huMAb4D5-2, huMAb4D5-3,
- huMAb4D5-4 huMAb4D5-5, huMAb4D5-6, huMAb4D5-7 and huMAb4D5-8 (trastuzumab, HERCEPTIN®) as in US Patent No. 5821337.
- Phage display is a technique by which variant polypeptides are displayed as fusion proteins to a coat protein on the surface of phage, e.g., filamentous phage, particles.
- phage display One utility of phage display lies in the fact that large libraries of randomized protein variants can be rapidly and efficiently sorted for those sequences that bind to a target molecule with high affinity. Display of peptide and protein libraries on phage has been used for screening millions of polypeptides for ones with specific binding properties. Polyvalent phage display methods have been used for displaying small random peptides and small proteins, typically through fusions to either pill or pVIII of filamentous phage (Wells and Lowman, (1992) Curr. Opin. Struct.
- phagemid vectors are used, which simplify DNA manipulations. Lowman and Wells, Methods: A companion to Methods in Enzymology, 3:205-0216 (1991).
- Phage display includes techniques for producing antibody- like molecules (Janeway, C, Travers, P., Walport, M., Shlomchik (2001) Immunobiology, 5th Ed., Garland Publishing, New York, p627-628; Lee et al ).
- a "phagemid” is a plasmid vector having a bacterial origin of replication, e.g., ColEl, and a copy of an intergenic region of a bacteriophage.
- the phagemid may be used on any known bacteriophage, including filamentous bacteriophage and lambdoid bacteriophage.
- the plasmid will also generally contain a selectable marker for antibiotic resistance. Segments of DNA cloned into these vectors can be propagated as plasmids. When cells harboring these vectors are provided with all genes necessary for the production of phage particles, the mode of replication of the plasmid changes to rolling circle replication to generate copies of one strand of the plasmid DNA and package phage particles.
- the phagemid may form infectious or non-infectious phage particles.
- This term includes phagemids which contain a phage coat protein gene or fragment thereof linked to a heterologous polypeptide gene as a gene fusion such that the heterologous polypeptide is displayed on the surface of the phage particle.
- Linker means a chemical moiety comprising a covalent bond or a chain of atoms that covalently attaches an antibody to a drug moiety.
- a linker is specified as L.
- Linkers include a divalent radical such as an alkyldiyl, an arylene, a heteroarylene, moieties such as: -(CR 2 ) n O(CR 2 ) n -, repeating units of alkyloxy (e.g. polyethylenoxy, PEG, polymethyleneoxy) and alkylamino (e.g.
- polyethyleneamino, JeffamineTM polyethyleneamino, JeffamineTM
- diacid ester and amides including succinate, succinamide, diglycolate, malonate, and caproamide.
- label means any moiety which can be covalently attached to an antibody and that functions to: (i) provide a detectable signal; (ii) interact with a second label to modify the detectable signal provided by the first or second label, e.g. FRET (fluorescence resonance energy transfer); (iii) stabilize interactions or increase affinity of binding, with antigen or ligand; (iv) affect mobility, e.g. electrophoretic mobility, or cell-permeability, by charge, hydrophobicity, shape, or other physical parameters, or (v) provide a capture moiety, to modulate ligand affinity, antibody/antigen binding, or ionic complexation.
- FRET fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- d and 1 or (+) and (-) are employed to designate the sign of rotation of plane-polarized light by the compound, with (-) or 1 meaning that the compound is levorotatory.
- a compound prefixed with (+) or d is dextrorotatory.
- these stereoisomers are identical except that they are mirror images of one another.
- a specific stereoisomer may also be referred to as an enantiomer, and a mixture of such isomers is often called an enantiomeric mixture.
- a 50:50 mixture of enantiomers is referred to as a racemic mixture or a racemate, which may occur where there has been no stereoselection or stereospecificity in a chemical reaction or process.
- racemic mixture and racemate refer to an equimolar mixture of two enantiomeric species, devoid of optical activity.
- organic or inorganic salts of an AZC include, but are not limited, to sulfate, citrate, acetate, oxalate, chloride, bromide, iodide, nitrate, bisulfate, phosphate, acid phosphate, isonicotinate, lactate, salicylate, acid citrate, tartrate, oleate, tannate, pantothenate, bitartrate, ascorbate, succinate, maleate, gentisinate, fumarate, gluconate, glucuronate, saccharate, formate, benzoate, glutamate, methanesulfonate, ethanesulfonate, benzenesulfonate, /?-toluenesulfonate, and pamoate (i.e., 1,1 ' -methyl ene-bis -(2-hydroxy-3- naphthoate)) salts.
- exemplary salts include, but are not limited
- a pharmaceutically acceptable salt may involve the inclusion of another molecule such as an acetate ion, a succinate ion or other counterion.
- the counterion may be any organic or inorganic moiety that stabilizes the charge on the parent compound.
- a pharmaceutically acceptable salt may have more than one charged atom in its structure. Instances where multiple charged atoms are part of the pharmaceutically acceptable salt can have multiple counter ions. Hence, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt can have one or more charged atoms and/or one or more counterion.
- “Pharmaceutically acceptable solvate” refers to an association of one or more solvent molecules and an AZC.
- solvents that form pharmaceutically acceptable solvates include, but are not limited to, water, isopropanol, ethanol, methanol, DMSO, ethyl acetate, acetic acid, and ethanolamine.
- BME beta-mercaptoethanol
- Boc N-(t-butoxycarbonyl)
- cit citrulline (2-amino-5-ureido pentanoic acid)
- dap is dolaproine
- DCC 1,3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
- DCM dichloromethane
- DEA diethylamine
- DEAD diethylazodicarboxylate
- DEPC diethylphosphorylcyanidate
- DIAD diisopropylazodicarboxylate
- DIEA N,N- diisopropylethylamine
- dil dolaisoleucine
- DMA is dimethylacetamide
- DMAP 4- dimethylaminopyridine
- DME is ethyleneglycol dimethyl ether (or 1 ,2-dimethoxyethane)
- DMF is N,N-dimethylformamide
- DMSO dimethylsulfoxide
- doe is
- DTT dithiothreitol
- EDCI l-(3- dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
- EEDQ 2-ethoxy-l- ethoxycarbonyl-l,2-dihydroquinoline
- ES-MS electrospray mass spectrometry
- EtOAc ethyl acetate
- Fmoc is N-(9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl)
- gly glycine
- HATU 0-(7- azabenzotriazol-l-yl)-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate
- HOBt 1- hydroxybenzotriazole
- HPLC high pressure liquid chromatography
- ile is isoleucine
- lys is lysine
- MeCN (CH 3 CN) is acetonitrile
- MeOH MeOH
- the compounds of the invention include cysteine engineered antibodies where one or more amino acids of a wild-type or parent antibody are replaced with a cysteine amino acid. Any form of antibody may be so engineered, i.e. mutated.
- a parent Fab antibody fragment may be engineered to form a cysteine engineered Fab, referred to herein as "ThioFab.”
- a parent monoclonal antibody may be engineered to form a
- ThioMab “ThioMab.” It should be noted that a single site mutation yields a single engineered cysteine residue in a ThioFab, while a single site mutation yields two engineered cysteine residues in a ThioMab, due to the dimeric nature of the IgG antibody. Mutants with replaced
- cysteine (Cys) residues are evaluated for the reactivity of the newly introduced, engineered cysteine thiol groups.
- the thiol reactivity value is a relative, numerical term in the range of 0 to 1.0 and can be measured for any cysteine engineered antibody.
- Thiol reactivity values of cysteine engineered antibodies of the invention are in the ranges of 0.6 to 1.0; 0.7 to 1.0; or 0.8 to 1.0.
- the design, selection, and preparation methods of the invention enable cysteine engineered antibodies which are reactive with electrophilic functionality. These methods further enable antibody conjugate compounds such as antibody-zirconium conjugate (AZC) compounds with zirconium atoms at designated, designed, selective sites. Reactive cysteine residues on an antibody surface allow specifically conjugating a zirconium moiety through a thiol reactive group such as maleimide or haloacetyl.
- a thiol reactive group such as maleimide or haloacetyl.
- the nucleophilic reactivity of the thiol functionality of a Cys residue to a maleimide group is about 1000 times higher compared to any other amino acid functionality in a protein, such as amino group of lysine residues or the N-terminal amino group.
- Thiol specific functionality in iodoacetyl and maleimide reagents may react with amine groups, but higher pH (>9.0) and longer reaction times are required (Garman, 1997, Non-Radioactive Labelling: A Practical Approach, Academic Press, London).
- cysteine engineered antibodies of the invention preferably retain the antigen binding capability of their wild type, parent antibody counterparts.
- cysteine engineered antibodies are capable of binding, preferably specifically, to antigens.
- antigens include, for example, tumor-associated antigens (TAA), cell surface receptor proteins and other cell surface molecules, transmembrane proteins, signalling proteins, cell survival regulatory factors, cell proliferation regulatory factors, molecules associated with (for e.g., known or suspected to contribute functionally to) tissue development or differentiation, lymphokines, cytokines, molecules involved in cell cycle regulation, molecules involved in vasculogenesis and molecules associated with (for e.g., known or suspected to contribute functionally to) angiogenesis.
- TAA tumor-associated antigens
- cell surface receptor proteins and other cell surface molecules include, for example, tumor-associated antigens (TAA), cell surface receptor proteins and other cell surface molecules, transmembrane proteins, signalling proteins, cell survival regulatory factors, cell proliferation regulatory factors, molecules associated with (for e.g., known or
- the tumor-associated antigen may be a cluster differentiation factor (i.e., a CD protein).
- An antigen to which a cysteine engineered antibody is capable of binding may be a member of a subset of one of the above-mentioned categories, wherein the other subset(s) of said category comprise other molecules/antigens that have a distinct characteristic (with respect to the antigen of interest).
- the parent antibody may also be a humanized antibody selected from huMAb4D5-l, huMAb4D5-2, huMAb4D5-3, huMAb4D5-4, huMAb4D5-5, huMAb4D5-6, huMAb4D5-7 and huMAb4D5-8 (Trastuzumab, HERCEPTIN®) as described in Table 3 of US 5821337, expressly incorporated herein by reference; humanized 520C9 (WO 93/21319) and humanized 2C4 antibodies as described herein.
- Cysteine engineered antibodies of the invention may be site-specifically and efficiently coupled with a thiol-reactive reagent.
- the thiol-reactive reagent may be a multifunctional linker reagent, a capture, i.e. affinity, label reagent (e.g. a biotin-linker reagent), a detection label (e.g. a fluorophore reagent), a solid phase immobilization reagent (e.g. SEPHAROSETM, polystyrene, or glass), or a zirconium-linker intermediate.
- label reagent e.g. a biotin-linker reagent
- detection label e.g. a fluorophore reagent
- solid phase immobilization reagent e.g. SEPHAROSETM, polystyrene, or glass
- zirconium-linker intermediate e.g. SEPHAROSETM, polystyrene, or glass
- reaction of a ThioFab with a biotin-linker reagent provides a biotinylated ThioFab by which the presence and reactivity of the engineered cysteine residue may be detected and measured.
- Reaction of a ThioFab with a multifunctional linker reagent provides a ThioFab with a functionalized linker which may be further reacted with a zirconium moiety reagent or other label.
- Reaction of a ThioFab with a zirconium-linker intermediate provides a ThioFab zirconium conjugate.
- the exemplary methods described here may be applied generally to the identification and production of antibodies, and more generally, to other proteins through application of the design and screening steps described herein.
- Such an approach may be applied to the conjugation of other thiol-reactive agents in which the reactive group is, for example, a maleimide, an iodoacetamide, a pyridyl disulfide, or other thiol-reactive conjugation partner (Haugland, 2003, Molecular Probes Handbook of Fluorescent Probes and Research Chemicals, Molecular Probes, Inc.; Brinkley, 1992, Bioconjugate Chem. 3:2; Garman, 1997, Non-Radioactive Labelling: A Practical Approach, Academic Press, London; Means (1990) Bioconjugate Chem. 1 :2; Hermanson, G. in
- the partner may be a cytotoxic agent (e.g. a toxin such as doxorubicin or pertussis toxin), a fluorophore such as a fluorescent dye like fluorescein or rhodamine, a chelating agent for an imaging or radiotherapeutic metal, a peptidyl or non-peptidyl label or detection tag, or a clearance-modifying agent such as various isomers of polyethylene glycol, a peptide that binds to a third component, or another carbohydrate or lipophilic agent.
- a cytotoxic agent e.g. a toxin such as doxorubicin or pertussis toxin
- a fluorophore such as a fluorescent dye like fluorescein or rhodamine
- a chelating agent for an imaging or radiotherapeutic metal e.g. a chelating agent for an imaging or radiotherapeutic metal
- a peptidyl or non-peptidyl label or detection tag
- the sites identified on the exemplary antibody fragment, hu4D5Fabv8, herein are primarily in the constant domain of an antibody which is well conserved across all species of antibodies. These sites should be broadly applicable to other antibodies, without further need of structural design or knowledge of specific antibody structures, and without interference in the antigen binding properties inherent to the variable domains of the antibody.
- Cysteine engineered antibodies which may be useful in the treatment of cancer include, but are not limited to, antibodies against cell surface receptors and tumor-associated antigens (TAA). Such antibodies may be used as naked antibodies (unconjugated to a label moiety) or as Formula I antibody-zirconium conjugates (AZC). Tumor-associated antigens are known in the art, and can prepared for use in generating antibodies using methods and information which are well known in the art. In attempts to discover effective cellular targets for cancer diagnosis and therapy, researchers have sought to identify transmembrane or otherwise tumor-associated polypeptides that are specifically expressed on the surface of one or more particular type(s) of cancer cell as compared to on one or more normal non- cancerous cell(s).
- tumor-associated polypeptides are more abundantly expressed on the surface of the cancer cells as compared to on the surface of the non-cancerous cells.
- the identification of such tumor-associated cell surface antigen polypeptides has given rise to the ability to specifically target cancer cells for destruction via antibody-based therapies.
- TAA examples include, but are not limited to, TAA (l)-(36) listed below.
- TAA examples include, but are not limited to, TAA (l)-(36) listed below.
- information relating to these antigens is listed below and includes names, alternative names, Genbank accession numbers and primary reference(s), following nucleic acid and protein sequence identification conventions of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).
- NCBI National Center for Biotechnology Information
- Nucleic acid and protein sequences corresponding to TAA (l)-(36) are available in public databases such as GenBank.
- Tumor- associated antigens targeted by antibodies include all amino acid sequence variants and isoforms possessing at least about 70%, 80%>, 85%, 90%>, or 95% sequence identity relative to the sequences identified in the cited references, or which exhibit substantially the same biological properties or characteristics as a TAA having a sequence found in the cited references.
- a TAA having a variant sequence generally is able to bind specifically to an antibody that binds specifically to the TAA with the corresponding sequence listed.
- the sequences and disclosure in the reference specifically recited herein are expressly incorporated by reference.
- BMPR1B bone morphogenetic protein receptor-type IB, Genbank accession
- NP 001194 bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type IB /pid NP_001194.1 - Cross-references: MIM:603248; NP 001194.1; AY065994
- WO2004048938 (Example 2); WO2004032842 (Example IV); WO2003042661 (Claim 12); WO2003016475 (Claim 1); WO200278524 (Example 2); WO200299074 (Claim 19; Page 127-129); WO200286443 (Claim 27; Pages 222, 393); WO2003003906 (Claim 10; Page 293); WO200264798 (Claim 33; Page 93-95); WO200014228 (Claim 5; Page 133-136); US2003224454 (Fig 3); WO2003025138 (Claim 12; Page 150);
- member 5 /pid NP_003477.3 - Homo sapiens
- EP1394274 (Example 11); WO2004016225 (Claim 2); WO2003042661 (Claim 12);
- WO200289747 (Example 5; Page 618-619); WO2003022995 (Example 9; Fig 13A, Example 53; Page 173, Example 2; Fig 2A); NP 036581 six transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate
- WO200292836 (Claim 6; Fig 12); WO200283866 (Claim 15; Page 116-121);
- MPF MPF
- MSLN MSLN
- SMR megakaryocyte potentiating factor
- mesothelin mesothelin
- Napi3b (NAPI-3B, NPTIIb, SLC34A2, solute carrier family 34 (sodium
- Sema 5b (FLJ10372, KIAA1445, Mm.42015, SEMA5B, SEMAG, Semaphorin 5b Hlog, sema domain, seven thrombospondin repeats (type 1 and type 1 -like), transmembrane domain (TM) and short cytoplasmic domain, (semaphorin) 5B, Genbank accession no. AB040878) Nagase T., et al (2000) DNA Res. 7 (2): 143-150); WO2004000997 (Claim 1);
- WO2003003984 (Claim 1); WO200206339 (Claim 1; Page 50); WO200188133 (Claim 1; Page 41-43, 48-58); WO2003054152 (Claim 20); WO2003101400 (Claim 11);
- PSCA hlg (2700050C12Rik, C530008O16Rik, RIKEN cDNA 2700050C12, RIKEN cDNA 2700050C12 gene, Genbank accession no. AY358628); Ross et al (2002) Cancer Res. 62:2546-2553; US2003129192 (Claim 2); US2004044180 (Claim 12); US2004044179 (Claim 11); US2003096961 (Claim 11); US2003232056 (Example 5); WO2003105758 (Claim 12); US2003206918 (Example 5); EP1347046 (Claim 1); WO2003025148 (Claim 20);
- ETBR Endothelin type B receptor, Genbank accession no. AY275463
- WO2004048938 (Example 2); WO2004040000 (Claim 151); WO2003087768 (Claim 1); WO2003016475 (Claim 1); WO2003016475 (Claim 1); WO200261087 (Fig 1);
- WO2003016494 (Fig 6); WO2003025138 (Claim 12; Page 144); WO200198351 (Claim 1; Page 124-125); EP522868 (Claim 8; Fig 2); WO200177172 (Claim 1; Page 297-299);
- WO2003104275 (Claim 1); WO2004046342 (Example 2); WO2003042661 (Claim 12); WO2003083074 (Claim 14; Page 61); WO2003018621 (Claim 1); WO2003024392 (Claim 2; Fig 93); WO200166689 (Example 6);
- LocusID 54894; NP_060233.2; NM_017763_1
- STEAP2 (HGNC 8639, IPCA-1, PCANAP1, STAMP1, STEAP2, STMP, prostate cancer associated gene 1 , prostate cancer associated protein 1 , six transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate 2, six transmembrane prostate protein, Genbank accession no.
- TrpM4 (BR22450, FLJ20041, TRPM4, TRPM4B, transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 4, Genbank accession no. NM 017636)
- WO200040614 (Claim 14; Page 100-103); WO200210382 (Claim 1; Fig 9A);
- WO2003042661 (Claim 12); WO200230268 (Claim 27; Page 391); US2003219806 (Claim 4); WO200162794 (Claim 14; Fig 1A-D);
- CRIPTO (CR, CRl, CRGF, CRIPTO, TDGFl, teratocarcinoma-derived growth factor, Genbank accession no. NP 003203 or NM 003212)
- WO200216413 (Claim 1; Page 94-95, 105); WO200222808 (Claim 2; Fig 1); US5854399 (Example 2; Col 17-18); US5792616 (Fig 2); Cross-references: MIM: 187395; NP_003203.1; NM_003212_1
- CD21 CR2 (Complement receptor 2) or C3DR (C3d/Epstein Barr virus
- WO9102536 (Fig 9.1-9.9); WO2004020595 (Claim 1);
- CD79b (CD79B, CD79 , IGb (immunoglobulin-associated beta), B29, Genbank accession no. NM 000626 or 11038674)
- WO2003048202 (claim 1, pages 306 and 309); WO 99/558658, US6534482 (claim 13, Fig 17A/B); WO200055351 (claim 11, pages 1145-1146);
- FcRH2 (IFGP4, IRTA4, SPAPIA (SH2 domain containing phosphatase anchor protein la), SPAP1B, SPAP1C, Genbank accession no. NM 030764, AY358130)
- WO2003055439 (Claim 29; Fig 1A-B); WO2003025228 (Claim 37; Fig 5C);
- WO200222636 (Example 13; Page 95-107); WO200212341 (Claim 68; Fig 7);
- NCA (CEACAM6, Genbank accession no. M18728);
- WO200222153 (Page 45-47); US2002042366 (Page 20-21); WO200146261 (Page
- EphB2R (DRT, ERK, Hek5, EPHT3, Tyro5, Genbank accession no. NM 004442) Chan,J. and Watt, V.M., Oncogene 6 (6), 1057-1061 (1991) Oncogene 10 (5):897-905 (1995), Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 21 :309-345 (1998), Int. Rev. Cytol.
- WO2002102235 (Claim 13; Page 299); US2003091580 (Example 2); WO200210187 (Claim 6; Fig 10); WO200194641 (Claim 12; Fig 7b); WO200202624 (Claim 13; Fig 1A-1B); US2002034749 (Claim 54; Page 45-46); WO200206317 (Example 2; Page 320-321, Claim 34; Page 321-322); WO200271928 (Page 468-469); WO200202587 (Example 1; Fig 1); WO200140269 (Example 3; Pages 190-192); WO200036107 (Example 2; Page 205-207); WO2004053079 (Claim 12); WO2003004989 (Claim 1); WO200271928 (Page 233-234, 452-453); WO 0116318;
- PSCA Prostate stem cell antigen precursor, Genbank accession no. AJ297436
- WO2003003906 (Claim 10; Page 288); WO200140309 (Example 1; Fig 17);
- WO9851805 (Claim 17; Page 97); W09851824 (Claim 10; Page 94); WO9840403 (Claim 2; Fig IB);
- AAP14954 lipoma HMGIC fusion-partner-like protein /pid AAP14954.1 - Homo sapiens Species: Homo sapiens (human)
- WO2003054152 (Claim 20); WO2003000842 (Claim 1); WO2003023013 (Example 3,
- WO2004011611; WO2003045422 (Example; Page 32-33); WO2003014294 (Claim 35; Fig 6B); WO2003035846 (Claim 70; Page 615-616); WO200294852 (Col 136-137);
- WO200238766 (Claim 3; Page 133); WO200224909 (Example 3; Fig 3);
- CD22 B-cell receptor CD22-B isoform, BL-CAM, Lyb-8, Lyb8, SIGLEC-2, FLJ22814, Genbank accession No. AK026467); Wilson et al (1991) J. Exp. Med. 173: 137-146; WO2003072036 (Claim 1; Fig 1);
- CD79a (CD79A, CD79a, immunoglobulin-associated alpha, a B cell-specific protein that covalently interacts with Ig beta (CD79B) and forms a complex on the surface with Ig M molecules, transduces a signal involved in B-cell differentiation), pi: 4.84, MW: 25028 TM: 2 [P] Gene Chromosome: 19ql3.2, Genbank accession No. NP 001774.10)
- CXCR5 Burkitt's lymphoma receptor 1, a G protein-coupled receptor that is activated by the CXCL13 chemokine, functions in lymphocyte migration and humoral defense, plays a role in HIV-2 infection and perhaps development of AIDS, lymphoma, myeloma, and leukemia); 372 aa, pi: 8.54 MW: 41959 TM: 7 [P] Gene Chromosome: l lq23.3, Genbank accession No. NP_001707.1)
- HLA-DOB Beta subunit of MHC class II molecule (la antigen) that binds peptides and presents them to CD4+ T lymphocytes); 273 aa, pi: 6.56 MW: 30820 TM: 1 [P] Gene Chromosome: 6p21.3, Genbank accession No. NP 002111.1)
- CD72 B-cell differentiation antigen CD72, Lyb-2) PROTEIN SEQUENCE Full maeaity...tafrfpd (1..359; 359 aa), pi: 8.66, MW: 40225 TM: 1 [P] Gene Chromosome: 9pl3.3, Genbank accession No. NP_001773.1)
- WO2004042346 (claim 65); WO2003026493 (pages 51-52, 57-58); WO200075655 (pages 105-106); Von Hoegen et al (1990) J. Immunol. 144(12):4870-4877; Strausberg et al (2002) Proc. Natl. Acad.
- LY64 Lymphocyte antigen 64 (RP105), type I membrane protein of the leucine rich repeat (LRR) family, regulates B-cell activation and apoptosis, loss of function is associated with increased disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosis); 661 aa, pi: 6.20, MW: 74147 TM: 1 [P] Gene Chromosome: 5ql2, Genbank accession No.
- FcRHl Fc receptor- like protein 1, a putative receptor for the immunoglobulin Fc domain that contains C2 type Ig-like and IT AM domains, may have a role in B-lymphocyte differentiation
- WO2003089624 (claim 7); (35) IRTA2 (Immunoglobulin superfamily receptor translocation associated 2, a putative immunoreceptor with possible roles in B cell development and lymphomagenesis;
- TENB2 tomoregulin, TPEF, HPP 1 , TR, putative transmembrane
- proteoglycan related to the EGF/heregulin family of growth factors and follistatin
- 374 aa NCBI Accession: AAD55776, AAF91397, AAG49451, NCBI RefSeq: NP 057276; NCBI Gene: 23671; OMIM: 605734; SwissProt Q9UIK5; Genbank accession No. AF179274; AY358907, CAF85723, CQ782436
- WO2004074320 (SEQ ID NO 810); JP2004113151 (SEQ ID NOS 2, 4, 8); WO2003042661 (SEQ ID NO 580); WO2003009814 (SEQ ID NO 411); EP1295944 (pages 69-70);
- WO200230268 page 329
- WO200190304 SEQ ID NO 2706
- US2004249130
- PMEL17 (silver homolog; SILV; D12S53E; PMEL17; (SI); (SIL); ME20; gplOO) BC001414; BT007202; M32295; M77348; NM 006928; McGlinchey,R.P. et al (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106 (33), 13731-13736; Kummer,M.P. et al (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284 (4), 2296-2306;
- TMEFF1 transmembrane protein with EGF-like and two follistatin-like domains 1; Tomoregulin- 1; H7365; C9orf2; C90RF2; U19878; X83961) NM 080655; NM 003692; Harms, P.W. (2003) Genes Dev. 17 (21), 2624-2629; Gery, S. et al (2003) Oncogene 22 (18):2723-2727;
- GDNF-Ral GDNF family receptor alpha 1 ; GFRA1; GDNFR; GDNFRA; RETL1; TRNR1; RET1L; GDNFR-alphal; GFR-ALPHA-1; U95847; BC014962; NM 145793)
- Ly6E lymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus E; Ly67,RIG-E,SCA-2,TSA-l
- TMEM46 shisa homolog 2 (Xenopus laevis); SHISA2) NP 001007539.1;
- Ly6G6D lymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus G6D; Ly6-D, MEGT1
- NP_067079.2 NP_067079.2
- NM_021246.2 Mallya, M. et al (2002) Genomics 80 (1): 113-123; Ribas,G. et al (1999) J. Immunol. 163 (l):278-287;
- LGR5 leucme-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5; GPR49, GPR67
- NP 003658.1 NM 003667.2
- Salanti,G. et al (2009) Am. J. Epidemiol. 170 (5):537-545; Yamamoto,Y. et al (2003) Hepatology 37 (3):528-533
- RET ret proto-oncogene; MEN2A; HSCR1; MEN2B; MTC1; (PTC); CDHF12;
- LY6K lymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus K; LY6K; HSJ001348; FLJ35226) NP_059997.3; NM_017527.3; Ishikawa,N. et al (2007) Cancer Res. 67 (24): 11601-11611; de Nooij-van Dalen,A.G. et al (2003) Int. J. Cancer 103 (6):768-774; (46) GPR19 (G protein-coupled receptor 19; Mm.4787) NP_006134.1; NM_006143.2;
- Tyrosinase (TYR; OCAIA; OCAIA; tyrosinase; SHEP3) NP 000363.1; NM 000372.4; Bishop,D.T. et al (2009) Nat. Genet. 41 (8):920-925; Nan, H. et al (2009) Int. J. Cancer 125 (4):909-917;
- TMEM118 ring finger protein, transmembrane 2; RNFT2; FLJ14627
- GPR172A G protein-coupled receptor 172A; GPCR41; FLJ11856; D15Ertd747e
- the parent antibody may also be a fusion protein comprising an albumin-binding peptide (ABP) sequence (Dennis et al. (2002) “Albumin Binding As A General Strategy For Improving The Pharmacokinetics Of Proteins” J Biol Chem. 277:35035-35043; WO
- ABSP albumin-binding peptide
- Antibodies of the invention include fusion proteins with ABP sequences taught by: (i) Dennis et al (2002) J Biol Chem. 277:35035-35043 at Tables III and IV, page 35038; (ii) US 20040001827 at [0076] SEQ ID NOS: 9-22; and (iii) WO 01/45746 at pages 12-13, SEQ ID NOS: zl-zl4, and all of which are incorporated herein by reference.
- DNA encoding an amino acid sequence variant of the starting polypeptide is prepared by a variety of methods known in the art. These methods include, but are not limited to, preparation by site-directed (or oligonucleotide-mediated) mutagenesis, PCR mutagenesis, and cassette mutagenesis of an earlier prepared DNA encoding the polypeptide. Variants of recombinant antibodies may be constructed also by restriction fragment manipulation or by overlap extension PCR with synthetic oligonucleotides. Mutagenic primers encode the cysteine codon replacement(s). Standard mutagenesis techniques can be employed to generate DNA encoding such mutant cysteine engineered antibodies.
- Site-directed mutagenesis is one method for preparing substitution variants, i.e.
- mutant proteins This technique is well known in the art (see for example, Carter (1985) et al Nucleic Acids Res. 13:4431-4443; Ho et al (1989) Gene (Amst.) 77:51-59; and Kunkel et al (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:488). Briefly, in carrying out site-directed mutagenesis of DNA, the starting DNA is altered by first hybridizing an oligonucleotide encoding the desired mutation to a single strand of such starting DNA.
- a DNA polymerase is used to synthesize an entire second strand, using the hybridized oligonucleotide as a primer, and using the single strand of the starting DNA as a template.
- the oligonucleotide encoding the desired mutation is incorporated in the resulting double-stranded DNA.
- Site-directed mutagenesis may be carried out within the gene expressing the protein to be mutagenized in an expression plasmid and the resulting plasmid may be sequenced to confirm the introduction of the desired cysteine replacement mutations (Liu et al (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273:20252-20260).
- Site-directed of protocols and formats including those commercially available, e.g. QuikChange® Multi Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA).
- PCR mutagenesis is also suitable for making amino acid sequence variants of the starting polypeptide. See Higuchi, (1990) in PCR Protocols, pp.177-183, Academic Press; Ito et al (1991) Gene 102:67-70; Bernhard et al (1994) Bioconjugate Chem. 5: 126-132; and Vallette et al (1989) Nuc. Acids Res. 17:723-733. Briefly, when small amounts of template DNA are used as starting material in a PCR, primers that differ slightly in sequence from the corresponding region in a template DNA can be used to generate relatively large quantities of a specific DNA fragment that differs from the template sequence only at the positions where the primers differ from the template.
- the starting material is the plasmid (or other vector) comprising the starting polypeptide DNA to be mutated.
- the codon(s) in the starting DNA to be mutated are identified. There must be a unique restriction endonuclease site on each side of the identified mutation site(s). If no such restriction sites exist, they may be generated using the above described oligonucleotide -mediated
- oligonucleotide encoding the sequence of the DNA between the restriction sites but containing the desired mutation(s) is synthesized using standard procedures, wherein the two strands of the oligonucleotide are synthesized separately and then hybridized together using standard techniques.
- This double-stranded oligonucleotide is referred to as the cassette.
- This cassette is designed to have 5' and 3' ends that are compatible with the ends of the linearized plasmid, such that it can be directly ligated to the plasmid.
- This plasmid now contains the mutated DNA sequence. Mutant DNA containing the encoded cysteine replacements can be confirmed by DNA sequencing.
- Single mutations are also generated by oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis using double stranded plasmid DNA as template by PCR based mutagenesis (Sambrook and Russel, (2001) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd edition; Zoller et al (1983) Methods Enzymol. 100:468-500; Zoller, M.J. and Smith, M. (1982) Nucl. Acids Res.
- hu4D5Fabv8 displayed on M13 phage (Gerstner et al (2002) "Sequence Plasticity In The Antigen-Binding Site Of A Therapeutic Anti-HER2 Antibody", J Mol Biol. 321 : 851-62) was used for experiments as a model system. Cysteine mutations were introduced in hu4D5Fabv8-phage, hu4D5Fabv8, and ABP-hu4D5Fabv8 constructs. The hu4D5-ThioFab-Phage preps were carried out using the polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation method as described earlier (Lowman, Henry B. (1998) Methods in Molecular Biology (Totowa, New Jersey) 87 (Combinatorial Peptide Library Protocols) 249-264).
- PEG polyethylene glycol
- Oligonucleotides are prepared by the phosphoramidite synthesis method (US
- the phosphoramidite method entails cyclical addition of nucleotide monomer units with a reactive 3 ' phosphoramidite moiety to an oligonucleotide chain growing on a solid-support comprised of controlled-pore glass or highly crosslinked polystyrene, and most commonly in the 3' to 5' direction in which the 3' terminus nucleoside is attached to the solid-support at the beginning of synthesis (US 5047524; US 5262530).
- Oligonucleotides can be chemically labelled with non-isotopic moieties for detection, capture, stabilization, or other purposes (Andrus, A. "Chemical methods for 5' non-isotopic labelling of PCR probes and primers” (1995) in PCR 2: A Practical Approach, Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 39-54; Hermanson, G. in Bioconjugate Techniques (1996) Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 40-55, 643-671; Keller, G. and Manak, M. in DNA Probes Second Edition (1993), Stockton Press, New York, pp. 121-23).
- PHESELECTOR ASSAY Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA.
- the PHESELECTOR Phage ELISA for Selection of Reactive Thiols assay allows for detection of reactive cysteine groups in antibodies in an ELISA phage format (US 7521541; Junutula JR et al. "Rapid identification of reactive cysteine residues for site- specific labeling of antibody-Fabs" J Immunol Methods 2008;332:41-52).
- the process of coating the protein (e.g. antibody) of interest on well surfaces, followed incubation with phage particles and then HRP labeled secondary antibody with absorbance detection is detailed in Example 2. Mutant proteins displayed on phage may be screened in a rapid, robust, and high-throughput manner. Libraries of cysteine engineered antibodies can be produced and subjected to binding selection using the same approach to identify
- FIG. 8 illustrates the PHESELECTOR Assay by a schematic representation depicting the binding of Fab or ThioFab to HER2 (top) and biotinylated ThioFab to streptavidin (bottom).
- DNA encoding the cysteine engineered antibodies is readily isolated and sequenced using conventional procedures (e.g., by using oligonucleotide probes that are capable of binding specifically to genes encoding the heavy and light chains of murine antibodies).
- the hybridoma cells serve as a source of such DNA.
- the DNA may be placed into expression vectors, which are then trans fected into host cells such as E.
- coli cells simian COS cells, Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells, or other mammalian host cells, such as myeloma cells (US 5807715; US 2005/0048572; US 2004/0229310) that do not otherwise produce the antibody protein, to obtain the synthesis of monoclonal antibodies in the recombinant host cells.
- myeloma cells US 5807715; US 2005/0048572; US 2004/0229310
- the yields of hu4D5Fabv8 cysteine engineered antibodies were similar to wild type hu4D5Fabv8.
- Review articles on recombinant expression in bacteria of DNA encoding the antibody include Skerra et al (1993) Curr. Opinion in Immunol. 5:256- 262 and Pluckthun (1992) Immunol. Revs. 130: 151-188.
- cysteine engineered antibodies e.g. ThioFabs, with highly reactive unpaired Cys residues
- a bacterial e.g. E. coli
- a mammalian cell culture system e.g. Chinese Hamster Ovary cells (CHO)
- CHO Chinese Hamster Ovary cells
- ThioFabs were expressed upon induction in 34B8, a non-suppressor E. coli strain (Baca et al (1997) Journal Biological Chemistry 272(16): 10678-84). See Example 3a.
- the harvested cell pellet was resuspended in PBS (phosphate buffered saline), total cell lysis was performed by passing through a microfluidizer and the ThioFabs were purified by affinity chromatography with protein G SEPHAROSETM (Amersham).
- ThioFabs were conjugated with biotin-PEO-maleimide as described above and the biotinylated-ThioFabs were further purified by Superdex-200TM (Amersham) gel filtration chromatography, which eliminated the free biotin-PEO-maleimide and the oligomeric fraction of ThioFabs.
- LC-ESI-MS Liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometric analysis was employed for the accurate molecular weight determination of biotin conjugated Fab (Cole, R.B. Electro Spray Ionization Mass Spectrometry: Fundamentals, Instrumentation And Applications. (1997) Wiley, New York).
- the antibody Fab fragment hu4D5Fabv8 contains about 445 amino acid residues, including 10 Cys residues (five on the light and five on the heavy chain).
- the high-resolution structure of the humanized 4D5 variable fragment (Fv4D5) has been established, see:
- Figure 1 A shows a three-dimensional representation of the hu4D5Fabv8 antibody fragment derived by X-ray crystal coordinates.
- the structure positions of the engineered Cys residues of the heavy and light chains are numbered according to a sequential numbering system.
- This sequential numbering system is correlated to the Kabat numbering system (Kabat et al., (1991) Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, 5th Ed. Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD) for the 4d5v7fabH variant of trastuzumab according to Figure IB which shows the sequential numbering scheme (top row), starting at the N-terminus, differs from the Kabat numbering scheme (bottom row) by insertions noted by a,b,c.
- the actual linear amino acid sequence may contain fewer or additional amino acids corresponding to a shortening of, or insertion into, a FR or CDR of the variable domain.
- the cysteine engineered heavy chain variant sites are identified by the sequential numbering and Kabat numbering schemes in the following chart:
- Ml 3 phagemid-Cys mutant Fabs ( Figures 3 A and 3B) can be rapidly screened compared to Fab proteins.
- Phagemid-ThioFab binding to antigen and to streptavidin can be tested by coating HER2 and streptavidin, respectively, onto ELISA plates followed by probing with anti-Fab-HRP (Horse radish peroxidase) as described in Example 2 and depicted in Figure 8.
- This method allowed simultaneous monitoring of the effect on the antigen binding and the reactivity of the thiol group by the engineered Cys
- the method can be applied to screen the reactive thiol groups for any protein displayed on Ml 3 phage.
- Conjugated or unconjugated phagemid-ThioFabs are purified by simple PEG precipitation.
- FIG. 8 is a graphical representation of the PHESELECTOR assay, depicting binding of a biotinylated ThioFab phage and an anti-phage HRP antibody to HER2 (top) and Streptavidin (bottom).
- Biotin conjugated and unconjugated variants were tested for HER2 and streptavidin binding using an ELISA based PHESELECTOR assay ( Figure 8, Example 2) with an HRP (horseradish peroxidase)-conjugated anti-phage antibody.
- HRP horseradish peroxidase
- the ThioFabs-phage samples showed varying levels of streptavidin binding activity. From all the tested phage-ThioFabs, the A121C cysteine engineered antibody exhibited maximal thiol reactivity. Even though wild type hu4D5Fabv8- phage was incubated with the same amounts of biotin-maleimide, these phage had little streptavidin binding indicating that preexisting cysteine residues (involved in disulfide bond formation) from the hu4D5Fabv8 and Ml 3 phage coat proteins did not interfere with the site- specific conjugation of biotin-maleimide. These results demonstrate that the phage ELISA assay can be used successfully to screen reactive thiol groups on the Fab surface.
- the PHESELECTOR assay allows screening of reactive thiol groups in antibodies.
- a parameter, fractional surface accessibility was employed to identify and quantitate the accessibility of solvent to the amino acid residues in a polypeptide.
- the surface accessibility can be expressed as the surface area (A 2 ) that can be contacted by a solvent molecule, e.g. water.
- a solvent molecule e.g. water.
- the occupied space of water is approximated as a 1.4 A radius sphere.
- Software is freely available or licensable (Secretary to CCP4, Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington, WA4 4 AD, United Kingdom, Fax: (+44) 1925 603825, or by internet:
- AREAIMOL defines the solvent accessible surface of a protein as the locus of the centre of a probe sphere (representing a solvent molecule) as it rolls over the Van der Waals surface of the protein.
- AREAIMOL calculates the solvent accessible surface area by generating surface points on an extended sphere about each atom (at a distance from the atom centre equal to the sum of the atom and probe radii), and eliminating those that lie within equivalent spheres associated with neighboring atoms.
- AREAIMOL finds the solvent accessible area of atoms in a PDB coordinate file, and summarizes the accessible area by residue, by chain and for the whole molecule. Accessible areas (or area differences) for individual atoms can be written to a pseudo-PDB output file.
- AREAIMOL assumes a single radius for each element, and only recognizes a limited number of different elements. Unknown atom types (i.e. those not in AREAIMOL's internal database) will be assigned the default radius of 1.8 A. The list of recognized atoms is:
- AREAIMOL and SURFACE report absolute accessibilities, i.e. the number of square Angstroms (A).
- Fractional surface accessibility is calculated by reference to a standard state relevant for an amino acid within a polypeptide.
- the reference state is tripeptide Gly-X-Gly, where X is the amino acid of interest, and the reference state should be an 'extended' conformation, i.e. like those in beta-strands.
- the extended conformation maximizes the accessibility of X.
- a calculated accessible area is divided by the accessible area in a Gly-X- Gly tripeptide reference state and reports the quotient, which is the fractional accessibility. Percent accessibility is fractional accessibility multiplied by 100.
- Another exemplary algorithm for calculating surface accessibility is based on the SOLV module of the program xsae (Broger, C, F. Hoffman-LaRoche, Basel) which calculates fractional accessibility of an amino acid residue to a water sphere based on the X- ray coordinates of the polypeptide.
- Residues are sorted based on their role in functional and structural interactions of
- Thiol reactivity may be generalized to any antibody where substitution of amino acids with reactive cysteine amino acids may be made within the ranges in the light chain selected from: L-10 to L-20; L-38 to L-48; L-105 to L-l 15; L-139 to L-149; L-163 to L-173; and within the ranges in the heavy chain selected from: H-35 to H-45; H-83 to H-93; H-l 14 to H- 127; and H-l 70 to H-l 84, and in the Fc region within the ranges selected from H-268 to H- 291; H-319 to H-344; H-370 to H-380; and H-395 to H-405.
- Thiol reactivity may also be generalized to certain domains of an antibody, such as the light chain constant domain (CL) and heavy chain constant domains, CHI, CH2 and CH3. Cysteine replacements resulting in thiol reactivity values of 0.6 and higher may be made in the heavy chain constant domains ⁇ , ⁇ , ⁇ , ⁇ , and ⁇ of intact antibodies: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM, respectively, including the IgG subclasses: IgGl, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4, IgA, and IgA2.
- Thiol reactivity data is shown in Figures 3A and 3B for amino acid residues of 4D5 ThioFab Cys mutants: (3 A) non-biotinylated (control) and (3B) biotinylated phage-ThioFabs. Reactive thiol groups on antibody/Fab surface were identified by PHESELECTOR assay analyses for the interaction of non-biotinylated phage-hu4D5Fabv8 (3 A) and biotinylated phage-hu4D5Fabv8 (3B) with BSA (open box), HER2 (grey box) or streptavidin (solid box). The assay was carried out as described in Example 2.
- Light chain variants are on the left side and heavy chain variants are on the right side.
- the binding of non-biotinylated 4D5 ThioFab Cys mutants is low as expected, but strong binding to HER2 is retained.
- the ratio of binding to streptavidin and to HER2 of the biotinylated 4D5 ThioFab Cys mutants gives the thiol reactivity values in Table 2.
- Background absorbance at 450 nm or small amounts of nonspecific protein binding of the biotinylated 4D5 ThioFab Cys mutants to BSA is also evident in Figure 3B. Fractional Surface Accessibility values of the selected amino acid residues that were replaced with a Cys residue are shown in Figure 4A.
- Amino acids at positions L-15, L-43, L-l 10, L-144, L-168, H-40, H-88, H-l 19, H- 121, H-l 22, H-l 75, and H-l 79 of an antibody may generally be mutated (replaced) with free cysteine amino acids. Ranges within about 5 amino acid residues on each side of these positions may also be replaced with free cysteine acids, i.e.
- L light chain
- H heavy chain
- A alanine
- S serine
- V valine
- C cysteine
- Thiol reactivity is measured as the ratio of OD 450 nm for streptavidin binding to OD 450 ancient for HER2 (antibody) binding (Example 2). Thiol reactivity value of 1 indicates complete biotinylation of the cysteine thiol.
- Fab preparation may require 2-3 days, depending on the scale of production. During this time, thiol groups may lose reactivity due to oxidation.
- stability of the thiol reactivity of phage-thioFabs was measured ( Figure 4B).
- ThioFab-phage purification on day 1, day 2 and day 4, all the samples were conjugated with biotin-PEO-maleimide and probed with phage ELISA assay (PHESELECTOR) to test HER2 and streptavidin binding.
- PESELECTOR phage ELISA assay
- the compounds of the invention include cysteine engineered antibodies where one or more amino acids of a parent antibody are replaced with a free cysteine amino acid.
- a cysteine engineered antibody comprises one or more free cysteine amino acids having a thiol reactivity value in the range of 0.6 to l .O.
- a free cysteine amino acid is a cysteine residue which has been engineered into the parent antibody and is not part of a disulfide bridge.
- cysteine engineered antibody is prepared by a process comprising:
- the cysteine engineered antibody may be more reactive than the parent antibody with the thiol-reactive reagent.
- the free cysteine amino acid residues may be located in the heavy or light chains, or in the constant or variable domains.
- Antibody fragments e.g. Fab, may also be engineered with one or more cysteine amino acids replacing amino acids of the antibody fragment, to form cysteine engineered antibody fragments.
- Another aspect of the invention provides a method of preparing (making) a cysteine engineered antibody, comprising:
- cysteine engineered antibody is more reactive than the parent antibody with the thiol-reactive reagent.
- Step (a) of the method of preparing a cysteine engineered antibody may comprise:
- Step (b) of the method of preparing a cysteine engineered antibody may comprise expressing the cysteine engineered antibody on a viral particle selected from a phage or a phagemid particle.
- Step (b) of the method of preparing a cysteine engineered antibody may also comprise:
- Another aspect of the invention is a method of screening cysteine engineered antibodies with highly reactive, unpaired cysteine amino acids for thiol reactivity
- Step (a) of the method of screening cysteine engineered antibodies may comprise:
- Step (b) of the method of screening cysteine engineered antibodies may comprise expressing the cysteine engineered antibody on a viral particle selected from a phage or a phagemid particle.
- Step (b) of the method of screening cysteine engineered antibodies may also comprise:
- the cysteine engineered antibodies of the invention may be conjugated with any label moiety which can be covalently attached to the antibody through a reactive cysteine thiol group (Singh et al (2002) Anal. Biochem. 304: 147-15; Harlow E. and Lane, D. (1999) Using Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Springs Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY; Lundblad R.L. (1991) Chemical Reagents for Protein Modification, 2nd ed. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL).
- the attached label may function to: (i) provide a detectable signal; (ii) interact with a second label to modify the detectable signal provided by the first or second label, e.g.
- FRET fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- Labelled cysteine engineered antibodies may be useful in diagnostic assays, e.g., for detecting expression of an antigen of interest in specific cells, tissues, or serum.
- the antibody will typically be labeled with a detectable moiety.
- Radioisotopes such as 3 H, n C, 14 C, 18 F, 32 P, 35 S, 64 Cu, 68 Ga,
- the antibody can be labeled with ligand reagents that bind, chelate or otherwise complex a radioisotope metal where the reagent is reactive with the engineered cysteine thiol of the antibody, using the techniques described in Current Protocols in Immunology, Volumes 1 and 2, Coligen et al, Ed. Wiley- Interscience, New York, NY, Pubs. (1991).
- Chelating ligands which may complex a metal ion include DOT A, DOPA, DOTP, DOTMA, DTP A and TETA (Macrocyclics, Dallas, TX).
- Radionuclides can be targetted via complexation with cysteine-engineered antibodies as antibody-zirconium conjugates of the invention (Wu et al (2005) Nature Biotechnology 23(9): 1137-1146).
- Metal-chelate complexes suitable as antibody labels for imaging experiments are disclosed: US 5342606; US 5428155; US 5316757; US 5480990; US 5462725; US 5428139; US 5385893; US 5739294; US 5750660; US 5834456; Hnatowich et al (1983) J. Immunol. Methods 65: 147-157; Meares et al (1984) Anal. Biochem. 142:68-78; Mirzadeh et al (1990) Bioconjugate Chem. 1 :59-65; Meares et al (1990) J. Cancerl990, Suppl. 10:21-26; Izard et al (1992) Bioconjugate Chem.
- Fluorescent labels such as rare earth chelates (europium chelates), fluorescein types including FITC, 5-carboxyfluorescein, 6-carboxy fluorescein; rhodamine types including TAMRA; dansyl; Lissamine; cyanines; phycoerythrins; Texas Red; and analogs thereof.
- the fluorescent labels can be conjugated to antibodies using the techniques disclosed in Current Protocols in Immunology, supra, for example. Fluorescent dyes and fluorescent label reagents include those which are commercially available from
- the enzyme generally catalyzes a chemical alteration of a chromogenic substrate that can be measured using various techniques. For example, the enzyme may catalyze a color change in a substrate, which can be measured spectrophotometrically. Alternatively, the enzyme may alter the fluorescence or chemiluminescence of the substrate. Techniques for quantifying a change in fluorescence are described above.
- the chemiluminescent substrate becomes electronically excited by a chemical reaction and may then emit light which can be measured (using a chemiluminometer, for example) or donates energy to a fluorescent acceptor.
- enzymatic labels include luciferases ⁇ e.g., firefly luciferase and bacterial luciferase; US 4737456), luciferin, 2,3-dihydrophthalazinediones, malate dehydrogenase, urease, peroxidase such as horseradish peroxidase (HRP), alkaline phosphatase (AP), ⁇ - galactosidase, glucoamylase, lysozyme, saccharide oxidases ⁇ e.g., glucose oxidase, galactose oxidase, and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase), heterocyclic oxidases (such as uricase and xanthine oxidase), lactoperoxidase, microperoxidase, and the like.
- luciferases ⁇ e.g., firefly luciferase and bacterial luciferase;
- enzyme-substrate combinations include, for example:
- HRP Horseradish peroxidase
- OPD orthophenylene diamine
- TMB 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine hydrochloride
- ⁇ -D-galactosidase ( ⁇ -D-Gal) with a chromogenic substrate ⁇ e.g., p- nitrophenyl- -D-galactosidase) or fluorogenic substrate 4-methylumbelliferyl- -D- galactosidase.
- a chromogenic substrate ⁇ e.g., p- nitrophenyl- -D-galactosidase
- fluorogenic substrate 4-methylumbelliferyl- -D- galactosidase 4-methylumbelliferyl- -D- galactosidase.
- a label may be indirectly conjugated with a cysteine engineered antibody.
- the antibody can be conjugated with biotin and any of the three broad categories of labels mentioned above can be conjugated with avidin or streptavidin, or vice versa. Biotin binds selectively to streptavidin and thus, the label can be conjugated with the antibody in this indirect manner.
- the polypeptide variant is conjugated with a small hapten (e.g., digoxin) and one of the different types of labels mentioned above is conjugated with an anti-hapten polypeptide variant ⁇ e.g., anti-digoxin antibody).
- a small hapten e.g., digoxin
- an anti-hapten polypeptide variant e.g., anti-digoxin antibody
- polypeptide variant of the present invention may be employed in any known assay method, such as ELISA, competitive binding assays, direct and indirect sandwich assays, and immunoprecipitation assays (Zola, (1987) Monoclonal Antibodies: A Manual of Techniques, pp.147-158, CRC Press, Inc.).
- a detection label may be useful for localizing, visualizing, and quantitating a binding or recognition event.
- the labelled antibodies of the invention can detect cell-surface receptors.
- Another use for detectably labelled antibodies is a method of bead-based immunocapture comprising conjugating a bead with a fluorescent labelled antibody and detecting a fluorescence signal upon binding of a ligand. Similar binding detection methodologies utilize the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) effect to measure and detect antibody-antigen interactions.
- SPR surface plasmon resonance
- Detection labels such as fluorescent dyes and chemiluminescent dyes (Briggs et al (1997) "Synthesis of Functionalised Fluorescent Dyes and Their Coupling to Amines and
- the labels preferably (iii) have good water-solubility to achieve effective conjugate concentration and detection sensitivity and (iv) are non-toxic to living cells so as not to disrupt the normal metabolic processes of the cells or cause premature cell death.
- fluorescently labelled events e.g. cell surface binding of peptide-dye conjugates may be conducted on an system (FMAT® 8100 HTS System, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, Calif.) that automates mix-and-read, non-radioactive assays with live cells or beads (Miraglia, "Homogeneous cell- and bead-based assays for high throughput screening using fluorometric microvolume assay technology", (1999) J. of Biomolecular Screening 4: 193-204).
- FMAT® 8100 HTS System Applied Biosystems, Foster City, Calif.
- labelled antibodies also include cell surface receptor binding assays, inmmunocapture assays, fluorescence linked immunosorbent assays (FLISA), caspase-cleavage (Zheng, "Caspase-3 controls both cytoplasmic and nuclear events associated with Fas-mediated apoptosis in vivo", (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:618-23; US 6372907), apoptosis (Vermes, "A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V" (1995) J. Immunol. Methods 184:39-51) and cytotoxicity assays. Fluorometric microvolume assay technology can be used to identify the up or down regulation by a molecule that is targeted to the cell surface
- Labelled cysteine engineered antibodies of the invention are useful as imaging biomarkers and probes by the various methods and techniques of biomedical and molecular imaging such as: (i) MRI (magnetic resonance imaging); (ii) MicroCT (computerized tomography); (iii) SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography); (iv) PET
- Imaging biomarkers may be objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacological responses to a therapeutic intervention.
- Biomarkers may be of several types: Type 0 are natural history markers of a disease and correlate longitudinally with known clinical indices, e.g.
- Imaging biomarkers thus can provide pharmacodynamic (PD) therapeutic information about: (i) expression of a target protein, (ii) binding of a therapeutic to the target protein, i.e. selectivity, and (iii) clearance and half-life pharmacokinetic data.
- PD pharmacodynamic
- in vivo imaging biomarkers relative to lab-based biomarkers include: non-invasive treatment, quantifiable, whole body assessment, repetitive dosing and assessment, i.e. multiple time points, and potentially transferable effects from preclinical (small animal) to clinical (human) results. For some applications, bioimaging supplants or minimizes the number of animal experiments in preclinical studies.
- Radionuclide imaging labels include radionuclides such as H, C, C, F, P, S,
- radionuclide metal ion can be complexed with a chelating linker such as DOTA.
- Linker reagents such as DOTA-maleimide (4-maleimidobutyramidobenzyl-DOTA) can be prepared by the reaction of aminobenzyl-DOTA with 4-maleimidobutyric acid (Fluka) activated with isopropylchloro formate (Aldrich), following the procedure of Axworthy et al (2000) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97(4): 1802-1807). DOTA-maleimide reagents react with the free cysteine amino acids of the cysteine engineered antibodies and provide a metal complexing ligand on the antibody (Lewis et al (1998) Bioconj. Chem. 9:72-86).
- Chelating linker labelling reagents such as DOTA-NHS (l,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-l,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid mono (N-hydroxysuccinimide ester) are commercially available (Macrocyclics, Dallas, TX).
- Receptor target imaging with radionuclide labelled antibodies can provide a marker of pathway activation by detection and quantitation of progressive accumulation of antibodies in tumor tissue (Albert et al (1998) Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 8: 1207-1210).
- the conjugated radio-metals may remain intracellular following lysosomal degradation.
- FRET fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- Reporter groups are typically fluorescent dyes that are excited by light at a certain wavelength and transfer energy to an acceptor, or quencher, group, with the appropriate Stokes shift for emission at maximal brightness.
- Fluorescent dyes include molecules with extended aromaticity, such as fluorescein and rhodamine, and their derivatives.
- the fluorescent reporter may be partially or significantly quenched by the quencher moiety in an intact peptide. Upon cleavage of the peptide by a peptidase or protease, a detectable increase in fluorescence may be measured (Knight, C. (1995) "Fluorimetric Assays of Proteolytic Enzymes", Methods in Enzymology, Academic Press, 248: 18-34).
- the labelled antibodies of the invention may also be used as an affinity purification agent.
- the labelled antibody is immobilized on a solid phase such a Sephadex resin or filter paper, using methods well known in the art.
- the immobilized antibody is contacted with a sample containing the antigen to be purified, and thereafter the support is washed with a suitable solvent that will remove substantially all the material in the sample except the antigen to be purified, which is bound to the immobilized polypeptide variant. Finally, the support is washed with another suitable solvent, such as glycine buffer, pH 5.0, that will release the antigen from the polypeptide variant.
- Labelling reagents typically bear reactive functionality which may react (i) directly with a cysteine thiol of a cysteine engineered antibody to form the labelled antibody, (ii) with a linker reagent to form a linker-label intermediate, or (iii) with a linker antibody to form the labelled antibody.
- Reactive functionality of labelling reagents include: maleimide, haloacetyl, iodoacetamide succinimidyl ester (e.g.
- An exemplary reactive functional group is N-hydroxysuccinimidyl ester (NHS) of a carboxyl group substituent of a detectable label, e.g. biotin or a fluorescent dye.
- the NHS ester of the label may be preformed, isolated, purified, and/or characterized, or it may be formed in situ and reacted with a nucleophilic group of an antibody.
- the carboxyl form of the label is activated by reacting with some combination of a carbodiimide reagent, e.g. dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, diisopropylcarbodiimide, or a uranium reagent, e.g.
- TSTU (0-(N-Succinimidyl)-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate
- HBTU O- benzotriazol-l-yl)-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate
- HATU (0-(7- azabenzotriazol-l-yl)-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate
- an activator such as 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBt)
- HOBt 1-hydroxybenzotriazole
- N-hydroxysuccinimide to give the NHS ester of the label.
- the label and the antibody may be coupled by in situ activation of the label and reaction with the antibody to form the label-antibody conjugate in one step.
- Other activating and coupling reagents include TBTU (2-(lH-benzotriazo-l-yl)-l-l,3,3- tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate), TFFH (N,N',N",N"'-tetramethyluronium 2- fluoro-hexafluorophosphate), PyBOP (benzotriazole- 1 -yl-oxy-tris-pyrrolidino-phosphonium hexafluorophosphate, EEDQ (2-ethoxy-l-ethoxycarbonyl-l,2-dihydro-quinoline), DCC (dicyclohexylcarbodiimide); DIPCDI (diisopropylcarbodiimide), MSNT (l-(mesitylene-2- sulfonyl)-3-nitro
- ThioFab constructs were cloned into an expression vector under alkaline phosphatase promoter (Chang et al (1987) Gene 55: 189-196) and the ThioFab expression was induced by growing E. coli cells in the phosphate-free medium.
- ThioFabs were purified on a Protein G SEPHAROSETM column and analyzed on reducing and non-reducing SDS-PAGE gels.
- ThioFabs L-V15C, L-Vl IOC, H-A88C, and H-A121C were expressed and purified by Protein-G SEPHAROSETM column chromatography (see methods sections for details). Purified proteins were analyzed on SDS-PAGE gel in reducing (with DTT) and non-reducing (without DTT) conditions. Other reducing agents such as BME (beta-mercaptoethanol) can used in the gel to cleave interchain disulfide groups. It is evident from SDS-PAGE gel analysis that the major (-90%) fraction of ThioFab is in the monomeric form, while wild type hu4D5Fabv8 is essentially in the monomeric form (47 kDa).
- ThioFab (A121C) and wild type hu4D5Fabv8 were incubated with 100 fold excess of biotin-maleimide for 3 hours at room temperature and the biotinylated Fabs were loaded onto a Superdex-200TM gel filtration column. This purification step was useful in separating monomeric Fab from oligomeric Fab and also from excess free biotin-maleimide (or free zirconium reagent).
- FIG. 5 shows validation of the properties of ThioFab variants in the absence of the phage context.
- the proteins without phage fusion, hu4D5Fabv8 and hu4D5Fabv8-A121C (ThioFab-A121C) were expressed and purified using protein-G agarose beads followed by incubation with 100 fold molar excess of biotin-maleimide.
- Streptavidin and HER2 binding of a biotinylated cys engineered ThioFab and a non-biotinylated wild type Fab was compared.
- the extent of biotin conjugation (interaction with streptavidin) and their binding ability to HER2 were monitored by ELISA analyses. Each Fab was tested at 2ng and 20ng.
- Biotinylated A121C ThioFab retained comparable HER2 binding to that of wild type hu4D5Fabv8 (Figure 5).
- Wild type Fab and A121C-ThioFab were purified by gel filtration column chromatography. The two samples were tested for HER2 and streptavidin binding by ELISA using goat anti-Fab-HRP as secondary antibody. Both wild type (open box) and
- ThioFab (dotted box) have similar binding to HER2 but only ThioFab retained streptavidin binding. Only a background level of interaction with streptavidin was observed with non- biotinylated wild type hu4D5Fabv8 ( Figure 5).
- Plasma-protein binding can be an effective means of improving the pharmacokinetic properties of short lived molecules.
- Albumin is the most abundant protein in plasma.
- Serum albumin binding peptides can alter the pharmacodynamics of fused active domain proteins, including alteration of tissue uptake, penetration, and diffusion.
- albumin binding peptide sequence US 20040001827.
- a series of albumin binding peptides were identified by phage display screening (Dennis et al. (2002) “Albumin Binding As A General Strategy For Improving The Pharmacokinetics Of Proteins” J Biol Chem. 277:35035-35043; WO 01/45746).
- Compounds of the invention include ABP sequences taught by: (i) Dennis et al (2002) J Biol Chem.
- Albumin Binding (ABP)-Fabs were engineered by fusing an albumin binding peptide to the C-terminus of Fab heavy chain in 1 : 1 stoichiometric ratio (1 ABP / 1 Fab). It was shown that association of these ABP-Fabs with albumin increased their half life by more than 25 fold in rabbits and mice. The above described reactive Cys residues can therefore be introduced in these ABP-Fabs and used for site-specific conjugation with zirconium reagents followed by in vivo animal studies.
- Exemplary albumin binding peptide sequences include, but are not limited to the amino acid sequences listed in SEQ ID NOS: 1-5:
- the albumin binding peptide does not compete with ligands known to bind albumin and has a half life (T1 ⁇ 2) in rabbit of 2.3 hr.
- ABP-ThioFab proteins were purified on BSA-SEPHAROSETM followed by biotin-maleimide conjugation and purification on Superdex-S200 column chromatography as described in previous sections. Purified biotinylated proteins were homogeneous and devoid of any oligomeric forms (Example 4).
- FIG. 6 shows the properties of Albumin Binding Peptide (ABP)-ThioFab variants.
- ELISA analyses were carried out to test the binding ability of ABP-hu4D5Fabv8-wt, ABP- hu4D5Fabv8-Vl IOC and ABP-hu4D5Fabv8-A121C with rabbit albumin, streptavidin and HER2.
- Biotinylated ABP-ThioFabs are capable of binding to albumin and HER2 with similar affinity to that of wild type ABP-hu4D5Fabv8 as confirmed by ELISA ( Figure 6) and BIAcore binding kinetics analysis (Table 3).
- An ELISA plate was coated with albumin, HER2 and SA as described.
- Biotinylated ABP-ThioFabs were capable of binding to streptavidin compared to non biotinylated control ABP-hu4D5Fabv8-wt indicating that ABP- ThioFabs were conjugated with biotin maleimide like ThioFabs in a site specific manner as the same Cys mutants were used for both the variants (Figure 6).
- Table 3 BIAcore kinetic analysis for HER2 and rabbit albumin binding to biotinylated
- ABP albumin binding peptide
- an albumin-binding peptide may be linked to the antibody by covalent attachment through a linker moiety.
- HER2/Fab, SA/Fab and SA/SA indicate that their interactions were monitored by anti-Fab-HRP, SA- HRP, respectively.
- SA/Fab monitors the presence of single biotin per Fab and more than one biotin per Fab is monitored by SA/SA analysis. Binding of HER2 with double cys mutants is similar to that of single Cys variants ( Figure 7). However the extent of biotinylation on double Cys mutants was higher compared to single Cys variants due to more than one free thiol group per Fab molecule ( Figure 7).
- the single cys mutants H-A88C, H- A121C and L-Vl IOC of trastuzumab, and double cys mutants VI 10C-A121C and VI 10C- A121C of trastuzumab were expressed in CHO (Chinese Hamster Ovary) cells by transient fermentation in media containing 1 mM cysteine.
- the A88C mutant heavy chain sequence (450 aa) is SEQ ID NO:6.
- the A121C mutant heavy chain sequence (450 aa) is SEQ ID NO:7.
- the VI IOC mutant light chain sequence (214 aa) is SEQ ID NO:8.
- the cysteine engineered thio-trastuzumab antibodies comprise one or more of the following variable region heavy chain sequences with a free cysteine amino acid (SEQ ID NOS: 9-16). Mutant Sequence SEQ ID NO
- cysteine engineered thio-trastuzumab antibodies comprise one or more of the following variable region light chain sequences with a free cysteine amino acid (SEQ ID NOS: 17-27).
- FIG. 13 A shows a cartoon depiction of biotinylated antibody binding to immobilized HER2 and HRP labeled secondary antibody for absorbance detection.
- Figure 13B shows binding measurements to immobilized HER2 with detection of absorbance at 450 nm of (left to right): non-biotinylated wild type trastuzumab (Wt), biotin- maleimide conjugated thio-trastuzumab variants VI IOC (single cys), A121C (single cys), and VI 10C-A121C (double cys).
- Wt non-biotinylated wild type trastuzumab
- VI IOC sino cys
- A121C single cys
- VI 10C-A121C double cys
- Figure 14A shows a cartoon depiction of a biotinylated antibody binding to immobilized HER2 with binding of biotin to anti-IgG-HRP for absorbance detection.
- Figure 14B shows binding measurements with detection of absorbance at 450 nm of biotin- maleimide conjugated thio-trastuzumab variants and non-biotinylated wild type trastuzumab in binding to streptavidin. From left to right: VI IOC (single cys), A121C (single cys), VI 10C/A121C (double cys), and trastuzumab. Each thio IgG trastuzumab variant and parent trastuzumab was tested at 1, 10, and 100 ng. The measurements show that the HER2
- ThioMabs have high thiol reactivity.
- Cysteine was introduced into the full-length 2H9 anti-EphB2R antibody at certain residues.
- the single cys mutant H-A121C of 2H9 was expressed in CHO (Chinese Hamster Ovary) cells by transient fermentation in media containing 1 mM cysteine.
- the A121C 2H9 mutant heavy chain sequence (450 aa) is SEQ ID NO:28.
- Cysteine engineered thio-2H9 antibodies comprise the following Fc constant region heavy chain sequences with a free cysteine amino acid (SEQ ID NOS: 29-38).
- Figure 16 shows non-reducing (top) and reducing (bottom) denaturing SDS-PAGE (polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) analysis of 2H9 ThioMab Fc variants (left to right, lanes 1-9): A339C; S337C; S324C; A287C; V284C; V282C; V279C; and V273C, with 2H9 wild type, after purification on immobilized Protein A.
- the lane on the right is a size marker ladder, indicating the intact proteins are about 150 kDa, heavy chain fragments about 50 kDa, and light chain fragments about 25 kDa.
- Figure 17A shows non-reducing (left) and reducing (right) denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis of 2H9 ThioMab variants (left to right, lanes 1-4): L-V15C; S179C; S375C; S400C, after purification on immobilized Protein A.
- Figure 17B shows non-reducing (left) and reducing (+DTT) (right) denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis of additional 2H9 and 3A5 ThioMab variants after purification on immobilized Protein A.
- the 2H9 ThioMab variants (in the Fab as well as Fc region) were expressed and purified as described.
- all the proteins are homogenous on SDS-PAGE followed by the reduction and oxidation procedure of Example 11 to prepare reactive ThioMabs for conjugation (Example 12).
- Cysteine was introduced into the full-length 3A5 anti-MUC16 antibody at certain residues.
- the single cys mutant H-A121C of 3A5 was expressed in CHO (Chinese Hamster Ovary) cells by transient fermentation in media containing 1 mM cysteine.
- the A121C 3A5 mutant heavy chain sequence (446 aa) comprises SEQ ID NO:39.
- Cysteine engineered thio-3A5 anti-MUC16 antibodies comprise the following variable region heavy chain sequences with a free cysteine amino acid (SEQ ID NOS: 40-44). Mutant Sequence SEQ ID NO:
- Cysteine engineered thio-3A5 anti-MUC16 antibodies comprise the following variable region light chain sequences with a free cysteine amino acid (SEQ ID NOS: 45-49).
- the thiol reactivity of full length, IgG cysteine engineered antibodies was measured by biotinylation and streptavidin binding.
- a western blot assay was set up to screen the ThioMab that is specifically conjugated with biotin-maleimide.
- the antibodies are analyzed on reducing SDS-PAGE and the presence of Biotin is specifically probed by incubating with streptavidin-HRP.
- streptavidin-HRP interaction is either observed in heavy chain or light chain depending on which engineered cys variant is being used and no interaction is seen with wild type, indicating that ThioMab variants specifically conjugated the biotin at engineered Cys residue.
- Figure 18 shows denaturing gel analysis of reduced, biotinylated Thio-IgG variants after capture on immobilized anti-IgG-HRP (top gel) and streptavidin-HRP (bottom gel).
- Lane 1 3A5 H- A121C.
- Lane 2 3A5 L-V110C.
- Lane 3 2H9 H-A121C.
- Lane 4 2H9 L-V110C.
- Lane 5 anti-EphB2R 2H9 parent, wild type.
- Each mutant (lanes 1-4) was captured by anti-IgG with HRP detection (top) indicating that selectivity and affinity were retained.
- Capture by immobilized streptavidin with HRP detection (bottom) confirmed the location of biotin on heavy and light chains.
- the location of cysteine mutation on the cysteine engineered antibodies in lanes 1 and 3 is the heavy chain.
- the location of cysteine mutation on the cysteine engineered antibodies in lanes 2 and 4 is the light chain.
- the cysteine mutation site undergoes conjugation with the biotin-maleimide reagent.
- Analysis of the ThioMab cysteine engineered antibodies of Figure 18 and a 2H9 V15C variant by LC/MS gave quantitative indication of thiol reactivity (Table 5).
- Cysteine engineering was conducted in the constant domain, i.e. Fc region, of IgG antibodies. A variety of amino acid sites were converted to cysteine sites and the expressed mutants, i.e. cysteine engineered antibodies, were assessed for their thiol reactivity.
- FIG. 19 schematic diagram, the streptavidin-biotin interaction is monitored by probing with anti-IgG-HRP followed by measuring absorbance at 450 nm.
- These results confirmed 2H9- ThioFc variants V282C, A287C, A339C, S375C and S400C had moderate to highest Thiol reactivity.
- the extent of biotin conjugation of 2H9 ThioMab Fc variants was quantitated by LS/MS analysis as reported in Table 6.
- the LS/MS analysis confirmed that the A282C, S375C and S400C variants had 100% biotin conjugation and V284C and A339C had 50% conjugation, indicating the presence of a reactive cysteine thiol group.
- the other ThioFc variants, and the parent, wild type 2H9 had either very little biotinylation or none.
- Desferoxamine B ( ⁇ '- ⁇ 5-[acetyl(hydroxy)amino]pentyl ⁇ -N-[5-( ⁇ 4-[(5- aminopentyl)(hydroxy)amino]-4-oxobutanoyl ⁇ amino)pentyl]-N-hydroxysuccinamide (CAS Reg. No. 70-51-9); and also known as Deferoxamine, desferoxamine B, DFO-B, DFOA, DFB or desferal) is a bacterial siderophore produced by the actinobacter Streptomyces pilosus ( Figure 20 top). Desferoxamine B has medical applications as a chelating agent used to remove excess iron from the body (Miller, Marvin J.
- TFP-N-Suc-Df Figure 20 center
- mAb-N-Suc-Df was chelated with 89 Zr.
- Embodiments of zirconium complexes also include zirconium-binding (chelating) ligands such as DTP A (CAS Reg. No. 67-43-6), DOP A(l, 4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane- 1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid) (Liu, Shuang (2008) Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 60(12): 1347-1370), cyclopentadienyl, and allyl groups (Erker, G. (1991) Pure and Applied Chemistry 63(6):797-806; Erker, G. (1990) Jour, of Organometallic Chem. 400(1-2): 185- 203), each of which are incorporated by reference herein.
- DTP A CAS Reg. No. 67-43-6
- DOP A(l, 4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane- 1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid) Liu, Shuang (2008) Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 60(12): 1347-1370
- Zirconium complexes (Z) and other radionuclides may be conjugated to antibodies (Ab), including monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) through ⁇ -amino group in lysine side chain or through thiol group of cysteine. Since approximately 40 lysine side chains (Wang L et al "Structural characterization of the maytansinoid-monoclonal antibody immunoconjugate, huN901-DMl, by mass spectrometry” (2005) Protein Sci. 14:2436-46) or 8 cysteines (Hamblett KJ et al. "Effects of drug loading on the antitumor activity of a monoclonal antibody drug conjugate" (2004) Clin Cancer Res.
- THlOMABs site-specifically radiolabeled cysteine- engineered antibodies
- One aspect of the present invention is a method for site-specific radiolabeling of THIOMABs using novel Df-based thiol reactive bifunctional reagents
- trastuzumab trastuzumab
- Zr zinc-reacted calcium
- One metastable isomer of zirconium is 89 Zr with a half-life of 78.4 hours with decay modes of beta (electron emission), positron (beta plus), and gamma radiation.
- radioisotope or other labels may be incorporated in the conjugate in known ways (Fraker et al (1978) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 80: 49-57; "Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunoscintigraphy” Chatal, CRC Press 1989).
- Carbon- 14-labeled 1-isothiocyanatobenzyl- 3-methyldiethylene triaminepentaacetic acid (MX-DTPA) is an exemplary chelating agent for conjugation of a radionuclide to the antibody (WO 94/11026).
- a “Linker” (L) is a bifunctional or multifunctional moiety which can be used to link one or more zirconium complex moieties (Z) and an antibody unit (Ab) to form antibody- zirconium conjugates (AZC) of Formula I.
- Antibody-zirconium conjugates (AZC) can be conveniently prepared using a Linker having reactive functionality for binding to zirconium and to the Antibody.
- a cysteine thiol of a cysteine engineered antibody (Ab) can form a bond with a functional group of a linker reagent, a zirconium label moiety or zirconium- linker intermediate.
- a Linker has a reactive site which has an electrophilic group that is reactive to a nucleophilic cysteine present on an antibody.
- the cysteine thiol of the antibody is reactive with an electrophilic group on a Linker and forms a covalent bond to a Linker.
- Useful electrophilic groups include, but are not limited to, maleimide and haloacetamide groups.
- Cysteine engineered antibodies may react with linker reagents or zirconium-linker intermediates, with electrophilic functional groups such as maleimide or a-halo carbonyl, according to the conjugation method at page 766 of Klussman, et al (2004), Bioconjugate Chemistry 15(4):765-773, and according to the protocols of Examples 17-19.
- the Z moieties are the same.
- Z moieties are different.
- Exemplary embodiments of the Formula I antibody-zirconium conjugate (AZC) compounds include:
- R is independently H or Ci-C 6 alkyl; and n is 1 to 12.
- a Linker has a reactive functional group which has a nucleophilic group that is reactive to an electrophilic group present on an antibody.
- Useful electrophilic groups on an antibody include, but are not limited to, aldehyde and ketone carbonyl groups.
- the heteroatom of a nucleophilic group of a Linker can react with an electrophilic group on an antibody and form a covalent bond to an antibody unit.
- Useful nucleophilic groups on a Linker include, but are not limited to, hydrazide, oxime, amino, hydrazine, thiosemicarbazone, hydrazine carboxylate, and arylhydrazide.
- the electrophilic group on an antibody provides a convenient site for attachment to a Linker.
- the Linker may be substituted with groups which modulated solubility or reactivity.
- a charged substituent such as sulfonate (-SO 3 ) or ammonium, may increase water solubility of the reagent and facilitate the coupling reaction of the linker reagent with the antibody or the zirconium moiety, or facilitate the coupling reaction of Ab-L (antibody-linker intermediate) with Z, or Z-L (zirconium-linker
- the compounds of the invention expressly contemplate, but are not limited to, AZC prepared with linker reagents: BMPEO, BMPS, EMCS, GMBS, HBVS, LC-SMCC, MBS, MPBH, SBAP, SIA, SIAB, SMCC, SMPB, SMPH, sulfo-EMCS, sulfo-GMBS, sulfo-KMUS, sulfo-MBS, sulfo-SIAB, sulfo-SMCC, and sulfo-SMPB, and SVSB (succinimidyl-(4- vinylsulfone)benzoate), and including bis-maleimide reagents: DTME, BMB, BMDB, BMH, BMOE, BM(PEO) 2 , and BM(PEO) 4 3, which are commercially available from Pierce
- Bis-maleimide reagents allow the attachment of the thiol group of a cysteine engineered antibody to a thiol-containing zirconium moiety, label, or linker intermediate, in a sequential or concurrent fashion.
- Other functional groups besides maleimide, which are reactive with a thiol group of a cysteine engineered antibody, zirconium moiety, label, or linker intermediate include iodoacetamide, bromoacetamide, vinyl pyridine, disulfide, pyridyl disulfide isocyanate, and isothiocyanate.
- linker reagents can also be obtained via other commercial sources, such as Molecular Biosciences Inc. (Boulder, CO), or synthesized in accordance with procedures described in Toki et al (2002) J. Org. Chem. 67: 1866-1872; Walker, M.A. (1995) J. Org. Chem. 60:5352-5355; Frisch et al (1996) Bioconjugate Chem. 7: 180-186; US 6214345; WO 02/088172; US 2003130189; US2003096743; WO 03/026577; WO 03/043583; and WO 04/032828.
- Exemplary linker reagents include:
- n is an integer ranging from 1-10 and T is -H or -S0 3 Na;
- n is an integer ranging from 0-3;
- linker L may be a dendritic type linker for covalent attachment of more than one zirconium moiety through a branching, multifunctional linker moiety to an antibody (Sun et al (2002) Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 12:2213- 2215; Sun et al (2003) Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 11 : 1761-1768).
- Dendritic linkers can increase the molar ratio of zirconium to antibody, i.e. loading of the AZC.
- a cysteine engineered antibody bears only one reactive cysteine thiol group, a multitude of zirconium moieties may be attached through a dendritic linker.
- branched, dendritic linkers include those with self-immolative 2,6-bis(hydroxymethyl)-p-cresol and 2,4,6-tris(hydroxymethyl)-phenol dendrimer units (WO 2004/01993; Szalai et al (2003) J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 125: 15688-15689; Shamis et al (2004) J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 126: 1726-1731; Amir et al (2003) Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42:4494- 4499).
- An aspect of the invention is a desferrioxamine-labelled, cysteine-engineered antibody comprising a cysteine engineered antibody (Ab) conjugated through a free cysteine amino acid to a linker (L) and a desferoxamine moiety (Df), having Formula II:
- L-Df is selected from:
- p 1 to 4.
- the antibody-zirconium conjugates (AZC) of Formula I may be prepared by several routes, employing organic chemistry reactions, conditions, and reagents known to those skilled in the art, including: (1) reaction of a cysteine group of a cysteine engineered antibody with a linker reagent, to form antibody-linker intermediate Ab-L, via a covalent bond, followed by reaction with an activated zirconium label moiety Z; and (2) reaction of a nucleophilic group of a zirconium moiety with a linker reagent, to form zirconium label- linker intermediate Z-L, via a covalent bond, followed by reaction with a cysteine group of a cysteine engineered antibody. Conjugation methods (1) and (2) may be employed with a variety of cysteine engineered antibodies, zirconium label moieties, and linkers to prepare the antibody-zirconium conjugates of Formula I.
- Antibody cysteine thiol groups are nucleophilic and capable of reacting to form covalent bonds with electrophilic groups on linker reagents and zirconium-linker
- intermediates including: (i) active esters such as NHS esters, HOBt esters, haloformates, and acid halides; (ii) alkyl and benzyl halides, such as haloacetamides; (iii) aldehydes, ketones, carboxyl, and maleimide groups; and (iv) disulfides, including pyridyl disulfides, via sulfide exchange.
- active esters such as NHS esters, HOBt esters, haloformates, and acid halides
- alkyl and benzyl halides such as haloacetamides
- aldehydes ketones
- carboxyl and maleimide groups
- disulfides including pyridyl disulfides, via sulfide exchange.
- Nucleophilic groups on a zirconium lable moiety include, but are not limited to: amine, thiol, hydroxyl, hydrazide, oxime, hydrazine, thiosemicarbazone, hydrazine carboxylate, and arylhydrazide groups capable of reacting to form covalent bonds with electrophilic groups on linker moieties and linker reagents.
- the cysteine engineered antibodies may be made reactive for conjugation with linker reagents by treatment with a reducing agent such as DTT (Cleland's reagent, dithiothreitol) or TCEP (tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride; Getz et al (1999) Anal. Biochem. Vol 273:73-80; Soltec Ventures, Beverly, MA).
- a reducing agent such as DTT (Cleland's reagent, dithiothreitol) or TCEP (tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride; Getz et al (1999) Anal. Biochem. Vol 273:73-80; Soltec Ventures, Beverly, MA).
- a reducing agent such as DTT (Cleland's reagent, dithiothreitol) or TCEP (tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydroch
- the reduced ThioMab was diluted and loaded onto HiTrap S column in 10 mM sodium acetate, pH 5, and eluted with PBS containing 0.3M sodium chloride. Disulfide bonds were reestablished between cysteine residues present in the parent Mab with dilute (200 nM) aqueous copper sulfate (CuS0 4 ) at room temperature, overnight.
- Other oxidants i.e.
- oxidizing agents and oxidizing conditions, which are known in the art may be used.
- Ambient air oxidation is also effective. This mild, partial reoxidation step forms intrachain disulfides efficiently with high fidelity.
- An approximate 10 fold excess of zirconium-linker intermediate is added, mixed, and let stand for about an hour at room temperature to effect conjugation and form the ThioMab antibody-zirconium conjugate.
- the conjugation mixture is gel filtered and loaded and eluted through a HiTrap S column to remove excess zirconium- linker intermediate and other impurities.
- Figure 15 shows the general process to prepare a cysteine engineered antibody expressed from cell culture for conjugation.
- Cysteine adducts presumably along with various interchain disulfide bonds, are reductively cleaved to give a reduced form of the antibody.
- the interchain disulfide bonds between paired cysteine residues are reformed under partial oxidation conditions, such as exposure to ambient oxygen.
- the newly introduced, engineered, and unpaired cysteine residues remain available for reaction with linker reagents or zirconium-linker intermediates to form the antibody conjugates of the invention.
- the ThioMabs expressed in mammalian cell lines result in externally conjugated Cys adduct to an engineered Cys through -S-S- bond formation. Hence the purified
- ThioMabs have to be treated with reduction and oxidation procedures as described in Example 11 to produce reactive ThioMabs. These ThioMabs are used to conjugate with maleimide containing radiolabels, cytotoxic drugs, fluorophores, and other labels.
- TFP-N-SucDf-Fe The protected active ester TFP-N-SucDf-Fe was prepared according to the previously described procedure (Verel I et al "89Zr Immuno-PET: Comprehensive Procedures For The Production Of 89Zr-Labeled Monoclonal Antibodies” (2003) J Nucl Med 44: 1271-81) and conjugated to trastuzumab using a 5-fold molar excess of TFP-N-SucDf-Fe to yield N-SucDf- trastuzumab with an average of 1.6 molecules of desferoxamine (Table 8).
- Df-Bz-SCN- trastuzumab was obtained by coupling an 8-fold molar excess of Df-Bz-SCN at pH 8.5 (Perk LR, et al. "Facile radiolabeling of monoclonal antibodies and other proteins with zirconium- 89 or gallium-68 for PET Imaging using p-isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine” (2008) Nature Protocols; published online:DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2008.22).
- the reaction provided Df- Bz-SCN-trastuzumab decorated in average with 2.4 molecules of desferoxamine (Table 1).
- novel maleimide based thiol reactive bifunctional linker Df-Chx-Mal was prepared from equimolar amounts of desferoxamine mesylate and SMCC ( Figure 21,
- Example 13 The reaction was complete within 30 min at room temperature and the product was isolated by precipitation upon addition of water in 45% yield and more than 95% purity.
- the reaction of an 8.5-fold molar excess of Df-Chx-Mal with freshly prepared thio- trastuzumab (Figure 21 Example 17) provided Df-Chx-Mal-thio-trastuzumab conjugate with exactly 2 molecules of desferoxamine in 1 h (Table 1, Figure 21). Bromoacetyl
- BDf-Bac desferoxamine
- Df-Iac desferoxamine mesylate and bromoacetyl bromide at 0°C
- the product was obtained in 14% yield after HPLC purification.
- the alkylation of freshly prepared thio- trastuzumab ( Figure 21, Example 16) with a 12-fold molar excess of Df-Bac provided the conjugate (Df-Ac-thio-trastuzumab) with 1.8 molecules of Df per antibody within 5 h (Table 8, Figure 21, Example 18).
- the low reactivity of bromide prompted us to explore the more reactive iodoacetyl derivative (Df-Iac).
- Df-Iac was prepared in 53% yield by the reaction of desferoxamine mesylate with a slight excess of N-hydroxysuccinimidyl iodoacetate ( Figure 21, Example 15). The product was obtained in more than 95% purity by precipitation from the reaction mixture. The subsequent reaction of an 11 -fold excess of Df-Iac provided Df-Ac- thio-trastuzumab decorated with 1.8 molecules of Df within 2 h (Table 1, Figure 21, Example 19). Based on our experience, Df-Chx-Mal is the preferred reagent of the three compounds investigated.
- the Zr was chelated as 89-zirconium oxalatewith all four variants of Df- trastuzumab using previously described experimental procedure (Verel I et al "89Zr immuno- PET: comprehensive procedures for the production of 89Zr-labeled monoclonal antibodies” (2003) J Nucl Med. 44: 1271-81).
- the radiolabeled proteins were purified on a desalting column and the final solution was concentrated to the required volume by membrane
- the yield, purity, and final specific activity of the Zr conjugates are summarized in Table 9.
- the chelation yield was over 80% with the exception of the Df-N-Suc linker obtained in lower yield presumably due to the lower amount of Df per antibody molecule and/or incomplete removal of Fe(III) used to protect the chelator during activation and conjugation.
- the product purity was over 90% with a small amount (1-6%) of high molecular weight
- Df-Chx-Mal-thio-trastuzumab provided the Zr complex in 99% purity (Table 9) as opposed to Df-Ac conjugate which was contaminated with approximately 8% of a low molecular weight impurity and 2% of high molecular weight aggregates.
- the contaminant resisted removal using NAP- 10 column but the removal was possible using repeated buffer exchange on Amicon filter.
- the obtained K D values were compared to non-modified trastuzumab (0.91 ⁇ 0.20 nM).
- the K D for the thio-trastuzumab conjugate containing Chx-Mal linker was 0.93 ⁇ 0.15 nM and the values for the conjugates containing Ac linker were 1.22 ⁇ 0.22 nM for conjugate prepared using Df-Bac and 0.87 ⁇ 0.15 nM prepared using Df-Iac.
- the results of the biological activity analyses indicate that the modification of thio-trastuzumab did not affect the binding affinity of the antibody to HER2.
- Fig. 3 The Zr-trastuzumab uptake in selected tissues is summarized in Fig 4.
- the images at 1 h (not shown) were dominated by the high blood pool uptake with the exception of Df-Bac where rapid hepatobiliary excretion of the lipophilic impurity resulted in an elevated uptake in intestine.
- the impurity was totally cleared within the first 24 h and elevated small and large intestine uptake was not detected at 24 h or later time after tracer injection.
- the tissue uptake of Df-Ac conjugate was resultantly slightly (-8%) lower, the tumor to blood ratios (Table 10) were not affected by the loss of injected radioactivity.
- the images at 96 h were dominated by the high tumor uptake
- BT474 (3+ expression level of HER2) xenografts exhibited lower absolute uptake of the tracer (15 %ID/g) than measured previously by Dijkers et al in SKOV3 (3+ expression level of HER2) 33.4 ⁇ 7.7%ID/g (Dijkers EC, et al. "Development and Characterization of Clinical-Grade 89Zr-Trastuzumab for HER2/neu ImmunoPET Imaging" (2009) J Nucl Med 50(6):974-981).
- the tumor to blood ratio of 5.7-7.1 (Table 10) is comparable to the value obtained with SKOV3 (tumor to blood of 7.6).
- the difference in tumor uptake may be attributed to the tumor model and total dose of trastuzumab.
- a material with higher specific activity was used hence so significantly less antibody was injected (35 ⁇ g, 1.4 mg/kg) compared to the Dijkers et al study with SKOV3 (100 ⁇ g, 4 mg/kg).
- the difference in trastuzumab was attributed to the tumor model and total dose of trastuzumab.
- the bone uptake may originate from the breakdown of the Zr-
- thiol specific reagents Three thiol specific reagents are exemplified herein for the chemoselective conjugation of desferrioxamine (Df) to monoclonal antibodies through the thiol group of cysteine of cysteine-engineered antibodies.
- the thiol-specific Df-reagents were obtained by the acylation of the amino group of desferrioxamine B in 14% (Df-Bac), 53% (Df-Iac) and 45% (Df-Chx-Mal) yields and conjugated to thio-trastuzumab resulting in site-specific modification on both engineered cysteines within 1-5 h.
- the binding activities of site-specific thio-trastuzumab conjugates to HER2 were identical to the activity of non-modified trastuzumab.
- the Df-modified thio-trastuzumabs (Df-Ac-thio-trastuzumab and Df-Chx-Mal-
- Df-Chx-Mal is a useful reagent for conjugation of Df to antibodies through cysteine side chain and showed several advantages over Df-Bac and Df-Iac.
- moderate pH 7.5 was required for complete conjugation of Df-Chx-Mal within 1 h as compared to pH 9 and 2 or 5 h required for Df-Bac
- the site specifically Zr labeled engineered THIOMAB conjugates can be used similarly as 18 F labeled THIOFAB conjugates (Gill HS, et al. "A modular platform for the rapid site-specific radiolabeling of proteins with 18F exemplified by quantitative positron emission tomography of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2" (2009) Jour, of Med. Chem. 52:5816-25) as valuable tools for PET imaging applications in biomedical research.
- the antibody-zirconium conjugates (AZC) of the invention may be administered by any route appropriate to the condition to be treated.
- the AZC will typically be administered parenterally, i.e. infusion, subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous, intradermal, intrathecal and epidural.
- compositions of diagnostic antibody-zirconium conjugates (AZC) of the invention are typically prepared for parenteral administration, i.e. bolus, intravenous, intratumor injection with a pharmaceutically acceptable parenteral vehicle and in a unit dosage injectable form.
- An antibody-zirconium conjugate (AZC) having the desired degree of purity is optionally mixed with pharmaceutically acceptable diluents, carriers, excipients or stabilizers (Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences (1980) 16th edition, Osol, A. Ed.), in the form of a lyophilized formulation or an aqueous solution.
- Acceptable diluents, carriers, excipients, and stabilizers are nontoxic to recipients at the dosages and concentrations employed, and include buffers such as phosphate, citrate, and other organic acids; antioxidants including ascorbic acid and methionine; preservatives (such as octadecyldimethylbenzyl ammonium chloride; hexamethonium chloride; benzalkonium chloride, benzethonium chloride; phenol, butyl or benzyl alcohol; alkyl parabens such as methyl or propyl paraben; catechol; resorcinol; cyclohexanol; 3-pentanol; and m-cresol); low molecular weight (less than about 10 residues) polypeptides; proteins, such as serum albumin, gelatin, or immunoglobulins; hydrophilic polymers such as polyvinylpyrrolidone; amino acids such as glycine, glutamine, asparag
- Zn-protein complexes Zn-protein complexes
- non-ionic surfactants such as TWEENTM, PLURONICSTM or polyethylene glycol (PEG).
- TWEENTM TWEENTM
- PLURONICSTM polyethylene glycol
- PEG polyethylene glycol
- the active pharmaceutical ingredients may also be entrapped in microcapsules prepared, for example, by coacervation techniques or by interfacial polymerization, for example, hydroxymethylcellulose or gelatin-microcapsules and poly-(methylmethacylate) microcapsules, respectively, in colloidal drug delivery systems (for example, liposomes, albumin microspheres, microemulsions, nano-particles and nanocapsules) or in
- sustained-release preparations may be prepared. Suitable examples of sustained- release preparations include semi permeable matrices of solid hydrophobic polymers containing the AZC, which matrices are in the form of shaped articles, e.g. films, or microcapsules.
- sustained-release matrices include polyesters, hydrogels (for example, poly(2-hydroxyethyl-methacrylate), or polyvinyl alcohol)), polylactides (US 3773919), copolymers of L-glutamic acid and gamma-ethyl-L-glutamate, non-degradable ethylene-vinyl acetate, degradable lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymers such as the LUPRON DEPOTTM (injectable microspheres composed of lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer and leuprolide acetate), and poly-D-(-)-3-hydroxybutyric acid.
- polyesters for example, poly(2-hydroxyethyl-methacrylate), or polyvinyl alcohol
- polylactides US 3773919
- copolymers of L-glutamic acid and gamma-ethyl-L-glutamate non-degradable ethylene-vinyl acetate
- the formulations to be used for in vivo administration must be sterile, which is readily accomplished by filtration through sterile filtration membranes.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Peptides Or Proteins (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
- Preparation Of Compounds By Using Micro-Organisms (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (8)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA2780216A CA2780216A1 (en) | 2009-11-05 | 2010-11-04 | Zirconium-desferrioxamine-labelled and desferrioxamine-labelled, cysteine-engineered antibodies and methods of making said antibodies |
| JP2012537224A JP5850843B2 (en) | 2009-11-05 | 2010-11-04 | Zirconium radiolabeled cysteine engineered antibody conjugate |
| KR1020177034613A KR20170136652A (en) | 2009-11-05 | 2010-11-04 | Zirconium-radiolabeled, cysteine engineered antibody conjugates |
| EP10776064.7A EP2496270B1 (en) | 2009-11-05 | 2010-11-04 | Zirconium-radiolabeled, cysteine engineered antibody conjugates |
| RU2012123007/10A RU2562862C2 (en) | 2009-11-05 | 2010-11-04 | Radioactive zirconium- labelled engineered cysteine antibodies conjugates |
| CN201080050134.4A CN102596260B (en) | 2009-11-05 | 2010-11-04 | Radiolabeled, the cysteine engineered antibody conjugates of zirconium |
| BR112012007774A BR112012007774A2 (en) | 2009-11-05 | 2010-11-04 | cysteine modified antibody, desferrioxamine labeling reagent, production method of a cysteine modified antibody production method of a zirconium labeled cysteine modified antibody and imaging method |
| MX2012005211A MX340674B (en) | 2009-11-05 | 2010-11-04 | Zirconium-radiolabeled, cysteine engineered antibody conjugates. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/612,912 | 2009-11-05 | ||
| US12/612,912 US20100111856A1 (en) | 2004-09-23 | 2009-11-05 | Zirconium-radiolabeled, cysteine engineered antibody conjugates |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2011056983A1 true WO2011056983A1 (en) | 2011-05-12 |
Family
ID=43383591
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2010/055465 WO2011056983A1 (en) | 2009-11-05 | 2010-11-04 | Zirconium-radiolabeled, cysteine engineered antibody conjugates |
Country Status (10)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US20100111856A1 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP2496270B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP5850843B2 (en) |
| KR (2) | KR20170136652A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN102596260B (en) |
| BR (1) | BR112012007774A2 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2780216A1 (en) |
| MX (1) | MX340674B (en) |
| RU (1) | RU2562862C2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2011056983A1 (en) |
Cited By (96)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013149159A1 (en) | 2012-03-30 | 2013-10-03 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-lgr5 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| WO2013165940A1 (en) | 2012-05-01 | 2013-11-07 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-pmel17 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US8772459B2 (en) | 2009-12-02 | 2014-07-08 | Imaginab, Inc. | J591 minibodies and Cys-diabodies for targeting human prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and methods for their use |
| WO2014159835A1 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2014-10-02 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-b7-h4 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US8877897B2 (en) | 2010-02-23 | 2014-11-04 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| US8911732B2 (en) | 2010-12-20 | 2014-12-16 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-mesothelin antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US8940298B2 (en) | 2007-09-04 | 2015-01-27 | The Regents Of The University Of California | High affinity anti-prostate stem cell antigen (PSCA) antibodies for cancer targeting and detection |
| US8940871B2 (en) | 2006-03-20 | 2015-01-27 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Engineered anti-prostate stem cell antigen (PSCA) antibodies for cancer targeting |
| US8951737B2 (en) | 1996-05-06 | 2015-02-10 | Cornell Research Foundation, Inc. | Treatment and diagnosis of cancer |
| WO2015042108A1 (en) | 2013-09-17 | 2015-03-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-lgr5 antibodies |
| WO2015089344A1 (en) | 2013-12-13 | 2015-06-18 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-cd33 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| WO2015095227A2 (en) | 2013-12-16 | 2015-06-25 | Genentech, Inc. | Peptidomimetic compounds and antibody-drug conjugates thereof |
| WO2015112909A1 (en) | 2014-01-24 | 2015-07-30 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-steap1 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| JP2015528692A (en) * | 2012-05-21 | 2015-10-01 | ジェネンテック, インコーポレイテッド | Anti-Ly6E antibody, immunoconjugate and method of use |
| JP2015528818A (en) * | 2012-08-02 | 2015-10-01 | ジェネンテック, インコーポレイテッド | Anti-ETBR antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| JP2015529656A (en) * | 2012-08-02 | 2015-10-08 | ジェネンテック, インコーポレイテッド | Anti-ETBR antibodies and immune complexes |
| WO2015179658A2 (en) | 2014-05-22 | 2015-11-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-gpc3 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| WO2015191715A1 (en) | 2014-06-11 | 2015-12-17 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-lgr5 antibodies and uses thereof |
| WO2016040868A1 (en) | 2014-09-12 | 2016-03-17 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-cll-1 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US9290578B2 (en) | 2013-10-21 | 2016-03-22 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-Ly6E antibodies and methods of use |
| US9562099B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2017-02-07 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-B7-H4 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| WO2017181152A2 (en) | 2016-04-15 | 2017-10-19 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Cd80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2017181148A2 (en) | 2016-04-15 | 2017-10-19 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Icos ligand variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2017197234A1 (en) | 2016-05-13 | 2017-11-16 | Bioatla, Llc | Anti-ror2 antibodies, antibody fragments, their immunoconjugates and uses thereof |
| WO2017223405A1 (en) | 2016-06-24 | 2017-12-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-polyubiquitin multispecific antibodies |
| WO2018023100A2 (en) | 2016-07-29 | 2018-02-01 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-idiotypic antibodies and related methods |
| WO2018022945A1 (en) | 2016-07-28 | 2018-02-01 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Cd112 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2018022946A1 (en) | 2016-07-28 | 2018-02-01 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Cd155 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US9896506B2 (en) | 2008-01-31 | 2018-02-20 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-CD79B antibodies and immunoconjugates and methods of use |
| EP3207027A4 (en) * | 2014-10-16 | 2018-04-18 | The University of Melbourne | Novel imaging composition and uses thereof |
| WO2018091724A1 (en) | 2016-11-21 | 2018-05-24 | Cureab Gmbh | Anti-gp73 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| WO2018102682A1 (en) | 2016-12-01 | 2018-06-07 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Radiolabeled anti-pd-l1 antibodies for immuno-pet imaging |
| WO2018102787A1 (en) | 2016-12-03 | 2018-06-07 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for determining car-t cells dosing |
| US10011658B2 (en) | 2015-04-03 | 2018-07-03 | Eureka Therapeutics, Inc. | Constructs targeting AFP peptide/MHC complexes and uses thereof |
| WO2018148476A1 (en) | 2017-02-10 | 2018-08-16 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Radiolabeled anti-lag3 antibodies for immuno-pet imaging |
| US10059768B2 (en) | 2014-09-12 | 2018-08-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-B7-H4 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US10058613B2 (en) | 2015-10-02 | 2018-08-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Pyrrolobenzodiazepine antibody drug conjugates and methods of use |
| US10077318B2 (en) | 2014-09-12 | 2018-09-18 | Genentech, Inc. | Cysteine engineered antibodies and conjugates |
| WO2018170021A1 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2018-09-20 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Pd-l1 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2018170023A1 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2018-09-20 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Pd-l2 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2018170026A2 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2018-09-20 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Cd80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US10137212B2 (en) * | 2013-03-13 | 2018-11-27 | The United States Of America, As Represented By The Secretary, Department Of Health And Human Services | Tetrahydroxamate chelators of zirconium89 and niobium90 for use in diagnostic applications |
| WO2018223098A1 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2018-12-06 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Articles of manufacture and methods related to toxicity associated with cell therapy |
| US10179820B2 (en) | 2014-09-12 | 2019-01-15 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-HER2 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| WO2019023148A1 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2019-01-31 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Anti-cd8 antibodies and uses thereof |
| WO2019074983A1 (en) | 2017-10-10 | 2019-04-18 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Ctla-4 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2019079520A2 (en) | 2017-10-18 | 2019-04-25 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Variant icos ligand immunomodulatory proteins and related compositions and methods |
| WO2019089858A2 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2019-05-09 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods of assessing or monitoring a response to a cell therapy |
| WO2019089848A1 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2019-05-09 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods associated with tumor burden for assessing response to a cell therapy |
| WO2019109053A1 (en) | 2017-12-01 | 2019-06-06 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for dosing and for modulation of genetically engineered cells |
| US10494432B2 (en) | 2007-07-16 | 2019-12-03 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-CD79B antibodies and immunoconjugates and methods of use |
| WO2019241758A1 (en) | 2018-06-15 | 2019-12-19 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Pd-1 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US10517969B2 (en) | 2009-02-17 | 2019-12-31 | Cornell University | Methods and kits for diagnosis of cancer and prediction of therapeutic value |
| US10533058B2 (en) | 2013-12-16 | 2020-01-14 | Genentech Inc. | Peptidomimetic compounds and antibody-drug conjugates thereof |
| US10604557B2 (en) | 2010-06-08 | 2020-03-31 | Genentech, Inc. | Cysteine engineered antibodies and conjugates |
| WO2020077257A1 (en) | 2018-10-11 | 2020-04-16 | Inhibrx, Inc. | Pd-1 single domain antibodies and therapeutic compositions thereof |
| WO2020076992A1 (en) | 2018-10-11 | 2020-04-16 | Inhibrx, Inc. | 5t4 single domain antibodies and therapeutic compositions thereof |
| WO2020076970A1 (en) | 2018-10-11 | 2020-04-16 | Inhibrx, Inc. | B7h3 single domain antibodies and therapeutic compositions thereof |
| WO2020076977A2 (en) | 2018-10-11 | 2020-04-16 | Inhibrx, Inc. | Dll3 single domain antibodies and therapeutic compositions thereof |
| WO2020113194A2 (en) | 2018-11-30 | 2020-06-04 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for treatment using adoptive cell therapy |
| WO2020113141A2 (en) | 2018-11-30 | 2020-06-04 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Cd86 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2020117257A1 (en) | 2018-12-06 | 2020-06-11 | Genentech, Inc. | Combination therapy of diffuse large b-cell lymphoma comprising an anti-cd79b immunoconjugates, an alkylating agent and an anti-cd20 antibody |
| EP3689910A2 (en) | 2014-09-23 | 2020-08-05 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG | Method of using anti-cd79b immunoconjugates |
| WO2020205623A1 (en) | 2019-03-29 | 2020-10-08 | Rakuten Medical, Inc. | Methods for photoimmunotherapy and related biomarkers |
| WO2020232169A1 (en) | 2019-05-14 | 2020-11-19 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-cd79b immunoconjugates to treat follicular lymphoma |
| WO2020257604A1 (en) | 2019-06-21 | 2020-12-24 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Use of bispecific antigen-binding molecules that bind muc16 and cd3 in combination with 4-1bb co-stimulation |
| WO2020257681A1 (en) | 2019-06-21 | 2020-12-24 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Use of bispecific antigen-binding molecules that bind psma and cd3 in combination with 4-1bb co-stimulation |
| WO2021055350A1 (en) | 2019-09-16 | 2021-03-25 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Radiolabeled met binding proteins for immuno-pet imaging |
| US10981987B2 (en) | 2007-07-16 | 2021-04-20 | Genentech, Inc. | Humanized anti-CD79b antibodies and immunoconjugates and methods of use |
| WO2021076196A1 (en) | 2019-10-18 | 2021-04-22 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-cd79b immunoconjugates to treat diffuse large b-cell lymphoma |
| WO2021113776A1 (en) | 2019-12-06 | 2021-06-10 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-idiotypic antibodies to bcma-targeted binding domains and related compositions and methods |
| WO2021113780A1 (en) | 2019-12-06 | 2021-06-10 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-idiotypic antibodies to gprc5d-targeted binding domains and related compositions and methods |
| WO2021155071A1 (en) | 2020-01-29 | 2021-08-05 | Inhibrx, Inc. | Cd28 single domain antibodies and multivalent and multispecific constructs thereof |
| US11142578B2 (en) | 2016-11-16 | 2021-10-12 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Anti-MET antibodies, bispecific antigen binding molecules that bind MET, and methods of use thereof |
| US11149088B2 (en) | 2016-04-15 | 2021-10-19 | Bioatla, Inc. | Anti-Axl antibodies, antibody fragments and their immunoconjugates and uses thereof |
| WO2021217051A1 (en) | 2020-04-24 | 2021-10-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-cd79b immunoconjugates |
| WO2022029660A1 (en) | 2020-08-05 | 2022-02-10 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-idiotypic antibodies to ror1-targeted binding domains and related compositions and methods |
| US11254744B2 (en) | 2015-08-07 | 2022-02-22 | Imaginab, Inc. | Antigen binding constructs to target molecules |
| US11266745B2 (en) | 2017-02-08 | 2022-03-08 | Imaginab, Inc. | Extension sequences for diabodies |
| US11274157B2 (en) | 2017-01-12 | 2022-03-15 | Eureka Therapeutics, Inc. | Constructs targeting histone H3 peptide/MHC complexes and uses thereof |
| WO2022147463A2 (en) | 2020-12-31 | 2022-07-07 | Alamar Biosciences, Inc. | Binder molecules with high affinity and/ or specificity and methods of making and use thereof |
| US11447564B2 (en) | 2017-04-26 | 2022-09-20 | Eureka Therapeutics, Inc. | Constructs specifically recognizing glypican 3 and uses thereof |
| US11471488B2 (en) | 2016-07-28 | 2022-10-18 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CD155 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2022241446A1 (en) | 2021-05-12 | 2022-11-17 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-cd79b immunoconjugates to treat diffuse large b-cell lymphoma |
| WO2023019092A1 (en) | 2021-08-07 | 2023-02-16 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-cd79b immunoconjugates to treat diffuse large b-cell lymphoma |
| US11584927B2 (en) | 2014-08-28 | 2023-02-21 | Bioatla, Inc. | Conditionally active chimeric antigen receptors for modified T-cells |
| US11596695B2 (en) | 2013-02-08 | 2023-03-07 | Novartis Ag | Specific sites for modifying antibodies to make immunoconjugates |
| WO2023034750A1 (en) | 2021-08-30 | 2023-03-09 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-polyubiquitin multispecific antibodies |
| US11667724B2 (en) | 2017-07-07 | 2023-06-06 | Astellas Pharma Inc. | Anti-human CEACAM5 antibody Fab fragment |
| US11679166B2 (en) | 2016-11-18 | 2023-06-20 | Astellas Pharma Inc. | Anti-human MUC1 antibody Fab fragment |
| WO2023172883A1 (en) | 2022-03-07 | 2023-09-14 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Immunomodulatory proteins of variant cd80 polypeptides, cell therapies thereof and related methods and uses |
| US11993661B2 (en) | 2018-06-18 | 2024-05-28 | Eureka Therapeutics, Inc. | Constructs targeting prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and uses thereof |
| WO2024151515A2 (en) | 2023-01-09 | 2024-07-18 | Odyssey Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-tnfr2 antigen-binding proteins and uses thereof |
| US12065503B2 (en) | 2018-10-10 | 2024-08-20 | Astellas Pharma Inc. | Pharmaceutical composition containing tagged site-antihuman antibody fab fragment complex |
| WO2024173876A1 (en) | 2023-02-17 | 2024-08-22 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Radiolabeled anti-lag3 antibodies for immuno-pet imaging |
| WO2024192065A1 (en) | 2023-03-14 | 2024-09-19 | Odyssey Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-cd25 antigen-binding proteins and uses thereof |
Families Citing this family (56)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9701754B1 (en) | 2002-10-23 | 2017-07-11 | City Of Hope | Covalent disulfide-linked diabodies and uses thereof |
| JP5951929B2 (en) * | 2007-10-03 | 2016-07-13 | コーネル ユニヴァーシティー | Treatment of proliferative disorders using PSMA antibodies |
| GB0803076D0 (en) | 2008-02-20 | 2008-03-26 | Univ Ghent | Mucosal Membrane Receptor and uses thereof |
| US20100008978A1 (en) * | 2008-05-09 | 2010-01-14 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Nanoparticles effective for internalization into cells |
| US20100009390A1 (en) * | 2008-05-09 | 2010-01-14 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Mutant antibodies with high affinity for egfr |
| WO2010014222A1 (en) * | 2008-07-30 | 2010-02-04 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Compositions for detecting cell death and methods of use thereof |
| EP2400992B1 (en) * | 2009-02-27 | 2015-07-22 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods and compositions for protein labelling |
| EP2577310B1 (en) * | 2010-06-03 | 2018-11-14 | F.Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Immuno-pet imaging of antibodies and immunoconjugates and uses therefor |
| TW201302793A (en) | 2010-09-03 | 2013-01-16 | Glaxo Group Ltd | Novel antigen binding proteins |
| EP2786151B1 (en) | 2011-11-29 | 2019-07-03 | F.Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Methods for prostate cancer analysis |
| KR102006997B1 (en) * | 2012-07-03 | 2019-08-02 | 한국생명공학연구원 | A site-selective binding peptide for IgG Fc and a hybrid molecule comprising the same |
| RU2017128512A (en) | 2012-07-04 | 2019-02-15 | Ф. Хоффманн-Ля Рош Аг | ANTIBODIES TO THEOPHYLLIN AND WAYS OF THEIR APPLICATION |
| CN107973856B (en) | 2012-07-04 | 2021-11-23 | 弗·哈夫曼-拉罗切有限公司 | Covalently linked antigen-antibody conjugates |
| CN104411725B (en) | 2012-07-04 | 2018-09-28 | 弗·哈夫曼-拉罗切有限公司 | Anti-biotin antibodies and application method |
| WO2014011327A1 (en) * | 2012-07-12 | 2014-01-16 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Radiolabeled probes for the non-invasive detection and imaging of cell death |
| WO2014069647A1 (en) * | 2012-11-05 | 2014-05-08 | 全薬工業株式会社 | Antibody and antibody composition production method |
| US20140147381A1 (en) * | 2012-11-29 | 2014-05-29 | Gregory David Espenan | 89zr compounds, to include somatostatin, apparatus and products comprising such compounds, methods of making same, and methods of using same for radio imaging and/or treatment |
| CA2898146C (en) | 2012-12-19 | 2020-12-01 | Charles Andrew BOSWELL | Methods and compositions for radiohalogen protein labeling |
| ES2699599T3 (en) * | 2013-03-15 | 2019-02-11 | Abbvie Biotherapeutics Inc | Fc variants |
| EP3008212A4 (en) * | 2013-06-10 | 2017-05-24 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods of treatment of cancer |
| MX2016007958A (en) | 2013-12-17 | 2016-08-03 | Genentech Inc | Anti-cd3 antibodies and methods of use. |
| EP3089759B1 (en) | 2014-01-03 | 2018-12-05 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG | Covalently linked polypeptide toxin-antibody conjugates |
| RU2694981C2 (en) | 2014-01-03 | 2019-07-18 | Ф. Хоффманн-Ля Рош Аг | Covalently linked conjugates chelicar-antibody against chelicar and use thereof |
| PL3089996T3 (en) | 2014-01-03 | 2021-12-13 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Bispecific anti-hapten/anti-blood brain barrier receptor antibodies, complexes thereof and their use as blood brain barrier shuttles |
| WO2015138615A2 (en) * | 2014-03-12 | 2015-09-17 | Irm Llc | Specific sites for modifying antibodies to make immunoconjugates |
| ES2768762T3 (en) * | 2014-11-05 | 2020-06-23 | Illumina Cambridge Ltd | Reduction of DNA damage during sample preparation and sequencing using siderophore chelating agents |
| CN107001447B (en) | 2014-12-17 | 2021-07-23 | 豪夫迈·罗氏有限公司 | Novel enzyme-mediated polypeptide conjugation method using sortase |
| CN104645364A (en) * | 2015-01-27 | 2015-05-27 | 南京江原安迪科正电子研究发展有限公司 | Mark product of <89>Zr marked denosumab, and preparation method and application thereof |
| WO2016179003A1 (en) | 2015-05-01 | 2016-11-10 | Genentech, Inc. | Masked anti-cd3 antibodies and methods of use |
| EP3307780A1 (en) | 2015-06-15 | 2018-04-18 | Genentech, Inc. | Antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| CN107849145B (en) | 2015-06-16 | 2021-10-26 | 基因泰克公司 | anti-CD 3 antibodies and methods of use thereof |
| CN108138158B (en) | 2015-09-25 | 2021-11-09 | 豪夫迈·罗氏有限公司 | Soluble sortase A |
| JP6895953B2 (en) | 2015-09-25 | 2021-06-30 | エフ.ホフマン−ラ ロシュ アーゲーF. Hoffmann−La Roche Aktiengesellschaft | Method for making thioester using sortase A |
| WO2017050889A1 (en) | 2015-09-25 | 2017-03-30 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Recombinant immunoglobulin heavy chains comprising a sortase conjugation loop and conjugates thereof |
| WO2017050872A1 (en) | 2015-09-25 | 2017-03-30 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Transamidation employing sortase a in deep eutectic solvents |
| WO2017161356A1 (en) * | 2016-03-18 | 2017-09-21 | Wake Forest University | Compounds, compositions and associated methods using zirconium-89 in immuno-positron emission tomography |
| CN109072212B (en) | 2016-03-30 | 2022-10-04 | 豪夫迈·罗氏有限公司 | Improved sortase |
| CN109069657B (en) * | 2016-04-06 | 2022-04-12 | 阿特根公司 | Antibody-drug conjugates comprising modified antibodies |
| EP3609897A1 (en) | 2017-04-12 | 2020-02-19 | H. Hoffnabb-La Roche Ag | A method for labeling of aldehyde containing target molecules |
| EP3652214A1 (en) | 2017-07-13 | 2020-05-20 | H. Hoffnabb-La Roche Ag | New binding agent and assay for pivka |
| AU2018321893A1 (en) | 2017-08-23 | 2020-03-19 | Wayne State University | In vivo immunoimaging of interferon-gamma |
| JP7403444B2 (en) | 2017-10-20 | 2023-12-22 | エフ. ホフマン-ラ ロシュ アーゲー | Antibody copy protection measures |
| WO2019165143A1 (en) * | 2018-02-21 | 2019-08-29 | Cytomx Therapeutics, Inc. | Positron emission tomography imaging of activatable binding polypeptides and related compositions thereof |
| WO2019175127A1 (en) | 2018-03-14 | 2019-09-19 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Novel anti-troponint antibodies |
| JP7333332B2 (en) | 2018-03-14 | 2023-08-24 | エフ. ホフマン-ラ ロシュ アーゲー | Methods for Affinity Maturation of Antibodies |
| WO2019201901A1 (en) | 2018-04-18 | 2019-10-24 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Novel anti-thymidine kinase antibodies |
| WO2020043868A1 (en) | 2018-08-31 | 2020-03-05 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Thymidine kinase (tk-1) in prognostic indices for dlbcl |
| JOP20210159A1 (en) | 2018-12-21 | 2023-01-30 | Novartis Ag | Antibodies to pmel17 and conjugates thereof |
| EP3921443A1 (en) | 2019-02-08 | 2021-12-15 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG | Diagnostic and therapeutic methods for cancer |
| WO2020236679A1 (en) * | 2019-05-17 | 2020-11-26 | Cytomx Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods and compositions for determining the biodistribution of activatable anti-cd166 antibody conjugates |
| JP2022537543A (en) * | 2019-06-17 | 2022-08-26 | タグワークス ファーマシューティカルス ビー.ブイ. | Compounds for fast and efficient click release |
| WO2022036146A1 (en) | 2020-08-12 | 2022-02-17 | Genentech, Inc. | Diagnostic and therapeutic methods for cancer |
| CN116457660A (en) | 2020-10-30 | 2023-07-18 | 豪夫迈·罗氏有限公司 | TIMP1 as a marker for cholangiocarcinoma |
| EP4448564A1 (en) | 2021-12-17 | 2024-10-23 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG | A novel antibody for detection of amyloid beta 42 (a-beta42) |
| AU2023236386A1 (en) | 2022-03-18 | 2024-10-10 | Evolveimmune Therapeutics, Inc. | Bispecific antibody fusion molecules and methods of use thereof |
| CN117198390B (en) * | 2023-09-08 | 2024-03-12 | 中国科学院广州生物医药与健康研究院 | Preparation method of SLC (SLC) membrane protein complex by designing and modifying disulfide bond crosslinking site |
Citations (286)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3773919A (en) | 1969-10-23 | 1973-11-20 | Du Pont | Polylactide-drug mixtures |
| US4275149A (en) | 1978-11-24 | 1981-06-23 | Syva Company | Macromolecular environment control in specific receptor assays |
| US4318980A (en) | 1978-04-10 | 1982-03-09 | Miles Laboratories, Inc. | Heterogenous specific binding assay employing a cycling reactant as label |
| US4415732A (en) | 1981-03-27 | 1983-11-15 | University Patents, Inc. | Phosphoramidite compounds and processes |
| US4458066A (en) | 1980-02-29 | 1984-07-03 | University Patents, Inc. | Process for preparing polynucleotides |
| US4737456A (en) | 1985-05-09 | 1988-04-12 | Syntex (U.S.A.) Inc. | Reducing interference in ligand-receptor binding assays |
| US4816567A (en) | 1983-04-08 | 1989-03-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Recombinant immunoglobin preparations |
| EP0404097A2 (en) | 1989-06-22 | 1990-12-27 | BEHRINGWERKE Aktiengesellschaft | Bispecific and oligospecific, mono- and oligovalent receptors, production and applications thereof |
| WO1991002536A1 (en) | 1989-08-23 | 1991-03-07 | Scripps Clinic And Research Foundation | Compositions and methods for detection and treatment of epstein-barr virus infection and immune disorders |
| US5047524A (en) | 1988-12-21 | 1991-09-10 | Applied Biosystems, Inc. | Automated system for polynucleotide synthesis and purification |
| US5091178A (en) | 1986-02-21 | 1992-02-25 | Oncogen | Tumor therapy with biologically active anti-tumor antibodies |
| WO1992007574A1 (en) | 1990-10-25 | 1992-05-14 | Tanox Biosystems, Inc. | Glycoproteins associated with membrane-bound immunoglobulins as antibody targets on b cells |
| WO1992017497A1 (en) | 1991-03-29 | 1992-10-15 | Genentech, Inc. | Human pf4a receptors and their use |
| EP0522868A1 (en) | 1991-07-12 | 1993-01-13 | SHIONOGI SEIYAKU KABUSHIKI KAISHA trading under the name of SHIONOGI & CO. LTD. | A human endothelin receptor |
| JPH053790B2 (en) | 1983-11-02 | 1993-01-18 | Canon Kk | |
| US5183884A (en) | 1989-12-01 | 1993-02-02 | United States Of America | Dna segment encoding a gene for a receptor related to the epidermal growth factor receptor |
| WO1993011161A1 (en) | 1991-11-25 | 1993-06-10 | Enzon, Inc. | Multivalent antigen-binding proteins |
| WO1993016185A2 (en) | 1992-02-06 | 1993-08-19 | Creative Biomolecules, Inc. | Biosynthetic binding protein for cancer marker |
| WO1993021319A1 (en) | 1992-04-08 | 1993-10-28 | Cetus Oncology Corporation | HUMANIZED C-erbB-2 SPECIFIC ANTIBODIES |
| US5262530A (en) | 1988-12-21 | 1993-11-16 | Applied Biosystems, Inc. | Automated system for polynucleotide synthesis and purification |
| WO1994010312A1 (en) | 1992-10-23 | 1994-05-11 | Chugai Seiyaku Kabushiki Kaisha | Gene coding for megakaryocyte potentiator |
| WO1994011026A2 (en) | 1992-11-13 | 1994-05-26 | Idec Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Therapeutic application of chimeric and radiolabeled antibodies to human b lymphocyte restricted differentiation antigen for treatment of b cell lymphoma |
| US5316757A (en) | 1984-10-18 | 1994-05-31 | Board Of Regents, The University Of Texas System | Synthesis of polyazamacrocycles with more than one type of side-chain chelating groups |
| EP0599274A1 (en) | 1992-11-24 | 1994-06-01 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | HER4, a human receptor tyrosine kinase of the epidermal growth factor receptor family |
| US5342606A (en) | 1984-10-18 | 1994-08-30 | Board Of Regents, The University Of Texas System | Polyazamacrocyclic compounds for complexation of metal ions |
| WO1994028931A1 (en) | 1993-06-11 | 1994-12-22 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods for treating inflammatory disorders |
| US5385893A (en) | 1993-05-06 | 1995-01-31 | The Dow Chemical Company | Tricyclopolyazamacrocyclophosphonic acids, complexes and derivatives thereof, for use as contrast agents |
| US5428139A (en) | 1991-12-10 | 1995-06-27 | The Dow Chemical Company | Bicyclopolyazamacrocyclophosphonic acid complexes for use as radiopharmaceuticals |
| US5440021A (en) | 1991-03-29 | 1995-08-08 | Chuntharapai; Anan | Antibodies to human IL-8 type B receptor |
| WO1995025167A1 (en) | 1994-03-17 | 1995-09-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Anti-egfr single-chain fvs and anti-egfr antibodies |
| US5462725A (en) | 1993-05-06 | 1995-10-31 | The Dow Chemical Company | 2-pyridylmethylenepolyazamacrocyclophosphonic acids, complexes and derivatives thereof, for use as contrast agents |
| US5480990A (en) | 1991-12-10 | 1996-01-02 | The Dow Chemical Company | Bicyclopolyazamacrocyclocarboxylic acid complexes for use as contrast agents |
| US5500362A (en) | 1987-01-08 | 1996-03-19 | Xoma Corporation | Chimeric antibody with specificity to human B cell surface antigen |
| WO1996030514A1 (en) | 1995-03-31 | 1996-10-03 | University Of Washington | Intracellular domain of the her-2/neu protein for prevention or treatment of malignancies |
| US5571894A (en) | 1991-02-05 | 1996-11-05 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Recombinant antibodies specific for a growth factor receptor |
| US5587458A (en) | 1991-10-07 | 1996-12-24 | Aronex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Anti-erbB-2 antibodies, combinations thereof, and therapeutic and diagnostic uses thereof |
| WO1997004801A1 (en) | 1995-07-27 | 1997-02-13 | Genentech, Inc. | Stabile isotonic lyophilized protein formulation |
| WO1997007198A2 (en) | 1995-08-11 | 1997-02-27 | Genetics Institute, Inc. | Dna sequences and secreted proteins encoded thereby |
| US5644033A (en) | 1992-12-22 | 1997-07-01 | Health Research, Inc. | Monoclonal antibodies that define a unique antigen of human B cell antigen receptor complex and methods of using same for diagnosis and treatment |
| WO1997035885A1 (en) | 1996-03-27 | 1997-10-02 | Genentech, Inc. | ErbB3 ANTIBODIES |
| US5677171A (en) | 1988-01-12 | 1997-10-14 | Genentech, Inc. | Monoclonal antibodies directed to the HER2 receptor |
| WO1997044452A1 (en) | 1996-05-17 | 1997-11-27 | Schering Corporation | Human b-cell antigens, related reagents |
| US5739294A (en) | 1991-12-10 | 1998-04-14 | The Dow Chemical Company | Bicyclopol yazamacrocyclophosphonic acid complexes for use as contrast agents |
| US5773223A (en) | 1993-09-02 | 1998-06-30 | Chiron Corporation | Endothelin B1, (ETB1) receptor polypeptide and its encoding nucleic acid methods, and uses thereof |
| US5792616A (en) | 1990-05-29 | 1998-08-11 | The United States Of America | Antibodies to human cripto protein |
| WO1998037193A1 (en) | 1997-02-20 | 1998-08-27 | Zymogenetics, Inc. | Zcytor7 cytokine receptor |
| US5807715A (en) | 1984-08-27 | 1998-09-15 | The Board Of Trustees Of The Leland Stanford Junior University | Methods and transformed mammalian lymphocyte cells for producing functional antigen-binding protein including chimeric immunoglobulin |
| WO1998040403A1 (en) | 1997-03-10 | 1998-09-17 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Psca: prostate stem cell antigen |
| US5821337A (en) | 1991-06-14 | 1998-10-13 | Genentech, Inc. | Immunoglobulin variants |
| EP0875569A1 (en) | 1997-04-28 | 1998-11-04 | Smithkline Beecham Corporation | A human sodium dependent phosphate transporter (IPT-1) |
| US5834456A (en) | 1996-02-23 | 1998-11-10 | The Dow Chemical Company | Polyazamacrocyclofluoromonoalkylphosphonic acids, and their complexes, for use as contrast agents |
| WO1998051824A1 (en) | 1997-05-15 | 1998-11-19 | Abbott Laboratories | Reagents and methods useful for detecting disease of the urinary tract |
| WO1998051805A1 (en) | 1997-05-15 | 1998-11-19 | Abbott Laboratories | Reagents and methods useful for detecting diseases of the prostate |
| US5854399A (en) | 1991-08-23 | 1998-12-29 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Department Of Health And Human Services | Antibodies specific for human cripto-related polypeptide CR-3 |
| US5869445A (en) | 1993-03-17 | 1999-02-09 | University Of Washington | Methods for eliciting or enhancing reactivity to HER-2/neu protein |
| WO1999019488A1 (en) | 1997-10-15 | 1999-04-22 | Children's Medical Center Corporation | Novel human egf receptors and use thereof |
| WO1999028468A1 (en) | 1997-12-02 | 1999-06-10 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Modulating b lymphocyte chemokine/receptor interactions |
| WO1999046284A2 (en) | 1998-03-13 | 1999-09-16 | The Burnham Institute | Molecules that home to various selected organs or tissues |
| US5976551A (en) | 1991-11-15 | 1999-11-02 | Institut Pasteur And Institut Nationale De La Sante Et De La Recherche Medicale | Altered major histocompatibility complex (MHC) determinant and method of using the determinant |
| WO1999058658A2 (en) | 1998-05-13 | 1999-11-18 | Epimmune, Inc. | Expression vectors for stimulating an immune response and methods of using the same |
| WO2000012130A1 (en) | 1998-08-27 | 2000-03-09 | Smithkline Beecham Corporation | Rp105 agonists and antagonists |
| WO2000014228A1 (en) | 1998-09-03 | 2000-03-16 | Japan Science And Technology Corporation | Neutral amino acid transporter and gene thereof |
| WO2000020579A1 (en) | 1998-10-02 | 2000-04-13 | Mcmaster University | Spliced form of erbb-2/neu oncogene |
| WO2000022129A1 (en) | 1998-10-13 | 2000-04-20 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Non-endogenous, constitutively activated human g protein-coupled receptors |
| WO2000032752A1 (en) | 1998-12-02 | 2000-06-08 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Psca: prostate stem cell antigen and uses thereof |
| WO2000036107A2 (en) | 1998-12-17 | 2000-06-22 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| WO2000040614A2 (en) | 1998-12-30 | 2000-07-13 | Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Inc. | Characterization of the soc/crac calcium channel protein family |
| WO2000044899A1 (en) | 1999-01-29 | 2000-08-03 | Corixa Corporation | Her-2/neu fusion proteins |
| WO2000053216A2 (en) | 1999-03-05 | 2000-09-14 | Smithkline Beecham Biologicals S.A. | Use of casb616 polypeptides and polynucleotides for cancer treatment |
| WO2000055351A1 (en) | 1999-03-12 | 2000-09-21 | Human Genome Sciences, Inc. | Human colon cancer associated gene sequences and polypeptides |
| US6153408A (en) | 1991-11-15 | 2000-11-28 | Institut Pasteur And Institut National De La Sante Et De La Recherche Medicale | Altered major histocompatibility complex (MHC) determinant and methods of using the determinant |
| WO2000075655A1 (en) | 1999-06-03 | 2000-12-14 | Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd. | Screening method with the use of cd100 |
| WO2001000245A2 (en) | 1999-06-25 | 2001-01-04 | Genentech, Inc. | HUMANIZED ANTI-ErbB2 ANTIBODIES AND TREATMENT WITH ANTI-ErbB2 ANTIBODIES |
| WO2001000244A2 (en) | 1999-06-25 | 2001-01-04 | Genentech, Inc. | METHODS OF TREATMENT USING ANTI-ErbB ANTIBODY-MAYTANSINOID CONJUGATES |
| WO2001016318A2 (en) | 1999-09-01 | 2001-03-08 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US6214345B1 (en) | 1993-05-14 | 2001-04-10 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Co. | Lysosomal enzyme-cleavable antitumor drug conjugates |
| WO2001038490A2 (en) | 1999-11-29 | 2001-05-31 | The Trustees Of Columbia University In The City Of New York | ISOLATION OF FIVE NOVEL GENES CODING FOR NEW Fc RECEPTORS-TYPE MELANOMA INVOLVED IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF LYMPHOMA/MELANOMA |
| WO2001040269A2 (en) | 1999-11-30 | 2001-06-07 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for therapy and diagnosis of breast cancer |
| WO2001040309A2 (en) | 1999-10-29 | 2001-06-07 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-prostate stem cell antigen (psca) antibody compositions and methods of use |
| WO2001041787A1 (en) | 1999-12-10 | 2001-06-14 | Epimmune Inc. | INDUCING CELLULAR IMMUNE RESPONSES TO HER2/neu USING PEPTIDE AND NUCLEIC ACID COMPOSITIONS |
| US6248564B1 (en) | 1997-08-29 | 2001-06-19 | Harvard University | Mutant MHC class I molecules |
| WO2001046232A2 (en) | 1999-12-23 | 2001-06-28 | Zymogenetics, Inc. | Soluble interleukin-20 receptor |
| WO2001045746A2 (en) | 1999-12-24 | 2001-06-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods and compositions for prolonging elimination half-times of bioactive compounds |
| WO2001046261A1 (en) | 1999-12-23 | 2001-06-28 | Zymogenetics, Inc. | Method for treating inflammation |
| WO2001048204A1 (en) | 1999-12-23 | 2001-07-05 | Agresearch Limited | Mutated bmp1b receptor as regulator of ovulation rate |
| WO2001053463A2 (en) | 2000-01-21 | 2001-07-26 | Corixa Corporation | COMPOUNDS AND METHODS FOR PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF HER-2/neu ASSOCIATED MALIGNANCIES |
| WO2001057188A2 (en) | 2000-02-03 | 2001-08-09 | Hyseq, Inc. | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| WO2001062794A2 (en) | 2000-02-22 | 2001-08-30 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 18607, a human calcium channel |
| WO2001066689A2 (en) | 2000-03-07 | 2001-09-13 | Hyseq, Inc. | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| WO2001072962A2 (en) | 2000-03-24 | 2001-10-04 | Fahri Saatcioglu | Novel prostate-specific or testis-specific nucleic acid molecules, polypeptides, and diagnostic and therapeutic methods |
| WO2001072830A2 (en) | 2000-03-31 | 2001-10-04 | Ipf Pharmaceuticals Gmbh | Diagnostic and medicament for analysing the cell surface proteome of tumour and inflammatory cells and for treating tumorous and inflammatory diseases, preferably using a specific chemokine receptor analysis and the chemokine receptor-ligand interaction |
| WO2001075177A2 (en) | 2000-04-03 | 2001-10-11 | The Government Of The United States Of America, As Represented By The Secretary, Department Of Health And Human Services | Tumor markers in ovarian cancer |
| WO2001077172A2 (en) | 2000-04-07 | 2001-10-18 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Non-endogenous, constitutively activated known g protein-coupled receptors |
| WO2001088133A2 (en) | 2000-05-18 | 2001-11-22 | Lexicon Genetics Incorporated | Human semaphorin homologs and polynucleotides encoding the same |
| WO2001090304A2 (en) | 2000-05-19 | 2001-11-29 | Human Genome Sciences, Inc. | Nucleic acids, proteins, and antibodies |
| WO2001094641A2 (en) | 2000-06-09 | 2001-12-13 | Idec Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Gene targets and ligands that bind thereto for treatment and diagnosis of ovarian carcinomas |
| WO2001098351A2 (en) | 2000-06-16 | 2001-12-27 | Incyte Genomics, Inc. | G-protein coupled receptors |
| US20010055751A1 (en) | 1997-03-10 | 2001-12-27 | Reiter Robert E | PSCA: Prostate stem cell antigen and uses thereof |
| WO2002002634A2 (en) | 2000-06-30 | 2002-01-10 | Incyte Genomics, Inc. | Human extracellular matrix and cell adhesion polypeptides |
| WO2002002624A2 (en) | 2000-06-30 | 2002-01-10 | Amgen, Inc. | B7-like molecules and uses thereof |
| WO2002002587A1 (en) | 2000-06-30 | 2002-01-10 | Human Genome Sciences, Inc. | B7-like polynucleotides, polypeptides, and antibodies |
| WO2002006339A2 (en) | 2000-07-03 | 2002-01-24 | Curagen Corporation | Proteins and nucleic acids encoding same |
| WO2002006317A2 (en) | 2000-07-17 | 2002-01-24 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| WO2002010187A1 (en) | 2000-07-27 | 2002-02-07 | Mayo Foundation For Medical Education And Research | B7-h3 and b7-h4, novel immunoregulatory molecules |
| WO2002010382A2 (en) | 2000-07-28 | 2002-02-07 | Ulrich Wissenbach | Trp8, trp9 and trp10, markers for cancer |
| WO2002012341A2 (en) | 2000-08-03 | 2002-02-14 | Corixa Corporation | Her-2/neu fusion proteins |
| WO2002013847A2 (en) | 2000-08-14 | 2002-02-21 | Corixa Corporation | Methods for diagnosis and therapy of hematological and virus-associated malignancies |
| WO2002014503A2 (en) | 2000-08-14 | 2002-02-21 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of her-2/neu-associated malignancies |
| WO2002016413A2 (en) | 2000-08-24 | 2002-02-28 | Glaxosmithkline Biologicals S.A. | Cripto tumour polypeptide |
| WO2002016429A2 (en) | 2000-08-24 | 2002-02-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| WO2002018444A2 (en) | 2000-09-01 | 2002-03-07 | Genentech, Inc. | Erbb4 antagonists |
| WO2002022808A2 (en) | 2000-09-18 | 2002-03-21 | Biogen, Inc. | Cripto mutant and uses thereof |
| WO2002022636A1 (en) | 2000-09-15 | 2002-03-21 | Isis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Antisense modulation of her-2 expression |
| WO2002022660A2 (en) | 2000-09-11 | 2002-03-21 | Hyseq, Inc. | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| WO2002022153A2 (en) | 2000-09-15 | 2002-03-21 | Zymogenetics, Inc. | Use of a polypeptide comprising the extracellular domains of il-20rb for the treatment of inflammation |
| US20020034749A1 (en) | 1997-11-18 | 2002-03-21 | Billing-Medel Patricia A. | Reagents and methods useful for detecting diseases of the breast |
| WO2002024909A2 (en) | 2000-09-18 | 2002-03-28 | Biogen, Inc. | Receptor nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| US20020042366A1 (en) | 1999-12-23 | 2002-04-11 | Penny Thompson | Method for treating inflammation |
| US6372907B1 (en) | 1999-11-03 | 2002-04-16 | Apptera Corporation | Water-soluble rhodamine dye peptide conjugates |
| WO2002030268A2 (en) | 2000-10-13 | 2002-04-18 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of prostate cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of prostate cancer |
| WO2002038766A2 (en) | 2000-11-07 | 2002-05-16 | Zymogenetics, Inc. | Human tumor necrosis factor receptor |
| US6399743B1 (en) | 1999-05-14 | 2002-06-04 | Dept. Of Veterans Affairs | Isolation and characterization of a rat epidermal growth factor related protein |
| WO2002054940A2 (en) | 2001-01-12 | 2002-07-18 | University Of Medicine & Dentistry Of New Jersey | Bone morphogenetic protein-2 in the treatment and diagnosis of cancer |
| WO2002059377A2 (en) | 2001-01-24 | 2002-08-01 | Protein Design Labs | Methods of diagnosis of breast cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of breast cancer |
| WO2002060317A2 (en) | 2001-01-30 | 2002-08-08 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of pancreatic cancer |
| WO2002061087A2 (en) | 2000-12-19 | 2002-08-08 | Lifespan Biosciences, Inc. | Antigenic peptides, such as for g protein-coupled receptors (gpcrs), antibodies thereto, and systems for identifying such antigenic peptides |
| WO2002064798A1 (en) | 2001-02-12 | 2002-08-22 | Bionomics Limited | Dna sequences differentially expressed in tumour cell lines |
| WO2002072596A1 (en) | 2001-03-09 | 2002-09-19 | Incyte Genomics, Inc. | Steap-related protein |
| WO2002071928A2 (en) | 2001-03-14 | 2002-09-19 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Nucleic acid molecules and proteins for the identification, assessment, prevention, and therapy of ovarian cancer |
| WO2002078524A2 (en) | 2001-03-28 | 2002-10-10 | Zycos Inc. | Translational profiling |
| US20020150573A1 (en) | 2000-11-10 | 2002-10-17 | The Rockefeller University | Anti-Igalpha-Igbeta antibody for lymphoma therapy |
| WO2002081646A2 (en) | 2001-04-06 | 2002-10-17 | Mannkind Corporation | Epitope sequences |
| WO2002083866A2 (en) | 2001-04-17 | 2002-10-24 | The Board Of Trustees Of The University Of Arkansas | Repeat sequences of the ca125 gene and their use for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions |
| WO2002086443A2 (en) | 2001-04-18 | 2002-10-31 | Protein Design Labs, Inc | Methods of diagnosis of lung cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of lung cancer |
| WO2002088170A2 (en) | 2001-04-26 | 2002-11-07 | Biogen, Inc. | Cripto blocking antibodies and uses thereof |
| WO2002088172A2 (en) | 2001-04-30 | 2002-11-07 | Seattle Genetics, Inc. | Pentapeptide compounds and uses related thereto |
| WO2002089747A2 (en) | 2001-05-09 | 2002-11-14 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of prostate cancer |
| WO2002092836A2 (en) | 2001-05-11 | 2002-11-21 | Sloan-Kettering Institute For Cancer Research | Nucleic acid sequence encoding ovarian antigen, ca125, and uses thereof |
| WO2002094852A2 (en) | 2001-05-24 | 2002-11-28 | Zymogenetics, Inc. | Taci-immunoglobulin fusion proteins |
| WO2002099074A2 (en) | 2001-06-05 | 2002-12-12 | Exelixis, Inc. | Slc7s as modifiers of the p53 pathway and methods of use |
| WO2002098358A2 (en) | 2001-06-04 | 2002-12-12 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis and treatment of androgen-dependent prostate cancer, prostate cancer undergoing androgen-withdrawal, and androgen-independent prostate cancer |
| WO2002099122A1 (en) | 2001-06-05 | 2002-12-12 | Exelixis, Inc. | Modifiers of the p53 pathway and methods of use |
| WO2002101075A2 (en) | 2001-06-13 | 2002-12-19 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Novel genes, compositions, kits, and methods for identification, assessment, prevention, and therapy of cervical cancer |
| US20020193567A1 (en) | 1995-08-11 | 2002-12-19 | Genetics Institute, Inc. | Secreted proteins and polynucleotides encoding them |
| WO2002102235A2 (en) | 2001-06-18 | 2002-12-27 | Eos Biotechnology Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of ovarian cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of ovarian cancer |
| WO2003000842A2 (en) | 2001-06-04 | 2003-01-03 | Curagen Corporation | Novel proteins and nucleic acids encoding same |
| WO2003002717A2 (en) | 2001-06-28 | 2003-01-09 | Schering Corporation | Biological activity of ak155 |
| WO2003004989A2 (en) | 2001-06-21 | 2003-01-16 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Compositions, kits, and methods for identification, assessment, prevention, and therapy of breast cancer |
| WO2003003984A2 (en) | 2001-07-05 | 2003-01-16 | Curagen Corporation | Novel proteins and nucleic acids encoding same |
| WO2003004529A2 (en) | 2001-07-02 | 2003-01-16 | Licentia Ltd. | Ephrin-tie receptor materials and methods |
| WO2003003906A2 (en) | 2001-07-03 | 2003-01-16 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Diagnostic and screening methods for bladder cancer |
| WO2003009814A2 (en) | 2001-07-25 | 2003-02-06 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Novel genes, compositions, kits, and methods for identification, assessment, prevention, and therapy of prostate cancer |
| US6518404B1 (en) | 1994-10-17 | 2003-02-11 | Human Genome Sciences, Inc. | Human endothelin-bombesin receptor antibodies |
| WO2003014294A2 (en) | 2001-08-03 | 2003-02-20 | Genentech, Inc. | Tacis and br3 polypeptides and uses thereof |
| WO2003016475A2 (en) | 2001-08-14 | 2003-02-27 | The General Hospital Corporation | Nucleic acid and amino acid sequences involved in pain |
| WO2003016494A2 (en) | 2001-08-16 | 2003-02-27 | Vitivity, Inc. | Diagnosis and treatment of vascular disease |
| US6528624B1 (en) | 1998-04-02 | 2003-03-04 | Genentech, Inc. | Polypeptide variants |
| WO2003018621A2 (en) | 2001-08-23 | 2003-03-06 | Oxford Biomedica (Uk) Limited | Genes |
| WO2003023013A2 (en) | 2001-09-13 | 2003-03-20 | Nuvelo, Inc. | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| WO2003022995A2 (en) | 2001-09-06 | 2003-03-20 | Agensys, Inc. | Nucleic acid and corresponding protein entitled steap-1 useful in treatment and detection of cancer |
| EP1295944A2 (en) | 1996-03-19 | 2003-03-26 | Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | GDP dissociation stimulating protein, brain-specific nucleosome assembly protein, skeletal muscle specific ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, cell proliferation protein, phosphatidylinositolkinase, nel related proteins |
| WO2003025138A2 (en) | 2001-09-17 | 2003-03-27 | Protein Design Labs, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of cancer compositions and methods of screening for modulators of cancer |
| WO2003025148A2 (en) | 2001-09-19 | 2003-03-27 | Nuvelo, Inc. | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| WO2003025228A1 (en) | 2001-09-18 | 2003-03-27 | Proteologics, Inc. | Methods and compositions for treating hcap associated diseases |
| WO2003024392A2 (en) | 2001-09-18 | 2003-03-27 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| US20030060612A1 (en) | 1997-10-28 | 2003-03-27 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| WO2003026493A2 (en) | 2001-09-28 | 2003-04-03 | Bing Yang | Diagnosis and treatment of diseases caused by mutations in cd72 |
| WO2003026577A2 (en) | 2001-09-24 | 2003-04-03 | Seattle Genetics, Inc. | P-amidobenzylethers in drug delivery agents |
| US20030064397A1 (en) | 1998-05-22 | 2003-04-03 | Incyte Genomics, Inc. | Transmembrane protein differentially expressed in prostate and lung tumors |
| US20030065143A1 (en) | 1998-12-30 | 2003-04-03 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| WO2003029262A2 (en) | 2001-08-29 | 2003-04-10 | Vanderbilt University | The human mob-5 (il-24) receptors and uses thereof |
| WO2003029421A2 (en) | 2001-10-03 | 2003-04-10 | Origene Technologies, Inc. | Regulated breast cancer genes |
| WO2003029277A2 (en) | 2001-10-03 | 2003-04-10 | Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Modulators of lymphocyte activation and migration |
| WO2003034984A2 (en) | 2001-10-19 | 2003-05-01 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disorders |
| WO2003035846A2 (en) | 2001-10-24 | 2003-05-01 | National Jewish Medical And Research Center | Structure of tall-1 and its cognate receptor |
| US20030091580A1 (en) | 2001-06-18 | 2003-05-15 | Mitcham Jennifer L. | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| US20030096373A1 (en) | 1999-05-14 | 2003-05-22 | Majumdar Adhip P. N. | Antibodies to a novel EGF-receptor related protein (ERRP) |
| US20030096961A1 (en) | 2001-06-01 | 2003-05-22 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030096743A1 (en) | 2001-09-24 | 2003-05-22 | Seattle Genetics, Inc. | p-Amidobenzylethers in drug delivery agents |
| WO2003042661A2 (en) | 2001-11-13 | 2003-05-22 | Protein Design Labs, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of cancer |
| WO2003043583A2 (en) | 2001-11-20 | 2003-05-30 | Seattle Genetics, Inc. | Treatment of immunological disorders using anti-cd30 antibodies |
| WO2003045422A1 (en) | 2001-11-29 | 2003-06-05 | Genset S.A. | Agonists and antagonists of prolixin for the treatment of metabolic disorders |
| WO2003048202A2 (en) | 2001-12-03 | 2003-06-12 | Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation | Nf-kappab activating genes |
| US20030119126A1 (en) | 2001-01-16 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030119128A1 (en) | 1999-07-20 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030119130A1 (en) | 1999-08-17 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030119122A1 (en) | 1999-05-11 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030119129A1 (en) | 1999-08-10 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030119131A1 (en) | 2000-01-20 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030118592A1 (en) | 2001-01-17 | 2003-06-26 | Genecraft, Inc. | Binding domain-immunoglobulin fusion proteins |
| US20030119125A1 (en) | 2001-01-16 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030119121A1 (en) | 2000-09-15 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030124140A1 (en) | 1998-12-17 | 2003-07-03 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| US20030124579A1 (en) | 2001-09-05 | 2003-07-03 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of ovarian cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of ovarian cancer |
| WO2003054152A2 (en) | 2001-12-10 | 2003-07-03 | Nuvelo, Inc. | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| WO2003055439A2 (en) | 2001-07-18 | 2003-07-10 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Her2/neu target antigen and use of same to stimulate an immune response |
| WO2003055443A2 (en) | 2001-10-31 | 2003-07-10 | Alcon, Inc. | Bone morphogenic proteins (bmp), bmp receptors and bmp binding proteins and their use in the diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma |
| US20030129192A1 (en) | 1999-09-10 | 2003-07-10 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| US20030134790A1 (en) | 2002-01-11 | 2003-07-17 | University Of Medicine And Dentistry Of New Jersey | Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 And Bone Morphogenetic Protein-4 In The Treatment And Diagnosis Of Cancer |
| WO2003062401A2 (en) | 2002-01-22 | 2003-07-31 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the detection, diagnosis and therapy of hematological malignancies |
| US20030143557A1 (en) | 2002-01-25 | 2003-07-31 | Reinhold Penner | Methods of screening for TRPM4b modulators |
| US20030157089A1 (en) | 1997-02-25 | 2003-08-21 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of prostate cancer |
| US20030165504A1 (en) | 1999-09-24 | 2003-09-04 | Retter Marc W. | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| WO2003072036A2 (en) | 2002-02-21 | 2003-09-04 | Duke University | Treatment methods using anti-cd22 antibodies |
| WO2003072035A2 (en) | 2002-02-22 | 2003-09-04 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the treatment of immune related diseases |
| EP1347046A1 (en) | 2002-03-22 | 2003-09-24 | Research Association for Biotechnology | Full-length cDNA sequences |
| WO2003077836A2 (en) | 2001-11-06 | 2003-09-25 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the detection, diagnosis and therapy of hematological malignancies |
| US20030186372A1 (en) | 2000-02-11 | 2003-10-02 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030185830A1 (en) | 1997-02-25 | 2003-10-02 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of prostate cancer |
| WO2003081210A2 (en) | 2002-03-21 | 2003-10-02 | Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Identification of kinase inhibitors |
| WO2003083041A2 (en) | 2002-03-22 | 2003-10-09 | Biogen, Inc. | Cripto-specific antibodies |
| WO2003083074A2 (en) | 2002-03-28 | 2003-10-09 | Idec Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Novel gene targets and ligands that bind thereto for treatment and diagnosis of colon carcinomas |
| WO2003083047A2 (en) | 2002-03-01 | 2003-10-09 | Exelixis, Inc. | MP53s AS MODIFIERS OF THE p53 PATHWAY AND METHODS OF USE |
| US20030194704A1 (en) | 2002-04-03 | 2003-10-16 | Penn Sharron Gaynor | Human genome-derived single exon nucleic acid probes useful for gene expression analysis two |
| WO2003087768A2 (en) | 2002-04-12 | 2003-10-23 | Mitokor | Targets for therapeutic intervention identified in the mitochondrial proteome |
| WO2003087306A2 (en) | 2002-04-05 | 2003-10-23 | Agensys, Inc. | Nucleic acid and corresponding protein entitled 98p4b6 useful in treatment and detection of cancer |
| WO2003089624A2 (en) | 2002-03-25 | 2003-10-30 | Uab Research Foundation | Fc receptor homolog, reagents, and uses thereof |
| WO2003088808A2 (en) | 2002-04-16 | 2003-10-30 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| WO2003089904A2 (en) | 2002-04-17 | 2003-10-30 | Baylor College Of Medicine | Aib1 as a prognostic marker and predictor of resistance to encocrine therapy |
| US20030206918A1 (en) | 1999-09-10 | 2003-11-06 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| WO2003093444A2 (en) | 2002-05-03 | 2003-11-13 | Incyte Corporation | Transporters and ion channels |
| WO2003097803A2 (en) | 2002-05-15 | 2003-11-27 | Avalon Pharmaceuticals | Cancer-linked gene as target for chemotherapy |
| US20030219806A1 (en) | 2000-02-22 | 2003-11-27 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Novel 18607, 15603, 69318, 12303, 48000, 52920, 5433, 38554, 57301, 58324, 55063, 52991, 59914, 59921 and 33751 molecules and uses therefor |
| US20030224411A1 (en) | 2003-03-13 | 2003-12-04 | Stanton Lawrence W. | Genes that are up- or down-regulated during differentiation of human embryonic stem cells |
| US20030224454A1 (en) | 2002-05-30 | 2003-12-04 | Ryseck Rolf Peter | Human solute carrier family 7, member 11 (hSLC7A11) |
| WO2003101400A2 (en) | 2002-06-04 | 2003-12-11 | Avalon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Cancer-linked gene as target for chemotherapy |
| WO2003101283A2 (en) | 2002-06-04 | 2003-12-11 | Incyte Corporation | Diagnostics markers for lung cancer |
| US20030232056A1 (en) | 1999-09-10 | 2003-12-18 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| WO2003104270A2 (en) | 2002-06-06 | 2003-12-18 | Ingenium Pharmaceuticals Ag | Dudulin 2 genes, expression products, non-human animal model: uses in human hematological disease |
| US20030232350A1 (en) | 2001-11-13 | 2003-12-18 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of cancer |
| WO2003104399A2 (en) | 2002-06-07 | 2003-12-18 | Avalon Pharmaceuticals, Inc | Cancer-linked gene as target for chemotherapy |
| WO2003104275A2 (en) | 2002-06-06 | 2003-12-18 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Genes and polypeptides relating to human colon cancers |
| WO2003105758A2 (en) | 2002-06-12 | 2003-12-24 | Avalon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Cancer-linked gene as target for chemotherapy |
| WO2004001004A2 (en) | 2002-06-21 | 2003-12-31 | Johns Hopkins University School Of Medicine | Membrane associated tumor endothelium markers |
| WO2004000997A2 (en) | 2002-03-19 | 2003-12-31 | Curagen Corporation | Therapeutic polypeptides, nucleic acids encoding same, and methods of use |
| WO2004001993A1 (en) | 2002-06-20 | 2003-12-31 | Snaptrack Incorporated | Reducing cross-interference in a combined gps receiver and communication system |
| WO2004000221A2 (en) | 2002-06-20 | 2003-12-31 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Compositions and methods for modulating lymphocyte activity |
| US20040001827A1 (en) | 2002-06-28 | 2004-01-01 | Dennis Mark S. | Serum albumin binding peptides for tumor targeting |
| US20040005538A1 (en) | 2001-04-11 | 2004-01-08 | Xiaojiang Chen | Three-dimensional structure of complement receptor type 2 and uses thereof |
| US20040005563A1 (en) | 2001-06-18 | 2004-01-08 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of ovarian cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of ovarian cancer |
| WO2004009622A2 (en) | 2002-07-19 | 2004-01-29 | Cellzome Ag | Protein complexes of cellular networks underlying the development of cancer and other diseases |
| US20040022727A1 (en) | 2002-06-18 | 2004-02-05 | Martin Stanton | Aptamer-toxin molecules and methods for using same |
| WO2004011611A2 (en) | 2002-07-25 | 2004-02-05 | Genentech, Inc. | Taci antibodies and uses thereof |
| WO2004015426A1 (en) | 2002-08-06 | 2004-02-19 | Bayer Healthcare Ag | Diagnostics and therapeutics for diseases associated with human cxc chemokine receptor 5(cxcr5) |
| WO2004016225A2 (en) | 2002-08-19 | 2004-02-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| EP1394274A2 (en) | 2002-08-06 | 2004-03-03 | Genox Research, Inc. | Methods of testing for bronchial asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| US20040044179A1 (en) | 2000-07-25 | 2004-03-04 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| WO2004020595A2 (en) | 2002-08-29 | 2004-03-11 | Five Prime Therapeutics, Inc. | Novel human polypeptides encoded by polynucleotides |
| WO2004020583A2 (en) | 2002-08-27 | 2004-03-11 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Polynucleotide predictor set for identifying protein tyrosine kinase modulators |
| WO2004022709A2 (en) | 2002-09-06 | 2004-03-18 | Mannkind Corporation | Epitope sequences |
| WO2004022778A1 (en) | 2002-09-05 | 2004-03-18 | Garvan Institute Of Medical Research | Methods of diagnosis and prognosis of ovarian cancer |
| WO2004027049A2 (en) | 2002-09-20 | 2004-04-01 | Astral, Inc. | Methods and compositions to generate and control the effector profile of t cells by simultaneous loading and activation of selected subsets of antigen presenting cells |
| JP2004113151A (en) | 2002-09-27 | 2004-04-15 | Sankyo Co Ltd | Oncogene and its application |
| WO2004031238A2 (en) | 2002-10-03 | 2004-04-15 | Mcgill Univeristy | Antibodies and cyclic peptides which bind cea (carcinoembryonic antigen) and their use as cancer therapeutics |
| WO2004032828A2 (en) | 2002-07-31 | 2004-04-22 | Seattle Genetics, Inc. | Anti-cd20 antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of cancer and immune disorders |
| WO2004032842A2 (en) | 2002-10-04 | 2004-04-22 | Van Andel Research Institute | Molecular sub-classification of kidney tumors and the discovery of new diagnostic markers |
| WO2004040000A2 (en) | 2002-09-09 | 2004-05-13 | Nura, Inc | G protein coupled receptors and uses thereof |
| WO2004042346A2 (en) | 2002-04-24 | 2004-05-21 | Expression Diagnostics, Inc. | Methods and compositions for diagnosing and monitoring transplant rejection |
| WO2004044178A2 (en) | 2002-11-13 | 2004-05-27 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods and compositions for diagnosing dysplasia |
| WO2004043361A2 (en) | 2002-11-08 | 2004-05-27 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the treatment of natural killer cell related diseases |
| WO2004046342A2 (en) | 2002-11-20 | 2004-06-03 | Biogen Idec Inc. | Novel gene targets and ligands that bind thereto for treatment and diagnosis of carcinomas |
| WO2004045520A2 (en) | 2002-11-15 | 2004-06-03 | Musc Foundation For Research Development | Complement receptor 2 targeted complement modulators |
| WO2004045516A2 (en) | 2002-11-15 | 2004-06-03 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| WO2004045553A2 (en) | 2002-11-15 | 2004-06-03 | The Board Of Trustees Of The University Of Arkansas | Ca125 gene and its use for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions |
| WO2004047749A2 (en) | 2002-11-21 | 2004-06-10 | University Of Utah Research Foundation | Purinergic modulation of smell |
| WO2004048938A2 (en) | 2002-11-26 | 2004-06-10 | Protein Design Labs, Inc. | Methods of detecting soft tissue sarcoma, compositions and methods of screening for soft tissue sarcoma modulators |
| WO2004053079A2 (en) | 2002-12-06 | 2004-06-24 | Diadexus, Inc. | Compositions, splice variants and methods relating to ovarian specific genes and proteins |
| WO2004058309A1 (en) | 2002-12-23 | 2004-07-15 | Human Genome Sciences, Inc. | Neutrokine-alpha conjugate, neutrokine-alpha complex, and uses thereof |
| EP1439393A2 (en) | 2002-12-13 | 2004-07-21 | Bayer Healthcare LLC | Detection methods using TIMP 1 for colon cancer diagnosis |
| WO2004063709A2 (en) | 2003-01-08 | 2004-07-29 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Biomarkers and methods for determining sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor modulators |
| WO2004063355A2 (en) | 2003-01-10 | 2004-07-29 | Protein Design Labs, Inc. | Novel methods of diagnosis of metastatic cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of matastatic cancer |
| WO2004063362A2 (en) | 2003-01-10 | 2004-07-29 | Cyclacel Limited | Cell cycle progression proteins |
| WO2004065576A2 (en) | 2003-01-15 | 2004-08-05 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods and compositions for the treatment of urological disorder using differential expressed polypeptides |
| WO2004065577A2 (en) | 2003-01-14 | 2004-08-05 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Polynucleotides and polypeptides associated with the nf-kb pathway |
| WO2004074320A2 (en) | 2003-02-14 | 2004-09-02 | Sagres Discovery, Inc. | Therapeutic targets in cancer |
| US20040197325A1 (en) | 2002-12-20 | 2004-10-07 | Debbie Law | Antibodies against GPR64 and uses thereof |
| US20040229310A1 (en) | 2003-01-23 | 2004-11-18 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods for producing humanized antibodies and improving yield of antibodies or antigen binding fragments in cell culture |
| US20040249130A1 (en) | 2002-06-18 | 2004-12-09 | Martin Stanton | Aptamer-toxin molecules and methods for using same |
| US20050048572A1 (en) | 2002-10-31 | 2005-03-03 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods and compositions for increasing antibody production |
| WO2006034488A2 (en) * | 2004-09-23 | 2006-03-30 | Genentech, Inc. | Cysteine engineered antibodies and conjugates |
| US20080050310A1 (en) | 2006-05-30 | 2008-02-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Antibodies and immunoconjugates and uses therefor |
| US20080247951A1 (en) | 2007-02-09 | 2008-10-09 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-robo4 antibodies and uses therefor |
| WO2008141044A2 (en) * | 2007-05-08 | 2008-11-20 | Genentech, Inc. | Cysteine engineered anti-muc16 antibodies and antibody drug conjugates |
| US20090028856A1 (en) | 2007-07-16 | 2009-01-29 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-CD79B Antibodies and Immunoconjugates and Methods of Use |
| US20090068202A1 (en) | 2007-07-16 | 2009-03-12 | Genentech, Inc. | Humanized Anti-CD79B Antibodies and Immunoconjugates and Methods of Use |
| US20090117100A1 (en) | 2007-10-19 | 2009-05-07 | Weiguang Mao | Cysteine engineered anti-TENB2 antibodies and antibody drug conjugates |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB8720833D0 (en) * | 1987-09-04 | 1987-10-14 | Celltech Ltd | Recombinant dna product |
| AU7075496A (en) * | 1995-09-18 | 1997-04-09 | Intracel Corporation | Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to respiratory syncytial virus |
| US6753165B1 (en) * | 1999-01-14 | 2004-06-22 | Bolder Biotechnology, Inc. | Methods for making proteins containing free cysteine residues |
| US7097840B2 (en) * | 2000-03-16 | 2006-08-29 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of treatment using anti-ErbB antibody-maytansinoid conjugates |
| US20040235068A1 (en) * | 2001-09-05 | 2004-11-25 | Levinson Arthur D. | Methods for the identification of polypeptide antigens associated with disorders involving aberrant cell proliferation and compositions useful for the treatment of such disorders |
-
2009
- 2009-11-05 US US12/612,912 patent/US20100111856A1/en not_active Abandoned
-
2010
- 2010-11-04 KR KR1020177034613A patent/KR20170136652A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2010-11-04 JP JP2012537224A patent/JP5850843B2/en active Active
- 2010-11-04 RU RU2012123007/10A patent/RU2562862C2/en active
- 2010-11-04 CN CN201080050134.4A patent/CN102596260B/en active Active
- 2010-11-04 CA CA2780216A patent/CA2780216A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2010-11-04 EP EP10776064.7A patent/EP2496270B1/en active Active
- 2010-11-04 KR KR1020127011607A patent/KR20120102625A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2010-11-04 WO PCT/US2010/055465 patent/WO2011056983A1/en active Application Filing
- 2010-11-04 MX MX2012005211A patent/MX340674B/en active IP Right Grant
- 2010-11-04 BR BR112012007774A patent/BR112012007774A2/en not_active IP Right Cessation
-
2014
- 2014-06-10 US US14/300,630 patent/US20150017094A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (307)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3773919A (en) | 1969-10-23 | 1973-11-20 | Du Pont | Polylactide-drug mixtures |
| US4318980A (en) | 1978-04-10 | 1982-03-09 | Miles Laboratories, Inc. | Heterogenous specific binding assay employing a cycling reactant as label |
| US4275149A (en) | 1978-11-24 | 1981-06-23 | Syva Company | Macromolecular environment control in specific receptor assays |
| US4458066A (en) | 1980-02-29 | 1984-07-03 | University Patents, Inc. | Process for preparing polynucleotides |
| US4415732A (en) | 1981-03-27 | 1983-11-15 | University Patents, Inc. | Phosphoramidite compounds and processes |
| US4816567A (en) | 1983-04-08 | 1989-03-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Recombinant immunoglobin preparations |
| JPH053790B2 (en) | 1983-11-02 | 1993-01-18 | Canon Kk | |
| US5807715A (en) | 1984-08-27 | 1998-09-15 | The Board Of Trustees Of The Leland Stanford Junior University | Methods and transformed mammalian lymphocyte cells for producing functional antigen-binding protein including chimeric immunoglobulin |
| US5428155A (en) | 1984-10-18 | 1995-06-27 | Board Of Regents, The University Of Texas System | Synthesis of polyazamacrocycles with more than one type of side-chain chelating groups |
| US5316757A (en) | 1984-10-18 | 1994-05-31 | Board Of Regents, The University Of Texas System | Synthesis of polyazamacrocycles with more than one type of side-chain chelating groups |
| US5342606A (en) | 1984-10-18 | 1994-08-30 | Board Of Regents, The University Of Texas System | Polyazamacrocyclic compounds for complexation of metal ions |
| US4737456A (en) | 1985-05-09 | 1988-04-12 | Syntex (U.S.A.) Inc. | Reducing interference in ligand-receptor binding assays |
| US5091178A (en) | 1986-02-21 | 1992-02-25 | Oncogen | Tumor therapy with biologically active anti-tumor antibodies |
| US5500362A (en) | 1987-01-08 | 1996-03-19 | Xoma Corporation | Chimeric antibody with specificity to human B cell surface antigen |
| US5677171A (en) | 1988-01-12 | 1997-10-14 | Genentech, Inc. | Monoclonal antibodies directed to the HER2 receptor |
| US5047524A (en) | 1988-12-21 | 1991-09-10 | Applied Biosystems, Inc. | Automated system for polynucleotide synthesis and purification |
| US5262530A (en) | 1988-12-21 | 1993-11-16 | Applied Biosystems, Inc. | Automated system for polynucleotide synthesis and purification |
| EP0404097A2 (en) | 1989-06-22 | 1990-12-27 | BEHRINGWERKE Aktiengesellschaft | Bispecific and oligospecific, mono- and oligovalent receptors, production and applications thereof |
| WO1991002536A1 (en) | 1989-08-23 | 1991-03-07 | Scripps Clinic And Research Foundation | Compositions and methods for detection and treatment of epstein-barr virus infection and immune disorders |
| US5183884A (en) | 1989-12-01 | 1993-02-02 | United States Of America | Dna segment encoding a gene for a receptor related to the epidermal growth factor receptor |
| US5480968A (en) | 1989-12-01 | 1996-01-02 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Department Of Health And Human Services | Isolated polypeptide erbB-3, related to the epidermal growth factor receptor and antibody thereto |
| US5792616A (en) | 1990-05-29 | 1998-08-11 | The United States Of America | Antibodies to human cripto protein |
| WO1992007574A1 (en) | 1990-10-25 | 1992-05-14 | Tanox Biosystems, Inc. | Glycoproteins associated with membrane-bound immunoglobulins as antibody targets on b cells |
| US5571894A (en) | 1991-02-05 | 1996-11-05 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Recombinant antibodies specific for a growth factor receptor |
| US5440021A (en) | 1991-03-29 | 1995-08-08 | Chuntharapai; Anan | Antibodies to human IL-8 type B receptor |
| WO1992017497A1 (en) | 1991-03-29 | 1992-10-15 | Genentech, Inc. | Human pf4a receptors and their use |
| US5821337A (en) | 1991-06-14 | 1998-10-13 | Genentech, Inc. | Immunoglobulin variants |
| US6407213B1 (en) | 1991-06-14 | 2002-06-18 | Genentech, Inc. | Method for making humanized antibodies |
| EP0522868A1 (en) | 1991-07-12 | 1993-01-13 | SHIONOGI SEIYAKU KABUSHIKI KAISHA trading under the name of SHIONOGI & CO. LTD. | A human endothelin receptor |
| US5854399A (en) | 1991-08-23 | 1998-12-29 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Department Of Health And Human Services | Antibodies specific for human cripto-related polypeptide CR-3 |
| US5587458A (en) | 1991-10-07 | 1996-12-24 | Aronex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Anti-erbB-2 antibodies, combinations thereof, and therapeutic and diagnostic uses thereof |
| US6153408A (en) | 1991-11-15 | 2000-11-28 | Institut Pasteur And Institut National De La Sante Et De La Recherche Medicale | Altered major histocompatibility complex (MHC) determinant and methods of using the determinant |
| US5976551A (en) | 1991-11-15 | 1999-11-02 | Institut Pasteur And Institut Nationale De La Sante Et De La Recherche Medicale | Altered major histocompatibility complex (MHC) determinant and method of using the determinant |
| US6011146A (en) | 1991-11-15 | 2000-01-04 | Institut Pasteur | Altered major histocompatibility complex (MHC) determinant and methods of using the determinant |
| WO1993011161A1 (en) | 1991-11-25 | 1993-06-10 | Enzon, Inc. | Multivalent antigen-binding proteins |
| US5480990A (en) | 1991-12-10 | 1996-01-02 | The Dow Chemical Company | Bicyclopolyazamacrocyclocarboxylic acid complexes for use as contrast agents |
| US5750660A (en) | 1991-12-10 | 1998-05-12 | The Dow Chemical Company | Bicyclopolyazamacrocyclophosphonic acid half esters |
| US5739294A (en) | 1991-12-10 | 1998-04-14 | The Dow Chemical Company | Bicyclopol yazamacrocyclophosphonic acid complexes for use as contrast agents |
| US5428139A (en) | 1991-12-10 | 1995-06-27 | The Dow Chemical Company | Bicyclopolyazamacrocyclophosphonic acid complexes for use as radiopharmaceuticals |
| WO1993016185A2 (en) | 1992-02-06 | 1993-08-19 | Creative Biomolecules, Inc. | Biosynthetic binding protein for cancer marker |
| WO1993021319A1 (en) | 1992-04-08 | 1993-10-28 | Cetus Oncology Corporation | HUMANIZED C-erbB-2 SPECIFIC ANTIBODIES |
| WO1994010312A1 (en) | 1992-10-23 | 1994-05-11 | Chugai Seiyaku Kabushiki Kaisha | Gene coding for megakaryocyte potentiator |
| WO1994011026A2 (en) | 1992-11-13 | 1994-05-26 | Idec Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Therapeutic application of chimeric and radiolabeled antibodies to human b lymphocyte restricted differentiation antigen for treatment of b cell lymphoma |
| EP0599274A1 (en) | 1992-11-24 | 1994-06-01 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | HER4, a human receptor tyrosine kinase of the epidermal growth factor receptor family |
| US5644033A (en) | 1992-12-22 | 1997-07-01 | Health Research, Inc. | Monoclonal antibodies that define a unique antigen of human B cell antigen receptor complex and methods of using same for diagnosis and treatment |
| US5869445A (en) | 1993-03-17 | 1999-02-09 | University Of Washington | Methods for eliciting or enhancing reactivity to HER-2/neu protein |
| US5462725A (en) | 1993-05-06 | 1995-10-31 | The Dow Chemical Company | 2-pyridylmethylenepolyazamacrocyclophosphonic acids, complexes and derivatives thereof, for use as contrast agents |
| US5385893A (en) | 1993-05-06 | 1995-01-31 | The Dow Chemical Company | Tricyclopolyazamacrocyclophosphonic acids, complexes and derivatives thereof, for use as contrast agents |
| US6214345B1 (en) | 1993-05-14 | 2001-04-10 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Co. | Lysosomal enzyme-cleavable antitumor drug conjugates |
| WO1994028931A1 (en) | 1993-06-11 | 1994-12-22 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods for treating inflammatory disorders |
| US5773223A (en) | 1993-09-02 | 1998-06-30 | Chiron Corporation | Endothelin B1, (ETB1) receptor polypeptide and its encoding nucleic acid methods, and uses thereof |
| WO1995025167A1 (en) | 1994-03-17 | 1995-09-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Anti-egfr single-chain fvs and anti-egfr antibodies |
| US6518404B1 (en) | 1994-10-17 | 2003-02-11 | Human Genome Sciences, Inc. | Human endothelin-bombesin receptor antibodies |
| US20030109676A1 (en) | 1994-10-17 | 2003-06-12 | Human Genome Sciences, Inc. | Human endothelin-bombesin receptor |
| WO1996030514A1 (en) | 1995-03-31 | 1996-10-03 | University Of Washington | Intracellular domain of the her-2/neu protein for prevention or treatment of malignancies |
| WO1997004801A1 (en) | 1995-07-27 | 1997-02-13 | Genentech, Inc. | Stabile isotonic lyophilized protein formulation |
| WO1997007198A2 (en) | 1995-08-11 | 1997-02-27 | Genetics Institute, Inc. | Dna sequences and secreted proteins encoded thereby |
| US20020193567A1 (en) | 1995-08-11 | 2002-12-19 | Genetics Institute, Inc. | Secreted proteins and polynucleotides encoding them |
| US5834456A (en) | 1996-02-23 | 1998-11-10 | The Dow Chemical Company | Polyazamacrocyclofluoromonoalkylphosphonic acids, and their complexes, for use as contrast agents |
| EP1295944A2 (en) | 1996-03-19 | 2003-03-26 | Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | GDP dissociation stimulating protein, brain-specific nucleosome assembly protein, skeletal muscle specific ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, cell proliferation protein, phosphatidylinositolkinase, nel related proteins |
| WO1997035885A1 (en) | 1996-03-27 | 1997-10-02 | Genentech, Inc. | ErbB3 ANTIBODIES |
| WO1997044452A1 (en) | 1996-05-17 | 1997-11-27 | Schering Corporation | Human b-cell antigens, related reagents |
| WO1998037193A1 (en) | 1997-02-20 | 1998-08-27 | Zymogenetics, Inc. | Zcytor7 cytokine receptor |
| US20030185830A1 (en) | 1997-02-25 | 2003-10-02 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of prostate cancer |
| US20030157089A1 (en) | 1997-02-25 | 2003-08-21 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of prostate cancer |
| US20010055751A1 (en) | 1997-03-10 | 2001-12-27 | Reiter Robert E | PSCA: Prostate stem cell antigen and uses thereof |
| WO1998040403A1 (en) | 1997-03-10 | 1998-09-17 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Psca: prostate stem cell antigen |
| US20030105292A1 (en) | 1997-04-14 | 2003-06-05 | Liaw Chen W. | Non-endogenous, constitutively activated human G protein-coupled receptors |
| US6555339B1 (en) | 1997-04-14 | 2003-04-29 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Non-endogenous, constitutively activated human protein-coupled receptors |
| EP0875569A1 (en) | 1997-04-28 | 1998-11-04 | Smithkline Beecham Corporation | A human sodium dependent phosphate transporter (IPT-1) |
| US20040018553A1 (en) | 1997-05-15 | 2004-01-29 | Patricia A. Billing-Medel | Reagents and methods useful for detecting diseases of the prostate |
| WO1998051805A1 (en) | 1997-05-15 | 1998-11-19 | Abbott Laboratories | Reagents and methods useful for detecting diseases of the prostate |
| WO1998051824A1 (en) | 1997-05-15 | 1998-11-19 | Abbott Laboratories | Reagents and methods useful for detecting disease of the urinary tract |
| US6248564B1 (en) | 1997-08-29 | 2001-06-19 | Harvard University | Mutant MHC class I molecules |
| WO1999019488A1 (en) | 1997-10-15 | 1999-04-22 | Children's Medical Center Corporation | Novel human egf receptors and use thereof |
| US20030060612A1 (en) | 1997-10-28 | 2003-03-27 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| US20020034749A1 (en) | 1997-11-18 | 2002-03-21 | Billing-Medel Patricia A. | Reagents and methods useful for detecting diseases of the breast |
| WO1999028468A1 (en) | 1997-12-02 | 1999-06-10 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Modulating b lymphocyte chemokine/receptor interactions |
| WO1999046284A2 (en) | 1998-03-13 | 1999-09-16 | The Burnham Institute | Molecules that home to various selected organs or tissues |
| US6528624B1 (en) | 1998-04-02 | 2003-03-04 | Genentech, Inc. | Polypeptide variants |
| US6534482B1 (en) | 1998-05-13 | 2003-03-18 | Epimmune, Inc. | Expression vectors for stimulating an immune response and methods of using the same |
| WO1999058658A2 (en) | 1998-05-13 | 1999-11-18 | Epimmune, Inc. | Expression vectors for stimulating an immune response and methods of using the same |
| US20030064397A1 (en) | 1998-05-22 | 2003-04-03 | Incyte Genomics, Inc. | Transmembrane protein differentially expressed in prostate and lung tumors |
| WO2000012130A1 (en) | 1998-08-27 | 2000-03-09 | Smithkline Beecham Corporation | Rp105 agonists and antagonists |
| WO2000014228A1 (en) | 1998-09-03 | 2000-03-16 | Japan Science And Technology Corporation | Neutral amino acid transporter and gene thereof |
| WO2000020579A1 (en) | 1998-10-02 | 2000-04-13 | Mcmaster University | Spliced form of erbb-2/neu oncogene |
| WO2000022129A1 (en) | 1998-10-13 | 2000-04-20 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Non-endogenous, constitutively activated human g protein-coupled receptors |
| WO2000032752A1 (en) | 1998-12-02 | 2000-06-08 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Psca: prostate stem cell antigen and uses thereof |
| WO2000036107A2 (en) | 1998-12-17 | 2000-06-22 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| US20030124140A1 (en) | 1998-12-17 | 2003-07-03 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| WO2000040614A2 (en) | 1998-12-30 | 2000-07-13 | Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Inc. | Characterization of the soc/crac calcium channel protein family |
| US20030065143A1 (en) | 1998-12-30 | 2003-04-03 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| WO2000044899A1 (en) | 1999-01-29 | 2000-08-03 | Corixa Corporation | Her-2/neu fusion proteins |
| WO2000053216A2 (en) | 1999-03-05 | 2000-09-14 | Smithkline Beecham Biologicals S.A. | Use of casb616 polypeptides and polynucleotides for cancer treatment |
| WO2000055351A1 (en) | 1999-03-12 | 2000-09-21 | Human Genome Sciences, Inc. | Human colon cancer associated gene sequences and polypeptides |
| US20030119122A1 (en) | 1999-05-11 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US6399743B1 (en) | 1999-05-14 | 2002-06-04 | Dept. Of Veterans Affairs | Isolation and characterization of a rat epidermal growth factor related protein |
| US20030096373A1 (en) | 1999-05-14 | 2003-05-22 | Majumdar Adhip P. N. | Antibodies to a novel EGF-receptor related protein (ERRP) |
| WO2000075655A1 (en) | 1999-06-03 | 2000-12-14 | Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd. | Screening method with the use of cd100 |
| WO2001000245A2 (en) | 1999-06-25 | 2001-01-04 | Genentech, Inc. | HUMANIZED ANTI-ErbB2 ANTIBODIES AND TREATMENT WITH ANTI-ErbB2 ANTIBODIES |
| WO2001000244A2 (en) | 1999-06-25 | 2001-01-04 | Genentech, Inc. | METHODS OF TREATMENT USING ANTI-ErbB ANTIBODY-MAYTANSINOID CONJUGATES |
| US20030119128A1 (en) | 1999-07-20 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030119129A1 (en) | 1999-08-10 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030119130A1 (en) | 1999-08-17 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| WO2001016318A2 (en) | 1999-09-01 | 2001-03-08 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030129192A1 (en) | 1999-09-10 | 2003-07-10 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| US20030206918A1 (en) | 1999-09-10 | 2003-11-06 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| US20030232056A1 (en) | 1999-09-10 | 2003-12-18 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| US20030165504A1 (en) | 1999-09-24 | 2003-09-04 | Retter Marc W. | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| WO2001040309A2 (en) | 1999-10-29 | 2001-06-07 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-prostate stem cell antigen (psca) antibody compositions and methods of use |
| US6372907B1 (en) | 1999-11-03 | 2002-04-16 | Apptera Corporation | Water-soluble rhodamine dye peptide conjugates |
| WO2001038490A2 (en) | 1999-11-29 | 2001-05-31 | The Trustees Of Columbia University In The City Of New York | ISOLATION OF FIVE NOVEL GENES CODING FOR NEW Fc RECEPTORS-TYPE MELANOMA INVOLVED IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF LYMPHOMA/MELANOMA |
| WO2001040269A2 (en) | 1999-11-30 | 2001-06-07 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for therapy and diagnosis of breast cancer |
| US20040101899A1 (en) | 1999-11-30 | 2004-05-27 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of breast cancer |
| WO2001041787A1 (en) | 1999-12-10 | 2001-06-14 | Epimmune Inc. | INDUCING CELLULAR IMMUNE RESPONSES TO HER2/neu USING PEPTIDE AND NUCLEIC ACID COMPOSITIONS |
| WO2001046261A1 (en) | 1999-12-23 | 2001-06-28 | Zymogenetics, Inc. | Method for treating inflammation |
| WO2001048204A1 (en) | 1999-12-23 | 2001-07-05 | Agresearch Limited | Mutated bmp1b receptor as regulator of ovulation rate |
| WO2001046232A2 (en) | 1999-12-23 | 2001-06-28 | Zymogenetics, Inc. | Soluble interleukin-20 receptor |
| US20020042366A1 (en) | 1999-12-23 | 2002-04-11 | Penny Thompson | Method for treating inflammation |
| US20040005320A1 (en) | 1999-12-23 | 2004-01-08 | Penny Thompson | Method for treating inflammation |
| WO2001045746A2 (en) | 1999-12-24 | 2001-06-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods and compositions for prolonging elimination half-times of bioactive compounds |
| US20030119131A1 (en) | 2000-01-20 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| WO2001053463A2 (en) | 2000-01-21 | 2001-07-26 | Corixa Corporation | COMPOUNDS AND METHODS FOR PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF HER-2/neu ASSOCIATED MALIGNANCIES |
| WO2001057188A2 (en) | 2000-02-03 | 2001-08-09 | Hyseq, Inc. | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| US20030186372A1 (en) | 2000-02-11 | 2003-10-02 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030219806A1 (en) | 2000-02-22 | 2003-11-27 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Novel 18607, 15603, 69318, 12303, 48000, 52920, 5433, 38554, 57301, 58324, 55063, 52991, 59914, 59921 and 33751 molecules and uses therefor |
| WO2001062794A2 (en) | 2000-02-22 | 2001-08-30 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 18607, a human calcium channel |
| WO2001066689A2 (en) | 2000-03-07 | 2001-09-13 | Hyseq, Inc. | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| WO2001072962A2 (en) | 2000-03-24 | 2001-10-04 | Fahri Saatcioglu | Novel prostate-specific or testis-specific nucleic acid molecules, polypeptides, and diagnostic and therapeutic methods |
| WO2001072830A2 (en) | 2000-03-31 | 2001-10-04 | Ipf Pharmaceuticals Gmbh | Diagnostic and medicament for analysing the cell surface proteome of tumour and inflammatory cells and for treating tumorous and inflammatory diseases, preferably using a specific chemokine receptor analysis and the chemokine receptor-ligand interaction |
| WO2001075177A2 (en) | 2000-04-03 | 2001-10-11 | The Government Of The United States Of America, As Represented By The Secretary, Department Of Health And Human Services | Tumor markers in ovarian cancer |
| WO2001077172A2 (en) | 2000-04-07 | 2001-10-18 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Non-endogenous, constitutively activated known g protein-coupled receptors |
| WO2001088133A2 (en) | 2000-05-18 | 2001-11-22 | Lexicon Genetics Incorporated | Human semaphorin homologs and polynucleotides encoding the same |
| WO2001090304A2 (en) | 2000-05-19 | 2001-11-29 | Human Genome Sciences, Inc. | Nucleic acids, proteins, and antibodies |
| WO2001094641A2 (en) | 2000-06-09 | 2001-12-13 | Idec Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Gene targets and ligands that bind thereto for treatment and diagnosis of ovarian carcinomas |
| WO2001098351A2 (en) | 2000-06-16 | 2001-12-27 | Incyte Genomics, Inc. | G-protein coupled receptors |
| WO2002002634A2 (en) | 2000-06-30 | 2002-01-10 | Incyte Genomics, Inc. | Human extracellular matrix and cell adhesion polypeptides |
| WO2002002624A2 (en) | 2000-06-30 | 2002-01-10 | Amgen, Inc. | B7-like molecules and uses thereof |
| WO2002002587A1 (en) | 2000-06-30 | 2002-01-10 | Human Genome Sciences, Inc. | B7-like polynucleotides, polypeptides, and antibodies |
| WO2002006339A2 (en) | 2000-07-03 | 2002-01-24 | Curagen Corporation | Proteins and nucleic acids encoding same |
| WO2002006317A2 (en) | 2000-07-17 | 2002-01-24 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| US20040044179A1 (en) | 2000-07-25 | 2004-03-04 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| WO2002010187A1 (en) | 2000-07-27 | 2002-02-07 | Mayo Foundation For Medical Education And Research | B7-h3 and b7-h4, novel immunoregulatory molecules |
| WO2002010382A2 (en) | 2000-07-28 | 2002-02-07 | Ulrich Wissenbach | Trp8, trp9 and trp10, markers for cancer |
| WO2002012341A2 (en) | 2000-08-03 | 2002-02-14 | Corixa Corporation | Her-2/neu fusion proteins |
| WO2002013847A2 (en) | 2000-08-14 | 2002-02-21 | Corixa Corporation | Methods for diagnosis and therapy of hematological and virus-associated malignancies |
| WO2002014503A2 (en) | 2000-08-14 | 2002-02-21 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of her-2/neu-associated malignancies |
| WO2002016413A2 (en) | 2000-08-24 | 2002-02-28 | Glaxosmithkline Biologicals S.A. | Cripto tumour polypeptide |
| WO2002016429A2 (en) | 2000-08-24 | 2002-02-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| WO2002018444A2 (en) | 2000-09-01 | 2002-03-07 | Genentech, Inc. | Erbb4 antagonists |
| WO2002022660A2 (en) | 2000-09-11 | 2002-03-21 | Hyseq, Inc. | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| US20030186373A1 (en) | 2000-09-15 | 2003-10-02 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| WO2002022636A1 (en) | 2000-09-15 | 2002-03-21 | Isis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Antisense modulation of her-2 expression |
| US20030119121A1 (en) | 2000-09-15 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| WO2002022153A2 (en) | 2000-09-15 | 2002-03-21 | Zymogenetics, Inc. | Use of a polypeptide comprising the extracellular domains of il-20rb for the treatment of inflammation |
| WO2002022808A2 (en) | 2000-09-18 | 2002-03-21 | Biogen, Inc. | Cripto mutant and uses thereof |
| WO2002024909A2 (en) | 2000-09-18 | 2002-03-28 | Biogen, Inc. | Receptor nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| WO2002026822A2 (en) | 2000-09-26 | 2002-04-04 | Genentech, Inc. | Pumpcn compositions and uses thereof |
| US20040005598A1 (en) | 2000-09-26 | 2004-01-08 | Genentech, Inc. | PUMPCn compositions and uses thereof |
| WO2002030268A2 (en) | 2000-10-13 | 2002-04-18 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of prostate cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of prostate cancer |
| WO2002038766A2 (en) | 2000-11-07 | 2002-05-16 | Zymogenetics, Inc. | Human tumor necrosis factor receptor |
| US20020150573A1 (en) | 2000-11-10 | 2002-10-17 | The Rockefeller University | Anti-Igalpha-Igbeta antibody for lymphoma therapy |
| WO2002061087A2 (en) | 2000-12-19 | 2002-08-08 | Lifespan Biosciences, Inc. | Antigenic peptides, such as for g protein-coupled receptors (gpcrs), antibodies thereto, and systems for identifying such antigenic peptides |
| WO2002054940A2 (en) | 2001-01-12 | 2002-07-18 | University Of Medicine & Dentistry Of New Jersey | Bone morphogenetic protein-2 in the treatment and diagnosis of cancer |
| US20030119125A1 (en) | 2001-01-16 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030119126A1 (en) | 2001-01-16 | 2003-06-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20030118592A1 (en) | 2001-01-17 | 2003-06-26 | Genecraft, Inc. | Binding domain-immunoglobulin fusion proteins |
| WO2002059377A2 (en) | 2001-01-24 | 2002-08-01 | Protein Design Labs | Methods of diagnosis of breast cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of breast cancer |
| WO2002060317A2 (en) | 2001-01-30 | 2002-08-08 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of pancreatic cancer |
| WO2002064798A1 (en) | 2001-02-12 | 2002-08-22 | Bionomics Limited | Dna sequences differentially expressed in tumour cell lines |
| WO2002072596A1 (en) | 2001-03-09 | 2002-09-19 | Incyte Genomics, Inc. | Steap-related protein |
| WO2002071928A2 (en) | 2001-03-14 | 2002-09-19 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Nucleic acid molecules and proteins for the identification, assessment, prevention, and therapy of ovarian cancer |
| WO2002078524A2 (en) | 2001-03-28 | 2002-10-10 | Zycos Inc. | Translational profiling |
| WO2003008537A2 (en) | 2001-04-06 | 2003-01-30 | Mannkind Corporation | Epitope sequences |
| WO2002081646A2 (en) | 2001-04-06 | 2002-10-17 | Mannkind Corporation | Epitope sequences |
| US20040005538A1 (en) | 2001-04-11 | 2004-01-08 | Xiaojiang Chen | Three-dimensional structure of complement receptor type 2 and uses thereof |
| WO2002083866A2 (en) | 2001-04-17 | 2002-10-24 | The Board Of Trustees Of The University Of Arkansas | Repeat sequences of the ca125 gene and their use for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions |
| WO2002086443A2 (en) | 2001-04-18 | 2002-10-31 | Protein Design Labs, Inc | Methods of diagnosis of lung cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of lung cancer |
| WO2002088170A2 (en) | 2001-04-26 | 2002-11-07 | Biogen, Inc. | Cripto blocking antibodies and uses thereof |
| WO2002088172A2 (en) | 2001-04-30 | 2002-11-07 | Seattle Genetics, Inc. | Pentapeptide compounds and uses related thereto |
| WO2002089747A2 (en) | 2001-05-09 | 2002-11-14 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of prostate cancer |
| WO2002092836A2 (en) | 2001-05-11 | 2002-11-21 | Sloan-Kettering Institute For Cancer Research | Nucleic acid sequence encoding ovarian antigen, ca125, and uses thereof |
| WO2002094852A2 (en) | 2001-05-24 | 2002-11-28 | Zymogenetics, Inc. | Taci-immunoglobulin fusion proteins |
| US20030096961A1 (en) | 2001-06-01 | 2003-05-22 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| US20040044180A1 (en) | 2001-06-01 | 2004-03-04 | Genentech, Inc. | Secreted and transmembrane polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| WO2002098358A2 (en) | 2001-06-04 | 2002-12-12 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis and treatment of androgen-dependent prostate cancer, prostate cancer undergoing androgen-withdrawal, and androgen-independent prostate cancer |
| WO2003000842A2 (en) | 2001-06-04 | 2003-01-03 | Curagen Corporation | Novel proteins and nucleic acids encoding same |
| WO2002099074A2 (en) | 2001-06-05 | 2002-12-12 | Exelixis, Inc. | Slc7s as modifiers of the p53 pathway and methods of use |
| WO2002099122A1 (en) | 2001-06-05 | 2002-12-12 | Exelixis, Inc. | Modifiers of the p53 pathway and methods of use |
| WO2002101075A2 (en) | 2001-06-13 | 2002-12-19 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Novel genes, compositions, kits, and methods for identification, assessment, prevention, and therapy of cervical cancer |
| US20040005563A1 (en) | 2001-06-18 | 2004-01-08 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of ovarian cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of ovarian cancer |
| US20030091580A1 (en) | 2001-06-18 | 2003-05-15 | Mitcham Jennifer L. | Compositions and methods for the therapy and diagnosis of ovarian cancer |
| WO2002102235A2 (en) | 2001-06-18 | 2002-12-27 | Eos Biotechnology Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of ovarian cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of ovarian cancer |
| WO2003004989A2 (en) | 2001-06-21 | 2003-01-16 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Compositions, kits, and methods for identification, assessment, prevention, and therapy of breast cancer |
| WO2003002717A2 (en) | 2001-06-28 | 2003-01-09 | Schering Corporation | Biological activity of ak155 |
| WO2003004529A2 (en) | 2001-07-02 | 2003-01-16 | Licentia Ltd. | Ephrin-tie receptor materials and methods |
| WO2003003906A2 (en) | 2001-07-03 | 2003-01-16 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Diagnostic and screening methods for bladder cancer |
| WO2003003984A2 (en) | 2001-07-05 | 2003-01-16 | Curagen Corporation | Novel proteins and nucleic acids encoding same |
| WO2003055439A2 (en) | 2001-07-18 | 2003-07-10 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Her2/neu target antigen and use of same to stimulate an immune response |
| WO2003009814A2 (en) | 2001-07-25 | 2003-02-06 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Novel genes, compositions, kits, and methods for identification, assessment, prevention, and therapy of prostate cancer |
| WO2003014294A2 (en) | 2001-08-03 | 2003-02-20 | Genentech, Inc. | Tacis and br3 polypeptides and uses thereof |
| WO2003016475A2 (en) | 2001-08-14 | 2003-02-27 | The General Hospital Corporation | Nucleic acid and amino acid sequences involved in pain |
| WO2003016494A2 (en) | 2001-08-16 | 2003-02-27 | Vitivity, Inc. | Diagnosis and treatment of vascular disease |
| WO2003018621A2 (en) | 2001-08-23 | 2003-03-06 | Oxford Biomedica (Uk) Limited | Genes |
| WO2003029262A2 (en) | 2001-08-29 | 2003-04-10 | Vanderbilt University | The human mob-5 (il-24) receptors and uses thereof |
| US20030124579A1 (en) | 2001-09-05 | 2003-07-03 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of ovarian cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of ovarian cancer |
| WO2003022995A2 (en) | 2001-09-06 | 2003-03-20 | Agensys, Inc. | Nucleic acid and corresponding protein entitled steap-1 useful in treatment and detection of cancer |
| WO2003023013A2 (en) | 2001-09-13 | 2003-03-20 | Nuvelo, Inc. | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| WO2003025138A2 (en) | 2001-09-17 | 2003-03-27 | Protein Design Labs, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of cancer compositions and methods of screening for modulators of cancer |
| WO2003024392A2 (en) | 2001-09-18 | 2003-03-27 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| WO2003025228A1 (en) | 2001-09-18 | 2003-03-27 | Proteologics, Inc. | Methods and compositions for treating hcap associated diseases |
| WO2003025148A2 (en) | 2001-09-19 | 2003-03-27 | Nuvelo, Inc. | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| US20030130189A1 (en) | 2001-09-24 | 2003-07-10 | Senter Peter D. | P-amidobenzylethers in drug delivery agents |
| WO2003026577A2 (en) | 2001-09-24 | 2003-04-03 | Seattle Genetics, Inc. | P-amidobenzylethers in drug delivery agents |
| US20030096743A1 (en) | 2001-09-24 | 2003-05-22 | Seattle Genetics, Inc. | p-Amidobenzylethers in drug delivery agents |
| WO2003026493A2 (en) | 2001-09-28 | 2003-04-03 | Bing Yang | Diagnosis and treatment of diseases caused by mutations in cd72 |
| WO2003029421A2 (en) | 2001-10-03 | 2003-04-10 | Origene Technologies, Inc. | Regulated breast cancer genes |
| WO2003029277A2 (en) | 2001-10-03 | 2003-04-10 | Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Modulators of lymphocyte activation and migration |
| WO2003034984A2 (en) | 2001-10-19 | 2003-05-01 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disorders |
| WO2003035846A2 (en) | 2001-10-24 | 2003-05-01 | National Jewish Medical And Research Center | Structure of tall-1 and its cognate receptor |
| WO2003055443A2 (en) | 2001-10-31 | 2003-07-10 | Alcon, Inc. | Bone morphogenic proteins (bmp), bmp receptors and bmp binding proteins and their use in the diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma |
| WO2003077836A2 (en) | 2001-11-06 | 2003-09-25 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the detection, diagnosis and therapy of hematological malignancies |
| US20030232350A1 (en) | 2001-11-13 | 2003-12-18 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of cancer |
| WO2003042661A2 (en) | 2001-11-13 | 2003-05-22 | Protein Design Labs, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of cancer |
| WO2003043583A2 (en) | 2001-11-20 | 2003-05-30 | Seattle Genetics, Inc. | Treatment of immunological disorders using anti-cd30 antibodies |
| WO2003045422A1 (en) | 2001-11-29 | 2003-06-05 | Genset S.A. | Agonists and antagonists of prolixin for the treatment of metabolic disorders |
| WO2003048202A2 (en) | 2001-12-03 | 2003-06-12 | Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation | Nf-kappab activating genes |
| WO2003054152A2 (en) | 2001-12-10 | 2003-07-03 | Nuvelo, Inc. | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| US20030134790A1 (en) | 2002-01-11 | 2003-07-17 | University Of Medicine And Dentistry Of New Jersey | Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 And Bone Morphogenetic Protein-4 In The Treatment And Diagnosis Of Cancer |
| WO2003062401A2 (en) | 2002-01-22 | 2003-07-31 | Corixa Corporation | Compositions and methods for the detection, diagnosis and therapy of hematological malignancies |
| US20030143557A1 (en) | 2002-01-25 | 2003-07-31 | Reinhold Penner | Methods of screening for TRPM4b modulators |
| WO2003072036A2 (en) | 2002-02-21 | 2003-09-04 | Duke University | Treatment methods using anti-cd22 antibodies |
| WO2003072035A2 (en) | 2002-02-22 | 2003-09-04 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the treatment of immune related diseases |
| WO2003083047A2 (en) | 2002-03-01 | 2003-10-09 | Exelixis, Inc. | MP53s AS MODIFIERS OF THE p53 PATHWAY AND METHODS OF USE |
| WO2004000997A2 (en) | 2002-03-19 | 2003-12-31 | Curagen Corporation | Therapeutic polypeptides, nucleic acids encoding same, and methods of use |
| WO2003081210A2 (en) | 2002-03-21 | 2003-10-02 | Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Identification of kinase inhibitors |
| EP1347046A1 (en) | 2002-03-22 | 2003-09-24 | Research Association for Biotechnology | Full-length cDNA sequences |
| WO2003083041A2 (en) | 2002-03-22 | 2003-10-09 | Biogen, Inc. | Cripto-specific antibodies |
| WO2003089624A2 (en) | 2002-03-25 | 2003-10-30 | Uab Research Foundation | Fc receptor homolog, reagents, and uses thereof |
| WO2003083074A2 (en) | 2002-03-28 | 2003-10-09 | Idec Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Novel gene targets and ligands that bind thereto for treatment and diagnosis of colon carcinomas |
| US20030194704A1 (en) | 2002-04-03 | 2003-10-16 | Penn Sharron Gaynor | Human genome-derived single exon nucleic acid probes useful for gene expression analysis two |
| WO2003087306A2 (en) | 2002-04-05 | 2003-10-23 | Agensys, Inc. | Nucleic acid and corresponding protein entitled 98p4b6 useful in treatment and detection of cancer |
| US20040101874A1 (en) | 2002-04-12 | 2004-05-27 | Mitokor Inc. | Targets for therapeutic intervention identified in the mitochondrial proteome |
| WO2003087768A2 (en) | 2002-04-12 | 2003-10-23 | Mitokor | Targets for therapeutic intervention identified in the mitochondrial proteome |
| US20030228319A1 (en) | 2002-04-16 | 2003-12-11 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| WO2003088808A2 (en) | 2002-04-16 | 2003-10-30 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| WO2003089904A2 (en) | 2002-04-17 | 2003-10-30 | Baylor College Of Medicine | Aib1 as a prognostic marker and predictor of resistance to encocrine therapy |
| WO2004042346A2 (en) | 2002-04-24 | 2004-05-21 | Expression Diagnostics, Inc. | Methods and compositions for diagnosing and monitoring transplant rejection |
| WO2003093444A2 (en) | 2002-05-03 | 2003-11-13 | Incyte Corporation | Transporters and ion channels |
| WO2003097803A2 (en) | 2002-05-15 | 2003-11-27 | Avalon Pharmaceuticals | Cancer-linked gene as target for chemotherapy |
| US20030224454A1 (en) | 2002-05-30 | 2003-12-04 | Ryseck Rolf Peter | Human solute carrier family 7, member 11 (hSLC7A11) |
| WO2003101283A2 (en) | 2002-06-04 | 2003-12-11 | Incyte Corporation | Diagnostics markers for lung cancer |
| WO2003101400A2 (en) | 2002-06-04 | 2003-12-11 | Avalon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Cancer-linked gene as target for chemotherapy |
| WO2003104270A2 (en) | 2002-06-06 | 2003-12-18 | Ingenium Pharmaceuticals Ag | Dudulin 2 genes, expression products, non-human animal model: uses in human hematological disease |
| WO2003104275A2 (en) | 2002-06-06 | 2003-12-18 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Genes and polypeptides relating to human colon cancers |
| WO2003104399A2 (en) | 2002-06-07 | 2003-12-18 | Avalon Pharmaceuticals, Inc | Cancer-linked gene as target for chemotherapy |
| WO2003105758A2 (en) | 2002-06-12 | 2003-12-24 | Avalon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Cancer-linked gene as target for chemotherapy |
| US20040249130A1 (en) | 2002-06-18 | 2004-12-09 | Martin Stanton | Aptamer-toxin molecules and methods for using same |
| US20040022727A1 (en) | 2002-06-18 | 2004-02-05 | Martin Stanton | Aptamer-toxin molecules and methods for using same |
| WO2004000221A2 (en) | 2002-06-20 | 2003-12-31 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Compositions and methods for modulating lymphocyte activity |
| WO2004001993A1 (en) | 2002-06-20 | 2003-12-31 | Snaptrack Incorporated | Reducing cross-interference in a combined gps receiver and communication system |
| WO2004001004A2 (en) | 2002-06-21 | 2003-12-31 | Johns Hopkins University School Of Medicine | Membrane associated tumor endothelium markers |
| US20040001827A1 (en) | 2002-06-28 | 2004-01-01 | Dennis Mark S. | Serum albumin binding peptides for tumor targeting |
| WO2004009622A2 (en) | 2002-07-19 | 2004-01-29 | Cellzome Ag | Protein complexes of cellular networks underlying the development of cancer and other diseases |
| WO2004011611A2 (en) | 2002-07-25 | 2004-02-05 | Genentech, Inc. | Taci antibodies and uses thereof |
| WO2004032828A2 (en) | 2002-07-31 | 2004-04-22 | Seattle Genetics, Inc. | Anti-cd20 antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of cancer and immune disorders |
| WO2004015426A1 (en) | 2002-08-06 | 2004-02-19 | Bayer Healthcare Ag | Diagnostics and therapeutics for diseases associated with human cxc chemokine receptor 5(cxcr5) |
| EP1394274A2 (en) | 2002-08-06 | 2004-03-03 | Genox Research, Inc. | Methods of testing for bronchial asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| WO2004016225A2 (en) | 2002-08-19 | 2004-02-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| WO2004020583A2 (en) | 2002-08-27 | 2004-03-11 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Polynucleotide predictor set for identifying protein tyrosine kinase modulators |
| WO2004020595A2 (en) | 2002-08-29 | 2004-03-11 | Five Prime Therapeutics, Inc. | Novel human polypeptides encoded by polynucleotides |
| WO2004022778A1 (en) | 2002-09-05 | 2004-03-18 | Garvan Institute Of Medical Research | Methods of diagnosis and prognosis of ovarian cancer |
| WO2004022709A2 (en) | 2002-09-06 | 2004-03-18 | Mannkind Corporation | Epitope sequences |
| WO2004040000A2 (en) | 2002-09-09 | 2004-05-13 | Nura, Inc | G protein coupled receptors and uses thereof |
| WO2004027049A2 (en) | 2002-09-20 | 2004-04-01 | Astral, Inc. | Methods and compositions to generate and control the effector profile of t cells by simultaneous loading and activation of selected subsets of antigen presenting cells |
| JP2004113151A (en) | 2002-09-27 | 2004-04-15 | Sankyo Co Ltd | Oncogene and its application |
| WO2004031238A2 (en) | 2002-10-03 | 2004-04-15 | Mcgill Univeristy | Antibodies and cyclic peptides which bind cea (carcinoembryonic antigen) and their use as cancer therapeutics |
| WO2004032842A2 (en) | 2002-10-04 | 2004-04-22 | Van Andel Research Institute | Molecular sub-classification of kidney tumors and the discovery of new diagnostic markers |
| US20050048572A1 (en) | 2002-10-31 | 2005-03-03 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods and compositions for increasing antibody production |
| WO2004043361A2 (en) | 2002-11-08 | 2004-05-27 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the treatment of natural killer cell related diseases |
| WO2004044178A2 (en) | 2002-11-13 | 2004-05-27 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods and compositions for diagnosing dysplasia |
| WO2004045516A2 (en) | 2002-11-15 | 2004-06-03 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| WO2004045553A2 (en) | 2002-11-15 | 2004-06-03 | The Board Of Trustees Of The University Of Arkansas | Ca125 gene and its use for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions |
| WO2004045520A2 (en) | 2002-11-15 | 2004-06-03 | Musc Foundation For Research Development | Complement receptor 2 targeted complement modulators |
| WO2004046342A2 (en) | 2002-11-20 | 2004-06-03 | Biogen Idec Inc. | Novel gene targets and ligands that bind thereto for treatment and diagnosis of carcinomas |
| WO2004047749A2 (en) | 2002-11-21 | 2004-06-10 | University Of Utah Research Foundation | Purinergic modulation of smell |
| WO2004048938A2 (en) | 2002-11-26 | 2004-06-10 | Protein Design Labs, Inc. | Methods of detecting soft tissue sarcoma, compositions and methods of screening for soft tissue sarcoma modulators |
| WO2004053079A2 (en) | 2002-12-06 | 2004-06-24 | Diadexus, Inc. | Compositions, splice variants and methods relating to ovarian specific genes and proteins |
| EP1439393A2 (en) | 2002-12-13 | 2004-07-21 | Bayer Healthcare LLC | Detection methods using TIMP 1 for colon cancer diagnosis |
| US20040197325A1 (en) | 2002-12-20 | 2004-10-07 | Debbie Law | Antibodies against GPR64 and uses thereof |
| WO2004058309A1 (en) | 2002-12-23 | 2004-07-15 | Human Genome Sciences, Inc. | Neutrokine-alpha conjugate, neutrokine-alpha complex, and uses thereof |
| WO2004063709A2 (en) | 2003-01-08 | 2004-07-29 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Biomarkers and methods for determining sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor modulators |
| WO2004063355A2 (en) | 2003-01-10 | 2004-07-29 | Protein Design Labs, Inc. | Novel methods of diagnosis of metastatic cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of matastatic cancer |
| WO2004063362A2 (en) | 2003-01-10 | 2004-07-29 | Cyclacel Limited | Cell cycle progression proteins |
| WO2004065577A2 (en) | 2003-01-14 | 2004-08-05 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Polynucleotides and polypeptides associated with the nf-kb pathway |
| WO2004065576A2 (en) | 2003-01-15 | 2004-08-05 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods and compositions for the treatment of urological disorder using differential expressed polypeptides |
| US20040229310A1 (en) | 2003-01-23 | 2004-11-18 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods for producing humanized antibodies and improving yield of antibodies or antigen binding fragments in cell culture |
| WO2004074320A2 (en) | 2003-02-14 | 2004-09-02 | Sagres Discovery, Inc. | Therapeutic targets in cancer |
| US20030224411A1 (en) | 2003-03-13 | 2003-12-04 | Stanton Lawrence W. | Genes that are up- or down-regulated during differentiation of human embryonic stem cells |
| WO2006034488A2 (en) * | 2004-09-23 | 2006-03-30 | Genentech, Inc. | Cysteine engineered antibodies and conjugates |
| US20080050310A1 (en) | 2006-05-30 | 2008-02-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Antibodies and immunoconjugates and uses therefor |
| US20080247951A1 (en) | 2007-02-09 | 2008-10-09 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-robo4 antibodies and uses therefor |
| WO2008141044A2 (en) * | 2007-05-08 | 2008-11-20 | Genentech, Inc. | Cysteine engineered anti-muc16 antibodies and antibody drug conjugates |
| US20080311134A1 (en) | 2007-05-08 | 2008-12-18 | Junutula Jagath R | Cysteine engineered anti-muc16 antibodies and antibody drug conjugates |
| US20090028856A1 (en) | 2007-07-16 | 2009-01-29 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-CD79B Antibodies and Immunoconjugates and Methods of Use |
| US20090068202A1 (en) | 2007-07-16 | 2009-03-12 | Genentech, Inc. | Humanized Anti-CD79B Antibodies and Immunoconjugates and Methods of Use |
| US20090117100A1 (en) | 2007-10-19 | 2009-05-07 | Weiguang Mao | Cysteine engineered anti-TENB2 antibodies and antibody drug conjugates |
Non-Patent Citations (368)
| Title |
|---|
| "Current Protocols in Immunology", vol. 1, 2, 1991, WILEY-INTERSCIENCE |
| "McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Chemical Terms", 1984, MCGRAW-HILL BOOK COMPANY |
| "The CCP4 Suite: Programs for Protein Crystallography", ACTA. CRYST., vol. D50, 1994, pages 760 - 763 |
| AERTS HJ ET AL.: "Disparity between in vivo EGFR expression and 89Zr-labeled cetuximab uptake assessed with PET", J NUCL MED., vol. 50, 2009, pages 123 - 31, XP055026510, DOI: doi:10.2967/jnumed.108.054312 |
| ALBERT ET AL., BIOORG. MED. CHEM. LETT., vol. 8, 1998, pages 1207 - 1210 |
| AM. J. HUM. GENET., vol. 49, no. 3, 1991, pages 555 - 565 |
| AMIEL J. ET AL., HUM. MOL. GENET., vol. 5, 1996, pages 355 - 357 |
| AMIR ET AL., ANGEW. CHEM. INT. ED., vol. 42, 2003, pages 4494 - 4499 |
| ANDRUS, A.: "PCR 2: A Practical Approach", 1995, OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS, article "Chemical methods for 5' non-isotopic labelling of PCR probes and primers", pages: 39 - 54 |
| ANNU. REV. NEUROSCI., vol. 21, 1998, pages 309 - 345 |
| ARAI H. ET AL., J. BIOL. CHEM., vol. 268, 1993, pages 3463 - 3470 |
| ARAI H. ET AL., JPN. CIRC. J., vol. 56, 1992, pages 1303 - 1307 |
| ATTIE T. ET AL., HUM. MOL. GENET., vol. 4, 1995, pages 2407 - 2409 |
| AURICCHIO A. ET AL., HUM. MOL. GENET., vol. 5, 1996, pages 351 - 354 |
| AUSUBEL ET AL.: "Current Protocols in Molecular Biology", 1993, GREENE PUBLISHING AND WILEY-INTERSCIENCE |
| AXWORTHY ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. USA, vol. 97, no. 4, 2000, pages 1802 - 1807 |
| B.LEEF.M.RICHARDS, J.MOL.BIOL., vol. 55, 1971, pages 379 - 400 |
| BACA ET AL., JOURNAL BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY, vol. 272, no. 16, 1997, pages 10678 - 84 |
| BAREL M. ET AL., MOL. IMMUNOL., vol. 35, 1998, pages 1025 - 1031 |
| BARELLA ET AL., BIOCHEM. J., vol. 309, 1995, pages 773 - 779 |
| BARNETT T. ET AL., GENOMICS, vol. 3, 1988, pages 59 - 66 |
| BEAUCAGE, S.IYER, R.: "Advances in the synthesis of oligonucleotides by the phosphoramidite approach", TETRAHEDRON, vol. 48, 1992, pages 2223 - 2311, XP000915225, DOI: doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)88752-4 |
| BECK ET AL., J. MOL. BIOL., vol. 228, 1992, pages 433 - 441 |
| BECK, J. MOL. BIOL., vol. 255, 1996, pages 1 - 13 |
| BERNHARD ET AL., BIOCONJUGATE CHEM., vol. 5, 1994, pages 126 - 132 |
| BETTER ET AL., J. BIOL. CHEM., vol. 269, no. 13, 1994, pages 9644 - 9650 |
| BIOCHEM. BIOPHYS. RES. COMMUN., vol. 255, no. 2, 1999, pages 283 - 288 |
| BIOCHEM. BIOPHYS. RES. COMMUN., vol. 275, no. 3, 2000, pages 783 - 788 |
| BIOCONJUGATE CHEM., vol. 3, 1992, pages 2 |
| BISHOP,D.T. ET AL., NAT. GENET., vol. 41, no. 8, 2009, pages 920 - 925 |
| BLEND ET AL., CANCER BIOTHERAPY & RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS, vol. 18, 2003, pages 355 - 363 |
| BLOOD, vol. 100, no. 9, 2002, pages 3068 - 3076 |
| BLOOD, vol. 99, no. 8, 2002, pages 2662 - 2669 |
| BLUMBERG H. ET AL., CELL, vol. 104, 2001, pages 9 - 19 |
| BOIJESSON PK ET AL.: "Performance ofimmuno- positron emission tomography with zirconium-89-labeled chimeric monoclonal antibody U36 in the detection of lymph node metastases in head and neck cancer patients", CLIN CANCER RES., vol. 12, 2006, pages 2133 - 40 |
| BOURGEOIS C. ET AL., J. CLIN. ENDOCRINOL. METAB., vol. 82, 1997, pages 3116 - 3123 |
| BRIGGS ET AL.: "Synthcsis of Functionaliscd Fluorescent Dyes and Their Coupling to Amincs and Amino Acids", J. CHEM. SOC., PERKIN-TRANS., vol. 1, 1997, pages 1051 - 1058 |
| BRINKLEY, BIOCONJUGATE CHEM., vol. 3, 1992, pages 2 |
| CAI W ET AL.: "PET imaging of colorectal cancer in xenograft-bearing mice by use of an 18F-labeled T84.66 anti-carcinoembryonic antigen diabody", J NUCL MED., vol. 48, 2007, pages 304 - 10, XP055003542, DOI: doi:10.2967/jnumed.107.043216 |
| CAMERA ET AL., NUCL. MED. BID., vol. 20, 1993, pages 955 - 62 |
| CAMERA, J. NUCL. MCD., vol. 21, 1994, pages 640 - 646 |
| CANCER RES., vol. 61, no. 15, 2001, pages 5857 - 5860 |
| CAPEL ET AL., IMMUNOMETHODS, vol. 4, 1994, pages 25 - 34 |
| CARPENTER ET AL., ANN. REV. BIOCHEM., vol. 56, 1987, pages 881 - 914 |
| CARTER ET AL., NUCLEIC ACIDS RES., vol. 13, 1985, pages 4431 - 4443 |
| CELL, vol. 109, no. 3, 2002, pages 397 - 407 |
| CHAN,J.WATT, V.M., ONCOGENE, vol. 6, no. 6, 1991, pages 1057 - 1061 |
| CHANG ET AL., GENE, vol. 55, 1987, pages 189 - 196 |
| CHATAL: "Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunoscintigraphy", 1989, CRC PRESS |
| CHEN ET AL., BIOCONJUGATE CHEM., vol. 15, 2004, pages 41 - 49 |
| CHMURA ET AL., PROC. NAT. ACAD. SCI. USA, vol. 98, no. 15, 2001, pages 8480 - 8484 |
| CHO H.-S., NATURE, vol. 421, 2003, pages 756 - 760 |
| CHOTHIA ET AL., NATURE, vol. 342, 1989, pages 877 |
| CHOTHIALESK, J. MOL. BIOL., vol. 196, 1987, pages 901 - 917 |
| CICCODICOLA, A. ET AL., EMBO J., vol. 8, no. 7, 1989, pages 1987 - 1991 |
| CLACKSON ET AL., NATURE, vol. 352, 1991, pages 624 - 628 |
| CLARK H.F. ET AL., GENOME RES., vol. 13, 2003, pages 2265 - 2270 |
| CLARK, H.F. ET AL., GENOME RES., vol. 13, no. 10, 2003, pages 2265 - 2270 |
| CLARK,H.F. ET AL., GENOME RES., vol. 13, no. 10, 2003, pages 2265 - 2270 |
| CLYNES ET AL., PROC. NAT. ACAD. SCI., vol. 95, 1998, pages 652 - 656 |
| COLE, R.B.: "Electro Spray Ionization Mass Spectrometry: Fundamentals, Instrumentation And Applications", 1997, WILEY |
| COUSSENS L. ET AL., SCIENCE, vol. 230, no. 4730, 1985, pages 1132 - 1139 |
| DAVIS ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI USA, vol. 98, no. 17, 2001, pages 9772 - 9777 |
| DE HAAS ET AL., J. LAB. CLIN. MED., vol. 126, 1995, pages 330 - 41 |
| DE LEON-RODRIGUEZ ET AL., CHEM.EUR. J., vol. 10, 2004, pages 1149 - 1155 |
| DE NOOIJ-VAN DALEN,A.G. ET AL., INT. J. CANCER, vol. 103, no. 6, 2003, pages 768 - 774 |
| DENARDO ET AL., CLINICAL CANCER RESEARCH, vol. 4, 1998, pages 2483 - 90 |
| DENNIS ET AL., J BIOL CHEM., vol. 277, 2002, pages 35035 - 35043 |
| DENNIS ET AL.: "Albumin Binding As A General Strategy For Improving The Pharmacokinetics Of Proteins", J BIOL CHEM., vol. 277, 2002, pages 35035 - 35043 |
| DIJKE,P. ET AL., SCIENCE, vol. 264, no. 5155, 1994, pages 101 - 104 |
| DIJKERS EC ET AL.: "Development and Characterization of Clinical-Grade 89Zr-Trastuzumab for HER2/neu ImmunoPET Imaging", J NUCL MED, vol. 50, no. 6, 2009, pages 974 - 981, XP002615664, DOI: doi:10.2967/JNUMED.108.060392 |
| DIJKERS ELI C F ET AL: "Development and characterization of clinical-grade 89Zr-trastuzumab for HER2/neu immunoPET imaging.", JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE : OFFICIAL PUBLICATION, SOCIETY OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE JUN 2009 LNKD- PUBMED:19443585, vol. 50, no. 6, June 2009 (2009-06-01), pages 974 - 981, XP002615664, ISSN: 0161-5505 * |
| DIVGI CR ET AL.: "Preoperative characterisation of clear-cell renal carcinoma using iodine-124-labelled antibody chimeric G250 (124I-cG250) and PET in patients with renal masses: a phase I trial", LANCET ONCOL, vol. 8, 2007, pages 304 - 10, XP002615898, DOI: doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70044-X |
| DOBNER ET AL., EUR. J. IMMUNOL., vol. 22, 1992, pages 2795 - 2799 |
| DREBIN ET AL., NATURE, vol. 312, 1984, pages 545 - 548 |
| D'SOUZA ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI., vol. 91, 1994, pages 7202 - 7206 |
| DUMOUTIER L. ET AL., J. IMMUNOL., vol. 167, 2001, pages 3545 - 3549 |
| EHSANI A. ET AL., GENOMICS, vol. 15, 1993, pages 426 - 429 |
| EIGCNBROT, J MOL BIOL., vol. 229, 1993, pages 969 - 995 |
| EIGENBROT ET AL., J MOL BIOL., vol. 229, 1993, pages 969 - 995 |
| EIGENBROT ET AL.: "X-Ray Structures Of The Antigen-Binding Domains From Three Variants Of Humanized Anti-P185her2 Antibody 4D5 And Comparison With Molecular Modeling", J MOL BIOL., vol. 229, 1993, pages 969 - 995, XP024009357, DOI: doi:10.1006/jmbi.1993.1099 |
| ELIEL, E.WILEN, S.: "Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds", 1994, JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. |
| ELSHOURBAGY N.A. ET AL., J. BIOL. CHEM., vol. 268, 1993, pages 3873 - 3879 |
| ERICSSON, T.A. ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 100, no. 11, 2003, pages 6759 - 6764 |
| ERKCR, G., PURE AND APPLIED CHEMISTRY, vol. 63, no. 6, 1991, pages 797 - 806 |
| ERKER, G., JOUR. OF ORGANOMETALLIC CHEM., vol. 400, no. 1-2, 1990, pages 185 - 203 |
| FCILD, J.A. ET AL., BIOCHEM. BIOPHYS. RES. COMMUN., vol. 258, no. 3, 1999, pages 578 - 582 |
| FENDLY ET AL., CANCER RESEARCH, vol. 50, 1990, pages 1550 - 1558 |
| FLETCHER CR: "The radiological hazards of zirconium-95 and niobium-95", HEALTH PHYS., vol. 16, 1969, pages 209 - 20 |
| FOOTEWINTER, J. MOL. BIOL., vol. 224, 1992, pages 487 - 499 |
| FRAKER ET AL., BIOCHEM. BIOPHYS. RES. COMMUN., vol. 80, 1978, pages 49 - 57 |
| FRISCH ET AL., BIOCONJUGATE CHEM., vol. 7, 1996, pages 180 - 186 |
| FUCHS S. ET AL., MOL. MED., vol. 7, 2001, pages 115 - 124 |
| FUJISAKU, J. BIOL. CHCM., vol. 264, no. 4, 1989, pages 2118 - 2125 |
| FURUSHIMA,K. ET AL., DEV. BIOL., vol. 306, no. 2, 2007, pages 480 - 492 |
| GARMAN: "Non-Radioactive Labelling: A Practical Approach", 1997, ACADEMIC PRESS |
| GARMAN: "Non-Radioactive Labelling: A Practical Approach", 1997, ACADEMIC PRESS, pages: 55 |
| GARRARD ET AL., GENE, vol. 128, 1993, pages 103 - 109 |
| GARY S.C. ET AL., GENE, vol. 256, 2000, pages 139 - 147 |
| GAUGITSCH, H.W. ET AL., J. BIOL. CHEM., vol. 267, no. 16, 1992, pages 11267 - 11273 |
| GAZZANO-SANTORO ET AL., J. IMMUNOL. METHODS, vol. 202, 1996, pages 163 |
| GCNOMICS, vol. 62, no. 2, 1999, pages 281 - 284 |
| GCRSTNCR: "Sequence Plasticity In The Antigen-Binding Site Of A Therapeutic Anti-HER2 Antibody", J MOL BIOL., vol. 321, 2002, pages 851 - 62, XP002972421, DOI: doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00677-0 |
| GENOME RES., vol. 13, no. 10, 2003, pages 2265 - 2270 |
| GERHARD,D.S. ET AL., GENOME RES., vol. 14, no. 1 OB, 2004, pages 2121 - 2127 |
| GERY, S. ET AL., ONCOGENE, vol. 22, no. 18, 2003, pages 2723 - 2727 |
| GETZ ET AL., ANAL. BIOCHEM., vol. 273, 1999, pages 73 - 80 |
| GILL HS ET AL.: "A modular platform for the rapid site-specific radiolabeling of proteins with 18F exemplified by quantitative positron emission tomography of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2", JOUR. OFMED. CHEM., vol. 52, 2009, pages 5816 - 25, XP055238938, DOI: doi:10.1021/jm900420c |
| GLAZER ET AL.: "Chemical Modification of Proteins. Laboratory Techniques in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology", 1975, AMERICAN ELSEVIER PUBLISHING CO. |
| GLYNNE-JONES ET AL., INT J CANCER., vol. 94, no. 2, 15 October 2001 (2001-10-15), pages 178 - 84 |
| GONZALEZ TROTTER DE ET AL.: "Quantitation of small-animal (124)1 activity distributions using a clinical PET/CT scanncr", J NUCL MED, vol. 45, 2004, pages 1237 - 44 |
| GOVINDAN S V ET AL: "Deferoxamine as a chelator for <67>Ga in the preparation of antibody conjugates", NUCLEAR MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY, ELSEVIER, NY, US, vol. 32, no. 5, 1 July 2005 (2005-07-01), pages 513 - 519, XP004952403, ISSN: 0969-8051, DOI: DOI:10.1016/J.NUCMEDBIO.2005.04.009 * |
| GREENWOOD ET AL., THERAPEUTIC IMMUNOLOGY, vol. 1, 1994, pages 247 - 255 |
| GU Z. ET AL., ONCOGENE, vol. 19, 2000, pages 1288 - 1296 |
| GUYER ET AL., J. IMMUNOL., vol. 117, 1976, pages 587 |
| HA ET AL., J. IMMUNOL., vol. 148, no. 5, 1992, pages 1526 - 1531 |
| HAENDLER B. ET AL., J. CARDIOVASC. PHARMACOL., vol. 20, 1992, pages S1 - S4 |
| HAMBLETT KJ ET AL.: "Effects of drug loading on the antitumor activity of a monoclonal antibody drug conjugate", CLIN CANCER RES., vol. 10, 2004, pages 7063 - 70, XP002726047, DOI: doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0789 |
| HARLOW E.LANE, D.: "Using Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual", 1999, COLD SPRINGS HARBOR LABORATORY PRESS |
| HARMS, P.W., GENES DEV., vol. 17, no. 21, 2003, pages 2624 - 2629 |
| HASHIMOTO ET AL., IMMUNOGENETICS, vol. 40, no. 4, 1994, pages 287 - 295 |
| HATA, K. ET AL., ANTICANCER RES., vol. 29, no. 2, 2009, pages 617 - 623 |
| HAUGLAND: "Molecular Probes Handbook of Fluorescent Probes and Research Chemicals", 2003, MOLECULAR PROBES, INC. |
| HERMANSON, G.: "Bioconjugate Techniques", 1996, ACADEMIC PRESS |
| HERMANSON, G.: "Bioconjugate Techniques", 1996, ACADEMIC PRESS, pages: 40 - 55,643-6 |
| HIGUCHI: "PCR Protocols", 1990, ACADEMIC PRESS, pages: 177 - 183 |
| HNATOWICH ET AL., J. IMMUNOL. METHODS, vol. 65, 1983, pages 147 - 157 |
| HO ET AL., GENE, vol. 77, 1989, pages 51 - 59 |
| HOFSTRA R.M.W. ET AL., EUR. J. HUM. GENET., vol. 5, 1997, pages 180 - 185 |
| HOFSTRA R.M.W. ET AL., NAT. GENET., vol. 12, 1996, pages 445 - 447 |
| HOLLAND JP: "Standardizcd methods for the production of high specific-activity zirconium-89", NUCL MED BIOL., vol. 36, 2009, pages 729 - 39, XP026545224, DOI: doi:10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2009.05.007 |
| HOLLIGER ET AL., NAT BIOTECHNOL, vol. 23, 2005, pages 1126 - 36 |
| HOLLINGER ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. USA, vol. 90, 1993, pages 6444 - 6448 |
| HORIE ET AL., GENOMICS, vol. 67, 2000, pages 146 - 152 |
| HUBERT, R.S. ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 96, no. 25, 1999, pages 14523 - 14528 |
| HUDZIAK ET AL., MOL. CELL. BIOL., vol. 9, no. 3, 1989, pages 1165 - 1172 |
| HUMPHREY ET AL., PROC. NAT. ACAD. SCI., vol. 87, 1990, pages 4207 - 4211 |
| IMMUNOGENETICS, vol. 54, no. 2, 2002, pages 87 - 95 |
| INT. REV. CYTOL., vol. 196, 2000, pages 177 - 244 |
| ISHIKAWA,N. ET AL., CANCER RES., vol. 67, no. 24, 2007, pages 11601 - 11611 |
| ITO ET AL., GENE, vol. 102, 1991, pages 67 - 70 |
| IZARD ET AL., BIOCONJUGATE CHEM., vol. 3, 1992, pages 346 - 350 |
| J. BIOL. CHCM., vol. 276, no. 29, 2001, pages 27371 - 27375 |
| J. BIOL. CHCM., vol. 277, no. 22, 2002, pages 19665 - 19672 |
| J. BIOL. CHCM., vol. 278, no. 33, 2003, pages 30813 - 30820 |
| J. BIOL. CHEM., vol. 270, no. 37, 1995, pages 21984 - 21990 |
| JAIN MBATRA SK: "Genetically engineered antibody fragments and PET imaging: a new era of radioimmunodiagnosis", J NUCL MED, vol. 44, 2003, pages 1970 - 2 |
| JANEWAY, C.TRAVERS, P.WALPORT, M.SHLOMCHIK. 5TH ED.: "Immunobiology", 2001, GARLAND PUBLISHING |
| JANEWAY, C.TRAVERS, P.WALPORT, M.SHLOMCHIK: "Immunobiology. 5th Ed.", 2001, GARLAND PUBLISHING, pages: 627 - 628 |
| JAYSON GC ET AL.: "Molecular imaging and biological evaluation of HuMV833 anti-VEGF antibody: implications for trial design of antiangiogenic antibodies", J NATL CANCER INST, vol. 94, 2002, pages 1484 - 93, XP002472298 |
| JONES ET AL., NATURE, vol. 321, 1986, pages 522 - 525 |
| JONSSON ET AL., IMMUNOGENETICS, vol. 29, no. 6, 1989, pages 411 - 413 |
| JUNUTULA ET AL: "Rapid identification of reactive cysteine residues for site-specific labeling of antibody-Fabs", JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGICAL METHODS, ELSEVIER SCIENCE PUBLISHERS B.V.,AMSTERDAM, NL, vol. 332, no. 1-2, 14 January 2008 (2008-01-14), pages 41 - 52, XP022527824, ISSN: 0022-1759, DOI: DOI:10.1016/J.JIM.2007.12.011 * |
| JUNUTULA J R ET AL: "Site-specific conjugation of a cytotoxic drug to an antibody improves the therapeutic index", NATURE BIOTECHNOLOGY, NATURE PUBLISHING GROUP, NEW YORK, NY, US, vol. 26, no. 8, 1 August 2008 (2008-08-01), pages 925 - 932, XP002499771, ISSN: 1087-0156, [retrieved on 20080720], DOI: DOI:10.1038/NBT.1480 * |
| JUNUTULA JR ET AL.: "Rapid identification of reactive cysteine residues for site-specific labeling of antibody-Fabs", J IMMUNOL METHODS, vol. 332, 2008, pages 41 - 52, XP022527824, DOI: doi:10.1016/j.jim.2007.12.011 |
| JUNUTULA JR ET AL.: "Site-specific conjugation of a cytotoxic drug to an antibody improves the therapeutic index", NAT BIOTECHNOL, vol. 26, 2008, pages 925 - 32 |
| JUNUTULA JR ET AL.: "Site-specific conjugation of a cytotoxic drug to an antibody improves the therapeutic index", NAT BIOTECHNOL., vol. 26, 2008, pages 925 - 32 |
| KABAT ET AL.: "Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest. 5th Ed.", 1991, NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH |
| KANNO ET AL., J. OF BIOTECHNOLOGY, vol. 76, 2000, pages 207 - 214 |
| KASAHARA ET AL., IMMUNOGENETICS, vol. 30, no. 1, 1989, pages 66 - 68 |
| KELLER, G.MANAK, M.: "DNA Probes", 1993, STOCKTON PRESS, pages: 121 - 23 |
| KIM ET AL., J. IMMUNOL., vol. 24, 1994, pages 249 |
| KIM,M.H. ET AL., MOL. CELL. BIOL., vol. 29, no. 8, 2009, pages 2264 - 2277 |
| KLUSSMAN ET AL., BIOCONJUGATE CHEMISTRY, vol. 15, no. 4, 2004, pages 765 - 773 |
| KNIGHT, C.: "Methods in Enzymology", vol. 248, 1995, ACADEMIC PRESS, article "Fluorimetric Assays of Proteolytic Enzymes", pages: 18 - 34 |
| KOBAYASHI ET AL., BIOCONJUGATE CHEM., vol. 10, 1999, pages 103 - 111 |
| KOBAYASHI ET AL., J. NUCL. MED., vol. 39, 1998, pages 829 - 36 |
| KOHLER ET AL., NATURE, vol. 256, 1975, pages 495 |
| KOTTS ET AL., IN VITRO, vol. 26, no. 3, 1990, pages 59A |
| KRAUS ET AL., PROC. NAT. ACAD. SCI., vol. 86, 1989, pages 9193 - 9197 |
| KUHNS J.J. ET AL., J. BIOL. CHCM., vol. 274, 1999, pages 36422 - 36427 |
| KUKIS ET AL., J. NUCL. MED., vol. 39, 1998, pages 2105 - 2110 |
| KUMAR ET AL., MOL. CELL. BIOL., vol. 11, no. 2, 1991, pages 979 - 986 |
| KUMMER,M.P. ET AL., J. BIOL. CHEM., vol. 284, no. 4, 2009, pages 2296 - 2306 |
| KUNKEL ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. USA, vol. 82, 1987, pages 488 |
| LAB. INVEST., vol. 82, no. 11, 2002, pages 1573 - 1582 |
| LARHAMMAR ET AL., J. BIOL. CHEM., vol. 260, no. 26, 1985, pages 14111 - 14119 |
| LARSON SM ET AL.: "PET scanning of iodine-124-3F9 as an approach to tumor dosimetry during treatment planning for radioimmunotherapy in a child with neuroblastoma", J NUCL MED, vol. 33, 1992, pages 2020 - 3 |
| LE ET AL., FEBS LETT., vol. 418, no. 1-2, 1997, pages 195 - 199 |
| LEE ET AL., CANCER RES., vol. 61, 2001, pages 4474 - 4482 |
| LEE FT ET AL.: "Immuno-PET of human colon xenograft- bearing BALB/c nude mice using 124I-CDR-grafted humanized A33 monoclonal antibody", J NUCL MED, vol. 42, 2001, pages 764 - 9, XP001023782 |
| LEWIS ET AL., BIOCONJ. CHEM., vol. 9, 1998, pages 72 - 86 |
| LEWIS ET AL., BIOCONJUGATE CHEM., vol. 12, 2001, pages 320 - 324 |
| LEWIS ET AL., CANCER RESEARCH, vol. 56, 1996, pages 1457 - 1465 |
| LEWIS, CANCER IMMUNOL. IMMUNOTHER, vol. 37, 1993, pages 255 - 263 |
| LI ET AL., BIOCONJUGATE CHEM., vol. 13, 2002, pages 110 - 115 |
| LIANG ET AL., CANCER RES., vol. 60, 2000, pages 4907 - 12 |
| LIU ET AL., J. BIOL. CHEM., vol. 273, 1998, pages 20252 - 20260 |
| LIU, SHUANG, ADVANCED DRUG DELIVERY REVIEWS, vol. 60, no. 12, 2008, pages 1347 - 1370 |
| LOWMAN ET AL., J. BIOL. CHEM., vol. 266, no. 17, 1991, pages 10982 - 10988 |
| LOWMAN, HENRY B., METHODS IN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY, vol. 87, 1998, pages 249 - 264 |
| LOWMANWELLS, METHODS: A COMPANION TO METHODS IN ENZYMOLOGY, vol. 3, 1991, pages 205 - 0216 |
| LUND ET AL., EUR. J. BIOCHEM., vol. 267, 2000, pages 7246 - 7256 |
| LUNDBLAD R.L.: "Chemical Reagents for Protein Modification. 2nd Ed.", 1991, CRC PRESS |
| LUNDBLAD, R. L.NOYES, C. M.: "Chemical Reagents for Protein Modification", vol. I, II, 1984, CRC PRESS |
| M. IN DAERON, ANNU. REV. IMMUNOL, vol. 15, 1997, pages 203 - 234 |
| MALLYA, M. ET AL., GENOMICS, vol. 80, no. 1, 2002, pages 113 - 123 |
| MARDIROSSIAN ET AL., NUCL. MED. BIOL., vol. 20, 1993, pages 65 - 74 |
| MARKS ET AL., J. MOL. BIOL., vol. 222, 1991, pages 581 - 597 |
| MCGLINCHEY,R.P. ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 106, no. 33, 2009, pages 13731 - 13736 |
| MCIJS WE: "A facile method for the labeling of proteins with zirconium isotopes", NUCL MED BIOL., vol. 23, 1996, pages 439 - 48, XP004051812, DOI: doi:10.1016/0969-8051(96)00020-0 |
| MEALEY J, JR: "Turn-over of carrier-free zirconium-89 in man", NATURE, vol. 179, 1957, pages 673 - 4 |
| MEANS, BIOCONJUGATE CHEM., vol. 1, 1990, pages 2 |
| MEARES ET AL., ANAL. BIOCHEM., vol. 142, 1984, pages 68 - 78 |
| MEARES ET AL., J. CANCER, vol. 1990, 1990, pages 21 - 26 |
| MEIJS WE ET AL.: "Zirconium-labeled monoclonal antibodies and their distribution in tumor-bearing nude mice", J. NUCL. MCD., vol. 38, 1997, pages 112 - 8 |
| MIEDERER ET AL., J. NUCL. MED., vol. 45, 2004, pages 129 - 137 |
| MIER ET AL., BIOCONJUGATE CHEM., vol. 16, 2005, pages 240 - 237 |
| MILLER ET AL., JOUR. OF IMMUNOLOGY, vol. 170, 2003, pages 4854 - 4861 |
| MILLER, MARVIN J: "Syntheses and therapeutic potential of hydroxamic acid based siderophores and analogs", CHEMICAL REVIEWS, vol. 89, no. 7, 1989, pages 1563 - 1579, XP002713430, DOI: doi:10.1021/cr00097a011 |
| MIRAGLIA: "Homogeneous cell- and bead-based assays for high throughput screening using fluorometric microvolume assay technology", J. OF BIOMOLECULAR SCREENING, vol. 4, 1999, pages 193 - 204 |
| MIRZADEH ET AL., BIOCONJUGATE CHEM., vol. 1, 1990, pages 59 - 65 |
| MITCHELL ET AL., J. NUCL. MED., vol. 44, 2003, pages 1105 - 1112 |
| MIURA ET AL., BLOOD, vol. 92, 1998, pages 2815 - 2822 |
| MIURA ET AL., GENOMICS, vol. 38, no. 3, 1996, pages 299 - 304 |
| MONTPETIT, A.SINNETT,D., HUM. GENET., vol. 105, no. 1-2, 1999, pages 162 - 164 |
| MOORE M. ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 84, 1987, pages 9194 - 9198 |
| MORRISON ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. USA, vol. 81, 1984, pages 6851 - 6855 |
| MUELLER ET AL., EUR. J. BIOCHEM., vol. 22, 1992, pages 1621 - 1625 |
| MULLER ET AL., EUR. J. IMMUNOL., vol. 22, no. 6, 1992, pages 1621 - 1625 |
| MUNGALL A.J. ET AL., NATURE, vol. 425, 2003, pages 805 - 811 |
| MURTHY ET AL., ARCH. BIOCHEM. BIOPHYS., vol. 252, 1987, pages 549 - 560 |
| NAGASE T. ET AL., DNA RES., vol. 7, no. 2, 2000, pages 143 - 150 |
| NAGENGAST WB ET AL.: "In vivo VEGF imaging with radiolabeled bevacizumab in a human ovarian tumor xenograft", J NUCL MED., vol. 48, 2007, pages 1313 - 9 |
| NAKAMUTA M. ET AL., BIOCHEM. BIOPHYS. RES. COMMUN., vol. 177, 1991, pages 34 - 39 |
| NAKAYAMA ET AL., BIOCHEM. BIOPHYS. RES. COMMUN., vol. 277, no. 1, 2000, pages 124 - 127 |
| NAN, H. ET AL., INT. J. CANCER, vol. 125, no. 4, 2009, pages 909 - 917 |
| NARITA,N. ET AL., ONCOGENE, vol. 28, no. 34, 2009, pages 3058 - 3068 |
| NARUSC, TISSUE ANTIGENS, vol. 59, 2002, pages 512 - 519 |
| NATURE, vol. 395, no. 6699, 1998, pages 288 - 291 |
| NAVENOT, J.M. ET AL., MOL. PHARMACOL., vol. 75, no. 6, 2009, pages 1300 - 1306 |
| NIKULA ET AL., J. NUCL. MED., vol. 40, 1999, pages 166 - 76 |
| NIKULA ET AL., NUCL. MED. BIOL., vol. 22, 1995, pages 387 - 90 |
| ODA ET AL.: "Nature Biotechnology", vol. 19, 2001, PIERCE BIOTECHNOLOGY, INC., pages: 379 - 382 |
| O'DOWD, B.F. ET AL., FEBS LETT., vol. 394, no. 3, 1996, pages 325 - 329 |
| OGAWA Y. ET AL., BIOCHEM. BIOPHYS. RES. COMMUN., vol. 178, 1991, pages 248 - 255 |
| OKAMOTO Y., BIOL. CHCM., vol. 272, 1997, pages 21589 - 21596 |
| OLAFSEN ET AL., PROTEIN ENG. DESIGN & SEL., vol. 17, no. 4, 2004, pages 315 - 323 |
| ONCOGENE, vol. 10, no. 5, 1995, pages 897 - 905 |
| ONCOGENE, vol. 14, no. 11, 1997, pages 1377 - 1382 |
| OSOL, A: "Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th Ed.", 1980 |
| O'SULLIVAN ET AL.: "Methods in Enzym.", vol. 73, 1981, ACADEMIC PRESS, article "Methods for the Preparation of Enzyme-Antibody Conjugates for use in Enzyme Immunoassay", pages: 147 - 166 |
| PARRISH-NOVAK J. ET AL., J. BIOL. CHEM., vol. 277, 2002, pages 47517 - 47523 |
| PERERA RM ET AL.: "Internalization, intracellular trafficking, and biodistribution of monoclonal antibody 806: a novel anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody", NEOPLASIA, vol. 9, 2007, pages 1099 - 110 |
| PERK LR ET AL., EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE AND MOLECULAR IMAGING, vol. 35, no. 10, 2009, pages 1857 - 1867 |
| PERK LR ET AL.: "(89)Zr as a PET surrogate radioisotope for scouting biodistribution of the therapeutic radiomctals (90)Y and (177)Lu in tumor-bearing nude mice after coupling to the internalizing antibody cetuximab", J NUCL MED., vol. 46, 2005, pages 1898 - 906, XP008068580 |
| PERK LR ET AL.: "Facile radio labeling of monoclonal antibodies and other proteins with zirconium-89 or gallium-68 for PET Imaging using p-isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine", NATURE PROTOCOLS, 2008 |
| PERK LR ET AL.: "Facile radiolabeling of monoclonal antibodies and other proteins with zirconium-89 or gallium-68 for PET Imaging using p-isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine", NATURE PROTOCOLS, 2008 |
| PERK LR ET AL.: "p-Isothiocyanatobcnzyl-dcsfcrrioxaminc: a new bifunctional chclatc for facile radiolabcling of monoclonal antibodies with zirconium-89 for immuno-PET imaging", EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE AND MOLECULAR IMAGING, 2009 |
| PERK LR ET AL.: "Preparation and evaluation of (89)Zr-Zevalin for monitoring of (90)Y-Zevalin biodistribution with positron emission tomography", EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE AND MOLECULAR IMAGING, vol. 33, 2006, pages 1337 - 45, XP019441788, DOI: doi:10.1007/s00259-006-0160-0 |
| PERK LR ET AL.: "Quantitative PET imaging of Met- expressing human cancer xenografts with (89)Zr-labelled monoclonal antibody DN30", EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE AND MOLECULAR IMAGING, vol. 35, 2008, pages 1857 - 67, XP019654427, DOI: doi:10.1007/s00259-008-0774-5 |
| PFLEIDERER, G.: "Modern Methods in Protein Chemistry", 1985, WALTER DEGRYTER, article "Chemical Modification of Proteins" |
| PIETRAS ET AL., ONCOGENE, vol. 9, 1994, pages 1829 - 1838 |
| PINGAULT V. ET AL., HUM. GENET., vol. 111, 2002, pages 198 - 206 |
| PLETNEV S. ET AL., BIOCHEMISTRY, vol. 42, 2003, pages 12617 - 12624 |
| PLIICKTHUN: "The Pharmacology of Monoclonal Antibodies", vol. 113, 1994, SPRINGER-VERLAG, pages: 269 - 315 |
| PLOWMAN ET AL., NATURE, vol. 366, 1993, pages 473 - 475 |
| PLOWMAN ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. USA, vol. 90, 1993, pages 1746 - 1750 |
| PLUCKTHUN, IMMUNOL. REVS., vol. 130, 1992, pages 151 - 188 |
| PRESTA ET AL., J. IMMUNOL., vol. 151, 1993, pages 2623 - 2632 |
| PRESTA ET AL., THROMB. HAEMOST., vol. 85, 2001, pages 379 - 389 |
| PRESTA, CURR. OP. STRUCT. BIOL., vol. 2, 1992, pages 593 - 596 |
| PREUD'HOMME ET AL., CLIN. EXP. IMMUNOL., vol. 90, no. 1, 1992, pages 141 - 146 |
| PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 100, no. 7, 2003, pages 4126 - 4131 |
| PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 93, no. 1, 1996, pages 136 - 140 |
| PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 96, no. 20, 1999, pages 11531 - 11536 |
| PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 98, no. 17, 2001, pages 9772 - 9777 |
| PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 99, no. 26, 2002, pages 16899 - 16903 |
| PUFFENBERGER E.G. ET AL., CELL, vol. 79, 1994, pages 1257 - 1266 |
| RAVETCHKINET, ANNU. REV. IMMUNOL, vol. 9, 1991, pages 457 - 92 |
| REITER R.E. ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 95, 1998, pages 1735 - 1740 |
| RIBAS,G. ET AL., J. IMMUNOL., vol. 163, no. 1, 1999, pages 278 - 287 |
| RIECHMANN ET AL., J. MOL. BIOL., vol. 224, 1992, pages 487 - 499 |
| RIECHMANN ET AL., NATURE, vol. 332, 1988, pages 323 - 329 |
| ROBINSON MK: "Quantitativc immuno-positron emission tomography imaging of HER2-positive tumor xenografts with an iodine-124 labeled anti-HER2 diabody", CANCER RES, vol. 65, 2005, pages 1471 - 8, XP002458366, DOI: doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2008 |
| ROSELLI ET AL., CANCER BIOTHERAPY & RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS, vol. 14, 1999, pages 209 - 20 |
| ROSS ET AL., CANCER RES., vol. 62, 2002, pages 2546 - 2553 |
| ROUX ET AL., J. IMMUNOL., vol. 161, 1998, pages 4083 - 4090 |
| RUEGG ET AL., CANCER RES., vol. 50, 1990, pages 4221 - 4226 |
| SAKAGUCHI ET AL., EMBO J., vol. 7, no. 11, 1988, pages 3457 - 3464 |
| SAKAMOTO A.YANAGISAWA M. ET AL., BIOCHEM. BIOPHYS. RES. COMMUN., vol. 178, 1991, pages 656 - 663 |
| SALANTI,G., AM. J. EPIDCMIOL., vol. 170, no. 5, 2009, pages 537 - 545 |
| SAMBROOK ET AL.: "Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual", 1989, COLD SPRING HARBOR LABORATORY PRESS |
| SAMBROOKRUSSEL: "Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 3rd Ed.", 2001 |
| SARUP ET AL., GROWTH REGULATION, vol. 1, 1991, pages 72 - 82 |
| SCHAEFER ET AL., ONCOGENE, vol. 15, 1997, pages 1385 - 1394 |
| SCHECTER ET AL., NATURE, vol. 312, 1984, pages 513 |
| SCHELLENBERGER EA ET AL.: "Optical imaging of apoptosis as a biomarker of tumor response to chemotherapy", NEOPLASIA, vol. 5, 2003, pages 187 - 92, XP009162585, DOI: doi:10.1016/S1476-5586(03)80050-7 |
| SCHERER,S.E. ET AL., NATURE, vol. 440, no. 7082, 2006, pages 346 - 351 |
| SCMBA, PROC. NAT. ACAD. SCI., vol. 82, 1985, pages 6497 - 6501 |
| SCOTT ET AL., J. BIOL. CHEM., vol. 266, 1991, pages 14300 - 5 |
| SEMBA K. ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 82, 1985, pages 6497 - 6501 |
| SERVENIUS ET AL., J. BIOL. CHEM., vol. 262, 1987, pages 8759 - 8766 |
| SHAMIS ET AL., J. AMER. CHEM. SOC., vol. 126, 2004, pages 1726 - 1731 |
| SHEIKH F. ET AL., J. IMMUNOL., vol. 172, 2004, pages 2006 - 2010 |
| SHEPARD ET AL., CLIN. IMMUNOL., vol. 11, no. 3, 1991, pages 117 - 127 |
| SHIRAISHI YICHIKAWA R: "Absorption and retention of 144 Ce and 95 Zr- 95 Nb in newborn, juvenile and adult rats", HEALTH PHYS., vol. 22, 1972, pages 373 - 8 |
| SHIVELY ET AL., J NUCL MED, vol. 48, 2007, pages 170 - 2 |
| SHIVELY JE.: "18F labeling for immuno-PET: where speed and contrast meet", J NUCL MED., vol. 48, 2007, pages 170 - 2 |
| SINGH ET AL., ANAL. BIOCHEM., vol. 304, 2002, pages 147 - 15 |
| SINGH ET AL., ANAL. BIOCHEM., vol. 304, 2002, pages 147 - 156 |
| SINGLETON ET AL.: "Dictionary of Microbiology and Molecular Biology. 2nd Ed.", 1994, J. WILEY & SONS |
| SINHA S.K. ET AL., J. IMMUNOL., vol. 150, 1993, pages 5311 - 5320 |
| SKERRA ET AL., CURR. OPINION IN IMMUNOL., vol. 5, 1993, pages 256 - 262 |
| SLIWKOWSKI ET AL., J. BIOL. CHEM., vol. 269, no. 20, 1994, pages 14661 - 14665 |
| STRAUSBERG ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI USA, vol. 99, 2002, pages 16899 - 16903 |
| STRAUSBERG R.L. ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 99, 2002, pages 16899 - 16903 |
| SUN ET AL., BIOORGANIC & MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY LETTERS, vol. 12, 2002, pages 2213 - 2215 |
| SUN ET AL., BIOORGANIC & MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY, vol. 11, 2003, pages 1761 - 1768 |
| SUNDARESAN G ET AL.: "124I-labeled engineered anti-CEA minibodies and diabodies allow high-contrast, antigen-specific small-animal PET imaging ofxenografts in athymic mice", J NUCL MED, vol. 44, 2003, pages 1962 - 9 |
| SVENSSON P.J. ET AL., HUM. GENET., vol. 103, 1998, pages 145 - 148 |
| SWARTZMAN: "A homogeneous and multiplexed immunoassay for high-throughput screening using fluorometric microvolume assay technology", ANAL. BIOCHEM., vol. 271, 1999, pages 143 - 51, XP055271863, DOI: doi:10.1006/abio.1999.4128 |
| SWIERCZ J.M. ET AL., J. CELL BIOL., vol. 165, 2004, pages 869 - 880 |
| SZALAI ET AL., J. AMER. CHEM. SOC., vol. 125, 2003, pages 15688 - 15689 |
| TAIT JF ET AL.: "Improved detection of cell death in vivo with anncxin V radiolabclcd by site-specific methods", J NUCL MED., vol. 47, 2006, pages 1546 - 53 |
| TAKCDA, S., FEBS LCTT., vol. 520, no. 1-3, 2002, pages 97 - 101 |
| TAWARAGI Y. ET AL., BIOCHEM. BIOPHYS. RES. COMMUN., vol. 150, 1988, pages 89 - 96 |
| THOMPSON, J.S. ET AL., SCIENCE, vol. 293, no. 5537, 2001, pages 2108 - 2111 |
| TINIANOW JEFF N ET AL: "Site-specifically 89Zr-labeled monoclonal antibodies for ImmunoPET.", NUCLEAR MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY APR 2010 LNKD- PUBMED:20346868, vol. 37, no. 3, April 2010 (2010-04-01), pages 289 - 297, XP002615665, ISSN: 1872-9614 * |
| TOKI ET AL., J. ORG. CHEM., vol. 67, 2002, pages 1866 - 1872 |
| TONNELLE ET AL., EMBO J., vol. 4, no. 11, 1985, pages 2839 - 2847 |
| TOUCHMAN ET AL., GENOME RES., vol. 10, 2000, pages 165 - 173 |
| TREANOR, J.J. ET AL., NATURE, vol. 382, no. 6586, 1996, pages 80 - 83 |
| TSUKAMOTO,H. ET AL., CANCER SCI., vol. 100, no. 10, 2009, pages 1895 - 1901 |
| TSUTSUMI M. ET AL., GENE, vol. 228, 1999, pages 43 - 49 |
| TU ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI USA, vol. 96, 1999, pages 4862 - 4867 |
| UCHIDA ET AL., BIOCHEM. BIOPHYS. RES. COMMUN., vol. 266, 1999, pages 593 - 602 |
| VALLETTE ET AL., NUC. ACIDS RES., vol. 17, 1989, pages 723 - 733 |
| VAN DONGEN ET AL., ONCOLOGIST, vol. 12, 2007, pages 1379 - 89 |
| VAN DONGEN GA ET AL.: "Immuno- PET: a navigator in monoclonal antibody development and applications", ONCOLOGIST, vol. 12, 2007, pages 1379 - 89, XP002492359, DOI: doi:10.1634/theoncologist.12-12-1379 |
| VAN DONGEN GA ET AL.: "Immuno-PET: a navigator in monoclonal antibody development and applications", ONCOLOGIST, vol. 12, 2007, pages 1379 - 89, XP002492359, DOI: doi:10.1634/theoncologist.12-12-1379 |
| VCRCL, J. NUCL. MCD., vol. 44, 2003, pages 1663 - 1670 |
| VCRHCIJ J.B., AM. J. MED. GENET., vol. 108, 2002, pages 223 - 225 |
| VEREL ET AL., J. NUCL. MED., vol. 44, 2003, pages 1663 - 1670 |
| VEREL I ET AL.: "89Zr immuno- PET: comprehensive procedures for the production of 89Zr-labeled monoclonal antibodies", J NUCL MED., vol. 44, 2003, pages 1271 - 81 |
| VEREL I ET AL.: "89Zr Immuno-PET: Comprehensive Procedures For The Production Of 89Zr-Labeled Monoclonal Antibodies", J NUCL MED, vol. 44, 2003, pages 1271 - 81 |
| VEREL I ET AL.: "89Zr immuno-PET: comprehensive procedures for the production of 89Zr-labeled monoclonal antibodies", J NUCL MED., vol. 44, 2003, pages 1271 - 81 |
| VEREL I ET AL.: "High-quality 124I-labelled monoclonal antibodies for use as PET scouting agents prior to 131I-radioimmunotherapy", EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE AND MOLECULAR IMAGING, vol. 31, 2004, pages 1645 - 52 |
| VEREL I ET AL.: "Long-lived positron emitters zirconium-89 and iodine-124 for scouting of therapeutic radioimmunoconjugates with PET", CANCER BIOTHER RADIOPHARM., vol. 18, 2003, pages 655 - 61 |
| VEREL I ET AL.: "The promise of immuno-PET in radioimmunothcrapy", J NUCL MED, vol. 46, no. 1, 2005, pages 164S - 71S, XP008103691 |
| VEREL IRIS ET AL: "89Zr immuno-PET: comprehensive procedures for the production of 89Zr-labeled monoclonal antibodies.", JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE : OFFICIAL PUBLICATION, SOCIETY OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE AUG 2003 LNKD- PUBMED:12902418, vol. 44, no. 8, August 2003 (2003-08-01), pages 1271 - 1281, XP002615666, ISSN: 0161-5505 * |
| VERMES: "A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V", J. IMMUNOL. METHODS, vol. 184, 1995, pages 39 - 51, XP004021001, DOI: doi:10.1016/0022-1759(95)00072-I |
| VITETTA ET AL., CANCER RESEARCH, vol. 54, 1994, pages 5301 - 5309 |
| VON HOEGEN ET AL., J. IMMUNOL., vol. 144, no. 12, 1990, pages 4870 - 4877 |
| WALKER, M.A., J. ORG. CHEM., vol. 60, 1995, pages 5352 - 5355 |
| WANG L ET AL.: "Structural characterization of the maytansinoid-monoclonal antibody immunoconjugate, huN901-DM1, by mass spectrometry", PROTEIN SCI., vol. 14, 2005, pages 2436 - 46, XP008081802, DOI: doi:10.1110/ps.051478705 |
| WCIS J.J., J. EXP. MED., vol. 167, 1988, pages 1047 - 1066 |
| WEIS J.J. ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 83, 1986, pages 5639 - 5643 |
| WELLS ET AL., GENE, vol. 34, 1985, pages 315 - 323 |
| WELLSLOWMAN, CURR. OPIN. STRUCT. BIOL., vol. 3, 1992, pages 355 - 362 |
| WERTHER ET AL., J. IMMUNOL. METHODS, vol. 157, 1996, pages 4986 - 4995 |
| WILLIAMS, CANCER BIOTHER RADIOPHARM, vol. 16, 2001, pages 25 - 35 |
| WILSON ET AL., J. EXP. MED., vol. 173, 1991, pages 137 - 146 |
| WONG: "Chemistry of Protein Conjugation and Cross-linking", 1991, CRC PRESS |
| WU ET AL., NATURE BIOTECHNOLOGY, vol. 23, no. 9, 2005, pages 1137 - 1146 |
| XU, M.J. ET AL., BIOCHEM. BIOPHYS. RES. COMMUN., vol. 280, no. 3, 2001, pages 768 - 775 |
| XU, X.Z. ET AL., PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. U.S.A., vol. 98, no. 19, 2001, pages 10692 - 10697 |
| YAMAGUCHI, N. ET AL., BIOL. CHEM., vol. 269, no. 2, 1994, pages 805 - 808 |
| YAMAMOTO ET AL., NATURE, vol. 319, 1986, pages 230 - 234 |
| YAMAMOTO T. ET AL., NATURE, vol. 319, 1986, pages 230 - 234 |
| YAMAMOTO,Y. ET AL., HEPATOLOGY, vol. 37, no. 3, 2003, pages 528 - 533 |
| YU ET AL., J. IMMUNOL., vol. 148, no. 2, 1992, pages 633 - 637 |
| ZAMMIT,D.J. ET AL., MOL. CELL. BIOL., vol. 22, no. 3, 2002, pages 946 - 952 |
| ZHANG ET AL., ANAL. BIOCHEM., vol. 311, 2002, pages 1 - 9 |
| ZHENG: "Caspase-3 controls both cytoplasmic and nuclear events associated with Fas-mediated apoptosis in vivo", PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. USA, vol. 95, 1998, pages 618 - 23 |
| ZOLA: "Monoclonal Antibodies: A Manual of Techniques", 1987, CRC PRESS, INC., pages: 147 - 158 |
| ZOLLER ET AL., METHODS ENZYMOL., vol. 100, 1983, pages 468 - 500 |
| ZOLLER, M.J.SMITH, M., NUCL. ACIDS RES., vol. 10, 1982, pages 6487 - 6500 |
Cited By (172)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8951737B2 (en) | 1996-05-06 | 2015-02-10 | Cornell Research Foundation, Inc. | Treatment and diagnosis of cancer |
| US8940871B2 (en) | 2006-03-20 | 2015-01-27 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Engineered anti-prostate stem cell antigen (PSCA) antibodies for cancer targeting |
| US10981987B2 (en) | 2007-07-16 | 2021-04-20 | Genentech, Inc. | Humanized anti-CD79b antibodies and immunoconjugates and methods of use |
| US10494432B2 (en) | 2007-07-16 | 2019-12-03 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-CD79B antibodies and immunoconjugates and methods of use |
| USRE48558E1 (en) | 2007-07-16 | 2021-05-18 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-CD79B antibodies and immunoconjugates and methods of use |
| US11866496B2 (en) | 2007-07-16 | 2024-01-09 | Genentech, Inc. | Humanized anti-CD79B antibodies and immunoconjugates and methods of use |
| US9527919B2 (en) | 2007-09-04 | 2016-12-27 | The Regents Of The University Of California | High affinity anti-prostate stem cell antigen (PSCA) antibodies for cancer targeting and detection |
| US8940298B2 (en) | 2007-09-04 | 2015-01-27 | The Regents Of The University Of California | High affinity anti-prostate stem cell antigen (PSCA) antibodies for cancer targeting and detection |
| US10544218B2 (en) | 2008-01-31 | 2020-01-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-CD79B antibodies and immunoconjugates and methods of use |
| US9896506B2 (en) | 2008-01-31 | 2018-02-20 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-CD79B antibodies and immunoconjugates and methods of use |
| US10517969B2 (en) | 2009-02-17 | 2019-12-31 | Cornell University | Methods and kits for diagnosis of cancer and prediction of therapeutic value |
| US11180570B2 (en) | 2009-12-02 | 2021-11-23 | Imaginab, Inc. | J591 minibodies and cys-diabodies for targeting human prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and methods for their use |
| US8772459B2 (en) | 2009-12-02 | 2014-07-08 | Imaginab, Inc. | J591 minibodies and Cys-diabodies for targeting human prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and methods for their use |
| US9815905B2 (en) | 2010-02-23 | 2017-11-14 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| US8877897B2 (en) | 2010-02-23 | 2014-11-04 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| US11873330B2 (en) | 2010-06-08 | 2024-01-16 | Genentech, Inc. | Cysteine engineered antibodies and conjugates |
| US10604557B2 (en) | 2010-06-08 | 2020-03-31 | Genentech, Inc. | Cysteine engineered antibodies and conjugates |
| US8911732B2 (en) | 2010-12-20 | 2014-12-16 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-mesothelin antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US10022452B2 (en) | 2010-12-20 | 2018-07-17 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-mesothelin antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US9719996B2 (en) | 2010-12-20 | 2017-08-01 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-mesothelin antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US9175089B2 (en) | 2012-03-30 | 2015-11-03 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-LGR5 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| WO2013149159A1 (en) | 2012-03-30 | 2013-10-03 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-lgr5 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US9597411B2 (en) | 2012-05-01 | 2017-03-21 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-PMEL17 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| WO2013165940A1 (en) | 2012-05-01 | 2013-11-07 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-pmel17 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US10196454B2 (en) | 2012-05-01 | 2019-02-05 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-PMEL17 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US9056910B2 (en) | 2012-05-01 | 2015-06-16 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-PMEL17 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US10653792B2 (en) | 2012-05-21 | 2020-05-19 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-Ly6E antibodies and immunoconjugates and methods of use |
| US9724427B2 (en) | 2012-05-21 | 2017-08-08 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-Ly6E antibodies and immunoconjugates and methods of use |
| JP2017169572A (en) * | 2012-05-21 | 2017-09-28 | ジェネンテック, インコーポレイテッド | ANTI-Ly6E ANTIBODIES AND IMMUNOCONJUGATES AND METHODS OF USE |
| JP2015528692A (en) * | 2012-05-21 | 2015-10-01 | ジェネンテック, インコーポレイテッド | Anti-Ly6E antibody, immunoconjugate and method of use |
| US9463251B2 (en) | 2012-08-02 | 2016-10-11 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-ETBR antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US9464141B2 (en) | 2012-08-02 | 2016-10-11 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-ETBR antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| JP2015529656A (en) * | 2012-08-02 | 2015-10-08 | ジェネンテック, インコーポレイテッド | Anti-ETBR antibodies and immune complexes |
| JP2015528818A (en) * | 2012-08-02 | 2015-10-01 | ジェネンテック, インコーポレイテッド | Anti-ETBR antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US11596695B2 (en) | 2013-02-08 | 2023-03-07 | Novartis Ag | Specific sites for modifying antibodies to make immunoconjugates |
| US10137212B2 (en) * | 2013-03-13 | 2018-11-27 | The United States Of America, As Represented By The Secretary, Department Of Health And Human Services | Tetrahydroxamate chelators of zirconium89 and niobium90 for use in diagnostic applications |
| US10150813B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2018-12-11 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-B7-H4 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| WO2014159835A1 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2014-10-02 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-b7-h4 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US9562099B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2017-02-07 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-B7-H4 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| EP3299391A1 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2018-03-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-b7-h4 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US11230600B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2022-01-25 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-B7-H4 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US10246515B2 (en) | 2013-09-17 | 2019-04-02 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of treating hedgehog-related diseases with an anti-LGR5 antibody |
| WO2015042108A1 (en) | 2013-09-17 | 2015-03-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-lgr5 antibodies |
| US9290578B2 (en) | 2013-10-21 | 2016-03-22 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-Ly6E antibodies and methods of use |
| US10889651B2 (en) | 2013-10-21 | 2021-01-12 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-Ly6E antibodies and methods of use |
| US10066022B2 (en) | 2013-10-21 | 2018-09-04 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-Ly6E antibodies and methods of use |
| WO2015089344A1 (en) | 2013-12-13 | 2015-06-18 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-cd33 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| EP3461845A1 (en) | 2013-12-13 | 2019-04-03 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-cd33 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US10533058B2 (en) | 2013-12-16 | 2020-01-14 | Genentech Inc. | Peptidomimetic compounds and antibody-drug conjugates thereof |
| US11692043B2 (en) | 2013-12-16 | 2023-07-04 | Medimmune Limited | Peptidomimetic compounds and antibody-drug conjugates thereof |
| WO2015095227A2 (en) | 2013-12-16 | 2015-06-25 | Genentech, Inc. | Peptidomimetic compounds and antibody-drug conjugates thereof |
| WO2015112909A1 (en) | 2014-01-24 | 2015-07-30 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-steap1 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| WO2015179658A2 (en) | 2014-05-22 | 2015-11-26 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-gpc3 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| WO2015191715A1 (en) | 2014-06-11 | 2015-12-17 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-lgr5 antibodies and uses thereof |
| US11584927B2 (en) | 2014-08-28 | 2023-02-21 | Bioatla, Inc. | Conditionally active chimeric antigen receptors for modified T-cells |
| US10556966B2 (en) | 2014-09-12 | 2020-02-11 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-HER2 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US10059768B2 (en) | 2014-09-12 | 2018-08-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-B7-H4 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US10179820B2 (en) | 2014-09-12 | 2019-01-15 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-HER2 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| EP3782654A1 (en) | 2014-09-12 | 2021-02-24 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-her2 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US10077318B2 (en) | 2014-09-12 | 2018-09-18 | Genentech, Inc. | Cysteine engineered antibodies and conjugates |
| EP3693391A1 (en) | 2014-09-12 | 2020-08-12 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-cll-1 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US11286302B2 (en) | 2014-09-12 | 2022-03-29 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-B7-H4 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| WO2016040868A1 (en) | 2014-09-12 | 2016-03-17 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-cll-1 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| US11000510B2 (en) | 2014-09-23 | 2021-05-11 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-CD79b immunoconjugates |
| EP3689910A2 (en) | 2014-09-23 | 2020-08-05 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG | Method of using anti-cd79b immunoconjugates |
| US12016842B2 (en) | 2014-09-23 | 2024-06-25 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-CD79b immunoconjugates |
| EP3207027A4 (en) * | 2014-10-16 | 2018-04-18 | The University of Melbourne | Novel imaging composition and uses thereof |
| EP3543226A1 (en) * | 2014-10-16 | 2019-09-25 | The University of Melbourne | Novel imaging composition and uses thereof |
| US10011658B2 (en) | 2015-04-03 | 2018-07-03 | Eureka Therapeutics, Inc. | Constructs targeting AFP peptide/MHC complexes and uses thereof |
| US11254744B2 (en) | 2015-08-07 | 2022-02-22 | Imaginab, Inc. | Antigen binding constructs to target molecules |
| US10632196B2 (en) | 2015-10-02 | 2020-04-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Pyrrolobenzodiazepine antibody drug conjugates and methods of use |
| US10639373B2 (en) | 2015-10-02 | 2020-05-05 | Genentech, Inc. | Pyrrolobenzodiazepine antibody drug conjugates and methods of use |
| US10058613B2 (en) | 2015-10-02 | 2018-08-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Pyrrolobenzodiazepine antibody drug conjugates and methods of use |
| US11078282B2 (en) | 2016-04-15 | 2021-08-03 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CD80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2017181152A2 (en) | 2016-04-15 | 2017-10-19 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Cd80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11479609B2 (en) | 2016-04-15 | 2022-10-25 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CD80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2017181148A2 (en) | 2016-04-15 | 2017-10-19 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Icos ligand variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11149088B2 (en) | 2016-04-15 | 2021-10-19 | Bioatla, Inc. | Anti-Axl antibodies, antibody fragments and their immunoconjugates and uses thereof |
| US11359022B2 (en) | 2016-04-15 | 2022-06-14 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CD80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11498967B2 (en) | 2016-04-15 | 2022-11-15 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CD80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US12110339B2 (en) | 2016-04-15 | 2024-10-08 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | ICOS ligand variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11897959B2 (en) | 2016-04-15 | 2024-02-13 | Bioatla, Inc. | Anti-AXL antibodies, antibody fragments and their immunoconjugates and uses thereof |
| US10882914B2 (en) | 2016-04-15 | 2021-01-05 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | ICOS ligand variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| EP4122958A1 (en) | 2016-05-13 | 2023-01-25 | BioAtla, Inc. | Anti-ror2 antibodies, antibody fragments, their immunoconjugates and uses thereof |
| US11879011B2 (en) | 2016-05-13 | 2024-01-23 | Bioatla, Inc. | Anti-ROR2 antibodies, antibody fragments, their immunoconjucates and uses thereof |
| WO2017197234A1 (en) | 2016-05-13 | 2017-11-16 | Bioatla, Llc | Anti-ror2 antibodies, antibody fragments, their immunoconjugates and uses thereof |
| US11254742B2 (en) | 2016-05-13 | 2022-02-22 | Bioatla, Inc. | Anti-Ror2 antibodies, antibody fragments, their immunoconjugates and uses thereof |
| WO2017223405A1 (en) | 2016-06-24 | 2017-12-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-polyubiquitin multispecific antibodies |
| WO2018022946A1 (en) | 2016-07-28 | 2018-02-01 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Cd155 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11834490B2 (en) | 2016-07-28 | 2023-12-05 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CD112 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11471488B2 (en) | 2016-07-28 | 2022-10-18 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CD155 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2018022945A1 (en) | 2016-07-28 | 2018-02-01 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Cd112 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2018023100A2 (en) | 2016-07-29 | 2018-02-01 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-idiotypic antibodies and related methods |
| US11142578B2 (en) | 2016-11-16 | 2021-10-12 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Anti-MET antibodies, bispecific antigen binding molecules that bind MET, and methods of use thereof |
| US11679166B2 (en) | 2016-11-18 | 2023-06-20 | Astellas Pharma Inc. | Anti-human MUC1 antibody Fab fragment |
| WO2018091724A1 (en) | 2016-11-21 | 2018-05-24 | Cureab Gmbh | Anti-gp73 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| EP4015532A1 (en) | 2016-11-21 | 2022-06-22 | cureab GmbH | Anti-gp73 antibodies and immunoconjugates |
| WO2018102682A1 (en) | 2016-12-01 | 2018-06-07 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Radiolabeled anti-pd-l1 antibodies for immuno-pet imaging |
| US12053534B2 (en) | 2016-12-01 | 2024-08-06 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Radiolabeled anti-PD-L1 antibodies for immuno-PET imaging |
| US10736976B2 (en) | 2016-12-01 | 2020-08-11 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Radiolabeled anti-PD-L1 antibodies for immuno-PET imaging |
| EP4279136A2 (en) | 2016-12-03 | 2023-11-22 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for determining car-t cells dosing |
| WO2018102787A1 (en) | 2016-12-03 | 2018-06-07 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for determining car-t cells dosing |
| US11274157B2 (en) | 2017-01-12 | 2022-03-15 | Eureka Therapeutics, Inc. | Constructs targeting histone H3 peptide/MHC complexes and uses thereof |
| US11266745B2 (en) | 2017-02-08 | 2022-03-08 | Imaginab, Inc. | Extension sequences for diabodies |
| US10905784B2 (en) | 2017-02-10 | 2021-02-02 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Radiolabeled anti-LAG3 antibodies for immuno-PET imaging |
| WO2018148476A1 (en) | 2017-02-10 | 2018-08-16 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Radiolabeled anti-lag3 antibodies for immuno-pet imaging |
| US11511001B2 (en) | 2017-02-10 | 2022-11-29 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Radiolabeled anti-LAG3 antibodies for immuno-PET imaging |
| WO2018170026A2 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2018-09-20 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Cd80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| EP4306537A2 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2024-01-17 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Pd-l1 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11117948B2 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2021-09-14 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CD80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2018170021A1 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2018-09-20 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Pd-l1 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11117949B2 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2021-09-14 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CD80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11096988B2 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2021-08-24 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CD80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11117950B2 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2021-09-14 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CD80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11732022B2 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2023-08-22 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | PD-L2 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11230588B2 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2022-01-25 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CD80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2018170023A1 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2018-09-20 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Pd-l2 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11639375B2 (en) | 2017-03-16 | 2023-05-02 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CD80 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11447564B2 (en) | 2017-04-26 | 2022-09-20 | Eureka Therapeutics, Inc. | Constructs specifically recognizing glypican 3 and uses thereof |
| US11740231B2 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2023-08-29 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Articles of manufacture and methods related to toxicity associated with cell therapy |
| WO2018223098A1 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2018-12-06 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Articles of manufacture and methods related to toxicity associated with cell therapy |
| US11667724B2 (en) | 2017-07-07 | 2023-06-06 | Astellas Pharma Inc. | Anti-human CEACAM5 antibody Fab fragment |
| US10730944B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2020-08-04 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Anti-CD8 antibodies and uses thereof |
| US12077587B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2024-09-03 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Anti-CD8 antibodies and uses thereof |
| WO2019023148A1 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2019-01-31 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Anti-cd8 antibodies and uses thereof |
| US11525001B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2022-12-13 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Anti-CD8 antibodies and uses thereof |
| EP4442268A2 (en) | 2017-10-10 | 2024-10-09 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Ctla-4 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11753458B2 (en) | 2017-10-10 | 2023-09-12 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | CTLA-4 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| EP4219540A2 (en) | 2017-10-10 | 2023-08-02 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Ctla-4 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2019074983A1 (en) | 2017-10-10 | 2019-04-18 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Ctla-4 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2019079520A2 (en) | 2017-10-18 | 2019-04-25 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Variant icos ligand immunomodulatory proteins and related compositions and methods |
| US11613566B2 (en) | 2017-10-18 | 2023-03-28 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Variant ICOS ligand immunomodulatory proteins and related compositions and methods |
| US11564946B2 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2023-01-31 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods associated with tumor burden for assessing response to a cell therapy |
| US12031975B2 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2024-07-09 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods of assessing or monitoring a response to a cell therapy |
| WO2019089858A2 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2019-05-09 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods of assessing or monitoring a response to a cell therapy |
| WO2019089848A1 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2019-05-09 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods associated with tumor burden for assessing response to a cell therapy |
| WO2019109053A1 (en) | 2017-12-01 | 2019-06-06 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for dosing and for modulation of genetically engineered cells |
| US12065476B2 (en) | 2018-06-15 | 2024-08-20 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | PD-1 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2019241758A1 (en) | 2018-06-15 | 2019-12-19 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Pd-1 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| US11993661B2 (en) | 2018-06-18 | 2024-05-28 | Eureka Therapeutics, Inc. | Constructs targeting prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and uses thereof |
| US12065503B2 (en) | 2018-10-10 | 2024-08-20 | Astellas Pharma Inc. | Pharmaceutical composition containing tagged site-antihuman antibody fab fragment complex |
| US11945869B2 (en) | 2018-10-11 | 2024-04-02 | Inhibrx, Inc. | PD-1 single domain antibodies and therapeutic compositions thereof |
| WO2020076977A2 (en) | 2018-10-11 | 2020-04-16 | Inhibrx, Inc. | Dll3 single domain antibodies and therapeutic compositions thereof |
| WO2020077257A1 (en) | 2018-10-11 | 2020-04-16 | Inhibrx, Inc. | Pd-1 single domain antibodies and therapeutic compositions thereof |
| US11208485B2 (en) | 2018-10-11 | 2021-12-28 | Inhibrx, Inc. | PD-1 single domain antibodies and therapeutic compositions thereof |
| WO2020076992A1 (en) | 2018-10-11 | 2020-04-16 | Inhibrx, Inc. | 5t4 single domain antibodies and therapeutic compositions thereof |
| WO2020076970A1 (en) | 2018-10-11 | 2020-04-16 | Inhibrx, Inc. | B7h3 single domain antibodies and therapeutic compositions thereof |
| WO2020113141A2 (en) | 2018-11-30 | 2020-06-04 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Cd86 variant immunomodulatory proteins and uses thereof |
| EP4427810A2 (en) | 2018-11-30 | 2024-09-11 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for treatment using adoptive cell therapy |
| WO2020113194A2 (en) | 2018-11-30 | 2020-06-04 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for treatment using adoptive cell therapy |
| WO2020117257A1 (en) | 2018-12-06 | 2020-06-11 | Genentech, Inc. | Combination therapy of diffuse large b-cell lymphoma comprising an anti-cd79b immunoconjugates, an alkylating agent and an anti-cd20 antibody |
| WO2020205623A1 (en) | 2019-03-29 | 2020-10-08 | Rakuten Medical, Inc. | Methods for photoimmunotherapy and related biomarkers |
| WO2020232169A1 (en) | 2019-05-14 | 2020-11-19 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-cd79b immunoconjugates to treat follicular lymphoma |
| WO2020257681A1 (en) | 2019-06-21 | 2020-12-24 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Use of bispecific antigen-binding molecules that bind psma and cd3 in combination with 4-1bb co-stimulation |
| WO2020257604A1 (en) | 2019-06-21 | 2020-12-24 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Use of bispecific antigen-binding molecules that bind muc16 and cd3 in combination with 4-1bb co-stimulation |
| US12091460B2 (en) | 2019-06-21 | 2024-09-17 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Use of bispecific antigen-binding molecules that bind MUC16 and CD3 in combination with 4-1BB co-stimulation |
| US11896682B2 (en) | 2019-09-16 | 2024-02-13 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Radiolabeled MET binding proteins for immuno-PET imaging and methods of use thereof |
| WO2021055350A1 (en) | 2019-09-16 | 2021-03-25 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Radiolabeled met binding proteins for immuno-pet imaging |
| WO2021076196A1 (en) | 2019-10-18 | 2021-04-22 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-cd79b immunoconjugates to treat diffuse large b-cell lymphoma |
| WO2021113776A1 (en) | 2019-12-06 | 2021-06-10 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-idiotypic antibodies to bcma-targeted binding domains and related compositions and methods |
| WO2021113780A1 (en) | 2019-12-06 | 2021-06-10 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-idiotypic antibodies to gprc5d-targeted binding domains and related compositions and methods |
| WO2021155071A1 (en) | 2020-01-29 | 2021-08-05 | Inhibrx, Inc. | Cd28 single domain antibodies and multivalent and multispecific constructs thereof |
| WO2021217051A1 (en) | 2020-04-24 | 2021-10-28 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-cd79b immunoconjugates |
| WO2022029660A1 (en) | 2020-08-05 | 2022-02-10 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-idiotypic antibodies to ror1-targeted binding domains and related compositions and methods |
| WO2022147463A2 (en) | 2020-12-31 | 2022-07-07 | Alamar Biosciences, Inc. | Binder molecules with high affinity and/ or specificity and methods of making and use thereof |
| WO2022241446A1 (en) | 2021-05-12 | 2022-11-17 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-cd79b immunoconjugates to treat diffuse large b-cell lymphoma |
| WO2023019092A1 (en) | 2021-08-07 | 2023-02-16 | Genentech, Inc. | Methods of using anti-cd79b immunoconjugates to treat diffuse large b-cell lymphoma |
| WO2023034750A1 (en) | 2021-08-30 | 2023-03-09 | Genentech, Inc. | Anti-polyubiquitin multispecific antibodies |
| WO2023172883A1 (en) | 2022-03-07 | 2023-09-14 | Alpine Immune Sciences, Inc. | Immunomodulatory proteins of variant cd80 polypeptides, cell therapies thereof and related methods and uses |
| WO2024151515A2 (en) | 2023-01-09 | 2024-07-18 | Odyssey Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-tnfr2 antigen-binding proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2024173876A1 (en) | 2023-02-17 | 2024-08-22 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Radiolabeled anti-lag3 antibodies for immuno-pet imaging |
| WO2024192065A1 (en) | 2023-03-14 | 2024-09-19 | Odyssey Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-cd25 antigen-binding proteins and uses thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| RU2562862C2 (en) | 2015-09-10 |
| JP2013510093A (en) | 2013-03-21 |
| CA2780216A1 (en) | 2011-05-12 |
| EP2496270A1 (en) | 2012-09-12 |
| CN102596260B (en) | 2017-04-05 |
| KR20120102625A (en) | 2012-09-18 |
| CN102596260A (en) | 2012-07-18 |
| BR112012007774A2 (en) | 2016-11-22 |
| US20100111856A1 (en) | 2010-05-06 |
| KR20170136652A (en) | 2017-12-11 |
| US20150017094A1 (en) | 2015-01-15 |
| MX2012005211A (en) | 2012-06-13 |
| EP2496270B1 (en) | 2018-01-31 |
| MX340674B (en) | 2016-07-20 |
| JP5850843B2 (en) | 2016-02-03 |
| RU2012123007A (en) | 2013-12-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2496270B1 (en) | Zirconium-radiolabeled, cysteine engineered antibody conjugates | |
| US11873330B2 (en) | Cysteine engineered antibodies and conjugates | |
| AU2005286607B2 (en) | Cysteine engineered antibodies and conjugates | |
| MX2007003404A (en) | Cysteine engineered antibodies and conjugates |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201080050134.4 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 10776064 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2010776064 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2012537224 Country of ref document: JP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 3939/CHENP/2012 Country of ref document: IN Ref document number: MX/A/2012/005211 Country of ref document: MX |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2780216 Country of ref document: CA Ref document number: 20127011607 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2012123007 Country of ref document: RU |
|
| REG | Reference to national code |
Ref country code: BR Ref legal event code: B01A Ref document number: 112012007774 Country of ref document: BR |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 112012007774 Country of ref document: BR Kind code of ref document: A2 Effective date: 20120404 |