US3579679A - Tensionless liquid treating apparatus and method - Google Patents
Tensionless liquid treating apparatus and method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US3579679A US3579679A US782587A US3579679DA US3579679A US 3579679 A US3579679 A US 3579679A US 782587 A US782587 A US 782587A US 3579679D A US3579679D A US 3579679DA US 3579679 A US3579679 A US 3579679A
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- web material
- fluid
- fabric
- supporting surface
- treatment
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06B—TREATING TEXTILE MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS, GASES OR VAPOURS
- D06B3/00—Passing of textile materials through liquids, gases or vapours to effect treatment, e.g. washing, dyeing, bleaching, sizing, impregnating
- D06B3/10—Passing of textile materials through liquids, gases or vapours to effect treatment, e.g. washing, dyeing, bleaching, sizing, impregnating of fabrics
- D06B3/16—Passing of textile materials through liquids, gases or vapours to effect treatment, e.g. washing, dyeing, bleaching, sizing, impregnating of fabrics in superimposed, i.e. stack-packed, form
Definitions
- a further object of the present invention is to provide a method of and apparatus for fluid treating a textile fabric wherein the fabric is passed through a fluid treating zone by a foraminous supporting surface in a substantially undulating path of travel while both faces of the fabric are being sprayed with fluid and wherein the fabric is maintained in a substantially tensionless state and with any given portion thereof only intermittently engaging the supporting surface whereby shrinkage of the fabric is not retarded and no appreciable tensional forces are ap plied thereto during the fluid treatment.
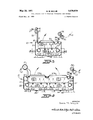
- FIG. 1 is a side elevation view of a first form of apparatus in accordance with the present invention
- FIG. 2 is a view similar to FIG. 1, of a second form of apparatus in accordance with the present invention.
- FIG. 3 is a sectional view through the apparatus of FIG. 1, taken similarly to FIG. 1;
- FIG. 4 is a view of the apparatus of FIG. 2 taken similarly to FIG. 3;
- FIG. 5 is a plan view, partly broken away and in section, of the first form of apparatus in accordance with the present invention, taken generally as indicated by the line 55 in FIG. 3;
- FIG. 6 is a schematic elevation view, in section, through the apparatus of FIG. 5, taken generally as indicated by the line 6-6 in that figure;
- FIG. 7 is an enlarged detail of a spray nozzle as incorporated in the apparatus of FIGS. 5 and 6.
- FIGS. 1, 3 and 5 through 7 a first form of apparatu in accordance with the present invention has been shown in FIGS. 1, 3 and 5 through 7, while a second form of apparatus in accordance with the present invention is shown in FIGS. 2 and 4.
- the following discussion will proceed first with reference to the apparatus of FIGS. 1, 3 and 5 through 7, with the distinctions of the apparatus 20 of FIGS. 2 and 4 being pointed out thereafter.
- the first form of apparatus, generally indicated at 10, for fluid treating a running length of flexible web material in a substantially tension-free condition comprises a housing 11, including a pivotally mounted door member 12 closing the upper side of the housing 11 and providing for access into the interior of the housing when desired.
- the housing 11 encloses a fluid treatment zone, as pointed out more fully hereinafter, through which flexible web material such as textile fabric F (FIGS. 1 and 3) is advanced and in which the textile fabric is subjected to fluid treatment.
- slot openings 14 and 15 are provided therein to serve respectively as an entrance and an exit for the material F.
- Web material handling means are provided to advance web material such as the material F to and into the apparatus 10, and include a pair of overfeeding rollers 17 and 18 supported by standards 19 and 20 rising at the entrance side of the casing 11.
- the overfeeding rollers 17 and 18 are driven in rotation at a speed and in a manner discussed more fully hereinafter, to pass web material therebetween and downwardly through the entrance slot 14 into the interior of the casing 11.
- Textile material F passing into the interior of the casing 11 is received and transported through the fluid treatment zone contained within the casing 11 by web material transporting means including a driven, horizontally movable, foraminous supporting surface preferably defined by at least one endless belt member 21 (FIGS. 3 and 5).
- the endless belt member 21 is supported for movement along a predetermined closed path of travel by a pair of rollers 22 and 23 mounted within the casing 11 for rotation about parallel, spaced apart, horizontally extending axes. Inasmuch as the endless belt member 21 passes about both of the rollers 22 and 23, the belt member 21 is guided thereby for movement in a horizontal direction through a fluid treatment zone as pointed out more fully hereinafter.
- the material from which the belt 21 is formed is both flexible and foraminous or perforate, as by being a woven Wire screening or the like.
- the belt member 21 is supported in its travel by a plurality of secondary supporting rollers 25,
- the belt 21 is driven at a predetermined rate less than and correlated to the linear surface speed of the overfeeding rollers 17 and 18, so as to receive the material F in a loose, substantially tension-free state.
- treating means including a plurality of fluid spray nozzles 30, mounted upon spray header pipes 31 and supplied therethrough with fluid under pressure.
- the spray patterns of the nozzles 30 are directed by slot formed orifices 32 therein (FIG. 7), releasing fluid in a fan-shaped spray.
- Each of the nozzles 30 is mounted in an associated header pipe 31 for rotational adjustment relative thereto (as indicated by the double-headed arrows on the nozzle 30 in FIG. 7) thus permitting adjustment of the fan angle of fluid directed by the Orifice 32 relative to the header pipe 31, or aiming of each nozzle relative to others in each group.
- each of the header pipes 31 is supported in the casing 11 of the apparatus for at least limited rotation (as indicated by the double-headed arrow on the pipe 31 in FIG. 7) thereby permitting collective aiming of the spray patterns of each group of nozzles 30 relative to the sprays of the other groups.
- the header pipes and nozzles are divided into first and second banks, positioned on opposite sides of the foraminous supporting surface defined by the upper horizontal reach of the path of travel of the belt 21.
- the first bank of spray nozzles 30 are positioned above the foraminous supporting surface defined by the belt 21, and are positioned to direct flowing streams of treatment fluid downwardly onto the upper face of the fabric F passing thereover.
- the second bank of spray nozzles 30 are mounted below the supporting surface defined by the belt 21 and positioned to direct flowing streams of fluid upwardly through the foraminous surface for impingement on the lower face of the fabric F moving thereover.
- the flowing streams of fluid impinged on the upper and lower faces of the web material F are so balanced that the material F is buoyed thereby and floats above the supporting surface 21 without the imposition of any appreciable tensional force thereon.
- the force of impingement of fluid against the lower face of the material is at least suflicient to balance the downward forces of gravity and of fluid impinging on the upper face, to prevent matting of the material against the supporting surface.
- the engagement between the moving supporting surface provided by the belt 21 and the web material is only that suflicient to transport the material F through the fluid treatment zone wherein the flowing streams of fluid impinge thereon.
- the engagement with the supporting surface is intermittent rather than continuous and, upon such intermittent engagement, the engagement is only transient in nature.
- treatment fluid is sprayed against the lower face of the material with suflicient force to move localized areas thereof out of engagement with the supporting surface and to cause the material to follow an undulating path of travel through the treatment zone.
- header pipes 31 are operatively connected to a pumping system for circulating a treatment fluid, such as a liquid.
- a treatment fluid such as a liquid.
- liquid sprayed against the material F through the nozzles 30 drains to the lower portion of the housing 11, and is pumped from the housing 11 through a drain conduit 38 by a drain pump 39.
- the drain pump 39 delivers liquid to a surge tank 40, provided in order to insure an adequate supply of treatment to a spray pump 41.
- the drain pump 39 and the spray pump 41 are powered in any appropriate manner, such as by independent electrical motors, and that additional appropriate accessory items may be interposed in the flow conduit 42 between the drain pump 39 and the surge tank 40 if desired.
- a filter may be interposed in the conduit 42 should it be considered appropriate to filter the treatment fluid before the same is impinged upon the material F.
- the spray pump 41 delivers treatment fluid under pressure to a main header pipe 44 (FIG. 6) from which liquid is distributed to the header pipes 31 for discharge through the nozzles 30.
- pressure control valves 45 and 46 may be interposed between the main fluid distribution header 44 and the header pipes 31 to provide control over the force with which fluid impinges upon the upper and lower faces of the material F.
- heating coils 48 will be mounted within the casing 11 below the level of treatment liquid retained therein as a reservoir.
- the heating coils may be formed in any appropriate manner, such as by being fabricated from suitable pipe, and are supplied with a heating media from an appropriate source.
- the heating media provided is steam from a suitable steam source such as a boiler.
- the material After passage of the web material through the fluid treatment zone defined by the opposed first and second banks of spray nozzles 30, the material is removed from the supporting surface defined by the belt 21 through the exit slot 15 by the provision of a set of lift-off rollers 34, 35, and 36.
- the lift-off rollers 34, 35 and 36 are supported by appropriate standard means rising adjacent the casing 11. Upon leaving the apparatus 10, the fabric may be advanced to any subsequent processing step.
- the engagement of any incremental length portion of the running length of material F with the supporting surface is intermittent rather than continuous and, upon such intermittent engagement, the engagement is only transient in nature.
- This important feature of the present invention is accomplished in part by overfeeding the web material onto the supporting surface provided by the foraminous belt 21 with a linear speed relation which is at least suflicient to accommodate any shrinkage occurring upon subjection of the web material to the fluid treatment.
- drive for the rotating elements of the apparatus 10 may be derived from a common motive power source, such as an electric motor 50 (FIG. 1). Rotational motive force originating with the motor 50 is transmitted to and applied to the various rotating elements through a drive train arrangement operatively connecting the rotating elements together.
- a common motive power source such as an electric motor 50 (FIG. 1). Rotational motive force originating with the motor 50 is transmitted to and applied to the various rotating elements through a drive train arrangement operatively connecting the rotating elements together.
- the drive train arrangement includes a plurality of endless flexible members 51, 52, 53 and 54 each supported for movement along a predetermined closed path of travel and each providing an operative interconnection between or among two or more sprocket members.
- a plurality of adjustable transmission means 56, 57 and 58 Interposed in the drive train thus provided by the endless flexible members or chains are a plurality of adjustable transmission means 56, 57 and 58.
- the linear speed ratios of the various rotating elements of the apparatus may be adjusted in any desired manner.
- the rate of overfeed of material F from the overfeeding rollers 17 and 18 onto the moving supporting surface provided by the foraminous belt 21 is at least suflicient to accommodate the highest shrinkage anticipated for the fabric being processed, and is obtained by driving the overfeeding rollers 17 and 18 at a higher linear surface speed than that at which the surface of the belt 21 is moving.
- an extended dwell time may be obtained through the use of a second form of the apparatus of the present invention, generally indicated at 20 and shown in FIGS. 2 and 4, wherein similar elements are identified by the addition of prime notation to reference characters heretofore used with reference to the apparatus 10.
- the principal distinction between the first form of apparatus 10 and the second form of apparatus 20 lies in the enclosure, within the housing 11' of the apparatus 20, of a pair of endless flexible foraminous belt members 21A and 21'B.
- first and second forms of the apparatus of the present invention it is anticipated that material being advanced from an apparatus of the first form, namely the apparatus 10, may then be supplied to an apparatus of the second form, namely an apparatus 20.
- a sequence of different fluid treatment processes may be successively applied to the same running length of material.
- the full sequence of fluid treatment processes involved in a finishing operation for textile fabrics may be accommodated by passage of a running length of fabric through a succession or range of the apparatus in accordance with the present invention.
- a method of treating a running length of textile web material in a substantially tension-free condition comprising the steps of overfeeding the textile web material in a substantially tensionless condition onto a horizontally moving, foraminous supporting surface,
- a method of treating a running length of textile fabric in a substantially tension-free condition comprising the steps of feeding the fabric at a first linear rate and in a substantially tensionless condition onto a foraminous supporting surface moving horizontally at a second linear rate independently determined to be less than said first linear rate so that the fabric is overfed onto the moving supporting surface, advancing the supported, overfed fabric through a liquid treatment zone while spraying treatment liquid against both the upper and lower faces of the fabric and while causing the fabric to follow an undulating path of travel through the treatment zone with any given portion of the fabric only intermittently engaging the supporting surface so that the fabric is subjected to liquid treatment without imposition of any appreciable tension force thereon and while in a substantially tension-free state,
- a method according to claim 3 wherein the fabric is overfed onto a first horizontally moving foraminous supporting surface and is sprayed with treatment liquid while being supported thereon, and including overfeeding the treated fabric from the first horizontally moving supporting surface onto a second horizontally moving foraminous supporting surface, advancing the supported, overfed fabric through a second liquid treatment zone while spraying treatment liquid against both the upper and lower faces of the fabric and While causing the fabric to follow an undulating path of travel through the second treatment zone with any given portion of the fabric only intermittently engaging the second supporting surface, and then removing the treated fabric from the second supporting surface.
- liquid sprayed onto the fabric in the second liquid treatment zones is of the same type as the liquid sprayed onto the fabric in the first liquid treatment zone.
- Apparatus for treating a running length of textile web material in a substantially tension-free condition comprising web material transporting means including a driven,
- web material handling means for advancing web material to said transporting means and for overfeeding the web material in a substantially tensionless condition onto said supporting surface for transport through the treatment zone
- common drive means operatively connected to both said web material transporting means and said web material handling means for driving the same at coordinated speeds and thereby governing the linear rate of overfeed of web material onto said supporting surface
- said drive means including at least one variable transmission device for independent variation of the linear rate of speed of one of said web material transporting means and said web material handling means for varying the ratio of linear rates of speed of said supporting surface and the web material
- web material treating means for impinging treatment liquid against both the upper and lower faces of the overfed web material passing through said zone, so that the web material is subjected to treatment Without imposition of any appreciable tensional force thereon and while in a substantially tension-free state.
- said feed material supporting means comprises first and second endless flexible members as supported for movement along a representative predetermined closed path of travel and defining a representative portion of said driven, horizontally movable, foraminous supporting surface, said first and second members respectively extending through first and second fluid treatment zones and said first member advancing web material to said second member and overfeeding advanced material thereonto, and further wherein said common drive means includes two variable transmission devices for independent variation of the linear rates of speed of said first and second members for varying the linear rates at which web material is advanced thereby.
- Apparatus according to claim 6 further comprising housing means for enclosing said fluid treatment zone and for collecting any excess treatment liquid following application thereof to web material and recirculating means operatively communicating with said housing means and said web material treating means for reimpinging collected treatment liquid against the Web material.
- said web material treating means includes first and second banks of liquid spray nozzles respectively mounted above said supporting surface for directing flowing streams of treatment liquid downwardly onto the upper face of web material passing through said fluid treatment zone and mounted below said supporting surface for directing flowing streams of treatment liquid upwardly therethrough onto the lower face of Web material passing through said fluid treatment zone.
- said web material treating means further includes header pipe means operatively connecting said banks of spray nozzles for supplying treatment liquid thereto and pump means operatively connected to said header pipe means for delivering thereto and to said banks of nozzles a flow of treatment liquid under pressure.
- each nozzle of said banks of nozzles directs a corresponding stream of treatment liquid in a shaped spray and further wherein said nozzles are mounted in groups for individual aiming of the shaped sprays of each nozzle relative to the sprays of other nozzles Within a common group and for collective aiming of the shaped sprays of each group of nozzles relative to the sprays of the other groups of nozzles.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US78258768A | 1968-12-10 | 1968-12-10 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US3579679A true US3579679A (en) | 1971-05-25 |
Family
ID=25126525
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US782587A Expired - Lifetime US3579679A (en) | 1968-12-10 | 1968-12-10 | Tensionless liquid treating apparatus and method |
Country Status (14)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US3579679A (es) |
| JP (1) | JPS4812111B1 (es) |
| AT (1) | AT304427B (es) |
| BE (1) | BE742825A (es) |
| CH (2) | CH528626A (es) |
| DE (2) | DE6947701U (es) |
| ES (1) | ES374554A1 (es) |
| FR (1) | FR2025788A1 (es) |
| GB (1) | GB1294471A (es) |
| IE (1) | IE33425B1 (es) |
| IL (1) | IL33472A (es) |
| LU (1) | LU59973A1 (es) |
| NL (1) | NL6918482A (es) |
| SE (1) | SE373892B (es) |
Cited By (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3640099A (en) * | 1969-12-02 | 1972-02-08 | Riggs & Lombard Inc | Apparatus for continuously scouring webs of knit material or the like |
| US3828587A (en) * | 1972-04-03 | 1974-08-13 | Riggs & Lombard Inc | Fabric treatment apparatus |
| US3886769A (en) * | 1973-02-26 | 1975-06-03 | Fulvio Conti | Width washing plant, particularly for delicate fabrics |
| US4005590A (en) * | 1975-04-15 | 1977-02-01 | C.D.B. Europ | Hank dyeing |
| US4047405A (en) * | 1976-10-13 | 1977-09-13 | Champagne-Dye Works | Apparatus for applying dye liquor to knit/deknit tubular rolls |
| US4124923A (en) * | 1976-09-03 | 1978-11-14 | Advanced Textiles Exploitation Ag | Apparatus for texturing yarn and textile fabric containing synthetic fibers |
| US4277860A (en) * | 1975-11-03 | 1981-07-14 | Sando Iron Works Co. Ltd. | Method of heat fulling and water washing of cloth |
| US4339856A (en) * | 1979-05-16 | 1982-07-20 | Sando Iron Works Co., Ltd. | Apparatus for continuous untwisting and crimping of a cloth |
| US4364248A (en) * | 1980-02-20 | 1982-12-21 | Sando Iron Works Co., Ltd. | Method and apparatus for wet-heat treating a knitted fabric |
| US4387476A (en) * | 1979-12-12 | 1983-06-14 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | Method and an apparatus for a washing process subsequent to the spinning of synthetic fibers |
| US4409709A (en) * | 1979-05-16 | 1983-10-18 | Sando Iron Works Co., Ltd. | Apparatus for continuous untwisting and crimping of a cloth |
| US4614096A (en) * | 1979-10-01 | 1986-09-30 | Arioli & C S.R.L. | System for the continuous and open-width washing of a fabric |
| EP0531868A1 (en) * | 1991-09-09 | 1993-03-17 | Gaston County Dyeing Machine Company | Apparatus for low liquid wet treatment of a textile material |
| US20060216427A1 (en) * | 2005-03-22 | 2006-09-28 | Conductive Inkjet Technology Limited | Treatment of flexible web material |
| WO2006100467A1 (en) | 2005-03-22 | 2006-09-28 | Conductive Inkjet Technology Limited | Treatment of flexible web material |
| CN113882093A (zh) * | 2021-08-23 | 2022-01-04 | 浙江常鑫纺织品有限公司 | 一种吸湿抗菌再生聚酯仿棉床品面料生产用蒸汽预缩装置 |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2285485A1 (fr) * | 1974-09-19 | 1976-04-16 | Artos Meier Windhorst Kg | Procede et dispositif pour le traitement, notamment pour le retrecissement de bandes textiles |
| DE2606873A1 (de) * | 1976-02-20 | 1977-09-01 | Osthoff Fa Walter | Flutungseinrichtung in jiggern, waschmaschinen o.dgl. zur nassbehandlung von textilbahnen |
| JPS597454B2 (ja) * | 1976-10-27 | 1984-02-18 | 木村寝台工業株式会社 | 患者用マツト |
| JPS5354889A (en) * | 1976-10-27 | 1978-05-18 | Kimura Shindai Kogyo Kk | Mat for patient |
| JPS596823Y2 (ja) * | 1976-12-03 | 1984-03-02 | 木村寝台工業株式会社 | 患者用マツト |
| JPS56162063U (es) * | 1980-05-02 | 1981-12-02 | ||
| DE3127052C2 (de) * | 1981-07-09 | 1983-09-29 | Küsters, Eduard, 4150 Krefeld | "Vorrichtung zur Verweilbehandlung von bahnförmigem Textilgut" |
-
1968
- 1968-12-10 US US782587A patent/US3579679A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1969
- 1969-12-02 IE IE1618/69A patent/IE33425B1/xx unknown
- 1969-12-02 IL IL33472A patent/IL33472A/en unknown
- 1969-12-05 ES ES374554A patent/ES374554A1/es not_active Expired
- 1969-12-08 SE SE6916909A patent/SE373892B/xx unknown
- 1969-12-08 BE BE742825D patent/BE742825A/xx unknown
- 1969-12-09 FR FR6942537A patent/FR2025788A1/fr not_active Withdrawn
- 1969-12-09 DE DE6947701U patent/DE6947701U/de not_active Expired
- 1969-12-09 JP JP44098986A patent/JPS4812111B1/ja active Pending
- 1969-12-09 NL NL6918482A patent/NL6918482A/xx not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1969-12-09 GB GB60125/69A patent/GB1294471A/en not_active Expired
- 1969-12-09 AT AT1144169A patent/AT304427B/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1969-12-09 LU LU59973D patent/LU59973A1/xx unknown
- 1969-12-09 DE DE19691961782 patent/DE1961782B2/de not_active Withdrawn
- 1969-12-10 CH CH1834969A patent/CH528626A/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1969-12-10 CH CH1834969D patent/CH1834969A4/xx unknown
Cited By (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3640099A (en) * | 1969-12-02 | 1972-02-08 | Riggs & Lombard Inc | Apparatus for continuously scouring webs of knit material or the like |
| US3828587A (en) * | 1972-04-03 | 1974-08-13 | Riggs & Lombard Inc | Fabric treatment apparatus |
| US3886769A (en) * | 1973-02-26 | 1975-06-03 | Fulvio Conti | Width washing plant, particularly for delicate fabrics |
| US4005590A (en) * | 1975-04-15 | 1977-02-01 | C.D.B. Europ | Hank dyeing |
| US4277860A (en) * | 1975-11-03 | 1981-07-14 | Sando Iron Works Co. Ltd. | Method of heat fulling and water washing of cloth |
| US4124923A (en) * | 1976-09-03 | 1978-11-14 | Advanced Textiles Exploitation Ag | Apparatus for texturing yarn and textile fabric containing synthetic fibers |
| US4047405A (en) * | 1976-10-13 | 1977-09-13 | Champagne-Dye Works | Apparatus for applying dye liquor to knit/deknit tubular rolls |
| US4339856A (en) * | 1979-05-16 | 1982-07-20 | Sando Iron Works Co., Ltd. | Apparatus for continuous untwisting and crimping of a cloth |
| US4409709A (en) * | 1979-05-16 | 1983-10-18 | Sando Iron Works Co., Ltd. | Apparatus for continuous untwisting and crimping of a cloth |
| US4614096A (en) * | 1979-10-01 | 1986-09-30 | Arioli & C S.R.L. | System for the continuous and open-width washing of a fabric |
| US4387476A (en) * | 1979-12-12 | 1983-06-14 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | Method and an apparatus for a washing process subsequent to the spinning of synthetic fibers |
| US4364248A (en) * | 1980-02-20 | 1982-12-21 | Sando Iron Works Co., Ltd. | Method and apparatus for wet-heat treating a knitted fabric |
| EP0531868A1 (en) * | 1991-09-09 | 1993-03-17 | Gaston County Dyeing Machine Company | Apparatus for low liquid wet treatment of a textile material |
| US20060216427A1 (en) * | 2005-03-22 | 2006-09-28 | Conductive Inkjet Technology Limited | Treatment of flexible web material |
| WO2006100467A1 (en) | 2005-03-22 | 2006-09-28 | Conductive Inkjet Technology Limited | Treatment of flexible web material |
| CN113882093A (zh) * | 2021-08-23 | 2022-01-04 | 浙江常鑫纺织品有限公司 | 一种吸湿抗菌再生聚酯仿棉床品面料生产用蒸汽预缩装置 |
| CN113882093B (zh) * | 2021-08-23 | 2024-02-06 | 浙江常鑫纺织品有限公司 | 一种吸湿抗菌再生聚酯仿棉床品面料生产用蒸汽预缩装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| NL6918482A (es) | 1970-06-12 |
| JPS4812111B1 (es) | 1973-04-18 |
| DE1961782B2 (de) | 1977-05-18 |
| SE373892B (es) | 1975-02-17 |
| CH528626A (de) | 1972-06-15 |
| CH1834969A4 (es) | 1972-06-15 |
| DE1961782A1 (de) | 1970-06-18 |
| LU59973A1 (es) | 1970-06-09 |
| ES374554A1 (es) | 1972-04-01 |
| BE742825A (es) | 1970-06-08 |
| IE33425L (en) | 1970-06-10 |
| IE33425B1 (en) | 1974-06-26 |
| GB1294471A (en) | 1972-10-25 |
| IL33472A (en) | 1972-10-29 |
| FR2025788A1 (es) | 1970-09-11 |
| AT304427B (de) | 1973-01-10 |
| IL33472A0 (en) | 1970-02-19 |
| DE6947701U (de) | 1971-05-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US3579679A (en) | Tensionless liquid treating apparatus and method | |
| US3614796A (en) | Method and apparatus for treating textile materials | |
| US3518848A (en) | Device for the continuous treatment of a web of fabric with fluid | |
| US3990274A (en) | Apparatus for continuously processing fabric | |
| US4087993A (en) | Heat fulling and water washing apparatus | |
| US3618226A (en) | Apparatus for continuously drying web material especially textile material | |
| US4059974A (en) | Apparatus for the continuous treatment of endless material, especially the shrinking thereof | |
| US338096A (en) | Island | |
| US3470571A (en) | Process of and apparatus for treating sheet materials | |
| US2268590A (en) | Treating textile material to remove gum, etc., therefrom | |
| US4137045A (en) | Method for treating a textile web with steam | |
| US3771952A (en) | Web scouring method and apparatus | |
| US3640099A (en) | Apparatus for continuously scouring webs of knit material or the like | |
| US4614096A (en) | System for the continuous and open-width washing of a fabric | |
| US6176884B1 (en) | Continuous fabric rinsing method and apparatus | |
| US3729958A (en) | Liquid treating apparatus for textile materials and method therefor | |
| US3776005A (en) | Apparatus for dyeing and/or washing fabric | |
| EP1007776A1 (en) | Wet grinding method for textile material and relative device | |
| JPS5848663B2 (ja) | 布を洗浄する方法および装置 | |
| KR900007094B1 (ko) | 기다란 테이프를 열수로 세척하는 방법 및 장치 | |
| GB2051899A (en) | Dyeing cloth | |
| SU1384638A1 (ru) | Устройство дл жидкостной обработки бесконечного текстильного полотна в жгуте | |
| JPS6123303B2 (es) | ||
| US664275A (en) | Machine for mercerizing. | |
| US3690814A (en) | Method for continuous wet treatment of a textile web |