KR880001970B1 - Ion exchange-electrolyte layer stiching method as electrochromic devices - Google Patents
Ion exchange-electrolyte layer stiching method as electrochromic devices Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR880001970B1 KR880001970B1 KR8201579A KR820001579A KR880001970B1 KR 880001970 B1 KR880001970 B1 KR 880001970B1 KR 8201579 A KR8201579 A KR 8201579A KR 820001579 A KR820001579 A KR 820001579A KR 880001970 B1 KR880001970 B1 KR 880001970B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- film
- punch
- piece
- die
- ion exchange
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/15—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on an electrochromic effect
- G02F1/1514—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on an electrochromic effect characterised by the electrochromic material, e.g. by the electrodeposited material
- G02F1/1523—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on an electrochromic effect characterised by the electrochromic material, e.g. by the electrodeposited material comprising inorganic material
- G02F1/1525—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on an electrochromic effect characterised by the electrochromic material, e.g. by the electrodeposited material comprising inorganic material characterised by a particular ion transporting layer, e.g. electrolyte
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/17—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on variable-absorption elements not provided for in groups G02F1/015 - G02F1/169
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/15—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on an electrochromic effect
- G02F1/153—Constructional details
- G02F1/1533—Constructional details structural features not otherwise provided for
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09F—DISPLAYING; ADVERTISING; SIGNS; LABELS OR NAME-PLATES; SEALS
- G09F9/00—Indicating arrangements for variable information in which the information is built-up on a support by selection or combination of individual elements
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Nonlinear Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Electrochromic Elements, Electrophoresis, Or Variable Reflection Or Absorption Elements (AREA)
- Devices For Indicating Variable Information By Combining Individual Elements (AREA)
Abstract
Description
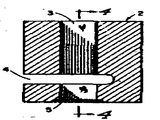
제1도는 펀치의 측면도.1 is a side view of the punch.
제2도는 상기 펀치의 저면도.2 is a bottom view of the punch.
제3도는 다이의 수직 단면도.3 is a vertical section of the die.
제4도는 제3도의 선 4-4에 따라 취한 단면도.4 is a sectional view taken along line 4-4 of FIG.
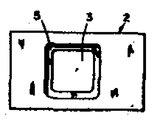
제5도는 제3도에 도시된 다이의 저면도이다.5 is a bottom view of the die shown in FIG.
* 도면의 주요부분에 대한 부호의 설명* Explanation of symbols for main parts of the drawings
1 : 펀치 2 : 다이1: Punch 2: Die
3 : 수직구멍 4 : 수평 슬로트3: vertical hole 4: horizontal slot
5 : 홈 6 : 펀치끝의 면5: groove 6: face of punch end
본 발명은 전기발생 장치(electrochromic device)의 개량된 제조방법에 관한 것으로, 더 구체적으로는, 적층된 전기발색장치의 제조에 있어서 전해질 층으로서 중합체 이온 교환수지 필름을 부착하는 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to an improved method of manufacturing an electrochromic device, and more particularly, to a method of attaching a polymer ion exchange resin film as an electrolyte layer in the production of laminated electrochromic devices.
본 발명은 전기 발색 시계 디이얼이나 다른 작은 전기발색 디스플레이 장치를 제조하는데 특히 유용하다.The present invention is particularly useful for making electrochromic watch dials or other small electrochromic display devices.
지속성 전기발색층과 전해질층의 두가지 층이 서로 이온 전도 가능하게 면접촉하여 구성되고, 전기발색층과 전해질층 사이에 가역적인 이온 흐름을 제공하기 위해 전극들 사이에 전류를 가역적으로 부여하는 수단을 가진 두개의 전극 표면 사이에 배치되는 전기발색 장치들이 알려져 있다. 이러한 장치에 전류을 가함으로서 전기발색층의 색영상(color image)이 전류의 방향에 따라 발현 또는 소멸될 수 있다. 전류가 가해지지 않을 때는 전기발색층은 어떤 상태가 마지막으로 유발되어 있든지 지속성을 가지게 된다. 그리하여, 적당한 극성의 작은 전류전하를 전극 도선들에 인가함으로서 디지탈 색 영상이 시계 표면에서 형성, 소멸 및 변화될 수 있다.The two layers of the persistent electrochromic layer and the electrolyte layer are configured to be ionically conductive in surface contact with each other, and means for reversibly imparting current between the electrodes to provide a reversible ion flow between the electrochromic layer and the electrolyte layer. Electrochromic devices are known that are disposed between two electrode surfaces having a diameter. By applying a current to such a device, a color image of the electrochromic layer can be expressed or disappeared along the direction of the current. When no current is applied, the electrochromic layer has a persistence no matter what state was last caused. Thus, by applying small current charges of appropriate polarity to the electrode leads, a digital color image can be formed, dissipated and changed at the field of view.
이러한 장치에서 전해질층을 형성시키기 위해 사용되는 재료는 이온 교환수지의 얇은 필름이고, 이 수지는 그 수지의 이온 교환 기능을 활성화시키는데 충분한 소량의 물을 흡수하여 함유하여야 한다.The material used to form the electrolyte layer in such an apparatus is a thin film of ion exchange resin, which must absorb and contain a small amount of water sufficient to activate the ion exchange function of the resin.
이러한 전기 발색장치에 그러한 수지층을 부착시키는 종래의 한가지 방법은, 전도성 유리판 또는 그와 같은 것의 전극 기판위에 지지된 전기발색층위에 가용성 수지층을 용매 피복하는 것이다. 전기 발색장치에 이온 교환수지 필름을 형성시키는 다른 방법은, 수지로 된 자립(self-supporting)필름을 일정한 크기의 조각으로 잘라내어 이것을 지지 기판상에 있는 전기발색층 위에 배치시키는 것이다. 본 발명은 이 후자의 방법을 개선한 것이다. 자립하는 필름층을 부착시키는데 있어서의 문제점은 접촉면들을 모든 지점들에서 전기접촉이 이루어지도록 하는데 있다. 필름과 기판 사이에 공기가 들어가면 그 층들 사이의 면접촉이 불연속적으로 되는 경향이 있다. 이러한 불연속성은 완성된 장치에서 스폿트(spot)들로 나타나는데, 이 스폿트들에서는 전류를 가한때 전기 발색층이 색을 변화시키지 않게 된다.One conventional method of adhering such a resin layer to such an electrochromic device is to solvent coat a soluble resin layer on an electrochromic layer supported on an electrode substrate of a conductive glass plate or the like. Another method of forming an ion exchange resin film in an electrochromic device is to cut a self-supporting film of resin into pieces of uniform size and place it on an electrochromic layer on a support substrate. The present invention improves on this latter method. The problem with attaching a self-supporting film layer is that the contact surfaces are in electrical contact at all points. If air enters between the film and the substrate, the surface contact between the layers tends to be discontinuous. This discontinuity appears as spots in the finished device, where the electrochromic layer does not change color when current is applied.
본 발명은 자립하는 이온 교환수지 필름을 전해질층 물질로 이용하여 전기발색 장치에 전해질층을 전단하여 부착하는 방법을 제공한다. 편치와 다이에 의해 필름 조각이 적당한 크기로 절단된 후, 이 절단된 필름이 기판에 대해 압착될때 필름과 기판 사이의 공기를 배출시키도록 하는 방식으로 그 필름 조각이 지지 기판상의 전기발색층위 제 위치에 부착된다. 본 발명은 대량 생산에 쉽게 적용될 수 있다.The present invention provides a method of shearing and attaching an electrolyte layer to an electrochromic device using a freestanding ion exchange resin film as an electrolyte layer material. After the pieces of film are cut to the appropriate size by the bias and the die, the pieces of film are placed on the electrochromic layer on the supporting substrate in such a way that the cut film releases air between the film and the substrate when pressed against the substrate. Is attached to. The present invention can be easily applied to mass production.
본 발명은 가장 바람직한 예를 첨부도면을 참조하여 이하 상술한다.The present invention will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings, the most preferred example.
제1도에서, 펀치(1)는 그 펀치에 의해 절단되어 전기 발색 장치에 배치될 필름조각의 형상 및 크기와 동일한 형상 및 크기의 단면을 가진 직선의 막대이다. 예를 들어, 그 펀치의 단면은 제2도에서 볼수 있는 바와같이 약간 둥근 모서리를 가진 정4각형으로 되어 있다. 필름을 절단하는 펀치 끝의 면(6)은 약간 둥글게된 측면 형상을 가진다. 비람직한 예에서, 그러한 둥글게 된 면(6)의 곡률 반경은 2인치(5.08㎝)이고, 펀치의 길이는 약 3.5인치(8.08㎝) 정도이며, 그 펀치의 단면 크기는 0.5인치(약 1.27㎝) 평방이다.In FIG. 1, the punch 1 is a straight rod having a cross section of the same shape and size as the shape and size of the film piece to be cut by the punch and placed in the electrochromic device. For example, the cross section of the punch is a square with slightly rounded corners as can be seen in FIG. The face 6 of the punch end for cutting the film has a slightly rounded side shape. In a preferred example, the radius of curvature of such rounded face 6 is 2 inches (5.08 cm), the length of the punch is about 3.5 inches (8.08 cm), and the cross section size of the punch is 0.5 inches (about 1.27). Cm) square.
제3도, 제4도 및 제5도는 수지필름 조각을 잘라내어 이것을 전기발색 장치에 배치시키기 위해 펀치(1)과 함께 사용하기 위한 다이(2)를 나타내는 도면이다. 즉, 제3도는 다이(2)의 수직 단면을 나타내고, 제4도는 제3도의 선 4-4에 따른 단면을 나타내며, 제5도는 다이의 저면을 나타낸다.3, 4 and 5 show a
모서리가 둥근 정사각형의 수직 구명(3)이 다이(2)의 길이방향으로 관통하여 있고, 펀치(1)가 이 수직 구멍(3)을 통과한다. 이 수직구멍(3)은 다이의 길이 방향으로의 펀치의 통과를 안내하도록 하는 형상으로 되어 있다. 즉, 이 수직 구멍(23)은 위에서 볼때 펀치(1)의 단면 형상 및 크기와 동일한 형상 및 크기고 되어 있다. 수평슬로트(4)가 그 수직 구멍(3)에 직교하여 다이(2)의 일 수직측면으로 부터 그 수직구멍(3)을 지나 다이 내측으로 절삭되어 있다. 그 수평 슬로트(4)의 평편한 저면은 수지 필름이 펀치에 의해 절단 되기 위해 놓이는 대(臺)를 제공한다. 도면들에서는, 다이의 명료한 도시를 위해 수지필름은 나타내지 않았다. 작동에 있어서는, 수지필름을 슬로트(4)속에 삽입하여 그 슬로트의 평편한 저면위에서 수직구멍(3)을 덮도록 배치한 후, 펀치(1)를 다이(2)의 상방으로부터 수직구멍(3)속으로 넣어 하방으로 눌러준다. 펀치 끝의 면(6)이 수지필름에 넣고 슬로트의 평편한 저면으로 지나 수직구멍(3)속으로 계속 들어감에 따라, 그 구멍(3)을 덮고 있는 수지필름이 펀치 끝의 면(6)의 가장자리에 의해 절단되고 그 펀치 끝의 면(6)에 지탱되어 다이(2)의 수직 구멍(43)속을 통해 하방으로 이동된다. 다이(2)의 저면에는 수직구멍(3)의 주위에 턱을 이루도록 홈(5)이 형성되어 있고, 그 홈(5)은 수지필름이 부착될 얇은 전도성 유리 기판을 그 홈내에 배치시키도록 하는 형상으로 되어 있다.A square vertical life 3 with rounded corners penetrates in the longitudinal direction of the
도면에 도시된 예에 있어서, 이 홈(5)은 둥근 모서리를 가진 3/4인치(약 1.9㎝) 평방 크기의 정사각형이고 수직구멍(3)과 동심적이다. 즉, 이홈(5)은 수직구멍(3)의 저부에 있는 카운터싱크(countersink)형태이다. 이 홈(5)속에 정사각형의 기판을 배치한 다음, 다이(2)의 바닥이 견고하고 평편한 면에 놓이도록 다이를 배치한 다음, 펀치(1)를 수직 구멍(3)을 통하여 하방을 누르면, 펀치 끝의 면(6)에 의해 슬로트(4)내의 필름이 절단된 다음, 그 절단된 필름 조각이 펀치 끝의 면에 살짝 부착되어 있는 채로 그 펀치(1)가 슬로트(4) 아래쪽 수직 구멍(3)을 통해 계속 아래쪽으로 이동되며, 펀치 끝이 기판에 도달한 때 펀치(1)가 상기 절단된 필름 조각을 기판에 대해 누른다. 펀치 끝의 면(6)이 약간 만곡되어 있기 때문에, 필름 조각은 그러한 만곡된 면(6)에 의해 먼저 중앙선을 따라 평편한 기판 표면에 대해 눌리어 진다. 다음, 그 필름 조각은 펀치 끝의 면(6)으로 부터 기판쪽으로 접착에 의해 옮겨지고, 그후 펀치(1)를 수직(2)의 수직구멍(3)으로부터 철회시킨다.In the example shown in the figure, this groove 5 is a square 3/4 inch square with rounded corners and concentric with the vertical hole 3. In other words, the groove 5 is in the form of a countersink at the bottom of the vertical hole 3. A square substrate is placed in the groove 5, and then the die is placed so that the bottom of the
상기한 펀치(1)와 같은 형태이지만, 그필름을 절단하는 펀치끝 대신에, 상기한 펀치끝의 면(6)과 동일한 형상 및 크기의 둥근면이 있는 탄성의 끝을 가진 다른 펀치(도시하지 않음)를 수직구명(3)속으로 삽입함으로서, 상기한 바와같이 기판상에 배치된 필름 조각을 제자리에 더 견고히 압착할 수 있다. 다른 펀치의 탄성의 둥근면이 기판위의 필름과 접하게 되면, 필름이 처음 기판에 부착된 중앙선을 따라 그 탄성의 둥근면이 먼저 필름을 기판에 대해 압박하게되고, 다음, 펀치에 더 많은 힘을 주게 되면, 그 펀치의 탄성의 둥근면이 상기 중앙선으로 부터 바깥쪽으로 펑탄하게 되면서 필름을 중앙으로 부터 바깥쪽으로 기판에 대해 점차로 눌러주게 되며, 필름이 기판 표면위에서 점차로 눌려짐에 따라 그 필름 아래의 공기가 바깥쪽으로 밀려나게 된다. 이렇게 하여 부착된 전해질 수지층(필름)을 가진 기판을 다이(2)로 부터 분리한 후, 전기 발색 디스플레이 장치에 공지의 방법으로 조립하게 된다.Another punch (not shown) having the same shape as the punch 1 described above, but having a rounded surface of the same shape and size as the face 6 of the punch tip, instead of the punch tip for cutting the film. By inserting into the vertical lifespan 3, the piece of film disposed on the substrate can be more firmly pressed into place as described above. When the elastic rounded surface of another punch comes into contact with the film on the substrate, the elastic rounded surface first presses the film against the substrate along the centerline where the film is first attached to the substrate, and then applies more force to the punch. When pressed, the elastic rounded surface of the punch is pushed outward from the centerline, gradually pushing the film against the substrate from the center outwards, and as the film is pressed gradually over the substrate surface, the air beneath the film Will be pushed outward. In this way, the substrate having the attached electrolyte resin layer (film) is separated from the
본 발명에 따라 전기발색 장치를 제조하는데 유용한 몇가지 특히 바람직한 중합체 이온 교환수지 들로서는, 2-아크릴아미도-2-메틸프로판 설폰산(AMPS)의 단독 중합체와 AMPS와 비닐설폰산(VAS)과의 공중합체가 있다. VAS의 단독 중합체, AMPS 또는 VAS 또는 다른 비닐 단량체(산 성분을 가진)와 또 다른 비닐 단량체, 폴리스티렌 설폰산, 및 그와 같은 것과의 다른 공중합체들은 사용할 수 도 있다.Some particularly preferred polymeric ion exchange resins useful for preparing electrochromic devices according to the invention include homopolymers of 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid (AMPS) with AMPS and vinylsulfonic acid (VAS). Copolymers. Homopolymers of VAS, AMPS or VAS or other vinyl monomers (with acid components) and other vinyl monomers, polystyrene sulfonic acids, and other copolymers of such may also be used.
선택된 수지는 본 발명에 사용할 경우 반드시 자립하는 수지필름을 형성할 수 있는 것이라야 한다. 이러한 용도에 적합한 필름은 주조(캐스팅), 성형(모울딩) 또는 다른 적당한 필름 성형법으로 만들어질 수 있다. 상술한 바와 같은 필름의 옮겨짐을 돕도록 표면 접착성을 약간 가진 수지필름을 사용하는 것이 좋고, 그러한 접착성은, 수지필름이 전해질로 사용하기 위해 가져야 하는 양의 흡수된 수분을 가질 때 대부분의 수지 필름에서 얻어질 수 있다. 그 필름은 또한, 안료, 통상의 흡습제 또는 다른 기능적 첨가제를 함유할 수도 있다.The resin selected should be one capable of forming a self-supporting resin film when used in the present invention. Films suitable for this use can be made by casting (casting), molding (moulding) or other suitable film forming method. It is advisable to use a resin film with some surface adhesion to assist in the transfer of the film as described above, and such adhesion is most resin film when the resin film has the amount of absorbed moisture that it should have for use as an electrolyte. Can be obtained from The film may also contain pigments, conventional humectants or other functional additives.
본 발명의 변형예로써, 필름을 기판에 대해 눌러주기 위해 탄성의 끝을 가진 펀치를 이용하는 대신, 전술한 절단 펀치에 의해 필름이 부착된 후 다이로 부터 기판을 제거한 다음, 그 필름을 로울링, 프레싱 또는 다른 적당한 수단에 의해 기판에 더 견고하게 부착 시킬 수 있다. 전기 발색 장치의 조립은 전기 발색 전극 반대편의 이온 전도성 필름 측면에 대전극(counter-electrode)를 부가하고 그의 모서리들에서 그 조립물을 밀봉시키는 것에 의해 완료된다.As a variant of the invention, instead of using a punch with elastic ends to press the film against the substrate, the substrate is removed from the die after the film is attached by the above-described cutting punch, and then the film is rolled, It can be more firmly attached to the substrate by pressing or other suitable means. Assembly of the electrochromic device is completed by adding a counter-electrode to the side of the ion conductive film opposite the electrochromic electrode and sealing the assembly at its corners.
전술한 장치 및 방법을 사용하여 본 발명을 구체화한 특정 실시예들을 이하 상세히 설명한다.Particular embodiments embodying the present invention using the apparatus and method described above are described in detail below.
[실시예 1]Example 1
진공 증착법에 의해 산화주석의 전도성 표면층을 가진 NESA 유리의 기판위에 스텐실 마스크(stencil massk)를 통하여 산화 텅스텐의 전기 발색 영상(image)층을 부착시킨다. 분자량이 100,000인 폴리에틸렌 옥사이드 2.7g, TiO2안료 3g 및 폴리아크릴아미도 메틸 프로판 설폰산 27g을 물 37g에 가해서 혼합물을 만든다. 이 혼합물을 실리콘 고무 필름 금형에서 주조한 후, 상대습도 50-55%이며 온도가 22℃인 질소 함유 분위기에서 건조시킨다. 주조 및 건조된 필름 시이트는 두께가 0.7㎜이다. 그 필름 시이트를 금형에서 꺼내고 상대습도가 60%인 질소분위기중에서 습윤시켜 그 필름 시이트의 가소성과 표면 접착성을 향상시키도록 한다. 전술한 펀치-다이 장치와 방법을 이용하여 상기 필름을 다이의 수평 슬로트내에 끼우고 산화 텅스텐의 영상층을 가진 전도성 유리 기판을 다이 저면에 있는 홈속에 배치한 다음, 펀치를 다이속에서 통과시켜 수평슬로트내의 필름을 절단하고 수지 필름의 절단된 조각이 펀치 끝에 부착된채 그 펀치를 기판의 표면쪽 아래로 계속 나가게 한다. 펀치 끝이 기판에 도달함에 따라, 펀치 끝에 있는 절단된 필름 조각은 기판위의 전기발색층을 덮도록 배치되고, 펀치끝의 만곡된 면과 평탄한 기판면 사이의 접촉선을 따라 기판에 대하여 눌리어지게 된다. 절단된 필름 조각을 기판상에 남겨놓은 채 펀치를 제거한다. 다음, 상기한 절단 펀치와 동일한 형상이지만 끝에 탄성의 만곡면을 가지는 다른 편치를 다이속을 통해 기판위에 있는 절단된 필름 조각에 대해 눌려준다. 이때의 누르는 힘은 만곡면을 변형시키고 필름을 중앙선으로 부터 바깥쪽으로 점차로 기판면에 대해 눌러 주는데 충분하여야 한다. 필름은 기판에 고정적으로 부착되는데 충분히 접착성이 있다.An electrochromic image layer of tungsten oxide is deposited on a substrate of NESA glass with a conductive surface layer of tin oxide by a vacuum deposition method through a stencil mask. 2.7 g of polyethylene oxide with a molecular weight of 100,000, 3 g of TiO 2 pigment and 27 g of polyacrylamido methyl propane sulfonic acid were added to 37 g of water to form a mixture. The mixture is cast in a silicone rubber film mold and then dried in a nitrogen containing atmosphere with a relative humidity of 50-55% and a temperature of 22 ° C. The cast and dried film sheets are 0.7 mm thick. The film sheet is taken out of the mold and wetted in a nitrogen atmosphere with a relative humidity of 60% to improve the plasticity and surface adhesion of the film sheet. Using the above-described punch-die apparatus and method, the film is placed in a horizontal slot of the die and a conductive glass substrate having an image layer of tungsten oxide is placed in the groove on the bottom of the die, and then the punch is passed through the die. The film in the horizontal slot is cut and the cut piece of resin film is attached to the punch end and the punch continues out below the surface of the substrate. As the punch tip reaches the substrate, the cut film piece at the punch tip is disposed to cover the electrochromic layer on the substrate and is pressed against the substrate along the contact line between the curved and flat substrate surface of the punch tip. You lose. The punch is removed leaving the cut piece of film on the substrate. Next, another knitting piece having the same shape as the above cutting punch but having an elastic curved surface at the end is pressed against the cut film piece on the substrate through the die. The pressing force at this time should be sufficient to deform the curved surface and press the film against the substrate surface gradually outward from the center line. The film is adhesive enough to adhere securely to the substrate.
상술된 바와 같이 절단된 필름이 부착된 기판은 65% 상대습도의 질소분위기중에서 최소한 24시간 동안 상태조절(conditioning)처리하여 수지층의 이온 전도성을 향상시키도록 한다. 이러한 처리를 한후, 수지층에 디전극 층을 압착하여 부착하고, 그렇게 하여 만들어진 전기 발색 소자를 밀봉하여 전기발색 장치를 완성한다.The substrate to which the cut film is attached as described above is conditioned in a nitrogen atmosphere at 65% relative humidity for at least 24 hours to improve the ion conductivity of the resin layer. After this treatment, the electrode layer is pressed onto the resin layer and adhered to the resin layer, and the electrochromic device thus produced is sealed to complete the electrochromic device.
Claims (5)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US25400781A | 1981-04-13 | 1981-04-13 | |
| US254,007 | 1981-04-13 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR830010397A KR830010397A (en) | 1983-12-30 |
| KR880001970B1 true KR880001970B1 (en) | 1988-10-08 |
Family
ID=22962568
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR8201579A KR880001970B1 (en) | 1981-04-13 | 1982-04-10 | Ion exchange-electrolyte layer stiching method as electrochromic devices |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JPS57181528A (en) |
| KR (1) | KR880001970B1 (en) |
| CH (1) | CH649641A5 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0428939A (en) * | 1990-05-21 | 1992-01-31 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | Ceiling cooling and heating system |
| JPH05223287A (en) * | 1991-04-08 | 1993-08-31 | Hitachi Air Conditioning & Refrig Co Ltd | Radiation air conditioner |
| JPH0543033U (en) * | 1991-11-15 | 1993-06-11 | 東京電気株式会社 | Electronic charge balance |
-
1982
- 1982-04-05 CH CH2094/82A patent/CH649641A5/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1982-04-10 KR KR8201579A patent/KR880001970B1/en active
- 1982-04-12 JP JP57059801A patent/JPS57181528A/en active Granted
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH0148525B2 (en) | 1989-10-19 |
| CH649641A5 (en) | 1985-05-31 |
| JPS57181528A (en) | 1982-11-09 |
| KR830010397A (en) | 1983-12-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CA2207801A1 (en) | Nonaqueous electrolyte battery | |
| CA1019039A (en) | Thin film devices having a low ohmic contact resistance | |
| KR880001970B1 (en) | Ion exchange-electrolyte layer stiching method as electrochromic devices | |
| AU2127288A (en) | Process for manufacturing a light-modulation device | |
| JPS55144404A (en) | Manufacture of discharge electrode for flat plate type ozonizer | |
| JPS57156292A (en) | Heat-sensitive recording sheet | |
| AU3516478A (en) | A laminar structure having a base layer of a fluorinated ion exchange polymer containing carboxylic groups | |
| JPH0517534B2 (en) | ||
| GB2062274A (en) | Electrochromic display device | |
| ES474189A1 (en) | Electrochromic device | |
| JPH0346421Y2 (en) | ||
| JPS5730818A (en) | Electrochromic display device | |
| JPS57176022A (en) | Liquid crystal display device and its manufacture | |
| JPS55104071A (en) | Extra thin cell | |
| ATE99077T1 (en) | PROCESS FOR MAKING A STRIP-SUPPORTED THIN ELECTRODE. | |
| JPH0533132U (en) | Liquid crystal cell manufacturing equipment | |
| JPS55165576A (en) | Manufacture of electrode plate for storage battery | |
| JPS57125924A (en) | Electrochromic display element | |
| SU925211A1 (en) | Device for paste-coating of strip blanks of electrodes of alkaline storage batteries | |
| JPS5713424A (en) | Spacer material and its manufacture | |
| JPS6260685B2 (en) | ||
| JPS5350761A (en) | Electrode base plate for electrochemical color forming display element | |
| JPH0326495Y2 (en) | ||
| JPS55154187A (en) | Heat-sensitive head | |
| JPS5752030A (en) | Electrochromic display device |