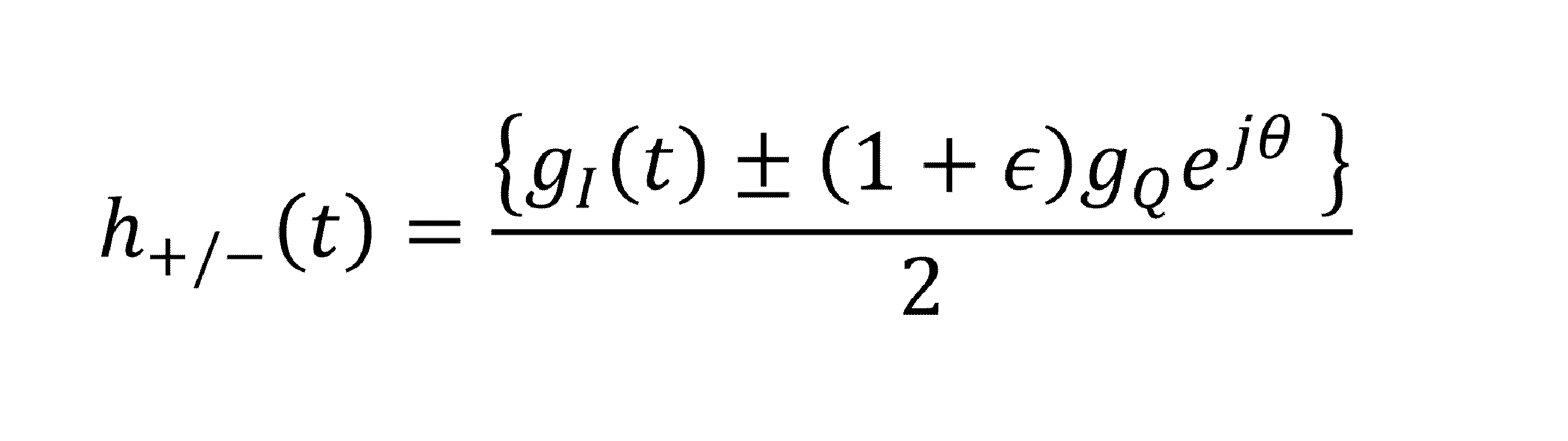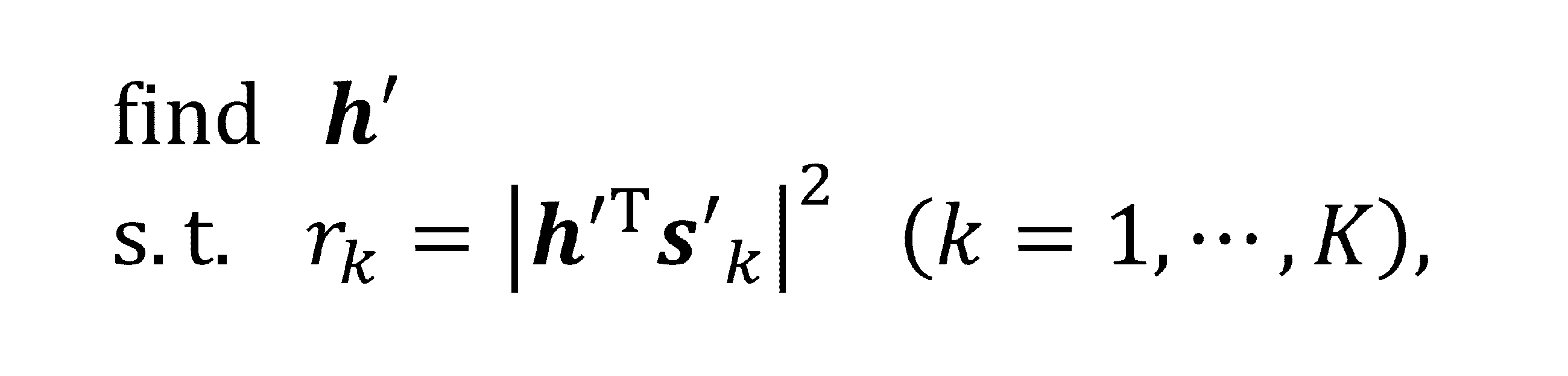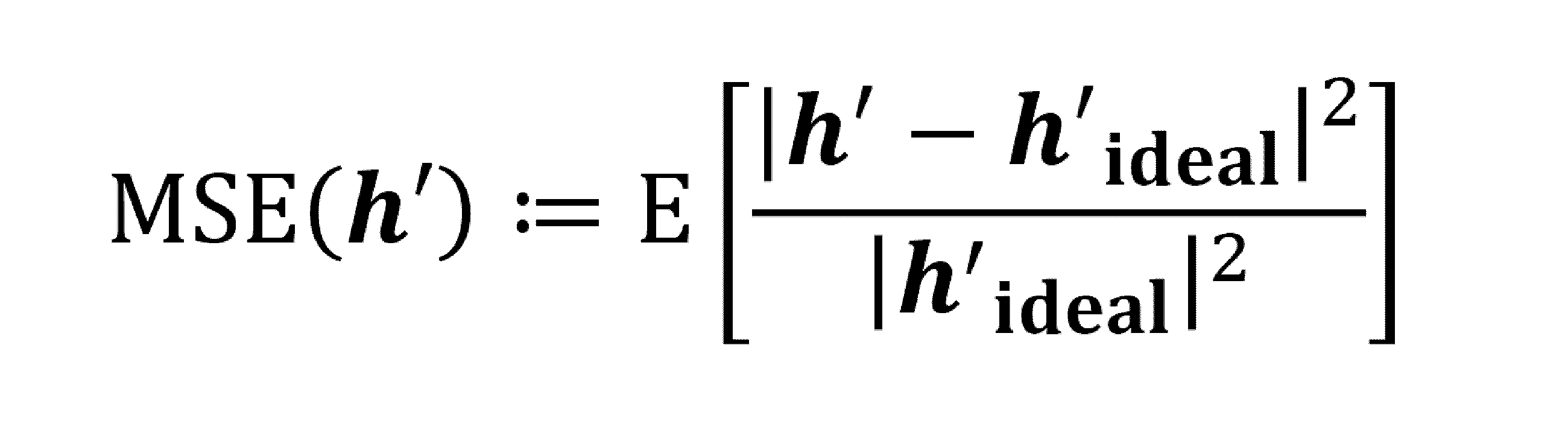JP7616628B2 - 位相回復に基づく光変調器評価技術 - Google Patents
位相回復に基づく光変調器評価技術 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7616628B2 JP7616628B2 JP2020048731A JP2020048731A JP7616628B2 JP 7616628 B2 JP7616628 B2 JP 7616628B2 JP 2020048731 A JP2020048731 A JP 2020048731A JP 2020048731 A JP2020048731 A JP 2020048731A JP 7616628 B2 JP7616628 B2 JP 7616628B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- optical
- modulator
- channel
- imbalance
- information
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 title claims description 152
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 44
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 title description 8
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 claims description 87
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 claims description 72
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 claims description 21
- 230000010363 phase shift Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000001427 coherent effect Effects 0.000 description 14
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 10
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000013598 vector Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000010183 spectrum analysis Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 3
- 108010076504 Protein Sorting Signals Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003190 augmentative effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000010287 polarization Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003044 adaptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002050 diffraction method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002068 genetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011478 gradient descent method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000013307 optical fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012634 optical imaging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000017105 transposition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B10/00—Transmission systems employing electromagnetic waves other than radio-waves, e.g. infrared, visible or ultraviolet light, or employing corpuscular radiation, e.g. quantum communication
- H04B10/07—Arrangements for monitoring or testing transmission systems; Arrangements for fault measurement of transmission systems
- H04B10/073—Arrangements for monitoring or testing transmission systems; Arrangements for fault measurement of transmission systems using an out-of-service signal
- H04B10/0731—Testing or characterisation of optical devices, e.g. amplifiers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B10/00—Transmission systems employing electromagnetic waves other than radio-waves, e.g. infrared, visible or ultraviolet light, or employing corpuscular radiation, e.g. quantum communication
- H04B10/60—Receivers
- H04B10/61—Coherent receivers
- H04B10/616—Details of the electronic signal processing in coherent optical receivers
- H04B10/6165—Estimation of the phase of the received optical signal, phase error estimation or phase error correction
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01M—TESTING STATIC OR DYNAMIC BALANCE OF MACHINES OR STRUCTURES; TESTING OF STRUCTURES OR APPARATUS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G01M11/00—Testing of optical apparatus; Testing structures by optical methods not otherwise provided for
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B10/00—Transmission systems employing electromagnetic waves other than radio-waves, e.g. infrared, visible or ultraviolet light, or employing corpuscular radiation, e.g. quantum communication
- H04B10/07—Arrangements for monitoring or testing transmission systems; Arrangements for fault measurement of transmission systems
- H04B10/075—Arrangements for monitoring or testing transmission systems; Arrangements for fault measurement of transmission systems using an in-service signal
- H04B10/079—Arrangements for monitoring or testing transmission systems; Arrangements for fault measurement of transmission systems using an in-service signal using measurements of the data signal
- H04B10/0799—Monitoring line transmitter or line receiver equipment
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B10/00—Transmission systems employing electromagnetic waves other than radio-waves, e.g. infrared, visible or ultraviolet light, or employing corpuscular radiation, e.g. quantum communication
- H04B10/50—Transmitters
- H04B10/501—Structural aspects
- H04B10/503—Laser transmitters
- H04B10/505—Laser transmitters using external modulation
- H04B10/5053—Laser transmitters using external modulation using a parallel, i.e. shunt, combination of modulators
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B10/00—Transmission systems employing electromagnetic waves other than radio-waves, e.g. infrared, visible or ultraviolet light, or employing corpuscular radiation, e.g. quantum communication
- H04B10/50—Transmitters
- H04B10/516—Details of coding or modulation
- H04B10/5161—Combination of different modulation schemes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B10/00—Transmission systems employing electromagnetic waves other than radio-waves, e.g. infrared, visible or ultraviolet light, or employing corpuscular radiation, e.g. quantum communication
- H04B10/50—Transmitters
- H04B10/564—Power control
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B10/00—Transmission systems employing electromagnetic waves other than radio-waves, e.g. infrared, visible or ultraviolet light, or employing corpuscular radiation, e.g. quantum communication
- H04B10/60—Receivers
- H04B10/61—Coherent receivers
- H04B10/613—Coherent receivers including phase diversity, e.g., having in-phase and quadrature branches, as in QPSK coherent receivers
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Nonlinear Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Optical Communication System (AREA)
- Optical Modulation, Optical Deflection, Nonlinear Optics, Optical Demodulation, Optical Logic Elements (AREA)
Description
既知の変調信号入力に対する光直交振幅変調器におけるのI(同相)チャネル及びQ(直交位相)チャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡を求める問題を,位相回復問題として定式化する。すると,単一の光検出器を用いても,変調器の周波数依存性IQ不均衡及びバイアスずれの推定を行うことができる。
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルのインパルス応答及び周波数応答,
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの電気―光応答の位相ずれの周波数依存性,
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの電気―光応答の強度ずれの周波数依存性,
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの直流バイアス成分,及び
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの非線形歪の周波数依存性のいずれか1つ又は2つ以上の不均衡に関するパラメータを含む。
不均衡演算部11は,
第1の変調信号に関する情報を受け取る入力信号情報受信部13と,
アナログ-ディジタル変換器(ADC)5からディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を受け取る強度情報受信部15とを有する。
そして,不均衡演算部は,第1の変調信号に関する情報及びディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を用いて,光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡を推定する。
不均衡演算部11は,上記の演算を行うため,例えば,位相回復演算部17と,不均衡係数演算部19とをさらに有する。
位相回復演算部17は,第1の変調信号に関する情報(s(t))を基に,ディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報(|E(t)|2)から出力信号の位相情報を回復するための位相回復演算を行う要素である。
不均衡係数演算部19は,位相回復された出力信号(E(t))と第1の変調信号に関する情報(s(t))から,不均衡のパラメータを算出するための要素である。
位相回復演算部17は,位相回復演算部が得た位相回復された出力信号(E(t))に対し,不均衡係数演算部19が不均衡係数の算出を行うことにより,光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡を推定する。
光IQ変調器へ,第1の変調信号が入力する。
光IQ変調器へ入力した光信号が,光IQ変調器により第1の変調信号に基づくIQ変調を受けて,第1の出力信号が出力される。
光検出器(PD)が第1の出力信号を受け取り,第1の出力信号の強度成分を計測する。
アナログ-ディジタル変換器(ADC)が,光検出器(PD)が計測した第1の出力信号の強度成分をディジタル信号に変換し,ディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を得る。
不均衡推定装置が,第1の変調信号に関する情報を受け取る。
不均衡推定装置が,ADCからディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を受け取る。
不均衡推定装置が,第1の変調信号に関する情報及びディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を用いて,光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡を推定する。
不均衡演算部11は,入力信号情報受信部13と,強度情報受信部15とを有する。そして,不均衡演算部11は,第1の変調信号に関する情報及びディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を用いて,光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡を推定する。上記の推定を行うため,不均衡演算部11は,例えば,位相回復演算部17と,不均衡係数演算部19とをさらに有してもよい。
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルのインパルス応答及び周波数応答,
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの電気―光応答の位相ずれの周波数依存性,
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの電気―光応答の強度ずれの周波数依存性,
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの直流バイアス成分,及び
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの非線形歪の周波数依存性のいずれか1つ又は2つ以上の不均衡に関するパラメータを含む。
Iチャネル及びQチャネルのインパルス応答は,それらの共通成分h+(t)及び誤差成分h-(t)で表すことができる。後述するように,h+(t)及びh-(t)を推測することで,Iチャネル及びQチャネルのインパルス応答を求めることができる。
また、インパルス応答をフーリエ変換、ピリオドグラム法などの手法でスペクトル解析することで、Iチャネル及びQチャネルの周波数応答を推定することができる。周波数応答は、IチャネルあるいはQチャネルにある周波数の正弦波入力を加えた際の出力振幅及び出力位相を与える。
誤差成分h-(t)をスペクトラム解析し、周波数応答の振幅成分を算出することで、光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの電気―光応答の強度ずれの周波数依存性を推測できる。
誤差成分h-(t)をスペクトラム解析し、周波数応答の位相成分を算出することで、光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの電気―光応答の強度ずれの周波数依存性を推測できる。
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの直流バイアス成分とは,変調信号の直流成分と光変調器出力における直流成分のずれである。
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの直流バイアス成分をδで表すことができる。後述するようにδを推測することで,光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの直流バイアスを推測できる。
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの非線形歪とは,光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの応答のうち、インパルス応答などの線形システムの形で表現できない、変調信号の振幅や位相状態に依存した応答である。
不均衡係数演算部19において、ボルテラフィルタなど非線形応答を表現する関数を採用することで、不均衡演算部11は位相回復演算部17及び不均衡係数演算部19に所定の演算を行わせて,光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの非線形歪を推測できる。
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルのインパルス応答及び周波数応答,
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの電気―光応答の位相ずれの周波数依存性,
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの電気―光応答の強度ずれの周波数依存性,
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの直流バイアス成分,及び
光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの非線形歪の周波数依存性のいずれか1つ又は2つ以上の不均衡に関するパラメータを含む。
図3は,電気―光応答の不均衡を推定するための処理の例を示すフローチャートである。 図3に示されるように,この方法は,以下の工程を含む。Sは,ステップを示す。
光IQ変調器へ,第1の変調信号が入力する(S101)。
光IQ変調器へ入力した光信号が,光IQ変調器により第1の変調信号に基づくIQ変調を受けて,第1の出力信号が出力される(S102)。
光検出器(PD)が第1の出力信号を受け取り,第1の出力信号の強度成分を計測する(S103)。
アナログ-ディジタル変換器(ADC)が,光検出器(PD)が計測した第1の出力信号の強度成分をディジタル信号に変換し,ディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を得る(S104)。
不均衡推定装置が,第1の変調信号に関する情報を受け取る(S105)。
不均衡推定装置が,ADCからディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を受け取る(S106)。
不均衡推定装置が,第1の変調信号に関する情報及びディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を用いて,光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡を推定する(S107)。
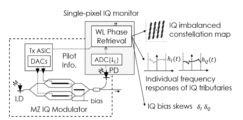
マッハ・ツェンダー干渉計(MZI)を用いた光IQ変調器,変調器を駆動するための92GSa/sの任意RF波形生成器(AWG),1550nm帯狭線幅光源を用いて,63.25Gbaud 偏波多重光16QAM変調信号を生成する。信号系列はデータ系列を想定しランダム系列とし,うち80,000シンボル程度を不均衡推定のためのパイロット信号として用いた。光信号は,エルビウムドープトファイバー増幅器(EDFA)で増幅されたのち,パワースプリッタにより2つに分岐される。一つは偏波ビームスプリッタ(PBS)によりX偏波成分のみを分離した後,SP-IQMに入力される。SP-IQMは3dB帯域70GHzのPDと160GSa/sのリアルタイムサンプリングオシロスコープ(DSO)からなり,位相回復,不均衡推定を行う演算部はオフライン処理としてワークステーション上に実装された。位相回復アルゴリズムには,前記PhareADMMを用いた。なお,本原理検証実験では,PD及びDSOの帯域制限の影響を無視するため広帯域の測定系を用いているが,位相回復処理における実効的なサンプリングレートは4.2GSa/sである。もう一つのパワースプリッタ出力はコヒーレント受信機を用いた光変調アナライザに入力される。コヒーレント受信機は,4チャンネルの80GSa/s DSOと狭線幅光源及び光ハイブリッド回路からなり,変調アナライザにおける演算処理はSP-IQMと同じく,オフラインにて実装した。コヒーレント受信の場合は,送受信機光源の周波数偏差(CFO)が問題となるが,これは不均衡推定に先立って信号スペクトル解析を行い補償した。変調アナライザにおける不均衡推定には,T. Adali, P. J. Schreier, and L. L. Scharf, "Complex-Valued Signal Processing: The Proper Way to Deal With Impropriety," IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(11), 5101-5125 (2011).などに示されたWLモデルを用いた最小平均二乗誤差推定(WL-MMSE)を用いた。なお,SP-IQM,変調器アナライザのアナログ回路に起因する周波数応答のずれについては,固定の線形等化器により補償している。実際のIQ変調器において,IQ不均衡,とくにその周波数依存性を厳密に制御することは容易ではないため,本実証実験では,送信機側AWGにおいて離散時間WLモデルをもとにディジタルフィルタで不均衡を模擬した。以降では,このディジタルフィルタのインパルス応答をh’ideal, SP-IQMによる推定結果をh’PR,コヒーレント受信機を用いた変調アナライザの推定結果をh’cohとし,平均推定誤差を
3 光検出器(PD)
5 アナログ-ディジタル変換器
11 不均衡演算部
13 入力信号情報受信部
15 強度情報受信部
17 位相回復演算部
19 不均衡係数演算部
Claims (2)
- 光直交振幅変調器(光IQ変調器)のI(同相)チャネル及びQ(直交位相)チャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡を推定するためのシステムであって,
光IQ変調器に第1の変調信号が入力された際の前記光IQ変調器からの第1の出力信号の強度成分を計測するための光検出器(PD)と,
前記光検出器(PD)が受信した第1の出力信号の強度成分をディジタル信号に変換し,ディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を得るためのアナログ-ディジタル変換器(ADC)と,
前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡を推定する不均衡演算部であって,
第1の変調信号に関する情報を受け取る入力信号情報受信部と,
前記ADCから前記ディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を受け取る強度情報受信部とを有し,
第1の変調信号に関する情報及び前記ディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を用いて,前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡を推定するものと,
を有するシステムであって,
第1の変調信号に関する情報は,第1変調の信号の強度及び位相の時間変化に関する情報(s(t))であり,
前記前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡は,
前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルのインパルス応答及び周波数応答,
前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの電気―光応答の位相ずれの周波数依存性,
前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの電気―光応答の強度ずれの周波数依存性,
前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの直流バイアス成分,及び
前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの非線形歪の周波数依存性のいずれか1つ又は2つ以上の不均衡に関するパラメータを含み,
前記不均衡演算部は,
第1の変調信号に関する情報(s(t))を基に,前記ディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報(|E(t)|2)から前記出力信号の位相情報を回復するための位相回復演算を行う位相回復演算部と,
前記位相回復された出力信号(E(t))と第1の変調信号に関する情報(s(t))から,前記不均衡のパラメータを算出する不均衡係数演算部と,
をさらに有し,
前記位相回復演算部が得た位相回復された出力信号(E(t))に対し,不均衡係数演算部が不均衡係数の算出を行うことにより,前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡を推定する,
システム。 - 光直交振幅変調器(光IQ変調器)のI(同相)チャネル及びQ(直交位相)チャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡を推定するための方法であって,
光IQ変調器へ,第1の変調信号を入力する工程と,
前記光IQ変調器へ入力した光信号が,光IQ変調器により第1の変調信号に基づくIQ変調を受けて,第1の出力信号が出力される工程と,
光検出器(PD)が第1の出力信号を受け取り,第1の出力信号の強度成分を計測する工程と,
アナログ-ディジタル変換器(ADC)が,前記光検出器(PD)が計測した第1の出力信号の強度成分をディジタル信号に変換し,ディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を得る工程と,
不均衡推定装置が,第1の変調信号に関する情報を受け取る工程と,
前記不均衡推定装置が,前記ADCから前記ディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を受け取る工程と,
前記不均衡推定装置が,第1の変調信号に関する情報及び前記ディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報を用いて,前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡を推定する工程と,
を含む,方法であって,
前記前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡は,
前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルのインパルス応答及び周波数応答,
前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの電気―光応答の位相ずれの周波数依存性,
前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの電気―光応答の強度ずれの周波数依存性,
前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの直流バイアス成分の周波数依存性,及び
前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネルの非線形歪の周波数依存性のいずれか1つ又は2つ以上の不均衡に関するパラメータを含み,
前記光IQ変調器のIチャネル及びQチャネル間の電気―光応答の不均衡を推定する工程は,
第1の変調信号に関する情報(s(t))を基に,前記ディジタル化された出力信号の強度情報(|E(t)|2)から出力信号の位相情報を回復するための位相回復演算を行う工程と,
前記位相回復された出力信号(E(t))と第1の変調信号に関する情報(s(t))から,前記不均衡のパラメータを算出する工程と,
を含む,
方法。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020048731A JP7616628B2 (ja) | 2020-03-19 | 2020-03-19 | 位相回復に基づく光変調器評価技術 |
| US17/910,891 US11791905B2 (en) | 2020-03-19 | 2021-03-05 | Technology for optical modulator evaluation on basis of phase recovery |
| PCT/JP2021/008819 WO2021187177A1 (ja) | 2020-03-19 | 2021-03-05 | 位相回復に基づく光変調器評価技術 |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020048731A JP7616628B2 (ja) | 2020-03-19 | 2020-03-19 | 位相回復に基づく光変調器評価技術 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2021148954A JP2021148954A (ja) | 2021-09-27 |
| JP7616628B2 true JP7616628B2 (ja) | 2025-01-17 |
Family
ID=77768463
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020048731A Active JP7616628B2 (ja) | 2020-03-19 | 2020-03-19 | 位相回復に基づく光変調器評価技術 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11791905B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP7616628B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2021187177A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US12381630B2 (en) * | 2020-10-28 | 2025-08-05 | Nec Corporation | Communication system, receiver, distortion detection device, and method |
| CN114189286B (zh) * | 2021-10-28 | 2023-02-14 | 华中科技大学 | 同时校准相干光收发机频率响应和iq时延差的方法及系统 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002244091A (ja) | 2001-02-19 | 2002-08-28 | Communication Research Laboratory | 光変調器の特性評価方法、およびそれを用いた高周波発振装置の制御方法 |
| WO2009113128A1 (ja) | 2008-03-13 | 2009-09-17 | 独立行政法人情報通信研究機構 | 複数マッハツェンダー干渉計を有する光変調器の特性評価方法 |
| JP2015516706A (ja) | 2012-02-20 | 2015-06-11 | タイコ エレクトロニクス サブシー コミュニケーションズ エルエルシー | 直交振幅変調システムにおけるブラインド等化およびキャリア位相復元のためのシステムおよび方法 |
| US20190123832A1 (en) | 2017-10-20 | 2019-04-25 | Roshmere, Inc. | Phase recovery for signals with quadrature amplitude modulation |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9124364B1 (en) * | 2012-05-30 | 2015-09-01 | Ciena Corporation | Quadrature power balance control in optical transmitters |
| US9729244B2 (en) * | 2014-10-20 | 2017-08-08 | Adva Optical Networking Se | Apparatus and method for monitoring signal quality of a modulated optical signal |
| US10218446B2 (en) * | 2015-12-19 | 2019-02-26 | Finisar Corporation | Method and apparatus for characterization and compensation of optical impairments in InP-based optical transmitter |
| US9979472B1 (en) * | 2016-12-29 | 2018-05-22 | Juniper Networks, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for detecting and compensating power imbalance and modulation imperfection for a coherent optical transmitter |
| CN109728856B (zh) * | 2017-10-27 | 2021-12-31 | 富士通株式会社 | 光发射机iq不平衡的估计装置、补偿装置及电子设备 |
-
2020
- 2020-03-19 JP JP2020048731A patent/JP7616628B2/ja active Active
-
2021
- 2021-03-05 US US17/910,891 patent/US11791905B2/en active Active
- 2021-03-05 WO PCT/JP2021/008819 patent/WO2021187177A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002244091A (ja) | 2001-02-19 | 2002-08-28 | Communication Research Laboratory | 光変調器の特性評価方法、およびそれを用いた高周波発振装置の制御方法 |
| WO2009113128A1 (ja) | 2008-03-13 | 2009-09-17 | 独立行政法人情報通信研究機構 | 複数マッハツェンダー干渉計を有する光変調器の特性評価方法 |
| JP2015516706A (ja) | 2012-02-20 | 2015-06-11 | タイコ エレクトロニクス サブシー コミュニケーションズ エルエルシー | 直交振幅変調システムにおけるブラインド等化およびキャリア位相復元のためのシステムおよび方法 |
| US20190123832A1 (en) | 2017-10-20 | 2019-04-25 | Roshmere, Inc. | Phase recovery for signals with quadrature amplitude modulation |
Non-Patent Citations (4)
| Title |
|---|
| C.R.S.Fludger,Low Cost Transmitter Self-Calibration of Time Delay and Frequency Response for High Baud-Rate QAM Transceivers,Optical Fiber Communication Conference, OSA Technical Digest,2017年,Th1D.3-1~3 |
| Julio Cesar Mederiros Diniz,Optimization of DP-M-QAM Transmitter Using Cooperative Coevolutionary Genetic Algorithm,JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY,2018年,Vol.36 No.12,pp.2450-2462 |
| Yuki Yoshida,A Phase-Retrieving Coherent Receiver Based on Two-Dimensional Photodetector Array,JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY,2020年01月01日,Vol.38 No.1,pp.90-100 |
| 酒井学,OFDM/OQAMにおけるプリアンブルを用いたI/Q不均衡推定法,第31回信号処理シンポジウム講演論文集,2016年12月14日,pp.352-357 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2021148954A (ja) | 2021-09-27 |
| US20230120581A1 (en) | 2023-04-20 |
| US11791905B2 (en) | 2023-10-17 |
| WO2021187177A1 (ja) | 2021-09-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. | Dual polarization full-field signal waveform reconstruction using intensity only measurements for coherent communications | |
| US10574362B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for transmitter IQ skew and insertion loss detection for coherent optical systems | |
| JP5238881B2 (ja) | コヒーレント受信機における適応非線形補償 | |
| US9906309B2 (en) | System and method for determining nonlinear mitigation perturbative distortion coefficients using a received optical signal | |
| US9544060B2 (en) | Optical transmitter and method for controlling the same | |
| JP7169980B2 (ja) | スペクトル相関を使用した変調信号のスペクトル形状の無雑音測定 | |
| JP2011089945A (ja) | 非線形歪検出回路、光受信機、光伝送システム、および非線形歪検出方法 | |
| US20120281981A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for detecting chromatic dispersion, and method and apparatus for compensating chromatic dispersion | |
| Sunnerud et al. | Characterization of complex optical modulation formats at 100 Gb/s and beyond by coherent optical sampling | |
| JP7616628B2 (ja) | 位相回復に基づく光変調器評価技術 | |
| JP6818698B2 (ja) | プラグ接続可能な光モジュールの較正 | |
| EP2683101A1 (en) | Polarization multilevel signal optical receiving apparatus, polarization multilevel signal optical transmitting apparatus, and polarization multilevel signal optical transmission apparatus | |
| Tao et al. | Characterization, modelling and measurement of device imperfections in advanced coherent transceivers | |
| US9479252B2 (en) | Pre-equalization using phase correction | |
| US10756822B1 (en) | Digital fiber nonlinearity compensation | |
| US12081271B2 (en) | Digital tone-based apparatus and method for measuring the frequency response of coherent optical transmitters | |
| US12166852B2 (en) | Self-calibrating device and method for in-phase and quadrature time skew and conjugation in a coherent transmitter | |
| Liu et al. | Practical Kramers-Kronig phase retrieval FIR filter with the Gibbs phenomenon | |
| US11381444B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for coherent transmitter calibration | |
| EP3345314B1 (en) | Phase retrieval for compensation of chromatic dispersion-induced inter-symbol interference | |
| Cabrera et al. | Universal bias controller testbed for dp-iq modulators in coherent optical links | |
| Yoshida et al. | Single-pixel IQ monitor via computational coherent reception with widely linear phase retrieval | |
| JP2013183214A (ja) | 光信号検査装置及び光信号検査方法 | |
| Kashi et al. | High resolution characterization of the spectral broadening due to fiber nonlinearities | |
| Gerard et al. | Self-suppression of signal-signal beating interference using a split-carrier transmitter |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20230214 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20240305 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20240425 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20240730 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20240905 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20241217 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20241223 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7616628 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |