JP7103953B2 - 薬物としてアマトキシンの誘導体を有する抗体薬物コンジュゲート - Google Patents
薬物としてアマトキシンの誘導体を有する抗体薬物コンジュゲート Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7103953B2 JP7103953B2 JP2018562186A JP2018562186A JP7103953B2 JP 7103953 B2 JP7103953 B2 JP 7103953B2 JP 2018562186 A JP2018562186 A JP 2018562186A JP 2018562186 A JP2018562186 A JP 2018562186A JP 7103953 B2 JP7103953 B2 JP 7103953B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- adc
- pharmaceutically acceptable
- acceptable salt
- formula
- pab
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000000611 antibody drug conjugate Substances 0.000 title claims description 62
- 229940049595 antibody-drug conjugate Drugs 0.000 title claims description 62
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 title claims description 12
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 title claims description 12
- WVHGJJRMKGDTEC-WCIJHFMNSA-N 2-[(1R,4S,8R,10S,13S,16S,27R,34S)-34-[(2S)-butan-2-yl]-8,22-dihydroxy-13-[(2R,3S)-3-hydroxybutan-2-yl]-2,5,11,14,27,30,33,36,39-nonaoxo-27lambda4-thia-3,6,12,15,25,29,32,35,38-nonazapentacyclo[14.12.11.06,10.018,26.019,24]nonatriaconta-18(26),19(24),20,22-tetraen-4-yl]acetamide Chemical class CC[C@H](C)[C@@H]1NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@@H]2Cc3c([nH]c4cc(O)ccc34)[S@](=O)C[C@H](NC(=O)CNC1=O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(N)=O)C(=O)N1C[C@H](O)C[C@H]1C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)[C@H](C)O)C(=O)N2 WVHGJJRMKGDTEC-WCIJHFMNSA-N 0.000 title claims description 11
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 25
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 24
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims description 19
- VEGGTWZUZGZKHY-GJZGRUSLSA-N (2s)-2-[[(2s)-2-amino-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-5-(carbamoylamino)-n-[4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]pentanamide Chemical compound NC(=O)NCCC[C@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](N)C(C)C)C(=O)NC1=CC=C(CO)C=C1 VEGGTWZUZGZKHY-GJZGRUSLSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 231100000729 Amatoxin Toxicity 0.000 claims description 7
- 108010014709 amatoxin Proteins 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 3
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 3
- 150000002431 hydrogen Chemical class 0.000 claims 2
- 125000001449 isopropyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 claims 1
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 38
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 31
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 26
- 150000001413 amino acids Chemical group 0.000 description 25
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 21
- JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) Chemical compound CCN(C(C)C)C(C)C JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 17
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 17
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical class [H]* 0.000 description 14
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 14
- 125000002947 alkylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 13
- 108090000765 processed proteins & peptides Proteins 0.000 description 13
- 238000004007 reversed phase HPLC Methods 0.000 description 13
- 230000004614 tumor growth Effects 0.000 description 12
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 11
- 238000000338 in vitro Methods 0.000 description 11
- 241000699670 Mus sp. Species 0.000 description 10
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trifluoroacetic acid Chemical group OC(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 201000011510 cancer Diseases 0.000 description 10
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 10
- NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Piperidine Chemical compound C1CCNCC1 NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 230000003013 cytotoxicity Effects 0.000 description 8
- 231100000135 cytotoxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 8
- 230000004580 weight loss Effects 0.000 description 8
- 101800002638 Alpha-amanitin Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 125000005647 linker group Chemical group 0.000 description 7
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 7
- NNWYWNRCBPYLML-GWCFXTLKSA-N (2s)-2-amino-n-[(2s)-1-[4-(hydroxymethyl)anilino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]-3-methylbutanamide Chemical compound CC(C)[C@H](N)C(=O)N[C@@H](C)C(=O)NC1=CC=C(CO)C=C1 NNWYWNRCBPYLML-GWCFXTLKSA-N 0.000 description 6
- LMDZBCPBFSXMTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide Chemical compound CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C LMDZBCPBFSXMTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 230000004663 cell proliferation Effects 0.000 description 6
- 229940125782 compound 2 Drugs 0.000 description 6
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 5
- 241000699666 Mus <mouse, genus> Species 0.000 description 5
- RXGJTYFDKOHJHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N S-deoxo-amaninamide Natural products CCC(C)C1NC(=O)CNC(=O)C2Cc3c(SCC(NC(=O)CNC1=O)C(=O)NC(CC(=O)N)C(=O)N4CC(O)CC4C(=O)NC(C(C)C(O)CO)C(=O)N2)[nH]c5ccccc35 RXGJTYFDKOHJHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000004007 alpha amanitin Substances 0.000 description 5
- CIORWBWIBBPXCG-SXZCQOKQSA-N alpha-amanitin Chemical compound O=C1N[C@@H](CC(N)=O)C(=O)N2C[C@H](O)C[C@H]2C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)CO)C(=O)N[C@@H](C2)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@H]1C[S@@](=O)C1=C2C2=CC=C(O)C=C2N1 CIORWBWIBBPXCG-SXZCQOKQSA-N 0.000 description 5
- CIORWBWIBBPXCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N alpha-amanitin Natural products O=C1NC(CC(N)=O)C(=O)N2CC(O)CC2C(=O)NC(C(C)C(O)CO)C(=O)NC(C2)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(C(C)CC)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC1CS(=O)C1=C2C2=CC=C(O)C=C2N1 CIORWBWIBBPXCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- CIORWBWIBBPXCG-JZTFPUPKSA-N amanitin Chemical class O=C1N[C@@H](CC(N)=O)C(=O)N2CC(O)C[C@H]2C(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)[C@@H](O)CO)C(=O)N[C@@H](C2)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)CC)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@H]1CS(=O)C1=C2C2=CC=C(O)C=C2N1 CIORWBWIBBPXCG-JZTFPUPKSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 230000022534 cell killing Effects 0.000 description 5
- 229940127121 immunoconjugate Drugs 0.000 description 5
- 239000003112 inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 5
- -1 p-aminobenzyl Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- 108020003175 receptors Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 102000005962 receptors Human genes 0.000 description 5
- 239000003053 toxin Substances 0.000 description 5
- 231100000765 toxin Toxicity 0.000 description 5
- 108700012359 toxins Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 229960005502 α-amanitin Drugs 0.000 description 5
- 125000004169 (C1-C6) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 108010027164 Amanitins Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 238000003556 assay Methods 0.000 description 4
- 231100000433 cytotoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 4
- 230000001472 cytotoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000004108 freeze drying Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000002953 preparative HPLC Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 4
- 125000003161 (C1-C6) alkylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- BDNKZNFMNDZQMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-diisopropylcarbodiimide Chemical compound CC(C)N=C=NC(C)C BDNKZNFMNDZQMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- NQTADLQHYWFPDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Hydroxysuccinimide Chemical compound ON1C(=O)CCC1=O NQTADLQHYWFPDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 210000001015 abdomen Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 150000008064 anhydrides Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229940125773 compound 10 Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229940125898 compound 5 Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 239000000562 conjugate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 3
- BGRWYRAHAFMIBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N diisopropylcarbodiimide Natural products CC(C)NC(=O)NC(C)C BGRWYRAHAFMIBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 description 3
- ZLVXBBHTMQJRSX-VMGNSXQWSA-N jdtic Chemical compound C1([C@]2(C)CCN(C[C@@H]2C)C[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)[C@@H]2NCC3=CC(O)=CC=C3C2)=CC=CC(O)=C1 ZLVXBBHTMQJRSX-VMGNSXQWSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000008685 targeting Effects 0.000 description 3
- UAOUIVVJBYDFKD-XKCDOFEDSA-N (1R,9R,10S,11R,12R,15S,18S,21R)-10,11,21-trihydroxy-8,8-dimethyl-14-methylidene-4-(prop-2-enylamino)-20-oxa-5-thia-3-azahexacyclo[9.7.2.112,15.01,9.02,6.012,18]henicosa-2(6),3-dien-13-one Chemical compound C([C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@]23C(C1=C)=O)C[C@H]2[C@]12C(N=C(NCC=C)S4)=C4CC(C)(C)[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@]3(O)OC2 UAOUIVVJBYDFKD-XKCDOFEDSA-N 0.000 description 2
- AOSZTAHDEDLTLQ-AZKQZHLXSA-N (1S,2S,4R,8S,9S,11S,12R,13S,19S)-6-[(3-chlorophenyl)methyl]-12,19-difluoro-11-hydroxy-8-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-9,13-dimethyl-6-azapentacyclo[10.8.0.02,9.04,8.013,18]icosa-14,17-dien-16-one Chemical compound C([C@@H]1C[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@]([C@]4(C=CC(=O)C=C4[C@@H](F)C3)C)(F)[C@@H](O)C[C@@]2([C@@]1(C1)C(=O)CO)C)N1CC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 AOSZTAHDEDLTLQ-AZKQZHLXSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SZUVGFMDDVSKSI-WIFOCOSTSA-N (1s,2s,3s,5r)-1-(carboxymethyl)-3,5-bis[(4-phenoxyphenyl)methyl-propylcarbamoyl]cyclopentane-1,2-dicarboxylic acid Chemical compound O=C([C@@H]1[C@@H]([C@](CC(O)=O)([C@H](C(=O)N(CCC)CC=2C=CC(OC=3C=CC=CC=3)=CC=2)C1)C(O)=O)C(O)=O)N(CCC)CC(C=C1)=CC=C1OC1=CC=CC=C1 SZUVGFMDDVSKSI-WIFOCOSTSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GHYOCDFICYLMRF-UTIIJYGPSA-N (2S,3R)-N-[(2S)-3-(cyclopenten-1-yl)-1-[(2R)-2-methyloxiran-2-yl]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]-3-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-[[(2S)-2-[(2-morpholin-4-ylacetyl)amino]propanoyl]amino]propanamide Chemical compound C1(=CCCC1)C[C@@H](C(=O)[C@@]1(OC1)C)NC([C@H]([C@@H](C1=CC=C(C=C1)OC)O)NC([C@H](C)NC(CN1CCOCC1)=O)=O)=O GHYOCDFICYLMRF-UTIIJYGPSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IWZSHWBGHQBIML-ZGGLMWTQSA-N (3S,8S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-isoquinolin-7-yl-N,N,10,13-tetramethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-amine Chemical compound CN(C)[C@H]1CC[C@]2(C)C3CC[C@@]4(C)[C@@H](CC[C@@H]4c4ccc5ccncc5c4)[C@@H]3CC=C2C1 IWZSHWBGHQBIML-ZGGLMWTQSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000000008 (C1-C10) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- KQZLRWGGWXJPOS-NLFPWZOASA-N 1-[(1R)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]-6-[(4S,5R)-4-[(2S)-2-(hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]-5-methylcyclohexen-1-yl]pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyrazine-3-carbonitrile Chemical compound ClC1=C(C=CC(=C1)Cl)[C@@H](C)N1N=C(C=2C1=NC(=CN=2)C1=CC[C@@H]([C@@H](C1)C)N1[C@@H](CCC1)CO)C#N KQZLRWGGWXJPOS-NLFPWZOASA-N 0.000 description 2
- ONBQEOIKXPHGMB-VBSBHUPXSA-N 1-[2-[(2s,3r,4s,5r)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy-4,6-dihydroxyphenyl]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1OC1=CC(O)=CC(O)=C1C(=O)CCC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 ONBQEOIKXPHGMB-VBSBHUPXSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RTQWWZBSTRGEAV-PKHIMPSTSA-N 2-[[(2s)-2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]-3-[4-(methylcarbamoylamino)phenyl]propyl]-[2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]propyl]amino]acetic acid Chemical compound CNC(=O)NC1=CC=C(C[C@@H](CN(CC(C)N(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O)N(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O)C=C1 RTQWWZBSTRGEAV-PKHIMPSTSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000001674 Agaricus brunnescens Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 101800001350 Beta-amanitin Proteins 0.000 description 2
- CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon dioxide Chemical compound O=C=O CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229940126657 Compound 17 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 102000004163 DNA-directed RNA polymerases Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108090000626 DNA-directed RNA polymerases Proteins 0.000 description 2
- AOJJSUZBOXZQNB-TZSSRYMLSA-N Doxorubicin Chemical compound O([C@H]1C[C@@](O)(CC=2C(O)=C3C(=O)C=4C=CC=C(C=4C(=O)C3=C(O)C=21)OC)C(=O)CO)[C@H]1C[C@H](N)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)O1 AOJJSUZBOXZQNB-TZSSRYMLSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OPFJDXRVMFKJJO-ZHHKINOHSA-N N-{[3-(2-benzamido-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-5-yl)-pyrazol-5-yl]carbonyl}-G-dR-G-dD-dD-dD-NH2 Chemical compound S1C(C=2NN=C(C=2)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@H](CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@H](CC(O)=O)C(N)=O)=C(C)N=C1NC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 OPFJDXRVMFKJJO-ZHHKINOHSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000009572 RNA Polymerase II Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010009460 RNA Polymerase II Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000004243 Tubulin Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108090000704 Tubulin Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 239000013543 active substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001093 anti-cancer Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004080 beta amanitin Substances 0.000 description 2
- IEQCUEXVAPAFMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N beta-amanitin Natural products O=C1NC(CC(O)=O)C(=O)N2CC(O)CC2C(=O)NC(C(C)C(O)CO)C(=O)NC(C2)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(C(C)CC)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC1CS(=O)C1=C2C2=CC=C(O)C=C2N1 IEQCUEXVAPAFMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000027455 binding Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000010261 cell growth Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- NEHMKBQYUWJMIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N chloromethane Chemical compound ClC NEHMKBQYUWJMIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229940125797 compound 12 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229940126543 compound 14 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229940126142 compound 16 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229940126086 compound 21 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229940125877 compound 31 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229940127089 cytotoxic agent Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 239000002254 cytotoxic agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 231100000599 cytotoxic agent Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 230000034994 death Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012377 drug delivery Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- IEQCUEXVAPAFMQ-SXZCQOKQSA-N g729ypp47l Chemical compound O=C1N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N2C[C@H](O)C[C@H]2C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)CO)C(=O)N[C@@H](C2)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@H]1C[S@@](=O)C1=C2C2=CC=C(O)C=C2N1 IEQCUEXVAPAFMQ-SXZCQOKQSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WVHGJJRMKGDTEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N gamma-amanitin Natural products O=C1NC(CC(N)=O)C(=O)N2CC(O)CC2C(=O)NC(C(C)C(C)O)C(=O)NC(C2)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(C(C)CC)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC1CS(=O)C1=C2C2=CC=C(O)C=C2N1 WVHGJJRMKGDTEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004128 high performance liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229960001001 ibritumomab tiuxetan Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 230000007154 intracellular accumulation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002147 killing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 231100000053 low toxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000011275 oncology therapy Methods 0.000 description 2
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012552 review Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 241000894007 species Species 0.000 description 2
- UCSJYZPVAKXKNQ-HZYVHMACSA-N streptomycin Chemical compound CN[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](CO)O[C@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@](C=O)(O)[C@H](C)O[C@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@@H](NC(N)=N)[C@H](O)[C@@H](NC(N)=N)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O UCSJYZPVAKXKNQ-HZYVHMACSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000007910 systemic administration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000000999 tert-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 238000004809 thin layer chromatography Methods 0.000 description 2
- UMGDCJDMYOKAJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiourea Chemical group NC(N)=S UMGDCJDMYOKAJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000001988 toxicity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 231100000419 toxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 210000004881 tumor cell Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 230000003442 weekly effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- OFILNAORONITPV-ZUROAWGWSA-N ε-amanitin Chemical compound O=C1N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N2C[C@H](O)C[C@H]2C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)[C@H](C)O)C(=O)N[C@@H](C2)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@H]1CS(=O)C1=C2C2=CC=C(O)C=C2N1 OFILNAORONITPV-ZUROAWGWSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ASOKPJOREAFHNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-Hydroxybenzotriazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2N(O)N=NC2=C1 ASOKPJOREAFHNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YEDUAINPPJYDJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-hydroxybenzothiazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2SC(O)=NC2=C1 YEDUAINPPJYDJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- STQGQHZAVUOBTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-Cyan-hept-2t-en-4,6-diinsaeure Natural products C1=2C(O)=C3C(=O)C=4C(OC)=CC=CC=4C(=O)C3=C(O)C=2CC(O)(C(C)=O)CC1OC1CC(N)C(O)C(C)O1 STQGQHZAVUOBTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000134916 Amanita Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000948470 Amanita phalloides Species 0.000 description 1
- 102100022005 B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 231100000699 Bacterial toxin Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 206010006187 Breast cancer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000026310 Breast neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 101100314454 Caenorhabditis elegans tra-1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000004568 DNA-binding Effects 0.000 description 1
- WEAHRLBPCANXCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Daunomycin Natural products CCC1(O)CC(OC2CC(N)C(O)C(C)O2)c3cc4C(=O)c5c(OC)cccc5C(=O)c4c(O)c3C1 WEAHRLBPCANXCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 101150029707 ERBB2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 208000010201 Exanthema Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241001562173 Galerina marginata Species 0.000 description 1
- JRZJKWGQFNTSRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Geldanamycin Natural products C1C(C)CC(OC)C(O)C(C)C=C(C)C(OC(N)=O)C(OC)CCC=C(C)C(=O)NC2=CC(=O)C(OC)=C1C2=O JRZJKWGQFNTSRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000007821 HATU Substances 0.000 description 1
- 101000897405 Homo sapiens B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 125000000998 L-alanino group Chemical group [H]N([*])[C@](C([H])([H])[H])([H])C(=O)O[H] 0.000 description 1
- FBOZXECLQNJBKD-ZDUSSCGKSA-N L-methotrexate Chemical compound C=1N=C2N=C(N)N=C(N)C2=NC=1CN(C)C1=CC=C(C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C(O)=O)C=C1 FBOZXECLQNJBKD-ZDUSSCGKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241001503562 Lepiota Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000004472 Lysine Substances 0.000 description 1
- KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lysine Natural products NCCCCC(N)C(O)=O KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229930182555 Penicillin Natural products 0.000 description 1
- JGSARLDLIJGVTE-MBNYWOFBSA-N Penicillin G Chemical compound N([C@H]1[C@H]2SC([C@@H](N2C1=O)C(O)=O)(C)C)C(=O)CC1=CC=CC=C1 JGSARLDLIJGVTE-MBNYWOFBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 231100000742 Plant toxin Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 102000014450 RNA Polymerase III Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010078067 RNA Polymerase III Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000012980 RPMI-1640 medium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241000283984 Rodentia Species 0.000 description 1
- 101710183280 Topoisomerase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000004142 Trypsin Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000631 Trypsin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Urea Natural products NC(N)=O XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LJOOWESTVASNOG-UFJKPHDISA-N [(1s,3r,4ar,7s,8s,8as)-3-hydroxy-8-[2-[(4r)-4-hydroxy-6-oxooxan-2-yl]ethyl]-7-methyl-1,2,3,4,4a,7,8,8a-octahydronaphthalen-1-yl] (2s)-2-methylbutanoate Chemical compound C([C@H]1[C@@H](C)C=C[C@H]2C[C@@H](O)C[C@@H]([C@H]12)OC(=O)[C@@H](C)CC)CC1C[C@@H](O)CC(=O)O1 LJOOWESTVASNOG-UFJKPHDISA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002777 acetyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 1
- 239000000427 antigen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108091007433 antigens Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000036639 antigens Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 230000006907 apoptotic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000003719 b-lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000000688 bacterial toxin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000002619 bicyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000037396 body weight Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012267 brine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000337 buffer salt Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001718 carbodiimides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000001569 carbon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910002092 carbon dioxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- VQLODVNDDHYECU-UHFFFAOYSA-N carbonic acid;4-nitrophenol Chemical compound OC(O)=O.OC1=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1.OC1=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1 VQLODVNDDHYECU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940127204 compound 29 Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940126214 compound 3 Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000012043 crude product Substances 0.000 description 1
- STQGQHZAVUOBTE-VGBVRHCVSA-N daunorubicin Chemical compound O([C@H]1C[C@@](O)(CC=2C(O)=C3C(=O)C=4C=CC=C(C=4C(=O)C3=C(O)C=21)OC)C(C)=O)[C@H]1C[C@H](N)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)O1 STQGQHZAVUOBTE-VGBVRHCVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010013023 diphtheria Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000004090 dissolution Methods 0.000 description 1
- CETRZFQIITUQQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N dmso dimethylsulfoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O.CS(C)=O CETRZFQIITUQQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960004679 doxorubicin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 201000005884 exanthem Diseases 0.000 description 1
- QTQAWLPCGQOSGP-GBTDJJJQSA-N geldanamycin Chemical compound N1C(=O)\C(C)=C/C=C\[C@@H](OC)[C@H](OC(N)=O)\C(C)=C/[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](OC)C[C@@H](C)CC2=C(OC)C(=O)C=C1C2=O QTQAWLPCGQOSGP-GBTDJJJQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000036541 health Effects 0.000 description 1
- NPZTUJOABDZTLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydroxybenzotriazole Substances O=C1C=CC=C2NNN=C12 NPZTUJOABDZTLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002596 immunotoxin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011081 inoculation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003211 malignant effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- BCVXHSPFUWZLGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N mecn acetonitrile Chemical compound CC#N.CC#N BCVXHSPFUWZLGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002609 medium Substances 0.000 description 1
- COTNUBDHGSIOTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N meoh methanol Chemical compound OC.OC COTNUBDHGSIOTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960000485 methotrexate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940050176 methyl chloride Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000002636 mycotoxin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000013642 negative control Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011580 nude mouse model Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001543 one-way ANOVA Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012044 organic layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000004430 oxygen atom Chemical group O* 0.000 description 1
- 229940049954 penicillin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- 239000003123 plant toxin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003389 potentiating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002035 prolonged effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002285 radioactive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 206010037844 rash Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102000027426 receptor tyrosine kinases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108091008598 receptor tyrosine kinases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000010898 silica gel chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005808 skin problem Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000046 skin rash Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 150000003384 small molecules Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;chloride;hydrate Chemical compound O.[Na+].[Cl-] HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 238000007619 statistical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229960005322 streptomycin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000010254 subcutaneous injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007929 subcutaneous injection Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000005931 tert-butyloxycarbonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(OC(*)=O)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- WHRNULOCNSKMGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran thf Chemical compound C1CCOC1.C1CCOC1 WHRNULOCNSKMGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WROMPOXWARCANT-UHFFFAOYSA-N tfa trifluoroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(F)(F)F.OC(=O)C(F)(F)F WROMPOXWARCANT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000013518 transcription Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035897 transcription Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002103 transcriptional effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001052 transient effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000014616 translation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012588 trypsin Substances 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002689 xenotransplantation Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/68—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment
- A61K47/6801—Drug-antibody or immunoglobulin conjugates defined by the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent
- A61K47/6803—Drugs conjugated to an antibody or immunoglobulin, e.g. cisplatin-antibody conjugates
- A61K47/6811—Drugs conjugated to an antibody or immunoglobulin, e.g. cisplatin-antibody conjugates the drug being a protein or peptide, e.g. transferrin or bleomycin
- A61K47/6817—Toxins
- A61K47/6831—Fungal toxins, e.g. alpha sarcine, mitogillin, zinniol or restrictocin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/68—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment
- A61K47/6835—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site
- A61K47/6851—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site the antibody targeting a determinant of a tumour cell
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/68—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment
- A61K47/6835—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site
- A61K47/6851—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site the antibody targeting a determinant of a tumour cell
- A61K47/6855—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site the antibody targeting a determinant of a tumour cell the tumour determinant being from breast cancer cell
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/68—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment
- A61K47/6835—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site
- A61K47/6851—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site the antibody targeting a determinant of a tumour cell
- A61K47/6857—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site the antibody targeting a determinant of a tumour cell the tumour determinant being from lung cancer cell
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/68—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment
- A61K47/6835—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site
- A61K47/6851—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site the antibody targeting a determinant of a tumour cell
- A61K47/6863—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site the antibody targeting a determinant of a tumour cell the tumour determinant being from stomach or intestines cancer cell
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/68—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment
- A61K47/6835—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site
- A61K47/6883—Polymer-drug antibody conjugates, e.g. mitomycin-dextran-Ab; DNA-polylysine-antibody complex or conjugate used for therapy
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/68—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment
- A61K47/6889—Conjugates wherein the antibody being the modifying agent and wherein the linker, binder or spacer confers particular properties to the conjugates, e.g. peptidic enzyme-labile linkers or acid-labile linkers, providing for an acid-labile immuno conjugate wherein the drug may be released from its antibody conjugated part in an acidic, e.g. tumoural or environment
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P43/00—Drugs for specific purposes, not provided for in groups A61P1/00-A61P41/00
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K14/00—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
- C07K14/415—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from plants
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K16/00—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies
- C07K16/18—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans
- C07K16/32—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against translation products of oncogenes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K19/00—Hybrid peptides, i.e. peptides covalently bound to nucleic acids, or non-covalently bound protein-protein complexes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K7/00—Peptides having 5 to 20 amino acids in a fully defined sequence; Derivatives thereof
- C07K7/64—Cyclic peptides containing only normal peptide links
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K2039/505—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies comprising antibodies
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2319/00—Fusion polypeptide
Description
本出願は、2016年5月31日に出願された米国仮特許出願第62/343,825号に対する優先権を主張し、この出願の内容は本明細書において参照として援用される。
本開示は、標的化抗体にコンジュゲートしてADC(抗体薬物コンジュゲート)を形成するアマニチンの誘導体を提供する。
アマトキシンは、8個のアミノ酸単位を有する剛性二環式ペプチドである。これらの化合物は、様々なキノコ種(例えば、Amanita phalloides(タマゴテングダケとしても公知)、Galerina marginata、Lepiota brunneo-incamata)から単離されるか、または合成により調製される。様々なキノコ種が、多様な量の様々なアマトキシンファミリーメンバーを含有している。このファミリーの一員であるアルファ-アマニチンは、真核生物RNAポリメラーゼII(EC2.7.7.6)の阻害剤であり、比較的程度は低いがRNAポリメラーゼIIIの阻害剤であり、それによって、転写およびタンパク質生合成を阻害することが公知である。Wieland(1983年)Int. J. Pept. Protein Res.22巻(3号):257~276頁。アルファ-アマニチンは、RNAポリメラーゼIIに非共有結合的に結合し、ゆっくり解離するため、酵素が回復する可能性は低い。転写阻害が長引くと、細胞アポトーシスが誘発されると考えられる。
本開示は、ADC(抗体薬物コンジュゲート)構造で使用される、改善されたアマトキシン誘導体を提供する。より具体的には、本開示は、式Iの構造を有する抗体薬物コンジュゲート(ADC)
[式中、
Abは、モノクローナル抗体であり、
L1-L2は、
L2-Xは、
波線は、Dとの結合点を示し、
Dは、アマトキシンから誘導された薬物部分の活性薬剤であり、以下の構造を有するアルファ-アマニチン、ベータ-アマニチン、ガンマ-アマニチン、およびイプシロン-アマニチンからなる群から選択され、
L2は、アミノ酸、10個までのアミノ酸からなるペプチド、-(CH2)p-、-(CH2CH2O)m-、-C(O)NH-、-NHC(O)-、PAB(p-アミノベンジル)、Val-Cit-PAB、Val-Ala-PAB、Ala-Ala-Asn-PAB、-R6OC(O)NR5-、-R8-S-S-R7、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択されるリンカーであり、
R5は、水素、C1~6アルキル、-(CH2)p-、-(CH2CH2O)m-、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R6は、アミノ酸、10個までのアミノ酸からなるペプチド、C1~6アルキル、-(CH2)p-、-(CH2CH2O)m-、-C(O)NH-、-NHC(O)-、PAB、Val-Cit-PAB、Val-Ala-PAB、Ala-Ala-Asn-PAB、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R7は、C2~6アルキレン、または-(CH2CH2O)m-であり、
R8は、アミノ酸、10個までのアミノ酸からなるペプチド、C1~6アルキル、C1~6アルキレン、置換C1~6アルキレン、-C(O)NH-、-C(O)-NH-CHR9-CR10R11-、-NHC(O)-CHR9-CR10R11-、-(CH2CH2O)m-、PAB、Val-Cit-PAB、Val-Ala-PAB、Ala-Ala-Asn-PAB、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R9は、水素、C1~6アルキル、C1~6アルキレン、-(CH2CH2O)m-、-C(O)NH-、-NHC(O)-、-C(O)NH-(CH2)p-SO3H、C(O)NH-(CH2)p-CO2H、-NHC(O)-(CH2)p-SO3H、-NHC(O)-(CH2)p-CO2Hおよびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R10およびR11は、それぞれ独立に、水素、C1~6アルキル、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
-R6OC(O)NR5-は、R5またはR6を介してL1と接続し、
-R8-S-S-R7-は、R8を介してL1と接続し、
mは、1~24の整数であり、
pは、1~6の整数である]。
R5は、水素、C1~6アルキル、-(CH2)p-、-(CH2CH2O)m-、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R6は、アミノ酸、10個までのアミノ酸からなるペプチド、C1~6アルキル、-(CH2)p-、-(CH2CH2O)m-、-C(O)NH-、-NHC(O)-、PAB、-Val-Cit-PAB-、-Val-Ala-PAB-、-Ala-Ala-Asn-PAB-、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R7は、C2~6アルキレン、または-(CH2CH2O)m-であり、
R8は、アミノ酸、10個までのアミノ酸からなるペプチド、C1~6アルキル、C1~6アルキレン、置換C1~6アルキレン、-C(O)NH-、-C(O)-NH-CHR9-CR10R11-、-NHC(O)-CHR9-CR10R11-、-(CH2CH2O)m-、PAB、-Val-Cit-PAB-、-Val-Ala-PAB-、-Ala-Ala-Asn-PAB-、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R9は、水素、C1~6アルキル、C1~6アルキレン、-(CH2CH2O)m-、-C(O)NH-、-NHC(O)-、-C(O)NH-(CH2)p-SO3H、C(O)NH-(CH2)p-CO2H、-NHC(O)-(CH2)p-SO3H、-NHC(O)-(CH2)p-CO2Hおよびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R10およびR11は、それぞれ独立に、水素、C1~6アルキル、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
-R6OC(O)NR5-は、R5またはR6を介してL1と接続し、
-R8-S-S-R7-は、R8を介してL1と接続し、
mは、1~24の整数であり、
pは、1~6の整数であり、残りの値は、式Iについて前述される通りである。
R5は、水素、C1~6アルキル、-(CH2)p-、-(CH2CH2O)m-、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R6は、アミノ酸、10個までのアミノ酸からなるペプチド、C1~6アルキル、-(CH2)p-、-(CH2CH2O)m-、-C(O)NH-、-NH(4-フェニル)CH2-、-Val-Cit-NH(4-フェニル)CH2-、-Val-Ala-NH(4-フェニル)CH2-、-Ala-Ala-Asn-NH(4-フェニル)CH2-、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R7は、C2~6アルキレン、または-(CH2CH2O)m-であり、
R8は、アミノ酸、10個までのアミノ酸からなるペプチド、C1~6アルキル、C1~6アルキレン、置換C1~6アルキレン、-C(O)-NH-CHR9-CR10R11-、-NHC(O)-CHR9-CR10R11-、-(CH2CH2O)m-、-PAB-、-Val-Cit-NH(4-フェニル)CH2-、-Val-Ala-NH(4-フェニル)CH2-、-Ala-Ala-Asn-NH(4-フェニル)CH2-、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R9は、水素、C1~6アルキル、C1~6アルキレン、-(CH2CH2O)m-、-C(O)NH-、-NHC(O)-、-C(O)NH-(CH2)p-SO3H、-C(O)NH-(CH2)p-CO2H、-NHC(O)-(CH2)p-SO3H、-NHC(O)-(CH2)p-CO2Hおよびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R10およびR11は、それぞれ独立に、水素、C1~6アルキル、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
-R6OC(O)NR5-は、R6を介してL1と接続し、
-R8-S-S-R7-は、R8を介してL1と接続し、
mは、1~24の整数であり、
pは、1~6の整数であり、残りの値は、式Iについて前述される通りである。
本明細書で使用される場合、一般的な有機に関する略語は、以下の通り定義される。
Ac アセチル
aq. 水性
BOCまたはBoc tert-ブトキシカルボニル
Bu n-ブチル
℃ 摂氏温度
Cit シトルリン
DCM 塩化メチレン
DEPC ジエチルシアノホスホネート
DIC ジイソプロピルカルボジイミド
DIEA ジイソプロピルエチルアミン
DMA N,N’-ジメチルアセトアミド
DMF N,N’-ジメチルホルムアミド
DMSO ジメチルスルホキシド
EDC 1-エチル-3-(3-ジメチルアミノプロピル)カルボジイミド
Et エチル
EtOAc 酢酸エチル
Eq 当量
Fmoc 9-フルオレニルメトキシカルボニル
g グラム
h 時間
HATU 2-(1H-7-アザベンゾトリアゾール-1-イル)-1,1,3,3-テトラメチルウロニウムヘキサフルオロホスフェート
HOBT N-ヒドロキシベンゾトリアゾール
HOSu N-ヒドロキシスクシンイミド
HPLC 高速液体クロマトグラフィー
LC/MS 液体クロマトグラフィー-質量分析
Me メチル
MeOH メタノール
MeCN アセトニトリル
mL ミリリットル
MS 質量分析
PAB p-アミノベンジル
RP-HPLC 逆相HPLC
rt 室温
t-Bu tert-ブチル
TEA トリエチルアミン
Tert、t 第三級
TFA トリフルオロ酢酸(Trifluoracetic acid)
THF テトラヒドロフラン
TLC 薄層クロマトグラフィー
μL マイクロリットル
酸を、DCM(塩化メチレン)に溶解させ、必要に応じてDMF(N,N’ジメチルホルムアミド)を添加して溶解を助けた。N-ヒドロキシスクシンイミド(1.5当量)を添加した後、EDC.HCl(1-エチル-3-(3-ジメチルアミノプロピル)カルボジイミド)(1.5当量)を添加した。酸の大部分が消費されるまで、反応混合物を室温で1時間撹拌した。反応の進行を、RP-HPLCによってモニタリングした。次に、混合物をDCMで希釈し、クエン酸(10%水溶液)およびブラインで逐次的に洗浄した。有機層を乾燥させ、濃縮乾固させた。粗製生成物を、RP-HPLCまたはシリカゲルカラムクロマトグラフィーによって任意選択で精製した。
この実施例は、以下「A」および「B」と示される2つの異なるアマニチン(amatinin)コンジュゲートを比較する比較研究を提供する。
この実施例は、特定の細胞においてin vitroで測定された、指定された薬物とコンジュゲートした抗体のEC50アッセイの結果(nM)を提供する。使用した抗体は、抗HER2 IgGクラスの抗体であった。以下の表においてプラスまたはマイナスの印で示される通り、様々なHer2発現レベルの7種の乳がん細胞系を、96ウェルプレートに蒔いた。ADCを連続希釈し、処理のために細胞上に添加し5日間置いた。研究の最後に、細胞増殖をPromega製CellTitreGloによって測定した。EC50(nM)を、50%細胞成長阻害濃度として決定した。成果を挙げる化合物の選択基準には、標的受容体の高い発現を伴って3nM未満のEC50で細胞系を死滅させるなどの高い有効性が含まれていた。また、成果を挙げる候補は、標的受容体の低度の発現と共に対照細胞系(MDA468)の相対的に低度の死滅によって決定される通り、低毒性および良好な治療ウィンドウを有するはずである。ADC22(図3)および24(図2)の両方を、高い有効性および良好な治療ウィンドウを伴う成果を挙げる候補として選択した。
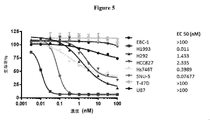
この実施例は、特定の細胞においてin vitroで測定された、本明細書に記載の指定されたADCのEC50アッセイの結果(nM)を提供する。使用した抗体は、細胞表面上の受容体チロシンキナーゼを標的とする。以下の表においてプラスまたはマイナスの印で示される通り、様々なレベルの受容体発現を伴う8種のがん細胞系を、96ウェルプレートに蒔いた。ADCを連続希釈し、処理のために細胞上に添加し5日間置いた。研究の最後に、細胞増殖をPromega製CellTitreGloによって測定した。EC50(nM)を、以下に示し、50%細胞成長阻害濃度として決定した。成果を挙げる化合物の選択基準には、標的受容体の高い発現を伴って3nM未満のEC50で細胞系を死滅させるなどの高い有効性が含まれる。また、成果を挙げる候補は、標的受容体の低度の発現と共に対照細胞系(T-47D)の相対的に低度の死滅によって決定される通り、低毒性および良好な治療ウィンドウを有するはずである。ADC25(図6)は、細胞系H1993、HCC827、SNU-5、およびH292において良好な細胞死滅有効性を示すが、Hs746T、EBC-1およびU87において有効性を示さなかった。ADC25は、陰性対照細胞系T-47Dを死滅させなかったので、良好な治療ウィンドウを示した。ADC26(図4)は、H1993およびSNu-5において良好な細胞死滅活性を示す。しかし、その他の6種の細胞系において活性ではない。ADC27(図5)は、H1993(EC50=11pM)およびSNu-5(EC50=75pM)において優れた細胞死滅活性を示す。ADC27はまた、Hs746Tおいて良好な有効性を示す(EC50=0.4nM)。ADC29(図7)は、細胞系Hs746Tにおいて良好な細胞死滅有効性を示すが、EBC-1、U87、HCC827、H1993およびT-47において有効性を示さなかった。
この実施例は、ヌードマウスのH292、HCC827、およびH1975ヒト異種移植腫瘍成長モデルにおける、低分子22、23、25、または27とコンジュゲートしたADCの有効性に関する結果を提供する。HCC827、H292、H1975細胞系を、ATCCから得た。細胞を、10%FBS(Seradigm 1500-500)およびペニシリンストレプトマイシン(Corning 30-002-CI)を含むRPMI1640 1×(Corning 10-041-CV)培地中、37℃において5%二酸化炭素加湿環境で培養した。細胞を2週間培養し、4回継代した後、収集した。細胞を、0.25%トリプシン(Corning 25-050-CI)を用いて収集した。注射前に、HCC827細胞を1:1比のHBSS(ハンクス緩衝塩溶液;Ward製470180-784)およびマトリゲル(Corning 354234)混合物に混合し、0.2ml当たり700万個の細胞を、各マウスの右上側腹部に皮下注射した。H292細胞をHBSSに再懸濁させ、0.2ml当たり500万個の細胞を、各マウスの右上側腹部に皮下注射した。H1975細胞をHBSSに再懸濁させ、0.2ml当たり300万個の細胞を、各マウスの右上側腹部に皮下注射した。
本発明の実施形態において、例えば以下の項目が提供される。
(項目1)
式Iの構造を有する抗体薬物コンジュゲート(ADC)
または薬学的に許容されるその塩
[式中、
Abは、モノクローナル抗体であり、
L 1 -L 2 は、
からなる群から選択されるリンカーであり、波線は、Abとの結合点を示し、
L 2 -Xは、
の構造を有し、R 4 は、水素、C 1~6 アルキル、または-(CH 2 CH 2 O) m -であり、mは、1~24の整数であり、波線は、Dとの結合点を示し、
L 2 は、単一アミノ酸、2~10個のアミノ酸長を有するペプチド、-(CH 2 ) p -、-(CH 2 CH 2 O) m -、-C(O)NH-、-NHC(O)-、PAB(p-アミノベンジル)、Val-Cit-PAB、Val-Ala-PAB、Ala-Ala-Asn-PAB、-R 6 OC(O)NR 5 -、-R 8 -S-S-R 7 、またはそれらの組合せからなる群から選択されるリンカーであり、R 5 は、水素、C 1~6 アルキル、-(CH 2 ) p -、-(CH 2 CH 2 O) m -、またはそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、R 6 は、アミノ酸、10個までのアミノ酸からなるペプチド、C 1~6 アルキル、-(CH 2 ) p -、-(CH 2 CH 2 O) m -、-C(O)NH-、-NHC(O)-、PAB、Val-Cit-PAB、Val-Ala-PAB、Ala-Ala-Asn-PAB、またはそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、R 7 は、C 2~6 アルキレン、-(CH 2 CH 2 O) m -からなる群から選択され、R 8 は、アミノ酸、10個までのアミノ酸からなるペプチド、C 1~6 アルキル、C 1~6 アルキレン、置換C 1~6 アルキレン、-C(O)NH-、-C(O)-NH-CHR 9 -CR 10 R 11 -、-NHC(O)-CHR 9 -CR 10 R 11 -、-(CH 2 CH 2 O) m -、PAB、Val-Cit-PAB、Val-Ala-PAB、Ala-Ala-Asn-PAB、またはそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R 9 は、水素、C 1~6 アルキル、C 1~6 アルキレン、-(CH 2 CH 2 O) m -、-C(O)NH-、-NHC(O)-、-C(O)NH-(CH 2 )p-SO 3 H、C(O)NH-(CH 2 )p-CO 2 H、-NHC(O)-(CH 2 )p-SO 3 H、-NHC(O)-(CH 2 )p-CO 2 H、またはそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
R 10 およびR 11 は、それぞれ独立に、水素、C 1~6 アルキル、またはそれらの組合せからなる群から選択され、
-R 6 OC(O)NR 5 -は、R 5 またはR 6 を介してL 1 と接続し、
-R 8 -S-S-R 7 -は、R 8 を介してL 1 と接続し、
Dは、アマトキシンから誘導された薬物部分の活性薬剤であり、アルファ-アマニチン、ベータ-アマニチン、ガンマ-アマニチン、およびイプシロン-アマニチンからなる群から選択され、
nは、1~10の整数であり、
mは、1~24の整数であり、
pは、1~6の整数である]。
(項目2)
Dが、式IIの構造
を有し、波線が、Xとの結合点を示し、
R 1 が、NH 2 またはOR 2 であり、R2が、H、またはC1~C10アルキルであり、R3が、HまたはOHである、項目1に記載のADC。
(項目3)
前記ADCが、
からなる群から選択される、項目1に記載のADC。
(項目4)
式
を有するADC。
(項目5)
式
を有するADC。
(項目6)
式
を有するADC。
(項目7)
式
を有するADC。
(項目8)
式
を有するADC。
(項目9)
式
を有するADC。
(項目10)
式
を有するADC。
Claims (21)
- 式(I)の構造を有する抗体薬物コンジュゲート(ADC)
[式中、
Abは、モノクローナル抗体であり、
L1-L2は、
L2-Xは、
L2は、(a)-R6OC(O)NR5-、および(b)-(CH2)p-、-(CH2CH2O)m-、-C(O)NH-、-NHC(O)-、またはそれらの2つ以上の組合せを含むリンカーであり、
R5は、水素、C1~6アルキル、-(CH2)p-、-(CH2CH2O)m-、または-(CH 2 ) p -および水素、-(CH 2 ) p -およびC 1-6 アルキル、-(CH 2 CH 2 O) m -および水素、-(CH 2 CH 2 O) m -およびC 1-6 アルキル、または-(CH 2 ) p -および-(CH 2 CH 2 O) m -の組合せであり、
ここで、R 5 が、-(CH 2 ) p -、-(CH 2 CH 2 O) m -、または-(CH 2 ) p -および-(CH 2 CH 2 O) m -の組合せである場合、R 5 は、L 1 、水素、またはC 1-6 アルキルと接続しており、
R6は、Val-Cit-PABまたはAla-Ala-Asn-PABであり、
ここで、-R6OC(O)NR5-は、R5またはR6を介してL1と接続し、
Dは、式(II):
ここで、R1は、NH2またはOR2であり、R2は、HまたはC1~10アルキルであり、そしてR3は、HまたはOHであり、そして
波線は、Xとの結合点を示し、
nは、1~10の整数であり、
mは、1~24の整数であり、
pは、1~6の整数である]。 - R4がC1~6である、請求項1に記載のADCまたは薬学的に許容されるその塩。
- R4がイソプロピルである、請求項9に記載のADCまたは薬学的に許容されるその塩。
- R4がメチルである、請求項9に記載のADC。
- L2が、(a)-R6OC(O)NR5-および(b)-(CH2)p-を含む、請求項1および9~12のいずれか1項に記載のADCまたは薬学的に許容されるその塩。
- R5がC1~6アルキルである、請求項1および9~13のいずれか1項に記載のADCまたは薬学的に許容されるその塩。
- R5がメチルである、請求項14に記載のADCまたは薬学的に許容されるその塩。
- R5が-(CH2)p-である、請求項1および9~13のいずれか1項に記載のADCまたは薬学的に許容されるその塩。
- nが1である、請求項1および9~16のいずれか1項に記載のADCまたは薬学的に許容されるその塩。
- R6が、Ala-Ala-Asn-PABである、請求項1および9~17のいずれか1項に記載のADCまたは薬学的に許容されるその塩。
- R6が、Val-Cit-PABである、請求項1および9~17のいずれか1項に記載のADCまたは薬学的に許容されるその塩。
- Abが、抗HER2抗体である、請求項1~20のいずれか1項に記載のADCまたは薬学的に許容されるその塩、または薬学的に許容されるその塩。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021143103A JP7403507B2 (ja) | 2016-05-31 | 2021-09-02 | 薬物としてアマトキシンの誘導体を有する抗体薬物コンジュゲート |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201662343825P | 2016-05-31 | 2016-05-31 | |
| US62/343,825 | 2016-05-31 | ||
| PCT/US2017/035206 WO2017210288A1 (en) | 2016-05-31 | 2017-05-31 | Antibody drug conjugates having derivatives of amatoxin as the drug |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021143103A Division JP7403507B2 (ja) | 2016-05-31 | 2021-09-02 | 薬物としてアマトキシンの誘導体を有する抗体薬物コンジュゲート |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2019523761A JP2019523761A (ja) | 2019-08-29 |
| JP2019523761A5 JP2019523761A5 (ja) | 2020-07-09 |
| JP7103953B2 true JP7103953B2 (ja) | 2022-07-20 |
Family
ID=60421192
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018562186A Active JP7103953B2 (ja) | 2016-05-31 | 2017-05-31 | 薬物としてアマトキシンの誘導体を有する抗体薬物コンジュゲート |
| JP2021143103A Active JP7403507B2 (ja) | 2016-05-31 | 2021-09-02 | 薬物としてアマトキシンの誘導体を有する抗体薬物コンジュゲート |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021143103A Active JP7403507B2 (ja) | 2016-05-31 | 2021-09-02 | 薬物としてアマトキシンの誘導体を有する抗体薬物コンジュゲート |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US11013816B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3471771A4 (ja) |
| JP (2) | JP7103953B2 (ja) |
| CN (2) | CN109195631B (ja) |
| CA (1) | CA3025931A1 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2017210288A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017210288A1 (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2017-12-07 | Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. | Antibody drug conjugates having derivatives of amatoxin as the drug |
| KR20230082055A (ko) | 2016-06-17 | 2023-06-08 | 마젠타 테라퓨틱스 인코포레이티드 | 세포의 고갈을 위한 조성물 및 방법 |
| TWI825007B (zh) | 2017-01-20 | 2023-12-11 | 德商海德堡醫藥研究有限責任公司 | 用於cd137+細胞耗盡(depletion)之組合物及方法 |
| CN111989122A (zh) * | 2018-04-13 | 2020-11-24 | 海德堡医药研究有限责任公司 | 用于治疗实体瘤的靶向鹅膏毒素缀合物 |
| CA3128264A1 (en) * | 2019-01-31 | 2020-08-06 | Hangzhou Dac Biotech Co., Ltd | A conjugate of an amanita toxin with branched linkers |
| EP3958908A1 (en) * | 2019-04-24 | 2022-03-02 | Heidelberg Pharma Research GmbH | Amatoxin antibody-drug conjugates and uses thereof |
| TW202144014A (zh) * | 2020-03-25 | 2021-12-01 | 大陸商江蘇恆瑞醫藥股份有限公司 | 一種抗體藥物偶聯物的製備方法 |
| JP2024509169A (ja) | 2021-03-03 | 2024-02-29 | ソレント・セラピューティクス・インコーポレイテッド | 抗bcma抗体を含む抗体-薬物コンジュゲート |
| CN113980909B (zh) * | 2021-11-16 | 2022-06-14 | 江南大学 | 一种α-鹅膏蕈碱人工抗原、单克隆抗体、杂交瘤细胞株及应用 |
| WO2023173026A1 (en) | 2022-03-10 | 2023-09-14 | Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. | Antibody-drug conjugates and uses thereof |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20120100161A1 (en) | 2009-04-08 | 2012-04-26 | Heinz Faulstich | Amatoxin-Armed Therapeutic Cell Surface Binding Components Designed for Tumour Therapy |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2947320B1 (fr) * | 2009-06-30 | 2011-07-22 | Valeo Systemes Thermiques | Vanne de commande pour un circuit de refroidissement d'un moteur de vehicule automobile |
| ES2402254T3 (es) * | 2010-09-30 | 2013-04-30 | Heidelberg Pharma Ag | Conjugados de amatoxinas con ligadores mejorados |
| JP6280103B2 (ja) * | 2012-05-15 | 2018-02-14 | ソレント・セラピューティクス・インコーポレイテッドSorrento Therapeutics, Inc. | 薬物コンジュゲート、コンジュゲーション方法およびその使用 |
| WO2014043403A1 (en) * | 2012-09-12 | 2014-03-20 | Agensys, Inc. | Amatoxin derivatives and cell-permeable conjugates thereof as inhibitors of rna polymerase |
| RU2687044C2 (ru) * | 2013-05-31 | 2019-05-06 | Дженентек, Инк. | Антитела против стеночной тейхоевой кислоты и их конъюгаты |
| EP3057610B1 (en) * | 2013-10-15 | 2021-09-22 | Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. | Drug-conjugates with a targeting molecule and two different drugs |
| US9239324B2 (en) | 2013-12-06 | 2016-01-19 | Gang Chen | Antibody-binding protein-drug conjugate and methods of use |
| EA201691023A1 (ru) * | 2013-12-16 | 2016-10-31 | Дженентек, Инк. | Пептидомиметические соединения и их конъюгаты антитела с лекарственным средством |
| US10973920B2 (en) * | 2014-06-30 | 2021-04-13 | Glykos Finland Oy | Saccharide derivative of a toxic payload and antibody conjugates thereof |
| WO2016004043A1 (en) | 2014-06-30 | 2016-01-07 | Blend Therapeutics, Inc. | Targeted conjugates and particles and formulations thereof |
| WO2017210288A1 (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2017-12-07 | Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. | Antibody drug conjugates having derivatives of amatoxin as the drug |
-
2017
- 2017-05-31 WO PCT/US2017/035206 patent/WO2017210288A1/en unknown
- 2017-05-31 JP JP2018562186A patent/JP7103953B2/ja active Active
- 2017-05-31 CA CA3025931A patent/CA3025931A1/en active Pending
- 2017-05-31 US US15/609,858 patent/US11013816B2/en active Active
- 2017-05-31 EP EP17807392.0A patent/EP3471771A4/en active Pending
- 2017-05-31 CN CN201780033085.5A patent/CN109195631B/zh active Active
- 2017-05-31 CN CN202211405532.4A patent/CN115645544A/zh active Pending
-
2021
- 2021-04-26 US US17/240,700 patent/US20210260211A1/en active Pending
- 2021-09-02 JP JP2021143103A patent/JP7403507B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20120100161A1 (en) | 2009-04-08 | 2012-04-26 | Heinz Faulstich | Amatoxin-Armed Therapeutic Cell Surface Binding Components Designed for Tumour Therapy |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| Kuhn, James L.,The Design and Synthesis of Small-Molecule Anticancer Agents Targeted Through Antibody-Drug Conjugates,A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of Baylor University In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Honors Program,2014年05月 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US11013816B2 (en) | 2021-05-25 |
| JP2019523761A (ja) | 2019-08-29 |
| CA3025931A1 (en) | 2017-12-07 |
| US20210260211A1 (en) | 2021-08-26 |
| CN109195631A (zh) | 2019-01-11 |
| WO2017210288A1 (en) | 2017-12-07 |
| JP7403507B2 (ja) | 2023-12-22 |
| JP2021183646A (ja) | 2021-12-02 |
| EP3471771A1 (en) | 2019-04-24 |
| EP3471771A4 (en) | 2020-04-15 |
| CN109195631B (zh) | 2022-11-29 |
| US20170340750A1 (en) | 2017-11-30 |
| CN115645544A (zh) | 2023-01-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7103953B2 (ja) | 薬物としてアマトキシンの誘導体を有する抗体薬物コンジュゲート | |
| US10590165B2 (en) | Antibody drug conjugates | |
| US20210283210A1 (en) | Hydrophilic antibody-drug conjugates | |
| JP2024038168A (ja) | 生物活性分子コンジュゲート、その調製法及び使用 | |
| CN109316605B (zh) | 叶酸受体结合配体-药物偶联物 | |
| KR101413955B1 (ko) | 아지리디닐-에포틸론 화합물 | |
| US20170224835A1 (en) | Antibody Drug Conjugates | |
| KR102085798B1 (ko) | 베타-갈락토사이드가 도입된 자가-희생 기를 포함하는 화합물 | |
| JP2019501141A (ja) | 受容体媒介化学療法による癌の治療のためのペプチド化合物およびペプチドコンジュゲート | |
| CA2338000C (en) | Water-soluble 4-thio-maleimido derivatives and methods for their production | |
| US6747055B1 (en) | Water-soluble drugs and methods for their production | |
| WO2017172907A1 (en) | Calicheamicin antibody drug conjugates linking an amidoacetyl group to a sugar moiety on calicheamicin | |
| US20230277676A1 (en) | Camptothecine antibody-drug conjugates and methods of use thereof | |
| CN116036303A (zh) | 一种抗体-药物偶联物及其制备方法和应用 | |
| CN113941007A (zh) | 一种串联的双药物链接组装单元及其应用 | |
| EP3442979A1 (en) | Topoisomerase poisons | |
| TW202327570A (zh) | 蒽環黴素衍生接合劑、抗體-藥物結合物及方法 | |
| CA3210473A1 (en) | Branched linkers for antibody-drug conjugates and methods of use thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200529 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20200529 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20210602 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210902 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20220301 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220531 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20220613 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20220707 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7103953 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |