JP7054587B2 - Drilling equipment and drilling method - Google Patents
Drilling equipment and drilling method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7054587B2 JP7054587B2 JP2016228477A JP2016228477A JP7054587B2 JP 7054587 B2 JP7054587 B2 JP 7054587B2 JP 2016228477 A JP2016228477 A JP 2016228477A JP 2016228477 A JP2016228477 A JP 2016228477A JP 7054587 B2 JP7054587 B2 JP 7054587B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- drill
- drilling
- printed circuit
- circuit board
- feed rate
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Drilling And Boring (AREA)
- Perforating, Stamping-Out Or Severing By Means Other Than Cutting (AREA)
Description
本発明は、多層プリント基板にドリルで穴あけを行うドリル加工装置及びドリル加工方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a drilling apparatus and a drilling method for drilling holes in a multilayer printed circuit board.
穴あけ加工においては、種々の加工条件の最適値を事前に実験的に求めておき、その最適加工条件をオペレータが装置に設定して加工を開始するのが一般的であるが、異なるワークに対して、その都度オペレータが加工条件を設定するのは面倒であり、また間違った条件設定をしてしまうおそれもある。
そこで、穴あけツールであるドリルの送り速度については、例えば特許文献1に開示されているように、その都度オペレータが設定しなくても、装置が自動的に設定することができるようにする方法もある。
In drilling, it is common to experimentally obtain the optimum values for various machining conditions in advance, and the operator sets the optimum machining conditions in the device to start machining, but for different workpieces. Therefore, it is troublesome for the operator to set the machining conditions each time, and there is a possibility that the wrong conditions are set.
Therefore, as disclosed in
ところが、特許文献1に開示されているような単純な構造のワークを堅固なドリルで加工する場合は加工条件の自動設定が可能かもしれないが、導体層と絶縁層とが交互に積層され、また導体層の厚みに変化のある多層プリント基板に耐荷重力の小さい小径ドリルで加工する場合は、全く様相が異なる。
すなわち、このような多層プリント基板の場合、切削抵抗としては、金属層である導体層を加工している時が圧倒的に大きく、またそれも導体層の厚みが厚いほど大きくなるので、加工開始時と加工終了時の負荷の差は何の意味を持たない。従って、ワークとなる多層プリント基板の内部構造に対応して加工条件を設定する必要があり、そうしないと、加工品質を落としたり、ドリルを破損したり、スピンドルでのモータ発熱、回転数低下、空気軸受の破損等の不具合を起こしたりする問題点がある。
However, when machining a workpiece with a simple structure as disclosed in
That is, in the case of such a multilayer printed circuit board, the cutting resistance is overwhelmingly large when the conductor layer, which is a metal layer, is processed, and the thicker the conductor layer, the greater the cutting resistance. The difference between the time and the load at the end of machining has no meaning. Therefore, it is necessary to set the machining conditions according to the internal structure of the multi-layer printed circuit board that is the workpiece, otherwise the machining quality will deteriorate, the drill will be damaged, the motor heat generated by the spindle, and the rotation speed will drop. There is a problem of causing problems such as damage to the air bearing.
そこで本発明は、ワークとなる多層プリント基板の特に導体層の状況を自動的に検出して加工条件を設定することができるようにすることを目的とするものである。 Therefore, it is an object of the present invention to be able to automatically detect the condition of the multi-layer printed circuit board as a work, particularly the conductor layer, and set the processing conditions.
本願において開示される代表的なドリル加工装置は、設定された加工条件で多層プリント基板のドリル加工を行うようにしたドリル加工装置において、穴あけ方向に到来する導体層を前記ドリルが通過する時間とその際の前記ドリルの送り速度とに基づいて前記導体層の厚みの合計値を検出する厚み検出部と、前記厚み検出部で検出された合計値に基づいて当該合計値に対応する最適なドリルの送り速度が実験的に求めて格納された記憶部と、前記多層プリント基板を加工する場合、前記厚み検出部で求められた当該多層プリント基板の導体層の厚みの合計値に基づいて前記記憶部から対応した前記最適なドリルの送り速度を自動的に決定し新たに設定する条件設定部とを有することを特徴とする。
A typical drilling apparatus disclosed in the present application is a drilling apparatus in which a multi-layer printed circuit board is drilled under set machining conditions, and the time required for the drill to pass through a conductor layer arriving in the drilling direction. The thickness detection unit that detects the total thickness of the conductor layer based on the feed speed of the drill at that time, and the optimum drill corresponding to the total value based on the total value detected by the thickness detection unit. When the multi-layer printed circuit board is processed, the storage unit is stored based on the total thickness of the conductor layer of the multi-layer printed circuit board obtained by the thickness detection unit. It is characterized by having a condition setting unit that automatically determines and newly sets the optimum drill feed speed corresponding to the unit.
また本願において開示される代表的なドリル加工方法は、設定された加工条件で多層プリント基板のドリル加工を行うようにしたドリル加工方法において、穴あけ方向に到来する導体層を前記ドリルが通過する時間とその際の前記ドリルの送り速度とに基づいて前記導体層の厚みの合計値を検出する厚み検出ステップと、前記厚み検出部で検出された合計値に基づいて当該合計値に対応する最適なドリルの送り速度を実験的に求めて記憶部に格納する記憶ステップと、前記多層プリント基板を加工する場合、前記厚み検出ステップで求められた当該多層プリント基板の導体層の厚みの合計値に基づいて前記記憶部から対応した前記最適なドリルの送り速度を自動的に決定し新たに設定する加工条件設定ステップと、を有することを特徴とする。
Further, a typical drilling method disclosed in the present application is a drilling method in which a multilayer printed circuit board is drilled under set processing conditions, and the time for the drill to pass through a conductor layer arriving in the drilling direction. And the thickness detection step of detecting the total value of the thickness of the conductor layer based on the feed speed of the drill at that time, and the optimum value corresponding to the total value based on the total value detected by the thickness detection unit. Based on the total value of the thickness of the conductor layer of the multilayer printed circuit board obtained in the thickness detection step and the storage step in which the feed speed of the drill is experimentally obtained and stored in the storage unit and the multilayer printed circuit board is processed. It is characterized by having a machining condition setting step for automatically determining and newly setting the optimum drill feed speed corresponding to the storage unit.
本発明によれば、多層プリント基板に対し、その都度オペレータが加工条件を設定しなくても、装置が自動的に設定することができるようにすることが可能となる。 According to the present invention, it is possible for the apparatus to automatically set the processing conditions for the multilayer printed circuit board without the operator setting the processing conditions each time.
以下、本発明の一実施例を図1~5を用いて説明する。
図2は本発明の一実施例となるドリル加工装置の構成を示す図である。図2での各構成要素や接続線は、主に本実施例を説明するために必要と考えられるものを示してあり、ドリル加工装置として必要な全てを示している訳ではない。
図2において、1は穴あけ加工をすべき多層プリント基板、2は多層プリント基板1を樹脂材から成る下板3を介して載置する加工テーブル、4は多層プリント基板1に穴をあけるためのドリル、5はドリル4を回転させるモータ内蔵型のスピンドル6を保持するスピンドルユニットである。スピンドルユニット5は、スピンドル垂直駆動部8により垂直方向に駆動される。
加工テーブル2は、多層プリント基板1に穴をあけようとする位置にドリル4が向くよう、加工テーブル駆動部7により水平方向に駆動され、位置決めされるようになっている。下板3は多層プリント基板1と加工テーブル2との間に介在する下板であり、ドリル4が多層プリント基板1を突き抜けて加工テーブル2に接触するのを防止する役目をするものである。
Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 5.
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a configuration of a drilling apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. Each component and connecting line in FIG. 2 mainly show what is considered necessary for explaining the present embodiment, and does not show all necessary for a drilling apparatus.
In FIG. 2, 1 is a multi-layer printed circuit board to be drilled, 2 is a processing table on which the multi-layer printed
The processing table 2 is horizontally driven and positioned by the processing
スピンドル6の下方側には穴あけ加工時に多層プリント基板1を押付けるためのプレッシャフット9が係合している。このプレッシャフット9はシリンダ10を介してスピンドルユニット5に連結されており、スピンドルユニット5が下降する場合、多層プリント基板1の上面位置に当接するまではスピンドルユニット5と共に下降する。
スピンドルユニット5とプレッシャフット9は互いに高さ方向に所定の間隔を保って係合していて、スピンドルユニット5が下降する場合、途中までは共に下降し、プレッシャフット9が多層プリント基板1の上面位置に当接すると、その後はプレッシャフット9がその位置にとどまり、スピンドルユニット5だけ独立に下降し、ドリル4で穴あけができるようになる。穴あけを終え、スピンドルユニット5を上昇させると、ある位置からプレッシャフット9も共に上昇するようになっている。
A
The
11は、スピンドルユニット5に固定された検出器12とプレッシャフット9に固定されたロッド13とから構成される基板上面センサである。プレッシャフット9が上昇して検出器12がロッド13の先端を光学的に検出するとON信号、プレッシャフット9が下降して検出器12がロッド13の先端を検出しなくなるとOFF信号を出力するようになっている。
従って、スピンドルユニット5を下降させた場合、プレッシャフット9が多層プリント基板1の表面に到達し、プレッシャフット9だけがそれ以上下降できなくなって、スピンドルユニット5とプレッシャフット9が垂直方向に互いにずれたことを検出した時、基板上面センサ11はON信号を出力する。また、その後スピンドルユニット5を上昇させた場合、プレッシャフット9が多層プリント基板1の上面位置から離れる時、基板上面センサ11はOFF信号を出力する。
Reference numeral 11 denotes a substrate top surface sensor composed of a
Therefore, when the
14はスピンドル6の回転や加工テーブル駆動部7、スピンドル垂直駆動部8等を制御してドリル加工装置の全体を制御する全体制御部である。全体制御部14の内部には、多層プリント基板1内にある導体層の厚みの合計Tを検出する厚み検出部15、導体層の厚みの合計値Tとその多層プリント基板1の穴あけ加工に最適なドリル4の送り速度との関係を事前に実験的に求めておいた情報が格納される最適送り速度記憶部16及びスピンドル垂直駆動部8の送り速度を選択する送り速度選択部17が設けられている。
全体制御部14は、ここで説明する以外の制御機能を有し、図示されていないブロックにも接続されている。全体制御部14は、例えばプログラム制御の処理装置を中心にして構成され、その中の各構成要素や接続線は、論理的なものも含むものとする。また各構成要素の一部は全体制御部14と別個に設けられていてもよい。
The
全体制御部14は、加工テーブル駆動部7の内部にある送り位置情報により、加工テーブル2の2次元位置を認識しながら加工テーブル駆動部7を制御するようになっており、またスピンドル垂直駆動部8の内部にある送り位置情報により、ドリル4の先端の現在の高さ位置を認識しながらスピンドル垂直駆動部8を制御するようになっている。
The
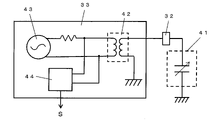
図3は図2におけるスピンドル6をさらに詳しく説明するための図であり、図2と同じものには同じ番号を付けてある。図3において、スピンドル6はモータを内蔵する構造となっており、ロータシャフト31がモータの回転子となっている。32はロータシャフト31と静電結合させるために固定子側にロータシャフト31に近接して取付けられた電極で、アースとの間で検出されるキャパシタの端子でもある。33は電極32に接続された共振検出部で、全体制御部14は共振検出部33からの共振検出信号Sを受信するようになっている。
FIG. 3 is a diagram for explaining the
図4は図3における共振検出部33を詳しく説明するための図である。図3と同じものには同じ番号をつけてある。図4において、41は電極32とアース間で検出されるキャパシタで、そのキャパシタンスは、ドリル4の先端が多層プリント基板1の導体層に接触した状態と接触していない状態では大きく変動し、前者では小さくなる。
42は二次側が電極32と接続されたトランスで、その二次側がキャパシタ41と接続された状態となっている。43はドリル4の先端が多層プリント基板1の導体層に接触した状態でのキャパシタ41が並列共振を起こす周波数の交流を発振させる発振回路、44はキャパシタ41に並列共振が起きてトランス42の一次側からみたインピーダンスが上がって一次側の両端電圧が下がったことを検出し、共振検出信号Sを送出する共振検出回路である。
FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining the
上記ドリル加工装置は以下のように動作する。加工すべき多層プリント基板1が、例えば、図1に示すように、導体層L1~L4と樹脂からなる絶縁層R1~R3が、導体層と絶縁層とが交互になるように積層されている場合を例にとり、図1及び図2を用いて説明する。導体層L1~L4の各々は銅箔、絶縁層R1~R3の各々は樹脂から成っているとする。
The drilling device operates as follows. The multilayer printed
全体制御部14は、スピンドル制御線Rによりスピンドル6を制御し、ドリル4を後述する所定の送り速度V0で回転させながら、スピンドルユニット5をスピンドル垂直駆動部8により下降させていく。先ず、プレッシャフット9が多層プリント基板1の表面に接触すると、基板上面センサ11からの検出信号が全体制御部14に入力され、全体制御部14はその時のスピンドル垂直駆動部8の送り位置情報に基づいて、多層プリント基板1の表面の高さ位置を認識できるようになっている。
The
スピンドルユニット5がさらに下降して、ドリル4が加工方向に進むと、ドリル4が導体層L1~L4の各々を通過する毎に共振検出回路44から共振検出信号Sが発生し、全体制御部14の厚み検出部15で受信される。
厚み検出部15では、共振検出信号Sの発生期間tとこの時のドリル4の送り速度V0との積から導体層L1~L4の各々の厚みを求めるとともに、それらを加算することにより導体層L1~L4の厚みの合計値Tを求め、最適送り速度記憶部16に格納する。
なお、厚みの合計値Tは、導体層L1~L4の各々での共振検出信号Sの発生期間tを加算して合計値を求め、この合計値とこの時のドリル4の送り速度の積から求めてもよい。
導体層L1~L4の厚みの合計値Tを求めたら、次に、その多層プリント基板1の穴あけ加工に対応する最適なドリル4の送り速度を実験的に求め、最適送り速度記憶部16における導体層L1~L4の厚みの合計値Tに対応させて格納する。
When the
The
The total thickness T is obtained by adding the generation periods t of the resonance detection signals S in each of the conductor layers L1 to L4 to obtain the total value, and from the product of this total value and the feed rate of the
After obtaining the total value T of the thicknesses of the conductor layers L1 to L4, the optimum feed rate of the
以上の動作を、加工する予定の各種の多層プリント基板の各々について行い、上記と同様にして、導体層の厚みの合計値Tと最適送り速度とを互いに対応させて最適送り速度記憶部16に格納する。この状態の最適送り速度記憶部16の内容を図5に示す。
最適送り速度としては、厚みが厚くなるほど切削抵抗が大きくなるので、低くするようになっている。例えば合計値TがT2以上でT3未満であれば、最適送り速度としてはV3となる。
The above operation is performed for each of the various multilayer printed circuit boards to be processed, and in the same manner as described above, the total value T of the thicknesses of the conductor layers and the optimum feed rate are made to correspond to each other in the optimum feed rate storage unit 16. Store. The contents of the optimum feed rate storage unit 16 in this state are shown in FIG.
The optimum feed rate is set to be low because the cutting resistance increases as the thickness increases. For example, if the total value T is T2 or more and less than T3, the optimum feed rate is V3.
次に、最適なドリル4の送り速度が最適送り速度記憶部16に格納されている多層プリント基板を加工する場合、ドリル加工装置は以下のように動作する。加工すべき多層プリント基板1は、図1に示す構造になっているものとする。
全体制御部14の厚み検出部15は、上記と同様の方法で多層プリント基板1の導体層L1~L4の厚みの合計値Tを求める。次に、送り速度設定部17は、厚みの合計値Tに基づいて最適送り速度記憶部16から対応する最適送り速度を選択し、ドリル4の先端の高さが基準位置Hに戻って次の穴の加工を行う前のPの時点で、スピンドル垂直駆動部8におけるドリル4の送り速度を新たに設定する。
なお、上記の所定の送り速度V0としては、装置が設定するもののなかで一番低い送り速度V4と等しい速度が設定されるものとする。
Next, when processing a multilayer printed circuit board in which the optimum feed rate of the
The
It should be noted that the predetermined feed rate V0 is set to a speed equal to the lowest feed rate V4 among those set by the apparatus.
以上の実施例によれば、自動的に導体層の厚みの合計値を検出し、それに基づいてドリル4の送り速度を厚みの合計値に対応する最適な速度に自動的に設定するようにしているので、加工品質を落としたり、ドリル4を破損したり、スピンドル6でのモータ発熱、回転数低下、空気軸受の破損等の不具合を起こしたりすることを防止できる。
また、初期動作における送り速度V0は、装置が設定するもののなかで一番低い送り速度V4としているので、当初の送り速度が速すぎて、上記の如き支障をきたすようなことを防止できる。
According to the above embodiment, the total value of the thickness of the conductor layer is automatically detected, and the feed speed of the
Further, since the feed rate V0 in the initial operation is set to the lowest feed rate V4 among those set by the apparatus, it is possible to prevent the initial feed rate from being too fast and causing the above - mentioned problems.
なお、以上の実施例において、多層プリント基板1の上に、ドリル4の食いつきを良くし、バリ等の発生を防ぐための上板を乗せるようにしてもよい。上板が例えばアルミニウムの如き金属導体から成る場合、この上板は導体層となるので、多層プリント基板1内の導体層L1~L4の場合と同様、ドリル4がここを通過する時に共振検出回路44から共振検出信号Sが発生し、厚み検出部15が算出する厚みの合計値Tには上板の厚みも含まれる。
上板は金属層なので、多層プリント基板1の導体層L1~L4と同様に絶縁層30より切削抵抗は大きく、導体層L1~L4と同様にその厚みを考慮する必要があるが、最適送り速度記憶部16には、上板の厚みも含んだ厚みの合計値Tとその場合に最適なドリル4の送り速度との関係を事前に実験的に求めて格納しておけば、上板を乗せた場合でも最適なドリル4の送り速度を選択できるようになる。
In the above embodiment, the upper plate for improving the bite of the
Since the upper plate is a metal layer, the cutting resistance is larger than that of the insulating layer 30 like the conductor layers L1 to L4 of the multilayer printed
また、以上の実施例においては、多層プリント基板1を加工する場合、導体層の厚みの合計値の検出を一つの穴あけで行い、次の穴あけから送り速度を最適値に設定するようにしたが、厚みの合計値の検出を複数の穴あけで行い、複数の穴の厚みの合計値の平均をとって最適値を選択するようにしてもよい。
Further, in the above embodiment, when processing the multilayer printed
また、以上の実施例においては、送り速度設定部17は、多層プリント基板1の導体層の厚みの合計値に基づいて最適送り速度記憶部16から対応する最適送り速度Vを選択するようにしたが、厚みの合計値に演算処理を行う等をして、対応する最適送り速度Vを決定するようにしてもよい。
Further, in the above embodiment, the feed
以上、本発明を多層プリント基板の導体層の状況に基づいて、それに対応する最適なドリルの送り速度の選択に適用する実施例を説明したが、本発明はドリルの回転数や交換時期、あるいはステップ加工を行うか否かを含めたステップ回数等、各種の加工条件の最適なものを選択する場合にも適用できる。この場合、加工条件は一つだけでなく、複数の加工条件を選択するようにしてもよい。 In the above, an embodiment in which the present invention is applied to the selection of the optimum drill feed rate corresponding to the situation of the conductor layer of the multilayer printed circuit board has been described. It can also be applied when selecting the optimum one for various machining conditions such as the number of steps including whether or not step machining is performed. In this case, not only one machining condition but also a plurality of machining conditions may be selected.
1:多層プリント基板、2:加工テーブル、3:下板 4:ドリル
5:スピンドルユニット 6:スピンドル、7:加工テーブル駆動部
8:スピンドル垂直駆動部、14:全体制御部、15:厚み検出部
16:最適送り速度記憶部、17:送り速度設定部
31:ロータシャフト、32:電極、33:共振検出部、41:キャパシタ、
42:トランス、43:発振回路、44:共振検出回路、
L1~L4:導体層、R1~R3:絶縁層、S:共振検出信号、
R:スピンドル制御線
1: Multi-layer printed circuit board 2: Machining table 3: Bottom plate 4: Drill 5: Spindle unit 6: Spindle, 7: Machining table drive unit 8: Spindle vertical drive unit, 14: Overall control unit, 15: Thickness detection unit 16: Optimal feed rate storage unit, 17: Feed speed setting unit
31: Rotor shaft, 32: Electrode, 33: Resonance detector, 41: Capacitor,
42: Transformer, 43: Oscillation circuit, 44: Resonance detection circuit,
L1 to L4: conductor layer, R1 to R3: insulating layer, S: resonance detection signal,
R: Spindle control line
Claims (4)
穴あけ方向に到来する導体層を前記ドリルが通過する時間とその際の前記ドリルの送り速度とに基づいて前記導体層の厚みの合計値を検出する厚み検出部と、
前記厚み検出部で検出された合計値に基づいて当該合計値に対応する最適なドリルの送り
速度が実験的に求めて格納された記憶部と、
前記多層プリント基板を加工する場合、前記厚み検出部で求められた当該多層プリント基
板の導体層の厚みの合計値に基づいて前記記憶部から対応した前記最適なドリルの送り速度を自動的に決定し新たに設定する条件設定部とを有することを特徴とするドリル加工装置。 In a drilling machine that drills a multilayer printed circuit board under the set machining conditions.
A thickness detection unit that detects the total thickness of the conductor layer based on the time for the drill to pass through the conductor layer arriving in the drilling direction and the feed rate of the drill at that time.
A storage unit in which the optimum drill feed rate corresponding to the total value is experimentally obtained and stored based on the total value detected by the thickness detection unit.
When processing the multilayer printed circuit board, the optimum drill feed rate corresponding to the storage unit is automatically determined from the storage unit based on the total thickness of the conductor layers of the multilayer printed circuit board obtained by the thickness detection unit. A drilling machine characterized by having a condition setting unit to be newly set.
前記厚み検出部で厚みを検出する際の前記ドリルの送り速度を、装置が設定する送り速度のなかで一番低いものとすることを特徴とするドリル加工装置。 In the drilling apparatus according to claim 1,
A drilling apparatus characterized in that the feed speed of the drill when the thickness is detected by the thickness detection unit is set to be the lowest among the feed speeds set by the apparatus.
前記導体層を前記ドリルが通過する際の前記導体層と前記ドリルとの接触を、前記ドリルが前記導体層を通過する時のアースとの間のキャパシタンスの変化に基づいて検出することを特徴とするドリル加工装置。 In the drilling apparatus according to claim 1 or 2.
It is characterized in that the contact between the conductor layer and the drill when the drill passes through the conductor layer is detected based on the change in capacitance between the drill and the ground when the drill passes through the conductor layer. Drilling equipment.
において、
穴あけ方向に到来する導体層を前記ドリルが通過する時間とその際の前記ドリルの送り速度とに基づいて前記導体層の厚みの合計値を検出する厚み検出ステップと、
前記厚み検出部で検出された合計値に基づいて当該合計値に対応する最適なドリルの送り
速度を実験的に求めて記憶部に格納する記憶ステップと、
前記多層プリント基板を加工する場合、前記厚み検出ステップで求められた当該多層プリント基板の導体層の厚みの合計値に基づいて前記記憶部から対応した前記最適なドリルの送り速度を自動的に決定し新たに設定する加工条件設定ステップとを有することを特徴とするドリル加工方法。
In the drilling method in which the multi-layer printed circuit board is drilled under the set machining conditions.
A thickness detection step for detecting the total thickness of the conductor layer based on the time for the drill to pass through the conductor layer arriving in the drilling direction and the feed rate of the drill at that time.
A storage step in which the optimum drill feed rate corresponding to the total value is experimentally obtained based on the total value detected by the thickness detection unit and stored in the storage unit .
When processing the multilayer printed circuit board, the optimum drill feed rate corresponding to the storage unit is automatically determined from the storage unit based on the total thickness of the conductor layers of the multilayer printed circuit board obtained in the thickness detection step . A drilling method characterized by having a newly set machining condition setting step.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016228477A JP7054587B2 (en) | 2016-11-25 | 2016-11-25 | Drilling equipment and drilling method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016228477A JP7054587B2 (en) | 2016-11-25 | 2016-11-25 | Drilling equipment and drilling method |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018083264A JP2018083264A (en) | 2018-05-31 |
| JP2018083264A5 JP2018083264A5 (en) | 2019-11-07 |
| JP7054587B2 true JP7054587B2 (en) | 2022-04-14 |
Family
ID=62237833
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016228477A Active JP7054587B2 (en) | 2016-11-25 | 2016-11-25 | Drilling equipment and drilling method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7054587B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7386034B2 (en) * | 2018-12-11 | 2023-11-24 | ビアメカニクス株式会社 | Drilling equipment and drilling method |
| TWI825238B (en) * | 2018-12-11 | 2023-12-11 | 日商維亞機械股份有限公司 | Drilling device and drilling method |
| CN113518505B (en) * | 2020-04-10 | 2022-10-28 | 苏州维嘉科技股份有限公司 | Circuit board drilling processing method |
| CN112372739B (en) * | 2020-10-22 | 2022-04-05 | 广东鼎泰高科技术股份有限公司 | Using method and preparation method of drill bit |
| CN112917583A (en) * | 2020-12-29 | 2021-06-08 | 吴思 | Processing method of polyurethane insulation board |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004063771A (en) | 2002-07-29 | 2004-02-26 | Hitachi Via Mechanics Ltd | Multilayer circuit board, method of processing blind hole therein and probe for measurement |
| JP2006095656A (en) | 2004-09-30 | 2006-04-13 | Doshisha | Boring machine for printed board and method for deciding boring condition of printed board using it |
| JP2008055536A (en) | 2006-08-30 | 2008-03-13 | Daihatsu Motor Co Ltd | Deep hole cutting method and machining device used therefor |
| JP2012016793A (en) | 2010-07-09 | 2012-01-26 | Sugino Machine Ltd | Piercing control method and piercing device |
| US20140093321A1 (en) | 2012-09-28 | 2014-04-03 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Printed circuit board, and method and apparatus for drilling printed circuit board |
| JP2014226764A (en) | 2013-05-25 | 2014-12-08 | 大船企業日本株式会社 | Spindle drop distance information detection mechanism and substrate processing apparatus incorporating the same |
| US20150078848A1 (en) | 2013-08-28 | 2015-03-19 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Method for Implementing High-Precision Backdrilling Stub Length Control |
| JP2015223685A (en) | 2014-05-30 | 2015-12-14 | ビアメカニクス株式会社 | Processing method and processing device |
| JP2016122825A (en) | 2014-02-21 | 2016-07-07 | ビアメカニクス株式会社 | Back drilling method and back drilling device |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3220219B2 (en) * | 1992-03-17 | 2001-10-22 | 株式会社オーエム製作所 | How to drill printed circuit boards |
| JPH05337895A (en) * | 1992-06-10 | 1993-12-21 | Hitachi Seiko Ltd | Printed circuit board drilling machine |
| JPH07223198A (en) * | 1994-02-08 | 1995-08-22 | Hitachi Ltd | Drilling method and drilling device |
| JPH09207099A (en) * | 1996-02-05 | 1997-08-12 | Ibiden Co Ltd | Commanding device for drill |
| JP3286522B2 (en) * | 1996-03-14 | 2002-05-27 | 日立ビアメカニクス株式会社 | Printed circuit board processing equipment |
| JPH10135647A (en) * | 1996-10-30 | 1998-05-22 | Hitachi Ltd | Pattern cutter |
-
2016
- 2016-11-25 JP JP2016228477A patent/JP7054587B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004063771A (en) | 2002-07-29 | 2004-02-26 | Hitachi Via Mechanics Ltd | Multilayer circuit board, method of processing blind hole therein and probe for measurement |
| JP2006095656A (en) | 2004-09-30 | 2006-04-13 | Doshisha | Boring machine for printed board and method for deciding boring condition of printed board using it |
| JP2008055536A (en) | 2006-08-30 | 2008-03-13 | Daihatsu Motor Co Ltd | Deep hole cutting method and machining device used therefor |
| JP2012016793A (en) | 2010-07-09 | 2012-01-26 | Sugino Machine Ltd | Piercing control method and piercing device |
| US20140093321A1 (en) | 2012-09-28 | 2014-04-03 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Printed circuit board, and method and apparatus for drilling printed circuit board |
| JP2014226764A (en) | 2013-05-25 | 2014-12-08 | 大船企業日本株式会社 | Spindle drop distance information detection mechanism and substrate processing apparatus incorporating the same |
| US20150078848A1 (en) | 2013-08-28 | 2015-03-19 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Method for Implementing High-Precision Backdrilling Stub Length Control |
| JP2016122825A (en) | 2014-02-21 | 2016-07-07 | ビアメカニクス株式会社 | Back drilling method and back drilling device |
| JP2015223685A (en) | 2014-05-30 | 2015-12-14 | ビアメカニクス株式会社 | Processing method and processing device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2018083264A (en) | 2018-05-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7054587B2 (en) | Drilling equipment and drilling method | |
| TWI554176B (en) | A device and a method for machining printed circuit boards | |
| KR101084517B1 (en) | Deep hole drilling apparatus | |
| CN108323019B (en) | Back drilling method on PCB | |
| US20120243952A1 (en) | On line vibration detected and intelligent control apparatus for cutting process which integrated with machine tool's i/o module and method thereof | |
| JP2020157469A (en) | Drilling device and drilling method | |
| JP2008543583A (en) | Apparatus and method for monitoring a production method for producing a through hole | |
| JP2016122825A (en) | Back drilling method and back drilling device | |
| CN114393639B (en) | Multilayer circuit board drilling method and multilayer circuit board drilling device | |
| KR20190065540A (en) | Back-drilling apparatus and back-drilling method | |
| CN111300147B (en) | Drill machining device and drill machining method | |
| WO2012063621A1 (en) | Machining apparatus | |
| JP2015223685A (en) | Processing method and processing device | |
| JP4034612B2 (en) | Blind hole machining method for multilayer circuit boards | |
| JP6909535B2 (en) | Substrate processing equipment and substrate processing method | |
| JP2020179445A (en) | Drilling device and drilling method | |
| JP6339428B2 (en) | Drill processing apparatus and drill processing method | |
| JPH09248797A (en) | Printed circuit board finishing device | |
| JP7386034B2 (en) | Drilling equipment and drilling method | |
| JP7046684B2 (en) | Drilling equipment and drilling method | |
| KR20100060414A (en) | Apparatus and method for making a printed circuit board | |
| CN111726942B (en) | Drilling device and drilling method | |
| CN109109077B (en) | Drilling device and drilling method | |
| JP6277857B2 (en) | Cutting apparatus and cutting method | |
| JP6846086B2 (en) | Drilling equipment and drilling method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190924 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190927 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20200630 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20200804 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200831 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20210217 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210419 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20211004 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20211107 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20220401 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20220401 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7054587 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |