JP7053390B2 - Damper device - Google Patents
Damper device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7053390B2 JP7053390B2 JP2018128751A JP2018128751A JP7053390B2 JP 7053390 B2 JP7053390 B2 JP 7053390B2 JP 2018128751 A JP2018128751 A JP 2018128751A JP 2018128751 A JP2018128751 A JP 2018128751A JP 7053390 B2 JP7053390 B2 JP 7053390B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- plate
- friction
- flange
- damper device
- hysteresis torque
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Mechanical Operated Clutches (AREA)
Description
本発明は、ダンパ装置、特に、入力されたトルクを出力側に伝達するとともに、トルク変動を減衰するダンパ装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a damper device, particularly a damper device that transmits an input torque to an output side and attenuates torque fluctuations.
車輌におけるアイドリング時及び走行時には、例えばエンジンから伝達されるトルク変動に起因する振動及び異音が発生する場合がある。この問題を解決するために、特許文献1に示されるようなダンパ装置が設けられている。
When the vehicle is idling and running, vibration and abnormal noise due to torque fluctuations transmitted from the engine, for example, may occur. In order to solve this problem, a damper device as shown in
特許文献1のダンパ装置は、クラッチプレートとリティニングプレートの軸方向間にスプラインハブが設けられている。そして、スプラインハブのフランジと各プレートとの間に、トーションスプリングやヒステリシストルクを発生するための摩擦部材、付勢部材等が設けられている。また、スプラインハブのボスの外周面には、ヒステリシストルクを発生するための摩擦ワッシャが設けられている。この摩擦ワッシャは、外周面がクラッチプレートの内周面に接触しており、スプラインハブに対してクラッチプレートのミスアライメントを防止する機能も有している。
The damper device of
特許文献1の装置では、クラッチプレートとリティニングプレートの軸方向間にスプラインハブが設けられ、さらにスプラインハブのフランジと各プレートとの間に摩擦部材及び付勢部材が設けられているので、スプラインハブは軸方向に所定の範囲で移動が可能である。
In the apparatus of
このため、摩擦部材等が摩耗してくると、装置の作動中にスプラインハブが軸方向に大きく移動する場合がある。そして、スプラインハブが軸方向に大きく移動すると、スプラインハブのボス外周面に設けられた摩擦ワッシャが、ボスとクラッチプレートとの間に噛み込むおそれがある。このような状況が発生すると、摩擦ワッシャが損傷したり、摩擦ワッシャの動作不良が発生したりすることになる。 Therefore, when the friction member or the like is worn, the spline hub may move significantly in the axial direction during the operation of the device. If the spline hub moves significantly in the axial direction, the friction washer provided on the outer peripheral surface of the boss of the spline hub may get caught between the boss and the clutch plate. When such a situation occurs, the friction washer may be damaged or the friction washer may malfunction.
本発明の課題は、ダンパ装置において、プレートの内周面に接触する摩擦部材の姿勢を安定させ、摩擦部材の損傷や動作不良を抑えることにある。 An object of the present invention is to stabilize the posture of a friction member in contact with the inner peripheral surface of a plate in a damper device, and to suppress damage or malfunction of the friction member.
(1)本発明に係るダンパ装置は、入力されたトルクを出力側に伝達するとともに、トルク変動を減衰する装置である。このダンパ装置は、第1回転部材と、第2回転部材と、複数の弾性部材と、第1ヒステリシストルク発生機構と、第2ヒステリシストルク発生機構と、緩衝部材と、を備えている。第1回転部材は環状の第1プレートを有する。第2回転部材は、トランスミッション側の部材に連結可能なハブと、ハブから径方向外方に延び第1プレートと軸方向に対向するフランジと、を有し、第1回転部材と相対回転可能である。複数の弾性部材は、第1回転部材と第2回転部材とを回転方向に弾性的に連結する。第1ヒステリシストルク発生機構は、弾性部材の径方向内方において第1プレートとフランジとの軸方向間に配置され、第1プレートとフランジとの相対回転時に第1ヒステリシストルクを発生する。第2ヒステリシストルク発生機構は、ハブの外周面に設けられ第1プレートの内周面と摩擦接触する環状の第1摩擦部材を有し、第1回転部材と第2回転部材との相対回転時に第2ヒステリシストルクを発生させる。緩衝部材は、第1ヒステリシストルク発生機構に設けられ、第1摩擦部材の外周面と所定の隙間をあけて配置されている。 (1) The damper device according to the present invention is a device that transmits the input torque to the output side and attenuates the torque fluctuation. This damper device includes a first rotating member, a second rotating member, a plurality of elastic members, a first hysteresis torque generating mechanism, a second hysteresis torque generating mechanism, and a cushioning member. The first rotating member has an annular first plate. The second rotating member has a hub that can be connected to a member on the transmission side, and a flange that extends radially outward from the hub and faces the first plate in the axial direction, and can rotate relative to the first rotating member. be. The plurality of elastic members elastically connect the first rotating member and the second rotating member in the rotational direction. The first hysteresis torque generation mechanism is arranged in the radial direction of the elastic member between the first plate and the flange in the axial direction, and generates the first hysteresis torque when the first plate and the flange rotate relative to each other. The second hysteresis torque generation mechanism has an annular first friction member provided on the outer peripheral surface of the hub and in frictional contact with the inner peripheral surface of the first plate, and during relative rotation between the first rotating member and the second rotating member. A second hysteresis torque is generated. The cushioning member is provided in the first hysteresis torque generation mechanism, and is arranged with a predetermined gap from the outer peripheral surface of the first friction member.
この装置では、トルク変動によって第1回転部材と第2回転部材とが相対回転し、この際、第1及び第2ヒステリシストルク発生機構によって発生するヒステリシストルクによって、トルク変動が減衰される。このような装置の作動中に、第2回転部材のフランジが軸方向に移動し、第1プレートの内周面と第1摩擦部材とが離れたとしても、緩衝部材によって第1摩擦部材の姿勢が安定する。このため、第1摩擦部材が第1プレートの内周部に噛み込む等の不具合が防止され、第1摩擦部材の損傷や、第1摩擦部材の動作不良を抑えることができる。 In this device, the first rotating member and the second rotating member rotate relative to each other due to the torque fluctuation, and at this time, the torque fluctuation is attenuated by the hysteresis torque generated by the first and second hysteresis torque generating mechanisms. Even if the flange of the second rotating member moves in the axial direction during the operation of such a device and the inner peripheral surface of the first plate and the first friction member are separated from each other, the posture of the first friction member is caused by the cushioning member. Is stable. Therefore, problems such as the first friction member getting caught in the inner peripheral portion of the first plate can be prevented, and damage to the first friction member and malfunction of the first friction member can be suppressed.
(2)好ましくは、第1ヒステリシストルク発生機構は、第1プレートに摩擦接触する環状の摩擦プレートを有している。そして、緩衝部材は、摩擦プレートの内周面に設けられている。 (2) Preferably, the first hysteresis torque generation mechanism has an annular friction plate that is in frictional contact with the first plate. The cushioning member is provided on the inner peripheral surface of the friction plate.
この場合は、第1ヒステリシストルク発生機構を構成する摩擦プレートの内周面に緩衝部材が設けられているので、構成が簡単になる。また、同様の理由により、緩衝部材を設けることによる装置の大型化を避けることができる。 In this case, since the cushioning member is provided on the inner peripheral surface of the friction plate constituting the first hysteresis torque generation mechanism, the configuration becomes simple. Further, for the same reason, it is possible to avoid increasing the size of the device by providing the cushioning member.
(3)好ましくは、緩衝部材は、軸方向に延び第1摩擦部材の外周面と対向する第1対向部を有している。 (3) Preferably, the cushioning member has a first facing portion that extends in the axial direction and faces the outer peripheral surface of the first friction member.
ここでは、第1摩擦部材が正規の位置からずれた場合、第1摩擦部材の外周面が緩衝部材の第1対向部に当接する。このため、第1摩擦部材の姿勢が大きく変化するのを抑えることができる。 Here, when the first friction member deviates from the normal position, the outer peripheral surface of the first friction member comes into contact with the first facing portion of the cushioning member. Therefore, it is possible to suppress a large change in the posture of the first friction member.
(4)好ましくは、緩衝部材は、径方向に延び第1摩擦部材の側面と対向する第2対向部を有している。 (4) Preferably, the cushioning member has a second facing portion that extends radially and faces the side surface of the first friction member.
この場合も、前記同様に、第1摩擦部材が正規の位置からずれた場合、緩衝部材の第2対向部によって、第1摩擦部材の姿勢が大きく変化するのを抑えることができる。 Also in this case, similarly, when the first friction member deviates from the normal position, the posture of the first friction member can be suppressed from being greatly changed by the second facing portion of the cushioning member.
(5)好ましくは、緩衝部材は、第1ヒステリシストルク発生機構を構成する部材よりも高い輻射率を有する。 (5) Preferably, the cushioning member has a higher emissivity than the member constituting the first hysteresis torque generation mechanism.
ここで、第1摩擦部材は熱によって変形する樹脂で形成されることが多い。したがって、第1摩擦部材が摩擦熱によって高温になると、第1摩擦部材が熱変形し、予定した摩擦抵抗が得られない。しかし、ここでは、第1摩擦部材で発生した熱を、高い輻射率を有する緩衝部材によって吸収することで、第1摩擦部材が高温になるのを抑えることができる。 Here, the first friction member is often formed of a resin that is deformed by heat. Therefore, when the temperature of the first friction member becomes high due to the frictional heat, the first friction member is thermally deformed and the expected frictional resistance cannot be obtained. However, here, by absorbing the heat generated by the first friction member by the cushioning member having a high emissivity, it is possible to suppress the temperature of the first friction member from becoming high.
(6)好ましくは、摩擦プレートは、フランジに係合する係合部を有し、フランジと相対回転不能である。 (6) Preferably, the friction plate has an engaging portion that engages with the flange and is non-rotatable relative to the flange.
摩擦プレートは摩擦により発熱する。また、第1摩擦部材からの熱が伝達される。しかし、摩擦プレートの係合部はフランジに係合しているので、摩擦プレートの熱を、係合部を介してフランジに直接伝達することができ。したがって摩擦プレートが高温になるのを避けることができる。 The friction plate generates heat due to friction. In addition, heat from the first friction member is transferred. However, since the engaging portion of the friction plate is engaged with the flange, the heat of the friction plate can be directly transferred to the flange via the engaging portion. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the friction plate from becoming hot.
(7)好ましくは、緩衝部材は、第1摩擦部材より低い弾性を有する。この場合は、第1摩擦部材が緩衝部材に当接しても、第1摩擦部材が損傷するのを避けることができる。 (7) Preferably, the cushioning member has lower elasticity than the first friction member. In this case, even if the first friction member comes into contact with the cushioning member, it is possible to prevent the first friction member from being damaged.
(8)好ましくは、緩衝部材は、第1摩擦部材よりも大きい摩擦係数を有する。この場合は、第1摩擦部材が緩衝部材に当接すると、緩衝部材の表面に対してすべりにくくなる。 (8) Preferably, the cushioning member has a higher coefficient of friction than the first friction member . In this case, when the first friction member comes into contact with the cushioning member, it becomes difficult to slip on the surface of the cushioning member.
(9)好ましくは、第1摩擦部材の第1プレートの内周面に接触する摩擦面は、第1回転部材及び第2回転部材の回転軸線に対して傾斜する傾斜面である。 (9) Preferably, the friction surface in contact with the inner peripheral surface of the first plate of the first friction member is an inclined surface inclined with respect to the rotation axes of the first rotating member and the second rotating member.
ここでは、第1プレートの内周面は傾斜面であり、この傾斜面に第1摩擦部材が摩擦接触する。このため、摩擦面積を大きく確保して面圧を小さくすることができ、摩擦部分の摩耗及び発熱を抑えることができる。 Here, the inner peripheral surface of the first plate is an inclined surface, and the first friction member is in frictional contact with the inclined surface. Therefore, a large friction area can be secured and the surface pressure can be reduced, and wear and heat generation of the friction portion can be suppressed.
また、第1摩擦部材と第1プレートとが傾斜面で当接しているので、第1摩擦部材が装着されたハブに対する第1プレートのミスアライメントを小さくしやすい。 Further, since the first friction member and the first plate are in contact with each other on an inclined surface, it is easy to reduce the misalignment of the first plate with respect to the hub on which the first friction member is mounted.
(10)好ましくは、第1摩擦部材の第1プレートの内周面に接触する摩擦面は、径方向外方に膨らむ球面の一部である。 (10) Preferably, the friction surface in contact with the inner peripheral surface of the first plate of the first friction member is a part of a spherical surface that swells outward in the radial direction.
この場合は、第1摩擦部材は第1プレートの球面に接触するので、前記同様に、摩擦面積を大きく確保することができ、摩擦部分の摩耗及び発熱を抑えることができる。また、第1摩擦部材の位置がずれたとしても、球面によって、ハブ(すなわち第2回転部材)と第1プレート(すなわち第1回転部材)とのミスアライメントを抑えることができる。 In this case, since the first friction member comes into contact with the spherical surface of the first plate, a large friction area can be secured and wear and heat generation of the friction portion can be suppressed as described above. Further, even if the position of the first friction member is displaced, the spherical surface can suppress misalignment between the hub (that is, the second rotating member) and the first plate (that is, the first rotating member).
(11)好ましくは、第1回転部材は、第2回転部材のフランジを挟んで第1プレートと軸方向において対向する第2プレートを有している。また、第2ヒステリシストルク発生機構は、環状の第2摩擦部材と、付勢部材と、を有している。第2摩擦部材は、フランジと第2プレートとの軸方向間に配置され、フランジの側面に摩擦接触する側面を有する。付勢部材は、第2摩擦部材をフランジ側に付勢する。 (11) Preferably, the first rotating member has a second plate that faces the first plate in the axial direction with the flange of the second rotating member interposed therebetween. Further, the second hysteresis torque generation mechanism has an annular second friction member and an urging member. The second friction member is arranged between the flange and the second plate in the axial direction, and has a side surface that is in frictional contact with the side surface of the flange. The urging member urges the second friction member toward the flange side.
以上のような本発明では、ダンパ装置において、プレートの内周面に接触する摩擦部材の姿勢を安定させ、摩擦部材の損傷や動作不良を抑えることができる。 In the present invention as described above, in the damper device, the posture of the friction member in contact with the inner peripheral surface of the plate can be stabilized, and damage or malfunction of the friction member can be suppressed.
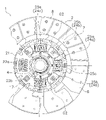
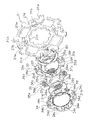
図1は、本発明の第1実施形態によるダンパ装置を有するクラッチディスク組立体の断面図である。図1のO-O線は、クラッチディスク組立体1の回転軸線である。このクラッチディスク組立体1は、図1の左側に配置されるエンジン及びフライホイールからのトルクを、図1の右側に配置されるトランスミッションに伝達し、かつトルク変動を減衰する。また、図2はクラッチディスク組立体1の正面部分図である。
FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view of a clutch disc assembly having a damper device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The OO line in FIG. 1 is the rotation axis of the
[全体構成]
クラッチディスク組立体1は、摩擦係合によりフライホイールからトルクが入力されるクラッチディスク2と、クラッチディスク2から入力されるトルク変動を減衰及び吸収するダンパ機構3(ダンパ装置)と、スプラインハブ4と、を有している。
[overall structure]
The
[クラッチディスク2]
クラッチディスク2は、図示しないプレッシャプレートによってフライホイールに押し付けられる。クラッチディスク2は、クッショニングプレート6と、クッショニングプレート6の両面にリベット7によって固定される1対の摩擦フェーシング8と、を有している。クッショニングプレート6はダンパ機構3の外周部に固定されている。
[Clutch disc 2]
The
[ダンパ機構3]
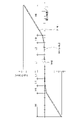
ダンパ機構3は、エンジンから伝達されるトルク変動を効果的に減衰及び吸収するために、図3に示すように、正側(駆動側の回転方向)及び負側において4段の捩り特性を有している。具体的には、捩り特性の正側及び負側において、1段目(L1)領域及び2段目(L2)領域は低捩り剛性及び低ヒステリシストルクの領域であり、3段目(H3)領域及び4段目(H4)領域は高捩り剛性及び高ヒステリシストルクの領域である。
[Damper mechanism 3]
As shown in FIG. 3, the
ダンパ機構3は、低剛性ダンパ11と、高剛性ダンパ12と、全領域ヒステリシストルク発生機構(以下、「L-Hヒス発生機構」と記す)13(第2ヒステリシストルク発生機構の一例)と、低捩り角度領域ヒステリシストルク発生機構(以下、「Lヒス発生機構」と記す)14と、中捩り角度領域ヒステリシストルク発生機構(以下、「L2ヒス発生機構」と記す)15と、高捩り角度領域ヒステリシストルク発生機構(以下、「Hヒス発生機構」と記す)16(第1ヒステリシストルク発生機構の一例)と、ストッパ機構17と、を有している。
The
低剛性ダンパ11は、低捩り角度領域(L1+L2)で作動する。高剛性ダンパ12は、低捩り角度領域よりも捩り角度の大きい高捩り角度領域(H3+H4)で作動する。また、高剛性ダンパ12は低剛性ダンパ11よりも高い捩り剛性を有する。
The low-
L-Hヒス発生機構13は、低捩り角度領域(L1+L2)及び高捩り角度領域(H3+H4)の全捩り角度領域においてヒステリシストルクを発生する機構である。Lヒス発生機構14は、低捩り角度領域の全領域(L1+L2)でのみヒステリシストルクを発生する機構である。L2ヒス発生機構15は、2段目の第2捩り角度領域(L2)でのみヒステリシストルクを発生する機構である。Hヒス発生機構16は、高捩り角度領域(H3+H4)でのみヒステリシストルクを発生する機構である。
The LH
ストッパ機構17は、入力側の部材であるクラッチディスク2と、出力側の部材であるスプラインハブ4と、の捩り角度(相対回転角度)が所定の角度になると、それ以上の両部材の相対回転角度を禁止する機構である。
When the twist angle (relative rotation angle) of the
<高剛性ダンパ12>
高剛性ダンパ12は、図4に示すように、入力側回転部材20(第1回転部材の一例)と、ハブフランジ21と、複数の高剛性スプリング22と、を有している。
<
As shown in FIG. 4, the high-
-入力側回転部材20-
入力側回転部材20には、クラッチディスク2を介してエンジンからトルクが入力され、クラッチプレート24(第1プレートの一例)及びリティニングプレート25を有している。
-Input side rotating member 20-
Torque is input to the input-
クラッチプレート24及びリティニングプレート25は、実質的に環状に形成され、軸方向に間隔を隔てて配置されている。クラッチプレート24はエンジン側に配置され、リティニングプレート25はトランスミッション側に配置されている。クラッチプレート24及びリティニングプレート25は、外周部がストップピン26によって連結されており、一体で回転する。
The
クラッチプレート24及びリティニングプレート25には、図2に示すように、それぞれ4個の第1保持部24a,25a及び第2保持部24b,25bが円周方向に間隔を隔てて形成されている。第1保持部24a,25aと第2保持部24b,25bとは円周方向に交互に配置されている。また、リティニングプレート25には、複数の係合孔25cが形成されている。
As shown in FIG. 2, four
なお、図2では、リティニングプレート25を示しているが、各保持部24a,24b,24b,25bに関しては、逆側に配置されたクラッチプレート24も同様の構成である。また、図2では、リティニングプレート25の一部を破断して示している。
Although the thinning
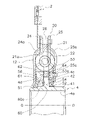
-ハブフランジ21-
ハブフランジ21は、略円板状の部材であり(図7参照)、スプラインハブ4の外周に配置されている。ハブフランジ21は、クラッチプレート24とリティニングプレート25との軸方向間に配置され、これらの両プレート24,25と所定の角度範囲内で相対回転可能である。図5に示すように、ハブフランジ21とスプラインハブ4とは、互いの内周部及び外周部に形成された複数の歯21c,4cによって噛み合っている。すなわち、ハブフランジ21とスプラインハブ4とが第2回転部材の一例である。なお、互いの歯21c,4cの間には所定の隙間G1が設定されている。すなわち、ハブフランジ21とスプラインハブ4とは、歯21c,4cの隙間G1の角度分(低捩り角度領域(L1+L2)に相当)だけ相対回転が可能である。
-Hub flange 21-
The
ハブフランジ21には、図5に示すように、クラッチプレート24及びリティニングプレート25の第1保持部24a,25a及び第2保持部24b,25bと対向する位置に、それぞれ第1窓孔21a及び第2窓孔21bが形成されている。そして、第1窓孔21aに第1高剛性スプリング22aが収容され、この第1高剛性スプリング22aがクラッチプレート24及びリティニングプレート25の第1保持部24a,25aによって軸方向及び径方向に保持されている。また、第2窓孔21bに第2高剛性スプリング22bが収容され、この第2高剛性スプリング22bがクラッチプレート24及びリティニングプレート25の第2保持部24b,25bによって軸方向及び径方向に保持されている。
As shown in FIG. 5, the
なお、クラッチプレート24及びリティニングプレート25の第1保持部24a,25a及び第2保持部24b,25bの円周方向の両端は、各高剛性スプリング22a,22bの端面に係合可能である。
Both ends of the
ここで、ハブフランジ21の第1窓孔21aには第1高剛性スプリング22aが、第2窓孔21bには第2高剛性スプリング22bが、それぞれ円周方向に隙間なく配置されている。一方、クラッチプレート24及びリティニングプレート25の第1保持部24a,25aには第1高剛性スプリング22aが円周方向に隙間なく配置されているが、両プレート24,25の第2保持部24b,25bには、第2高剛性スプリング22bが円周方向に隙間G2(図2及び図5参照)を介して配置されている。この隙間G2が3段目の捩り角度分(角度領域H3)に相当している。
Here, the first high-
なお、ハブフランジ21の第2窓孔21bのそれぞれの内周側には、軸方向に貫通する係合孔21eが形成されている。
An
以上の構成により、詳細は後述するが、高捩り角度領域H3,H4では、まず第1高剛性スプリング22aのみが圧縮され(H3領域)、その後、第1高剛性スプリング22aに加えて第2高剛性スプリング22bが圧縮される(H4領域)ことになる。
With the above configuration, although details will be described later, in the high torsion angle regions H3 and H4, only the first high-
<ストッパ機構17>
ストッパ機構17は、図5に示すように、ハブフランジ21の外周部に形成された複数のストッパ用切欠21dと、前述のストップピン26と、から構成されている。ストッパ用切欠21dは、所定の角度範囲にわたって形成されており、径方向外方に開いている。そして、このストッパ用切欠21dをストップピン26が軸方向に貫通している。
<
As shown in FIG. 5, the
また、切欠21dは、円周方向の両端部が内周側に向かって深く形成され、中央部分が浅く形成されている。この浅い部分の内周側に、第2窓孔21bが形成されている。
Further, in the
<低剛性ダンパ11>
低剛性ダンパ11は、図6及び図7に示すように、サブプレート34及びスプリングホルダ35と、ドライブプレート36と、複数の低剛性スプリング37と、を有している。
<
As shown in FIGS. 6 and 7, the low-
-サブプレート34-
サブプレート34は、クラッチプレート24とハブフランジ21との軸方向間に配置され、ほぼ矩形であって、角部が円弧状に形成されている。サブプレート34は、図7に示すように、中央部に円形の開口を有しており、それぞれ2個の第1保持部34a及び第2保持部34bと、4個の第1係合突起34cと、第1係合突起34cより突起長さが短い4個の第2係合突起34dと、環状溝34eと、を有している。
-Sub-plate 34-
The sub-plate 34 is arranged between the
第1保持部34a及び第2保持部34bは、各係合突起34cの内周側に形成されている。4個の第1係合突起34cは、4つの角部外周にハブフランジ21側に突出して形成されている。環状溝34eは第1保持部34a及び第2保持部34bの内周側で、開口部の縁に形成されている。
The
-スプリングホルダ35-
スプリングホルダ35は、サブプレート34とハブフランジ21との軸方向間で、サブプレート34と間隔をあけて対向して配置されている。スプリングホルダ35はサブプレート34とほぼ同様の形状である。スプリングホルダ35は、中央部に円形の開口を有しており、それぞれ2個の第1保持部35a及び第2保持部35bと、4個のボス部35cと、4個の切欠35dと、を有している。各ボス部35cには切欠35eが形成されている。また、第2保持部35bの円周方向両端には、円周方向に延びる円弧状溝35fが形成されている。
-Spring holder 35-
The
第1保持部35a及び第2保持部35bは、それぞれサブプレート34の第1保持部34a及び第2保持部34bと対向する位置に形成されている。4個のボス部35cは、4つの角部外周に形成されている。この4個のボス部35cの切欠35eにサブプレート34の第1係合突起34cが係合し、さらにボス部35cがハブフランジ21の係合孔21eに係合している。このように、第1係合突起34c及びボス部35cが係合孔21eに圧入されることで、サブプレート34はハブフランジ21に対して軸方向に移動不能になっている。また、切欠35dは、サブプレート34の第2係合突起34dに対応して形成されており、この切欠35dに第2係合突起34dが係合している。
The
なお、サブプレート34の第1係合突起34cは先端に爪を有していてもよい。この場合、第1係合突起34cの先端部は、切欠35e及びハブフランジ21の係合孔21eを貫通し、先端の爪がハブフランジ21の側面に係合する。これにより、サブプレート34はハブフランジ21に対して軸方向に移動不能となる。
The first
以上のように、サブプレート34とスプリングホルダ35とが、第1係合突起34cと切欠35eとの係合、及び第2係合突起34dと切欠35dとの係合、によって一体化されている。そして、スプリングホルダ35とハブフランジ21とが、第1係合突起34c及びボス部35cと係合孔21eとの係合によって一体化されている。したがって、サブプレート34及びスプリングホルダ35はハブフランジ21と一体に回転する。
As described above, the sub-plate 34 and the
-ドライブプレート36-
ドライブプレート36は、サブプレート34とスプリングホルダ35との軸方向間に配置され、サブプレート34及びスプリングホルダ35と所定の角度範囲内で相対回転可能である。ドライブプレート36は、中央部に開口を有しており、それぞれ2個の第1窓孔36a及び第2窓孔36bと、ドライブプレート36の内周面に形成された複数の係合凹部36cと、を有している。
-Drive plate 36-
The
また、第1窓孔36aの内周端部の両側には、それぞれ円周方向に延びる第1係合溝36dが形成されている。第2窓孔36bの内周端部の一方側には、円周方向に延びる第2係合溝36eが形成されている。
Further, first engaging
第1窓孔36a及び第2窓孔36bは、それぞれサブプレート34及びスプリングホルダ35の第1保持部34a,35a及び第2保持部34b,35bと対向する位置に形成されている。そして、第1窓孔36aに第1低剛性スプリング37aが収容され、この第1低剛性スプリング37aがサブプレート34及びスプリングホルダ35の第1保持部34a,35aによって軸方向及び径方向に保持されている。また、第2窓孔36bに第2低剛性スプリング37bが収容され、この第2低剛性スプリング37bがサブプレート34及びスプリングホルダ35の第2保持部34b,35bによって軸方向及び径方向に保持されている。
The
なお、サブプレート34及びスプリングホルダ35の第1保持部34a,35a及び第2保持部34b,35bの円周方向の両端は、各低剛性スプリング37a,37bの端面に係合可能である。
Both ends of the
ここで、ドライブプレート36の第1窓孔36aには第1低剛性スプリング37aが、第2窓孔36bには第2低剛性スプリング37bが、それぞれ円周方向に隙間なく配置されている。一方、サブプレート34及びスプリングホルダ35の第1保持部34a,35aには第1低剛性スプリング37aが円周方向に隙間なく配置されているが、両部材34,35の第2保持部34b,35bには、第2低剛性スプリング37bが円周方向に隙間を介して配置されている。この隙間が1段目の捩り角度分(低捩り角度領域L1)に相当している。
Here, the first low-
低剛性スプリング37のバネ定数は、高剛性スプリング22のバネ定数に比べて大幅に小さく設定されている。すなわち、高剛性スプリング22は低剛性スプリング37よりもはるかに剛性が高い。このため、1段目領域(L1)及び2段目領域(L2)では、高剛性スプリング22は圧縮されず、低剛性スプリング37のみが圧縮される。
The spring constant of the low-
[スプラインハブ4]
スプラインハブ4は、クラッチプレート24及びリティニングプレート25の内周側に配置されている。スプラインハブ4は、図4及び図6に示すように、軸方向に延びる筒状のボス41と、ボス41から径方向外側に延びるフランジ42と、を有している。ボス41の内周部には、トランスミッションの入力シャフト(図示せず)に係合するスプライン孔4aが形成されている。
[Spline Hub 4]
The
ボス41の外周面において、フランジ42のエンジン側には複数の係合凸部4dが形成されている。係合凸部4dはドライブプレート36の係合凹部36cに、実質的に隙間なく係合している。また、フランジ42の外周面には、歯4cが形成されている。図5で説明したように、この歯4cが、ハブフランジ21の歯21cと噛合可能であり、両歯4c,21cの円周方向間には隙間G1が存在する。
On the outer peripheral surface of the
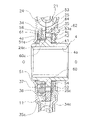
<L-Hヒス発生機構13>
L-Hヒス発生機構13は、捩り角度領域の全領域(L1+L2+H3+H4)においてヒステリシストルクHを発生する。
<LH
The LH
L-Hヒス発生機構13は、図6に示すように、第1摩擦ワッシャ51(第1摩擦部材の一例)と、第2摩擦ワッシャ52と、第1コーンスプリング54と、を有している。
As shown in FIG. 6, the LH
第1摩擦ワッシャ51は、樹脂製であり、スプラインハブ4のボス41の外周において、係合凸部4dの側面とクラッチプレート24の内周端部との間に配置されている。より詳細には、第1摩擦ワッシャ51の外周面において、クラッチプレート24側の角部は、軸方向の外側(クラッチプレート24側)に向かって径が小さくなる傾斜面51aとなっている。また、クラッチプレート24の内周端面は、この傾斜面51aに当接する傾斜面24cとなっている。
The
第2摩擦ワッシャ52は、樹脂製であり、スプラインハブ4のフランジ42とリティニングプレート25の内周端部との軸方向間に配置されている。第2摩擦ワッシャ52の外周部には、後述する第3摩擦ワッシャ53に係合する係合部(図示せず)を有しており、両部材は一体回転する。
The
また、第1コーンスプリング54は、第2摩擦ワッシャ52とリティニングプレート25の内周端部との軸方向間に配置され、第2摩擦ワッシャ52とリティニングプレート25とが互いに離れるように、両部材25,52を付勢している。
Further, the
以上から、クラッチプレート24及びリティニングプレート25と、スプラインハブ4と、が相対回転する全捩り角度領域において、第1摩擦ワッシャ51とクラッチプレート24又はスプラインハブ4との間に摩擦抵抗が発生するとともに、第2摩擦ワッシャ52とスプラインハブ4との間に摩擦抵抗が発生する。これらの摩擦抵抗によって、全捩り角度領域においてヒステリシストルクHが発生する。
From the above, frictional resistance is generated between the
<Lヒス発生機構14>
Lヒス発生機構14は、1段目領域及び2段目領域である低捩り角度領域の全領域(L1+L2)でのみヒステリシストルクhLを発生する。
<L
The L
Lヒス発生機構14は、図7に示すように、サブプレート34の環状溝34eに装着された付勢部材としての波線56を有している。波線56は、一部に欠落部を有する環状の線材で形成されている。波線56は、円周方向に所定の間隔で複数の押圧部56aを有している。押圧部56aはドライブプレート36側に突出して形成されており、弾性変形が可能である。また、押圧部56aの先端部は、ドライブプレート36の各窓孔36a,36bに形成された第1及び第2係合溝36d,36eに係合可能である。このように、波線56は、ドライブプレート36に対して相対回転不能であり、かつ環状溝34e内で円周方向に移動可能である。そして、波線56の弾性変形によって、ドライブプレート36がスプリングホルダ35側に付勢されている。
As shown in FIG. 7, the L-his
ここで、前述のように、サブプレート34及びスプリングホルダ35はハブフランジ21と一体回転する。また、ドライブプレート36はスプラインハブ4と一体回転する。そして、ハブフランジ21とスプラインハブ4とは、前述のように、隙間G1の角度分だけ相対回転可能である。言い換えれば、ハブフランジ21(スプリングホルダ35と一体回転)とスプラインハブ4(ドライブプレート36と一体回転)とは、捩り特性の1段目領域と2段目領域の低捩り角度領域の全領域(L1+L2)においてのみ相対回転可能である。
Here, as described above, the sub-plate 34 and the
そして、スプリングホルダ35とドライブプレート36とは、波線56によって互いに押圧されているので、スプリングホルダ35とドライブプレート36とは低捩り角度の全領域(L1+L2)においてのみ相対回転して摩擦抵抗が生じる。また、波線56とサブプレート34の環状溝34eの底部との間にも摩擦抵抗が生じる。これらの摩擦抵抗によって、ヒステリシストルクhLが発生する。
Since the
ここでは、サブプレート34の環状溝34eに波線56が埋め込まれるように装着されているので、軸方向寸法を抑えて、ヒステリシストルク発生機構を実現できる。また、スプリングホルダ35とドライブプレート36との間だけではなく、波線56とサブプレート34の環状溝34eの底部との間にも摩擦抵抗が生じるので、各部における摩擦抵抗を小さくして所望のヒステリシストルクが得られる。したがって、各部の磨耗を抑えることができる。
Here, since the
<L2ヒス発生機構15>
L2ヒス発生機構15は、2段目の捩り角度領域(L2)でのみヒステリシストルクhL2を発生する。
<L2
The L2
L2ヒス発生機構15はウェーブスプリング60を有している。ウェーブスプリング60は、軸方向に弾性変形可能な環状の弾性体であり、軸方向に圧縮された状態でスプラインハブ4のフランジ42とスプリングホルダ35との間に配置されている。ウェーブスプリング60は、ハブフランジ21及びスプリングホルダ35に当接しており、ハブフランジ21に対して回転すると摩擦抵抗を発生する。
The L2
図8に、ウェーブスプリング60及びその周辺の部材を抽出して示している。ウェーブスプリング60は、環状の本体部60aと、本体部60aから径方向外側へ延びる2対の爪部60bと、を有している。爪部60bの先端部は、軸方向に折り曲げられており、スプリングホルダ35に形成された円弧状溝35fを通過して第2低剛性スプリング37bの両端部に当接している。2つの爪部60b間の円周方向の距離は、第2低剛性スプリング37bの自由長とほぼ一致している。これにより、第2低剛性スプリング37bによりウェーブスプリング60の円周(回転)方向の位置決めが行われるとともに、第2低剛性スプリング37b及びウェーブスプリング60は一体で回転可能となっている。なお、溝35fの円周方向の距離は、2つの爪部60b間の円周方向の距離より長い。
FIG. 8 shows the
また、本体部60aの内周部には、複数の係合凹部60cが形成されている。係合凹部60cは、スプラインハブ4の係合凸部4dに所定の隙間を介して係合している。この隙間が、1段目の捩り角度領域(L1)の角度分に相当している。したがって、1段目領域ではウェーブスプリング60によるヒステリシストルクは発生しないが、2段目領域(L2)でのみウェーブスプリング60によるヒステリシストルクhL2が得られる。
Further, a plurality of engaging
<Hヒス発生機構16>
Hヒス発生機構16は、3段目領域及び4段目領域である高捩り角度領域(H3+H4)でのみヒステリシストルクhHを発生する。
<H
The H
Hヒス発生機構16は、図4及び図6に示すように、サブプレート34に装着された環状の第1摩擦材61(サブプレート34及び第1摩擦材61が摩擦プレートの一例である)と、環状の第2摩擦材62を有する第3摩擦ワッシャ53と、第2コーンスプリング64と、を有している。
As shown in FIGS. 4 and 6, the H-his
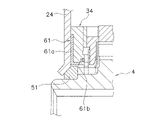
第1摩擦材61は、サブプレート34のエンジン側の側面に固定されており、サブプレート34とともにハブフランジ21と一体回転する。そして、第1摩擦材61は、クラッチプレート24の内周部の側面に当接可能である。また、第1摩擦材61は、図9に拡大して示すように、断面がL字状に形成されている。
The
より詳細には、第1摩擦材61は、摩擦部61a及び緩衝部61b(緩衝部材の一例)を有している。第1摩擦材61は、例えば、熱可塑性エラストマー等の樹脂材料で形成されており、第1摩擦ワッシャ51よりも弾性が低く、かつ摩擦係数が大きい。また、第1摩擦材61は、Hヒス発生機構16を構成する他の部材よりも、高い輻射率を有している。
More specifically, the
摩擦部61aは、クラッチプレート24の側面に摩擦接触する部分であり、円板状に形成されている。緩衝部61bは、摩擦部61aの内周端からリティニングプレート25側に軸方向に延びている。緩衝部61bは、第1摩擦ワッシャ51の外周面に対して、径方向に所定の隙間をあけて対向する位置に配置されている。
The
第3摩擦ワッシャ53は、ハブフランジ21内周部とリティニングプレート25内周部との間に配置されており、リティニングプレート25側に突出する複数の係合突起53aを有している。この係合突起53aがリティニングプレート25の係合孔25cに係合している。したがって、第3摩擦ワッシャ53はリティニングプレート25と一体回転する。第2摩擦材62は、第3摩擦ワッシャ53のハブフランジ21側の側面に固定され、ハブフランジ21の内周部の側面に摩擦接触する。
The
第2コーンスプリング64は、第3摩擦ワッシャ53とリティニングプレート25との間に配置されている。第2コーンスプリング64は、第3摩擦ワッシャ53とリティニングプレート25とを、両者が軸方向に互いに離れる方向に付勢している。したがって、第2コーンスプリング64により、第1摩擦材61とクラッチプレート24とが互いに押圧され、第2摩擦材62とハブフランジ21とが互いに押圧される。
The
以上から、クラッチプレート24及びリティニングプレート25と、ハブフランジ21と、が相対回転する高捩り角度領域の全領域(H3+H4)において、第1摩擦材61とクラッチプレート24との間、及び第2摩擦材62とハブフランジ21との間において摩擦抵抗が生じる。これらの摩擦抵抗によって、ヒステリシストルクhHが発生する。
From the above, in the entire region (H3 + H4) of the high torsional angle region where the
以上をまとめると、図3に示すように、各角度領域では以下のようなヒステリシストルクが発生する。 Summarizing the above, as shown in FIG. 3, the following hysteresis torques are generated in each angle region.
1段目領域(L1):H(L-Hヒス発生機構13)+hL(Lヒス発生機構14)
2段目領域(L2):H+hL+hL2(L2ヒス発生機構15)
3段目領域及び4段目領域(H3+H4):H+hH(Hヒス発生機構16)
以上のヒステリシストルク発生機構13~16によるヒステリシストルクについて、低捩り角度領域(L1+L2)におけるL-Hヒス発生機構13によるヒステリシストルクHと、Lヒス発生機構14によるヒステリシストルクhLと、の割合は、ヒステリシストルクhLが50%以上であることが望ましい。
First stage region (L1): H (L—H hiss generation mechanism 13) + hL (L hiss generation mechanism 14)
Second stage region (L2): H + hL + hL2 (L2 hiss generation mechanism 15)
3rd stage region and 4th stage region (H3 + H4): H + hH (H hiss generation mechanism 16)
Regarding the hysteresis torque by the above-mentioned hysteresis
[動作]
本実施形態のクラッチディスク組立体1の捩り特性は、角度範囲の大きさは異なるが基本的に正側と負側とで対称である。したがって、ここでは正側のみの動作を説明し、負側の動作についての説明は省略する。
[motion]
The torsional characteristics of the
<1段目>
伝達トルク及びトルク変動が小さい場合は、本装置は捩り特性の1段目(L1)で作動する。この1段目では、剛性の低い第1及び第2低剛性スプリング37a,37bのうち、自由長が長い第1低剛性スプリング37aのみが圧縮される。このため、サブプレート34及びスプリングホルダ35と、ドライブプレート36と、が相対回転する。一方で、第1及び第2高剛性スプリング22a,22bは剛性が高いためにほとんど圧縮されない。したがって、入力側回転部材20(クラッチプレート24及びリティニングプレート25)とハブフランジ21とは一体回転する。
<1st stage>
When the transmission torque and torque fluctuation are small, this device operates in the first stage (L1) of the torsion characteristics. In this first stage, of the low-rigidity first and second low-
以上から、捩り特性の1段目では、{入力側回転体20+ハブフランジ21+サブプレート34+スプリングホルダ35}が一体回転し、これらの部材に対して{ドライブプレート36+スプラインハブ4}が回転する。
From the above, in the first stage of the twisting characteristic, {input
この場合は、L-Hヒス発生機構13によるヒステリシストルクHと、Lヒス発生機構14によるヒステリシストルクhLとが発生する。具体的には、第1摩擦ワッシャ51とクラッチプレート24又はスプラインハブ4との間、及び第2摩擦ワッシャ52とスプラインハブ4との間、において摩擦抵抗が発生する。また、同時に、波線56とサブプレート34との間、及びドライブプレート36とスプリングホルダ35との間においても摩擦抵抗が発生する。
In this case, the hysteresis torque H by the LH
なお、ウェーブスプリング60は爪部60bが第2低剛性スプリング37bに係合しているので、この1段目ではウェーブスプリング60は自由に回転し得る状態であり、ウェーブスプリング60とハブフランジ21との間には摩擦抵抗は発生しない。
Since the
<2段目>
伝達トルク又はトルク変動がより大きくなると、第1低剛性スプリング37aが圧縮されつつ、さらに自由長の短い第2低剛性スプリング37bも圧縮され始める。第1低剛性スプリング37aと第2低剛性スプリング37bとは並列に配置されているので、第2低剛性スプリング37bが圧縮され始めると、第1低剛性スプリング37aのみが圧縮されている場合(1段目)に比較して捩り剛性は高くなる。すなわち、捩り特性の2段目に移行する。
<2nd stage>
When the transmission torque or the torque fluctuation becomes larger, the first low-
この2段目においては、1段目と同様のヒステリシストルク発生機構13,14に加えて、L2ヒス発生機構15が作動する。
In this second stage, the L2
すなわち、1段目と同様の部材間に摩擦抵抗が発生するとともに、ウェーブスプリング60とハブフランジ21との間においても摩擦抵抗が発生する。具体的には、第2低剛性スプリング37bが圧縮されると、第2低剛性スプリング37bが圧縮された分だけウェーブスプリング60がハブフランジ21に対して回転し、両部材60,21間に摩擦抵抗が発生する。したがって、2段目においては、1段目と同様のヒステリシストルクH+hLに加えて、ウェーブスプリング60とハブフランジ21との間の摩擦抵抗によるヒステリシストルクhL2が発生する。
That is, frictional resistance is generated between the same members as in the first stage, and frictional resistance is also generated between the
<3段目>
伝達トルク又はトルク変動がさらに大きくなると、第1及び第2低剛性スプリング37a,37bがさらに圧縮され、スプラインハブ4に対して入力側回転部材20がさらに回転する。すると、ハブフランジ21の歯21cとスプラインハブ4の歯4cとが当接し、ハブフランジ21とスプラインハブ4とは一体に回転することになる。この状態では、第1及び第2低剛性スプリング37a,37bは先の状態以上に圧縮されることはなく、高剛性スプリング22のうちの自由長の長い第1高剛性スプリング22aの圧縮が開始される。第1高剛性スプリング22aは第1及び第2低剛性スプリング37a,37bよりも剛性が高いので、2段目よりもさらに高い3段目の捩り剛性が得られる。
<Third stage>
When the transmission torque or the torque fluctuation becomes larger, the first and second low-
3段目においては、第1高剛性スプリング22aが圧縮されるので、入力側回転部材20とハブフランジ21(及びスプラインハブ4)との間で相対回転が発生する。一方で、リティニングプレート25と第3摩擦ワッシャ53とは一体回転し、ハブフランジ21とサブプレート34とは一体回転する。したがって、この3段目では、L-Hヒス発生機構13及びHヒス発生機構16が作動する。
In the third stage, since the first high-
すなわち、第3摩擦ワッシャ53に固定された第2摩擦材62とハブフランジ21との間で摩擦抵抗が発生する。また、サブプレート34に固定された第1摩擦材61とクラッチプレート24との間で摩擦抵抗が発生する。これらの摩擦抵抗によって、ヒステリシストルクhHが発生する。すなわち、合計でヒステリシストルクH+hHが発生する。
That is, frictional resistance is generated between the
ここで、この3段目では、サブプレート34及びスプリングホルダ35と、ドライブプレート36と、は相対回転せず、これらの部材の間では摩擦抵抗は発生しない。すなわち、Lヒス発生機構14及びL2ヒス発生機構15は作動しない。
Here, in this third stage, the sub-plate 34, the
<4段目>
伝達トルク又はトルク変動がさらに大きくなると、第1高剛性スプリング22aが圧縮されつつ、さらに自由長の短い第2高剛性スプリング22bも圧縮され始める。第1高剛性スプリング22aと第2高剛性スプリング22bとは並列に配置されているので、第2高剛性スプリング22bが圧縮され始めると、第1高剛性スプリング22aのみが圧縮されている場合(3段目)に比較して捩り剛性は高くなる。すなわち、捩り特性の4段目に移行する。
<4th stage>
When the transmission torque or the torque fluctuation becomes larger, the first high-
この4段目において、相対回転する部材は3段目と同様であり、L-Hヒス発生機構13及びHヒス発生機構16が作動し、ヒステリシストルクH+hHが得られる。
In this fourth stage, the relative rotating member is the same as in the third stage, the LH
<第1摩擦ワッシャ51の姿勢変動>
スプラインハブ4は、クラッチプレート24とリティニングプレート25との軸方向間に配置されている。また、スプラインハブ4とリティニングプレート25との間には第1コーンスプリング54が配置されている。したがって、装置の作動中には、スプラインハブ4は軸方向に移動する。特に、各部の摩耗が大きくなると、スプラインハブ4の軸方向の移動も大きくなる。このような状況では、スプラインハブ4とクラッチプレート24との軸方向間の隙間が大きくなり、第1摩擦ワッシャ51の姿勢が大きく変動するおそれがある。
<Posture change of the
The
しかし、第1摩擦ワッシャ51の外周面と対向するように第1摩擦材61の緩衝部61bが配置されているので、第1摩擦ワッシャ51の姿勢が変動すると、緩衝部61bによってその動きが規制される。このため、装置の作動中に、第1摩擦ワッシャ51が正規の位置からずれてセットされることが防止され、第1摩擦ワッシャ51の損傷が抑えられ、また第1摩擦ワッシャ51の動作不良を抑えることができる。
However, since the
また、第1摩擦材61は第1摩擦ワッシャ51より低い弾性を有するので、第1摩擦ワッシャ51が第1摩擦材61の緩衝部61bに当接しても、第1摩擦摩擦ワッシャ51が損傷するのを避けることができる。さらに、緩衝部61bは第1摩擦ワッシャ51よりも大きい摩擦係数を有しているので、第1摩擦ワッシャ51が緩衝部61bに当接しても、第1摩擦ワッシャ51がすべりにくく、第1摩擦ワッシャ51の姿勢が変動するのを抑えることができる。
Further, since the
ここで、第1摩擦ワッシャ51はクラッチプレート24と摩擦接触するので、第1摩擦ワッシャ51は発熱する。第1摩擦ワッシャ51で発生した熱は、高い輻射率を有する第1摩擦材61の緩衝部61bによって吸収される。また、第1摩擦材61自体もクラッチプレート24と摩擦接触するので、発熱する。これらの熱は、第1摩擦材61が固定されたサブプレート34の第1係合突起34cを介してハブフランジ21に直接伝達される。このため、第1摩擦ワッシャ51及び第1摩擦材61が高温になるのを抑えることができる。
Here, since the
また、第1摩擦ワッシャ51はクラッチプレート24の内周端面に傾斜面で当接しているので、摩擦面積を大きく確保することができる。このため、面圧を比較的小さくでき、摩耗及び発熱を抑えることができる。
Further, since the
[他の実施形態]
本発明は以上のような実施形態に限定されるものではなく、本発明の範囲を逸脱することなく種々の変形又は修正が可能である。
[Other embodiments]
The present invention is not limited to the above embodiments, and various modifications or modifications can be made without departing from the scope of the present invention.
(a)図10に緩衝部材の第2実施形態を示している。この例では、第1摩擦材70は、摩擦部70aと、第1対向部70bと、第2対向部70cと、を有している。
(A) FIG. 10 shows a second embodiment of the cushioning member. In this example, the
摩擦部70aは第1実施形態の摩擦部61aに相当し、第1対向部70bは第1実施形態の緩衝部61bに相当している。すなわち、摩擦部70aは、円板状に形成され、クラッチプレート24の側面に当接可能である。第1対向部70bは、摩擦部70aの内周端からリティニングプレート25側に軸方向に延び、第1摩擦ワッシャ51の外周面に対して、径方向に所定の隙間をあけて対向する位置に配置されている。また、第2対向部70cは、第1対向部70bの先端から径方向内方に延び、第1摩擦ワッシャ51の側面と所定の隙間をあけて対向して配置されている。
The
このような実施形態では、第1対向部70b及び第2対向部70cによって、第1摩擦ワッシャ51の姿勢変動をより抑えることが可能になる。
In such an embodiment, the first facing
(b)図11に緩衝部材の第3実施形態を示している。この例では、第1摩擦材72は、摩擦部72a及び緩衝部72bを有している。摩擦部72aは前記実施形態における摩擦部61aと同様である。緩衝部72bは、摩擦部72aの内周端から、径方向内方に、かつリティニングプレート25側に向かって傾斜している。
(B) FIG. 11 shows a third embodiment of the cushioning member. In this example, the
一方、この例では、第1摩擦ワッシャ74は、外周面の両方の角部に傾斜面を有している。すなわち、第1摩擦ワッシャ74の外周面には、クラッチプレート24側の角部と、リティニングプレート25側の角部の両方に、中央部から側方に向かって径が小さくなる第1傾斜面74a及び第2傾斜面74bを有している。そして、第1傾斜面74aはクラッチプレート24の内周端面に接触し、第2傾斜面74bは緩衝部72bに所定の隙間を介して対向している。
On the other hand, in this example, the first friction washer 74 has inclined surfaces at both corners of the outer peripheral surface. That is, on the outer peripheral surface of the first friction washer 74, both the corner portion on the
このような実施形態によっても、前記各実施形態と同様の作用効果を得ることができる。 Even with such an embodiment, the same effect as that of each of the above-described embodiments can be obtained.
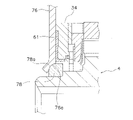
(c)図12に第4実施形態を示している。この第4実施形態は、クラッチプレート及び第1摩擦ワッシャの構成が異なっている。ここでは、クラッチプレート76の内周端面76aは、径方向の斜め外方に凹む球面に一部である。また、第1摩擦ワッシャ78の外周面の角部、すなわちクラッチプレート76の内周端面76aに接触する摩擦面78aは、径方向外方に膨らむ球面の一部である。
(C) FIG. 12 shows a fourth embodiment. In this fourth embodiment, the configurations of the clutch plate and the first friction washer are different. Here, the inner
このように、クラッチプレート76の内周端面76aと第1摩擦ワッシャ78の外周面の一部である摩擦面78aとを球面の一部とし、それらを摩擦接触させることにより、スプラインハブ4に対するクラッチプレート76を含む構成部分のミスアライメントをより小さくすることができる。
In this way, the inner
(d)前記実施形態では、4段の捩り特性を有するクラッチディスク組立体に本発明を適用したが、捩じり特性の段数は限定されない。ダンパ装置を有するすべての動力伝達装置に本発明を同様に適用することができる。 (D) In the above embodiment, the present invention is applied to a clutch disc assembly having four stages of twisting characteristics, but the number of stages of twisting characteristics is not limited. The present invention can be similarly applied to all power transmission devices having a damper device.
(e)各ヒステリシストルク発生機構で発生するヒステリシストルクの大きさは限定されない。求められる捩じり特性に応じてヒステリシストルクの大きさを適宜変更が可能である。 (E) The magnitude of the hysteresis torque generated by each hysteresis torque generation mechanism is not limited. The magnitude of the hysteresis torque can be appropriately changed according to the required torsional characteristics.
(f)上記の各実施形態を、各々組み合わせて採用することができる。 (F) Each of the above embodiments can be adopted in combination.
1 クラッチディスク組立体
2 クラッチディスク
3 ダンパ機構
4 スプラインハブ
12 高剛性ダンパ
13 全領域(L-H:第2)ヒステリシストルク発生機構
16 高捩り角度領域(H:第1)ヒステリシストルク発生機構
21 ハブフランジ
24,76 クラッチプレート
25 リティニングプレート
34 サブプレート
34c 第1係合突起
51,74,78 第1摩擦ワッシャ
61,70,72 第1摩擦材
61b 緩衝部
70b 第1対向部
70c 第2対向部
1
Claims (11)
環状の第1プレートを有する第1回転部材と、
前記トランスミッション側の部材に連結可能なハブと、前記ハブから径方向外方に延び前記第1プレートと軸方向に対向するフランジと、を有し、前記第1回転部材と相対回転可能な第2回転部材と、
前記第1回転部材と前記第2回転部材とを回転方向に弾性的に連結する複数の弾性部材と、
前記弾性部材の径方向内方において前記第1プレートと前記フランジとの軸方向間に配置され、前記第1プレートと前記フランジとの相対回転時に第1ヒステリシストルクを発生する第1ヒステリシストルク発生機構と、
前記ハブの外周面に設けられ前記第1プレートの内周面と摩擦接触する環状の第1摩擦部材を有し、前記第1回転部材と前記第2回転部材との相対回転時に第2ヒステリシストルクを発生させる第2ヒステリシストルク発生機構と、
前記第1ヒステリシストルク発生機構に設けられ、前記第1摩擦部材の外周面と所定の隙間をあけて配置された緩衝部材と、
を備えたダンパ装置。 It is a damper device that transmits torque from the drive source to the transmission side and attenuates torque fluctuations.
A first rotating member having an annular first plate and
A second that has a hub that can be connected to the transmission-side member and a flange that extends radially outward from the hub and faces the first plate in the axial direction, and is rotatable relative to the first rotating member. Rotating member and
A plurality of elastic members that elastically connect the first rotating member and the second rotating member in the rotational direction, and
A first hysteresis torque generation mechanism that is arranged in the radial direction of the elastic member between the first plate and the flange in the axial direction and generates a first hysteresis torque when the first plate and the flange rotate relative to each other. When,
It has an annular first friction member provided on the outer peripheral surface of the hub and in frictional contact with the inner peripheral surface of the first plate, and has a second hysteresis torque during relative rotation between the first rotating member and the second rotating member. The second hysteresis torque generation mechanism that generates
A cushioning member provided in the first hysteresis torque generation mechanism and arranged with a predetermined gap from the outer peripheral surface of the first friction member.
A damper device equipped with.
前記緩衝部材は、前記摩擦プレートの内周面に設けられている、
請求項1に記載のダンパ装置。 The first hysteresis torque generation mechanism has an annular friction plate that is in frictional contact with the first plate.
The cushioning member is provided on the inner peripheral surface of the friction plate.
The damper device according to claim 1.
前記第2ヒステリシストルク発生機構は、
前記フランジと前記第2プレートとの軸方向間に配置され、前記フランジの側面に摩擦接触する側面を有する環状の第2摩擦部材と、
前記第2摩擦部材を前記フランジ側に付勢する付勢部材と、
を有する、
請求項2に記載のダンパ装置。 The first rotating member has a second plate that faces the first plate in the axial direction with the flange of the second rotating member interposed therebetween.
The second hysteresis torque generation mechanism is
An annular second friction member arranged between the flange and the second plate in the axial direction and having a side surface in frictional contact with the side surface of the flange.
An urging member that urges the second friction member to the flange side, and
Have,
The damper device according to claim 2.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018128751A JP7053390B2 (en) | 2018-07-06 | 2018-07-06 | Damper device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018128751A JP7053390B2 (en) | 2018-07-06 | 2018-07-06 | Damper device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2020008061A JP2020008061A (en) | 2020-01-16 |
| JP2020008061A5 JP2020008061A5 (en) | 2021-08-12 |
| JP7053390B2 true JP7053390B2 (en) | 2022-04-12 |
Family
ID=69151215
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018128751A Active JP7053390B2 (en) | 2018-07-06 | 2018-07-06 | Damper device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7053390B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114992280B (en) * | 2022-05-09 | 2024-05-07 | 浙江吉利控股集团有限公司 | Transmission device, dual-mass flywheel and clutch transmission structure and vehicle |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000170790A (en) | 1998-12-08 | 2000-06-20 | Exedy Corp | Friction mechanism, damper disk assembly and clutch disk |
| JP2009019746A (en) | 2007-07-13 | 2009-01-29 | Exedy Corp | Damper mechanism |
| JP2015175440A (en) | 2014-03-14 | 2015-10-05 | 株式会社エクセディ | Damper disc assembly |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0649940Y2 (en) * | 1989-05-16 | 1994-12-14 | 三菱自動車工業株式会社 | Clutch device |
-
2018
- 2018-07-06 JP JP2018128751A patent/JP7053390B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000170790A (en) | 1998-12-08 | 2000-06-20 | Exedy Corp | Friction mechanism, damper disk assembly and clutch disk |
| JP2009019746A (en) | 2007-07-13 | 2009-01-29 | Exedy Corp | Damper mechanism |
| JP2015175440A (en) | 2014-03-14 | 2015-10-05 | 株式会社エクセディ | Damper disc assembly |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2020008061A (en) | 2020-01-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2008089089A (en) | Damper mechanism | |
| JP7181737B2 (en) | Torque converter lockup device | |
| US8454446B2 (en) | Damper mechanism | |
| JP4495936B2 (en) | Clutch disc assembly | |
| JP7053390B2 (en) | Damper device | |
| JP2009019746A (en) | Damper mechanism | |
| JP4445529B2 (en) | Damper mechanism | |
| JP7299828B2 (en) | damper device | |
| JP7040974B2 (en) | Damper device | |
| JP7040962B2 (en) | Damper device | |
| JP7012564B2 (en) | Damper device | |
| JP7148419B2 (en) | damper device | |
| JP6976874B2 (en) | Power transmission structure and power transmission device | |
| JP2022052126A (en) | Hysteresis torque generating mechanism and power transmission device | |
| JP7384654B2 (en) | damper device | |
| JP7376334B2 (en) | damper device | |
| JP3986266B2 (en) | Clutch disc assembly | |
| JP2019132288A (en) | Power transmission device | |
| JP6545972B2 (en) | Damper disc assembly | |
| CN209818581U (en) | Pin for caulking and power transmission structure | |
| JP6782349B2 (en) | Damper disc assembly | |
| JP7306890B2 (en) | damper device | |
| JP5060269B2 (en) | Torsional vibration reduction device | |
| WO2005028915A1 (en) | Flexible flywheel | |
| JP2022184493A (en) | damper device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210621 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20210621 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20220311 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20220329 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20220331 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7053390 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |