JP6891528B2 - Circuit devices, physical quantity measuring devices, electronic devices and mobile objects - Google Patents
Circuit devices, physical quantity measuring devices, electronic devices and mobile objects Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6891528B2 JP6891528B2 JP2017027463A JP2017027463A JP6891528B2 JP 6891528 B2 JP6891528 B2 JP 6891528B2 JP 2017027463 A JP2017027463 A JP 2017027463A JP 2017027463 A JP2017027463 A JP 2017027463A JP 6891528 B2 JP6891528 B2 JP 6891528B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- signal
- phase difference
- reference clock
- unit
- pulse
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Measurement Of Unknown Time Intervals (AREA)
Description
本発明は、回路装置、物理量測定装置、電子機器及び移動体等に関する。 The present invention relates to a circuit device, a physical quantity measuring device, an electronic device, a mobile body, and the like.
送信信号と受信信号の位相差を検出し、その位相差に基づいてTOF(Time Of Flight)の測定等を行う位相差検出方式の時間デジタル変換器が知られている。従来の位相差検出方式では、送信信号と受信信号の位相差をセンサーで電荷に変換(位相差の積分値に相当する電荷量を蓄積)し、その電荷に基づいて位相差を検出している。 A phase difference detection type time digital converter that detects the phase difference between a transmission signal and a reception signal and measures TOF (Time Of Flight) based on the phase difference is known. In the conventional phase difference detection method, the phase difference between the transmitted signal and the received signal is converted into an electric charge by a sensor (the amount of electric charge corresponding to the integrated value of the electric charge is accumulated), and the phase difference is detected based on the electric charge. ..
例えば特許文献1〜3には、測定対象に向けて発光し、測定対象物からの反射光をセンサーで受光し、発光タイミングと受光タイミングの位相差に対応する電荷量がセンサーに蓄積され、センサーから読み出した電荷量に基づいて測定対象の距離を測定する手法が開示されている。
For example, in
上述した従来技術では、発光タイミングを基準として得られた受光信号をセンサーで電荷(積分値)に変換して距離を測定するため、時間デジタル変換器が送信信号を自発する必要がある。そのため、時間デジタル変換回路の外部から任意のタイミングで入力された2つの信号の間の時間を測定することができなかった。 In the above-mentioned conventional technique, since the received light signal obtained based on the light emission timing is converted into an electric charge (integral value) by the sensor and the distance is measured, it is necessary for the time digital converter to spontaneously generate the transmission signal. Therefore, it is not possible to measure the time between two signals input from the outside of the time-digital conversion circuit at an arbitrary timing.
本発明は、上記の課題の少なくとも一部を解決するためになされたものであり、以下の形態又は態様として実現することが可能である。 The present invention has been made to solve at least a part of the above problems, and can be realized as the following forms or embodiments.
本発明の一態様は、第1の信号が入力され、基準クロック信号と前記第1の信号の位相差を表す第1の位相差信号を出力する第1の位相差信号出力部と、第2の信号が入力され、前記基準クロック信号と前記第2の信号の位相差を表す第2の位相差信号を出力する第2の位相差信号出力部と、前記第1の位相差信号と前記第2の位相差信号に基づいて、前記第1の信号と前記第2の信号の時間差を測定する測定部と、を含む回路装置に関係する。 One aspect of the present invention includes a first phase difference signal output unit, which receives a first signal and outputs a first phase difference signal representing the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the first signal, and a second phase difference signal output unit. A second phase difference signal output unit that inputs the signal of the above and outputs a second phase difference signal representing the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the second signal, the first phase difference signal, and the first phase difference signal. It relates to a circuit apparatus including a measuring unit for measuring a time difference between the first signal and the second signal based on the phase difference signal of 2.
本発明の一態様によれば、基準クロック信号と第1の信号の位相差を表す第1の位相差信号が出力され、基準クロック信号と第2の信号の位相差を表す第2の位相差信号が出力される。これにより、基準クロック信号に対して任意のタイミングで入力される(いわゆる自発でない)第1の信号に基づいて、基準クロック信号と第1の信号の位相差を検出でき、基準クロック信号に対して任意のタイミングで入力される第2の信号に基づいて、基準クロック信号と第2の信号の位相差を検出できる。そして、これらの位相差を表す第1の位相差信号と第2の位相差信号に基づいて、第1の信号と第2の信号の時間差を測定できる。このようにして本発明の一態様では、自発でない2つの信号の間の時間を測定できる。 According to one aspect of the present invention, a first phase difference signal representing the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the first signal is output, and a second phase difference representing the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the second signal. A signal is output. As a result, the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the first signal can be detected based on the first signal (so-called non-spontaneous) input at an arbitrary timing with respect to the reference clock signal, and the reference clock signal can be detected. The phase difference between the reference clock signal and the second signal can be detected based on the second signal input at an arbitrary timing. Then, the time difference between the first signal and the second signal can be measured based on the first phase difference signal and the second phase difference signal representing these phase differences. In this way, in one aspect of the invention, the time between two non-spontaneous signals can be measured.
また本発明の一態様では、前記第1の位相差信号出力部は、前記基準クロック信号と前記第1の信号に基づく積分処理を行って、前記第1の位相差信号を出力し、前記第2の位相差信号出力部は、前記基準クロック信号と前記第2の信号に基づく積分処理を行って、前記第2の位相差信号を出力してもよい。 Further, in one aspect of the present invention, the first phase difference signal output unit performs integration processing based on the reference clock signal and the first signal, outputs the first phase difference signal, and outputs the first phase difference signal. The phase difference signal output unit of 2 may output the second phase difference signal by performing integration processing based on the reference clock signal and the second signal.
このようにすれば、基準クロック信号と第1の信号に基づく積分処理を行うことで、基準クロック信号と第1の信号の位相差を表す第1の位相差信号を出力できる。また、基準クロック信号と第2の信号に基づく積分処理を行うことで、基準クロック信号と第2の信号の位相差を表す第2の位相差信号を出力できる。 In this way, the first phase difference signal representing the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the first signal can be output by performing the integration process based on the reference clock signal and the first signal. Further, by performing the integration process based on the reference clock signal and the second signal, it is possible to output a second phase difference signal representing the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the second signal.
また本発明の一態様では、前記第1の位相差信号出力部は、前記第1の信号に基づいて、前記基準クロック信号のパルス幅に対応するパルス幅の第1のパルス信号を生成する第1のパルス信号生成部を有し、前記第2の位相差信号出力部は、前記第2の信号に基づいて、前記基準クロック信号の前記パルス幅に対応するパルス幅の第2のパルス信号を生成する第2のパルス信号生成部を有してもよい。 Further, in one aspect of the present invention, the first phase difference signal output unit generates a first pulse signal having a pulse width corresponding to the pulse width of the reference clock signal based on the first signal. The second phase difference signal output unit has one pulse signal generation unit, and the second phase difference signal output unit generates a second pulse signal having a pulse width corresponding to the pulse width of the reference clock signal based on the second signal. It may have a second pulse signal generator to generate.
このようにすれば、第1のパルス信号により規定される積分期間において基準クロック信号を積分することが可能になり、その積分値により第1の位相差信号を生成できるようになる。また第2のパルス信号により規定される積分期間において基準クロック信号を積分することが可能になり、その積分値により第2の位相差信号を生成できるようになる。即ち、第1の信号から第1のパルス信号を生成し、第2の信号から第2のパルス信号を生成することで、第1の信号及び第2の信号が任意のタイミングで入力される場合であっても、積分処理が可能となり、位相差を検出できる。 In this way, the reference clock signal can be integrated in the integration period defined by the first pulse signal, and the first phase difference signal can be generated from the integrated value. Further, the reference clock signal can be integrated in the integration period defined by the second pulse signal, and the second phase difference signal can be generated by the integrated value. That is, when the first signal and the second signal are input at an arbitrary timing by generating the first pulse signal from the first signal and generating the second pulse signal from the second signal. Even if it is, the integration process becomes possible and the phase difference can be detected.
また本発明の一態様では、前記第1の位相差信号出力部は、前記基準クロック信号と前記第1のパルス信号に基づく積分処理を行う第1の積分処理部を有し、前記第2の位相差信号出力部は、前記基準クロック信号と第2のパルス信号に基づく積分処理を行う第2の積分処理部を有してもよい。 Further, in one aspect of the present invention, the first phase difference signal output unit has a first integration processing unit that performs integration processing based on the reference clock signal and the first pulse signal, and the second The phase difference signal output unit may have a second integration processing unit that performs integration processing based on the reference clock signal and the second pulse signal.
このようにすれば、第1の積分処理部が基準クロック信号と第1のパルス信号に基づく積分処理を行うことで、基準クロック信号と第1の信号の位相差を表す第1の位相差信号を出力できる。また、第2の積分処理部が基準クロック信号と第2のパルス信号に基づく積分処理を行うことで、基準クロック信号と第2の信号の位相差を表す第2の位相差信号を出力できる。 In this way, the first integration processing unit performs integration processing based on the reference clock signal and the first pulse signal, so that the first phase difference signal representing the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the first signal. Can be output. Further, the second integration processing unit performs integration processing based on the reference clock signal and the second pulse signal, so that a second phase difference signal representing the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the second signal can be output.
また本発明の一態様では、前記第1のパルス信号生成部は、第1の遅延回路を有し、前記第1の位相差信号出力部は、前記第1の遅延回路の遅延時間を、前記基準クロック信号の前記パルス幅に対応する遅延時間に設定する第1の遅延制御回路を有し、前記第2のパルス信号生成部は、第2の遅延回路を有し、前記第2の位相差信号出力部は、前記第2の遅延回路の遅延時間を、前記基準クロック信号の前記パルス幅に対応する遅延時間に設定する第2の遅延制御回路を有してもよい。 Further, in one aspect of the present invention, the first pulse signal generation unit has a first delay circuit, and the first phase difference signal output unit sets the delay time of the first delay circuit. The second delay control circuit for setting the delay time corresponding to the pulse width of the reference clock signal, the second pulse signal generation unit has the second delay circuit, and the second phase difference. The signal output unit may have a second delay control circuit that sets the delay time of the second delay circuit to a delay time corresponding to the pulse width of the reference clock signal.
このようにすれば、基準クロック信号のパルス幅に対応する遅延時間に設定された第1の遅延回路を用いて、基準クロック信号のパルス幅に対応するパルス幅の第1のパルス信号を生成できる。また、基準クロック信号のパルス幅に対応する遅延時間に設定された第2の遅延回路を用いて、基準クロック信号のパルス幅に対応するパルス幅の第2のパルス信号を生成できる。 In this way, the first pulse signal having a pulse width corresponding to the pulse width of the reference clock signal can be generated by using the first delay circuit set to the delay time corresponding to the pulse width of the reference clock signal. .. Further, a second pulse signal having a pulse width corresponding to the pulse width of the reference clock signal can be generated by using the second delay circuit set to the delay time corresponding to the pulse width of the reference clock signal.
また本発明の一態様では、前記第1の位相差信号出力部は、パルス幅測定モードでは、前記第1の遅延回路に前記基準クロック信号を出力し、位相差検出モードでは、前記第1のパルス信号生成部に前記第1の信号を出力する第1のセレクターを有し、前記第2の位相差信号出力部は、前記パルス幅測定モードでは、前記第2の遅延回路に前記基準クロック信号を出力し、前記位相差検出モードでは、前記第2のパルス信号生成部に前記第2の信号を出力する第2のセレクターを有してもよい。 Further, in one aspect of the present invention, the first phase difference signal output unit outputs the reference clock signal to the first delay circuit in the pulse width measurement mode, and the first phase difference detection mode. The pulse signal generation unit has a first selector that outputs the first signal, and the second phase difference signal output unit has the reference clock signal in the second delay circuit in the pulse width measurement mode. In the phase difference detection mode, the second pulse signal generation unit may have a second selector that outputs the second signal.
このようにすれば、パルス幅測定モードにおいて第1の遅延回路と第1の遅延制御回路により第1の遅延回路の遅延時間を設定し、第2の遅延回路と第2の遅延制御回路により第2の遅延回路の遅延時間を設定できる。そして、位相差検出モードにおいて第1のパルス信号生成部が第1の遅延回路を用いて第1の信号から第1のパルス信号を生成し、第2のパルス信号生成部が第2の遅延回路を用いて第2の信号から第2のパルス信号を生成し、これらのパルス信号に基づいて位相差を検出できる。 In this way, in the pulse width measurement mode, the delay time of the first delay circuit is set by the first delay circuit and the first delay control circuit, and the second delay circuit and the second delay control circuit set the delay time. The delay time of the delay circuit of 2 can be set. Then, in the phase difference detection mode, the first pulse signal generation unit generates the first pulse signal from the first signal using the first delay circuit, and the second pulse signal generation unit is the second delay circuit. Can be used to generate a second pulse signal from the second signal and detect the phase difference based on these pulse signals.
また本発明の一態様では、回路装置は、前記基準クロック信号に基づいて、互いに位相が異なる第1〜第nのクロック信号(nは2以上の整数)を生成するクロック信号生成部を含み、前記第1の位相差信号出力部は、前記第1〜第nのクロック信号と前記第1の信号に基づく積分処理を行う第1〜第nの積分器を有し、前記第2の位相差信号出力部は、前記第1〜第nのクロック信号と前記第2の信号に基づく積分処理を行う第n+1〜第2nの積分器を有してもよい。 Further, in one aspect of the present invention, the circuit device includes a clock signal generation unit that generates first to nth clock signals (n is an integrator of 2 or more) having different phases from each other based on the reference clock signal. The first phase difference signal output unit has the first to nth clock signals and the first to nth integrators that perform integrator processing based on the first signal, and the second phase difference. The signal output unit may have an n + 1 to 2n integrator that performs an integrating process based on the first to nth clock signals and the second signal.
このようにすれば、互いに位相が異なる第1〜第nの積分値の特性が得られる。これにより、入力位相差に対して、位相が異なるn個の特性に基づくn個の積分値が得られる。積分処理は積分器の特性ばらつき等によって非線形性を有する可能性があり、それによって入力位相差と出力位相差の間に非線形性が生じる可能性がある。この点、本発明の一態様によれば、n個の積分値を例えば平均して位相差を求めることで、入力位相差と出力位相差の間に非線形性を低減できる。 In this way, the characteristics of the first to nth integrated values having different phases from each other can be obtained. As a result, n integral values based on n characteristics having different phases can be obtained with respect to the input phase difference. The integration process may have non-linearity due to variations in the characteristics of the integrator, etc., which may cause non-linearity between the input phase difference and the output phase difference. In this regard, according to one aspect of the present invention, the non-linearity between the input phase difference and the output phase difference can be reduced by, for example, averaging n integrated values to obtain the phase difference.
また本発明の一態様では、前記測定部は、前記第1〜第nの積分器の出力信号及び前記第n+1〜第2nの積分器の出力信号のいずれかを選択するセレクターと、前記セレクターからの信号をA/D変換するA/D変換回路と、A/D変換された前記第1〜第nの積分器の出力信号及び前記第n+1〜第2nの積分器の出力信号に基づいて、前記時間差を求める処理部と、を有してもよい。 Further, in one aspect of the present invention, the measuring unit has a selector for selecting one of the output signal of the first to nth integrators and the output signal of the n + 1 to 2n integrators, and the selector. Based on the A / D conversion circuit that A / D converts the signal, the output signal of the first to nth integrators that have been A / D converted, and the output signal of the n + 1 to 2n integrators. It may have a processing unit for obtaining the time difference.
このようにすれば、第1〜第nの積分器の出力信号及び第n+1〜第2nの積分器の出力信号を時分割にA/D変換できる。これにより、回路規模を節約できる。また、このようなA/D変換を行うことで、デジタル信号処理により積分器の出力信号(積分値)に基づいて時間差を求めることができる。 In this way, the output signal of the first to nth integrators and the output signal of the n + 1 to 2n integrators can be A / D converted into time division. As a result, the circuit scale can be saved. Further, by performing such A / D conversion, the time difference can be obtained based on the output signal (integrated value) of the integrator by digital signal processing.
また本発明の一態様では、回路装置は、前記第1の信号がアクティブになってから、前記第2の信号がアクティブになるまでの前記基準クロック信号のクロック数をカウントするカウンターを含み、前記測定部は、前記カウンターのカウント値と前記第1の位相差信号と前記第2の位相差信号に基づいて、前記第1の信号と前記第2の信号の時間差を測定してもよい。 Further, in one aspect of the present invention, the circuit device includes a counter that counts the number of clocks of the reference clock signal from the activation of the first signal to the activation of the second signal. The measuring unit may measure the time difference between the first signal and the second signal based on the count value of the counter, the first phase difference signal, and the second phase difference signal.
従来の位相差検出方式ではセンサーで積分処理を行うため、ダイナミックレンジを広げることが困難である。この点、本発明の一態様によれば、第1の信号がアクティブになってから、第2の信号がアクティブになるまでの基準クロック信号のクロック数がカウントされ、そのカウント値を用いて第1の信号と第2の信号の時間差が測定される。これにより、第1の信号と第2の信号の位相差が基準クロック信号の1周期より大きい場合であっても、位相差を検出できる。これにより、広いダイナミックレンジの測定が可能になる。 In the conventional phase difference detection method, it is difficult to widen the dynamic range because the integration process is performed by the sensor. In this regard, according to one aspect of the present invention, the number of clocks of the reference clock signal from the activation of the first signal to the activation of the second signal is counted, and the count value is used to count the number of clocks. The time difference between the first signal and the second signal is measured. Thereby, even when the phase difference between the first signal and the second signal is larger than one cycle of the reference clock signal, the phase difference can be detected. This makes it possible to measure a wide dynamic range.
また本発明の他の態様は、上記のいずれかに記載の回路装置を含む物理量測定装置に関係する。 Further, another aspect of the present invention relates to a physical quantity measuring device including the circuit device according to any one of the above.
また本発明の更に他の態様は、上記のいずれかに記載の回路装置を含む電子機器に関係する。 Yet another aspect of the present invention relates to an electronic device including the circuit device according to any of the above.
また本発明の更に他の態様は、上記のいずれかに記載の回路装置を含む移動体に関係する。 Yet another aspect of the invention relates to a mobile body comprising the circuit device according to any of the above.
以下、本発明の好適な実施の形態について詳細に説明する。なお以下に説明する本実施形態は特許請求の範囲に記載された本発明の内容を不当に限定するものではなく、本実施形態で説明される構成の全てが本発明の解決手段として必須であるとは限らない。 Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail. The present embodiment described below does not unreasonably limit the content of the present invention described in the claims, and all the configurations described in the present embodiment are indispensable as a means for solving the present invention. Not necessarily.
1.第1の構成例
上述したように、従来の位相差検出方式では信号の積分がセンサーで行われており、センサーの出力信号が位相差信号となっている。この方式は、例えば3次元計測等に利用されている。即ち、2次元センサーを用いて各画素での測距を行い、測定対象の3次元情報を取得する。
1. 1. First Configuration Example As described above, in the conventional phase difference detection method, the signal is integrated by the sensor, and the output signal of the sensor is the phase difference signal. This method is used for, for example, three-dimensional measurement. That is, the distance is measured at each pixel using the two-dimensional sensor, and the three-dimensional information of the measurement target is acquired.
位相差検出方式は、送信信号と受信信号の位相差(時間差)を測定するので、一種の時間デジタル変換器と考えられる。しかしながら、送信信号を自発する必要があることや、センサーで位相差に変換していることから、時間デジタル変換器として用途が限られている。例えば、2つの信号経路の遅延差や、PLLにおける位相差検出等の、自発でない2つの信号の時間差を測定することは、従来の位相差検出方式では困難である。 Since the phase difference detection method measures the phase difference (time difference) between the transmitted signal and the received signal, it can be considered as a kind of time digital converter. However, since it is necessary to spontaneously generate a transmission signal and it is converted into a phase difference by a sensor, its use as a time digital converter is limited. For example, it is difficult to measure the time difference between two non-spontaneous signals such as the delay difference between two signal paths and the phase difference detection in the PLL by the conventional phase difference detection method.
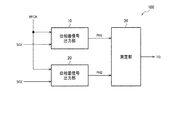
図1は、本実施形態の回路装置の第1の構成例である。回路装置100は、第1の位相差信号出力部10(第1の位相差信号出力回路)、第2の位相差信号出力部20(第2の位相差信号出力回路)、測定部30(測定回路)を含む。なお、本実施形態は図1の構成に限定されず、その構成要素の一部を省略したり、他の構成要素を追加したりする等の種々の変形実施が可能である。例えば、図1では基準クロック信号RFCKが位相差信号出力部10、20に入力されているが、これに限定されず、基準クロック信号RFCKを位相又は周波数の基準として生成されたクロック信号が位相差信号出力部10、20に入力されてもよい。
FIG. 1 is a first configuration example of the circuit device of the present embodiment. The
図1の回路装置100は、第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の遷移タイミングの時間差をデジタル値(時間差データTQ)に変換する時間デジタル変換回路である。
The
具体的には、第1の位相差信号出力部10は、第1の信号SG1が入力され、基準クロック信号RFCKと第1の信号SG1の位相差を表す第1の位相差信号PH1を出力する。第2の位相差信号出力部20は、第2の信号SG2が入力され、基準クロック信号RFCKと第2の信号SG2の位相差を表す第2の位相差信号PH2を出力する。測定部30は、第1の位相差信号PH1と第2の位相差信号PH2に基づいて、第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の遷移タイミングの時間差を測定する。測定部30は、測定された時間差を表す時間差データTQを出力する。
Specifically, the first phase difference
図2は、本実施形態における時間差測定の手法を説明する図である。なお以下では、各信号の遷移タイミングが信号の立ち上がりエッジである場合を例に説明するが、信号の遷移タイミングはこれに限定されない。即ち、遷移タイミングは信号レベルが変化するタイミングであればよい。 FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a method of measuring the time difference in the present embodiment. In the following, the case where the transition timing of each signal is the rising edge of the signal will be described as an example, but the transition timing of the signal is not limited to this. That is, the transition timing may be any timing at which the signal level changes.
第1の位相差信号出力部10は、基準クロック信号RFCKの立ち上がりエッジと第1の信号SG1の立ち上がりエッジの間の位相差に対応する第1の位相差信号PH1を生成する。例えば、基準クロック信号RFCKの1周期を360度として、位相差が60度だったとする。第2の位相差信号出力部20は、基準クロック信号RFCKの立ち上がりエッジと第2の信号SG2の立ち上がりエッジの間の位相差に対応する第2の位相差信号PH2を生成する。例えば、位相差が150度だったとする。測定部30は、2つの位相差信号PH1、PH2から、第1の信号SG1の立ち上がりエッジと第2の信号SG2の立ち上がりエッジの間の位相差を求める。具体的には、第1の位相差信号PH1から位相差(60度)を求め、第2の位相差信号PH2から位相差(150度)を求め、2つの位相差の差分150度−60度=90度を求める。例えば、測定部30は、位相差90度を表すデジタル値を時間差データTQとして出力する。或いは、基準クロック信号RFCKの1周期をTRFとした場合に、位相差90度を時間差TDF=(90度/360度)×TRFに変換し、その時間差TDFを表す時間差データTQを出力する。
The first phase difference
第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2としては種々の信号を想定できる。例えば、信号SG1、SG2は、TOF方式の測距センサーにおけるスタート信号とストップ信号であってもよい。この場合、先に入力される第1の信号SG1(スタート信号)から、後に入力される第2の信号SG2(ストップ信号)までの時間を測定することになる。或いは、信号SG1、SG2は、基準信号(例えば基準クロック、時刻パルス等)と、その基準信号に同期すべき信号(例えば、基準クロック又は時刻パルスに同期するタイミング信号、クロック信号等)であってもよい。或いは、第1の信号経路を通過した信号(遅延信号)と、第2の信号経路を通過した信号(遅延信号)であってもよい。これらの例では、第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の前後関係は決まっていない。例えば、第1の信号SG1、第2の信号SG2の順に入力された場合には正の値の時間差TDFを出力し、第2の信号SG2、第1の信号SG1の順に入力された場合には負の値の時間差TDFを出力する。 Various signals can be assumed as the first signal SG1 and the second signal SG2. For example, the signals SG1 and SG2 may be a start signal and a stop signal in the TOF type distance measuring sensor. In this case, the time from the first signal SG1 (start signal) input first to the second signal SG2 (stop signal) input later is measured. Alternatively, the signals SG1 and SG2 are a reference signal (for example, a reference clock, a time pulse, etc.) and a signal to be synchronized with the reference signal (for example, a timing signal, a clock signal, etc. that are synchronized with the reference clock or the time pulse). May be good. Alternatively, it may be a signal that has passed through the first signal path (delay signal) and a signal that has passed through the second signal path (delay signal). In these examples, the context of the first signal SG1 and the second signal SG2 is not determined. For example, when the first signal SG1 and the second signal SG2 are input in this order, a positive time difference TDF is output, and when the second signal SG2 and the first signal SG1 are input in this order, the time difference TDF is output. Outputs a negative time difference TDF.
位相差信号(PH1、PH2の各々)は、信号値が0度〜360度の位相差に対応した信号であり、例えば信号値と0度〜360度の位相差が1対1に対応する信号である。例えば、位相差信号は、位相差のサインとコサインの組み合わせ、又はそれらに類似した信号の組み合わせ(例えば図4のPHQ、PHI)である。なお、位相差信号はこれに限定されず、位相差信号から位相差を特定できる信号であればよい。 The phase difference signal (each of PH1 and PH2) is a signal whose signal value corresponds to a phase difference of 0 to 360 degrees, for example, a signal whose phase difference of 0 to 360 degrees corresponds to 1: 1. Is. For example, the phase difference signal is a combination of phase difference sine and cosine, or a combination of signals similar to them (for example, PHQ, PHI in FIG. 4). The phase difference signal is not limited to this, and any signal that can specify the phase difference from the phase difference signal may be used.
本実施形態によれば、基準クロック信号RFCKと第1の信号SG1の位相差が検出され、基準クロック信号RFCKと第2の信号SG2の位相差が検出され、それらの位相差に基づいて、第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の遷移タイミングの時間差が測定される。これにより、第1の信号SG1(例えばスタート信号)を時間デジタル変換回路が自発しない場合であっても、第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の遷移タイミングの時間差を測定できる。また、従来の位相差検出方式のようにTOF方式の測距センサーに限らず、2つの信号の時間差を測定する時間デジタル変換回路として種々の用途に適用できるようになる。 According to the present embodiment, the phase difference between the reference clock signal RFCK and the first signal SG1 is detected, the phase difference between the reference clock signal RFCK and the second signal SG2 is detected, and the first is based on the phase difference. The time difference between the transition timings of the first signal SG1 and the second signal SG2 is measured. Thereby, even when the time digital conversion circuit does not spontaneously generate the first signal SG1 (for example, the start signal), the time difference between the transition timings of the first signal SG1 and the second signal SG2 can be measured. Further, it can be applied to various applications as a time digital conversion circuit for measuring the time difference between two signals, not limited to the TOF type ranging sensor as in the conventional phase difference detection method.
また本実施形態では、第1の位相差信号出力部10は、基準クロック信号RFCKと第1の信号SG1に基づく積分処理を行って、第1の位相差信号PH1を出力する。第2の位相差信号出力部20は、基準クロック信号RFCKと第2の信号SG2に基づく積分処理を行って、第2の位相差信号PH2を出力する。
Further, in the present embodiment, the first phase difference
図3は、第1の位相差信号出力部の動作を説明するタイミングチャートである。なお、ここでは第1の位相差信号出力部10を例に説明するが、第2の位相差信号出力部20についても同様な動作を行う。
FIG. 3 is a timing chart illustrating the operation of the first phase difference signal output unit. Although the first phase difference
第1の位相差信号出力部10は、第1の信号SG1から第1のパルス信号PSG1を生成する。第1の信号SG1と第1のパルス信号PSG1の立ち上がりエッジ(遷移タイミング)は、同じタイミングであり、第1のパルス信号PSG1のパルス幅TPSは、基準クロック信号RFCKのパルス幅TH(ハイレベルの期間)と同じである。第1の位相差信号出力部10は、第1のパルス信号PSG1がアクティブ(ハイレベル、第1の論理レベル)である積分期間において基準クロック信号RFCKを積分する。具体的には、積分期間において基準クロック信号RFCKがローレベルの期間TAMでは負の信号レベルを積分し、基準クロック信号RFCKがハイレベルの期間TAPでは正の信号レベルを積分し、その積分値PHI(信号)を出力する。積分される負の信号レベルと正の信号レベルは絶対値が同じ信号レベルである。また第1の位相差信号出力部10は、基準クロック信号RFCKと位相が90度異なるクロック信号RFCK’を積分期間において積分する。具体的には、積分期間においてクロック信号RFCK’がローレベルの期間TBMでは負の信号レベルを積分し、クロック信号RFCK’がハイレベルの期間TBPでは正の信号レベルを積分し、その積分値PHQ(信号)を出力する。第1の位相差信号出力部10は、積分値PHI、PHQを第1の位相差信号PH1として出力する。
The first phase difference
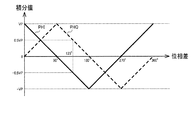
図4は、積分値の特性を示す図である。積分値が変化する範囲の上限を+VPとし、下限を−VPとする。積分値PHIは疑似的なコサイン波の特性を有する。具体的には、コサイン波と同位相の三角波であり、コサイン波の頂点(0度、180度、360度)とゼロクロス点(90度、270度)の間を直線補間(直線近似)した波形である。また積分値PHQは疑似的なサイン波の特性を有する。具体的には、サイン波と同位相の三角波であり、サイン波のゼロクロス点(0度、180度、360度)と頂点(90度、270度)の間を直線補間(直線近似)した波形である。サインとコサインの値に対して、0度〜360度の範囲で角度(位相差)を一意に決めることができるので、積分値PHI、PHQから位相差を決定できる。例えば、図4に示すように積分値(PHI,PHQ)=(−VP/2、+VP/2)の場合、位相差は135度と決定できる。 FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the characteristics of the integrated value. The upper limit of the range in which the integrated value changes is + VP, and the lower limit is -VP. The integrated value PHI has the characteristics of a pseudo cosine wave. Specifically, it is a triangular wave having the same phase as the cosine wave, and is a waveform obtained by linearly interpolating (straight line approximation) between the vertices of the cosine wave (0 degrees, 180 degrees, 360 degrees) and the zero crossing point (90 degrees, 270 degrees). Is. Further, the integrated value PHQ has a pseudo sine wave characteristic. Specifically, it is a triangular wave having the same phase as the sine wave, and is a waveform obtained by linearly interpolating (straight line approximation) between the zero cross point (0 degree, 180 degree, 360 degree) and the apex (90 degree, 270 degree) of the sine wave. Is. Since the angle (phase difference) can be uniquely determined in the range of 0 degrees to 360 degrees with respect to the sine and cosine values, the phase difference can be determined from the integrated values PHI and PHQ. For example, when the integral value (PHI, PHQ) = (-VP / 2, + VP / 2) as shown in FIG. 4, the phase difference can be determined to be 135 degrees.
このように、基準クロック信号RFCKと第1の信号SG1に基づく積分処理を行うことで、基準クロック信号RFCKと第1の信号SG1の位相差を表す第1の位相差信号PH1を出力できる。同様に、基準クロック信号RFCKと第2の信号SG2に基づく積分処理を行うことで、基準クロック信号RFCKと第2の信号SG2の位相差を表す第2の位相差信号PH2を出力できる。 By performing the integration process based on the reference clock signal RFCK and the first signal SG1 in this way, the first phase difference signal PH1 representing the phase difference between the reference clock signal RFCK and the first signal SG1 can be output. Similarly, by performing the integration process based on the reference clock signal RFCK and the second signal SG2, the second phase difference signal PH2 representing the phase difference between the reference clock signal RFCK and the second signal SG2 can be output.
また本実施形態では、第1の位相差信号出力部10は、第1の信号SG1に基づいて、基準クロック信号RFCKのパルス幅THに対応するパルス幅TPSの第1のパルス信号PSG1を生成する第1のパルス信号生成部(図7の第1のパルス信号生成部40)を有する。第2の位相差信号出力部20は、第2の信号SG2に基づいて、基準クロック信号RFCKのパルス幅THに対応するパルス幅の第2のパルス信号PSG2を生成する第2のパルス信号生成部(図7の第2のパルス信号生成部70)を有する。
Further, in the present embodiment, the first phase difference
このようにすれば、第1のパルス信号PSG1により規定される積分期間(図3のTPS)において基準クロック信号RFCKを積分することで、第1の位相差信号PH1を生成できるようになる。また第2のパルス信号PSG2により規定される積分期間において基準クロック信号RFCKを積分することで、第2の位相差信号PH2を生成できるようになる。即ち、第1の信号SG1から第1のパルス信号PSG1を生成し、第2の信号SG2から第2のパルス信号PSG2を生成することで、第1の信号SG1及び第2の信号SG2が外部から入力される場合であっても、積分処理が可能となり、位相差を検出できる。 In this way, the first phase difference signal PH1 can be generated by integrating the reference clock signal RFCK in the integration period (TPS in FIG. 3) defined by the first pulse signal PSG1. Further, by integrating the reference clock signal RFCK in the integration period defined by the second pulse signal PSG2, the second phase difference signal PH2 can be generated. That is, by generating the first pulse signal PSG1 from the first signal SG1 and generating the second pulse signal PSG2 from the second signal SG2, the first signal SG1 and the second signal SG2 are externally generated. Even when it is input, integration processing is possible and the phase difference can be detected.
また本実施形態では、第1の位相差信号出力部10は、基準クロック信号RFCKと第1のパルス信号PSG1に基づく積分処理を行う第1の積分処理部(図7の第1の積分処理部60)を有する。第2の位相差信号出力部20は、基準クロック信号RFCKと第2のパルス信号PSG2に基づく積分処理を行う第2の積分処理部(図7の第2の積分処理部90)を有する。
Further, in the present embodiment, the first phase difference
このようにすれば、基準クロック信号RFCKと第1のパルス信号PSG1に基づく積分処理を行って、基準クロック信号RFCKと第1の信号SG1の位相差を表す第1の位相差信号PH1を出力できる。また、基準クロック信号RFCKと第2のパルス信号PSG2に基づく積分処理を行って、基準クロック信号RFCKと第2の信号SG2の位相差を表す第2の位相差信号PH2を出力できる。 In this way, integration processing based on the reference clock signal RFCK and the first pulse signal PSG1 can be performed, and the first phase difference signal PH1 representing the phase difference between the reference clock signal RFCK and the first signal SG1 can be output. .. Further, the integration process based on the reference clock signal RFCK and the second pulse signal PSG2 can be performed to output the second phase difference signal PH2 representing the phase difference between the reference clock signal RFCK and the second signal SG2.
また本実施形態では、第1のパルス信号生成部は、第1の遅延回路(図7の第1の遅延回路41)を有する。第1の位相差信号出力部10は、第1の遅延回路の遅延時間を、基準クロック信号RFCKのパルス幅THに対応する遅延時間に設定する第1の遅延制御回路(図7の第1の遅延制御回路50)を有する。そして、第1の遅延回路と第1の遅延制御回路を含んで第1のDLL(Delay Locked Loop)回路(図7の第1のDLL回路130)が構成される。第2のパルス信号生成部は、第2の遅延回路(図7の第2の遅延回路71)を有する。第2の位相差信号出力部20は、第2の遅延回路の遅延時間を、基準クロック信号RFCKのパルス幅THに対応する遅延時間に設定する第2の遅延制御回路(図7の第2の遅延制御回路80)を有する。そして、第2の遅延回路と第2の遅延制御回路を含んで第2のDLL(Delay Locked Loop)回路(図7の第2のDLL回路140)が構成される。
Further, in the present embodiment, the first pulse signal generation unit has a first delay circuit (
このようにすれば、基準クロック信号RFCKのパルス幅THに対応する遅延時間に設定された第1の遅延回路により、基準クロック信号RFCKのパルス幅THに対応するパルス幅TPSの第1のパルス信号PSG1を生成できる。また、基準クロック信号RFCKのパルス幅THに対応する遅延時間に設定された第2の遅延回路により、基準クロック信号RFCKのパルス幅THに対応するパルス幅の第2のパルス信号PSG2を生成できる。 In this way, the first pulse signal of the pulse width TPS corresponding to the pulse width TH of the reference clock signal RFCK is provided by the first delay circuit set to the delay time corresponding to the pulse width TH of the reference clock signal RFCK. PSG1 can be generated. Further, the second delay circuit set to the delay time corresponding to the pulse width TH of the reference clock signal RFCK can generate the second pulse signal PSG2 having the pulse width corresponding to the pulse width TH of the reference clock signal RFCK.
また本実施形態では、第1の位相差信号出力部10は第1のセレクター(図7の第1のセレクター15)を有する。第1のセレクターは、パルス幅測定モード(図8のステップS1、図9)では、第1の遅延回路に基準クロック信号RFCKを出力し、位相差検出モード(図8のステップS2、図10)では、第1のパルス信号生成部に第1の信号SG1を出力する。第2の位相差信号出力部20は第2のセレクター(図7の第2のセレクター25)を有する。第2のセレクターは、パルス幅測定モードでは、第2の遅延回路に基準クロック信号RFCKを出力し、位相差検出モードでは、第2のパルス信号生成部に第2の信号SG2を出力する。
Further, in the present embodiment, the first phase difference
例えば、パルス幅測定モードは間欠的に設定される。即ち、パルス幅測定モードが設定される第1の期間と、位相差検出モードが設定される第2の期間が交互に繰り返され、第2の期間において位相差の検出(時間差の測定)が行われる。第2の期間は第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の入力を待機する待機期間に相当する。この待機期間中に第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2が入力されると、時間差が測定される。1つの第2の期間中に1回の測定が行われてもよいし、複数回の測定が行われてもよい。 For example, the pulse width measurement mode is set intermittently. That is, the first period in which the pulse width measurement mode is set and the second period in which the phase difference detection mode is set are alternately repeated, and the phase difference is detected (measurement of the time difference) in the second period. It is said. The second period corresponds to a waiting period for waiting for input of the first signal SG1 and the second signal SG2. When the first signal SG1 and the second signal SG2 are input during this standby period, the time difference is measured. One measurement may be made during one second period, or multiple measurements may be made.
このようにすれば、パルス幅測定モードにおいて第1の遅延回路と第1の遅延制御回路により第1の遅延回路の遅延時間を設定し、第2の遅延回路と第2の遅延制御回路により第2の遅延回路の遅延時間を設定できる。そして、位相差検出モードにおいて第1のパルス信号生成部が第1の信号SG1に基づいて第1のパルス信号PSG1を生成し、第2のパルス信号生成部が第2の信号SG2に基づいて第2のパルス信号PSG2を生成し、これらのパルス信号に基づいて位相差を検出(時間差を測定)できる。 In this way, in the pulse width measurement mode, the delay time of the first delay circuit is set by the first delay circuit and the first delay control circuit, and the second delay circuit and the second delay control circuit set the delay time. The delay time of the delay circuit of 2 can be set. Then, in the phase difference detection mode, the first pulse signal generation unit generates the first pulse signal PSG1 based on the first signal SG1, and the second pulse signal generation unit generates the first pulse signal SG2 based on the second signal SG2. 2 pulse signals PSG2 can be generated, and the phase difference can be detected (time difference is measured) based on these pulse signals.
また本実施形態では、回路装置100は、基準クロック信号RFCKに基づいて、互いに位相が異なる第1〜第nのクロック信号(図12のクロック信号CKAI1、CKBI1、CKCI1)を生成するクロック信号生成部(図7のクロック信号生成部120)を含む。第1の位相差信号出力部10は、第1〜第nのクロック信号と第1の信号SG1に基づく積分処理を行う第1〜第nの積分器(図11の積分器61〜63)を有する。第2の位相差信号出力部20は、第1〜第nのクロック信号と第2の信号SG2に基づく積分処理を行う第n+1〜第2nの積分器を有する。
Further, in the present embodiment, the
具体的には、第1〜第nのクロック信号の位相は、基準クロック信号RFCKを基準として360度/n刻みである。例えば、図12ではn=3であり、第1〜第3のクロック信号(CKAI1、CKBI1、CKCI1)の位相は360度/3=120度刻みである。なお、第1〜第3のクロック信号(CKAI1、CKBI1、CKCI1)と位相が90度異なるクロック信号(CKAQ1、CKBQ1、CKCQ1)、それらと位相が180度異なるクロック信号(CKAI2、CKBI2、CKCI2、CKAQ2、CKBQ2、CKCQ2)を加えると、360度/12=30度の多相クロックになっている。 Specifically, the phase of the first to nth clock signals is in increments of 360 degrees / n with reference to the reference clock signal RFCK. For example, in FIG. 12, n = 3, and the phases of the first to third clock signals (CKAI1, CKBI1, CKCI1) are in 360 degree / 3 = 120 degree increments. The clock signals (CKAQ1, CKBQ1, CKCQ1) whose phase is 90 degrees different from that of the first to third clock signals (CKAI1, CKBI1, CKCI1), and the clock signals (CKAI2, CKBI2, CKCI2, CKAQ2) whose phase is 180 degrees different from them. , CKBQ2, CCKQ2), it becomes a multi-phase clock of 360 degrees / 12 = 30 degrees.
このようにすれば、図13〜図15で後述するように、互いに位相が異なる第1〜第nの積分値の特性(PHAI1、PHBI1、PHCI1)が得られる。これにより、入力位相差に対して、位相が異なるn個の特性に基づくn個の積分値が得られる。積分処理は積分器の特性ばらつき等によって非線形性を有する可能性があり、それによって入力位相差と出力位相差の間に非線形性が生じる可能性がある。この点、本実施形態によれば、n個の積分値を例えば平均して位相差を求めることで、入力位相差と出力位相差の間に非線形性を低減できる。 In this way, as will be described later in FIGS. 13 to 15, the characteristics (PHAI1, PHBI1, PHCI1) of the first to nth integrated values having different phases from each other can be obtained. As a result, n integral values based on n characteristics having different phases can be obtained with respect to the input phase difference. The integration process may have non-linearity due to variations in the characteristics of the integrator, etc., which may cause non-linearity between the input phase difference and the output phase difference. In this regard, according to the present embodiment, the non-linearity between the input phase difference and the output phase difference can be reduced by, for example, averaging n integrated values to obtain the phase difference.
また本実施形態では、測定部30は、第1〜第nの積分器の出力信号及び第n+1〜第2nの積分器の出力信号のいずれかを選択するセレクター(図16のセレクター31)と、セレクターからの信号をA/D変換するA/D変換回路(図16のA/D変換回路32)と、A/D変換された第1〜第nの積分器の出力信号及び第n+1〜第2nの積分器の出力信号に基づいて、時間差を求める処理部(図16の処理部33)と、を有する。
Further, in the present embodiment, the measuring
このようにすれば、第1〜第nの積分器の出力信号及び第n+1〜第2nの積分器の出力信号を時分割にA/D変換できる。これにより、回路規模を節約できる。また、このようなA/D変換を行うことで、デジタル信号処理により積分器の出力信号(積分値)に基づいて時間差を求めることができる。また、デジタル信号処理において、例えば、図19〜図21で後述する積分器のばらつき補正等の種々の処理を簡素な構成で実現できる。 In this way, the output signal of the first to nth integrators and the output signal of the n + 1 to 2n integrators can be A / D converted into time division. As a result, the circuit scale can be saved. Further, by performing such A / D conversion, the time difference can be obtained based on the output signal (integrated value) of the integrator by digital signal processing. Further, in digital signal processing, various processes such as correction of variation of the integrator, which will be described later in FIGS. 19 to 21, can be realized with a simple configuration.
2.第2の構成例
図5は、本実施形態の回路装置の第2の構成例である。図5では、回路装置100が更にカウンター110を含む。
2. Second Configuration Example FIG. 5 is a second configuration example of the circuit device of the present embodiment. In FIG. 5, the
カウンター110は、第1の信号SG1がアクティブになってから、第2の信号SG2がアクティブになるまでの基準クロック信号RFCKのクロック数をカウントする。そして、測定部30は、カウンター110のカウント値CNQと第1の位相差信号PH1と第2の位相差信号PH2に基づいて、第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の時間差を測定する。
The
図6は、第2の構成例の回路装置の動作を説明するタイミングチャートである。カウンター110は、第1の信号SG1がアクティブになったことを検出してカウント動作を開始し、第2の信号SG2がアクティブになったことを検出してカウント動作を停止する。図6の例では、第1の信号SG1の立ち上がりエッジから第2の信号SG2の立ち上がりエッジまでの間に基準クロック信号RFCKが1クロック入力されるので、カウント値CNQ=1となる。
FIG. 6 is a timing chart illustrating the operation of the circuit device of the second configuration example. The
なお、第1のパルス信号PSG1がアクティブになったことを検出してカウント動作を開始し、第2のパルス信号PSG2がアクティブになったことを検出してカウント動作を停止してもよい。 The counting operation may be started by detecting that the first pulse signal PSG1 has become active, and may stop the counting operation by detecting that the second pulse signal PSG2 has become active.
図6に示すように、第1の信号SG1と基準クロック信号RFCKの位相差が60度と検出され、第2の信号SG2と基準クロック信号RFCKの位相差が270度と検出されたとする。この場合、測定部30は、第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の位相差を、−60度+(CNQ×360度)+270度と求める。図6ではCNQ=1なので、位相差は570度となる。
As shown in FIG. 6, it is assumed that the phase difference between the first signal SG1 and the reference clock signal RFCK is detected as 60 degrees, and the phase difference between the second signal SG2 and the reference clock signal RFCK is detected as 270 degrees. In this case, the measuring
第2の信号SG2が第1の信号SG1よりも前に入力された場合には、カウンター110は、第2の信号SG2がアクティブになったことを検出してカウント動作を開始し、第1の信号SG1がアクティブになったことを検出してカウント動作を停止する。この場合、カウント値CNQの符号を負にする。
When the second signal SG2 is input before the first signal SG1, the
従来の位相差検出方式ではセンサーで積分処理を行うため、ダイナミックレンジ(測定できる位相差や距離、時間のレンジ)を広げることが困難である。この点、本実施形態によれば、第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の位相差が360度より大きい(時間差が基準クロック信号RFCKの1周期より大きい)場合であっても、位相差を検出できる。これにより、広いダイナミックレンジの測定が可能になる。 In the conventional phase difference detection method, since the integration process is performed by the sensor, it is difficult to widen the dynamic range (measureable phase difference, distance, and time range). In this regard, according to the present embodiment, even when the phase difference between the first signal SG1 and the second signal SG2 is larger than 360 degrees (the time difference is larger than one cycle of the reference clock signal RFCK), the phase difference Can be detected. This makes it possible to measure a wide dynamic range.
3.詳細な構成例
図7は、本実施形態の回路装置の詳細な構成例である。回路装置100は、第1の位相差信号出力部10、第2の位相差信号出力部20、測定部30、クロック信号生成部120(クロック信号生成回路)を含む。なお、本実施形態は図7の構成に限定されず、その構成要素の一部を省略したり、他の構成要素(例えば図5のカウンター110)を追加したりする等の種々の変形実施が可能である。
3. 3. Detailed Configuration Example FIG. 7 is a detailed configuration example of the circuit device of the present embodiment. The
クロック信号生成部120は、クロック信号MCK(マスタークロック信号)からクロック信号RFCK2、CKI、CKQを生成する。クロック信号RFCK2は、基準クロック信号RFCKの2倍の周波数を有するクロック信号である。クロック信号CKI、CKQは、基準クロック信号RFCKから位相がシフトされたクロック信号(多相クロック信号)である。クロック信号MCKは、基準クロック信号RFCKよりも周波数が高いクロック信号であり、回路装置100の内部で生成されるクロック信号、又は回路装置100の外部から供給されるクロック信号である。例えば、クロック信号生成部120は分周器等から構成される。
The clock
第1の位相差信号出力部10は、第1のセレクター15、第1のDLL回路130、第1の積分処理部60(第1の積分処理回路)を含む。第1のDLL回路130は、第1のパルス信号生成部40(第1のパルス信号生成回路)、第1の遅延制御回路50を含む。
The first phase difference
第1のセレクター15は、第1の信号SG1とクロック信号RFCK2のいずれかを選択し、その選択した信号SLQ1を出力する。第1のパルス信号生成部40は、第1の遅延回路41を含み、パルス幅が第1の遅延回路41の遅延時間で設定される第1のパルス信号PSG1を生成する。第1の遅延制御回路50は、第1の遅延回路41の遅延時間を制御する制御信号CT1を出力し、その遅延時間が基準クロック信号RFCKのパルス幅となるように制御する。例えば、第1の遅延回路41は、複数の遅延素子が直列に接続された回路である。遅延素子は、例えばインバーターと、インバーターの出力に設けられた可変容量キャパシター(負荷容量)である。そして可変容量キャパシターの容量値が制御信号CT1により制御され、第1の遅延回路41の遅延時間が制御される。第1の遅延制御回路50は、第1の遅延回路41の出力信号DLQ1とクロック信号RFCK2との位相差を検出して信号DT1を出力する位相差検出部51(位相差検出回路)と、信号DT1に基づいて制御信号CT1を出力する制御部52(制御回路)とを含む。第1の積分処理部60は、第1のパルス信号PSG1とクロック信号CKI、CKQに基づいて積分処理を行い、第1の位相差信号PH1を出力する。
The
第2の位相差信号出力部20は、第2のセレクター25、第2のDLL回路140、第2の積分処理部90(第2の積分処理回路)を含む。第2のDLL回路140は、第2のパルス信号生成部70(第2のパルス信号生成回路)、第2の遅延制御回路80を含む。
The second phase difference
第2のセレクター25は、第2の信号SG2とクロック信号RFCK2のいずれかを選択し、その選択した信号SLQ2を出力する。第2のパルス信号生成部70は、第2の遅延回路71を含み、パルス幅が第2の遅延回路71の遅延時間で設定される第2のパルス信号PSG2を生成する。第2の遅延制御回路80は、第2の遅延回路71の遅延時間を制御する制御信号CT2を出力し、その遅延時間が基準クロック信号RFCKのパルス幅となるように制御する。第2の遅延回路71は第1の遅延回路41と同様な構成である。第2の遅延制御回路80は、第2の遅延回路71の出力信号DLQ2とクロック信号RFCK2との位相差を検出して信号DT2を出力する位相差検出部81(位相差検出回路)と、信号DT2に基づいて制御信号CT2を出力する制御部82(制御回路)とを含む。第2の積分処理部90は、第2のパルス信号PSG2とクロック信号CKI、CKQに基づいて積分処理を行い、第2の位相差信号PH2を出力する。
The
図8は、詳細な構成例の回路装置の動作を説明するフローチャートである。動作を開始すると測定部30(図16の処理部33)はパルス幅測定モードを設定する(S1)。パルス幅測定モードでは、第1の位相差信号出力部10及び第2の位相差信号出力部20は、基準クロック信号RFCKのパルス幅を測定して遅延回路の遅延時間(遅延量)を設定(ロック)するパルス幅測定モードを設定する(S1)。
FIG. 8 is a flowchart illustrating the operation of the circuit device of the detailed configuration example. When the operation is started, the measurement unit 30 (processing
図9は、パルス幅測定モードにおける第1の位相差信号出力部の動作を説明する図である。ここでは第1の位相差信号出力部10を例に説明するが、第2の位相差信号出力部20の動作も同様である。なお、図9では動作に関わる構成要素を図示し、他の構成要素は図示を省略する。
FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating the operation of the first phase difference signal output unit in the pulse width measurement mode. Here, the first phase difference
パルス幅測定モードでは、第1のセレクター15は、クロック信号RFCK2を選択し、信号SLQ1として出力する。遅延回路41は、信号SLQ1(=RFCK2)を遅延させた信号DLQ1を出力する。位相差検出部51は、クロック信号RFCK2と信号DLQ1の位相差を検出し、その検出された位相差を表す信号DT1を出力する。制御部52は、信号DT1に基づいて、クロック信号RFCK2と信号DLQ1の位相差がゼロとなるように制御信号CT1を生成する。クロック信号RFCK2の周波数は、基準クロック信号RFCKの周波数の2倍なので、第1の遅延回路41の遅延時間は、基準クロック信号RFCKの半周期(基準クロック信号RFCKのデューティーが50%の場合において基準クロック信号RFCKのハイパルスの幅)にロックされる。
In the pulse width measurement mode, the
図8に示すように、測定部30は位相差検出モードを設定する(S2)。位相差検出モードでは、第1の位相差信号出力部10及び第2の位相差信号出力部20は、第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の位相差を検出する。
As shown in FIG. 8, the measuring
図10は、位相差検出モードにおける第1の位相差信号出力部の動作を説明する図である。ここでは第1の位相差信号出力部10を例に説明するが、第2の位相差信号出力部20の構成及び動作も同様である。なお、図10では動作に関わる構成要素を図示し、他の構成要素は図示を省略する。
FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating the operation of the first phase difference signal output unit in the phase difference detection mode. Here, the first phase difference
第1のパルス信号生成部40は、第1の遅延回路41、ラッチ回路42、NOR回路43を含む。位相差検出モードでは、第1のセレクター15は、第1の信号SG1を選択し、信号SLQ1として出力する。ラッチ回路42は、信号SLQ1(=SG1)の立ち上がりエッジでハイレベルを取り込み、信号LQ1をローレベルからハイレベルに変化させ、信号LQB1(LQ1の論理反転信号)をハイレベルからローレベルに変化させる。第1の遅延回路41は、制御信号CT1で設定される遅延時間で信号LQ1を遅延させ、信号DLQ1を出力する。制御信号CT1は、パルス幅測定モードで設定された値が維持されている。NOR回路43は、信号LQB1と信号DLQ1の否定論理和信号を第1のパルス信号PSG1として出力する。制御信号CT1は、パルス幅測定モードで設定された値が維持されており、第1のパルス信号PSG1のパルス幅は基準クロック信号RFCKのパルス幅と同じになる。第1の積分処理部60は、第1のパルス信号PSG1に基づいて積分処理を行い、第1の位相差信号PH1を出力する。
The first pulse
図8に示すように、測定部30は、位相差検出モードにおいて出力される第1の位相差信号PH1と第2の位相差信号PH2を第1の位相差データと第2の位相差データにA/D変換する(S3)。次に、測定部30は、デジタル信号処理により第1の位相差データと第2の位相差データから第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の遷移タイミングの時間差を求める(S4)。
As shown in FIG. 8, the measuring
4.積分処理部
図11は、第1の積分処理部の詳細な構成例である。第1の積分処理部60は、積分器61〜66(複数の積分器、第1〜第6の積分器)を含む。なお、ここでは第1の積分処理部60を例に説明するが、第2の積分処理部90も同様に複数の積分器(第7〜第12の積分器)を含み、同様に動作により第2のパルス信号PSG2に基づく積分処理を行う。
4. Integral processing unit FIG. 11 is a detailed configuration example of the first integral processing unit. The first
クロック信号生成部120は、クロック信号CKAI、CKBI、CKCI、CKAQ、CKBQ、CKCQを生成し、積分器61、62、63、64、65、66に供給する。クロック信号CKAI、CKBI、CKCIは図7のクロック信号CKIに対応し、クロック信号CKAQ、CKBQ、CKCQは図7のクロック信号CKQに対応する。積分器61、62、63、64、65、66は、供給されるクロック信号と第1のパルス信号PSG1に基づいて積分処理を行い、積分値PHAI1、PHBI1、PHCI1、PHAQ1、PHBQ1、PHCQ1を出力する。積分値PHAI1、PHBI1、PHCI1、PHAQ1、PHBQ1、PHCQ1は、図7の第1の位相差信号PH1に対応する。
The clock
図12は、クロック信号生成部が生成するクロック信号のタイミングチャートである。 FIG. 12 is a timing chart of the clock signal generated by the clock signal generation unit.
クロック信号CKAI、CKBI、CKCI、CKAQ、CKBQ、CKCQの各々は、位相が反転した(位相が180度異なる)2つのクロック信号の組み合わせである。例えば、クロック信号CKAIは、クロック信号CKAI1、CKAI2から構成される。そして、これら12個のクロック信号は、基準クロック信号RFCKに対して30度(=360度/12)ずつ位相がずれた多相クロック信号になっている。 Clock signals Each of CKAI, CKBI, CKCI, CKAQ, CKBQ, and CKCQ is a combination of two clock signals whose phases are inverted (phases differ by 180 degrees). For example, the clock signal CKAI is composed of clock signals CKAI1 and CKAI2. The 12 clock signals are multi-phase clock signals that are out of phase by 30 degrees (= 360 degrees / 12) with respect to the reference clock signal RFCK.
具体的には、クロック信号CKAI1は基準クロック信号RFCKと同位相であり、クロック信号CKBI1、CKCI1は、基準クロック信号RFCKに対して位相が120度、240度だけ遅れている。クロック信号CKAQ1、CKBQ1、CKCQ1は、クロック信号CKAI1、CKBI1、CKCI1に対して位相が90度だけ遅れている。そしてクロック信号CKAI2、CKBI2、CKCI2、CKAQ2、CKBQ2、CKCQ2は、クロック信号CKAI1、CKBI1、CKCI1、CKAQ1、CKBQ1、CKCQ1に対して位相が反転されている(位相が180度異なっている)。 Specifically, the clock signal CKAI1 has the same phase as the reference clock signal RFCK, and the clock signals CKBI1 and CKCI1 are delayed by 120 degrees and 240 degrees from the reference clock signal RFCK. The clock signals CKAQ1, CKBQ1, and CKCQ1 are 90 degrees out of phase with the clock signals CKAI1, CKBI1, and CKCI1. The phases of the clock signals CKAI2, CKBI2, CKCI2, CKAQ2, CKBQ2, and CKCQ2 are inverted with respect to the clock signals CKAI1, CKBI1, CKCI1, CKAQ1, CKBQ1, and CKCQ1 (the phases are 180 degrees different).
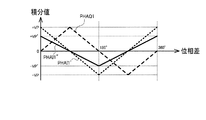
図13〜図15は、多相クロックによる積分処理の積分値の特性を示す図である。横軸の位相差は、基準クロック信号RFCKと第1の信号SG1の位相差である。図12で説明したように、基準クロック信号RFCKを基準としてクロック信号CKAI、CKBI、CKCIの位相は0度、120度、240度になっている。そのため、図13〜図15に示すように、積分値PHAI1の特性に対して、積分値PHBI1、PHCI1の特性は120度、240度ずれている。同様に、積分値PHAQ1の特性に対して、積分値PHBQ1、PHCQ1の特性は120度、240度ずれている。 13 to 15 are diagrams showing the characteristics of the integrated value of the integral processing by the polymorphic clock. The phase difference on the horizontal axis is the phase difference between the reference clock signal RFCK and the first signal SG1. As described with reference to FIG. 12, the phases of the clock signals CKAI, CKBI, and CKCI are 0 degrees, 120 degrees, and 240 degrees with reference to the reference clock signal RFCK. Therefore, as shown in FIGS. 13 to 15, the characteristics of the integrated values PHBI1 and PHCI1 deviate from the characteristics of the integrated value PHAI1 by 120 degrees and 240 degrees. Similarly, the characteristics of the integrated values PHBQ1 and PHCQ1 deviate from the characteristics of the integrated value PHAQ1 by 120 degrees and 240 degrees.
測定部30は、積分値PHAI1、PHAQ1から第1の位相差を求め、積分値PHBI1、PHBQ1から第2の位相差を求め、積分値PHCI1、PHCQ1から第3の位相差を求める。そして、第1〜第3の位相差の平均値を、第1の信号SG1と基準クロック信号RFCKの位相差として求める。
The measuring
理想的には、積分値PHAI1、PHAQ1の組だけでも、入力位相差に対して線形な特性の出力位相差が得られる。入力位相差は、入力された基準クロック信号RFCKと第1の信号SG1の位相差であり、出力位相差は、積分処理に基づく位相差である。しかしながら、積分器の誤差(例えば積分値のフルスケール誤差やオフセット等)によって、入力位相差と出力位相差が線形にならない可能性がある。 Ideally, the output phase difference having a characteristic linear with respect to the input phase difference can be obtained only with the set of the integrated values PHAI1 and PHAQ1. The input phase difference is the phase difference between the input reference clock signal RFCK and the first signal SG1, and the output phase difference is the phase difference based on the integration process. However, there is a possibility that the input phase difference and the output phase difference will not be linear due to the error of the integrator (for example, the full-scale error of the integrated value, the offset, etc.).
この点、本実施形態では、位相を異ならせた多相クロックで積分処理を行って複数の位相差(第1〜第3の位相差)を求め、その複数の位相差を平均するので、入力位相差と出力位相差の間の非線形性を平均化できる。例えば、入力位相差が180度の場合、図13において積分値PHAI1の特性が−VPで折り返す点になっている。このような特性が折り返す点では非線形性が出やすくなる。しかし、図14、図15では、位相差180度における積分値PHBI1、PHCI1の特性は直線になっている。このため、第1〜第3の位相差を平均することで、非線形性を低減できる。 In this regard, in the present embodiment, a plurality of phase differences (first to third phase differences) are obtained by performing integration processing with polyphase clocks having different phases, and the plurality of phase differences are averaged. The non-linearity between the phase difference and the output phase difference can be averaged. For example, when the input phase difference is 180 degrees, the characteristic of the integrated value PHAI1 in FIG. 13 is a point that folds back at −VP. Non-linearity is likely to occur at the point where such characteristics are folded back. However, in FIGS. 14 and 15, the characteristics of the integrated values PHBI1 and PHCI1 at a phase difference of 180 degrees are linear. Therefore, the non-linearity can be reduced by averaging the first to third phase differences.
5.測定部
図16は、測定部の詳細な構成例である。測定部30は、セレクター31(マルチプレクサー)、A/D変換回路32、処理部33(デジタル信号処理部、処理回路、ロジック回路)を含む。
5. Measuring unit FIG. 16 is a detailed configuration example of the measuring unit. The measuring
セレクター31には、第1の位相差信号出力部10から積分値PHAI1、PHAQ1、PHBI1、PHBQ1、PHCI1、PHCQ1が入力され、第2の位相差信号出力部20から積分値PHAI2、PHAQ2、PHBI2、PHBQ2、PHCI2、PHCQ2が入力される。セレクター31は、これらの信号を1つずつ時分割に選択し、その選択した信号を信号MXQとして出力する。A/D変換回路32は、信号MXQとして入力される積分値PHAI1、PHAQ1、PHBI1、PHBQ1、PHCI1、PHCQ1、PHAI2、PHAQ2、PHBI2、PHBQ2、PHCI2、PHCQ2を時分割にA/D変換し、そのA/D変換された積分値(積分データ)をデータADQとして出力する。処理部33は、デジタル信号処理により、データADQに基づいて時間差データTQを求める。
Integral values PHAI1, PHAQ1, PHBI1, PHBQ1, PHCI1, PHCQ1 are input to the
具体的には、処理部33は、位相差算出部34と時間差算出部35を含む。位相差算出部34は、積分値PHAI1、PHAQ1から第1の位相差を求め、積分値PHBI1、PHBQ1から第2の位相差を求め、積分値PHCI1、PHCQ1から第3の位相差を求める。また積分値PHAI2、PHAQ2から第4の位相差を求め、積分値PHBI2、PHBQ2から第5の位相差を求め、積分値PHCI2、PHCQ1から第6の位相差を求める。位相差算出部34は、第1〜第3の位相差を平均して、第1の信号SG1と基準クロック信号RFCKの位相差を求め、第4〜第6の位相差を平均して、第2の信号SG2と基準クロック信号RFCKの位相差を求める。時間差算出部35は、第1の信号SG1と基準クロック信号RFCKの位相差と、第2の信号SG2と基準クロック信号RFCKの位相差とから、第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の位相差を求め、その位相差に基づいて時間差データTQを出力する。位相差を時間差に変換する手法は、図2等で説明した手法と同様である。
Specifically, the
6.積分器
図17は、積分器の詳細な構成例である。また図18は、積分器の動作を説明するタイミングチャートである。なお、ここでは図11の積分器61を例に説明するが、他の積分器(図11の積分器62〜66、第2の積分処理部90の積分器)も同様の構成である。
6. The integrator FIG. 17 is a detailed configuration example of the integrator. Further, FIG. 18 is a timing chart illustrating the operation of the integrator. Although the
図17に示すように、積分器61は、積分信号生成部GIS、電流生成部IGEN、積分部CINTを含む。
As shown in FIG. 17, the
積分信号生成部GISは、第1のパルス信号PSG1とクロック信号CKAI(CKAI1、CKAI2)から積分信号INCKA、INCKBを生成する。図18に示すように、第1のパルス信号PSG1とクロック信号CKAI1の論理積を積分信号INCKAとして出力し、第1のパルス信号PSG1とクロック信号CKAI2の論理積を積分信号INCKBとして出力する。 The integration signal generation unit GIS generates integration signals INCKA and INCKB from the first pulse signal PSG1 and clock signals CKAI (CKAI1, CKAI2). As shown in FIG. 18, the logical product of the first pulse signal PSG1 and the clock signal CKAI1 is output as the integrated signal INCKA, and the logical product of the first pulse signal PSG1 and the clock signal CKAI2 is output as the integrated signal INCKB.
電流生成部IGENは、積分信号INCKA、INCKBに基づいて電流IP、INを生成し、その電流IP、INを積分部CINTの入力ノードNINP、NINNに供給する。具体的には、積分信号INCKAがハイレベル(アクティブ)であり、積分信号INCKBがローレベル(非アクティブ)である場合には、スイッチ素子SWA1、SWA2がオンになり、スイッチ素子SWB1、SWB2がオフになる。そして、電流源IBBから一定電流値の負電流が電流IPとしてノードNINPに供給され、電流源IBAから一定電流値の正電流が電流INとしてノードNINNに供給され、IP−IN<0となる。一方、積分信号INCKAがローレベル(非アクティブ)であり、積分信号INCKBがハイレベル(アクティブ)である場合には、スイッチ素子SWA1、SWA2がオフになり、スイッチ素子SWB1、SWB2がオンになる。そして、電流源IBAから一定電流値の正電流が電流IPとしてノードNINPに供給され、電流源IBBから一定電流値の負電流が電流INとしてノードNINNに供給され、IP−IN>0となる。 The current generation unit IGEN generates currents IP and IN based on the integration signals INCKA and INCKB, and supplies the currents IP and IN to the input nodes NINP and NINN of the integration unit CINT. Specifically, when the integration signal INCKA is high level (active) and the integration signal INCKB is low level (inactive), the switch elements SWA1 and SWA2 are turned on, and the switch elements SWB1 and SWB2 are turned off. become. Then, a negative current having a constant current value is supplied to the node NINP as a current IP from the current source IBB, and a positive current having a constant current value is supplied to the node NINN as a current IN from the current source IBA, so that IP-IN <0. On the other hand, when the integration signal INCKA is low level (inactive) and the integration signal INCKB is high level (active), the switch elements SWA1 and SWA2 are turned off, and the switch elements SWB1 and SWB2 are turned on. Then, a positive current having a constant current value is supplied to the node NINP as a current IP from the current source IBA, and a negative current having a constant current value is supplied to the node NINN as a current IN from the current source IBB, and IP-IN> 0.
積分部CINTは、差動入力された電流IP、INを積分し、その積分値を電圧VOUT、VOUTNとして差動出力する。即ち、電流IP、INにより供給される電荷を電圧VOUTP、VOUTNに変換する電荷電圧変換を行う。積分部CINTは、負の入力電荷を正の電圧に変換する反転増幅を行う。即ち、積分信号INCKAがハイレベルであり、積分信号INCKBがローレベルである場合、上述のようにIP−IN<0なので、図18に示すようにVOUTP−VOUTNが増加する方向に電圧VOUTP、VOUTNが変化する。一方、積分信号INCKAがローレベルであり、積分信号INCKBがハイレベルである場合、上述のようにIP−IN>0なので、図18に示すようにVOUTP−VOUTNが減少する方向に電圧VOUTP、VOUTNが変化する。このようにして第1のパルス信号PSG1が積分値PHAI1に変換され、図13に示す積分値PHAI1の特性が得られる。 The integrating unit CINT integrates the differentially input currents IP and IN, and differentially outputs the integrated values as voltages VOUT and VOUTN. That is, charge-voltage conversion is performed to convert the electric charge supplied by the currents IP and IN into the voltages VOUTP and VOUTN. The integrator CINT performs inverting amplification that converts a negative input charge into a positive voltage. That is, when the integration signal INCKA is at a high level and the integration signal INCKB is at a low level, since IP-IN <0 as described above, the voltages VOUTP and VOUTN increase in the direction in which VOUTP-VOUTN increases as shown in FIG. Changes. On the other hand, when the integration signal INCKA is at a low level and the integration signal INCKB is at a high level, IP-IN> 0 as described above, so that the voltages VOUTP and VOUTN decrease in the direction in which VOUTP-VOUTN decreases as shown in FIG. Changes. In this way, the first pulse signal PSG1 is converted into the integrated value PHAI1, and the characteristics of the integrated value PHAI1 shown in FIG. 13 are obtained.
積分部CINTにおいて、制御信号APCK(クロック信号)がローレベル(非アクティブ)であり、制御信号APCKの論理反転信号である制御信号XAPCK(クロック信号)がハイレベル(アクティブ)である場合、スイッチ素子SWP1〜SWP4がオフになり、スイッチ素子SWP5〜SWP8がオンになる。この場合、キャパシターCP1〜CP4、アンプ回路AMPにより差動の積分回路(差動の電荷電圧変換回路)が構成され、上述の積分動作が行われる。一方、制御信号APCKがハイレベル(アクティブ)であり、制御信号XAPCKがローレベル(非アクティブ)である場合、スイッチ素子SWP1〜SWP4がオンになり、スイッチ素子SWP5〜SWP8がオフになる。この場合、入力ノードNINP、NINNがコモン電圧VCMに設定され、入力電荷がリセットされ、電圧VOUTP、VOUTNがコモン電圧VCMにリセットされる。 In the integrating unit CINT, when the control signal APCK (clock signal) is low level (inactive) and the control signal XAPCK (clock signal) which is a logical inversion signal of the control signal APCK is high level (active), the switch element. SWP1 to SWP4 are turned off, and switch elements SWP5 to SWP8 are turned on. In this case, the capacitors CP1 to CP4 and the amplifier circuit AMP form a differential integrator circuit (differential charge-voltage conversion circuit), and the above-mentioned integration operation is performed. On the other hand, when the control signal APCK is at a high level (active) and the control signal XAPCK is at a low level (inactive), the switch elements SWP1 to SWP4 are turned on and the switch elements SWP5 to SWP8 are turned off. In this case, the input nodes NINP and NINN are set to the common voltage VCM, the input charge is reset, and the voltages VOUTP and VOUTN are reset to the common voltage VCM.
7.積分器のばらつき補正
図19は、積分器間における積分値の特性のばらつきを説明する図である。図20は、入力位相差に対する出力位相差の特性例である。
7. Correction of integrator variation FIG. 19 is a diagram illustrating variations in the characteristics of integrated values between integrators. FIG. 20 is an example of the characteristics of the output phase difference with respect to the input phase difference.
図19に示すように、積分値PHAQ1の変化範囲の上限が+VPであり、下限が−VPであるとする。即ち、積分値PHAQ1のフルスケール(出力フルスケール)が2VPであるとする。このとき、積分値PHAI1’のように、積分値PHAI1も同一のフルスケール2VPであることが理想である。この理想の場合には、図20の特性CHAのように、入力位相差に対して出力位相差が線形な特性となる。 As shown in FIG. 19, it is assumed that the upper limit of the change range of the integrated value PHAQ1 is + VP and the lower limit is −VP. That is, it is assumed that the full scale (output full scale) of the integrated value PHAQ1 is 2VP. At this time, it is ideal that the integrated value PHAI1 is also the same full-scale 2VP as in the integrated value PHAI1'. In this ideal case, as shown in the characteristic CHA of FIG. 20, the output phase difference has a linear characteristic with respect to the input phase difference.
しかしながら、図19に示す積分値PHAI1”のように、積分値PHAI1のフルスケールが2VP’≠2VPとなる可能性がある。例えば、図17において電流源IBA、IBBが出力する電流の大きさが積分器間でばらつくことで、積分器間でのフルスケールのばらつきが生じる。このようなフルスケールのばらつきが生じた場合、図20の特性CHA’のように、入力位相差に対して出力位相差が非線形な特性となる。 However, as shown in FIG. 19, the full scale of the integrated value PHAI1 may be 2VP'≠ 2VP. For example, in FIG. 17, the magnitude of the current output by the current sources IBA and IBB is large. The variation between the integrators causes a full-scale variation between the integrators. When such a full-scale variation occurs, the output position is relative to the input phase difference as shown in the characteristic CHA'in FIG. The phase difference has a non-linear characteristic.
またフルスケールのばらつきだけでなく、オフセットのばらつきが生じる可能性がある。オフセットのばらつきによっても、入力位相差に対して出力位相差が非線形な特性となる可能性がある。 Moreover, not only full-scale variation but also offset variation may occur. Due to the variation in offset, the output phase difference may have a non-linear characteristic with respect to the input phase difference.
図21は、積分器のばらつき補正を説明する図である。なお、図21では参考に第1のパルス信号PSG1を図示しているが、ばらつき補正時には第1のパルス信号PSG1は積分器に供給されなくてよい。 FIG. 21 is a diagram illustrating variation correction of the integrator. Although the first pulse signal PSG1 is shown in FIG. 21 for reference, the first pulse signal PSG1 does not have to be supplied to the integrator at the time of variation correction.
図21に示すように、回路装置100は各積分器について上限測定、下限測定、オフセット測定を行う。これらの測定は、第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の時間差を測定する前に行っておく。例えば回路装置100の電源投入時などに行う。
As shown in FIG. 21, the
上限測定時には、積分信号生成部GISが、第1のパルス信号PSG1と同じパルス幅でハイレベルになる積分信号INCKAを出力し、ローレベルの積分信号INCKBを出力する。これは積分値の上限を測定することに相当するので、例えば図19では+VP’が積分値として得られる。下限測定時には、積分信号生成部GISが、ローレベルの積分信号INCKAを出力し、第1のパルス信号PSG1と同じパルス幅でハイレベルになる積分信号INCKBを出力する。これは積分値の下限を測定することに相当するので、例えば図19では−VP’が積分値として得られる。オフセット測定時には、積分信号生成部GISが、ローレベルの積分信号INCKA、INCKBを出力する。これは積分値のオフセットを測定することに相当するので、例えば図19では0が積分値として得られる。 At the time of upper limit measurement, the integration signal generation unit GIS outputs an integration signal INCKA that has the same pulse width as the first pulse signal PSG1 and has a high level, and outputs a low-level integration signal INCKB. Since this corresponds to measuring the upper limit of the integrated value, for example, in FIG. 19, + VP'is obtained as the integrated value. At the time of lower limit measurement, the integration signal generation unit GIS outputs a low-level integration signal INCKA and outputs an integration signal INCKB that has the same pulse width as the first pulse signal PSG1 and becomes a high level. Since this corresponds to measuring the lower limit of the integrated value, for example, in FIG. 19, -VP'is obtained as the integrated value. At the time of offset measurement, the integration signal generation unit GIS outputs low-level integration signals INCKA and INCKB. Since this corresponds to measuring the offset of the integrated value, for example, in FIG. 19, 0 is obtained as the integrated value.
上記の測定で得られた積分値の上限をIMAXとし、下限をIMINとし、オフセットをIOFとし、フルスケールの期待値をFLSとする。また、第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の時間差を測定した際に得られた積分値をMESとする。測定部30の処理部33は、補正された積分値MES’を例えばMES’=(FLS/(IMAX−IMIN))×(MES−IOF)により求める。例えば図19の例ではMES’=(VP/VP’)×MESとなる。このような補正を、各積分器について行う。そして、この補正された積分値に基づいて位相差を求め、その位相差に基づいて時間差を求める。
The upper limit of the integrated value obtained in the above measurement is IMAX, the lower limit is IMIN, the offset is IOF, and the expected value of full scale is FLS. Further, the integrated value obtained when the time difference between the first signal SG1 and the second signal SG2 is measured is defined as MES. The
なお、オフセット測定を行わず、上限と下限の測定値で積分値を補正してもよい。この場合、MES’=(FLS/(IMAX−IMIN))×MESである。 The integrated value may be corrected by the measured values of the upper limit and the lower limit without performing the offset measurement. In this case, MES'= (FLS / (IMAX-IMIN)) × MES.
8.物理量測定装置、電子機器、移動体
図22は、本実施形態の回路装置100を含む物理量測定装置の構成例である。物理量測定装置200は、信号供給部210(信号供給回路)、回路装置100、処理部220(処理回路、処理装置)を含む。なお、本実施形態は図22の構成に限定されず、その構成要素の一部(例えば信号供給部)を省略したり、他の構成要素を追加したりする等の種々の変形実施が可能である。
8. Physical quantity measuring device, electronic device, mobile body FIG. 22 is a configuration example of a physical quantity measuring device including the
図22の物理量測定装置200は、時間デジタル変換の結果に基づいて種々の物理量を測定する装置である。例えば、測定される物理量は時間や距離等であるが、これらに限定されない。
The physical
信号供給部210は、回路装置100に対して第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2を供給する。例えば物理量測定装置200が測距センサーである場合、信号供給部210は、発光部、受光部、制御部を含む。そして、制御部が送信信号により発光部を発光させると共に送信信号を第1の信号SG1として回路装置100に供給する。また制御部は、受光部からの受光信号を波形成形して受信信号を生成し、その受信信号を第2の信号SG2として回路装置100に供給する。或いは物理量測定装置200が時間デジタル変換器である場合、信号供給部210は、外部から入力される2つの信号を波形成形して第1の信号SG1、第2の信号SG2として出力する。或いは、外部から入力される2つの信号をバッファリングして第1の信号SG1、第2の信号SG2として出力する。或いは、信号供給部210は、外部から第1の信号SG1、第2の信号SG2を入力するケーブル等を接続するコネクターであってもよい。
The
回路装置100は、第1の信号SG1と第2の信号SG2の時間差を測定し、時間差データTQを出力する。処理部220は、時間差データTQに基づいて種々のデジタル信号処理を行う。例えば、処理部220は、時間差データTQを物理量に変換する処理を行い、その物理量のデータを出力する。
The
図23は、本実施形態の回路装置100を含む電子機器の構成例である。電子機器300は、回路装置100、アンテナANT、通信部510(通信装置)、処理部520(処理装置)を含む。また操作部530(操作装置)、表示部540(表示装置)、記憶部550(メモリー)を含むことができる。例えば回路装置100と処理部520により物理量測定装置が構成される。なお電子機器300は図23の構成に限定されず、これらの一部の構成要素(例えばアンテナANT、通信部510等)を省略したり、他の構成要素を追加するなどの種々の変形実施が可能である。
FIG. 23 is a configuration example of an electronic device including the
図23の電子機器300としては、例えば、ECU(Electronic Control Unit)等の車載の電子装置や、医療用又は工業用の超音波検査装置等の超音波測定装置や、電波や超音波を用いたレーダーを想定できる。また、電子機器300として、ゲーム装置や、デジタルカメラ又はビデオカメラ等の映像機器や、スマートフォン、携帯電話機、携帯型ゲーム装置、ノートPC又はタブレットPC等の携帯情報端末(移動端末)や、コンテンツを配信するコンテンツ提供端末や、或いは基地局又はルーター等のネットワーク関連機器などの種々の機器を想定できる。
As the
通信部510(無線回路)は、アンテナANTを介して外部からデータを受信したり、外部にデータを送信する処理を行う。処理部520は、電子機器300の制御処理や、通信部510を介して送受信されるデータの種々のデジタル処理、回路装置100が出力する時間差データを用いたデジタル処理などを行う。この処理部520の機能は、例えばマイクロコンピューターなどのプロセッサーにより実現できる。操作部530は、ユーザーが入力操作を行うためのものであり、操作ボタンやタッチパネルディスプレイをなどにより実現できる。表示部540は、各種の情報を表示するものであり、液晶や有機ELなどのディスプレイにより実現できる。なお操作部530としてタッチパネルディスプレイを用いる場合には、このタッチパネルディスプレイが操作部530及び表示部540の機能を兼ねることになる。記憶部550は、データを記憶するものであり、その機能はRAMやROMなどの半導体メモリーやHDD(ハードディスクドライブ)などにより実現できる。
The communication unit 510 (wireless circuit) performs a process of receiving data from the outside or transmitting data to the outside via the antenna ANT. The
図24は、本実施形態の回路装置を含む移動体の例を示す。本実施形態の回路装置100(物理量測定装置)は、例えば、車、飛行機、バイク、自転車、或いは船舶等の種々の移動体に組み込むことができる。移動体は、例えばエンジンやモーター等の駆動機構、ハンドルや舵等の操舵機構、各種の電子機器(車載機器)を備えて、地上や空や海上を移動する機器・装置である。図24は移動体の具体例としての自動車206を概略的に示している。自動車206には、本実施形態の回路装置100を有する物理量測定装置(不図示)が組み込まれる。制御装置208は、この物理量測定装置により生成された物理量に基づいて動作する。例えば、制御装置208は、自動車206と物体との距離に応じて運転アシスト制御や自動運転制御を行うECUであってもよい。なお本実施形態の回路装置や物理量測定装置が組み込まれる機器は、このような制御装置208には限定されず、自動車206等の移動体に設けられる種々の機器(車載機器)に組み込むことが可能である。
FIG. 24 shows an example of a mobile body including the circuit device of the present embodiment. The circuit device 100 (physical quantity measuring device) of the present embodiment can be incorporated into various moving bodies such as a car, an airplane, a motorcycle, a bicycle, or a ship. A moving body is a device / device that is provided with, for example, a drive mechanism such as an engine or a motor, a steering mechanism such as a handle or a rudder, and various electronic devices (vehicle-mounted devices), and moves on the ground, in the air, or on the sea. FIG. 24 schematically shows an
なお、上記のように本実施形態について詳細に説明したが、本発明の新規事項および効果から実体的に逸脱しない多くの変形が可能であることは当業者には容易に理解できるであろう。従って、このような変形例はすべて本発明の範囲に含まれるものとする。例えば、明細書又は図面において、少なくとも一度、より広義または同義な異なる用語と共に記載された用語は、明細書又は図面のいかなる箇所においても、その異なる用語に置き換えることができる。また本実施形態及び変形例の全ての組み合わせも、本発明の範囲に含まれる。また回路装置、物理量測定装置、電子機器、移動体の構成・動作等も、本実施形態で説明したものに限定されず、種々の変形実施が可能である。 Although the present embodiment has been described in detail as described above, those skilled in the art will easily understand that many modifications that do not substantially deviate from the novel matters and effects of the present invention are possible. Therefore, all such modifications are included in the scope of the present invention. For example, a term described at least once in a specification or drawing with a different term in a broader or synonymous manner may be replaced by that different term anywhere in the specification or drawing. All combinations of the present embodiment and modifications are also included in the scope of the present invention. Further, the configuration / operation of the circuit device, the physical quantity measuring device, the electronic device, the moving body, and the like are not limited to those described in the present embodiment, and various modifications can be performed.
10…第1の位相差信号出力部、15…第1のセレクター、
20…第2の位相差信号出力部、25…第2のセレクター、30…測定部、
31…セレクター、32…A/D変換回路、33…処理部、34…位相差算出部、
35…時間差算出部、40…第1のパルス信号生成部、41…遅延回路、
41…第1の遅延回路、42…ラッチ回路、43…NOR回路、
50…第1の遅延制御回路、51…位相差検出部、52…制御部、
60…第1の積分処理部、61〜66…積分器、70…第2のパルス信号生成部、
71…第2の遅延回路、80…第2の遅延制御回路、81…位相差検出部、
82…制御部、90…第2の積分処理部、100…回路装置、110…カウンター、
120…クロック信号生成部、130…第1のDLL回路、
140…第2のDLL回路、200…物理量測定装置、206…自動車(移動体)、
208…制御装置、210…信号供給部、220…処理部、300…電子機器、
510…通信部、520…処理部、530…操作部、540…表示部、550…記憶部、
PH1…第1の位相差信号、PH2…第2の位相差信号、PSG1…第1のパルス信号、
PSG2…第2のパルス信号、RFCK…基準クロック信号、SG1…第1の信号、
SG2…第2の信号、TDF…時間差、TH…パルス幅、TPS…パルス幅、
TQ…時間差データ
10 ... 1st phase difference signal output unit, 15 ... 1st selector,
20 ... 2nd phase difference signal output unit, 25 ... 2nd selector, 30 ... Measuring unit,
31 ... Selector, 32 ... A / D conversion circuit, 33 ... Processing unit, 34 ... Phase difference calculation unit,
35 ... Time difference calculation unit, 40 ... First pulse signal generation unit, 41 ... Delay circuit,
41 ... 1st delay circuit, 42 ... latch circuit, 43 ... NOR circuit,
50 ... First delay control circuit, 51 ... Phase difference detection unit, 52 ... Control unit,
60 ... 1st integrator processing unit, 61-66 ... integrator, 70 ... second pulse signal generator,
71 ... second delay circuit, 80 ... second delay control circuit, 81 ... phase difference detector,
82 ... control unit, 90 ... second integration processing unit, 100 ... circuit device, 110 ... counter,
120 ... Clock signal generator, 130 ... First DLL circuit,
140 ... second DLL circuit, 200 ... physical quantity measuring device, 206 ... automobile (mobile body),
208 ... control device, 210 ... signal supply unit, 220 ... processing unit, 300 ... electronic device,
510 ... Communication unit, 520 ... Processing unit, 530 ... Operation unit, 540 ... Display unit, 550 ... Storage unit,
PH1 ... 1st phase difference signal, PH2 ... 2nd phase difference signal, PSG1 ... 1st pulse signal,
PSG2 ... second pulse signal, RFCK ... reference clock signal, SG1 ... first signal,
SG2 ... second signal, TDF ... time difference, TH ... pulse width, TPS ... pulse width,
TQ ... Time difference data
Claims (12)
第2の信号が入力され、前記基準クロック信号と前記第2の信号の位相差を表す第2の位相差信号を出力する第2の位相差信号出力部と、
前記第1の位相差信号と前記第2の位相差信号に基づいて、前記第1の信号と前記第2の信号の時間差を測定する測定部と、
を含み、
前記第1の位相差信号出力部は、
前記第1の信号に基づいて、前記基準クロック信号のパルス幅に対応するパルス幅の第1のパルス信号を生成する第1のパルス信号生成部を有し、
前記第2の位相差信号出力部は、
前記第2の信号に基づいて、前記基準クロック信号の前記パルス幅に対応するパルス幅の第2のパルス信号を生成する第2のパルス信号生成部を有することを特徴とする回路装置。 A first phase difference signal output unit that receives a first signal and outputs a first phase difference signal that represents the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the first signal.
A second phase difference signal output unit that receives a second signal and outputs a second phase difference signal that represents the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the second signal.
A measuring unit that measures the time difference between the first signal and the second signal based on the first phase difference signal and the second phase difference signal.
Including
The first phase difference signal output unit is
It has a first pulse signal generation unit that generates a first pulse signal having a pulse width corresponding to the pulse width of the reference clock signal based on the first signal.
The second phase difference signal output unit is
A circuit device including a second pulse signal generation unit that generates a second pulse signal having a pulse width corresponding to the pulse width of the reference clock signal based on the second signal.
前記第1の位相差信号出力部は、
前記基準クロック信号と前記第1の信号に基づく積分処理を行って、前記第1の位相差信号を出力し、
前記第2の位相差信号出力部は、
前記基準クロック信号と前記第2の信号に基づく積分処理を行って、前記第2の位相差信号を出力することを特徴とする回路装置。 In the circuit device according to claim 1,
The first phase difference signal output unit is
Integral processing based on the reference clock signal and the first signal is performed, and the first phase difference signal is output.
The second phase difference signal output unit is
A circuit device characterized in that an integration process based on the reference clock signal and the second signal is performed to output the second phase difference signal.
前記第1のパルス信号生成部は、
第1の遅延回路を有し、
前記第1の位相差信号出力部は、
前記第1の遅延回路の遅延時間を、前記基準クロック信号の前記パルス幅に対応する遅延時間に設定する第1の遅延制御回路を有し、
前記第2のパルス信号生成部は、
第2の遅延回路を有し、
前記第2の位相差信号出力部は、
前記第2の遅延回路の遅延時間を、前記基準クロック信号の前記パルス幅に対応する遅延時間に設定する第2の遅延制御回路を有することを特徴とする回路装置。 In the circuit device according to claim 1 or 2.
The first pulse signal generation unit
It has a first delay circuit and
The first phase difference signal output unit is
It has a first delay control circuit that sets the delay time of the first delay circuit to a delay time corresponding to the pulse width of the reference clock signal.
The second pulse signal generation unit
Has a second delay circuit,
The second phase difference signal output unit is
A circuit device comprising a second delay control circuit that sets the delay time of the second delay circuit to a delay time corresponding to the pulse width of the reference clock signal.
前記第1の位相差信号出力部は、
パルス幅測定モードでは、前記第1の遅延回路に前記基準クロック信号を出力し、位相差検出モードでは、前記第1のパルス信号生成部に前記第1の信号を出力する第1のセレクターを有し、
前記第2の位相差信号出力部は、
前記パルス幅測定モードでは、前記第2の遅延回路に前記基準クロック信号を出力し、前記位相差検出モードでは、前記第2のパルス信号生成部に前記第2の信号を出力する第2のセレクターを有することを特徴とする回路装置。 In the circuit device according to claim 3,
The first phase difference signal output unit is
In the pulse width measurement mode, the reference clock signal is output to the first delay circuit, and in the phase difference detection mode, the first pulse signal generation unit has a first selector that outputs the first signal. And
The second phase difference signal output unit is
In the pulse width measurement mode, the reference clock signal is output to the second delay circuit, and in the phase difference detection mode, the second signal is output to the second pulse signal generation unit. A circuit device characterized by having.
第2の信号が入力され、前記基準クロック信号と前記第2の信号の位相差を表す第2の位相差信号を出力する第2の位相差信号出力部と、
前記第1の位相差信号と前記第2の位相差信号に基づいて、前記第1の信号と前記第2の信号の時間差を測定する測定部と、
を含み、
前記第1の位相差信号出力部は、
前記第1の信号に基づいて、所定パルス幅の第1のパルス信号を生成する第1のパルス信号生成部と、
前記基準クロック信号と前記第1のパルス信号に基づく積分処理を行う第1の積分処理部と、
を有し、
前記第2の位相差信号出力部は、
前記第2の信号に基づいて、前記所定パルス幅の第2のパルス信号を生成する第2のパルス信号生成部と、
前記基準クロック信号と前記第2のパルス信号に基づく積分処理を行う第2の積分処理部と、
を有することを特徴とする回路装置。 A first phase difference signal output unit that receives a first signal and outputs a first phase difference signal that represents the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the first signal.
A second phase difference signal output unit that receives a second signal and outputs a second phase difference signal that represents the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the second signal.
A measuring unit that measures the time difference between the first signal and the second signal based on the first phase difference signal and the second phase difference signal.
Including
The first phase difference signal output unit is
A first pulse signal generation unit that generates a first pulse signal having a predetermined pulse width based on the first signal, and a first pulse signal generation unit .
A first integration processing unit that performs integration processing based on the reference clock signal and the first pulse signal, and
Have,
The second phase difference signal output unit is
A second pulse signal generation unit that generates a second pulse signal having the predetermined pulse width based on the second signal.
A second integration processing unit that performs integration processing based on the reference clock signal and the second pulse signal, and
A circuit device characterized by having.
前記所定パルス幅は、前記基準クロック信号のパルス幅に対応するパルス幅であることを特徴とする回路装置。 In the circuit device according to claim 5,
A circuit device characterized in that the predetermined pulse width is a pulse width corresponding to the pulse width of the reference clock signal.
第2の信号が入力され、前記基準クロック信号と前記第2の信号の位相差を表す第2の位相差信号を出力する第2の位相差信号出力部と、
前記第1の位相差信号と前記第2の位相差信号に基づいて、前記第1の信号と前記第2の信号の時間差を測定する測定部と、
前記基準クロック信号に基づいて、互いに位相が異なる第1〜第nのクロック信号(nは2以上の整数)を生成するクロック信号生成部と、
を含み、
前記第1の位相差信号出力部は、
前記第1〜第nのクロック信号と前記第1の信号に基づく積分処理を行う第1〜第nの積分器を有し、
前記第2の位相差信号出力部は、
前記第1〜第nのクロック信号と前記第2の信号に基づく積分処理を行う第n+1〜第2nの積分器を有することを特徴とする回路装置。 A first phase difference signal output unit that receives a first signal and outputs a first phase difference signal that represents the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the first signal.
A second phase difference signal output unit that receives a second signal and outputs a second phase difference signal that represents the phase difference between the reference clock signal and the second signal.
A measuring unit that measures the time difference between the first signal and the second signal based on the first phase difference signal and the second phase difference signal.
A clock signal generation unit that generates first to nth clock signals (n is an integer of 2 or more) having different phases based on the reference clock signal.
Including
The first phase difference signal output unit is
It has the first to nth clock signals and the first to nth integrators that perform integration processing based on the first signal.
The second phase difference signal output unit is
A circuit device including an n + 1 to 2n integrator that performs an integration process based on the first to second clock signals and the second signal.
前記測定部は、
前記第1〜第nの積分器の出力信号及び前記第n+1〜第2nの積分器の出力信号のいずれかを選択するセレクターと、
前記セレクターからの信号をA/D変換するA/D変換回路と、
A/D変換された前記第1〜第nの積分器の出力信号及び前記第n+1〜第2nの積分器の出力信号に基づいて、前記時間差を求める処理部と、
を有することを特徴とする回路装置。 In the circuit device according to claim 7.
The measuring unit
A selector that selects one of the output signal of the first to nth integrators and the output signal of the n + 1 to 2n integrators, and
An A / D conversion circuit that A / D converts the signal from the selector,
A processing unit that obtains the time difference based on the output signal of the first to nth integrators and the output signal of the n + 1 to second n integrators that have been A / D converted.
A circuit device characterized by having.
前記第1の信号がアクティブになってから、前記第2の信号がアクティブになるまでの前記基準クロック信号のクロック数をカウントするカウンターを含み、
前記測定部は、
前記カウンターのカウント値と前記第1の位相差信号と前記第2の位相差信号に基づいて、前記第1の信号と前記第2の信号の前記時間差を測定することを特徴とする回路装置。 In the circuit device according to any one of claims 1 to 8.
A counter that counts the number of clocks of the reference clock signal from the activation of the first signal to the activation of the second signal is included.
The measuring unit
A circuit device for measuring the time difference between the first signal and the second signal based on the count value of the counter, the first phase difference signal, and the second phase difference signal.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017027463A JP6891528B2 (en) | 2017-02-17 | 2017-02-17 | Circuit devices, physical quantity measuring devices, electronic devices and mobile objects |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017027463A JP6891528B2 (en) | 2017-02-17 | 2017-02-17 | Circuit devices, physical quantity measuring devices, electronic devices and mobile objects |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018132461A JP2018132461A (en) | 2018-08-23 |
| JP2018132461A5 JP2018132461A5 (en) | 2019-12-26 |
| JP6891528B2 true JP6891528B2 (en) | 2021-06-18 |
Family
ID=63247343
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017027463A Active JP6891528B2 (en) | 2017-02-17 | 2017-02-17 | Circuit devices, physical quantity measuring devices, electronic devices and mobile objects |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6891528B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7375420B2 (en) | 2019-09-27 | 2023-11-08 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Circuit devices, physical quantity measuring devices, electronic equipment and moving objects |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6295487A (en) * | 1985-10-22 | 1987-05-01 | Yokogawa Electric Corp | Time width measuring instrument |
| JPS62299786A (en) * | 1986-06-20 | 1987-12-26 | Yokogawa Electric Corp | Time measuring instrument |
| JPS63309888A (en) * | 1987-06-11 | 1988-12-16 | Yokogawa Electric Corp | Time measuring instrument |
| JP3941274B2 (en) * | 1998-01-28 | 2007-07-04 | 株式会社ニコン | Distance measuring device |
| US7330803B2 (en) * | 2005-06-22 | 2008-02-12 | Ametek, Inc. | High resolution time interval measurement apparatus and method |
-
2017
- 2017-02-17 JP JP2017027463A patent/JP6891528B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2018132461A (en) | 2018-08-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6878943B2 (en) | Circuit devices, physical quantity measuring devices, electronic devices and mobile objects | |
| TW469370B (en) | PWM control circuit, microcomputer and electronic equipment | |
| US6232595B1 (en) | Position detecting apparatus | |
| US8143926B2 (en) | Data signal generating apparatus | |
| JP5948195B2 (en) | Clock generation device and clock data restoration device | |
| JP2019027843A (en) | Circuit device, physical quantity measuring device, electronic apparatus, and mobile entity | |
| US11105632B2 (en) | Method and device for demodulating gyroscope signals | |
| JP2019039673A (en) | Time digital conversion circuit, circuit device, physical quantity measuring device, electronic apparatus, and mobile entity | |
| US20170153279A1 (en) | Lock-in amplifier, integrated circuit and portable measurement device including the same | |
| JP4794596B2 (en) | Physical quantity detection circuit, physical quantity sensor device | |
| JP2017103511A (en) | Circuit device, oscillator, electronic apparatus, movable body and manufacturing method for oscillator | |
| JP6891528B2 (en) | Circuit devices, physical quantity measuring devices, electronic devices and mobile objects | |
| JP4836985B2 (en) | Physical quantity detection circuit | |
| US20100301906A1 (en) | Multiphase signal divider | |
| US9000855B2 (en) | Circuit and method for detecting oscillating frequency drift | |
| US9261364B2 (en) | Driving circuit, system, and driving method for gyro sensor | |
| CN108253953B (en) | Demodulation system and demodulation device of MEMS gyroscope | |
| JP2019020204A (en) | Circuit device, oscillator, physical quantity measuring device, electronic apparatus, and mobile entity | |
| JP2006194703A (en) | Ac power measurement apparatus and program | |
| CN112655151B (en) | Duty cycle calibration circuit, electronic equipment and method | |
| US20160077193A1 (en) | High resolution timing device and radar detection system having the same | |
| JP2019174368A (en) | Circuit device, physical quantity measuring device, electronic apparatus, moving body, and phase adjustment method | |
| JP2002131084A (en) | Position detector | |
| JP2012080382A (en) | Switched capacitor circuit, filter circuit, physical amount measurement device and electronic equipment | |
| US8860592B2 (en) | Signal generating circuit |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20191115 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20191115 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20201022 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20201124 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210106 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20210224 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210407 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20210427 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20210510 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6891528 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |