JP6184805B2 - Interrupting element and interrupting element circuit - Google Patents
Interrupting element and interrupting element circuit Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6184805B2 JP6184805B2 JP2013177058A JP2013177058A JP6184805B2 JP 6184805 B2 JP6184805 B2 JP 6184805B2 JP 2013177058 A JP2013177058 A JP 2013177058A JP 2013177058 A JP2013177058 A JP 2013177058A JP 6184805 B2 JP6184805 B2 JP 6184805B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- soluble conductor
- circuit
- melting point
- point metal
- conductor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 claims description 182
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 claims description 114
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 claims description 114
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 109
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 109
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 82
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 claims description 77
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 56
- 239000003870 refractory metal Substances 0.000 claims description 16
- 230000020169 heat generation Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 15
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 5
- HBBGRARXTFLTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lithium ion Chemical compound [Li+] HBBGRARXTFLTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910001416 lithium ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910010293 ceramic material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000003628 erosive effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004593 Epoxy Substances 0.000 description 2
- MCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zirconium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Zr]=O MCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000005336 cracking Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 2
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1 ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007664 blowing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- KZHJGOXRZJKJNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N dioxosilane;oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Si]=O.O=[Si]=O.O=[Al]O[Al]=O.O=[Al]O[Al]=O.O=[Al]O[Al]=O KZHJGOXRZJKJNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000002500 effect on skin Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010304 firing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002241 glass-ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003475 lamination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052863 mullite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001737 promoting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007634 remodeling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052707 ruthenium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000007650 screen-printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035939 shock Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001169 thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H37/00—Thermally-actuated switches
- H01H37/74—Switches in which only the opening movement or only the closing movement of a contact is effected by heating or cooling
- H01H37/76—Contact member actuated by melting of fusible material, actuated due to burning of combustible material or due to explosion of explosive material
- H01H37/761—Contact member actuated by melting of fusible material, actuated due to burning of combustible material or due to explosion of explosive material with a fusible element forming part of the switched circuit
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H61/00—Electrothermal relays
- H01H61/02—Electrothermal relays wherein the thermally-sensitive member is heated indirectly, e.g. resistively, inductively
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M50/00—Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of electrochemical cells other than fuel cells, e.g. hybrid cells
- H01M50/50—Current conducting connections for cells or batteries
- H01M50/572—Means for preventing undesired use or discharge
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M2200/00—Safety devices for primary or secondary batteries
- H01M2200/20—Pressure-sensitive devices
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Fuses (AREA)
- Emergency Protection Circuit Devices (AREA)
Description
本発明は、電源ラインや信号ラインを電気的且つ物理的に遮断することにより安全性を保障する遮断素子、及び遮断素子回路に関する。 The present invention relates to a cutoff element and a cutoff element circuit that ensure safety by electrically and physically shutting off a power supply line and a signal line.
充電して繰り返し利用することのできる二次電池の多くは、バッテリパックに加工されてユーザに提供される。特に重量エネルギー密度の高いリチウムイオン二次電池においては、ユーザ及び電子機器の安全を確保するために、一般的に、過充電保護、過放電保護等のいくつもの保護回路をバッテリパックに内蔵し、所定の場合にバッテリパックの出力を遮断する機能を有している。 Many secondary batteries that can be charged and used repeatedly are processed into battery packs and provided to users. Particularly in lithium ion secondary batteries with high weight energy density, in order to ensure the safety of users and electronic devices, in general, a battery pack incorporates a number of protection circuits such as overcharge protection and overdischarge protection, It has a function of shutting off the output of the battery pack in a predetermined case.
この種の遮断素子には、バッテリパックに内蔵されたFETスイッチを用いて出力のON/OFFを行うことにより、バッテリパックの過充電保護又は過放電保護動作を行うものがある。しかしながら、何らかの原因でFETスイッチが短絡破壊した場合、雷サージ等が印加されて瞬間的な大電流が流れた場合、あるいはバッテリセルの寿命によって出力電圧が異常に低下したり、逆に過大異常電圧を出力した場合であっても、バッテリパックや電子機器は、発火等の事故から保護されなければならない。そこで、このような想定し得るいかなる異常状態においても、バッテリセルの出力を安全に遮断するために、外部からの信号によって電流経路を遮断する機能を有するヒューズ素子からなる遮断素子が用いられている。 Some of these types of shut-off elements perform an overcharge protection or overdischarge protection operation of the battery pack by turning on / off the output using an FET switch built in the battery pack. However, when the FET switch is short-circuited for some reason, when a lightning surge or the like is applied and an instantaneous large current flows, the output voltage drops abnormally due to the life of the battery cell, or conversely an excessively abnormal voltage Even when a battery pack is output, battery packs and electronic devices must be protected from accidents such as fire. Therefore, in order to safely shut off the output of the battery cell in any possible abnormal state, a shut-off element made of a fuse element having a function of shutting off the current path by an external signal is used. .
図17に示すように、このようなリチウムイオン二次電池等向けの保護回路の遮断素子80としては、電流経路上に接続された第1及び第2の電極81,82間に亘って可溶導体83を接続して電流経路の一部をなし、この電流経路上の可溶導体83を、過電流による自己発熱、あるいは遮断素子80内部に設けた発熱体84によって溶断するものが提案されている。
As shown in FIG. 17, the
具体的に、遮断素子80は、絶縁基板85と、絶縁基板85に積層され、絶縁部材86に覆われた発熱体84と、絶縁基板85の両端に形成された第1、第2の電極81,82と、絶縁部材86上に発熱体84と重畳するように積層された発熱体引出電極88と、両端が第1、第2の電極81,82にそれぞれ接続され、中央部が発熱体引出電極88に接続された可溶導体83とを備える。
Specifically, the
図18は、遮断素子80の回路図である。すなわち、遮断素子80は、発熱体引出電極88を介して直列接続された可溶導体83と、可溶導体83の接続点を介して通電して発熱させることによって可溶導体83を溶融する発熱体84とからなる回路構成である。また、遮断素子80では、たとえば、可溶導体83が充放電電流経路上に直列接続され、発熱体84が電流制御素子87と接続される。電流制御素子87は、例えば電界効果トランジスタ(以下、FETと呼ぶ。)により構成され、リチウムイオン二次電池が異常電圧を示したときには、可溶導体83を介して発熱体84に電流が流れるように制御される。
FIG. 18 is a circuit diagram of the
これにより遮断素子80は、発熱体84の発熱により、電流経路上の可溶導体83を溶断させ、この溶融導体を発熱体引出電極88に集めることにより、第1及び第2の電極81,82間の電流経路を遮断し、バッテリパックの充放電経路を電気的且つ物理的に遮断することができる。
Thereby, the
ここで、図17、図18に示す遮断素子80においては、発熱体84を発熱させる電力を、可溶導体83を介して供給するものであるが、第1の電極81〜可溶導体83〜第2の電極82にわたる電流経路はバッテリの充放電経路であることから、発熱体84の通電時においても発熱体84に可溶導体83を溶断させるのに十分な熱量を得ることができる。
Here, in the interruption | blocking
しかし、遮断素子80を、電源ラインよりも微弱な電流を流す信号ラインにおいて用いる場合には、発熱体84に可溶導体83を溶断させるのに十分な発熱量を得るほどの電力を供給することができず、遮断素子80の用途が大電流用途に限られていた。
However, when the
また、電流経路を発熱体84側に切り替える電流制御素子87も、電流定格の向上に伴って同様に定格の向上が求められる。そして、高定格の電流制御素子は、一般的に高価であり、コスト上も不利となる。
Also, the
そこで、本発明は、微弱な電流経路に組み込まれた場合にも、発熱体に可溶導体を溶断させるのに十分な電力を供給することができ、あらゆる用途に用いることができる遮断素子、及び遮断素子回路を提供することを目的とする。 Therefore, the present invention can supply sufficient power for fusing a soluble conductor to a heating element even when incorporated in a weak current path, and can be used for any application, and An object is to provide a breaker circuit.
上述した課題を解決するために、本発明に係る遮断素子は、絶縁基板と、上記絶縁基板に形成され、第1の回路を構成する第1及び第2の電極と、上記絶縁基板に形成され、上記第1の回路と電気的に独立して形成された第2の回路を構成する第3〜第5の電極と、上記第1及び第2の電極間にわたって搭載された第1の可溶導体と、上記第3及び第4の電極間に接続された発熱体と、上記第4及び第5の電極間にわたって搭載された第2の可溶導体とを備えたものである。
In order to solve the above-described problems, a blocking element according to the present invention is formed on an insulating substrate, the first and second electrodes that are formed on the insulating substrate and constitute the first circuit, and the insulating substrate. A first fusible electrode mounted between the first and second electrodes, and third to fifth electrodes constituting a second circuit formed electrically independent of the first circuit. A conductor, a heating element connected between the third and fourth electrodes, and a second soluble conductor mounted across the fourth and fifth electrodes.
また、本発明に係る遮断素子回路は、第1の可溶導体を有する第1の回路と、上記第1の回路と電気的に独立して形成され、発熱体と、上記発熱体の一端と接続された第2の可溶導体とを有する第2の回路とを備えたものである。 The interrupting element circuit according to the present invention includes a first circuit having a first fusible conductor, and is electrically independent of the first circuit, and includes a heating element and one end of the heating element. it is obtained by a second circuit having a second fusible conductor connected.
本発明によれば、第1の回路と、第1の回路を遮断させる第2の回路とが、電気的に独立しているため、第1の回路が組み込まれる外部回路の種類によらず、発熱体に対して第1の可溶導体を溶断させるのに十分な発熱量を得る電力を供給することができる。したがって、本発明によれば、第1の回路が組み込まれる外部回路として、微弱な電流を流すデジタル信号回路等にも適用することができる。 According to the present invention, since the first circuit and the second circuit that shuts off the first circuit are electrically independent, regardless of the type of external circuit in which the first circuit is incorporated, Electric power for obtaining a heat generation amount sufficient to melt the first soluble conductor with respect to the heating element can be supplied. Therefore, according to the present invention, the present invention can also be applied to a digital signal circuit for passing a weak current as an external circuit in which the first circuit is incorporated.
以下、本発明が適用された遮断素子、及び遮断素子回路について、図面を参照しながら詳細に説明する。なお、本発明は、以下の実施形態のみに限定されるものではなく、本発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲内において種々の変更が可能であることは勿論である。また、図面は模式的なものであり、各寸法の比率等は現実のものとは異なることがある。具体的な寸法等は以下の説明を参酌して判断すべきものである。また、図面相互間においても互いの寸法の関係や比率が異なる部分が含まれていることは勿論である。 Hereinafter, a shut-off element and a shut-off element circuit to which the present invention is applied will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. It should be noted that the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments, and various modifications can be made without departing from the scope of the present invention. Further, the drawings are schematic, and the ratio of each dimension may be different from the actual one. Specific dimensions should be determined in consideration of the following description. Moreover, it is a matter of course that portions having different dimensional relationships and ratios are included between the drawings.
[第1の形態]
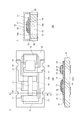
本発明が適用された遮断素子1は、図1に示すように、絶縁基板10と、絶縁基板10に形成され、第1の回路2を構成する第1の電極11及び第2の電極12と、絶縁基板10に形成され、第2の回路3を構成する第3の電極13、第4の電極14及び第5の電極15と、第1及び第2の電極11,12間にわたって搭載された第1の可溶導体17(ヒューズ)と、第3及び第4の電極13,14間に接続された発熱体18と、第4及び第5の電極14,15間にわたって搭載された第2の可溶導体(ヒューズ)19とを備える。図1(A)は、遮断素子1の平面図であり、図1(B)は、A−A‘断面図であり、(C)は断面図である。
[First embodiment]
As shown in FIG. 1, a blocking
絶縁基板10は、たとえば、アルミナ、ガラスセラミックス、ムライト、ジルコニアなどの絶縁性を有する部材によって形成される。その他、ガラスエポキシ基板、フェノール基板等のプリント配線基板に用いられる材料を用いてもよいが、ヒューズ溶断時の温度に留意する必要がある。
The insulating
[第1及び第2の電極:第1の回路]
第1及び第2の電極11,12は、絶縁基板10の表面10a上に形成されるとともに、後述する絶縁部材21上に積層されている。また、第1及び第2の電極11,12は、スルーホール20を介して絶縁基板10の裏面10bに形成された外部接続端子と連続されている。
[First and second electrodes: first circuit]
The first and
第1及び第2の電極11,12は、第1の可溶導体17が搭載されることにより電気的に接続されている。これにより、遮断素子1は、第1の電極11〜第1の可溶導体17〜第2の電極12に至る第1の回路2を構成し、第1の回路2は、遮断素子1が実装される回路基板上に形成された回路の一部に組み込まれる。
The first and
第1の回路2が組み込まれる回路は、遮断素子1が実装される電子機器の電流ラインであり、例えばリチウムイオン二次電池のバッテリパックにおける充放電回路、各種電子機器の電源回路、あるいは、デジタル信号回路等、電流の強弱に関わらず物理的な電流経路の遮断が求められるあらゆる回路に適用することができる。
A circuit in which the
[発熱体]
発熱体18は、絶縁基板10の表面10aに積層され、絶縁部材21に覆われている。発熱体18は、比較的抵抗値が高く通電すると発熱する導電性を有する部材であって、例えばW、Mo、Ru等からなる。これらの合金あるいは組成物、化合物の粉状体を樹脂バインダ等と混合して、ペースト状にしたものを絶縁基板10上にスクリーン印刷技術を用いてパターン形成して、焼成する等によって形成される。発熱体18は、一端が第3の電極13と接続され、他端が第4の電極14と接続されている。
[Heating element]
The
発熱体18を覆うように絶縁部材21が配置され、この絶縁部材21を介して発熱体18と重畳するように第1の電極11、第2の電極12、第4の電極14及び第5の電極15が積層されている。絶縁部材21としては、例えばガラスを用いることができる。なお、遮断素子1は、発熱体18の熱を効率良く第1の可溶導体13に伝えるために、発熱体18と絶縁基板10の間にも絶縁部材を積層し、発熱体18を絶縁基板10の表面に形成された絶縁部材21の内部に設けても良い。
An insulating
[第3〜第5の電極:第2の回路]
第3の電極13は、絶縁基板10の表面10a上に形成され、発熱体18の一端と接続されている。第4の電極14は、絶縁基板10の表面10a上に形成されることにより発熱体18の他端と接続されるとともに、絶縁部材21上に積層されている。第5の電極15は、絶縁部材10の表面10a上に形成されるとともに、絶縁部材21上に積層されている。なお、第3の電極13及び第5の電極15は、スルーホール20を介して絶縁基板10の裏面10bに形成された外部接続端子と連続されている。
[Third to fifth electrodes: second circuit]
The
第4及び第5の電極14,15は、絶縁部材21上において、第2の可溶導体19が搭載されることにより電気的に接続されている。これにより、第3〜第5の電極13〜15は、上記第1の回路2と電気的に独立した第2の回路3を構成する。第2の回路3は、第1の回路2の第1の可溶導体17を加熱、溶断するための回路であり、第1の可溶導体17を溶断し第1の回路2を遮断した後は、第2の可溶導体19を溶断することで自身も遮断し、発熱体18への給電を停止する。
The fourth and
[可溶導体]
第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、発熱体18の発熱により速やかに溶断されるいずれの金属を用いることができ、例えば、Snを主成分とするPbフリーハンダ等の低融点金属を好適に用いることができる。
[Soluble conductor]
The first and second
また、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、低融点金属と高融点金属とを含有してもよい。低融点金属としては、Pbフリーハンダなどのハンダを用いることが好ましく、高融点金属としては、Ag、Cu又はこれらを主成分とする合金などを用いることが好ましい。高融点金属と低融点金属とを含有することによって、遮断素子1をリフロー実装する場合に、リフロー温度が低融点金属の溶融温度を超えて、低融点金属が溶融しても、内層の低融点金属の外部への流出を抑制し、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19の形状を維持することができる。また、溶断時も、低融点金属が溶融することにより、高融点金属を溶食(ハンダ食われ)することで、高融点金属の融点以下の温度で速やかに溶断することができる。なお、第1〜第3の可溶導体21〜23は、後に説明するように、様々な構成によって形成することができる。
Moreover, the 1st, 2nd
第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、低融点金属層を内層とし、高融点金属層を外層として構成することができる。このような第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、低融点金属箔に、高融点金属層をメッキ技術を用いて成膜することによって形成することができ、あるいは、他の周知の積層技術、膜形成技術を用いて形成することもできる。また、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、高融点金属層を内層とし、低融点金属層を外層として構成してもよく、また低融点金属層と高融点金属層とが交互に積層された4層以上の多層構造としてもよい。
The first and second
なお、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、第1及び第2の電極11,12上、第4及び第5の電極14,15上へ、ハンダ等を用いて接続されている。また、第1の回路2を、デジタル信号回路に適用する場合、第1の可溶導体17の外層として、高周波特性の良好な銀メッキ層を形成することが好ましい。これにより、第1の可溶導体17は、表皮効果による低抵抗化を図り高周波特性を向上させるとともに、瞬間的な大電流が流れた際にも外層の銀メッキ層を流れ、自己発熱による溶断を防止する耐パルス性を向上させることができる。
The first and second
[第1の可溶導体の先溶融]
ここで、遮断素子1は、第1の回路2の第1の可溶導体17が、第2の回路3の第2の可溶導体19よりも先に溶断するように形成されている。第1の可溶導体17よりも先に第2の可溶導体19が溶断すると、発熱体18への給電が停止され、第1の可溶導体17を溶断することができなくなるからである。
[First melting of the first soluble conductor]
Here, the blocking
そこで、遮断素子1は、発熱体18が発熱すると、第1の可溶導体17が先に溶断するように形成されている。具体的に、遮断素子1の第1の可溶導体17は、第2の可溶導体19よりも、発熱体18の発熱中心に近い位置に搭載されている。
Therefore, the blocking
ここで、発熱体18の発熱中心とは、発熱体18が発熱することにより発現する熱分布のうち、発熱初期の段階で最も高温となる領域をいう。発熱体18より発せされる熱は絶縁基板10からの放熱量が最も多く、絶縁基板10を、耐熱衝撃性に優れるが熱伝導率も高いセラミックス材料により形成した場合などには、絶縁基板10に熱が拡散してしまう。そのため、発熱体18は通電が開始された発熱初期の段階では、絶縁基板10と接する外縁から最も遠い中心が最も熱く、絶縁基板10と接する外縁に向かうにつれて放熱されて温度が上がりにくくなる。
Here, the heat generation center of the
そこで、遮断素子1は、第1の可溶導体17を、第2の可溶導体19よりも、発熱体18の発熱初期において最も高温となる発熱中心に近い位置に搭載することにより、第2の可溶導体19よりも早く熱が伝わり、溶断するようにする。第2の可溶導体19は、第1の可溶導体17より遅れて加熱されるため、第1の可溶導体17が溶断した後に溶断される。
Therefore, the blocking
また、遮断素子1は、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19の形状を変えることにより、第1の可溶導体17が先に溶断するようにしてもよい。例えば、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、断面積が小さいほど溶断が容易となることから、遮断素子1は、第1の可溶導体17の断面積を第2の可溶導体19の断面積よりも小さくすることにより、第2の可溶導体19よりも先に溶断させることができる。
Moreover, the interruption | blocking
また、遮断素子1は、第1の可溶導体17を第1、第2の電極11,12間の電流経路に沿って幅狭かつ長く形成し、第2の可溶導体19を第4,第5の電極14,15間の電流経路に沿って幅広かつ短く形成してもよい。これにより、第1の可溶導体17は、第2の可溶導体19よりも相対的に溶断しやすい形状となり、発熱体18の発熱により、第2の可溶導体19よりも先に溶断する。
Moreover, the interruption | blocking
また、遮断素子1は、第1の可溶導体17の材料として、第2の可溶導体19の材料よりも融点の低いもので形成してもよい。これによっても、発熱体18の発熱により第1の可溶導体17を第2の可溶導体19よりも溶断しやすくし、確実に第1の可溶導体17を第2の可溶導体19よりも先に溶断させることができる。
Moreover, you may form the interruption | blocking
その他にも、遮断素子1は、第1の可溶導体17と第2の可溶導体19の層構造を変えることによって融点に差を設け、相対的に第1の可溶導体17を第2の可溶導体19よりも溶断しやすくし、発熱体18の発熱により、第1の可溶導体17を第2の可溶導体19よりも先に溶断させるようにしてもよい。
In addition, the blocking
[その他]
なお、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19の酸化防止、及び第1、第2の可溶導体17,19の溶融時における濡れ性を向上させるために、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19の上にはフラックス22が塗布されている。
[Others]
In order to prevent oxidation of the first and second
また、遮断素子1は、絶縁基板10がカバー部材23に覆われることによりその内部が保護されている。カバー部材23は、上記絶縁基板10と同様に、たとえば、熱可塑性プラスチック,セラミックス,ガラスエポキシ基板等の絶縁性を有する部材を用いて形成されている。
Further, the inside of the blocking
[回路構成]
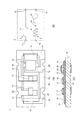
次いで、遮断素子1の回路構成について説明する。図2に遮断素子1の回路図を示す。図3に、遮断素子1が適用された遮断素子回路30の一例を示す。遮断素子1は、第1の電極11と第2の電極12とが第1の可溶導体17を介して連続することにより形成される第1の回路2を有する。第1の回路2は、遮断素子1が実装される回路基板の電流経路上に直列接続されることにより、電源回路やデジタル信号回路等の各種外部回路31に組み込まれる。
[Circuit configuration]
Next, the circuit configuration of the blocking
また、遮断素子1は、第4の電極14を介して発熱体18と第2の可溶導体19とが直列接続された第2の回路3を有する。第2の回路3は、第1の回路2と電気的に独立し、熱的に接続可能とされている。発熱体18は、一端を第3の電極13と接続され、他端を第4の電極14と接続されている。また、第2の可溶導体19は、第4の電極14と第5の電極15との間にわたって搭載されている。第3の電極13は、外部接続端子を介して第2の回路3への給電を制御する電流制御素子25に接続され、第5の電極15は、外部接続端子を介して外部電源26と接続される。
Moreover, the interruption | blocking
電流制御素子25は、第2の回路3への給電を制御するスイッチ素子であり、例えばFETにより構成され、第1の回路2の電気的に且つ物理的な遮断の要否を検出する検出回路27と接続されている。検出回路27は、遮断素子1の第1の回路2が組み込まれた各種回路を遮断する必要がある事態を検出する回路であり、例えばバッテリパックの異常電圧、ネットワーク通信機器におけるハッキングやクラッキング、あるいはソフトウェアのライセンス期間の満了等、第1の回路2の遮断により物理的、不可逆的に電流経路を絶ち、外部と遮断する必要が生じた場合に電流制御素子25を動作させる。
The
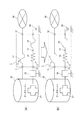
これにより、第2の回路3に外部電源26の電力が供給され、発熱体18が発熱することにより第1の可溶導体17が溶断される(図4(A)(B)(C))。第1の可溶導体17の溶融導体は、濡れ性の高い第1の電極11及び第2の電極12上に引き寄せられる。したがって、第1の可溶導体17は、確実に第1の回路2を遮断することができる。また、第1の可溶導体17が第2の可溶導体19よりも先に溶断されるため、第2の回路3は、第1の回路2が遮断するまで確実に発熱体18に給電し、発熱させることができる。
Thereby, the electric power of the
発熱体18は、第1の可溶導体17の溶断後も発熱を続けるが、第1の可溶導体17に続き第2の可溶導体19も溶断することにより、第2の回路3も遮断される(図5(A)(B)(C))。これにより、発熱体18への給電も停止される。
The
このような遮断素子1及び遮断素子回路30によれば、外部回路31に組み込まれる第1の回路2と、第1の回路を遮断させる第2の回路3とが、電気的に独立しているため、外部回路31の種類によらず、発熱体18に対して第1の可溶導体17を溶断させるのに十分な発熱量を得る電力を供給することができる。したがって、遮断素子1及び遮断素子回路30によれば、第1の回路2が組み込まれる外部回路31として、微弱な電流を流すデジタル信号回路に適用することもできる。
According to such a
例えば、図6(A)に示すように、遮断素子1及び遮断素子回路30は、情報セキュリティを目的として、第1の回路2をデータサーバ33とインターネット回線34との間に組み込み、検出回路27によってハッキングやクラッキングを検出した時には、図6(B)に示すように、第1の回路2を遮断することで物理的、不可逆的に信号ラインをインターネット回線34から切り離し、情報の流出を防止することができる。
For example, as shown in FIG. 6A, the blocking
その他にも、遮断素子1及び遮断素子回路30は、デバイスの物理的なライセンス認証の取り消し、PL対策としてデバイスの改造行為に対する機能停止などに応用することもできる。
In addition, the blocking
また、遮断素子1及び遮断素子回路30によれば、第1の回路2と電気的に独立して第2の回路3を形成しているため、発熱体18への給電を制御する電流制御素子25を、第1の回路2の定格に関わらず、発熱体18の定格に応じて選択することができ、より安価に製造することができる。
Moreover, according to the interruption | blocking
[第2の形態]
遮断素子は、図1に示すように、発熱体18を絶縁基板10の第1〜第5の電極11〜15が形成されている表面10a上に形成し、第1及び第2の電極11,12、並びに第4及び第5の電極14,15を重畳させる他にも、図7に示すように、絶縁基板10の第1〜第5の電極11〜15が形成されている表面10aと反対側の裏面10bに形成してもよい。図7(A)は、発熱体18が絶縁基板10の裏面に形成された遮断素子40の平面図であり、図7(B)は、A−A‘断面図である。なお、上述した遮断素子1と同じ部材については同一の符号を付してその詳細を省略する。
[Second form]
As shown in FIG. 1, the blocking element includes a
遮断素子40は、第3の電極13及び第4の電極14の一端も、絶縁基板10の裏面10b側に形成される。第4の電極14の他端は、絶縁基板10の表面10aに形成され、第5の電極15との間で第2の可溶導体19が搭載される。第4の電極14の一端と他端とは、スルーホール20を介して連続されている。
As for the interruption | blocking
遮断素子40は、発熱体18を絶縁基板10の裏面10bに形成することにより、絶縁基板10の表面10aが平坦となり、第1、第2の電極11,12や、第4の電極14の他端側、第5の電極15を簡易な工程で形成することができる。なお、この場合、発熱体18上には、絶縁部材21が形成され、発熱体18の保護を図るとともに、遮断素子1の実装時の絶縁性を確保することができる。
In the blocking
また、このとき、発熱体18と第1及び第2の電極11,12とを重畳させ、第1の可溶導体17を第2の可溶導体19よりも発熱体18の発熱中心に近い位置に配置することが好ましい。また、発熱体18と第4及び第5の電極14,15とを重畳させ、第2の可溶導体19にも発熱体18の熱を効率よく伝達するようにしてもよい。
At this time, the
[第3の形態]
また、遮断素子は、図8に示すように、発熱体18を、絶縁基板10の内部に形成してもよい。図8(A)は、発熱体18が絶縁基板10の内部に形成された遮断素子50の平面図であり、図8(B)は、A−A‘断面図である。なお、上述した遮断素子1と同じ部材については同一の符号を付してその詳細を省略する。
[Third embodiment]
Moreover, the interruption | blocking element may form the
遮断素子50は、例えば、絶縁基板10をセラミックス材料で形成する場合、表面に発熱体18、第3の電極13、第4の電極14の一端を形成した後、さらにセラミックス材を積層することにより、発熱体18が内部に形成された絶縁基板10を得ることができる。第3の電極13及び第4の電極14の各一端は、それぞれスルーホール20を介して絶縁基板10の表面10a又は裏面10bに形成された他端と接続されている。
For example, when the insulating
遮断素子50は、発熱体18を絶縁基板10の内部に形成することによっても、絶縁基板10の表面10aが平坦となり、第1及び第2の電極11,12や、第4の電極14の他端側、第5の電極15を簡易な工程で形成することができる。なお、遮断素子50は、発熱体18が絶縁基板10の内部に形成されているため、絶縁部材21を設ける必要はない。
In the blocking
また、このとき、発熱体18と第1及び第2の電極11,12とを重畳させ、第1の可溶導体17を第2の可溶導体19よりも発熱体18の発熱中心に近い位置に配置することが好ましい。また、発熱体18と第4及び第5の電極14,15とを重畳させ、第2の可溶導体19にも発熱体18の熱を効率よく伝達するようにしてもよい。
At this time, the
[第4の形態]
また、遮断素子1は、図9に示すように、発熱体18を、絶縁基板10の表面10a上において、第1及び第2の電極11,12、並びに第4及び第5の電極14,15と並んで形成してもよい。図9(A)は、発熱体18が絶縁基板10の表面上において第1及び第2の電極11,12、並びに第4及び第5の電極14,15と並んで形成された遮断素子60の平面図であり、図9(B)は、A−A‘断面図である。なお、上述した遮断素子1と同じ部材については同一の符号を付してその詳細を省略する。
[Fourth form]
Further, as shown in FIG. 9, the interrupting
遮断素子60は、第1の可溶導体17を第2の可溶導体19よりも発熱体18の発熱中心の近くに配置することが好ましい。また、図10(A)(B)に示すように、第1及び第2の電極11,12のみを絶縁部材21を介して発熱体18上と重畳させ、第1の可溶導体17のみを発熱体18の上に重畳配置してもよい。これにより、第1の可溶導体17は、第2の可溶導体19よりも発熱体18に近い位置に配置され、第2の可溶導体19よりも先に溶断されることができる。
It is preferable that the interruption | blocking
[第1、第2の可溶導体]
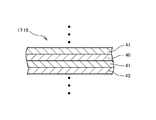
上述したように、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19のいずれか又は全部は、低融点金属と高融点金属とを含有してもよい。このとき、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、図11(A)に示すように、内層としてAg、Cu又はこれらを主成分とする合金等からなる高融点金属層40が設けられ、外層としてSnを主成分とするPbフリーハンダ等からなる低融点金属層41が設けられた可溶導体を用いてもよい。この場合、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、高融点金属層40の全面が低融点金属層41によって被覆された構造としてもよく、相対向する一対の側面を除き被覆された構造であってもよい。高融点金属層40や低融点金属層41による被覆構造は、メッキ等の公知の成膜技術を用いて形成することができる。
[First and second soluble conductors]
As described above, any or all of the first and second
また、図11(B)に示すように、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、内層として低融点金属層41が設けられ、外層として高融点金属層40が設けられた可溶導体を用いてもよい。この場合も、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、低融点金属層41の全面が高融点金属層40によって被覆された構造としてもよく、相対向する一対の側面を除き被覆された構造であってもよい。
Further, as shown in FIG. 11B, the first and second
また、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、図12に示すように、高融点金属層40と低融点金属層41とが積層された積層構造としてもよい。
Moreover, the 1st, 2nd
この場合、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、図12(A)に示すように、第1、第2の電極11,12や第4、第5の電極14,15に搭載される下層と、下層の上に積層される上層からなる2層構造として形成され、下層となる高融点金属層40の上面に上層となる低融点金属層41を積層してもよく、反対に下層となる低融点金属層41の上面に上層となる高融点金属層40を積層してもよい。あるいは、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、図12(B)に示すように、内層と内層の上下面に積層される外層とからなる3層構造として形成してもよく、内層となる高融点金属層40の上下面に外層となる低融点金属層41を積層してもよく、反対に内層となる低融点金属層41の上下面に外層となる高融点金属層40を積層してもよい。
In this case, the first and second
また、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、図13に示すように、高融点金属層40と低融点金属層41とが交互に積層された4層以上の多層構造としてもよい。この場合、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、最外層を構成する金属層によって、全面又は相対向する一対の側面を除き被覆された構造としてもよい。
Moreover, the 1st, 2nd
また、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、内層を構成する低融点金属層41の表面に高融点金属層40をストライプ状に部分的に積層させてもよい。図14は、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19の平面図である。
In the first and second
図14(A)に示す第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、低融点金属層41の表面に、幅方向に所定間隔で、線状の高融点金属層40が長手方向に複数形成されることにより、長手方向に沿って線状の開口部42が形成され、この開口部42から低融点金属層41が露出されている。第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、低融点金属層41が開口部42より露出することにより、溶融した低融点金属と高融点金属との接触面積が増え、高融点金属層40の浸食作用をより促進させて溶断性を向上させることができる。開口部42は、例えば、低融点金属層41に高融点金属層40を構成する金属の部分メッキを施すことにより形成することができる。
The first and second
また、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、図14(B)に示すように、低融点金属層41の表面に、長手方向に所定間隔で、線状の高融点金属層40を幅方向に複数形成することにより、幅方向に沿って線状の開口部42を形成してもよい。
Further, as shown in FIG. 14B, the first and second
また、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、図15に示すように、低融点金属層41の表面に高融点金属層40を形成するとともに、高融点金属層40の全面に亘って円形の開口部43が形成され、この開口部43から低融点金属層41を露出させてもよい。開口部43は、例えば、低融点金属層41に高融点金属層40を構成する金属の部分メッキを施すことにより形成することができる。
Further, as shown in FIG. 15, the first and second
第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、低融点金属層41が開口部43より露出することにより、溶融した低融点金属と高融点金属との接触面積が増え、高融点金属の浸食作用をより促進させて溶断性を向上させることができる。
In the first and second
また、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、図16に示すように、内層となる高融点金属層40に多数の開口部44を形成し、この高融点金属層40に、メッキ技術等を用いて低融点金属層41を成膜し、開口部44内に充填してもよい。これにより、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、溶融する低融点金属が高融点金属に接する面積が増大するので、より短時間で低融点金属が高融点金属を溶食することができるようになる。
Further, as shown in FIG. 16, the first and second
また、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、低融点金属層41の体積を、高融点金属層40の体積よりも多く形成することが好ましい。第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、発熱体18によって加熱されることにより、低融点金属が溶融することにより高融点金属を溶食し、これにより速やかに溶融、溶断することができる。したがって、第1、第2の可溶導体17,19は、低融点金属層41の体積を、高融点金属層40の体積よりも多く形成することにより、この溶食作用を促進し、速やかに第1、第2の電極11,12間の遮断、及び第4、第5の電極14,15間の遮断を行うことができる。
Further, the first and second
1,40,50,60 遮断素子、2 第1の回路、3 第2の回路、10 絶縁基板、10a 表面、10b 裏面、11 第1の電極、12 第2の電極、13 第3の電極、14 第4の電極、15 第5の電極、17 第1の可溶導体、18 発熱体、19 第2の可溶導体、20 スルーホール、21 絶縁部材、22 フラックス、23 カバー部材、25 電流制御素子、26 外部電源、27 検出回路、30 遮断素子回路、31 外部回路、33 データサーバ、34 インターネット回線、40 高融点金属層、41 低融点金属層、42〜44 開口部 1, 40, 50, 60 blocking element, 2 first circuit, 3 second circuit, 10 insulating substrate, 10a surface, 10b back surface, 11 first electrode, 12 second electrode, 13 third electrode, 14 4th electrode, 15 5th electrode, 17 1st soluble conductor, 18 Heating element, 19 2nd soluble conductor, 20 Through hole, 21 Insulating member, 22 Flux, 23 Cover member, 25 Current control Element, 26 External power source, 27 Detection circuit, 30 Shut-off element circuit, 31 External circuit, 33 Data server, 34 Internet line, 40 High melting point metal layer, 41 Low melting point metal layer, 42 to 44 Opening
Claims (25)
上記絶縁基板に形成され、第1の回路を構成する第1及び第2の電極と、
上記絶縁基板に形成され、上記第1の回路と電気的に独立して形成された第2の回路を構成する第3〜第5の電極と、
上記第1及び第2の電極間にわたって搭載された第1の可溶導体と、
上記第3及び第4の電極間に接続された発熱体と、
上記第4及び第5の電極間にわたって搭載された第2の可溶導体とを備えた遮断素子。 An insulating substrate;
First and second electrodes formed on the insulating substrate and constituting a first circuit;
Third to fifth electrodes forming a second circuit formed on the insulating substrate and formed electrically independent of the first circuit ;
A first fusible conductor mounted across the first and second electrodes;
A heating element connected between the third and fourth electrodes;
The interruption | blocking element provided with the 2nd soluble conductor mounted ranging between the said 4th and 5th electrodes.
上記発熱体は、上記絶縁基板と上記絶縁層の間、又は上記絶縁層の内部に形成されている請求項1〜6のいずれか1項に記載の遮断素子。 An insulating layer is provided on the surface of the surface on which the first to fifth electrodes of the insulating substrate are formed,
The interruption element according to any one of claims 1 to 6, wherein the heating element is formed between the insulating substrate and the insulating layer or inside the insulating layer.
上記発熱体は、上記絶縁基板と上記絶縁層の間に形成されるとともに、上記第1及び第2の電極、並びに上記第4及び第5の電極と並んで形成されている請求項1〜6のいずれか1項に記載の遮断素子。 An insulating layer is provided on the surface of the surface on which the first to fifth electrodes of the insulating substrate are formed,
The heating element is formed between the insulating substrate and the insulating layer, and is formed side by side with the first and second electrodes and the fourth and fifth electrodes. The interruption | blocking element of any one of these.
上記低融点金属が上記発熱体からの加熱により溶融し、上記高融点金属を溶食する請求項1〜12のいずれか1項に記載の遮断素子。 The first soluble conductor and / or the second soluble conductor contains a low melting point metal and a high melting point metal,
The interruption | blocking element of any one of Claims 1-12 by which the said low melting metal melt | dissolves by the heating from the said heat generating body, and corrodes the said high melting metal.
上記高融点金属は、Ag、Cu又はAg若しくはCuを主成分とする合金である請求項14記載の遮断素子。 The low melting point metal is solder,
The breaker element according to claim 14, wherein the refractory metal is Ag, Cu, or an alloy containing Ag or Cu as a main component.
上記第1の回路と電気的に独立して形成され、発熱体と、上記発熱体の一端と接続された第2の可溶導体とを有する第2の回路とを備えた遮断素子回路。 A first circuit having a first fusible conductor;
A breaker element circuit comprising: a second circuit formed electrically independent of the first circuit and having a heating element and a second fusible conductor connected to one end of the heating element.
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013177058A JP6184805B2 (en) | 2013-08-28 | 2013-08-28 | Interrupting element and interrupting element circuit |
| CN201911368547.6A CN110957188A (en) | 2013-08-28 | 2014-08-27 | Disconnecting element and disconnecting element circuit |
| TW103129444A TWI629702B (en) | 2013-08-28 | 2014-08-27 | Blocking element and blocking element circuit |
| CN201480047053.7A CN105493219A (en) | 2013-08-28 | 2014-08-27 | Shutoff element and shutoff element circuit |
| KR1020157035050A KR102275927B1 (en) | 2013-08-28 | 2014-08-27 | Shutoff element and shutoff element circuit |
| PCT/JP2014/072348 WO2015030020A1 (en) | 2013-08-28 | 2014-08-27 | Shutoff element and shutoff element circuit |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013177058A JP6184805B2 (en) | 2013-08-28 | 2013-08-28 | Interrupting element and interrupting element circuit |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015046316A JP2015046316A (en) | 2015-03-12 |
| JP2015046316A5 JP2015046316A5 (en) | 2016-07-28 |
| JP6184805B2 true JP6184805B2 (en) | 2017-08-23 |
Family
ID=52586572
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013177058A Active JP6184805B2 (en) | 2013-08-28 | 2013-08-28 | Interrupting element and interrupting element circuit |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6184805B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR102275927B1 (en) |
| CN (2) | CN105493219A (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI629702B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2015030020A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6483524B2 (en) * | 2015-05-22 | 2019-03-13 | デクセリアルズ株式会社 | Protection element, secondary battery protection circuit, battery pack and battery state management system |
| US20230207241A1 (en) | 2020-05-29 | 2023-06-29 | Dexerials Corporation | Protective circuit |
| JP2024049240A (en) * | 2022-09-28 | 2024-04-09 | デクセリアルズ株式会社 | Protection element and manufacturing method for protection element |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3774871B2 (en) * | 1995-10-16 | 2006-05-17 | 松尾電機株式会社 | Delay type thin film fuse |
| JPH1056742A (en) * | 1996-08-06 | 1998-02-24 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Overcharge protective circuit for secondary circuit |
| JP2000200529A (en) * | 1999-01-07 | 2000-07-18 | Nec Kansai Ltd | Protection element and its manufacture |
| JP4244452B2 (en) * | 1999-07-19 | 2009-03-25 | ソニー株式会社 | Battery pack |
| JP4464554B2 (en) * | 2000-12-14 | 2010-05-19 | 北陸電気工業株式会社 | Fuse element and chip type fuse |
| EP1300867A1 (en) * | 2001-10-03 | 2003-04-09 | Metalor Technologies International S.A. | Fuse link and method of manufacture |
| JP2004185960A (en) * | 2002-12-03 | 2004-07-02 | Kamaya Denki Kk | Circuit protection element and its manufacturing method |
| JP4624489B2 (en) * | 2005-08-05 | 2011-02-02 | 内橋エステック株式会社 | Manufacturing method of case type alloy type thermal fuse and case type alloy type thermal fuse |
| CN101313382A (en) * | 2005-10-03 | 2008-11-26 | 保险丝公司 | Fuse with cavity forming enclosure |
| JP4511449B2 (en) * | 2005-11-11 | 2010-07-28 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Protection element and battery pack provided with the protection element |
| JP5072796B2 (en) | 2008-05-23 | 2012-11-14 | ソニーケミカル&インフォメーションデバイス株式会社 | Protection element and secondary battery device |
| JP5301298B2 (en) * | 2009-01-21 | 2013-09-25 | デクセリアルズ株式会社 | Protective element |
| JP5656466B2 (en) | 2010-06-15 | 2015-01-21 | デクセリアルズ株式会社 | Protective element and method of manufacturing protective element |
| CN102290301B (en) * | 2010-06-18 | 2014-04-02 | 厦门赛尔特电子有限公司 | High-current fuse |
-
2013
- 2013-08-28 JP JP2013177058A patent/JP6184805B2/en active Active
-
2014
- 2014-08-27 TW TW103129444A patent/TWI629702B/en active
- 2014-08-27 CN CN201480047053.7A patent/CN105493219A/en active Pending
- 2014-08-27 CN CN201911368547.6A patent/CN110957188A/en active Pending
- 2014-08-27 KR KR1020157035050A patent/KR102275927B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2014-08-27 WO PCT/JP2014/072348 patent/WO2015030020A1/en active Application Filing
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2015030020A1 (en) | 2015-03-05 |
| CN110957188A (en) | 2020-04-03 |
| CN105493219A (en) | 2016-04-13 |
| KR20160046762A (en) | 2016-04-29 |
| KR102275927B1 (en) | 2021-07-12 |
| JP2015046316A (en) | 2015-03-12 |
| TWI629702B (en) | 2018-07-11 |
| TW201523680A (en) | 2015-06-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6249602B2 (en) | Protective element | |
| KR102277298B1 (en) | Electric power fuse | |
| KR102523229B1 (en) | Protection element and mounted body | |
| JP6336725B2 (en) | Protective element and protective circuit board using the same | |
| JP6576618B2 (en) | Protective element | |
| JP6173859B2 (en) | Short circuit element | |
| JP6231324B2 (en) | Protection circuit board | |
| JP6184805B2 (en) | Interrupting element and interrupting element circuit | |
| KR102263795B1 (en) | Interrupting element and interrupting-element circuit | |
| JP6621255B2 (en) | Protection element, fuse element | |
| JP6184238B2 (en) | Short circuit element and short circuit | |
| TWI670739B (en) | Switching element and switching circuit | |
| JP2015230804A (en) | Short circuit element | |
| JP2018018835A (en) | Protection element and fuse element | |
| JP6202992B2 (en) | Protective circuit, battery circuit, protective element, and driving method of protective element | |
| JP6231323B2 (en) | Protective element and protective circuit board using the same | |
| KR102418683B1 (en) | Short circuit element and compensation circuit using same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20160607 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20160607 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20160608 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20170207 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170322 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20170711 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20170726 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6184805 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |