JP5929121B2 - Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus - Google Patents
Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5929121B2 JP5929121B2 JP2011257161A JP2011257161A JP5929121B2 JP 5929121 B2 JP5929121 B2 JP 5929121B2 JP 2011257161 A JP2011257161 A JP 2011257161A JP 2011257161 A JP2011257161 A JP 2011257161A JP 5929121 B2 JP5929121 B2 JP 5929121B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- transistor
- period
- region
- potential
- electro
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 claims description 65
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 claims description 52
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 36
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 19
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 description 14
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 13
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 12
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 12
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 10
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 10
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 10
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 241000750042 Vini Species 0.000 description 5
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910000838 Al alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000593 degrading effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000012447 hatching Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000644 propagated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
- Control Of Indicators Other Than Cathode Ray Tubes (AREA)
- Control Of El Displays (AREA)
Description
本発明は、例えば画素回路が微細化されたときに有効な電気光学装置および電子機器に
関する。
The present invention relates to an electro-optical device and an electronic apparatus that are effective when a pixel circuit is miniaturized, for example.
近年、有機発光ダイオード(Organic Light Emitting Diode、以下「OLED」という
)素子などの発光素子を用いた電気光学装置が各種提案されている。この電気光学装置で
は、走査線とデータ線との交差に対応して、上記発光素子やトランジスターなどを含む画
素回路が、表示すべき画像の画素に対応して設けられる構成が一般的である。このような
構成において、画素の階調レベルに応じた電位のデータ信号が当該トランジスターのゲー
トに印加されると、当該トランジスターは、ゲート・ソース間の電圧に応じた電流を発光
素子に供給する。これにより、当該発光素子は、階調レベルに応じた輝度で発光する。こ
のとき、トランジスターの閾値電圧などの特性が画素回路毎にばらついていると、表示画
面の一様性を損なうような表示ムラが発生する。このため、トランジスターの特性を補償
する技術が提案されている(例えば特許文献1参照)。
また、電気光学装置に対して、表示サイズの小型化や表示の高精細化が要求されること
が多い。表示サイズの小型化と表示の高精細化とを両立するためには、画素回路を微細化
する必要があるので、電気光学装置を例えばシリコン集積回路に設ける技術が提案されて
いる(例えば特許文献2参照)。
In recent years, various electro-optical devices using light emitting elements such as organic light emitting diode (hereinafter referred to as “OLED”) elements have been proposed. In this electro-optical device, a configuration in which a pixel circuit including the light emitting element, the transistor, and the like is provided corresponding to the pixel of the image to be displayed corresponding to the intersection of the scanning line and the data line. In such a configuration, when a data signal having a potential corresponding to the gray level of the pixel is applied to the gate of the transistor, the transistor supplies a current corresponding to the voltage between the gate and the source to the light emitting element. Accordingly, the light emitting element emits light with luminance according to the gradation level. At this time, if the characteristics such as the threshold voltage of the transistor vary from pixel circuit to pixel circuit, display unevenness that impairs the uniformity of the display screen occurs. For this reason, a technique for compensating the characteristics of a transistor has been proposed (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
In many cases, electro-optical devices are required to have a smaller display size and higher display definition. In order to achieve both a reduction in display size and an increase in display definition, it is necessary to miniaturize the pixel circuit. Therefore, a technique for providing an electro-optical device in, for example, a silicon integrated circuit has been proposed (for example, Patent Documents). 2).
ところで、画素回路には、発光素子に電流を供給するトランジスターのほかに、様々な
トランジスターが存在する。画素回路が微細化されたとき、トランジスター同士が接近す
るので、互いに容量カップリングしやすくなる。このため、あるトランジスターで発生し
たノイズが、他のトランジスターに影響を及ぼすことになり、結果的に、表示品位を低下
させる要因になり得る。
本発明は、上述した事情に鑑みてなされたもので、その目的の一つは、画素回路が微細
化されてトランジスター同士が接近しても、表示品位の低下を防止することが可能な電気
光学装置および電子機器を提供することにある。
By the way, in the pixel circuit, there are various transistors in addition to the transistor that supplies current to the light emitting element. When the pixel circuit is miniaturized, the transistors are close to each other, so that capacitive coupling is facilitated. For this reason, noise generated in a certain transistor affects other transistors, and as a result, the display quality can be reduced.
The present invention has been made in view of the above-described circumstances, and one of its purposes is an electro-optic that can prevent deterioration in display quality even when a pixel circuit is miniaturized and transistors are brought close to each other. It is to provide an apparatus and an electronic device.
上記目的を達成するために本発明に係る電気光学装置にあっては、複数の走査線と複数
のデータ線との交差に対応して設けられた画素回路と、を有し、前記画素回路は、ゲート
・ソース間の電圧に応じた電流を供給する第1トランジスターと、前記第1トランジスタ
ーにより供給された電流に応じた輝度で発光する二端子型の発光素子と、前記データ線と
前記第1トランジスターのゲートとの間でオンまたはオフする第2トランジスターと、前
記第1トランジスターのゲートとドレインとの間でオンまたはオフする第3トランジスタ
ーと、前記第1トランジスターによって前記発光素子に供給される電流経路でオンまたは
オフする第4トランジスターと、前記発光素子における二端子のうち、前記第1トランジ
スター側の端子と、所定のリセット電位を給電する第1給電線との間でオンまたはオフす
る第5トランジスターと、を含み、前記第1トランジスターと前記発光素子とは、高位側
の電源と低位側の電源との間で直列に接続され、前記画素回路が形成される領域は第1領
域および第2領域を含み、前記第1領域には、前記第1トランジスター、前記第2トラン
ジスターおよび前記第3トランジスターが配置され、前記第2領域には、前記第4トラン
ジスターおよび前記第5トランジスターが配置されたことを特徴とする。本発明によれば
、第1トランジスターを含む第1領域が、第4トランジスターおよび第5トランジスター
を含む第2領域から分離されている。このため、第4トランジスターおよび第5トランジ
スターのオンオフ動作に伴うノイズが第1トランジスターにおけるゲートに重畳され難い
ので、表示品位の低下を防止することができる。
なお、第1領域と第2領域とは、画素回路が形成される領域を走査線の延在方向である
行方向に沿って分割した構成が好ましい。
In order to achieve the above object, the electro-optical device according to the present invention has a pixel circuit provided corresponding to the intersection of the plurality of scanning lines and the plurality of data lines, and the pixel circuit is A first transistor that supplies a current according to a voltage between a gate and a source; a two-terminal light emitting element that emits light with a luminance according to a current supplied by the first transistor; the data line; A second transistor that is turned on or off between the gate of the transistor, a third transistor that is turned on or off between the gate and the drain of the first transistor, and a current supplied to the light emitting element by the first transistor A fourth transistor that is turned on or off along a path; a terminal on the first transistor side of two terminals of the light emitting element; and a predetermined reset. A fifth transistor that is turned on or off with respect to a first power supply line that supplies power to the first potential, and the first transistor and the light emitting element are connected in series between a high-order power source and a low-order power source. The region where the pixel circuit is formed includes a first region and a second region, and the first region, the second transistor, and the third transistor are disposed in the first region, The fourth transistor and the fifth transistor are arranged in two regions. According to the present invention, the first region including the first transistor is separated from the second region including the fourth transistor and the fifth transistor. For this reason, since the noise accompanying the on / off operation of the fourth transistor and the fifth transistor is difficult to be superimposed on the gate of the first transistor, it is possible to prevent display quality from being deteriorated.
Note that the first region and the second region preferably have a configuration in which the region where the pixel circuit is formed is divided along the row direction, which is the extending direction of the scanning lines.
本発明において、一端が前記データ線に接続された第1保持容量と、一端が前記データ
線に接続され、他端が前記第1給電線に接続された第2保持容量と、前記画素回路を駆動
する駆動回路を、有し、前記駆動回路は、第1期間に、前記データ線と初期電位を給電す
る第2給電線とを電気的に接続し、前記第1保持容量の他端と所定電位を給電する第3給
電線とを電気的に接続し、前記第1期間に続く第2期間に、前記データ線と前記第2給電
線とを電気的に非接続とし、前記第1保持容量の他端と第3給電線との接続を維持した状
態で前記第2トランジスターおよび前記第3トランジスターをオンさせ、前記第2期間に
続く第3期間に、前記第1保持容量の他端と第3給電線とを電気的に非接続として、前記
輝度に応じた電位の信号を前記第1保持容量の他端に供給し、前記第3期間の終了時に前
記第2トランジスターをオフさせ、前記第3期間に続く第4期間に、前記第4トランジス
ターをオンさせ、前記第3トランジスターを、前記第3期間の終了時までにオフさせ、前
記第5トランジスターを、第1期間の開始時から第4期間の開始時までの一部または全部
の期間でオンさせる構成が好ましい。この構成によれば、第1期間に、データ線、第1保
持容量および第2保持容量が初期化される。第2期間に、第2トランジスターおよび第3
トランジスターがそれぞれオンしたとき、データ線および第1トランジスターのゲートは
、当該第1トランジスターの閾値電圧に対応した電位となる。第3期間において、第2ト
ランジスターをオンさせた状態で、輝度に応じた電位の信号が第1保持容量の他端に供給
されたとき、データ線および第1トランジスターのゲートは、閾値電圧に応じた電位から
、当該第1保持容量の他端における電位変動を容量比で分圧した分だけシフトする。この
ため、第1トランジスターのゲートにおける電位範囲は、第1保持容量の他端における電
位範囲に対し狭められる。したがって、この構成によれば、細かい精度のデータ信号を必
要としない一方で、トランジスターの特性を補償しつつ、発光素子に供給する電流を精度
良く供給することができる。
In the present invention, a first storage capacitor having one end connected to the data line, a second storage capacitor having one end connected to the data line and the other end connected to the first power supply line, and the pixel circuit A driving circuit for driving, wherein the driving circuit electrically connects the data line and a second feeding line for feeding an initial potential in a first period, and connects the other end of the first storage capacitor to a predetermined amount. Electrically connecting a third power supply line for supplying a potential, and electrically disconnecting the data line and the second power supply line in a second period following the first period; The second transistor and the third transistor are turned on while maintaining the connection between the other end of the first power supply line and the third power supply line, and the other end of the first storage capacitor and the second storage capacitor are turned on in a third period following the second period. 3 is electrically disconnected from the feeder line, and a signal having a potential corresponding to the luminance is 1 is supplied to the other end of the storage capacitor, the second transistor is turned off at the end of the third period, the fourth transistor is turned on in the fourth period following the third period, and the third transistor is It is preferable that the third transistor is turned off by the end of the third period, and the fifth transistor is turned on for a part or all of the period from the start of the first period to the start of the fourth period. According to this configuration, the data line, the first storage capacitor, and the second storage capacitor are initialized in the first period. In the second period, the second transistor and the third
When each transistor is turned on, the data line and the gate of the first transistor are at a potential corresponding to the threshold voltage of the first transistor. In the third period, when a signal having a potential corresponding to luminance is supplied to the other end of the first storage capacitor while the second transistor is turned on, the data line and the gate of the first transistor are in accordance with the threshold voltage. The potential variation at the other end of the first storage capacitor is shifted from the potential by the amount divided by the capacitance ratio. For this reason, the potential range at the gate of the first transistor is narrower than the potential range at the other end of the first storage capacitor. Therefore, according to this configuration, a current to be supplied to the light emitting element can be supplied with high accuracy while compensating for the characteristics of the transistor while not requiring a data signal with fine accuracy.
本発明において、前記第1領域と第2領域との間にシールド配線が設けられ、前記発光
素子に電流が流れないときに、前記シールド配線の電位が固定されていても良い。これに
よれば、第1領域および第2領域の一方で発生したノイズ等が他方に伝播するのを、より
確実に抑えることができる。
ここで、前記シールド配線には、前記電源の一方が給電される態様としても良いし、前
記リセット電位が給電される態様としても良い。いずれの態様においても、別途の画素回
路に給電される電位を流用するので、構成の複雑化を避けることができる。
また、本発明において、前記第1トランジスターと前記第4トランジスターとは、導電
配線を介して互いに接続された構成としても良い。この構成によれば、発光素子への電流
経路の低抵抗化を図ることができる。なお、導電配線としては、例えばアルミニウム単体
またはアルミニウム合金などが好ましい。
なお、本発明は、電気光学装置のほか、当該電気光学装置を有する電子機器として概念
することも可能である。電子機器としては、典型的にはヘッドマウント・ディスプレイ(
HMD)や電子ビューファイダーなどの表示装置が挙げられる。
In the present invention, a shield wiring may be provided between the first region and the second region, and the potential of the shield wiring may be fixed when no current flows through the light emitting element. According to this, it can suppress more reliably that the noise etc. which generate | occur | produced by one side of the 1st area | region and the 2nd area | region are propagated to the other side.
Here, either one of the power supplies may be supplied to the shield wiring, or the reset potential may be supplied. In any aspect, since the potential supplied to the separate pixel circuit is used, the configuration can be prevented from becoming complicated.
In the present invention, the first transistor and the fourth transistor may be connected to each other through a conductive wiring. According to this configuration, the resistance of the current path to the light emitting element can be reduced. As the conductive wiring, for example, aluminum alone or an aluminum alloy is preferable.
In addition to the electro-optical device, the present invention can be conceptualized as an electronic apparatus having the electro-optical device. Typically, electronic devices include head-mounted displays (
Display devices such as HMD) and electronic viewfinders.
以下、本発明を実施するための形態について図面を参照して説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments for carrying out the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
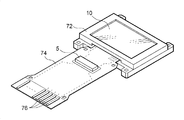
図1は、本発明の実施形態に係る電気光学装置10の構成を示す斜視図である。
電気光学装置10は、例えばヘッドマウント・ディスプレイにおいて画像を表示するマ
イクロ・ディスプレイである。電気光学装置10の詳細については後述するが、複数の画
素回路や当該画素回路を駆動する駆動回路などが例えばシリコン基板に形成された有機E
L装置であり、画素回路には、発光素子の一例であるOLEDが用いられている。
電気光学装置10は、表示部で開口する枠状のケース72に収納されるとともに、FP
C(Flexible Printed Circuits)基板74の一端が接続されている。FPC基板74に
は、半導体チップの制御回路5が、COF(Chip On Film)技術によって実装されるとと
もに、複数の端子76が設けられて、上位回路(図示省略)に接続される。当該上位回路
から複数の端子76を介して画像データが同期信号に同期して供給される。同期信号には
、垂直同期信号や、水平同期信号、ドットクロック信号が含まれる。また、画像データは
、表示すべき画像の画素の階調レベルを例えば8ビットで規定する。
制御回路5は、電気光学装置10の電源回路とデータ信号出力回路との機能を兼用する
ものである。詳細には、制御回路5は、同期信号にしたがって生成した各種の制御信号や
各種電位を電気光学装置10に供給するほか、デジタルの画像データをアナログのデータ
信号に変換して、電気光学装置10に供給する。
FIG. 1 is a perspective view showing a configuration of an electro-
The electro-
The L device is an OLED which is an example of a light emitting element.
The electro-
One end of a C (Flexible Printed Circuits)
The control circuit 5 combines the functions of the power supply circuit and the data signal output circuit of the electro-
図2は、第1実施形態に係る電気光学装置10の構成を示す図である。この図に示され
るように、電気光学装置10は、走査線駆動回路20と、デマルチプレクサ30と、レベ
ルシフト回路40と、表示部100とに大別される。
このうち、表示部100には、表示すべき画像の画素に対応した画素回路110がマト
リクス状に配列されている。詳細には、表示部100において、m行の走査線12が図に
おいて横方向に延在して設けられ、また、3列毎にグループ化された(3n)列のデータ
線14が図において縦方向に延在し、かつ、各走査線12と互いに電気的な絶縁を保って
設けられている。そして、m行の走査線12と(3n)列のデータ線14との交差部に対
応して画素回路110が設けられている。このため、本実施形態において画素回路110
は、縦m行×横(3n)列でマトリクス状に配列されている。
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of the electro-
Among these, in the
Are arranged in a matrix with vertical m rows × horizontal (3n) columns.
ここで、m、nは、いずれも自然数である。走査線12および画素回路110のマトリ
クスのうち、行(ロウ)を区別するために、図において上から順に1、2、3、…、(m
−1)、m行と呼ぶ場合がある。同様にデータ線14および画素回路110のマトリクス
の列(カラム)を区別するために、図において左から順に1、2、3、…、(3n−1)
、(3n)列と呼ぶ場合がある。また、データ線14のグループを一般化して説明するた
めに、1以上n以下の整数jを用いると、左から数えてj番目のグループには、(3j−
2)列目、(3j−1)列目および(3j)列目のデータ線14が属している、というこ
とになる。
なお、同一行の走査線12と同一グループに属する3列のデータ線14との交差に対応
した3つの画素回路110は、それぞれR(赤)、G(緑)、B(青)の画素に対応して
、これらの3画素が表示すべきカラー画像の1ドットを表現する。すなわち、本実施形態
では、RGBに対応したOLEDの発光によって1ドットのカラーを加法混色で表現する
構成となっている。
Here, m and n are both natural numbers. In order to distinguish rows in the matrix of the
-1), sometimes called m rows. Similarly, in order to distinguish the column of the matrix of the
, (3n) columns. In order to generalize and describe the group of
2) The
Note that the three
本実施形態では、列毎に給電線16がデータ線14に沿ってそれぞれ設けられている。
各給電線16にはリセット電位としての電位Vorstが給電されているので、当該給電線1
6が第1給電線として機能する。また、列毎に保持容量50が設けられている。詳細には
、保持容量50の一端はデータ線14に接続され、他端が給電線16に接続されている。
このため、保持容量50は、第2保持容量として機能する。
なお、保持容量50については、データ線14を構成する配線と、給電線16を構成す
る配線とで、絶縁体(誘電体)を挟持することによって形成される構成が好ましい。また
、保持容量50については、図2では表示部100の外側に設けられているが、これはあ
くまでも等価回路であり、表示部100の内側に、または、内側から外側にわたって設け
られても良いのはもちろんである。また、図2では省略しているが、保持容量50の容量
をCdtとする。
In the present embodiment, the
Since each of the
6 functions as a first feeder. Further, a holding
For this reason, the
Note that the
さて、電気光学装置10には、次のような制御信号が制御回路5によって供給される。
詳細には、電気光学装置10には、走査線駆動回路20を制御するための制御信号Ctrと
、デマルチプレクサ30での選択を制御するための制御信号Sel(1)、/Sel(1)、Sel(2
)、/Sel(2)、Sel(3)、/Sel(3)と、レベルシフト回路40を制御するための制御信号
/Gini、Gref、Gcpl、/Gcplとが供給される。
なお、制御信号Ctrには、実際にはパルス信号や、クロック信号、イネーブル信号など
、複数の信号が含まれる。また、制御信号Sel(1)および/Sel(1)は互いに論理反転の関
係にある。同様に、制御信号Sel(2)および/Sel(2)と、制御信号Sel(3)および/Sel(
3)と、制御信号Gcplおよび/Gcplとについても、互いに論理反転の関係にある。
The following control signals are supplied to the electro-
Specifically, the electro-
), / Sel (2), Sel (3), / Sel (3) and control signals / Gini, Gref, Gcpl, / Gcpl for controlling the
Note that the control signal Ctr actually includes a plurality of signals such as a pulse signal, a clock signal, and an enable signal. The control signals Sel (1) and / Sel (1) are in a logically inverted relationship with each other. Similarly, control signals Sel (2) and / Sel (2) and control signals Sel (3) and / Sel (
3) and the control signals Gcpl and / Gcpl are also in a logically inverted relationship with each other.
電気光学装置10には、デマルチプレクサ30での選択タイミングに合わせてデータ信
号Vd(1)、Vd(2)、…、Vd(n)が、1、2、…、n番目のグループに対応して制御回路5
によって供給される。なお、データ信号Vd(1)〜Vd(n)が取り得る電位の最高値をVmax
とし、最低値をVminとする。
In the electro-
Supplied by The maximum potential of the data signals Vd (1) to Vd (n) can be expressed as Vmax.
And the minimum value is Vmin.
走査線駆動回路20は、フレームの期間にわたって走査線12を1行毎に順番に走査す
るための走査信号を、制御信号Ctrにしたがって生成するものである。ここで、1、2、
3、…、(m−1)、m行目の走査線12に供給される走査信号を、それぞれGwr(1)、
Gwr(2)、Gwr(3)、…、Gwr(m-1)、Gwr(m)と表記している。
なお、走査線駆動回路20は、走査信号Gwr(1)〜Gwr(m)のほかにも、当該走査信号に
同期した各種の制御信号を行毎に生成して表示部100に供給するが、図2においては図
示を省略している。また、フレームの期間とは、電気光学装置10が1カット(コマ)分
の画像を表示するのに要する期間をいい、例えば同期信号に含まれる垂直同期信号の周波
数が120Hzであれば、その1周期分の8.3ミリ秒の期間である。
The scanning
3,..., (M−1), and the scanning signals supplied to the m-
Gwr (2), Gwr (3), ..., Gwr (m-1), Gwr (m) are written.
In addition to the scanning signals Gwr (1) to Gwr (m), the scanning
デマルチプレクサ30は、列毎に設けられたトランスミッションゲート34の集合体で
あり、各グループを構成する3列に、データ信号を順番に供給するものである。
ここで、j番目のグループに属する(3j−2)列、(3j−1)列、(3j)列に対
応したトランスミッションゲート34の入力端は互いに共通接続されて、その共通端子に
それぞれデータ信号Vd(j)が供給される。
j番目のグループにおいて左端列である(3j−2)列に設けられたトランスミッショ
ンゲート34は、制御信号Sel(1)がHレベルであるとき(制御信号/Sel(1)がLレベル
であるとき)にオン(導通)する。同様に、j番目のグループにおいて中央列である(3
j−1)列に設けられたトランスミッションゲート34は、制御信号Sel(2)がHレベル
であるとき(制御信号/Sel(2)がLレベルであるとき)にオンし、j番目のグループに
おいて右端列である(3j)列に設けられたトランスミッションゲート34は、制御信号
Sel(3)がHレベルであるとき(制御信号/Sel(3)がLレベルであるとき)にオンする。
The
Here, the input terminals of the
The
j-1) The
レベルシフト回路40は、保持容量41、44と、トランスミッションゲート42と、
NチャネルMOS型のトランジスター43と、PチャネルMOS型のトランジスター45
との組を列毎に有し、各列のトランスミッションゲート34の出力端から出力されるデー
タ信号を一旦保持した後に、電位をシフトしてデータ線14に供給するものである。
各列において保持容量44の一端は、対応する列のデータ線14とトランジスター45
のドレインノードとに接続される一方、保持容量44の他端は、トランスミッションゲー
ト34の出力端とトランジスター43のソースノードとに接続される。このため、保持容
量44は、一端がデータ線14に接続された第1保持容量として機能する。
一方、各列においてトランスミッションゲート42の入力端はトランスミッションゲー
ト34の出力端に接続され、トランスミッションゲート42の出力端は保持容量44の他
端に接続されている。
The
N-
For each column, after temporarily holding the data signal output from the output terminal of the
In each column, one end of the
The other end of the
On the other hand, in each column, the input end of the
各列においてトランジスター45のソースノードは、初期電位として電位Viniを給電
する第2給電線としての給電線61に各列にわたって共通に接続され、ゲートノードには
、制御信号/Giniが各列にわたって共通に供給される。このため、トランジスター45
は、データ線14と給電線61とを、制御信号/GiniがLレベルのときに電気的に接続
し、制御信号/GiniがHレベルのときに電気的に非接続とする構成となっている。
各列においてトランジスター43のドレインノードは、電位Vrefを給電する第3給電
線としての給電線62に各列にわたって共通に接続され、ゲートノードには、制御信号G
refが各列にわたって共通に供給される。このため、トランジスター43は、保持容量4
4の他端(ノードh)と給電線62とを、制御信号GrefがHレベルのときに電気的に接
続し、制御信号GrefがLレベルのときに電気的に非接続とする構成となっている。
各列においてトランスミッションゲート42は、制御信号GcplがHレベルであるとき
(制御信号/GcplがLレベルであるとき)に一斉にオンする。
In each column, the source node of the
Is configured such that the
In each column, the drain node of the
ref is supplied in common across each column. For this reason, the
4 is electrically connected when the control signal Gref is at the H level and electrically disconnected when the control signal Gref is at the L level. Yes.
In each column, the
なお、図2では省略しているが、保持容量44の容量をCrf1とする。
また、保持容量41の他端は、固定電位、例えば電位Vssに共通に接地されている。な
お、電位Vssは、論理信号である走査信号や制御信号のLレベルに相当する。
図2では省略しているが、保持容量41の容量をCrf2とする。
Although omitted in FIG. 2, the capacity of the
The other end of the
Although omitted in FIG. 2, the capacity of the
本実施形態では、便宜的に走査線駆動回路20、デマルチプレクサ30およびレベルシ
フト回路40に分けているが、これらについては、画素回路110を駆動する駆動回路と
してまとめて概念することが可能である。
In the present embodiment, the scanning
図3を参照して画素回路110の電気的な構成について説明する。図3は、画素回路1
10の等価回路を示す図である。各画素回路110については電気的にみれば互いに同一
構成なので、ここでは、i行目であって、j番目のグループのうち左端列の(3j−2)
列目に位置するi行(3j−2)列の画素回路110を例にとって説明する。
なお、図3は、画素回路110の等価回路を示すに留まり、実際の回路レイアウトを反
映させた図ではない。また、iは、画素回路110が配列する行を一般的に示す場合の記
号であって、1以上m以下の整数である。
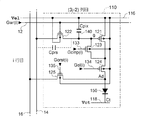
The electrical configuration of the
10 is a diagram showing an equivalent circuit of FIG. Since each
A description will be given by taking the
Note that FIG. 3 only shows an equivalent circuit of the
図3に示されるように、画素回路110は、PチャネルMOS型のトランジスター12
1〜125と、保持容量140と、OLED150と、を含む。この画素回路110には
、走査信号Gwr(i)、制御信号Gel(i)、Gcmp(i)、Gorst(i)が供給される。ここで、走
査信号Gwr(i)、制御信号Gel(i)、Gcmp(i)、Gorst(i)は、それぞれi行目に対応して
走査線駆動回路20によって供給されるものである。このうち、制御信号Gel(i)は制御
線134を介して供給され、同様に、制御信号Gcmp(i)、Gorst(i)は、それぞれ制御線
133、135を介して供給される。
なお、走査信号Gwr(i)、制御信号Gel(i)、Gcmp(i)、Gorst(i)は、i行目に対応し
て供給されるので、i行目であれば、着目している(3j−2)列以外の他の列の画素回
路にも共通に供給される。
As shown in FIG. 3, the
1 to 125, a
Note that the scanning signal Gwr (i), the control signals Gel (i), Gcmp (i), and Gorst (i) are supplied corresponding to the i-th row. (3j-2) It is also supplied in common to the pixel circuits in other columns than the column.
さて、i行(3j−2)列の画素回路110におけるトランジスター122にあっては
、ゲートノードがi行目の走査線12に接続され、ドレインまたはソースノードの一方が
(3j−2)列目のデータ線14に接続され、他方がトランジスター121におけるゲー
トノードと、保持容量140の一端と、トランジスター123のドレインノードとにそれ
ぞれ接続されている。ここで、トランジスター121のゲートノードについては、他のノ
ードと区別するためにgと表記する。
トランジスター121にあっては、ソースノードが給電線116に接続され、ドレイン
ノードがトランジスター123のソースノードと、トランジスター124のソースノード
とにそれぞれ接続されている。ここで、給電線116には、画素回路110において電源
の高位側となる電位Velが給電される。
トランジスター123にあっては、ゲートノードがi行目の制御線133に接続されて
制御信号Gcmp(i)が供給される。
トランジスター124にあっては、ゲートノードがi行目の制御線134に接続されて
制御信号Gel(i)が供給され、ドレインノードがトランジスター125のソースノードと
OLED150のアノードAdとにそれぞれ接続されている。
トランジスター125にあっては、ゲートノードがi行目の制御線135に接続されて
i行目に対応した制御信号Gorst(i)が供給され、ドレインノードが(3j−2)列目に
対応した給電線16に接続されて電位Vorstに保たれている。
Now, in the
In the
In the
In the
In the
ここで、トランジスター121が第1トランジスターに相当し、トランジスター122
が第2トランジスターに相当し、トランジスター123が第3トランジスターに相当する
。また、トランジスター124が第4トランジスターに相当し、トランジスター125が
第5トランジスターに相当する。
Here, the
Corresponds to the second transistor, and the
保持容量140の他端は、給電線116に接続される。このため、保持容量140は、
トランジスター121のソース・ドレイン間の電圧を保持することになる。ここで、保持
容量140の容量をCpixと表記したとき、保持容量50の容量Cdtと、保持容量44の
容量Crf1と、保持容量140の容量Cpixとは、
Cdt>Crf1>>Cpix
となるように設定される。
すなわち、CdtはCrf1よりも大きく、CpixはCdtおよびCrf1よりも十分に小さくな
るように設定される。なお、Crf2は、Crf1と同程度であるか、Crf1よりもやや小さい
程度である。また、保持容量140としては、トランジスター121のゲートノードgに
寄生する容量を用いても良いし、シリコン基板において互いに異なる導電層で絶縁層を挟
持することによって形成される容量を用いても良い。
The other end of the
The voltage between the source and drain of the
Cdt >> Crf1 >> Cpix
Is set to be
That is, Cdt is set to be larger than Crf1, and Cpix is set to be sufficiently smaller than Cdt and Crf1. Note that Crf2 is about the same as Crf1 or slightly smaller than Crf1. As the
OLED150のアノードAdは、画素回路110毎に個別に設けられる画素電極であ
る。これに対して、OLED150のカソードCtは、画素回路110のすべてにわたっ
て共通の共通電極118であり、画素回路110において電源の低位側となる電位Vctに
保たれている。
OLED150は、上記シリコン基板において、アノードAdと光透過性を有するカソ
ードCtとで白色有機EL層を挟持した二端子型素子である。そして、OLED150の
出射側(カソード側)にはRGBのいずれかに対応したカラーフィルターが重ねられる。
このようなOLED150において、アノードAdからカソードCtに電流が流れると、
アノードAdから注入された正孔とカソードCtから注入された電子とが有機EL層で再結
合して励起子が生成され、白色光が発生する。このときに発生した白色光は、シリコン基
板(アノード)とは反対側のカソードを透過し、カラーフィルターによる着色を経て、観
察者側に視認される構造(トップエミッション構造)となっている。
The anode Ad of the
The
In such an
The holes injected from the anode Ad and the electrons injected from the cathode Ct are recombined in the organic EL layer to generate excitons, and white light is generated. The white light generated at this time is transmitted through the cathode opposite to the silicon substrate (anode), and is colored by a color filter so as to be visually recognized by the viewer (top emission structure).
本実施形態において電気光学装置10はシリコン基板に形成されるので、トランジスタ
ー121〜125の基板電位については電位Velとしている。
In the present embodiment, since the electro-
ここで、画素回路110の製造工程を簡易的に説明する。
まず、P型のシリコン基板において画素回路110が形成される予定領域に、トランジ
スター121〜125の基礎となる島状のNウェル(N−)が形成された後、ゲート絶縁
膜を介し、多結晶シリコン膜などがパターニングされてゲート配線が形成される。この後
、ゲート配線をマスクとしたイオンの打ち込み等によって、ソースノードまたはドレイン
ノードとなるP型拡散層(P+)が形成される。
この後、第1層間絶縁膜を介して、アルミニウムや銅などの導電配線層(第1配線層)
がパターニングされて、後述する各種の配線が第1配線として設けられる。このとき、ソ
ースノードまたはドレインノードと、第1配線とは、第1層間絶縁膜を開孔するコンタク
トホールを介して接続される。
続いて、第2層間絶縁膜を介して、同じくアルミニウムや銅などの導電配線層(第2配
線層)がパターニングされて、各種の配線が第2配線として設けられる。このとき、第1
配線と、第2配線とは、第2層間絶縁膜を開孔するコンタクトホールを介して接続される
。
そして、第3層間絶縁膜および遮光層を介して、矩形形状の画素電極が、OLED15
0のアノードAdとして形成される。以降については上述した通りである。
Here, a manufacturing process of the
First, after an island-shaped N well (N−) serving as a base of the
Thereafter, a conductive wiring layer (first wiring layer) such as aluminum or copper via the first interlayer insulating film.
Are patterned, and various wirings to be described later are provided as the first wiring. At this time, the source node or the drain node and the first wiring are connected through a contact hole that opens the first interlayer insulating film.
Subsequently, a conductive wiring layer (second wiring layer) such as aluminum or copper is similarly patterned through the second interlayer insulating film, and various wirings are provided as second wirings. At this time, the first
The wiring and the second wiring are connected via a contact hole that opens the second interlayer insulating film.
The rectangular pixel electrode is connected to the OLED 15 via the third interlayer insulating film and the light shielding layer.
Formed as zero anode Ad. The subsequent steps are as described above.
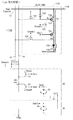
図4は、トップエミッション構造の画素回路110を観察側から平面視したときにのト
ランジスター121〜125の配置を示す平面図であり、配線についてはゲート配線まで
を示している。図5は、図4に対してさらに第1配線層および第2配線層による各種の配
線を付加したときの構造を示す平面図である。なお、図6は、図5における構造を回路で
置き換えて示す説明図であり、回路的には図3と同一である。
FIG. 4 is a plan view showing the arrangement of the
図4および図5に示されるように、画素回路110が形成される領域は、図において横
方向(走査線12の延在方向)に沿って、下側の第1領域110aと上側の第2領域11
0bとに分離されている。このうち、第1領域110aには、トランジスター121〜1
23が設けられ、第2領域110bには、トランジスター124、125が設けられる。
As shown in FIGS. 4 and 5, the region where the
It is separated into 0b. Among these, in the
23, and
トランジスター121は、図4に示されるように、平面視で列方向に長手の矩形形状と
なっており、島状のNウェルに対して絶縁膜を介して形成されたゲート配線121gと、
当該ゲート配線121gをマスクとして形成された2つのP型拡散層(図においてハッチ
ングで示した領域)とを有する。トランジスター121における2つの拡散層のうち、図
において下側がソースノードであり、上側がドレインノードである。
As shown in FIG. 4, the
And two P-type diffusion layers (regions indicated by hatching in the drawing) formed using the
トランジスター122、123は、図においてトランジスター121の右側に配置し、
共通化された島状のNウェルが、平面視で列方向に長手の矩形形状となっている。トラン
ジスター122、123の共通Nウェルには、互いに分離したゲート配線122g、12
3gが形成され、これをマスクとして3つのP型拡散層が形成される。これらの3つの拡
散層のうち、図において下側がトランジスター122におけるドレインまたはソースノー
ドの一方であり、中央がトランジスター122におけるドレインまたはソースノードの他
方と、トランジスター123におけるドレインノードとの共通ノードであり、上側がトラ
ンジスター123におけるソースノードである。
The
The common island-shaped N-well has a rectangular shape elongated in the column direction in plan view. In the common N well of the
3g is formed, and three P-type diffusion layers are formed using this as a mask. Of these three diffusion layers, the lower side in the figure is one of the drain or source node in the
トランジスター124は、図4に示されるように、平面視で列方向に長手の矩形形状と
なっており、トランジスター122、123に対して列方向で揃った地点に位置している
。トランジスター124における島状のNウェルには、ゲート配線124gが形成されて
、これをマスクとして2つのP型拡散層が形成されている。2つの拡散層のうち、図にお
いて下側がトランジスター124におけるソースノードであり、上側がドレインノードで
ある。
トランジスター125は、図においてトランジスター124の左側であって、トランジ
スター121に対して列方向で揃った地点に位置している。トランジスター125におけ
る島状のNウェルには、ゲート配線125gが形成されて、これをマスクとして2つのP
型拡散層が形成されている。2つの拡散層のうち、図において下側がトランジスター12
5におけるドレインノードであり、上側がソースノードである。
As shown in FIG. 4, the
The
A mold diffusion layer is formed. Of the two diffusion layers, the lower side is the
5 is a drain node, and the upper side is a source node.
このように設けられるトランジスター121〜125に対して、第1層間絶縁膜が設け
られた後、第1配線層がパターニングされて、図5に示されるように走査線12、配線8
1〜86、給電線116、配線116b、制御線133〜135が上記第1配線として設
けられる。このうち、走査線12、給電線116、制御線133〜135は、それぞれ上
述したように行方向に延在して設けられる。
走査線12は、ゲート配線122gの上面側(紙面において手前側)を通過する。走査
線12は、第1層間絶縁膜を開孔するコンタクトホール(図における□)12fを介して
ゲート配線122gに接続される。制御線133は、ゲート配線123gの上面側を通過
するとともに、コンタクトホール133fを介してゲート配線123gに接続される。
給電線116は、第1領域110aと第2領域110bとの境界を含むように設けられ
る。制御線134、135は、いずれもゲート配線124g、125gの上面側を通過す
るとともに、このうち、制御線134がコンタクトホール134fを介してゲート配線1
24gに接続され、制御線135がコンタクトホール135fを介してゲート配線125
gに接続される。
After the first interlayer insulating film is provided for the
1 to 86, a
The
The
The
connected to g.
配線81は、データ線14とトランジスター122におけるドレインまたはソースノー
ドの一方とを接続する。
配線82は、トランジスター122におけるドレインまたはソースノードの他方と、ト
ランジスター123におけるドレインノードとの共通ノードを、トランジスター121に
おけるゲート配線121gに、コンタクトホール82fを介して接続する。配線82は、
ゲート配線121gの上面側において幅広となっており、保持容量140における一対の
電極のうち、一方を構成する。
配線83は、トランジスター121におけるドレインノードとトランジスター123に
おけるソースノードとを接続する。
配線84は、トランジスター124におけるソースノードを、後述する第2配線層の配
線91に接続するための中継電極である。配線85は、トランジスター125におけるド
レインノードと、給電線16とを接続する。配線86は、トランジスター124における
ドレインノードと、トランジスター125におけるソースノードと、OLED150(図
5において図示省略)におけるアノードAdとを接続する。
配線116bは、トランジスター121におけるソースノードを、後述する第2配線層
の配線116aを介して、給電線116に接続するための中継配線である。
The
The
It is wide on the upper surface side of the gate wiring 121 g and constitutes one of the pair of electrodes in the
The
The
The
続いて、第2層間絶縁膜が設けられた後、第2配線層がパターニングされて、図5に示
されるようにデータ線14、給電線16、配線91、116aが上記第2配線として設け
られる。
データ線14、給電線16は、それぞれ列方向に延在して設けられる。データ線14は
、平面視でトランジスター122、123、124の右側に位置し、第2層間絶縁膜を開
孔するコンタクトホール14fを介して、配線81に接続される。これにより、データ線
14は、配線81を介して、トランジスター122におけるドレインまたはソースノード
の一方に接続されることになる。
給電線16は、平面視でトランジスター122、123、124と、トランジスター1
21、125との間に位置し、コンタクトホール16fを介して配線85に接続される。
これにより、給電線16は、配線85を介して、トランジスター125におけるドレイン
ノードに接続されることになる。
Subsequently, after the second interlayer insulating film is provided, the second wiring layer is patterned, and the
The
The
21 and 125, and is connected to the
As a result, the
一方、配線116aは、平面視でトランジスター121の左側に設けられ、制御線13
3および走査線12を跨いだ状態で、給電線116とコンタクトホール116eを介して
接続され、配線116bとはコンタクトホール116fを介して接続される。配線116
aは、平面視で配線82と重なる領域を有し、保持容量140における一対の電極のうち
、他方を構成する。これにより、保持容量140は、配線82と配線116aとで第2層
間絶縁膜を挟持した構成になる。また、給電線116は、配線116a、116bを介し
て、トランジスター121におけるソースノードに接続されることになる。
配線91は、配線83、84同士を、給電線116を跨いだ状態で接続する。
On the other hand, the
3 and the
a has a region overlapping the
The
このように画素回路110では、第1領域110aと第2領域110bとに、固定電位
の給電線116によって隔てられる。また、トランジスター121におけるドレインノー
ドと、トランジスター123におけるドレインノードと、トランジスター124における
ソースノードは、配線83、84、91によって互いに接続される。一方、トランジスタ
ー121のゲートノードgにあっては、配線116aによって図において左側がシールド
されるとともに、給電線16によって右側がシールドされた構成となる。
As described above, in the
<第1実施形態の動作>
図7を参照して電気光学装置10の動作について説明する。図7は、電気光学装置10
における各部の動作を説明するためのタイミングチャートである。
この図に示されるように、走査信号Gwr(1)〜Gwr(m)が順次Lレベルに切り替えられて
、1フレームの期間において1〜m行目の走査線12が1水平走査期間(H)毎に順番に
走査される。
1水平走査期間(H)での動作は、各行の画素回路110にわたって共通である。そこ
で以下については、i行目が水平走査される走査期間において、特にi行(3j−2)列
の画素回路110について着目して動作を説明する。
<Operation of First Embodiment>
The operation of the electro-
6 is a timing chart for explaining the operation of each part in FIG.
As shown in this figure, the scanning signals Gwr (1) to Gwr (m) are sequentially switched to the L level, and the
The operation in one horizontal scanning period (H) is common to the
本実施形態ではi行目の走査期間について大別すると、図7において(b)で示される
初期化期間と、(c)で示される補償期間と、(d)で示される書込期間とに分けられる
。そして、(d)の書込期間の後、間をおいて(a)で示されるの発光期間となり、1フ
レームの期間経過後に再びi行目の走査期間に至る。このため、時間の順でいえば、(発
光期間)→初期化期間→補償期間→書込期間→(発光期間)というサイクルの繰り返しと
なる。
なお、図7において、i行目に対し1行前の(i−1)行目に対応する走査信号Gwr(i
-1)、制御信号Gel(i-1)、Gcmp(i-1)、Gorst(i-1)の各々については、i行目に対応す
る走査信号Gwr(i)、制御信号Gel(i)、Gcmp(i)、Gorst(i)よりも、それぞれ時間的に
1水平走査期間(H)だけ時間的に先行した波形となる。
In this embodiment, the scanning period of the i-th row is roughly classified into an initialization period shown in FIG. 7B, a compensation period shown in FIG. 7C, and a writing period shown in FIG. Divided. Then, after the writing period of (d), the light emission period shown in (a) is reached, and the scanning period of the i-th row is reached again after the elapse of one frame period. Therefore, in the order of time, a cycle of (light emission period) → initialization period → compensation period → writing period → (light emission period) is repeated.
In FIG. 7, the scanning signal Gwr (i) corresponding to the (i−1) th row before the i-th row.
-1), the control signals Gel (i-1), Gcmp (i-1), and Gorst (i-1), the scanning signal Gwr (i) and the control signal Gel (i) corresponding to the i-th row. , Gcmp (i) and Gorst (i) are temporally preceded by one horizontal scanning period (H).
<発光期間>
説明の便宜上、初期化期間の前提となる発光期間から説明する。図7に示されるように
、i行目の発光期間では、走査信号Gwr(i)がHレベルであり、また、論理信号である制
御信号Gel(i)、Gcmp(i)、Gorst(i)のうち、制御信号Gel(i)がLレベルであり、制御
信号Gcmp(i)、Gorst(i)がHレベルである。
このため、図8に示されるようにi行(3j−2)列の画素回路110においては、ト
ランジスター124がオンする一方、トランジスター122、123、125がオフする
。したがって、トランジスター121は、ゲート・ソース間の電圧Vgsに応じた電流Ids
をOLED150に供給する。後述するように、本実施形態において発光期間での電圧V
gsは、トランジスター121の閾値電圧から、データ信号の電位に応じてレベルシフトし
た値である。このため、OLED150には、階調レベルに応じた電流がトランジスター
121の閾値電圧を補償した状態で供給されることになる。
<Light emission period>
For convenience of explanation, the light emission period which is the premise of the initialization period will be described. As shown in FIG. 7, in the light emission period of the i-th row, the scanning signal Gwr (i) is at the H level, and the control signals Gel (i), Gcmp (i), and Gorst (i) that are logic signals. Among them, the control signal Gel (i) is at the L level, and the control signals Gcmp (i) and Gorst (i) are at the H level.
For this reason, as shown in FIG. 8, in the
Is supplied to the
gs is a value obtained by level shifting from the threshold voltage of the
なお、i行目の発光期間は、i行目以外が水平走査される期間であるから、データ線1
4の電位は適宜変動する。ただし、i行目の画素回路110においては、トランジスター
122がオフしているので、ここでは、データ線14の電位変動を考慮していない。また
、図8においては、動作説明で重要となる経路を太線で示している(以下の図9〜図11
においても同様である)。
Note that since the light emission period of the i-th row is a period during which horizontal scanning is performed except for the i-th row, the
The potential of 4 varies as appropriate. However, in the
The same applies to the above).
<初期化期間>
次にi行目の走査期間に至ると、まず、第1期間として(b)の初期化期間が開始する
。初期化期間では、発光期間と比較して、制御信号Gel(i)がHレベルに、制御信号Gors
t(i)がLレベルに、それぞれ変化する。
このため、図9に示されるように、i行(3j−2)列の画素回路110においてはト
ランジスター124がオフし、トランジスター125がオンする。これによってOLED
150に供給される電流の経路が遮断されるとともに、OLED150のアノードAdが
電位Vorstにリセットされる。
OLED150は、上述したようにアノードAdとカソードCtとで有機EL層を挟持し
た構成であるので、アノードAd・カソードCtの間には、図において破線で示されるよう
に容量Coledが並列に寄生する。発光期間においてOLED150に電流が流れていたと
きに、当該OLED150のアノード・カソード間の両端電圧が当該容量Coledによって
保持されるが、この保持電圧は、トランジスター125のオンによってリセットされる。
このため、本実施形態では、後の発光期間においてOLED150に再び電流が流れると
きに、当該容量Coledで保持されている電圧の影響を受けにくくなる。
<Initialization period>
Next, when the scanning period of the i-th row is reached, first, the initialization period (b) is started as the first period. In the initialization period, the control signal Gel (i) is at the H level compared to the light emission period, and the control signal Gors
t (i) changes to L level.
Therefore, as shown in FIG. 9, in the
The path of the current supplied to 150 is interrupted, and the anode Ad of the
Since the
For this reason, in this embodiment, when a current flows again through the
詳細には、例えば高輝度の表示状態から低輝度の表示状態に転じるときに、リセットし
ない構成であると、輝度が高い(大電流が流れた)ときの高電圧が保持されてしまうので
、次に、小電流を流そうとしても、過剰な電流が流れてしまって、低輝度の表示状態にさ
せることができなくなる。これに対して、本実施形態では、トランジスター125のオン
によってOLED150のアノードAdの電位がリセットされるので、低輝度側の再現性
が高められることになる。
なお、本実施形態において、電位Vorstについては、当該電位Vorstと共通電極118
の電位Vctとの差がOLED150の発光閾値電圧を下回るように設定される。このため
、初期化期間(次に説明する補償期間および書込期間)において、OLED150はオフ
(非発光)状態である。
Specifically, for example, when switching from a high-brightness display state to a low-brightness display state, if the configuration does not reset, the high voltage when the luminance is high (a large current flows) is retained. In addition, even if a small current is applied, an excessive current flows and the display state with low luminance cannot be achieved. On the other hand, in this embodiment, the potential of the anode Ad of the
In the present embodiment, the potential Vorst and the
Is set so that the difference from the potential Vct is lower than the light emission threshold voltage of the
一方、初期化期間では、制御信号/GiniがLレベルになり、制御信号GrefがHレベル
になるとともに、制御信号GcplがLレベルになる。このため、レベルシフト回路40に
おいては、図9に示されるようにトランジスター45、43がそれぞれオンするとともに
、トランスミッションゲート42がオフする。したがって、保持容量44の一端であるデ
ータ線14は電位Viniに、保持容量44の他端であるノードhは電位Vrefに、それぞれ
初期化される。
ここで、電位Viniについては、(Vel−Vini)がトランジスター121の閾値電圧|
Vth|よりも大きくなるように設定される。なお、トランジスター121はPチャネル型
であるので、ソースノードの電位を基準とした閾値電圧Vthは負である。そこで、高低関
係の説明で混乱が生じるのを避けるために、閾値電圧については、絶対値の|Vth|で表
し、大小関係で規定することにする。
また、電位Vrefについては、データ信号Vd(1)〜Vd(n)が取り得る電位に対して、後
の書込期間においてノードhの電位が上昇変化するような値に、例えば最低値Vminより
も低くなるように設定される。
On the other hand, in the initialization period, the control signal / Gini becomes L level, the control signal Gref becomes H level, and the control signal Gcpl becomes L level. For this reason, in the
Here, for the potential Vini, (Vel−Vini) is the threshold voltage of the
It is set to be larger than Vth |. Note that since the
Further, the potential Vref is set to such a value that the potential of the node h rises and changes in the subsequent writing period with respect to the potential that the data signals Vd (1) to Vd (n) can take, for example, from the minimum value Vmin. Is set to be low.
また、制御回路5は、初期化期間および補償期間にわたってデータ信号を供給する。す
なわち、制御回路5は、j番目のグループでいえばデータ信号Vd(j)を順番に、i行(3
j−2)列、i行(3j−1)列、i行(3j)列の画素の階調レベルに応じた電位に切
り替える一方、データ信号の電位の切り替えに合わせて制御信号Sel(1)、Sel(2)、Sel
(3)を順番に排他的にHレベルとする。これによって、デマルチプレクサ30では、各グ
ループにおいてトランスミッションゲート34がそれぞれ左端列、中央列、右端列の順番
でオンする。
ここで、初期化期間において、j番目のグループに属する左端列のトランスミッション
ゲート34が制御信号Sel(1)によってオンする場合、図9に示されるように、データ信
号Vd(j)が保持容量41の一端に供給されるので、当該データ信号は、保持容量41によ
って保持される。
The control circuit 5 supplies a data signal over the initialization period and the compensation period. That is, in the j-th group, the control circuit 5 sequentially outputs the data signal Vd (j) in i rows (3
While switching to the potential corresponding to the gradation level of the pixels in the j-2) column, i row (3j-1) column, i row (3j) column, the control signal Sel (1) , Sel (2), Sel
Set (3) to the H level exclusively in order. As a result, in the
When the
<補償期間>
i行目の走査期間では、次に第2期間として(c)の補償期間となる。補償期間では初
期化期間と比較して、走査信号Gwr(i)および制御信号Gcmp(i)がLレベルとなる。一方
、補償期間では、制御信号GrefがHレベルに維持された状態で制御信号/GiniがHレベ
ルになる。
このため、図10に示されるように、i行(3j−2)列の画素回路110ではトラン
ジスター122がオンして、ゲートノードgがデータ線14に電気的に接続される一方、
トランジスター123のオンによって、トランジスター121がダイオード接続となる。
したがって、電流が、給電線116→トランジスター121→トランジスター123→
トランジスター122→(3j−2)列目のデータ線14という経路で流れるので、ゲー
トノードgは、電位Viniから上昇する。ただし、上記経路に流れる電流は、ゲートノー
ドgが電位(Vel−|Vth|)に近づくにつれて流れにくくなるので、補償期間の終了に
至るまでに、データ線14およびゲートノードgは電位(Vel−|Vth|)で飽和する。
したがって、保持容量140は、補償期間の終了に至るまでにトランジスター121の閾
値電圧|Vth|を保持することになる。
<Compensation period>
In the i-th scanning period, the second period is the compensation period (c). In the compensation period, the scanning signal Gwr (i) and the control signal Gcmp (i) are at the L level as compared with the initialization period. On the other hand, in the compensation period, the control signal / Gini becomes H level while the control signal Gref is maintained at H level.
Therefore, as shown in FIG. 10, in the
When the
Therefore, the current is fed from the
Since the
Therefore, the
一方、レベルシフト回路40においては、制御信号GrefがHレベルを維持した状態で
制御信号/GiniがHレベルになるので、レベルシフト回路40においてノードhは電位
Vrefに固定される。
また、補償期間において、j番目のグループに属する左端列のトランスミッションゲー
ト34が制御信号Sel(1)によってオンする場合、図10に示されるように、データ信号
Vd(j)が保持容量41によって保持される。
On the other hand, in the
In the compensation period, when the
すでに初期化期間において、j番目のグループに属する左端列のトランスミッションゲ
ート34が制御信号Sel(1)によってオンした場合には、補償期間において、当該トラン
スミッションゲート34はオンすることはないが、保持容量41にデータ信号Vd(j)が保
持されている点において変わりはない。
また、補償期間が終了すると、制御信号Gcmp(i)がHレベルになるので、トランジスタ
ー121のダイオード接続が解除される。
If the
When the compensation period ends, the control signal Gcmp (i) becomes H level, so that the diode connection of the
なお、補償期間が終了してから次の書込期間が開始するまでの間において制御信号Gre
fがLレベルになるので、トランジスター43がオフになる。このため、(3j−2)列
目のデータ線14からi行(3j−2)列の画素回路110におけるゲートノードgに至
るまでの経路は、フローティング状態になるものの、当該経路の電位は、保持容量50、
140によって(Vel−|Vth|)に維持される。
The control signal Gre is between the end of the compensation period and the start of the next writing period.
Since f becomes L level, the
140 maintains (Vel− | Vth |).
<書込期間>
i行目の走査期間では、補償期間の後に、第3期間として(c)の書込期間となる。書
込期間では、制御信号Gcmp(i)がHレベルになる一方、補償期間では、制御信号Grefが
Lレベルとなった状態で制御信号/GiniがHレベル(制御信号/GcplがLレベルとなる
)。
このため、図11に示されるようにレベルシフト回路40においては、トランスミッシ
ョンゲート42がオンするので、保持容量41に保持されたデータ信号が保持容量44の
他端であるノードhに供給される。すなわち、ノードhには、OLED150の輝度に応
じた電位の信号が供給される。このため、ノードhは、補償期間における電位Vrefから
シフトする。このときのノードhの電位変化分をΔVとして、変化後の電位を(Vref+
ΔV)として表すことにする。
<Writing period>
In the i-th scanning period, the third period is the writing period (c) after the compensation period. In the writing period, the control signal Gcmp (i) is at the H level, while in the compensation period, the control signal / Gini is at the H level (the control signal / Gcpl is at the L level) while the control signal Gref is at the L level. ).
Therefore, as shown in FIG. 11, in the
It will be expressed as ΔV).
一方、ゲートノードgは、保持容量44の一端にデータ線14を介して接続されている
ので、補償期間における電位(Vel−|Vth|)から、ノードhの電位変化分ΔVに容量
比k2を乗じた値だけ上昇する方向にシフトした値となる。すなわち、ゲートノードgの
電位は、補償期間における電位(Vel−|Vth|)から、ノードhの電位変化分ΔVに容
量比k2を乗じた値だけ、上昇方向にシフトした値(Vel−|Vth|+k2・ΔV)となる
。これをトランジスター121の電圧Vgsで絶対値で表現すると、閾値電圧|Vth|から
ゲートノードgの電位上昇したシフト分だけ減じた値(|Vth|−k2・ΔV)となる。
なお、容量比k2とは、Cdt、Crf1、Crf2の容量比である。厳密にいえば、保持容量
140の容量Cpixも考慮しなければならないが、容量Cpixは、容量Cdt、Crf1、Crf2
と比較して十分に小さくなるように設定しているので、無視している。
On the other hand, since the gate node g is connected to one end of the
The capacity ratio k2 is a capacity ratio of Cdt, Crf1, and Crf2. Strictly speaking, the capacitance Cpix of the
Since it is set to be sufficiently small compared to, it is ignored.
図12は、書込期間におけるデータ信号の電位とゲートノードgの電位との関係を示す
図である。制御回路5から供給されるデータ信号は、上述したように画素の階調レベルに
応じて最小値Vminから最大値Vmaxまでの電位範囲を取り得る。本実施形態では、当該デ
ータ信号が直接ゲートノードgに書き込まれるのではなく、図に示されるようにレベルシ
フトされて、ゲートノート゛gに書き込まれる。
このとき、ゲートノードgの電位範囲ΔVgateは、データ信号の電位範囲ΔVdata(=
Vmax−Vmin)に容量比k2を乗じた値に圧縮される。
また、ゲートノードgの電位範囲ΔVgateを、データ信号の電位範囲ΔVdataに対して
どの方向にどれだけシフトさせるかについては、電位Vp(=Vel−|Vth|)、Vrefで
定めることができる。これは、データ信号の電位範囲ΔVdataが、電位Vrefを基準にし
て容量比k2で圧縮されるとともに、その圧縮範囲が電位Vpを基準にシフトされたものが
、ゲートノードgの電位範囲ΔVgateとなるためである。
FIG. 12 is a diagram showing the relationship between the potential of the data signal and the potential of the gate node g in the writing period. As described above, the data signal supplied from the control circuit 5 can take a potential range from the minimum value Vmin to the maximum value Vmax according to the gradation level of the pixel. In this embodiment, the data signal is not directly written to the gate node g, but is level-shifted and written to the gate notebook g as shown in the figure.
At this time, the potential range ΔVgate of the gate node g is equal to the potential range ΔVdata (=
Vmax−Vmin) is multiplied by a capacity ratio k2.
In addition, the potential Vp (= Vel− | Vth |) and Vref can determine how much the potential range ΔVgate of the gate node g is shifted with respect to the potential range ΔVdata of the data signal. This is because the potential range ΔVdata of the data signal is compressed with the capacitance ratio k2 with respect to the potential Vref, and the compression range shifted with reference to the potential Vp becomes the potential range ΔVgate of the gate node g. Because.
このようにi行目の書込期間において、i行目の画素回路110のゲートノードgには
、補償期間における電位(Vel−|Vth|)から、ノードhの電位変化分ΔVに容量比k
2を応じた分だけシフトした電位(Vel−|Vth|+k2・ΔV)が書き込まれる。
やがて走査信号Gwr(i)がHレベルになり、トランジスター122がオフする。これに
よって書込期間が終了して、ゲートノードgの電位は、シフトされた値に確定する。
Thus, in the writing period of the i-th row, the gate node g of the
A potential (Vel− | Vth | +
Eventually, the scanning signal Gwr (i) becomes H level, and the
<発光期間>
本実施形態では、i行目の書込期間の終了後、1水平走査期間(H)経過後において第
4期間として発光期間に至る。この発光期間では、上述したように制御信号Gel(i)がL
レベルになるので、i行(3j−2)列の画素回路110においては、トランジスター1
24がオンする。ゲート・ソース間の電圧Vgsは、(|Vth|−k2・ΔV)であるから
、OLED150には、先の図8に示したように、階調レベルに応じた電流がトランジス
ター121の閾値電圧を補償した状態で供給されることになる。
このような動作は、i行目の走査期間において、(3j−2)列目の画素回路110以
外のi行目の他の画素回路110においても時間的に並列して実行される。さらに、この
ようなi行目の動作は、実際には、1フレームの期間において1、2、3、…、(m−1
)、m行目の順番で実行されるとともに、フレーム毎に繰り返される。
<Light emission period>
In the present embodiment, after the end of the writing period of the i-th row, the light emission period is reached as the fourth period after one horizontal scanning period (H) has elapsed. In this light emission period, the control signal Gel (i) is L as described above.
Therefore, in the
24 turns on. Since the voltage Vgs between the gate and the source is (| Vth | −
Such an operation is also executed in parallel in time in
), Executed in the order of the m-th row, and repeated for each frame.
本実施形態によれば、ゲートノードgにおける電位範囲ΔVgateは、データ信号の電位
範囲ΔVdataに対し狭められるので、データ信号を細かい精度で刻まなくても、階調レベ
ルを反映した電圧を、トランジスター121のゲート・ソース間に印加することができる
。このため、微細な画素回路110においてトランジスター121のゲート・ソース間の
電圧Vgsの変化に対しOLED150に流れる微小電流が相対的に大きく変化する場合で
あっても、OLED150に供給する電流を精度良く制御することが可能になる。
According to the present embodiment, the potential range ΔVgate at the gate node g is narrowed with respect to the potential range ΔVdata of the data signal, so that the voltage reflecting the gradation level can be applied to the
また、図3において破線で示されるようにデータ線14と画素回路110におけるゲー
トノードgとの間には容量Cprsが実際には寄生する。このため、データ線14の電位変
化幅が大きいと、当該容量Cprsを介してゲートノードgに伝播し、いわゆるクロストー
クやムラなどが発生して表示品位を低下させてしまう。当該容量Cprsの影響は、画素回
路110が微細化されたときに顕著に現れる。
これに対して、本実施形態においては、データ線14の電位変化範囲についても、デー
タ信号の電位範囲ΔVdataに対し狭められるので、容量Cprsを介した影響を抑えること
ができる。
Further, as indicated by a broken line in FIG. 3, a capacitance Cprs is actually parasitic between the
On the other hand, in the present embodiment, the potential change range of the
本実施形態によれば、トランジスター125をオンさせる期間、すなわちOLED15
0のリセット期間として、走査期間よりも長い期間、例えば2水平走査期間を確保するこ
とができるので、発光期間においてOLED150の寄生容量に保持された電圧を十分に
初期化することができる。
According to this embodiment, the period during which the
Since a period longer than the scanning period, for example, two horizontal scanning periods can be secured as the reset period of 0, the voltage held in the parasitic capacitance of the
また、本実施形態によれば、トランジスター121によってOLED150に供給され
る電流Idsは、閾値電圧の影響が相殺される。このため、本実施形態によれば、トランジ
スター121の閾値電圧が画素回路110毎にばらついても、そのばらつきが補償されて
、階調レベルに応じた電流がOLED150に供給されるので、表示画面の一様性を損な
うような表示ムラの発生を抑えられる結果、高品位の表示が可能になる。
Further, according to the present embodiment, the current Ids supplied to the
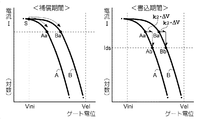
この相殺について図13を参照して説明する。この図に示されるように、トランジスタ
ー121は、OLED150に供給する微小電流を制御するために、弱反転領域(サブス
レッショルド領域)で動作する。
図において、Aは閾値電圧|Vth|が大きいトランジスターを、Bは閾値電圧|Vth|
が小さいトランジスターを、それぞれ示している。なお、図13において、ゲート・ソー
ス間の電圧Vgsは、実線で示される特性と電位Velとの差である。また、図13において
、縦スケールの電流は、ソースからドレインに向かう方向を正(上)とした対数で示され
ている。
補償期間においてゲートノードgは、電位Viniから電位(Vel−|Vth|)となる。
このため、閾値電圧|Vth|が大きいトランジスターAは、動作点がSからAaに移動す
る一方、閾値電圧|Vth|が小さいトランジスターBは、動作点がSからBaに移動する
。
次に、2つのトランジスターが属する画素回路110へのデータ信号の電位が同じ場合
、つまり同じ階調レベルが指定された場合に、書込期間においては、動作点Aa、Baか
らの電位シフト量は、ともに同じk2・ΔVである。このため、トランジスターAについ
ては動作点がAaからAbに移動し、トランジスターBについては動作点がBaからBb
に移動するが、電位シフト後の動作点における電流は、トランジスターA、Bともに、ほ
ぼ同じIdsで揃うことになる。
これにより、本実施形態によれば、トランジスター121の閾値電圧が画素回路110
毎にばらついても、そのばらつきが補償されるのである。
This cancellation will be described with reference to FIG. As shown in this figure, the
In the figure, A is a transistor having a large threshold voltage | Vth |, and B is a threshold voltage | Vth |.
Each shows a transistor with a small. In FIG. 13, the gate-source voltage Vgs is the difference between the characteristic indicated by the solid line and the potential Vel. In FIG. 13, the current on the vertical scale is shown as a logarithm with the direction from the source to the drain being positive (upper).
In the compensation period, the gate node g changes from the potential Vini to the potential (Vel− | Vth |).
Therefore, the transistor A having a large threshold voltage | Vth | moves from S to Aa while the transistor B having a small threshold voltage | Vth | moves from S to Ba.
Next, when the potential of the data signal to the
However, the currents at the operating point after the potential shift are aligned at substantially the same Ids in both the transistors A and B.
Thus, according to the present embodiment, the threshold voltage of the
Even if there is variation every time, the variation is compensated.
また、本実施形態によれば、初期化期間から補償期間までにわたって制御回路5から供
給されるデータ信号を、一旦、保持容量41に保持させた後、書込期間にその保持電位を
レベルシフトした上でデータ線14に供給する。このため、制御回路5からみれば、デー
タ信号を、書込期間ではなく、初期化期間から補償期間までの比較的長い期間にわたって
供給すれば良いので、データ信号の供給動作について低速化することができる。
Further, according to the present embodiment, the data signal supplied from the control circuit 5 is once held in the holding
ところで、トランジスター121におけるドレインノードと、トランジスター123に
おけるドレインノードと、トランジスター124におけるソースノードとは、電気的に互
いに接続される。このため、トランジスター121、124、125については、トラン
ジスター122、123のようにNウェル領域およびP型拡散層を一部供用化した構成と
することも可能ではある。
しかしながら、本実施形態では、図4または図5に示されるように画素回路110が第
1領域110aと第2領域110bとに分けられるとともに、第1領域110aにトラン
ジスター121〜123が設けられ、第2領域110bにトランジスター124、125
が設けられる。このため、トランジスター121と、トランジスター124、125とは
、領域的に分離されている。これは、次の理由による。
By the way, the drain node in the
However, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 4 or FIG. 5, the
Is provided. For this reason, the
すなわち、i行目でいえば、(a)の発光期間に至る際に、制御信号Gel(i)がLレベ
ルに変化してトランジスター124がオンになり、制御信号Gorst(i)がHレベルに変化
してトランジスター125がオフになる。このオンオフ動作(制御信号の電位変化)に伴
うノイズが、トランジスター121におけるゲートノードgに重畳されると、(d)の書
込期間での電位から変動してしまうことになり、表示品位が低下してしまう。
本実施形態では、トランジスター121を含む第1領域110aが、トランジスター1
24、125を含む第2領域110bから分離されている。このため、トランジスター1
24、125のオンオフ動作に伴うノイズがトランジスター121におけるゲートノード
gに重畳され難い構成としているのである。
That is, in the i-th row, when the light emission period (a) is reached, the control signal Gel (i) changes to L level, the
In the present embodiment, the
It is separated from the
The noise accompanying the on / off operation of 24 and 125 is not easily superimposed on the gate node g in the
一方、(d)の書込期間において、データ線14からゲートノードgに至る書込経路は
第1領域110aの範囲内に限られている。このため、トランジスター124、125か
らみれば、書込期間における第1領域110aでの電界変動による影響が低減されること
になる。
また、アノードAd(トランジスター125のソースノード、トランジスター124の
ドレインノード)は、(b)の初期化期間から(d)の書込期間に至るまで、電位Vorst
に固定されるが、ノイズ等によって、当該電位Vorstから変動してしまうと、閾値補償と
ゲートノードgへのデータ書き込みとが正確に実行できなくなる。
本実施形態によれば、アノードAdを含むトランジスター124、125が、トランジ
スター121を含む第1領域110aから分離されているので、当該第1領域110aで
発生するノイズ等の影響を受けにくくなる。このため、閾値補償やデータ書き込みを、分
離しない構成と比較して、より正確に実行することができる。
On the other hand, in the writing period (d), the writing path from the
The anode Ad (the source node of the
However, if the potential Vorst varies due to noise or the like, threshold compensation and data writing to the gate node g cannot be performed accurately.
According to the present embodiment, since the
さらに、本実施形態では、第1領域110aと第2領域110bとの間に、固定電位の
給電線116が配置している。このため、第1領域110aおよび第2領域110bのう
ち、一方から他方へのノイズや電界変動の影響がシールドされる、という効果も期待でき
る。
Further, in the present embodiment, a fixed
トランジスター121のドレインノードからトランジスター124のソースノードまで
は、OLED150への電流経路の一部である。ここで、トランジスター121、124
について一部供用化した構成とした場合、特に拡散層部分での抵抗損失が大きくなる。そ
こで、本実施形態では、第1領域110aに設けられたトランジスター121のドレイン
ノードから第2領域110bに設けられたトランジスター124のソースノードまでを、
導電配線層である第1配線としての配線83、84、および、同じく導電配線層である第
2配線としての配線91を介して接続した構成としている。配線83、84、91で接続
した構成では、コンタクトホールでの抵抗増加分を考慮しても、トランジスター121、
124について一部供用化した構成と比較して、トランジスター121のドレインノード
からトランジスター124のソースノードまでの経路の低抵抗化を図ることができる。
なお、実施形態では、第2領域110bにおいてトランジスター124が右側に、トラ
ンジスター125が左側に、それぞれ配置しているが、トランジスター124をトランジ
スター121と同じ左側に配置させて電流経路をほぼ一直線化しても良い。
From the drain node of the
When a part of the structure is used, the resistance loss particularly in the diffusion layer portion increases. Therefore, in the present embodiment, from the drain node of the
The
Compared with the configuration in which 124 is partially used, the resistance from the drain node of the
In the embodiment, the
<応用・変形例>
本発明は、上述した実施形態や応用例などの実施形態等に限定されるものではなく、例
えば次に述べるような各種の変形が可能である。また、次に述べる変形の態様は、任意に
選択された一または複数を適宜に組み合わせることもできる。
<Application and modification>
The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments and application examples, and various modifications as described below are possible. Moreover, the aspect of the deformation | transformation described below can also combine suitably arbitrarily selected 1 or several.
<第1領域と第2領域との境界>
実施形態では、第1領域110aと第2領域110bとの境界に、シールド配線として
の給電線116が配置された構成であったが、なんらかの固定電位を給電する配線が設け
られていれば、シールド配線として機能させることができる。このため、例えば図14に
示されるように、当該境界を含むように配線16aを設けるとともに、電位Vorstを給電
する構成として、配線16aをシールド配線として機能させても良い。
ここで、配線16aは、行方向に延在するように形成され、給電線16とは、第2層間
絶縁膜を開孔するコンタクトホール16eを介して接続される。このため、電位Vorstは
、列方向に延在する給電線16と行方向に延在する配線16aとのメッシュ状の配線によ
って給電されることになる。なお、配線16aは、短冊状であっても良い。
給電線116は、図において第1領域110aの下側に位置し、当該給電線116から
分岐した部分がトランジスター121のソースノードに接続されている。また、配線11
6cは、第2配線層をパターニングしたものであり、一端がトランジスター121のソー
スノードに接続される一方、他端が走査線12を跨いで、平面視で配線82と重なってい
る。すなわち、図14の例において保持容量140は、配線82と配線116cとで第2
層間絶縁膜を挟持した構成である。
<Boundary between first area and second area>
In the embodiment, the
Here, the
The
Reference numeral 6c denotes a pattern of the second wiring layer. One end of the second wiring layer is connected to the source node of the
In this configuration, an interlayer insulating film is sandwiched.
また、トランジスター121におけるゲート・ドレイン間には寄生容量が少なからず存
在する。このため、i行目でいえば、制御信号Gel(i)がHレベルであってトランジスタ
ー124がオフしているとき(OLED150に電流が流れていないとき)であっても、
トランジスター121のドレインノードは、発光期間で電流が流れていたときの電位に当
該寄生容量によって保たれる。
このため、図15に示されるように、第1領域110aと第2領域110bとの境界に
、給電線116や配線16aを設けなくても、トランジスター121のドレインノードに
接続される配線83を、シールド配線として機能させることができる。
In addition, there is a considerable parasitic capacitance between the gate and drain of the
The drain node of the
Therefore, as shown in FIG. 15, the
なお、保持容量140については、第1配線層の配線82と、第2配線層の配線116
a(116c)とで第2層間絶縁膜を挟持する構成に限られず、トランジスター121の
ソースノードとなる拡散層を拡大して、当該拡散層と第1配線層からなる配線とで第1層
間絶縁膜を挟持する構成としても良い。
For the
The first interlayer insulation is not limited to the configuration in which the second interlayer insulating film is sandwiched between a (116c) and the diffusion layer serving as the source node of the
<制御回路>
実施形態において、データ信号を供給する制御回路5については電気光学装置10とは
別体としたが、制御回路5についても、走査線駆動回路20やデマルチプレクサ30、レ
ベルシフト回路40とともに、シリコン基板に集積化しても良い。
<Control circuit>
In the embodiment, the control circuit 5 that supplies the data signal is separated from the electro-
<基板>
実施形態においては、電気光学装置10をシリコン基板に集積した構成としたが、他の
半導体基板に集積した構成しても良い。また、ポリシリコンプロセスを適用してガラス基
板等に形成しても良い。いずれにしても、画素回路110が微細化した構成に有効である
。
<Board>
In the embodiment, the electro-
<制御信号Gcmp(i)>
実施形態等において、i行目でいえば、書込期間において制御信号Gcmp(i)をHレベル
としたが、Lレベルとしても良い。すなわち、トランジスター123をオンさせることに
よる閾値補償とノードゲートgへの書き込みとを並行して実行する構成としても良い。
<Control signal Gcmp (i)>
In the embodiment and the like, in the i-th row, the control signal Gcmp (i) is set to the H level in the writing period, but may be set to the L level. That is, the threshold compensation by turning on the
<デマルチプレクサ>
実施形態等では、データ線14を3列毎にグループ化するとともに、各グループにおい
てデータ線14を順番に選択して、データ信号を供給する構成としたが、グループを構成
するデータ線数については「2」であっても良いし、「4」以上であっても良い。
また、グループ化せずに、すなわちデマルチプレクサ30を用いないで各列のデータ線
14にデータ信号を一斉に線順次で供給する構成でも良い。
<Demultiplexer>
In the embodiment and the like, the data lines 14 are grouped every three columns, and the data lines 14 are sequentially selected in each group to supply data signals. However, the number of data lines constituting the group is as follows. "2" may be sufficient and "4" or more may be sufficient.
Further, a configuration may be adopted in which data signals are supplied to the data lines 14 of each column all at once without grouping, that is, without using the
<トランジスターのチャネル型>
上述した実施形態等では、画素回路110におけるトランジスター121〜125をP
チャネル型で統一したが、Nチャネル型で統一しても良い。また、Pチャネル型およびN
チャネル型を適宜組み合わせても良い。
<Transistor channel type>
In the above-described embodiment, the
The channel type is unified, but the N channel type may be unified. Also, P channel type and N
The channel types may be combined as appropriate.
<その他>
実施形態等では、電気光学素子として発光素子であるOLEDを例示したが、例えば無
機発光ダイオードやLED(Light Emitting Diode)など、電流に応じた輝度で発光する
ものであれば良い。
<Others>
In the embodiments and the like, an OLED that is a light emitting element is illustrated as an electro-optical element, but any light emitting element may be used as long as it emits light with a luminance according to current, such as an inorganic light emitting diode or LED (Light Emitting Diode).
<電子機器>
次に、実施形態等や応用例に係る電気光学装置10を適用した電子機器について説明す
る。電気光学装置10は、画素が小サイズで高精細な表示な用途に向いている。そこで、
電子機器として、ヘッドマウント・ディスプレイを例に挙げて説明する。
<Electronic equipment>
Next, an electronic apparatus to which the electro-
As an electronic apparatus, a head mounted display will be described as an example.
図16は、ヘッドマウント・ディスプレイの外観を示す図であり、図17は、その光学
的な構成を示す図である。
まず、図16に示されるように、ヘッドマウント・ディスプレイ300は、外観的には
、一般的な眼鏡と同様にテンプル310や、ブリッジ320、レンズ301L、301R
を有する。また、ヘッドマウント・ディスプレイ300は、図17に示されるように、ブ
リッジ320近傍であってレンズ301L、301Rの奥側(図において下側)には、左
眼用の電気光学装置10Lと右眼用の電気光学装置10Rとが設けられる。
電気光学装置10Lの画像表示面は、図17において左側となるように配置している。
これによって電気光学装置10Lによる表示画像は、光学レンズ302Lを介して図にお
いて9時の方向に出射する。ハーフミラー303Lは、電気光学装置10Lによる表示画
像を6時の方向に反射させる一方で、12時の方向から入射した光を透過させる。
電気光学装置10Rの画像表示面は、電気光学装置10Lとは反対の右側となるように
配置している。これによって電気光学装置10Rによる表示画像は、光学レンズ302R
を介して図において3時の方向に出射する。ハーフミラー303Rは、電気光学装置10
Rによる表示画像を6時方向に反射させる一方で、12時の方向から入射した光を透過さ
せる。
FIG. 16 is a diagram showing the external appearance of the head-mounted display, and FIG. 17 is a diagram showing its optical configuration.
First, as shown in FIG. 16, the head mounted
Have Further, as shown in FIG. 17, the head mounted
The image display surface of the electro-
Accordingly, the display image by the electro-
The image display surface of the electro-
Through 3 o'clock in the figure. The
While the display image by R is reflected in the 6 o'clock direction, light incident from the 12 o'clock direction is transmitted.
この構成において、ヘッドマウント・ディスプレイ300の装着者は、電気光学装置1
0L、10Rによる表示画像を、外の様子と重ね合わせたシースルー状態で観察すること
ができる。
また、このヘッドマウント・ディスプレイ300において、視差を伴う両眼画像のうち
、左眼用画像を電気光学装置10Lに表示させ、右眼用画像を電気光学装置10Rに表示
させると、装着者に対し、表示された画像があたかも奥行きや立体感を持つかのように知
覚させることができる(3D表示)。
In this configuration, the wearer of the head mounted
Display images by 0L and 10R can be observed in a see-through state superimposed on the outside.
In the head-mounted
なお、電気光学装置10については、ヘッドマウント・ディスプレイ300のほかにも
、ビデオカメラやレンズ交換式のデジタルカメラなどにおける電子式ビューファインダー
にも適用可能である。
The electro-
10…電気光学装置、12…走査線、14…データ線、16…給電線、20…走査線駆動
回路、30…デマルチプレクサ、40…レベルシフト回路、41、44、50…保持容量
、100…表示部、110…画素回路、110a…第1領域、110b…第2領域、11
6…給電線、118…共通電極、121〜125…トランジスター、140…保持容量、
150…OLED、300…ヘッドマウント・ディスプレイ。
DESCRIPTION OF
6 ... feeder line, 118 ... common electrode, 121-125 ... transistor, 140 ... holding capacity,
150 ... OLED, 300 ... head-mounted display.
Claims (5)
前記画素回路は、
ゲート・ソース間の電圧に応じた電流を供給する第1トランジスターと、
前記第1トランジスターにより供給された電流に応じた輝度で発光する二端子型の発光素子と、
前記データ線と前記第1トランジスターのゲートとの間でオンまたはオフする第2トランジスターと、
前記第1トランジスターにおけるゲートとドレインとの間でオンまたはオフする第3トランジスターと、
前記第1トランジスターによって前記発光素子に供給される電流の経路でオンまたはオフする第4トランジスターと、
前記発光素子における二端子のうち、前記第1トランジスター側の端子と、所定のリセット電位を給電する第1給電線との間でオンまたはオフする第5トランジスターと、
を含み、
前記第1トランジスターと前記発光素子とは、高位側の電源と低位側の電源との間で直列に接続され、
前記画素回路が形成される領域は第1領域および第2領域を含み、
前記第1領域には、前記第1トランジスター、前記第2トランジスターおよび前記第3トランジスターが配置され、
前記第2領域には、前記第4トランジスターおよび前記第5トランジスターが配置され、
前記第1領域と第2領域との間にシールド配線が設けられ、
前記発光素子に電流が流れないときに、前記シールド配線の電位が固定され、
前記シールド配線には、前記リセット電位が給電される
ことを特徴とする電気光学装置。 And a pixel circuits provided corresponding to intersections of a plurality of scanning lines and a plurality of data lines,
The pixel circuit includes:
A first transistor for supplying a current according to a voltage between the gate and the source;
A two-terminal type light emitting element that emits light at a luminance corresponding to the current supplied by the first transistor;
A second transistor that is turned on or off between the data line and the gate of the first transistor;
A third transistor that is turned on or off between a gate and a drain of the first transistor;
A fourth transistor which is turned on or off in the path of current supplied to the light emitting element by the first transistor,
Of the two terminals of the light emitting element, a fifth transistor that is turned on or off between a terminal on the first transistor side and a first feeder that feeds a predetermined reset potential;
Including
The first transistor and the light emitting element are connected in series between a high-order power supply and a low-order power supply,
The region where the pixel circuit is formed includes a first region and a second region,
In the first region, the first transistor, the second transistor, and the third transistor are disposed,
The fourth transistor and the fifth transistor are disposed in the second region ,
A shield wiring is provided between the first region and the second region;
When no current flows through the light emitting element, the potential of the shield wiring is fixed,
The electro-optical device , wherein the shield wiring is supplied with the reset potential .
一端が前記データ線に接続され、他端が前記第1給電線に接続された第2保持容量と、
前記画素回路を駆動する駆動回路を、有し、
前記駆動回路は、
第1期間に、
前記データ線と初期電位を給電する第2給電線とを電気的に接続し、前記第1保持容量の他端と所定電位を給電する第3給電線とを電気的に接続し、
前記第1期間に続く第2期間に、
前記データ線と前記第2給電線とを電気的に非接続とし、前記第1保持容量の他端と第3給電線とを電気的に接続した状態で前記第2トランジスターおよび前記第3トランジスターをオンさせ、
前記第2期間に続く第3期間に、
前記第1保持容量の他端と第3給電線とを電気的に非接続として、前記輝度に応じた電位の信号を前記第1保持容量の他端に供給し、
前記第3期間の終了時に前記第2トランジスターをオフさせ、
前記第3期間に続く第4期間に、前記第4トランジスターをオンさせ、
前記第3トランジスターを、前記第3期間の終了時までにオフさせ、
前記第5トランジスターを、第1期間の開始時から第4期間の開始時までの一部または全部の期間でオンさせる
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の電気光学装置。 A first storage capacitor having one end connected to the data line;
A second storage capacitor having one end connected to the data line and the other end connected to the first power feed line;
A driving circuit for driving the pixel circuit;
The drive circuit is
In the first period,
Electrically connecting the data line and a second power supply line for supplying an initial potential; electrically connecting the other end of the first storage capacitor and a third power supply line for supplying a predetermined potential;
In a second period following the first period,
The data line and the second power supply line are electrically disconnected, and the second transistor and the third transistor are connected in a state where the other end of the first storage capacitor and the third power supply line are electrically connected. Turn on
In a third period following the second period,
Electrically connecting the other end of the first storage capacitor and the third feeder to the other end of the first storage capacitor with a signal having a potential corresponding to the luminance;
Turning off the second transistor at the end of the third period;
Turning on the fourth transistor in a fourth period following the third period;
Turning off the third transistor by the end of the third period;
2. The electro-optical device according to claim 1, wherein the fifth transistor is turned on during a part or all of a period from the start of the first period to the start of the fourth period.
ことを特徴とする請求項1又は請求項2に記載の電気光学装置。 Wherein the first transistor and the fourth transistor, the electro-optical device according to claim 1 or claim 2 through a conductive wire, characterized in that connected to each other.
前記画素回路は、
ゲート・ソース間の電圧に応じた電流を供給する第1トランジスターと、
前記第1トランジスターにより供給された電流に応じた輝度で発光する二端子型の発光素子と、
前記データ線と前記第1トランジスターのゲートとの間でオンまたはオフする第2トランジスターと、
前記発光素子における二端子のうち、前記第1トランジスター側の端子と、所定のリセット電位を給電する第1給電線との間でオンまたはオフする第3トランジスターと、
を有し、
前記第1トランジスターと前記発光素子とは、高位側の電源と低位側の電源との間で直列に接続され、
前記画素回路が形成される領域は第1領域および第2領域を含み、
前記第1領域には、前記第1トランジスターおよび前記第2トランジスターが配置され、
前記第2領域には、前記第3トランジスターが配置され、
前記第1領域と第2領域との間にシールド配線が設けられ、
前記発光素子に電流が流れないときに、前記シールド配線の電位が固定され、
前記シールド配線には、前記リセット電位が給電される
ことを特徴とする電気光学装置。 And a pixel circuits provided corresponding to intersections of a plurality of scanning lines and a plurality of data lines,
The pixel circuit includes:
A first transistor for supplying a current according to a voltage between the gate and the source;
A two-terminal type light emitting element that emits light at a luminance corresponding to the current supplied by the first transistor;
A second transistor that is turned on or off between the data line and the gate of the first transistor;
A third transistor that is turned on or off between a terminal on the first transistor side of the two terminals of the light emitting element and a first feeder that feeds a predetermined reset potential;
Have
The first transistor and the light emitting element are connected in series between a high-order power supply and a low-order power supply,
The region where the pixel circuit is formed includes a first region and a second region,
In the first region, the first transistor and the second transistor are disposed,
The third transistor is disposed in the second region,
A shield wiring is provided between the first region and the second region;
When no current flows through the light emitting element, the potential of the shield wiring is fixed,
The electro-optical device , wherein the shield wiring is supplied with the reset potential .
ことを特徴とする電子機器。 An electronic apparatus comprising the electro-optical device according to any one of claims 1 to 4.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011257161A JP5929121B2 (en) | 2011-11-25 | 2011-11-25 | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011257161A JP5929121B2 (en) | 2011-11-25 | 2011-11-25 | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013113868A JP2013113868A (en) | 2013-06-10 |
| JP2013113868A5 JP2013113868A5 (en) | 2014-11-06 |
| JP5929121B2 true JP5929121B2 (en) | 2016-06-01 |
Family
ID=48709501
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011257161A Active JP5929121B2 (en) | 2011-11-25 | 2011-11-25 | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5929121B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6225511B2 (en) * | 2013-07-02 | 2017-11-08 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Display device and electronic device |
| KR102107565B1 (en) * | 2013-12-18 | 2020-05-08 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | Organic light emitting diode display |
| JP6372084B2 (en) | 2014-01-22 | 2018-08-15 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Light emitting device and electronic device |
| JP6459316B2 (en) | 2014-09-03 | 2019-01-30 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Organic electroluminescence device and electronic device |
| JP6432223B2 (en) * | 2014-09-03 | 2018-12-05 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Organic electroluminescence device and electronic device |
| JP6432222B2 (en) | 2014-09-03 | 2018-12-05 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Organic electroluminescence device and electronic device |
| KR102307813B1 (en) | 2014-12-22 | 2021-10-01 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | Organic light emitting diode display |
| CN109074768B (en) | 2016-09-09 | 2022-12-16 | 索尼半导体解决方案公司 | Display device and electronic device |
Family Cites Families (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH113048A (en) * | 1997-06-10 | 1999-01-06 | Canon Inc | Electroluminescent element and device and their production |
| JP2003308030A (en) * | 2002-02-18 | 2003-10-31 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Display device |
| JP2006243176A (en) * | 2005-03-01 | 2006-09-14 | Sony Corp | Display device, signal line driving method |
| JP5025242B2 (en) * | 2005-12-02 | 2012-09-12 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | Semiconductor device, display device, module, and electronic device |
| JP2007316513A (en) * | 2006-05-29 | 2007-12-06 | Toshiba Matsushita Display Technology Co Ltd | Active matrix type display device |
| JP2007316510A (en) * | 2006-05-29 | 2007-12-06 | Toshiba Matsushita Display Technology Co Ltd | Active matrix type display device |
| JP4259556B2 (en) * | 2006-09-13 | 2009-04-30 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus |
| JP2009109853A (en) * | 2007-10-31 | 2009-05-21 | Toshiba Matsushita Display Technology Co Ltd | Active matrix type display device |
| JP5286992B2 (en) * | 2008-07-09 | 2013-09-11 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus |
| JP2010019950A (en) * | 2008-07-09 | 2010-01-28 | Seiko Epson Corp | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus |
| KR101082283B1 (en) * | 2009-09-02 | 2011-11-09 | 삼성모바일디스플레이주식회사 | Organic Light Emitting Display Device and Driving Method Thereof |
| JP5682385B2 (en) * | 2011-03-10 | 2015-03-11 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus |
| JP6141590B2 (en) * | 2011-10-18 | 2017-06-07 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus |
| JP6064313B2 (en) * | 2011-10-18 | 2017-01-25 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Electro-optical device, driving method of electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus |
| JP5929087B2 (en) * | 2011-10-19 | 2016-06-01 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus |
| JP5853614B2 (en) * | 2011-11-10 | 2016-02-09 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus |
| JP5998458B2 (en) * | 2011-11-15 | 2016-09-28 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Pixel circuit, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus |
| JP5879944B2 (en) * | 2011-11-16 | 2016-03-08 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus |
-
2011
- 2011-11-25 JP JP2011257161A patent/JP5929121B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013113868A (en) | 2013-06-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6015095B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP5853614B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP6064313B2 (en) | Electro-optical device, driving method of electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP6056175B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP6141590B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP5998458B2 (en) | Pixel circuit, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus | |
| KR102051357B1 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP5879944B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP5887973B2 (en) | Electro-optical device, driving method of electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP5929121B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP6213644B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP6079859B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP6152902B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP6583464B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP5929087B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP5845963B2 (en) | Electro-optical device, driving method of electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP6673406B2 (en) | Electro-optical devices and electronic equipment | |
| JP6376258B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP6315072B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP2022177027A (en) | Electro-optic device and electronic equipment | |
| JP2016212445A (en) | Electro-optic device | |
| JP2015004907A (en) | Electro-optic device, method for driving electro-optic device, and electronic equipment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140918 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140918 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20150107 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20150730 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150901 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20151015 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20160405 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20160418 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5929121 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |