JP5901348B2 - Seismic isolation structure - Google Patents
Seismic isolation structure Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5901348B2 JP5901348B2 JP2012041208A JP2012041208A JP5901348B2 JP 5901348 B2 JP5901348 B2 JP 5901348B2 JP 2012041208 A JP2012041208 A JP 2012041208A JP 2012041208 A JP2012041208 A JP 2012041208A JP 5901348 B2 JP5901348 B2 JP 5901348B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- seismic isolation
- weight
- superstructure
- mass damper
- damper
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 title claims description 64
- 238000013016 damping Methods 0.000 description 31
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 13
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 10
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000033001 locomotion Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000008094 contradictory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005316 response function Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Buildings Adapted To Withstand Abnormal External Influences (AREA)
- Vibration Prevention Devices (AREA)
Description
本発明は、免震構造物の高次モードの振動を選択的に低減することが可能な免震構造物に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a seismic isolation structure that can selectively reduce higher-order mode vibrations of the seismic isolation structure.
一般的に、基礎部分や中間階に免震層を形成した免震構造物においては、上記免震層に鋼材ダンパー、鉛ダンパー、粘弾性ダンパー、オイルダンパー等の減衰ダンパーを介装して、上部構造の振動を減衰させている。 Generally, in a base isolation structure with base isolation layers formed on the base and intermediate floors, steel dampers, lead dampers, viscoelastic dampers, oil dampers and other damping dampers are interposed in the base isolation layers. Damping the vibration of the superstructure.
ところで、上記減衰ダンパーの減衰力の設定においては、上記免震層における上下部構造間の相対変位と、上部構造への振動伝達率には、相反する関係がある。
すなわち、上記減衰力を低く設定すると、上部構造への振動伝達率を下げ、上部構造の加速度応答を低減させることはできるものの、反面上記免震層における相対変位が大きくなるため、上部構造と周囲の建物との間に大きなクリアランスを設定する必要が生じてしまう。
By the way, in setting the damping force of the damping damper, there is a contradictory relationship between the relative displacement between the upper and lower structures in the seismic isolation layer and the vibration transmissibility to the upper structure.
That is, if the damping force is set low, the vibration transmission rate to the superstructure can be lowered and the acceleration response of the superstructure can be reduced. However, since the relative displacement in the seismic isolation layer is large, It becomes necessary to set a large clearance with the building.
これに対して、上記減衰力を高く設定すると、免震層における相対変位を小さくすることができるが、上部構造への2次モード以上の高い振動数成分の伝達率が大きくなって加速度応答が増大する。 On the other hand, if the damping force is set high, the relative displacement in the seismic isolation layer can be reduced, but the transmission rate of high frequency components higher than the secondary mode to the superstructure is increased, resulting in an acceleration response. Increase.
したがって、敷地が狭い等の理由から、充分な上記クリアランスを確保することが難しい場合には、上記減衰力を高く設定せざるを得ず、この結果上部構造に対する加速度低減効果が小さくなってしまうという問題点があった。
そこで、上記問題点を解決する手段として、上記免震構造物の免震装置に、減衰力を可変とした減衰装置を設置し、振動の大小によって上記減衰力を制御する各種のシステムや方法が提案されている。
Therefore, if it is difficult to ensure sufficient clearance due to the fact that the site is small, the damping force has to be set high, and as a result, the acceleration reduction effect on the superstructure is reduced. There was a problem.
Therefore, as means for solving the above problems, there are various systems and methods for installing a damping device with variable damping force in the seismic isolation device of the seismic isolation structure and controlling the damping force according to the magnitude of vibration. Proposed.
例えば、下記特許文献1において、本出願人は、免震層に減衰力が可変な減衰装置を介装し、予め上下部構造間における基準振幅値を設定するとともに、センサ等によって上下部構造間の相対的な振幅値および速度を測定し、これら振幅値および速度から振動の一定時間後の予測振幅値を算出して、上記予測振幅値が上記基準振幅値よりも大きい場合に上記減衰力を増加させ、上記予測振幅値が上記基準振幅値よりも小さい場合に上記減衰力を減少させる免震制御方法を提案した。
For example, in the following
しかしながら、上記免震制御方法にあっては、センサ等によって上下部構造間の相対的な振幅値および速度を時々刻々測定して、これらから上記振動の一定時間後の予測振幅値を常時算出しておく必要があるために、大地震時における制御の信頼性やコストの観点から問題があり、より一層簡易で、しかも保守・信頼性に優れたセミアクティブ免震システムに代わる免震システムの開発が望まれていた。 However, in the above seismic isolation control method, the relative amplitude value and speed between the upper and lower structures are measured momentarily by a sensor or the like, and the predicted amplitude value after a certain time of the vibration is constantly calculated from these. Development of a seismic isolation system that replaces the semi-active seismic isolation system that is even easier and more maintenance-reliable. Was desired.
そこで、本出願人は、下記特許文献2において、上記免震層に減衰係数を2段階または3段階に切り換え可能な可変減衰ダンパーを設け、上部構造の応答検出手段からの検出信号に基づいて、地震発生時に上記可変減衰ダンパーの減衰係数を最小にし、設定値を超える上部構造の応答量を検出した際に、可変減衰ダンパーの減衰係数を上げて減衰力を増大させることにより、大地震時等に上下部構造間に過度の相対変位を生じることを防ぐようにした免震システムを提案した。
Therefore, in the following
上記構成からなる免震システムによれば、演算装置や複雑な制御装置等を要することなく、簡易な設備によって地震時に高い振動絶縁効果を発揮させることができ、かつ大地震時等には上下部構造間に過度の相対変位を生じることを防ぐことができるという効果が得られる。 According to the seismic isolation system having the above-described configuration, it is possible to exhibit a high vibration insulation effect during an earthquake with simple equipment without requiring an arithmetic device or a complicated control device, and the upper and lower parts during a large earthquake. An effect of preventing an excessive relative displacement between the structures can be obtained.
ところが、上記免震システムにおいては、可変減衰ダンパーの減衰係数が大きく切り替わった後は、復旧されるまで加速度の低減効果が小さいままの状態が続くことになる。このため、大地震後に、再度可変減衰ダンパーの減衰係数を最小値に設定する必要があるという欠点があった。また、大地震時における過度の相対変位を抑制することを優先するものであるために、中小地震時には上部構造の加速度応答を低減することができるものの、大地震時には当該加速度応答低減効果を十分に得ることができないという問題もあった。 However, in the above seismic isolation system, after the damping coefficient of the variable damping damper is largely switched, the acceleration reduction effect remains small until it is restored. For this reason, there has been a drawback that it is necessary to set the damping coefficient of the variable damping damper to the minimum value again after a large earthquake. In addition, since priority is given to suppressing excessive relative displacement during a large earthquake, the acceleration response of the superstructure can be reduced during small and medium-sized earthquakes. There was also a problem that it could not be obtained.
他方、下記特許文献3においては、高次モードの振動を選択的に低減させる免震構造物として、免震層に、上部構造物の高次モードの振動に対して応答低減効果を発揮する回転慣性質量ダンパーを、免震装置と並列に設置したものが提案されている。
On the other hand, in
しかしながら、上記免震構造物においては、回転慣性質量ダンパーを免震装置と並列に設置して、上下部構造間に生じる相対変位により錘を回転させて応答低減効果を発揮させるものであるために、構造が複雑化するとともに、地震時に確実に錘の機械的な回転運動を生じるように、平常時においても回転慣性質量ダンパーのボールネジ部分等の保護やメンテナンスが必要になるという欠点があった。加えて、一般的に、回転慣性質量ダンパーは、高次モードの振動に対しては、地盤から入力された揺れを増幅させる傾向にあるため、逆に構造物の加速度応答を増幅させるおそれもある。 However, in the above-mentioned seismic isolation structure, the rotary inertia mass damper is installed in parallel with the seismic isolation device, and the weight is rotated by the relative displacement generated between the upper and lower structures to exert the response reduction effect. In addition to the complexity of the structure, there is a drawback in that it is necessary to protect and maintain the ball screw part of the rotary inertia mass damper even in normal times so that the mechanical rotational movement of the weight is surely generated in the event of an earthquake. In addition, in general, the rotary inertia mass damper tends to amplify the vibration input from the ground with respect to the vibration of the higher order mode, and may conversely amplify the acceleration response of the structure. .
本発明は、上記事情に鑑みてなされたものであり、簡易な設備によって、構造物の高次モードの振動に対する加速度応答の低減効果を得ることができるとともに、保守管理も容易な免震構造物を提供することを課題とするものである。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and with a simple facility, it is possible to obtain an effect of reducing acceleration response to vibrations of higher-order modes of the structure, and also a seismic isolation structure that is easy to maintain and manage. It is a problem to provide.
上記課題を解決するため、請求項1に記載の発明は、上部構造と下部構造との間に免震層が形成された免震構造物において、上記免震層における上記上部構造の下面に、当該上部構造のn次モード(nは1以上の整数)の固有振動数に同調させた同調質量ダンパーを設置してなり、上記同調質量ダンパーは、錘と、当該錘と上記上部構造の柱との間に介装されたスプリングおよびオイルダンパーとを有し、かつ上記錘は、上記上部構造の四方の柱間に移動自在に設けられるとともに、上記スプリングおよびオイルダンパーは、それぞれ上記錘の中心に対して点対称となる位置に配置されていることを特徴とするものである。
In order to solve the above-mentioned problem, the invention according to
また、請求項2に記載の発明は、請求項1に記載の発明において、上記nが2以上の整数であることを特徴とするものである。
The invention described in
さらに、請求項3に記載の発明は、請求項1または2に記載の発明において、上記下部構造が地盤上に構築された基礎であるとともに、上記上部構造の下面に設置した上記同調質量ダンパーの錘を、上記基礎上において水平方向に移動自在に支持したことを特徴とするものである。
Further, the invention according to
これに対して、請求項4に記載の発明は、請求項1または2に記載の発明において、上記免震層が、中間階に設けられるとともに、上記上部構造の下面に設置した上記同調質量ダンパーの錘を、上記下部構造となる下階の壁の上面において水平方向に移動自在に支持したことを特徴とするものである。
On the other hand, the invention according to
図7に示すように、構造物が地震や強風等の外乱を受けて揺れを生じる場合には、各モードが合成された振動となる。この際に、1次モード、2次モード、3次モードは、各々1次固有振動数、2次固有振動数、3次固有振動数で振動する。そして、同図に示す免震構造物においては、一般的に、免震層が大きく変形する1次モードによる振動の占める割合が大きいものの、免震構造物自体の固有振動数や、地震動等の条件によっては、2次モード以上の高次モードによる振動が無視できない場合もある。 As shown in FIG. 7 , when the structure is shaken due to a disturbance such as an earthquake or strong wind, the vibrations are a combination of the modes. At this time, the primary mode, the secondary mode, and the tertiary mode vibrate at the primary natural frequency, the secondary natural frequency, and the tertiary natural frequency, respectively. In the seismic isolation structure shown in the figure, although the proportion of vibration due to the primary mode in which the seismic isolation layer greatly deforms is large, the natural frequency of the seismic isolation structure itself, seismic motion, etc. Depending on conditions, vibrations caused by higher-order modes higher than the second-order mode may not be ignored.
そして、請求項1〜4のいずれかに記載の発明によれば、免震構造物の上部構造の下面に、当該上部構造の1次以上のモードの固有振動数に同調させた同調質量ダンパーを設置しているために、大地震時のみならず中小地震や強風時においても、演算装置や複雑な制御装置等を要することなく、簡易な設備によって地震時に高い振動絶縁効果を発揮させることができるとともに、大地震時等には上下部構造間に過度の相対変位を生じることを防ぐことができる。 And according to invention of any one of Claims 1-4, the tuned mass damper tuned to the natural frequency of the 1st or more mode of the said upper structure on the lower surface of the upper structure of a seismic isolation structure Because it is installed, not only during a large earthquake, but also during small and medium earthquakes and strong winds, it is possible to demonstrate a high vibration isolation effect during an earthquake with a simple facility without the need for arithmetic devices or complex control devices. At the same time, it is possible to prevent excessive relative displacement between the upper and lower structures during a large earthquake.
さらに、請求項2に記載の発明によれば、2次モード以上の固有振動数に同調させた同調質量ダンパーを設置しているために、上部構造への伝達率が大きい2次モード以上の高い振動数成分を吸収して、上部構造物の加速度応答を確実に低減させることができる。
Furthermore, according to the invention described in
加えて、減衰係数を切り替える可変減衰ダンパーとは異なり、切替操作を必要としないうえに、さらに回転慣性質量ダンパーのような錘の機械的な回転運動を要しないために、構造が簡易であるとともに、作動の確実性や保守の容易性に優れる。 In addition, unlike the variable damping damper that switches the damping coefficient, the switching operation is not required, and further, the mechanical rotation movement of the weight like the rotary inertia mass damper is not required. Excellent operation reliability and ease of maintenance.
また、上部構造の下面に設置されている同調質量ダンパーは、水平方向において下部構造と力学的に縁が切れているために、可変減衰ダンパーや回転慣性質量ダンパーのように地盤(下部構造)の揺れを上部構造に伝えることが無く、確実に上部構造における加速度応答を低減させることができる。
しかも、上記同調質量ダンパーを、本来デッドスペースとなる免震層に配置しているために、構造物全体としてのスペースの有効利用にも資する。
In addition, the tuned mass damper installed on the lower surface of the upper structure is mechanically disconnected from the lower structure in the horizontal direction, so that the ground (lower structure) can be used like a variable damping damper or a rotary inertia mass damper. The vibration is not transmitted to the superstructure, and the acceleration response in the superstructure can be reliably reduced.
In addition, since the tuned mass damper is disposed in the seismic isolation layer that originally becomes a dead space, it contributes to the effective use of the space as the entire structure.
また、請求項3または請求項4に記載の発明によれば、同調質量ダンパーの錘の鉛直荷重を、下部構造となる基礎あるいは下階の壁において支持しているために、当該錘を揚重する必要が無く、施工性にも優れる。
Further, according to the invention described in
なお、請求項1〜4のいずれかに記載の発明において、上記同調質量ダンパーを、揺れが大きくなり易い構造物の短辺方向に作動するように設置すれば、より一層効果的に上部構造の加速度応答を低減することができるために好適である。
In addition, in the invention according to any one of
(第1の実施形態)
図1および図2は、本発明に係る免震構造物の一実施形態を示すものであり、図3〜図6は、その変形例を示すものである。
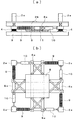
図1および図2において、この免震構造物は、構造物(上部構造)1の柱2aが積層ゴムによる免震装置4および減衰ダンパー5を介して地盤上に構築された基礎(下部構造)3上に支持されることにより、構造物1と基礎3との間に免震層6が形成されたものである。
(First embodiment)
1 and 2 show an embodiment of a seismic isolation structure according to the present invention, and FIGS. 3 to 6 show modifications thereof.
In FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, this seismic isolation structure is a foundation (lower structure) in which a pillar 2a of a structure (upper structure) 1 is constructed on the ground via a
そして、免震層6における床梁2bの下面に、同調質量ダンパー7が設置されている。この同調質量ダンパー7は、錘8と、当該錘8と柱2aとの間に介装されたスプリング9およびオイルダンパー10とによって概略構成されたものである。ここで、錘8は、ローラやガイドレール等の滑動手段11を介して、基礎3と床梁2bとの間に力を伝達することなく、当該基礎3上を水平2方向に移動自在に設けられている。
A tuned
また、この錘8には、各々四方に位置する柱2a間に向けて直交4方向に延出する支持部材8aが一体化されており、各支持部材8aの先端部と、当該先端部を間に挟む一方の柱2aとの間にスプリング9が介装され、他方の柱2aとの間にオイルダンパー10が介装されている。ちなみに、これらスプリング9およびオイルダンパー10は、図2(b)に示す平面視において、それぞれ錘8の中心に対して点対称となる位置に配置されている。
Further, the
そして、上記同調質量ダンパー7は、錘8、スプリング9およびオイルダンパー10の諸元が、構造物1の2次モードの固有振動数に同調するように設定されている。この際に、一般的には、構造物1におけるX方向とY方向との振動特性が異なるために、X方向に作用するスプリング9およびオイルダンパー10並びにY方向に作用するスプリング9およびオイルダンパー10は、各々当該X方向およびY方向の振動特性に応じて設定されている。
The tuning
以上の構成からなる免震構造物にあっては、構造物1の床梁2bの下面に、この構造物1の2次モードの固有振動数に同調させた同調質量ダンパー7を設置しているために、大地震時のみならず中小地震や強風時においても、図6の解析結果に示すように、構造物1への伝達率が大きい2次モードの振動数成分を吸収して、構造物1の加速度応答を確実に低減させることができる。
In the seismic isolation structure having the above configuration, the tuned
しかも、同調質量ダンパー7は、従来の減衰係数を切り替える可変減衰ダンパーとは異なり、切替操作を必要としないうえに、さらに回転慣性質量ダンパーのような錘の機械的な回転運動を要しないために、構造が簡易であるとともに、作動の確実性や保守の容易性に優れる。
In addition, unlike the conventional variable damping damper that switches the damping coefficient, the tuned
また、構造物1の床梁2bの下面に設置されている同調質量ダンパー7は、水平方向において基礎3と力学的に縁が切れているために、回転慣性質量ダンパーのように基礎3の揺れを構造物1に伝えることが無く、確実に構造物1における加速度応答を低減させることができる。加えて、同調質量ダンパー7を、本来デッドスペースとなる免震層6に配置しているために、構造物全体としてのスペースの有効利用にも資する。
Further, since the tuned
さらに、同調質量ダンパー7の錘8の鉛直荷重を、基礎3において支持しているために、錘8を構造物1側に揚重する必要が無く、施工性にも優れる。
さらに、本発明に係る免震構造は、免震層6に同調質量ダンパー7を設置しているために、様々な形態を採ることが可能である。
Furthermore, since the vertical load of the
Furthermore, since the tuned
例えば、図3は、上記第1の実施形態の第1変形例を示すもので、この免震構造は、第1の実施形態と同様に、四方の柱2a間に錘8を水平2方向に移動自在に設けるとともに、この錘8と、当該錘8を間に挟む対角方向の柱2aとの間に、それぞれスプリング9およびオイルダンパー10を介装することにより、錘8の慣性力をX方向およびY方向の両方向に作用させるものである。
For example, FIG. 3 shows a first modification of the first embodiment. This seismic isolation structure is similar to the first embodiment in that the
また、図4に示す第2変形例においては、同調質量ダンパー7の錘8をX方向(図中左右方向)に敷設されたレール(図示を略す。)上を当該X方向にのみ移動自在に設け、両端部と上記移動方向に対向する柱2aとの間に、スプリング9とオイルダンパー10を介装したものである。
Further, in the second modification shown in FIG. 4, the
ちなみに、この変形例においては、上記同調質量ダンパー7の錘8を、揺れが大きくなり易い構造物1の短辺方向に移動自在に設置して、当該錘8、スプリング9およびオイルダンパー10の諸元を、構造物1の短辺方向における2次モードの固有振動数に同調するように設定することが好ましい。
Incidentally, in this modified example, the
(第2の実施形態)
なお、上記第1の実施形態においては、本発明を、免震層6を構造物1と地盤上に構築された基礎3との間に形成した基礎免震の免震構造物に適用した場合について示したが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではなく、図5に示す第2の実施形態のように、構造物の中間階に免震層を形成した場合にも同様に適用することができる。
(Second Embodiment)
In the first embodiment, the present invention is applied to a base-isolated base isolation structure in which the
すなわち、この免震構造物においては、構造物20の中間階において、その下部構造21の柱21aと、その上階(上部構造)の梁22との間に免震装置4が介装されることにより、柱21a間に構築された壁23と、上記梁22との間に免震層24が形成されている。
That is, in this seismic isolation structure, the
そして、上階の梁22の下面に、同調質量ダンパー25が設置されている。
図中符号26は、この同調質量ダンパー25の錘を示すもので、この錘26は、壁23の上面に敷設されたレール27上を図中左右方向に走向自在に設けられている。また、この錘26の上面には、間隔をおいて取付板28a、28bが立設されるとともに、梁22の下面には、各々の取付板28a、28bと間隔をおいて対向するように、支持板29a、29bが垂設されている。そして、取付板28aと支持板29aとの間に、スプリング30が介装されるとともに、取付板28bと支持板29bとの間にオイルダンパー31が介装されることにより、上記同調質量ダンパー25が構成されている。
A tuned
そして、上記同調質量ダンパー25においても、錘26、スプリング30およびオイルダンパー31等の諸元が、免震層24の上部構造の2次モードの固有振動数に同調するように設定されている。
したがって、上記構成からなる免震構造物によっても、免震層24の上部構造に対して図1および図2に示したものと同様の作用効果を得ることができる。
Also in the tuned
Therefore, even with the seismic isolation structure having the above-described configuration, the same effects as those shown in FIGS. 1 and 2 can be obtained for the upper structure of the
なお、上記第1および第2の実施形態においては、いずれも同調質量ダンパー7、25を、構造物(上部構造)1の2次モードの固有振動数に同調するように設定した場合についてのみ説明したが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではなく、構造物の構造等の特性によって、1次モードによる振動の占める割合が大きい場合には、上記同調質量ダンパーを1次モードの固有振動するに同調するように設定してもよい。
In the first and second embodiments, only the case where the tuned
1 構造物(上部構造)
3 基礎(下部構造)
6、24 免震層
7、25 同調質量ダンパー
8、26 錘
9、30 スプリング
10、31 オイルダンパー
1 Structure (superstructure)
3 Foundation (under structure)
6, 24
Claims (4)
上記免震層における上記上部構造の下面に、当該上部構造のn次モード(nは1以上の整数)の固有振動数に同調させた同調質量ダンパーを設置してなり、
上記同調質量ダンパーは、錘と、当該錘と上記上部構造の柱との間に介装されたスプリングおよびオイルダンパーとを有し、
かつ上記錘は、上記上部構造の四方の柱間に移動自在に設けられるとともに、上記スプリングおよびオイルダンパーは、それぞれ上記錘の中心に対して点対称となる位置に配置されていることを特徴とする免震構造物。 In a base-isolated structure in which a base isolation layer is formed between the superstructure and the substructure,
A tuned mass damper tuned to the natural frequency of the n-order mode (n is an integer of 1 or more) of the superstructure is installed on the bottom surface of the superstructure in the seismic isolation layer,
The tuned mass damper includes a weight, and a spring and an oil damper interposed between the weight and the column of the superstructure ,
The weight is provided movably between the four pillars of the superstructure, and the spring and the oil damper are respectively arranged at positions that are point-symmetric with respect to the center of the weight. Seismic isolation structure.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012041208A JP5901348B2 (en) | 2012-02-28 | 2012-02-28 | Seismic isolation structure |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012041208A JP5901348B2 (en) | 2012-02-28 | 2012-02-28 | Seismic isolation structure |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013177744A JP2013177744A (en) | 2013-09-09 |
| JP5901348B2 true JP5901348B2 (en) | 2016-04-06 |
Family
ID=49269616
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012041208A Active JP5901348B2 (en) | 2012-02-28 | 2012-02-28 | Seismic isolation structure |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5901348B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9366810B2 (en) * | 2012-08-29 | 2016-06-14 | Ofs Fitel, Llc | Double-clad, gain-producing fibers with increased cladding absoroption while maintaining single-mode operation |
| JP6033200B2 (en) * | 2013-08-27 | 2016-11-30 | オーエフエス ファイテル,エルエルシー | Fiber that provides gain with increased cladding absorption while maintaining single mode operation |
| JP6378494B2 (en) * | 2014-02-06 | 2018-08-22 | 鹿島建設株式会社 | Seismic isolation structure |
| JP2016056875A (en) * | 2014-09-10 | 2016-04-21 | オイレス工業株式会社 | Seismic base isolation structure with vibration control function |
| JP7248243B2 (en) * | 2019-07-16 | 2023-03-29 | 国立大学法人京都工芸繊維大学 | Damping device and damping structure |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2903075B2 (en) * | 1990-04-18 | 1999-06-07 | 清水建設株式会社 | Multi-degree-of-freedom dynamic vibration absorber |
| JPH10280726A (en) * | 1997-04-08 | 1998-10-20 | Tatsuji Ishimaru | Vibration control mechanism |
| JP4803620B2 (en) * | 2000-09-20 | 2011-10-26 | オイレス工業株式会社 | Seismic isolation structure with damping function |
| JP2005337283A (en) * | 2004-05-24 | 2005-12-08 | Bridgestone Corp | Support and base isolation device |
-
2012
- 2012-02-28 JP JP2012041208A patent/JP5901348B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013177744A (en) | 2013-09-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5901348B2 (en) | Seismic isolation structure | |
| JP2020101081A (en) | Vibration control device and building equipped with the same | |
| JP2009007916A (en) | Damping structure and its specification method | |
| JP5621101B1 (en) | Seismic foundation for buildings | |
| JP5961057B2 (en) | Seismic isolation structure, seismic isolation floor structure and clean room equipped with the same | |
| JP2009155801A (en) | Vibration control structure | |
| JP5059708B2 (en) | Structural seismic control structure | |
| JP6456774B2 (en) | Vibration control structure | |
| JP5617905B2 (en) | Damping building, damping system, damping method | |
| JP5252227B2 (en) | Seismic isolation system | |
| JP6308741B2 (en) | Intermediate seismic isolation structure | |
| JP5801139B2 (en) | Shock damper | |
| JP5839820B2 (en) | Vibration control system | |
| Keerthana et al. | Seismic response control using base isolation strategy | |
| JP2001003982A (en) | Non-resonant semi-active seismic isolation structure and seismic isolation method | |
| JP6502116B2 (en) | Vibration control device | |
| JP5327647B2 (en) | Damping structure | |
| JP5917291B2 (en) | Mass damper type damping device | |
| JP2022107290A (en) | Additional mass type vibration control device | |
| JP6526782B2 (en) | Damping structure of structure and method of providing damping structure in existing structure | |
| JP2016056875A (en) | Seismic base isolation structure with vibration control function | |
| JP6298402B2 (en) | Partial seismic isolation structure | |
| JP6505272B2 (en) | Intermediate seismic isolation structure | |
| JP2012202510A (en) | Base isolation structure | |
| JP2024090144A (en) | Vibration damping structure |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140311 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20150128 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150203 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150326 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150721 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150828 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20160308 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20160308 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5901348 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |