JP5372079B2 - Game machine - Google Patents
Game machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5372079B2 JP5372079B2 JP2011157896A JP2011157896A JP5372079B2 JP 5372079 B2 JP5372079 B2 JP 5372079B2 JP 2011157896 A JP2011157896 A JP 2011157896A JP 2011157896 A JP2011157896 A JP 2011157896A JP 5372079 B2 JP5372079 B2 JP 5372079B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- effect
- determination
- gaming state
- variation pattern
- determined
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は、遊技領域に設けられた始動領域に遊技球が進入したことを条件として、遊技者に有利な特別遊技の実行可否が決定される遊技機に関する。 The present invention relates to a gaming machine in which whether or not to execute a special game advantageous to a player is determined on the condition that a game ball has entered a starting area provided in the game area.
従来、始動口に遊技球が入球すると大当たりの抽選が行われ、この大当たりの抽選により大当たりに当選すると、多量の賞球を獲得可能な特別遊技が実行可能となる遊技機が知られている。こうした遊技機においては、液晶画面等の演出表示部に、数字等が記された演出図柄が変動表示された後、最終的にハズレ図柄もしくは大当たり図柄が停止表示されることで大当たりの抽選結果が遊技者に報知される。 Conventionally, when a game ball enters the start opening, a jackpot lottery is performed, and when a jackpot is won by this jackpot lottery, a gaming machine that can execute a special game capable of acquiring a large amount of prize balls is known. . In such a gaming machine, after the effect symbol with numbers etc. is displayed in a variable manner on the effect display unit such as a liquid crystal screen, the lottery symbol or jackpot symbol is finally stopped and the jackpot lottery result is displayed. Informed to the player.
このようにして行われる変動演出中には、演出図柄の変動表示中にさまざまなキャラクタ画像等を演出表示部に表示することにより、演出効果ならびに遊技の興趣を向上するようにしている。また、近年では、さらなる演出効果の向上を図るべく、例えば特許文献1、2に示されるように、所謂、先読み演出が広く採用されている。先読み演出というのは、始動口に遊技球が入球して大当たりの抽選の権利が保留として留保された場合に、当該保留についての変動演出が開始されるよりも前に、当該保留についての大当たりの期待度を示唆する演出である。
During the variation effect performed in this way, various character images and the like are displayed on the effect display unit during the variation display of the effect symbol, thereby improving the effect of the effect and the interest of the game. In recent years, so-called prefetching effects have been widely adopted, for example, as shown in
具体的には、始動口に遊技球が入球すると、大当たりの抽選に係る乱数と、変動演出の態様を決定するための乱数と、が記憶される。そして、先読み演出を行う場合には、保留が留保された時点でこれらの乱数を事前判定(先読み)して記憶部に記憶するとともに、記憶部に記憶された事前判定情報に基づいて先読み演出を実行することとなる。このように、先読み演出が行われると、遊技者に対して、変動演出が開始される前から長期にわたって期待感を付与することができ、全体として演出効果の向上を図ることができる。 Specifically, when a game ball enters the start opening, a random number related to the jackpot lottery and a random number for determining the mode of variation effect are stored. And when performing pre-reading effects, these random numbers are pre-determined (pre-reading) at the time when the suspension is reserved and stored in the storage unit, and the pre-reading effects are performed based on the pre-determination information stored in the storage unit. Will be executed. As described above, when the pre-reading effect is performed, it is possible to give the player a sense of expectation over a long period before the changing effect is started, and it is possible to improve the effect of the effect as a whole.
上記の特許文献1、2に示される遊技機においては、初期設定として通常遊技状態に設定されるとともに、通常遊技状態において大当たりに当選すると、大当たりの当選確率が高確率になる高確率遊技状態や、始動口に遊技球が入球しやすくなる時短遊技状態にて遊技を進行可能となる。このように、複数の遊技状態が設けられる遊技機において先読み演出を採用すると、次のような問題が生じる。
In the gaming machines shown in
例えば、通常遊技状態において4つの保留が記憶された状態で大当たりに当選し、特別遊技の終了後に、高確率遊技状態および時短遊技状態に設定されたとする。このとき、特別遊技が実行される前に記憶された保留については、通常遊技状態を前提とした事前判定情報が記憶されており、現在の遊技状態(高確率遊技状態や時短遊技状態)において事前判定した場合に導出される事前判定情報と異なる情報となっている。 For example, suppose that a big win is won in a state in which four holds are stored in the normal gaming state, and a high probability gaming state and a short-time gaming state are set after the end of the special game. At this time, with respect to the hold stored before the special game is executed, pre-determination information based on the normal game state is stored, and the hold in advance in the current game state (high probability game state or short-time game state). This information is different from the prior determination information derived when the determination is made.
そのため、特別遊技の終了直後においては、先読み演出と大当たりの期待度との対応関係が不正確になり、特別遊技の終了後、しばらくの間は先読み演出を実行することができず、演出効果が低下してしまうという実態がある。そこで、常時、複数の遊技状態それぞれの事前判定情報を導出するとともに、現在設定されている遊技状態に対応する事前判定情報に基づいて、先読み演出を実行することが考えられる。しかしながら、保留が記憶されるたびに、複数の遊技状態それぞれの事前判定情報を導出することとなると、処理負担が大きくなってしまうという問題が生じる。 Therefore, immediately after the end of the special game, the correspondence between the pre-reading effect and the expectation of the jackpot becomes inaccurate, and after the special game ends, the pre-reading effect cannot be executed for a while, and the effect is There is a reality that it will decline. Therefore, it is conceivable to always derive advance determination information for each of a plurality of gaming states and execute a prefetch effect based on the advance determination information corresponding to the currently set gaming state. However, there is a problem in that the processing load increases if the prior determination information for each of the plurality of gaming states is derived each time the hold is stored.
本発明は、処理負担の増大を抑制しながらも、特に遊技状態が変更された場合の演出効果を向上することができる遊技機の提供を目的とする。 It is an object of the present invention to provide a gaming machine that can improve the effect of production when the gaming state is changed, while suppressing an increase in processing load.
上記課題を解決するために、本発明の遊技機は、遊技者の有利度合いを異にする第1の遊技状態および第2の遊技状態が少なくとも含まれる複数の遊技状態の中からいずれかの遊技状態に設定される遊技機であって、遊技球が流下する遊技領域が設けられた遊技盤と、前記遊技領域に設けられた始動領域と、前記始動領域に遊技球が進入したことを条件として、遊技者に有利な特別遊技の実行可否を決定するための特別遊技判定用乱数、および、当該特別遊技の実行可否を報知する変動演出の態様が対応付けられた変動パターンを決定するための第1変動パターン乱数および第2変動パターン乱数を少なくとも取得するとともに、当該取得した前記各乱数を保留として記憶部に記憶する乱数記憶手段と、始動条件の成立により、前記乱数記憶手段によって記憶部に記憶された特別遊技判定用乱数を読み出して、予め設定された判定条件にしたがって前記特別遊技の実行可否を判定する特別遊技実行判定手段と、前記特別遊技実行判定手段の判定結果、当該判定の際に読み出された特別遊技判定用乱数とともに記憶部に記憶された前記第1変動パターン乱数、および、設定されている遊技状態に対応付けて予め設定された決定条件にしたがって、前記変動パターンの所定要素に基づいて分類され遊技状態ごとに設定された複数の演出分類の中からいずれかの演出分類を決定する演出分類決定手段と、前記特別遊技実行判定手段の判定の際に読み出された特別遊技判定用乱数とともに記憶部に記憶された前記第2変動パターン乱数に基づいて、前記演出分類決定手段によって決定された演出分類に対応付けられた変動パターンの中からいずれかの変動パターンを決定する変動パターン決定手段と、前記変動パターン決定手段によって決定された変動パターンにしたがって前記変動演出を実行する変動演出実行手段と、前記特別遊技実行判定手段によって前記特別遊技の実行を可能とする判定結果が導出されるとともに、前記変動演出実行手段によって実行される前記変動演出が終了した場合に、当該特別遊技を実行する特別遊技実行手段と、前記特別遊技が実行された場合に、当該特別遊技の終了後の遊技状態を複数の遊技状態の中からいずれかの遊技状態に設定する遊技状態設定手段と、前記記憶部に前記各乱数が記憶された場合に、設定されている遊技状態に対応する前記判定条件および決定条件にしたがって、前記特別遊技判定用乱数、前記第1変動パターン乱数および第2変動パターン乱数を事前判定して、当該設定されている遊技状態における変動パターンに係る第1事前判定情報を導出するとともに、遊技状態が前記第1の遊技状態に設定されている場合には、前記第2の遊技状態に対応する前記決定条件にしたがって前記第1変動パターン乱数を仮判定して、当該第2の遊技状態における演出分類に係る第2事前判定情報を当該第1の遊技状態における前記第1事前判定情報に加えて導出する事前判定手段と、前記事前判定手段によって導出された第1事前判定情報および第2事前判定情報を記憶する事前判定情報記憶手段と、前記事前判定情報記憶手段に記憶された前記第1事前判定情報または前記第2事前判定情報に基づいて、当該事前判定情報が導出された保留に基づく変動演出が開始されるよりも前に開始される予兆演出の実行可否を判定する予兆演出実行判定手段と、前記予兆演出実行判定手段によって前記予兆演出を実行する判定結果が導出された場合に、前記予兆演出を実行する予兆演出実行手段と、を備え、前記予兆演出実行判定手段は、前記第2の遊技状態に設定されている場合には、前記第1の遊技状態に設定されているときに記憶された保留については前記第2事前判定情報に基づいて前記予兆演出の実行可否を判定し、前記第2の遊技状態に設定された後に記憶された保留については前記第1事前判定情報に基づいて前記予兆演出の実行可否を判定することを特徴とする。
In order to solve the above-described problems, the gaming machine according to the present invention is any one of a plurality of gaming states including at least a first gaming state and a second gaming state that have different degrees of player advantage. A gaming machine that is set to a state, provided that a gaming board is provided with a gaming area in which gaming balls flow down, a starting area provided in the gaming area, and a gaming ball has entered the starting area. First, a random number for determining a special game for determining whether or not to execute a special game advantageous to the player, and a variation pattern for determining a variation pattern associated with a variation effect mode for notifying whether or not the special game can be performed. The random number storage means for acquiring at least the first variation pattern random number and the second variation pattern random number and storing the acquired random numbers in the storage unit as a hold, and the random number storage by the establishment of the start condition The special game determination random number stored in the storage unit by the stage and the determination result of the special game execution determination unit that determines whether or not the special game can be executed according to a predetermined determination condition, and the determination result of the special game execution determination unit In accordance with the first variation pattern random number stored in the storage unit together with the special game determination random number read at the time of the determination, and the determination condition set in advance in association with the set game state, At the time of determination by the effect classification determining means for determining any effect classification from among a plurality of effect classifications classified according to predetermined elements of the variation pattern and set for each gaming state, and the special game execution determining means Based on the second variation pattern random number stored in the storage unit together with the read special game determination random number, determined by the effect classification determining means A variation pattern determining means for determining any one of the variation patterns associated with the outgoing classification; a variation effect executing means for executing the variation effect according to the variation pattern determined by the variation pattern determining means; The special game execution determination means derives a determination result that enables execution of the special game, and the special game is executed when the variation effect executed by the variation effect execution means ends. A game execution means; a game state setting means for setting a game state after the end of the special game to any one of a plurality of game states when the special game is executed; and When each random number is stored, the special game is performed according to the determination condition and the determination condition corresponding to the set gaming state. The technique determination random number, the first variation pattern random number, and the second variation pattern random number are preliminarily determined to derive first prior determination information related to the variation pattern in the set gaming state, and the gaming state is the first When the gaming state is set to 1, the first variation pattern random number is provisionally determined according to the determination condition corresponding to the second gaming state, and the effect classification in the second gaming state is concerned. Predetermining means for deriving second predetermination information in addition to the first predetermination information in the first gaming state, first predetermination information and second predetermination information derived by the predetermination means Based on the preliminary determination information storage means to be stored and the first preliminary determination information or the second preliminary determination information stored in the preliminary determination information storage means, the preliminary determination information is A determination result of executing the indication effect by the indication effect execution determining means for determining whether or not to execute the indication effect that is started before the start of the variation effect based on the put on hold is performed, and the indication effect execution determining means. If derived, and a indication effect execution means for executing the indication effect, the indication effect execution determining means, if it is set before Symbol second gaming state, the first game With respect to the hold stored when the state is set, whether or not the indication effect can be executed is determined based on the second prior determination information, and the hold stored after being set to the second gaming state. Whether or not the indication effect is executable is determined based on the first prior determination information.
また、本発明の遊技機は、前記事前判定手段が、遊技状態が前記第2の遊技状態に設定されている場合には、当該第2の遊技状態に対応する前記判定条件および決定条件にしたがって、前記特別遊技判定用乱数、前記第1変動パターン乱数および第2変動パターン乱数を事前判定して、当該第2の遊技状態における変動パターンに係る第1事前判定情報を導出するとともに、前記第1の遊技状態に対応する前記決定条件にしたがって前記第1変動パターン乱数を仮判定して、当該第1の遊技状態における演出分類に係る第2事前判定情報を前記第1事前判定情報に加えて導出してもよい。 Further, in the gaming machine of the present invention, when the prior determination means sets the determination condition and the determination condition corresponding to the second gaming state when the gaming state is set to the second gaming state. Therefore, the special game determination random number, the first variation pattern random number, and the second variation pattern random number are determined in advance to derive first determination information related to the variation pattern in the second gaming state, and the first The first variation pattern random number is provisionally determined according to the determination condition corresponding to one gaming state, and second prior determination information relating to the effect classification in the first gaming state is added to the first prior determination information. It may be derived.
また、本発明の遊技機は、前記演出分類決定手段によって決定される演出分類には、少なくとも通常演出分類および特定演出分類が設けられ、前記通常演出分類は、前記特別遊技実行判定手段によって前記特別遊技を実行しないとする判定結果が導出された場合に、前記特定演出分類よりも高確率で決定され、前記特定演出分類は、前記特別遊技実行判定手段によって前記特別遊技の実行を可能とする判定結果が導出された場合に、前記通常演出分類よりも高確率で決定され、前記通常演出分類に対応付けられた変動パターンによる変動演出の平均時間は、前記特定演出分類に対応付けられた変動パターンによる変動演出の平均時間よりも短くしてもよい。 In the gaming machine of the present invention, at least the normal effect category and the specific effect category are provided in the effect category determined by the effect category determining means, and the normal effect category is determined by the special game execution determining means. When a determination result that the game is not to be executed is derived, the determination is made with a higher probability than the specific effect classification, and the specific effect classification is determined to enable the execution of the special game by the special game execution determination means. When the result is derived, it is determined with a higher probability than the normal effect category, and the average time of the change effect according to the change pattern associated with the normal effect category is the variation pattern associated with the specific effect category. It may be shorter than the average time of the fluctuating production.
また、本発明の遊技機は、前記変動パターンに対応して前記特別遊技の実行可否を報知する演出表示画像が前記変動演出実行手段によって表示される演出表示部を備え、前記通常演出分類に対応付けられる変動パターンには、前記演出表示部に第1の表示態様の演出表示画像が表示されることなく変動演出が終了する変動パターンが含まれ、前記特定演出分類に対応付けられる変動パターンには、前記演出表示部に第1の表示態様の演出表示画像が表示された後に、第2の表示態様の演出表示画像が表示されて変動演出が終了する変動パターンが含まれてもよい。 Further, the gaming machine of the present invention includes an effect display unit that displays an effect display image for notifying whether or not the special game can be executed corresponding to the change pattern, and displays the change effect executing means, and corresponds to the normal effect classification. The variation pattern to be attached includes a variation pattern in which the variation effect ends without displaying the effect display image of the first display mode on the effect display unit, and the variation pattern associated with the specific effect category includes In addition, after the effect display image of the first display mode is displayed on the effect display unit, a variation pattern in which the effect display image of the second display mode is displayed and the variation effect ends may be included.
以下に添付図面を参照しながら、本発明の好適な実施形態について詳細に説明する。かかる実施形態に示す寸法、材料、その他具体的な数値等は、発明の理解を容易とするための例示にすぎず、特に断る場合を除き、本発明を限定するものではない。なお、本明細書及び図面において、実質的に同一の機能、構成を有する要素については、同一の符号を付することにより重複説明を省略し、また本発明に直接関係のない要素は図示を省略する。 Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. The dimensions, materials, and other specific numerical values shown in the embodiments are merely examples for facilitating the understanding of the invention, and do not limit the present invention unless otherwise specified. In the present specification and drawings, elements having substantially the same function and configuration are denoted by the same reference numerals, and redundant description is omitted, and elements not directly related to the present invention are not illustrated. To do.
本発明の実施形態の理解を容易にするため、まず、遊技機の機械的構成および電気的構成を簡単に説明し、その後、各基板における具体的な処理を説明する。 In order to facilitate understanding of the embodiment of the present invention, first, the mechanical configuration and electrical configuration of the gaming machine will be briefly described, and then specific processing on each board will be described.
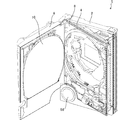
図1は、本実施形態の遊技機1の斜視図であり、扉が開放された状態を示している。図示のように、遊技機1は、略矩形状に組まれた四辺によって囲繞空間が形成される外枠2と、この外枠2にヒンジ機構によって開閉自在に取り付けられた中枠4と、この中枠4と同様に、ヒンジ機構によって外枠2に開閉自在に取り付けられた前枠6と、を備えている。
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of the
中枠4は、外枠2と同様に、略矩形状に組まれた四辺によって囲繞空間が形成されており、この囲繞空間に遊技盤8が保持されている。また、前枠6には、ガラス製または樹脂製の透過板10が保持されている。そして、これら中枠4および前枠6を外枠2に対して閉じると、遊技盤8と透過板10とが所定の間隔を維持して略平行に対面するとともに、遊技機1の正面側から、透過板10を介して遊技盤8が視認可能となる。
As with the
図2は、遊技機1の正面図である。この図に示すように、前枠6の下部には、遊技機1の正面側に突出する操作ハンドル12が設けられている。この操作ハンドル12は、遊技者が回転操作可能に設けられており、遊技者が操作ハンドル12を回転させて発射操作を行うと、当該操作ハンドル12の回転角度に応じた強度で、不図示の発射機構によって遊技球が発射される。このようにして発射された遊技球は、遊技盤8に設けられたレール14a、14b間を上昇して遊技領域16に導かれることとなる。
FIG. 2 is a front view of the
遊技領域16は、遊技盤8と透過板10との間隔に形成される空間であって、遊技球が流下または転動可能な領域である。遊技盤8には、多数の釘や風車が設けられており、遊技領域16に導かれた遊技球が釘や風車に衝突して、不規則な方向に流下、転動するようにしている。
The
また、遊技領域16には、遊技球が入球可能な一般入賞口18、第1始動口20、第2始動口22が設けられており、これら一般入賞口18、第1始動口20、第2始動口22に遊技球が入球すると、それぞれ所定の賞球が遊技者に払い出される。
Further, the
なお、詳しくは後述するが、第1始動口20または第2始動口22に遊技球が入球すると、予め設けられた複数の特別図柄の中からいずれか1の特別図柄を決定するための抽選が行われる。各特別図柄には、遊技者にとって有利な特別遊技の実行可否や、以後の遊技状態をどのような遊技状態にするかといった種々の遊技利益(状態)が対応付けられている。したがって、遊技者は、第1始動口20または第2始動口22に遊技球が入球すると、所定の賞球を獲得するのと同時に、種々の遊技利益を受ける権利獲得の機会を獲得することとなる。
As will be described in detail later, when a game ball enters the
また、第2始動口22は、遊技盤8の裏面側から正面側に向けて出没可能な可動片22bを有しており、この可動片22bの状態に応じて、第2始動口22への遊技球の進入容易性が変化するようになっている。具体的には、可動片22bが遊技盤8の裏面側に没入して、遊技領域16から退避した状態、すなわち、閉状態にある場合には、可動片22bの正面を遊技球が流下する構成となっており、第2始動口22への遊技球の入球が不可能もしくは困難となっている。
The
これに対して、遊技領域16に設けられたゲート24を遊技球が通過すると、後述する普通図柄の抽選が行われ、この抽選によって当たりに当選すると、可動片22bが所定時間、遊技領域16に向けて突出した開状態に制御される。このように、可動片22bが開状態になると、当該可動片22bが遊技球を第2始動口22に導く受け皿として機能し、第2始動口22への遊技球の入球が容易となる。
On the other hand, when the game ball passes through the
さらに、第1始動口20および第2始動口22よりも下方にはアタッカー装置26が設けられている。このアタッカー装置26は、遊技球が入球可能な大入賞口28と、この大入賞口28を開閉する開閉扉28bと、を備えており、通常、開閉扉28bが閉扉して、大入賞口28への遊技球の入球が不可能となっている。これに対して、前述の特別遊技が実行されると、開閉扉28bが所定の態様で開放されるとともに、この開閉扉28bが遊技球を大入賞口28内に導く受け皿として機能する。そして、大入賞口28に遊技球が入球すると、所定の賞球が遊技者に払い出される。
Further, an
なお、遊技領域16の最下部には、一般入賞口18、第1始動口20、第2始動口22、大入賞口28のいずれにも入球しなかった遊技球を、遊技領域16から遊技盤8の背面側に排出する排出口30が設けられている。
At the bottom of the
そして、遊技盤8には、遊技の進行中等に演出を行う演出装置として、液晶表示装置からなる演出表示装置50と、可動装置からなる演出役物装置52とが設けられている。演出表示装置50は、画像を表示する演出表示部50aを備えており、この演出表示部50aを、遊技盤8の略中央部分において、遊技機1の正面側から視認可能に配置している。
The
また、遊技盤8の裏面側であって、かつ、演出表示部50aよりも遊技機1の正面側には、演出役物装置52が設けられている。この演出役物装置52は、図示のように剣を模した形状に構成されており、演出表示部50aの前面から退避して遊技機1に正対する遊技者から視認できない初期位置から、図示のように演出表示部50aの前面に臨む変位位置へと変位可能に設けられている。
In addition, an
また、前枠6には、点灯態様や発光色をさまざまに制御して演出を行うためのランプからなる演出照明装置54が設けられている。さらに、遊技機1の幅方向略中央位置であって、かつ、透過板10よりも下方位置には、遊技者の押下操作を受け付けるボタンからなる演出操作装置56が設けられている。そして、前枠6の上部位置や外枠2の最下部位置には、遊技機1の正面側に向けられたスピーカからなる音声出力装置58が設けられている。
In addition, the
なお、図中符号70は、遊技機1から払い出される賞球や、遊技球貸出装置から貸し出される遊技球が導かれる上皿であり、この上皿70が遊技球で一杯になると、遊技球は下皿72に導かれることとなる。また、この下皿72の底面には、当該下皿72から遊技球を排出するための球抜き孔(不図示)が形成されている。この球抜き孔は、通常、開閉板(不図示)によって閉じられているが、球抜きつまみ72aを図中左右方向にスライドさせることにより、当該球抜きつまみ72aと一体となって開閉板がスライドし、球抜き孔から下皿72の下方に遊技球を排出することが可能となっている。
また、遊技盤8には、遊技領域16の外方であって、かつ、遊技者が視認可能な位置に、第1特別図柄表示器80、第2特別図柄表示器82、第1特別図柄保留表示器84、第2特別図柄保留表示器86、普通図柄表示器88、普通図柄保留表示器90が設けられている。これら各表示器80〜90は、遊技に係る種々の状況を表示するための装置であるが、その詳細については後述する。
Further, the
(制御手段の内部構成)
図3は、遊技の進行を制御する制御手段の内部構成を示すブロック図である。
(Internal structure of control means)
FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing the internal configuration of the control means for controlling the progress of the game.
主制御基板100は遊技の基本動作を制御する。この主制御基板100は、メインCPU100a、メインROM100b、メインRAM100cを備えている。メインCPU100aは、各検出スイッチやタイマからの入力信号に基づいて、メインROM100bに格納されたプログラムを読み出して演算処理を行うとともに、各装置や表示器を直接制御したり、あるいは演算処理の結果に応じて他の基板にコマンドを送信したりする。メインRAM100cは、メインCPU100aの演算処理時におけるデータのワークエリアとして機能する。
The
上記主制御基板100には、一般入賞口18に遊技球が入球したことを検出する一般入賞口検出スイッチ18a、第1始動口20に遊技球が入球したことを検出する第1始動口検出スイッチ20a、第2始動口22に遊技球が入球したことを検出する第2始動口検出スイッチ22a、ゲート24を遊技球が通過したことを検出するゲート検出スイッチ24a、大入賞口28に遊技球が入球したことを検出する大入賞口検出スイッチ28aが接続されており、これら各検出スイッチから主制御基板100に検出信号が入力されるようになっている。
The
また、主制御基板100には、第2始動口22の可動片22bを作動する始動口開閉ソレノイド22cと、大入賞口28を開閉する開閉扉28bを作動する大入賞口開閉ソレノイド28cと、が接続されており、主制御基板100によって、第2始動口22および大入賞口28の開閉制御がなされるようになっている。
The
さらに、主制御基板100には、第1特別図柄表示器80、第2特別図柄表示器82、第1特別図柄保留表示器84、第2特別図柄保留表示器86、普通図柄表示器88、普通図柄保留表示器90が接続されており、主制御基板100によって、これら各表示器の表示制御がなされるようになっている。
Further, the
また、本実施形態の遊技機1は、主に第1始動口20または第2始動口22への遊技球の入球によって開始される特別図柄遊技と、ゲート24を遊技球が通過することによって開始される普通図柄遊技とに大別される。そして、主制御基板100のメインROM100bには、特別図柄遊技および普通図柄遊技を進行するための種々のプログラムや、各種の遊技に必要なデータ、テーブルが記憶されている。
In addition, the
また、主制御基板100には、払出制御基板120および副制御基板200が接続されている。
The
払出制御基板120は、遊技球を発射させるための制御、および、賞球を払い出すための制御を行う。この払出制御基板120も、CPU、ROM、RAMを備えており、主制御基板100に対して双方向に通信可能に接続されている。この払出制御基板120には遊技情報出力端子板110が接続されており、主制御基板100から出力される遊技進行上の種々の情報が、払出制御基板120および遊技情報出力端子板110を介して、遊技店のホールコンピュータ等に出力されることとなる。
The
また、払出制御基板120には、貯留部に貯留された遊技球を賞球として遊技者に払い出すための払出モータ121が接続されている。払出制御基板120は、主制御基板100から送信された払出個数指定コマンドに基づいて払出モータ121を制御して所定の賞球を遊技者に払い出すように制御する。このとき、払い出された遊技球数が払出球計数スイッチ122によって検出され、払い出すべき賞球が遊技者に払い出されたかが把握されるようになっている。
Further, the
また、払出制御基板120には、下皿72の満タン状態を検出する皿満タン検出スイッチ123が接続されている。この皿満タン検出スイッチ123は、賞球として払い出される遊技球を下皿72に導く通路に設けられており、当該通路を遊技球が通過するたびに、遊技球検出信号が払出制御基板120に入力されるようになっている。
Further, a dish full
そして、下皿72に所定量以上の遊技球が貯留されて満タン状態になると、下皿72に向かう通路内に遊技球が滞留し、皿満タン検出スイッチ123から払出制御基板120に向けて、遊技球検出信号が連続的に入力される。払出制御基板120は、遊技球検出信号が所定時間連続して入力された場合に、下皿72が満タン状態であると判断し、皿満タンコマンドを主制御基板100に送信する。一方、皿満タンコマンドを送信した後、遊技球検出信号の連続入力が途絶えた場合には、満タン状態が解除されたと判断し、皿満タン解除コマンドを主制御基板100に送信する。
Then, when a predetermined amount or more of game balls are stored in the
また、払出制御基板120には、発射制御基板130が双方向に通信可能に接続されている。この発射制御基板130は、払出制御基板120から発射制御データを受信すると発射の許可を行う。この発射制御基板130には、操作ハンドル12に設けられ、当該操作ハンドル12に遊技者が触れたことを検出するタッチセンサ12aと、操作ハンドル12の操作角度を検出する操作ボリューム12bと、が接続されている。そして、タッチセンサ12aおよび発射ボリューム12bから信号が入力されると、発射制御基板130において、遊技球発射装置に設けられた発射用ソレノイド131を通電して遊技球を発射させる制御がなされる。
In addition, a
副制御基板200は、主に遊技中や待機中等の各演出を制御する。この副制御基板200は、サブCPU200a、サブROM200b、サブRAM200cを備えており、主制御基板100に対して、当該主制御基板100から副制御基板200への一方向に通信可能に接続されている。サブCPU200aは、主制御基板100から送信されたコマンドやタイマからの入力信号等に基づいて、サブROM200bに格納されたプログラムを読み出して演算処理を行うとともに、演出を実行するためのコマンドを、画像制御基板210または電飾制御基板220に送信する。このとき、サブRAM200cは、サブCPU200aの演算処理時におけるデータのワークエリアとして機能する。
The
画像制御基板210は、上記演出表示部50aに画像を表示させる画像表示制御を行うものであり、CPU、ROM、RAM、VRAMを備えている。この画像制御基板210のROMには、演出表示部50aに表示される図柄や背景等の画像データが多数格納されており、副制御基板200から送信されたコマンドに基づいて、CPUが、画像データをROMからVRAMに読み出して、演出表示部50aの画像表示を制御する。
The
電飾制御基板220は、副制御基板200から送信されたコマンドに基づいて、音声出力装置58から音声を出力させる音声出力制御を行う。また、電飾制御基板220は、副制御基板200から送信されるコマンドに基づいて、演出役物装置52を可動したり演出照明装置54を点灯制御したりする。さらには、演出操作装置56が押下操作されたことを検出する演出操作装置検出スイッチ56aから操作検出信号が入力された際に、所定のコマンドを副制御基板200に送信する。
Based on the command transmitted from the
なお、各基板には、不図示の電源基板が接続されている。この電源基板は、コンデンサからなるバックアップ電源を備えており、遊技機に供給する電源電圧を監視し、電源電圧が所定値以下となったときに、電断検知信号を主制御基板100に出力するようになっている。
A power supply board (not shown) is connected to each board. This power supply board has a backup power supply composed of a capacitor, monitors the power supply voltage supplied to the gaming machine, and outputs a power interruption detection signal to the
次に、本実施形態の遊技機1における遊技について、メインROM100bに記憶されている各種テーブルを参照しながら説明する。
Next, games in the
前述したように、本実施形態の遊技機1は、特別図柄遊技と普通図柄遊技の2種類の遊技が並行して進行するものであり、これら両遊技を進行する際の遊技状態として、低確率遊技状態または高確率遊技状態のいずれかの遊技状態と、非時短遊技状態または時短遊技状態のいずれかの遊技状態と、が組み合わされたいずれかの遊技状態にて遊技が進行する。
As described above, in the
各遊技状態の詳細については後述するが、低確率遊技状態というのは、大入賞口28が開放される特別遊技を実行する権利獲得の確率が低く(本実施形態では1/273)設定された遊技状態であり、高確率遊技状態というのは、特別遊技を実行する権利獲得の確率が高く(本実施形態では1/27.3)設定された遊技状態である。
The details of each gaming state will be described later, but the low probability gaming state is set with a low probability of acquiring a right to execute a special game in which the special winning
また、非時短遊技状態というのは、可動片22bが開状態になりにくく、第2始動口22に遊技球が入球しにくい遊技状態であり、時短遊技状態というのは、非時短遊技状態よりも可動片22bが開状態になりやすく、第2始動口22に遊技球が入球しやすい遊技状態である。
In addition, the non-short game state is a game state in which the
遊技者が操作ハンドル12を操作して遊技領域16に遊技球を発射させるとともに、遊技領域16を流下する遊技球が第1始動口20または第2始動口22に入球すると、遊技者に付与される遊技利益が対応付けられた特別図柄の決定処理(以下、「大当たりの抽選」という)が行われる。この大当たりの抽選において、大当たりに当選すると、大入賞口28が開放されるとともに当該大入賞口28への遊技球の入球が可能となる特別遊技が実行され、また、当該特別遊技の終了後の遊技状態が、上記のいずれかの遊技状態に設定される。以下では、大当たりの抽選方法について説明する。
When the player operates the operation handle 12 to fire a game ball in the
なお、詳しくは後述するが、第1始動口20または第2始動口22に遊技球が入球すると、大当たりの抽選に係る種々の乱数値(特別図柄乱数、大当たり乱数、第1変動パターン乱数、第2変動パターン乱数A、B)が取得されるとともに、これら各乱数値がメインRAM100cの保留記憶領域に記憶される。以下では、第1始動口20に遊技球が入球して保留記憶領域に記憶された種々の乱数を総称して第1保留とよび、第2始動口22に遊技球が入球して保留記憶領域に記憶された種々の乱数を総称して第2保留とよぶ。
As will be described in detail later, when a game ball enters the
この保留記憶領域は、8つの記憶部(第1〜第8記憶部)を有しており、第1始動口20または第2始動口22に遊技球が入球すると、第1保留または第2保留を、保留記憶領域の第1記憶部から順に記憶する。具体的には、第1始動口20または第2始動口22に遊技球が入球したとき、第1〜第8記憶部のいずれにも保留が記憶されていない場合には、第1記憶部に保留を記憶する。また、例えば、第1〜第3記憶部に第1保留または第2保留が記憶されている状態で、第1始動口20または第2始動口22に遊技球が入球した場合には、当該保留を第4記憶部に記憶する。
This reserved storage area has eight storage units (first to eighth storage units), and when a game ball enters the
このとき、各記憶部に記憶される保留は、第1保留であるか第2保留であるかを識別可能に記憶される。そして、第1保留および第2保留は、いずれも4個を上限として保留記憶領域に記憶される。したがって、例えば、保留記憶領域の第1記憶部〜第4記憶部に第1保留が記憶されており、第2保留が1つも記憶されていない状態で、第1始動口20に遊技球が入球した場合には、当該入球によって新たに第1保留が記憶されることはない。
At this time, the hold stored in each storage unit is stored so that it can be identified whether it is the first hold or the second hold. The first hold and the second hold are both stored in the hold storage area with an upper limit of four. Thus, for example, the first storage unit is stored in the first storage unit to the fourth storage unit of the storage unit, and no game ball enters the
図4は、特別図柄判定テーブルを説明する図である。第1始動口20または第2始動口22に遊技球が入球すると、0〜545の範囲内から1つの特別図柄乱数が取得される。そして、遊技球が入球した始動口と、大当たりの抽選を開始するとき、すなわち、大当たりの判定を行うときの遊技状態と、に応じて特別図柄判定テーブルが選択され、当該選択された特別図柄判定テーブルと取得された特別図柄乱数とによって大当たりの判定が行われる。
FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining the special symbol determination table. When a game ball enters the
低確率遊技状態において、第1保留に基づいて大当たりの抽選を開始する場合には、図4(a)に示す特別図柄判定テーブル1が参照される。この特別図柄判定テーブル1によれば、特別図柄乱数が7または107であった場合に大当たりと判定し、その他の特別図柄乱数であった場合にはハズレと判定する。したがって、この場合の大当たり確率は1/273となる。 In the low-probability gaming state, when starting the jackpot lottery based on the first hold, the special symbol determination table 1 shown in FIG. According to this special symbol determination table 1, when the special symbol random number is 7 or 107, it is determined that it is a big hit, and when it is any other special symbol random number, it is determined that it is lost. Therefore, the jackpot probability in this case is 1/273.
また、高確率遊技状態において、第1保留に基づいて大当たりの抽選を開始する場合には、図4(b)に示す特別図柄判定テーブル2が参照される。この特別図柄判定テーブル2によれば、特別図柄乱数が7、17、27、37、47、57、67、77、87、97、107、117、127、137、147、157、167、177、187、197であった場合に大当たりと判定する。したがって、この場合の大当たり確率は1/27.3となる。このように、高確率遊技状態である場合には、低確率遊技状態である場合に比べて、大当たり確率が10倍となる。 Further, in the high-probability gaming state, when starting the big win lottery based on the first hold, the special symbol determination table 2 shown in FIG. 4B is referred to. According to the special symbol determination table 2, the special symbol random numbers are 7, 17, 27, 37, 47, 57, 67, 77, 87, 97, 107, 117, 127, 137, 147, 157, 167, 177, When it is 187, 197, it is determined that the jackpot. Therefore, the jackpot probability in this case is 1 / 27.3. Thus, in the case of a high probability gaming state, the jackpot probability is 10 times that in the case of a low probability gaming state.
また、低確率遊技状態において、第2保留に基づいて大当たりの抽選を開始する場合には、図4(c)に示す特別図柄判定テーブル3が参照される。この特別図柄判定テーブル3も、特別図柄判定テーブル1と同様に、特別図柄乱数が7または107であった場合に大当たりと判定する。したがって、この場合の大当たり確率は1/273となる。 In the low-probability gaming state, when the big win lottery is started based on the second hold, the special symbol determination table 3 shown in FIG. Similarly to the special symbol determination table 1, the special symbol determination table 3 is also determined to be a big hit when the special symbol random number is 7 or 107. Therefore, the jackpot probability in this case is 1/273.
また、高確率遊技状態において、第2保留に基づいて大当たりの抽選を開始する場合には、図4(d)に示す特別図柄判定テーブル4が参照される。この特別図柄判定テーブル4も、特別図柄判定テーブル2と同様に、特別図柄乱数が7、17、27、37、47、57、67、77、87、97、107、117、127、137、147、157、167、177、187、197であった場合に大当たりと判定する。したがって、この場合の大当たり確率は1/27.3となる。 Further, in the high-probability gaming state, when starting the big win lottery based on the second hold, the special symbol determination table 4 shown in FIG. As with the special symbol determination table 2, the special symbol determination table 4 has special symbol random numbers of 7, 17, 27, 37, 47, 57, 67, 77, 87, 97, 107, 117, 127, 137, 147. 157, 167, 177, 187, 197, the jackpot is determined. Therefore, the jackpot probability in this case is 1 / 27.3.
図5は、特別図柄の種別を決定するための図柄種別判定テーブルを説明する図である。第1始動口20または第2始動口22に遊技球が入球すると、0〜299の範囲内から1つの大当たり乱数が取得される。そして、遊技球が入球した始動口と、上記の大当たりまたはハズレの判定結果と、に応じて図柄種別判定テーブルが選択され、当該選択された図柄種別判定テーブルと取得された大当たり乱数とによって特別図柄の種別が決定される。なお、大当たり乱数は、大当たりの判定結果が導出された場合に限らず、ハズレの判定結果が導出された場合にも、特別図柄の種別を決定する際に取得されるものである。以下では、大当たり乱数によって決定される特別図柄のうち、大当たりの判定結果が得られた場合に決定される特別図柄を大当たり図柄とよび、ハズレの判定結果が得られた場合に決定される特別図柄をハズレ図柄とよぶ。
FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining a symbol type determination table for determining the type of a special symbol. When a game ball enters the
ここで、上記した特別図柄判定テーブルによって第1保留を判定した結果、大当たりの判定結果が得られた場合には、図柄種別判定テーブル1が参照される。この図柄種別判定テーブル1によれば、図示のとおり、0〜299の各大当たり乱数に特別図柄A、B、C、D、E、F、G、H、Iの9種類の特別図柄が対応付けられており、例えば、大当たり乱数が「0」であった場合には、特別図柄Aが決定されることとなる。 Here, as a result of determining the first hold based on the above-described special symbol determination table, if a jackpot determination result is obtained, the symbol type determination table 1 is referred to. According to the symbol type determination table 1, nine special symbols A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I are associated with each jackpot random number from 0 to 299 as illustrated. For example, when the jackpot random number is “0”, the special symbol A is determined.
また、上記した特別図柄判定テーブルによって第2保留を判定した結果、大当たりの判定結果が得られた場合には、図柄種別判定テーブル2が参照される。この図柄種別判定テーブル2によっても、上記図柄種別判定テーブル1と同様の確率で各特別図柄が決定される。 In addition, as a result of determining the second hold based on the special symbol determination table described above, when the jackpot determination result is obtained, the symbol type determination table 2 is referred to. Also according to the symbol type determination table 2, each special symbol is determined with the same probability as the symbol type determination table 1.
また、上記した特別図柄判定テーブルによって第1保留または第2保留を判定した結果、ハズレの判定結果が得られた場合には、図柄種別判定テーブル3が参照される。この図柄種別判定テーブル3によれば、第1保留についてハズレの判定結果が得られた場合には、特別図柄の種別として必ず特別図柄Xが決定され、第2保留についてハズレの判定結果が得られた場合には、特別図柄の種別として必ず特別図柄Yが決定される。 In addition, when the determination result of the loss is obtained as a result of determining the first hold or the second hold by using the special symbol determination table described above, the symbol type determination table 3 is referred to. According to the symbol type determination table 3, when the determination result of the first hold is obtained, the special symbol X is always determined as the special symbol type, and the determination result of the loss is obtained for the second hold. In such a case, the special symbol Y is always determined as the special symbol type.
図6は、大当たりに当選した場合に実行される特別遊技を制御するための特別電動役物作動テーブルを説明する図である。特別電動役物作動テーブルは、特別遊技の実行中に大入賞口開閉ソレノイド28cを通電制御するために参照されるものであり、本実施形態においては、特別電動役物作動テーブルとして、作動テーブル1、2が設けられている。
FIG. 6 is a diagram for explaining a special electric accessory operating table for controlling a special game that is executed when a jackpot is won. The special electric accessory operating table is referred to for energization control of the special prize opening /
そして、特別図柄A、B、E、Fのいずれかが決定されると、作動テーブル1を参照して特別遊技が実行される。この作動テーブル1によれば、大入賞口28が29秒開放すること、または、大入賞口28に8個の遊技球が入球する(カウントC=8)ことのいずれかの条件が成立することによって終了するラウンド遊技が5回実行される。なお、各ラウンド遊技間に設定される大入賞口28の閉鎖時間すなわちインターバル時間は、2.0秒に設定されている。この作動テーブル1を参照して特別遊技が実行された場合、賞球数から遊技球の発射数を差し引いた平均純増数は450個となる。
When any of the special symbols A, B, E, and F is determined, the special game is executed with reference to the operation table 1. According to this operation table 1, the condition that either the special winning
また、特別図柄C、D、G、H、Iが決定されると、作動テーブル2を参照して特別遊技が実行される。この作動テーブル2によれば、大入賞口28が29秒開放すること、または、大入賞口28に8個の遊技球が入球する(カウントC=8)ことのいずれかの条件が成立することによって終了するラウンド遊技が15回実行される。なお、各ラウンド遊技間に設定される大入賞口28の閉鎖時間すなわちインターバル時間は、2.0秒に設定されている。この作動テーブル2を参照して特別遊技が実行された場合、賞球数から遊技球の発射数を差し引いた平均純増数は1350個となる。
When the special symbols C, D, G, H, and I are determined, the special game is executed with reference to the operation table 2. According to this operation table 2, the condition that either the winning prize opening 28 is released for 29 seconds or that eight game balls enter the winning prize opening 28 (count C = 8) is satisfied. Thus, the round game that ends is executed 15 times. Note that the closing time of the special winning
図7は、上記のようにして特別遊技が実行された場合に、当該特別遊技の終了後の遊技状態を設定するための遊技状態設定テーブルを説明する図である。特別遊技の終了後の遊技状態は、大当たりの抽選によって決定された特別図柄の種別によって決定される。 FIG. 7 is a diagram for explaining a game state setting table for setting the game state after the special game when the special game is executed as described above. The gaming state after the end of the special game is determined by the type of special symbol determined by the jackpot lottery.
図示のとおり、特別図柄A、B、C、Dが決定された場合には、特別遊技の終了後に低確率遊技状態に設定され、特別図柄E、F、G、H、Iが決定された場合には、特別遊技の終了後に高確率遊技状態に設定される。なお、高確率遊技状態の継続回数(以下、「高確回数」という)は10000回に設定される。これは、高確率遊技状態が、大当たりの抽選結果が10000回確定するまで継続することを意味している。高確率遊技状態においては、大当たりの当選確率が1/27.3に設定されていることから、実質的には、大当たりに再度当選するまで高確率遊技状態が継続することとなる。ただし、上記した高確回数は1の高確率遊技状態における最大継続回数を示すものであり、上記の継続回数に到達するまでの間に大当たりに当選した場合には、再度、高確回数の設定が行われることとなる。 As shown in the figure, when special symbols A, B, C, D are determined, the special probability E, F, G, H, I are determined after the special game is finished and set to the low probability gaming state Is set to a high-probability gaming state after the end of the special game. Note that the number of continuations of the high-probability gaming state (hereinafter referred to as “high-probability number”) is set to 10,000. This means that the high probability gaming state continues until the jackpot lottery result is determined 10,000 times. In the high probability gaming state, since the jackpot winning probability is set to 1 / 27.3, the high probability gaming state will continue until the jackpot is won again. However, the above-mentioned high-accuracy count indicates the maximum number of continuations in the high probability gaming state of 1. If the big hit is won before reaching the above-mentioned continuation count, the high-probability count is set again. Will be performed.
また、特別遊技の終了後には、高確率遊技状態または低確率遊技状態のいずれかに設定されるとともに、必ず時短遊技状態に設定されることとなるが、この時短遊技状態の継続回数(以下、「時短回数」という)は、特別図柄の種別と、大当たり当選時の遊技状態とに応じて次のようにして決定される。 In addition, after the end of the special game, it is set to either the high probability game state or the low probability game state, and is always set to the short-time game state. The “number of times saved” is determined as follows according to the type of the special symbol and the game state at the time of winning the jackpot.
すなわち、大当たり当選時の遊技状態が非時短遊技状態である場合において、特別図柄A、C、E、Gが決定されて特別遊技が実行されたときには、時短回数が9回に設定され、特別図柄B、D、F、Hが決定されて特別遊技が実行されたときには、時短回数が17回に設定され、特別図柄Iが決定されて特別遊技が実行されたときには、時短回数が10000回に設定される。 That is, in the case where the game state at the time of winning the jackpot is a non-short-time game state, when the special symbols A, C, E, and G are determined and the special game is executed, the number of hour / hours is set to nine, and the special symbol is set. When B, D, F, H are determined and a special game is executed, the number of time reductions is set to 17 times, and when special symbol I is determined and a special game is executed, the number of time reductions is set to 10,000 times. Is done.
また、大当たり当選時の遊技状態が時短遊技状態である場合において、特別図柄A、B、C、D、E、F、Gが決定されて特別遊技が実行されたときには、時短回数が100回に設定され、特別図柄H、Iが決定されて特別遊技が実行されたときには、時短回数が10000回に設定される。なお、上記のように設定された高確回数や時短回数だけ特別図柄の変動表示が行われると、高確率遊技状態が終了して低確率遊技状態に設定され、また、時短遊技状態が終了して非時短遊技状態に設定されることとなる。 Also, when the game state at the time of winning the jackpot is the short-time game state, when the special symbols A, B, C, D, E, F, G are determined and the special game is executed, the number of time reductions is 100 times. When the special symbols H and I are set and the special game is executed, the number of time reductions is set to 10,000. Note that if the special symbols are displayed in a variable manner for the high-accuracy count or short-time count set as described above, the high-probability gaming state ends and the low-probability gaming state is set, and the short-time gaming state ends. Will be set to a non-time-saving gaming state.
図8は、遊技者に付与される遊技利益(特別遊技の内容、特別遊技終了後の遊技状態の内容)を大当たり図柄ごとに説明する図である。この図に示すように、本実施形態においては、大当たりに当選した場合に、5回もしくは15回のラウンド遊技が実行され、以後の遊技状態が70%の確率で高確率遊技状態に設定される。また、大当たりに当選した場合には、必ず時短遊技状態に設定されるが、非時短遊技状態に設定されているときに大当たりに当選するよりも、時短遊技状態に設定されているときに大当たりに当選した場合の方が、時短回数が有利に設定されることとなる。 FIG. 8 is a diagram for explaining the game profit (contents of special game, content of game state after completion of special game) given to the player for each jackpot symbol. As shown in this figure, in the present embodiment, when the jackpot is won, five or fifteen round games are executed, and the subsequent gaming state is set to the high probability gaming state with a probability of 70%. . In addition, if you win a jackpot, you will always be set to the short-time gaming state, but if you are set to the short-time gaming state, rather than winning the jackpot when the non-time-saving gaming state is set, In the case of winning, the number of time reductions will be advantageously set.
図9(a)は、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合の大当たり時に参照される演出分類決定テーブル1および演出分類コマンド決定テーブル1を説明する図であり、図9(b)は、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合のハズレ時に参照される演出分類決定テーブル2および演出分類コマンド決定テーブル2を説明する図である。上記のように、大当たりの抽選結果が導出されると、当該大当たりの抽選結果を報知する変動演出の態様を決定する処理が行われる。変動演出の態様を決定するための処理として、主制御基板100においては、まず、演出分類が決定され、決定された演出分類に属する発展前変動パターンおよび発展後変動パターンが決定されることとなる。
FIG. 9A is a diagram for explaining the effect classification determination table 1 and the effect classification command determination table 1 that are referred to when the big hit is set when the non-time-saving gaming state is set, and FIG. It is a figure explaining the effect classification | category determination table 2 and the effect classification | category command determination table 2 referred at the time of a loss in the case of being set to a time-saving game state. As described above, when the jackpot lottery result is derived, a process for determining a variation effect mode for notifying the jackpot lottery result is performed. In the
ここで、演出分類というのは、大当たりの当否、変動演出の時間(以下、「変動時間」という)、変動演出の態様、演出出現時の大当たり確率(以下、「信頼度」という)等、予め設定された条件に基づいて演出を区分けするものである。本実施形態においては、非時短遊技状態と時短遊技状態とで変動演出の態様を異にしており、したがって遊技状態ごとに演出分類が設定されている。 Here, the effect classification is, for example, whether or not the jackpot is won, the time of the fluctuating effect (hereinafter referred to as “variable time”), the mode of the fluctuating effect, the jackpot probability at the appearance of the effect (hereinafter referred to as “reliability”), etc. The effects are divided based on the set conditions. In the present embodiment, the mode of varying effects is different between the non-time-saving gaming state and the time-saving gaming state, and accordingly, the effect classification is set for each gaming state.
上記したように、第1始動口20または第2始動口22に遊技球が入球すると、第1保留または第2保留として、特別図柄乱数、大当たり乱数、第1変動パターン乱数、第2変動パターン乱数A、Bが記憶される。そして、特別図柄乱数および大当たり乱数によって大当たり図柄もしくはハズレ図柄が決定されると、これら特別図柄乱数および大当たり乱数と同時に取得(記憶)された第1変動パターン乱数に基づいて演出分類が決定される。
As described above, when a game ball enters the
具体的には、大当たりの抽選により、大当たり図柄(特別図柄A〜I)が決定された場合には、図9(a)に示す演出分類決定テーブル1を参照して第1変動パターン乱数の判定が行われる。第1変動パターン乱数は、0〜999の範囲から1つ取得されており、この第1変動パターン乱数が0〜199の範囲内である場合には、「固定弱リーチ大当たり」の演出分類が決定され、第1変動パターン乱数が200〜999の範囲内である場合には、「固定強リーチ大当たり」の演出分類が決定される。 Specifically, when the jackpot symbol (special symbols A to I) is determined by the jackpot lottery, the first variation pattern random number is determined with reference to the effect classification determination table 1 shown in FIG. Is done. One first variation pattern random number is acquired from the range of 0 to 999. When this first variation pattern random number is in the range of 0 to 199, the effect classification of “fixed weak reach jackpot” is determined. When the first variation pattern random number is in the range of 200 to 999, the effect classification of “fixed strong reach jackpot” is determined.
一方、大当たりの抽選により、ハズレ図柄(特別図柄X、Y)が決定された場合には、図9(b)に示す演出分類決定テーブル2を参照して第1変動パターン乱数の判定が行われる。この図9(b)に示す演出分類決定テーブル2によれば、第1変動パターン乱数に応じて、「不定通常ハズレ」、「不定弱リーチハズレ」、「不定強リーチハズレ」、「固定通常ハズレ」、「固定弱リーチハズレ」、「固定強リーチハズレ」のいずれかが決定される。 On the other hand, when the lost symbol (special symbol X, Y) is determined by the big win lottery, the first variation pattern random number is determined with reference to the effect classification determination table 2 shown in FIG. 9B. . According to the effect classification determination table 2 shown in FIG. 9B, in accordance with the first variation pattern random number, “indefinite normal loss”, “indefinite weak reach loss”, “indefinite strong reach loss”, “fixed normal loss”, Either “fixed weak reach loss” or “fixed strong reach loss” is determined.
なお、図9(b)に示すハズレ時の演出分類決定テーブル2によれば、演出分類を決定するとき、すなわち、変動パターンを決定するときの第1保留および第2保留の合計数に応じて、異なる演出分類が決定され得る。この保留数と演出分類との関係について、図10を用いて詳細に説明する。 According to the effect classification determination table 2 at the time of the loss shown in FIG. 9B, when determining the effect classification, that is, according to the total number of the first hold and the second hold when determining the variation pattern. Different performance categories can be determined. The relationship between the number of holds and the effect classification will be described in detail with reference to FIG.
図10(a)は、非時短遊技状態における大当たり時の演出分類と第1変動パターン乱数との関係を説明する図であり、図10(b)は、非時短遊技状態におけるハズレ時の演出分類と第1変動パターン乱数との関係を説明する図である。この図に示すように、非時短遊技状態において、大当たりの抽選結果が導出された場合には、保留数とは無関係に、第1変動パターン乱数に基づいて演出分類が決定される。 FIG. 10A is a diagram for explaining the relationship between the effect category at the time of jackpot in the non-short game state and the first variation pattern random number, and FIG. 10B is the effect category at the time of loss in the non-time game state. It is a figure explaining the relationship between a 1st fluctuation pattern random number. As shown in this figure, in the non-time-saving gaming state, when the jackpot lottery result is derived, the effect classification is determined based on the first variation pattern random number regardless of the number of holds.
これに対して、非時短遊技状態において、ハズレの抽選結果が導出された場合には、第1変動パターン乱数が同一であったとしても、保留数に応じて異なる演出分類が決定される場合がある。例えば、第1変動パターン乱数が「770」であった場合に、第1保留および第2保留の合計数が2以下であれば「不定弱リーチハズレ」の演出分類が決定され、第1保留および第2保留の合計数が3以上であれば「不定通常ハズレ」が決定されることとなる。 On the other hand, if the lottery result is derived in the non-time-saving gaming state, even if the first variation pattern random number is the same, a different effect category may be determined depending on the number of holds. is there. For example, when the first variation pattern random number is “770”, if the total number of the first hold and the second hold is 2 or less, the effect classification of “undefined weak reach loss” is determined, and the first hold and the first hold If the total number of 2 suspensions is 3 or more, “indefinite normal loss” is determined.
なお、演出分類の名称のうち「固定」と称されるものは、保留の数とは無関係に、後述する発展前変動パターンおよび発展後変動パターンとして、同一の変動パターンが決定されることを示し、「不定」と称されるものは、保留の数に応じて異なる変動パターンが決定されることを示している。したがって、非時短遊技状態において、大当たりの抽選結果が導出された場合には、保留の数を問わず、第1変動パターン乱数の値に対応する1の変動パターンが決定されることとなる。また、非時短遊技状態において、ハズレの抽選結果が導出された場合であっても、第1変動パターン乱数が800〜999の範囲内の値である場合には、保留の数を問わず、第1変動パターン乱数に対応する1の変動パターンが決定されることとなる。 In addition, what is called “fixed” in the name of the effect category indicates that the same variation pattern is determined as a variation pattern before development and a variation pattern after development, which will be described later, regardless of the number of holds. , “Undetermined” indicates that a different variation pattern is determined depending on the number of suspensions. Therefore, when the jackpot lottery result is derived in the non-time-saving gaming state, one variation pattern corresponding to the value of the first variation pattern random number is determined regardless of the number of holds. Further, even if the lottery result is derived in the non-time-saving gaming state, the first variation pattern random number is a value within the range of 800 to 999, regardless of the number of holds. One fluctuation pattern corresponding to one fluctuation pattern random number is determined.
また、演出分類の名称のうち「強」および「弱」は、大当たりの信頼度を示しており、「弱」は信頼度が低いことを示し、「強」は信頼度が高いことを示している。したがって、「強」の演出分類が決定された場合には、後述する発展前変動パターンおよび発展後変動パターンの中で、信頼度の高い変動パターンが決定され、「弱」の演出分類が決定された場合には、信頼度の低い変動パターンが決定されることとなる。さらに、演出分類の名称のうち「通常」および「リーチ」は、変動演出の具体的な態様を示しているが、その詳細については後述する。 In addition, “Strong” and “Weak” in the name of the production category indicate the reliability of the jackpot, “Weak” indicates that the reliability is low, and “Strong” indicates that the reliability is high. Yes. Therefore, when the “strong” performance category is determined, a highly reliable variation pattern is determined from the pre-development variation pattern and the post-development variation pattern described later, and the “weak” performance category is determined. In such a case, a variation pattern with low reliability is determined. Furthermore, “normal” and “reach” among the names of the effect classifications indicate specific modes of the variable effects, the details of which will be described later.
なお、図9に示す演出分類決定テーブル1、2は、大当たりの抽選結果が導出されたとき、すなわち、変動演出の開始時において、変動パターンを決定するために参照される。一方、演出分類コマンド決定テーブル1、2は、保留記憶領域に第1保留または第2保留が記憶されたときに用いられる。すなわち、遊技機1においては、変動演出の開始時に変動パターンが決定されるが、このとき決定される変動パターンを、第1保留または第2保留が記憶された時点で事前に判定することで、当該保留による大当たりの当否や、当該保留の変動パターンを事前に示唆することが可能となる。
The effect classification determination tables 1 and 2 shown in FIG. 9 are referred to when determining the variation pattern when the jackpot lottery result is derived, that is, at the start of the variation effect. On the other hand, the effect classification command determination tables 1 and 2 are used when the first hold or the second hold is stored in the hold storage area. That is, in the
そこで、本実施形態においては、第1保留または第2保留が記憶された時点で、図9に示す演出分類コマンド決定テーブルを参照して、第1変動パターン乱数の判定を行うこととしている。以下では、変動演出の開始時の判定と区別するために、保留が記憶された時点で行われる判定を「事前判定」という。 Therefore, in the present embodiment, when the first hold or the second hold is stored, the first variation pattern random number is determined with reference to the effect classification command determination table shown in FIG. In the following, in order to distinguish from the determination at the start of the variation effect, the determination performed at the time when the hold is stored is referred to as “preliminary determination”.
図示のように、演出分類決定テーブルによって「固定」と称される演出分類が対応付けられた第1変動パターン乱数には、演出分類コマンド決定テーブルによっても、同様の演出分類コマンドが対応付けられている。一方、演出分類決定テーブルによって「不定」と称される演出分類が対応付けられた第1変動パターン乱数には、演出分類コマンド決定テーブルにおいて、いずれも同一の「不定値コマンド」が対応付けられている。 As shown in the drawing, the same effect classification command is also associated with the first variation pattern random number associated with the effect classification called “fixed” by the effect classification determination table also with the effect classification command determination table. Yes. On the other hand, the first variation pattern random number associated with the effect classification called “indefinite” by the effect classification determination table is associated with the same “indefinite value command” in the effect classification command determination table. Yes.
上記のように、変動演出の開始時に大当たりの抽選結果が導出されて演出分類が決定されると、決定された演出分類に対応する発展前変動パターンおよび発展後変動パターンがそれぞれ1つずつ決定される。そして、発展前変動パターンに対応する発展前変動パターンコマンド、および、発展後変動パターンに対応する発展後変動パターンコマンドが副制御基板200に送信され、副制御基板200において、受信した変動パターンコマンドに基づいて、演出表示部50aに表示する画像等、具体的な変動演出の態様を決定することとなる。
As described above, when the lottery lottery result is derived at the start of the variation effect and the effect classification is determined, the pre-development variation pattern and the post-development variation pattern corresponding to the determined effect classification are determined one by one. The Then, the pre-development variation pattern command corresponding to the pre-development variation pattern and the post-development variation pattern command corresponding to the post-development variation pattern are transmitted to the
ここで、大当たりの抽選結果を遊技者に報知するための変動演出の態様(変動パターン)は、発展前の演出(前半)と発展後の演出(後半)とに分けられる。そして、変動パターンを決定する際には、発展前変動パターンコマンド決定テーブルに基づいて、発展前の変動演出が対応付けられた発展前変動パターンが決定され、発展後変動パターンコマンド決定テーブルに基づいて、発展後の変動演出が対応付けられた発展後変動パターンが決定される。 Here, the variation effect mode (variation pattern) for notifying the player of the jackpot lottery result is divided into an effect before development (first half) and an effect after development (second half). Then, when determining the variation pattern, the variation pattern before development associated with the variation effect before development is determined based on the variation pattern command determination table before development, and based on the variation pattern command determination table after development. A post-development variation pattern associated with the post-development variation effect is determined.
図11(a)は、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合の大当たり時に参照される発展前変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル1および発展前事前判定コマンド決定テーブル1を説明する図であり、図11(b)は、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合のハズレ時に参照される発展前変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル2および発展前事前判定コマンド決定テーブル2を説明する図である。変動演出の開始時に「固定弱リーチ大当たり」または「固定強リーチ大当たり」の演出分類が決定された場合には、図11(a)に示す発展前変動パターンコマンド決定テーブルを参照して、第2変動パターン乱数Aの判定が行われる。 FIG. 11A is a diagram for explaining the pre-development variation pattern command determination table 1 and the pre-development advance determination command determination table 1 that are referred to at the time of the big hit when the non-time-saving gaming state is set. b) is a diagram for explaining the pre-development variation pattern command determination table 2 and the pre-development advance judgment command determination table 2 that are referred to when a game is lost when the non-time-saving gaming state is set. When the production category of “fixed weak reach jackpot” or “fixed strong reach jackpot” is determined at the start of the fluctuation production, the second variation pattern command decision table before development shown in FIG. The variation pattern random number A is determined.
この図11(a)に示す発展前変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル1によれば、第2変動パターン乱数Aに発展前変動パターンコマンドが対応付けられている。より詳細には、「固定弱リーチ大当たり」の演出分類が決定された場合には、第2変動パターン乱数Aの値に応じて、「ノーマルリーチ1」、「ノーマルリーチ2」、「疑似1リーチ」、「特殊パターン1」、「特殊パターン2」、「特殊パターン3」のいずれかが決定され、「固定強リーチ大当たり」の演出分類が決定された場合には、第2変動パターン乱数Aの値に応じて「疑似2リーチ」、「疑似3リーチ」が決定される。このようにして発展前変動パターンコマンドが決定されると、当該決定された発展前変動パターンコマンドが副制御基板200に送信されることとなる。
According to the undeveloped variation pattern command determination table 1 shown in FIG. 11A, the undeveloped variation pattern command is associated with the second variation pattern random number A. More specifically, when the production classification of “fixed weak reach jackpot” is determined, “
また、図11(b)に示す発展前変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル2によれば、「不定通常ハズレ」の演出分類が決定された場合には、第2変動パターン乱数Aがいずれの値であろうとも、保留数に応じて「12秒ハズレ」、「7秒ハズレ」、「4秒ハズレ」のいずれかの発展前変動パターンコマンドが決定される。また、その他の各演出分類が決定された場合には、第2変動パターン乱数Aの値に応じて、それぞれ図示の発展前変動パターンコマンドが決定されることとなる。 In addition, according to the pre-development variation pattern command determination table 2 shown in FIG. 11B, when the production classification of “indefinite normal loss” is determined, the second variation pattern random number A will be any value. Also, a pre-development variation pattern command of “12-second loss”, “7-second loss”, or “4-second loss” is determined according to the number of holds. Further, when each other effect category is determined, the pre-development variation pattern command shown in the figure is determined in accordance with the value of the second variation pattern random number A.
そして、上記したように、第1保留または第2保留が記憶された場合には、これらの保留が記憶された時点で、発展前変動パターンの事前判定が行われる。そして、発展前変動パターンの事前判定によって導出された発展前事前判定コマンドが副制御基板200に送信されることとなる。
As described above, when the first hold or the second hold is stored, the pre-development variation pattern is determined in advance at the time when these holds are stored. Then, a pre-development pre-determination command derived by pre-development variation pattern pre-determination is transmitted to the
なお、演出分類の事前判定によって、不定値コマンドが導出された場合(図9参照)には、発展前変動パターンについての事前判定を行わないこととしているが、その他の演出分類については、変動演出の開始時と、保留が記憶されたときとで、同様の発展前変動パターンが導出されることとなる。 In addition, when an indefinite value command is derived by the prior determination of the effect classification (see FIG. 9), the prior determination of the pre-development variation pattern is not performed. A similar pre-development variation pattern is derived at the time of starting and when the hold is stored.
図12(a)は、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合の大当たり時に参照される発展後変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル1および発展後事前判定コマンド決定テーブル1を説明する図であり、図12(b)は、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合のハズレ時に参照される発展後変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル2および発展後事前判定コマンド決定テーブル2を説明する図である。変動演出の開始時に「固定弱リーチ大当たり」または「固定強リーチ大当たり」の演出分類が決定された場合には、図12(a)に示す発展後変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル1を参照して、第2変動パターン乱数Bの判定が行われる。 FIG. 12 (a) is a diagram for explaining the post-development variation pattern command determination table 1 and the post-development advance determination command determination table 1 that are referred to at the time of jackpot when the non-time-saving gaming state is set. b) is a diagram for explaining the post-development variation pattern command determination table 2 and the post-development advance determination command determination table 2 that are referred to at the time of losing when the non-time-saving gaming state is set. When the production classification of “fixed weak reach jackpot” or “fixed strong reach jackpot” is determined at the start of the fluctuation production, the developed variation pattern command determination table 1 shown in FIG. The determination of the two fluctuation pattern random number B is performed.
この図12(a)に示す発展後変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル1によれば、第2変動パターン乱数Bに発展後変動パターンが対応付けられている。より詳細には、「固定弱リーチ大当たり」の演出分類が決定された場合には、第2変動パターン乱数Bの値に応じて、「大当たり発展1〜4」のいずれかが決定され、「固定強リーチ大当たり」の演出分類が決定された場合には、第2変動パターン乱数Bの値に応じて「大当たりSP発展1、2」が決定される。このようにして発展後変動パターンが決定されると、当該決定された発展後変動パターンに対応する発展後変動パターンコマンドが副制御基板200に送信されることとなる。
According to the developed variation pattern command determination table 1 shown in FIG. 12A, the developed variation pattern is associated with the second variation pattern random number B. More specifically, when the production classification of “fixed weak reach jackpot” is determined, one of “
また、図12(b)に示す発展後変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル2によれば、「不定通常ハズレ」の演出分類が決定された場合には、第2変動パターン乱数Bがいずれの値であろうとも、発展後の変動演出が行われない(変動演出が発展前で終了する)ことを示す「後半なし1」の発展後変動パターンコマンドが決定される。つまり、演出分類として「不定通常ハズレ」が決定された場合には、保留数に応じて「12秒ハズレ」、「7秒ハズレ」、「4秒ハズレ」のいずれかの発展前変動パターンに対応する変動演出のみが行われることとなる(図11参照)。 Further, according to the post-development variation pattern command determination table 2 shown in FIG. 12B, when the production classification of “indefinite normal loss” is determined, the second variation pattern random number B is any value. In addition, a post-development variation pattern command of “no second half” indicating that the post-development variation effect is not performed (the variation effect ends before the development) is determined. In other words, when “indefinite normal loss” is determined as the production category, it corresponds to the pre-development variation pattern of “12 second loss”, “7 second loss”, or “4 second loss” depending on the number of holds. Only the changing effect is performed (see FIG. 11).
また、その他の各演出分類が決定された場合には、第2変動パターン乱数Bの値に応じて、それぞれ図示の発展後変動パターンコマンドが決定されることとなる。このとき、演出分類が「固定通常ハズレ」であった場合には、「特殊パターン1〜3」のいずれかの発展前変動パターンに対応する変動演出のみが行われ、発展後の変動演出が行われないため、上記と同様に、「後半なし1」の発展後変動パターンコマンドが決定されることとなる。
Further, when each other effect classification is determined, the post-development variation pattern command shown is determined according to the value of the second variation pattern random number B. At this time, if the effect classification is “fixed normal loss”, only the change effect corresponding to any of the pre-development change patterns of “
そして、上記したように、第1保留または第2保留が記憶された場合には、これらの保留が記憶された時点で、発展後変動パターンの事前判定が行われる。そして、発展後変動パターンの事前判定によって導出された発展後変動パターンに対応する発展後事前判定コマンドが副制御基板200に送信されることとなる。
As described above, when the first hold or the second hold is stored, the post-development variation pattern is determined in advance at the time when these holds are stored. Then, a post-development pre-determination command corresponding to the post-development variation pattern derived by pre-determination of the post-development variation pattern is transmitted to the
なお、演出分類の事前判定によって、不定値コマンドが事前判定された場合には、発展後変動パターンについての事前判定を行わないこととしているが、その他の演出分類については、変動演出の開始時と、保留が記憶されたときとで、同様の発展後変動パターンが導出されることとなる。 In addition, when the indefinite value command is pre-determined by the pre-determination of the effect category, the pre-determination for the post-development variation pattern is not performed, but for other effect categories, A similar post-development variation pattern is derived when the hold is stored.
図13(a)は、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合の大当たり時に参照される演出分類決定テーブル3および演出分類コマンド決定テーブル3を説明する図であり、図13(b)は、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合のハズレ時に参照される演出分類決定テーブル4および演出分類コマンド決定テーブル4を説明する図である。変動演出の開始時、および、第1保留または第2保留が記憶されたときに、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合には、図9のテーブルが参照されるが、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合には、この図13に示すテーブルが参照される。演出分類の具体的な決定方法は上記と同じであるため、ここでは詳細な説明を省略するが、図示のように、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合と、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合とでは、第1変動パターン乱数が同じであったとしても、異なる演出分類が決定されることとなる。 FIG. 13A is a diagram for explaining the effect classification determination table 3 and the effect classification command determination table 3 that are referred to when the jackpot is set in the time-saving gaming state A, and FIG. It is a figure explaining the effect classification | category determination table 4 and the effect classification | category command determination table 4 which are referred at the time of loss in the case of being set to the gaming state A. If the non-time-saving gaming state is set when the variation effect is started and when the first hold or the second hold is stored, the table of FIG. If set, the table shown in FIG. 13 is referred to. Since the specific method of determining the effect classification is the same as described above, detailed description is omitted here, but when the non-short game state is set and the short game state A is set as shown in the figure. In this case, even if the first variation pattern random number is the same, a different effect category is determined.
なお、時短遊技状態は、時短遊技状態A、B、Cに区別される。これら時短遊技状態A、B、Cは、いずれも変動パターンを決定する際に参照するテーブルを異にしているが、第2始動口22の開閉条件(可動片22bの制御条件)は同じである。時短遊技状態Aは、特別遊技の終了後の時短回数が9回もしくは17回の場合に、当該特別遊技の終了後に設定される。また、時短遊技状態Bは、特別遊技の終了後の時短回数が100回の場合に、当該特別遊技の終了後に設定され、時短遊技状態Cは、特別遊技の終了後の時短回数が10000回の場合に、当該特別遊技の終了後に設定される。これらの時短遊技状態A、B、Cは、上記の時短回数内で大当たりに当選しなかった場合に、非時短遊技状態に変更されることによって終了となる。
The short-time gaming state is classified into short-time gaming states A, B, and C. These short game states A, B, and C all have different tables to be referred to when determining the variation pattern, but the opening / closing conditions of the second start port 22 (control conditions of the
図14(a)は、時短遊技状態Aにおける大当たり時の演出分類と第1変動パターン乱数との関係を説明する図であり、図14(b)は、時短遊技状態Aにおけるハズレ時の演出分類と第1変動パターン乱数との関係を説明する図である。この図に示すように、時短遊技状態Aにおいても、非時短遊技状態と同様に、大当たりの抽選結果が導出された場合には、保留数とは無関係に、第1変動パターン乱数に基づいて演出分類が決定される。これに対して、時短遊技状態Aにおいて、ハズレの抽選結果が導出された場合には、非時短遊技状態と同様に、保留数に応じて異なる演出分類が決定される場合がある。 FIG. 14A is a diagram for explaining the relationship between the effect category at the time of jackpot in the short-time gaming state A and the first variation pattern random number, and FIG. 14B is the effect category at the time of loss in the short-time gaming state A. It is a figure explaining the relationship between a 1st fluctuation pattern random number. As shown in this figure, even in the short-time gaming state A, similar to the non-short-time gaming state, when the jackpot lottery result is derived, the performance is based on the first variation pattern random number regardless of the number of holds. Classification is determined. On the other hand, when the lottery result is derived in the short-time gaming state A, different effect classifications may be determined depending on the number of holds, as in the non-short-time gaming state.
図15(a)は、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合の大当たり時に参照される発展前変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル3および発展前事前判定コマンド決定テーブル3を説明する図であり、図15(b)は、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合のハズレ時に参照される発展前変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル4および発展前事前判定コマンド決定テーブル4を説明する図である。この図に示すように、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合に決定され得る演出分類には、それぞれ発展前変動パターンが対応付けられており、非時短遊技状態と同様に、決定された演出分類と第2変動パターン乱数Aとによって、1の発展前変動パターンが決定されることとなる。 FIG. 15A is a diagram for explaining the pre-development variation pattern command determination table 3 and the pre-development advance determination command determination table 3 that are referred to at the time of the big hit when the short-time gaming state A is set. b) is a diagram for explaining the pre-development variation pattern command determination table 4 and the pre-development prior determination command determination table 4 that are referred to when a loss occurs when the short-time gaming state A is set. As shown in this figure, the effect classification that can be determined when the short-time game state A is set is associated with a pre-development variation pattern, and the determined effect is similar to the non-short-time game state. One pre-development variation pattern is determined by the classification and the second variation pattern random number A.
図16(a)は、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合の大当たり時に参照される発展後変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル3および発展後事前判定コマンド決定テーブル3を説明する図であり、図16(b)は、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合のハズレ時に参照される発展後変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル4および発展後事前判定コマンド決定テーブル4を説明する図である。この図に示すように、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合に決定され得る演出分類には、それぞれ発展後変動パターンが対応付けられており、非時短遊技状態と同様に、決定された演出分類と第2変動パターン乱数Bとによって、1の発展後変動パターンが決定されることとなる。 FIG. 16 (a) is a diagram for explaining the post-development variation pattern command determination table 3 and the post-development advance determination command determination table 3 that are referred to at the time of the big hit when the short-time gaming state A is set. b) is a diagram for explaining the post-development variation pattern command determination table 4 and the post-development pre-determination command determination table 4 that are referred to at the time of losing when the short-time gaming state A is set. As shown in this figure, the development classification that can be determined when the short-time gaming state A is set is associated with a variation pattern after development, and the determined performance is similar to the non-short-time gaming state. One developed variation pattern is determined by the classification and the second variation pattern random number B.
以上のように、主制御基板100においては、変動演出の開始時に、そのときの遊技状態に基づいて、演出分類、発展前変動パターンおよび発展後変動パターンが判定され、発展前変動パターンコマンドおよび発展後変動パターンコマンドが副制御基板200に送信される。また、第1保留または第2保留が記憶された場合にも、そのときの遊技状態に基づいて、演出分類、発展前変動パターンおよび発展後変動パターンが事前判定され、演出分類コマンド、発展前変動パターンコマンドおよび発展後変動パターンコマンドが副制御基板200に送信されることとなる。
As described above, in the
このとき、変動演出の開始時と、第1保留または第2保留が記憶されたときとでは、演出分類が「不定」である場合を除いて、同一の発展前変動パターンおよび発展後変動パターンが導出されることとなる。また、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合と、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合とでは、各乱数の値が同一であったとしても、演出分類、発展前変動パターンおよび発展後変動パターンが異なるものとなっている。 At this time, the same pre-development variation pattern and post-development variation pattern are obtained at the start of the variation production and when the first hold or the second hold is stored, except when the production classification is “indefinite”. Will be derived. Further, even when the random time value is the same between the case where the non-time saving gaming state is set and the case where the time saving gaming state A is set, the effect classification, the pre-development variation pattern, and the post-development variation The pattern is different.
そのため、例えば、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合に保留Bが記憶され、それ以前に処理がなされる保留Aによって遊技状態が時短遊技状態Aに変更されると、保留Bの変動演出の開始時に決定される実際の発展前変動パターンおよび発展後変動パターンと、事前判定された発展前変動パターンおよび発展後変動パターンとが全く異なったものになるおそれがある。そこで、本実施形態においては、例えば、非時短遊技状態において第1保留または第2保留が記憶された場合には、当該時短遊技状態における演出分類、発展前変動パターン、発展後変動パターンに加えて、時短遊技状態Aにおける演出分類の事前判定結果も導出することとしている。なお、こうした主制御基板100における処理については、後で詳しく説明することとする。
Therefore, for example, when the non-short-time gaming state is set, the hold B is stored, and when the game state is changed to the short-time gaming state A by the hold A that is processed before that, There is a possibility that the actual pre-development variation pattern and the post-development variation pattern determined at the start and the pre-development variation pattern and the post-development variation pattern determined in advance may be completely different. Therefore, in the present embodiment, for example, when the first hold or the second hold is stored in the non-short game state, in addition to the effect classification, the pre-development variation pattern, and the post-development variation pattern in the short time game state. In addition, the prior determination result of the effect classification in the short time gaming state A is also derived. Such processing on the
また、上記したように、演出分類コマンド決定テーブル、発展前変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル、発展後変動パターンコマンド決定テーブル等は、非時短遊技状態、時短遊技状態A、B、Cごとにそれぞれ設けられているが、ここでは、時短遊技状態B、Cについては説明を省略する。また、例えば、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合には、高確率遊技状態に設定されている場合と、低確率遊技状態に設定されている場合とがあるが、ここでは、大当たりの確率(高確率、低確率)を問わず、共通のテーブルが参照されることとする。 In addition, as described above, the effect classification command determination table, the pre-development variation pattern command determination table, the post-development variation pattern command determination table, and the like are provided for each of the non-short-time gaming state, the short-time gaming state A, B, and C, respectively. However, description of the short-time gaming states B and C is omitted here. In addition, for example, when the short-time gaming state A is set, there are a case where the high-probability gaming state is set and a case where the low-probability gaming state is set. A common table is referred to regardless of (high probability, low probability).
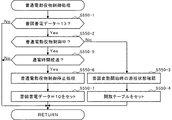
図17は、普通図柄判定テーブルを説明する図である。遊技領域16を流下する遊技球がゲート24を通過すると、第2始動口22の可動片22bを通電制御するか否かが対応付けられた普通図柄の決定処理(以下、「普図抽選」という)が行われる。
FIG. 17 is a diagram for explaining a normal symbol determination table. When a game ball flowing down the
なお、詳しくは後述するが、遊技球がゲート24を通過すると、0〜19の範囲内から1つの普通図柄乱数が取得されるとともに、この乱数値がメインRAM100cの普図保留記憶領域に4つを上限として記憶される。したがって、普図保留記憶領域に4つの乱数値が記憶された状態で、遊技球がゲート24を通過した場合には、当該遊技球の通過に基づいて乱数値が記憶されることはない。以下では、ゲート24を遊技球が通過して普図保留記憶領域に記憶された乱数値(普通図柄乱数)を普図保留とよぶ。
As will be described in detail later, when the game ball passes through the
非時短遊技状態において普図抽選を開始する場合には、図17(a)に示す普通図柄判定テーブル1が参照される。この普通図柄判定テーブル1によれば、普通図柄乱数が0であった場合に当選と判定し、普通図柄乱数が1〜19あった場合にはハズレと判定する。したがって、この場合の当選確率は1/20となる。 When the general drawing lottery is started in the non-time-saving gaming state, the normal symbol determination table 1 shown in FIG. According to this normal symbol determination table 1, when the normal symbol random number is 0, it is determined to be a win, and when the normal symbol random number is 1 to 19, it is determined to be lost. Therefore, the winning probability in this case is 1/20.
また、時短遊技状態において普図抽選を開始する場合には、図17(b)に示す普通図柄判定テーブル2が参照される。この普通図柄判定テーブル2によれば、普通図柄乱数が0〜18であった場合に当選と判定し、普通図柄乱数が19であった場合にはハズレと判定する。したがって、この場合の当選確率は19/20となる。なお、普図抽選によって当選の判定結果が得られた場合には当たり図柄が決定され、ハズレの判定結果が得られた場合にはハズレ図柄が決定される。 In addition, when the general drawing lottery is started in the short-time gaming state, the normal symbol determination table 2 shown in FIG. According to the normal symbol determination table 2, when the normal symbol random number is 0 to 18, it is determined that the winning is selected, and when the normal symbol random number is 19, it is determined that the game is lost. Therefore, the winning probability in this case is 19/20. In addition, a winning symbol is determined when the winning determination result is obtained by the regular drawing lottery, and a lost symbol is determined when the losing determination result is obtained.
図18(a)は、普通図柄変動パターン決定テーブルを説明する図であり、図18(b)は、第2始動口開放制御テーブルを説明する図である。上記のように、普図抽選が行われると、普通図柄の変動パターンが決定される。ここでは、遊技状態が非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合には変動時間が20秒に決定され、遊技状態が時短遊技状態に設定されている場合には変動時間が1秒に決定される。このようにして変動時間が決定されると、当該決定された時間にわたって普通図柄表示器88が変動表示(点滅表示)される。そして、当たり図柄が決定された場合には普通図柄表示器88が点灯し、ハズレ図柄が決定された場合には普通図柄表示器88が消灯する。
FIG. 18A is a diagram illustrating a normal symbol variation pattern determination table, and FIG. 18B is a diagram illustrating a second start port opening control table. As described above, when the regular drawing lottery is performed, the variation pattern of the normal symbol is determined. Here, when the gaming state is set to the non-short-time gaming state, the variation time is determined to be 20 seconds, and when the gaming state is set to the short-time gaming state, the variation time is determined to be 1 second. . When the variation time is determined in this way, the
そして、普図抽選によって当たり図柄が決定されるとともに、普通図柄表示器88が点灯した場合には、第2始動口22の可動片22bが、普図抽選が行われたときの遊技状態に応じて図18(b)に示すように通電制御される。
When the winning symbol is determined by the general symbol lottery and the
すなわち、非時短遊技状態において当たり図柄が決定された場合には、始動口開閉ソレノイド22cが0.1秒×1回=0.1秒のみ通電され、第2始動口22の可動片22bが0.1秒のみ開放する。また、時短遊技状態において当たり図柄が決定された場合には、始動口開閉ソレノイド22cが2.9秒×2回=5.8秒通電され、第2始動口22の可動片22bが合計で5.8秒開放する。
That is, when the winning symbol is determined in the non-short game state, the start opening /
このように、時短遊技状態においては、非時短遊技状態よりも第2始動口22に遊技球が入球しやすくなる。つまり、時短遊技状態においては、ゲート24を遊技球が通過する限りにおいて、次々と普図抽選がなされるとともに、第2始動口22が頻繁に開放状態となるため、遊技者は遊技球の費消を低減しながら、大当たりの抽選を行うことが可能となる。
Thus, in the short-time gaming state, it becomes easier for the game ball to enter the
次に、遊技機1における遊技の進行について、フローチャートを用いて説明する。
Next, the progress of the game in the
(主制御基板のメイン処理)
図19を用いて、主制御基板100のメイン処理を説明する。
(Main processing of main control board)
The main process of the
電源基板より電源が供給されると、メインCPU100aにシステムリセットが発生し、メインCPU100aは、以下のメイン処理を行う。
When power is supplied from the power supply board, a system reset occurs in the
(ステップS1)
メインCPU100aは、初期化処理として、電源投入に応じて、メインROM100bから起動プログラムを読み込むとともに、メインRAM100cに記憶されるフラグ等を初期化したり、副制御基板200に送信する各種のコマンドを演出用伝送データ格納領域に記憶したりする。
(Step S1)
As an initialization process, the
(ステップS2)
次に、メインCPU100aは、変動パターン乱数(第1変動パターン乱数、第2変動パターン乱数A、B)を更新する変動パターン乱数更新処理を行う。
(Step S2)
Next, the
(ステップS3)
次に、メインCPU100aは、特別図柄乱数および大当たり乱数を更新する際に参照される初期値乱数の更新を行う。以降は、所定の割込み処理が行われるまで、ステップS2とステップS3との処理を繰り返し行う。
(Step S3)
Next, the
(主制御基板のタイマ割込処理)
図20を用いて、主制御基板100のタイマ割込処理を説明する。
(Timer interrupt processing of main control board)
The timer interrupt process of the
主制御基板100に設けられたリセット用クロックパルス発生回路によって、所定の周期(2ミリ秒、以下「2ms」という)毎にクロックパルスが発生されることで、以下のタイマ割込処理が実行される。
A clock pulse is generated at a predetermined cycle (2 milliseconds, hereinafter referred to as “2 ms”) by the reset clock pulse generation circuit provided on the
(ステップS100)
まず、メインCPU100aは、各種タイマカウンタを更新する時間制御処理を行う。
(Step S100)
First, the
(ステップS200)
次に、メインCPU100aは、特別図柄乱数、大当たり乱数、普通図柄乱数を更新する処理を行う。具体的には、それぞれの乱数カウンタを1加算して、乱数カウンタを更新する。なお、加算した結果が乱数範囲の最大値を超えた場合には、乱数カウンタを0に戻し、乱数カウンタが1周した場合には、その時の初期値乱数の値から乱数を更新する。
(Step S200)
Next, the
(ステップS300)
次に、メインCPU100aは、一般入賞口検出スイッチ18a、第1始動口検出スイッチ20a、第2始動口検出スイッチ22a、ゲート検出スイッチ24a、大入賞口検出スイッチ28aに入力があったか否か判定する入力制御処理を行う。
(Step S300)
Next, the
(ステップS400)
次に、メインCPU100aは、特別図柄、特別電動役物の制御を行うための特図特電処理を行う。
(Step S400)
Next, the
(ステップS500)
次に、メインCPU100aは、普通図柄、普通電動役物の制御を行うための普図普電処理を行う。
(Step S500)
Next, the
(ステップS600)
次に、メインCPU100aは、一般入賞口18、第1始動口20、第2始動口22、大入賞口28に遊技球が入球したか否かを確認するとともに、遊技球の入球があった場合には、それぞれに対応する払出個数指定コマンドを払出制御基板120に送信する。
(Step S600)
Next, the
(ステップS700)
次に、メインCPU100aは、外部情報データ、第2始動口開閉ソレノイドデータ、大入賞口開閉ソレノイドデータ、各表示器80、82、84、86、88、90の表示データを作成する処理を行う。
(Step S700)
Next, the
(ステップS800)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS700で作成した各データの信号を出力させるポート出力処理、および、上記各ステップでメインRAM100cの演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットされたコマンドを送信するコマンド送信処理を行う。
(Step S800)
Next, the
以下に、上記したタイマ割込処理のうち、ステップS300の入力制御処理、ステップS400の特図特電処理、ステップS500の普図普電処理について、詳細に説明する。 Below, among the above-mentioned timer interruption processes, the input control process in step S300, the special figure special electric process in step S400, and the common figure ordinary electric process in step S500 will be described in detail.
図21は、上記ステップS300の入力制御処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 21 is a flowchart for explaining the input control processing in step S300.
(ステップS310)
まず、メインCPU100aは、一般入賞口検出スイッチ18aから検出信号が入力されたか、すなわち、遊技球が一般入賞口18に入球したか否かを判定する。メインCPU100aは、一般入賞口検出スイッチ18aから検出信号が入力された場合には、賞球のために用いる一般入賞口賞球カウンタに所定のデータを加算して更新する。
(Step S310)
First, the
(ステップS320)
次に、メインCPU100aは、大入賞口検出スイッチ28aから検出信号が入力されたか、すなわち、遊技球が大入賞口28に入球したか否かを判定する。メインCPU100aは、大入賞口検出スイッチ28aから検出信号が入力された場合には、賞球のために用いる大入賞口賞球カウンタに所定のデータを加算して更新するとともに、大入賞口28に入球した遊技球を計数するための大入賞口入球カウンタを加算して更新する。
(Step S320)
Next, the
(ステップS330)
次に、メインCPU100aは、第1始動口検出スイッチ20aから検出信号が入力されたか、すなわち、遊技球が第1始動口20に入球したか否かを判定して、大当たりの抽選を行うための所定のデータをセットする。詳しくは、図22を用いて後述する。
(Step S330)
Next, the
(ステップS340)
次に、メインCPU100aは、第2始動口検出スイッチ22aから検出信号が入力されたか、すなわち、遊技球が第2始動口22に入球したか否かを判定する。なお、この第2始動口検出スイッチ入力処理は、各種データを異にする点を除いて、上記ステップS330の第1始動口検出スイッチ入力処理と同じである。
(Step S340)
Next, the
(ステップS350)
次に、メインCPU100aは、ゲート検出スイッチ24aから信号が入力されたか、すなわち、遊技球がゲート24を通過したか否かを判定する。このゲート検出スイッチ入力処理については、図24を用いて後述する。
(Step S350)
Next, the
図22は、上記ステップS330の第1始動口検出スイッチ入力処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 22 is a flowchart for explaining the first start port detection switch input process in step S330.
(ステップS330−1)
まず、メインCPU100aは、第1始動口検出スイッチ20aから検出信号が入力されたか否かを判定する。第1始動口検出スイッチ20aから検出信号が入力されたと判定した場合にはステップS330−2に処理を移し、第1始動口検出スイッチ20aから検出信号が入力されていないと判定した場合には、第1始動口検出スイッチ入力処理を終了する。
(Step S330-1)
First, the
(ステップS330−2)
上記ステップS330−1において、第1始動口検出スイッチ20aから検出信号が入力されたと判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、賞球のために用いる賞球カウンタに所定のデータを加算して更新する処理を行う。
(Step S330-2)
When it is determined in step S330-1 that a detection signal is input from the first start
(ステップS330−3)
次に、メインCPU100aは、保留記憶領域に記憶されている第1保留数(X1)が4未満であるか否かを判定する。その結果、第1保留数(X1)<4と判定した場合にはステップS330−4に処理を移し、第1保留数(X1)≧4と判定した場合には第1始動口検出スイッチ入力処理を終了する。
(Step S330-3)
Next, the
(ステップS330−4)
上記ステップS330−3において、第1保留数(X1)<4と判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、第1保留数(X1)に「1」加算した値を新たな第1保留数(X1)として記憶する。
(Step S330-4)
If it is determined in step S330-3 that the first hold number (X1) <4, the
(ステップS330−5)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS200で更新された特別図柄乱数を取得して、保留記憶領域にある第1記憶部から第8記憶部まで順に空いている記憶部を検索し、空いている記憶部に取得した特別図柄乱数を記憶する。
(Step S330-5)
Next, the
(ステップS330−6)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS200で更新された大当たり乱数を取得するとともに、当該取得した大当たり乱数を、上記ステップS330−5で特別図柄乱数を記憶したのと同じ記憶部に記憶する。
(Step S330-6)
Next, the
(ステップS330−7)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS2で更新された変動パターン乱数(第1変動パターン乱数、第2変動パターン乱数A、B)を取得するとともに、上記ステップS330−5およびステップS330−6で各乱数を記憶したのと同じ記憶部に記憶する。
(Step S330-7)
Next, the
(ステップS331)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS330−5〜ステップS330−7で記憶部に記憶された各乱数を判定する事前判定処理を実行し、当該第1始動口検出スイッチ入力処理を終了する。
(Step S331)
Next, the
図23は、上記ステップS331の事前判定処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 23 is a flowchart for explaining the prior determination process in step S331.
(ステップS331−1)
まず、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS330−5で記憶部に記憶された特別図柄乱数を、上記した特別図柄判定テーブル1または特別図柄判定テーブル2に基づいて判定する。具体的には、現在の遊技状態に応じて、図4に示す特別図柄判定テーブル1または特別図柄判定テーブル2を選択するとともに、選択したテーブルと特別図柄乱数とから事前判定を行い、当該事前判定結果(大当たり情報またはハズレ情報)をメインRAM100cの所定の処理領域に記憶する。
(Step S331-1)
First, the
(ステップS331−2)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS330−6で記憶部に記憶された大当たり乱数を事前判定する。具体的には、上記ステップS331−1の事前判定によって「大当たり」の結果が導出された場合には、図5に示す図柄種別判定テーブル1を選択するとともに、当該選択したテーブルと大当たり乱数とから事前判定を行う。そして、当該事前判定によって導出された特別図柄の種別を、メインRAM100cの所定の処理領域に記憶する。一方、上記ステップS331−1の事前判定によって「大当たり」の結果が導出されなかった場合には、特別図柄Xに係るデータを、メインRAM100cの所定の処理領域に記憶する。
(Step S331-2)
Next, the
(ステップS331−3)
次に、メインCPU100aは、現在の遊技状態、および、上記ステップS331−2で導出された特別図柄種別に係る事前判定情報に応じて、演出分類コマンド決定テーブルを選択する。具体的には、現在の遊技状態が非時短遊技状態である場合には、図9(a)または図9(b)に示す演出分類コマンド決定テーブル1、2を選択し、現在の遊技状態が時短遊技状態Aである場合には、図13(a)または図13(b)に示す演出分類コマンド決定テーブル3、4を選択する。なお、現在の遊技状態が時短遊技状態B、Cである場合には、それぞれの遊技状態専用の演出分類コマンド決定テーブルを選択することとなる。
(Step S331-3)
Next, the
(ステップS331−4)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS331−3で選択されたテーブルと、第1変動パターン乱数とから、現在の遊技状態に基づく演出分類の事前判定を行う。
(Step S331-4)
Next, the
(ステップS331−5)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS331−4で導出された演出分類コマンドを演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットする。
(Step S331-5)
Next, the
(ステップS331−6)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS331−5でセットされた演出分類コマンドが、不定値コマンド(図9、図13参照)であるかを判定する。その結果、上記ステップS331−5でセットされた演出分類コマンドが不定値コマンドであると判定した場合にはステップS331−13に処理を移し、演出分類コマンドは不定値コマンドではないと判定した場合にはステップS331−7に処理を移す。
(Step S331-6)
Next, the
(ステップS331−7)
上記ステップS331−6において、演出分類コマンドは不定値コマンドではないと判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、現在の遊技状態、および、上記ステップS331−4で導出された演出分類に応じて、発展前事前判定コマンド決定テーブルを選択する。具体的には、現在の遊技状態が非時短遊技状態である場合には、図11(a)または図11(b)に示す発展前事前判定コマンド決定テーブル1、2を選択し、現在の遊技状態が時短遊技状態Aである場合には、図15(a)または図15(b)に示す発展前事前判定コマンド決定テーブル3、4を選択する。なお、現在の遊技状態が時短遊技状態B、Cである場合には、それぞれの遊技状態専用の演出分類コマンド決定テーブルを選択することとなる。
(Step S331-7)
If it is determined in step S331-6 that the effect classification command is not an indefinite value command, the
(ステップS331−8)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS331−7で選択されたテーブルと、第2変動パターン乱数Aとから、現在の遊技状態に基づく発展前変動パターンの事前判定を行う。
(Step S331-8)
Next, the
(ステップS331−9)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS331−8で導出された発展前事前判定コマンドを演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットする。
(Step S331-9)
Next, the
(ステップS331−10)
次に、メインCPU100aは、現在の遊技状態、および、上記ステップS331−4で導出された演出分類に応じて、発展後事前判定コマンド決定テーブルを選択する。具体的には、現在の遊技状態が非時短遊技状態である場合には、図12(a)または図12(b)に示す発展後事前判定コマンド決定テーブル1、2を選択し、現在の遊技状態が時短遊技状態Aである場合には、図16(a)または図16(b)に示す発展後事前判定コマンド決定テーブル3、4を選択する。なお、現在の遊技状態が時短遊技状態B、Cである場合には、それぞれの遊技状態専用の演出分類コマンド決定テーブルを選択することとなる。
(Step S331-10)
Next, the
(ステップS331−11)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS331−10で選択されたテーブルと、第2変動パターン乱数Bとから、現在の遊技状態に基づく発展後変動パターンの事前判定を行う。
(Step S331-11)
Next, the
(ステップS331−12)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS331−11で導出された発展後事前判定コマンドを演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットする。
(Step S331-12)
Next, the
(ステップS331−13)
次に、メインCPU100aは、現在の遊技状態が非時短遊技状態であるかを判定する。その結果、現在の遊技状態が非時短遊技状態であると判定した場合にはステップS331−14に処理を移し、現在の遊技状態は非時短遊技状態ではないと判定した場合にはステップS331−16に処理を移す。
(Step S331-13)
Next, the
(ステップS331−14)
上記ステップS331−13において、現在の遊技状態は非時短遊技状態であると判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、低確率遊技状態かつ時短遊技状態Aであると仮定した場合の演出分類と、高確率遊技状態かつ時短遊技状態Aであると仮定した場合の演出分類とを仮判定する。
(Step S331-14)
In step S331-13, if it is determined that the current gaming state is the non-short-time gaming state, the
具体的には、まず、特別図柄乱数と特別図柄判定テーブル1とから大当たり、ハズレの判定結果を導出し、その判定結果に基づいて図柄種別判定テーブル1または3を選択して特別図柄種別を仮判定する。そして、仮判定された特別図柄種別に応じて、図13(a)または図13(b)に示す時短遊技状態A用の演出分類コマンド決定テーブルを選択し、当該選択したテーブルと、第1変動パターン乱数とから演出分類を仮判定する。 Specifically, first, a jackpot and loss determination result is derived from the special symbol random number and the special symbol determination table 1, and based on the determination result, the symbol type determination table 1 or 3 is selected and the special symbol type is temporarily set. judge. Then, according to the provisionally determined special symbol type, an effect classification command determination table for the short-time gaming state A shown in FIG. 13A or 13B is selected, and the selected table and the first variation are selected. The effect classification is provisionally determined from the pattern random number.
また、これと同様に、特別図柄乱数と特別図柄判定テーブル2とから大当たり、ハズレの判定結果を導出し、その判定結果に基づいて図柄種別判定テーブル1または3を選択して特別図柄種別を仮判定する。そして、仮判定された特別図柄種別に応じて、図13(a)または図13(b)に示す時短遊技状態A用の演出分類コマンド決定テーブルを選択し、当該選択したテーブルと、第1変動パターン乱数とから演出分類を仮判定する。 Similarly, a big hit and loss determination result is derived from the special symbol random number and the special symbol determination table 2, and the symbol type determination table 1 or 3 is selected based on the determination result, and the special symbol type is temporarily set. judge. Then, according to the provisionally determined special symbol type, an effect classification command determination table for the short-time gaming state A shown in FIG. 13A or 13B is selected, and the selected table and the first variation are selected. The effect classification is provisionally determined from the pattern random number.
このように、時短遊技状態Aであると仮定した場合の演出分類情報を予め導出しておくことにより、当該保留が処理される前に遊技状態が時短遊技状態Aに設定されたとしても、正確な演出分類情報に基づく演出が実行できるようにしている。 In this way, by deriving in advance the effect classification information when it is assumed that the short-time gaming state A, even if the gaming state is set to the short-time gaming state A before the suspension is processed, Production based on various production classification information can be executed.
(ステップS331−15)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS331−14で導出された演出分類コマンドを、演出分類仮判定コマンドとして演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットする。より詳細には、低確率遊技状態、かつ、時短遊技状態Aであると仮定した場合の低確用演出分類仮判定コマンドと、高確率遊技状態、かつ、時短遊技状態Aであると仮定した場合の高確用演出分類仮判定コマンドとを、演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットする。
(Step S331-15)
Next, the
これにより、遊技状態が非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合には、非時短遊技状態に対応する演出分類コマンド、発展前事前判定コマンド、発展後事前判定コマンドと、時短遊技状態Aに対応する2つの演出分類仮判定コマンドと、が送信されることとなる。 Thereby, when the gaming state is set to the non-short-time gaming state, it corresponds to the effect classification command corresponding to the non-time-short gaming state, the pre-development pre-determination command, the post-development pre-determination command, and the short-time gaming state A. Two effect classification provisional determination commands are transmitted.
(ステップS331−16)
一方、上記ステップS331−13において、現在の遊技状態は非時短遊技状態ではないと判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、現在の遊技状態が時短遊技状態Aであるかを判定する。その結果、現在の遊技状態が時短遊技状態Aであると判定した場合にはステップS331−17に処理を移し、現在の遊技状態は時短遊技状態Aではないと判定した場合にはステップS331−19に処理を移す。
(Step S331-16)
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S331-13 that the current gaming state is not the non-short-time gaming state, the
(ステップS331−17)
上記ステップS331−16において、現在の遊技状態は時短遊技状態Aであると判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、低確率遊技状態かつ非時短遊技状態であると仮定した場合の演出分類と、高確率遊技状態かつ非時短遊技状態であると仮定した場合の演出分類とを仮判定する。
(Step S331-17)
If it is determined in step S331-16 that the current gaming state is the short-time gaming state A, the
具体的には、まず、特別図柄乱数と特別図柄判定テーブル1とから大当たり、ハズレの判定結果を導出し、その判定結果に基づいて図柄種別判定テーブル1または3を選択して特別図柄種別を仮判定する。そして、仮判定された特別図柄種別に応じて、図9(a)または図9(b)に示す非時短遊技状態用の演出分類コマンド決定テーブルを選択し、当該選択したテーブルと、第1変動パターン乱数とから演出分類を仮判定する。 Specifically, first, a jackpot and loss determination result is derived from the special symbol random number and the special symbol determination table 1, and based on the determination result, the symbol type determination table 1 or 3 is selected and the special symbol type is temporarily set. judge. Then, according to the tentatively determined special symbol type, an effect classification command determination table for the non-short game state shown in FIG. 9A or 9B is selected, and the selected table and the first variation are selected. The effect classification is provisionally determined from the pattern random number.
また、これと同様に、特別図柄乱数と特別図柄判定テーブル2とから大当たり、ハズレの判定結果を導出し、その判定結果に基づいて図柄種別判定テーブル1または3を選択して特別図柄種別を仮判定する。そして、仮判定された特別図柄種別に応じて、図9(a)または図9(b)に示す非時短遊技状態用の演出分類コマンド決定テーブルを選択し、当該選択したテーブルと、第1変動パターン乱数とから演出分類を仮判定する。 Similarly, a big hit and loss determination result is derived from the special symbol random number and the special symbol determination table 2, and the symbol type determination table 1 or 3 is selected based on the determination result, and the special symbol type is temporarily set. judge. Then, according to the tentatively determined special symbol type, an effect classification command determination table for the non-short game state shown in FIG. 9A or 9B is selected, and the selected table and the first variation are selected. The effect classification is provisionally determined from the pattern random number.
このように、非時短遊技状態であると仮定した場合の演出分類情報を予め導出しておくことにより、当該保留が処理される前に遊技状態が非時短遊技状態に設定されたとしても、正確な演出分類情報に基づく演出が実行できるようにしている。 Thus, by deriving in advance the effect classification information when it is assumed that it is a non-short game state, even if the game state is set to a non-short game state before the suspension is processed, Production based on various production classification information can be executed.
(ステップS331−18)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS331−17で導出された演出分類コマンドを、演出分類仮判定コマンドとして演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットする。より詳細には、低確率遊技状態、かつ、非時短遊技状態であると仮定した場合の低確用演出分類仮判定コマンドと、高確率遊技状態、かつ、非時短遊技状態であると仮定した場合の高確用演出分類仮判定コマンドとを、演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットする。
(Step S331-18)
Next, the
これにより、遊技状態が時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合には、時短遊技状態Aに対応する演出分類コマンド、発展前事前判定コマンド、発展後事前判定コマンドと、非時短遊技状態に対応する2つの演出分類仮判定コマンドと、が送信されることとなる。 Thereby, when the gaming state is set to the short-time gaming state A, it corresponds to the effect classification command, the pre-development advance judgment command, the post-evolution advance judgment command corresponding to the short-time gaming state A, and the non-short-time gaming state. Two effect classification provisional determination commands are transmitted.
(ステップS331−19)
次に、メインCPU100aは、第1保留または第2保留が記憶されたことを示す始動入賞コマンドを生成して演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットし、事前判定処理(第1始動口検出スイッチ入力処理)を終了する。
(Step S331-19)
Next, the
なお、この事前判定処理は第2始動口22に遊技球が入球した場合にも同様に行われる。
This pre-determination process is similarly performed when a game ball enters the
図24は、上記ステップS350のゲート検出スイッチ入力処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 24 is a flowchart for explaining the gate detection switch input process in step S350.
(ステップS350−1)
まず、メインCPU100aは、ゲート検出スイッチ24aから検出信号が入力されたか否かを判定する。その結果、ゲート検出スイッチ24aから検出信号が入力されたと判定した場合にはステップS350−2に処理を移し、ゲート検出スイッチ24aから検出信号が入力されていないと判定した場合には、当該ゲート検出スイッチ入力処理を終了する。
(Step S350-1)
First, the
(ステップS350−2)
上記ステップS350−1において、ゲート検出スイッチ24aから検出信号が入力されたと判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、普図保留数(Y)が4未満であるかを判定する。その結果、普図保留数(Y)<4と判定した場合にはステップS350−3に処理を移し、普図保留数(Y)≧4と判定した場合には、当該ゲート検出スイッチ入力処理を終了する。
(Step S350-2)
If it is determined in step S350-1 that a detection signal has been input from the
(ステップS350−3)
上記ステップS350−2において、普図保留数(Y)<4と判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、普図保留数(Y)に「1」加算した値を新たな普図保留数(Y)として記憶する。
(Step S350-3)
If it is determined in step S350-2 that the number of reserved maps (Y) <4, the
(ステップS350−4)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS200で更新された普通図柄乱数を取得して普通図柄保留記憶領域に記憶して、当該ゲート検出スイッチ入力処理を終了する。なお、普通図柄保留記憶領域は、第1記憶部〜第4記憶部の4つの記憶部を有しており、普通図柄乱数が取得されると、第1記憶部から順に普通図柄乱数が記憶されていない空きの記憶部が検索され、空いている記憶部のうちもっとも番号(序数)の小さい記憶部に、取得した普通図柄乱数が記憶される。以下では、普通図柄保留記憶領域の記憶部に記憶された普通図柄乱数を普図保留とよぶ。
(Step S350-4)
Next, the
次に、図25〜図31を用いて、主制御基板100において実行される上記の特別図柄遊技に係る処理について説明する。
Next, a process related to the special symbol game executed on the
図25は、上記ステップS400の特図特電処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 25 is a flowchart for explaining the special figure special electric processing in step S400.
(ステップS410)
まず、メインCPU100aは、特図特電データの値をロードする。この特図特電データとしては、特別図柄変動開始処理の実行を示すデータ「00」と、特別図柄変動停止処理の実行を示すデータ「01」と、停止後処理の実行を示すデータ「02」と、特別電動役物制御処理の実行を示すデータ「03」と、特別遊技終了処理の実行を示すデータ「04」と、が設けられている。
(Step S410)
First, the
次に、メインCPU100aは、特別図柄変動開始処理(ステップS420)、特別図柄変動停止処理(ステップS430)、停止後処理(ステップS440)、特別電動役物制御処理(ステップS450)、特別遊技終了処理を実行するが、これら各処理について、以下に、図面を参照して説明する。
Next, the
図26は、上記ステップS420の特別図柄変動開始処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 26 is a flowchart for explaining the special symbol variation start process in step S420.
(ステップS420−1)
まず、メインCPU100aは、特図特電データが、特別図柄変動開始処理の実行を示すデータ「00」であるか否かを判定する。その結果、特図特電データ=00と判定した場合にはステップS420−2に処理を移し、特図特電データ=00ではないと判定した場合には当該特別図柄変動開始処理を終了する。
(Step S420-1)
First, the
(ステップS420−2)
上記ステップS420−1において、特図特電データ=00であると判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、保留記憶領域に第1保留または第2保留が記憶されているかを判定する。その結果、第1保留または第2保留が記憶されていると判定した場合にはステップS420−3に処理を移し、第1保留または第2保留は記憶されていないと判定した場合にはステップS420−8に処理を移す。
(Step S420-2)
If it is determined in step S420-1 that the special figure special electricity data = 00, the
(ステップS420−3)
上記ステップS420−2において、保留記憶領域に第1保留または第2保留が記憶されていると判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、保留記憶領域に記憶されている保留をシフトする処理を行う。具体的には、第1記憶部に記憶されている乱数を所定の処理領域に複写するとともに、第2記憶部に記憶されている各乱数を第1記憶部にシフトさせて記憶する。同様に、第2記憶部〜第8記憶部に各乱数が記憶されている場合には、これら各乱数を番号(序数)の1つ小さい記憶部にシフトさせる。これにより、第1保留および第2保留は、留保された順に処理領域に書き込まれることとなる。したがって、記憶部に記憶された第1保留および第2保留は、先に記憶された乱数から順に読み出されて、大当たりの抽選を行う際の判定に用いられることとなる。また、このとき、第1保留数(X1)または第2保留数(X2)から「1」減算した値を新たな第1保留数(X1)または第2保留数(X2)として記憶する。
(Step S420-3)
If it is determined in step S420-2 that the first hold or the second hold is stored in the hold storage area, the
(ステップS420−4)
次に、メインCPU100aは、特別図柄判定テーブル(図4参照)および図柄種別判定テーブル(図5参照)のうち、現在の遊技状態に対応するテーブルを選択する。そして、上記ステップS420−3において処理領域に書き込まれた特別図柄乱数および大当たり乱数を、それぞれ選択したテーブルに基づいて判定して、いずれかの特別図柄を決定するとともに、当該決定した特別図柄に対応するデータを、メインRAM100cの所定の領域に記憶する。また、この特別図柄決定処理においては、現在の遊技状態、すなわち、特別図柄を決定したときの遊技状態が遊技状態バッファに記憶される。
(Step S420-4)
Next, the
(ステップS421)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS420−3において処理領域に上書きされた変動パターン乱数を、各テーブルに基づいて判定することにより変動パターンを決定する。この変動パターン決定処理については、図27を用いて後述する。
(ステップS420−5)
次に、メインCPU100aは、第1特別図柄表示器80または第2特別図柄表示器82において、特別図柄の変動表示を開始するための変動表示データをセットする。これにより、第1保留に基づいて特別図柄の変動表示が行われる場合には、第1特別図柄表示器80が点滅表示を開始するとともに、第2保留に基づいて特別図柄の変動表示が行われる場合には、第2特別図柄表示器82が点滅表示を開始する。なお、ここで制御される点滅表示とは、各表示器82、84において「−」が所定の間隔で点滅することをいうものである。また、第1保留に基づいて特別図柄の変動表示が行われる場合には、変動表示の開始と同時に、第1保留が1つ減ることを示すように、第1特別図柄保留表示器84が表示制御され、第2保留に基づいて特別図柄の変動表示が行われる場合には、変動表示の開始と同時に、第2保留が1つ減ることを示すように、第2特別図柄保留表示器86が表示制御される。
(Step S421)
Next, the
(Step S420-5)
Next, the
(ステップS420−6)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS421で決定した変動時間を変動時間カウンタにセットする。
(Step S420-6)
Next, the
(ステップS420−7)
次に、メインCPU100aは、特図特電処理において特別図柄変動停止処理が実行されるように、特図特電データに「01」をセットし、当該特別図柄変動開始処理を終了する。
(Step S420-7)
Next, the
(ステップS420−8)
また、上記ステップS420−2において、第1保留および第2保留のいずれも記憶されていないと判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、デモ判定処理を実行する。このデモ判定処理において、メインCPU100aは、特別図柄の変動表示が行われていない時間を計時するとともに、所定時間にわたって特別図柄の変動表示が行われない場合には、演出表示部50aにデモ画面を表示するためのデモコマンドを演出用伝送データ格納領域に記憶する。
(Step S420-8)
If it is determined in step S420-2 that neither the first hold nor the second hold is stored, the
図27は、上記ステップS421の変動パターン決定処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 27 is a flowchart for explaining the variation pattern determination process in step S421.
(ステップS421−1)
まず、メインCPU100aは、始動口種別(第1始動口または第2始動口)、特別図柄決定処理によって決定された特別図柄の種別、および設定されている遊技状態を判定し、演出分類決定テーブル(図9、図13参照)を選択する。
(Step S421-1)
First, the
(ステップS421−2)
次に、メインCPU100aは、処理領域に記憶された第1変動パターン乱数と、上記ステップS421−1で選択した演出分類決定テーブルとに基づいて演出分類を判定する。
(Step S421-2)
Next, the
(ステップS421−3)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS421−2で判定された演出分類に対応する発展前変動パターンコマンド決定テーブルを選択する(図11、図15参照)。
(Step S421-3)
Next, the
(ステップS421−4)
次に、メインCPU100aは、処理領域に記憶された第2変動パターン乱数Aと、上記ステップS421−3で選択した発展前変動パターンコマンド決定テーブルとに基づいて、発展前変動パターンコマンドを判定する。
(Step S421-4)
Next, the
(ステップS421−5)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS421−4で判定された発展前変動パターンコマンドを演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットする。
(Step S421-5)
Next, the
(ステップS421−6)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS421−2で判定された演出分類に対応する発展後変動パターンコマンド決定テーブルを選択する(図12、図16参照)。
(Step S421-6)
Next, the
(ステップS421−7)
次に、メインCPU100aは、処理領域に記憶された第2変動パターン乱数Bと、上記ステップS421−6で選択した発展後変動パターンコマンド決定テーブルとに基づいて、発展後変動パターンコマンドを判定する。
(Step S421-7)
Next, the
(ステップS421−8)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS421−7で判定された発展後変動パターンコマンドを演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットする。
(Step S421-8)
Next, the
(ステップS421−9)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS421−4で判定された発展前変動パターンの変動時間と、上記ステップS421−7で判定された発展後変動パターンの変動時間とから、合計変動時間を演算して当該変動パターン決定処理を終了する。
(Step S421-9)
Next, the
図28は、上記ステップS430の特別図柄変動停止処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 28 is a flowchart for explaining the special symbol variation stopping process in step S430.
(ステップS430−1)
まず、メインCPU100aは、特図特電データが、特別図柄変動停止処理の実行を示すデータ「01」であるか否かを判定する。その結果、特図特電データ=01と判定した場合にはステップS430−2に処理を移し、特図特電データ=01ではないと判定した場合には当該特別図柄変動停止処理を終了する。
(Step S430-1)
First, the
(ステップS430−2)
上記ステップS430−1において、特図特電データ=01と判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、変動時間(ステップS420−6でセット)が経過したか否かを判定する。その結果、変動時間が経過したと判定した場合にはステップS430−3に処理を移し、変動時間は経過していないと判定した場合には当該特別図柄変動停止処理を終了する。
(Step S430-2)
If it is determined in step S430-1 that special figure special electricity data = 01, the
(ステップS430−3)
上記ステップS430−2において、変動時間が経過したと判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS420−4で決定、記憶された特別図柄を、第1特別図柄表示器80または第2特別図柄表示器82に停止表示するための停止表示データをセットする。
(Step S430-3)
If it is determined in step S430-2 that the variation time has elapsed, the
(ステップS430−4)
次に、メインCPU100aは、図柄が確定したことを示す図柄確定コマンドを演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットする。
(Step S430-4)
Next, the
(ステップS430−5)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記のようにして特別図柄の停止表示を開始したら、停止表示時間カウンタに図柄を停止表示する時間をセットする。
(Step S430-5)
Next, when the
(ステップS430−6)
次に、メインCPU100aは、特図特電処理において停止後処理が実行されるように、特図特電データに「02」をセットし、当該特別図柄変動停止処理を終了する。
(Step S430-6)
Next, the
図29は、上記ステップS440の停止後処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 29 is a flowchart for explaining the post-stop processing in step S440.
(ステップS440−1)
まず、メインCPU100aは、特図特電データが、停止後処理の実行を示すデータ「02」であるか否かを判定する。その結果、特図特電データ=02と判定した場合にはステップS440−2に処理を移し、特図特電データ=02ではないと判定した場合には当該停止後処理を終了する。
(Step S440-1)
First, the
(ステップS440−2)
上記ステップS440−1において、特図特電データ=02と判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、停止表示時間(ステップS430−5でセット)が経過したか否かを判定する。その結果、停止表示時間は経過していないと判定した場合には当該停止後処理を終了し、停止表示時間を経過したと判定した場合にはステップS440−3に処理を移す。
(Step S440-2)
If it is determined in step S440-1 that special figure special electricity data = 02, the
(ステップS440−3)
上記ステップS440−2において、停止表示時間が経過したと判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、時短遊技状態設定処理を行う。ここでは、メインCPU100aは、現在の遊技状態が時短遊技状態Aであることを示す時短遊技フラグAや、時短遊技状態Bであることを示す時短遊技フラグB等がオンしているか否かを判定する。そして、いずれかの時短遊技フラグがオンしている場合には、メインRAM100cに設けられた時短回数記憶領域を更新する。この時短回数記憶領域には、当該時短遊技状態が終了するまでの残り変動回数(継続回数)が記憶されており、ここでは、現在、記憶されている残り変動回数から「1」減算した値を新たな残り変動回数として記憶することとなる。なお、残り変動回数を更新した結果、残り変動回数=0となった場合には、同時に時短遊技フラグをオフする処理が行われることとなる。また、時短遊技フラグはオンしていないと判定した場合には、そのまま次のステップS440−4に処理を移す。
(Step S440-3)
If it is determined in step S440-2 that the stop display time has elapsed, the
(ステップS440−4)
次に、メインCPU100aは、高確率遊技状態設定処理を行う。ここでは、メインCPU100aは、現在の遊技状態が高確率遊技状態であることを示す高確遊技フラグがオンしているか否かを判定する。そして、高確遊技フラグがオンしている場合には、メインRAM100cに設けられた高確回数記憶領域を更新する。この高確回数記憶領域には、高確率遊技状態が終了するまでの残り変動回数(継続回数)が記憶されており、ここでは、現在、記憶されている残り変動回数から「1」減算した値を新たな残り変動回数として記憶することとなる。なお、残り変動回数を更新した結果、残り変動回数=0となった場合には、同時に高確遊技フラグをオフする処理が行われることとなる。また、高確遊技フラグはオンしていないと判定した場合には、そのまま次のステップS440−5に処理を移す。
(Step S440-4)
Next, the
(ステップS440−5)
次に、メインCPU100aは、停止表示されている図柄が大当たり図柄であるかを判定する。その結果、停止表示されている図柄は大当たり図柄ではないと判定した場合にはステップS440−6に処理を移し、停止表示されている図柄は大当たり図柄であると判定した場合にはステップS440−7に処理を移す。
(Step S440-5)
Next, the
(ステップS440−6)
上記ステップS440−5において、停止表示されている図柄は大当たり図柄ではないと判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、特図特電処理において特別図柄変動開始処理が実行されるように、特図特電データに「00」をセットし、当該停止後処理を終了する。これにより、次の特別図柄の変動表示が開始可能となる。
(Step S440-6)
If it is determined in step S440-5 that the symbol that has been stopped is not a jackpot symbol, the
(ステップS440−7)
一方、上記ステップS440−5において、停止表示されている図柄は大当たり図柄であると判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、現在の遊技状態を遊技状態バッファに記憶した後、遊技状態(高確遊技フラグ、高確残り変動回数、時短遊技フラグ、時短残り変動回数)をリセットする処理を行う。
(Step S440-7)
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S440-5 that the symbol that has been stopped is a jackpot symbol, the
(ステップS440−8)
次に、メインCPU100aは、特図特電処理において特別電動役物制御処理が実行されるように、特図特電データに「03」をセットする。これにより、大当たり図柄が停止表示した後に特別遊技が開始されることとなる。
(Step S440-8)
Next, the
(ステップS440−9)
次に、メインCPU100aは、現在の遊技状態を確認し、遊技状態コマンドを演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットして当該停止後処理を終了する。
(Step S440-9)
Next, the
図30は、上記ステップS450の特別電動役物制御処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 30 is a flowchart for explaining the special electric accessory control process in step S450.
(ステップS450−1)
まず、メインCPU100aは、特図特電データが、特別電動役物制御処理の実行を示すデータ「03」であるか否かを判定する。その結果、特図特電データ=03と判定した場合にはステップS450−2に処理を移し、特図特電データ=03ではないと判定した場合には当該特別電動役物制御処理を終了する。
(Step S450-1)
First, the
(ステップS450−2)
上記ステップS450−1において、特図特電データ=03と判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、特別遊技実行処理を行う。ここでは、ラウンド遊技が開始する前のオープニング処理、図6に示す作動テーブル1、2を参照して行われるラウンド遊技実行処理、ラウンド遊技の終了後のエンディング処理が行われる。また、ここでは、オープニング処理の開始時にオープニングコマンドがセットされ、各ラウンド遊技の開始時にラウンド開始コマンドがセットされ、エンディング処理の開始時にエンディングコマンドがセットされる。そして、これらの各コマンドを受信すると、副制御基板200において特別遊技中の演出が実行される。
(Step S450-2)
If it is determined in step S450-1 that special figure special electricity data = 03, the
(ステップS450−3)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS450−2における特別遊技実行処理によって特別遊技が終了したか、より具体的には、全てのラウンド遊技が終了するとともに、エンディング処理によって計時されるエンディング時間が経過したかを判定する。その結果、特別遊技が終了したと判定した場合にはステップS450−4に処理を移し、特別遊技は終了していないと判定した場合には、そのまま当該特別電動役物制御処理を終了する。
(Step S450-3)
Next, the
(ステップS450−4)
上記ステップS450−3において、特別遊技は終了したと判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、特図特電処理において特別遊技終了処理が実行されるように、特図特電データに「04」をセットし、当該特別電動役物制御処理を終了する。
(Step S450-4)
If it is determined in step S450-3 that the special game has ended, the
図31は、上記ステップS460の特別遊技終了処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 31 is a flowchart for explaining the special game end processing in step S460.
(ステップS460−1)
まず、メインCPU100aは、特図特電データが、特別遊技終了処理の実行を示すデータ「04」であるか否かを判定する。その結果、特図特電データ=04と判定した場合にはステップS460−2に処理を移し、特図特電データ=04ではないと判定した場合には当該特別遊技終了処理を終了する。
(Step S460-1)
First, the
(ステップS460−2)
上記ステップS460−1において、特図特電データ=04であると判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、メインRAM100cに記憶された特別図柄データおよび遊技状態バッファにある遊技状態データをロードする。そして、図7に示す遊技状態設定テーブルを参照し、これら特別図柄データに基づいて、特別遊技の終了後の遊技状態を設定する。具体的には、高確遊技フラグ、高確継続回数(残り変動回数)、時短遊技フラグ、時短継続回数(残り変動回数)を設定する。
(Step S460-2)
If it is determined in step S460-1 that the special figure special power data = 04, the
(ステップS460−3)
次に、メインCPU100aは、遊技状態を確認し、遊技状態指定コマンドを演出用伝送データ格納領域にセットする。この遊技状態指定コマンドは、上記ステップS460−2で設定された高確遊技フラグ、高確継続回数(残り変動回数)、時短遊技フラグ、時短継続回数(残り変動回数)、特別遊技の実行契機となった大当たり図柄の種別に係る情報を有している。
(Step S460-3)
Next, the
(ステップS460−4)
次に、メインCPU100aは、特図特電処理において特別図柄変動開始処理が実行されるように、特図特電データに「00」をセットし、当該特別遊技終了処理を終了する。
(Step S460-4)
Next, the
次に、図32〜図36を用いて、主制御基板100において実行される上記の普通図柄遊技に係る処理について説明する。
Next, processing related to the above-described normal symbol game executed on the
図32は、上記ステップS500の普図普電処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 32 is a flow chart for explaining the ordinary power transmission process in step S500.
(ステップS510)
まず、メインCPU100aは、普図普電データの値をロードする。この普図普電データは、普通図柄変動開始処理の実行を示すデータ「10」と、普通図柄変動停止処理の実行を示すデータ「11」と、普通図柄停止後処理の実行を示すデータ「12」と、普通電動役物制御処理の実行を示すデータ「13」と、が設けられている。
(Step S510)
First, the
次に、メインCPU100aは、普通図柄変動開始処理(ステップS520)、普通図柄変動停止処理(ステップS530)、普通図柄停止後処理(ステップS540)、普通電動役物制御処理(ステップS550)を実行する。これら各処理について、以下に、図面を参照して説明する。
Next, the
図33は、上記ステップS520の普通図柄変動開始処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 33 is a flowchart for explaining the normal symbol variation start process in step S520.
(ステップS520−1)
まず、メインCPU100aは、普図普電データが、普通図柄変動開始処理の実行を示すデータ「10」であるか否かを判定する。その結果、普図普電データ=10と判定した場合にはステップS520−2に処理を移し、普図普電データ=10ではないと判定した場合には当該普通図柄変動開始処理を終了する。
(Step S520-1)
First, the
(ステップS520−2)
上記ステップS520−1において、普図普電データ=10と判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、普図保留数(Y)が1以上であるかを判定する。その結果、普図保留数(Y)≧1と判定した場合にはステップS520−3に処理を移し、普図保留数(Y)<1と判定した場合には当該普通図柄変動開始処理を終了する。
(Step S520-2)
If it is determined in step S520-1 that the normal map / general power data = 10, the
(ステップS520−3)
上記ステップS520−2において、普図保留数(Y)≧1と判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、普図保留数(Y)から「1」減算した値を新たな普図保留数(Y)として記憶する。
(Step S520-3)
If it is determined in step S520-2 that the number of reserved maps (Y) ≧ 1, the
(ステップS520−4)
次に、メインCPU100aは、普通図柄保留記憶領域に記憶されている普図保留をシフトする処理を行う。具体的には、第1記憶部に記憶されている普通図柄乱数を所定の処理領域に複写するとともに、第2記憶部〜第4記憶部に普通図柄乱数が記憶されている場合には、これら各乱数を1つ番号(序数)の小さい記憶部にシフトさせる。具体的には、第1記憶部に記憶されている乱数を所定の処理領域に複写するとともに、第2記憶部に記憶されている乱数を第1記憶部にシフトさせて記憶する。同様に、第3記憶部および第4記憶部に乱数が記憶されている場合には、これら各乱数を番号(序数)の1つ小さい記憶部にシフトさせる。これにより、普通図柄保留記憶領域に記憶された普図保留は、記憶された順に処理領域に書き込まれることとなる。つまり、普通図柄保留記憶領域に記憶された乱数は、先に記憶された乱数から順に読み出されて、当選判定処理に用いられることとなる。
(Step S520-4)
Next, the
(ステップS520−5)
次に、メインCPU100aは、処理領域に複写された普通図柄乱数の当選判定処理を行う。具体的には、現在の遊技状態が非時短遊技状態である場合には、図17(a)に示す普通図柄判定テーブル1を参照して、処理領域に複写された普通図柄乱数を判定する。また、現在の遊技状態が時短遊技状態である場合には、図17(b)に示す普通図柄判定テーブル2を参照して、処理領域に複写された普通図柄乱数を判定する。
(Step S520-5)
Next, the
(ステップS520−6)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS520−5の当選判定処理の結果が当選であるか否かを判定する。その結果、当選の判定結果が得られた場合にはステップS520−7に処理を移し、当選ではなくハズレの判定結果が得られた場合にはステップS520−8に処理を移す。
(Step S520-6)
Next, the
(ステップS520−7)
上記ステップS520−6において、判定結果が当選であると判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、当たり図柄データをメインRAM100cの所定の領域に記憶する。
(Step S520-7)
If it is determined in step S520-6 that the determination result is winning, the
(ステップS520−8)
一方、上記ステップS520−6において、判定結果がハズレであると判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、ハズレ図柄データをメインRAM100cの所定の領域に記憶する。
(Step S520-8)
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S520-6 that the determination result is a loss, the
(ステップS520−9)
次に、メインCPU100aは、現在の遊技状態が、非時短遊技状態または時短遊技状態のいずれに設定されているかを確認するとともに、現在の遊技状態に応じて普図変動時間をセットする。具体的には、図18(a)に示すように、現在の遊技状態が非時短遊技状態である場合には、普図変動時間カウンタに20秒をセットし、時短遊技状態である場合には普図変動時間カウンタに1秒をセットする。
(Step S520-9)
Next, the
(ステップS520−10)
次に、メインCPU100aは、普通図柄の変動表示を開始するための変動表示データをセットする。これにより、普通図柄の変動表示が行われる場合には、普通図柄表示器88が点滅表示を開始する。また、普通図柄の変動表示が開始するのと同時に、普図保留が1つ減ることを示すように、普通図柄保留表示器90が表示制御される。
(Step S520-10)
Next, the
(ステップS520−11)
次に、メインCPU100aは、現在の遊技状態を変動開始時の遊技状態として遊技状態バッファに記憶する。
(Step S520-11)
Next, the
(ステップS520−12)
次に、メインCPU100aは、普図普電処理において普通図柄変動停止処理が実行されるように、普図普電データに「11」をセットし、当該普通図柄変動開始処理を終了する。
(Step S520-12)
Next, the
図34は、上記ステップS530の普通図柄変動停止処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 34 is a flowchart for explaining the normal symbol fluctuation stopping process in step S530.
(ステップS530−1)
まず、メインCPU100aは、普図普電データが、普通図柄変動停止処理の実行を示すデータ「11」であるか否かを判定する。その結果、普図普電データ=11と判定した場合にはステップS530−2に処理を移し、普図普電データ=11ではないと判定した場合には当該普通図柄変動停止処理を終了する。
(Step S530-1)
First, the
(ステップS530−2)
上記ステップS530−1において、普図普電データ=11と判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、普図変動時間(ステップS520−9でセット)が経過したかを判定する。その結果、普図変動時間が経過したと判定した場合にはステップS530−3に処理を移し、普図変動時間は経過していないと判定した場合には当該普通図柄変動停止処理を終了する。
(Step S530-2)
If it is determined in step S530-1 that the normal map power transmission data = 11, the
(ステップS530−3)
上記ステップS530−2において、普図変動時間が経過したと判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、普通図柄表示器88に普通図柄を停止表示するための停止表示データをセットする。
(Step S530-3)
If it is determined in step S530-2 that the normal symbol change time has elapsed, the
(ステップS530−4)
次に、メインCPU100aは、上記のようにして普通図柄の停止表示を開始したら、停止表示時間カウンタに図柄を停止表示する時間をセットする。
(Step S530-4)
Next, when the
(ステップS530−5)
次に、メインCPU100aは、普図普電処理において普通図柄停止後処理が実行されるように、普図普電データに「12」をセットし、当該普通図柄変動停止処理を終了する。
(Step S530-5)
Next, the
図35は、上記ステップS540の普通図柄停止後処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 35 is a flowchart for explaining the normal symbol stop post-processing in step S540.
(ステップS540−1)
まず、メインCPU100aは、普図普電データが、普通図柄停止後処理の実行を示すデータ「12」であるか否かを判定する。その結果、普図普電データ=12と判定した場合にはステップS540−2に処理を移し、普図普電データ=12ではないと判定した場合には当該普通図柄停止後処理を終了する。
(Step S540-1)
First, the
(ステップS540−2)
上記ステップS540−1において、普図普電データ=12と判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、停止表示時間(ステップS530−4でセット)が経過したか否かを判定する。その結果、停止表示時間は経過していないと判定した場合には当該普通図柄停止後処理を終了し、停止表示時間を経過したと判定した場合にはステップS540−3に処理を移す。
(Step S540-2)
If it is determined in step S540-1 that the normal power data is 12, the
(ステップS540−3)
上記ステップS540−2において、停止表示時間が経過したと判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、停止表示されている図柄が当たり図柄であるかを判定する。その結果、停止表示されている図柄は当たり図柄ではないと判定した場合にはステップS540−5に処理を移し、停止表示されている図柄は当たり図柄であると判定した場合にはステップS540−4に処理を移す。
(Step S540-3)
If it is determined in step S540-2 that the stop display time has elapsed, the
(ステップS540−4)
上記ステップS540−3において、停止表示されている図柄は当たり図柄であると判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、普図普電処理において普通電動役物制御処理が実行されるように、普図普電データに「13」をセットし、当該普通図柄停止後処理を終了する。
(Step S540-4)
If it is determined in step S540-3 that the symbol that has been stopped is a winning symbol, the
(ステップS540−5)
一方、上記ステップS540−3において、停止表示されている図柄は当たり図柄ではない(ハズレ図柄である)と判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、普図普電処理において普通図柄変動開始処理が実行されるように、普図普電データに「10」をセットし、当該普通図柄停止後処理を終了する。
(Step S540-5)
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S540-3 that the symbol that has been stopped is not a winning symbol (is a lost symbol), the
図36は、上記ステップS550の普通電動役物制御処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 36 is a flowchart for explaining the ordinary electric accessory control process in step S550.
(ステップS550−1)
まず、メインCPU100aは、普図普電データが、普通電動役物制御処理の実行を示すデータ「13」であるか否かを判定する。その結果、普図普電データ=13と判定した場合にはステップS550−2に処理を移し、普図普電データ=13ではないと判定した場合には当該普通電動役物制御処理を終了する。
(Step S550-1)
First, the
(ステップS550−2)
上記ステップS550−1において、普図普電データ=13と判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、普通電動役物が制御中であるか、すなわち、すでに始動口開閉ソレノイド22cが通電制御中であるかを判定する。その結果、普通電動役物が制御中であると判定した場合には、ステップS550−5に処理を移し、普通電動役物は制御中ではないと判定した場合にはステップS550−3に処理を移す。
(Step S550-2)
If it is determined in step S550-1 that the ordinary power / general power data = 13, the
(ステップS550−3)
上記ステップS550−2において、普通電動役物は制御中ではないと判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、普通図柄の変動開始時の遊技状態が、非時短遊技状態または時短遊技状態のいずれであったかを判定する。
(Step S550-3)
If it is determined in step S550-2 that the normal electric accessory is not being controlled, the
(ステップS550−4)
次に、メインCPU100aは、始動口開閉ソレノイド22cの通電制御を開始すべく、上記ステップS550−3において確認した遊技状態に応じて通電制御データをセットする。具体的には、普通図柄の変動開始時の遊技状態が非時短遊技状態であった場合には始動口開閉ソレノイド22cの通電制御データとして、開放回数=1回、1回の開放時間=0.1秒となる通電制御データをセットする。また、普通図柄の変動開始時の遊技状態が時短遊技状態であった場合には、開放回数=2回、1回の開放時間=2.9秒となる通電制御データをセットする。
(Step S550-4)
Next, the
(ステップS550−5)
また、上記ステップS550−2において、普通電動役物が制御中であると判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS550−4でセットされた通電時間を経過したかを判定する。その結果、通電時間を経過したと判定した場合にはステップS550−6に処理を移し、通電時間は経過していないと判定した場合には当該普通電動役物制御処理を終了する。
(Step S550-5)
If it is determined in step S550-2 that the ordinary electric accessory is being controlled, the
(ステップS550−6)
上記ステップS550−5において、通電時間が経過したと判定した場合には、メインCPU100aは、始動口開閉ソレノイド22cの通電を停止する処理を行う。
(Step S550-6)
If it is determined in step S550-5 that the energization time has elapsed, the
(ステップS550−7)
次に、メインCPU100aは、普図普電処理において普通図柄変動開始処理が実行されるように、普図普電データに「10」をセットし、当該普通図柄停止後処理を終了する。
(Step S550-7)
Next, the
以上のように、主制御基板100において各種の処理が実行されることにより、特別図柄遊技および普通図柄遊技が進行することとなるが、こうした遊技の進行中には、主制御基板100から送信されるコマンドに基づいて、副制御基板200において、さまざまな演出を実行するための制御が行われる。以下では、副制御基板200において決定、制御され、特別図柄の変動表示中に演出表示部50aに表示される変動演出について、具体的に説明する。
As described above, the special symbol game and the normal symbol game are progressed by executing various processes in the
本実施形態においては、遊技状態ごとに種々の演出が行われるが、ここではまず、非時短遊技状態における演出の一例について説明する。 In this embodiment, various effects are performed for each gaming state. Here, an example of effects in the non-time-saving gaming state will be described first.
図37は、非時短遊技状態における変動演出の一例を説明する図である。この図に示すように、非時短遊技状態においては、演出表示部50aに表示される3つの演出図柄40a、40b、40cの組み合わせによって、大当たりの抽選結果を遊技者に報知するようにしている。
FIG. 37 is a diagram for explaining an example of the variation effect in the non-time-saving gaming state. As shown in this figure, in the non-time-saving gaming state, the player is notified of the jackpot lottery result by a combination of the three
演出図柄40a、40b、40cのそれぞれは、1〜8の数字が記された8種類の図柄から構成されている。そして、特別図柄の変動表示中には、演出図柄40a、40b、40cのそれぞれが、8種類の図柄を縦方向にスクロール表示(変動表示)する。なお、図37(b)における矢印は、演出図柄40a、40b、40cが変動表示中(縦方向のスクロール表示中)であることを示している。そして、特別図柄の変動表示が終了して、第1特別図柄表示器80または第2特別図柄表示器82に特別図柄が停止表示するのとほぼ同じタイミングで、演出表示部50aに、全ての演出図柄40a、40b、40cが停止表示される。
Each of the
図38は、大当たり時に演出表示部50aに停止表示される演出図柄40a、40b、40cの組み合わせパターンを示す図である。この図に示すように、本実施形態においては、大当たり時の図柄組み合わせパターンとして8パターン設けられており、大当たりに当選した場合には、最終的に演出表示部50aに演出図柄40a、40b、40cが全て同一の図柄で停止表示されることとなる。
FIG. 38 is a diagram illustrating a combination pattern of
そして、演出図柄40a、40b、40cが停止表示するまでの間には、演出図柄40a、40b、40cがさまざまな態様で変動表示されるとともに、演出表示部50aにさまざまな画像が表示されることとなる。
Then, until the
図39は、非時短遊技状態における「リーチなし演出」の一例を示す図である。「リーチなし演出」においては、図39(a)に示すように、演出図柄40a、40b、40cが変動表示を開始してから所定時間経過後に、図39(b)に示すように、まず、演出図柄40aが停止表示する。その後、さらに所定時間経過後に、図39(c)に示すように、演出図柄40cが演出図柄40aと異なる図柄で停止表示し、その後、さらに所定時間が経過したところで、図39(d)に示すように、最後に演出図柄40bが停止表示する。このとき、演出図柄40a、40b、40cの全てが同一の図柄で停止表示することはなく、これによって大当たりの抽選結果がハズレであったことが遊技者に報知される。
FIG. 39 is a diagram illustrating an example of the “no reach effect” in the non-time-saving gaming state. In the “no reach effect”, as shown in FIG. 39 (a), as shown in FIG. 39 (b), as shown in FIG. 39 (b), after the predetermined time elapses after the
なお、この「リーチなし演出」は、主制御基板100において、「不定通常ハズレ」、「固定通常ハズレ」の演出分類が決定されて(図9参照)、「12秒ハズレ」、「7秒ハズレ」、「4秒ハズレ」、「特殊パターン1〜3」の発展前変動パターンコマンドを受信した場合に実行される(図11参照)。「不定通常ハズレ」、「固定通常ハズレ」の演出分類が決定された場合には、必ず、「後半なし1」の発展後変動パターンコマンドがセットされて送信される。「後半なし1」の発展後変動パターンコマンドを受信した場合には、発展後の変動演出が行われず(決定されず)、発展前の変動演出のみで終了するため、「リーチなし演出」の具体的な内容は、発展前変動パターンコマンドのみによって決定されることとなる。
The “reach-less effect” is determined on the
図40は、非時短遊技状態における「リーチ演出」の一例を示す図である。「リーチ演出」においては、図40(a)に示すように、演出図柄40a、40b、40cが変動表示を開始してから所定時間経過後に、図40(b)に示すように、まず、演出図柄40aが停止表示する。その後、さらに所定時間経過後に、図40(c)に示すように、演出図柄40cが演出図柄40aと同じ図柄で停止表示する。
FIG. 40 is a diagram illustrating an example of “reach effect” in the non-time-saving gaming state. In the “reach effect”, as shown in FIG. 40 (a), as shown in FIG. 40 (b), after the predetermined time has elapsed since the
このとき、図40(d)に示すように、演出図柄40bが変動表示を継続したままの状態で、演出表示部50aにおいて、「リーチ」という文字が、演出図柄40a、40b、40cに重畳表示される。その後、図40(e)に示すように、演出表示部50aがブラックアウトするとともに演出図柄40a、40b、40cの表示面積が小さくなって、演出表示部50aの右上の表示領域に表示される。そして、図40(f)に示すように、演出表示部50aにおいて、種々のキャラクタが登場するキャラクタ演出画像が表示され、図40(g)に示すように、演出図柄40a、40b、40cの表示面積が元の大きさとなったところで、演出図柄40bが停止表示し、このときの演出図柄40a、40b、40cの停止表示態様によって大当たりの抽選結果が報知されることとなる。
At this time, as shown in FIG. 40 (d), the effect “reach” is superimposed on the
なお、この「リーチ演出」は、主制御基板100において、「リーチ」という文言が含まれる演出分類が決定され(図9参照)、当該演出分類に基づいて決定された発展前変動パターンコマンドおよび発展後変動パターンコマンドを受信した場合に実行される(図11、図12参照)。このとき、図40(a)〜図40(d)までの具体的な表示内容が、発展前変動パターンコマンドに基づいて決定され、図40(e)〜図40(g)までの具体的な表示内容が、発展後変動パターンコマンドに基づいて決定される。 For the “reach effect”, an effect category including the word “reach” is determined on the main control board 100 (see FIG. 9), and the pre-development variation pattern command and the development determined based on the effect category are determined. This is executed when a post-variation pattern command is received (see FIGS. 11 and 12). At this time, the specific display contents from FIG. 40A to FIG. 40D are determined based on the pre-development variation pattern command, and the specific display contents from FIG. 40E to FIG. The display content is determined based on the post-development variation pattern command.
図41は、時短遊技状態Aにおける「リーチなし演出」の一例を示す図である。時短遊技状態Aにおいては、図41(a)に示すように、「CHANCE」、「NEXT」、「リプレイ」等の表示図柄41が演出表示部50aに表示される。これらの表示図柄41は、図41(b)に示すように、変動演出の開始にともなって、縦方向にスクロール表示され、所定時間経過後に、図41(c)に示すように、いずれかの表示図柄41が演出表示部50aの中央に停止表示される。ここでは、「NEXT」の表示図柄41が、「ハズレ」を意味しており、表示図柄41が停止表示するタイミングで、演出図柄40a、40b、40cも、演出表示部50aの右上に小さく停止表示される。
FIG. 41 is a diagram illustrating an example of the “no reach effect” in the short-time gaming state A. In the short-time gaming state A, as shown in FIG. 41A,
なお、この「リーチなし演出」は、主制御基板100において、「不定通常ハズレ」、「固定通常ハズレ」の演出分類が決定されて(図13参照)、「8秒ハズレ」、「3秒ハズレ」、「2秒ハズレ」、「特殊パターンA」の発展前変動パターンコマンドを受信した場合に実行される(図15参照)。「不定通常ハズレ」、「固定通常ハズレ」の演出分類が決定された場合には、必ず、「後半なし2」の発展後変動パターンコマンドがセットされて送信される。上記と同様に、「後半なし2」の発展後変動パターンコマンドを受信した場合には、発展後の変動演出が行われず(決定されず)、発展前の変動演出のみで終了するため、「リーチなし演出」の具体的な内容は、発展前変動パターンコマンドのみによって決定されることとなる。
The “reach-less effect” is determined in the
図42は、時短遊技状態Aにおける「リーチ演出」の一例を示す図である。「リーチ演出」においては、図42(a)に示すように、表示図柄41が変動表示を開始してから所定時間経過後に、図42(b)に示すように、「リプレイ」もしくは「CHANCE」と記された表示図柄41が、演出表示部50aの中央に停止表示する。
FIG. 42 is a diagram illustrating an example of “reach effect” in the short-time gaming state A. In the “reach effect”, as shown in FIG. 42 (a), after a predetermined time has elapsed since the
その後、図42(c)に示すように、演出表示部50aにおいて、種々のキャラクタが登場するキャラクタ演出画像が表示される。このとき、演出図柄40a、40b、40cが、演出表示部50aの右上の表示領域に表示される。そして、図42(d)に示すように、演出図柄40a、40b、40cの表示面積が元の大きさとなったところで、演出図柄40bが停止表示し、このときの演出図柄40a、40b、40cの停止表示態様によって大当たりの抽選結果が報知されることとなる。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 42 (c), a character effect image in which various characters appear is displayed in the
なお、この「リーチ演出」は、主制御基板100において、「リーチ」という文言が含まれる演出分類が決定され(図13参照)、当該演出分類に基づいて決定された発展前変動パターンコマンドおよび発展後変動パターンコマンドを受信した場合に実行される(図15、図16参照)。このとき、図42(a)〜図42(b)までの具体的な表示内容が、発展前変動パターンコマンドに基づいて決定され、図42(c)〜図42(d)までの具体的な表示内容が、発展後変動パターンコマンドに基づいて決定される。 For the “reach effect”, an effect category including the word “reach” is determined on the main control board 100 (see FIG. 13), and the pre-development variation pattern command and the development determined based on the effect category are determined. This is executed when a post-change pattern command is received (see FIGS. 15 and 16). At this time, the specific display contents from FIG. 42A to FIG. 42B are determined based on the pre-development variation pattern command, and the specific display contents from FIG. 42C to FIG. The display content is determined based on the post-development variation pattern command.
以上のように、本実施形態においては、非時短遊技状態と時短遊技状態Aとで、変動演出の態様を異にしている。換言すれば、特別遊技の終了後の9回もしくは17回の変動演出については、専用の変動演出を実行すべく、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合と、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合とで、全く異なる変動パターンが決定されるようにしている。 As described above, in the present embodiment, the non-time saving gaming state and the time saving gaming state A are different in the mode of variation effect. In other words, for the 9th or 17th variation effect after the end of the special game, in order to execute a dedicated variation effect, it is set in the short-time game state A and in the non-short-time game state. In this case, a completely different variation pattern is determined.
ただし、非時短遊技状態および時短遊技状態Aのいずれの場合においても、「リーチなし演出」というのは、発展前変動パターンコマンドによってのみ変動演出の態様が決定されるものである。また、「リーチ演出」というのは、発展前変動パターンコマンドによって決定される「リーチなし演出」と同様の演出に続いて、発展後変動パターンコマンドによって決定される変動演出が行われるものである。このように、本実施形態においては、特定の演出態様で変動演出が終了するものを「リーチなし演出」とし、特定の演出態様となった後にさらに変動演出が発展的に継続するものを「リーチ演出」とする。また、「リーチなし演出」と「リーチ演出」とでは平均変動時間が異なっており、「リーチなし演出」は所定時間以下で変動演出が終了し、「リーチ演出」は所定時間以上、変動演出が行われるものである。つまり、「リーチ演出」は「リーチなし演出」よりも平均変動時間が長く設定されている。 However, in both the non-short-time gaming state and the short-time gaming state A, the “reach-less effect” is a mode in which the variation effect is determined only by the pre-development variation pattern command. The “reach effect” is a change effect determined by the post-development variation pattern command, following the same effect as the “non-reach effect” determined by the pre-development change pattern command. As described above, in the present embodiment, an effect in which a variation effect ends in a specific effect mode is referred to as an “unreachable effect”, and an event in which the variable effect continues to develop after becoming a specific effect mode is referred to as “reach”. "Direction". In addition, the average fluctuation time differs between the “no reach production” and the “reach production”. The “no reach production” ends the fluctuation production in a predetermined time or less, and the “reach production” exceeds the predetermined time. Is to be done. That is, the “reach effect” is set to have a longer average fluctuation time than the “reach effect”.
次に、図43〜図48を用いて、本実施形態の予兆演出(所謂「先読み演出」)について説明する。 Next, the sign effect (the so-called “prefetch effect”) of the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 43 to 48.
図43は、保留表示の一例を示す図である。図43(a)に示すように、本実施形態においては、演出表示部50aに保留表示領域60a〜60hが設けられており、第1保留または第2保留がいくつ記憶されているかを遊技者に報知するようにしている。上記したように、主制御基板100には第1保留および第2保留を記憶する保留記憶領域が設けられているが、副制御基板200にも、第1保留および第2保留に係る大当たり情報、演出分類情報、発展前変動パターン情報、発展後変動パターン情報、演出分類仮判定情報等(以下、「保留情報」という)が記憶される保留記憶領域が設けられている。
FIG. 43 is a diagram illustrating an example of a hold display. As shown in FIG. 43 (a), in the present embodiment, hold
この副制御基板200のサブRAM200cに設けられる保留記憶領域も、主制御基板100の保留記憶領域と同様に、第1記憶部〜第8記憶部を備えている。そして、第1記憶部が保留表示領域60aに対応し、以下、第2記憶部〜第8記憶部が、それぞれ保留表示領域60b〜60hに対応している。各保留表示領域60a〜60hは、対応する記憶部に保留情報が記憶されると保留表示がなされ、対応する記憶部に保留情報が記憶されていない場合には保留表示が非表示(背景画像の表示)となる。例えば、3つの保留が記憶されている場合には、第1記憶部〜第3記憶部に保留情報が記憶されるため、図43(b)に示すように、各記憶部に対応する保留表示領域60a、60b、60cのみに保留表示がなされることとなる。
Similarly to the reserved storage area of the
図44は、副制御基板200の保留記憶領域を説明する図である。この図に示すように、保留記憶領域には第1記憶部〜第8記憶部が設けられており、各記憶部には、それぞれ「保留種別」、「記憶時の遊技状態」、「保留表示決定乱数」、「演出分類情報」、「発展前事前判定情報」、「発展後事前判定情報」、「低確用演出分類仮判定情報」、「高確用演出分類仮判定情報」、「保留表示種別」が記憶される領域が設けられている。これらの各記憶領域には、主制御基板100から送信されるコマンドに基づいて情報が記憶されることとなる。
FIG. 44 is a diagram for explaining the reserved storage area of the
各記憶部の保留種別記憶領域には、当該保留が第1保留であるか第2保留であるかが記憶され、遊技状態記憶領域には、コマンド受信時の遊技状態すなわち保留が記憶されたときの遊技状態が記憶される。各記憶部の保留表示決定乱数記憶領域には、保留表示の態様を決定するための保留表示決定乱数が記憶される。この保留表示決定乱数は、主制御基板100から送信される始動入賞コマンドを受信した際に、0〜255の範囲内から1つ取得して記憶される。
Whether the hold is the first hold or the second hold is stored in the hold type storage area of each storage unit, and the game state at the time of receiving the command, that is, the hold is stored in the game state storage area Is stored. The hold display determination random number storage area of each storage unit stores a hold display determination random number for determining a hold display mode. The hold display determination random number is acquired and stored in the range of 0 to 255 when the start winning command transmitted from the
各記憶部の演出分類情報記憶領域には、当該保留が記憶されたときの遊技状態に基づいて導出された演出分類情報が記憶される。例えば、非時短遊技状態に設定されているときに保留が記憶された場合には、非時短遊技状態における演出分類情報が記憶される。各記憶部の発展前事前判定情報記憶領域、および、発展後事前判定情報記憶領域には、当該保留が記憶されたときの遊技状態に基づいて導出された発展前事前判定情報および発展後事前判定情報が記憶される。なお、すでに説明したとおり、演出分類として「不定値」が決定された場合には、発展前事前判定情報および発展後事前判定情報は記憶されない。 In the effect category information storage area of each storage unit, effect category information derived based on the gaming state when the hold is stored is stored. For example, when the hold is stored when the non-short-time gaming state is set, the effect classification information in the non-short-time gaming state is stored. The pre-development pre-determination information storage area and the post-development pre-determination information storage area of each storage unit are pre-development pre-determination information and post-development pre-determination derived based on the gaming state when the hold is stored. Information is stored. As already described, when “indefinite value” is determined as the effect classification, the pre-development advance determination information and the post-development advance determination information are not stored.
そして、各記憶部の低確用演出分類仮判定情報記憶領域には、次のようにして情報が記憶される。すなわち、保留が記憶されたときの遊技状態が非時短遊技状態であった場合には、時短遊技状態Aであって、かつ、低確率遊技状態であると仮定した場合に決定される演出分類仮判定情報が記憶され、保留が記憶されたときの遊技状態が時短遊技状態Aであった場合には、非時短遊技状態であって、かつ、低確率遊技状態であると仮定した場合に決定される演出分類仮判定情報が記憶される。 Information is stored as follows in the low-reliability effect classification provisional determination information storage area of each storage unit. In other words, if the game state when the hold is stored is the non-short-time game state, the effect classification temporary determined when it is assumed that the game state is the short-time game state A and the low-probability game state. When the determination information is stored and the gaming state when the hold is stored is the short-time gaming state A, it is determined when it is assumed that the gaming state is a non-short-time gaming state and a low-probability gaming state. Effect classification provisional determination information is stored.
また、各記憶部の高確用演出分類仮判定情報記憶領域には、次のようにして情報が記憶される。すなわち、保留が記憶されたときの遊技状態が非時短遊技状態であった場合には、時短遊技状態Aであって、かつ、高確率遊技状態であると仮定した場合に決定される演出分類仮判定情報が記憶され、保留が記憶されたときの遊技状態が時短遊技状態Aであった場合には、非時短遊技状態であって、かつ、高確率遊技状態であると仮定した場合に決定される演出分類仮判定情報が記憶される。 In addition, information is stored as follows in the high-accuracy production category temporary determination information storage area of each storage unit. In other words, if the game state when the hold is stored is the non-short-time game state, the effect classification temporary determined when it is assumed that the game state is the short-time game state A and the high-probability game state. When the determination information is stored and the gaming state when the hold is stored is the short-time gaming state A, it is determined when it is assumed that the gaming state is a non-short-time gaming state and a high-probability gaming state. Effect classification provisional determination information is stored.
また、各記憶部の保留表示種別記憶領域には、上記の各情報に基づいて決定された保留表示種別が記憶される。この保留表示種別は、演出表示部50aの各保留表示領域60a〜60hになされる保留表示の態様を示すものであるが、保留表示種別は、副制御基板200の各記憶領域に記憶された保留情報に基づいて次のように決定される。
The hold display type storage area of each storage unit stores the hold display type determined based on each of the above information. The hold display type indicates a hold display mode performed in each
図45は、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合に参照される保留表示決定テーブル1〜3を説明する図であり、図46は、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合の特殊表示の実行条件判定テーブルを説明する図である。保留記憶領域に保留情報が記憶されると、サブCPU200aは、0〜255の範囲内から1つの保留表示決定乱数を取得するとともに、当該保留表示決定乱数を、上記の保留情報が記憶された記憶部と同じ記憶部に記憶する。
FIG. 45 is a diagram for explaining the hold display determination tables 1 to 3 that are referred to when the non-short game state is set, and FIG. 46 is a special display when the non-short game state is set. It is a figure explaining an execution condition determination table. When the hold information is stored in the hold storage area, the
そして、サブCPU200aは、新たに記憶部に記憶された演出分類情報、発展後事前判定情報(発展後変動パターン)、演出分類仮判定情報と、取得した保留表示決定乱数とに基づいて、保留表示の態様を決定する。
Then, the
すなわち、記憶部に記憶された演出分類情報が「不定値」の場合には、図45(a)に示す保留表示決定テーブル1を参照して保留表示種別が決定される。この保留表示決定テーブル1によれば、保留表示決定乱数が0〜249のときに「通常表示」と決定し、保留表示決定乱数が250〜255のときに「特殊表示1」と決定する。
That is, when the effect classification information stored in the storage unit is “indefinite value”, the hold display type is determined with reference to the hold display determination table 1 shown in FIG. According to the hold display determination table 1, “normal display” is determined when the hold display determination random number is 0 to 249, and “
また、記憶部に記憶された演出分類情報が「不定値」以外の場合には、図45(b)に示す保留表示決定テーブル2を参照して保留表示種別が決定される。この保留表示決定テーブル2には、非時短遊技状態に設定されているときに受信し得る発展後変動パターン(発展後事前判定情報)ごとに、保留表示決定乱数と保留表示種別とが対応付けて記憶されている。この保留表示決定テーブル2によれば、例えば、記憶部に記憶された発展後事前判定情報が「後半なし1」である場合には、保留表示決定乱数が0〜199のときに「通常表示」と決定し、保留表示決定乱数が200〜255のときに「特殊表示1」と決定する。
If the effect classification information stored in the storage unit is other than “undefined value”, the hold display type is determined with reference to the hold display determination table 2 shown in FIG. In the hold display determination table 2, a hold display determination random number and a hold display type are associated with each developed variation pattern (post-development advance determination information) that can be received when the non-time-saving gaming state is set. It is remembered. According to the hold display determination table 2, for example, when the post-development advance determination information stored in the storage unit is “no
なお、本実施形態においては、変動演出が行われて保留が処理された場合に、再度、各記憶部の保留情報を判定して保留表示種別を決定する。例えば、第1記憶部〜第4記憶部に4つの保留情報が記憶されている場合に、第1記憶部に記憶された保留についての変動演出が行われたとする。このとき、第2記憶部〜第4記憶部に記憶された保留情報は、それぞれ第1記憶部〜第3記憶部にシフトされる。したがって、この場合には、サブCPU200aが、シフトされた後の第1記憶部〜第3記憶部の保留情報に基づいて、再度、保留表示種別を決定することとなる。
In the present embodiment, when a change effect is performed and the hold is processed, the hold information of each storage unit is determined again to determine the hold display type. For example, it is assumed that, when four pieces of hold information are stored in the first storage unit to the fourth storage unit, a variation effect regarding the hold stored in the first storage unit is performed. At this time, the hold information stored in the second storage unit to the fourth storage unit is shifted to the first storage unit to the third storage unit, respectively. Therefore, in this case, the
そして、時短遊技状態Aに設定されているときに記憶された保留であって、当該保留についての変動演出が行われる前に、遊技状態が非時短遊技状態に変更された保留については、保留表示決定テーブル3に基づいて保留の表示態様が決定される。時短遊技状態Aに設定されているときに記憶された保留については、非時短遊技状態用の発展後事前判定情報は記憶されていないものの、非時短遊技状態に設定されていると仮定した場合の演出分類仮判定情報が記憶されている(図23のステップS331−16〜ステップS331−18、図44参照)。 And about the hold which was memorize | stored when it is set to the short-time game state A, and the game state was changed into the non-short-time game state before the variation | change effect about the said hold is performed, hold display Based on the determination table 3, the display mode of the hold is determined. As for the hold stored when the short-time gaming state A is set, the post-development advance determination information for the non-short-time gaming state is not stored, but it is assumed that the non-short-time gaming state is set. The effect classification provisional determination information is stored (see steps S331-16 to S331-18 in FIG. 23 and FIG. 44).
そこで、時短遊技状態Aに設定されているときに記憶された保留であって、当該保留が処理される前に遊技状態が非時短遊技状態に設定された場合には、当該保留について、図45(c)に示す保留表示決定テーブル3を参照して保留表示種別が決定される。具体的には、当該保留については、演出分類仮判定情報(演出分類仮判定コマンド)として、低確率遊技状態、かつ、非時短遊技状態であると仮定した場合の低確用演出分類仮判定情報と、高確率遊技状態、かつ、非時短遊技状態であると仮定した場合の高確用演出分類仮判定情報とが記憶されている。そして、2つの演出分類仮判定情報のうち、現在の遊技状態(高確か低確か)に対応する演出分類仮判定情報に基づいて、保留表示種別が決定されることとなる。 Therefore, in the case where the hold is stored when the short-time gaming state A is set and the game state is set to the non-short-time gaming state before the hold is processed, the hold is illustrated in FIG. The hold display type is determined with reference to the hold display determination table 3 shown in FIG. Specifically, for the hold, the low-probability effect classification temporary determination information when it is assumed that the low-probability gaming state and the non-short-time gaming state are provided as the effect classification temporary determination information (effect classification temporary determination command). And high-probability effect classification provisional determination information when it is assumed that the high-probability gaming state and the non-time-saving gaming state are stored. And a pending | holding display type will be determined based on the production | presentation classification provisional determination information corresponding to the present game state (high certainty certainty) among two production | generation classification provisional determination information.
保留表示決定テーブル3によれば、非時短遊技状態に設定されているときに受信し得る仮演出分類コマンド(演出分類仮判定情報)に応じて、保留表示決定乱数と保留表示種別とが対応付けて記憶されている。この保留表示決定テーブル3によれば、例えば、記憶部に記憶された演出分類仮判定情報が「固定弱リーチハズレ」である場合には、保留表示決定乱数が0〜99のときに「通常表示」と決定し、保留表示決定乱数が100〜255のときに「特殊表示2」と決定する。
According to the hold display determination table 3, the hold display determination random number and the hold display type are associated with each other according to a temporary effect classification command (effect classification temporary determination information) that can be received when the non-time-saving gaming state is set. Is remembered. According to the hold display determination table 3, for example, when the effect classification temporary determination information stored in the storage unit is “fixed weak reach loss”, “normal display” when the hold display determination random number is 0 to 99. And “
なお、図45に示す保留表示決定テーブル1〜3を参照して決定された保留表示種別が「特殊表示」であった場合には、さらに、図46に示す特殊表示の実行条件判定テーブルに基づいて、「特殊表示」の実行可否が判定される。ここでは、「特殊表示」の決定がなされた保留(対象保留)よりも前に処理される保留(対象前保留)の非時短遊技状態における演出分類情報および演出分類仮判定情報が、全て「固定通常ハズレ」である場合に、対象保留について「特殊表示」がなされることとなる。一方で、対象前保留に「固定通常ハズレ」以外の演出分類情報および演出分類仮判定情報が含まれている場合には、対象保留について「通常表示」がなされることとなる。 If the hold display type determined with reference to the hold display determination tables 1 to 3 shown in FIG. 45 is “special display”, it is further based on the special display execution condition determination table shown in FIG. Whether or not “special display” can be executed is determined. Here, all of the effect classification information and the effect classification provisional judgment information in the non-time-saving gaming state of the hold (hold before target) processed before the hold (target hold) for which “special display” is determined are all “fixed”. In the case of “normally lost”, “special display” is made for the target hold. On the other hand, when the pre-target hold includes effect classification information other than “fixed normal lose” and effect classification provisional determination information, “normal display” is made for the target hold.
図47は、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合に参照される保留表示決定テーブル4〜6を説明する図であり、図48は、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合の特殊表示の実行条件判定テーブルを説明する図である。時短遊技状態Aにおいて、記憶部に記憶された演出分類情報が「不定値」の場合には、図47(a)に示す保留表示決定テーブル4を参照して保留表示種別が決定される。この保留表示決定テーブル4によれば、保留表示決定乱数が0〜249のときに「通常表示」と決定し、保留表示決定乱数が250〜255のときに「特殊表示A」と決定する。 FIG. 47 is a diagram for explaining the hold display determination tables 4 to 6 that are referred to when the short-time gaming state A is set, and FIG. 48 shows the special display when the short-time gaming state A is set. It is a figure explaining an execution condition determination table. In the short-time gaming state A, when the effect classification information stored in the storage unit is “indefinite value”, the hold display type is determined with reference to the hold display determination table 4 shown in FIG. According to the hold display determination table 4, “normal display” is determined when the hold display determination random number is 0 to 249, and “special display A” is determined when the hold display determination random number is 250 to 255.
また、記憶部に記憶された演出分類情報が「不定値」以外の場合には、図47(b)に示す保留表示決定テーブル5を参照して保留表示種別が決定される。この保留表示決定テーブル5には、時短遊技状態Aに設定されているときに受信し得る発展後変動パターン(発展後事前判定情報)ごとに、保留表示決定乱数と保留表示種別とが対応付けて記憶されている。この保留表示決定テーブル5によれば、例えば、記憶部に記憶された発展後事前判定情報が「後半なし2」である場合には、必ず「通常表示」と決定する。また、発展後事前判定情報が「ハズレチャンスAまたはB」である場合には、保留表示決定乱数が0〜99のときに「通常表示」と決定し、保留表示決定乱数が100〜255のときに「特殊表示A」と決定する。
When the effect classification information stored in the storage unit is other than “undefined value”, the hold display type is determined with reference to the hold display determination table 5 shown in FIG. In the hold display determination table 5, a hold display determination random number and a hold display type are associated with each of the developed variation patterns (post-development advance determination information) that can be received when the short-time gaming state A is set. It is remembered. According to the hold display determination table 5, for example, when the post-development advance determination information stored in the storage unit is “no
そして、非時短遊技状態に設定されているときに記憶された保留であって、当該保留についての変動演出が行われる前に、遊技状態が時短遊技状態Aに変更された保留については、保留表示決定テーブル6に基づいて保留の表示態様が決定される。非時短遊技状態に設定されているときに記憶された保留については、時短遊技状態A用の発展後事前判定情報は記憶されていないものの、時短遊技状態Aに設定されていると仮定した場合の演出分類仮判定情報が記憶されている(図23のステップS331−13〜ステップS331−15、図44参照)。 The hold stored when the non-short game state is set, and the hold in which the game state is changed to the short-time game state A before the fluctuating effect on the hold is performed, is displayed as a hold. Based on the determination table 6, the display mode of the hold is determined. As for the hold stored when the non-short game state is set, the post-development advance determination information for the short time game state A is not stored, but it is assumed that it is set to the short time game state A. The effect classification provisional determination information is stored (see steps S331-13 to S331-15 in FIG. 23, FIG. 44).
そこで、非時短遊技状態に設定されているときに記憶された保留であって、当該保留が処理される前に遊技状態が時短遊技状態Aに設定された場合には、当該保留について、図47(c)に示す保留表示決定テーブル6を参照して保留表示種別が決定される。具体的には、当該保留については、演出分類仮判定情報(演出分類仮判定コマンド)として、低確率遊技状態、かつ、時短遊技状態Aであると仮定した場合の低確用演出分類仮判定情報と、高確率遊技状態、かつ、時短遊技状態Aであると仮定した場合の高確用演出分類仮判定情報とが記憶されている。そして、2つの演出分類仮判定情報のうち、現在の遊技状態(高確か低確か)に対応する演出分類仮判定情報に基づいて、保留表示種別が決定されることとなる。 Therefore, if the hold is stored when the non-short game state is set, and the game state is set to the short-time game state A before the hold is processed, the hold is illustrated in FIG. The hold display type is determined with reference to the hold display determination table 6 shown in FIG. Specifically, for the suspension, the low-probability effect classification temporary determination information when it is assumed that the low-probability gaming state and the short-time gaming state A are provided as the effect classification temporary determination information (effect classification temporary determination command). And high-probability effect classification provisional determination information when it is assumed that the high-probability gaming state and the short-time gaming state A are stored. And a pending | holding display type will be determined based on the production | presentation classification provisional determination information corresponding to the present game state (high certainty certainty) among two production | generation classification provisional determination information.
保留表示決定テーブル6によれば、時短遊技状態Aに設定されているときに受信し得る演出分類仮判定コマンド(演出分類仮判定情報)に応じて、保留表示決定乱数と保留表示種別とが対応付けて記憶されている。この保留表示決定テーブル6によれば、例えば、記憶部に記憶された演出分類仮判定情報が「固定強リーチ大当たり」である場合には、保留表示決定乱数が0〜99のときに「通常表示」と決定し、保留表示決定乱数が100〜255のときに「特殊表示A」と決定する。 According to the hold display determination table 6, the hold display determination random number and the hold display type correspond according to the effect classification provisional determination command (production effect provisional determination information) that can be received when the time-saving gaming state A is set. It is remembered. According to the hold display determination table 6, for example, when the effect classification tentative determination information stored in the storage unit is “fixed strong reach jackpot”, when the hold display determination random number is 0 to 99, “normal display” ”And“ special display A ”when the hold display determination random number is 100 to 255.
なお、図47に示す保留表示決定テーブル4〜6を参照して決定された保留表示種別が「特殊表示」であった場合には、さらに、図48に示す特殊表示の実行条件判定テーブルに基づいて、「特殊表示」の実行可否が判定される。ここでは、「特殊表示」の決定がなされた保留(対象保留)よりも前に処理される保留(対象前保留)の時短遊技状態Aにおける演出分類情報および演出分類仮判定情報が、全て「固定通常ハズレ」である場合に、対象保留について「特殊表示」がなされることとなる。一方で、対象前保留に「固定通常ハズレ」以外の演出分類情報および演出分類仮判定情報が含まれている場合には、対象保留について「通常表示」がなされることとなる。 If the hold display type determined with reference to the hold display determination tables 4 to 6 shown in FIG. 47 is “special display”, the special display execution condition determination table shown in FIG. 48 is used. Whether or not “special display” can be executed is determined. Here, all the effect classification information and the effect classification provisional determination information in the short-time gaming state A of the hold (hold before target) processed before the hold (target hold) for which “special display” is determined are all “fixed”. In the case of “normally lost”, “special display” is made for the target hold. On the other hand, when the pre-target hold includes effect classification information other than “fixed normal lose” and effect classification provisional determination information, “normal display” is made for the target hold.
なお、図45に示す保留表示種別のうち、「通常表示」は保留表示を青色で表示することを示し、「特殊表示1」は保留表示を緑色で表示することを示し、「特殊表示2」は保留表示を黄色で表示することを示し、「特殊表示3」は保留表示を赤色で表示することを示し、「特殊表示4」は保留表示をキャラクタAで表示することを示し、「特殊表示5」は保留表示をキャラクタBで表示することを示している。
45, “normal display” indicates that the hold display is displayed in blue, “
また、図47に示す保留表示種別のうち、「通常表示」は保留表示を青色で表示することを示し、「特殊表示A」は保留表示を白星で表示することを示し、「特殊表示B」は保留表示を黒星で表示することを示している。このように、本実施形態においては、非時短遊技状態と時短遊技状態Aとで、予兆演出の態様が異なるように設定されている。 47, “normal display” indicates that the hold display is displayed in blue, “special display A” indicates that the hold display is displayed as a white star, and “special display B”. Indicates that the hold display is displayed as a black star. As described above, in the present embodiment, the non-time-saving gaming state and the time-saving gaming state A are set so that the indication effects differ.
以上説明したように、本実施形態においては、保留表示の表示態様によって、対象保留についての大当たりの信頼度を示唆するようにしている。そして、遊技状態が変更された場合であっても、変更後の遊技状態に対応する保留情報(演出分類仮判定情報)を備えているので、予兆演出の正確な信頼度を担保することができる。以下では、上記の予兆演出を実行するための副制御基板200における具体的な制御処理について説明する。
As described above, in the present embodiment, the reliability of the jackpot for the target hold is suggested by the display mode of the hold display. And even if it is a case where a game state is changed, since the hold information (effect classification provisional judgment information) corresponding to the game state after a change is provided, the exact reliability of an indication effect can be ensured. . Hereinafter, a specific control process in the
(副制御基板200のメイン処理)
図49は、副制御基板200のメイン処理を説明するフローチャートである。
(Main processing of sub-control board 200)
FIG. 49 is a flowchart for explaining the main process of the
(ステップS1000)
サブCPU200aは、電源投入に応じて、サブROM200bからメイン処理プログラムを読み込むとともに、サブRAM200cに記憶されるフラグ等の初期化、設定処理を行う。
(Step S1000)
The
(ステップS1001)
次に、サブCPU200aは、各演出乱数を更新する処理を行うとともに、以後は、割込み処理が行われるまで当該ステップS1001の処理を繰り返し行う。
(Step S1001)
Next, the
(副制御基板200のタイマ割込処理)
図50は、副制御基板200のタイマ割込処理を説明するフローチャートである。副制御基板200には、所定の周期(2ms)でクロックパルスを発生するリセット用クロックパルス発生回路(不図示)が設けられている。そして、このリセット用クロックパルス発生回路によるクロックパルスの発生により、サブCPU200aはタイマ割込処理プログラムを読み込んで当該タイマ割込処理を開始する。
(Timer interrupt processing of sub control board 200)
FIG. 50 is a flowchart for explaining timer interrupt processing of the
(ステップS1100)
まず、サブCPU200aは、副制御基板200で用いられる各種タイマカウンタの更新処理を行う。
(Step S1100)
First, the
(ステップS1200)
次に、サブCPU200aは、サブRAM200cの受信バッファに格納されているコマンドを解析するとともに、受信したコマンドに応じた種々の処理を行う。副制御基板200においては、主制御基板100からコマンドが送信されると、コマンド受信割込処理が行われ、主制御基板100から送信されたコマンドが受信バッファに格納される。ここでは、コマンド受信割込処理によって受信バッファに格納されたコマンドを解析することとなる。
(Step S1200)
Next, the
(ステップS1300)
次に、サブCPU200aは、実行中の演出進行状況に応じて、演出操作装置56の操作の受け付け可否を判定するとともに、演出操作装置検出スイッチ56aの信号のチェックを行う。そして、演出操作装置検出スイッチ56aから操作信号が入力されたときに、演出操作装置56の操作受け付け中であった場合には、演出操作装置56が操作されたことを画像制御基板210に送信すべく、送信バッファにコマンドを格納する。
(Step S1300)
Next, the
(ステップS1400)
次に、サブCPU200aは、サブRAM200cの送信バッファにセットされているコマンドを画像制御基板210や電飾制御基板220へ送信し、タイマ割込処理を終了する。
(Step S1400)
Next, the
図51は、上記コマンド解析処理のうち、始動入賞コマンドを受信した場合に実行される始動入賞コマンド受信処理を説明するフローチャートである。上記したとおり、この始動入賞コマンドは、主制御基板100において、事前判定処理のステップS331−19(図23参照)でセットされた後、ステップS800の出力制御処理(図20参照)によって副制御基板200に送信される。
FIG. 51 is a flowchart for explaining a start winning command reception process executed when a start winning command is received in the command analysis process. As described above, this start winning command is set in step S331-19 (see FIG. 23) of the pre-determination process in the
(ステップS1210−1)
始動入賞コマンドを受信したと判定した場合には、まず、サブCPU200aは、同時に受信した演出分類コマンドを解析し、当該受信した演出分類コマンドに対応する演出分類情報を、第1記憶部〜第8記憶部の中で保留情報が記憶されていないもっとも番号(序数)の小さい記憶部に記憶する。
(Step S1210-1)
If it is determined that the start winning command has been received, the
(ステップS1210−2)
次に、サブCPU200aは、始動入賞コマンドと同時に受信した発展前事前判定コマンドを解析し、上記演出分類情報を記憶したのと同じ記憶部に発展前事前判定情報を記憶する。なお、発展前事前判定コマンドを受信していない場合には、そのまま次のステップに処理が移される。
(Step S1210-2)
Next, the
(ステップS1210−3)
次に、サブCPU200aは、始動入賞コマンドと同時に受信した発展後事前判定コマンドを解析し、上記演出分類情報を記憶したのと同じ記憶部に発展後事前判定情報を記憶する。なお、発展後事前判定コマンドを受信していない場合には、そのまま次のステップに処理が移される。
(Step S1210-3)
Next, the
(ステップS1210−4)
次に、サブCPU200aは、始動入賞コマンドと同時に受信した低確用演出分類仮判定コマンドおよび高確用演出分類仮判定コマンドを解析し、上記演出分類情報を記憶したのと同じ記憶部に低確用演出分類仮判定情報および高確用演出分類仮判定情報を記憶する。
(Step S1210-4)
Next, the
(ステップS1210−5)
次に、サブCPU200aは、0〜255の範囲から1の保留表示決定乱数を取得する。
(Step S1210-5)
Next, the
(ステップS1210−6)
次に、サブCPU200aは、上記ステップS1210−1で記憶した演出分類情報と、現在設定されている遊技状態とに基づいて、保留表示決定テーブルをセットする。具体的には、上記ステップS1210−1で記憶した演出分類情報が「不定値」である場合において、遊技状態が非時短遊技状態であれば、図45(a)に示す保留表示決定テーブル1をセットし、遊技状態が時短遊技状態であれば、図47(a)に示す保留表示決定テーブル4をセットする。また、上記ステップS1210−1で記憶した演出分類情報が「不定値」以外である場合において、遊技状態が非時短遊技状態であれば、図45(b)に示す保留表示決定テーブル2をセットし、遊技状態が時短遊技状態であれば、図47(b)に示す保留表示決定テーブル5をセットする。
(Step S1210-6)
Next, the
(ステップS1210−7)
次に、サブCPU200aは、上記ステップS1210−5で取得した保留表示決定乱数と、上記ステップS1210−6でセットしたテーブルとに基づいて、保留表示種別を判定する。
(Step S1210-7)
Next, the
(ステップS1210−8)
次に、サブCPU200aは、上記ステップS1210−7で導出された保留表示種別が「通常表示」であるかを判定する。その結果、「通常表示」であると判定した場合にはステップS1210−9に処理を移し、「通常表示」ではないと判定した場合にはステップS1210−11に処理を移す。
(Step S1210-8)
Next, the
(ステップS1210−9)
上記ステップS1210−8において、保留表示種別が「通常表示」であると判定した場合には、サブCPU200aは、保留表示種別記憶領域に「通常表示」に係る情報を記憶する。
(Step S1210-9)
When it is determined in step S1210-8 that the hold display type is “normal display”, the
(ステップS1210−10)
次に、サブCPU200aは、新たに記憶された当該対象保留についての保留表示を通常表示(青色表示)すべく、通常表示コマンドをセットする。ここでセットされたコマンドは画像制御基板210に送信され、画像制御基板210において、演出表示部50aに保留表示を通常表示するための処理が行われることとなる。
(Step S1210-10)
Next, the
(ステップS1210−11)
一方、上記ステップS1210−8において、保留表示種別が「通常表示」ではない(「特殊表示」である)と判定した場合には、サブCPU200aは、当該保留よりも前に変動演出が行われる対象前保留の演出分類が、全て「固定通常ハズレ」であるかを判定する。
(Step S1210-11)
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S1210-8 that the hold display type is not “normal display” (ie, “special display”), the
より詳細には、現在の遊技状態が非時短遊技状態、低確率遊技状態である場合において、対象前保留が現在と同じ遊技状態に設定されているときに記憶されたものであるときには、各対象前保留の演出分類情報が「固定通常ハズレ」であるかを判定する。一方、対象前保留が時短遊技状態Aに設定されているときに記憶されたものであるときには、各対象前保留の低確用演出分類仮判定情報が「固定通常ハズレ」であるかを判定する。こうした判定を全ての対象前保留について行った結果、全ての演出分類情報(演出分類仮判定情報)が固定通常ハズレであると判定した場合にはステップS1210−12に処理を移し、固定通常ハズレ以外の情報が1つでもあると判定した場合にはステップS1210−9に処理を移す。 More specifically, when the current gaming state is a non-time-saving gaming state or a low-probability gaming state, each subject is stored when the pre-submission is set to the same gaming state as the current one. It is determined whether the pre-pending performance classification information is “fixed normal loss”. On the other hand, when the pre-target hold is stored when the short-time gaming state A is set, it is determined whether the low-probability effect classification provisional determination information of each pre-target hold is “fixed normal lose”. . As a result of performing such determination for all pre-subject suspensions, if it is determined that all the production category information (production category provisional judgment information) is fixed normal loss, the process proceeds to step S1210-12, and other than fixed normal loss If it is determined that there is even one piece of information, the process proceeds to step S1210-9.
(ステップS1210−12)
上記ステップS1210−11において、全ての演出分類情報(演出分類仮判定情報)が固定通常ハズレであると判定した場合には、サブCPU200aは、保留表示種別記憶領域に「特殊表示」に係る情報を記憶する。
(Step S1210-12)
If it is determined in step S1210-11 that all the effect classification information (effect classification provisional determination information) is fixed normal loss, the
(ステップS1210−13)
次に、サブCPU200aは、新たに記憶された当該対象保留についての保留表示を特殊表示すべく、特殊表示コマンドをセットする。ここでセットされたコマンドは画像制御基板210に送信され、画像制御基板210において、演出表示部50aに保留表示を特殊表示するための処理が行われることとなる。
(Step S1210-13)
Next, the
上記の始動入賞コマンド受信処理により、新たに記憶された保留について、通常表示もしくは特殊表示がなされることとなる。 With the start winning command reception process described above, a normal display or a special display is made for the newly stored suspension.
図52は、上記コマンド解析処理のうち、変動パターンコマンドを受信した場合に実行される変動パターンコマンド受信処理を説明するフローチャートである。上記したとおり、この変動パターンコマンドは、主制御基板100において、変動パターン決定処理(図27参照)のうち、ステップS421−5およびステップS421−8でセットされた後、ステップS800の出力制御処理(図20参照)によって副制御基板200に送信される。
FIG. 52 is a flowchart for explaining a variation pattern command reception process executed when a variation pattern command is received in the command analysis process. As described above, this variation pattern command is set in step S421-5 and step S421-8 in the variation pattern determination processing (see FIG. 27) on the
(ステップS1220)
変動パターンコマンドを受信したと判定した場合には、まず、サブCPU200aは、保留更新処理を行う。この保留更新処理については、図53を用いて後述する。
(Step S1220)
When it is determined that the variation pattern command has been received, the
(ステップS1230)
次に、サブCPU200aは、発展前演出決定処理を行う。この発展前演出決定処理においては、発展前演出決定乱数を取得するとともに、当該取得した乱数と、受信した発展前変動パターンコマンドに対応する演出決定テーブルとに基づいて、具体的な発展前変動演出の態様を決定する。そして、決定した発展前変動演出を実行すべく、画像制御基板210や電飾制御基板220にコマンドを送信し、これによって変動演出が開始されることとなる。
(Step S1230)
Next, the
(ステップS1240)
次に、サブCPU200aは、発展後演出決定処理を行う。この発展後演出決定処理においては、発展後演出決定乱数を取得するとともに、当該取得した乱数と、受信した発展後変動パターンコマンドに対応する演出決定テーブルとに基づいて、具体的な発展後変動演出の態様を決定する。そして、決定した発展後変動演出を実行すべく、画像制御基板210や電飾制御基板220にコマンドを送信する。これにより、発展前変動演出に続いて、発展後変動演出が実行されることとなる。
(Step S1240)
Next, the
図53は、保留更新処理を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 53 is a flowchart for explaining the pending update process.
(ステップS1220−1)
変動パターンコマンドを受信すると、サブCPU200aは、まず、保留記憶領域の各記憶部のシフト処理を行う。ここでは、第1記憶部に記憶されている保留情報を所定の処理領域に記憶するとともに、第2記憶部〜第8記憶部に記憶されている保留情報を1つ番号(序数)の小さい記憶部にシフトする。
(Step S1220-1)
When receiving the variation pattern command, the
(ステップS1220−2)
次に、サブCPU200aは、サブRAM200cに設けられた記憶部番号(N)記憶領域に1を記憶する。なお、この記憶部番号(N)は、当該保留更新処理を行う際に、いずれの記憶部に対する処理を行っているかを示すものである。例えば、記憶部番号(N)として「1」が記憶されている場合には、第1記憶部についての処理を行うことを示し、記憶部番号(N)として「8」が記憶されている場合には、第8記憶部についての処理を行うことを示すものである。
(Step S1220-2)
Next, the
(ステップS1220−3)
次に、サブCPU200aは、第1記憶部に保留情報が記憶されているかを判定する。その結果、第1記憶部に保留情報が記憶されている場合にはステップS1220−4に処理を移し、第1記憶部に保留情報が記憶されていない場合には当該保留更新処理を終了する。
(Step S1220-3)
Next, the
(ステップS1220−4)
上記ステップS1220−3において、第1記憶部に保留情報が記憶されていると判定した場合には、サブCPU200aは、第N記憶部(第1記憶部)の保留情報と現在の遊技状態とに基づいて、保留表示決定テーブルをセットする。
(Step S1220-4)
If it is determined in step S1220-3 that the hold information is stored in the first storage unit, the
具体的には、現在の遊技状態と、第N記憶部(第1記憶部)に記憶された遊技状態(保留が記憶されたときの遊技状態)とが一致するかを判定し、一致する場合には、当該記憶部の演出分類情報を参照する。そして、「不定値」の演出分類情報が記憶されている場合には、遊技状態に応じて保留表示決定テーブル1、4をセットし、その他の演出分類情報が記憶されている場合には、遊技状態に応じて保留表示決定テーブル2、5をセットする。また、現在の遊技状態と、第N記憶部(第1記憶部)に記憶された遊技状態(保留が記憶されたときの遊技状態)とが一致しない場合には、現在の遊技状態に応じて保留表示決定テーブル3、6をセットする。 Specifically, it is determined whether the current gaming state matches the gaming state stored in the Nth storage unit (first storage unit) (the gaming state when the hold is stored). Is referred to the effect classification information of the storage unit. When the “indefinite value” effect classification information is stored, the hold display determination tables 1 and 4 are set according to the game state, and when other effect classification information is stored, the game The hold display determination tables 2 and 5 are set according to the state. If the current gaming state does not match the gaming state stored in the Nth storage unit (first storage unit) (the gaming state when the hold is stored), the current gaming state depends on the current gaming state. The hold display determination tables 3 and 6 are set.
(ステップS1220−5)
次に、サブCPU200aは、第N記憶部に記憶されている保留表示決定乱数と、上記ステップS1220−4でセットしたテーブルとに基づいて、保留表示種別を判定する。
(Step S1220-5)
Next, the
(ステップS1220−6)
次に、サブCPU200aは、上記ステップS1220−5で導出された保留表示種別が「通常表示」であるかを判定する。その結果、「通常表示」であると判定した場合にはステップS1220−7に処理を移し、「通常表示」ではないと判定した場合にはステップS1220−9に処理を移す。
(Step S1220-6)
Next, the
(ステップS1220−7)
上記ステップS1220−6において、保留表示種別が「通常表示」であると判定した場合には、サブCPU200aは、保留表示種別記憶領域に「通常表示」に係る情報を上書きする。
(Step S1220-7)
If it is determined in step S1220-6 that the hold display type is “normal display”, the
(ステップS1220−8)
次に、サブCPU200aは、第N記憶部にシフトされた対象保留についての保留表示を通常表示(青色表示)すべく、通常表示コマンドをセットする。ここでセットされたコマンドは画像制御基板210に送信され、画像制御基板210において、演出表示部50aに保留表示を通常表示するための処理が行われることとなる。
(Step S1220-8)
Next, the
(ステップS1220−9)
一方、上記ステップS1220−6において、保留表示種別が「通常表示」ではない(「特殊表示」である)と判定した場合には、サブCPU200aは、当該保留よりも前に変動演出が行われる対象前保留の演出分類が、全て「固定通常ハズレ」であるかを判定する。
(Step S1220-9)
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S1220-6 that the hold display type is not “normal display” (ie, “special display”), the
より詳細には、現在の遊技状態が非時短遊技状態、低確率遊技状態である場合において、対象前保留が現在と同じ遊技状態に設定されているときに記憶されたものであるときには、各対象前保留の演出分類情報が「固定通常ハズレ」であるかを判定する。一方、対象前保留が時短遊技状態Aに設定されているときに記憶されたものであるときには、各対象前保留の低確用演出分類仮判定情報が「固定通常ハズレ」であるかを判定する。こうした判定を全ての対象前保留について行った結果、全ての演出分類情報(演出分類仮判定情報)が固定通常ハズレであると判定した場合にはステップS1220−10に処理を移し、固定通常ハズレ以外の情報が1つでもあると判定した場合にはステップS1220−7に処理を移す。 More specifically, when the current gaming state is a non-time-saving gaming state or a low-probability gaming state, each subject is stored when the pre-submission is set to the same gaming state as the current one. It is determined whether the pre-pending performance classification information is “fixed normal loss”. On the other hand, when the pre-target hold is stored when the short-time gaming state A is set, it is determined whether the low-probability effect classification provisional determination information of each pre-target hold is “fixed normal lose”. . As a result of performing such determination for all pre-subject suspensions, if it is determined that all the production category information (production category provisional judgment information) is a fixed normal loss, the process moves to step S1220-10, and other than the fixed normal loss. If it is determined that there is even one piece of information, the process proceeds to step S1220-7.
(ステップS1220−10)
上記ステップS1220−9において、全ての演出分類情報(演出分類仮判定情報)が固定通常ハズレであると判定した場合には、サブCPU200aは、保留表示種別記憶領域に「特殊表示」に係る情報を上書きする。
(Step S1220-10)
If it is determined in step S1220-9 that all the effect classification information (effect classification provisional determination information) is fixed normal loss, the
(ステップS1220−11)
次に、サブCPU200aは、第N記憶部にシフトされた対象保留についての保留表示を特殊表示すべく、特殊表示コマンドをセットする。ここでセットされたコマンドは画像制御基板210に送信され、画像制御基板210において、演出表示部50aに保留表示を特殊表示するための処理が行われることとなる。
(Step S1220-11)
Next, the
(ステップS1220−12)
次に、サブCPU200aは、サブRAM200cに設けられた記憶部番号(N)に記憶されている現在の値に「1」を加算した値を、新たな記憶部番号(N)として記憶する。
(Step S1220-12)
Next, the
(ステップS1220−13)
次に、サブCPU200aは、上記ステップS1220−12で更新された記憶部番号(N)に保留情報があるかを判定する。その結果、保留情報があると判定した場合には、上記ステップS1220−4から上記の処理を繰り返し行う。これにより、第1記憶部〜第8記憶部に記憶された全ての保留について、それぞれ保留表示を再度決定する処理が行われることとなる。そして、記憶部番号(N)に保留情報がないと判定した場合には、当該保留更新処理を終了する。
(Step S1220-13)
Next, the
上記の副制御基板200における制御処理により、新たに保留が記憶されたときと、保留が処理されたときとで、保留表示が更新され、このときの保留表示の態様によって、予兆演出が行われることとなる。
The hold display is updated when the hold is newly stored by the control process in the
以上のように、本実施形態によれば、保留表示の態様によって予兆演出が行われることとなるが、通常は、各保留の発展後事前判定情報に基づいて、予兆演出の実行可否や出現頻度、あるいは表示態様等が最適に決定されるように設計している。そして、各保留については、遊技状態が変更されたと仮定した場合の演出分類仮判定情報を導出することとしているので、遊技状態が変更されたとしても、この演出分類仮判定情報に基づいて、予兆演出を実行することが可能となっている。これにより、遊技状態の変更直後から予兆演出を実行することが可能となり、演出効果を向上して遊技の興趣をさらに向上することができる。 As described above, according to the present embodiment, the sign effect is performed according to the mode of the hold display, but usually, whether or not the sign effect can be executed and the appearance frequency based on the post-development advance determination information of each hold. Alternatively, the display mode is designed to be determined optimally. And for each hold, the effect classification provisional determination information when it is assumed that the gaming state has been changed is derived. Therefore, even if the gaming state has been changed, an indication is made based on this effect classification provisional determination information. Production can be performed. As a result, it is possible to execute the indication effect immediately after the change of the game state, and the effect of the effect can be improved and the interest of the game can be further improved.
なお、保留が記憶されたときに、全ての遊技状態の発展後変動パターン情報(発展後事前判定情報)を事前判定すれば、常に、予兆演出を高精度に実行することが可能であるが、このようにすると、主制御基板100の処理負担が極めて大きくなる。なぜなら、遊技状態ごとに、特別図柄乱数、大当たり図柄乱数の判定を行い、その後、第1変動パターン乱数、第2変動パターン乱数A、第2変動パターン乱数Bの判定を行わなければならないからである。本実施形態においては、遊技状態が変更された場合の予兆演出を担保するために、第1変動パターン乱数の判定までを行い、第2変動パターン乱数A、Bの判定は行わないこととしたので、予兆演出の精度をある程度担保しつつ、処理負担の増大を抑制することが可能となる。
In addition, when the hold is stored, if the post-development variation pattern information (post-development pre-determination information) of all game states is pre-determined, it is always possible to execute the predictive effect with high accuracy. In this way, the processing burden on the
なお、上記実施形態における非時短遊技状態が本発明の第1の遊技状態に相当し、時短遊技状態Aが本発明の第2の遊技状態に相当する。上記実施形態においては、非時短遊技状態、時短遊技状態Aのいずれの遊技状態においても、大当たりの当選確率を異にする低確率遊技状態または高確率遊技状態に設定されることとしたが、大当たりの当選確率は常に一定としても構わない。また、遊技者の有利度合いが異なる2以上の遊技状態が設けられていればよく、各遊技状態の内容等は特に限定されるものではない。 Note that the non-short game state in the above embodiment corresponds to the first game state of the present invention, and the short-time game state A corresponds to the second game state of the present invention. In the above embodiment, in both the non-time-saving gaming state and the time-saving gaming state A, it is set to a low-probability gaming state or a high-probability gaming state with different jackpot winning probabilities. The winning probability may be always constant. Further, it is only necessary to provide two or more gaming states having different degrees of advantage of the player, and the contents of each gaming state are not particularly limited.
また、上記実施形態において、特別図柄乱数および大当たり乱数が本発明の特別遊技判定用乱数に相当し、図22に示す第1始動口検出スイッチ入力処理を実行するメインCPU100aが本発明の乱数記憶手段に相当する。上記実施形態においては、変動パターンを決定するための乱数として、演出分類を決定する乱数、発展前変動パターンを決定する乱数、発展後変動パターンを決定する乱数を設けることとした。しかしながら、例えば、変動パターンを発展前、発展後に分ける必要はなく、変動演出の開始から終了までを1の変動パターンで決定することとしてもよい。
In the above embodiment, the special symbol random number and the jackpot random number correspond to the special game determination random number of the present invention, and the
また、上記実施形態において、図26のステップS420−4の特別図柄決定処理を実行するメインCPU100aが本発明の特別遊技実行判定手段に相当する。
また、上記実施形態において、図27のステップS421−1〜ステップS421−2の処理を実行するメインCPU100aが本発明の演出分類決定手段に相当する。
また、上記実施形態において、図27のステップS421−3〜ステップS421−8の処理を実行するメインCPU100aが本発明の変動パターン決定手段に相当する。
また、上記実施形態において、図52のステップS1230およびステップS1240の処理を実行するサブCPU200aおよび画像制御基板210、電飾制御基板220が本発明の変動演出実行手段に相当する。
Moreover, in the said embodiment, main CPU100a which performs the special symbol determination process of step S420-4 of FIG. 26 is equivalent to the special game execution determination means of this invention.
Moreover, in the said embodiment, main CPU100a which performs the process of FIG.27 S421-1-step S421-2 is equivalent to the effect classification | category determination means of this invention.
In the above-described embodiment, the
In the above-described embodiment, the
また、上記実施形態において、図30の特別電動役物制御処理を実行するメインCPU100aが本発明の特別遊技実行手段に相当する。
また、上記実施形態において、図31の特別遊技終了処理を実行するメインCPU100aが本発明の遊技状態設定手段に相当する。
また、上記実施形態において、図23の事前判定処理を実行するメインCPU100aが本発明の事前判定手段に相当する。また、上記実施形態における発展後事前判定情報が本発明の第1事前判定情報に相当し、演出分類仮判定情報が本発明の第2事前判定情報に相当する。
また、上記実施形態における保留記憶領域が本発明の事前判定情報記憶手段に相当する。
In the above embodiment, the
In the above embodiment, the
Moreover, in the said embodiment, main CPU100a which performs the prior determination process of FIG. 23 corresponds to the prior determination means of this invention. Further, the post-development preliminary determination information in the above embodiment corresponds to the first preliminary determination information of the present invention, and the effect classification provisional determination information corresponds to the second preliminary determination information of the present invention.
The reserved storage area in the above embodiment corresponds to the prior determination information storage means of the present invention.
また、上記実施形態における保留表示の特殊表示が本発明の予兆演出に相当し、図51のステップS1210−7の処理を実行するサブCPU200aが本発明の予兆演出実行判定手段に相当する。なお、上記実施形態においては、所定の事前判定情報が記憶された場合に、当該保留についての保留表示を特殊表示するか否か(予兆演出の実行可否)について、抽選により決定することとしたが、所定の事前判定情報が記憶された場合には、必ず予兆演出を実行することとしてもよい。
Further, the special display of the hold display in the above embodiment corresponds to the sign effect of the present invention, and the
また、上記実施形態においては、保留表示の表示態様によって予兆演出を実行することとしたが、予兆演出の具体的な内容はこれに限らない。例えば、対象保留よりも前に行われる対象前保留の変動演出開始時に、所定の演出が連続的に実行されるようにしてもよい。いずれにしても、本発明の予兆演出は、対象保留に基づく変動演出が開始されるよりも前に開始される演出を広く含むものである。 Moreover, in the said embodiment, although the sign effect was performed with the display mode of a hold display, the specific content of a sign effect is not restricted to this. For example, a predetermined effect may be continuously executed at the start of the variable effect of the hold before target performed before the target hold. In any case, the indication effect of the present invention includes a wide range of effects that are started before the change effect based on the target suspension is started.
また、上記実施形態においては、非時短遊技状態に設定されている場合には、非時短遊技状態における事前判定情報と、時短遊技状態Aの演出分類仮判定情報とを導出し、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合には、時短遊技状態Aにおける事前判定情報と、非時短遊技状態の演出分類仮判定情報とを導出することとした。しかしながら、例えば、上記実施形態において、時短遊技状態Aに設定されている場合には、時短遊技状態Aにおける事前判定情報のみを導出し、非時短遊技状態の演出分類仮判定情報は導出しないこととしてもよい。
また、上記実施形態において、「通常」と称される演出分類が本発明の通常演出分類に相当し、「リーチ」と称される演出分類が本発明の特定演出分類に相当する。
Further, in the above embodiment, when the non-time-saving gaming state is set, the prior determination information in the non-time-saving gaming state and the effect classification provisional judgment information of the time-saving gaming state A are derived, and the time-saving gaming state A In the case where it is set, the prior determination information in the short-time gaming state A and the effect classification provisional determination information in the non-short-time gaming state are derived. However, for example, in the above embodiment, when the short-time gaming state A is set, only the preliminary determination information in the short-time gaming state A is derived, and the effect classification provisional determination information of the non-short-time gaming state is not derived. Also good.
In the above-described embodiment, the effect category called “normal” corresponds to the normal effect category of the present invention, and the effect category called “reach” corresponds to the specific effect category of the present invention.
以上、添付図面を参照しながら本発明の好適な実施形態について説明したが、本発明はかかる実施形態に限定されないことは言うまでもない。当業者であれば、特許請求の範囲に記載された範疇において、各種の変更例または修正例に想到し得ることは明らかであり、それらについても当然に本発明の技術的範囲に属するものと了解される。 As mentioned above, although preferred embodiment of this invention was described referring an accompanying drawing, it cannot be overemphasized that this invention is not limited to this embodiment. It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that various changes and modifications can be made within the scope of the claims, and these are naturally within the technical scope of the present invention. Is done.
1 遊技機
8 遊技盤
16 遊技領域
20 第1始動口
22 第2始動口
50 演出表示装置
50a 演出表示部
100 主制御基板
100a メインCPU
100b メインROM
100c メインRAM
200 副制御基板
200a サブCPU
200b サブROM
200c サブRAM
210 画像制御基板
220 電飾制御基板
1
100b Main ROM
100c main RAM
200
200b Sub ROM
200c Sub RAM
210
Claims (4)
遊技球が流下する遊技領域が設けられた遊技盤と、
前記遊技領域に設けられた始動領域と、
前記始動領域に遊技球が進入したことを条件として、遊技者に有利な特別遊技の実行可否を決定するための特別遊技判定用乱数、および、当該特別遊技の実行可否を報知する変動演出の態様が対応付けられた変動パターンを決定するための第1変動パターン乱数および第2変動パターン乱数を少なくとも取得するとともに、当該取得した前記各乱数を保留として記憶部に記憶する乱数記憶手段と、
始動条件の成立により、前記乱数記憶手段によって記憶部に記憶された特別遊技判定用乱数を読み出して、予め設定された判定条件にしたがって前記特別遊技の実行可否を判定する特別遊技実行判定手段と、
前記特別遊技実行判定手段の判定結果、当該判定の際に読み出された特別遊技判定用乱数とともに記憶部に記憶された前記第1変動パターン乱数、および、設定されている遊技状態に対応付けて予め設定された決定条件にしたがって、前記変動パターンの所定要素に基づいて分類され遊技状態ごとに設定された複数の演出分類の中からいずれかの演出分類を決定する演出分類決定手段と、
前記特別遊技実行判定手段の判定の際に読み出された特別遊技判定用乱数とともに記憶部に記憶された前記第2変動パターン乱数に基づいて、前記演出分類決定手段によって決定された演出分類に対応付けられた変動パターンの中からいずれかの変動パターンを決定する変動パターン決定手段と、
前記変動パターン決定手段によって決定された変動パターンにしたがって前記変動演出を実行する変動演出実行手段と、
前記特別遊技実行判定手段によって前記特別遊技の実行を可能とする判定結果が導出されるとともに、前記変動演出実行手段によって実行される前記変動演出が終了した場合に、当該特別遊技を実行する特別遊技実行手段と、
前記特別遊技が実行された場合に、当該特別遊技の終了後の遊技状態を複数の遊技状態の中からいずれかの遊技状態に設定する遊技状態設定手段と、
前記記憶部に前記各乱数が記憶された場合に、設定されている遊技状態に対応する前記判定条件および決定条件にしたがって、前記特別遊技判定用乱数、前記第1変動パターン乱数および第2変動パターン乱数を事前判定して、当該設定されている遊技状態における変動パターンに係る第1事前判定情報を導出するとともに、遊技状態が前記第1の遊技状態に設定されている場合には、前記第2の遊技状態に対応する前記決定条件にしたがって前記第1変動パターン乱数を仮判定して、当該第2の遊技状態における演出分類に係る第2事前判定情報を当該第1の遊技状態における前記第1事前判定情報に加えて導出する事前判定手段と、
前記事前判定手段によって導出された第1事前判定情報および第2事前判定情報を記憶する事前判定情報記憶手段と、
前記事前判定情報記憶手段に記憶された前記第1事前判定情報または前記第2事前判定情報に基づいて、当該事前判定情報が導出された保留に基づく変動演出が開始されるよりも前に開始される予兆演出の実行可否を判定する予兆演出実行判定手段と、
前記予兆演出実行判定手段によって前記予兆演出を実行する判定結果が導出された場合に、前記予兆演出を実行する予兆演出実行手段と、を備え、
前記予兆演出実行判定手段は、
前記第2の遊技状態に設定されている場合には、前記第1の遊技状態に設定されているときに記憶された保留については前記第2事前判定情報に基づいて前記予兆演出の実行可否を判定し、前記第2の遊技状態に設定された後に記憶された保留については前記第1事前判定情報に基づいて前記予兆演出の実行可否を判定することを特徴とする遊技機。 A gaming machine that is set to any one of a plurality of gaming states including at least a first gaming state and a second gaming state with different degrees of advantage of the player,
A game board with a game area where game balls flow down;
A starting area provided in the gaming area;
On condition that a game ball has entered the starting area, a random number for determining a special game for determining whether or not to execute a special game advantageous to the player, and a variation effect mode for notifying whether or not the special game can be executed Random number storage means for obtaining at least a first variation pattern random number and a second variation pattern random number for determining a variation pattern associated with each other, and storing the obtained random numbers in a storage unit as a hold,
A special game execution determination unit that reads out a special game determination random number stored in the storage unit by the random number storage unit when the start condition is satisfied, and determines whether or not the special game can be executed according to a predetermined determination condition;
In correspondence with the determination result of the special game execution determination means, the first variation pattern random number stored in the storage unit together with the special game determination random number read at the time of the determination, and the set game state Effect classification determining means for determining any effect classification from among a plurality of effect classifications classified according to predetermined elements of the variation pattern and set for each gaming state according to a predetermined determination condition;
Corresponds to the effect classification determined by the effect classification determination means based on the second variation pattern random number stored in the storage unit together with the random number for special game determination read at the time of determination by the special game execution determination means A variation pattern determining means for determining any variation pattern from the variation patterns attached;
Fluctuation effect execution means for executing the fluctuation effect according to the fluctuation pattern determined by the fluctuation pattern determination means;
A special game for executing the special game when the special game execution determination means derives a determination result that enables the execution of the special game and when the variable effect executed by the variable effect execution means ends. Execution means;
A game state setting means for setting a game state after the end of the special game to any one of a plurality of game states when the special game is executed;
When each random number is stored in the storage unit, the special game determination random number, the first variation pattern random number, and the second variation pattern according to the determination condition and determination condition corresponding to the set gaming state A random number is preliminarily determined to derive first prior determination information related to the variation pattern in the set gaming state, and when the gaming state is set to the first gaming state, the second The first variation pattern random number is provisionally determined according to the determination condition corresponding to the gaming state, and second pre-determining information related to the effect classification in the second gaming state is the first in the first gaming state. A pre-determination means for deriving in addition to the pre-determination information;
A pre-determination information storage unit that stores first pre-determination information and second pre-determination information derived by the pre-determination unit;
Based on the first pre-determination information or the second pre-determination information stored in the pre-determination information storage means, start before the change effect based on the hold from which the pre-determination information is derived is started Predictive effect execution determining means for determining whether or not to execute the predictive effect,
When the determination result for executing the indication effect is derived by the indication effect execution determination means, the indication effect execution means for executing the indication effect,
The sign production execution determination means includes :
Before SL if it is set to the second gaming state, executability of the predictive effect on the basis of the second pre-determination information about stored pending when set to the first game status And determining whether or not the indication effect can be executed based on the first pre-determination information for the hold stored after the second gaming state is set.
遊技状態が前記第2の遊技状態に設定されている場合には、当該第2の遊技状態に対応する前記判定条件および決定条件にしたがって、前記特別遊技判定用乱数、前記第1変動パターン乱数および第2変動パターン乱数を事前判定して、当該第2の遊技状態における変動パターンに係る第1事前判定情報を導出するとともに、前記第1の遊技状態に対応する前記決定条件にしたがって前記第1変動パターン乱数を仮判定して、当該第1の遊技状態における演出分類に係る第2事前判定情報を前記第1事前判定情報に加えて導出することを特徴とする請求項1記載の遊技機。 The prior determination means includes
When the gaming state is set to the second gaming state, the special gaming determination random number, the first variation pattern random number, and the special gaming determination random number according to the determination condition and the determination condition corresponding to the second gaming state The second variation pattern random number is preliminarily determined to derive first prior determination information related to the variation pattern in the second gaming state, and the first variation according to the determination condition corresponding to the first gaming state. The gaming machine according to claim 1, wherein a pattern random number is provisionally determined, and second prior determination information related to the effect classification in the first gaming state is derived in addition to the first prior determination information.
前記通常演出分類は、
前記特別遊技実行判定手段によって前記特別遊技を実行しないとする判定結果が導出された場合に、前記特定演出分類よりも高確率で決定され、
前記特定演出分類は、
前記特別遊技実行判定手段によって前記特別遊技の実行を可能とする判定結果が導出された場合に、前記通常演出分類よりも高確率で決定され、
前記通常演出分類に対応付けられた変動パターンによる変動演出の平均時間は、前記特定演出分類に対応付けられた変動パターンによる変動演出の平均時間よりも短いことを特徴とする請求項1または2記載の遊技機。 The effect category determined by the effect category determining means is provided with at least a normal effect category and a specific effect category,
The normal performance category is
When the determination result that the special game is not to be executed is derived by the special game execution determination means, it is determined with a higher probability than the specific effect classification,
The specific performance category is
When the determination result that enables execution of the special game is derived by the special game execution determination means, it is determined with a higher probability than the normal performance classification,
The average time of the variation effect by the variation pattern associated with the normal effect category is shorter than the average time of the variation effect by the variation pattern associated with the specific effect category. Game machines.
前記通常演出分類に対応付けられる変動パターンには、前記演出表示部に第1の表示態様の演出表示画像が表示されることなく変動演出が終了する変動パターンが含まれ、
前記特定演出分類に対応付けられる変動パターンには、前記演出表示部に第1の表示態様の演出表示画像が表示された後に、第2の表示態様の演出表示画像が表示されて変動演出が終了する変動パターンが含まれることを特徴とする請求項3記載の遊技機。 An effect display image for notifying whether or not the special game can be executed corresponding to the change pattern is provided with an effect display unit displayed by the change effect executing means,
The variation pattern associated with the normal effect classification includes a variation pattern in which the variation effect ends without displaying the effect display image of the first display mode on the effect display unit,
In the variation pattern associated with the specific effect classification, after the effect display image of the first display mode is displayed on the effect display unit, the effect display image of the second display mode is displayed and the variation effect ends. The gaming machine according to claim 3, wherein a variation pattern is included.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011157896A JP5372079B2 (en) | 2011-07-19 | 2011-07-19 | Game machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011157896A JP5372079B2 (en) | 2011-07-19 | 2011-07-19 | Game machine |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013191646A Division JP5782080B2 (en) | 2013-09-17 | 2013-09-17 | Game machine |
| JP2013191647A Division JP5782081B2 (en) | 2013-09-17 | 2013-09-17 | Game machine |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013022126A JP2013022126A (en) | 2013-02-04 |
| JP2013022126A5 JP2013022126A5 (en) | 2013-09-05 |
| JP5372079B2 true JP5372079B2 (en) | 2013-12-18 |
Family
ID=47781151
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011157896A Expired - Fee Related JP5372079B2 (en) | 2011-07-19 | 2011-07-19 | Game machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5372079B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6240935B2 (en) * | 2013-02-22 | 2017-12-06 | 株式会社ソフイア | Game machine |
| JP2017023356A (en) * | 2015-07-21 | 2017-02-02 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP2017023357A (en) * | 2015-07-21 | 2017-02-02 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP6192705B2 (en) * | 2015-12-28 | 2017-09-06 | 株式会社ソフイア | Game machine |
| JP6368300B2 (en) * | 2015-12-28 | 2018-08-01 | 株式会社ソフイア | Game machine |
| JP6491116B2 (en) * | 2016-01-27 | 2019-03-27 | 株式会社ソフイア | Game machine |
| JP6221104B2 (en) * | 2016-01-27 | 2017-11-01 | 株式会社ソフイア | Game machine |
| JP2019013572A (en) * | 2017-07-07 | 2019-01-31 | サミー株式会社 | Pachinko game machine |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5305998B2 (en) * | 2009-03-13 | 2013-10-02 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP5297891B2 (en) * | 2009-05-25 | 2013-09-25 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP4876177B2 (en) * | 2010-02-23 | 2012-02-15 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP2013009952A (en) * | 2011-05-27 | 2013-01-17 | Takao Co Ltd | Pinball game machine |
-
2011
- 2011-07-19 JP JP2011157896A patent/JP5372079B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013022126A (en) | 2013-02-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5758689B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5850638B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5775441B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5372079B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5829853B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5858632B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6085334B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5887093B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5897326B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5722206B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5894455B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5855352B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6074526B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5782081B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5996028B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6085333B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5782080B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5879375B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6386502B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6046689B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6124972B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6298482B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6162840B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5953011B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2016182455A (en) | Game machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130723 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20130723 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20130723 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20130816 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130820 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130917 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5372079 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |