JP5023907B2 - Actuator, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus - Google Patents
Actuator, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5023907B2 JP5023907B2 JP2007236298A JP2007236298A JP5023907B2 JP 5023907 B2 JP5023907 B2 JP 5023907B2 JP 2007236298 A JP2007236298 A JP 2007236298A JP 2007236298 A JP2007236298 A JP 2007236298A JP 5023907 B2 JP5023907 B2 JP 5023907B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- coil
- movable plate
- wiring
- actuator
- pair
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 title claims description 27
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 35
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 24
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 108091008695 photoreceptors Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920006332 epoxy adhesive Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000001579 optical reflectometry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Facsimile Scanning Arrangements (AREA)
- Apparatuses For Generation Of Mechanical Vibrations (AREA)
- Mechanical Optical Scanning Systems (AREA)
- Mechanical Light Control Or Optical Switches (AREA)
Description
本発明は、アクチュエータ、光スキャナ、および画像形成装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to an actuator, an optical scanner, and an image forming apparatus.
例えば、レーザープリンタ等にて光走査により描画を行うための光スキャナとして、捩り振動子を構成する構造体を有するアクチュエータを用いたものが知られている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。
特許文献1に開示されたアクチュエータでは、ミラーを有する可動板が1対のトーションバーを介して基板に対し連結されている。そして、コイルが可動板に設けられているとともに、磁石が可動板に対向して設けられている。また、コイルに通電するための配線がトーションバーに設けられており、この配線を介してコイルに通電することにより、トーションバーの捩れ変形を伴って、磁石の磁界中に配された可動板を回動させる。
For example, an optical scanner for performing drawing by optical scanning with a laser printer or the like is known that uses an actuator having a structure constituting a torsional vibrator (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
In the actuator disclosed in Patent Document 1, a movable plate having a mirror is connected to a substrate via a pair of torsion bars. The coil is provided on the movable plate, and the magnet is provided to face the movable plate. In addition, a wiring for energizing the coil is provided in the torsion bar. By energizing the coil via this wiring, a movable plate disposed in the magnetic field of the magnet is accompanied by torsional deformation of the torsion bar. Rotate.
しかしながら、特許文献1にかかる光スキャナでは、トーションバー上に配線が設けられているため、トーションバーの捩れ変形によって配線に大きな応力が生じてしまう。そのため、配線の断線が生じやすく、アクチュエータの信頼性を低下させてしまう。
また、配線から生じる熱の影響によりトーションバーのバネ特性(バネ定数)が変動するため、可動板を所望の周波数で安定して動作するように制御することが難しい。
However, in the optical scanner according to Patent Document 1, since the wiring is provided on the torsion bar, a large stress is generated in the wiring due to torsional deformation of the torsion bar. Therefore, disconnection of the wiring is likely to occur, and the reliability of the actuator is lowered.
Further, since the spring characteristics (spring constant) of the torsion bar fluctuate due to the influence of heat generated from the wiring, it is difficult to control the movable plate so as to operate stably at a desired frequency.
本発明の目的は、電磁駆動(ムービングコイル)方式において、配線の断線を防止して、優れた信頼性を発揮することができるアクチュエータ、光スキャナ、および画像形成装置を提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to provide an actuator, an optical scanner, and an image forming apparatus that can exhibit excellent reliability by preventing disconnection of wiring in an electromagnetic drive (moving coil) system.
このような目的は、下記の本発明により達成される。
本発明のアクチュエータは、可動板と、該可動板を支持する1対の軸部材とを備えた振動部と、
前記振動部に設けられたコイルと、
前記コイルに通電するための配線と、
前記コイルに対向して設置された磁石とを有し、
前記磁石の磁界中に配された前記コイルに通電することにより、前記可動板を前記各軸部材の捩れ変形を伴って回動させるように構成され、
前記配線は、その一部が前記各軸部材に対し離間するように配設されていることを特徴とする。
Such an object is achieved by the present invention described below.
An actuator according to the present invention includes a vibrating part including a movable plate and a pair of shaft members that support the movable plate;
A coil provided in the vibrating section;
Wiring for energizing the coil;
A magnet installed facing the coil,
By energizing the coil disposed in the magnetic field of the magnet, the movable plate is configured to rotate with torsional deformation of each shaft member,
The wiring is characterized in that a part of the wiring is arranged so as to be separated from each shaft member.
これにより、各軸部材の捩れ変形によって配線に生じる応力を低減して、アクチュエータの信頼性を向上させることができる。
また、各軸部材に対する配線からの熱の影響を防止または抑制することができる。そのため、各軸部材のバネ特性(バネ定数)の変動を防止または抑制して、長期にわたり簡単に、可動板を所望の周波数で安定して動作させることができる。
さらに、軸部材上に可動板の挙動検知のためのPZR等のセンサを設けた際、コイルからの配線を軸部材上に設けることが難しい場合であっても、コイルからの配線の取り出しが簡単となる。
Thereby, the stress which arises in wiring by the torsional deformation of each shaft member can be reduced, and the reliability of an actuator can be improved.
Moreover, the influence of the heat from the wiring with respect to each shaft member can be prevented or suppressed. Therefore, fluctuations in the spring characteristics (spring constant) of each shaft member can be prevented or suppressed, and the movable plate can be easily operated stably at a desired frequency over a long period of time.
Further, when a sensor such as PZR for detecting the behavior of the movable plate is provided on the shaft member, it is easy to take out the wiring from the coil even when it is difficult to provide the wiring from the coil on the shaft member. It becomes.
本発明のアクチュエータでは、前記配線は、前記1対の軸部材のうちの少なくとも一方の軸部材に沿って設けられていることが好ましい。
これにより、可動板の回動によって配線に生じる応力を低減して、アクチュエータの信頼性を向上させることができる。
本発明のアクチュエータでは、前記振動部を支持する支持部を有しており、前記配線は、前記振動部上に接合された第1の接合点と、前記支持部上に接合された第2の接合点とを有し、前記第1の接合点と前記第2の接合点との間をワイヤーボンディングすることにより形成されたものであることが好ましい。
これにより、配線の形成を比較的簡単なものとしつつ、アクチュエータの信頼性を向上させることができる。
In the actuator according to the aspect of the invention, it is preferable that the wiring is provided along at least one shaft member of the pair of shaft members.
Thereby, the stress which arises in wiring by rotation of a movable plate can be reduced and the reliability of an actuator can be improved.
In the actuator of the present invention, the actuator has a support part that supports the vibration part, and the wiring has a first joining point joined on the vibration part and a second joint joined on the support part. It is preferable that it is formed by wire bonding between the first joint point and the second joint point.
Thereby, the reliability of the actuator can be improved while the formation of the wiring is relatively simple.
本発明のアクチュエータでは、前記コイルは、絶縁膜を介して前記振動部上に設けられ、当該絶縁膜は、前記各軸部材に対し離間しつつ延長された延長部を有し、前記配線は、当該延長部上に設けられていることが好ましい。
これにより、コイルおよび配線の形成を比較的簡単なものとしつつ、アクチュエータの信頼性を向上させることができる。
In the actuator according to the aspect of the invention, the coil is provided on the vibrating portion via an insulating film, the insulating film has an extended portion that is extended while being separated from the shaft members, and the wiring is It is preferable to be provided on the extension.
Thereby, the reliability of the actuator can be improved while making the formation of the coil and the wiring relatively simple.
本発明のアクチュエータでは、前記コイルは、前記可動板に設けられていることが好ましい。
これにより、振動部を可動板および1対の軸部材からなる1自由度振動系とすることができる。
本発明のアクチュエータでは、前記コイルは、前記可動板の板面に沿って渦巻状に形成されていることが好ましい。
これにより、コイルの構成を比較的簡単なものとするとともに、駆動電圧を抑えつつ、コイルに生じる磁力を大きくすることができる。
本発明のアクチュエータでは、前記配線は、前記可動板と前記各軸部材との境界部付近に接合された1対の第1の接合点を有していることが好ましい。
これにより、可動板の回動によって配線に生じる応力を低減して、アクチュエータの信頼性を向上させることができる。
In the actuator of the present invention, it is preferable that the coil is provided on the movable plate.
Thereby, a vibration part can be made into the 1 degree-of-freedom vibration system which consists of a movable plate and a pair of shaft members.
In the actuator according to the aspect of the invention, it is preferable that the coil is formed in a spiral shape along the plate surface of the movable plate.
Thereby, while making the structure of a coil comparatively simple, the magnetic force which arises in a coil can be enlarged, suppressing a drive voltage.
In the actuator according to the aspect of the invention, it is preferable that the wiring has a pair of first joining points joined in the vicinity of a boundary portion between the movable plate and each shaft member.
Thereby, the stress which arises in wiring by rotation of a movable plate can be reduced and the reliability of an actuator can be improved.
本発明のアクチュエータでは、前記振動部を支持する支持部を有しており、前記配線は、前記支持部と前記各軸部材との境界部付近に接合された1対の第2の接合点を有していることが好ましい。
これにより、可動板の回動によって配線に生じる応力を簡単かつ確実に低減して、アクチュエータの信頼性を向上させることができる。
In the actuator according to the aspect of the invention, the actuator includes a support portion that supports the vibration portion, and the wiring includes a pair of second joining points joined in the vicinity of a boundary portion between the support portion and each shaft member. It is preferable to have.
Thereby, the stress which arises in wiring by rotation of a movable plate can be reduced easily and reliably, and the reliability of an actuator can be improved.
本発明のアクチュエータでは、前記1対の第1の接合点および前記1対の第2の接合点は、前記1対の軸部材に対する前記配線の影響が互いに等しくなるように設けられていることが好ましい。
これにより、アクチュエータの設計を簡単なものとしつつ、振動部の振動特性を優れたものとすることができる。
本発明のアクチュエータでは、前記配線は、前記1対の軸部材に対する影響が互いに等しくなるように設けられていることが好ましい。
これにより、アクチュエータの設計を簡単なものとしつつ、振動部の振動特性を優れたものとすることができる。
In the actuator of the present invention, the pair of first joining points and the pair of second joining points may be provided so that the influence of the wiring on the pair of shaft members is equal to each other. preferable.
Thereby, it is possible to make the design of the actuator simple and to make the vibration characteristics of the vibration part excellent.
In the actuator according to the aspect of the invention, it is preferable that the wiring is provided so that influences on the pair of shaft members are equal to each other.
Thereby, it is possible to make the design of the actuator simple and to make the vibration characteristics of the vibration part excellent.
本発明のアクチュエータでは、前記可動板および前記各軸部材は、シリコンで一体的に形成されていることが好ましい。
これにより、振動部の振動特性および耐久性を優れたものとすることができる。
本発明のアクチュエータでは、前記コイルおよび前記配線は、それぞれ、金属で構成されていることが好ましい。
金属は一般に優れた電気伝導性を有するものの変形を繰り返すことにより金属疲労が生じる。したがって、金属で構成されたコイルや配線を用いた場合に、本発明を適用することによる効果が顕著となる。
In the actuator of the present invention, it is preferable that the movable plate and the shaft members are integrally formed of silicon.
Thereby, the vibration characteristics and durability of the vibration part can be made excellent.
In the actuator according to the aspect of the invention, it is preferable that each of the coil and the wiring is made of metal.
Although metal generally has excellent electrical conductivity, metal fatigue is caused by repeated deformation. Therefore, when the coil and wiring comprised with the metal are used, the effect by applying this invention becomes remarkable.
本発明の光スキャナは、光反射部が設けられた可動板と、該可動板を支持する1対の軸部材とを備えた振動部と、
前記振動部に設けられたコイルと、
前記コイルに通電するための配線と、
前記コイルに対向して設置された磁石とを有し、
前記磁石の磁界中に配された前記コイルに通電することにより、前記可動板を前記各軸部材の捩れ変形を伴って回動させ、前記光反射部で反射した光を走査するように構成され、
前記配線は、その一部が前記各軸部材に対し離間するように配設されていることを特徴とする。
これにより、本発明の光スキャナは、電磁駆動(ムービングコイル)方式において、優れた信頼性を発揮することができる。
An optical scanner according to the present invention includes a movable portion provided with a light reflecting portion, and a vibrating portion including a pair of shaft members that support the movable plate,
A coil provided in the vibrating section;
Wiring for energizing the coil;
A magnet installed facing the coil,
By energizing the coil disposed in the magnetic field of the magnet, the movable plate is rotated with torsional deformation of each shaft member, and the light reflected by the light reflecting portion is scanned. ,
The wiring is characterized in that a part of the wiring is arranged so as to be separated from each shaft member.
Thereby, the optical scanner of the present invention can exhibit excellent reliability in the electromagnetic drive (moving coil) system.
本発明の画像形成装置は、光反射部が設けられた可動板と、該可動板を支持する1対の軸部材とを備えた振動部と、
前記振動部に設けられたコイルと、
前記コイルに通電するための配線と、
前記コイルに対向して設置された磁石とを有し、
前記磁石の磁界中に配された前記コイルに通電することにより、前記可動板を前記各軸部材の捩れ変形を伴って回動させ、前記光反射部で反射した光を走査して、画像を形成するように構成され、
前記配線は、その一部が前記各軸部材に対し離間するように配設されていることを特徴とする。
これにより、本発明の画像形成装置は、優れた信頼性を発揮することができる。
An image forming apparatus according to the present invention includes a movable portion provided with a light reflecting portion, and a vibration portion including a pair of shaft members that support the movable plate,
A coil provided in the vibrating section;
Wiring for energizing the coil;
A magnet installed facing the coil,
By energizing the coil arranged in the magnetic field of the magnet, the movable plate is rotated with torsional deformation of each shaft member, and the light reflected by the light reflecting portion is scanned to scan the image. Configured to form,
The wiring is characterized in that a part of the wiring is arranged so as to be separated from each shaft member.
As a result, the image forming apparatus of the present invention can exhibit excellent reliability.
以下、本発明のアクチュエータの好適な実施形態について、添付図面を参照しつつ説明する。
<第1実施形態>
図1は、本発明のアクチュエータの第1実施形態を示す斜視図、図2は、図1に示すアクチュエータの平面図、図3は、図1に示すアクチュエータの断面図((a)は図2中のA−A線断面図、(b)は図2中のB−B線断面図)、図4は、図1に示すアクチュエータに備えられたコイルを説明するための部分拡大斜視図である。
なお、以下では、説明の便宜上、図3中の上側を「上」、下側を「下」と言う。
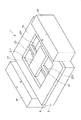
図1に示すように、本実施形態のアクチュエータ1は、電磁駆動方式(より具体的にはムービングコイル方式)を採用するアクチュエータであって、振動系(振動部)を有する基体2と、この基体2を支持する支持体3と、1対の磁石(永久磁石)41、42とを有している。
DESCRIPTION OF EXEMPLARY EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of an actuator of the invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
<First Embodiment>
FIG. 1 is a perspective view showing a first embodiment of the actuator of the present invention, FIG. 2 is a plan view of the actuator shown in FIG. 1, and FIG. 3 is a sectional view of the actuator shown in FIG. A sectional view taken along the line AA in FIG. 2, (b) is a sectional view taken along the line BB in FIG. 2, and FIG. 4 is a partially enlarged perspective view for explaining the coil provided in the actuator shown in FIG. .
In the following, for convenience of explanation, the upper side in FIG. 3 is referred to as “upper” and the lower side is referred to as “lower”.
As shown in FIG. 1, the actuator 1 of this embodiment is an actuator that employs an electromagnetic drive system (more specifically, a moving coil system), and includes a
以下、アクチュエータ1を構成する各部を順次説明する。
基体2は、図1に示すように、可動板21と、可動板21を支持する1対の軸部材22、23と、これらを囲むように枠状に形成された支持部24とを有している。
可動板21は、板状をなし、本実施形態では、平面視形状が長方形をなしている。そして、可動板21の板面(上面)には、光反射性を有する光反射部211が設けられている。これにより、アクチュエータ1を光スキャナ、光アッテネータ、光スイッチ等の光学デバイスに適用することができる。
Hereinafter, each part which comprises the actuator 1 is demonstrated sequentially.
As shown in FIG. 1, the
The
また、図2に示すように、可動板21の下面には、コイル212が設けられている。このコイル212は、後述する1対の磁石41、42の磁界中に配され、通電により可動板21に電磁力を作用させることができる。
このコイル212は、可動板21の光反射部211とは反対側の面に設けられているため、光反射部211の設計の自由度が低下することはない。
Further, as shown in FIG. 2, a
Since the
また、本実施形態では、コイル212は、図2および図4に示すように、可動板21の板面に沿って渦巻状に形成されている。このような渦巻状のコイル212は、単に環状に形成したコイルに比し大きな磁力を発生させることができ、また、可動板21の厚さ方向に積層して形成したコイルに比し構成が簡単で製造も容易である。すなわち、コイル212の構成を比較的簡単なものとするとともに、駆動電圧を抑えつつ、コイル212に生じる磁力を大きくすることができる。
In the present embodiment, the
また、コイル212を構成する素線の一端(渦巻きの外周側の端)は、可動板21と軸部材23との境界部付近に位置し、後述する配線231に電気的に接続されている。また、コイル212を構成する素線の他端(渦巻きの中心側の端)は、可動板21の板面の中心付近に位置しているが、ワイヤーボンディングで構成された配線214を介して、可動板21と軸部材22との境界部付近で、後述する配線221に電気的に接続されている。
なお、コイル212を構成する素線の他端(渦巻きの中心側の端)と配線221との接続は、ワイヤーボンディングに限定されず、例えば、振動部上に絶縁膜を介して配線パターンを成膜するとともに、その絶縁膜に配線パターンに導通する貫通電極を設けた構成でもよい。
In addition, one end of the wire constituting the coil 212 (end on the outer peripheral side of the spiral) is located near the boundary between the
The connection between the other end of the wire constituting the coil 212 (the end on the center side of the spiral) and the
ここで、前述した配線214は、その一端がコイル212を構成する素線の他端(渦巻きの中心側の端)付近の接合点で可動板21に接合・固定され、他端が可動板21と軸部材22との境界部付近の第1の接合点222に接合・固定されている。
また、可動板21(振動部)とコイル212との間には、絶縁膜が介在しているのが好ましい。これにより、コイル212と可動板21と間の絶縁性を優れたものとし、信頼性を向上させることができる。この場合、コイル212を構成する素線の外周に絶縁膜を形成してもよいし、可動板21の下面(コイル212側の面)の全面に絶縁膜を形成してもよい。また、この絶縁膜の構成材料としては、絶縁性を有していれば特に限定されないが、樹脂、金属酸化物等が挙げられる。
また、コイル212の構成材料としては、導電性を有するものであれば、特に限定されないが、アルミニウム等の金属が好適に用いられる。
Here, the
In addition, an insulating film is preferably interposed between the movable plate 21 (vibrating portion) and the
The constituent material of the
このような可動板21は、1対の軸部材22、23によって支持(両持ち支持)されている。
1対の軸部材22、23は、それぞれ、弾性変形可能であるとともに、可動板21と支持部24とを連結している。
また、1対の軸部材22、23は、互いに同軸的に設けられており、これらを回動中心軸(回転軸)Xとして、可動板21が各軸部材22、23の捩れ変形を伴って支持部24に対して回動可能となっている。
Such a
Each of the pair of
In addition, the pair of
支持部24の下面には、各軸部材22、23との境界部付近に、端子241、242が設けられている。
そして、端子241は、前述したコイル212と配線221を介して電気的に接続され、端子242は、コイル212と配線231を介して電気的に接続されている。これにより、配線221、231を介してコイル212に通電することができる。
The terminal 241 is electrically connected to the
配線221は、その一端が可動板21と軸部材22との境界部付近の第1の接合点222で、可動板21に接合・固定され、他端が端子241上の第2の接合点223で支持部24に接合・固定されている。
このような配線221は、第1の接合点222と第2の接合点223とをワイヤーボンディングすることにより形成されたものである。
One end of the
Such a
同様に、配線231は、その一端が可動板21と軸部材23との境界部付近の第1の接合点232で、可動板21に接合・固定され、他端が端子242上の第2の接合点233で支持部24に接合・固定されている。
このような配線231は、前述した配線221と同様、第1の接合点232と第2の接合点233とをワイヤーボンディングすることにより形成されたものである。
なお、配線221、231は、ワイヤーボンディング法により形成されたものに限定されない。
Similarly, the
Such a
Note that the
このような各配線221、231は、各軸部材22、23に対し離間するように配設されている。これにより、各軸部材22、23の捩れ変形によって配線221、231に生じる応力を低減して、アクチュエータ1の信頼性を向上させることができる。
また、配線221が軸部材22に沿って設けられているとともに、配線231が軸部材23に沿って設けられているため、可動板21の回動によって配線221、231に生じる応力を低減して、アクチュエータ1の信頼性を向上させることができる。
In addition, since the
また、各配線221、231は前述したようにワイヤーボンディングを用いて形成されたものであるため、配線221、231の形成を比較的簡単なものとしつつ、アクチュエータ1の信頼性を向上させることができる。
また、配線221、231が前述したような1対の第1の接合点222、232を有しているため、可動板21の回動によって配線221に、231生じる応力を低減して、アクチュエータ1の信頼性を向上させることができる。
その上、配線221、231が前述したような1対の第2の接合点223、233を有しているため、可動板21の回動によって配線に生じる応力を簡単かつ確実に低減して、アクチュエータ1の信頼性を向上させることができる。
Further, since the
Further, since the
In addition, since the
また、各接合点222、223、232、233が回動中心軸X上に位置するとともに、第1の接合点222と第2の接合点223との間の距離と、第1の接合点232と第2の接合点233との間の距離とが等しくなっている。したがって、1対の第1の接合点222、232および1対の第2の接合点223、233は、1対の軸部材22、23に対する配線221、231の影響が互いに等しくなるように設けられている。これにより、アクチュエータ1の設計を簡単なものとしつつ、振動部の振動特性を優れたものとすることができる。
In addition, each
また、各配線221、231は、1対の軸部材22、23に対する影響が互いに等しくなるように設けられている。より具体的には、配線221の長さと配線231の長さとが等しく設定され、また、配線221の横断面形状と配線231の横断面形状とが等しく設定され、さらに、配線221の横断面積(太さ)と配線231の横断面積(太さ)とが等しく設定されている。言い換えすれば、配線221と配線231とは対称的に構成されている。これにより、アクチュエータ1の設計を簡単なものとしつつ、振動部の振動特性を優れたものとすることができる。
Further, the
また、配線221は第1の接合点222と第2の接合点223との間の距離よりも長く、また、配線231は第1の接合点232と第2の接合点233との間の距離よりも長くなっている。これにより、各配線221、231に生じる張力を小さくして、配線221、231に生じる応力を低減することができる。
このような各配線221、231についても、前述したコイル212と同様に、軸部材22(振動部)と配線221との間や、軸部材23(振動部)と配線231との間には、絶縁膜が介在しているのが好ましい。これにより、配線221、231と振動部と間の絶縁性を優れたものとし、信頼性を向上させることができる。
Further, the
For each of these
また、各配線221、231の構成材料としては、導電性を有するものであれば、特に限定されないが、本実施形態のようにワイヤーボンディング法を用いる場合、金のような金属が好適に用いられる。
金属は一般に優れた電気伝導性を有するものの変形を繰り返すことにより金属疲労が生じる。したがって、金属で構成された配線を用いた場合、本発明を適用することによる効果が顕著となる。
Further, the constituent material of each of the
Although metal generally has excellent electrical conductivity, metal fatigue is caused by repeated deformation. Therefore, when the wiring comprised with the metal is used, the effect by applying this invention becomes remarkable.
このような可動板21および1対の軸部材22、23は、振動系(振動部)を構成している。すなわち、本実施形態では、振動部が可動板21および1対の軸部材22、23からなる1つの振動系(すなわち1自由度振動系)を有するものである。
このような振動系を有する基体2は、例えば、シリコンを主材料として構成されていて、可動板21と1対の軸部材22、23と支持部24が一体的に形成されている。これにより、振動部の振動特性および耐久性を優れたものとすることができる。
Such a
The
また、このような振動部は、1つの基板をエッチングすることにより一体的に形成されたものである。これにより、シリコンで一体的に形成された振動部を簡単に製造することができる。
この基板の平均厚さ(すなわち可動板21や軸部材22、23の厚さ)は、それぞれ、特に限定されないが、1〜1500μmであるのが好ましく、10〜300μmであるのがより好ましい。
Moreover, such a vibration part is integrally formed by etching one substrate. Thereby, the vibration part integrally formed with silicon can be easily manufactured.
The average thickness of the substrate (that is, the thickness of the
また、前述したような振動系(振動部)を支持するための支持部24は、可動板21の外周を囲むように枠状をなしている。そして、この支持部24の下面に、支持体3が接合されている。
支持体3は、例えば、ガラスやシリコンを主材料として構成されている。そして、基体2と支持体3とは直接接合または陽極接合により接合されている。なお、基体2と支持体3とは、例えば、ガラス、シリコン、またはSiO2を主材料として構成された接合層を介して接合されていてもよいし、接着剤を介して接合されていてもよい。
Further, the
The support 3 is made of, for example, glass or silicon as a main material. The
支持体3は、前述した支持部24に沿って枠状をなしている。なお、支持体3の形状は、前述したものに限定されない。
このような支持体3にあっては、その内側の空間が、基体2の振動系の振動、すなわち可動板21が回動(振動)する際に、支持体3に接触するのを防止する逃げ部を構成する。このような逃げ部を設けることにより、アクチュエータ1全体の大型化を防止しつつ、可動板21の振れ角(振幅)をより大きく設定することができる。
The support 3 has a frame shape along the
In such a support 3, the space inside thereof prevents the contact with the support 3 when the vibration of the vibration system of the
このような支持体3の側面には、1対の磁石41、42が接合・固定されている。
この1対の磁石41、42は、可動板21の回動中心軸Xを介して互いに対向するとともに、それぞれ非回動時の可動板21の端面に対向するように設けられている。このようにして各磁石41、42は、コイル212に対向している。
また、磁石41は、可動板21側をS極とし、磁石42は、可動板21側をN極とするように設置されている。したがって、1対の磁石41、42は、可動板21付近に、非回動時の可動板21の板面に平行で、かつ、可動板21の回動中心軸Xに直角な方向の磁界を発生させる。
なお、磁石41、42は、永久磁石ではなく、電磁石であってもよい。また、磁石41、42の極性は、図示のものに限定されないことは言うまでもない。
A pair of
The pair of
Moreover, the
以上のような構成を有するアクチュエータ1は、次のようにして作動する。
図示しない電源回路が配線221、231を介してコイル212に交番電圧を印加することにより、コイル212に生じる磁界の方向が上方向と下方向とで交互に切り換わる。
そのため、1対の磁石41、42の磁界中に配された可動板21は、各軸部材22、23の捩れ変形を伴いながら、可動板21が支持部24に対し回動(振動)する。
The actuator 1 having the above configuration operates as follows.
When a power supply circuit (not shown) applies an alternating voltage to the
Therefore, the
ここで、可動板21と1対の軸部材22、23とからなる振動系の固有振動数ω1は、可動板21の慣性モーメントJ1と、1対の軸部材22、23のばね定数k1とにより、ω1=(k1/J1)1/2によって与えられる。コイル212に印加する交番電圧の周波数は、固有振動数ω1と同じであっても異なっていてもよいが、固有振動数ω1と同じである場合、効率よくアクチュエータ1を作動させることができる。
Here, the natural frequency ω 1 of the vibration system composed of the
以上説明したように構成されたアクチュエータ1によれば、コイル212に通電するための各配線221、231が各軸部材22、23に対し離間するように配設されているため、各軸部材22、23の捩れ変形によって配線221、231に生じる応力を低減して、アクチュエータ1の信頼性を向上させることができる。
特に、本実施形態では、ワイヤーボンディングを用いて各配線221、231を形成することにより、配線221、231の形成を比較的簡単なものとすることができる。
According to the actuator 1 configured as described above, since the
In particular, in the present embodiment, the
また、各軸部材22、23に対する配線221、231からの熱の影響を防止または抑制することができる。そのため、各軸部材22、23のバネ特性(バネ定数)の変動を防止または抑制して、長期にわたり簡単に、可動板21を所望の周波数で安定して動作させることができる。
さらに、軸部材22、23上に可動板21の挙動検知のためのPZR等のセンサを設けた際、コイル212からの配線221、231を軸部材22、23上に設けることが難しい場合であっても、コイル212からの配線221、231の取り出しが簡単となる。
Moreover, the influence of the heat from the
Furthermore, when sensors such as PZR for detecting the behavior of the
<第2実施形態>
次に、本発明のアクチュエータの第2実施形態について説明する。
図5は、本発明のアクチュエータの第2実施形態を示す断面図、図6は、本発明のアクチュエータの第2実施形態を示す部分拡大斜視図である。
以下、第2実施形態について説明するが、前述した第1実施形態との相違点を中心に説明し、同様の事項については、その説明を省略する。
本実施形態のアクチュエータは、コイルの設置方法および配線の構成が異なる以外は、前述した第1実施形態と同様である。
Second Embodiment
Next, a second embodiment of the actuator of the present invention will be described.
FIG. 5 is a sectional view showing a second embodiment of the actuator of the present invention, and FIG. 6 is a partially enlarged perspective view showing the second embodiment of the actuator of the present invention.
In the following, the second embodiment will be described, but the description will focus on the differences from the first embodiment described above, and description of similar matters will be omitted.
The actuator of this embodiment is the same as that of 1st Embodiment mentioned above except the installation methods of a coil, and the structure of wiring differing.
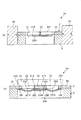
本実施形態のアクチュエータ1Aでは、図5および図6に示すように、コイル212が絶縁膜25を介して可動板21(振動部)上に設けられている。
この絶縁膜25は、可動板21に接合・固定された本体部251と、各軸部材22、23に対し離間しつつ延長された延長部252、253とを有している。
そして、軸部材22に沿って設けられた延長部252上には、配線221Aが設けられ、軸部材23に沿って設けられた延長部253上には、配線231Aが設けられている。
In the
The insulating
A
このような配線221Aは、その一端が第1の接合点222で絶縁膜25を介して可動板21に接合・固定され、他端が第2の接合点223で絶縁膜25を介して支持部24に接合・固定されている。これと同様に、配線231Aは、一端が第1の接合点232で絶縁膜25を介して可動板21に接合され、他端が第2の接合点233で絶縁膜25を介して支持部24に接合・固定されている。
One end of the
このような配線221A、231Aは各軸部材22、23に対し離間しているため、各軸部材22、23の捩れ変形によって配線221A、231Aに生じる応力を低減して、アクチュエータ1Aの信頼性を向上させることができる。
ここで、配線221Aは、薄膜形成された配線214Aを介して、コイル212を構成する素線の他端(渦巻きの中心側の端)に電気的に接続されている。また、配線231Aは、コイル212を構成する素線の一端(渦巻きの外周側の端)に接続されている。
Since
Here, the
また、配線214Aは、絶縁膜254を介してコイル212上に設けられている。絶縁膜254には、図示しないが、配線214と配線221Aとの接合、および、配線214とコイル212との接合のための貫通電極が挿通されている。
このように各配線221A、231Aおよびコイル212(さらには絶縁膜254、配線214)は、蒸着、メッキなどの各種薄膜形成方法を用いて絶縁膜25上に形成することができる。したがって、コイル212および配線221A、231Aの形成を比較的簡単なものとしつつ、アクチュエータ1の信頼性を向上させることができる。
このような各配線221A、231Aおよびコイル212は、絶縁膜25上に形成した後に、基体2に接合する。
The
As described above, the
Each of the wirings 221A, 231A and the
絶縁膜25の構成材料としては、絶縁性を有していれば、特に限定されないが、樹脂材料が好適に用いられる。
また、絶縁膜25と基体2との接合は、特に限定されず、例えば、エポキシ系の接着剤等を用いて行うことができる。
以上説明したような、第2実施形態のアクチュエータ1Aによっても、前述した第1実施形態のアクチュエータ1と同様の効果を発揮することができる。
The constituent material of the insulating
Further, the bonding between the insulating
The effect similar to that of the actuator 1 of the first embodiment described above can also be exhibited by the
以上説明したようなアクチュエータ1、1Aは、例えば、光スキャナ、光スイッチ、光アッテネータなどに適用することができる。
アクチュエータ1、1Aを光スキャナとして用いた場合、アクチュエータ1(本発明にかかる光スキャナ)は、光反射部211で反射した光を走査する。このような本発明にかかる光スキャナは、優れた信頼性を発揮することができる。
このような光スキャナは、例えば、レーザープリンタ、イメージング用ディスプレイ、バーコードリーダー、走査型共焦点顕微鏡などの画像形成装置に好適に適用することができる。
The
When the
Such an optical scanner can be suitably applied to an image forming apparatus such as a laser printer, an imaging display, a barcode reader, or a scanning confocal microscope.
以下、本発明の光スキャナを備えた画像形成装置の具体例を説明する。
まず、電子写真方式を採用するプリンタに本発明を適用した例を説明する。
図7は、本発明の光スキャナを備える画像形成装置(プリンタ)の一例を示す全体構成の模式的断面図、図8は、図7に示す画像形成装置に備えられた露光ユニットの概略構成を示す図である。
Hereinafter, a specific example of an image forming apparatus provided with the optical scanner of the present invention will be described.
First, an example in which the present invention is applied to a printer that employs an electrophotographic system will be described.
FIG. 7 is a schematic cross-sectional view of the overall configuration showing an example of an image forming apparatus (printer) including the optical scanner of the present invention, and FIG. 8 is a schematic configuration of an exposure unit provided in the image forming apparatus shown in FIG. FIG.
図7に示す画像形成装置110(プリンタ)は、露光・現像・転写・定着を含む一連の画像形成プロセスによって、トナーからなる画像を紙やOHPシートなどの記録媒体に記録するものである。このような画像形成装置110は、図7に示すように、図示矢印方向に回転する感光体111を有し、その回転方向に沿って順次、帯電ユニット112、露光ユニット113、現像ユニット114、転写ユニット115、クリーニングユニット116が配設されている。また、画像形成装置110は、図7にて、下部に、紙などの記録媒体Pを収容する給紙トレイ117が設けられ、上部に、定着装置118が設けられている。
An image forming apparatus 110 (printer) shown in FIG. 7 records an image made of toner on a recording medium such as paper or an OHP sheet by a series of image forming processes including exposure, development, transfer, and fixing. As shown in FIG. 7, such an
このような画像形成装置110にあっては、まず、図示しないホストコンピュータからの指令により、感光体111、現像ユニット114に設けられた現像ローラ(図示せず)、および中間転写ベルト151が回転を開始する。そして、感光体111は、回転しながら、帯電ユニット112により順次帯電される。
感光体111の帯電された領域は、感光体111の回転に伴って露光位置に至り、露光ユニット113によって、第1色目、例えばイエローYの画像情報に応じた潜像が前記領域に形成される。
In such an
The charged region of the
感光体111上に形成された潜像は、感光体111の回転に伴って現像位置に至り、イエロー現像のための現像装置144によってイエロートナーで現像される。これにより、感光体111上にイエロートナー像が形成される。このとき、現像ユニット114は、現像装置144が選択的に前記現像位置にて感光体111と対向している。なお、この選択は、保持体145の軸146まわりの回転により、現像装置141〜144の相対位置関係を維持しつつそれぞれの位置を変えることで行う。
The latent image formed on the
感光体111上に形成されたイエロートナー像は、感光体111の回転に伴って一次転写位置(すなわち、感光体111と一次転写ローラ152との対向部)に至り、一次転写ローラ152によって、中間転写ベルト151に転写(一次転写)される。このとき、一次転写ローラ152には、トナーの帯電極性とは逆の極性の一次転写電圧(一次転写バイアス)が印加される。なお、この間、二次転写ローラ155は、中間転写ベルト151から離間している。
The yellow toner image formed on the
前述の処理と同様の処理が、第2色目、第3色目および第4色目について繰り返して実行されることにより、各画像信号に対応した各色のトナー像が、中間転写ベルト151に重なり合って転写される。これにより、中間転写ベルト151上にはフルカラートナー像が形成される。
一方、記録媒体Pは、給紙トレイ117から、給紙ローラ171、レジローラ172によって二次転写位置(すなわち、二次転写ローラ155と駆動ローラ154との対向部)へ搬送される。
The same processing as described above is repeatedly executed for the second color, the third color, and the fourth color, so that the toner images of the respective colors corresponding to the respective image signals are transferred onto the
On the other hand, the recording medium P is conveyed from the
中間転写ベルト151上に形成されたフルカラートナー像は、中間転写ベルト151の回転に伴って二次転写位置に至り、二次転写ローラ155によって記録媒体Pに転写(二次転写)される。このとき、二次転写ローラ155は中間転写ベルト151に押圧されるとともに二次転写電圧(二次転写バイアス)が印加される。また、中間転写ベルト151は、駆動ローラ154を回転させることで一次転写ローラ152および従動ローラ153を従動回転させながら回転する。
The full color toner image formed on the
記録媒体Pに転写されたフルカラートナー像は、定着装置118によって加熱および加圧されて記録媒体Pに融着される。その後、片面プリントの場合には、記録媒体Pは、排紙ローラ対173によって画像形成装置110の外部へ排出される。
一方、感光体111は一次転写位置を経過した後に、クリーニングユニット116のクリーニングブレード161によって、その表面に付着しているトナーが掻き落とされ、次の潜像を形成するための帯電に備える。掻き落とされたトナーは、クリーニングユニット116内の残存トナー回収部に回収される。
The full-color toner image transferred to the recording medium P is heated and pressurized by the fixing
On the other hand, after the primary transfer position has elapsed, the toner adhering to the surface of the
両面プリントの場合には、定着装置118によって一方の面に定着処理された記録媒体Pを一旦排紙ローラ対173により挟持した後に、排紙ローラ対173を反転駆動するとともに、搬送ローラ対174、176を駆動して、当該記録媒体Pを搬送路175を通じて表裏反転して二次転写位置へ帰還させ、前述と同様の動作により、記録媒体Pの他方の面に画像を形成する。
In the case of double-sided printing, after the recording medium P fixed on one surface by the fixing
このような画像形成装置に備えられた露光ユニット113は、図示しないパーソナルコンピュータなどのホストコンピュータから画像情報を受けこれに応じて、一様に帯電された感光体111上に、レーザーを選択的に照射することによって、静電的な潜像を形成する装置である。
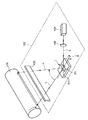
より具体的に説明すると、露光ユニット113は、図8に示すように、光スキャナであるアクチュエータ1と、レーザー光源131と、コリメータレンズ132と、fθレンズ133とを有している。
The
More specifically, as shown in FIG. 8, the
露光ユニット113にあっては、レーザー光源131からコリメータレンズ132を介してアクチュエータ1(光反射部211)にレーザー光Lが照射される。そして、光反射部211で反射したレーザー光Lがfθレンズを介して感光体111上に照射される。
その際、アクチュエータ1の駆動(可動板21の回動中心軸Xまわりの回動)により、光反射部211で反射した光(レーザーL)は、感光体111の軸線方向に走査(主走査)される。一方、感光体111の回転により、光反射部211で反射した光(レーザーL)は、感光体111の周方向に走査(副走査)される。また、レーザー光源131から出力されるレーザー光Lの強度は、図示しないホストコンピュータから受けた画像情報に応じて変化する。
このようにして露光ユニット113は、感光体111上を選択的に露光して画像形成(描画)を行う。
In the
At that time, the light (laser L) reflected by the
In this way, the
次に、イメージングディスプレイ(表示装置)に本発明を適用した例を説明する。
図9は、本発明の画像形成装置(イメージングディスプレイ)の一例を示す概略図である。
図9に示す画像形成装置119は、光スキャナであるアクチュエータ1と、R(赤)、G(緑)、B(青)の3色の光源191、192、193と、クロスダイクロイックプリズム(Xプリズム)194と、ガルバノミラー195と、固定ミラー196と、スクリーン197とを備えている。
Next, an example in which the present invention is applied to an imaging display (display device) will be described.
FIG. 9 is a schematic view showing an example of an image forming apparatus (imaging display) of the present invention.
An
このような画像形成装置119にあっては、光源191、192、193からクロスダイクロイックプリズム194を介してアクチュエータ1(光反射部211)に各色の光が照射される。このとき、光源191からの赤色の光と、光源192からの緑色の光と、光源193からの青色の光とが、クロスダイクロイックプリズム194にて合成される。
そして、光反射部211で反射した光(3色の合成光)は、ガルバノミラー195で反射した後に、固定ミラー196で反射し、スクリーン197上に照射される。
In such an
Then, the light (three colors of combined light) reflected by the
その際、アクチュエータ1の駆動(可動板21の回動中心軸Xまわりの回動)により、光反射部211で反射した光は、スクリーン197の横方向に走査(主走査)される。一方、ガルバノミラー195の軸線Yまわりの回転により、光反射部211で反射した光は、スクリーン197の縦方向に走査(副走査)される。また、各色の光源191、192、193から出力される光の強度は、図示しないホストコンピュータから受けた画像情報に応じて変化する。
このようにして画像形成装置119は、スクリーン197上に画像形成(描画)を行う。
At that time, the light reflected by the
In this way, the
以上、本発明のアクチュエータ、光スキャナ、および画像形成装置について、図示の実施形態に基づいて説明したが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではない。例えば、本発明のアクチュエータ等では、各部の構成は、同様の機能を発揮する任意の構成のものに置換することができ、また、任意の構成を付加することもできる。
前述した実施形態では、配線221、231が軸部材22、23の略全長にわたって離間している構成を説明したが、コイル212に通電するための配線の一部が軸部材22、23に離間していればよく、例えば、配線221、231が軸部材22、23の一部で接合していてもよい。
The actuator, the optical scanner, and the image forming apparatus of the present invention have been described based on the illustrated embodiment. However, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, in the actuator of the present invention, the configuration of each part can be replaced with an arbitrary configuration that exhibits the same function, and an arbitrary configuration can be added.
In the above-described embodiment, the configuration in which the
また、前述した実施形態では、振動部が1自由度振動系を構成するものについて説明したが、振動部が2次自由度以上の振動系を構成していてもよい。例えば、振動部が2自由度振動系を構成する場合、振動部は、各軸部材の途中に駆動部材(質量部)を設けることにより構成する。これにより、振動部が2自由度振動系を構成し、駆動電圧を低減しつつ、可動板の振れ角を大きくすることができる。この場合、電磁駆動用のコイルは、1つまたは1対の駆動部材に設け、また、配線の接合点を駆動部材上に設ける。 In the above-described embodiment, the description has been given of the vibration unit constituting the one-degree-of-freedom vibration system. For example, when a vibration part comprises a 2 degree-of-freedom vibration system, a vibration part is comprised by providing a drive member (mass part) in the middle of each shaft member. Thereby, the vibration part constitutes a two-degree-of-freedom vibration system, and the deflection angle of the movable plate can be increased while reducing the drive voltage. In this case, the coil for electromagnetic drive is provided in one or a pair of drive members, and the junction of wiring is provided on the drive member.
1、1A‥‥‥アクチュエータ 2‥‥‥基体 21‥‥‥可動板 22、23‥‥‥軸部材 24‥‥‥支持部 211‥‥‥光反射部 212‥‥‥コイル 221、221A、231、231A‥‥‥配線 222、232‥‥‥第1の接合点 223、233‥‥‥第2の接合点 241、242‥‥‥端子 214、214A‥‥‥配線 25、254‥‥‥絶縁膜 252、253‥‥‥延長部 41、42‥‥‥磁石 3‥‥‥支持体 110、119‥‥‥画像形成装置 110‥‥‥感光体 112‥‥‥帯電ユニット 113‥‥‥露光ユニット 114‥‥‥現像ユニット 115‥‥‥転写ユニット 116‥‥‥クリーニングユニット 117‥‥‥給紙トレイ 118‥‥‥定着装置 131‥‥‥レーザー光源 132‥‥‥コリメータレンズ 133‥‥‥fθレンズ 141〜144‥‥‥現像装置 145‥‥‥保持体 146‥‥‥軸 151‥‥‥中間転写ベルト 152‥‥‥一次転写ローラ 153‥‥‥従動ローラ 154‥‥‥駆動ローラ 155‥‥‥二次転写ローラ 161‥‥‥クリーニングブレード 171‥‥‥給紙ローラ 172‥‥‥レジローラ 173‥‥‥排紙ローラ対 174、176‥‥‥搬送ローラ対 175‥‥‥搬送路 191〜193‥‥‥光源 194‥‥‥クロスダイクロイックプリズム 195‥‥‥ガルバノミラー 196‥‥‥固定ミラー 197‥‥‥スクリーン 251‥‥‥本体部 P‥‥‥記録媒体 X‥‥‥回動中心軸
1, 1A ...
Claims (9)
前記振動部に設けられたコイルと、
前記コイルに通電するための配線と、
前記コイルに対向して設置された磁石とを有し、
前記磁石の磁界中に配された前記コイルに通電することにより、前記可動板を前記各軸部材の捩れ変形を伴って回動させるように構成され、
前記コイルは、絶縁膜を介して前記振動部上に設けられ、
前記絶縁膜は、前記各軸部材に対し離間しつつ延長された延長部を有し、
前記配線は、前記延長部上かつ前記1対の軸部材のうちの少なくとも一方の軸部材に沿って設けられていることを特徴とするアクチュエータ。 A vibrating portion including a movable plate and a pair of shaft members that support the movable plate;
A coil provided in the vibrating section;
Wiring for energizing the coil;
A magnet installed facing the coil,
By energizing the coil disposed in the magnetic field of the magnet, the movable plate is configured to rotate with torsional deformation of each shaft member,
The coil is provided on the vibration part via an insulating film,
The insulating film has an extended portion that is extended while being separated from the shaft members,
The actuator is characterized in that the wiring is provided on the extension portion and along at least one shaft member of the pair of shaft members .
前記振動部に設けられたコイルと、
前記コイルに通電するための配線と、
前記コイルに対向して設置された磁石とを有し、
前記磁石の磁界中に配された前記コイルに通電することにより、前記可動板を前記各軸部材の捩れ変形を伴って回動させ、前記光反射部で反射した光を走査するように構成され、
前記コイルは、絶縁膜を介して前記振動部上に設けられ、
前記絶縁膜は、前記各軸部材に対し離間しつつ延長された延長部を有し、
前記配線は、前記延長部上かつ前記1対の軸部材のうちの少なくとも一方の軸部材に沿って設けられていることを特徴とする光スキャナ。 A vibrating portion including a movable plate provided with a light reflecting portion and a pair of shaft members that support the movable plate;
A coil provided in the vibrating section;
Wiring for energizing the coil;
A magnet installed facing the coil,
By energizing the coil disposed in the magnetic field of the magnet, the movable plate is rotated with torsional deformation of each shaft member, and the light reflected by the light reflecting portion is scanned. ,
The coil is provided on the vibration part via an insulating film,
The insulating film has an extended portion that is extended while being separated from the shaft members,
The optical scanner, wherein the wiring is provided on the extension and along at least one shaft member of the pair of shaft members .
前記振動部に設けられたコイルと、
前記コイルに通電するための配線と、
前記コイルに対向して設置された磁石とを有し、
前記磁石の磁界中に配された前記コイルに通電することにより、前記可動板を前記各軸部材の捩れ変形を伴って回動させ、前記光反射部で反射した光を走査して、画像を形成するように構成され、
前記コイルは、絶縁膜を介して前記振動部上に設けられ、
前記絶縁膜は、前記各軸部材に対し離間しつつ延長された延長部を有し、
前記配線は、前記延長部上かつ前記1対の軸部材のうちの少なくとも一方の軸部材に沿って設けられていることを特徴とする画像形成装置。 A vibrating portion including a movable plate provided with a light reflecting portion and a pair of shaft members that support the movable plate;
A coil provided in the vibrating section;
Wiring for energizing the coil;
A magnet installed facing the coil,
By energizing the coil arranged in the magnetic field of the magnet, the movable plate is rotated with torsional deformation of each shaft member, and the light reflected by the light reflecting portion is scanned to scan the image. Configured to form,
The coil is provided on the vibration part via an insulating film,
The insulating film has an extended portion that is extended while being separated from the shaft members,
The image forming apparatus, wherein the wiring is provided on the extension and along at least one shaft member of the pair of shaft members .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007236298A JP5023907B2 (en) | 2007-09-12 | 2007-09-12 | Actuator, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007236298A JP5023907B2 (en) | 2007-09-12 | 2007-09-12 | Actuator, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009069340A JP2009069340A (en) | 2009-04-02 |
| JP2009069340A5 JP2009069340A5 (en) | 2010-10-07 |
| JP5023907B2 true JP5023907B2 (en) | 2012-09-12 |
Family
ID=40605692
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007236298A Expired - Fee Related JP5023907B2 (en) | 2007-09-12 | 2007-09-12 | Actuator, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5023907B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013076844A1 (en) * | 2011-11-24 | 2013-05-30 | パイオニア株式会社 | Actuator |
| DE102012206269B4 (en) | 2012-04-17 | 2023-12-14 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Micromechanical component and manufacturing process for a micromechanical component |
| WO2014002183A1 (en) * | 2012-06-26 | 2014-01-03 | パイオニア株式会社 | Actuator |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH01200322A (en) * | 1988-02-05 | 1989-08-11 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Oscillatory mirror device |
| JP2005099063A (en) * | 2000-12-11 | 2005-04-14 | Miwa Engineering:Kk | Deflection actuator, optical scanning element, and light receiving scanning element |
| JP2002345230A (en) * | 2001-05-16 | 2002-11-29 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Linear driver |
| JP2003311695A (en) * | 2002-04-26 | 2003-11-05 | Nippon Signal Co Ltd:The | Planar type actuator and its manufacturing method |
| JP2005245074A (en) * | 2004-02-25 | 2005-09-08 | Alps Electric Co Ltd | Linear driving device |
-
2007
- 2007-09-12 JP JP2007236298A patent/JP5023907B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009069340A (en) | 2009-04-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4241791B2 (en) | Actuator, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP4232835B2 (en) | Actuator, optical scanner and image forming apparatus | |
| JP4337862B2 (en) | Optical device, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| EP2157467A2 (en) | MEMS Mirror, Mirror Scanner, Optical Scanning Unit and Image Forming Apparatus including the Optical Scanning Unit | |
| JP2011107675A (en) | Light deflecting element, light deflector and image forming device | |
| JP5233221B2 (en) | Actuator, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP6614276B2 (en) | Piezoelectric light deflector, optical scanning device, image forming device, and image projection device | |
| JP4983266B2 (en) | Optical device, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP5023907B2 (en) | Actuator, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2011095290A (en) | Optical deflection element, optical deflector and image forming apparatus | |
| JP4720723B2 (en) | Optical device, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2008070863A (en) | Vibrating mirror, light writing device, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2008228436A (en) | Actuator, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP4910668B2 (en) | Optical device, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2009198702A (en) | Oscillating structure, and oscillator device using oscillating structure | |
| JP2008145542A (en) | Optical device, optical scanner and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2009069341A (en) | Actuator, optical scanner and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2009069339A (en) | Actuator, method for manufacturing actuator, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP4525652B2 (en) | Actuator, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP4983281B2 (en) | Actuator, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2008145543A (en) | Optical device, optical scanner and image forming apparatus | |
| JP4720729B2 (en) | Optical device, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2010002783A (en) | Optical scanner and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP4720725B2 (en) | Optical device, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2011069860A (en) | Optical deflector, method of adjusting temperature of optical deflection element, method of manufacturing optical deflector and image forming apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100820 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100820 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120209 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120306 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120427 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20120522 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20120604 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150629 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5023907 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |