JP4654521B2 - Solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method of solid-state imaging device - Google Patents
Solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method of solid-state imaging device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4654521B2 JP4654521B2 JP2001029148A JP2001029148A JP4654521B2 JP 4654521 B2 JP4654521 B2 JP 4654521B2 JP 2001029148 A JP2001029148 A JP 2001029148A JP 2001029148 A JP2001029148 A JP 2001029148A JP 4654521 B2 JP4654521 B2 JP 4654521B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- photoelectric conversion
- solid
- trench
- semiconductor substrate
- imaging device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 title claims description 40
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 11
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 95
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 38
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 37
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 claims description 16
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005036 potential barrier Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001312 dry etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000873 masking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Solid State Image Pick-Up Elements (AREA)
- Transforming Light Signals Into Electric Signals (AREA)
- Element Separation (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は固体撮像素子及び固体撮像素子の製造方法に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
図2は従来の固体撮像素子の一例を示す平面図、図3は図2における点線の矩形領域Rを詳しく示す部分拡大平面図、図4の(A)は図3におけるA−A’線に沿った部分断面側面図、図4の(B)は図3におけるB−B’線に沿った部分断面側面図である。
【0003】
図2に示した固体撮像素子102は一例としてインターライン型の固体撮像素子であり、シリコンから成る半導体基板104上に多数の光電変換素子106を相互に間隔をおきマトリクス状に配列して構成されている。そして光電変換素子106の各列ごとに垂直電荷転送レジスター108が、光電変換素子106の列方向(矢印V)に延設され、垂直電荷転送レジスター108の一端部に水平電荷転送レジスター110が、光電変換素子106の行方向(矢印H)に延設されている。水平電荷転送レジスター110の一方の端部にはアンプ部112が形成されている。
【0004】
このような構成において、各列の各光電変換素子106が光を受けて生成した電荷は、光電変換素子106と垂直電荷転送レジスター108との間に介在する不図示の読み出し領域を経て、対応する垂直電荷転送レジスター108に出力され、垂直電荷転送レジスター108はこの電荷を順次、水平電荷転送レジスター110に向けて転送する。水平電荷転送レジスター110は各垂直電荷転送レジスター108から電荷を受け取ってアンプ部112に転送し、アンプ部112は転送されてきた電荷にもとづき出力端子114を通じて映像信号を出力する。
【0005】
断面図を参照して光電変換素子106周辺を詳しく説明すると、図4の(B)に示したように、光電変換素子106はp型の半導体基板104の表面部に局所的に積層されたp型領域115およびn型領域116を含み、図4の(B)ではその左側の半導体基板表面部に、対応する垂直電荷転送レジスター108が形成されている。垂直電荷転送レジスター108の上には第2層目の転送電極118が絶縁膜120を介して形成され、その上には絶縁膜120を介して遮光膜122が形成されている。
【0006】
また、図4の(B)において光電変換素子106の右側にはチャネルストップ領域として高濃度のp型不純物をたとえばイオン注入法により導入したp型領域124が形成されている。このp型領域124は、図3に示したように、平面視では各光電変換素子106を、垂直電荷転送レジスター108側を除いて囲む形で形成されている。
【0007】
したがって、光電変換素子106の列方向の断面では、図4の(A)に示したように、隣接する光電変換素子106の間にチャネルストップ領域としてのp型領域124が配置されている。
また、図4の(A)に示した断面位置では、p型領域124の上に第1層目の転送電極126、および第2層目の転送電極118が絶縁膜120を介して積層され、その上を遮光膜122が覆っている。
【0008】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
上述のように各光電変換素子106の周囲、すなわち画素の周囲に高濃度の不純物によるp型領域124を形成することで画素間に高いポテンシャルバリアが生成され、各画素が分離される。その結果、各光電変換素子106が受光して生成した信号電荷は各光電変換素子106ごとに独立して垂直電荷転送レジスター108に供給されることになる。
【0009】
しかしながら、このp型領域124によるポテンシャルバリアは基板表面から深い位置へ向かうにしたがってしだいに均一化される。そのため、光電変換素子106のn型領域116が深く形成されるような構造の場合には、p型領域124が充分に作用せず、隣接する光電変換素子106間で信号電荷が混合する結果となる。このような信号電荷の混合が発生すると固体撮像素子102の解像度が低下し、またカラー画像を撮影する固体撮像素子の場合には、隣接する光電変換素子106は相互に異なる色に対応しているため画素間の混色が発生してしまう。
【0010】
この問題は、高エネルギーでp型不純物を導入し、p型領域124を深く形成することで回避できる。しかし、高エネルギーのイオン注入は制御性が悪く、横方向への広がりも大きいことから、光電変換素子106が高密度で配列され個々の光電変換素子106のサイズが小さい場合には、この手法を用いることは困難である。さらに、イオン注入時のマスキングのためのレジスト層は、高エネルギーのイオン注入に耐えられるよう厚く形成しなければならず、この点からも微細加工が難しくなり、光電変換素子106のサイズが小さい場合にはp型領域124を深く形成することは困難である。
【0011】
本発明はこのような問題を解決するためになされたもので、その目的は、サイズの小さい光電変換素子を高密度で配列する場合でも、各光電変換素子を容易かつ確実に分離して信号電荷の混合にともなう解像度の低下や混色を防止できる固体撮像素子を提供することにある。
【0012】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記目的を達成するため、本発明に係る固体撮像素子は、半導体基板上に相互に近接して配列された複数の光電変換素子を備え、前記光電変換素子は前記半導体基板の表面部に局所的に積層された第1導電型および第2導電型の領域を含み、前記第2導電型の領域は前記半導体基板の表面側に形成されている固体撮像素子であって、各光電変換素子の周囲の半導体基板表面部に、前記第1導電型の領域の底部より深い位置に至るトレンチが形成され、前記光電変換素子と、同光電変換素子に隣接する前記トレンチとの間の半導体基板表面部に、前記第2導電型の領域と接して当該トレンチよりも浅い高濃度の第2導電型の不純物を含む領域が形成されていることを特徴とする。
また、本発明に係る固体撮像素子の製造方法は、半導体基板上に相互に近接して配列された複数の光電変換素子を備え、前記光電変換素子は前記半導体基板の表面部に局所的に積層された第1導電型および第2導電型の領域を含み、前記第2導電型の領域は前記半導体基板の表面側に形成された固体撮像素子の製造方法であって、各光電変換素子の周囲の半導体基板表面部に、前記第1導電型の領域の底部より深い位置に至るトレンチを形成し、前記光電変換素子と、同光電変換素子に隣接する前記トレンチとの間の半導体基板表面部に、前記第2導電型の領域と接して当該トレンチよりも浅い高濃度の第2導電型の不純物を含む領域を形成することを特徴とする。
【0013】
このように本発明の固体撮像素子、並びに本発明の製造方法により製造した固体撮像素子では、各光電変換素子の周囲の半導体基板表面部に、前記第1導電型の領域の底部より深い位置に至るトレンチが形成されているので、各光電変換素子により生成された信号電荷は、このトレンチにより阻止されて、隣接する他の光電変換素子による信号電荷と混合することがない。その結果、解像度が低下したり画素間で混色が起こるといった問題は発生しない。
【0014】
【発明の実施の形態】
次に本発明の実施の形態例について図面を参照して説明する。
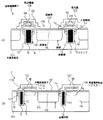
図1の(A)および(B)は本発明による固体撮像素子の一例を示す部分断面側面図である。図中、図2ないし図4と同一の要素には同一の符号が付されている。
ここで説明する実施の形態例としての固体撮像素子は、一例としてインターライン型の固体撮像素子であり、基本的な構成は図2に示した固体撮像素子102と同様の構成となっている。すなわち、シリコンから成る半導体基板上に多数の光電変換素子を相互に間隔をおきマトリクス状に配列して構成され、光電変換素子の各列ごとに垂直電荷転送レジスターが、光電変換素子の列方向に延設され、垂直電荷転送レジスターの一端部に水平電荷転送レジスターが配置されている。また水平電荷転送レジスターの一方の端部にはアンプ部が形成されている。なお、光電変換素子はここではフォトダイオードであるとする。
【0015】
そして、図1の(A)は図4の(A)と同様、光電変換素子の列方向における光電変換素子周辺の詳しい断面を示し、図1の(B)は図4の(B)と同様、光電変換素子の行方向における光電変換素子周辺の詳しい断面を示している。
本実施の形態例は、チャネルストップ領域としてトレンチを形成する点で、従来の固体撮像素子と異なっている。すなわち、図1の(A)、(B)に示したように、実施の形態例の固体撮像素子2では、n型領域116(本発明に係わる第1導電型の領域)およびp型領域115(本発明に係わる第2導電型の領域)から成る光電変換素子106のそれぞれの周囲の半導体基板表面部に、n型領域116の底部6より深い位置に至るトレンチ8が形成されている。
【0016】
トレンチ8は、従来の固体撮像素子におけるp型領域124と同様の位置に形成されており、したがって平面視においても図3に示した従来の固体撮像素子102のp型領域124と同様、垂直電荷転送レジスター108と、同垂直電荷転送レジスター108に対応する光電変換素子106との間の箇所を除いて、光電変換素子106を囲む形で形成されている。
【0017】
トレンチ8の内面には、図1の(A)および(B)に示したように、本実施の形態例では絶縁膜10が被着され、そして内側に金属材料12が充填されている。トレンチ8の内面に被着させる上記絶縁膜10は、たとえば、半導体基板104の熱酸化によるシリコンの酸化膜として形成することができ、トレンチ8内に充填する金属材料12はたとえばアルミニウムを堆積させることで形成することができる。
【0018】
また、光電変換素子106と、この光電変換素子106に隣接するトレンチ8との間における半導体基板表面部に、高濃度の不純物を含むp型領域14(本発明に係わる高濃度の第2導電型の不純物を含む領域)が比較的浅く形成されている。この高濃度の不純物を含むp型領域14は、光電変換素子106と、対応する垂直電荷転送レジスター108との間の箇所を除いて、光電変換素子106の周囲に形成されている。また、図1(B)から明らかなように、光電変換素子106のp型領域115と、高濃度の不純物を含むp型領域14とは、互いに接して形成されている。
【0019】
電極や遮光膜に関しては従来の固体撮像素子と同様であり、図1の(B)に示したように、垂直電荷転送レジスター108の上に第2層目の転送電極118が絶縁膜120を介して形成され、その上に絶縁膜120を介して遮光膜122が形成されている。また、図1の(A)に示した断面位置では、トレンチ8および高濃度の不純物を含むp型領域14の上に転送電極126、118が絶縁膜120を介して積層され、その上を遮光膜122が覆っている。
【0020】
このように本実施の形態例の固体撮像素子2では、光電変換素子106のそれぞれの周囲の半導体基板表面部に、光電変換素子106を構成するn型領域116の底部6より深い位置に至るトレンチ8が形成されているので、各光電変換素子106により生成された信号電荷は、このトレンチ8により阻止されて、隣接する他の光電変換素子106による信号電荷と混合することがない。そのため、解像度が低下したり画素間で混色が起こるといった問題は発生しない。
【0021】
また、本実施の形態例では、トレンチ8内に金属材料12が充填されているので、光電変換素子106の受光部に斜めに入射した光、あるいは光電変換素子106内で散乱した光などは、光電変換素子106の側部から出射した後、金属材料12の側面で反射されて再度光電変換素子106内に入射し、その結果、光電変換素子106の感度が向上する。
【0022】
このようなトレンチ8は、エッチングなど従来から広く用いられている技術により容易に形成することができる。具体的には、たとえば、転送電極126、118や斜光膜122を形成する前の段階で、まず従来通り、たとえばイオン注入法によって高濃度の不純物を含むp型領域14を形成する。その後、半導体基板表面にたとえばシリコン窒化膜を形成し、パターン化してトレンチ8の形成箇所のみ開口させ、そしてこのパターン化したシリコン窒化膜をマスクとして選択的エッチング(たとえばドライエッチング)を行い、トレンチ8を必要な深さに形成する。
【0023】
本実施の形態例の固体撮像素子2では、トレンチ8の形成がこのように容易であることから、サイズの小さい光電変換素子106を高密度で配列するような場合でも、各光電変換素子106を確実に分離して解像度の低下や混色を防止することができる。
【0024】
なお、本実施の形態例では、トレンチ8内に金属材料12を充填するとしたが、金属材料12を充填せず、絶縁材料を充填したり、あるいは空洞構造とすることも可能である。その場合にも、トレンチ8はチャネルストップ領域としての機能を果たすため、各光電変換素子106により生成された信号電荷は、トレンチ8により阻止されて、隣接する他の光電変換素子106による信号電荷と混合することがない。そのため、解像度が低下したり画素間で混色が起こるといった問題は発生しない。
ただし、光電変換素子106の側部などから出射した光がトレンチ部で反射して再度光電変換素子106内に入射するという作用は得られないか、あるい弱まるので、この点では、高い光反射率を得るためにトレンチ8内に金属材料12を充填する構造とすることが望ましい。
【0025】
本実施の形態例では、トレンチ8とともに高濃度の不純物を含むp型領域14をも形成するとしたが、この高濃度の不純物を含むp型領域14を形成する目的は画素を分離することではなく、光電変換素子106を構成するn型領域116の下方に溜まった正孔を速やかに排出するためのものである。したがって、特に深いものとする必要はなく、その形成は容易である。
トレンチ8を形成する際にシリコン窒化膜によるマスクを用いるとしたが、マスクの材料としては、エッチングの際に半導体基板104よりエッチングレートが低い材料であれば、必ずしもシリコン窒化膜でなくてもよい。
【0026】
また、本実施の形態例では、光電変換素子106はマトリクス状に配列されているとしたが、リニアイメージセンサーなどのように、光電変換素子が直線的に配列されている場合にも本発明は有効であり、各光電変換素子106の周囲にトレンチを形成することで同様の効果を得ることができる。
本実施の形態例では、固体撮像素子2は、インターライン型であるとしたが、以上の説明から明らかなように本発明が各光電変換素子106周辺の構造に係わるものであるため、電荷の転送方式がインターライン型以外の方式であっても本発明は適用可能である。
【0027】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように本発明の固体撮像素子、並びに本発明の製造方法により製造した固体撮像素子では、各光電変換素子の周囲の半導体基板表面部に、光電変換素子を構成する第1導電型の領域の底部より深い位置に至るトレンチが形成されているので、各光電変換素子により生成された信号電荷は、このトレンチにより阻止されて、隣接する他の光電変換素子による信号電荷と混合することがない。その結果、解像度が低下したり画素間で混色が起こるといった問題は発生しない。
そして、上記トレンチはエッチングなど従来から広く用いられている技術により容易に形成することができるので、サイズの小さい光電変換素子を高密度で配列するような場合でも解像度の低下や混色を確実に防止することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 (A)および(B)は本発明による固体撮像素子の一例を示す部分断面側面図である。
【図2】 従来の固体撮像素子の一例を示す平面図である。
【図3】 図2の固体撮像素子の一部を詳しく示す部分拡大平面図である。
【図4】 (A)は図3におけるA−A’線に沿った部分断面側面図、(B)は図3におけるB−B’線に沿った部分断面側面図である。
【符号の説明】
2……固体撮像素子、6……光電変換素子のn型領域の底部、8……トレンチ、10……絶縁膜、12……金属材料、14……高濃度の不純物を含むp型領域、102……固体撮像素子、104……半導体基板、106……光電変換素子、108……垂直電荷転送レジスター、110……水平電荷転送レジスター、112……アンプ部、114……出力端子、115……光電変換素子のp型領域、116……光電変換素子のn型領域、118……転送電極、120……絶縁膜、122……遮光膜、124……p型領域、126……転送電極。[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a solid-state imaging device and a method for manufacturing the solid-state imaging device .
[0002]
[Prior art]
2 is a plan view showing an example of a conventional solid-state imaging device, FIG. 3 is a partially enlarged plan view showing in detail a dotted-line rectangular region R in FIG. 2, and FIG. 4A is a line AA ′ in FIG. 4B is a partial cross-sectional side view taken along the line BB ′ in FIG.
[0003]
The solid-
[0004]
In such a configuration, the charges generated by the
[0005]
The periphery of the
[0006]
4B, a p-
[0007]
Therefore, in the cross section in the column direction of the
4A, the first-
[0008]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
As described above, by forming the p-
[0009]
However, the potential barrier formed by the p-
[0010]
This problem can be avoided by introducing p-type impurities with high energy and forming the p-
[0011]
The present invention has been made to solve such problems, and its purpose is to easily and reliably separate each photoelectric conversion element even when small-sized photoelectric conversion elements are arranged at a high density, thereby to charge signal charges. It is an object of the present invention to provide a solid-state imaging device capable of preventing a reduction in resolution and color mixing due to mixing.
[0012]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to achieve the above object, a solid-state imaging device according to the present invention includes a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements arranged close to each other on a semiconductor substrate, and the photoelectric conversion elements are locally provided on a surface portion of the semiconductor substrate. Including a first conductive type region and a second conductive type region, wherein the second conductive type region is a solid-state imaging device formed on a surface side of the semiconductor substrate, and is around each photoelectric conversion device. A trench reaching a position deeper than the bottom of the first conductivity type region is formed in the semiconductor substrate surface portion of the semiconductor substrate, and the semiconductor substrate surface portion between the photoelectric conversion element and the trench adjacent to the photoelectric conversion element is formed. A region containing a second conductivity type impurity having a high concentration shallower than the trench is formed in contact with the second conductivity type region .
The method for manufacturing a solid-state imaging device according to the present invention includes a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements arranged in proximity to each other on a semiconductor substrate, and the photoelectric conversion elements are locally stacked on a surface portion of the semiconductor substrate. A region of the first conductivity type and a region of the second conductivity type, wherein the second conductivity type region is a method of manufacturing a solid-state imaging device formed on the surface side of the semiconductor substrate. Forming a trench reaching a position deeper than the bottom of the first conductivity type region on the surface of the semiconductor substrate, and on the surface of the semiconductor substrate between the photoelectric conversion element and the trench adjacent to the photoelectric conversion element. A region containing a second conductivity type impurity having a high concentration shallower than the trench is formed in contact with the second conductivity type region .
[0013]
Thus, in the solid-state imaging device of the present invention and the solid-state imaging device manufactured by the manufacturing method of the present invention, the surface of the semiconductor substrate around each photoelectric conversion element is positioned deeper than the bottom of the first conductivity type region. Since the reaching trench is formed, the signal charge generated by each photoelectric conversion element is blocked by this trench and is not mixed with the signal charge by other adjacent photoelectric conversion elements. As a result, there is no problem that the resolution is lowered or color mixture occurs between pixels.
[0014]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Next, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
1A and 1B are partial cross-sectional side views showing an example of a solid-state imaging device according to the present invention. In the figure, the same elements as those in FIGS. 2 to 4 are denoted by the same reference numerals.
The solid-state imaging device as an embodiment described here is an interline type solid-state imaging device as an example, and the basic configuration is the same as that of the solid-
[0015]
1A shows a detailed cross section around the photoelectric conversion element in the column direction of the photoelectric conversion elements, as in FIG. 4A, and FIG. 1B is the same as FIG. 4B. 2 shows a detailed cross section around the photoelectric conversion element in the row direction of the photoelectric conversion element.
This embodiment is different from the conventional solid-state imaging device in that a trench is formed as a channel stop region. That is, as shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B, in the solid-state imaging device 2 of the embodiment, the n-type region 116 (the first conductivity type region according to the present invention) and the p-
[0016]
The
[0017]
As shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B, an insulating
[0018]
Further, a p-
[0019]
The electrodes and the light-shielding film are the same as those of the conventional solid-state imaging device. As shown in FIG. 1B, the second-
[0020]
As described above, in the solid-state imaging device 2 according to the present embodiment, a trench reaching a position deeper than the
[0021]
Further, in this embodiment, since the
[0022]
Such a
[0023]
In the solid-state imaging device 2 according to the present embodiment, the
[0024]
In the present embodiment, the
However, the light emitted from the side portion of the
[0025]
In this embodiment, the p-
Although a silicon nitride mask is used when forming the
[0026]
In this embodiment, the
In the present embodiment, the solid-state imaging device 2 is an interline type. However, as is apparent from the above description, the present invention relates to the structure around each
[0027]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, in the solid-state imaging device of the present invention and the solid-state imaging device manufactured by the manufacturing method of the present invention, the first conductivity type constituting the photoelectric conversion device is formed on the surface of the semiconductor substrate around each photoelectric conversion device. Since a trench reaching a position deeper than the bottom of the region is formed, the signal charge generated by each photoelectric conversion element can be blocked by this trench and mixed with the signal charge by another adjacent photoelectric conversion element. Absent. As a result, there is no problem that the resolution is lowered or color mixture occurs between pixels.
The trench can be easily formed by a conventionally widely used technique such as etching, so that even when small-sized photoelectric conversion elements are arranged at a high density, a reduction in resolution and color mixing are surely prevented. can do.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIGS. 1A and 1B are partial cross-sectional side views showing an example of a solid-state imaging device according to the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a plan view showing an example of a conventional solid-state imaging device.
3 is a partial enlarged plan view showing in detail a part of the solid-state imaging device of FIG. 2;
4A is a partial cross-sectional side view taken along the line AA ′ in FIG. 3, and FIG. 4B is a partial cross-sectional side view taken along the line BB ′ in FIG. 3;
[Explanation of symbols]
2 ...... solid-state imaging device, the bottom of the n-
Claims (11)
前記光電変換素子は前記半導体基板の表面部に局所的に積層された第1導電型および第2導電型の領域を含み、前記第2導電型の領域は前記半導体基板の表面側に形成されている固体撮像素子であって、
各光電変換素子の周囲の半導体基板表面部に、前記第1導電型の領域の底部より深い位置に至るトレンチが形成され、
前記光電変換素子と、同光電変換素子に隣接する前記トレンチとの間の半導体基板表面部に、前記第2導電型の領域と接して当該トレンチよりも浅い高濃度の第2導電型の不純物を含む領域が形成されている
固体撮像素子。A plurality of photoelectric conversion elements arranged close to each other on a semiconductor substrate,
The photoelectric conversion element includes a first conductivity type region and a second conductivity type region locally stacked on a surface portion of the semiconductor substrate, and the second conductivity type region is formed on a surface side of the semiconductor substrate. A solid-state imaging device,
A trench reaching a position deeper than the bottom of the region of the first conductivity type is formed on the surface of the semiconductor substrate around each photoelectric conversion element ,
On the surface of the semiconductor substrate between the photoelectric conversion element and the trench adjacent to the photoelectric conversion element, a second conductivity type impurity having a high concentration shallower than the trench is in contact with the second conductivity type region. A solid-state imaging device in which a region to be formed is formed .
請求項1記載の固体撮像素子。An insulating film is deposited on the inner surface of the trench
The solid-state imaging device according to claim 1 .
請求項2記載の固体撮像素子。The trench is filled with a metal material
The solid-state imaging device according to claim 2 .
請求項1記載の固体撮像素子。The trench is filled with an insulating material
The solid-state imaging device according to claim 1 .
請求項2記載の固体撮像素子。The semiconductor substrate is made of silicon, and the insulating film is made of silicon oxide.
The solid-state imaging device according to claim 2 .
請求項3記載の固体撮像素子。The metal material is aluminum.
The solid-state imaging device according to claim 3 .
請求項1〜6の何れかに記載の固体撮像素子。The photoelectric conversion elements are arranged in a matrix on the semiconductor substrate, and a vertical charge transfer register extends in the column direction of the photoelectric conversion elements for each column of the photoelectric conversion elements, and the vertical charge transfer registers correspond to each other. Charges are taken in and transferred from the photoelectric conversion elements in a row, and the trenches except for the portions between the vertical charge transfer registers and the photoelectric conversion elements corresponding to the vertical charge transfer registers. Formed around
The solid-state image sensor in any one of Claims 1-6 .
各光電変換素子の周囲の半導体基板表面部に、前記第1導電型の領域の底部より深い位置に至るトレンチを形成し、
前記光電変換素子と、同光電変換素子に隣接する前記トレンチとの間の半導体基板表面部に、前記第2導電型の領域と接して当該トレンチよりも浅い高濃度の第2導電型の不純物を含む領域を形成する
固体撮像素子の製造方法。A plurality of photoelectric conversion elements arranged close to each other on a semiconductor substrate, the photoelectric conversion elements having first conductivity type and second conductivity type regions locally stacked on a surface portion of the semiconductor substrate The second conductivity type region is a method of manufacturing a solid-state imaging device formed on the surface side of the semiconductor substrate,
Forming a trench reaching a position deeper than the bottom of the first conductivity type region on the surface of the semiconductor substrate around each photoelectric conversion element ;
On the surface of the semiconductor substrate between the photoelectric conversion element and the trench adjacent to the photoelectric conversion element, a high-concentration second conductivity type impurity that is in contact with the second conductivity type region and is shallower than the trench. A method for manufacturing a solid-state imaging device for forming a region to be included .
請求項8記載の固体撮像素子の製造方法。A silicon nitride film is formed on the surface of the semiconductor substrate, patterned to open the trench formation portion, and the trench is formed by performing selective etching using the patterned silicon nitride film as a mask.
The manufacturing method of the solid-state image sensor of Claim 8 .
請求項8または9記載の固体撮像素子の製造方法。The trench is filled with a metal material through an insulating film or filled with an insulating material.
The manufacturing method of the solid-state image sensor of Claim 8 or 9 .
請求項8または9記載の固体撮像素子の製造方法。The trench has a hollow structure
The manufacturing method of the solid-state image sensor of Claim 8 or 9 .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001029148A JP4654521B2 (en) | 2001-02-06 | 2001-02-06 | Solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method of solid-state imaging device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001029148A JP4654521B2 (en) | 2001-02-06 | 2001-02-06 | Solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method of solid-state imaging device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002231929A JP2002231929A (en) | 2002-08-16 |
| JP2002231929A5 JP2002231929A5 (en) | 2008-03-06 |
| JP4654521B2 true JP4654521B2 (en) | 2011-03-23 |
Family
ID=18893527
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001029148A Expired - Fee Related JP4654521B2 (en) | 2001-02-06 | 2001-02-06 | Solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method of solid-state imaging device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4654521B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100748326B1 (en) * | 2001-06-26 | 2007-08-09 | 매그나칩 반도체 유한회사 | Image sensor and its manufacturing method |
| JP4496753B2 (en) * | 2003-10-20 | 2010-07-07 | ソニー株式会社 | Solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method thereof |
| KR100678269B1 (en) | 2004-10-18 | 2007-02-02 | 삼성전자주식회사 | CMOS image sensor and its manufacturing method |
| JP4742602B2 (en) | 2005-02-01 | 2011-08-10 | ソニー株式会社 | Solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP5123701B2 (en) * | 2008-03-13 | 2013-01-23 | キヤノン株式会社 | Photoelectric conversion device, imaging system, and method of manufacturing photoelectric conversion device |
| JP2010067827A (en) * | 2008-09-11 | 2010-03-25 | Fujifilm Corp | Solid-state imaging device and imaging apparatus |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5286782A (en) * | 1976-01-13 | 1977-07-19 | Nec Corp | Production of semiconductor integrated circuit |
| JPS60147131A (en) * | 1984-01-11 | 1985-08-03 | Seiko Epson Corp | Semiconductor device |
| JPH01161757A (en) * | 1987-12-18 | 1989-06-26 | Nec Corp | Solid-state image pickup element |
| JPH02105460A (en) * | 1988-10-14 | 1990-04-18 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Manufacture of solid-state image sensing device |
| JPH03273679A (en) * | 1990-03-23 | 1991-12-04 | Matsushita Electron Corp | Solid-state image sensing device |
| JPH03273678A (en) * | 1990-03-23 | 1991-12-04 | Matsushita Electron Corp | Solid-state image sensing device |
-
2001
- 2001-02-06 JP JP2001029148A patent/JP4654521B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5286782A (en) * | 1976-01-13 | 1977-07-19 | Nec Corp | Production of semiconductor integrated circuit |
| JPS60147131A (en) * | 1984-01-11 | 1985-08-03 | Seiko Epson Corp | Semiconductor device |
| JPH01161757A (en) * | 1987-12-18 | 1989-06-26 | Nec Corp | Solid-state image pickup element |
| JPH02105460A (en) * | 1988-10-14 | 1990-04-18 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Manufacture of solid-state image sensing device |
| JPH03273679A (en) * | 1990-03-23 | 1991-12-04 | Matsushita Electron Corp | Solid-state image sensing device |
| JPH03273678A (en) * | 1990-03-23 | 1991-12-04 | Matsushita Electron Corp | Solid-state image sensing device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2002231929A (en) | 2002-08-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JPH07120779B2 (en) | Overflow drain structure of solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| TWI363420B (en) | Solid state imaging device and imaging apparatus | |
| JP2004273640A (en) | Solid-state imaging device and its manufacturing method | |
| JP4654521B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method of solid-state imaging device | |
| JPH10135439A (en) | Solid-state imaging device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP5030323B2 (en) | Solid-state image sensor | |
| JPH08255888A (en) | Solid state image sensor and fabrication thereof | |
| WO2004055896A1 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and method for producing solid-state imaging device | |
| JPH02278874A (en) | Solid state image sensor and manufacture thereof | |
| JP2000174251A (en) | Photoelectric conversion element and solid-state imaging device using the same | |
| JP2010153603A (en) | Solid state imaging apparatus | |
| JPS63312669A (en) | Solid-state image sensor | |
| JP2897689B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device | |
| JP3562128B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device | |
| JP2012204492A (en) | Solid state image pickup device | |
| JPS60173978A (en) | Solid-state image pickup device | |
| US6383834B1 (en) | Charge coupled device | |
| JPH0465165A (en) | Charge coupled device and manufacture thereof | |
| JP2980196B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device | |
| JPH1126745A (en) | Solid-state image pick-up device | |
| JPH02278767A (en) | Solid-state image sensing device | |
| JP2671151B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JPS6251256A (en) | Solid-state image pickup device | |
| JPH0570947B2 (en) | ||
| JPS62181465A (en) | CCD solid-state image sensor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080117 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20080117 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20090817 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20091009 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100910 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100914 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20101104 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20101124 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20101207 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140107 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140107 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |