JP2017092191A - Silicon carbide semiconductor device - Google Patents
Silicon carbide semiconductor device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2017092191A JP2017092191A JP2015218815A JP2015218815A JP2017092191A JP 2017092191 A JP2017092191 A JP 2017092191A JP 2015218815 A JP2015218815 A JP 2015218815A JP 2015218815 A JP2015218815 A JP 2015218815A JP 2017092191 A JP2017092191 A JP 2017092191A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- trench
- insulating film
- silicon carbide
- gate insulating
- semiconductor device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 55
- HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon carbide Chemical compound [Si+]#[C-] HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title claims description 50
- 229910010271 silicon carbide Inorganic materials 0.000 title claims description 50
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 24
- 229910052735 hafnium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 25
- VBJZVLUMGGDVMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N hafnium atom Chemical compound [Hf] VBJZVLUMGGDVMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 25
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 23
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 23
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 22
- 229910052746 lanthanum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 21
- FZLIPJUXYLNCLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N lanthanum atom Chemical compound [La] FZLIPJUXYLNCLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 21
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 claims description 15
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 11
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052727 yttrium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- VWQVUPCCIRVNHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N yttrium atom Chemical compound [Y] VWQVUPCCIRVNHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910052684 Cerium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zirconium Chemical compound [Zr] QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- GWXLDORMOJMVQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N cerium Chemical compound [Ce] GWXLDORMOJMVQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052712 strontium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- CIOAGBVUUVVLOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N strontium atom Chemical compound [Sr] CIOAGBVUUVVLOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052715 tantalum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N tantalum atom Chemical compound [Ta] GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052726 zirconium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000002431 hydrogen Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 3
- 238000003763 carbonization Methods 0.000 claims 3
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 3
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 claims 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 abstract description 30
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 abstract description 12
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 abstract description 12
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 88
- MRELNEQAGSRDBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N lanthanum(3+);oxygen(2-) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[La+3].[La+3] MRELNEQAGSRDBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 27
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 23
- 229910000449 hafnium oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 23
- WIHZLLGSGQNAGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N hafnium(4+);oxygen(2-) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[Hf+4] WIHZLLGSGQNAGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 23
- TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Al]O[Al]=O TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 23
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 17
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 12
- 229910018072 Al 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 10
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 8
- 229910021193 La 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 4
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000012298 atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000000231 atomic layer deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012299 nitrogen atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002344 surface layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910017109 AlON Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910003855 HfAlO Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- CJNBYAVZURUTKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N hafnium(iv) oxide Chemical compound O=[Hf]=O CJNBYAVZURUTKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000000116 mitigating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- VSZWPYCFIRKVQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N selanylidenegallium;selenium Chemical compound [Se].[Se]=[Ga].[Se]=[Ga] VSZWPYCFIRKVQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/12—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、トレンチゲート構造の半導体素子を有する炭化珪素(以下、SiCという)半導体装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a silicon carbide (hereinafter referred to as SiC) semiconductor device having a semiconductor element having a trench gate structure.
従来より、大電流が流せるようにチャネル密度を高くした構造としてトレンチゲート構造の半導体素子を有するSiC半導体装置がある。このようなトレンチゲート構造の半導体素子を有するSiC半導体装置では、SiCの破壊電界強度が高いことから、トレンチ底部に高電界が加わって絶縁破壊が生じる可能性がある。このため、例えばSiCを用いたトレンチゲート構造のMOSFETでは、ゲート絶縁膜に加わる電界(以下、ゲート電界という)を緩和するために、対向するトレンチゲート間のベース層の下部にp型の電界緩和層を形成し、トレンチ底部への電界の入り込みを緩和することで、絶縁破壊を防止している。 Conventionally, there is a SiC semiconductor device having a semiconductor element having a trench gate structure as a structure in which a channel density is increased so that a large current can flow. In an SiC semiconductor device having such a semiconductor element having a trench gate structure, since the breakdown electric field strength of SiC is high, there is a possibility that a high electric field is applied to the bottom of the trench to cause dielectric breakdown. For this reason, in a MOSFET having a trench gate structure using SiC, for example, a p-type electric field relaxation is provided below a base layer between opposing trench gates in order to reduce an electric field applied to a gate insulating film (hereinafter referred to as a gate electric field). By forming a layer and mitigating the entry of the electric field into the bottom of the trench, dielectric breakdown is prevented.
また、ゲート絶縁膜を誘電率の高いAl2O3、AlONで構成することで、ゲート電界を弱め、ゲート信頼性を高めることも行われている。特許文献1では、ゲート絶縁膜をシリコン酸化膜(SiO2)よりも高誘電率膜で構成しつつ、ゲート絶縁膜のうちトレンチ側壁部に位置している側壁絶縁膜をトレンチ底部に位置している底部絶縁膜よりも高誘電率にするという条件を満たすようにしている。このように、ゲート絶縁膜を誘電率の高い膜で構成することでMOSFETの電流駆動能力も高めることが可能になる。
In addition, by configuring the gate insulating film with Al 2 O 3 or AlON having a high dielectric constant, the gate electric field is weakened and the gate reliability is improved. In
しかしながら、単にゲート絶縁膜の誘電率を高くしてもゲート絶縁膜が絶縁破壊される破壊電界が低いため、結果的に高耐圧が得られず、SiC半導体装置を構成する素子の信頼性確保が困難という問題がある。 However, even if the dielectric constant of the gate insulating film is simply increased, the breakdown electric field at which the gate insulating film breaks down is low. As a result, a high breakdown voltage cannot be obtained, and the reliability of the elements constituting the SiC semiconductor device can be ensured. There is a problem of difficulty.
また、特許文献1に記載されたMOSFETでは、上記の条件を満たすようにしているが、この条件では、MOSFETのオフ時に高電界が印加されたときに、トレンチ底部においてゲート絶縁膜に印加される電界を十分に緩和できない。このため、高耐圧を得ることができず、SiC半導体装置を構成する半導体素子の信頼性確保が困難である。
In the MOSFET described in
本発明は上記点に鑑みて、高耐圧かつ信頼性の高いトレンチゲート構造の半導体素子を有するSiC半導体装置を提供することを目的とする。 An object of the present invention is to provide a SiC semiconductor device having a semiconductor element having a trench gate structure with high breakdown voltage and high reliability.
上記目的を達成するため、請求項1に記載のトレンチゲート構造の半導体素子を有するSiC半導体装置では、炭化珪素からなる第1または第2導電型の基板(1)と、基板の上に形成され、基板よりも低不純物濃度とされた第1導電型の炭化珪素からなるドリフト層(2)と、ドリフト層の上に形成された第2導電型の炭化珪素からなるベース領域(4)と、ベース領域の上に形成され、ドリフト層よりも高濃度の第1導電型の炭化珪素からなるソース領域(5)と、ソース領域およびベース領域よりも深く、かつ、ドリフト層まで達し、ソース領域およびベース領域が両側に配置されるように形成されたトレンチ(7)と、トレンチの表面に形成されたゲート絶縁膜(8)と、トレンチ内において、ゲート絶縁膜の上に形成されたゲート電極(9)と、ソース領域およびベース領域に電気的に接続されたソース電極(10)と、基板の裏面側に形成されたドレイン電極(12)と、を有するトレンチゲート構造の半導体素子を備えている。このような構成において、ゲート絶縁膜は、少なくともトレンチの底部に位置している部分が高誘電率膜によって構成されており、該ゲート絶縁膜は単位面積辺りの容量をCox、絶縁破壊電圧をVb,oxとしてCox×Vb,oxが7.6×10-6C/cm2以上とされている。
In order to achieve the above object, an SiC semiconductor device having a trench gate structure semiconductor element according to
このように、ゲート絶縁膜の少なくとも一部にシリコン酸化膜よりも誘電率の高い材料を用い、Cox×Vb,oxが7.6×10-6C/cm2以上となる関係を満たす材料によって構成している。このような条件を満たす材料の高誘電率膜によってゲート絶縁膜を構成することにより、高耐圧かつ信頼性の高いトレンチゲート構造の縦型MOSFETを有するSiC半導体装置とすることが可能となる。 In this way, a material having a dielectric constant higher than that of the silicon oxide film is used for at least a part of the gate insulating film, and a material satisfying the relationship that Cox × Vb, ox is 7.6 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 or more is satisfied. It is composed. By configuring the gate insulating film with a high dielectric constant film made of a material that satisfies such conditions, it is possible to obtain a SiC semiconductor device having a vertical MOSFET having a trench gate structure with high breakdown voltage and high reliability.
なお、上記各手段の括弧内の符号は、後述する実施形態に記載の具体的手段との対応関係の一例を示すものである。 In addition, the code | symbol in the bracket | parenthesis of each said means shows an example of a corresponding relationship with the specific means as described in embodiment mentioned later.
以下、本発明の実施形態について図に基づいて説明する。なお、以下の各実施形態相互において、互いに同一もしくは均等である部分には、同一符号を付して説明を行う。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. In the following embodiments, parts that are the same or equivalent to each other will be described with the same reference numerals.
(第1実施形態)
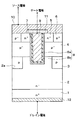
第1実施形態について説明する。本実施形態では、トレンチゲート構造の半導体素子を有するSiC半導体装置として、図1に示す反転型のトレンチゲート構造の縦型MOSFETを有するSiC半導体装置を例に挙げて説明する。なお、図1では、縦型MOSFETの1セル分しか記載していないが、図1に示す縦型MOSFETと同様の構造のものが複数セル隣り合うように配置されている。
(First embodiment)
A first embodiment will be described. In the present embodiment, an SiC semiconductor device having a vertical MOSFET having an inverted trench gate structure shown in FIG. 1 will be described as an example of the SiC semiconductor device having a semiconductor element having a trench gate structure. In FIG. 1, only one cell of the vertical MOSFET is shown, but a plurality of cells having the same structure as the vertical MOSFET shown in FIG. 1 are arranged adjacent to each other.
図1に示すように、SiC半導体装置は、リンもしくは窒素などのn型不純物が高濃度、例えば1×1019〜1×1020cm-3の不純物濃度でドープされたSiC単結晶からなるn+型半導体基板1を用いて形成されている。n+型半導体基板1の上には、n+型半導体基板1よりも低不純物濃度とされ、n型不純物が例えば1×1015〜1×1016cm-3の不純物濃度でドープされた厚さが5〜15μm程度のSiCからなるn型ドリフト層2が形成されている。
As shown in FIG. 1, the SiC semiconductor device includes an n-type impurity made of SiC single crystal doped with an n-type impurity such as phosphorus or nitrogen at a high concentration, for example, an impurity concentration of 1 × 10 19 to 1 × 10 20 cm −3. It is formed using a +
n型ドリフト層2には部分的に凹まされた凹部2aが形成されている。凹部2aは、一方向、すなわち図1の紙面垂直方向を長手方向とした直線形状で構成されており、後述するトレンチゲート構造を構成するトレンチ7よりも深い位置まで、かつ、トレンチ7と同方向を長手方向として形成されている。
The n-
凹部2a内には、凹部2aの長手方向と同方向を長手方向として、ボロンもしくはアルミニウムなどのp型不純物がドープされた電界緩和層3が形成されている。電界緩和層3は、トレンチ7の底部への電界の入り込みを抑制することでゲート電界を緩和するものであり、例えば1×1017〜1×1019cm-3程度とされ、トレンチ7の底部よりも深い位置まで形成されている。
In the
また、n型ドリフト層2および電界緩和層3の表面上に、p型ベース領域4が形成されている。p型ベース領域4は、縦型MOSFETのチャネルを構成する層であり、後述するトレンチゲート構造を構成するトレンチ7の両側において、トレンチ7の側面に接するように形成されている。
A p-
p型ベース領域4の表層部のうち電界緩和層3と対応する位置よりもトレンチゲート構造側には、トレンチゲート構造に接するように、n型ドリフト層2よりもn型不純物が高濃度にドープされたn+型ソース領域5が形成されている。本実施形態の場合、例えばn+型ソース領域5を不純物濃度が1×1021cm-3程度、厚さが0.3μm程度で形成している。また、p型ベース領域4の表層部のうち電界緩和層3と対応する位置、つまりn+型ソース領域5を挟んでトレンチゲート構造の反対側には、p型不純物が高濃度にドープされたp+型コンタクト領域6が形成されている。本実施形態の場合、例えばp+型コンタクト領域6を不純物濃度が1×1021cm-3程度、厚さが0.3μm程度で形成している。
The n-type impurity is doped at a higher concentration than the n-
さらに、図1の断面において、隣り合って配置された電界緩和層3の中央位置に、p型ベース領域4およびn+型ソース領域5を貫通してn型ドリフト層2に達し、かつ、電界緩和層3の底部よりも浅くされたトレンチ7が形成されている。このトレンチ7の側面と接するようにp型ベース領域4およびn+型ソース領域5が配置されている。トレンチ7の内壁面は高誘電率膜などによって構成されたゲート絶縁膜8で覆われている。そして、ゲート絶縁膜8の表面に形成されたドープトPoly−Siにて構成されたゲート電極9により、トレンチ7内が埋め尽くされている。このように、トレンチ7内にゲート絶縁膜8およびゲート電極9を備えた構造により、トレンチゲート構造が構成されている。
Further, in the cross section of FIG. 1, the n-
本実施形態では、ゲート絶縁膜8を多層構造によって構成しており、ここではゲート絶縁膜8を第1層8aと第2層8bの2層構造としている。具体的には、ゲート絶縁膜8のうちの第1層8aと第2層8bの両方共にトレンチ7の底部および側壁部に形成されるようにしており、第2層8bが第1層8aの表面に形成される構造としている。そして、第1層8aについてはシリコン酸化膜によって構成し、第2層8bを第1実施形態で説明した高誘電率膜によって構成している。このように、ゲート絶縁膜8を多層構造としつつ、トレンチ7の底部、つまりゲート電極9のうちの少なくとも底部が覆われるように高誘電率膜で構成される第2層8bが備えられるようにしている。
In this embodiment, the
なお、ゲート絶縁膜8のうちの第2層8bの詳細構成については後述する。また、図1では示されていないが、トレンチゲート構造は、例えば紙面垂直方向を長手方向とした短冊状とされており、複数本のトレンチゲート構造が紙面左右方向に等間隔にストライプ状に並べられることで複数セルが備えられた構造とされている。
The detailed configuration of the
また、n+型ソース領域5およびp+型コンタクト領域6の表面には、ソース電極10が形成されている。ソース電極10は、複数の金属(例えばニッケル(Ni)やアルミニウム(Al)等)にて構成されている。具体的には、n+型ソース領域5に接続される部分はn型SiCとオーミック接触可能な金属で構成され、p+型コンタクト領域6を介してp型ベース領域4に接続される部分はp型SiCとオーミック接触可能な金属で構成されている。なお、ソース電極10は、層間絶縁膜11を介して、ゲート電極9に電気的に接続される図示しないゲート配線と電気的に分離されている。そして、層間絶縁膜11に形成されたコンタクトホールを通じて、ソース電極10はn+型ソース領域5およびp+型コンタクト領域6と電気的に接触させられている。
A
さらに、n+型半導体基板1の裏面側にはn+型半導体基板1と電気的に接続されたドレイン電極12が形成されている。このような構造により、nチャネルタイプの反転型のトレンチゲート構造の縦型MOSFETが構成されている。
Further, on the back side of the n + -type semiconductor substrate 1 n + -
このように構成される反転型のトレンチゲート構造の縦型MOSFETにおいて、上記したようにゲート絶縁膜8のうち高誘電率膜で構成される第2層8bが第1層8a上におけるトレンチ7の底部から側壁部に至るすべての領域に形成されるようにしている。さらに、本実施形態の場合、アモルファス構造を有するアモルファス膜によって第2層8bを構成している。そして、第2層8bをシリコン酸化膜(SiO2)よりも誘電率の高い材料で構成しており、該ゲート絶縁膜8は単位面積当たりの容量をCox、絶縁破壊電圧をVb,oxとして、Cox×Vb,oxが7.6×10-6C/cm2以上となる関係を満たす材料によって構成している。このような条件を満たす材料でゲート絶縁膜8を構成することにより、高耐圧かつ信頼性の高いトレンチゲート構造の縦型MOSFETを有するSiC半導体装置としている。以下、この効果が得られる理由について説明する。
In the vertical MOSFET having the inverted trench gate structure configured as described above, the
MOS構造の素子のゲート絶縁膜が破壊するとき、ゲート絶縁膜には絶縁破壊電圧Vb,ox以上の電界が印加される。ゲート絶縁膜が一般的に用いられるシリコン酸化膜のみによって構成される場合、絶縁破壊電界は約11MV/cmとなる。このため、例えば、素子のオフ時にドレイン電極に1200Vが印加されると想定した場合、素子のゲート絶縁膜が破壊するとき、破壊箇所のシリコン酸化膜には11MV/cm以上の電界が印加されることになる。 When the gate insulating film of the element having the MOS structure is broken, an electric field equal to or higher than the breakdown voltage Vb, ox is applied to the gate insulating film. In the case where the gate insulating film is composed only of a commonly used silicon oxide film, the dielectric breakdown electric field is about 11 MV / cm. For this reason, for example, assuming that 1200 V is applied to the drain electrode when the device is turned off, when the gate insulating film of the device is broken, an electric field of 11 MV / cm or more is applied to the silicon oxide film at the broken portion. It will be.
この時、ゲート絶縁膜の容量をCox、絶縁破壊電圧をVb,oxとすると、Cox×Vb,ox[C/cm2]は絶縁膜が破壊するときに耐えうる電荷量を表しており、この値が大きいほど絶縁膜が壊れにくいと言える。例えばシリコン酸化膜の場合、ゲート絶縁膜の厚さが50nmとすると、絶縁破壊電圧は50nm×11MV/cmで60Vとなる。このとき、Cox×Vb,oxは3.8×10-6C/cm2程度の値となる。 At this time, when the capacity of the gate insulating film is Cox and the breakdown voltage is Vb, ox, Cox × Vb, ox [C / cm 2 ] represents the amount of charge that can be withstood when the insulating film breaks. It can be said that the larger the value, the harder the insulating film is broken. For example, in the case of a silicon oxide film, if the thickness of the gate insulating film is 50 nm, the dielectric breakdown voltage is 60 V at 50 nm × 11 MV / cm. At this time, Cox × Vb, ox becomes a value of about 3.8 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 .
容量が大きいほど電流駆動能力が高く、絶縁破壊電圧が大きいほど絶縁膜が壊れにくいため、Cox×Vb,oxが大きいほどゲート絶縁膜としてより望ましい特性を有していると言えるが、単位面積当たりの容量、絶縁破壊電圧は材料物性で決まるため、シリコン酸化膜を用いてこの値を大きくすることは困難である。 The larger the capacity, the higher the current drive capability, and the higher the breakdown voltage, the more difficult the insulation film breaks.Therefore, the larger the Cox x Vb, ox, the more desirable characteristics as a gate insulation film. Therefore, it is difficult to increase this value by using a silicon oxide film.
一方、ゲート絶縁膜8の一部、もしくは全部に高誘電率膜を使用し、容量はシリコン酸化膜の場合と同じでC×Vb,oxを2倍の値にした場合、ゲート絶縁膜8が破壊するまでに印加できる電圧を2倍にすることができ、同じドレイン電圧が印加された時の余裕度を大幅に上げることができる。
On the other hand, when a high dielectric constant film is used for part or all of the
なお、本実施形態では、ゲート絶縁膜8のうちの第2層8bをトレンチ7の底部から側壁部に至るすべての領域で同じ組成の高誘電率膜としているが、特に電界の集中するトレンチ7の底部における角部と接する部分を高誘電率膜にすれば良い。このようにすれば、高耐圧の素子にできるため、より絶縁破壊に対するゲート絶縁膜8の信頼性を高めることが可能になるし、仮に電界緩和層3を無くしたとしても、オフ時の絶縁膜破壊を抑制でき、信頼性の高い素子を実現することができる。
In the present embodiment, the
このような第2層8bを構成する高誘電率膜としては、例えばハフニウム(Hf)、アルミニウム(Al)、ランタン(La)、セリウム(Ce)、ジルコニウム(Zr)、イットリウム(Y)、タンタル(Ta)、ストロンチウム(Sr)等のうちの1種もしくは2種以上を含む絶縁材料が挙げられる。例えば、ハフニウムを含む絶縁材料である酸化ハフニウム(HfO2)、アルミニウムを含む絶縁材料である酸化アルミニウム(Al2O3)、ランタンを含む絶縁材料である酸化ランタン(La2O3)などの高誘電率膜を第2層8bとして適用できる。また、ハフニウムとアルミニウムもしくはランタンのいずれか複数を含むHfAlO、HfLaO、AlLaO、HfAlLaOなどの高誘電率膜を第2層8bとして適用できる。さらに、ハフニウム、アルミニウムおよびランタンに加えて上記した各金属材料のいずれか複数が含まれる高誘電率膜についても第2層8bとして適用できる。
Examples of the high dielectric constant film constituting the
例えば、第2層8bの構成材料としてハフニウム、アルミニウムおよびランタンを用いて実験を行い、各構成材料の元素含有率(atomic%)を変えてCox×Vb,ox[C/cm2]を求めた。図2は、その実験結果を示している。なお、この実験については、シリコン酸化膜上に成膜した酸化ハフニウム、酸化アルミニウムおよび酸化ランタンを構成材料として、各構成材料の含有率を変えて行っている。図2が示す三角形の各頂点は、それぞれ各構成材料の含有率を100%とした場合を表しており、各頂点から1升ずれる毎に10%ずつ構成材料の含有率が増減することを示している。具体的には、三角形の上頂点を酸化ランタン100%、左下頂点を酸化ハフニウム100%、右下頂点を酸化アルミニウム100%としており、例えば左下頂点から右側に1升ずれると、酸化ハフニウム90%と酸化アルミニウム10%の含有率になることを示している。なお、ここでいう構成材料の含有率は、以下のように表される。
For example, experiments were performed using hafnium, aluminum, and lanthanum as the constituent material of the
第2層8bを例えば酸化アルミニウムと酸化ハフニウムとを混在させた合成膜によって構成する場合、酸化アルミニウムにおいて含有率がx、酸化ハフニウムの含有率がyであると、酸化アルミニウムと酸化ハフニウムとの合成膜は、次の化学式で表される。ただし、x、yについては、不純物を無視して、x+y=1が成り立つものとする。
In the case where the
(化1)
(Al2O3)x(HfO2)y
図2に示されるように、酸化ハフニウムや酸化アルミニウムについても他の構成材料と共に含ませることでCox×Vb,ox>7.6×10-6C/cm2を満たすことができる。特に、酸化アルミニウムと酸化ハフニウムとを含ませた合成膜についてはCox×Vb,oxの値が大きくなった。
(Chemical formula 1)
(Al 2 O 3 ) x (HfO 2 ) y
As shown in FIG. 2, it is possible to satisfy Cox × Vb, ox> 7.6 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 by including hafnium oxide and aluminum oxide together with other constituent materials. In particular, the value of Cox × Vb, ox increased for the synthetic film containing aluminum oxide and hafnium oxide.
具体的には、図2中の領域(1)に示すように、酸化アルミニウムの含有率が0.05〜0.75、酸化ハフニウムの含有率が0.25〜0.95の場合に、Cox×Vb,ox>7.6×10-6C/cm2を満たしていた。この場合、化学式は(Al2O3)0.05〜0.75(HfO2)0.25〜0.95で表される。特に、酸化アルミニウムの含有率が0.3、酸化ハフニウムの含有率が0.7の場合においてはCox×Vb,oxが9.7×10-6C/cm2という高い数値が得られた。 Specifically, as shown in the region (1) in FIG. 2, when the content of aluminum oxide is 0.05 to 0.75 and the content of hafnium oxide is 0.25 to 0.95, Cox × Vb, ox> 7.6 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 was satisfied. In this case, the chemical formula is represented by (Al 2 O 3 ) 0.05 to 0.75 (HfO 2 ) 0.25 to 0.95 . In particular, when the aluminum oxide content was 0.3 and the hafnium oxide content was 0.7, a high value of Cox × Vb, ox of 9.7 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 was obtained.
図2中の領域(2)に示すように、酸化ハフニウムの含有率が0.45〜0.75、酸化ランタンの含有率が0.25〜0.55の場合においては、Cox×Vb,ox>7.6×10-6C/cm2を満たしていた。 As shown in the region (2) in FIG. 2, when the content of hafnium oxide is 0.45 to 0.75 and the content of lanthanum oxide is 0.25 to 0.55, Cox × Vb, ox > 7.6 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 was satisfied.
図2中の領域(3)に示すように、酸化アルミニウムの含有率が0.1、酸化ハフニウムの含有率が0.25〜0.75、酸化ランタンの含有率が0.15〜0.65の場合においては、Cox×Vb,ox>7.6×10-6C/cm2を満たしていた。この場合、化学式は(Al2O3)0.1(HfO2)0.25〜0.75(La2O3)0.15〜0.65で表される。 As shown in the region (3) in FIG. 2, the aluminum oxide content is 0.1, the hafnium oxide content is 0.25 to 0.75, and the lanthanum oxide content is 0.15 to 0.65. In this case, Cox × Vb, ox> 7.6 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 was satisfied. In this case, the chemical formula is represented by (Al 2 O 3 ) 0.1 (HfO 2 ) 0.25 to 0.75 (La 2 O 3 ) 0.15 to 0.65 .
図2中の領域(4)に示すように、酸化アルミニウムの含有率が0.2、酸化ハフニウムの含有率が0.05〜0.75、酸化ランタンの含有率が0.05〜0.75の場合においても、Cox×Vb,ox>7.6×10-6C/cm2を満たしていた。この場合、化学式は(Al2O3)0.2(HfO2)0.05〜0.75(La2O3)0.05〜0.75で表される。 As shown in region (4) in FIG. 2, the content of aluminum oxide is 0.2, the content of hafnium oxide is 0.05 to 0.75, and the content of lanthanum oxide is 0.05 to 0.75. In this case, Cox × Vb, ox> 7.6 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 was satisfied. In this case, the chemical formula is represented by (Al 2 O 3 ) 0.2 (HfO 2 ) 0.05 to 0.75 (La 2 O 3 ) 0.05 to 0.75 .
図2中の領域(5)に示すように、酸化アルミニウムの含有率が0.3、酸化ハフニウムの含有率が0.35〜0.55、酸化ランタンの含有率が0.15〜0.35の場合においても、Cox×Vb,ox>7.6×10-6C/cm2を満たしていた。この場合、化学式は(Al2O3)0.3(HfO2)0.35〜0.55(La2O3)0.15〜0.35で表される。 As shown in region (5) in FIG. 2, the aluminum oxide content is 0.3, the hafnium oxide content is 0.35 to 0.55, and the lanthanum oxide content is 0.15 to 0.35. In this case, Cox × Vb, ox> 7.6 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 was satisfied. In this case, the chemical formula is represented by (Al 2 O 3 ) 0.3 (HfO 2 ) 0.35 to 0.55 (La 2 O 3 ) 0.15 to 0.35 .
図2中の領域(6)に示すように、酸化アルミニウムの含有率が0.4、酸化ハフニウムの含有率が0.35〜0.55、酸化ランタンの含有率が0.05〜0.25の場合においても、Cox×Vb,ox>7.6×10-6C/cm2を満たしていた。この場合、化学式は(Al2O3)0.4(HfO2)0.35〜0.55(La2O3)0.05〜0.25で表される。 As shown in region (6) in FIG. 2, the aluminum oxide content is 0.4, the hafnium oxide content is 0.35 to 0.55, and the lanthanum oxide content is 0.05 to 0.25. In this case, Cox × Vb, ox> 7.6 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 was satisfied. In this case, the chemical formula is represented by (Al 2 O 3 ) 0.4 (HfO 2 ) 0.35 to 0.55 (La 2 O 3 ) 0.05 to 0.25 .
図2中の領域(7)に示すように、酸化アルミニウムの含有率が0.5、酸化ハフニウムの含有率が0.35〜0.45、酸化ランタンの含有率が0.05〜0.15の場合においても、Cox×Vb,ox>7.6×10-6C/cm2を満たしていた。この場合、化学式は(Al2O3)0.5(HfO2)0.35〜0.45(La2O3)0.05〜0.15で表される。 As shown in the region (7) in FIG. 2, the content of aluminum oxide is 0.5, the content of hafnium oxide is 0.35 to 0.45, and the content of lanthanum oxide is 0.05 to 0.15. In this case, Cox × Vb, ox> 7.6 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 was satisfied. In this case, the chemical formula is represented by (Al 2 O 3 ) 0.5 (HfO 2 ) 0.35 to 0.45 (La 2 O 3 ) 0.05 to 0.15 .
このように、図2中の各領域(1)〜(7)で示した構成材料の含有率において、Cox×Vb,ox>7.6×10-6C/cm2を満たすことができる。したがって、酸化ハフニウム、酸化アルミニウムおよび酸化ランタンを構成材料のいずれか2つ以上を構成材料として第2層8bを構成した場合には、少なくとも領域(1)〜(7)に示した含有率となる場合において、縦型MOSFETの高耐圧化を実現できる。
Thus, in the content ratios of the constituent materials shown in the regions (1) to (7) in FIG. 2, Cox × Vb, ox> 7.6 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 can be satisfied. Therefore, when the
また、上記では、酸化ハフニウム、酸化アルミニウムおよび酸化ランタンを構成材料として第2層8bを構成した場合における酸化ハフニウム、酸化アルミニウムおよび酸化ランタンの含有率を示した。これをハフニウム、アルミニウムおよびランタンの元素含有率で示すと、以下のようになる。なお、ここでいう元素含有率は、以下のようにして求められる。
In the above description, the contents of hafnium oxide, aluminum oxide, and lanthanum oxide in the case where the
例えば、第2層8bを酸化ハフニウムと酸化アルミニウムとの合成膜によって構成した場合には、上記したように、酸化ハフニウムにおいて含有率がx、酸化アルミニウムの含有率がyであると、酸化ハフニウムと酸化アルミニウムとの合成膜は、上記した化学式1で表される。
For example, when the
このような化学式で表される合成膜において、ハフニウムの元素含有率は1×x、アルミニウムの元素含有率は2×y、酸素の元素含有率は2×x+3×yとなる。例えば、図2中の(3)で示した酸化アルミニウムの含有率が0.1、酸化ハフニウムの含有率が0.4、酸化ランタンの含有率が0.5の場合には、化学式が次式となる。 In the synthetic film represented by such a chemical formula, the element content of hafnium is 1 × x, the element content of aluminum is 2 × y, and the element content of oxygen is 2 × x + 3 × y. For example, when the aluminum oxide content shown by (3) in FIG. 2 is 0.1, the hafnium oxide content is 0.4, and the lanthanum oxide content is 0.5, the chemical formula is: It becomes.
(化2)
(Al2O3)0.1(HfO2)0.4(La2O3)0.5
この場合には、アルミニウムは2×0.1、ハフニウムの元素含有率は1×0.4、ランタンの元素含有率は2×0.5、酸素の元素含有率は3×0.1+2×0.4+3×0.5となる。これを計算すると、アルミニウムの元素含有率は4.8%、ハフニウムの元素含有率は9.5%、ランタンの元素含有率は23.8%、酸素の元素含有率は61.9%となる。このような元素含有率の計算手法に基づいて、上記した各元素含有率を導出している。なお、ここでは理解を容易にするために酸素についても元素含有率を計算したが、下記の各領域(1)〜(7)についての元素含有率では酸素の元素含有率を省略してある。
(Chemical formula 2)
(Al 2 O 3 ) 0.1 (HfO 2 ) 0.4 (La 2 O 3 ) 0.5
In this case, aluminum is 2 × 0.1, hafnium element content is 1 × 0.4, lanthanum element content is 2 × 0.5, and oxygen element content is 3 × 0.1 + 2 × 0. 4 + 3 × 0.5. When this is calculated, the element content of aluminum is 4.8%, the element content of hafnium is 9.5%, the element content of lanthanum is 23.8%, and the element content of oxygen is 61.9%. . Based on such an element content calculation method, each element content described above is derived. In addition, although element content rate was calculated also about oxygen here for easy understanding, the element content rate of oxygen is abbreviate | omitted in the element content rate about following each area | region (1)-(7).
領域(1)の場合、つまり第2層8bをハフニウムとアルミニウムを含む高誘電率膜によって構成する場合、元素含有率がハフニウムについては5〜31%、アルミニウムについては3〜34%となる。
In the case of the region (1), that is, when the
領域(2)の場合、つまり第2層8bをハフニウムとランタンを含む高誘電率膜によって構成する場合、元素含有率がハフニウムについては10〜22%、ランタンについては14〜27%となる。
In the case of the region (2), that is, when the
領域(3)〜(7)の場合、つまり第2層8bをハフニウム、アルミニウムおよびランタンを含む高誘電率膜によって構成する場合、元素含有率がハフニウムについては1〜22%、アルミニウムについては4〜25%、ランタンについては2〜31%となる。
In the case of the regions (3) to (7), that is, when the
このように、図2中の各領域(1)〜(7)における各元素含有率については上記の通りとなり、このような元素含有率となる場合において、Cox×Vb,ox>7.6×10-6C/cm2を満たすことができて、縦型MOSFETの高耐圧化を図ることが可能となる。 As described above, the element content in each of the regions (1) to (7) in FIG. 2 is as described above. In such an element content, Cox × Vb, ox> 7.6 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 can be satisfied, and the high breakdown voltage of the vertical MOSFET can be increased.
なお、酸化ランタンが水分を吸収し易く、安定した素子特性が得られないため、ランタンの含有量についてはできるだけ少ない方が良い。 Since lanthanum oxide easily absorbs moisture and stable device characteristics cannot be obtained, the lanthanum content is preferably as small as possible.
さらに、上記の材料に加えて、第2層8bの構成材料として窒素(N)や水素(H)を含ませることもできる。第2層8bの構成材料に窒素を加える場合、窒素の元素含有率を1〜30%とする。このように窒素を加えることで、第2層8bの結晶化温度を高くでき、プロセス中に適用可能な温度を高くできるため、よりプロセス自由度を高めることが可能となる。また、第2層8b中に形成される酸素空孔などの欠陥に窒素元素が入り込んで欠陥修復を行うことが可能になる。第2層8bの構成材料に水素を加える場合、水素の元素含有率を1〜10%とする。このように水素を加えることで、トレンチ界面での欠陥が水素によって修復され、ストレスを与えたときに発生する欠陥に起因する縦型MOSFETの閾値電圧の変動を抑制できるため、縦型MOSFETの電気特定の安定性を高めることが可能となる。窒素と水素はいずれか一方のみを第2層8bに含有させても良いし、両方とも含有させても良い。
Further, in addition to the above materials, nitrogen (N) or hydrogen (H) may be included as a constituent material of the
以上説明したように、本実施形態にかかる縦型MOSFETを有するSiC半導体装置では、ゲート絶縁膜8のうちの第2層8bをトレンチ7の底部から側壁部に至るすべての領域を高誘電率膜によって構成している。そして、シリコン酸化膜(SiO2)よりも誘電率の高い材料であって、ゲート絶縁膜8をCox×Vb,ox>7.6×10-6C/cm2以上となる関係を満たす材料によって構成している。このような条件を満たす材料によってゲート絶縁膜8を構成することにより、高耐圧かつ信頼性の高いトレンチゲート構造の縦型MOSFETを有するSiC半導体装置とすることが可能となる。
As described above, in the SiC semiconductor device having the vertical MOSFET according to the present embodiment, the entire region from the bottom of the
なお、本実施形態にかかる縦型MOSFETを有するSiC半導体装置の製造方法は、基本的には従来の製造方法と同様であり、ゲート絶縁膜8を形成する際の構成材料を従来に対して変更したり、形成方法を変更するだけでよい。例えば、ゲート絶縁膜8については、第1層8aおよび第2層8b共に、CVD(chemical vapor deposition)法、ALD(atomic layer deposition)法などによって形成することができる。第1層8aについては、熱酸化法や堆積法によって形成しても良い。また、上記したように、第2層8b中に窒素や水素を含有する場合には、第2層8bの形成時の雰囲気を窒素雰囲気もしくは水素雰囲気としたり、窒素や水素を含まない状態の第2層8bの形成後に窒素雰囲気や水素雰囲気中で加熱処理を行えば良い。
The manufacturing method of the SiC semiconductor device having the vertical MOSFET according to the present embodiment is basically the same as the conventional manufacturing method, and the constituent material for forming the
(第2実施形態)
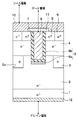
第2実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、第1実施形態に対してゲート絶縁膜8の構造を変更したものであり、その他については第1実施形態と同様であるため、第1実施形態と異なる部分についてのみ説明する。
(Second Embodiment)
A second embodiment will be described. In the present embodiment, the structure of the
図3に示すように、本実施形態では、ゲート絶縁膜8を単層構造によって構成しており、ゲート絶縁膜8がトレンチ7の底部および側壁部に形成されるようにしている。そして、ゲート絶縁膜8の全体を第1実施形態で説明した第2層8bを構成する高誘電率膜によって構成している。本実施形態のゲート絶縁膜8として用いられる高誘電率膜の材料については第1実施形態で説明した第2層8bの構成材料と同様である。
As shown in FIG. 3, in this embodiment, the
このように、ゲート絶縁膜8を単層構造とする場合においても、トレンチ7の底部、つまりゲート電極9のうちの少なくとも底部が覆われるように高誘電率膜で構成される第2層8bが備えられているため、第1実施形態と同様の効果を得ることができる。
As described above, even when the
なお、このような構造の縦型MOSFETを有するSiC半導体装置の製造方法も、基本的には従来と同様であり、ゲート絶縁膜8の形成工程が異なるだけである。具体的には、ゲート絶縁膜8を第1実施形態で説明した高誘電率膜で構成される第2層8bの形成方法を用いて製造すれば良い。本実施形態のような構造とする場合、トレンチ7の底部および側壁部の表面全域にゲート絶縁膜8を1種類の膜で構成すれば良いため、容易にゲート絶縁膜8を形成できる。
The manufacturing method of the SiC semiconductor device having the vertical MOSFET having such a structure is basically the same as the conventional method, and only the formation process of the
(第3実施形態)
第3実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、第1実施形態に対してゲート絶縁膜8の構造を変更したものであり、その他については第1実施形態と同様であるため、第2実施形態と異なる部分についてのみ説明する。
(Third embodiment)
A third embodiment will be described. In the present embodiment, the structure of the
図4に示すように、本実施形態では、第1層8aをトレンチ7の側壁部のみに形成しており、底部には形成していない。そして、第2層8aがトレンチ7の底部においてn型ドリフト層2に接している。
As shown in FIG. 4, in the present embodiment, the
このような構造とする場合においても、トレンチ7の底部、つまりゲート電極9のうちの少なくとも底部が覆われるように高誘電率膜で構成される第2層8bが備えられているため、第1実施形態と同様の効果を得ることができる。また、トレンチ7の側壁部のみに第1層8aを形成することでゲート容量を小さくすることが可能となり、縦型MOSFETのスイッチング損失を低減することが可能となる。
Even in the case of such a structure, since the
なお、このような構造の縦型MOSFETを有するSiC半導体装置の製造方法は、基本的には第1実施形態と同様である。ただし、ゲート絶縁膜8の形成工程として、第1層8aを形成した後に、異方性エッチングなどによって第1層8aのうちトレンチ7の底部の部分を除去してから第2層8bを形成するという工程を行うことになる。
The manufacturing method of the SiC semiconductor device having the vertical MOSFET having such a structure is basically the same as that of the first embodiment. However, as a step of forming the
(第4実施形態)
第4実施形態について説明する。本実施形態も、第1実施形態に対してゲート絶縁膜8の構造を変更したものであり、その他については第1実施形態と同様であるため、第1実施形態と異なる部分についてのみ説明する。
(Fourth embodiment)
A fourth embodiment will be described. This embodiment is also a modification of the structure of the
図5に示すように、本実施形態では、第1層8aをトレンチ7の底部のみに形成しており、側壁部に形成していない。そして、第2層8aがトレンチ7の側壁部においてn型ドリフト層2やp型ベース領域4に接している。
As shown in FIG. 5, in the present embodiment, the
このような構造とする場合においても、トレンチ7の底部、つまりゲート電極9のうちの少なくとも底部が覆われるように高誘電率膜で構成される第2層8bが備えられているため、第1実施形態と同様の効果を得ることができる。また、トレンチ7の底部のみに第1層8aを形成することでゲート容量を小さくすることが可能となり、縦型MOSFETのスイッチング損失を低減することが可能となる。
Even in the case of such a structure, since the
なお、このような構造の縦型MOSFETを有するSiC半導体装置の製造方法は、基本的には第1実施形態と同様である。ただし、ゲート絶縁膜8の形成工程として、第1層8aを形成した後に、エッチバックによって第1層8aをトレンチ7の底部の部分にのみ残るようにしてから第2層8bを形成するという工程を行うことになる。
The manufacturing method of the SiC semiconductor device having the vertical MOSFET having such a structure is basically the same as that of the first embodiment. However, as the step of forming the
(他の実施形態)
本発明は上記した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、特許請求の範囲に記載した範囲内において適宜変更が可能である。
(Other embodiments)
The present invention is not limited to the embodiment described above, and can be appropriately changed within the scope described in the claims.
例えば、上記実施形態では、ゲート絶縁膜8の構造について幾つかの例を挙げて説明した。しかしながら、これらも一例を示したにすぎず、ゲート絶縁膜8のうちのトレンチ7の底部に位置している部分、換言すればゲート電極9のうち少なくともトレンチ7の底部に位置している部分と対応する部分が高誘電率膜で構成されていれば良い。
For example, in the above embodiment, the structure of the
また、ゲート絶縁膜8を構成する高誘電率膜を構成するハフニウム、アルミニウム、ランタン、セリウム、ジルコニウム、イットリウム、タンタル、ストロンチウム等の少なくとも1種を含む絶縁材料として酸化膜を例に挙げたが、酸窒化膜であっても良い。
In addition, although an oxide film is cited as an example of an insulating material containing at least one of hafnium, aluminum, lanthanum, cerium, zirconium, yttrium, tantalum, strontium, and the like constituting the high dielectric constant film constituting the
また、ゲート絶縁膜8については、アモルファス構造となるアモルファス膜によって構成することができるが、結晶構造を有する結晶膜によって構成することもできる。アモルファス構造の場合、結晶粒界が無いことから、リーク電流を抑制することが可能となる。結晶膜の場合、例えばジルコニウムやイットニウムなどをドープすると結晶性が変わって比誘電率をより高くできるという効果が得られる。
Further, the
また、上記各実施形態では、第1導電型をn型、第2導電型をp型としたnチャネルタイプのMOSFETを例に挙げて説明したが、各構成要素の導電型を反転させたpチャネルタイプのMOSFETに対しても本発明を適用することができる。さらに、上記説明では、トレンチゲート構造のMOSFETを例に挙げて説明したが、同様のトレンチゲート構造のIGBTに対しても本発明を適用することができる。IGBTは、上記各実施形態に対してn+型基板1の導電型をn型からp型に変更するだけであり、その他の構造や製造方法に関しては上記各実施形態と同様である。 In each of the above-described embodiments, an n-channel type MOSFET in which the first conductivity type is n-type and the second conductivity type is p-type has been described as an example. The present invention can also be applied to a channel type MOSFET. Furthermore, in the above description, the trench gate structure MOSFET has been described as an example. However, the present invention can be applied to a similar trench gate structure IGBT. The IGBT only changes the conductivity type of the n + type substrate 1 from the n-type to the p-type with respect to the above-described embodiments, and the other structures and manufacturing methods are the same as those of the above-described embodiments.
1 n+型半導体基板
2 n型ドリフト層
4 p型ベース領域
5 n+型ソース領域
7 トレンチ
8 ゲート絶縁膜
8a 第1層
8b 第2層
9 ゲート電極
10 ソース電極
12 ドレイン電極
1 n + type semiconductor substrate 2 n type drift layer 4 p type base region 5 n +
Claims (9)
炭化珪素からなる第1または第2導電型の基板(1)と、
前記基板の上に形成され、前記基板よりも低不純物濃度とされた第1導電型の炭化珪素からなるドリフト層(2)と、
前記ドリフト層の上に形成された第2導電型の炭化珪素からなるベース領域(4)と、
前記ベース領域の上に形成され、前記ドリフト層よりも高濃度の第1導電型の炭化珪素からなるソース領域(5)と、
前記ソース領域および前記ベース領域よりも深く、かつ、前記ドリフト層まで達し、前記ソース領域および前記ベース領域が両側に配置されるように形成されたトレンチ(7)と、
前記トレンチの表面に形成されたゲート絶縁膜(8)と、
前記トレンチ内において、前記ゲート絶縁膜の上に形成されたゲート電極(9)と、
前記ソース領域および前記ベース領域に電気的に接続されたソース電極(10)と、
前記基板の裏面側に形成されたドレイン電極(12)と、を有するトレンチゲート構造の前記半導体素子を備え、
前記ゲート絶縁膜は、少なくとも前記トレンチの底部に位置している部分が高誘電率膜によって構成されており、該ゲート絶縁膜は、単位面積当たりの容量をCoxとし、絶縁破壊電圧をVb,oxとしてCox×Vb,oxが7.6×10-6C/cm2以上とされている炭化珪素半導体装置。 A silicon carbide semiconductor device having a semiconductor element having a trench gate structure,
A first or second conductivity type substrate (1) made of silicon carbide;
A drift layer (2) made of silicon carbide of the first conductivity type formed on the substrate and having a lower impurity concentration than the substrate;
A base region (4) made of silicon carbide of the second conductivity type formed on the drift layer;
A source region (5) formed on the base region and made of silicon carbide of the first conductivity type having a higher concentration than the drift layer;
A trench (7) formed so as to be deeper than the source region and the base region and reach the drift layer, and the source region and the base region are disposed on both sides;
A gate insulating film (8) formed on the surface of the trench;
A gate electrode (9) formed on the gate insulating film in the trench;
A source electrode (10) electrically connected to the source region and the base region;
A drain electrode (12) formed on the back side of the substrate; and the semiconductor element having a trench gate structure,
In the gate insulating film, at least a portion located at the bottom of the trench is formed of a high dielectric constant film, and the gate insulating film has a capacitance per unit area as Cox and a dielectric breakdown voltage as Vb, ox. A silicon carbide semiconductor device in which Cox × Vb, ox is 7.6 × 10 −6 C / cm 2 or more.
炭化珪素からなる第1または第2導電型の基板(1)と、
前記基板の上に形成され、前記基板よりも低不純物濃度とされた第1導電型の炭化珪素からなるドリフト層(2)と、
前記ドリフト層の上に形成された第2導電型の炭化珪素からなるベース領域(4)と、
前記ベース領域の上に形成され、前記ドリフト層よりも高濃度の第1導電型の炭化珪素からなるソース領域(5)と、
前記ソース領域および前記ベース領域よりも深く、かつ、前記ドリフト層まで達し、前記ソース領域および前記ベース領域が両側に配置されるように形成されたトレンチ(7)と、
前記トレンチの表面に形成されたゲート絶縁膜(8)と、
前記トレンチ内において、前記ゲート絶縁膜の上に形成されたゲート電極(9)と、
前記ソース領域および前記ベース領域に電気的に接続されたソース電極(11)と、
前記基板の裏面側に形成されたドレイン電極(12)と、を有するトレンチゲート構造の前記半導体素子を備え、
前記ゲート絶縁膜は、少なくとも前記トレンチの底部に位置している部分が高誘電率膜によって構成されており、該高誘電率膜は、ハフニウム、アルミニウム、ランタン、セリウム、ジルコニウム、イットリウム、タンタル、ストロンチウムの少なくとも1種を含む絶縁材料によって構成されている炭化珪素半導体装置。 A silicon carbide semiconductor device having a semiconductor element having a trench gate structure,
A first or second conductivity type substrate (1) made of silicon carbide;
A drift layer (2) made of silicon carbide of the first conductivity type formed on the substrate and having a lower impurity concentration than the substrate;
A base region (4) made of silicon carbide of the second conductivity type formed on the drift layer;
A source region (5) formed on the base region and made of silicon carbide of the first conductivity type having a higher concentration than the drift layer;
A trench (7) formed so as to be deeper than the source region and the base region and reach the drift layer, and the source region and the base region are disposed on both sides;
A gate insulating film (8) formed on the surface of the trench;
A gate electrode (9) formed on the gate insulating film in the trench;
A source electrode (11) electrically connected to the source region and the base region;
A drain electrode (12) formed on the back side of the substrate; and the semiconductor element having a trench gate structure,
The gate insulating film is formed of a high dielectric constant film at least at a portion located at the bottom of the trench, and the high dielectric constant film is composed of hafnium, aluminum, lanthanum, cerium, zirconium, yttrium, tantalum, and strontium. A silicon carbide semiconductor device made of an insulating material containing at least one of the above.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015218815A JP2017092191A (en) | 2015-11-06 | 2015-11-06 | Silicon carbide semiconductor device |
| PCT/JP2016/077776 WO2017077780A1 (en) | 2015-11-06 | 2016-09-21 | Silicon carbide semiconductor device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015218815A JP2017092191A (en) | 2015-11-06 | 2015-11-06 | Silicon carbide semiconductor device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017092191A true JP2017092191A (en) | 2017-05-25 |
| JP2017092191A5 JP2017092191A5 (en) | 2018-03-01 |
Family
ID=58661812
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015218815A Pending JP2017092191A (en) | 2015-11-06 | 2015-11-06 | Silicon carbide semiconductor device |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2017092191A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2017077780A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2023058209A1 (en) * | 2021-10-07 | 2023-04-13 | Fuji Electric Co., Ltd. | Method of manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107706230B (en) * | 2017-09-28 | 2020-06-16 | 中国电子科技集团公司第五十五研究所 | Power groove gate MOS device and preparation method thereof |
| JP7062946B2 (en) * | 2017-12-25 | 2022-05-09 | 富士電機株式会社 | Semiconductor devices and methods for manufacturing semiconductor devices |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004214366A (en) * | 2002-12-27 | 2004-07-29 | Nec Electronics Corp | Semiconductor device and its fabricating process |
| JP2007194652A (en) * | 2001-06-21 | 2007-08-02 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Semiconductor device |
| JP2008091556A (en) * | 2006-09-29 | 2008-04-17 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor device |
| JP2008243994A (en) * | 2007-03-26 | 2008-10-09 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| WO2008139621A1 (en) * | 2007-05-15 | 2008-11-20 | Canon Anelva Corporation | Process for producing semiconductor device |
| JP2010045210A (en) * | 2008-08-13 | 2010-02-25 | Renesas Technology Corp | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device and semiconductor device |
| JP2013201308A (en) * | 2012-03-26 | 2013-10-03 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same |
-
2015
- 2015-11-06 JP JP2015218815A patent/JP2017092191A/en active Pending
-
2016
- 2016-09-21 WO PCT/JP2016/077776 patent/WO2017077780A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007194652A (en) * | 2001-06-21 | 2007-08-02 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Semiconductor device |
| JP2004214366A (en) * | 2002-12-27 | 2004-07-29 | Nec Electronics Corp | Semiconductor device and its fabricating process |
| JP2008091556A (en) * | 2006-09-29 | 2008-04-17 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor device |
| JP2008243994A (en) * | 2007-03-26 | 2008-10-09 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| WO2008139621A1 (en) * | 2007-05-15 | 2008-11-20 | Canon Anelva Corporation | Process for producing semiconductor device |
| JP2010045210A (en) * | 2008-08-13 | 2010-02-25 | Renesas Technology Corp | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device and semiconductor device |
| JP2013201308A (en) * | 2012-03-26 | 2013-10-03 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2023058209A1 (en) * | 2021-10-07 | 2023-04-13 | Fuji Electric Co., Ltd. | Method of manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device |
| JP7540596B2 (en) | 2021-10-07 | 2024-08-27 | 富士電機株式会社 | Method for manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2017077780A1 (en) | 2017-05-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10074728B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| US10128344B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| US20160079375A1 (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same | |
| US20120241761A1 (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same | |
| CN101626033A (en) | Structure and method for forming a shielded gate trench fet with an inter-electrode dielectric having a low-k dielectric therein | |
| US10236339B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| US10546931B2 (en) | Semiconductor device, inverter circuit, and vehicle | |
| WO2014087975A1 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| WO2016152059A1 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| TW201705300A (en) | Trench power transistor structure and manufacturing method thereof | |
| WO2017077780A1 (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device | |
| US20120241814A1 (en) | Power semiconductor device | |
| US20230231009A1 (en) | Power semiconductor device | |
| WO2023058209A1 (en) | Method of manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device | |
| WO2019003589A1 (en) | Semiconductor device and production method therefor | |
| US10847649B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP6052065B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| US20090289307A1 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP6945036B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| US11329137B2 (en) | Semiconductor devices and methods of manufacturing the same | |
| KR102399430B1 (en) | Power semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same | |
| JP6346341B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2018129558A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2007059818A (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180117 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20180117 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20181009 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20190402 |