JP2010273185A - Digital phase locked loop circuit - Google Patents
Digital phase locked loop circuit Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010273185A JP2010273185A JP2009124157A JP2009124157A JP2010273185A JP 2010273185 A JP2010273185 A JP 2010273185A JP 2009124157 A JP2009124157 A JP 2009124157A JP 2009124157 A JP2009124157 A JP 2009124157A JP 2010273185 A JP2010273185 A JP 2010273185A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- clock signal
- circuit
- phase
- signal
- value
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Manipulation Of Pulses (AREA)
- Stabilization Of Oscillater, Synchronisation, Frequency Synthesizers (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、デジタルフェーズロックドループ回路に関する。 The present invention relates to a digital phase locked loop circuit.
従来から知られているアナログフェーズロックドループ(以下、アナログPLLと称す)1は、図17に示すように、位相周波数比較器11と、チャージポンプ12と、アナログフィルタ13と、電圧制御発振器14と、N分周回路15とを有する。このような、アナログフィルタ13等のアナログ回路は、抵抗や容量といったアナログ素子により構成され、回路面積の増大が問題となる。このため、現在、半導体回路で主流であるCMOS技術の微細化の恩恵をアナログPLLは受けにくい。
A conventionally known analog phase-locked loop (hereinafter referred to as analog PLL) 1 includes a
また、アナログPLLは、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの1周期毎にアナログ信号で、フィードバッククロック信号FDとの位相比較動作を行う。このため、周波数ジャンプによる出力クロック信号への入力クロック信号の漏れが発生する問題が起こる。更に素子バラツキ等による入出力間の位相オフセットの問題等が発生する。このため、アナログPLLを、全てデジタル回路構成に置き換えた、完全デジタルフェーズロックドループ(以下、AD(ALL Digital)PLLと称す)が開発されている。 The analog PLL is an analog signal for each cycle of the reference clock signal FREF and performs a phase comparison operation with the feedback clock signal FD. For this reason, there arises a problem that leakage of the input clock signal to the output clock signal due to frequency jump occurs. Furthermore, a problem of phase offset between input and output due to element variation or the like occurs. Therefore, a completely digital phase-locked loop (hereinafter referred to as AD (ALL Digital) PLL) in which the analog PLL is entirely replaced with a digital circuit configuration has been developed.
ADPLLは、回路面積の増大要因であるアナログ素子を必要としない。代わりに、デジタル信号処理を行うデジタル回路で構成される。デジタル回路は、CMOS技術の微細化により回路面積の縮小が可能である利点を有する。また、位相比較もデジタルデータで行うため、アナログPLLのような、周波数ジャンプによる出力クロック信号への入力クロック信号の漏れも発生しない。加えて、正確な小数点逓倍等も可能になる。このような、ADPLLの例としては、特許文献1のような技術がある。
The ADPLL does not require an analog element that increases the circuit area. Instead, it is composed of a digital circuit that performs digital signal processing. The digital circuit has an advantage that the circuit area can be reduced by miniaturization of CMOS technology. Further, since the phase comparison is also performed with digital data, the leakage of the input clock signal to the output clock signal due to the frequency jump does not occur unlike the analog PLL. In addition, accurate decimal point multiplication is possible. As an example of such ADPLL, there is a technique as disclosed in
ここで、従来技術としてADPLL2のブロック構成図を図18に示す。ADPLL2は、図17のアナログPLL1をデジタル化したものを想定している。図18に示すように、ADPLL2は、カウンタ21、22と、TDC(Time-to-Digital Converter)回路23と、分周回路24と、加算器25と、位相誤差演算回路26と、デジタルフィルタ27と、DCO(Digitally-Controlled-Oscillator)回路28とを有する。
Here, FIG. 18 shows a block diagram of ADPLL2 as a conventional technique. ADPLL2 assumes that the analog PLL1 of FIG. 17 is digitized. As shown in FIG. 18, the ADPLL 2 includes
アナログPLL1の位相周波数比較器11及びチャージポンプ12にかかる部分(図17のUNIT10)がADPLL2のカウンタ21、22及びTDC回路23及び加算器25及び位相誤差演算回路26にかかる部分(図18のUNIT20)に相当する。以下同様に、アナログフィルタ13が、デジタルフィルタ27に相当する。電圧制御発振器14が、DCO回路28に相当する。N分周回路15が、分周回路24に相当する。
A portion related to the
ADPLL2では、カウンタ21は、リファレンスクロック信号FREFをカウントし、デジタル信号PFRCとして出力する。分周回路24は、出力クロック信号FOUTをN分周してフィードバック信号FDを出力し、且つ、Nカウント以内のカウント値をデジタル信号PFDC2として出力する。カウンタ22は、フィードバック信号FDをカウントし、デジタル信号PFDCとして出力する。加算器25は、デジタル信号PFDC1とPFDC2の値の和をとり、デジタル信号PFDCを出力する。TDC回路23は、出力クロック信号FOUTの1クロック以内の位相差(小数点以下の値)をデジタルデータ化して、デジタル信号PTDCと、位相差の正負を示す極性信号PTDC_SIGNとを出力する。
In ADPLL2, the
位相誤差演算回路26は、デジタル信号PFRC、PFDC、PTDCの値から、PFRC−(PFDC+PTDC)を演算する。その演算処理結果及びPTDC_SIGNからリファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバック信号FDの位相差分を、デジタル信号PERRとして出力する。デジタルフィルタ27は、デジタル信号PERRを平滑化し、デジタル信号DCONを出力する。DCO回路28は、デジタル信号DCONに応じた、周波数の出力クロック信号FOUTを出力する。ADPLL2は、(|PFRC−(PFDC+PTDC)|)の値が「0」となるように動作し、「0」となった時点でロック状態となる。
The phase
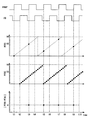
ここで、図19〜図21のグラフを用いて、カウント値PFRCとPFDCの関係を説明する。但し、カウンタ21、22は、4ビットカウンタ(16進数カウンタ)であるとする。つまり、0〜15をカウントする。なお、図19〜図21の同符号で示す時刻は、同じ時刻を指すものとする。
Here, the relationship between the count values PFRC and PFDC will be described with reference to the graphs of FIGS. However, the
まず、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとカウント値PFRCの関係を図19に示す。図19に示すように、時刻t1、t3、t5、t7、t9にリファレンスクロック信号FREFが立ち上がる。よって、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相データであるカウント値PFRCも、時刻t1、t3、t5、t7、t9に出力される。 First, the relationship between the reference clock signal FREF and the count value PFRC is shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 19, the reference clock signal FREF rises at times t1, t3, t5, t7, and t9. Accordingly, the count value PFRC that is the phase data of the reference clock signal FREF is also output at times t1, t3, t5, t7, and t9.
次に、フィードバッククロック信号FDとカウント値PFDCの関係を図20に示す。図20に示すように、時刻t2、t4、t6、t8、t10にフィードバッククロック信号FDが立ち上がる。よって、フィードバッククロック信号FDの位相データであるカウント値PFDC1も、時刻t2、t4、t6、t8、t10に出力される。また、分周回路24は、出力クロック信号FOUTのカウント毎にカウント値PFDC2を出力する。よって、加算器25により、PFDC1とPFDC2を加算したカウント値PFDCが出力される。
Next, the relationship between the feedback clock signal FD and the count value PFDC is shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 20, the feedback clock signal FD rises at times t2, t4, t6, t8, and t10. Therefore, the count value PFDC1 that is the phase data of the feedback clock signal FD is also output at times t2, t4, t6, t8, and t10. Further, the
最後に、図19、図20のグラフに示したリファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相データであるカウント値PFRC、フィードバッククロック信号FDの位相データであるカウント値PFDCとの位相差分である(|PFRC−PFDC|)の値を図21の最下段のグラフに示す。このように、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバック信号FDの位相差である値「4」のデータは、出力クロック信号FOUTよりも遅い周期のリファレンスクロック信号FREFのクロックタイミングで算出される。 Finally, it is the phase difference between the count value PFRC that is the phase data of the reference clock signal FREF and the count value PFDC that is the phase data of the feedback clock signal FD shown in the graphs of FIGS. 19 and 20 (| PFRC−PFDC | ) Is shown in the lowermost graph of FIG. As described above, the data of the value “4”, which is the phase difference between the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback signal FD, is calculated at the clock timing of the reference clock signal FREF having a cycle slower than that of the output clock signal FOUT.
なお、図19〜図21には、説明の簡略化のため、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバック信号FDの位相差が常に一定であり、且つ、出力クロック信号FOUTの1クロック以内の位相差もない(PTDC=0)場合を示した。しかし、本来は、上述したように(|PFRC−PFDC|)の値が「0」となるよう、ADPLL2が動作するため、時刻t3、t5、t7、t9で算出される(|PFRC−PFDC|)の値が減少することになる。 In FIG. 19 to FIG. 21, for simplification of description, the phase difference between the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback signal FD is always constant, and there is no phase difference within one clock of the output clock signal FOUT ( The case of PTDC = 0) is shown. However, as described above, since ADPLL2 operates so that the value of (| PFRC-PFDC |) becomes “0” as described above, it is calculated at times t3, t5, t7, and t9 (| PFRC-PFDC | ) Will decrease.
ここで、カウンタ21、TDC回路23は、リファレンスクロック信号FREFのクロックタイミングで動作し、データ更新される。カウンタ22、位相誤差演算回路26等その他の回路は、出力クロック信号FOUT、及びその分周クロックタイミングで動作し、データ更新される。しかし、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバック信号FDは、非同期の関係である。よって、位相データである上述した各デジタルのカウント値PFRC、PFDCの値も、それぞれ異なるタイミングで遷移する。
Here, the
図22、図23を用いて、このことによる問題点を説明する。まず、図22に、位相データの遷移タイミングに問題がない場合を示す。図22に示すように、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジに応じて、位相誤差演算回路26にデジタルデータPFDCが取り込まれる。ここで、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジのタイミングでは、デジタルデータPFDCの値が安定して「9」となっている。よって、位相誤差演算回路26が演算に用いる値も「9」で行える。なお、この例でのデジタルデータPFRCの値は「10」のため、位相差(|PFRC−PFDC|)の値が「1」生じていることになる。
Problems caused by this will be described with reference to FIGS. First, FIG. 22 shows a case where there is no problem in the phase data transition timing. As shown in FIG. 22, the digital data PFDC is taken into the phase
図23に、位相データの遷移タイミングに問題がある場合を示す。図23に示すように、図22同様、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジに応じて、位相誤差演算回路26にデジタルデータPFDCが取り込まれる。しかし、図22の場合と異なり、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジのタイミングでは、デジタルデータPFDCの値が「9」から「10」への遷移過程にある。この遷移過程のデジタルデータPFDCの値「X」は不定な値である。よって、この不定なデジタルデータPFDCの値「X」が、位相誤差演算回路26に取り込まれ、演算に用いられる。このため、演算結果が正確な値とならない問題が発生する。特に、この問題はリファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバック信号FDの立ち上がりエッジが同期しようとする、ロック状態の近傍で多く発生する。
FIG. 23 shows a case where there is a problem in the phase data transition timing. As shown in FIG. 23, the digital data PFDC is taken into the phase
このように、ADPLL2が、確実にPLLとして動作するためには、所定の時刻にそれぞれ安定した正確な位相データPFRC、PFDCを比較する必要がある。しかし、上述したように、所定の時刻に位相データPFRC、PFDCを比較したとき、一方の位相データが遷移過程である場合、正確な位相データの比較が行えない問題がある。 Thus, in order for ADPLL2 to operate reliably as a PLL, it is necessary to compare accurate and stable phase data PFRC and PFDC, respectively, at a predetermined time. However, as described above, when the phase data PFRC and PFDC are compared at a predetermined time, if one of the phase data is in a transition process, there is a problem that accurate phase data cannot be compared.
本発明は、第1のクロック信号をカウントする第1のカウンタと、第2のクロック信号をカウントする第2のカウンタと、第1のクロック信号を順次遅延させた第1、第2の遅延クロック信号を生成する遅延クロック生成回路と、前記第1のクロック信号及び第1、第2の遅延クロック信号のそれぞれで前記第2のカウンタのカウント値をサンプリングする第1のサンプル回路と、前記第1のクロック信号と、前記第2のクロック信号を所定の数で分周した第3のクロック信号との位相差、及び、前記第1のサンプル回路がサンプリングしたカウント値とに応じて、前記第1のサンプル回路がサンプリングしたカウント値のうち1つを選択する選択回路と、前記第1のカウンタのカウント値及び前記選択回路が選択したカウント値とに応じて前記第1のクロックと前記第3のクロックとの位相差を演算する位相誤差演算回路と、前記位相誤差演算回路の演算結果に応じて前記第2のクロックを出力するデジタル制御発振器と、を有するデジタルフェーズロックドループ回路である。 The present invention provides a first counter that counts a first clock signal, a second counter that counts a second clock signal, and first and second delayed clocks in which the first clock signal is sequentially delayed. A delay clock generation circuit for generating a signal; a first sample circuit for sampling a count value of the second counter with each of the first clock signal and the first and second delay clock signals; and the first According to the phase difference between the first clock signal and the third clock signal obtained by dividing the second clock signal by a predetermined number, and the count value sampled by the first sample circuit. According to the selection circuit that selects one of the count values sampled by the sample circuit, the count value of the first counter, and the count value selected by the selection circuit A phase error calculation circuit that calculates a phase difference between the first clock and the third clock, and a digitally controlled oscillator that outputs the second clock according to the calculation result of the phase error calculation circuit It is a digital phase locked loop circuit.
本発明にかかるデジタルフェーズロックドループ回路は、第2のカウンタのカウント値を前記第1のクロック信号及び第1、第2の遅延クロック信号のそれぞれでサンプリングする。そして、選択回路は、第1、第3のクロック信号の位相差、及び、前記第1のサンプル回路がサンプリングしたカウント値に応じて、そのサンプリングしたカウント値のうち1つを選択する。このため、そのサンプリングしたカウント値のうちある1つが遷移過程でサンプリングした値が不定であっても、他のサンプリングしたカウント値と、第1、第3のクロック信号の位相差の関係から正確なカウント値を選択回路が選択することができる。 The digital phase-locked loop circuit according to the present invention samples the count value of the second counter with each of the first clock signal and the first and second delayed clock signals. The selection circuit selects one of the sampled count values according to the phase difference between the first and third clock signals and the count value sampled by the first sample circuit. For this reason, even if one of the sampled count values is indeterminate during the transition process, it is accurate from the relationship between the other sampled count values and the phase difference between the first and third clock signals. The count value can be selected by the selection circuit.
本発明にかかるデジタルフェーズロックドループ回路は、安定した位相同期ループを構成することができる。 The digital phase locked loop circuit according to the present invention can constitute a stable phase locked loop.
発明の実施の形態 BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
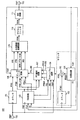
以下、本発明を適用した具体的な実施の形態について、図面を参照しながら詳細に説明する。図1に本実施の形態にかかる完全デジタルフェーズロックドループ(以下、ADPLLと称す)回路100の構成の一例を示す。図1に示すように、ADPLL回路100は、カウンタ101、102と、TDC(Time-to-Digital Converter)回路103と、分周回路104と、加算回路105と、PFDサンプル回路106と、PFDS選択回路107と、サンプリング回路108と、位相誤差演算回路109と、デジタルフィルタ110と、DCO(Digitally-Controlled-Oscillator)回路111と、リファレンスクロック入力端子112と、出力クロック出力端子113とを有する。
Hereinafter, specific embodiments to which the present invention is applied will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 shows an example of the configuration of a complete digital phase-locked loop (hereinafter referred to as ADPLL)
リファレンスクロック入力端子112はリファレンスクロック信号FREF(第1のクロック信号)を入力する。
The reference
カウンタ101(第1のカウンタ)は、リファレンスクロック信号FREFが入力されるごとに逓倍設定値をカウントする。例えば、10逓倍の設定であれば、カウンタ101は、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの1クロックが入力される度に、10ずつカウントアップしていく。そして、そのカウント値PFRCをサンプリング回路108に出力する。なお、符号「PFRC」は、カウント値を示すと同時に、そのカウント値を格納するデジタルのカウント値信号名を示すものとする。
The counter 101 (first counter) counts the multiplication set value every time the reference clock signal FREF is input. For example, if the setting is multiplied by 10, the
カウンタ102(第3のカウンタ)は、分周回路104が出力するフィードバッククロック信号FDをカウントする。そして、そのカウント値PFDC1を加算回路105に出力する。
The counter 102 (third counter) counts the feedback clock signal FD output from the
分周回路104は、DCO回路111が出力する出力クロック信号FOUTを上記逓倍設定値と等しい値で分周し出力する。その所定の値に分周されたクロックをフィードバッククロック信号FDとする。例えば、分周回路104が入力クロック信号を1/10に分周する機能を有する場合、100MHzの出力クロック信号FOUTが入力されると、クロック周波数が10MHzのフィードバッククロック信号FDを出力する。更に、分周回路104は、上述したフィードバッククロック信号FDの1周期以内の出力クロック信号FOUTのクロックをカウントする。そして、そのカウント値PFDC2を加算回路105に出力する。
The
ここで例えば、分周回路104が入力クロック信号を1/10に分周する機能を有する場合を考える。この場合、カウンタ102は、出力クロック信号FOUTのクロック数が10毎で1カウントし、そのカウント値をPFDC1として出力する。そして、分周回路104は、フィードバッククロック信号FDの1周期以内の出力クロック信号FOUTのクロックカウント値0〜9をカウント値PFDC2として出力する。つまり、10分周設定である本例では、カウンタ102は、出力クロック信号FOUTのクロック数の10の桁、分周回路104は、1の桁をカウントしていることになる。
Here, for example, consider a case where the
加算回路105は、カウンタ102からのカウント値PFDC1と、分周回路104からのカウント値PFDC2とを加算してカウント値PFDCとして、PFDサンプル回路106に出力する。符号「PFDC」は、カウント値を示すと同時に、そのカウント値を格納するデジタルのカウント値信号名を示すものとする。なお、上述したカウント値PFRC、PFDC1、PFDC2、PFDCの関係は、図19〜図21で説明したものと同様の関係となる。なお、カウンタ102、分周回路104、加算回路105で第2のカウンタを構成する。
The
TDC回路103(位相差検出器)は、上記カウンタ101、102では測定できないリファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDとの、出力クロックFOUT、1クロック以内の位相差を測定する。そして、その測定結果の値を、出力クロック信号FOUTの1周期のデジタルデータの値で正規化する。この正規化の結果をデジタルデータの位相差検出信号PTDCとして出力する。また、正規化の結果、PTDCの値が所定の値以上であるか否かの判定値をデジタルデータの位相差検出信号PTDCに付加する。また、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相に対するフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相の進み遅れを位相極性信号PTDC_SIGN(極性値)として出力する。さらに、リファレンスクロック信号FREFを所定の期間、順次遅延させた遅延クロック信号FR1、FR2を出力する。
The TDC circuit 103 (phase difference detector) measures the phase difference within one clock of the output clock FOUT between the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD that cannot be measured by the
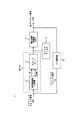
図2にTDC回路103の回路構成の一例を示す。図2に示すように、TDC回路103は、複数のフリップフロップ回路と、複数の遅延素子と、複数のインバータと、複数のAND回路と、比較選択回路201と、バイナリ化エンコーダ202と、正規化回路203とを有する。
FIG. 2 shows an example of the circuit configuration of the
TDC回路103は、遅延素子を2n+2個(n:正の整数)有する。この複数の遅延素子のうち、フィードバッククロック信号FDを順次遅延させる遅延素子はn+1個ある。この遅延素子をそれぞれBP1〜BPn+1とする。この遅延素子BP1〜BPn+1が、順次遅延させていくフィードバッククロック信号FDをそれぞれFD1〜FDn+1とする。また、複数の遅延素子のうち、リファレンスクロック信号FREFを順次遅延させる遅延素子はn+1個ある。この遅延素子をそれぞれBN1〜BNn+1とする。この遅延素子BN1〜BNn+1(遅延クロック生成回路)が、順次遅延させていくクロック信号FREFをそれぞれクロック信号FR1〜FRn+1とする。この遅延素子BN1〜BNn+1の遅延期間は、出力クロック信号FOUTの1/2周期以内であり、且つ、カウント値PFDCの値が変化する遷移時間以上となるものとする。なお、遅延素子BP1〜BPn+1、BN1〜BNn+1は入力信号に対して同様の遅延を生じさせるものとする。以下、フィードバッククロック信号FDを遅延させたクロック信号FD1〜FDn+1、リファレンスクロック信号FREFを遅延させたクロック信号FR1〜FRn+1を遅延クロック信号と称す。TDC回路103は、これら遅延クロック信号FR1〜FRn+1のうち、FR1、FR2をPFDサンプル回路106に出力する。
The
更に、TDC回路103は、フリップフロップ回路を2n+3個有する。この複数のフリップフロップ回路のうち、遅延クロック信号FD1〜FDn+1を入力データ端子に入力し、リファレンスクロック信号をクロック端子に入力するフリップフロップ回路をそれぞれFFP1〜FFPn+1とする。また、複数のフリップフロップ回路のうち、フィードバッククロック信号FDを入力データ端子に入力し、遅延クロック信号FR1〜FRn+1をクロック端子に入力するフリップフロップ回路をそれぞれFFN1〜FFNn+1とする。また、遅延しないフィードバッククロック信号FDを入力データ端子に、遅延しないリファレンスクロック信号をクロック端子に入力するフリップフロップ回路をFF0とする。
Further, the
フリップフロップ回路FFN1〜FFNn+1の出力データ端子から出力される信号をそれぞれPDN1〜PDNn+1、フリップフロップ回路FF0の出力データ端子から出力される信号をPD0、フリップフロップ回路FFP1〜FFPn+1の出力データ端子から出力される信号をそれぞれPDP1〜PDPn+1とする。以下、これらの信号PDN1〜PDNn+1、PDP1〜PDPn+1をサンプリング信号と称す。
Signals output from the output data terminals of the flip-flop circuits FFN1 to FFNn + 1 are respectively output from PDN1 to
TDC回路103は、インバータ素子を2n+2個有する。この複数のインバータ素子のうち、サンプリング信号PDN1〜PDNnが入力されるインバータ素子をそれぞれIVN1〜IVNnとする。そして、インバータ素子IVN1〜IVNnが出力する信号をそれぞれPDNB1〜PDNBnとする。また、複数のインバータ素子のうち、サンプリング信号PDP1〜PDPn+1が入力されるインバータ素子をそれぞれIVP1〜IVPn+1とする。そして、インバータ素子IVP1〜IVPnが出力する信号をそれぞれPDNB1〜PDNBnとする。更に、信号PD0が入力されるインバータ素子をIV0とし、インバータ素子IV0が出力する信号をPDB0とする。
The
TDC回路103は、AND回路を2n+2個有する。各AND回路は2つの入力の積を演算し、演算結果を出力する。この複数のAND回路のうち、n+1個をANDN1〜ANDNn+1、更に残りのn+1個をANDP1〜ANDPn+1とする。
The
AND回路ANDN1は、サンプリング信号PDN1と信号PDB0を入力し、演算結果を信号NEG[n]として出力する。AND回路ANDN2は、サンプリング信号PDN2と信号PDNB1を入力し、演算結果を信号NEG[n−1]として出力する。AND回路ANDN3は、サンプリング信号PDN3と信号PDNB2を入力し、演算結果を信号NEG[n−2]として出力する。以下、同様な構成を繰り返し、最終的にAND回路ANDNn+1は、サンプリング信号PDNn+1と信号PDNBnを入力し、演算結果を信号NEG[0]として出力する。 The AND circuit ANDN1 receives the sampling signal PDN1 and the signal PDB0 and outputs the calculation result as a signal NEG [n]. The AND circuit ANDN2 receives the sampling signal PDN2 and the signal PDNB1, and outputs the calculation result as a signal NEG [n−1]. The AND circuit ANDN3 receives the sampling signal PDN3 and the signal PDNB2, and outputs the calculation result as a signal NEG [n-2]. Thereafter, the same configuration is repeated, and finally, the AND circuit ANDNn + 1 receives the sampling signal PDNn + 1 and the signal PDNBn, and outputs the calculation result as a signal NEG [0].
一方、AND回路ANDP1は、サンプリング信号PD0と信号PDPB1を入力し、演算結果を信号POS[n]として出力する。AND回路ANDP2は、サンプリング信号PDP1と信号PDPB2を入力し、演算結果を信号POS[n−1]として出力する。AND回路ANDP3は、サンプリング信号PDP2と信号PDPB3を入力し、演算結果を信号POS[n−2]として出力する。以下、同様な構成を繰り返し、最終的にAND回路ANDPn+1は、サンプリング信号PDPnと信号PDPBn+1を入力し、演算結果を信号POS[0]として出力する。以下、信号NEG[n]〜NEG[0]、POS[n]〜POS[0]をエッジ抽出信号と称す。 On the other hand, the AND circuit ANDP1 receives the sampling signal PD0 and the signal PDPB1, and outputs the calculation result as a signal POS [n]. The AND circuit ANDP2 receives the sampling signal PDP1 and the signal PDPB2, and outputs the calculation result as a signal POS [n−1]. The AND circuit ANDP3 receives the sampling signal PDP2 and the signal PDPB3, and outputs the calculation result as a signal POS [n-2]. Thereafter, the same configuration is repeated, and finally, the AND circuit ANDPn + 1 receives the sampling signal PDPn and the signal PDPBn + 1, and outputs the calculation result as the signal POS [0]. Hereinafter, the signals NEG [n] to NEG [0] and POS [n] to POS [0] are referred to as edge extraction signals.
比較選択回路201は、上記エッジ抽出信号NEG[n]〜NEG[0]をバス化し、そのバスにより送信されるエッジ抽出信号NEG[n:0]と、上記エッジ抽出信号POS[n]〜POS[0]をバス化し、そのバスにより送信されるエッジ抽出信号POS[n:0]とを入力する。比較選択回路201は、エッジ抽出信号NEG[n:0]と、POS[n:0]とを比較する。後述する図3〜図5で説明するが、信号NEG[n:0]とPOS[n:0]は、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジを基準としたフィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がりエッジの位相差情報を有している。この信号NEG[n:0]と、POS[n:0]とを比較することで、リファレンスクロック信号FREFに対して、フィードバッククロック信号FDの位相の進み遅れを判定することができる。エッジ抽出信号NEG[n:0]とPOS[n:0]のどちらかの信号に「1」の値があるかを判定し、例えばPOS[n:0]に「1」がある場合、ハイレベルの位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNを出力し、且つエッジ抽出信号POS[n:0]を信号TDC[n:0]として出力する。反対にエッジ抽出信号NEG[n:0]側に「1」の値がある場合、ロウレベルの信号PTDC_SIGNを出力し、且つエッジ抽出信号NEG[n:0]を信号TDC[n:0]として出力する。 The comparison / selection circuit 201 converts the edge extraction signals NEG [n] to NEG [0] into a bus, the edge extraction signal NEG [n: 0] transmitted by the bus, and the edge extraction signals POS [n] to POS. [0] is converted into a bus, and an edge extraction signal POS [n: 0] transmitted by the bus is input. The comparison selection circuit 201 compares the edge extraction signal NEG [n: 0] with POS [n: 0]. As will be described later with reference to FIGS. 3 to 5, the signals NEG [n: 0] and POS [n: 0] are phase difference information of the rising edge of the feedback clock signal FD based on the rising edge of the reference clock signal FREF. have. By comparing this signal NEG [n: 0] with POS [n: 0], it is possible to determine the phase delay of the feedback clock signal FD with respect to the reference clock signal FREF. It is determined whether one of the edge extraction signals NEG [n: 0] and POS [n: 0] has a value of “1”. For example, when POS [n: 0] has “1”, the signal is high. The level phase polarity signal PTDC_SIGN is output, and the edge extraction signal POS [n: 0] is output as the signal TDC [n: 0]. Conversely, when the edge extraction signal NEG [n: 0] has a value of “1”, the low level signal PTDC_SIGN is output, and the edge extraction signal NEG [n: 0] is output as the signal TDC [n: 0]. To do.
バイナリ化エンコーダ202は、比較選択回路201からの信号TDC[n:0]に応じて、デジタルデータを生成する。正規化回路203は、出力クロック信号FOUTから、出力クロック信号FOUTの1周期をデジタルデータとして生成し、そのデータ値でバイナリ化エンコーダ202が生成したデジタルデータの値を正規化する。そして、正規化した値をデジタルデータの位相差検出信号PTDCとして出力する。なお、出力クロック信号FOUTの1周期のデジタルデータは、遅延素子BP1〜BPn+1と同様の遅延を発生させる遅延素子の段数として、正規化回路203が生成する。この位相差検出信号PTDCの値は、リファレンスクロック信号FREFに対して、フィードバッククロック信号FDの位相の進み遅れが、出力クロック信号FOUTの1周期以下なら、0以上1以下の少数値のデジタルデータとして出力される。また、正規化回路203は、正規化した結果の値(PTDCの値)が、0.5より小さければデジタルデータの位相差検出信号PTDCのMSB(most significant bit)は「0」となり、0.5以上ならばMSBは「1」となる。
The
例えば、正規化回路203が生成した出力クロック信号FOUTの1周期のデジタルデータの値が「10」、バイナリ化エンコーダ202のデジタルデータの値が「2」である場合、正規化後のデジタルデータの値は「0.2」となる。よって、デジタルデータの位相差検出信号PTDCは、MSBが「0」で、値が「0.2」となる。同様に、正規化回路203が生成した出力クロック信号FOUTの1周期のデジタルデータの値を「10」とし、バイナリ化エンコーダ202のデジタルデータの値が「7」ならば、正規化後のデジタルデータの値が「0.7」となる。よって、デジタルデータの位相差検出信号PTDCは、MSBが「1」で、値が「0.7」となる。
For example, when the value of the digital data of one cycle of the output clock signal FOUT generated by the
以上、TDC回路103は、出力クロック信号FOUTの1周期以下の誤差を小数点以下の値のデジタルデータを格納する位相差検出信号PTDCとして出力できる。また、位相差検出信号PTDCのMSBの値により、リファレンスクロック信号FREFに対して、フィードバッククロック信号FDの位相の位相差が、出力クロック信号FOUTの1/2周期より大きいか小さいかが判定できる。また、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNにより、リファレンスクロック信号FREFに対して、フィードバッククロック信号FDの位相の遅れ、進みが判定できる。但し、図2のTDC回路103の構成は一例であり、同一機能を有するなら、他の回路構成で実現してもよい。
As described above, the
以下、上述したTDC回路103の動作について簡単に説明する。図3〜図5にTDC回路103の動作を説明するタイミングチャートを示す。図3では、フィードバッククロック信号FDの位相が、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相に対して期間T1遅れている。図3に示すように、リファレンスクロック信号FREFが時刻t1にハイレベルに立ち上がるが、この立ち上がりエッジに対して、フィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がりエッジが期間T1遅れている。このため、時刻t1にリファレンスクロック信号FREF、時刻t2に遅延クロック信号FR1がハイレベルに立ち上がってもフリップフロップFFN1〜FFNn+1、FF0、FFP1〜FFPn+1が出力する全てのサンプリング信号PDN1〜PNPn+1、PD0、PDP1〜PDPn+1は、ロウレベルとなる。
Hereinafter, the operation of the
時刻t3にフィードバッククロック信号FDがハイレベルに立ち上がる。このフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相は、遅延クロック信号FR2より進んでいるため、時刻t4の遅延クロック信号FR2の立ち上がりエッジに応じてサンプリング信号PDN2がハイレベルに立ち上がる。以降、遅延クロック信号FR3〜FRn+1の立ち上がりエッジに応じて信号PDN3〜PDNn+1がハイレベルに立ち上がる。
At time t3, the feedback clock signal FD rises to a high level. Since the phase of the feedback clock signal FD is ahead of the delayed clock signal FR2, the sampling signal PDN2 rises to a high level in response to the rising edge of the delayed clock signal FR2 at time t4. Thereafter, the signals PDN3 to PDNn + 1 rise to a high level in response to the rising edges of the delayed clock signals FR3 to
このことからエッジ抽出信号NEG[n−1]のみが、時刻t4にハイレベルに立ち上がる、つまりAND回路ANDN2の出力値が「1」となる。更に、比較選択回路201は、NEG[n−1]が「1」の値を有するため、ロウレベルの位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNと、NEG[n:0]を信号TDC[n:0]として出力する。バイナリ化エンコーダ202は、この信号TDC[n:0]に応じて、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相に対して、フィードバッククロック信号FDの位相が遅延素子で3段分遅延を有していると判断し、「3」の値を出力する。正規化回路203は、この値を正規化し、位相差検出信号PTDCとして出力する。なお、位相差検出信号PTDCのMSBは、出力クロック信号FOUTの1周期分の値に応じて決まる。例えば、出力クロック信号FOUTの1周期分のデジタル値が「10」ならば、正規化後の値が、「0.3」となるため、位相差検出信号PTDCは「0」となる。出力クロック信号FOUTの1周期分のデジタル値が「5」ならば、正規化後の値が、「0.6」となるため、位相差検出信号PTDCのMSBの値は「1」となる。以下、位相差検出信号PTDCのMSBの値については、図4、図5の説明でも同様とする。
Therefore, only the edge extraction signal NEG [n−1] rises to a high level at time t4, that is, the output value of the AND circuit ANDN2 becomes “1”. Further, the comparison / selection circuit 201 outputs the low-level phase polarity signal PTDC_SIGN and NEG [n: 0] as the signal TDC [n: 0] because NEG [n−1] has a value of “1”. The
図4では、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がりエッジが時刻t1でほぼ同時にハイレベルに立ち上がっている。この場合、時刻t1にサンプリング信号PD0がハイレベルに立ち上がる。以降、遅延クロック信号FR1〜FRn+1の立ち上がりエッジに応じて信号PDN1〜PDNn+1がハイレベルに立ち上がる。一方、サンプリング信号PDP1〜PDPn+1は、全てロウレベルとなる。
In FIG. 4, the rising edges of the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD rise to the high level almost simultaneously at time t1. In this case, the sampling signal PD0 rises to a high level at time t1. Thereafter, the signals PDN1 to PDNn + 1 rise to a high level in response to rising edges of the delayed clock signals FR1 to
このことからエッジ抽出信号POS[n]のみが、時刻t1にハイレベルに立ち上がる。つまりAND回路ANDP1の出力値が「1」となる。更に、比較選択回路201は、POS[n]が「1」の値を有するため、ハイレベルの位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNと、POS[n:0]を信号TDC[n:0]として出力する。バイナリ化エンコーダ202は、この信号TDC[n:0]に応じて、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相に対して、フィードバッククロック信号FDの位相が遅延を有していないと判断し、「1」の値を生成する。正規化回路203は、この値を正規化し、位相差検出信号PTDCとして出力する。
For this reason, only the edge extraction signal POS [n] rises to a high level at time t1. That is, the output value of the AND circuit ANDP1 is “1”. Further, the comparison / selection circuit 201 outputs the high-level phase polarity signal PTDC_SIGN and POS [n: 0] as the signal TDC [n: 0] because POS [n] has a value of “1”. The
図5では、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相がフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相に対して期間T2遅れている。このため、時刻t1にフィードバッククロック信号FD、時刻t2に遅延クロック信号FD1がハイレベルに立ち上がってもフリップフロップFFN1〜FFNn+1、FF0、FFP1〜FFPn+1からのサンプリング信号PDN1、PD0、PDP1〜PDPn+1は、全てロウレベルとなる。時刻t3にリファレンスクロック信号FREFがハイレベルに立ち上がる。このため、時刻t3に、フリップフロップFF0、FFP1が出力するそれぞれのサンプリング信号PD0、PDP1がハイレベルとなる。以降、遅延クロック信号FR1〜FRn+1の立ち上がりエッジに応じて信号PDN1〜PDNn+1がハイレベルに立ち上がる。
In FIG. 5, the phase of the reference clock signal FREF is delayed by a period T2 with respect to the phase of the feedback clock signal FD. Therefore, even when the feedback clock signal FD at time t1 and the delayed clock signal FD1 rises to high level at time t2, the sampling signals PDN1, PD0, PDP1 to PDPn + 1 from the flip-flops FFN1 to
このことからエッジ抽出信号POS[n−1]のみが、時刻t3にハイレベルに立ち上がる。つまりAND回路ANDP2の出力値が「1」となる。更に、比較選択回路201は、POS[n−1]が「1」の値を有するため、ハイレベルの位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNと、POS[n:0]を信号TDC[n:0]として出力する。バイナリ化エンコーダ202は、この信号TDC[n:0]に応じて、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相に対して、フィードバッククロック信号FDの位相が遅延素子で2段分進んでいると判断し、「2」の値を生成する。正規化回路203は、この値を正規化し、位相差検出信号PTDCとして出力する。
For this reason, only the edge extraction signal POS [n−1] rises to a high level at time t3. That is, the output value of the AND circuit ANDP2 is “1”. Furthermore, since POS [n−1] has a value of “1”, the comparison / selection circuit 201 outputs the high-level phase polarity signal PTDC_SIGN and POS [n: 0] as the signal TDC [n: 0]. . The
なお、上述したNEG[n:0]、POS[n:0]を第1の比較結果、第2の比較結果とする。このように、TDC回路103は、クロック信号としてリファレンスクロック信号、データ信号としてフィードバッククロック信号FDを用い、それぞれの信号を遅延させる回路を持たせている。そして、それぞれ遅延させたリファレンスクロック信号とフィードバッククロック信号FDを比較し、その第1の比較結果と第2の比較結果に応じて、リファレンスクロック信号に対するフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相差、および、位相の遅れ進みを測定する。また、その位相差を出力クロック信号FOUTの1周期分で正規化する。
Note that the above-described NEG [n: 0] and POS [n: 0] are the first comparison result and the second comparison result. As described above, the
PFDサンプル回路106は、加算回路105からのカウント値PFDCの値を、リファレンスクロック信号FREF、遅延クロック信号FR1、FR2の立ち上がりエッジのタイミングで取り込む。そして、それぞれのタイミングで取り込んだ、カウント値を位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2として、PFD選択回路107へ出力する。リファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジのタイミングで、取り込んだカウント値PFDCの値を位相データ信号PFDS0、遅延クロック信号FR1の立ち上がりエッジのタイミングで取り込んだカウント値PFDCの値を位相データ信号PFDS1、遅延クロック信号FR2の立ち上がりエッジのタイミングで取り込んだカウント値PFDCの値を位相データ信号PFDS2とする。
The PFD sample circuit 106 takes in the value of the count value PFDC from the
ここで、フィードバッククロック信号FDとリファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジのタイミングの違いで、PFDサンプル回路106から出力される位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2の値も異なる。フィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がりタイミングとリファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジのタイミングの違いに応じた、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2の値の関係を図6〜図12に示す。 Here, the values of the phase data signals PFDS0, PFDS1, and PFDS2 output from the PFD sample circuit 106 differ depending on the timing of the rising edge of the feedback clock signal FD and the reference clock signal FREF. 6 to 12 show the relationship between the values of the phase data signals PFDS0, PFDS1, and PFDS2 in accordance with the difference between the rising timing of the feedback clock signal FD and the timing of the rising edge of the reference clock signal FREF.
ここで、図6にリファレンスクロック信号FREFから遅延クロック信号FR1の遅延量をtdFR、リファレンスクロック信号FREFから遅延クロック信号FR2の遅延量を2×tdFRとして示す。ここで、PFDサンプル回路106がリファレンスクロック信号FREF、遅延クロック信号FR1、FR2により、取り込むカウント値PFDCの値が全て不確定な値となることを避けるため、遅延量tdFRをフィードバッククロック信号FDが入力されてからPFDC値が確定するまでの遅延時間tdFD以上の遅延量とする必要がある。更に、出力クロック信号FOUTの2周期以上にわたって、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2を取り込むことを避けるため、2×tdFRは出力クロック信号FOUTの1周期(以後、tFOとする)の半分以内の遅延量であるものとする。このように、2×tdFRをtFOの半分以内の遅延量とする理由は、後述する位相データ判定時に上述した位相差検出信号PTDCを使用するためである。理想的には、tdFD<<tdFR<2×tdFR<<tFO(以後、条件式1と称す)を満たす必要がある。これにより、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2として捕獲されるデータは、確定した隣り合うデータ値かその遷移途中の不定値の3つの状態しかとりえないこととなる。但し、実際には、tdFDの遅延を小さくするには限界があり、さらに出力クロック信号FOUTが高速となる場合、前述した条件式を常に満たすことが困難となり、tdFDとtdFRが限りなく等しくなる場合が存在する。本実施例には、そのような場合でも以下に説明するように正しいデータを得る処理を行なうことでこの問題を解決している。なお、上述した説明は図6を元に行ったが、図7〜図12の場合でも同様である。 FIG. 6 shows the delay amount from the reference clock signal FREF to the delayed clock signal FR1 as tdFR, and the delay amount from the reference clock signal FREF to the delayed clock signal FR2 as 2 × tdFR. Here, the feedback clock signal FD is inputted with the delay amount tdFR in order to prevent the count value PFDC fetched from the reference clock signal FREF and the delayed clock signals FR1 and FR2 by the PFD sample circuit 106 from becoming uncertain values. It is necessary to set a delay amount equal to or longer than the delay time tdFD until the PFDC value is determined after being set. Further, in order to avoid capturing the phase data signals PFDS0, PFDS1, and PFDS2 over two or more cycles of the output clock signal FOUT, 2 × tdFR is a delay within half of one cycle of the output clock signal FOUT (hereinafter referred to as tFO). It is assumed that the amount. Thus, the reason why 2 × tdFR is set to a delay amount within half of tFO is that the above-described phase difference detection signal PTDC is used when phase data is determined later. Ideally, tdFD << tdFR << 2 × tdFR << tFO (hereinafter referred to as conditional expression 1) needs to be satisfied. As a result, the data captured as the phase data signals PFDS0, PFDS1, and PFDS2 can take only three states: a determined adjacent data value or an indefinite value during the transition. However, in practice, there is a limit to reducing the delay of tdFD, and when the output clock signal FOUT becomes high speed, it becomes difficult to always satisfy the above-described conditional expression, and tdFD and tdFR are infinitely equal. Exists. In this embodiment, even in such a case, this problem is solved by performing processing for obtaining correct data as described below. In addition, although the above-mentioned description was performed based on FIG. 6, it is the same also in the case of FIGS.
まず、図6では、時刻t1でリファレンスクロック信号FREFがハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t1時点でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCnを、位相データ信号PFDS0として出力する。時刻t2で遅延クロック信号FR1がハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t2でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCnを、位相データ信号PFDS1として出力する。時刻t3で遅延クロック信号FR2がハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t3でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCnを、位相データ信号PFDS2として出力する。その後、フィードバッククロック信号FDが立ち上がり、時刻t4において、カウント値PFDCの値がPFDCnからPFDCn+1となる。しかし、この時刻t4以前にカウント値PFDCが取り込まれており、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2の全ての値が同じ値のPFDCnとなっている。このため、PFDS0=PFDS1=PFDS2となる。なお、符号「PFDS0」「PFDS1」「PFDS2」は、それぞれ位相データ信号名を示すと同時に、その信号が格納するカウント値を示すものとする。
First, in FIG. 6, the reference clock signal FREF rises to a high level at time t1. The value PFDCn of the count value PFDC at the time t1 is output as the phase data signal PFDS0. At time t2, the delayed clock signal FR1 rises to a high level. The value PFDCn of the count value PFDC at time t2 is output as the phase data signal PFDS1. At time t3, the delayed clock signal FR2 rises to a high level. The value PFDCn of the count value PFDC at time t3 is output as the phase data signal PFDS2. Thereafter, the feedback clock signal FD rises, and at time t4, the count value PFDC changes from PFDCn to
図7では、時刻t1でリファレンスクロック信号FREFがハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t1時点でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCnを、位相データ信号PFDS0として出力する。時刻t2で遅延クロック信号FR1がハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t2でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCnを、位相データ信号PFDS1として出力する。その後、フィードバッククロック信号FDが立ち上がり、時刻t3において、カウント値PFDCの値がPFDCnからPFDCn+1となる。この時刻t3に遅延クロック信号FR2がハイレベルに立ち上がる。このため、位相データ信号PFDS2として、出力されるカウント値PFDCの値は、遷移状態の値であり不定な値として出力される。
In FIG. 7, the reference clock signal FREF rises to a high level at time t1. The value PFDCn of the count value PFDC at the time t1 is output as the phase data signal PFDS0. At time t2, the delayed clock signal FR1 rises to a high level. The value PFDCn of the count value PFDC at time t2 is output as the phase data signal PFDS1. Thereafter, the feedback clock signal FD rises, and at time t3, the count value PFDC changes from PFDCn to
図8では、時刻t1でリファレンスクロック信号FREFがハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t1時点でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCnを、位相データ信号PFDS0として出力する。時刻t2で遅延クロック信号FR1がハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t2でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCnを、位相データ信号PFDS1として出力する。その後、フィードバッククロック信号FDが立ち上がり、時刻t3において、カウント値PFDCの値がPFDCnからPFDCn+1に遷移する。時刻t4で、遅延クロック信号FR2がハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t4時点でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCn+1を、位相データ信号PFDS2として出力する。
In FIG. 8, the reference clock signal FREF rises to a high level at time t1. The value PFDCn of the count value PFDC at the time t1 is output as the phase data signal PFDS0. At time t2, the delayed clock signal FR1 rises to a high level. The value PFDCn of the count value PFDC at time t2 is output as the phase data signal PFDS1. Thereafter, the feedback clock signal FD rises, and at time t3, the count value PFDC changes from PFDCn to
ここで、図7、図8のパターンでは、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2の値が、PFDS0=PFDS1≠PFDS2となっている。 Here, in the patterns of FIGS. 7 and 8, the values of the phase data signals PFDS0, PFDS1, and PFDS2 are PFDS0 = PFDS1 ≠ PFDS2.
図9では、時刻t1でリファレンスクロック信号FREFがハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t1時点でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCnを、位相データ信号PFDS0として出力する。その後、フィードバッククロック信号FDが立ち上がり、時刻t2においてカウント値PFDCの値がPFDCnからPFDCn+1へ遷移する。この時刻t2において遅延クロック信号FR1がハイレベルに立ち上がる。このため、位相データ信号PFDS1として、出力されるカウント値PFDCの値は、遷移状態の値であり不定な値として出力される。時刻t3で遅延クロック信号FR2がハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t3時点でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCn+1を、位相データ信号PFDS2として出力する。このため、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2の値は、全て異なる値となる。よって、PFDS0≠PFDS1≠PFDS2となる。 In FIG. 9, the reference clock signal FREF rises to a high level at time t1. The value PFDCn of the count value PFDC at the time t1 is output as the phase data signal PFDS0. Thereafter, the feedback clock signal FD rises, and the value of the count value PFDC transits from PFDCn to PFDCn + 1 at time t2. At this time t2, the delayed clock signal FR1 rises to a high level. For this reason, the value of the count value PFDC output as the phase data signal PFDS1 is a transition state value and is output as an indefinite value. At time t3, the delayed clock signal FR2 rises to a high level. The value PFDCn + 1 of the count value PFDC at time t3 is output as the phase data signal PFDS2. For this reason, the values of the phase data signals PFDS0, PFDS1, and PFDS2 are all different values. Therefore, PFDS0 ≠ PFDS1 ≠ PFDS2.
図10では、時刻t1でリファレンスクロック信号FREFがハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t1時点でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCnを、位相データ信号PFDS0として出力する。その後、フィードバッククロック信号FDが立ち上がり、時刻t2において、カウント値PFDCの値がPFDCnからPFDCn+1へ遷移する。時刻t3で遅延クロック信号FR1がハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t3でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCn+1を、位相データ信号PFDS1として出力する。時刻t4で、遅延クロック信号FR2がハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t4時点でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCn+1を、位相データ信号PFDS2として出力する。
In FIG. 10, the reference clock signal FREF rises to a high level at time t1. The value PFDCn of the count value PFDC at the time t1 is output as the phase data signal PFDS0. Thereafter, the feedback clock signal FD rises, and at time t2, the count value PFDC changes from PFDCn to
図11では、フィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がり、時刻t1において、カウント値PFDCの値がPFDCnからPFDCn+1へ遷移する。この時刻t1においてリファレンスクロック信号FREFがハイレベルに立ち上がる。このため、位相データ信号PFDS0として、出力されるカウント値PFDCの値は、遷移状態の値であり不定な値として出力される。時刻t2で遅延クロック信号FR1がハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t2時点でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCn+1を、位相データ信号PFDS1として出力する。時刻t3で遅延クロック信号FR2がハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t3時点でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCn+1を、位相データ信号PFDS2として出力する。
In FIG. 11, at the rise of the feedback clock signal FD, at time t1, the value of the count value PFDC changes from PFDCn to
ここで、図10、図11のパターンでは、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2の値が、PFDS0≠PFDS1=PFDS2となっている。 Here, in the patterns of FIGS. 10 and 11, the values of the phase data signals PFDS0, PFDS1, and PFDS2 are PFDS0 ≠ PFDS1 = PFDS2.
図12では、フィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がり、時刻t1において、カウント値PFDCの値がPFDCnからPFDCn+1へ遷移する。時刻t2でリファレンスクロック信号FREFがハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t2時点でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCn+1を、位相データ信号PFDS0として出力する。時刻t3で遅延クロック信号FR1がハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t3時点でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCn+1を、位相データ信号PFDS1として出力する。時刻t4で遅延クロック信号FR2がハイレベルに立ち上がる。この時刻t4時点でのカウント値PFDCの値PFDCn+1を、位相データ信号PFDS2として出力する。本パターンでは、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2の全ての値が同じ値のPFDCn+1となっている。このため、PFDS0=PFDS1=PFDS2となる。 In FIG. 12, the value of the count value PFDC transits from PFDCn to PFDCn + 1 at time t1 when the feedback clock signal FD rises. At time t2, the reference clock signal FREF rises to a high level. The value PFDCn + 1 of the count value PFDC at time t2 is output as the phase data signal PFDS0. At time t3, the delayed clock signal FR1 rises to a high level. The value PFDCn + 1 of the count value PFDC at time t3 is output as the phase data signal PFDS1. At time t4, the delayed clock signal FR2 rises to a high level. The value PFDCn + 1 of the count value PFDC at time t4 is output as the phase data signal PFDS2. In this pattern, all values of the phase data signals PFDS0, PFDS1, and PFDS2 are PFDCn + 1 having the same value. Therefore, PFDS0 = PFDS1 = PFDS2.
以上のように、フィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がりタイミングとリファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりタイミングの違いで、上述した7つのパターンが存在する。 As described above, the seven patterns described above exist depending on the difference between the rising timing of the feedback clock signal FD and the rising timing of the reference clock signal FREF.
PFD選択回路107は、TDC回路103が出力する位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNと、位相差検出信号PTDCと、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2の値とに応じて、選択位相データ信号PFD_ONEを出力する。
The
PFD選択回路107の動作理論を下記に説明する。まず、上述したが、TDC回路103が出力する位相差検出信号PTDCは、カウンタ101、102では測定できないリファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDとの、出力クロックFOUTの1周期以内の位相差情報を有している。位相差検出信号PTDCには、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相差を出力クロックFOUTの1周期以内で正規化したデジタルデータの値と、その位相差が出力クロックFOUTの1/2周期以上か否かを示す値がMSBに格納されている。また、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNは、リファレンスクロック信号FREFに対して、フィードバッククロック信号FDの位相の進み遅れを示す判定信号である。例えば、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNは、リファレンスクロック信号FREFに対してフィードバッククロック信号FDが遅れている場合は、ロウレベル、つまり値が「0」として出力される。リファレンスクロック信号FREFに対してフィードバッククロック信号FDが進んでいる場合は、ハイレベル、つまり値が「1」として出力される。
The operation theory of the
このため、PFD選択回路107は、TDC回路103が出力する位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNと、位相差検出信号PTDCにより、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDとの位相の関係が、図13に示す4パターンのうちどれであるかが判定できる。
For this reason, the
まず、パターンAは、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDとの位相差が出力クロックFOUTの1/2周期以下、且つリファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相がフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相より進んでいる場合を示している。 First, the pattern A is a case where the phase difference between the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD is less than ½ period of the output clock FOUT, and the phase of the reference clock signal FREF is ahead of the phase of the feedback clock signal FD. Show.
パターンBは、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDとの位相差が出力クロックFOUTの1/2周期以上、且つリファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相がフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相より遅れている場合を示している。 Pattern B shows a case where the phase difference between the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD is ½ period or more of the output clock FOUT, and the phase of the reference clock signal FREF is delayed from the phase of the feedback clock signal FD. Yes.
パターンCは、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDとの位相差が出力クロックFOUTの1/2周期以下、且つリファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相がフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相より遅れている場合を示している。 Pattern C shows a case where the phase difference between the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD is less than ½ period of the output clock FOUT, and the phase of the reference clock signal FREF is delayed from the phase of the feedback clock signal FD. Yes.
パターンDは、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDとの位相差が出力クロックFOUTの1/2周期以上、且つリファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相がフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相より進んでいる場合を示している。 Pattern D shows a case where the phase difference between the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD is greater than or equal to ½ period of the output clock FOUT, and the phase of the reference clock signal FREF is ahead of the phase of the feedback clock signal FD. Yes.
ここで、図14に、図13に示したパターンA〜Dと、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNと位相差検出信号PTDCのMSBの関係をまとめた表を示す。このように、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNと位相差検出信号PTDCのMSBの値により、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDとの位相の関係を判断することができる。 Here, FIG. 14 shows a table summarizing the relationship between the patterns A to D shown in FIG. 13 and the MSBs of the phase polarity signal PTDC_SIGN and the phase difference detection signal PTDC. Thus, the phase relationship between the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD can be determined based on the MSB values of the phase polarity signal PTDC_SIGN and the phase difference detection signal PTDC.
ここで、図6〜図12に示した位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2と、パターンA〜Dとの関係を考える。まず、図6で示したリファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDのパターンは、リファレンスクロック信号FREFと、遅延クロック信号FR1、FR2の遅延関係から、パターンAもしくは、パターンDに該当することがわかる。また、図12で示したリファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDのパターンは、パターンBもしくはCに該当することがわかる。この図6、図12の両パターンとも、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2のデジタルデータ値が同じ値である(PFDS0=PFDS1=PFDS2)。つまり、パターンDもしくは、パターンBであれば、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相差が出力クロックFOUTの1/2周期以上あり、パターンAもしくは、パターンCであっても、フィードバッククロック信号FDのデータ遷移時間(tdFD)以上の位相差が存在していることが想定できる。よって、この場合は、位相データ信号PFDS0〜PFDS2のどの値を選択してもよく、その選択した位相データ信号を選択位相データ信号PFD_ONEとしてPFD選択回路107が出力する。
Here, the relationship between the phase data signals PFDS0, PFDS1, and PFDS2 shown in FIGS. 6 to 12 and the patterns A to D will be considered. First, it can be seen that the pattern of the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD shown in FIG. 6 corresponds to the pattern A or the pattern D from the delay relationship between the reference clock signal FREF and the delayed clock signals FR1 and FR2. Further, it can be seen that the patterns of the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD shown in FIG. 12 correspond to the pattern B or C. In both the patterns of FIGS. 6 and 12, the digital data values of the phase data signals PFDS0, PFDS1, and PFDS2 are the same value (PFDS0 = PFDS1 = PFDS2). That is, in the case of the pattern D or the pattern B, the phase difference between the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD is ½ period or more of the output clock FOUT. It can be assumed that a phase difference equal to or longer than the FD data transition time (tdFD) exists. Therefore, in this case, any value of the phase data signals PFDS0 to PFDS2 may be selected, and the
次に、図7、図8で示したリファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDのパターンは、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1が同じ値であるが、PFDS2はそれとは異なる値となっている(PFDS0=PFDS1≠PFDS2)。この場合、フィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がりエッジが、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジ近傍にあることが予測される。更に、フィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がりエッジが、遅延クロック信号FR1、FR2の立ち上がりエッジ近傍にあることが予測される。 Next, in the patterns of the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, the phase data signals PFDS0 and PFDS1 have the same value, but PFDS2 has a different value (PFDS0 = PFDS1 ≠ PFDS2). In this case, it is predicted that the rising edge of the feedback clock signal FD is in the vicinity of the rising edge of the reference clock signal FREF. Furthermore, it is predicted that the rising edge of the feedback clock signal FD is in the vicinity of the rising edges of the delayed clock signals FR1 and FR2.
ここで、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相の関係は、大半がパターンAの状態となっていることが想定される。よって、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNの値が「0」であれば、PFD選択回路107は、位相データ信号PFDS0を選択し、選択位相データ信号PFD_ONEとして出力する。但し、前述したような条件式1を十分満たすことが困難な場合は、想定とは異なり、TDC回路103が位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNの値として「1」を出力する場合も考えられる。この場合は、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相の関係は、パターンCの状態となっていることが想定される。よって、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNの値が「1」であれば、PFD選択回路107は、位相データ信号PFDS0の値に「1」を加えた値(PFDS0+1)のデジタルデータを選択位相データ信号PFD_ONEとして出力する。これにより、TDC回路103で測定した位相関係に合わせた正確な位相データを選択できることとなる。以降に示すその他の状態においても、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNの状態を用いてデータ選択を行なう。
Here, it is assumed that the phase relationship between the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD is mostly in the pattern A state. Therefore, if the value of the phase polarity signal PTDC_SIGN is “0”, the
次に、図9で示したリファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDのパターンは、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2が全て異なる値となっている(PFDS0≠PFDS1≠PFDS2)。この場合、フィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がりエッジが、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジ近傍にあることが予測される。ここで、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相の関係は、パターンAもしくは、パターンCの状態となっていることが想定される。PFD選択回路107は、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNの値が「0」であれば、パターンAであると判断して、位相データ信号PFDS0を選択し、選択位相データ信号PFD_ONEとして出力する。または、PFD選択回路107は、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNの値が「1」であれば、パターンCであると判断して、位相データ信号PFDS2を選択し、選択位相データ信号PFD_ONEとして出力する。
Next, in the patterns of the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD shown in FIG. 9, the phase data signals PFDS0, PFDS1, and PFDS2 are all different values (PFDS0 ≠ PFDS1 ≠ PFDS2). In this case, it is predicted that the rising edge of the feedback clock signal FD is in the vicinity of the rising edge of the reference clock signal FREF. Here, it is assumed that the phase relationship between the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD is in the state of pattern A or pattern C. If the value of the phase polarity signal PTDC_SIGN is “0”, the
次に、図10、図11で示したリファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDのパターンは、位相データ信号PFDS1、PFDS2が同じ値であるが、PFDS0はそれとは異なる値となっている(PFDS0≠PFDS1=PFDS2)。この場合、フィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がりエッジが、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジ近傍にあることが予測される。更に、この場合、図7、図8で示した場合とは逆の関係となっており、フィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がりエッジが、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジより進んでいることが予測される。 Next, in the patterns of the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD shown in FIGS. 10 and 11, the phase data signals PFDS1 and PFDS2 have the same value, but PFDS0 has a different value (PFDS0 ≠ PFDS1 = PFDS2). In this case, it is predicted that the rising edge of the feedback clock signal FD is in the vicinity of the rising edge of the reference clock signal FREF. Further, in this case, the relationship is opposite to that shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, and it is predicted that the rising edge of the feedback clock signal FD is ahead of the rising edge of the reference clock signal FREF.
ここで、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相の関係は、大半がパターンCの状態となっていることが想定される。よって、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNの値が「1」であれば、PFD選択回路107は、位相データ信号PFDS2を選択し、選択位相データ信号PFD_ONEとして出力する。但し、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNの値が「0」であれば、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相の関係は、パターンAの状態となっていることが想定される。よって、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNの値が「0」であれば、PFD選択回路107は、位相データ信号PFDS2の値から「1」を引いた値(PFDS2−1)のデジタルデータを選択位相データ信号PFD_ONEとして出力する。
Here, it is assumed that the phase relationship between the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD is mostly in the pattern C state. Therefore, if the value of the phase polarity signal PTDC_SIGN is “1”, the
以上がPFD選択回路107の動作理論の説明である。PFD選択回路107が上記動作により、出力する選択位相データ信号PFD_ONEのパターンをまとめた表を図15に示す。図15に示すように、PFD選択回路107は、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2の値及び位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNの値に応じて、選択位相データ信号PFD_ONEを生成し、出力する。
The above is the description of the operation theory of the
サンプリング回路108は、遅延クロック信号FRn+1の立ち上がりエッジ後、つまり各位相情報のデータの確定後、出力クロックFOUTのクロックタイミングで各位相情報を取り込む。そして、取り込んだ位相情報に応じたデジタル値を有する信号を位相誤差演算回路109に出力する。ここで言う各位相情報とは、位相差検出信号PTDC、カウント値信号PFRC、選択位相データ信号PFD_ONE、位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNであるとする。また、サンプリング回路108が出力するデジタル値を有する信号をPFR、PTD、DERR_PTDC_SIGN、PFDとする。なお、便宜上、符号「PFR」「PTD」「PFD」「DERR_PTDC_SIGN」は、デジタル信号名を示すと同時に、そのデジタル信号が格納する値を示すものとする。また、デジタル信号PFRは信号PFRCに対応し、デジタル信号PTDは位相差検出信号PTDCに対応し、デジタル信号DERR_PTDC_SIGNは位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNに対応し、デジタル信号PFDは選択位相データ信号PFD_ONEに対応する。
The
図16に、ADPLL回路100の特徴部分であるPFDサンプル回路106、PFD選択回路107の動作を説明するためのタイミングチャートを示す。図1と図16で示される符号のうち同じ符号のものは、同一の信号を指すものとする。また、本例では、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相が、フィードバッククロック信号FDより遅れており、且つ、フィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がりエッジが、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジ近傍にある場合を想定する。つまり、図13のパターンCに該等する。
FIG. 16 is a timing chart for explaining the operations of the PFD sample circuit 106 and the
図16に示すように、時刻t1にフィードバッククロック信号FDが立ち上がる。そのフィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がりエッジに対応して、時刻t2に加算回路105からのカウント値PFDCが「9」から「10」へ遷移する。時刻t2とほぼ同時刻にリファレンスクロック信号FREFも立ち上がる。このリファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりエッジに応じて、PFDサンプル回路106がカウント値PFDCを取り込む。しかし、時刻t2では、カウント値PFDCが「9」から「10」へ遷移途中である。このため、PFDサンプル回路106が取り込んだカウント値PFDCは、不定な値(図中の「X」)となる。この値は、位相データ信号PFDS0としてPFDサンプル回路106から出力される。
As shown in FIG. 16, the feedback clock signal FD rises at time t1. Corresponding to the rising edge of the feedback clock signal FD, the count value PFDC from the
次に、時刻t3に遅延クロック信号FR1が立ち上がる。この遅延クロック信号FR1の立ち上がりエッジに応じて、PFDサンプル回路106がカウント値PFDCを取り込む。このときのカウント値PFDCは、既に遷移が終わっており、値が「10」に確定している。このため、この値が「10」のカウント値PFDCが位相データ信号PFDS1としてPFDサンプル回路106から出力される。 Next, the delayed clock signal FR1 rises at time t3. In response to the rising edge of the delayed clock signal FR1, the PFD sample circuit 106 takes in the count value PFDC. The count value PFDC at this time has already transitioned, and the value is fixed to “10”. Therefore, the count value PFDC whose value is “10” is output from the PFD sample circuit 106 as the phase data signal PFDS1.
次に、時刻t4に遅延クロック信号FR2が立ち上がる。この遅延クロック信号FR2の立ち上がりエッジに応じて、PFDサンプル回路106がカウント値PFDC(値が「10」)を取り込む。この値が「10」のカウント値PFDCが位相データ信号PFDS2としてPFDサンプル回路106から出力される。これらのことから、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2の値は、PFDS0≠PFDS1=PFDS2となる。 Next, the delayed clock signal FR2 rises at time t4. In response to the rising edge of the delayed clock signal FR2, the PFD sample circuit 106 takes in the count value PFDC (value is “10”). The count value PFDC whose value is “10” is output from the PFD sample circuit 106 as the phase data signal PFDS2. Therefore, the values of the phase data signals PFDS0, PFDS1, and PFDS2 are PFDS0 ≠ PFDS1 = PFDS2.
ここで、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバッククロック信号FDの立ち上がりの位相差は、ほぼ時刻t1〜t2の期間であり、出力クロックFOUTの1/2周期以下である。このため、TDC回路103から出力される位相差検出信号PTDCのMSBは「0」となっている。また、リファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相が、フィードバッククロック信号FDより遅れているため、TDC回路103から出力される位相極性信号PTDC_SIGNの値は「1」となっている。また、上述のように、位相データ信号PFDS0、PFDS1、PFDS2の値は、PFDS0≠PFDS1=PFDS2となっている。このため、PFD選択回路107は、図15からもわかるように、位相データ信号PFDS2の値を選択し、選択位相データ信号PFD_ONEとして出力する。
Here, the phase difference between the rising edges of the reference clock signal FREF and the feedback clock signal FD is approximately the period from time t1 to t2, and is equal to or less than ½ period of the output clock FOUT. Therefore, the MSB of the phase difference detection signal PTDC output from the
サンプリング回路108は、TDC回路103から出力される遅延クロック信号FRn+1の立ち上がりエッジを検出すると、時刻t5に出力クロックFOUTのクロックタイミングで値が「10」のカウント値PFDCと、値が「10」の選択位相データ信号PFD_ONEを取り込む。
When the
位相誤差演算回路109は、サンプリング回路108からのデジタル信号PFR、PTD、DERR_PTDC_SIGN、PFDを入力する。位相誤差演算回路109は、上記信号の各値に応じて(PFR−(PFD+PTD))を演算する。そして、この演算結果に応じてリファレンスクロック信号FREFに対するフィードバッククロック信号FDの位相誤差データを得る。また、PTDの正負はDERR_PTDC_SIGNの値によって決まる。この演算により、位相誤差演算回路109は、出力クロック信号FOUTの1周期以内の位相差を導くことができる。位相誤差演算回路109は、その位相誤差データの値をデジタルデータの位相誤差信号PERRとして出力する。
The phase
デジタルフィルタ110は、入力した位相誤差信号PERRを任意の帯域でフィルタリングして、そのフィルタリングデータに応じてデジタル制御発振回路111の制御コードDCONを出力する。
The
デジタル制御発振(DCO)回路111(デジタル制御発振器)は、入力した制御コードDCONに応じた発振周波数で出力クロック信号FOUTを生成し、出力する。出力クロック出力端子113は、DCO回路111からの出力クロック信号FOUTを外部回路(不図示)へ出力する端子である。
A digitally controlled oscillation (DCO) circuit 111 (digitally controlled oscillator) generates and outputs an output clock signal FOUT at an oscillation frequency corresponding to the input control code DCON. The output
ここで、従来のADPLL回路2では、図23に示したように、フィードバッククロック信号FDと非同期関係にあるリファレンスクロック信号FREFの立ち上がりのタイミングで遷移過程にあるデジタルデータPFDCの値を位相誤差演算回路26が読み取る場合があった。この場合、遷移過程にある不定なデジタルデータPFDCの値を用いて、位相誤差演算回路26がフィードバッククロック信号FDとリファレンスクロック信号FREFの位相誤差を演算してしまっていた。この現象は、リファレンスクロック信号FREFとフィードバック信号FDの立ち上がりが同期しようとするロック状態の近傍で、多く発生する。このため、ADPLL回路2では、安定した位相同期ループを形成することができなかった。
Here, in the
本実施の形態のADPLL回路100では、フィードバッククロック信号FDと非同期関係にあるリファレンスクロック信号FREFと、そのリファレンスクロック信号FREFを順次遅延させた遅延クロック信号FR1、FR2を用いて、PFDサンプル回路106でカウント値PFDCの値を取り込む。そして、PFDサンプル回路106が取り込んだ、その3つのカウント値PFDCから最も適切な値をPFD選択回路107が選択する。その選択には、TDC回路103からのデータを利用する。そして、PFD選択回路107が選択した適切な値を位相誤差の演算に用いる。このことにより、遷移過程にある不定なデジタルデータを位相誤差の演算に用いることを防ぐことが可能になり、正しい位相誤差データを算出することで安定した位相同期ループを形成することが可能となる。
In the
なお、本発明は上記実施の形態に限られたものでなく、趣旨を逸脱しない範囲で適宜変更することが可能である。 Note that the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and can be changed as appropriate without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
100 ADPLL回路
101、102 カウンタ
103 TDC回路
104 分周回路
105 加算回路
106 PFDサンプル回路
107 PFD選択回路
108 サンプリング回路
109 位相誤差演算回路
110 デジタルフィルタ
111 DCO回路
112 入力端子
113 出力端子
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (8)
第2のクロック信号をカウントする第2のカウンタと、
第1のクロック信号を順次遅延させた第1、第2の遅延クロック信号を生成する遅延クロック生成回路と、
前記第1のクロック信号及び第1、第2の遅延クロック信号のそれぞれで前記第2のカウンタのカウント値をサンプリングするサンプル回路と、
前記第1のクロック信号と、前記第2のクロック信号を所定の数で分周した第3のクロック信号との位相差、及び、前記第1のサンプル回路がサンプリングしたカウント値とに応じて、前記第1のサンプル回路がサンプリングしたカウント値のうち1つを選択する選択回路と、
前記第1のカウンタのカウント値及び前記選択回路が選択したカウント値とに応じて前記第1のクロックと前記第3のクロックとの位相差を演算する位相誤差演算回路と、
前記位相誤差演算回路の演算結果に応じて前記第2のクロックを出力するデジタル制御発振器と、
を有するデジタルフェーズロックドループ回路。 A first counter for counting a first clock signal;
A second counter for counting a second clock signal;
A delay clock generating circuit for generating first and second delayed clock signals obtained by sequentially delaying the first clock signal;
A sample circuit that samples the count value of the second counter with each of the first clock signal and the first and second delayed clock signals;
According to the phase difference between the first clock signal and the third clock signal obtained by dividing the second clock signal by a predetermined number, and the count value sampled by the first sample circuit, A selection circuit for selecting one of the count values sampled by the first sample circuit;
A phase error calculation circuit for calculating a phase difference between the first clock and the third clock according to the count value of the first counter and the count value selected by the selection circuit;
A digitally controlled oscillator that outputs the second clock according to a calculation result of the phase error calculation circuit;
A digital phase-locked loop circuit.
前記第2のクロック信号を所定の数で分周した前記第3のクロック信号を生成する分周回路と、
前記第3のクロック信号をカウントする第3のカウンタと、を有する
請求項1に記載のデジタルフェーズロックドループ回路。 The second counter is
A frequency dividing circuit for generating the third clock signal obtained by dividing the second clock signal by a predetermined number;
The digital phase-locked loop circuit according to claim 1, further comprising a third counter that counts the third clock signal.
請求項2に記載のデジタルフェーズロックドループ回路。 The digital phase-locked loop circuit according to claim 2, further comprising a phase difference detector that detects a phase difference between the first clock signal and the third clock signal within one cycle of the second clock signal.
前記第1のクロック信号に対して前記第3のクロック信号の位相の遅れ進みを示す極性値と、
前記第1のクロック信号と前記第3のクロック信号との位相差が前記第2のクロック信号の半周期以内であるか否かの判定値と、を生成する
請求項3に記載のデジタルフェーズロックドループ回路。 The phase detector is
A polarity value indicating a phase advance of the third clock signal with respect to the first clock signal;
4. The digital phase lock according to claim 3, wherein a determination value as to whether or not a phase difference between the first clock signal and the third clock signal is within a half cycle of the second clock signal is generated. Droop circuit.
前記極性値と、前記判定値と、前記第1のサンプル回路がサンプリングしたカウント値と、に応じて、前記第1のサンプル回路がサンプリングしたカウント値のうち1つを選択する
請求項4に記載のデジタルフェーズロックドループ回路。 The selection circuit includes:
5. The count value sampled by the first sample circuit is selected according to the polarity value, the determination value, and the count value sampled by the first sample circuit. Digital phase locked loop circuit.
前記第3のクロック信号を順次遅延させ、その順次遅延させたクロック信号と前記第1のクロック信号を比較した第1の比較結果と、前記第1のクロック信号を順次遅延させ、その順次遅延させたクロック信号と前記第3のクロックを比較した第2の比較結果と、に応じて前記第1のクロック信号と前記第3のクロック信号の相対的な位相差を検出する
請求項3〜請求項5のいずれか1項に記載のデジタルフェーズロックドループ回路。 The phase detector is
A first comparison result obtained by sequentially delaying the third clock signal and comparing the sequentially delayed clock signal with the first clock signal, and sequentially delaying the first clock signal and sequentially delaying the first clock signal. 4. A relative phase difference between the first clock signal and the third clock signal is detected according to a second comparison result obtained by comparing the clock signal with the third clock. 6. The digital phase locked loop circuit according to any one of 5 above.
前記第1、第2の遅延クロック信号は、前記位相検出器が前記第1のクロック信号を順次遅延させたクロック信号から用いられる
請求項6に記載のデジタルフェーズロックドループ回路。 The phase detector includes the delay clock generation circuit,
7. The digital phase locked loop circuit according to claim 6, wherein the first and second delayed clock signals are used from a clock signal obtained by sequentially delaying the first clock signal by the phase detector.
請求項7に記載のデジタルフェーズロックドループ回路。 The amount of delay by which the phase detector sequentially delays the first clock signal is within a half period of the second clock signal, and more than a transition period in which the count value of the second counter transitions to the next value The digital phase-locked loop circuit according to claim 7.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009124157A JP2010273185A (en) | 2009-05-22 | 2009-05-22 | Digital phase locked loop circuit |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009124157A JP2010273185A (en) | 2009-05-22 | 2009-05-22 | Digital phase locked loop circuit |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010273185A true JP2010273185A (en) | 2010-12-02 |
| JP2010273185A5 JP2010273185A5 (en) | 2012-05-17 |
Family
ID=43420847
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009124157A Pending JP2010273185A (en) | 2009-05-22 | 2009-05-22 | Digital phase locked loop circuit |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2010273185A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013081084A (en) * | 2011-10-04 | 2013-05-02 | Renesas Electronics Corp | Digital pll circuit and semiconductor integrated circuit device |
| CN105356896A (en) * | 2015-09-29 | 2016-02-24 | 西安空间无线电技术研究所 | Multi-frequency switching system and method for miniature Ka double-frequency transmitter |
| US10686457B2 (en) | 2018-05-16 | 2020-06-16 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Circuit device, oscillator, electronic apparatus and vehicle |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH06120812A (en) * | 1992-10-01 | 1994-04-28 | Mitsubishi Denki Eng Kk | Semiconductor integrated circuit |
| JPH08288798A (en) * | 1995-04-18 | 1996-11-01 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Input signal latching circuit |
| JP2002076886A (en) * | 2000-06-30 | 2002-03-15 | Texas Instruments Inc | Digital fractional phase detector |
| US20020131538A1 (en) * | 2000-10-23 | 2002-09-19 | Staszewski Robert B. | Method and apparatus for asynchronous clock retiming |
| JP2003283476A (en) * | 2002-03-22 | 2003-10-03 | Nec Engineering Ltd | Burst data receiver |
-
2009
- 2009-05-22 JP JP2009124157A patent/JP2010273185A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH06120812A (en) * | 1992-10-01 | 1994-04-28 | Mitsubishi Denki Eng Kk | Semiconductor integrated circuit |
| JPH08288798A (en) * | 1995-04-18 | 1996-11-01 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Input signal latching circuit |
| JP2002076886A (en) * | 2000-06-30 | 2002-03-15 | Texas Instruments Inc | Digital fractional phase detector |
| US20020131538A1 (en) * | 2000-10-23 | 2002-09-19 | Staszewski Robert B. | Method and apparatus for asynchronous clock retiming |
| JP2003283476A (en) * | 2002-03-22 | 2003-10-03 | Nec Engineering Ltd | Burst data receiver |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013081084A (en) * | 2011-10-04 | 2013-05-02 | Renesas Electronics Corp | Digital pll circuit and semiconductor integrated circuit device |
| CN105356896A (en) * | 2015-09-29 | 2016-02-24 | 西安空间无线电技术研究所 | Multi-frequency switching system and method for miniature Ka double-frequency transmitter |
| CN105356896B (en) * | 2015-09-29 | 2018-02-09 | 西安空间无线电技术研究所 | A kind of multifrequency switching system and method for being used to minimize Ka double frequency emitters |
| US10686457B2 (en) | 2018-05-16 | 2020-06-16 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Circuit device, oscillator, electronic apparatus and vehicle |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5305935B2 (en) | Digital phase locked loop circuit | |
| US7859344B2 (en) | PLL circuit with improved phase difference detection | |
| JP5590867B2 (en) | Time / digital converter and digital phase lock loop | |
| US9742416B2 (en) | IC phase detector with re-timed reference clock controlling switches | |
| US9543970B2 (en) | Circuit for digitizing phase differences, PLL circuit and method for the same | |
| KR101632657B1 (en) | Time-to-digital convertoer and all-digital phase locked loop | |
| CN101640534B (en) | Full digital phase-locked loop applying rapid frequency capture method | |
| JP5347534B2 (en) | Phase comparator, PLL circuit, and phase comparator control method | |
| TWI392237B (en) | Timing error detecting device and method thereof | |
| US7595672B2 (en) | Adjustable digital lock detector | |
| US7924071B2 (en) | Synchronization detection circuit, pulse width modulation circuit using the same, and synchronization detection method | |
| JP5333439B2 (en) | Frequency synthesizer and oscillation frequency control method of oscillator | |
| JP2012049659A (en) | Digital phase lock loop circuit | |
| JP2013197898A (en) | Pll circuit, method of controlling pll circuit, and digital circuit | |
| JP2012049660A (en) | Phase lock loop | |
| US20100182049A1 (en) | Digital Phase Detection | |
| JP2010273185A (en) | Digital phase locked loop circuit | |
| WO2021036775A1 (en) | Signal generation circuit and method, and digital-to-time conversion circuit and method | |
| KR101710450B1 (en) | Phase locked loop and method for using the same | |
| TWI733415B (en) | Phase locked loop device and clock generation method | |
| WO2020246092A1 (en) | Phase synchronization circuit, electronic device, and method for controlling phase synchronization circuit | |
| CN111642138B (en) | Frequency locking ring, electronic equipment and frequency generation method | |
| JP2013077869A (en) | Time-digital converter and pll circuit | |
| KR101107722B1 (en) | Wide-range digital frequency synthesizer | |
| JP2531269B2 (en) | Sync detection method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120326 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20120326 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130319 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20130716 |