JP2010103802A - Electronic device - Google Patents
Electronic device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010103802A JP2010103802A JP2008273970A JP2008273970A JP2010103802A JP 2010103802 A JP2010103802 A JP 2010103802A JP 2008273970 A JP2008273970 A JP 2008273970A JP 2008273970 A JP2008273970 A JP 2008273970A JP 2010103802 A JP2010103802 A JP 2010103802A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- substrate
- frame
- package
- side wall
- electronic device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/0555—Shape
- H01L2224/05552—Shape in top view
- H01L2224/05554—Shape in top view being square
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/48221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/48225—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/48227—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation connecting the wire to a bond pad of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/49—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of a plurality of wire connectors
- H01L2224/491—Disposition
- H01L2224/4912—Layout
- H01L2224/49171—Fan-out arrangements
Landscapes
- Oscillators With Electromechanical Resonators (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、圧電発振器などの電子装置に関わり、特に大型化を招くことなく長期間の電
気的品質を得るのに好適なものである。
The present invention relates to an electronic device such as a piezoelectric oscillator, and is particularly suitable for obtaining long-term electrical quality without causing an increase in size.
近年、圧電発振器は、周波数安定度、小型軽量、堅牢性、低価格等により携帯電話等の
通信機器から水晶時計のような民生機器まで、多くの分野で用いられている。中でも圧電
振動子の周波数温度特性を補償した温度補償型圧電発振器(TCXO)は、周波数安定度
を必要とする携帯電話等に広く用いられている。
特許文献1には小型化、表面実装化を図った温度補償型水晶発振器が開示されている。
図6は、その分解斜視図であり、同図(a)は、金属キャップ、同図(b)は、水晶振動
素子、同図(c)は、金属キャップを取り除き、内部が見えるようにした温度補償型水晶
発振器の斜視図である。
図6に示すように温度補償型水晶発振器70は、封止室71を形成する多層セラミック
基板72と、封止室71に配設され発振回路及び補償回路を成す回路素子73と、封止室
71内の多層セラミック基板(以下、単に「基板」と称する)72に固着された水晶振動
素子Xと、基板72の上面に設けられたコバール製のシールリング75に溶接される金属
キャップ76等から構成されている。ここで、水晶振動素子Xは、封止室71に設けられ
た一対の保持器77、78上に導電性ペースト介して固着されている。
In recent years, piezoelectric oscillators have been used in many fields from communication devices such as mobile phones to consumer devices such as quartz watches due to their frequency stability, small size and light weight, robustness, and low price. In particular, a temperature compensated piezoelectric oscillator (TCXO) that compensates for the frequency temperature characteristics of a piezoelectric vibrator is widely used in mobile phones and the like that require frequency stability.
Patent Document 1 discloses a temperature-compensated crystal oscillator that is miniaturized and surface-mounted.
FIG. 6 is an exploded perspective view thereof. FIG. 6A is a metal cap, FIG. 6B is a crystal resonator element, and FIG. 6C is a metal cap removed so that the inside can be seen. It is a perspective view of a temperature compensation type crystal oscillator.
As shown in FIG. 6, a temperature-compensated
保持器77、78は、導電性の弾性材製で、先端部77a、78aと基端部77b、7
8bから成り、先端部77a、78aが曲った略フック形状に形成されている。保持器7
7、78は、その基端部77b、78bのみが基板72上に固定され、その先端部77a
、78aは基板72から浮いている。水晶振動素子Xの励振電極75a、75bに連なる
引き出し電極75c、75dは、夫々先端部77a、78aに導電性ペーストを介して固
定されている。仮に、水晶振動素子Xを基板72上に直接固着すると、シーム溶接によっ
て基板72に生じる微小な歪が、水晶振動素子Xに影響し、水晶振動素子Xの周波数のば
らつきの原因となる。そこで、周波数の高精度化を図る場合に、前記のように保持器77
、78を介して水晶振動素子Xを基板72に固着すると、保持器77、78の先端部77
a、78aが有するスプリング機能が、シーム溶接によって生じる基板72の微小歪を吸
収し、水晶振動素子Xに与える影響を低減する。
The
8b, and the
7 and 78, only the
, 78 a are floating from the
, 78, the crystal vibrating element X is fixed to the
The spring function of a and 78a absorbs minute distortion of the
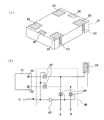
また、特許文献2には、DLD特性(ドライブレベル特性)の試験用端子を備えた水晶
発振器が開示されている。図7(a)はパッケージ81の上下を反転させた斜視図で、パ
ッケージ81の底面には一対のDLD特性の試験用端子86、86が、電源(Vcc)入
力用端子電極82、GND端子電極83、OUT端子電極84、Cont端子電極85と
共に配置されている。一対の試験用端子電極86、86は、図7(b)に示す切り替え器
98から引き出された端子A、Bに電気的に接続される。切り替え器98は、アナログス
イッチ95、96及びインバータ97から構成される。端子Cは、水晶発振器の電源入力
用端子電極82に接続しておく。水晶振動子の試験時は、電源入力用端子電極82を接地
すると、インバータ97の出力は「Hレベル」になり、アナログスイッチ96が「オン」
になって、端子A、Bに接続されたパッケージ81の試験用端子電極86、86と、ブラ
ンク電極93とが電気的に接続される。このため、この試験用端子電極86、86を使用
することにより、前記DLD特性試験ができる。
水晶発振器の動作時は、電源入力用端子電極82に電圧が印加されるので、端子Cが「
Hレベル」になる。このため、アナログスイッチ95が「オン」になって、ブランク電極
93がLSI91の振動子接続端子電極92へ接続されて、水晶発振器は発振動作状態に
なる。このとき、アナログスイッチ96は、インバータ97の出力が「Lレベル」になる
ため、「オフ」となって試験用端子電極86、86とブランク電極5とが電気的に切り離
される。
Thus, the
During operation of the crystal oscillator, a voltage is applied to the power
H level ”. For this reason, the
ところで、特許文献1又は2に開示された圧電発振器は、積層セラミックパッケージに
設けた保持器、あるいはパッケージ内の段差部に導電性接着剤を介して、パッケージに覆
われてない水晶振動素子を接着、固定する構成とされる。
しかしながら、このような従来の構成の圧電発振器を、小型(例えば7.0×5.0×
1.5mm)で、しかも長期間(例えば10年〜20年)に亘り電気的品質を保証する温
度補償型圧電発振器に用いた場合は、繰り返しの温度変化、あるいは経年変化により、パ
ッケージ内の半田、電子部品等からガスが発生する。そのガスが水晶振動素子の基板面、
電極等に付着して、周波数の変化を来し、発振周波数が要求規格を満たさない虞があると
いう問題があった。
本発明は上記問題を解決するためになされたもので、小型でしかも長期間の品質を得る
ことができる電子装置を提供することにある。
By the way, the piezoelectric oscillator disclosed in
However, the piezoelectric oscillator having such a conventional configuration is small (for example, 7.0 × 5.0 ×
1.5 mm), and when used in a temperature compensated piezoelectric oscillator that guarantees electrical quality over a long period of time (for example, 10 to 20 years), the solder in the package is subject to repeated temperature changes or aging changes. Gas is generated from electronic parts. The gas is the substrate surface of the crystal resonator element,
There has been a problem that the frequency is changed by adhering to an electrode or the like, and the oscillation frequency may not satisfy the required standard.
The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and it is an object of the present invention to provide an electronic device that is small in size and can obtain long-term quality.
本発明は、上記の課題の少なくとも一部を解決するためになされたものであり、以下の
形態又は適用例として実現することが可能である。
SUMMARY An advantage of some aspects of the invention is to solve at least a part of the problems described above, and the invention can be implemented as the following forms or application examples.
[適用例1]第1及び第2の主面と、該第1及び第2の主面と連続した側面と、前記側
面に前記第1の主面から前記第2の主面に達する第1の切欠部とを有する基板と、前記基
板上に配置され、上面及び下面と連続した側面に上面から下面に達する第2の切欠部を有
する枠状側壁と、前記基板と前記枠状側壁とからなる空間に収容された圧電振動子と、前
記基板と前記枠状側壁とからなる空間に収容された電子部品と、を備え、前記第2の切欠
部の少なくとも一部の深さが前記第1の切欠部の深さより浅い電子装置を特徴とする。
Application Example 1 First and second main surfaces, side surfaces continuous with the first and second main surfaces, and a first surface that reaches the second main surface from the first main surface to the side surface. A substrate having a notch, a frame-shaped side wall disposed on the substrate and having a second notch extending from the upper surface to the lower surface on a side surface continuous with the upper surface and the lower surface, and the substrate and the frame-shaped side wall A piezoelectric vibrator housed in a space and an electronic component housed in a space made up of the substrate and the frame-shaped side wall, and the depth of at least a part of the second notch is the first. The electronic device is shallower than the depth of the notch.
基板上に配置される枠状側壁に形成される第2の切欠部の一部の深さを、基板に形成す
る第1の切欠部の深さより浅く構成することで、枠状側壁の強度を低下させることなく、
その肉厚を薄くして、その内部空間を大きくすることが可能になる。
これにより、電子装置の内部に、気密封止された圧電振動子を搭載することが可能にな
るので、電子装置の大型化することなく、長期間に亘り電気的品質を保つことができる電
子装置を構成することができる。
By configuring the depth of a part of the second notch formed on the frame-shaped side wall disposed on the substrate to be shallower than the depth of the first notch formed on the substrate, the strength of the frame-shaped side wall is increased. Without lowering
It is possible to reduce the wall thickness and increase the internal space.
This makes it possible to mount a hermetically sealed piezoelectric vibrator inside the electronic device, so that the electronic device can maintain electrical quality for a long period of time without increasing the size of the electronic device. Can be configured.
[適用例2]前記第1の切欠部と前記第2の切欠部のうち、少なくとも前記第1の切欠
部にメッキを施した適用例1に記載の電子装置を特徴とする。
[Application Example 2] The electronic device according to Application Example 1 is characterized in that at least the first cutout portion is plated out of the first cutout portion and the second cutout portion.
第1の切欠部と第2の切欠部のうち、少なくとも第1の切欠部にメッキを施すようにす
れば、基板と枠状側壁とからなる空間に蓋体を封止した際に蓋体と第1の切欠部との短絡
を防止することができる。
If at least the first cutout portion is plated out of the first cutout portion and the second cutout portion, the lid body is sealed when the lid body is sealed in the space formed by the substrate and the frame-like side wall. A short circuit with the first notch can be prevented.
[適用例3]前記空間に不活性ガスが入った状態、または真空の状態であって、前記空
間を蓋体により封止した適用例1に記載の電子装置を特徴とする。
Application Example 3 The electronic device according to Application Example 1, wherein the space is filled with an inert gas or is in a vacuum state, and the space is sealed with a lid.
基板と枠状側壁とから形成される空間に不活性ガスを注入し、蓋体にて気密封止した電
子装置を構成することにより、空間内に収容された電子部品、接続導体、電極端子等の経
年変化が改善され、長期間の使用に耐える電子装置を構成できるという効果がある。
By injecting an inert gas into the space formed by the substrate and the frame-shaped side wall and forming an electronic device hermetically sealed with a lid, electronic components, connection conductors, electrode terminals, etc. accommodated in the space As a result, it is possible to construct an electronic device that can withstand long-term use.
[適用例4]前記空間に樹脂を注入して前記空間を封止する適用例1に記載の電子装置
を特徴とする。
Application Example 4 The electronic device according to Application Example 1 is characterized in that resin is injected into the space to seal the space.
基板と枠状側壁とから形成される空間を樹脂にて気密封止した電子装置を構成すること
により、空間に収容された電子部品、接続導体、電極端子等を振動、衝撃、酸化等から保
護し、品質のより安定した電子装置を構成できるという効果がある。
By constructing an electronic device in which the space formed by the substrate and the frame-shaped side wall is hermetically sealed with resin, the electronic components, connection conductors, electrode terminals, etc. accommodated in the space are protected from vibration, impact, oxidation, etc. In addition, there is an effect that an electronic device with more stable quality can be configured.
以下、本発明の実施の形態を図面に基づいて詳細に説明する。
なお、本実施形態では電子装置の一例として圧電発振器を例に挙げて説明する。
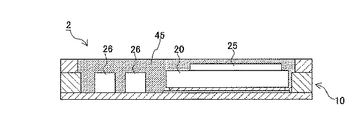
図1は、本発明の一実施形態に係る圧電発振器の内部構成を示した概略図であり、図1
(a)は平面図、図1(b)はQ−Qにおける断面図、図1(c)は左半分が側面図、右
半分がR−Rにおける断面図の合成図である。また図2は本実施形態の圧電発振器の外部
構成を示した概略図であり、図2(a)は側面図、図2(b)は底面図である。
本実施の形態の圧電発振器1は、気密容器として、セラミックを積層した積層セラミッ
クパッケージ(以下、単に「パッケージ」と称する)10を備えている。パッケージ10は
、基板11と、この基板11上に接合される第1の枠状側壁13と、第1の枠状側壁13
上に接合される第2の枠状側壁15とからなる。第2の枠状側壁15の上面15bには、
金属製(コバール材)のシールリング18が接合されている。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
In the present embodiment, a piezoelectric oscillator will be described as an example of an electronic device.
FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing the internal configuration of a piezoelectric oscillator according to an embodiment of the present invention.
1A is a plan view, FIG. 1B is a cross-sectional view taken along the line Q-Q, FIG. 1C is a composite view of a cross-sectional view taken along the left side of the left half and the right half of FIG. 2A and 2B are schematic views showing the external configuration of the piezoelectric oscillator of the present embodiment, in which FIG. 2A is a side view and FIG. 2B is a bottom view.
The piezoelectric oscillator 1 of the present embodiment includes a laminated ceramic package (hereinafter simply referred to as “package”) 10 in which ceramics are laminated as an airtight container. The
It consists of the 2nd frame-shaped
A metal (Kovar material)
基板11は、第1の主面(下面)11aと、第2の主面(上面)11bと、これら下面
11a及び上面11bと連続した側面11cとを有する平板状のセラミックにより構成さ
れる。基板11の側面11cには、図1(c)に示すように、その下面11aから上面1
1bに達するキャスタレーション(第1の切欠部)12が形成されている。
第1の枠状側壁13は、図1(b)に示すように、下面13a及び上面13bと連続し
た側面13cとからなり、基板11上に配置される。第1の枠状側壁13の側面13cに
は、図1(c)に示すように、下面13aから上面13bに達するキャスタレーション(
第1の切欠部)14が形成されている。
第2の枠状側壁15もまた、図1(b)に示すように、下面15a及び上面15bと連
続した側面15cとからなり、第1の枠状側壁13上に配置される。第2の枠状側壁15
の側面15cには、図1(c)に示すように、下面15aから上面15bに達するキャス
タレーション(第2の切欠部)16が形成されている。
本実施形態の圧電発振器1では、後述するように、少なくとも第2の枠状側壁15に形
成したキャスタレーション16の深さを、基板11に形成したキャスタレーション12の
深さより浅く形成した点に特徴がある。ここで、キャスタレーションの深さは、キャスタ
レーションの形状が半円筒状であれば、その半径が深さに相当する。
The
A castellation (first notch) 12 reaching 1b is formed.
As shown in FIG. 1B, the first frame-shaped
A first notch 14) is formed.
As shown in FIG. 1B, the second frame-shaped
As shown in FIG. 1C, a castellation (second notch portion) 16 reaching the upper surface 15b from the lower surface 15a is formed on the side surface 15c.
As will be described later, the piezoelectric oscillator 1 of the present embodiment is characterized in that at least the depth of the
パッケージ10の内部(空間)には、パッケージ化された圧電振動子20と各種電子部
品25、26とが収容されており、これら圧電振動子20と、各種電子部品25、26と
により、例えば電圧制御型温度補償圧電発振器を構成している。
圧電振動子20は、例えば上記図6(b)に示した圧電振動素子Xをセラミック製のパ
ッケージ内に収容して不活性ガス(N2)により気密封止したものとされ、図1(a)に
示す導体膜32上に導電性接着剤33を介して搭載されている。
また圧電振動子20のパッケージ端部には、図1(a)に示すような端子電極21a、
21bが形成されている。
電子部品26は、例えばチップコンデンサ等であり、パッケージ10内の配線導体31
、31に半田を介して実装されている。
A packaged
The
Further, a
21b is formed.
The
, 31 are mounted via solder.
電子部品25は、例えば、発振回路、温度センサー、可変容量素子、温度補償回路等を
内蔵したICである。また電子部品25は、圧電振動子20より小さいサイズとされ、パ
ッケージ10内に搭載された圧電振動子20の上面に端子電極21a、21bを避けて導
電性接着剤を介して搭載されている。
電子部品25の上面周縁部には、複数の端子電極25a、25a・・・が形成されてお
り、端子電極25aの1つがボンディングワイヤ34により端子電極21aに接続され、
端子電極25aの他の1つがボンディングワイヤ34により端子電極21bに接続されて
いる。また残りの端子電極25aがパッケージ10の段差部、つまり、第1の枠状側壁1
3の上面13bに形成されたパッド電極30にボンディングワイヤ34により接続されて
いる。
The
A plurality of
The other one of the
3 is connected to the
パッド電極30は、配線導体31、図示しない内部導体、キャスタレーション12、1
4により、図2(b)に示すパッケージ10の底面の端子電極VSS、VCO、CONT
、OUT等に導通されている。
パッケージ10の上面に形成されたシールリング18には、図示しない金属製(コバー
ル材)の蓋体40がシーム溶接されている。この際、パッケージ10の内部は、電子部品
25、26、配線導体、端子電極等の経年変化を抑えるべく不活性ガス(窒素ガスN2)
が封入されている。なお、パッケージ10の内部は真空状態にしてもよい。
このように構成された圧電発振器1では、不活性ガス雰囲気あるいは真空中で気密封止
するパッケージ10の空間内に、圧電振動素子をパッケージ(気密封止)した圧電振動子2
0を搭載することで、例えば10年から20年の長期間の使用に耐えられるように構成し
たものである。
The
4, terminal electrodes VSS, VCO, CONT on the bottom surface of the
, OUT, etc.
A metal (Kovar) lid 40 (not shown) is seam welded to the
Is enclosed. Note that the inside of the
In the piezoelectric oscillator 1 configured as described above, a
By mounting 0, for example, it is configured to withstand long-term use of 10 to 20 years.
しかしながら、このように構成した場合は、圧電発振器1のパッケージ10内にパッケ
ージ化した圧電振動子20を搭載する必要があるため、圧電振動素子だけを搭載する場合
に比べて、圧電振動子20のパッケージ分だけパッケージ10の内部空間を大きくする必
要があり、圧電発振器1の大型化を招くという問題点があった。
圧電発振器1のサイズを大型化することなく、パッケージ10の内部空間を大きくする
には、パッケージ10を構成する第1及び第2の枠状側壁13、15の肉厚を薄くするこ
とが考えられるが、この場合は、第1及び第2の枠状側壁13、15に形成したキャスタ
レーション14、16部分の肉厚、特に第2の枠状側壁15の肉厚が薄くなり、十分な強
度を確保することができなくなるおそれがあった。
However, in the case of such a configuration, since it is necessary to mount the packaged
In order to increase the internal space of the
そこで、本実施形態の圧電発振器1においては、圧電発振器1のサイズを大型化するこ
となく、パッケージ10の内部空間を確保するために、図1(c)の側面及び断面図、図
2(a)の側面図に示すように、基板11、第1の枠状側壁13に形成したキャスタレー
ション12、14の深さ(半円筒状であれはその半径)と、第2の枠状側壁15に形成し
たキャスタレーション16の深さを異ならせるようにした。つまり、本実施形態では、肉
厚が最も薄い第2の枠状側壁15のキャスタレーション16の深さを、基板11、及び第
1の枠状側壁13に形成したキャスタレーション12、14より浅くすることで、第2の
枠状側壁15を十分な強度の肉厚に保ちつつ、パッケージ10の内部空間(内部容積)を
大きくするようにした。これにより、圧電発振器1のパッケージ10を大型化することな
く、パッケージ10の内部にパッケージ化された圧電振動子20を搭載することが可能に
なる。つまり、小型で長期間に亘り電気的品質を保つことができる圧電発振器1を実現す
ることができるようになる。
Therefore, in the piezoelectric oscillator 1 of the present embodiment, in order to secure the internal space of the
図3は、本実施形態の圧電発振器のパッケージ用の積層シートを形成するときの断面図
である。この場合は、所定の大きさの複数の穴12’を空けたグリーンシートG1(基板
11となる)上に、所定の大きさの複数の穴14’と、開口部OP1とを設けたグリーン
シートG2(第1の枠状側壁13となる)を重ね、さらにその上に所定の大きさの複数の
穴16’と、開口部OP2とを設けたグリーンシートG3(第2の枠状側壁15となる)
を重ねて焼成する。このとき、グリーンシートG1の穴12’及びグリーンシートG2の
穴14’は、その内壁面12a、14aに導電材料を付着させた状態で、内部を貫通させ
ておくようにする。これは、グリーンシートG1、G2の穴12’、14’に導電材料を
充填した後、穴12’、14’内の導電材料を吸引することにより形成することができる
。
FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view when forming a laminated sheet for a package of the piezoelectric oscillator of this embodiment. In this case, a green sheet provided with a plurality of
Are fired. At this time, the
次に、メッキ液を穴12’、14’、16’を通して還流させることにより、所望とす
る内壁面12a、14aの導電材料にメッキを施すことができる。
従って、この後、B−Bにより積層したグリーンシートG1、G2、G3を分割すれば
キャスタレーション12、14、16を備えたセラミックパッケージ10が得られる。
一例として、穴12’が円筒形の場合、その直径は0.15mm、穴16’の直径は0
.08mmから0.1mm程度である。
Next, by plating the plating solution through the holes 12 ', 14', 16 ', it is possible to plate the conductive material of the desired
Therefore, after that, if the green sheets G1, G2, and G3 laminated by BB are divided, the
As an example, when the
. It is about 08 mm to 0.1 mm.
以上のように、穴12’、14’、16’の大きさを適切に選ぶことによりキャスタレ
ーション12、14、16の深さを所望の深さとすることができる。
また、キャスタレーション16のメッキも所定に位置(高さ)まで施すことが可能であ
り、パッケージ10のシールリング18に蓋体40をシーム溶接した場合に、蓋体40と
キャスタレーション16との短絡を防止することができるという利点もある。
また、穴12’、14’、16’の形状としては円筒形が一般的であるが、楕円形、矩
形等であってもよい。
As described above, the depth of the
The
Further, the shape of the holes 12 ', 14', 16 'is generally cylindrical, but may be oval, rectangular or the like.
本実施形態では、穴12’、14’の大きさを同じとし、穴16’の大きさを穴12’
、14’の大きさより小さくしているので、この場合はキャスタレーション12、14の
深さが同一で、キャスタレーション16の深さはキャスタレーション12、14の深さよ
り浅くなる。また、穴14’、16’の大きさを同じとし、穴12’の大きさより小さく
した場合は、キャスタレーション14、16の深さが同一で、キャスタレーション12の
深さより浅くなる。
いずれの場合もキャスタレーション12の深さは、従来のパッケージの深さと同じ程度
として実装基板との接合強度を維持できる程度に保つことが重要である。また、キャスタ
レーション16または14、16の深さは、パッケージの10の強度を従来と同程度の強
度を維持できる程度に保つことが重要である。
In the present embodiment, the sizes of the
In this case, the depth of the
In any case, it is important to keep the depth of the
なお、本実施形態では、グリーンシートの積層数が3層である場合を例に挙げて説明し
たが、3層に限定する必要はなく、所望とするパッケージに適した積層数でよい。
以上のように、本実施形態では、グリーンシートを分割してパッケージ10とした場合
に、基板11の側壁11cのキャスタレーション12、または基板11の側壁11cのキ
ャスタレーション12と、第1の枠状側壁14の側壁14cのキャスタレーション14の
深さを深くできるので、実装基板との接合強度を維持することができる。
また、実施形態では、第2の枠状側壁16の側壁16cのキャスタレーション16の深
さをキャスタレーション12、14より浅くすることができるので、パッケージ10の強
度を確保しつつ圧電発振器1を小型化することが可能である。
また、パッケージ10の空間に不活性ガスを注入し、蓋体にて気密封止した電子装置を
構成することにより、積層セラミックパッケージに収容された電子部品、接続導体、電極
端子等の経年変化が改善され、10年から20年の使用に耐える電子装置を構成できると
いう効果がある。
In the present embodiment, the case where the number of green sheets is three is described as an example. However, the number of green sheets is not limited to three, and may be a number suitable for a desired package.
As described above, in this embodiment, when the green sheet is divided into the
In the embodiment, since the depth of the
In addition, by injecting an inert gas into the space of the
図4は、第2の実施形態に係る圧電発振器の構成を示した断面図であり、図1、図2に
示した第1の実施形態の圧電発振器1と異なる点は、シールリング18と、金属製の蓋体
40とを除去し、パッケージ10の内部に耐湿性の樹脂45を充填した点である。
樹脂45の量としては、パッケージ10の第2の枠状側壁15の上面15b程度まで充
填する。
このように圧電発振器2のパッケージ10の空間を樹脂にて気密封止した電子装置を構
成することにより、パッケージ10に収容された電子部品、接続導体、電極端子等を振動
、衝撃、酸化等から保護し、品質のより安定した電子装置を構成できるという効果がある
。
なお、本実施形態では、基板11の側面11cに形成したキャスタレーション12と、
第1の枠状側壁13の側面13cに形成したキャスタレーション14との深さを同じとし
、肉厚が最も薄い第2の枠状側壁15の側面15cに形成したキャスタレーション16の
深さを、キャスタレーション12(14)の深さより浅くする場合を例に挙げて説明した
が、これはあくまでも一例であり、第1及び第2の枠状側壁13、15の側面13c、1
5cに形成するキャスタレーション14、16の深さを同じとし、基板11の側面11c
に形成するキャスタレーション12の深さより浅くしてもよい。
また、本実施形態では、電子装置の一例として圧電発振器を例に挙げて説明したが、こ
れはあくまでも一例であり、圧電発振器以外の電子装置にも適用可能である。
FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view showing the configuration of the piezoelectric oscillator according to the second embodiment. The difference from the piezoelectric oscillator 1 of the first embodiment shown in FIGS. The
The amount of the
Thus, by constructing an electronic device in which the space of the
In the present embodiment, a
The depth of the
The
The depth may be shallower than the depth of the
In the present embodiment, a piezoelectric oscillator has been described as an example of an electronic apparatus. However, this is merely an example, and the present invention can be applied to electronic apparatuses other than the piezoelectric oscillator.
次に、図5及び図1を用いて第1の実施形態の圧電発振器の製造方法を説明する。
先ず、パッド電極30、配線導体31、導体膜32、キャスタレーション12、14、
16等を備えた積層セラミック製のパッケージ10を用意する。
先ず、手順1として、図1に示したパッケージ10の容量用配線導体31上に、ディス
ペンサを用いて半田を塗布する。
次に、手順2として、マウント装置を用いて半田上に容量(チップコンデンサ)26を
搭載した後、次にこれを所定の温度分布のリフロー装置に通し、チップコンデンサ26を
半田で固定する。
次に、手順3として、圧電振動子20搭載用の導体膜32の中央部にディスペンサ等を
用いて、導電性接着剤33を塗布する。
次に、手順4として、導電性接着剤33上に圧電振動子20を搭載し、所定の温度で前
記導電性接着剤を乾燥、硬化させる。
次に、手順5として、圧電振動子20の端子電極21a、21bの中央寄りの端と、圧
電振動子20の長手方向の端との中央にディスペンサ等を用いて、導電性接着剤を塗布す
る。
Next, a manufacturing method of the piezoelectric oscillator according to the first embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS.
First,
A monolithic
First, as procedure 1, solder is applied onto the
Next, as
Next, as a procedure 3, a
Next, as procedure 4, the
Next, as a procedure 5, a conductive adhesive is applied to the center between the end of the
次に、手順6として、圧電振動子20上の前記導電性接着剤に電子部品(発振回路、温
度補償回路等を含むIC)25を搭載する。所定の温度(例えば150℃、0.5H)で
前記導電性接着剤を乾燥、硬化する。このとき、IC25が圧電振動子20の所定の位置
からずれないことに注意する。
次に、手順7として、圧電振動子20の端子電極21a、21bと、IC25上の所定
の端子電極25aとをボンディングワイヤ34で接続する。さらに、IC25上の所定の
端子電極25aと、パッケージ10の所定のパッド電極30とをボンディングワイヤ34
で接続する。
Next, as a
Next, as
Connect with.
次に、手順8として、パッケージ10のシールリング18にシーム溶接機等を用いて金
属製の蓋体40を溶接する。溶接後、気密性をチェックする。
次に、手順9として、蓋体40上に所定の表示をレーザーにて彫刻する。以上の工程を
経て本発明の圧電発振器が完成する。
なお、図4に示した第2の実施形態に係る圧電発振器2を製造する場合は、図4に示し
た工程手順のうち、手順8の封止工程を、樹脂45を充填する工程に変更するだけで実現
することができる。
以上のような圧電発振器の製造方法を採用することにより、小型で、電気的品質が10
年から20に使用に耐える圧電発振器を製造することが可能になる。
Next, as procedure 8, a
Next, as a
In the case of manufacturing the
By adopting the manufacturing method of the piezoelectric oscillator as described above, it is small in size and has an electrical quality of 10
It becomes possible to manufacture a piezoelectric oscillator that can be used for 20 to 20 years.
1、2…圧電発振器、10…パッケージ、11…基板、11a…第1の主面、11b…第
2の主面、11c…側面、12、14、16…キャスタレーション、12’、14’、1
6’ …穴、12a、14a、16a…内壁面、13…第1の枠状側壁、13a…上面、
13b…下面、13c…側面、15…第2の枠状側壁、15c…側面、18…シールリン
グ、20…圧電振動子、21a、21b…端子電極、25…電子部品(IC)、25a…
端子電極、26…電子部品(チップコンデンサ)、30…パッド電極、31…配線導体、
32…導体膜、33…導電性接着剤、34…ボンディングワイヤ、40…蓋体、45…樹
脂
DESCRIPTION OF
6 '... hole, 12a, 14a, 16a ... inner wall surface, 13 ... first frame-like side wall, 13a ... upper surface,
13b ... lower surface, 13c ... side surface, 15 ... second frame-like side wall, 15c ... side surface, 18 ... seal ring, 20 ... piezoelectric vibrator, 21a, 21b ... terminal electrode, 25 ... electronic component (IC), 25a ...
Terminal electrode, 26 ... electronic component (chip capacitor), 30 ... pad electrode, 31 ... wiring conductor,
32 ... Conductive film, 33 ... Conductive adhesive, 34 ... Bonding wire, 40 ... Lid, 45 ... Resin
Claims (4)
の主面から前記第2の主面に達する第1の切欠部とを有する基板と、
前記基板上に配置され、上面及び下面と連続した側面に上面から下面に達する第2の切
欠部を有する枠状側壁と、
前記基板と前記枠状側壁とからなる空間に収容された圧電振動子と、
前記基板と前記枠状側壁とからなる空間に収容された電子部品と、を備え、
前記第2の切欠部の少なくとも一部の深さが前記第1の切欠部の深さより浅いことを特
徴とする電子装置。 First and second main surfaces, side surfaces continuous with the first and second main surfaces, and the first surface on the side surfaces
A substrate having a first notch that reaches the second main surface from the main surface of
A frame-like side wall disposed on the substrate and having a second cutout portion extending from the upper surface to the lower surface on a side surface continuous with the upper surface and the lower surface;
A piezoelectric vibrator housed in a space composed of the substrate and the frame-shaped side wall;
An electronic component housed in a space composed of the substrate and the frame-shaped side wall,
An electronic device, wherein a depth of at least a part of the second notch is shallower than a depth of the first notch.
施したことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の電子装置。 2. The electronic device according to claim 1, wherein at least the first notch portion is plated out of the first notch portion and the second notch portion.
り封止したことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の電子装置。 The electronic device according to claim 1, wherein the space is filled with an inert gas or is in a vacuum state, and the space is sealed with a lid.
装置。 The electronic device according to claim 1, wherein resin is injected into the space to seal the space.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008273970A JP2010103802A (en) | 2008-10-24 | 2008-10-24 | Electronic device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008273970A JP2010103802A (en) | 2008-10-24 | 2008-10-24 | Electronic device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010103802A true JP2010103802A (en) | 2010-05-06 |
| JP2010103802A5 JP2010103802A5 (en) | 2011-12-01 |
Family
ID=42294026
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008273970A Withdrawn JP2010103802A (en) | 2008-10-24 | 2008-10-24 | Electronic device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2010103802A (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101191075B1 (en) | 2011-06-15 | 2012-10-16 | (주)에프씨아이 | Sip package and manufacturing method |
| CN103856183A (en) * | 2012-11-30 | 2014-06-11 | 精工爱普生株式会社 | Oscillator, electronic apparatus, and moving object |
| JP2015211361A (en) * | 2014-04-28 | 2015-11-24 | 日本電波工業株式会社 | Piezoelectric device |
| US10069499B2 (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2018-09-04 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Method of manufacturing oscillator, oscillator, electronic apparatus, and moving object |
| US10090843B2 (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2018-10-02 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Oscillator including first and second containers for housing resonator and semiconductor device |
| JP2018157377A (en) * | 2017-03-17 | 2018-10-04 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Oscillator, electronic apparatus, and movable body |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11214945A (en) * | 1998-01-22 | 1999-08-06 | Seiko Epson Corp | Electronic component |
| JP2003243934A (en) * | 2002-02-19 | 2003-08-29 | Toyo Commun Equip Co Ltd | Surface mount type piezoelectric oscillator, its manufacturing method and metallic die |
| JP2005191042A (en) * | 2003-12-24 | 2005-07-14 | Kyocera Corp | Wiring substrate |
| JP2006050529A (en) * | 2004-02-17 | 2006-02-16 | Seiko Epson Corp | Piezoelectric oscillator and its manufacturing method |
| JP2006067552A (en) * | 2004-07-27 | 2006-03-09 | Seiko Epson Corp | Piezoelectric oscillator, manufacturing method therefor and electronic equipment |
-
2008
- 2008-10-24 JP JP2008273970A patent/JP2010103802A/en not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11214945A (en) * | 1998-01-22 | 1999-08-06 | Seiko Epson Corp | Electronic component |
| JP2003243934A (en) * | 2002-02-19 | 2003-08-29 | Toyo Commun Equip Co Ltd | Surface mount type piezoelectric oscillator, its manufacturing method and metallic die |
| JP2005191042A (en) * | 2003-12-24 | 2005-07-14 | Kyocera Corp | Wiring substrate |
| JP2006050529A (en) * | 2004-02-17 | 2006-02-16 | Seiko Epson Corp | Piezoelectric oscillator and its manufacturing method |
| JP2006067552A (en) * | 2004-07-27 | 2006-03-09 | Seiko Epson Corp | Piezoelectric oscillator, manufacturing method therefor and electronic equipment |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101191075B1 (en) | 2011-06-15 | 2012-10-16 | (주)에프씨아이 | Sip package and manufacturing method |
| CN103856183A (en) * | 2012-11-30 | 2014-06-11 | 精工爱普生株式会社 | Oscillator, electronic apparatus, and moving object |
| US9362921B2 (en) | 2012-11-30 | 2016-06-07 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Oscillator, electronic apparatus, and moving object |
| US9432026B2 (en) | 2012-11-30 | 2016-08-30 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Oscillator, electronic apparatus, and moving object |
| CN103856183B (en) * | 2012-11-30 | 2018-04-27 | 精工爱普生株式会社 | Oscillator, electronic equipment and moving body |
| JP2015211361A (en) * | 2014-04-28 | 2015-11-24 | 日本電波工業株式会社 | Piezoelectric device |
| US10069499B2 (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2018-09-04 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Method of manufacturing oscillator, oscillator, electronic apparatus, and moving object |
| US10090843B2 (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2018-10-02 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Oscillator including first and second containers for housing resonator and semiconductor device |
| JP2018157377A (en) * | 2017-03-17 | 2018-10-04 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Oscillator, electronic apparatus, and movable body |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5339681B2 (en) | Surface mount crystal unit | |
| EP1257055A2 (en) | Piezoelectric device | |
| JP2010103802A (en) | Electronic device | |
| JP4204873B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing piezoelectric oscillator | |
| JP2003163540A (en) | Surface-mounted crystal oscillator | |
| JP2005244639A (en) | Temperature compensated crystal oscillator | |
| JP2001320240A (en) | Piezoelectric oscillator | |
| JP2005223640A (en) | Package, surface mounted piezoelectric oscillator using the same, and frequency adjusting method therefor | |
| JP2000124738A (en) | Piezoelectric oscillator and piezoelectric vibration device | |
| JP2007184965A (en) | Piezoelectric device and method of manufacturing piezoelectric device | |
| JP2007053808A (en) | Piezoelectric device and method of manufacturing piezoelectric device | |
| JP2010268439A (en) | Surface mounting crystal vibrator | |
| JP2008252467A (en) | Piezoelectric device for surface mounting | |
| JP4529623B2 (en) | Piezoelectric oscillator | |
| JP2005150786A (en) | Composite piezoelectric device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP4844659B2 (en) | Piezoelectric device | |
| JP2005253007A (en) | Temperature compensated crystal oscillator | |
| JP2017034328A (en) | Piezoelectric vibration device | |
| JP2007097040A (en) | Piezoelectric vibrator and piezoelectric oscillator | |
| JP4071889B2 (en) | Crystal oscillator | |
| JPH1075120A (en) | Crystal oscillator | |
| KR100790750B1 (en) | Crystal oscillator package | |
| JP2021002744A (en) | Piezoelectric device and method of manufacturing piezoelectric device | |
| JP2001320258A (en) | Piezoelectric vibrator and piezoelectric oscillator using the same | |
| JP2021002745A (en) | Piezoelectric device and method of manufacturing piezoelectric device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20110729 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20110729 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110819 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20111019 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20111019 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20121120 |
|
| A761 | Written withdrawal of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A761 Effective date: 20130117 |