JP2010096374A - Absorption heat pump - Google Patents
Absorption heat pump Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010096374A JP2010096374A JP2008265863A JP2008265863A JP2010096374A JP 2010096374 A JP2010096374 A JP 2010096374A JP 2008265863 A JP2008265863 A JP 2008265863A JP 2008265863 A JP2008265863 A JP 2008265863A JP 2010096374 A JP2010096374 A JP 2010096374A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- solution
- concentrated solution
- pipe
- regenerator
- pump
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 169
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 604
- 239000006096 absorbing agent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 102
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 79
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 79
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims description 219
- 239000003507 refrigerant Substances 0.000 claims description 162
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 claims description 98
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 claims description 25
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 claims description 19
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000005086 pumping Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 57
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 40
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 28
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 24
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000000498 cooling water Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 9
- 238000009795 derivation Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 8
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 8
- 239000002826 coolant Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000002745 absorbent Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000002250 absorbent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000007865 diluting Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000009897 systematic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000032258 transport Effects 0.000 description 4
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 2
- AMXOYNBUYSYVKV-UHFFFAOYSA-M lithium bromide Chemical compound [Li+].[Br-] AMXOYNBUYSYVKV-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009833 condensation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005494 condensation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001502 supplementing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002351 wastewater Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A30/00—Adapting or protecting infrastructure or their operation
- Y02A30/27—Relating to heating, ventilation or air conditioning [HVAC] technologies
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02B—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO BUILDINGS, e.g. HOUSING, HOUSE APPLIANCES OR RELATED END-USER APPLICATIONS
- Y02B30/00—Energy efficient heating, ventilation or air conditioning [HVAC]
- Y02B30/62—Absorption based systems
Abstract
Description
本発明は吸収ヒートポンプに関し、特に吸収ヒートポンプの吸収溶液の結晶防止に関する。 The present invention relates to an absorption heat pump, and more particularly to prevention of crystallization of an absorption solution of an absorption heat pump.
低温の熱源から熱を汲み上げて高温の熱源にする機器であるヒートポンプのうち、熱駆動のものとして、吸収ヒートポンプが知られている。吸収ヒートポンプは、吸収溶液が冷媒の蒸気を吸収する際に発生する吸収熱で被加熱媒体を加熱して熱を汲み上げる。吸収ヒートポンプは、吸収溶液に対して冷媒の吸収及び蒸発を適宜行わせることにより、吸収溶液の濃度及び露点温度を適宜変化させて吸収ヒートポンプサイクルを継続させている。 Among heat pumps that are devices that pump heat from a low-temperature heat source into a high-temperature heat source, an absorption heat pump is known as a heat pump. The absorption heat pump heats the medium to be heated with the absorption heat generated when the absorption solution absorbs the vapor of the refrigerant, and pumps up the heat. The absorption heat pump causes the absorption solution to appropriately absorb and evaporate the refrigerant, thereby changing the concentration of the absorption solution and the dew point temperature as appropriate to continue the absorption heat pump cycle.
吸収ヒートポンプサイクルにおいて、吸収ヒートポンプの運転中は温度が高い吸収溶液の濃度が高い部分は、そのままの濃度で温度が低下すると結晶してしまい、吸収溶液が流れなくなってしまう。このような不都合を回避するため、一般に、吸収ヒートポンプの運転を停止する際は、吸収溶液を循環させる溶液ポンプの運転を継続させて、吸収溶液の濃度が高い部分を希釈する希釈運転が行われる。吸収溶液の希釈が必要なのは、通常の停止工程における場合のみならず、停電や溶液ポンプが故障した場合でも同様である。停電の発生等があった場合でも吸収溶液を希釈する技術として、非通電時に解放する電磁弁が取り付けられた管で蒸発器の冷媒液貯留部と再生器から吸収器へ吸収溶液を搬送する管又は再生器とを接続し、溶液ポンプを運転することができなくなった場合に蒸発器の冷媒液を再生器に流入させて吸収溶液を希釈するものがある(例えば、特許文献1参照。)。
しかしながら、蒸発器の冷媒液を再生器に流入させる場合は、再生器から吸収器へ吸収溶液を搬送する管に高濃度の吸収溶液が残ってしまう。また、蒸発器の冷媒液を再生器から吸収器へ吸収溶液を搬送する管内に流入させる場合も、蒸発器内の冷媒液の量が再生器から吸収器へ吸収溶液を搬送する管内に保有される吸収溶液の量に比べて少ないので、再生器から吸収器へ吸収溶液を搬送する管内の吸収溶液を十分に希釈することができない場合があった。 However, when the refrigerant liquid of the evaporator is caused to flow into the regenerator, the high-concentration absorbing solution remains in the pipe that conveys the absorbing solution from the regenerator to the absorber. In addition, when the refrigerant liquid of the evaporator is caused to flow into the pipe that transports the absorbing solution from the regenerator to the absorber, the amount of the refrigerant liquid in the evaporator is held in the pipe that transports the absorbing solution from the regenerator to the absorber. In some cases, the absorbent solution in the tube that transports the absorbent solution from the regenerator to the absorber cannot be sufficiently diluted.
本発明は上述の課題に鑑み、吸収溶液の希釈運転が完了する前に溶液ポンプを運転することができなくなった場合でも吸収溶液が結晶することを安定的に回避することができる吸収ヒートポンプを提供することを目的とする。 In view of the above-described problems, the present invention provides an absorption heat pump that can stably avoid crystallization of an absorption solution even when the solution pump cannot be operated before the dilution operation of the absorption solution is completed. The purpose is to do.
上記目的を達成するために、本発明の第1の態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプは、例えば図1に示すように、吸収溶液Saが冷媒蒸気Veを吸収して濃度が低下した希溶液Swとなる際に発生する吸収熱で被加熱媒体Wqを加熱する吸収器10と;希溶液Swを導入し加熱して、希溶液Swから冷媒Vgを蒸発させて濃度が上昇した濃溶液Saを生成する再生器30と;希溶液Swを吸収器10から再生器30に導く希溶液ライン16と;濃溶液Saを再生器30から吸収器10に導く濃溶液ライン35であって、濃溶液Saを圧送する溶液ポンプ35pを有する濃溶液ライン35と;希溶液ライン16内の希溶液Swを濃溶液ライン35内に導く希釈管58A(58B)であって、希溶液ライン16側から濃溶液ライン35側への希溶液Swの流れを許し、濃溶液ライン35側から希溶液ライン16側への溶液ポンプ35pで圧送された濃溶液Saの流れを遮断する逆流防止手段59A(59B)を有する希釈管58A(58B)とを備える。
In order to achieve the above object, the absorption heat pump according to the first aspect of the present invention, for example, as shown in FIG. 1, the absorption solution Sa absorbs the refrigerant vapor Ve and becomes a diluted solution Sw having a reduced concentration. An absorber 10 that heats the medium Wq to be heated with absorption heat generated in the regenerator; a regenerator that generates a concentrated solution Sa having an increased concentration by introducing and heating the diluted solution Sw to evaporate the refrigerant Vg from the diluted
このように構成すると、希溶液ライン内の希溶液を濃溶液ライン内に導く希釈管であって、希溶液ライン側から濃溶液ライン側への希溶液の流れを許し、濃溶液ライン側から希溶液ライン側への溶液ポンプで圧送された濃溶液の流れを遮断する逆流防止手段を有する希釈管を備えるので、吸収溶液の希釈運転が完了する前に溶液ポンプを運転することができなくなった場合でも希溶液を濃溶液に混合させることができて濃溶液を希釈することができ、濃溶液が結晶することを安定的に回避することができる。 With this configuration, the dilution pipe guides the dilute solution in the dilute solution line into the concentrated solution line, allowing the dilute solution to flow from the dilute solution line side to the concentrated solution line side, and diluting from the concentrated solution line side. When equipped with a dilution tube with backflow prevention means that blocks the flow of concentrated solution pumped by the solution pump to the solution line side, the solution pump cannot be operated before the absorption solution dilution operation is completed However, the dilute solution can be mixed with the concentrated solution, the concentrated solution can be diluted, and the concentrated solution can be stably prevented from crystallizing.
また、本発明の第2の態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプは、例えば図1に示すように、上記本発明の第1の態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプ1において、冷媒液Vfを導入し加熱して、導入した冷媒液Vfの一部を蒸発させて吸収器10に供給する冷媒蒸気Veを生成し、導入した冷媒液Vfの残りを下部に貯留する蒸発器20と;蒸発器20の下部に貯留された冷媒液Vfを吸収器10に導く連通管28であって、吸収器10内の吸収溶液Swが蒸発器20に流入しないように構成された連通管28と;連通管28に配設された自動弁29であって、電気の供給が遮断されているときに流路を開放する自動弁29とを備え;自動弁29への電気の供給が遮断されているときには、蒸発器20の下部に貯留された冷媒液Vfが、連通管28及び吸収器10を介して希溶液ライン16に流入するように構成されている。
Further, for example, as shown in FIG. 1, the absorption heat pump according to the second aspect of the present invention is introduced in the
このように構成すると、自動弁への電気の供給が遮断されているときに、蒸発器の下部に貯留された冷媒液が、連通管及び吸収器を介して希溶液ラインに流入するので、希釈管を介して濃溶液ライン内に流入する希釈用の流体の量を、蒸発器に貯留された冷媒液を直接濃溶液ラインに供給する場合の量に比べて多くすることができて、濃溶液ラインのより広範囲にわたり希釈用の流体を行き渡らせることができる。 With this configuration, when the supply of electricity to the automatic valve is shut off, the refrigerant liquid stored in the lower part of the evaporator flows into the dilute solution line via the communication pipe and the absorber. The amount of the fluid for dilution flowing into the concentrated solution line through the pipe can be made larger than the amount when the refrigerant liquid stored in the evaporator is directly supplied to the concentrated solution line. Dilution fluid can be spread over a wider area of the line.
また、本発明の第3の態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプは、例えば図2に示すように、上記本発明の第1の態様又は第2の態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプ1(例えば図1参照)において、溶液ポンプ35pが、羽根車52pを回転させる電動機53mを収容するハウジング53を有し、吐出した流体の一部をハウジング53内に導入してハウジング53内を冷却するように構成され;希釈管58Bが、希溶液ライン16(例えば図1参照)内の希溶液Swをハウジング53内に導くように溶液ポンプ35pに接続されて構成されている。
Moreover, the absorption heat pump according to the third aspect of the present invention is a solution in the
このように構成すると、比較的流路の断面積が小さく濃溶液が留まりがちな溶液ポンプの冷却系統内の濃溶液を希溶液で確実に希釈することができる。 If comprised in this way, the concentrated solution in the cooling system of the solution pump with which the cross-sectional area of a flow path is comparatively small and a concentrated solution tends to stay can be reliably diluted with a diluted solution.
また、本発明の第4の態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプは、例えば図2、図3に示すように、上記本発明の第2の態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプにおいて、溶液ポンプ35pが、羽根車52pを回転させる電動機53mを収容するハウジング53を有し、吐出した流体の一部をハウジング53内に導入してハウジング53内を冷却するように構成され;蒸発器20の下部に貯留された冷媒液Vfをハウジング53内に導く溶液ポンプ希釈管58B’をさらに備える。
Moreover, the absorption heat pump which concerns on the 4th aspect of this invention is the absorption heat pump which concerns on the said 2nd aspect of this invention, for example, as shown to FIG. 2, FIG. 3, The
このように構成すると、比較的流路の断面積が小さく濃溶液が留まりがちな溶液ポンプの冷却系統内の濃溶液を冷媒液で確実に希釈することができる。 If comprised in this way, the concentrated solution in the cooling system of the solution pump with which the cross-sectional area of a flow path is comparatively small and a concentrated solution tends to stay can be reliably diluted with a refrigerant liquid.
また、本発明の第5の態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプは、例えば図1に示すように、上記本発明の第1の態様乃至第4の態様のいずれか1つの態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプ1において、再生器30で発生した冷媒蒸気Vgを導入し冷却し凝縮させる凝縮器40と;凝縮器40内に存在する不凝縮ガスNgを凝縮器40内から抜き出す抽気流路64、66と;抽気流路64、66を介して抜き出された不凝縮ガスNgを集める抽気タンク62と;再生器30から導出された濃溶液Saを抽気タンク62に導く抽気溶液流路65、66と;抽気タンク62内の吸収溶液Saを再生器30に導く戻り溶液流路67と;希溶液ライン16を流れる希溶液Swを抽気タンク62へ導く希溶液抽気希釈管68とを備え;濃溶液Saを抽気溶液流路65、66を介して抽気タンク62に搬送することにより凝縮器40内から抽気流路64、66を介して抽気タンク62へ不凝縮ガスNgを抜き出すように構成されている。
In addition, the absorption heat pump according to the fifth aspect of the present invention is regenerated in the
このように構成すると、濃溶液を抽気タンクに搬送することで不凝縮ガスを抽気する抽気系統内の吸収溶液を希溶液で希釈することができる。 If comprised in this way, the absorption solution in the extraction system which extracts a non-condensable gas by conveying a concentrated solution to an extraction tank can be diluted with a dilute solution.
また、本発明の第6の態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプは、例えば図3に示すように、上記本発明の第2の態様又は第4の態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプにおいて、再生器30で発生した冷媒蒸気Vgを導入し冷却し凝縮させる凝縮器40と;凝縮器40内に存在する不凝縮ガスNgを凝縮器40内から抜き出す抽気流路64、66と;抽気流路64、66を介して抜き出された不凝縮ガスNgを集める抽気タンク62と;再生器30から導出された濃溶液Saを抽気タンク62に導く抽気溶液流路65、66と;抽気タンク62内の吸収溶液Saを再生器30に導く戻り溶液流路67と;蒸発器20の下部に貯留された冷媒液Vfを抽気タンク62へ導く冷媒液抽気希釈管68Aとを備え;濃溶液Saを抽気溶液流路65、66を介して抽気タンク62に搬送することにより凝縮器40内から抽気流路64、66を介して抽気タンク62へ不凝縮ガスNgを抜き出すように構成されている。
Moreover, the absorption heat pump which concerns on the 6th aspect of this invention is the refrigerant | coolant vapor | steam which generate | occur | produced in the
このように構成すると、濃溶液を抽気タンクに搬送することで不凝縮ガスを抽気する抽気系統内の吸収溶液を冷媒液で希釈することができる。 If comprised in this way, the absorption solution in the extraction system which extracts non-condensable gas by conveying a concentrated solution to an extraction tank can be diluted with a refrigerant | coolant liquid.
また、本発明の第7の態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプは、例えば図1に示すように、上記本発明の第1の態様乃至第6の態様のいずれか1つの態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプ1において、溶液ポンプ35pで吐出された濃溶液Saが流れる方向を順方向として、溶液ポンプ35pの吐出側の濃溶液ライン35に設けられた逆流制限手段35cであって、逆方向に流れる流体の流量を溶液ポンプ35pに損傷を与えない流量に制限する逆流制限手段35cを備える。
Moreover, the absorption heat pump according to the seventh aspect of the present invention is the solution of the
このように構成すると、溶液ポンプが停止した際に吸収器と再生器との圧力差及び位置ヘッドにより生ずる濃溶液ライン内の吸収溶液の逆流によって溶液ポンプが損傷することを防ぐことができる。 If comprised in this way, when a solution pump stops, it can prevent that a solution pump is damaged by the backflow of the absorption solution in the concentrated solution line which arises by the pressure difference of an absorber and a regenerator, and a position head.
また、本発明の第8の態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプは、例えば図6に示すように、上記本発明の第1の態様乃至第7の態様のいずれか1つの態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプにおいて、濃溶液ライン35内の濃溶液Saと希溶液ライン16内の希溶液Swとで熱交換させる溶液熱交換器38であって、導入された濃溶液Sa及び希溶液Swが再生器30の下部に貯留される濃溶液Saの停止中の液位よりも高所に位置するように設けられた溶液熱交換器38を備える。
Moreover, the absorption heat pump according to the eighth aspect of the present invention is the concentrated heat solution according to any one of the first to seventh aspects of the present invention as shown in FIG. The
このように構成すると、溶液ポンプが停止した際に吸収器と再生器との圧力差及び位置ヘッドにより濃溶液ライン内の吸収溶液が逆流したときに、濃溶液が溶液熱交換器から導出されるので、溶液熱交換器内で吸収溶液が結晶することを回避することができる。 With this configuration, when the absorption pump in the concentrated solution line flows backward due to the pressure difference between the absorber and the regenerator and the position head when the solution pump is stopped, the concentrated solution is led out from the solution heat exchanger. Therefore, it is possible to avoid the absorption solution from being crystallized in the solution heat exchanger.
また、本発明の第9の態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプは、例えば図6に示すように、上記本発明の第1の態様乃至第7の態様のいずれか1つの態様に係る吸収ヒートポンプにおいて、濃溶液ライン35内の濃溶液Saと希溶液ライン16内の希溶液Swとで熱交換させる溶液熱交換器38を備え;希釈管58A’が、溶液熱交換器38よりも上流側の希溶液ライン16と溶液熱交換器38よりも下流側の濃溶液ライン35とを連絡するように接続されている。
In addition, the absorption heat pump according to the ninth aspect of the present invention is the concentrated heat pump according to any one of the first to seventh aspects of the present invention as shown in FIG. A
このように構成すると、希釈管から濃溶液ラインに合流した希溶液が再生器に向かって流れる際に濃溶液を溶液熱交換器から押し出すこととなり、溶液熱交換器内に濃溶液が滞留することを回避することができる。 With this configuration, the concentrated solution is pushed out of the solution heat exchanger when the dilute solution joined from the dilution pipe to the concentrated solution line flows toward the regenerator, and the concentrated solution stays in the solution heat exchanger. Can be avoided.
本発明によれば、希溶液ライン内の希溶液を濃溶液ライン内に導く希釈管であって、希溶液ライン側から濃溶液ライン側への希溶液の流れを許し、濃溶液ライン側から希溶液ライン側への溶液ポンプで圧送された濃溶液の流れを遮断する逆流防止手段を有する希釈管を備えるので、吸収溶液の希釈運転が完了する前に溶液ポンプを運転することができなくなった場合でも希溶液を濃溶液に混合させることができて濃溶液を希釈することができ、濃溶液が結晶することを安定的に回避することができる。 According to the present invention, a dilution pipe that guides a dilute solution in a dilute solution line into the concentrated solution line, allowing the flow of the dilute solution from the dilute solution line side to the concentrated solution line side, and diluting from the concentrated solution line side. When equipped with a dilution tube with backflow prevention means that blocks the flow of concentrated solution pumped by the solution pump to the solution line side, the solution pump cannot be operated before the absorption solution dilution operation is completed However, the dilute solution can be mixed with the concentrated solution, the concentrated solution can be diluted, and the concentrated solution can be stably prevented from crystallizing.
以下、図面を参照して本発明の実施の形態について説明する。なお、各図において互いに同一又は相当する部材には同一あるいは類似の符号を付し、重複した説明は省略する。 Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. In the drawings, the same or similar members are denoted by the same or similar reference numerals, and redundant description is omitted.
まず図1を参照して、本発明の第1の実施の形態に係る吸収ヒートポンプ1を説明する。図1は、吸収ヒートポンプ1の模式的系統図である。吸収ヒートポンプ1は、吸収ヒートポンプサイクルを行う主要構成機器である吸収器10、蒸発器20、再生器30、及び凝縮器40と、希溶液Swを吸収器10から再生器30に導く希溶液ラインとしての希溶液管16と、濃溶液Saを再生器30から吸収器10に導く濃溶液ラインとしての濃溶液管35及び溶液ポンプ35pと、希溶液管16内の希溶液Swを濃溶液管35に導く希釈管としての流路希釈管58A及び溶液ポンプ35pに導く希釈管としてのポンプ希釈管58Bと、制御装置99とを備えている。吸収ヒートポンプ1は、比較的利用価値の低い低温(例えば80℃〜90℃程度)の排温水を熱源媒体として再生器30及び蒸発器20に供給して、利用価値の高い蒸気(例えば、圧力が約0.1MPa(ゲージ圧)を超え、望ましくは0.8MPa(ゲージ圧)程度)を気液分離器80から取り出すことができるものである。
First, an
なお、以下の説明においては、吸収溶液に関し、ヒートポンプサイクル上における区別を容易にするために、性状やヒートポンプサイクル上の位置に応じて「希溶液Sw」や「濃溶液Sa」等と呼称するが、性状等を不問にするときは総称して「吸収溶液S」又は「溶液S」ということとする。同様に、冷媒に関し、ヒートポンプサイクル上における区別を容易にするために、性状やヒートポンプサイクル上の位置に応じて「蒸発器冷媒蒸気Ve」、「再生器冷媒蒸気Vg」、「冷媒液Vf」等と呼称するが、性状等を不問にするときは総称して「冷媒V」ということとする。本実施の形態では、吸収溶液S(吸収剤と冷媒Vとの混合物)としてLiBr水溶液が用いられており、冷媒Vとして水(H2O)が用いられている。また、被加熱媒体Wは、液体の被加熱媒体Wである被加熱媒体液Wq、気体の被加熱媒体である被加熱媒体蒸気Wv、被加熱媒体液Wqと被加熱媒体蒸気Wvとが混合した混合被加熱媒体Wmの総称である。本実施の形態では、被加熱媒体Wとして水(H2O)が用いられている。 In the following description, the absorption solution is referred to as “dilute solution Sw”, “concentrated solution Sa” or the like depending on the properties and the position on the heat pump cycle in order to facilitate the distinction on the heat pump cycle. When the properties are not questioned, they are collectively referred to as “absorbing solution S” or “solution S”. Similarly, in order to easily distinguish the refrigerant on the heat pump cycle, “evaporator refrigerant vapor Ve”, “regenerator refrigerant vapor Vg”, “refrigerant liquid Vf”, etc., depending on the properties and positions on the heat pump cycle. However, when the properties and the like are not asked, they are collectively referred to as “refrigerant V”. In the present embodiment, an LiBr aqueous solution is used as the absorbing solution S (a mixture of the absorbent and the refrigerant V), and water (H 2 O) is used as the refrigerant V. The heated medium W is a heated medium liquid Wq which is a liquid heated medium W, a heated medium vapor Wv which is a gaseous heated medium, and the heated medium liquid Wq and the heated medium vapor Wv are mixed. A general term for the mixed medium Wm to be heated. In the present embodiment, water (H 2 O) is used as the heating medium W.
吸収器10は、被加熱媒体Wの流路を構成する加熱管11と、濃溶液Saを散布する濃溶液散布ノズル12を内部に有している。濃溶液散布ノズル12は、散布した濃溶液Saが加熱管11に降りかかるように、加熱管11の上方に配設されている。吸収器10は、濃溶液散布ノズル12から濃溶液Saが散布され、濃溶液Saが蒸発器冷媒蒸気Veを吸収する際に吸収熱を発生させる。この吸収熱を、加熱管11を流れる被加熱媒体Wが受熱して、被加熱媒体Wが加熱されるように構成されている。吸収器10の下部には、散布された濃溶液Saが蒸発器冷媒蒸気Veを吸収して濃度が低下した希溶液Swが貯留される貯留部13が形成されている。加熱管11は、希溶液Swに没入しないように、貯留部13よりも上方に配設されている。このようにすると、加熱管11の表面に濡れ広がった濃溶液Saに蒸発器冷媒蒸気Veが吸収されるようになるため、濃溶液Saと蒸発器冷媒蒸気Veとの接触面積を大きくできると共に、発生した吸収熱が加熱管11を流れる被加熱媒体Wに速やかに伝わり、吸収能力の回復を早めることができる。貯留部13には、貯留された希溶液Swの液位を検出する吸収器液位検出器14が配設されている。
The
蒸発器20は、熱源媒体としての熱源温水hの流路を構成する熱源管21と、冷媒液Vfを散布する冷媒液散布ノズル22を内部に有している。冷媒液散布ノズル22は、散布した冷媒液Vfが熱源管21に降りかかるように、熱源管21の上方に配設されている。冷媒液散布ノズル22は、凝縮器40内の冷媒液Vfを蒸発器20に導く冷媒液管45と接続されている。蒸発器20は、冷媒液散布ノズル22から冷媒液Vfが散布され、散布された冷媒液Vfが熱源管21内を流れる熱源温水hの熱で蒸発して蒸発器冷媒蒸気Veが発生するように構成されている。蒸発器20は、散布された冷媒液Vfのうち蒸発しなかった冷媒液Vfが下部に貯留されるように構成されている。熱源管21は、典型的には、下部に貯留された冷媒液Vfに浸らないように配設されている。蒸発器20の下部には、貯留された冷媒液Vfの液位を検出する蒸発器液位検出器24が配設されている。蒸発器液位検出器24は、冷媒液管45に配設された二方弁45vと信号ケーブルで接続されており、検出した冷媒液Vfの液位に応じて蒸発器20に導入する冷媒液Vfの流量を調節することができるように構成されている。蒸発器20の底部には、貯留されている冷媒液Vfを凝縮器40に戻す冷媒液管25と、冷媒液Vfを吸収器10の貯留部13に導く連通管28が接続されている。冷媒液管25には、冷媒熱交換器48が配設されている。連通管28には、電気が供給されているときに閉となり、電気の供給が遮断されているときに開となる自動弁としての電磁弁29が配設されている。電磁弁29は、いわゆるノーマリオープンの電磁弁である。
The
吸収器10と蒸発器20とは、相互に連通するように1つの缶胴内に形成されている。吸収器10と蒸発器20とが連通することにより、蒸発器20で発生した蒸発器冷媒蒸気Veを吸収器10に供給することができるように構成されている。吸収器10と蒸発器20とは、典型的には、濃溶液散布ノズル12より上方及び冷媒液散布ノズル22より上方で連通している。また、蒸発器20は、連通管28を介して吸収器10内の吸収溶液Sが蒸発器20内に流入しないように、蒸発器20の底面が吸収器10の貯留部13の液面よりも高くなるように配設されている。換言すれば、連通管28は、吸収器10との接続部よりも蒸発器20との接続部の方が高所に位置するように構成されている。
The
再生器30は、希溶液Swを加熱する熱源媒体としての熱源温水hを内部に流す熱源管31と、希溶液Swを散布する希溶液散布ノズル32とを有している。再生器30は、散布された希溶液Swから冷媒Vが蒸発して濃度が上昇した濃溶液Saが下部に貯留されるように構成されている。再生器30では、希溶液Swが熱源温水hに加熱されることにより、濃溶液Saと再生器冷媒蒸気Vgとが生成されるように構成されている。再生器30の濃溶液Saが貯留される部分と吸収器10の濃溶液散布ノズル12とは、濃溶液Saを流す濃溶液管35で接続されている。濃溶液管35には、再生器30の濃溶液Saを吸収器10に圧送する溶液ポンプ35pが配設されている。溶液ポンプ35pは、吸収器液位検出器14と信号ケーブルで接続されたインバータ35vを有しており、吸収器液位検出器14が検出する液位に応じて回転速度が調節されて吸収器10に圧送する濃溶液Saの流量を調節することができるように構成されている。希溶液散布ノズル32と吸収器10の貯留部13とは希溶液Swを流す希溶液管16で接続されている。濃溶液管35及び希溶液管16には、濃溶液Saと希溶液Swとの間で熱交換を行わせる溶液熱交換器38が配設されている。
The
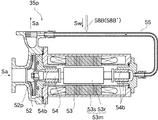
ここで図2を参照して、溶液ポンプ35pの構造について説明する。溶液ポンプ35pは、機外から供給された電力で稼働する遠心式のキャンドモータポンプであり、羽根車52pを収容するケーシング52と、電動機53mを収容するハウジング53とを有している。電動機53mは、ロータ53rと、ロータ53rを囲むように配設されたステータ53sとを有している。ロータ53rと羽根車52pとは軸受け54bに支持された軸54を介して接続されており、ロータ53rの回転により羽根車52pを回転させることができるように構成されている。また、溶液ポンプ35pは、羽根車52pの回転によって吐出された流体(本実施の形態では濃溶液Sa)の一部を、ケーシング52からハウジング53の反ケーシング52側に導く冷却用管55を有している。冷却用管55を流れる流体は、ハウジング53内に流入し、ロータ53rとステータ53sとの間を通ってケーシング52内の羽根車52p部分に到達するように構成されている。このように流体が流れることにより、電動機53m及び軸受け54bを冷却することができるように構成されている。冷却用管55には、ポンプ希釈管58Bが接続されている。
Here, the structure of the
再び図1に戻って吸収ヒートポンプ1の構成の説明を続ける。凝縮器40は、冷却媒体流路を形成する冷却水管41を有している。冷却水管41には、冷却媒体としての冷却水cが流れる。凝縮器40は、再生器30で発生した再生器冷媒蒸気Vgを導入し、これを冷却水cで冷却して凝縮させるように構成されている。冷却水管41は、再生器冷媒蒸気Vgを直接冷却することができるように、再生器冷媒蒸気Vgが凝縮した冷媒液Vfに浸らないように配設されている。凝縮器40には凝縮した冷媒液Vfを蒸発器20に送る冷媒液管45が接続されている。冷媒液管45には、冷媒液Vfを蒸発器20に圧送するための冷媒ポンプ46と、蒸発器20から凝縮器40に向かう冷媒液Vfと凝縮器40から蒸発器20に向かう冷媒液Vfとで熱交換を行わせる冷媒熱交換器48と、蒸発器20への冷媒液Vfの供給を調節する二方弁45vとが、冷媒液Vfの流れる方向にこの順で配設されている。
Returning to FIG. 1 again, the description of the configuration of the
再生器30と凝縮器40とは、相互に連通するように1つの缶胴内に形成されている。再生器30と凝縮器40とが連通することにより、再生器30で発生した再生器冷媒蒸気Vgを凝縮器40に供給することができるように構成されている。再生器30と凝縮器40とは、典型的には、希溶液散布ノズル32より上方で連通している。また、再生器30の下部と凝縮器40の下部とは、凝縮器40内の冷媒液Vfが所定の液位よりも上昇しようとしたときに冷媒液Vfを再生器30に導くオーバーフロー管44で接続されている。オーバーフロー管44は、凝縮器40側では、凝縮器40の底部を貫通して内部に立ち上げられ、端部が所定の液位に位置するように配設されている。また、再生器30の下部と凝縮器40の下部とは、ノーマリオープンの電磁弁47vが配設された連絡管47で接続されている。連絡管47は、再生器30側ではオーバーフロー管44を介して冷媒液Vfを再生器30に流入させることができるようにオーバーフロー管44に接続され、凝縮器40側ではオーバーフロー管44の立ち上がり高さよりも低い位置に管端が位置するように配設されている。吸収器10と再生器30とは、不凝縮ガス移動管15を介して連通可能に構成されている。不凝縮ガス移動管15は、吸収器10内に生じた不凝縮ガスNgを再生器30に移動させることができるように、吸収器10の気相部と再生器30の気相部とを連通している。不凝縮ガス移動管15には、連通を遮断する遮断弁15vが配設されている。また、吸収器10及び蒸発器20が再生器30及び凝縮器40よりも高所に配設されており、位置ヘッドで吸収器10内の吸収溶液Sを再生器30へ及び蒸発器20内の冷媒液Vfを凝縮器40へそれぞれ搬送可能に構成されている。
The
流路希釈管58Aは、溶液熱交換器38と希溶液散布ノズル32との間の希溶液管16と、溶液ポンプ35pと溶液熱交換器38との間の濃溶液管35とに接続されており、希溶液管16と濃溶液管35とを連絡している。流路希釈管58Aには、逆流防止手段としてのチェッキ弁59Aが設けられている。チェッキ弁59Aは、メカニカルな構造で流体の逆流を防止するように構成されており、希溶液管16から濃溶液管35への希溶液Swの流れを許し、濃溶液管35から希溶液管16への濃溶液Saの流れを遮断するように配設されている。流路希釈管58Aの接続部分と溶液熱交換器38との間の濃溶液管35には、逆流制限手段としての有孔チェッキ弁35cが設けられている。有孔チェッキ弁35cは、流体の逆流を防ぐための弁体に小孔が形成されており、所定流量の流体の逆流を許す点で一般的なチェッキ弁(逆止弁)と異なっている点以外は一般的なチェッキ弁(逆止弁)と同じ構造になっている。有孔チェッキ弁35cが逆流を許す所定の流量は、流体の逆流によって溶液ポンプ35pの羽根車52p(図2参照)が回転させられることにより溶液ポンプ35pが損傷することを回避することができる範囲内でできるだけ多い流量である。有孔チェッキ弁35cは、吸収器10側から再生器30側への吸収溶液Sが上記の逆流を許す所定の流量となるように配設されている。
The flow
ポンプ希釈管58Bは、流路希釈管58Aの接続部分よりも下流側の希溶液管16と、溶液ポンプ35pの冷却用管55(図2参照)とに接続されており、希溶液管16内の希溶液Swを溶液ポンプ35pのハウジング53(図2参照)内に導入することができるように構成されている。ポンプ希釈管58Bには、通電時に閉となり電気の供給が遮断されているときに開となる電磁弁59B(ノーマリオープンの電磁弁)が配設されている。
The
吸収ヒートポンプ1は、気液分離器80と、抽気系統60とをさらに備えている。気液分離器80は、吸収器10の加熱管11を流れて加熱された被加熱媒体Wを導入し、被加熱媒体蒸気Wvと被加熱媒体液Wqとを分離する機器である。気液分離器80には、内部に貯留する被加熱媒体液Wqの液位を検出する気液分離器液位検出器81が設けられている。気液分離器80の下部と吸収器10の加熱管11の一端とは、被加熱媒体液Wqを加熱管11に導く被加熱媒体液管82で接続されている。被加熱媒体液管82には、被加熱媒体液Wqを加熱管11に向けて圧送する被加熱媒体ポンプ83が配設されている。内部が気相部となる気液分離器80の側面と加熱管11の他端とは、加熱された被加熱媒体Wを気液分離器80に導く加熱後被加熱媒体管84で接続されている。
The
また、気液分離器80には、蒸気として系外に供給された分の被加熱媒体Wを補うための補給水Wsを系外から導入する補給水管85が接続されている。補給水管85には、気液分離器80に向けて補給水Wsを圧送する補給水ポンプ86と、逆止弁85cと、補給水Wsを温水で予熱する補給水熱交換器87Bと、希溶液Swと熱交換させて補給水Wsをさらに加熱する補給水熱交換器87Aとが、補給水Wsの流れ方向に向かってこの順に配設されている。補給水ポンプ86は、気液分離器液位検出器81と信号ケーブルで接続されており、気液分離器80内の被加熱媒体液Wqの液位に応じて発停が制御されるように構成されている。補給水熱交換器87Aは、補給水Wsと希溶液Swとを熱交換させるように、補給水管85及び溶液熱交換器38よりも上流側の希溶液管16に配設されている。また、気液分離器80には、被加熱媒体蒸気Wvを系外に供給する被加熱媒体蒸気供給管89が上部(典型的には頂部)に接続されている。
The gas-
気液分離器80は、加熱管11内で被加熱媒体液Wqの一部が蒸発して被加熱媒体液Wqと被加熱媒体蒸気Wvとが混合した混合被加熱媒体Wmを導入してもよく、被加熱媒体液Wqのまま気液分離器80に導いて減圧し一部を気化させて混合被加熱媒体Wmとしたものを気液分離させるようにしてもよい。被加熱媒体液Wqを減圧気化するには、オリフィス等の絞り手段を用いることができる。加熱管11内で被加熱媒体液Wqの一部を蒸発させるか否かは、典型的には、被加熱媒体ポンプ83及び/又は補給水ポンプ86の吐出圧力を調節することにより、加熱管11内の圧力を被加熱媒体液Wqの温度に相当する飽和圧力よりも高くするか否かによって調節することができる。
The gas-
抽気系統60は、エジェクタ61と抽気タンク62とを有している。エジェクタ61は、駆動源としての濃溶液Saを減圧して加速させるノズル(不図示)と、吸引物としての不凝縮ガスNgを導入する導入口61aとを有している。エジェクタ61の導入口61aには、抽気流路を構成する凝縮器抽気管64が接続されている。凝縮器抽気管64には、流体の流れを遮断する抽気逆流防止弁としての凝縮器抽気遮断弁64vが配設されている。凝縮器抽気遮断弁64vには、典型的にはノーマリオープンの電磁弁が用いられるが、手動の弁や、エジェクタ61側から凝縮器40側への流体の流れを遮断する逆止弁(チェッキ弁)が用いられてもよい。エジェクタ61のノズルの吸い込み側には、溶液ポンプ35pと有孔チェッキ弁35cとの間で濃溶液管35から分岐した抽気溶液流路を構成する駆動溶液供給管65が接続されている。エジェクタ61のノズルの吐出側には、駆動源の濃溶液Saと吸引物の不凝縮ガスNgとの混合流体を抽気タンク62へと導く抽気溶液流路を構成する気液混合管66が接続されている。つまり、抽気溶液流路は、再生器30から駆動溶液供給管65の接続部までの濃溶液管35と、駆動溶液供給管65と、気液混合管66とで構成されている。また、溶液ポンプ35pは、再生器30の濃溶液Saを吸収器10に圧送するポンプであると共に、再生器30の濃溶液Saを抽気タンク62に圧送する抽気溶液ポンプを兼ねている。抽気溶液ポンプとして機能する溶液ポンプ35pは、典型的には、再生器30内の吸収溶液Sを大気圧以上に昇圧できるヘッドを持つように構成されている。
The
抽気タンク62は、駆動源の濃溶液Saと吸引物の不凝縮ガスNgとを導入し、捕集した不凝縮ガスNgを溜めておくことができるタンクである。抽気タンク62は、天板に気体溜まり62cが形成されており、気体溜まり62cの上部に不凝縮ガスNgを導出する導出弁62vが設けられている。気体溜まり62cにはフロート62fが設けられており、抽気タンク62内の濃溶液Saの液位の上昇と共にフロート62fが上昇することにより、不凝縮ガスNgを機外に排出する排出口を閉塞するように構成されている。抽気タンク62の底部には、気液混合管66が接続されている。気液混合管66は、液トラップを形成するように、下に凸のU字状に配設されている。抽気タンク62の底部にはまた、抽気タンク62内の濃溶液Saを再生器30に戻す戻り溶液流路を構成する戻り溶液管67が接続されている。戻り溶液管67には、濃溶液Saの流れを遮断する戻り溶液遮断弁67v(ノーマリオープンの電磁弁)が配設されている。戻り溶液管67もまた、液トラップを形成するように、抽気タンク62の底部及び再生器30の底部よりも下方へ一旦下がるように配設されている。抽気タンク62の天板には、希溶液抽気希釈管68の一端が接続されている。希溶液抽気希釈管68の他端は、吸収器10近傍の希溶液管16に接続されており、希溶液管16を流れる希溶液Swを抽気タンク62へ流入させることができるように構成されている。希溶液抽気希釈管68には、通電時に閉となり電気の供給が遮断されているときに開となる電磁弁69(ノーマリオープンの電磁弁)が配設されている。
The
制御装置99は、吸収ヒートポンプ1の運転を制御する機器である。制御装置99は、冷媒ポンプ46及び被加熱媒体ポンプ83とそれぞれ信号ケーブルで接続されており、これらの発停や回転速度の調節を行うことができるように構成されている。これまでの説明では吸収器液位検出器14の出力を直接入力して制御されることとした溶液ポンプ35p、及び気液分離器液位検出器81の出力を直接入力して制御されることとした補給水ポンプ86も、制御装置99を介して(検出器の出力信号を一旦制御装置99に入力して)制御されることとしてもよい。また、制御装置99は、遮断弁15v、電磁弁29、電磁弁47v、電磁弁59B、凝縮器抽気遮断弁64v、戻り溶液遮断弁67v、電磁弁69にそれぞれ信号を送信して弁の開閉動作をさせることができるように構成されている。これまでの説明では蒸発器液位検出器24の出力を直接入力して制御されることとした二方弁45vも、制御装置99を介して(検出器の出力信号を一旦制御装置99に入力して)制御されることとしてもよい。
The
上述のノーマリオープンの電磁弁29、47v、59B、69、及び凝縮器抽気遮断弁64v、戻り溶液遮断弁67vは、溶液ポンプ35pに電気が供給されなくなると併せて電気の供給が遮断されるように構成されており、典型的には、溶液ポンプ35pに接続される電気ケーブルが接続された分電盤を介して機外から電気の供給を受ける(典型的には、溶液ポンプ35p及び各電磁弁29、47v、59B、69、64v、67v共に商用電源から電力の供給を受ける)ように構成されている。
The normally
引き続き図1を参照して、吸収ヒートポンプ1の作用を説明する。吸収ヒートポンプ1の被加熱媒体Wを昇温する運転中は、各電磁弁29、47v、59B、69に電気が供給されており、各電磁弁29、47v、59B、69は閉になっている。まず、冷媒側のサイクルを説明する。凝縮器40では、再生器30で蒸発した再生器冷媒蒸気Vgを受け入れて、冷却水管41を流れる冷却水cで冷却して凝縮し、冷媒液Vfとする。凝縮した冷媒液Vfは、冷媒ポンプ46で蒸発器20の冷媒液散布ノズル22に送られる。このとき、蒸発器20の下部に貯留される冷媒液Vfが所定の液位になるように、蒸発器液位検出器24の検出液位に応じて二方弁45vが制御される。冷媒液散布ノズル22に送られた冷媒液Vfは、熱源管21に向けて散布され、熱源管21内を流れる熱源温水hによって加熱され、蒸発して蒸発器冷媒蒸気Veとなる。蒸発器20で発生した蒸発器冷媒蒸気Veは、蒸発器20と連通する吸収器10へと移動する。凝縮器40内の冷媒液Vfが所定の液位を超える場合は、超える分の冷媒液Vfがオーバーフロー管44を介して再生器30に移動する。これにより、吸収ヒートポンプ1の運転中の吸収溶液Sの濃度が結晶しない濃度に維持される。
With continued reference to FIG. 1, the operation of the
次に吸収ヒートポンプ1の溶液側のサイクルを説明する。吸収器10では、濃溶液Saが濃溶液散布ノズル12から散布され、この散布された濃溶液Saが蒸発器20から移動してきた蒸発器冷媒蒸気Veを吸収する。蒸発器冷媒蒸気Veを吸収した濃溶液Saは、濃度が低下して希溶液Swとなる。吸収器10では、濃溶液Saが蒸発器冷媒蒸気Veを吸収する際に吸収熱が発生する。この吸収熱により、加熱管11を流れる被加熱媒体液Wqが加熱される。ここで、被加熱媒体蒸気Wvを取り出すための気液分離器80まわりの作用について説明する。
Next, the cycle on the solution side of the
気液分離器80には、系外から補給水Wsが補給水管85を介して導入される。補給水Wsは、補給水ポンプ86により補給水管85を圧送され、まず補給水熱交換器87Bで温度が上昇した後に、補給水熱交換器87Aで希溶液Swと熱交換してさらに温度が上昇して、気液分離器80に導入される。気液分離器80に導入された補給水Wsは、被加熱媒体液Wqとして気液分離器80の下部に貯留される。気液分離器80の下部に貯留される被加熱媒体液Wqが所定の液位になるように、補給水ポンプ86が制御される。気液分離器80の下部に貯留されている被加熱媒体液Wqは、被加熱媒体ポンプ83で吸収器10の加熱管11に送られる。加熱管11に送られた被加熱媒体液Wqは、吸収器10における上述の吸収熱により加熱される。加熱管11で加熱された被加熱媒体液Wqは、一部が蒸発して被加熱媒体蒸気Wvとなった混合被加熱媒体Wmとして、あるいは温度が上昇した被加熱媒体液Wqとして、気液分離器80に向けて加熱後被加熱媒体管84を流れる。加熱後被加熱媒体管84を、温度が上昇した被加熱媒体液Wqが流れる場合、被加熱媒体液Wqは、気液分離器80に導入される際に減圧され、一部が蒸発して被加熱媒体蒸気Wvとなった混合被加熱媒体Wmとして気液分離器80に導入される。気液分離器80に導入された混合被加熱媒体Wmは、被加熱媒体液Wqと被加熱媒体蒸気Wvとが分離される。分離された被加熱媒体液Wqは、気液分離器80の下部に貯留され、再び吸収器10の加熱管11に送られる。他方、分離された被加熱媒体蒸気Wvは、被加熱媒体蒸気供給管89に導出され、蒸気利用場所に供給される。
The gas-
再び吸収ヒートポンプ1の溶液側のサイクルの説明に戻る。吸収器10で蒸発器冷媒蒸気Veを吸収した濃溶液Saは、濃度が低下して希溶液Swとなり、貯留部13に貯留される。貯留部13内の希溶液Swは、重力及び吸収器10と再生器30との内圧の差により再生器30に向かって希溶液管16を流れ、補給水熱交換器87Aで補給水Wsと熱交換して温度が低下した後に、溶液熱交換器38で濃溶液Saと熱交換してさらに温度が低下して、再生器30に至る。このとき、溶液ポンプ35pの吐出圧力がチェッキ弁59Aにかかっているので、また、電磁弁59Bが閉になっているので、希溶液Swは流路希釈管58Aを介して及びポンプ希釈管58Bを介して濃溶液管35に流入することなく再生器30に達する。再生器30に送られた希溶液Swは、希溶液散布ノズル32から散布される。希溶液散布ノズル32から散布された希溶液Swは、熱源管31を流れる熱源温水h(本実施の形態では約80℃前後)によって加熱され、散布された希溶液Sw中の冷媒が蒸発して濃溶液Saとなり、再生器30の下部に貯留される。他方、希溶液Swから蒸発した冷媒Vは再生器冷媒蒸気Vgとして凝縮器40へと移動する。再生器30の下部に貯留された濃溶液Saは、溶液ポンプ35pにより、濃溶液管35を介して吸収器10の濃溶液散布ノズル12に圧送される。このとき、流路希釈管58Aにはチェッキ弁59Aが配設されているため流路希釈管58Aを介して濃溶液Saが希溶液管16に流入することがなく、またポンプ希釈管58Bの電磁弁59Bが閉じられているのでポンプ希釈管58Bを介して濃溶液Saが希溶液管16に流入することがない。また、吸収器10の貯留部13に貯留された希溶液Swが所定の液位になるように、吸収器液位検出器14の検出液位に応じてインバータ35vにより溶液ポンプ35pの回転速度(ひいては吐出流量)が調節される。濃溶液管35を流れる濃溶液Saは、溶液熱交換器38で希溶液Swと熱交換して温度が上昇してから吸収器10に流入し、濃溶液散布ノズル12から散布される。以降、同様のサイクルを繰り返す。
Returning to the description of the cycle on the solution side of the
上記のような吸収溶液S及び冷媒Vのサイクルを行う吸収ヒートポンプ1は、吸収ヒートポンプサイクルを行う主要構成機器である吸収器10、蒸発器20、再生器30、及び凝縮器40の内部が大気圧以下であるため大気が侵入する場合がある。大気はその中でも低圧となる再生器30及び凝縮器40に侵入しやすい。また、吸収ヒートポンプ1は、缶胴を構成する鋼材が吸収溶液と反応して水素ガスが発生する。水素ガスは吸収ヒートポンプサイクル内で比較的高温となる吸収器10で多く発生する。大気や水素ガスは、吸収ヒートポンプサイクル内及び大気圧下で凝縮しない不凝縮ガスNgである。吸収器10内の不凝縮ガスNgは、制御装置99が遮断弁15vを定期的に開くことによってより低圧の再生器30に移動する。他方、再生器30で発生した再生器冷媒蒸気Vgが凝縮器40に移動することから、全体のガスの流れは再生器30から凝縮器40に向かっているので、再生器30内の不凝縮ガスNgは凝縮器40に収集される傾向にある。不凝縮ガスNgが吸収ヒートポンプ1内に滞留すると能力が低下するため、吸収ヒートポンプ1は、以下に説明するように内部の不凝縮ガスNgを抽気することとしている。
The
凝縮器40内の不凝縮ガスNgを抽気タンク62に収集する際は、導出弁62vが閉となっており、凝縮器抽気遮断弁64v及び戻り溶液遮断弁67vが開となっている。溶液ポンプ35pの作動により、再生器30内の濃溶液Saは、濃溶液管35を流れて吸収器10に圧送されると共に、一部が分流して駆動溶液供給管65に流入する。駆動溶液供給管65に流入した濃溶液Saは、溶液ポンプ35pの圧力により、エジェクタ61を通過し、気液混合管66を流れて抽気タンク62に流入する。濃溶液Saがエジェクタ61を通過することで、導入口61aに接続された凝縮器抽気管64を介して凝縮器40内の不凝縮ガスNgがエジェクタ61に吸引される。
When collecting the non-condensable gas Ng in the
抽気タンク62に流入した濃溶液Sa及び不凝縮ガスNgは、抽気タンク62内で気液分離される。つまり、濃溶液Saと不凝縮ガスNgとは液体と気体とに分離される。抽気タンク62内で分離された濃溶液Saは、戻り溶液管67を流れて再生器30に戻される。他方、抽気タンク62内で分離された不凝縮ガスNgは、導出弁62vが閉じられており、気液混合管66及び戻り溶液管67が液シール構造になっているため、抽気タンク62内に滞留する。このようにして、不凝縮ガスNgは抽気タンク62内に収集される。なお、吸収ヒートポンプ1の停止中で、濃溶液Saの流れが停止している状態でも、気液混合管66及び戻り溶液管67が液シール構造になっているため、不凝縮ガスNgは抽気タンク62内に保持される。
The concentrated solution Sa and the non-condensable gas Ng flowing into the
抽気タンク62に収集された不凝縮ガスNgを抽気タンク62の外に排出する際は、制御装置99は、凝縮器抽気遮断弁64v及び戻り溶液遮断弁67vを閉にする。このとき、導出弁62vは閉じたままである。溶液ポンプ35pも作動している。すると、凝縮器40内の不凝縮ガスNgはエジェクタ61に吸引されないが、濃溶液Saは溶液ポンプ35pにより抽気タンク62に圧送される。これにより、抽気タンク62内の濃溶液Saの液位が上昇していき、抽気タンク62内の不凝縮ガスNgは圧縮される。そして、不凝縮ガスNgの圧力が大気圧以上となったら制御装置99は導出弁62vを開にする。導出弁62vが開になると、不凝縮ガスNgが導出弁62vを介して機外に排出される。このとき、抽気タンク62内の濃溶液Saの液位が上昇するが、濃溶液Saの液面の上昇と共に上昇するフロート62fが導出弁62vと連通する開口を塞ぐので、濃溶液Saが機外に流出することを防ぐことができる。フロート62fが導出弁62vと連通する開口を塞いだ場合は、抽気タンク62からの不凝縮ガスNgの導出も完了する。典型的には、上昇したフロート62fがスイッチ(不図示)を投入して、あるいは電極棒を利用した液面スイッチのような他の液面スイッチ(不図示)が作動して、制御装置99に信号を送信する構成としておくと、抽気タンク62からの不凝縮ガスNgの導出の完了を検出することができるので好ましい。あるいは、例えば制御装置99が導出弁62vを開にしてからの時間を計測し、あらかじめ測定しておいた不凝縮ガスNgの導出が完了するまでの時間に基づいて不凝縮ガスNgの導出の完了を検出してもよい。不凝縮ガスNgの導出が完了したら、制御装置99は、導出弁62vを閉じ、戻り溶液遮断弁67vを開放し、さらに凝縮器抽気遮断弁64vを開けて、凝縮器40内の不凝縮ガスNgの抽気タンク62への収集を再開する。
When discharging the non-condensable gas Ng collected in the
上述のように作用する吸収ヒートポンプ1は、被加熱媒体Wを昇温する運転中、吸収溶液Sが、昇温された被加熱媒体Wの温度前後の温度で濃度を変化させながら吸収器10と再生器30とを循環して吸収ヒートポンプサイクルを継続させる。そして、吸収ヒートポンプ1の運転を停止する際は、濃度が高い濃溶液Saがそのままの濃度で周囲環境温度(例えば室温)に近づいて吸収溶液Sが結晶してしまい次に起動することができなくなることを回避するために、希釈運転が行われる。吸収ヒートポンプ1の希釈運転は、典型的には、まず被加熱媒体Wの昇温を停止したときに熱源管21、31への熱源温水hの供給を停止し、電磁弁29を開にして蒸発器20内の冷媒を吸収溶液Sに戻し、溶液ポンプ35pの運転を継続することで吸収器10及び再生器30並びにこれらを連絡する希溶液管16及び濃溶液管35内の吸収溶液Sの濃度を希釈すると共にほぼ均一にすることにより行われる。このとき、電磁弁29が希釈弁として機能することになるが、希釈運転時に電磁弁29に代えて電磁弁47vを開にして、凝縮器40内の冷媒を吸収溶液Sに戻すこととしてもよい。希釈弁として電磁弁47vを用いた場合は、連絡管47の立ち上がりの高さの設定により、サイクル濃度を考慮して必要な冷媒量を戻すことができる。なお、希釈弁として電磁弁29を利用し電磁弁47vを利用しない場合は、電磁弁47vを設けなくてよい。
The
吸収ヒートポンプ1の被加熱媒体Wを昇温する運転中あるいは希釈運転中に停電が生じた場合は、吸収溶液Sが十分希釈されないままの状態で溶液ポンプ35pが停止してしまい、このままの状態で周囲環境温度(例えば室温)に近づくと吸収溶液Sが結晶してしまうこととなる。吸収ヒートポンプと類似の装置構成を持ち溶液サイクルの圧力及び露点温度が異なる吸収冷凍機では、一般に被冷却媒体である冷水の出口温度を一定にする運転をしており、蒸発器の冷媒温度はほぼ一定になっている。このような吸収冷凍機では、吸収器に導入される冷却水の温度が低下した場合には吸収器内の吸収溶液の温度が低下するので、蒸発温度と吸収器溶液温度とが関係する吸収溶液濃度が低下する。このような吸収冷凍機では、温度が低下した際に吸収溶液の濃度が結晶濃度以上になるのは、一般に冷却水温度が高く外気温度も高い夏季の短期間であり、この夏季において停電等が発生して吸収溶液の希釈が不完全な状態で停止していたとしても、温度が低下して結晶が生じるまでには一般に数時間の余裕があり復電後の再起動で結晶が避けられることが多い。これに対し、吸収ヒートポンプ1は、典型的には被加熱媒体Wの出口温度をほぼ一定にする運転をするので、被加熱媒体Wを加熱する吸収器10内の吸収溶液Sの温度がほぼ一定の高温(昇温された被加熱媒体Wの温度をやや上回る温度)の状態になっている。吸収器10に供給される蒸発器冷媒蒸気Veは蒸発器20において熱源温水hで加熱されるため、蒸発器20内はほぼ一定温度になっており、冷却水cの温度が低下した場合でも蒸発温度と吸収器溶液温度とが関係する吸収溶液濃度は全負荷状態のままほぼ一定となる。つまり、吸収ヒートポンプ1は、典型的には、年間を通じて、温度が低下した際に吸収溶液の濃度が結晶濃度以上になる高濃度サイクルとなっており、停電等が生じて溶液ポンプ35pが稼働しなくなった場合は吸収溶液Sが結晶してしまう可能性が高い。吸収ヒートポンプ1は、このような不都合を回避すべく以下に示す作用をするように構成されている。
When a power failure occurs during the operation of raising the temperature of the heated medium W of the
吸収ヒートポンプ1の被加熱媒体Wを昇温する運転中あるいは希釈運転中に停電等が生じて溶液ポンプ35pが停止した場合、吸収器10及び再生器30の内圧の差と位置ヘッドとにより、希溶液管16内の希溶液Sw及び濃溶液管35内の濃溶液Saの双方が吸収器10側から再生器30側へ向かって流れる。このとき、溶液ポンプ35pの吐出圧がチェッキ弁59Aにかからなくなっているので、希溶液管16内の希溶液Swが流路希釈管58Aを介して濃溶液管35に流入し、流入した希溶液Swが濃溶液管35内の濃溶液Saと混合して、濃溶液Saが希釈される。また、停電によりノーマリオープンの電磁弁59Bが開となり、ポンプ希釈管58Bを介して希溶液Swが溶液ポンプ35pのハウジング53内に流入して、ハウジング53内の濃溶液Saが希釈される。このように、吸収ヒートポンプ1では、濃溶液管35及び溶液ポンプ35p内の濃溶液Saが、吸収器10の貯留部13及び希溶液管16内に保有されている充分な量の希溶液Swで希釈されるため、希釈が不十分になることが抑制され、濃溶液Saが結晶することを安定的に回避することができる。
When a power failure or the like occurs during the operation of raising the temperature of the heated medium W of the
なお、濃溶液管35には、溶液ポンプ35pの損傷を防ぐために有孔チェッキ弁35cが設けられているが、有孔チェッキ弁35cには小孔が形成されているため、溶液ポンプ35pの損傷を防止しつつ濃溶液Saを逆流させることができ、有孔チェッキ弁35cよりも吸収器10側に位置する濃溶液管35内の濃溶液Saを希釈することができる。このとき、吸収器10内の気体(典型的には蒸発器冷媒蒸気Ve)が希溶液管16を介して再生器30に抜けるよりも濃溶液管35を介して再生器30に抜ける方が早くなる大きさに有孔チェッキ弁35cの小孔の口径が形成されている場合は、再生器30から濃溶液散布ノズル12までの濃溶液Sa(濃溶液系の濃溶液Sa)を一時的にすべて再生器30に戻すことができる。濃溶液系の濃溶液Saがすべて再生器30に戻ると、希溶液管16を介して再生器30に流入した希溶液Swと混合して希釈され、希釈された吸収溶液Sが再び濃溶液管35に流入して、吸収器10及び再生器30の内圧がバランスする位置で吸収溶液Sが静止する。静止した吸収溶液Sは、結晶濃度未満に希釈されていることとなる。
The
吸収ヒートポンプ1では、さらにノーマリオープンの電磁弁29が停電により開となり、蒸発器20の下部に貯留されていた冷媒液Vfが連通管28を介して貯留部13に流入し、貯留部13内の希溶液Swをさらに希釈する。貯留部13内の希溶液Swは濃溶液系の濃溶液Saを希釈するため、貯留部13内の希溶液Swの濃度が低下し及び量が増加することで、濃溶液系の濃溶液Saの希釈効果を向上させることができる。また、吸収ヒートポンプ1では、さらにノーマリオープンの電磁弁69が停電により開となり、希溶液管16内の希溶液Swが抽気タンク62に流入して、駆動溶液として導入された濃溶液Saを希釈する。駆動溶液供給管65、気液混合管66、及び戻り溶液管67は、これらを流れる濃溶液Saが吸収器10及び再生器30を循環する吸収溶液Sに比べて少量であるため口径が小さく、内部に濃溶液Saが滞留するとこの濃溶液Saが冷却されやすく結晶しやすい。吸収ヒートポンプ1は、抽気タンク62内の濃溶液Saが希釈されることにより、希釈された吸収溶液Sが、一部は気液混合管66及び駆動溶液供給管65を介して再生器30に流れ、その他は戻り溶液管67を介して再生器30に流れるため、駆動溶液供給管65、気液混合管66、及び戻り溶液管67内の吸収溶液Sを希釈することができ、吸収溶液Sの結晶を抑制することができる。
In the
次に図3を参照して、本発明の第2の実施の形態に係る吸収ヒートポンプ2を説明する。図3は、吸収ヒートポンプ2の模式的系統図である。吸収ヒートポンプ2の、吸収ヒートポンプ1(図1参照)との異なる点は、溶液ポンプ35p内に導入する流体を希溶液管16内の希溶液Swではなく蒸発器20内の冷媒液Vfとするように、ポンプ希釈管58B’の反溶液ポンプ35p側が蒸発器20の下部(典型的には底部)に接続されている。さらに、抽気タンク62に導入する流体を希溶液管16内の希溶液Swではなく蒸発器20内の冷媒液Vfとするように、希溶液抽気希釈管68に代えて冷媒液抽気希釈管68Aが蒸発器20の下部(典型的には底部)と抽気タンク62とを連絡するように設けられている。吸収ヒートポンプ2のその他の構成は、吸収ヒートポンプ1(図1参照)と同様である。吸収ヒートポンプ2では、冷媒液Vfを溶液ポンプ35p及び抽気タンク62に導入することとしているので、吸収溶液Sの流路断面積が小さく比較的結晶が生じやすいこれらの部分の吸収溶液Sを、効率よく希釈することができる。なお、吸収ヒートポンプ2では、溶液ポンプ35p及び抽気タンク62の双方に冷媒液Vfを導入することとしているが、冷媒液Vfを導入するのをいずれか一方とし、他方を吸収ヒートポンプ1(図1参照)のように希溶液Swを導入するように構成してもよい。
Next, an
次に図4を参照して、本発明の第2の実施の形態の変形例に係る吸収ヒートポンプ2Aを説明する。図4は、吸収ヒートポンプ2Aの模式的系統図である。吸収ヒートポンプ2Aの、吸収ヒートポンプ2(図3参照)との異なる点は、冷媒液Vfを貯留するのを凝縮器40に代えて蒸発器20の下部としている。そして、蒸発器20の冷媒液Vfを凝縮器40に導く冷媒液管25(図3参照)に代えて蒸発器20下部に貯留されている冷媒液Vfを冷媒液散布ノズル22に導く冷媒液管25Aが設けられ、冷媒液管25Aには蒸発器20下部の冷媒液Vfを冷媒液散布ノズル22に送液する冷媒ポンプ26が配設され、凝縮器40の冷媒液Vfを蒸発器20の冷媒液散布ノズル22に導く冷媒液管45(図3参照)に代えて凝縮器40の冷媒液Vfを蒸発器20の液溜まり部に導く冷媒液管45Aが設けられ、蒸発器液位検出器24(図3参照)に代えて凝縮器40下部の冷媒液Vfの液位を検出する凝縮器液位検出器42が設けられている。凝縮器液位検出器42と二方弁45vとは信号ケーブルで接続されており、凝縮器液位検出器42が検出した冷媒液Vfの液位に応じて蒸発器20に導入する冷媒液Vfの流量を調節することができるように構成されている。吸収ヒートポンプ2Aは、さらに、オーバーフロー管44(図1参照)に相当するオーバーフロー管27Aと、電磁弁47v(図1参照)が配設された連絡管47(図1参照)に相当する電磁弁27vが配設された連絡管27Bが、蒸発器20に設けられている。なお、吸収ヒートポンプ2(図3参照)では設けられていた冷媒熱交換器48が、吸収ヒートポンプ2Aでは設けられていない。吸収ヒートポンプ2Aのその他の構成は、吸収ヒートポンプ2(図3参照)と同様である。吸収ヒートポンプ2Aでは、希釈運転時は電磁弁27vを開け連絡管27Bを介して適量の冷媒を吸収溶液Sに戻すと共に溶液ポンプ35pで溶液系を循環混合させることができ、停電時等は電磁弁29が開となり連通管28を介して蒸発器20下部の冷媒液Vfを全量吸収溶液Sに戻して吸収溶液Sの結晶を防止することができる。なお、電磁弁29が希釈弁の機能を兼ねる場合は連絡管27B及び電磁弁27vを設けなくてもよい。
Next, an
次に図5を参照して、本発明の第3の実施の形態に係る吸収ヒートポンプ3について説明する。吸収ヒートポンプ3は、二段昇温型の吸収ヒートポンプとして構成されており、図1、3、4に示されている吸収ヒートポンプ1、2、2Aにおける吸収器10及び蒸発器20が、高温側の高温吸収器10H及び高温蒸発器20Hと、低温側の低温吸収器10L及び低温蒸発器20Lとに分かれている(図5では図4に示す吸収ヒートポンプ2Aを二段昇温型にした例を示しているが、吸収ヒートポンプ1(図1参照)あるいは吸収ヒートポンプ2(図2参照)を二段昇温型にしてもよい。)。高温吸収器10Hは低温吸収器10Lよりも内圧が高く、高温蒸発器20Hは低温蒸発器20Lよりも内圧が高い。高温吸収器10Hと高温蒸発器20Hとは、高温蒸発器20Hの冷媒Vの蒸気VeHを高温吸収器10Hに移動させることができるように上部で連通していると共に電磁弁29Hが配設された連通管28Hにより下部で連通している。低温吸収器10Lと低温蒸発器20Lとは、低温蒸発器20Lの冷媒Vの蒸気VeLを低温吸収器10Lに移動させることができるように上部で連通していると共に電磁弁29Lが配設された連通管28Lにより下部で連通している。被加熱媒体液Wqは、高温吸収器10Hで加熱される。熱源温水hは、低温蒸発器20Lに導入される。低温吸収器10Lは低温蒸発器20Lから移動してきた冷媒Vの蒸気を溶液Sが吸収する際の吸収熱で高温蒸発器20H内の冷媒液Vfを加熱して高温蒸発器20H内に冷媒Vの蒸気を発生させ、発生した高温蒸発器20H内の冷媒Vの蒸気は高温吸収器10Hに移動して高温吸収器10H内の溶液Sに吸収される際の吸収熱で被加熱媒体液Wqを加熱するように構成されている。吸収ヒートポンプ3では、低温吸収器10Lから導出されて希溶液管16を流れる希溶液Swが、流路希釈管58Aを介して濃溶液管35に流入することができ、ポンプ希釈管58Bを介して溶液ポンプ35pに流入することができるように構成されている。
Next, with reference to FIG. 5, the
図6には、吸収ヒートポンプ1、2、2A、3に適用可能な変形例の、溶液熱交換器38まわりの構成を示す。図6に示す変形例では、溶液熱交換器38内の吸収溶液Sの下端が、吸収ヒートポンプ1、2、2A、3の停止時の再生器30の吸収溶液Sの液面の停止位置よりも高所に位置するように、溶液熱交換器38が配設されている。このように構成すると、吸収ヒートポンプ1、2、2A、3の停止時に溶液熱交換器38内に吸収溶液Sが残らなくなり、溶液熱交換器38内での吸収溶液Sの結晶を避けることができる。また、機内のほとんどの吸収溶液S及び蒸発器20内の冷媒液Vfが再生器30内に集まるので、吸収溶液Sの平均濃度が低下し、再生器30内での吸収溶液Sの結晶が抑制される。
FIG. 6 shows a configuration around the
図6に示す変形例では、さらに、流路希釈管58A’が、溶液熱交換器38よりも上流側の希溶液管16と溶液熱交換器38よりも下流側の濃溶液管35とを連絡するように接続されている。換言すれば、希溶液管16と濃溶液管35とが、溶液熱交換器38よりも再生器30側ではなく、溶液熱交換器38よりも吸収器10側で連絡している。このように構成すると、流路希釈管58A’を介して濃溶液管35に流入した希溶液Swが再生器30に向かって流れる際に濃溶液Saを溶液熱交換器38から押し出すこととなり、溶液熱交換器38内に濃溶液Saが滞留することを回避することができる。また、流路希釈管58A’を介して濃溶液管35に流入した希溶液Swが濃溶液Saと共に再生器30に至るまでの距離が長くなるため、吸収溶液Sのより均一な希釈が可能となる。なお、図6に示す変形例では、上述の溶液熱交換器38内の吸収溶液Sの下端が停止時の再生器30の吸収溶液Sの液面の停止位置よりも高くなるように配置する溶液熱交換器38の配置的な特徴と、この段落で述べた溶液熱交換器38よりも吸収器10側で希溶液管16と濃溶液管35とを流路希釈管58A’を介して連絡するという流路希釈管58A’の接続に関する特徴との両方を示しているが、これらの変形例のいずれか一方を吸収ヒートポンプ1、2、2A、3に適用することとしてもよく、あるいは両方の特徴を適用してもよい。
In the modification shown in FIG. 6, the flow path dilution pipe 58 </ b> A ′ further connects the
以上の説明では、希釈管として流路希釈管58A(又は流路希釈管58A’)及びポンプ希釈管58B(又はポンプ希釈管58B’)を有していることとしたが、いずれか一方を設けることで他方の希釈管の機能を満たす場合は、他方を省略することとしてもよい。
In the above description, the
以上の説明では、流路希釈管58A(又は流路希釈管58A’)に配設された逆流防止手段がメカニカルな構造で流体の逆流を防止するチェッキ弁59Aであるとしたが、通電時に閉となり電気の供給が遮断されているときに開となる電磁弁をチェッキ弁59Aに代えて設けることとしてもよい。また、各所に設けられている電磁弁29、47v、59B、69をノーマリオープンのスプリングリターン弁に代えてもよい。
In the above description, the backflow prevention means provided in the flow
以上の説明では、逆流制限手段が、弁体に小孔が形成されたチェッキ弁(逆止弁)である有孔チェッキ弁35cであるとしたが、有孔チェッキ弁35cに代えて小孔が形成されていないチェッキ弁(逆止弁)を設け、チェッキ弁を迂回する迂回流路をチェッキ弁に並設し、この迂回流路にオリフィスを設ける構成としてもよい。この場合、オリフィスが有孔チェッキ弁35cの小孔に相当する。
In the above description, the backflow restricting means is the
以上の説明では、抽気タンク62内の圧力を大気圧以上に昇圧して不凝縮ガスNgを機外へ排出することとしたが、真空ポンプを設けて大気圧未満の抽気タンク62内の不凝縮ガスNgを真空引きすることにより機外へ排出してもよい。この場合は、凝縮器抽気遮断弁64v及び戻り溶液遮断弁67vを設けなくてもよい。また、以上の説明ではエジェクタ61により凝縮器40内の不凝縮ガスNgを吸引することとしたが、凝縮器抽気管64を抽気タンク62に直接接続すると共に駆動溶液供給管65内を流れる吸収溶液Sを冷却したうえで抽気タンク62に導入するように構成し、抽気タンク62内の圧力を低下させることで凝縮器40内の不凝縮ガスNgを抽気タンク62に導くこととしてもよい。駆動溶液供給管65内を流れる吸収溶液Sを冷却するには、例えば凝縮器40から導出された冷媒液Vfと熱交換を行わせる熱交換器を設けることにより行ってもよい。
In the above description, the pressure in the
1、2、2A、3 吸収ヒートポンプ
10 吸収器
16 希溶液管
20 蒸発器
28 連通管
29 電磁弁
30 再生器
35 濃溶液管
35c 有孔チェッキ弁
35p 溶液ポンプ
38 溶液熱交換器
40 凝縮器
52p 羽根車
53 ハウジング
53m 電動機
58A 流路希釈管
58B ポンプ希釈管
58B’ 溶液ポンプ希釈管
59A チェッキ弁
59B 電磁弁
62 抽気タンク
64 凝縮器抽気管
65 駆動溶液供給管
66 気液混合管
67 戻り溶液管
68 希溶液抽気希釈管
68A 冷媒液抽気希釈管
Ng 不凝縮ガス
S 吸収溶液
Sa 濃溶液
Sw 希溶液
Ve 蒸発器冷媒蒸気
Vg 再生器冷媒蒸気
Vf 冷媒液
Wq 被加熱媒体液
1, 2, 2A, 3
Claims (9)
前記希溶液を導入し加熱して、前記希溶液から冷媒を蒸発させて濃度が上昇した濃溶液を生成する再生器と;
前記希溶液を前記吸収器から前記再生器に導く希溶液ラインと;
前記濃溶液を前記再生器から前記吸収器に導く濃溶液ラインであって、前記濃溶液を圧送する溶液ポンプを有する濃溶液ラインと;
前記希溶液ライン内の前記希溶液を前記濃溶液ライン内に導く希釈管であって、前記希溶液ライン側から前記濃溶液ライン側への前記希溶液の流れを許し、前記濃溶液ライン側から前記希溶液ライン側への前記溶液ポンプで圧送された前記濃溶液の流れを遮断する逆流防止手段を有する希釈管とを備える;
吸収ヒートポンプ。 An absorber that heats the medium to be heated with the heat of absorption generated when the absorbing solution becomes a dilute solution having a reduced concentration by absorbing refrigerant vapor;
A regenerator that introduces and heats the dilute solution to evaporate a refrigerant from the dilute solution to produce a concentrated solution having increased concentration;
A dilute solution line leading the dilute solution from the absorber to the regenerator;
A concentrated solution line for guiding the concentrated solution from the regenerator to the absorber; a concentrated solution line having a solution pump for pumping the concentrated solution;
A dilution pipe for introducing the diluted solution in the diluted solution line into the concentrated solution line, allowing the flow of the diluted solution from the diluted solution line side to the concentrated solution line side; A dilution pipe having backflow prevention means for blocking the flow of the concentrated solution pumped by the solution pump to the dilute solution line side;
Absorption heat pump.
前記蒸発器の下部に貯留された冷媒液を前記吸収器に導く連通管であって、前記吸収器内の吸収溶液が前記蒸発器に流入しないように構成された連通管と;
前記連通管に配設された自動弁であって、電気の供給が遮断されているときに流路を開放する自動弁とを備え;
前記自動弁への電気の供給が遮断されているときには、前記蒸発器の下部に貯留された冷媒液が、前記連通管及び前記吸収器を介して前記希溶液ラインに流入するように構成された;
請求項1に記載の吸収ヒートポンプ。 An evaporator that introduces and heats a refrigerant liquid, evaporates a part of the introduced refrigerant liquid to generate the refrigerant vapor to be supplied to the absorber, and stores the remainder of the introduced refrigerant liquid in a lower part;
A communication pipe that guides the refrigerant liquid stored in the lower part of the evaporator to the absorber, the communication pipe configured to prevent the absorption solution in the absorber from flowing into the evaporator;
An automatic valve disposed in the communication pipe, wherein the automatic valve opens the flow path when the supply of electricity is interrupted;
When supply of electricity to the automatic valve is cut off, the refrigerant liquid stored in the lower part of the evaporator is configured to flow into the dilute solution line through the communication pipe and the absorber. ;
The absorption heat pump according to claim 1.
前記希釈管が、前記希溶液ライン内の前記希溶液を前記ハウジング内に導くように前記溶液ポンプに接続されて構成された;
請求項1又は請求項2に記載の吸収ヒートポンプ。 The solution pump has a housing that houses an electric motor that rotates an impeller, and is configured to introduce a part of the discharged fluid into the housing to cool the housing;
The dilution tube is configured to be connected to the solution pump to direct the dilute solution in the dilute solution line into the housing;
The absorption heat pump according to claim 1 or 2.
前記蒸発器の下部に貯留された冷媒液を前記ハウジング内に導く溶液ポンプ希釈管をさらに備える;
請求項2に記載の吸収ヒートポンプ。 The solution pump has a housing that houses an electric motor that rotates an impeller, and is configured to introduce a part of the discharged fluid into the housing to cool the housing;
A solution pump dilution pipe for guiding the refrigerant liquid stored in the lower part of the evaporator into the housing;
The absorption heat pump according to claim 2.
前記凝縮器内に存在する不凝縮ガスを前記凝縮器内から抜き出す抽気流路と;
前記抽気流路を介して抜き出された不凝縮ガスを集める抽気タンクと;
前記再生器から導出された前記濃溶液を前記抽気タンクに導く抽気溶液流路と;
前記抽気タンク内の吸収溶液を前記再生器に導く戻り溶液流路と;
前記希溶液ラインを流れる前記希溶液を前記抽気タンクへ導く希溶液抽気希釈管とを備え;
前記濃溶液を前記抽気溶液流路を介して前記抽気タンクに搬送することにより前記凝縮器内から前記抽気流路を介して前記抽気タンクへ不凝縮ガスを抜き出すように構成された;
請求項1乃至請求項4のいずれか1項に記載の吸収ヒートポンプ。 A condenser for introducing and cooling the refrigerant vapor generated in the regenerator to cool and condense;
A bleed passage for extracting non-condensable gas present in the condenser from the condenser;
An extraction tank for collecting the non-condensable gas extracted through the extraction passage;
An extraction solution channel for guiding the concentrated solution derived from the regenerator to the extraction tank;
A return solution flow path for guiding the absorbing solution in the extraction tank to the regenerator;
A dilute solution bleed dilution pipe that guides the dilute solution flowing through the dilute solution line to the bleed tank;
By transporting the concentrated solution to the extraction tank through the extraction solution flow path, the non-condensable gas is extracted from the condenser to the extraction tank through the extraction flow path;
The absorption heat pump according to any one of claims 1 to 4.
前記凝縮器内に存在する不凝縮ガスを前記凝縮器内から抜き出す抽気流路と;
前記抽気流路を介して抜き出された不凝縮ガスを集める抽気タンクと;
前記再生器から導出された前記濃溶液を前記抽気タンクに導く抽気溶液流路と;
前記抽気タンク内の吸収溶液を前記再生器に導く戻り溶液流路と;
前記蒸発器の下部に貯留された冷媒液を前記抽気タンクへ導く冷媒液抽気希釈管とを備え;
前記濃溶液を前記抽気溶液流路を介して前記抽気タンクに搬送することにより前記凝縮器内から前記抽気流路を介して前記抽気タンクへ不凝縮ガスを抜き出すように構成された;
請求項2又は請求項4に記載の吸収ヒートポンプ。 A condenser for introducing and cooling the refrigerant vapor generated in the regenerator to cool and condense;
A bleed passage for extracting non-condensable gas present in the condenser from the condenser;
An extraction tank for collecting the non-condensable gas extracted through the extraction passage;
An extraction solution channel for guiding the concentrated solution derived from the regenerator to the extraction tank;
A return solution flow path for guiding the absorbing solution in the extraction tank to the regenerator;
A refrigerant liquid extraction dilution pipe for introducing the refrigerant liquid stored in the lower part of the evaporator to the extraction tank;
By transporting the concentrated solution to the extraction tank through the extraction solution flow path, the non-condensable gas is extracted from the condenser to the extraction tank through the extraction flow path;
The absorption heat pump according to claim 2 or 4.
請求項1乃至請求項6のいずれか1項に記載の吸収ヒートポンプ。 The flow direction of the fluid flowing in the reverse direction is a reverse flow restricting means provided in the concentrated solution line on the discharge side of the solution pump, where the flow direction of the concentrated solution discharged by the solution pump is a forward direction. Comprising a backflow limiting means to limit the flow rate to a level that does not damage the pump;
The absorption heat pump according to any one of claims 1 to 6.
請求項1乃至請求項7のいずれか1項に記載の吸収ヒートポンプ。 A solution heat exchanger for exchanging heat between the concentrated solution in the concentrated solution line and the diluted solution in the diluted solution line, wherein the introduced concentrated solution and the diluted solution are stored in a lower part of the regenerator. A solution heat exchanger provided so as to be positioned higher than the liquid level when the concentrated solution is stopped;
The absorption heat pump according to any one of claims 1 to 7.
前記希釈管が、前記溶液熱交換器よりも上流側の希溶液ラインと前記溶液熱交換器よりも下流側の前記濃溶液ラインとを連絡するように接続された;
請求項1乃至請求項7のいずれか1項に記載の吸収ヒートポンプ。 A solution heat exchanger for exchanging heat between the concentrated solution in the concentrated solution line and the diluted solution in the diluted solution line;
The dilution pipe is connected to communicate the dilute solution line upstream of the solution heat exchanger and the concentrated solution line downstream of the solution heat exchanger;
The absorption heat pump according to any one of claims 1 to 7.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008265863A JP5501597B2 (en) | 2008-10-15 | 2008-10-15 | Absorption heat pump |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008265863A JP5501597B2 (en) | 2008-10-15 | 2008-10-15 | Absorption heat pump |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010096374A true JP2010096374A (en) | 2010-04-30 |
| JP5501597B2 JP5501597B2 (en) | 2014-05-21 |
Family
ID=42258189
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008265863A Active JP5501597B2 (en) | 2008-10-15 | 2008-10-15 | Absorption heat pump |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5501597B2 (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013253746A (en) * | 2012-06-07 | 2013-12-19 | Ebara Refrigeration Equipment & Systems Co Ltd | Absorption heat pump |
| CN104672397A (en) * | 2015-03-11 | 2015-06-03 | 镇江利德尔复合材料有限公司 | Highly-efficient unsaturated resin production device |
| CN108105795A (en) * | 2017-07-10 | 2018-06-01 | 昊姆(上海)节能科技有限公司 | Compression, absorption heat pump coupling fume treatment auxiliary |
| CN113566447A (en) * | 2021-08-11 | 2021-10-29 | 镇江市富来尔制冷工程技术有限公司 | Rapid crystal melting device for lithium bromide absorption type air conditioning unit and operation method |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104930747B (en) * | 2015-07-09 | 2018-02-23 | 荏原冷热系统(中国)有限公司 | A kind of second-kind absorption-type heat pump |
Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5774562A (en) * | 1980-10-28 | 1982-05-10 | Sanyo Electric Co | Absorption refrigerating machine |
| JPS5798767A (en) * | 1980-12-10 | 1982-06-19 | Hitachi Ltd | Absorption type refrigerating machine |
| JPS5831262A (en) * | 1981-08-19 | 1983-02-23 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Preventive device for crystallization of absorbing liquid of absorption heat pump |
| JPS649765U (en) * | 1987-07-08 | 1989-01-19 | ||
| JPS6418266U (en) * | 1987-02-06 | 1989-01-30 | ||
| JPH0379967A (en) * | 1989-08-22 | 1991-04-04 | Tokyo Gas Co Ltd | Double effect absorption refrigerating apparatus |
| JPH04347464A (en) * | 1991-05-24 | 1992-12-02 | Hitachi Zosen Corp | Absorption type heat pump device |
| JPH09257332A (en) * | 1996-03-21 | 1997-10-03 | Yazaki Corp | Method for preventing deposition of absorbing freezer |
| JPH11324971A (en) * | 1998-05-18 | 1999-11-26 | Ebara Corp | Canned motor pump |
| JP2002081785A (en) * | 2000-08-31 | 2002-03-22 | Ebara Corp | Absorption refrigerating machine and method for controlling the same |
| JP2007147148A (en) * | 2005-11-25 | 2007-06-14 | Ebara Corp | Absorption heat pump |
-
2008
- 2008-10-15 JP JP2008265863A patent/JP5501597B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5774562A (en) * | 1980-10-28 | 1982-05-10 | Sanyo Electric Co | Absorption refrigerating machine |
| JPS5798767A (en) * | 1980-12-10 | 1982-06-19 | Hitachi Ltd | Absorption type refrigerating machine |
| JPS5831262A (en) * | 1981-08-19 | 1983-02-23 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Preventive device for crystallization of absorbing liquid of absorption heat pump |
| JPS6418266U (en) * | 1987-02-06 | 1989-01-30 | ||
| JPS649765U (en) * | 1987-07-08 | 1989-01-19 | ||
| JPH0379967A (en) * | 1989-08-22 | 1991-04-04 | Tokyo Gas Co Ltd | Double effect absorption refrigerating apparatus |
| JPH04347464A (en) * | 1991-05-24 | 1992-12-02 | Hitachi Zosen Corp | Absorption type heat pump device |
| JPH09257332A (en) * | 1996-03-21 | 1997-10-03 | Yazaki Corp | Method for preventing deposition of absorbing freezer |
| JPH11324971A (en) * | 1998-05-18 | 1999-11-26 | Ebara Corp | Canned motor pump |
| JP2002081785A (en) * | 2000-08-31 | 2002-03-22 | Ebara Corp | Absorption refrigerating machine and method for controlling the same |
| JP2007147148A (en) * | 2005-11-25 | 2007-06-14 | Ebara Corp | Absorption heat pump |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013253746A (en) * | 2012-06-07 | 2013-12-19 | Ebara Refrigeration Equipment & Systems Co Ltd | Absorption heat pump |
| CN104672397A (en) * | 2015-03-11 | 2015-06-03 | 镇江利德尔复合材料有限公司 | Highly-efficient unsaturated resin production device |
| CN104672397B (en) * | 2015-03-11 | 2023-10-20 | 镇江利德尔复合材料有限公司 | High-efficient apparatus for producing of unsaturated resins |
| CN108105795A (en) * | 2017-07-10 | 2018-06-01 | 昊姆(上海)节能科技有限公司 | Compression, absorption heat pump coupling fume treatment auxiliary |
| CN113566447A (en) * | 2021-08-11 | 2021-10-29 | 镇江市富来尔制冷工程技术有限公司 | Rapid crystal melting device for lithium bromide absorption type air conditioning unit and operation method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5501597B2 (en) | 2014-05-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5501597B2 (en) | Absorption heat pump | |
| US5636526A (en) | Apparatus and method for automatically purging an absorption cooling system | |
| JP5923739B2 (en) | Refrigeration equipment | |
| WO2005071326A1 (en) | Absorptive chiller with evaporator protection | |
| CN113418310B (en) | Overall process anti-cavitation refrigeration system | |
| JP4542985B2 (en) | Absorption heat pump | |
| JP5816134B2 (en) | Absorption heat pump and operation method of absorption heat pump | |
| JP5395502B2 (en) | Absorption heat pump | |
| JP5543093B2 (en) | Compressive refrigerator and operation method thereof | |
| JP2010065917A (en) | Absorption heat pump | |
| JP2011027358A (en) | Heater | |
| JP6614873B2 (en) | Absorption refrigerator | |
| JP6111094B2 (en) | Absorption heat pump | |
| JP4390681B2 (en) | Absorption refrigerator | |
| JPH08121911A (en) | Absorption refrigerating machine utilizing engine exhaust heat | |
| CN106871487B (en) | Absorption heat pump | |
| CN220135761U (en) | Refrigerating system and drink equipment | |
| JP2862614B2 (en) | Bleed exhaust system for air-cooling absorption air conditioner | |
| JP3048817B2 (en) | Non-condensable gas discharge device | |
| JP4205896B2 (en) | Absorption refrigerator | |
| JP3133441B2 (en) | Bleeding device for absorption refrigerator | |
| JPS5828907B2 (en) | Absorption chiller bleed device | |
| JP3575580B2 (en) | Absorption cooling device | |
| JP2020204412A (en) | Absorption type refrigerator | |
| JPS6013017Y2 (en) | Absorption chiller with heating/cooling switching and automatic concentration adjustment mechanism |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110817 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20121019 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20121030 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20121225 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130702 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130830 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140304 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140312 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5501597 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |