JP2006128360A - Printed wiring board and its manufacturing method - Google Patents
Printed wiring board and its manufacturing method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2006128360A JP2006128360A JP2004313814A JP2004313814A JP2006128360A JP 2006128360 A JP2006128360 A JP 2006128360A JP 2004313814 A JP2004313814 A JP 2004313814A JP 2004313814 A JP2004313814 A JP 2004313814A JP 2006128360 A JP2006128360 A JP 2006128360A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- multilayer
- base substrate
- laminated
- printed wiring
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
- H05K3/22—Secondary treatment of printed circuits
- H05K3/28—Applying non-metallic protective coatings
- H05K3/281—Applying non-metallic protective coatings by means of a preformed insulating foil
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K1/00—Printed circuits
- H05K1/02—Details
- H05K1/11—Printed elements for providing electric connections to or between printed circuits
- H05K1/118—Printed elements for providing electric connections to or between printed circuits specially for flexible printed circuits, e.g. using folded portions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
- H05K3/02—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits in which the conductive material is applied to the surface of the insulating support and is thereafter removed from such areas of the surface which are not intended for current conducting or shielding
- H05K3/06—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits in which the conductive material is applied to the surface of the insulating support and is thereafter removed from such areas of the surface which are not intended for current conducting or shielding the conductive material being removed chemically or electrolytically, e.g. by photo-etch process
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
- H05K3/46—Manufacturing multilayer circuits
- H05K3/4688—Composite multilayer circuits, i.e. comprising insulating layers having different properties
- H05K3/4691—Rigid-flexible multilayer circuits comprising rigid and flexible layers, e.g. having in the bending regions only flexible layers
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Production Of Multi-Layered Print Wiring Board (AREA)
- Non-Metallic Protective Coatings For Printed Circuits (AREA)
- Structure Of Printed Boards (AREA)
- Shielding Devices Or Components To Electric Or Magnetic Fields (AREA)
Abstract
Description
この発明は、プリント配線板およびその製造方法に関し、特に、リジッド−フレックス基板等、ベース基板の部分的領域に多層部を有するプリント配線板およびその製造方法に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a printed wiring board and a manufacturing method thereof, and more particularly to a printed wiring board having a multilayer portion in a partial region of a base substrate such as a rigid-flex board and a manufacturing method thereof.
電子機器に用いれるプリント配線板として、ポリイミド等、可撓性を有する絶縁性のベースフィルムの少なくとも片面に銅箔等による導体層を有するベース基板の導体層の側の面に、その部分的領域を多層化するために、絶縁性フィルムの少なくとも片面に導体層を有する積層板を積層され、前記ベース基板の前記導体層と前記積層板の前記導体層とによってリジットな多層部が形成され、前記ベース基板の前記導体層による導通接続用のフレキシブルなケーブル部とを有するリジッド−フレックス基板が知られている(例えば、非特許文献1、2)。 As a printed wiring board used in an electronic device, a partial region on a surface of a base substrate having a conductive layer made of copper foil or the like on at least one surface of a flexible insulating base film such as polyimide. In order to make a multilayer, a laminated board having a conductor layer is laminated on at least one surface of the insulating film, and a rigid multilayer part is formed by the conductor layer of the base substrate and the conductor layer of the laminated board, A rigid-flex board having a flexible cable portion for conductive connection by the conductor layer of the base board is known (for example, Non-Patent Documents 1 and 2).
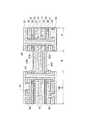
従来のリジッド−フレックス基板の具体例(6層)を、図8を参照して説明する。 A specific example (six layers) of a conventional rigid-flex board will be described with reference to FIG.
リジッド−フレックス6層基板は、断面図で見て中央(積層方向の中央)に、ベース基板として、FPC用の内層CCL(銅張積層板)100、つまり、ポリイミドフィルム101の両面に銅箔による導体パターン102、103を有する両面銅張の内層CCL100が配置され、その両面全面に各々CL(カバーレイ)110、120が配置されている。CL110、120は、ポリイミド等によるカバーフィルム111、121の片面に接着剤層112、122を有し、それぞれ接着剤層112、122によってCCL100の表面に貼り合わせられている。
The rigid-flex 6-layer substrate is made of copper foil on both sides of the FPC inner layer CCL (copper-clad laminate) 100, that is, the
さらに、それらの外側(外層側)の部分的領域(断面図で見て左右両側)には、層間接着シート(層間接着剤)131、132とプリプレグ133、134を介して両面銅張の外層CCL140、150が積層配置されている。外層CCL140、150は、各々、絶縁フィルム141、151の両面に銅箔による導体パターン142、143、152、153を形成されている。
Further, on the outer (outer layer side) partial region (on the left and right sides in the cross-sectional view), double-sided copper-clad outer layer CCL140 is provided via interlayer adhesive sheets (interlayer adhesive) 131, 132 and
これにより、内層CCL100、外層CCL140、150による多層部Aと、内層CCL100による導通接続用のフレキシブルなケーブル部Bが構成される。 Thereby, the multilayer part A by the inner layer CCL100 and the outer layers CCL140 and 150 and the flexible cable part B for conductive connection by the inner layer CCL100 are configured.
なお、多層部Aには層間導通用のめっきスルーホール135、136が形成される。そして、最外層には回路保護用の永久レジスト層(絶縁層)137、138が形成される。
In the multilayer portion A, plated through
このリジッド−フレックス6層基板は、製造プロセスは、例えば、以下の通りである。 The manufacturing process of this rigid-flex 6-layer substrate is, for example, as follows.
(1)中央に配するベース基板として、FPC用の内層CCL100の両面の回路形成(導体パターン102、103の形成)を行い、その両面にCL110、120を接着する。
(1) As a base substrate disposed in the center, circuit formation (formation of
(2)外層CCL140、150で、内層CCL100側に位置する回路(導体パターン142、152)を形成し、外層CCL140、150を層間接着シート131、132とプリプレグ133、134を介して(1)と貼り合せる。これにより、多層部Aを形成する。
(2) The
(3)多層部Aの層間回路の相互導通を取るために貫通穴を明け、銅箔表面および貫通穴内に銅めっきを行い、めっきスルーホール135、136を形成する。
(3) A through hole is made in order to establish mutual conduction between the interlayer circuits of the multilayer portion A, and copper plating is performed on the copper foil surface and the through hole to form plated through
(4)外層CCL140、150による最外層の回路形成(導体パターン143、153の形成)を行い、さらに、永久レジスト層(ソルダレジスト層)137、138を設け、リジッド−フレックス6層基板を完成する。
(4) Circuit formation of the outermost layer (formation of
なお、リジッド−フレックス6層基板の場合、プリプレグ133、134を省略し、層間接着シート131、132のみを介して、積層することもできる。また、FPC多層基板の場合には、プリプレグ133、134は省略し、外層CCL140、150として、内層CCL100と同様のFPC用のものを使用する。
In the case of a rigid-flex 6-layer substrate, the
この種の多層基板は、多層部Aとケーブル部Bを一体に設け、ケーブル部Bに可撓性を持たせることに、その特長がある。 This type of multilayer board is characterized in that the multilayer part A and the cable part B are integrally provided and the cable part B is flexible.
これらの多層基板は、上記プロセスで説明した通り、層間接着剤、プリプレグ等で積層するが、多層部Aとケーブル部Bの境界部分Cでの接着剤のしみ出しを抑える必要がある。層間接着剤は、多層部Aでは回路充填性を確保する必要があり、未硬化時の溶融粘度が低い方が好ましい。しかし、層間接着剤の溶融粘度が低すぎると、積層時に多層部Aとケーブル部Bの境界部分Cでのしみ出し量が多くなり、ケーブル部Bの可撓性を損なうことがある。 These multilayer substrates are laminated with an interlayer adhesive, a prepreg, or the like as described in the above process, but it is necessary to suppress the seepage of the adhesive at the boundary portion C between the multilayer portion A and the cable portion B. The interlayer adhesive needs to ensure circuit filling properties in the multilayer part A, and preferably has a low melt viscosity when uncured. However, if the melt viscosity of the interlayer adhesive is too low, the amount of seepage at the boundary portion C between the multilayer portion A and the cable portion B increases during lamination, and the flexibility of the cable portion B may be impaired.
これに対しては、回路充填性を確保でき、かつ樹脂流れを抑えるべく、接着剤やプリブレグ材の溶融粘度を調整したり、貼り合わせ時に使用するクッション材の組み合わせで防止する方法が一般的に取られており、このほか、境界部にダミーパターンを設けたり、境界部に樹脂流れ防止用のダム材を配置するなどしてケーブル部への樹脂の流出を防止する提案もなされている(例えば、特許文献1、2)。 For this, in order to ensure circuit fillability and suppress resin flow, it is generally possible to adjust the melt viscosity of the adhesive or prepreg material or prevent it by combining the cushion material used at the time of bonding. In addition to this, proposals have been made to prevent the outflow of resin to the cable part by providing a dummy pattern at the boundary part or arranging a dam material for preventing resin flow at the boundary part (for example, Patent Documents 1 and 2).
近年、電子機器の小型化、薄型化が進み、電子機器に搭載されるプリント基板についても一層の薄型化が求められている中で、従来の多層基板構造では、限界がある。 In recent years, electronic devices are becoming smaller and thinner, and printed circuit boards mounted on electronic devices are required to be thinner. Conventional multilayer substrate structures have limitations.
従来構造で基板を薄くするためには、使用する材料を薄くしていく必要がある。例えば、多層基板に使用されている材料としては次のものがある。 In order to make the substrate thinner with the conventional structure, it is necessary to make the material used thinner. For example, the following materials are used for the multilayer substrate.
(1)CCL(ポリイミドフィルムと回路銅箔)
ポリイミドフィルムは25μm厚さ(lmil)の材料が汎用的に使用されている。薄い基材として12.5μm(1/2mil)も使用されている。銅箔は35μm(1oz)を標準として、18μm(1/2oz)、12μm(1/3oz)、9μm(1/4oz)などがある。例えば、ポリイミドフィルムを1/2mil、銅箔を1/4ozとすれば、総厚21.5μmのCCLが実現するが、薄い銅箔は高価であり、CCLの製造も難しく、材料コストが高くなる。また、薄いため、ハンドリングが難しく、手作業では、折れ、しわによる不良が発生しやすい。
(1) CCL (polyimide film and circuit copper foil)
As the polyimide film, a material having a thickness of 25 μm (lmil) is generally used. 12.5 μm (1/2 mil) is also used as a thin substrate. The copper foil has a standard of 35 μm (1 oz) and includes 18 μm (1/2 oz), 12 μm (1/3 oz), 9 μm (1/4 oz), and the like. For example, if the polyimide film is 1/2 mil and the copper foil is 1/4 oz, a CCL with a total thickness of 21.5 μm is realized, but the thin copper foil is expensive, the CCL is difficult to manufacture, and the material cost is high. . Moreover, since it is thin, handling is difficult, and it is easy to generate | occur | produce the defect by bending and a wrinkle by manual work.
(2)CL(ポリイミドフィルと接着剤層)
CCL同様に、ボリイミドフィルムはlmilの材料が汎用的に使用されるが、薄い基材として1/2のmil材も使用される。接着剤は、任意の厚さに加工可能であり、回路間に充填するためには、回路銅箔より厚いことが望まれる。
(2) CL (polyimide fill and adhesive layer)
Like CCL, lmil material is generally used for polyimide film, but 1/2 mil material is also used as a thin substrate. The adhesive can be processed to an arbitrary thickness, and it is desirable that the adhesive is thicker than the circuit copper foil in order to fill between the circuits.
(3)ガラス繊維強化エポキシ樹脂板(GE板)
60μm程度の薄い基材があるが、中心にガラス繊維を挟んでいるため、薄くするには限界がある。
(3) Glass fiber reinforced epoxy resin board (GE board)
Although there is a thin substrate of about 60 μm, there is a limit to making it thin because a glass fiber is sandwiched in the center.
(4)層間の接着に使用する接着剤
CL用接着剤と同様、任意の厚さに加工可能であり、回路間に充填するためには、回路銅箔より厚いことが望まれる。
(4) Adhesive used for adhesion between layers Like the adhesive for CL, it can be processed to an arbitrary thickness, and is desired to be thicker than the circuit copper foil in order to fill between circuits.
(5)層間接綾するための銅めっき
接続信頼性を確保するためには、薄肉化に限界がある。限界厚さは、基板の材質や厚さ、穴の品質にも依存する。一般に、基板が薄くなると、めっき厚さを薄くすることができる。
(5) Copper plating for indirect layer traversal In order to ensure connection reliability, there is a limit to thinning. The critical thickness also depends on the material and thickness of the substrate and the quality of the hole. In general, as the substrate becomes thinner, the plating thickness can be reduced.
(6)表層の永久レジスト層
表層回路保護のため、一定の厚さが必要あり、回路厚さに依存する。
(6) Surface permanent resist layer A certain thickness is required to protect the surface layer circuit and depends on the circuit thickness.
いずれの材料も生産性やコスト、性能確保のために一定以上の厚さが要求される。また、多層部からケーブル部への樹脂の流出防止策については、樹脂の粘度を調整するダミーパターンを設ける、ダム材を設ける等、いずれの場合も通常と異なるプロセスが必要となり、コストアップの要因となる。
この発明が解決しようとする課題は、上記に鑑み、基板の構成材料を薄くするだけではなく、構造を見直して一層の薄型化を可能にすることである。 In view of the above, the problem to be solved by the present invention is not only to make the constituent material of the substrate thin, but also to review the structure to make it thinner.
この発明によるプリント配線板は、絶縁性のベースフィルムの少なくとも片面に導体層を有するベース基板の導体層の側の面に、その部分的領域を多層化するために、絶縁性フィルムの少なくとも片面に導体層を有する積層板を積層され、前記ベース基板の前記導体層と前記積層板の前記導体層とによる多層部と、前記ベース基板の前記導体層による導通接続用のケーブル部とを有するプリント配線板において、多層化のための前記積層板の前記絶縁性フィルムが前記ベース基板の前記ケーブル部にまで延在していて当該絶縁性フィルムが前記ケーブル部の前記導体層を保護被覆するカバーフィルムをなしている。 The printed wiring board according to the present invention is formed on at least one surface of the insulating film in order to multilayer the partial region on the surface of the base substrate having the conductor layer on at least one surface of the insulating base film. Printed wiring comprising a laminated board having a conductor layer, and having a multilayer part formed by the conductor layer of the base board and the conductor layer of the laminated board, and a cable part for conducting connection by the conductor layer of the base board. In the board, the insulating film of the laminated plate for multilayering extends to the cable portion of the base substrate, and the insulating film protects and covers the conductor layer of the cable portion. There is no.
この発明によるプリント配線板は、好ましくは、前記積層板の前記絶縁性フィルムは、その全面を接着剤層によって前記ベース基板の導体層の側の面に貼り合わせられている。 In the printed wiring board according to the present invention, preferably, the entire surface of the insulating film of the laminated board is bonded to the surface of the base substrate on the conductor layer side by an adhesive layer.
この発明によるプリント配線板は、好ましくは、前記ベース基板の前記ベースフィルムと前記積層板の前記絶縁性フィルムが、ともに可撓性樹脂フィルムにより構成されている。 In the printed wiring board according to the present invention, preferably, both the base film of the base substrate and the insulating film of the laminated board are made of a flexible resin film.
この発明によるプリント配線板は、好ましくは、前記多層部にプリプレグが積層されている。 In the printed wiring board according to the present invention, preferably, a prepreg is laminated on the multilayer portion.
この発明によるプリント配線板の製造方法は、絶縁性のベースフィルムの少なくとも片面に導体層を有するベース基板の導体層の側の面に、その部分的領域を多層化するために、絶縁性フィルムの少なくとも片面に導体層を有する積層板を貼り合わせ、前記ベース基板の前記導体層と前記積層板の前記導体層とによって多層部を形成し、それ以外の部分を前記ベース基板の前記導体層による導通接続用のケーブル部とする積層キュア工程を有し、前記積層板の前記絶縁性フィルムが前記ベース基板の前記ケーブル部にまで延在しており、当該絶縁性フィルムを前記積層キュア工程にて前記ケーブル部に貼り合わせ、当該絶縁性フィルムによって前記ケーブル部の前記導体層を保護被覆する。 In the printed wiring board manufacturing method according to the present invention, the insulating film is formed on a surface of the base substrate having a conductor layer on at least one side of the insulating base film. A laminated board having a conductor layer on at least one surface is bonded, a multilayer part is formed by the conductor layer of the base board and the conductor layer of the laminated board, and the other part is conducted by the conductor layer of the base board. It has a lamination curing process as a cable part for connection, the insulating film of the laminated board extends to the cable part of the base substrate, the insulating film in the lamination curing process Affixed to the cable part, the conductor layer of the cable part is protectively covered with the insulating film.
この発明によるプリント配線板は、多層部とケーブル部を一体形成したプリント配線板において、ケーブル部の保護被覆を、多層部を構成する絶縁性フィルムにより行い、ケーブル部の保護被覆をカバーレイを排除するから、カバーレイ分の材料コストを削減し、低コスト化を実現し、基板の薄型化を容易にする。 In the printed wiring board according to the present invention, in the printed wiring board in which the multilayer portion and the cable portion are integrally formed, the protective covering of the cable portion is performed by an insulating film constituting the multilayer portion, and the protective covering of the cable portion is eliminated. Therefore, the material cost for the coverlay is reduced, the cost is reduced, and the substrate can be easily made thinner.
この発明によるプリント配線板をリジッド−フレックス6層基板として適用して一つの実施形態を、図1を参照して説明する。 An embodiment in which the printed wiring board according to the present invention is applied as a rigid-flex 6-layer substrate will be described with reference to FIG.
本実施形態のリジッド−フレックス6層基板は、断面図で見て中央(積層方向の中央)に、ベース基板として、FPC用の内層CCL(銅張積層板)10、つまり、可撓性樹脂フィルムであるポリイミドフィルム(ポリイミド基材)11の両面に銅箔による導体パターン12、13を形成された両面銅張の内層CCL10を有する。
The rigid-flex 6-layer substrate of this embodiment has an inner layer CCL (copper-clad laminate) 10 for FPC as a base substrate at the center (center in the stacking direction) as viewed in a cross-sectional view, that is, a flexible resin film. The polyimide film (polyimide base material) 11 is a double-sided copper-clad inner layer CCL10 in which
内層CCL10の両面の部分的領域(断面図で見て左右両側)には、エポキシ系接着剤による層間接着シート21、22とエポキシ系のプリプレグ23、24を介して両面銅張の外層CCL30、40が積層配置されている。
In the partial areas (both left and right sides in the cross-sectional view) of the
外層CCL30、40は、多層化のための銅張積層板であり、各々、可撓性樹脂フィルムであるポリイミドフィルム(ポリイミド基材)31、41の両面に銅箔による導体パターン32、33、42、43を形成されている。
The
これにより、内層CCL10、外層CCL30、40による多層部Aと、内層CCL10による導通接続用のフレキシブルなケーブル部Bが構成される。 Thereby, the multilayer part A by the inner layer CCL10 and the outer layers CCL30 and 40 and the flexible cable part B for conductive connection by the inner layer CCL10 are configured.
多層部Aには層間導通用のめっきスルーホール25、26や表層バイア27、28が形成されている。
The multilayer portion A is formed with plated through
そして、最外層には、回路保護用の永久レジスト層(絶縁層)51、52が形成されている。 In the outermost layer, permanent resist layers (insulating layers) 51 and 52 for circuit protection are formed.
外層CCL30、40のポリイミドフィルム31、41は、ベース基板をなす内層CCL10のケーブル部Bにまで延在しており、このケーブル対応部分31B、41Bが、ケーブル部Bを含む内層CCL10の両面全面に設けられた層間接着シート21、22のケーブル対応部分21B、22Bによってケーブル部Bの表面に貼り合わせられている。
The
これにより、外層CCL30、40のポリイミドフィルム31、41が、ケーブル部Aの導体パターン(導体層)12、13を保護被覆するカバーフィルムをなす。
Thereby, the
この構造のリジッド−フレックス基板では、ケーブル部Bの導体パターンを保護被覆するためのCL(カバーレイ)が不要になり、多層部Aとケーブル部Bとに一様に積層されるCL(図8のCL110、120参照)を省略する分だけ、多層部Aを薄くすることができる。従来例を比べると、例えば、ポリイミドフィルム25μm、接着剤層25μmのCLを使用していた場合、両面で、合計100μm、多層部Aを薄くすることができる。 また、CLが不要となり、材料費のコストダウンが可能となる。 In the rigid-flex board having this structure, a CL (cover lay) for protecting and covering the conductor pattern of the cable portion B is not required, and CL is uniformly laminated on the multilayer portion A and the cable portion B (FIG. 8). The multilayer portion A can be made thinner by the amount of omission of CL110 and 120). Compared to the conventional example, for example, when CL having a polyimide film of 25 μm and an adhesive layer of 25 μm is used, the multilayer portion A can be thinned by 100 μm in total on both sides. Further, CL is not necessary, and the material cost can be reduced.
また、層間接着シート21、22は、すべて外層CCL30、40の内側に配置され、基板外部には露出しない。このため、通常の積層条件で、層間接着シート21、22のしみ出しがを抑えることができ、境界部での可撓性性が向上する。
The interlayer
プリプレグ23、24は、多層部Aの機械的強度が必要な場合(リジッド化)に使用し、必要に応じて薄くすることができる。さらには、省略することも可能である。あるいは、多層部Aの層間接着シート21、22をなくしてプリプレグ23、24だけとし、ケーブル部Bにのみポリイミドフィルム31、41を貼り付けるための層間接着シート21、22(部分21B、22Bだけ)を設けてもよい。
The
つぎに、本実施形態のリジッド−フレックス6層基板の製造プロセス例を、図2〜図7を参照して説明する。 Next, an example of a manufacturing process of the rigid-flex 6-layer substrate of the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS.
(ベース基板の製造)
図2(a)に示されているように、ポリイミドフィルム11の両面に銅箔14、15を有する両面銅張積層板19を出発材とし、図2(b)に示されているように、銅箔14、15をエッチングして導体パターン12、13を形成し、ベース基板としての内層CCL10を完成する。
(Manufacture of base substrate)
As shown in FIG. 2 (a), starting from a double-sided copper clad
(上側の多層化用の積層板の製造)
図3(a)に示されているように、ポリイミドフィルム31の両面に銅箔34、35を有する両面銅張積層板39を出発材とし、図3(b)に示されているように、下側の銅箔35をエッチングして導体パターン33を形成する。両面銅張積層板39はベース基板用の両面銅張積層板19と同等の大きさを有し、両面銅張積層板39の導体パターン33は多層化対応部分Aaにのみ形成し、ケーブル対応部分Baの銅箔35はすべて除去する。
(Manufacture of upper laminated board)
As shown in FIG. 3 (a), starting from a double-sided copper-clad
そして、図3(c)に示されているように、両面銅張積層板39の多層化対応部分Aaの導体パターン33の側に、多層化対応部分Aaの大きさに合った大きさのプリプレグ23をラミネートする。プリプレグ23は多層化対応部分Aaにのみ存在する。
Then, as shown in FIG. 3C, a prepreg having a size corresponding to the size of the multilayer corresponding portion Aa is formed on the
つぎに、図3(d)、(e)に示されているように、両面銅張積層板39のプリプレグ23の側に、両面銅張積層板39と同じ大きさ、換言すると、ベース基板用の両面銅張積層板19と同等の大きさの層間接着シート21をラミネートする。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 3D and 3E, on the side of the
なお、層間接着シート21は、内層CCL10の導体パターン12の側にラミネートしてもよい。
The interlayer
(下側の多層化用の積層板の製造)
図4(a)に示されているように、ポリイミドフィルム41の両面に銅箔44、45を有する両面銅張積層板49を出発材とし、図4(b)に示されているように、上側の銅箔44をエッチングして導体パターン42を形成する。両面銅張積層板49もベース基板用の両面銅張積層板19と同等の大きさを有し、両面銅張積層板49の導体パターン42は多層化対応部分Abにのみ形成し、ケーブル対応部分Bbの銅箔44はすべて除去する。
(Manufacture of laminated board for lower multilayer)
As shown in FIG. 4A, starting from a double-sided copper clad
そして、図4(c)に示されているように、両面銅張積層板49の多層化対応部分Abの導体パターン42の側に、多層化対応部分Abの大きさに合った大きさのプリプレグ24をラミネートする。プリプレグ24は多層化対応部分Abにのみ存在する。なお、多層化対応部分AaとAbは同じ大きさである。
Then, as shown in FIG. 4C, a prepreg having a size corresponding to the size of the multilayer corresponding part Ab is formed on the side of the
つぎに、図4(d)、(e)に示されているように、両面銅張積層板49のプリプレグ24の側に、両面銅張積層板49と同じ大きさ、つまりベース基板用の両面銅張積層板19と同等の大きさの層間接着シート22をラミネートする。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 4D and 4E, on the side of the
なお、層間接着シート22は、内層CCL10の導体パターン13の側にラミネートしてもよい。
The interlayer
(積層)
図5(a)に示されているように、内層CCL10の上側に、図3(e)の積層板38を、内層CCL10の下側に、図4(e)の積層板48を各々配置し、図5(b)に示されているように、これらを一括して積層キュアする。この積層キュアは、ホットプレス機により、積層板38、内層CCL10、積層板48の積層体を加熱、加圧し、層間接着シート21、22、プリプレグ23、24がCステージ状態まで硬化するように行う。
(Laminated)
As shown in FIG. 5A, the
これにより、内層CCL10、積層板38、48による多層部Aと、内層CCL10による導通接続用のフレキシブルなケーブル部Bとが構成される。
Thereby, the multilayer part A by the inner layer CCL10 and the
この積層キュアにより、上側の積層板38のポリイミドフィルム31(ケーブル対応部分31B)は、ケーブル部Bの部分において、層間接着シート21のケーブル対応部分21Bによって内層CCL10の上面にタイトに貼り合わせられる。また、下側の積層板48のポリイミドフィルム41(ケーブル対応部分41B)は、ケーブル部Bの部分において、層間接着シート22のケーブル対応部分22Bによって内層CCL10の下面にタイトに貼り合わせられる。
By this lamination curing, the polyimide film 31 (
つぎに、図6(c)に示されているように、多層部Aを貫通する層間導通穴61、62を明ける。また必要に応じて部分的な層間導通用の表層バイア用穴63、64の穴加工を行う。
Next, as shown in FIG. 6C, interlayer conduction holes 61 and 62 penetrating the multilayer portion A are opened. Further, drilling of the surface via
つぎに、図6(d)に示されているように、銅めっきを行い、銅めっき層65、66によって層間導通穴61、62、表層バイア用穴63、64における層間導通を得る。
Next, as shown in FIG. 6 (d), copper plating is performed to obtain interlayer conduction in the interlayer conduction holes 61 and 62 and the surface via
つぎに、図7(e)に示されているように、上側の積層板38の銅箔34、銅めっき層65をエッチングして上側の最外層の導体パターン32を形成すると共に、下側の積層板38の銅箔45、銅めっき層66をエッチングして下側の最外層の導体パターン42を形成する。これに同時に、多層部Aにおける層間導通用のめっきスルーホール25、26、表層バイア27、28が完成する。
Next, as shown in FIG. 7 (e), the
上側の積層板38の銅箔34と銅めっき層65、下側の積層板38の銅箔45と銅めっき層66は、ケーブル部Bにおいては、すべて除去される。これにより、ケーブル部Bには、ポリイミドフィルム31、41が残存し、ポリイミドフィルム31、41がケーブル部Bを保護被覆するカバーフィルムをなし、ケーブル部Bの可撓性が確保される。
The
つぎに、図7(f)に示されているように、最外層表面を永久レジスト層51、52によって被覆し、露出部分に必要な表面処理を行い、リジッド−フレックス6層基板を完成する。
Next, as shown in FIG. 7 (f), the outermost layer surface is covered with permanent resist
このような構成で作製されたリジッド−フレックス基板は、ケーブル部B両面構造の場合、CL×2枚分、薄くすることができる。 In the case of the cable part B double-sided structure, the rigid-flex board manufactured with such a configuration can be thinned by CL × 2.
下記のように作製した基板について、特性を評価した。特性評価は、ケーブル部への接着剤のしみ出し量、可撓性層間接続信頼性、耐マイグレーション性について行った。 The characteristics of the substrate produced as described below were evaluated. Characteristic evaluation was performed about the amount of the adhesive oozing out to the cable part, flexible interlayer connection reliability, and migration resistance.
可撓性の評価は、耐折性試験(JISC5016)を実施した。極率半径3mmで多層部とケーブル部の境界で折り曲げ、断線する回数を測定した。これは、比較例2の回数を1とした相対評価である。層間接続信頼性の評価は、気相ヒートショック試験を実施した(−25℃・125℃/60分サイクル×l000回)。貫通スルーホール部の導体抵抗測定で断線なきことを観察した。耐マイグレーション性の評価は、高温高湿直流電圧印加試験(85℃/85RH%/DC50V×1000時間)L/S=100μm/100μmの櫛歯電極パターン(回路総長2m)で、絶縁抵抗測定10MΩ以上とした。 For the evaluation of flexibility, a folding resistance test (JISC5016) was performed. The number of times of bending and disconnection at the boundary between the multilayer portion and the cable portion was measured with a radius of curvature of 3 mm. This is a relative evaluation in which the number of times of Comparative Example 2 is 1. For the evaluation of interlayer connection reliability, a gas phase heat shock test was performed (−25 ° C./125° C./60 minutes cycle × 1000 times). It was observed that there was no disconnection in the conductor resistance measurement of the through-hole portion. Evaluation of migration resistance is a high-temperature, high-humidity DC voltage application test (85 ° C / 85RH% / DC50V x 1000 hours) L / S = 100μm / 100μm comb-teeth electrode pattern (total circuit length 2m), insulation resistance measurement 10MΩ or more It was.
(実施例1)
構造:図1に示すリジッド−フレックス6層基板
使用した材料構成
・永久レジスト層:アルカリ現像型ドライフィルムタイプソルダレジスト(38μm厚)
・外層CCL:電解銅箔(12μm厚)、ポリイミド基材(25μm厚)
・プリプレグ:エポキシ系プリプレグ材(60μm厚)
・層間接着シート:エポキシ系接着剤(25μm厚)
・内層CCL:圧延銅箔(12μm厚)、ポリイミド基材(25μm厚)
・層間接続:銅メッキ(25μm厚)
(実施例2)
構造:図1に示すリジッド−フレックス6層基板からプリプレグ層を除いたFPC6層基板
使用した材料構成
・永久レジスト層:実施例1と同じ
・外層CCL:実施例1と同じ
・層間接着シート:エポキシ系接着剤(40μm厚)
・内層CCL:実施例1と同じ
・層間接続:実施例1と同じ
(実施例3)
構造:図1に示すリジッド−フレックス6層基板から多層部のみ層間接着剤層を抜いたリジッド−フレックス6層基板
・永久レジスト層:実施例1と同じ
・外層CCL:実施例1と同じ
・層間接着シート:実施例1と同じ
・内層CCL:実施例1と同じ
・プリプレグ:実施例1と同じ
・層間接続:実施例1と同じ
(比較例1):図8に示すジッド−フレックス6層基板
使用した材料構成
・永久レジスト層:実施例1と同じ
・外層CCL:実施例1と同じ
・プリプレグ:実施例1と同じ
・層間接着シート:実施例1と同じ
・CL:エポキシ系接着剤(25μm厚)、ポリイミド基材(25μm厚)
・内層CCL:実施例1と同じ
・層間接続:実施例1と同じ
(比較例2):図8に示すジッド−フレックス6層基板からプリプレグ層を除いたFPC6層基板
使用した材料構成
・永久レジスト層:実施例1と同じ
・外層CCL:実施例1と同じ
・層間接着シート:実施例1と同じ
・CL:実施例1と同じ
・内層CCL:実施例1と同じ
・層間接続:実施例1と同じ
実施例1〜3と比較例1、2の評価結果を表1に示す。
Example 1
Structure: Rigid-Flex 6-layer substrate shown in Fig. 1 Material structure used / Permanent resist layer: Alkali-developable dry film type solder resist (38μm thickness)
-Outer layer CCL: electrolytic copper foil (12 μm thickness), polyimide substrate (25 μm thickness)
・ Prepreg: Epoxy prepreg material (60μm thick)
・ Interlayer adhesive sheet: Epoxy adhesive (25μm thick)
Inner layer CCL: rolled copper foil (12 μm thickness), polyimide substrate (25 μm thickness)
・ Interlayer connection: Copper plating (25μm thickness)
(Example 2)
Structure: FPC 6-layer substrate obtained by removing the prepreg layer from the rigid-flex 6-layer substrate shown in FIG. 1. Material structure used: Permanent resist layer: Same as Example 1. Outer layer CCL: Same as Example 1. Interlayer adhesive sheet: Epoxy Adhesive (40μm thickness)
Inner layer CCL: Same as Example 1. Interlayer connection: Same as Example 1 (Example 3)
Structure: Rigid-flex 6-layer substrate in which the interlayer adhesive layer is removed from the rigid-flex 6-layer substrate shown in FIG. 1 only in the multilayer part. Permanent resist layer: same as Example 1. Outer layer CCL: Same as Example 1. Interlayer Adhesive sheet: Same as Example 1. Inner layer CCL: Same as Example 1. Prepreg: Same as Example 1. Interlayer connection: Same as Example 1 (Comparative Example 1): Gid-Flex 6-layer substrate shown in FIG. Material composition used: Permanent resist layer: Same as Example 1. Outer layer CCL: Same as Example 1. Prepreg: Same as Example 1. Interlayer adhesive sheet: Same as Example 1. CL: Epoxy adhesive (25 μm Thickness), polyimide substrate (25 μm thickness)
Inner layer CCL: Same as Example 1 Interlayer connection: Same as Example 1 (Comparative Example 2): FPC 6-layer substrate obtained by removing the prepreg layer from the Gid-Flex 6-layer substrate shown in FIG. 8 Material composition used Permanent resist Layer: Same as Example 1. Outer layer CCL: Same as Example 1. Interlayer adhesive sheet: Same as Example 1. CL: Same as Example 1. Inner layer CCL: Same as Example 1. Interlayer connection: Example 1 Same as
Table 1 shows the evaluation results of Examples 1 to 3 and Comparative Examples 1 and 2.
表1から明らかなように、実施例1〜3では、比較例1、2に比して基板厚さ(多層部の厚さ)が薄くなり、ケーブル部への接着剤のしみ出しがなくなり、多層部とケーブル部の境界で折り曲げ性(可撓性)が改善された。層間接続信頼性と耐マイグーション性については、実施例1〜3と比較例1、2とで、同等の性能を得られた。 As is apparent from Table 1, in Examples 1 to 3, the substrate thickness (thickness of the multilayer part) is reduced as compared with Comparative Examples 1 and 2, and no bleeding of the adhesive to the cable part occurs. Bendability (flexibility) was improved at the boundary between the multilayer part and the cable part. About interlayer connection reliability and migration resistance, the performance equivalent in Examples 1-3 and Comparative Examples 1 and 2 was acquired.
10 内層CCL
11 ポリイミドフィルム
12、13 導体パターン
14、15 銅箔
19 両面銅張積層板
21、22 層間接着シート
23、24 プリプレグ
25、26 めっきスルーホール
27、28 表層バイア
30 外層CCL
31 ポリイミドフィルム
32、33 導体パターン
34、35 銅箔
38 積層板
39 両面銅張積層板
40 外層CCL
41 ポリイミドフィルム
42、43 導体パターン
44、45 銅箔
48 積層板
49 両面銅張積層板
51、52 永久レジスト層
61、62 層間導通穴
63、64 表層バイア用穴
65、66 銅めっき層
10 Inner layer CCL
DESCRIPTION OF
31
41
Claims (5)
多層化のための前記積層板の前記絶縁性フィルムが前記ベース基板の前記ケーブル部にまで延在していて当該絶縁性フィルムが前記ケーブル部の前記導体層を保護被覆するカバーフィルムをなしているプリント配線板。 Laminate a laminated board having a conductor layer on at least one side of the insulating film in order to multilayer the partial area on the surface of the base substrate having the conductor layer on at least one side of the insulating base film. And a printed wiring board having a multilayer portion formed by the conductive layer of the base substrate and the conductive layer of the laminated plate, and a cable portion for conductive connection by the conductive layer of the base substrate.
The insulating film of the laminated plate for multilayering extends to the cable portion of the base substrate, and the insulating film forms a cover film that covers the conductor layer of the cable portion. Printed wiring board.
前記積層板の前記絶縁性フィルムが前記ベース基板の前記ケーブル部にまで延在しており、当該絶縁性フィルムを前記積層キュア工程にて前記ケーブル部に貼り合わせ、当該絶縁性フィルムによって前記ケーブル部の前記導体層を保護被覆する構造とするプリント配線板の製造方法。 A laminated board having a conductor layer on at least one side of the insulating film is pasted on the surface of the base substrate having the conductor layer on at least one side of the insulating base film in order to make the partial area multilayer. In addition, a multilayer curing step is performed in which a multilayer portion is formed by the conductor layer of the base substrate and the conductor layer of the laminate, and the other portion is a cable portion for conducting connection by the conductor layer of the base substrate. Have
The insulating film of the laminated plate extends to the cable portion of the base substrate, the insulating film is bonded to the cable portion in the laminated curing step, and the cable portion is bonded to the cable portion by the insulating film. A method of manufacturing a printed wiring board having a structure in which the conductor layer is covered with a protective coating.
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004313814A JP2006128360A (en) | 2004-10-28 | 2004-10-28 | Printed wiring board and its manufacturing method |
| TW094134841A TW200631483A (en) | 2004-10-28 | 2005-10-05 | Printed wiring board and manufacturing method thereof |
| KR1020050101764A KR100742679B1 (en) | 2004-10-28 | 2005-10-27 | Printed wiring board and production thereof |
| CNA200510118461XA CN1767720A (en) | 2004-10-28 | 2005-10-28 | Printing wiring board and its production method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004313814A JP2006128360A (en) | 2004-10-28 | 2004-10-28 | Printed wiring board and its manufacturing method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006128360A true JP2006128360A (en) | 2006-05-18 |
Family
ID=36722754
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004313814A Pending JP2006128360A (en) | 2004-10-28 | 2004-10-28 | Printed wiring board and its manufacturing method |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2006128360A (en) |
| KR (1) | KR100742679B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN1767720A (en) |
| TW (1) | TW200631483A (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2009113202A1 (en) | 2008-03-10 | 2009-09-17 | イビデン株式会社 | Flexible wiring board, and its manufacturing method |
| JP2010232585A (en) * | 2009-03-30 | 2010-10-14 | Toppan Printing Co Ltd | Multilayer wiring board and method of manufacturing the same |
| JP2011082317A (en) * | 2009-10-07 | 2011-04-21 | Sumitomo Electric Printed Circuit Inc | Flexible printed wiring board and electronic equipment with the same |
| US7982135B2 (en) | 2006-10-30 | 2011-07-19 | Ibiden Co., Ltd. | Flex-rigid wiring board and method of manufacturing the same |
| US8071883B2 (en) | 2006-10-23 | 2011-12-06 | Ibiden Co., Ltd. | Flex-rigid wiring board including flexible substrate and non-flexible substrate and method of manufacturing the same |
| JP2015161975A (en) * | 2014-02-26 | 2015-09-07 | レノボ・シンガポール・プライベート・リミテッド | Withdrawal structure, keyboard unit, and portable information apparatus |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100754080B1 (en) | 2006-07-13 | 2007-08-31 | 삼성전기주식회사 | Rigid-flexible printed circuit board and manufacturing method therefor |
| KR100771310B1 (en) | 2006-08-22 | 2007-10-29 | 삼성전기주식회사 | Rigid flexible printed circuit board and fabricating method of the same |
| CN103327738B (en) * | 2012-03-22 | 2016-03-09 | 富葵精密组件(深圳)有限公司 | Rigid-flexible circuit board and preparation method thereof |
| CN104602448B (en) * | 2013-10-30 | 2017-11-03 | 鹏鼎控股(深圳)股份有限公司 | Flexible circuit board and preparation method thereof |
| TWI517775B (en) | 2014-03-06 | 2016-01-11 | 相互股份有限公司 | Printed circuit board and method thereof |
| CN105592638B (en) * | 2014-10-20 | 2018-10-30 | 鹏鼎控股(深圳)股份有限公司 | Rigid-flex combined board and preparation method thereof |
| TWI713420B (en) * | 2019-04-01 | 2020-12-11 | 新揚科技股份有限公司 | Circuit board structure |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2841996B2 (en) * | 1992-01-13 | 1998-12-24 | 日立化成工業株式会社 | Manufacturing method of rigid flex wiring board |
| JPH0750455A (en) * | 1993-08-06 | 1995-02-21 | Mitsui Toatsu Chem Inc | Rigid/flexible printed wiring board and its manufacture |
| JPH07193370A (en) * | 1993-12-25 | 1995-07-28 | Ibiden Co Ltd | Flex rigid printed board and its manufacturing method |
| JPH0955562A (en) * | 1995-08-11 | 1997-02-25 | Cmk Corp | Printed wiring board |
| US6350387B2 (en) | 1997-02-14 | 2002-02-26 | Teledyne Industries, Inc. | Multilayer combined rigid/flex printed circuit board containing flexible soldermask |
-
2004
- 2004-10-28 JP JP2004313814A patent/JP2006128360A/en active Pending
-
2005
- 2005-10-05 TW TW094134841A patent/TW200631483A/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2005-10-27 KR KR1020050101764A patent/KR100742679B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2005-10-28 CN CNA200510118461XA patent/CN1767720A/en active Pending
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8071883B2 (en) | 2006-10-23 | 2011-12-06 | Ibiden Co., Ltd. | Flex-rigid wiring board including flexible substrate and non-flexible substrate and method of manufacturing the same |
| US8476531B2 (en) | 2006-10-23 | 2013-07-02 | Ibiden Co., Ltd | Flex-rigid wiring board and method of manufacturing the same |
| US8925194B2 (en) | 2006-10-23 | 2015-01-06 | Ibiden Co., Ltd. | Flex-rigid wiring board and method of manufacturing the same |
| US7982135B2 (en) | 2006-10-30 | 2011-07-19 | Ibiden Co., Ltd. | Flex-rigid wiring board and method of manufacturing the same |
| US8479389B2 (en) | 2006-10-30 | 2013-07-09 | Ibiden Co., Ltd. | Method of manufacturing a flex-rigid wiring board |
| US8525038B2 (en) | 2006-10-30 | 2013-09-03 | Ibiden Co., Ltd. | Flex-rigid wiring board and method of manufacturing the same |
| US9271405B2 (en) | 2006-10-30 | 2016-02-23 | Ibiden Co., Ltd. | Flex-rigid wiring board and method of manufacturing the same |
| WO2009113202A1 (en) | 2008-03-10 | 2009-09-17 | イビデン株式会社 | Flexible wiring board, and its manufacturing method |
| US8405999B2 (en) | 2008-03-10 | 2013-03-26 | Ibiden Co., Ltd. | Flexible wiring board and method of manufacturing same |
| JP2010232585A (en) * | 2009-03-30 | 2010-10-14 | Toppan Printing Co Ltd | Multilayer wiring board and method of manufacturing the same |
| JP2011082317A (en) * | 2009-10-07 | 2011-04-21 | Sumitomo Electric Printed Circuit Inc | Flexible printed wiring board and electronic equipment with the same |
| JP2015161975A (en) * | 2014-02-26 | 2015-09-07 | レノボ・シンガポール・プライベート・リミテッド | Withdrawal structure, keyboard unit, and portable information apparatus |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR100742679B1 (en) | 2007-07-25 |
| CN1767720A (en) | 2006-05-03 |
| TWI302080B (en) | 2008-10-11 |
| TW200631483A (en) | 2006-09-01 |
| KR20060052260A (en) | 2006-05-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100742679B1 (en) | Printed wiring board and production thereof | |
| JP5151265B2 (en) | Multilayer wiring board and method for manufacturing multilayer wiring board | |
| WO2006080073A1 (en) | Multi-layer circuit substrate manufacturing method and multi-layer circuit substrate | |
| JP5059950B2 (en) | Wiring board and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP4768059B2 (en) | Multilayer flexible printed wiring board | |
| CN109429441A (en) | Rigid Flex and preparation method thereof | |
| CN103582320A (en) | Multilayer circuit board and manufacturing method thereof | |
| WO2015166588A1 (en) | Rigid-flex substrate with embedded component | |
| WO2015014048A1 (en) | Rigid-flex printed circuit board and manufacturing method therefor | |
| JP2004319962A (en) | Flex rigid printed wiring board and its manufacturing method | |
| WO2015141004A1 (en) | Multilayer circuit board, semiconductor device, and multilayer circuit board manufacturing method | |
| US20140182899A1 (en) | Rigid-flexible printed circuit board and method for manufacturing same | |
| TW201406222A (en) | Multilayer printed circuit board and method for manufacturing same | |
| WO2010061752A1 (en) | Wiring board and method for manufacturing same | |
| JP2006059962A (en) | Rigid flex circuit board and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2007109697A (en) | Multilayer printed wiring board and method of manufacturing same | |
| JP2015162626A (en) | Printed wiring board and manufacturing method of the same | |
| JP2010040934A (en) | Rigid flex circuit board | |
| JPH11251703A (en) | Circuit board, both-sided circuit board, multilayered circuit board, and manufacture of circuit board | |
| JP2014068047A (en) | Method for manufacturing multilayer printed wiring board | |
| JP2018195657A (en) | Rigid-flex multilayer printed wiring board | |
| JP2008034702A (en) | Rigid flex circuit board and its manufacturing method | |
| KR101097504B1 (en) | The method for preparing multi layered circuit board | |
| KR101887754B1 (en) | Rigid flexible circuit board manufacturing method | |
| CN107889356B (en) | Soft and hard composite circuit board |