JP2006049057A - Organic el display device - Google Patents
Organic el display device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2006049057A JP2006049057A JP2004227500A JP2004227500A JP2006049057A JP 2006049057 A JP2006049057 A JP 2006049057A JP 2004227500 A JP2004227500 A JP 2004227500A JP 2004227500 A JP2004227500 A JP 2004227500A JP 2006049057 A JP2006049057 A JP 2006049057A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- organic
- display device
- light emitting
- recess
- aluminum plate
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 64
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 27
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 26
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 33
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 33
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 16
- 230000017525 heat dissipation Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical group [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 abstract description 8
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 58
- 238000005401 electroluminescence Methods 0.000 description 18
- 239000005394 sealing glass Substances 0.000 description 17
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 15
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 14
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 8
- 101100489584 Solanum lycopersicum TFT1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 6
- 101100214488 Solanum lycopersicum TFT2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 239000002274 desiccant Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000020169 heat generation Effects 0.000 description 5
- PQXKHYXIUOZZFA-UHFFFAOYSA-M lithium fluoride Chemical compound [Li+].[F-] PQXKHYXIUOZZFA-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 5
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 4
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000005525 hole transport Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005488 sandblasting Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000565 sealant Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000012298 atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000191 radiation effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004576 sand Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- FCNCGHJSNVOIKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9,10-diphenylanthracene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1C(C1=CC=CC=C11)=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 FCNCGHJSNVOIKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910003077 Ti−O Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910007541 Zn O Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910002065 alloy metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- XCJYREBRNVKWGJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N copper(II) phthalocyanine Chemical compound [Cu+2].C12=CC=CC=C2C(N=C2[N-]C(C3=CC=CC=C32)=N2)=NC1=NC([C]1C=CC=CC1=1)=NC=1N=C1[C]3C=CC=CC3=C2[N-]1 XCJYREBRNVKWGJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002019 doping agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- RBTKNAXYKSUFRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N heliogen blue Chemical compound [Cu].[N-]1C2=C(C=CC=C3)C3=C1N=C([N-]1)C3=CC=CC=C3C1=NC([N-]1)=C(C=CC=C3)C3=C1N=C([N-]1)C3=CC=CC=C3C1=N2 RBTKNAXYKSUFRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 1
- IBHBKWKFFTZAHE-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[4-(n-naphthalen-1-ylanilino)phenyl]phenyl]-n-phenylnaphthalen-1-amine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1N(C=1C2=CC=CC=C2C=CC=1)C1=CC=C(C=2C=CC(=CC=2)N(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C3=CC=CC=C3C=CC=2)C=C1 IBHBKWKFFTZAHE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000001579 optical reflectometry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000002080 perylenyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=C2C=CC=C3C4=CC=CC5=CC=CC(C1=C23)=C45)* 0.000 description 1
- CSHWQDPOILHKBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N peryrene Natural products C1=CC(C2=CC=CC=3C2=C2C=CC=3)=C3C2=CC=CC3=C1 CSHWQDPOILHKBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920006254 polymer film Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000001737 promoting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003566 sealing material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000013464 silicone adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001179 sorption measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004936 stimulating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- TVIVIEFSHFOWTE-UHFFFAOYSA-K tri(quinolin-8-yloxy)alumane Chemical compound [Al+3].C1=CN=C2C([O-])=CC=CC2=C1.C1=CN=C2C([O-])=CC=CC2=C1.C1=CN=C2C([O-])=CC=CC2=C1 TVIVIEFSHFOWTE-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 238000001771 vacuum deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、一対の電極間に有機発光層を設け、一対の電極により有機発光層に電界を印加させて発光させる有機EL表示装置に係り、特に発光領域を構成する有機発光層で生じた発熱による当該発光領域の効率低下を抑制して長寿命と信頼性向上を可能とした有機EL表示装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to an organic EL display device in which an organic light emitting layer is provided between a pair of electrodes, and an electric field is applied to the organic light emitting layer by the pair of electrodes to emit light, and particularly heat generated in the organic light emitting layer constituting the light emitting region. In particular, the present invention relates to an organic EL display device capable of suppressing a decrease in efficiency of the light emitting region due to a long life and improving reliability.
近年、フラットパネル型の表示装置として液晶表示装置(LCD)やプラズマ表示装置(PDP)、電界放出型表示装置(FED)、有機EL表示装置(OLED)などが実用化ないし実用化研究段階にある。その中でも、有機EL表示装置は、薄型・軽量の自発光型表示装置の典型としてこれからの表示装置として極めて有望な表示装置である。有機EL表示装置には、所謂ボトムエミッション型とトップエミッション型とがある。 In recent years, liquid crystal display devices (LCD), plasma display devices (PDP), field emission display devices (FED), organic EL display devices (OLED), etc. are in the practical application or practical application research stage as flat panel display devices. . Among them, the organic EL display device is a very promising display device as a future display device as a typical thin and lightweight self-luminous display device. Organic EL display devices include a so-called bottom emission type and a top emission type.
ボトムエミッション型の有機EL表示装置は、ガラス基板を好適とする絶縁性基板上に第1の電極または一方の電極としてのITOなどの透明電極、電界の印加により発光する有機多層膜(有機発光層とも言う)、第2の電極または他方の電極としての反射性の金属電極を順次積層した発光機構により有機EL発光素子が構成される。この有機EL発光素子をマトリクス状に多数配列し、それらの積層構造を覆って封止缶とも称する他の基板を設け、上記発光構造を外部の雰囲気から遮断している。 A bottom emission type organic EL display device includes a first electrode or a transparent electrode such as ITO as one electrode on an insulating substrate suitable for a glass substrate, an organic multilayer film that emits light by applying an electric field (organic light emitting layer) In other words, the organic EL light emitting element is configured by a light emitting mechanism in which reflective metal electrodes as the second electrode or the other electrode are sequentially stacked. A large number of organic EL light emitting elements are arranged in a matrix, and another substrate, which is also referred to as a sealing can, is provided to cover the laminated structure, thereby blocking the light emitting structure from the external atmosphere.
そして、例えば透明電極を陽極とし、金属電極を陰極として両者の電極間に電界を印加することにより、有機多層膜にキャリア(電子と正孔)が注入され、当該有機多層膜が発光する。この発光をガラス基板側から外部に出射する構成となっている。 Then, for example, by applying an electric field between the electrodes using the transparent electrode as the anode and the metal electrode as the cathode, carriers (electrons and holes) are injected into the organic multilayer film, and the organic multilayer film emits light. This light emission is emitted from the glass substrate side to the outside.
一方、トップエミッション型の有機EL表示装置は、上述した一方の電極を反射性を有する金属電極とし、他方の電極をITO等の透明電極として両者の電極間に電界を印加することにより、有機多層膜が発光し、この発光を上述した他方の電極側から出射する構成となっている。トップエミッション型では、ボトムエミッション型における封止缶としてガラス板を好適とする透明板が使用される。 On the other hand, in the top emission type organic EL display device, one of the electrodes described above is a reflective metal electrode, and the other electrode is a transparent electrode such as ITO, and an electric field is applied between the two electrodes. The film emits light, and the emitted light is emitted from the other electrode side described above. In the top emission type, a transparent plate suitable for a glass plate is used as a sealing can in the bottom emission type.
このように構成される有機EL表示装置では、有機EL発光素子の発光時に一方の電極と他方の電極との間に印加される電界に応じて発光機構の有機多層膜にキャリアが注入されて発光するが、注入されたキャリアの全てが発光に寄与するわけでなく、一部は発熱となって発光機構を加熱する。発光機構を構成する有機多層膜の材料は、一般に発熱によって発光特性が劣化し、寿命が低下する。このために発熱を除去する必要がある。このような発熱の対策を施したものとして、有機多層膜を形成した基板の背面に熱伝導性の高い金属放熱部材を貼り付けることにより、放熱効果を改善した構造が下記特許文献1に記載されている。
しかしながら、このように構成された有機EL表示装置では、基板自体がガラスなどの熱伝導性の低い基板を使用した場合、単に基板の背面に放熱部材を設けたり、または貼り付けた構造では、有機多層膜と放熱部材との間の距離が大きく、十分な放熱効果が期待できず、これによって発光機構を構成する有機多層膜は点灯時の発熱によって発光特性の劣化が促進される。また、この発熱は、有機EL表示装置の長寿命化を阻害する要因となっている。 However, in the organic EL display device configured as described above, when a substrate having a low thermal conductivity such as glass is used as the substrate itself, a structure in which a heat dissipation member is simply provided or pasted on the back surface of the substrate is organic. The distance between the multilayer film and the heat radiating member is large, and a sufficient heat radiation effect cannot be expected. As a result, the organic multilayer film constituting the light emitting mechanism is promoted to deteriorate in light emission characteristics due to heat generated during lighting. In addition, this heat generation is a factor that hinders the extension of the life of the organic EL display device.
したがって、本発明は前述した従来の課題を解決するためになされたものであり、その目的は、このような発光に伴う有機多層膜の温度上昇を抑制することによって発光効率を維持し、且つ長寿命化を図った有機EL表示装置を提供することにある。 Therefore, the present invention has been made to solve the above-described conventional problems, and the object thereof is to maintain the luminous efficiency by suppressing the temperature increase of the organic multilayer film due to such light emission and An object of the present invention is to provide an organic EL display device with a long life.
このような目的を達成するために本発明による有機EL表示装置は、複数の有機EL発光素子が形成された絶縁性基板の背面に薄肉となる凹部を設け、この凹部内に放熱部材を配設することにより、この放熱部材が発熱源に近い凹部の底面に近接配置されるので、放熱部材の熱拡散が促進されることで背景技術の課題を解決することができる。 In order to achieve such an object, the organic EL display device according to the present invention is provided with a thin concave portion on the back surface of an insulating substrate on which a plurality of organic EL light emitting elements are formed, and a heat dissipation member is disposed in the concave portion. By doing so, since this heat radiating member is arrange | positioned close to the bottom face of the recessed part near a heat generating source, the subject of background art can be solved by accelerating | stimulating the thermal diffusion of a heat radiating member.
本発明による他の有機EL表示装置は、好ましくは、上記構成において、上記放熱部材をアルミニウム板材とすることにより、アルミニウム板材が発熱源に近接配置されるので、アルミニウム板材の熱拡散が促進されことで背景技術の課題を解決することができる。 In another organic EL display device according to the present invention, preferably, in the above configuration, the heat radiating member is made of an aluminum plate, so that the aluminum plate is disposed close to the heat source, so that the thermal diffusion of the aluminum plate is promoted. Can solve the problems of the background art.
本発明による他の有機EL表示装置は、好ましくは、上記構成において、上記放熱部材を銅板材とすることにより、銅板材が発熱源に近接配置されるので、銅板材の熱拡散が促進されることで背景技術の課題を解決することができる。 In another organic EL display device according to the present invention, preferably, in the configuration described above, the heat dissipation member is a copper plate material, so that the copper plate material is disposed close to the heat source, so that the thermal diffusion of the copper plate material is promoted. This can solve the problems of the background art.
本発明による他の有機EL表示装置は、好ましくは、上記構成において、上記放熱部材を熱伝導性の高いシリコン接着材を用いて接着配置することにより、放熱部材が発熱源に近接配置されるので、放熱部材の熱拡散が促進されることで背景技術の課題を解決することができる。 In another organic EL display device according to the present invention, preferably, in the above configuration, the heat dissipating member is disposed close to the heat source by adhering and disposing the heat dissipating member using a silicon adhesive having high thermal conductivity. The problem of the background art can be solved by promoting the thermal diffusion of the heat dissipation member.
本発明による他の有機EL表示装置は、好ましくは、上記構成において、上記凹部内に配置される放熱部材の外面や内面に微細な凹凸面を形成することにより、放熱部材の熱拡散がさらに促進されることで背景技術の課題を解決することができる。 In another organic EL display device according to the present invention, preferably, in the above configuration, the heat diffusion of the heat radiating member is further promoted by forming fine uneven surfaces on the outer surface and the inner surface of the heat radiating member disposed in the concave portion. As a result, the problems of the background art can be solved.
本発明による他の有機EL表示装置は、好ましくは、上記構成において、上記放熱部材を金属膜とすることにより、金属膜が発熱源に近接配置されるので、金属膜の熱拡散が促進されることで背景技術の課題を解決することができる。 In another organic EL display device according to the present invention, preferably, in the above configuration, the heat dissipation member is a metal film, so that the metal film is disposed close to the heat source, so that the thermal diffusion of the metal film is promoted. This can solve the problems of the background art.
本発明による他の有機EL表示装置は、好ましくは、上記構成において、上記凹部内に配置された金属膜の外面に微細な凹凸面を形成することにより、金属膜の熱拡散がさらに促進されることで背景技術の課題を解決することができる。 In another organic EL display device according to the present invention, preferably, in the above configuration, the thermal diffusion of the metal film is further promoted by forming a fine uneven surface on the outer surface of the metal film disposed in the recess. This can solve the problems of the background art.
なお、本発明は、前記各構成及び後述する実施の形態に記載される構成に限定されるものではなく、本発明の技術思想を逸脱することなく、種々の変更が可能であることは言うまでもない。 The present invention is not limited to the configurations described in the above-described configurations and the embodiments described later, and it goes without saying that various modifications can be made without departing from the technical idea of the present invention. .
本発明による有機EL表示装置によれば、複数の有機EL発光素子を形成した絶縁性基板の背面に薄肉となる凹部を設け、この凹部内に放熱部材を設置することにより、この放熱部材が発熱源に近い凹部の底面に近接されるので、有機EL発光素子で発生した熱を効率良く拡散させ、放熱効率を高めることができる。これによって有機EL発光素子の発光効率を低下させることがなくなり、有機EL表示装置の長寿命化を図ることができるなどの極めて優れた効果が得られる。 According to the organic EL display device of the present invention, a thin concave portion is provided on the back surface of the insulating substrate on which a plurality of organic EL light emitting elements are formed, and the heat radiating member is heated by installing the heat radiating member in the concave portion. Since it is close to the bottom surface of the recess close to the source, it is possible to efficiently diffuse the heat generated in the organic EL light emitting device and to improve the heat radiation efficiency. As a result, the light emission efficiency of the organic EL light emitting element is not lowered, and an extremely excellent effect such that the life of the organic EL display device can be extended is obtained.
以下、本発明の具体的な実施の形態について、実施例の図面を参照して詳細に説明する。なお、ここでは、トップエミッション型の有機EL表示装置を例とする。 Hereinafter, specific embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings of the examples. Here, a top emission type organic EL display device is taken as an example.
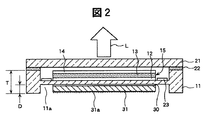
図1は、本発明による有機EL表示装置の実施例1による有機EL素子の層構造を模式的に説明する要部断面図である。また、図2は、本発明による有機EL表示装置の実施例1の全体構造を模式的に説明する要部断面図である。さらに、図3は、図2に示す有機EL表示装置の背面から見た要部斜視図である。なお、これらの図では、説明を簡単にするために1画素のみを示し、画素を選択するスイッチング素子及び発光輝度を制御する制御素子などが搭載されるが、ここでは省略されている。 FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view of an essential part schematically illustrating the layer structure of an organic EL element according to Example 1 of an organic EL display device according to the present invention. FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of an essential part for schematically explaining the overall structure of Example 1 of the organic EL display device according to the present invention. Further, FIG. 3 is a perspective view of a main part viewed from the back of the organic EL display device shown in FIG. In these drawings, only one pixel is shown for ease of explanation, and a switching element for selecting a pixel, a control element for controlling light emission luminance, and the like are mounted, but are omitted here.
図1に示した絶縁性基板11は、有機EL表示装置を構成するアクティブ・マトリクス基板(または薄膜トランジスタ基板、TFT基板とも称する)である。この絶縁性基板11は、セラミック板材またはガラス板材などから形成されている。この絶縁性基板11の主面には発光制御電極としての陰極12が画素毎に導電性金属膜のパターニングにより形成されている。この導電性金属膜としては、絶縁性基板11側から第1層としてアルミニウム(Al)層12aと、第2層として弗化リチウム(LiF)層12bとを用いた。なお、アルミニウム層12aの膜厚は例えば約200nm、弗化リチウム層12bの膜厚は例えば約1nm程度である。
The
なお、上記導電性金属膜は、この他にMg/AlまたはMg/Inなどを用いても良い。これらの導電性金属膜を蒸着法あるいはスパッタリング法もしくはCVD法などにより絶縁性基板11の主面に成膜し、フォトリソグラフィー工程などを用いて所要の大きさにパターニングを施し、画素毎の陰極12を形成する。この陰極12は光反射性が良好であることが望ましい。
In addition, Mg / Al or Mg / In may be used for the conductive metal film. These conductive metal films are formed on the main surface of the
また、この陰極12の上面には、有機EL発光素子の有機発光構造を構成する有機多層膜13が形成さている。この有機多層膜13は、陰極12側から電子輸送層13a,発光層13b,正孔輸送層13c,正孔注入層13dが順次積層されて形成されている。この有機多層膜13の膜厚は、例えば約150nm程度である。
An
なお、上記の有機多層膜13の材料の一例は、以下のとおりである。すなわち、電子輸送層13aは、Alq3(トリス(8−ヒドロキシキノリン)アルミニウム)などが用いられる。また、発光層13bは、ホスト材料に9,10−ジフェニルアントラセンなどを、ドーパント材料にペリレンなどを用いた発光材料が用いられる。また、正孔輸送層13cは、α−NPD(α−ナフチルフェニルジアミン)などが用いられる。また、正孔注入層13dは、CuPc(銅フタロシアニン)などが用いられる。
An example of the material of the
また、この有機多層膜13の上面には、陽極14が成膜されて有機EL発光素子15が形成されている。この陽極14には、ITO(In−Ti−O)やIZO(In−Zn−O)などの透明導電性薄膜を用いることができるが、ここでは、例えば膜厚約30nm以下のITO膜とした。なお、アクティブ・マトリクス型では、絶縁性基板11の主面にLTPS(低温ポリシリコン半導体膜)などで形成された薄膜トランジスタ(Thin Film Transistor:TFT)を有する画素選択回路または画素駆動回路が形成されるが、ここでは図示を省略した。
Further, an
また、この有機EL発光素子15の最上層には、これらの陰極12,有機多層膜13及び陽極14を覆ってガスバリア性膜16が形成されている。このガスバリア性膜16としては、例えばポリマー膜,窒化珪素膜,酸化珪素膜などのガス非透過性材料層で形成され、特に有機多層膜13が外部雰囲気中の水分及びガス成分などの吸着から保護されるので、これに起因する発光特性の劣化を防止する。また、ガスバリア性膜16を形成した後、このガスバリア性膜16の表面に図示しないが、熱伝導性の高い金属膜を成膜しても良い。この金属膜の形成により、発光に起因する内部からの発熱を絶縁性基板11に放熱させることができるので、有機多層膜13の長寿命化が図れる。なお、最上層に形成されるガスバリア性膜16及び金属膜の膜厚は、数μm程度である。
Further, a
また、この絶縁性基板11の内面には、乾燥剤23が収納されており、この乾燥剤23は既知の乾燥剤をシート状に成形し、絶縁性基板11の内面に貼り付け、またはゲル状として塗布しても良い。この乾燥剤23の厚さは、例えば約100μm程度である。また、封着剤22には紫外線硬化型樹脂が用いられるが、他のシール材であってもよい。
In addition, a
また、このように主面側に有機EL発光素子15が形成された絶縁性基板11上には、この有機EL発光素子15を覆うように絶縁性の透光性ガラス基板21がその周縁部に封止剤22を介在させて封止され、周囲環境からの湿気の侵入等による動作特性の劣化を防止し、安定した表示を可能にしている。この封止剤22には紫外線硬化型樹脂が用いられるが、他のシール材であってもよい。
Further, on the insulating
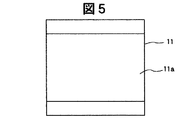
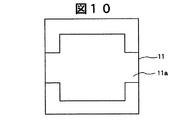
また、この絶縁性基板11には、有機EL素子15と反対向する背面側に凹部11aが一体的に形成されている。この絶縁性基板11の背面に形成される凹部11aは、例えばサンドブラスト法による掘り込みにより形成されている。この絶縁性基板11の板厚Tは、約700μm程度であり、また、この凹部11aの深さDは、板厚Tの約1/3〜1/4の範囲であり、例えば約200μm程度である。また、この凹部11aは絶縁性基板11の成形時に一体的に成形するなどの手段により形成することも可能である。
Further, the insulating
また、この絶縁性基板11の背面側に形成された凹部11aの内部底面には、熱伝導性の高いシリコン接着剤30を介して放熱部材として例えば熱拡散性の高いアルミニウム板31が接着配置されている。このアルミニウム板31の板厚は、約50μm〜約150μmの範囲である。さらにこのアルミニウム板31の外気と接触する最表面には微細な凹凸面31aが形成されており、この微細な凹凸面31aは、サンドブラスト法またはエッチンング法などにより形成される。なお、このアルミニウム板31は、絶縁性基板11の凹部11aに接着する以前に定型のアルミニウム板材の表面にサンドブラスト法またはエッチング法などにより微細な凹凸面を形成した後、所定の大きさに切断して形成しても良い。
Also, for example, an
このように構成された有機EL表示装置において、有機EL発光素子15を構成する陰極12と陽極14との間に所定の電圧を印加することによる正孔注入層13dから発光層13bへの正孔の移送と、電子輸送層13aから注入される電子とで発光層13bを発光させ、透光性ガラス基板21側から外部上方に向かって発光光Lとして出射される。
In the organic EL display device configured as described above, holes from the
このように構成された有機EL表示装置は、絶縁性基板11の背面側に凹部11aを設け、この凹部11a内にアルミニウム板31を貼り付けるのみの構成となるので、有機EL表示装置の全体を薄く構成することができる。また、有機EL発光素子15とアルミニウム板31とが凹部21aの底部に形成される薄肉の部分を介して近接配置されるので、アルミニウム板31が発熱源となる有機EL素子15により近い位置となるので、大きな放熱効果を得ることができる。
The organic EL display device configured as described above has a configuration in which the
さらに、アルミニウム板31の最表面に微細な凹凸面31aを設けたことにより、放熱効果をさらに向上させることができる。また、絶縁性基板21に放熱部材としてのアルミニウム板31を設置する場合、その背面側に凹部11aが形成されているので、単にアルミニウム板31を貼り付けるよりも、その位置決めが極めて容易となり、生産性を向上させることができる。
Furthermore, by providing the fine
なお、上記実施例では、放熱部材として熱拡散性の高いアルミニウム板31を用いたが、このアルミニウム板31に代えて銅板を用いてもよく、また、これらの合金金属板材を用いても良い。さらに、これらの金属板材に代えて熱拡散性を有する金属板材であれば特に限定されるものではない。
In the above embodiment, the
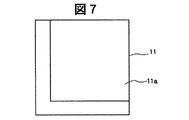
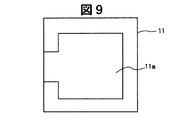
図4乃至図19は、絶縁性基板11の背面側に形成される凹部11aの他の実施例による構成を示す背面側から見た要部平面図である。これらの図4乃至図19に示すように絶縁性基板11に背面側に形成される凹部11aは、図2に示す有機EL発光素子15の配置個所等に対応して各種の形状が製作可能となるが、これらの凹部11aの形成方法としては、有機EL発光素子15の作製前では平板状に形成された絶縁性基板に例えばサンドブラスト法またはエッチング法の両方の手段によって形成することができるが、有機EL発光素子15の作製後では、有機EL発光素子15の損傷を考慮すると、サンドブラスト法により凹部11aを形成する手段の方がエッチング法よりも望ましい。
4 to 19 are plan views of the main part viewed from the back side showing the configuration of another embodiment of the
図20は、本発明による有機EL表示装置の実施例2による構成を模式的に説明する要部断面図であり、前述した図2と同一部分には同一符号を付し、その説明は省略する。図20において、図2と異なる点は、絶縁性基板11の背面側に形成された凹部11a内にはその内壁面の全面にわたって熱伝導性の高い金属材料、例えばアルミニウムまたは銅などの金属材料を真空蒸着法またはスパッタリング法により金属膜40が形成されている。なお、この金属膜40の膜厚は、約10μm〜約250μmの範囲である。また、この金属膜40の外面には微細な凹凸面40aが形成されている。この微細な凹凸面40aは、例えばサンドブラスト法,エッチング法またはラビング法などの手段により形成されている。
FIG. 20 is a cross-sectional view schematically illustrating a main part of the organic EL display device according to the second embodiment of the present invention. The same parts as those in FIG. . 20 differs from FIG. 2 in that a metal material having high thermal conductivity, for example, a metal material such as aluminum or copper, is formed in the
このように金属膜40を設けることにより、有機EL発光素子15と金属膜40とが凹部11aの底部に形成される薄肉の部分を介して近接配置されるので、金属膜40が発熱源となる有機EL発光素子15により近い位置となるので、有機EL発光素子15からの発熱を有効に外部に拡散させることができので、大きな放熱効果を得ることができる。さらに金属膜40の外面に微細な凹凸面40aを設けているので、熱拡散性をさらに向上させることができる。一方、絶縁性基板11の背面をサンドブラスト法等で粗くすれば、当該背面に形成される金属膜40の内面(絶縁性基板11に対向する面)にも凹凸が生じる。これにより、絶縁性基板11と金属膜40との接合面積が増し、有機EL発光素子15で生じた熱は、効率良く金属膜40に排出される。この金属膜40は、有機EL発光素子15を作製した後に形成することができるので、発熱対策が容易に実現可能となる。
By providing the
なお、この金属膜40に接地線を溶接などにより接続し、図示しないが画素を選択するスイッチング素子及び発光輝度を制御する制御素子などに電気的にアース接続しても良い。
Note that a ground line may be connected to the
図21は、本発明を適用したトップエミッション型有機EL表示装置の画素に構成例を説明する回路図である。この画素PXはカラー表示では副画素(サブピクセル)となる。画素PXは、走査線GLとデータ線DLとに接続したスイッチング用の薄膜トランジスタジスタTFT1と、走査線GLで選択されたスイッチング用薄膜トランジスタTFT1のオンでデータ線DLから供給される表示データを電荷として蓄積する蓄積容量CPRと、有機EL発光素子15の駆動用薄膜トランジスタTFT2と、電流供給線CSLとで構成される。
FIG. 21 is a circuit diagram illustrating a configuration example of a pixel of a top emission type organic EL display device to which the present invention is applied. This pixel PX becomes a sub-pixel (sub-pixel) in color display. The pixel PX accumulates display data supplied from the data line DL as an electric charge when the switching thin film transistor TFT1 connected to the scanning line GL and the data line DL and the switching thin film transistor TFT1 selected by the scanning line GL are turned on. A storage capacitor CPR for driving, a thin film transistor TFT2 for driving the organic EL
薄膜トランジスタTFT1のゲート電極は走査線GLに接続され、ドレイン電極はデータ線DLに接続されている。また、薄膜トランジスタTFT2のゲート電極は薄膜トランジスタTFT1のソース電極に接続され、この接続点に蓄積容量CPRの一方の電極(+極)が接続されている。薄膜トランジスタTFT2のドレイン電極は電流供給線CSLに接続され、ソース電極は有機EL発光素子15の陽極14に接続されている。
The gate electrode of the thin film transistor TFT1 is connected to the scanning line GL, and the drain electrode is connected to the data line DL. The gate electrode of the thin film transistor TFT2 is connected to the source electrode of the thin film transistor TFT1, and one electrode (+ electrode) of the storage capacitor CPR is connected to this connection point. The drain electrode of the thin film transistor TFT2 is connected to the current supply line CSL, and the source electrode is connected to the
画素PXが走査線GLで選択されて薄膜トランジスタTFT1がオンとなると、データ線DLから供給される表示データが蓄積容量CPRに蓄積される。そして、薄膜トランジスタTFT1がオフした時点で薄膜トランジスタTFT2がオンとなり、電流供給線CSLから有機EL表示素子15に流れ、ほぼ1フレームの期間(または1フィールド期間)にわたってこの電流を持続させる。この時に流れる電流は、蓄積容量CPRに蓄積されているデータ信号に対応する電荷で規定される。この回路は最も単純な構成であり、他に種々の回路構成が知られている。
When the pixel PX is selected by the scanning line GL and the thin film transistor TFT1 is turned on, the display data supplied from the data line DL is stored in the storage capacitor CPR. When the thin film transistor TFT1 is turned off, the thin film transistor TFT2 is turned on and flows from the current supply line CSL to the organic
図22は、図21に示した画素の回路を基板上で実現した構成例を説明する画素付近の平面図である。図中、図21と同一の符号は同一部分に対応し、DEは画素の開口部である。薄膜トランジスタTFT1と薄膜トランジスタTFT2とは画素の開口部DEに隣接する非表示部に配置される。 FIG. 22 is a plan view of the vicinity of a pixel for explaining a configuration example in which the circuit of the pixel shown in FIG. 21 is realized on a substrate. In the drawing, the same reference numerals as those in FIG. 21 correspond to the same portions, and DE is an opening of a pixel. The thin film transistors TFT1 and TFT2 are arranged in a non-display portion adjacent to the pixel opening DE.
図23は、有機EL表示装置の駆動回路を含めた等価回路である。画素PXはマトリクス状に配列されて表示領域ARを形成する。データ線DLはデータ線駆動回路DDRにより駆動される。また、走査線GLは走査線駆動回路GDRで駆動される。電流供給線CSLは電流供給バスラインCSLBを介して図示しない電流供給回路に接続している。なお、TMは外部入力端子を示す。 FIG. 23 is an equivalent circuit including a drive circuit of the organic EL display device. The pixels PX are arranged in a matrix to form a display area AR. The data line DL is driven by the data line driving circuit DDR. The scanning line GL is driven by the scanning line driving circuit GDR. The current supply line CSL is connected to a current supply circuit (not shown) via a current supply bus line CSLB. TM denotes an external input terminal.
なお、前述した実施例においては、トップエミッション型の有機EL表示装置について説明したが、ボトムエミッション型の有機EL表示装置においても、封止ガラス基板に凹部を設け、この凹部内に放熱部材を配設しても、前述とほぼ同様の効果が得られることは勿論である。 In the above-described embodiments, the top emission type organic EL display device has been described. However, also in the bottom emission type organic EL display device, a recess is provided in the sealing glass substrate, and a heat dissipation member is provided in the recess. Of course, the same effect as described above can be obtained even if it is provided.
また、前述した各実施例においては、有機EL表示装置を用いた有機ELパネルについて説明したが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではなく、携帯性を重視する小型情報端末(携帯,PDA等)用の有機ELパネルまたはモニタ用有機ELディスプレイの全般に適用できることは言うまでもない。 In each of the embodiments described above, the organic EL panel using the organic EL display device has been described. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and a small information terminal (portable, PDA, etc.) that places importance on portability. Needless to say, the present invention can be applied to the organic EL panel for monitoring) or the organic EL display for monitoring.
11・・・絶縁性基板、11a・・・凹部、12・・・陰極、12a・・・アルミニウム層、12b・・・弗化リチウム層、13・・・有機発光膜、13a・・・電子輸送層、13b・・・発光層、13c・・・正孔輸送層、13d・・・正孔注入層、14・・・陽極、15・・・有機EL発光素子、16・・・ガスバリア性膜、21・・・透光性ガラス基板、22・・・封止剤、23・・・乾燥剤、30・・・シリコン接着剤、31・・・アルミニウム板、31a・・・凹凸面、40・・・金属膜、41a・・・凹凸面。
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (7)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004227500A JP2006049057A (en) | 2004-08-04 | 2004-08-04 | Organic el display device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004227500A JP2006049057A (en) | 2004-08-04 | 2004-08-04 | Organic el display device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006049057A true JP2006049057A (en) | 2006-02-16 |
| JP2006049057A5 JP2006049057A5 (en) | 2007-09-06 |
Family
ID=36027371
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004227500A Pending JP2006049057A (en) | 2004-08-04 | 2004-08-04 | Organic el display device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2006049057A (en) |
Cited By (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2007139124A1 (en) * | 2006-06-01 | 2007-12-06 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device and an electronic device |
| JP2008058488A (en) * | 2006-08-30 | 2008-03-13 | Seiko Epson Corp | Light emitting device, method for manufacturing light emitting device, and electronic equipment |
| JP2008141404A (en) * | 2006-11-30 | 2008-06-19 | Toshiba Design & Manufacturing Service Corp | Image sensor and image forming apparatus |
| JP2009076389A (en) * | 2007-09-21 | 2009-04-09 | Panasonic Electric Works Co Ltd | Surface light-emitting device |
| WO2009066561A1 (en) | 2007-11-22 | 2009-05-28 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | Organic electroluminescent device and method for manufacturing the same |
| US7732811B2 (en) | 2006-12-04 | 2010-06-08 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device, and electronic device |
| JP2010146894A (en) * | 2008-12-19 | 2010-07-01 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Organic electroluminescence element |
| KR101024838B1 (en) | 2009-09-14 | 2011-03-28 | 김동수 | Oled radiant heat sheet manufacture method |
| EP2309312A1 (en) * | 2009-09-18 | 2011-04-13 | Panasonic Electric Works Co., Ltd | Light module |
| JP2011141979A (en) * | 2010-01-06 | 2011-07-21 | Seiko Epson Corp | Method of manufacturing electro-optical device, and electro-optical device |
| US8040047B2 (en) | 2007-10-19 | 2011-10-18 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting device |
| US8053980B2 (en) | 2007-03-23 | 2011-11-08 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting device and electronic device |
| US8278649B2 (en) | 2008-03-18 | 2012-10-02 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device and electronic device |
| US8362466B2 (en) | 2008-12-17 | 2013-01-29 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device, and electronic device |
| JP2013021357A (en) * | 2012-09-26 | 2013-01-31 | Seiko Epson Corp | Organic el device, manufacturing method of organic el device, and electronic apparatus |
| US8698131B2 (en) | 2009-03-26 | 2014-04-15 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Organic EL apparatus, method of manufacturing organic EL apparatus, electronic apparatus |
| WO2015097857A1 (en) * | 2013-12-27 | 2015-07-02 | パイオニアOledライティングデバイス株式会社 | Light emitting apparatus |
| US9192017B2 (en) | 2008-03-18 | 2015-11-17 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device and electronic device |
| US9397308B2 (en) | 2006-12-04 | 2016-07-19 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light emitting element, light emitting device, and electronic device |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH09260539A (en) * | 1996-03-27 | 1997-10-03 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Sub-mounter and semiconductor device as well as manufacture thereof |
| JPH1051065A (en) * | 1996-08-02 | 1998-02-20 | Matsushita Electron Corp | Semiconductor laser device |
| JP2002343555A (en) * | 2001-05-18 | 2002-11-29 | Rohm Co Ltd | Organic el display device |
| JP2002343559A (en) * | 2001-05-18 | 2002-11-29 | Rohm Co Ltd | Organic el display device |
-
2004
- 2004-08-04 JP JP2004227500A patent/JP2006049057A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH09260539A (en) * | 1996-03-27 | 1997-10-03 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Sub-mounter and semiconductor device as well as manufacture thereof |
| JPH1051065A (en) * | 1996-08-02 | 1998-02-20 | Matsushita Electron Corp | Semiconductor laser device |
| JP2002343555A (en) * | 2001-05-18 | 2002-11-29 | Rohm Co Ltd | Organic el display device |
| JP2002343559A (en) * | 2001-05-18 | 2002-11-29 | Rohm Co Ltd | Organic el display device |
Cited By (32)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7649211B2 (en) | 2006-06-01 | 2010-01-19 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Organic light emitting element |
| WO2007139124A1 (en) * | 2006-06-01 | 2007-12-06 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device and an electronic device |
| JP2008204934A (en) * | 2006-06-01 | 2008-09-04 | Semiconductor Energy Lab Co Ltd | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device, and electronic device |
| US8076676B2 (en) | 2006-06-01 | 2011-12-13 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device and an electronic device which include two layers including the same light-emitting organic compound |
| US8410492B2 (en) | 2006-06-01 | 2013-04-02 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device and an electronic device, which include two layers including same light-emitting organic compound |
| US8860019B2 (en) | 2006-06-01 | 2014-10-14 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting device comprising light-emitting layer including two layers |
| JP2008058488A (en) * | 2006-08-30 | 2008-03-13 | Seiko Epson Corp | Light emitting device, method for manufacturing light emitting device, and electronic equipment |
| JP2008141404A (en) * | 2006-11-30 | 2008-06-19 | Toshiba Design & Manufacturing Service Corp | Image sensor and image forming apparatus |
| US9397308B2 (en) | 2006-12-04 | 2016-07-19 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light emitting element, light emitting device, and electronic device |
| US7732811B2 (en) | 2006-12-04 | 2010-06-08 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device, and electronic device |
| US8916857B2 (en) | 2006-12-04 | 2014-12-23 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device, and electronic device |
| US8319210B2 (en) | 2006-12-04 | 2012-11-27 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device, and electronic device |
| US8053980B2 (en) | 2007-03-23 | 2011-11-08 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting device and electronic device |
| JP2009076389A (en) * | 2007-09-21 | 2009-04-09 | Panasonic Electric Works Co Ltd | Surface light-emitting device |
| US8251765B2 (en) | 2007-10-19 | 2012-08-28 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting device |
| US8040047B2 (en) | 2007-10-19 | 2011-10-18 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting device |
| WO2009066561A1 (en) | 2007-11-22 | 2009-05-28 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | Organic electroluminescent device and method for manufacturing the same |
| US9192017B2 (en) | 2008-03-18 | 2015-11-17 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device and electronic device |
| US8278649B2 (en) | 2008-03-18 | 2012-10-02 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device and electronic device |
| US9224960B2 (en) | 2008-03-18 | 2015-12-29 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device, and electronic device |
| US8362466B2 (en) | 2008-12-17 | 2013-01-29 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device, and electronic device |
| US9437824B2 (en) | 2008-12-17 | 2016-09-06 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light-emitting element, light emitting device, and electronic device |
| JP2010146894A (en) * | 2008-12-19 | 2010-07-01 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Organic electroluminescence element |
| US8698131B2 (en) | 2009-03-26 | 2014-04-15 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Organic EL apparatus, method of manufacturing organic EL apparatus, electronic apparatus |
| KR101024838B1 (en) | 2009-09-14 | 2011-03-28 | 김동수 | Oled radiant heat sheet manufacture method |
| EP2309312A1 (en) * | 2009-09-18 | 2011-04-13 | Panasonic Electric Works Co., Ltd | Light module |
| US8764209B2 (en) | 2009-09-18 | 2014-07-01 | Panasonic Corporation | Light module |
| CN102026434A (en) * | 2009-09-18 | 2011-04-20 | 松下电工株式会社 | Light module |
| JP2011141979A (en) * | 2010-01-06 | 2011-07-21 | Seiko Epson Corp | Method of manufacturing electro-optical device, and electro-optical device |
| JP2013021357A (en) * | 2012-09-26 | 2013-01-31 | Seiko Epson Corp | Organic el device, manufacturing method of organic el device, and electronic apparatus |
| WO2015097857A1 (en) * | 2013-12-27 | 2015-07-02 | パイオニアOledライティングデバイス株式会社 | Light emitting apparatus |
| JPWO2015097857A1 (en) * | 2013-12-27 | 2017-03-23 | パイオニアOledライティングデバイス株式会社 | Light emitting device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI557893B (en) | Organic light emitting diode display and manufacturing method of the same | |
| TW589915B (en) | Electroluminescence display device | |
| JP4776393B2 (en) | Organic EL display device | |
| JP2006049057A (en) | Organic el display device | |
| KR101147428B1 (en) | Organic light emitting diode display | |
| JP4060113B2 (en) | Light emitting device | |
| JP2007026970A (en) | Organic light emitting display device | |
| KR20110135734A (en) | Organic light emitting diode display | |
| JP2005235403A (en) | Organic el display device | |
| JP2011119223A (en) | Organic light-emitting display device | |
| JP2005317476A (en) | Display device | |
| KR100959106B1 (en) | Organic light emitting diode display | |
| JP2006351314A (en) | Top emission light-emitting display | |
| JP4742626B2 (en) | LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE HAVING THE SAME | |
| JP2004047458A (en) | Electroluminescence display | |
| JP2003264063A (en) | Display device | |
| KR101197758B1 (en) | Organic Light Emitting Diodes | |
| US8648335B2 (en) | Organic light emitting diode display | |
| JP2005166265A (en) | Organic el display device | |
| JP4652451B2 (en) | Optical device and method for manufacturing optical device | |
| JPH11297476A (en) | Organic light-emitting element, and manufacture thereof | |
| JP2003323973A (en) | Electroluminescent display device | |
| KR101564629B1 (en) | Organic electro-luminescence device | |
| JP2007053030A (en) | Organic electroluminescent element and its manufacturing method | |
| JP4755002B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of sealing member for optical device, manufacturing method of optical device, optical device, and sealing member for optical device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070723 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070723 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100324 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100427 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100625 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20100921 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20110218 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20110218 |