EP4100328B1 - Verfahren zur auswahl der abfälle einer automatischen maschine zur herstellung oder verpackung von verbraucherartikeln - Google Patents
Verfahren zur auswahl der abfälle einer automatischen maschine zur herstellung oder verpackung von verbraucherartikeln Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP4100328B1 EP4100328B1 EP21709093.5A EP21709093A EP4100328B1 EP 4100328 B1 EP4100328 B1 EP 4100328B1 EP 21709093 A EP21709093 A EP 21709093A EP 4100328 B1 EP4100328 B1 EP 4100328B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- component
- motion law
- article
- processed
- defective
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B19/00—Packaging rod-shaped or tubular articles susceptible to damage by abrasion or pressure, e.g. cigarettes, cigars, macaroni, spaghetti, drinking straws or welding electrodes
- B65B19/02—Packaging cigarettes
- B65B19/22—Wrapping the cigarettes; Packaging the cigarettes in containers formed by folding wrapping material around formers
- B65B19/223—Wrapping the cigarettes; Packaging the cigarettes in containers formed by folding wrapping material around formers in a curved path; in a combination of straight and curved paths, e.g. on rotary tables or other endless conveyors
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B57/00—Automatic control, checking, warning, or safety devices
- B65B57/10—Automatic control, checking, warning, or safety devices responsive to absence, presence, abnormal feed, or misplacement of articles or materials to be packaged
- B65B57/14—Automatic control, checking, warning, or safety devices responsive to absence, presence, abnormal feed, or misplacement of articles or materials to be packaged and operating to control, or stop, the feed of articles or material to be packaged
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a procedure for the selective management of the waste of an automatic machine for manufacturing or packing consumer articles.
- the present invention is advantageously but not exclusively applied in the selective management of the waste of an automatic packaging machine that manufactures cigarette packs, to which the following disclosure will explicitly refer without thereby losing generality.
- Document DE 36 39 972 describes a process and a device for separating out from a material web material web sections which are unusable as a result of defects.
- a processing station for example a packaging machine for cigarettes, is also disclosed, machine that is fed intermittently with material web sections of defined length which are cut off from the material web by means of a cutting device after each take-off cycle.
- An automatic packaging machine for cigarettes usually comprises a plurality of actuators which act on the articles in order to modify the shape, the structure or the position thereof and each actuator can assume a plurality of different positions.
- some actuators are used for conveying semi-finished articles through a plurality of processing stations.
- Such conveying systems in the majority of cases, are continuous systems, i.e. systems which move at a constant speed or according to periodic motion laws so as to respect predetermined concurrences between the article, the components to be added to the article in order to complete it and the processing operations to be carried out.
- the processing stations in turn comprise other actuators designed to feed the aforementioned components to be added to the semi-finished articles (for example a wrapping, a collar, a blank, an absorbent layer, etc.) and/or to process the articles.
- the environmental issue relating to industrial waste has become increasingly widespread.
- such issue falls within the interests of the manufacturer, as the reduction in waste generates (unless a machine stoppage of excessive duration) a considerable saving in raw materials, i.e. in the components to be processed and combined for forming a consumer article.
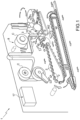
- the conveying system 4 comprises a belt 5 configured to receive some semi-finished articles 3 and transport them towards a processing station WS.
- the component 6 can be any type of element to be added to the article 3 such as, for example, a collar, a glue, a support, a fastening element, a label, a blank, an absorbent sheet, an elastic, a foodstuff, etc.
- reference numeral 3 will indicate the consumer articles in general and reference numeral 3' will indicate the consumer article being processed.
- reference numeral 6 will indicate the components in general, reference numeral 6' will indicate the defective components and reference numeral 6" will indicate the new components, succeeding the defective components 6'.
- the conveying system 4 also comprises one or more pushers 7.
- the pushers 7 are set in motion by actuators 13 independent of one another and by the belt 5.
- the pushers 7 are set in motion by a single actuating system that is independent of the belt 5.
- the pushers 7 are integral with the conveyor belt 5.
- the automatic machine 1 comprises at least one store (8) containing one or more components 6.
- the component 6 is a planar element, in particular a strip, a wrapping or a blank.
- the component 6 is obtained from a seamless strip, which is fed, cut and possibly rejected along a feeding path FP.
- the component 6 is a continuous strip of wrapping material and the store 8 is thus a reel C.
- the store 8 comprises a plurality of separate (for example collars or blanks) and stored (for example in piles) components.
- the part 2 of the automatic machine 1 further comprises a feeding system 9 configured to feed at least one component 6 from the respective store 8 towards the conveying path CP and along the feeding path FP and according to a second periodic motion law, in particular different from the first periodic motion law which governs the movement of the articles 3.
- the part 2 further comprises a wheel 10 mounted rotatable around a central rotation axis A and provided with seats 11 (in particular pockets) adapted to accommodate the semi-finished articles 3 (the cigarette packs) and (at least) one pusher 7 adapted to push the semi-finished articles 3 into the seats 11 of the movable wheel 10.
- the article 3 being processed i.e. the one inside the work station WS
- the actuators that set in motion the conveying device 4 (and/or the pushers 7) and/or the feeding system 9 comprise electric motors (in particular of brushless type) which are independent of one another.
- the actuators also comprise types of actuation different from the electric motors (for example pneumatic or hydraulic cylinders, electrically actuated cylinders, etc.).
- a first actuator 12 is coupled to the wheel 10 so as to control the rotation of the wheel 10 around the rotation axis A and it is provided with a rotating electric motor (for example of brushless type) which sets the wheel 10 into rotation through the interposition of a reducer (not illustrated);
- a second actuator 13 is coupled to the pusher 7 to control the linear movement of the pusher 7 along a direction D and for a predefined stroke and it is provided with a rotating electric motor (for example of brushless type) and with a reducer which transforms the circular movement into a linear movement (both not illustrated); and, in particular, a third actuator 14 connected to the store 8 and configured to feed the components 6 along the feeding path FP (obviously, the actuator 14 can be any other type of actuator comprising, for example, articulated quadrilaterals, robots, gripping and laying elements, etc.).
- the machine 1 further comprises a control system 15 configured to detect, during the feeding of the components 6, the quality and/or the position and/or the orientation of at least one component 6 so as to establish whether the component is usable or defective.
- a component 6 can be considered defective if it has wrinkles, creases, holes, tears, stains, non-constant thickness, unsuitable dampness, wrong position, incorrect inclination, etc.
- a component is to be considered suitable if it respects all the minimum specifications of quality and/or orientation and/or position.
- the control system 15 is a camera 16, which, for each component 6 passing in front of it, performs a scan (i.e. a photo) so as to determine the quality, the orientation and the position thereof and define whether it is defective or suitable.
- the camera 16 is comprised in a viewing system (in turn comprised in the control system 15) and in a processing system of the images of a known type and not illustrated to a greater extent.
- control system 15 is any type of sensor capable of establishing the quality and/or the position and/or the orientation of a product (for example, ultrasound sensors, capacitive sensors, microwave sensors, photoelectric cells, etc.).
- the automatic machine 1 further comprises a control unit 17 (schematically illustrated in Figure 1 ) configured to control at least the conveying system 4 (by means of the actuator 13) and feeding system 9 (by means of the actuator 14).
- the control unit 17 also controls the wheel 10 (by means of the actuator 12) and, in particular, all the actuators of the part 2 of the automatic machine 1.
- the control unit 17 is the processor of an industrial control unit or an industrial PC.
- control unit 17 is configured to control, in case the component 6' fed is defective, the conveying system 4 according to a first modified motion law, which is different from the first periodic motion law, so as to convey the article 3' being processed.
- control unit 17 is configured to control the feeding system 9 according to a second modified motion law, which is different from the second periodic motion law, so as to feed the new component 6" replacing the defective component 6'.
- the article 3' in the processing step slows down and/or the (usable) component 6" succeeding the defective component 6' accelerates so as to give the feeding system 9 the time necessary to position the succeeding component 6" in the work station WS before the article 3' goes through the feeding path and pushes it into the seat 11.
- the defective component 6' is previously conveyed towards a waste zone WZ (for example a container).
- control unit 17 is configured to process, in case a component 6' fed is defective (as illustrated in the non-limiting embodiment of Figure 3 ), the first and/or the second modified motion law, which comprise respectively (at least) a deceleration (at least) of the article 3' being processed and/or an acceleration of the new component 6".
- the first and/or the second modified motion law which comprise respectively (at least) a deceleration (at least) of the article 3' being processed and/or an acceleration of the new component 6".
- the part 2 of the automatic machine 1 comprises a separation device 18 that separates the components 6, 6', 6", in particular a cutting device 19 that cuts the components 6, 6', 6", which is provided, more precisely, with a knife and with a counter-knife.
- a procedure is provided for the selective management of the waste of at least a part of an automatic machine for manufacturing or packing consumer articles.
- the procedure comprises at least a step of conveying, according to the first periodic motion law, the plurality of semi-finished articles 3 along the conveying path CP through (at least) the work station (WS), where (at least) the component 6, 6" is added to an article 3' being processed.
- the procedure comprises the further step, in particular at least partially simultaneous with the conveying step, of feeding each component 6, 6', 6", according to a second periodic motion law, from the respective store 8 (in the non-limiting embodiment of Figures 2 and 3 , from the reel C) towards the conveying path CP and along the feeding path FP.
- the procedure comprises a step of checking, in a control area IA and during the step of feeding the component 6, 6' (i.e. before said component 6, 6' reaches the conveying path CP and not compulsorily during the movement of the component 6, 6' along the feeding path FP) the quality and/or the position and/or the orientation of the component and establishing whether the component is usable or defective.
- the control system 15 (more precisely, the camera 16) scans the component 6, 6', 6" directed towards the conveying path CP (and towards the article 3' being processed), determines whether the component 6, 6', 6" is suitable or defective (i.e. to be rejected) and communicates this to the control unit 17, for the possible variation of the motion laws of the component 3' being processed (i.e. the one which should have received the defective component 6', Figure 3 ) and/or of the succeeding component 6".
- the procedure also comprises a replacement step, during which the defective component 6' is conveyed from the control area IA to a waste zone WZ and replaced, inside the work station WS, by a new component 6", which is fed from the respective store 8 towards the conveying path CP and along the feeding path FP.
- a replacement step during which the defective component 6' is conveyed from the control area IA to a waste zone WZ and replaced, inside the work station WS, by a new component 6", which is fed from the respective store 8 towards the conveying path CP and along the feeding path FP.
- the new component 6" is fed according to a second modified motion law (different from the second periodic motion law with which it is normally conveyed), allowing the new component 6" to reach the work station WS in order to be added to the article 3' being processed.
- a second modified motion law different from the second periodic motion law with which it is normally conveyed
- the procedure comprises a further step, prior to the compensation step, of processing, by means of the control unit 17 and in case the component 6 is defective, the first modified motion law and/or the second modified motion law based on the current kinematics and/or on the size of the article 3' being processed.
- the modified motion laws are calculated by means of known methods of interpolation of points for an electric actuator such as, for example, splines or polynomials (or by imposing the maximum possible accelerations/decelerations for the actuators 12, 13 and 14).
- the modified motion law comprises at least a first step, during which there is both a deceleration of the article 3', and (or alternatively) an acceleration of the new component 6". More precisely, the modified motion law also comprises a second step, during which there is both an acceleration of the article 3', and (or alternatively) a deceleration of the new component 6", in particular so as to re-establish the same speeds provided for by the periodic motion law. In such manner, the disruption of the coupling between the component 6" and the article 3' inside the work station WS is prevented.
- the step of checking the quality and/or the position and/or the orientation of the component 6, 6', 6" is cyclically repeated for each new component 6" going along the feeding path (FP).
- the semi-finished articles 3 upstream of the article 3' being processed are conveyed according to a third modified motion law, different from the first modified motion law, the third modified motion law comprises a deceleration step having a peak which is smaller, in module, compared to the first modified motion law.
- the third modified motion law allows the semi-finished articles 3 upstream of the article 3' being processed to slow down in a differentiated manner (more precisely with a less abrupt deceleration) compared to the article 3' in the processing step (which, being the first in the line moving towards the work station WS and thus the one at a smaller distance from the work station WS, has less space to reduce its speed).
- the semi-finished articles 3 upstream of the article 3' being processed are controlled with a third periodic motion law, corresponding to the first periodic motion law.
- the stopping time has a predetermined upper limit, more precisely below five (preferably two) seconds.
- the upper limit of the stopping time is exceeded, the semi-finished articles 3 downstream of the stationary article 3' continue their possible further processing operations (until exiting the machine 1), in particular until the automatic machine 1 is emptied of all the articles 3 downstream of the article 3' in compensation step.
- the defective component 6' is rejected inside the zone WZ without going through the conveying path CP (for example by means of a suitable discharge, suction, exchange, etc. apparatus).
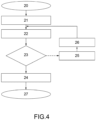
- the rectangular blocks are processing blocks in which operations are carried out by the control unit 15, while the rhomboidal blocks are six control or checking blocks in which certain conditions are checked; at the outlet of such blocks, the continuous arrows indicate that such conditions have been checked, while the broken arrows indicate that such conditions have not been checked.
- the modified motion law is imposed on the actuators 12, 13 and 14 in the block 26, after which the new component 6" is controlled. Such procedure continues in a recursive manner.
- the control of the component 6, 6" fed along the feeding path FP occurs at such a distance (from the work station) that, when processing the modified motion law, the control unit 17 knows the number of consecutive defective components 6' (up to a finite maximum, as described above) and thus of the following new usable component 6". In this case, in processing the modified motion law, the control unit 17 also considers the rejection of possible consecutive defective components, varying the deceleration of the article 3' being processed (and possibly the acceleration of the new component 6" to be fed) so as to compensate also the plurality of consecutive rejections.
- the automatic machine 1 is configured to carry out the procedure described in the foregoing.
- the present invention has multiple advantages. First of all, it allows rejecting only the defective components and not an entire article in which a plurality of usable components are also present. In such manner, it improves the efficiency of the manufacturer in terms of wastage of usable material, the waste is generally reduced and therefore there is a greater sustainability of the process and lower disposal and raw material costs.
- the possibility of independently controlling the various actuators and checking the number of consecutive rejections allows preventing that the machine jams out of control, enabling, simultaneously, the completion of the production of the articles downstream of the part of the machine that stops during a step.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Attitude Control For Articles On Conveyors (AREA)
- Control Of Conveyors (AREA)
Claims (14)
- Verfahren für das selektive Management des Abfalls wenigstens eines Teils (2) einer automatischen Maschine (1) zum Herstellen oder Verpacken von Verbraucherartikeln; wobei das Verfahren die Schritte umfasst:Fördern mehrerer Halbfertigartikel (3), gemäß einem ersten periodischen Bewegungsgesetz, entlang eines Förderwegs (CP) durch wenigstens eine Arbeitsstation (WS), wo zu einem Artikel (3'), der verarbeitet wird, wenigstens eine Komponente (6, 6") hinzugefügt wird;Zuführen jeder Komponente (6, 6', 6"), gemäß einem zweiten periodischen Bewegungsgesetz, aus einem jeweiligen Lager (8) in Richtung des Förderwegs (CP) und entlang eines Zuführungswegs (FP);Prüfen, in einem Kontrollbereich (IA) und während des Schritts des Zuführens der Komponente (6, 6', 6"), der Qualität und/oder der Position und/oder der Orientierung der Komponente (6, 6', 6") selbst und Feststellen, ob die Komponente (6, 6', 6") nutzbar oder defekt ist;wobei das Verfahren dadurch gekennzeichnet ist, dass es, falls die Komponente (6, 6', 6") fehlerhaft ist, einen Ersetzungsschritt, währenddessen die defekte Komponente (6') von dem Kontrollbereich (IA) zu einer Abfallzone (WZ) gefördert wird und innerhalb der Arbeitsstation (WS) durch eine neue Komponente (6"), die aus dem Lager (8) in Richtung des Förderwegs (CP) und entlang des Zuführungswegs (FP) zugeführt wird, ersetzt wird,; und einen Kompensationsschritt, währenddessen der Artikel (3'), der verarbeitet wird, gemäß einem ersten modifizierten Bewegungsgesetz gefördert wird und die neue Komponente (6") gemäß einem zweiten modifizierten Bewegungsgesetz gefördert wird, was somit ermöglicht, dass die neue Komponente (6") die Arbeitsstation (WS) in der Weise erreicht, dass sie zu dem Artikel (3'), der verarbeitet wird, hinzugefügt werden kann, umfasst;wobei das Verfahren vor dem Kompensationsschritt einen weiteren Schritt des Verarbeitens, mittels einer Steuereinheit und falls die zugeführte Komponente (6, 6', 6") defekt ist, wenigstens des ersten modifizierten Bewegungsgesetzes und/oder des zweiten modifizierten Bewegungsgesetzes auf der Grundlage der aktuellen Kinematik und/oder der Größe des Artikels (3'), der verarbeitet wird, umfasst.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 1, wobei das erste modifizierte Bewegungsgesetz, verglichen mit dem ersten periodischen Bewegungsgesetz, einen Schritt des Verzögerns des Artikels (3'), der verarbeitet wird, umfasst, wobei der Verzögerungsschritt insbesondere zu Beginn des Kompensationsschritts ausgeführt wird.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, wobei das zweite modifizierte Bewegungsgesetz, verglichen mit dem zweiten periodischen Bewegungsgesetz, einen Schritt des Beschleunigens der neuen Komponente (6") umfasst, wobei der Beschleunigungsschritt insbesondere zu Beginn des Kompensationsschritts ausgeführt wird.
- Verfahren nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, wobei die Halbfertigartikel (3) vor und/oder nach demjenigen (3'), der verarbeitet wird und dem Kompensationsschritt ausgesetzt wird, entlang des Förderwegs (CP), insbesondere gemäß dem ersten periodischen Bewegungsgesetz, weitergefördert werden.
- Verfahren nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, wobei der Ersetzungsschritt und der Kompensationsschritt wenigstens teilweise gleichzeitig sind.
- Verfahren nach einem der vorhergehenden Schritte, wobei der Schritt des Prüfens der Qualität und/oder der Position und/oder der Orientierung der Komponente (6, 6', 6") für jede neue Komponente (6"), die durch den Kontrollbereich (IA) und entlang des Zuführungswegs (FP) geht, zyklisch wiederholt wird.
- Verfahren nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, wobei, während des Kompensationsschritts, der Artikel (3'), der verarbeitet wird, verlangsamt wird, bis er vorübergehend für eine Haltezeit anhält.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 7, wobei die Haltezeit eine vorbestimmte Obergrenze, insbesondere unter fünf Sekunden, aufweist.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 8, wobei, falls die Obergrenze der Haltezeit überschritten wird, der Teil (2) der automatischen Maschine (1) auf gesteuerte Weise anhält, insbesondere einem Betreiber oder einem Managementsystem einen Fehler signalisiert.
- Verfahren nach einem der Ansprüche 7 bis 9, wobei, falls die Obergrenze der Haltezeit überschritten wird, die Halbfertigartikel (3) stromabseitig des Artikels (3'), der angehalten wird, mit möglichen Weiterverarbeitungsoperationen fortfahren, insbesondere bis die automatische Maschine (1) leer ist.
- Verfahren nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, wobei, während des Kompensationsschritts, die Halbfertigartikel (3) stromaufseitig des Artikels (3'), der verarbeitet wird, gemäß einem dritten modifizierten Bewegungsgesetz, das von dem ersten modifizierten Bewegungsgesetz verschieden ist, gefördert werden; wobei das dritte modifizierte Bewegungsgesetz insbesondere einen Verzögerungsschritt umfasst, der eine Spitze aufweist, die kleiner ist, in der Maßeinheit, verglichen mit dem ersten modifizierten Bewegungsgesetz.
- Verfahren nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, wobei, für jeden Artikel, der Förderweg (CP) in mögliche Kompensationszonen (VS), in denen der Artikel (3'), der verarbeitet wird, gemäß dem ersten modifizierten Bewegungsgesetz gefördert werden kann, und vordefinierte Geschwindigkeitszonen (CS), in denen der Artikel (3'), der verarbeitet wird, ausschließlich gemäß dem ersten periodischen Bewegungsgesetz gefördert wird, unterteilt ist.
- Verfahren nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, wobei eine defekte Komponente (6), die sich entlang des Zuführungswegs (FP) weiterbewegt und durch den Förderweg (CP) geht, zurückgewiesen wird.
- Automatische Maschine (1) zum Herstellen oder Verpacken von Verbraucherartikeln (3); wobei die automatische Maschine (1) umfasst:ein Fördersystem (4), das konfiguriert ist, mehrere Halbfertigartikel (3) einzeln oder in Gruppen entlang eines Förderwegs (CP) und gemäß einem ersten periodischen Fördergesetz zu fördern;wenigstens ein Lager (8), das eine oder mehrere Komponenten enthält;ein Zuführungssystem (9), das konfiguriert ist, wenigstens eine Komponente (6) aus dem jeweiligen Lager (8) in Richtung des Förderwegs (CP) und entlang eines Zuführungswegs (FP) sowie gemäß einem zweiten periodischen Bewegungsgesetz zuzuführen;ein Kontrollsystem (15), das konfiguriert ist, während des Zuführens der Komponenten, die Qualität und/oder die Position und/oder die Orientierung wenigstens einer Komponente (6) zu detektieren, um festzustellen, ob die Komponente (6) nutzbar oder defekt ist; undeine Steuereinheit (17), die konfiguriert ist, wenigstens das Fördersystem (4) und das Zuführungssystem (9) zu steuern;eine Abfallzone (WZ), die konfiguriert ist, mögliche defekte Komponenten zu empfangen;wobei die automatische Maschine (1) dadurch gekennzeichnet ist, dass:die Steuereinheit (17) konfiguriert ist, falls die zugeführte Komponente (6') defekt ist, das Fördersystem (4) gemäß einem ersten modifizierten Bewegungsgesetz, das von dem ersten periodischen Bewegungsgesetz verschieden ist, zu steuern, , um den Artikel (3'), der verarbeitet wird, zu fördern, und das Zuführungssystem (9) gemäß einem zweiten modifizierten Bewegungsgesetz, das von dem zweiten periodischen Bewegungsgesetz verschieden ist, zu steuern, um die neue Komponente (6"), die die defekte Komponente (6') ersetzt, zuzuführen;die Steuereinheit (17) konfiguriert ist, falls die zugeführte Komponente (6, 6', 6") defekt ist, wenigstens das erste modifizierte Bewegungsgesetz und/oder das zweite modifizierte Bewegungsgesetz auf der Grundlage der aktuellen Kinematik und/oder der Größe des Artikels (3'), der verarbeitet wird, zu verarbeiten.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT202000001993 | 2020-02-03 | ||
| PCT/IB2021/050865 WO2021156759A1 (en) | 2020-02-03 | 2021-02-03 | Procedure for the selective management of the waste of an automatic machine for manufacturing or packing consumer articles |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP4100328A1 EP4100328A1 (de) | 2022-12-14 |
| EP4100328B1 true EP4100328B1 (de) | 2025-04-09 |
Family
ID=70480486
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP21709093.5A Active EP4100328B1 (de) | 2020-02-03 | 2021-02-03 | Verfahren zur auswahl der abfälle einer automatischen maschine zur herstellung oder verpackung von verbraucherartikeln |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP4100328B1 (de) |
| PL (1) | PL4100328T3 (de) |
| WO (1) | WO2021156759A1 (de) |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3639972A1 (de) * | 1986-11-22 | 1988-05-26 | Hauni Werke Koerber & Co Kg | Verfahren und einrichtung zum aussondern von durch fehlerstellen unbrauchbaren materialbahnabschnitten aus einer materialbahn |
| EP0957028A1 (de) * | 1998-05-14 | 1999-11-17 | MARCHESINI GROUP S.p.A. | Verfahren zum Verpacken von Gegenständen in Behälter |
| DE102018105269A1 (de) * | 2018-03-07 | 2019-09-12 | Krones Aktiengesellschaft | Verpackungsvorrichtung für Artikel und Verfahren zum Bereitstellen von flächigen Verpackungszuschnitten für Artikel |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0311830B1 (de) * | 1987-10-16 | 1992-11-25 | Körber Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum gruppenweisen Verpacken von Einzelpackungen |
| IT1238549B (it) * | 1990-04-11 | 1993-08-18 | Gd Spa | Apparecchiatura per l'alimentazione di prodotti. |
| ITBO20060019A1 (it) * | 2006-01-16 | 2007-07-17 | Gd Spa | Metodo e macchina per confezionare/incartare un prodotto utilizzando almeno un foglio stampato |
| DE102012025158A1 (de) * | 2012-12-21 | 2014-06-26 | Focke & Co. (Gmbh & Co. Kg) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur automatischen Prüfung von flächigem Folienmaterial |
| IT201800004698A1 (it) * | 2018-04-19 | 2019-10-19 | Procedimento per il ripristino dello stato funzionale di una macchina automatica per la produzione di articoli dell’industria del tabacco |
-
2021
- 2021-02-03 EP EP21709093.5A patent/EP4100328B1/de active Active
- 2021-02-03 WO PCT/IB2021/050865 patent/WO2021156759A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2021-02-03 PL PL21709093.5T patent/PL4100328T3/pl unknown
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3639972A1 (de) * | 1986-11-22 | 1988-05-26 | Hauni Werke Koerber & Co Kg | Verfahren und einrichtung zum aussondern von durch fehlerstellen unbrauchbaren materialbahnabschnitten aus einer materialbahn |
| EP0957028A1 (de) * | 1998-05-14 | 1999-11-17 | MARCHESINI GROUP S.p.A. | Verfahren zum Verpacken von Gegenständen in Behälter |
| DE102018105269A1 (de) * | 2018-03-07 | 2019-09-12 | Krones Aktiengesellschaft | Verpackungsvorrichtung für Artikel und Verfahren zum Bereitstellen von flächigen Verpackungszuschnitten für Artikel |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP4100328A1 (de) | 2022-12-14 |
| PL4100328T3 (pl) | 2025-06-23 |
| WO2021156759A1 (en) | 2021-08-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2623305B1 (de) | Schachtelherstellungsmaschine und vorrichtung dafür zur entfernung defekter produkte | |
| US11834211B2 (en) | Packing machine for paper product converting line and method for packing of paper products | |
| EP1740460B1 (de) | Verfahren und werk zur herstellung von blisterpackungen durch schneiden eines blisterbands | |
| EP3115302B1 (de) | Verfahren, maschine und anlage zur vakuumverpackung von produkten | |
| AU2003266959B2 (en) | Installation for producing and packing tubes | |
| EP0957028B1 (de) | Verfahren zum Verpacken von Gegenständen in Behälter | |
| JPS5926532B2 (ja) | シガレツト包装機の包装材検出・廃棄装置 | |
| US7690498B2 (en) | Method for transferring a product in a packaging machine and transfer device for carrying out said method | |
| US20080138187A1 (en) | Method For Handling a Blister in a Blister Packaging Machine and Device For Carrying Out Said Method | |
| EP4100328B1 (de) | Verfahren zur auswahl der abfälle einer automatischen maschine zur herstellung oder verpackung von verbraucherartikeln | |
| US6122898A (en) | Packaging machine | |
| CN102015462A (zh) | 用于由物品组成的物品集的包装机、用于制造物品集的方法及物品集 | |
| JP3983756B2 (ja) | 打ち抜きステージ | |
| US8925713B2 (en) | Method for operating a processing system, in which product units having different product characteristics are processed | |
| EP1449770A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Herstellen von Streifenpackungen | |
| EP4371894A1 (de) | Verfahren zur abfallverwaltung mit halbfabrikatrückführung für eine automatische maschine zur herstellung oder verpackung von konsumartikeln | |
| US6971213B2 (en) | Method for the separate rejection of defective items, in particular strip packages, during transferring from a packaging line to a conveying line | |
| KR101965006B1 (ko) | 흡수성 물품의 배출 방법 | |
| EP1848637B1 (de) | Maschine zum füllen kastenartiger behälter mit nebeneinander und vertikal angeordneten artikeln | |
| JP6117739B2 (ja) | 横形製袋充填機およびその制御方法 | |
| JP2841204B2 (ja) | 包装方法及び装置 | |
| EP3713863B1 (de) | In schneidemaschinen integriertes dreifachantriebssystem | |
| ITSV980036A1 (it) | Metodo di azionamento e macchina operatrice, in particolare nelle macchine impaccettatrici di sigarette, o simili. | |
| JP2860344B2 (ja) | 包装方法及び装置 | |
| EP4594193A1 (de) | Maschine zur herstellung von filterbeuteln für aufbrühbare produkte |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: UNKNOWN |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE INTERNATIONAL PUBLICATION HAS BEEN MADE |
|
| TPAC | Observations filed by third parties |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNTIPA |
|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20220808 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20230130 |
|
| DAV | Request for validation of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230529 |
|
| TPAC | Observations filed by third parties |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNTIPA |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20240913 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602021028874 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: FP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 1783365 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20250409 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250409 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250811 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250409 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG9D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250709 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250710 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250409 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250409 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250409 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250709 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250809 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250409 |