EP3536769B1 - Wasch- und reinigungsmittelzusammensetzung enthaltend ein polyoxyalkylen carboxylat - Google Patents
Wasch- und reinigungsmittelzusammensetzung enthaltend ein polyoxyalkylen carboxylat Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3536769B1 EP3536769B1 EP19020100.4A EP19020100A EP3536769B1 EP 3536769 B1 EP3536769 B1 EP 3536769B1 EP 19020100 A EP19020100 A EP 19020100A EP 3536769 B1 EP3536769 B1 EP 3536769B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- fatty acid
- peg
- surfactants
- oil
- rco
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/66—Non-ionic compounds
- C11D1/72—Ethers of polyoxyalkylene glycols
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/02—Anionic compounds
- C11D1/04—Carboxylic acids or salts thereof
- C11D1/08—Polycarboxylic acids containing no nitrogen or sulfur
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/66—Non-ionic compounds
- C11D1/83—Mixtures of non-ionic with anionic compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D2111/00—Cleaning compositions characterised by the objects to be cleaned; Cleaning compositions characterised by non-standard cleaning or washing processes
- C11D2111/10—Objects to be cleaned
- C11D2111/12—Soft surfaces, e.g. textile
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D2111/00—Cleaning compositions characterised by the objects to be cleaned; Cleaning compositions characterised by non-standard cleaning or washing processes
- C11D2111/10—Objects to be cleaned
- C11D2111/14—Hard surfaces
- C11D2111/16—Metals
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D2111/00—Cleaning compositions characterised by the objects to be cleaned; Cleaning compositions characterised by non-standard cleaning or washing processes
- C11D2111/10—Objects to be cleaned
- C11D2111/14—Hard surfaces
- C11D2111/18—Glass; Plastics
Definitions
- washing and cleaning compositions which contain at least one polyoxyalkylene carboxylate and a further surfactant.
- the polyoxyalkylene carboxylate or polyoxyalkylene carboxylates and the at least one other surfactant are based on fatty acids from vegetable oils and have an exceptionally high proportion of long-chain ( ⁇ C17), mostly unsaturated hydrocarbon chains.
- the present invention relates to the use of a composition as a washing and cleaning agent with high cleaning performance using more environmentally friendly and less irritating surfactants and to a method for improving the cleaning performance of a washing and cleaning agent using the composition.
- protein contamination occurs in all areas of humans and animals, e.g. as fragments of hair, dander, milk residues, gluten, deposits on contact lenses, etc.
- the cleaning of proteins is particularly important in food areas, clinics, animal husbandry and many more.
- proteins can protect microorganisms and thus reduce the effectiveness of disinfectants. Effective protein soil removal is essential, especially in areas that require high levels of hygiene.
- a preferred embodiment variant is therefore a composition in which the removal of protein dirt takes place with a reduction or, in particular, with no proteases.
- the dispersing power is also important for a washing and cleaning agent.
- the dispersing power is the ability of a surface-active substance or an agent to keep dirt particles in the washing liquor, i.e. the dirt-carrying capacity, so that dirt particles cannot be deposited again on the textile or the surface.
- Nonionic surfactants are often used as dispersing agents.
- the anionic surfactants commonly used for the cleaning task are often sensitive to hard water.
- Biosurfactants which are produced by microorganisms, form a special class of nonionic surfactants. In many cases, microorganisms are genetically modified for an efficient production process of biosurfactants; Changes criticized by some environmental groups.
- Another disadvantage of the commonly used surfactants is their high potential for irritation.
- the most commonly used surfactants such as sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium laureth sulfate, cocoamidopropylamide or decyl glucoside cause serious eye damage. It is desirable, therefore, to replace these surfactants to the greatest extent possible with milder-on-the-eye surfactants.
- Skin-mild tenside systems are known from cosmetics, but, as listed below, are not suitable for industrial, institutional, textile and household cleaning due to their specific properties.
- US2004/0265264 discloses the use of sodium PEG-7 olive oil carboxylate in "catalytic" amounts to reduce skin irritation from the primary surfactant sodium laureth sulfate.
- WO2013098066 Sodium PEG-7 olive oil carboxylate is used in comparatively small amounts together with other surfactants based on lauryl and biosurfactants for a baby cleaning product.
- the exemplary embodiment reveals the positive sensory effect on the skin through the combination of biosurfactants with oleic acid, the cleaning performance is not mentioned.
- UK 10147049 discloses surfactant mixtures of sodium cocoyl glutamate, sodium myristyl ether sulfate and sodium PEG-7 olive oil carboxylate which selectively wash out surface lipids rather than sebum lipids and thus reduce skin roughness. Furthermore, detergents with combinations of sodium lauryl sulfate as the surfactant with the largest proportion and sodium PEG-7 olive oil carboxylate are known.
- the complex technical task of the invention was to provide compositions as detergents and cleaning agents that contain predominantly fatty acid surfactants based on vegetable raw materials, the proportion of surfactants based on palm oils (i.e. palm oil, palm kernel oil, coconut oil, babassu oil) being reduced as far as possible should be in favor of surfactants from less problematic sources, such as vegetable oils from European cultivation.
- palm oils i.e. palm oil, palm kernel oil, coconut oil, babassu oil
- the desired lauric acid (C12) which is usually used due to its technical properties such as advantageous foaming, washing and cleaning performance, cannot be obtained in sufficient quantities from available oils, for example from Central Europe.
- the desired surfactants contain a high proportion of unsaturated, long fatty acid residues ⁇ C18 instead of lauric acid, which, in the surfactant concentrations commonly used, result in completely new properties such as foam, stability, cleaning performance, compatibility, etc.
- the surfactant combinations should achieve good cleaning performance. Another goal was to use the surfactant mixture over a wide pH range and to combine it with different ingredients in order to have a base available for different uses.
- Irritation potential for skin irritation potential for eyes, biodegradability, water hazard, as can be seen, for example, in the hazard labeling obligation according to CLP.
- compositions When used according to the invention, the compositions should be based on natural raw materials to the greatest possible extent and should be readily biodegradable.
- compositions when used as defined in the claims and described below, achieve one or more of the stated objects.
- the compositions when used according to the invention, can achieve the same or better cleaning performance as the comparison agents while at the same time minimizing the medium-chain surfactants, in particular lauryl or coco, without having to increase the total concentration of surfactants.
- questionable ingredients such as strong eye-irritating surfactants, could be partially or completely substituted in the compositions when used according to the invention.
- the substitution of surfactants when used according to the invention is surprising insofar as surfactant systems only develop their full effect through interactions with one another and the substituted surfactant systems represent well-established systems.
- compositions when used according to the invention, exhibit a cleaning action on specific soiling that was in no way foreseeable by a person skilled in the art. This enables the use of environmentally friendly agents, even with stubborn dirt such as protein dirt or particle dirt.
- compositions show a very high cleaning performance on protein soil when used according to the invention.
- the cleaning performance for removing proteins thus also allows the use of an enzyme-free embodiment as a preferred embodiment, particularly preferably without proteases.
- compositions show an unforeseeably good dirt-carrying capacity during use, comparable to the surfactant systems commonly used for this task.
- the re-attachment to cleaned surfaces is reduced, which counteracts graying or crusting, for example when the compositions are used according to the invention as laundry detergents.
- the high dispersing power of the compositions when used according to the invention also allows stabilization of insoluble ingredients in the composition, such as abrasives or wax bodies or the like.
- a further advantage of the invention is that, unlike in commonly used anionic surfactant systems such as sodium laureth sulfate or sodium lauryl sulfate, the composition is insensitive to hard water when used according to the invention and therefore the dirt-carrying capacity is not reduced in the presence of calcium and magnesium ions .
- nonionic surfactants with medium-chain carbon chains with a high potential for irritation such as decyl glucoside, or surfactants from fermentation (biosurfactants), which are usually used for hard water, can also be excluded.
- the foaming behavior of the compositions when used according to the invention corresponds to a pure sodium laureth sulfate surfactant system, despite the fundamentally longer carbon chains of the fatty acid acyl radicals of the surfactants. Contrary to expectations, a stable foam can be achieved in the compositions when used according to the invention, as a result of which medium-chain alkylamidobetaines, monoethanolamides and diethanolamides, which have a considerable potential for irritation, are reduced.
- a preferred embodiment variant is therefore free from alkylamidobetaines, such as cocoamidopropyl betaine.
- Another preferred embodiment variant is free from mono- and diethanolamides, such as cocamide DEA, cocamide MEA, and others.
- composition is characterized by high stability when used according to the invention.
- composition is also disclosed in a preservative-free embodiment when used according to the invention.
- compositions as washing and cleaning agents for hard or flexible surfaces, and also for textiles, carpets or natural fibers in the areas of industrial, institutional, textile and household cleaning.
- Solid substrates such as cloths represent a preferred embodiment. These are impregnated with a preparation and have the advantage that the correct dosage is already specified.
- the agents When used according to the invention, the agents have a high level of compatibility with the specific ingredients (e.g. cationic surfactants) and show good adhesion to the substrate. Wipes meet the consumer's desire for convenience in particular, they are easy to handle, can be used directly without additional work steps and can also be used on the go, e.g. when travelling, even if there is no running water available.
- Cloths are made from textiles, which can be woven, knitted or warp-knitted or exist as a composite material in the form of fleece, paper, cotton wool or felt, with fleeces usually being made from polypropylene, polyester or viscose. Substrates and cloths impregnated with agents can be manufactured in a number of ways - dipping, wiping and spraying.
- the vegetable oils from oil palms, babassu, palm kernels, or coconuts differ significantly in the fatty acid composition from the C-18 vegetable oils according to the invention:
- the following vegetable oils, fats, waxes or resins are referred to as C-18 vegetable oil:
- the C-18 vegetable oils are natural triglycerides.
- C-18 vegetable oils have a mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, with the fatty acid distribution of fatty acids having 18 and more carbon atoms being greater than 60% by weight, more preferably greater than 72% by weight and most preferably greater than 77% by weight. % and wherein the proportion of unsaturated fatty acids is more than 55% by weight, preferably more than 65% by weight and particularly preferably more than 72% by weight.
- the proportion of fatty acids having 16 and fewer carbon atoms is preferably below 30% by weight, preferably below 27% by weight and particularly preferably below 17% by weight.
- the C-18 vegetable oils preferably contain ⁇ 0.5%, particularly preferably >0.05%, of fatty acids having 6 carbon atoms.
- the C-18 vegetable oils preferably contain ⁇ 75% by weight of hydroxy fatty acids, preferably ⁇ 25% by weight, particularly preferably ⁇ 5% by weight.
- C-18 vegetable oils preferably contain saturated or unsaturated fatty acids with 20 and more carbon atoms, the content of which can be up to 96% by weight.
- the C-18 vegetable oils contain less than 95% by weight oleic acid, more preferably less than 85% by weight oleic acid; % by weight in the definition of C-18 vegetable oil in each case based on the total content of fatty acids in the vegetable oil.
- C-18 vegetable oils can be obtained from the following plants or parts of plants, such as seeds, kernels, fruits, leaves, roots and others, hereinafter referred to as C-18 plants, which preferably meet the technical features relating to fatty acid compositions for the agents according to the invention be selected from the group comprising the plants: amaranth, aniseed, apple, apricot, argan, arnica, avocado, cotton, borage, nettle, broccoli, canola, chia, hemp, hazelnut, beech, boxwood, thistle, spelled, peanut, tiger nut , lilac, garden cress, barley, pomegranate, oat, hemp, hazelnut, blueberry, elderberry, jasmine, currant, St.
- the oil is selected from the group: apricot, avocado, cotton, broccoli, beech, thistle, spelled, tigernut, barley, hemp, hazelnut, jojoba, cherry, mullein, crab, cruciferous spurge, pumpkin, Iberian scorpionfish, camelina, linseed , lupine, alfalfa, macademia, almond, corn, poppy, evening primrose, olive, oil radish, oil rocket, peach, rapeseed, rice, calendula, turnip rape, safflower, sage, sea buckthorn, black cumin, sesame, sesame leaf, mustard, sunflower, soy, tobacco , walnut, grape and wheat, and combinations thereof.
- apricot avocado, cotton, broccoli, beech, thistle, spelled, tigernut, barley, hemp, hazelnut, jojoba, cherry, mullein, crab, cruciferous spurge, pumpkin, I
- the oil is very particularly preferably selected from the group of apricot, thistle, tiger nut, hemp, crambe, Iberian dragonhead, camelina, linseed, lupine, alfalfa, corn, almond, olive, oilseed radish, peach, rapeseed, rapeseed, sesame, sesame leaf, sunflower , soybean, grape and wheat, and combinations thereof.
- oils is used in this invention to represent fats, waxes and resins.
- medium-chain surfactants are understood to mean surfactants with saturated alkyl or acyl groups with chain lengths between 8-18 carbon atoms or mixtures of saturated alkyl or acyl groups with 8 to 18 carbon atoms and unsaturated C-18 alkenyl or acyl groups, such as those found in coconut oil , palm kernel oil or babassu oil can be obtained.
- alkyl and acyl represent saturated and unsaturated radicals.
- fats or waxes representing derivatives of fatty acids after chemical reactions - purified or as a mixture - and/or their synthetic reaction products, such as addition products the double bond, reactions at the fatty acid function, such as fatty alcohols and their ethers and/or carboxy ethers, amines or fatty acid amides, fatty acid esters, and imines.
- fatty acid derivatives are preferably present as a mixture according to the fatty acid distribution in the native oil or as they occur in the conversion of naturally occurring vegetable oils or fats.
- fatty acids or fatty alcohols or fatty acid acyls or derivatives thereof represent branched or unbranched, linear or substituted, in particular hydroxy-substituted, saturated, mono- or polyunsaturated carboxylic acids or alcohols or derivatives thereof preferably having 6 to 24 carbon atoms.
- Surfactants are understood in the context of this invention to be amphiphilic organic substances with surface-active properties, which adsorb to the interface between two liquids, such as oil and water, and have the ability to reduce the surface tension of water. In solution, surfactants tend to self-aggregate and form structures such as micelles, lamellar structures, etc. In connection with this invention, surfactants are compounds that have the ability to reduce the surface tension of water at 20°C and at a concentration of 0.5% by weight. % based on the total amount of the preparation to below 45 mN/m.
- PEGylated vegetable oils are ethoxylated vegetable oils as defined in " Safety Assessment of PEGylated Oils as Used in Cosmetics", International Journal of Toxicology November/December 2014, 33 .
- cosmetic ingredients which describes the etherification and esterification products of glycerides and fatty acids with ethylene oxide, is used.
- representatives derived from C-18 plants are particularly preferred here;
- PEGylated fatty acid glycerides are mono-, di- and/or triglycerides which have been modified with a specific number of alkylene glycol units, mostly ethylene glycol units, and may contain by-products of the reaction.
- PEGylated fatty acid glycerides are defined as in " Safety Assessment of PEGylated Alkyl Glycerides as Used in Cosmetics", Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) 2014 . It should be noted that CIR also considers unsaturated fatty acids under "alkyl".
- representatives derived from C-18 plants are particularly preferred here;
- biosurfactant means the biosurfactant glycolipids from fermentation production defined according to the invention.
- sulphur surfactants are understood to mean anionic or amphoteric surfactants with a sulfur-containing hydrophilic radical, such as, for example, alkyl sulfates, alkyl ether sulfates, (alkoxylated) sulfosuccinates, (alkoxylated) sulfonates, (alkoxylated) isethionates, (alkoxylated) taurates, sulfobetaines and sultaines.
- a sulfur-containing hydrophilic radical such as, for example, alkyl sulfates, alkyl ether sulfates, (alkoxylated) sulfosuccinates, (alkoxylated) sulfonates, (alkoxylated) isethionates, (alkoxylated) taurates, sulfobetaines and sultaines.
- sulphate-containing surfactants are sodium laureth sulphate, sodium lauryl sulphate, ammonium laureth sulphate, ammonium lauryl sulphate, sodium myreth sulphate, sodium coco sulphate, sodium trideceth sulphate or MIPA laureth sulphate.
- Free from sulfur surfactants, phosphates, phosphonates means that the formulation does not contain any appreciable amounts of sulfur surfactants, phosphates, phosphonates. In particular, this means that sulfur surfactants, phosphates, phosphonates are each contained in amounts of less than 0.1% by weight, preferably less than 0.01% by weight, based on the total formulation, in particular no detectable amounts.
- At least one refers to 1 or more, for example 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 or more.
- detergents and cleaning agents is understood to mean a means for removing unwanted soiling or coverings, such as stains, residues, impurities, metabolic products of biological processes from hard or flexible surfaces, as well as textiles, carpets or natural fibers in industrial, institutional , textile and household cleaning.
- the agents can be applied, diluted or undiluted, to the material to be cleaned by rubbing, dosing, spraying, foaming and other methods (e.g. laying on) directly or using a tool such as a cloth.
- detergents and cleaning agents preferably also comprise at least 4 other ingredients selected from the groups: solvents; other surfactants; softeners and complexing agents; viscosity regulators; pH adjusters and acids and bases; builders; solubilizer; abrasives; antioxidants; vitamins; UV filter; opacifiers; anti-corrosive agents; preservatives; fragrances; dyes; inorganic alkali metal or alkaline earth metal salts; optionally enzymes.
- cleaning performance or “detergent power” is understood as meaning the removal of one or more soilings.
- the distance can be measured or assessed visually via a lightening or reduction in soiling.
- the HLB (hydrophile-lipophile balance) value is a measure of the hydrophilicity or lipophilicity of a substance, usually a nonionic surfactant.
- the value can be measured theoretically as described in relevant literature (e.g. according to the Griffin method) or experimentally by comparing the solubility behavior of standard compositions with known HLB.
- a first object of the invention is directed to the use of a composition as a detergent for industrial, institutional, textile and household cleaning, preferably for hard surfaces and textiles, containing at least one compound of the formula (I), preferably a mixture of compounds of the formula (I), and one or more other surfactants (III).
- the fatty acid residue RCO with a proportion of 20 or more carbon atoms is preferably >0.01% by weight, particularly preferably >0.05% by weight and very particularly preferably ⁇ 0.1% by weight and extremely preferably ⁇ 0.2% by weight.
- the proportion of fatty acid residues RCO with fatty acids having 16 and fewer carbon atoms is preferably below 30% by weight, preferably below 27% by weight and particularly preferably below 17% by weight;
- the proportion of fatty acid residues RCO with fatty acids of 6 and fewer carbon atoms is preferably ⁇ 0.5%, particularly preferably ⁇ 0.05%;
- the proportion of hydroxy fatty acid residues is preferably ⁇ 75% by weight, preferably ⁇ 25% by weight, particularly preferably ⁇ 5% by weight;
- the proportion of fatty acid residues RCO with 20 and more carbon atoms can preferably be up to 96% by weight;
- the proportion of the oleic acid acyl residue is preferably less than 95% by weight, particularly preferably below 85% by weight,
- Surfactants of this class used according to the invention are preferably obtained by the reaction, known to those skilled in the art, of monochloroacetic acid at a terminal hydroxyl group of an alkoxylated fatty acid ester, an alkoxylated alkyl glyceride, preferably a mono- or diglyceride, an alkoxylated polyglyceride, or an alkoxylated C-18 vegetable oil, or their mixtures and then neutralized with a lye.
- Suitable types of surfactants for the compositions when used according to the invention include, but are not limited to: sodium PEG-6 almond oil carboxylate, sodium PEG-8 almond oil carboxylate, sodium PEG-8 apricot kernel oil carboxylate, sodium PEG-8 boxy chinensis oil carboxylate, sodium PEG -6 Apricot kernel oil carboxylate, sodium PEG-40 Apricot kernel oil carboxylate, sodium PEG-8 Argan oil carboxylate, sodium PEG-8 avocado oil carboxylate, sodium PEG-11 Avocado oil carboxylate, sodium PEG-8 Borage seed oil carboxylate, sodium PEG-8 Macademia tenuifolia oil carboxylate, sodium PEG-6 corn oil carboxylate, sodium PEG-8 corn oil carboxylate, sodium PEG-8 grapeseed oil carboxylate, Sodium PEG-8 hazelnut oil carboxylate, Sodium PEG-8 flaxseed oil carboxylate, Sodium PEG-6 olive oil carboxylate, Sodium PEG-7 olive oil carboxylate, Potassium PEG-7 olive oil carboxylate
- the compounds (I) are preferred, particularly preferably poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), .alpha.-carboxy.omega.-(olive oil fatty acids)oxy, sodium salt (with 7 mol EO average EO content), according to the invention used as a cleaning surfactant for protein dirt.
- the compounds (I) are preferred, particularly preferably poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), alpha.-carboxy-.omega.-(olive oil fatty acids)oxy-, Sodium salt (with 7 mol EO average EO content), used as a cleaning surfactant for improved dirt-carrying capacity.
- the compounds (I) are preferred, particularly preferably poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), .alpha.-carboxy-.omega.-(olive oil fatty acids)oxy, sodium salt (with 7 mol EO average EO content), for Reduction of eye irritation by surfactant systems used.
- composition containing the compound (I) with the INCI name: sodium olive oil PEG-7 carboxylate or sodium PEG-7 olive oil carboxylate, IUPC name poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), .alpha. -carboxy-.omega.-(olive oil fatty acids)oxy-, sodium salt with 7 mol EO average EO content), HLB 11.
- compound (I) is based on a mixture of fatty acid derivatives based on C18 vegetable oils with different chain lengths and degrees of saturation.
- the mixture preferably follows the distribution of fatty acids in the native oil or as they occur during the conversion of naturally occurring vegetable oils or fats.
- mixtures of fatty acid derivatives for the synthesis of the surfactant class - as they occur in the conversion of naturally occurring vegetable oils or fats - the surfactants can be produced cost-effectively, resource-efficiently and in an environmentally friendly manner. Additional purification processes, such as e.g. the separation of fatty acids or fatty acid esters by fractional distillation or additional synthesis steps, e.g. to fatty alcohol, are not required here.
- the surfactant mixtures used show an increased cleaning performance.
- the polyglycol chain of compound (I) is of plant origin.
- the compositions contain preferably from 0.01 to 50% by weight of one or more compounds (I), more preferably from 0.25 to 40% by weight, particularly preferably from 0.6 to 20% by weight and most preferably from 0.6% to 8 % by weight based on the total mass of the composition.
- Another object of the invention is directed to the use of a composition
- a composition comprising one or more additional surfactants (II) selected from the groups of alkyl ether sulfates, alkyl sulfates, acyl glutamates, acyl sarcosinates, sulfosuccinate esters, preferably ethoxylated or non-ethoxylated, alkyl glucosides, amidoalkyl betaines, alkanolamides and amphoacetates , wherein the surfactants are saturated alkyl or acyl groups having chain lengths between 8-18 carbon atoms, or mixtures of saturated alkyl or acyl groups having 8 to 18 carbon atoms and unsaturated C-18 alkenyl or contain acyl groups such as are obtained from coconut oil, palm kernel oil or babassu oil; and wherein the weight ratio of (I) to the sum of the surfactants (II) is ⁇ 2:1, preferably ⁇ 3.5:1 and
- Alkyl ether sulfates sodium laureth sulfate, sodium coceth sulfate; Sodium myristyl ether sulfate, Sodium trideceth sulfate.
- Preferred compounds from the group of alkyl sulfates are: sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium coco sulfate, ammonium lauryl sulfate;
- Preferred compounds from the group of acylglutamates are: sodium cocoyl glutamate, TEA cocoyl glutamate, sodium lauroyl glutamate;
- Preferred compounds from the group of acyl sarcosinates are sodium lauroyl sarcosinate, sodium myristoyl sarcosinate;
- Preferred compounds from the group of sulfosuccinate esters are preferably disodium lauryl sulfosuccinate, disodium laureth sulfosuccinate;
- Preferred compounds from the group of alkyl glucosides are coco glucoside, lauryl glucoside, decyl glucoside, C10-C16 alkyl glucoside;
- the agents When used, the agents preferably contain up to 25% by weight of one or more compounds (II), more preferably up to 15% by weight, particularly preferably up to 10% by weight and very particularly preferably up to 1% by weight, based on the total mass of the composition
- compositions used according to the invention are distinguished by a high dispersing effect.
- the composition used does not contain any biosurfactants.
- a preferred embodiment contains no group (II) surfactants.
- a preferred embodiment contains one or more surfactants of compound (I) and other surfactants (III) derived from C18 vegetable oils.
- the invention relates to the use of a composition additionally comprising one or more surfactants (III) selected from the group consisting of soaps (alkali metal or ammonium fatty acid carboxylates), ethoxylated fatty acid alkyl esters, fatty acid amides and fatty acid imines, the fatty acid residues of a C 18 vegetable oil derived.
- surfactants selected from the group consisting of soaps (alkali metal or ammonium fatty acid carboxylates), ethoxylated fatty acid alkyl esters, fatty acid amides and fatty acid imines, the fatty acid residues of a C 18 vegetable oil derived.
- It preferably contains at least one soap selected from alkali metal or ammonium salts of saturated or unsaturated fatty acids produced by saponification of C-18 vegetable oils as defined above.
- At least one of the ethoxylated fatty acid alkyl esters, derived from a C18 vegetable oil, selected from the group of ethoxylated fatty acid methyl esters or ethoxylated fatty acid ethyl esters is selected from the group consisting of N-acylamino acid derivatives, N-acylaspartate, N-acylglycinate, N-acylalaninate, N-acylsarcosinate, N-acylglutamate, acylated polypeptides, N-acylaminosulfonic acids, N-Acyltauride, alkoxylated fatty acid amides, polyhydroxy fatty acid amides, optionally ethoxylated or carboxylated, carboxamide ether sulfates, alkanolamine-carboxylic acid condensates, amidoalkylpyr
- At least one of the fatty acid imines derived from a C18 vegetable oil is selected from the group of imidazole carboxylates, alkyliminopropionic acid, amphoacetates.
- One or more surfactants (III) selected from the groups of amphoacetates (C) are particularly preferred.
- Fatty acid amides of the formula (A) derived from thistle, tiger nut, hemp, crambe, Iberian dragonhead, camelina, linseed, lupine, alfalfa, corn, olive, oil radish, rapeseed, turnip rape, sesame leaf, sunflower, soybean, grapes and wheat are particularly preferred. as well as their combinations.
- Fatty acid amides of the formula (A) with an HLB >10.5 and ⁇ 12.0 are particularly preferred.
- the polyglycol chain of compound (A) is preferably of vegetable origin.
- compositions preferably contain up to 30% by weight of one or more compounds (A), more preferably up to 10% by weight, particularly preferably 0.5-3% by weight and very particularly preferably 0.5% by weight. up to 2% by weight, based on the total mass of the composition.
- the ethoxylated fatty acid amide based on rapeseed oil IUPAC name: Amides, rape oil, N-(hydroxyethyl), ethoxylated; INCI name: PEG-4 rapeseed amide, or rapeseed amide or PEG-4 rapeseed amide.
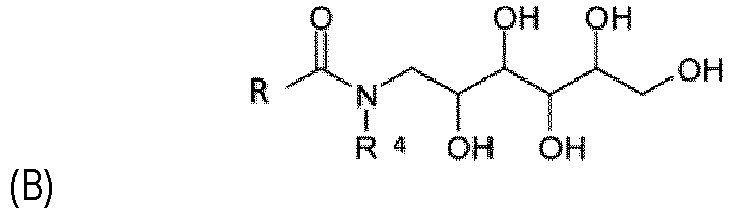
- Another object of the invention is directed to the use of a composition comprising one or more surfactants (III) selected from the group of polyhydroxy fatty acid amides of the formula (B) below,
- Extremely preferred according to the invention is the polyhydroxy fatty acid amide or glucamide according to formula (B) based on sunflower oil, INCI name: Sunfloweroyl Methylglucamide.
- sunfloweroyl methylglucamide has a significantly lower eye irritation potential and is therefore outstandingly suitable for the use of the compositions according to the invention.
- Another object of the invention is directed to the use of a composition
- a composition comprising one or more surfactants (III) selected from the group of amphoacetates (C) or amphoglycinates, wherein the surfactant (C) preferably consists of a mixture of different chain lengths and degrees of saturation of the fatty acid residue RCO such as defined for surfactant (I). and wherein RCO is preferably derived from a C-18 vegetable oil from the preferred group of plants disclosed according to definitions.
- Suitable amphoacetates include, but are not limited to, sodium oliveamphoacetate, sodium sunflowerseedamphoacetate, sodium grapeseedamphoacetate, sodium cottonseedamphoacetate, sodium ricebranamphoacetate, sodium sesamamphoacetate, sodium sweetalmondamphoacetate, sodium peanutamphoacetate, sodium wheat germmoacetate, and mixtures thereof.
- Amphoacetates (C) derived from thistle, tiger nut, hemp, crambe, Iberian dragonhead, camelina, linseed, lupine, alfalfa, corn, olive, oilseed radish, rapeseed, turnip rape, sesame leaf, sunflower, soybean, grapes and wheat are also particularly preferred according to the invention. as well as their combinations.
- compositions preferably contain up to 40% by weight of one or more compounds (C), more preferably 0.5-25% by weight, particularly preferably 0.5-10% by weight and very particularly preferably 0.5% by weight % to 5% by weight, based on the total mass of the composition.
- amphoacetates (C) derived from C-18 vegetable oils, in a concentration of ⁇ 5% by weight, preferably ⁇ 10% by weight, particularly preferably ⁇ 20% by weight, based on the total mass of the Surfactants in the composition used.
- amphoacetates (C) derived from C-18 vegetable oils are used as amphoteric surfactants in the washing and cleaning composition.
- Another object of the invention is the use of a composition comprising one or more additional surfactants selected from the group of alkoxylated fatty acid esters (D), where (D) preferably consists of a mixture of different chain lengths and degrees of saturation of the fatty acid residue RCO as defined above and where RCO is preferably derived from a C-18 vegetable oil from the preferred group of plants disclosed above.
- D alkoxylated fatty acid esters
- Suitable fatty acid esters include, but are not limited to: Vegetable oil PEG esters (i): PEG-6 almond oil, PEG-8 almond oil, PEG-8 apricot kernel oil, PEG-6 apricot kernel oil, PEG-40 apricot kernel oil, PEG-8 avocado oil, PEG -11 Avocado Oil, PEG-8 Borage Seed Oil, PEG-8 Macademia Tenuifolia Oil, PEG-6 Corn Oil, PEG-8 Corn Oil, PEG-8 Grape Seed Oil, PEG-8 Hazelnut Oil, PEG-8 Flaxseed Oil, PEG-6 Olive Oil, PEG-7 Olive Oil , PEG-7 Olive Oil, PEG-7 Olive Oil, PEG-8 Olea Europaea Oil, PEG-7 Olive Oil, PEG-7 Olive Oil, PEG-8 Olive Oil, PEG-10 Olive Oil, PEG-8 Oryza Sativa Oil, PEG-8 Prunus Dulcis, PEG-8 Persea gratissma oil, PEG-8 Passiflora edulis seed oil, PEG-6 peanut oil
- compositions When used, the compositions preferably contain up to 30% by weight of one or more compounds (D), more preferably up to 20% by weight, particularly preferably up to 10% by weight and very particularly preferably 1% to 3% by weight. % based on the total mass of the compositions.
- the composition preferably comprises one or more additional surfactants selected from the group of alkoxylated fatty acid esters (D), particularly preferably the weight ratio of (I) to the sum of C18 vegetable oil PEG esters (i), in particular preferably ⁇ 2:1 to PEG-7 olive oil ester, preferably ⁇ 3.5:1 and most preferably ⁇ 5:1.
- D alkoxylated fatty acid esters
- additional surfactants selected from the group of alkoxylated fatty acid esters (D), particularly preferably the weight ratio of (I) to the sum of C18 vegetable oil PEG esters (i), in particular preferably ⁇ 2:1 to PEG-7 olive oil ester, preferably ⁇ 3.5:1 and most preferably ⁇ 5:1.
- compositions contain, when used, preferably up to 5% by weight of one or more C18 vegetable oil PEG esters (i), more preferably up to 3%, most preferably up to 1% by weight. In a preferred embodiment of the compositions, no additional C18 vegetable oil PEG ester (i) is added to the compound (I) in use.
- compositions preferably contain up to 50% by weight of one or more compounds (III), more preferably up to 40% by weight, particularly preferably 0.6 to 20% by weight and very particularly preferably 0.6% by weight to 8% by weight, based on the total mass of the composition.
- Surfactants are understood in this context to be amphiphilic organic substances with surface-active properties, which adsorb to the interface between two liquids, such as oil and water, and have the ability to reduce the surface tension of water. In solution, surfactants tend to self-aggregate and form structures such as micelles, lamellar structures, etc. In connection with this invention, surfactants are compounds that have the ability to reduce the surface tension of water at 20°C and at a concentration of 0.5% by weight. % based on the total amount of the preparation to below 45 mN/m.
- surfactants which can be freely combined with the composition by a person skilled in the art when used according to the invention, reference is made to the relevant specialist literature such as Richard J. Farn, Chemistry and Technology of Surfactants, Blackwell Publishing.
- the surfactants include hydrocarbon chains derived from fatty acids or synthetic hydrocarbons, saturated or unsaturated, substituted or unsubstituted, linear or branched with 4-24 carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain.
- Optional surfactants preferably include, but are not limited to, other surfactants derived from C18 vegetable oils.
- compositions show a comparable cleaning performance to conventional agents with sulfur surfactants, even without their use.
- a preferred variant is free from all sulfur surfactants.
- the phosphates and phosphonates that pollute the water can be dispensed with without compromising on the cleaning performance.
- Another preferred embodiment is phosphate and phosphonate free in use.
- composition can optionally contain cationic surfactants when used, for example primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary alkylammonium salts of the formula (RI)(RII)(RIII)(RIV)N + X - , in which RI to RVI are independently the same or various alkyl radicals, branched and unbranched, saturated or unsaturated, unsubstituted, mono- or polysubstituted, or H, where X represents an anion.
- cationic surfactants when used, for example primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary alkylammonium salts of the formula (RI)(RII)(RIII)(RIV)N + X - , in which RI to RVI are independently the same or various alkyl radicals, branched and unbranched, saturated or unsaturated, unsubstituted, mono- or polysubstituted, or H, where X represents an anion.
- Surfactants are preferably used whose hydrophilic part originates from plants, very particularly preferably derived from plants from Central Europe, such as, for example, sugar surfactants or amino acid surfactants.
- compositions When used according to the invention, the compositions develop a stable foam and thus make the frequently used cocoamidopropyl betaine unnecessary. This substance has a significant potential for irritation. A preferred variant is therefore free of cocoamidopropyl betaine when used.
- Another preferably used variant is free from cocamide DEA and cocamide MEA, which are also used to stabilize foam and are known to be skin-irritating.
- composition of the surfactants on average when used according to the invention Composition of the surfactants on average when used according to the invention
- the sum of the surfactants derived from C18 fatty acids (I)+(III), based on the total mass of the surfactants present in the composition is preferably >50% by weight, preferably >65% by weight, particularly preferably >75% by weight %.
- the sum of the surfactants derived from C-18 fatty acids (I)+(III)+(IV), based on the total mass of the surfactants present in the composition is 100%.
- the composition can contain all the solvents customary in detergents and cleaning agents.
- the composition used contains water as the solvent, with more than 5% by weight, preferably more than 15% by weight and particularly preferably more than 25% by weight of water, based in each case on the total amount of Composition.
- particularly preferred compositions contain--based on their weight--from 5 to 98% by weight, preferably from 10 to 90% by weight, particularly preferably from 25 to 75% by weight, of water.
- the use may involve low-water or water-free compositions, the water content in a preferred embodiment being less than 10% by weight and more preferably less than 8% by weight, based on the total liquid Composition.
- the composition is anhydrous in use, the composition containing an organic solvent as the main solvent. It is preferred that the composition contains 5 to 98% by weight, preferably 10 to 90% by weight, particularly preferably 25 to 75% by weight, of solvent when used.
- At least one of the solvents is preferably selected from the group consisting of: aqua (water), alcohol denat. (Ethanol), alcohols, buteth-3, butoxydiglycol, butoxyethanol, butoxyisopropanol, butoxypropanol, n-butyl alcohol, t-butyl alcohol, butyl-3-hydroxybutyrate, butylene glycol, butyloctanol, C1-C6 alkanes, C7-C15 alkanes , Diethylene Glycol, Diethylene glycol monobutyl ether, Dimethoxydiglycol, dimethyl ether, dimethyl 2-methylglutarate, dipropylene glycol, dipropylene glycol phenyl ether, ethyl lactate, 2-ethyl lactate, ethyl levulinate glycerol ketal, ethyl levulinate propylene glycol ketal, Ethyl levulinate ethylene glycol ketal, ethoxy
- solvents from the group of solvents that are obtained from vegetable raw materials and are biodegradable are used. Solvents which do not contain any VOC (volatile organic compounds) are particularly preferred.
- a particularly preferred embodiment additionally contains fatty acid alkyl esters of the formula R-CO-OR 6 as a solvent, where the fatty acid alkyl ester consists of a mixture of different chain lengths and degrees of saturation of the fatty acid residue RCO as defined for surfactant (A) and is derived from a C-18 vegetable oil ; and wherein R 6 is a linear or branched hydrocarbon of 1-5 carbon atoms, preferably consisting of a methyl or ethyl group, most preferably methyl.
- Preferred representatives are rapeseed methyl ester, sunflower methyl ester, thistle methyl ester or soya methyl ester.
- complexing agents customary in detergents, care products and cleaning agents are suitable.
- Suitable for use according to the invention are, for example, softeners and complexing agents from the groups of phosphates and phosphonates, phyllosilicates, zeolites, carbonates and polycarboxylates, aminopolycarboxylic acids such as aminoacetic acids and polyaminoacetic acids and their salts, hydroxycarboxylic acids and their salts, polyglycosides and gluconic acids and their salts.
- At least one of the complexing agents is preferably selected from the group comprising aminotrimethylene phosphonic acid, beta-alanine acetoacetic acid, calcium disodium EDTA, chitosan, citric acid and its salts and hydrates, cyclodextrin, cyclohexanediamine tetraacetic acid, diammonium citrate, diammonium EDTA, diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid, diethylenetriamine pentamethylene phosphoric acid , Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium Azacycloheptane Diphosphonate, Disodium EDTA, Disodium Pyrophosphate, EDTA, Ethylenediamine- N , N' -disuccinic acid (EDDS), Etidronic Acid, Galactaric Acid, ⁇ -Glucan, Gluconic Acid, Glucuronic Acid, Glucoheptonic Acid, HEDTA, Hydroxypropyl Cyclodextrin, Methyl
- chelating agents can be freely combined with other ingredients mentioned here by a person skilled in the art.
- the compositions when used according to the invention, contain complexing agents that are biodegradable.
- the compositions therefore preferably contain no phosphates, no phosphonates, no EDTA and no polycarboxylates.
- the following complexing agents based on renewable raw materials are particularly preferred in this invention, such as beta-alanine diacetic acid, cyclodextrin, diammonium citrate, galactaric acid, gluconic acid, glucuronic acid, methylcyclodextrin, hydroxypropyl cyclodextrin, polyaspartic acid, alkali salts of gluconate, sodium carbonate, carboxymethyl inulin and sodium carboxymethyl inulin (NaCMI), sodium citrate, sodium dihydroxyethylglycinate, sodium gluconate, sodium glucoheptonate, sodium iminodisuccinate, sodium lactate, sodium lignosulfate, tetranatrium GLDA (I-glutamic acid, N,N-di (acetic acid), tetrasodium salt) , citric acid and its salts.
- beta-alanine diacetic acid such as beta-alanine diacetic acid, cyclodextr
- compositions When used according to the invention, preferred compositions contain at least one complexing agent in a total amount of 0.1-20% by weight, preferably 0.2-15% by weight, particularly preferably 0.5-10% by weight, based on the total amount of the composition.
- compositions are particularly suitable for stabilizing abrasives and polishing agents because of their high dispersibility.
- At least one of the abrasives and polishing agents is preferably selected from the group consisting of plastic abrasives based on polyethylene or polyurethane, organic polymers, mineral abrasives such as silicic acids, e.g.
- abrasives such as cellulose derivatives, wood flour or kernel and shell flour, and mixtures thereof.
- abrasives based on natural kernel and/or shell flours, in particular walnut shells, almond shells, hazelnut shells, olive kernel, apricot kernel and cherry kernel flour or pearls made of wax (e.g. jojoba wax).
- the concentration of the abrasives can be up to 50% by weight, preferably 0-30% by weight, based on the total amount of the composition.
- the composition can contain all the preservatives customary in washing, care and cleaning agents, which can be freely combined with other ingredients by a person skilled in the art for the purposes of this application.
- At least one preservative is preferably selected from the group consisting of alcohols, aldehydes, antimicrobial acids or their salts, carboxylic acid esters, acid amides, phenols, phenol derivatives, diphenyls, diphenylalkanes, urea derivatives, oxygen and nitrogen acetals and formals, benzamidines, isothiazoles and their derivatives such as isothiazolinones, phthalimide derivatives, pyridine derivatives, surface-active compounds, guanidines, antimicrobial amphoteric compounds, quinolines, 1,2-dibromo-2,4-dicyanobutane, iodo-2-propynyl-butyl-carbamate, iodine, iodophors and peroxides.
- compositions when used according to the invention based on antimicrobial active substances selected from antimicrobial peptides, ethanol, benzyl alcohol, dehydroacetic acid and their salts, sorbic acid and potassium sorbate, vegetable organic acids and their salts, formic acid, glycerol, citric acid, lactic acid, salicylic acid, and their salts.
- antimicrobial active substances selected from antimicrobial peptides, ethanol, benzyl alcohol, dehydroacetic acid and their salts, sorbic acid and potassium sorbate, vegetable organic acids and their salts, formic acid, glycerol, citric acid, lactic acid, salicylic acid, and their salts.
- the amount of the preservatives (one or more compounds) in the compositions when used is preferably 0.001 to 30% by weight, more preferably 0.05-20% by weight, particularly preferably 1-10% by weight, based on the total amount the composition.
- the embodiment used is extremely preferably free of chemical preservatives, as disclosed in the exemplary embodiments, i.e. in particular without parabens, without formaldehyde-containing preservatives or formaldehyde-releasing agents, without isothiazoles and their derivatives, without halogen-containing compounds, without phthalimides, without benzalkonium chloride, without benzoic acid, without phenoxyethanol .
- antioxidants are preferably added to the composition in order to protect the unsaturated hydrocarbon chains.
- At least one antioxidant is preferably selected from the group comprising amino acids (e.g. glycine, histidine, tyrosine, tryptophan) and their derivatives, imidazoles (e.g. urocanic acid) and their derivatives, peptides such as D,L-carnosine, D-carnosine, L-carnosine and their derivatives (e.g. anserine), carotenoids, carotenes and their derivatives, chlorogenic acid and its derivatives, lipoic acid and its derivatives, aurothioglucose, propylthiouracil and other thiols (e.g.
- thioredoxin glutathione, cysteine, cystine, cystamine and their glycosyl, N-acetyl -, methyl, ethyl, propyl, amyl, butyl and lauryl, palmitoyl, oleyl, [gamma]-linoleyl, cholesteryl and glyceryl esters) and their salts, dilauryl thiodipropionate, distearyl thiodipropionate, thiodipropionic acid and their derivatives (esters, ethers, peptides, lipids, nucleotides, nucleosides and salts) and sulfoximine compounds (e.g.
- buthionine sulfoximine homocysteine sulfoximine, buthionine sulfone, penta-, hexa-, heptathionine sulfoximine
- metal chelators e.g. [alpha]-hydroxy fatty acids, palmitic acid, phytic acid, lactoferrin), [alpha]-hydroxy acids (e.g. citric acid, lactic acid, malic acid), numic acid, bile acid, bile extracts, bilirubin, biliverdin, EDTA, EGTA and their derivatives, unsaturated fatty acids and their derivatives (e.g.
- vitamin E acetate
- vitamin A and derivatives vitamin A palmitate
- stilbenes and its derivatives e.g. stilbene oxide, trans-stilbene oxide
- superoxide dismutase and the derivatives suitable according to the invention salts, esters, ethers, sugars, nucleotides, nucleosides, peptides and lipids
- Antioxidants based on raw materials from plants preferably C-18 plants, such as antioxidants from the groups of amino acids, peptides, cartinoids, chelators, plant extracts and hydroxy acids, and mixtures thereof are preferred for the use according to the invention.
- the amount of antioxidants (one or more compounds) in the compositions when used is preferably 0.001 to 30% by weight, particularly preferably 0.05-20% by weight, in particular 1-10% by weight, based on the total amount of Composition.
- antioxidants can be combined with other ingredients mentioned here by a person skilled in the art.
- the composition may contain active ingredients against microorganisms such as fungi or bacteria in use.
- active ingredients against microorganisms such as fungi or bacteria in use.
- organohalogen compounds and halides, quaternary ammonium compounds, a number of plant extracts and zinc compounds can be used as germ-inhibiting or antimicrobial active ingredients.
- triclosan chlorhexidine and chlorhexidine gluconate
- 3,4,4'-trichlorocarbanilide bromochlorophene, dichlorophene, chlorothymol, chloroxylenol, hexachlorophene, dichloro-m-xylenol, dequalinium chloride, domiphenbromide, ammonium phenolsulfonate, benzalkonium halides, benzalkonium cetyl phosphate, benzalkonium saccharinates, benzethonium chloride, cetylpyridinium chloride , laurylpyridinium chloride, laurylisoquinolinium bromide, methylbenzedonium chloride.
- phenol phenoxyethanol, disodium dihydroxyethyl sulfosuccinyl undecylenate, sodium bicarbonate, zinc lactate, sodium phenol sulfonate and zinc phenol sulfonate, ketoglutaric acid, terpene alcohols such as. B.
- farnesol chlorophyllin-copper complexes
- active ingredients are selected from prebiotically active components.
- prebiotically active components include conifer extracts, in particular from the Pinaceae group, and plant extracts from the Sapindaceae, Araliaceae, Lamiaceae and Saxifragaceae groups, in particular extracts from Picea sp., Paullinia sp., Panax sp., Lamium album or Ribes nigrum and mixtures of these substances.
- compositions are selected from the germ-inhibiting perfume oils or essential oils.
- the amount of germ-inhibiting substances in the compositions is 0.1-10% by weight, preferably 0.2-7% by weight, in particular 0.3-5% by weight and extremely preferably 0.4-1% .0% by weight, based on the total amount of the composition.
- UVA and/or UVB filters can be added to the composition used.
- the composition is particularly suitable for stabilizing particles.
- compositions can therefore advantageously contain substances which absorb UV radiation in the UVA and UVB range, the total amount of filter substances in the entire composition preferably being between 0.1% by weight and 30% by weight.
- Commercially available water- or oil-soluble UV filters are preferred.
- combinations of UV filters are used, which can be combined with other ingredients mentioned here by a person skilled in the art.
- the composition can contain binders or consistency regulators, e.g. B. natural and / or synthetic water-soluble polymers such as alginates, carrageenates, tragacanth, starch and starch ethers, cellulose ethers such.
- they are preferably used in the compositions in amounts of 0.01-10% by weight, based on the total amount of the composition.
- oils oils, fats and waxes
- waxes u. a. natural waxes such as B. beeswax, rump fat, candelilla wax, carnauba wax, ceresin, esparto grass wax, guaruma wax, Japan wax, cork wax, lanolin (wool wax), microwax, montan wax, ozokerite (earth wax), petrolatum, paraffin wax, ouricoury wax, rice germ oil wax, shellac wax, sunflower wax, fruit waxes such as orange wax, Lemon waxes, grapefruit waxes, sugar cane wax, chemically modified waxes (hard waxes), such as e.g. B.
- hard waxes such as e.g. B.
- the waxes can be used in the compositions in amounts of 0.2 to 80% by weight, preferably amounts of 0.2 to 70% by weight, based on the total amount of the composition.
- suitable pearlescent waxes are: alkylene glycol esters, specifically ethylene glycol distearate; Fatty acid alkanolamides, partial glycerides, esters of polybasic, optionally hydroxy-substituted carboxylic acids with fatty alcohols having 6 to 24 carbon atoms, fatty substances such as fatty alcohols, fatty ketones, fatty aldehydes, fatty ethers and fatty carbonates, which have a total of at least 24 carbon atoms; Fatty acids such as stearic acid, hydroxystearic acid or behenic acid, ring-opening products of olefin epoxides having 12 to 24 carbon atoms with fatty alcohols having 12 to 24 carbon atoms and/or polyols having 2 to 15 carbon atoms and 2 to 10 hydroxyl groups, and mixtures thereof. When used according to the invention, preference is given to compositions with pearlescent waxes based on C18 plants.
- the amount of pearlescent wax used can be from 0.1 to 5% by weight, preferably from 0.5 to 3% by weight and in particular from 1 to 1.5% by weight, based on the total amount of the composition.
- the composition When used according to the invention, the composition is stable over a wide pH range. A pH range between 1 and 13 is preferred.
- the pH value of the composition can be adjusted using conventional pH regulators, with different pH ranges from acidic (pH 0-4) to neutral (pH 5 -7) to basic (pH 8-14). Acids and/or alkalis are used as pH adjusters. Suitable acids are, in particular, organic acids such as formic acid, acetic acid, citric acid, glycolic acid, lactic acid, succinic acid, Adipic acid, malic acid, tartaric acid and gluconic acid, amidosulfonic acid, methanesulfonic acid.
- Acids obtained from vegetable raw materials such as acetic acid, citric acid, lactic acid, malic acid and tartaric acid and the mineral acids hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid and nitric acid or mixtures thereof are particularly preferred.
- Preferred bases come from the group of alkali and alkaline earth metal hydroxides and carbonates and sodium metasilicates.
- the composition used may contain ammonia and alkanolamines.
- acidic cleaners such as bathroom, sanitary or toilet cleaners, neutral cleaners such as dishwashing detergents, and alkaline cleaners such as grease and oil cleaners or detergents are possible.
- compositions can also contain solubilizers, so-called hydrotropes, in addition to the substances already mentioned.
- solubilizers so-called hydrotropes
- Builders which are customarily used in detergents and cleaning agents are suitable. When used according to the invention, the builders can be freely combined with other ingredients in the composition by a person skilled in the art.
- builders based on renewable raw materials which can be obtained from plants in the temperate zone are particularly preferred in the composition, such as polyaspartates, polycarboxylates such as citrates, and gluconates, succinates or malonates.
- fragrances and dyes customary in detergents and cleaning agents can be added to the composition in the use according to the invention.
- Preferred dyes and fragrances the selection of which presents no difficulty to the person skilled in the art, have a high storage stability and are insensitive to the other ingredients of the detergent or cleaning agent.
- the dyes have no pronounced substantivity to textile fibers or hard surfaces and do not stain them.
- neither colorants nor fragrances are added.
- the compositions used have satisfactory aesthetics and a pleasant fragrance even without the addition of colorants or fragrances, so that embodiments without colorants and/or fragrances are possible, such as for consumers with allergies and/or sensitive skin.
- the composition When used, the composition exhibits such good cleaning performance that enzymes are unnecessary.
- the composition may optionally contain enzymes when used, particularly in the textile, specialty and dish cleaning embodiments used.
- the enzymes can be combined in the compositions by a person skilled in the art with all the other ingredients mentioned here. Proteases, lipases, amylases, hydrolases and/or cellulases are preferably used.
- they can be added to the composition in any form established according to the prior art. In the case of liquid or gel-like compositions, these include in particular solutions of the enzymes, preferably highly concentrated, low in water and/or mixed with stabilizers.
- the enzymes can be used in encapsulated form.
- enzyme stabilizers which are well known to the person skilled in the art can be added to the enzyme-containing agents.
- a particularly preferred embodiment of the invention is therefore the use of the composition without proteases; the use of the enzyme-free embodiment is very particularly preferred. This is particularly advantageous for consumers with allergies and/or sensitive skin. Uses of enzyme-free embodiments with comparable cleaning power are disclosed in the working examples.
- the liquid or gel-form embodiment of the compositions preferably has a viscosity of from 0.4 to 10,000 mPa.s. on.
- the composition may contain viscosity regulators.
- the amount of viscosity regulator is usually up to 1.5% by weight, preferably 0.001 to 1.0% by weight, in particular 0.01 to 0.5% by weight; % by weight of active substance based on the total composition.
- At least one of the viscosity regulators is preferably selected from the group consisting of organic modified natural substances (carboxymethyl cellulose and other cellulose ethers, hydroxyethyl and propyl cellulose and the like, gum ether), organic fully synthetic thickeners (polyacrylic and polymethacrylic compounds, vinyl polymers, polycarboxylic acids, polyethers, polyimines , polyamides) and inorganic thickeners (polysilicic acids, phyllosilicates, clay minerals such as montmorillonites, zeolites, silicic acids), as well as organic natural thickeners (agar-agar, carrageenan, xanthan, tragacanth, gum arabic, alginates, pectins, polyoses, guar flour, locust bean gum, starch, dextrins, gelatin, casein).
- organic modified natural substances carboxymethyl cellulose and other cellulose ethers, hydroxyethyl and propyl cellulose and the like,
- the viscosity regulators are natural organic thickeners from vegetable raw materials - including algae - for example polysaccharides such as pectins or starch.
- no fully synthetic organic thickeners such as polyacrylic and polymethacrylic compounds, vinyl polymers, polycarboxylic acids, polyethers, polyimines or polyamides are used.
- Inorganic thickeners are also preferred.
- compositions preferably used according to the invention thickened with xanthan gum are disclosed in the exemplary embodiments.
- the viscosity regulators can be freely combined by a person skilled in the art with other ingredients mentioned here.
- Methods for cleaning are generally characterized in that in one or more process steps different active cleaning substances are applied to the items to be cleaned and washed off after the exposure time, or that the items to be cleaned are otherwise treated with a detergent, care product or cleaning agent or a solution of this agent.
- temperatures of up to 90° C. and less are used in the embodiment of the detergent or laundry additive used. Temperatures below 60° C. are preferred and temperatures that do not require heating of the water temperature (about 20° C.) to save energy are particularly preferred. These temperature specifications relate to the temperatures used in the washing steps. All facts, objects and embodiments described for the use of the composition are also applicable to the washing and cleaning process and vice versa.
- compositions are used according to the invention to improve the cleaning performance of a detergent or cleaning agent to remove protein soil.
- Proteases can be dispensed with here.
- Preferred examples of this application are dishwashing detergents, textile detergents, surface cleaners, hygiene cleaners, cleaners in the food sector, hospitals, animal husbandry.
- compositions are preferably used according to the invention to improve the dirt-carrying capacity.
- Preferred products are dishwashing detergents, laundry detergents, floor cleaners, industrial cleaners for heavily soiled areas such as mining, coal, workshops, road construction and others.
- the compositions are preferably used to improve the dispersing power of a detergent or cleaning agent.
- Insoluble particles are stabilized in the composition.
- Preferred examples are abrasive cleaners, wax-based floor cleaners.
- the compositions are preferably used to improve the stability of the composition at high electrolyte contents.
- Examples are laundry detergents.
- the compositions are preferably used to improve washing performance in hard water.
- Examples are laundry detergents. Complexing agents and non-ionic surfactants can be reduced, graying and encrustations on laundry and in the machine are reduced.
- the compositions are preferably used to reduce eye irritation caused by a washing or cleaning agent.
- These compositions preferably have a pH of between 5 and 7.
- Preferred uses are dishwashing detergents and neutral cleaners for surfaces, and products which are applied using sprayers.
- compositions are preferably used according to the invention to improve the protection of materials.
- Preferred products are cleaners for sensitive surfaces, industrial cleaners, cleaners for displays.
- compositions are used according to the invention to assist in the removal of microbial contaminants from a detergent or cleaning product. Due to the high protein purification, hygiene cleaners are supported in the removal of biofilms.
- the composition can be used as a detergent and cleaning agent for hard and flexible surfaces, as well as textiles, carpets or natural fibers.
- detergents and cleaning agents also include washing aids which are metered into the actual agent during manual or machine cleaning.
- detergents within the scope of the invention also include pre- and post-treatment agents, ie agents that are used before the actual cleaning, for example to loosen stubborn dirt.
- the agents can be applied to the items to be cleaned, which are found in households, industry, commerce or institutions, port facilities, as well as industrial and leisure facilities and sports facilities.
- the composition is preferably used for cleaning hard surfaces or textiles.
- Hard surfaces in the context of this application are windows, mirrors and other glass surfaces, surfaces made of ceramic, plastic, metal or wood, flat or uneven, painted or unpainted, flexible surfaces are, for example, plastic sheets, foam, earth or others.
- Textiles and fibers within the meaning of the application are fabrics, clothing, upholstery, carpets, yarns, etc.
- the composition is used at an acidic pH between 0 and 6, preferably between 1 and 4.
- acidic pH between 0 and 6, preferably between 1 and 4.
- Typical examples of uses at acidic pH are toilet and sanitary cleaners, limescale cleaners, cement veil cleaners.
- the composition is used at an alkaline pH between 7 and 14, preferably between 8 and 12.
- alkaline pH between 7 and 14, preferably between 8 and 12.
- Typical examples of uses at alkaline pH are detergents, surface cleaners, kitchen cleaners, grill and oven cleaners, wheel rim cleaners and others.
- the composition is used at a neutral pH between 5 and 7, for example when a skin-neutral pH is desirable, such as in a dishwashing detergent.
- compositions are suitable for use in cleaning and washing preparations such as hand dishwashing detergents, machine dishwashing detergents, dishwasher cleaners, washing machine cleaners, toilet cleaners or toilet cleaners, universal or all-purpose cleaners, kitchen cleaners, bathroom or sanitary cleaners, floor cleaners, oven and grill cleaners , glass and window cleaners, metal cleaning agents, upholstery and carpet cleaners, heavy-duty detergents, color detergents, mild detergents, textile auxiliaries, pre-treatment agents, special detergents and cleaning agents, as well as other agents for industrial & commercial or institutional cleaning, agents for textile and fiber treatment, agents leather treatment, as well as other forms of preparation.
- cleaning and washing preparations such as hand dishwashing detergents, machine dishwashing detergents, dishwasher cleaners, washing machine cleaners, toilet cleaners or toilet cleaners, universal or all-purpose cleaners, kitchen cleaners, bathroom or sanitary cleaners, floor cleaners, oven and grill cleaners , glass and window cleaners, metal cleaning agents, upholstery and carpet cleaners, heavy-duty detergents, color detergents, mild detergents
- the composition can be used as a liquid, solution or dispersion, emulsion, lotion, gel, dip, spray or foam. So you can e.g. a solution, an emulsion (O/W), or a multiple emulsion, for example of the water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) type, a gel, a hydrodispersion, a lamellar phase, a liquid isotropic solution phase or a micellar phase. It can be adsorbed to powder, granules or tabs.
- the agents are suitable both for diluted use and for direct application to the substrate to be cleaned. It is suitable for direct application as well as for use with a tool such as a cloth.
- a preferred variant is the use of the composition on solid substrates, such as cloths. When used according to the invention, these are impregnated, sprayed or coated with the composition or applied by another method.
- Solid substrates have the advantage that the preparation is already specified in them in the correct dosage. This meets the consumer's desire for convenience in particular, they are easy to handle, can be used directly without additional work steps and can also be used on the go, e.g. when travelling, even if no water is available.
- compositions in liquid forms, particularly preferably in aqueous forms of administration.
- compound (I) is sodium PEG-7 olive oil carboxylate
- I, reference C12 sodium laureth-5 carboxylate
- reference oleyl sodium oleth-6 carboxylate
- SLES sodium laureth sulfate
- Soil holding capacity is measured as a 2% solution versus sodium laureth sulfate and references that
- the foam of SLES collapses; the particles flocculate and soil-carrying capacity is lost.
- the foam is unexpectedly retained and the soil-carrying capacity remains intact.
- the good dirt-carrying capacity of the mixtures is also maintained when CaCl 2 is added.
- the mixtures show synergistic behavior here (diagram 3)—the dirt-carrying capacity of the mixtures in the disclosed ratios is significantly higher than for the solutions of the individual compounds (I) or SLES (diagram 3).
- Foam formation and foam stability are additive in the agents. This ensures good foaming behavior. In hard water, the foam remains stable only with the agents disclosed.
- the tests were carried out with 84% dried egg white (mixture of animal and vegetable protein) and a 3% surfactant solution in water (diagram 4).
- a representative concentration of surfactants in a mild cleaning agent is taken as an example, analogously to alkyl ether sulfates, alkyl sulfates, acyl sarcosinates, alkyl glucosides, amidoalkyl betaines, alkanolamides and amphoacetates according to claim 2.
- composition of the surfactant system can reduce eye irritation by at least one label level.
- the surfactants AC from C-18 vegetable oils have a positive influence on dirt-carrying capacity.
- the already very good dirt-carrying capacity is not impaired by the addition of a further surfactant AD; on the contrary, the surfactants AC from C-18 vegetable oils improve the dirt-carrying capacity.
- the surfactants A and B from C-18 vegetable oils have a positive influence on the cleaning power.
- the already very good protein dissolving capacity is not impaired by the addition of a further surfactant AD.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Detergent Compositions (AREA)
Description
- Gegenstand dieser Anmeldung ist, wie in den Ansprüchen definiert, die Verwendung von Wasch- und Reinigungszusammensetzungen, die mindestens ein Polyoxyalkylen Carboxylat und ein weiteres Tensid enthalten. Das oder die Polyoxyalkylen Carboxylate und das mindestens eine weitere Tensid basieren auf Fettsäuren aus Pflanzenölen und weisen einen aussergewöhnlich hohen Anteil an langkettigen (≥ C17), mehrheitlich ungesättigten Kohlenwasserstoffketten auf.
- Die vorliegende Erfindung betrifft die Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung als Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel mit hoher Reinigungsleistung unter Verwendung von umweltfreundlicheren und geringer reizenden Tensiden und ein Verfahren zur Verbesserung der Reinigungsleistung eines Wasch- und Reinigungsmittels unter Verwendung der Zusammensetzung.
- So ist die Entfernung von proteinhaltigen Verunreinigungen (Eiweissverunreinigungen) in der Textilpflege und der Reinigung von Oberflächen gleichermassen wichtig. Verunreinigungen durch Proteine treten in allen Bereichen von Mensch und Tier auf, z.B. als Fragmente von Haaren, Hautschuppen, Milchreste, Gluten, Ablagerungen auf Kontaktlinsen, u.s.w. So ist die Reinigung von Proteinen besonders wichtig in Lebensmittelbereichen, Kliniken, Tierhaltung u.v.a.m. Weiterhin können Proteine Mikroorganismen als Schutz dienen und somit die Wirksamkeit von Desinfektionsmitteln herabsetzen. Eine effektive Proteinschmutzentfernung ist insbesondere in Bereichen, die eine hohe Hygiene erfordern, unerlässlich.
- Häufig erfolgt die Entfernung von Proteinschmutz durch Proteasezusätze in Waschmitteln, Geschirrspülmitteln, Oberflächen- und Hygienereinigern. Der Einsatz von Enzymen ist bei Umweltschützern umstritten. Zum einen erfolgt deren Produktion in der Regel über Gentechnik und ist energieaufwändig. Zum anderen ist die Verwendung von Enzymen aufgrund von Stabilitätsproblemen und Inkompatibilitäten mit vielen üblichen Inhaltsstoffen für den Formulierer aufwändig. Desweiteren stehen Enzyme im Verdacht, sensibilisierend zu wirken. Eine bevorzugte Ausführungsvariante stellt daher eine Zusammensetzung dar, bei der die Entfernung von Proteinschmutz unter Reduktion oder insbesondere unter Verzicht auf Proteasen erfolgt.
- Weiterhin ist ein gutes Dispergiervermögen für ein Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel wichtig. Unter dem Dispergiervermögen versteht man die Fähigkeit einer oberflächenaktiven Substanz oder eines Mittels, Schmutzpartikel in der Waschflotte zu halten, also das Schmutztragevermögen, so dass sich Schmutzteilchen nicht wieder auf dem Textil oder der Oberfläche ablagern können.
- Häufig werden nichtionische Tenside als Dispergiermittel eingesetzt. Die üblicherweise für die Reinigungsaufgabe eingesetzten anionischen Tenside zeigen oft Empfindlichkeiten gegenüber hartem Wasser. Eine spezielle nichtionische Tensidklasse bilden die Biotenside, welche durch Mikroorganismen produziert werden. Für einen effizienten Herstellungsprozess von Biotensiden werden in vielen Fällen Mikroorganismen gentechnisch verändert; Veränderungen, die von manchen Umweltgruppen kritisiert werden.
- Neben der Reinigungsleistung von Reinigungsmitteln spielen zunehmend ökologische und toxikologische Gesichtspunkte eine wichtige Rolle in der Kaufentscheidung der Kunden.
- Als Standard werden in der Reinigungsmittelindustrie für nachhaltige Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel Tenside mit einem hohen Laurinsäuregehalt (C12) eingesetzt. Jedoch wird die Nachhaltigkeit dieser Tenside zunehmend in Frage gestellt, da sie auf Erdöl oder pflanzlichen Ölen aus tropischen Monokulturen basieren. Diese Pflanzenöle, wie z.B. Kokos- oder Palmkernöl, werden aufgrund ihrer technischen Eigenschaften wie vorteilhafte Schaum-, Wasch- und Reinigungsleistung eingesetzt, die sie dank ihrem hohen Laurinsäuregehalt (C12) besitzen.
- Ein weiterer Nachteil der üblicherweise eingesetzten Tenside ist deren hohes Reizpotential. So verursachen beispielsweise die am häufigsten eingesetzten Tenside wie Natrium Lauryl Sulfate, Natrium Laureth Sulfate, Cocoamidopropylamid oder Decylglucosid schwere Augenschäden. Es ist wünschenswert, diese Tenside daher zu einem grösstmöglichen Mass mit augenmilderen Tensiden zu ersetzen. Hautmilde Tensidsysteme sind aus der Kosmetik bekannt, aber wie nachfolgend aufgeführt, wegen ihrer spezifischen Eigenschaften nicht geeignet für Industrie-, institutionelle, Textil- und Haushaltsreinigung.
- Anders als in der Kosmetik, in der Hautgefühl und rückfettende Eigenschaften eine wesentliche Rolle spielen, steht in der Industrie-, institutionellen, Textil- und Haushaltsreinigung die Reinigungskraft im Vordergrund. Zusätzlich besteht die Anforderung an Tensidsysteme, flexibel in einem breiten pH-Bereich einsetzbar zu sein. Industrie- Textil- und Haushaltsreinigung erfolgt oft in extremen pH-Bereichen, anders als die Körperreinigung, welche bevorzugt in einem hautneutralen pH-Wert erfolgt, d.h.in einem pH-Bereich zwischen 5 und 7.
-
US 2004/0265264 offenbart die Verwendung von Natrium PEG-7 Olivenölcarboxylat in "katalytischen" Mengen zur Reduktion von Hautirritation durch das primäre Tensid Natrium Laurethsulfat. InWO 2013098066 wird Natrium PEG-7 Olivenölcarboxylat in vergleichbar geringen Mengen zusammen mit weiteren Tensiden auf Basis Laurylbasis und Biotensid verwendet für ein Babyreinigungsmittel. Das Ausführungsbeispiel offenbart die sensorisch positive Auswirkung auf die Haut durch die Kombination von Biotensiden mit Ölsäure, die Reinigungsleistung wird nicht erwähnt. -
DE 10147049 offenbart Tensidgemische aus Natrium Cocoylglutamat, Natrium Myristylethersulfat und Natrium PEG-7 Olivenölcarboxylat, welche selektiv Oberflächenlipide statt Sebumlipide auswaschen und somit Hautrauigkeit vermindern. Weiterhin sind Reinigungsmittel mit Kombinationen aus Natrium Laurylsulfat als Tensid mit dem grössten Mengenanteil und Natrium PEG-7 Olivenölcarboxylat bekannt. - Damit ist aber das Problem nicht gelöst, Verwendungen von umweltfreundlicheren Zusammensetzungen für Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel, insbesondere für anspruchsvolle Reinigungsaufgaben in Industrie-, Textil- und Haushaltsreinigung bereitzustellen.
- Die komplexe technische Aufgabe der Erfindung hat darin bestanden, Zusammensetzungen als Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel bereitzustellen, die vorwiegend Fettsäuretenside auf Basis pflanzlicher Rohstoffe enthalten, wobei der Anteil an Tensiden, welche auf Palmölen (d.h. Palmöl, Palmkernöl, Kokosöl, Babassuöl) basieren, möglichst reduziert werden soll zugunsten von Tensiden aus weniger problematischen Quellen, wie zum Beispiel pflanzlichen Ölen aus europäischem Anbau.
- Dies ist technisch insofern anspruchsvoll, da aus verfügbaren Ölen, zum Beispiel aus Mitteleuropa, die gewünschte Laurinsäure (C12) nicht in ausreichendem Mass gewonnen werden kann, welche aufgrund ihrer technischen Eigenschaften wie vorteilhafte Schaum-, Wasch- und Reinigungsleistung üblicherweise eingesetzt wird. Dagegen enthalten die gewünschten Tenside statt Laurinsäure einen hohen Anteil an ungesättigten, langen Fettsäureresten ≥ C18, welche in üblich eingesetzten Tensidkonzentrationen komplett neue Eigenschaften wie Schaum, Stabilität, Reinigungsleistung, Kompatibilität u.a. mit sich bringen.
- Neben der verbesserten Nachhaltigkeit der Zusammensetzung bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung, sollen die Tensidkombinationen eine gute Reinigungsleistung erzielen. Weiterhin war es ein Ziel, die Tensidmischung über einen breiten pH-Bereich einzusetzen, sowie mit unterschiedlichen Inhaltsstoffen zu kombinieren um eine Basis für unterschiedliche Verwendungen zur Verfügung zu haben.
- Weiterhin sollten bevorzugt ein oder mehrere Nachteile der herkömmlichen Tensidmischungen betreffend Toxikologie,
- Reizpotential für Haut, Reizpotential für Augen, biologische Abbaubarkeit, Wassergefährdung, wie sie beispielsweise in der Gefahrenkennzeichnungspflicht nach CLP zu erkennen sind, beseitigt werden.
- Die Zusammensetzungen sollten bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung zu einem grösstmöglichen Umfang auf natürlichen Rohstoffen basieren und biologisch gut abbaubar sein.
- Überraschenderweise wurde gefunden, dass Zusammensetzungen, bei der Verwendung wie in den Ansprüchen definiert und nachfolgend beschrieben, eine oder mehrere der genannten Aufgaben lösen.
- Überraschenderweise und für den Fachmann in keiner Weise vorhersehbar, können die Zusammensetzungen bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung die gleiche oder bessere Reinigungsleistung wie die Vergleichsmitteln erzielen bei gleichzeitiger Minimierung der mittelkettigen Tensiden, insbesondere Lauryl bzw. Coco, ohne die Gesamtkonzentration an Tensiden erhöhen zu müssen. Dies bedeutet, dass bedenkliche Inhaltsstoffe, wie zum Beispiel stark augenreizende Tenside, in den Zusammensetzungen bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung teilweise oder ganz substituiert werden konnten. Die Substitution von Tensiden bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung ist insofern erstaunlich, da Tensidsysteme durch Wechselwirkungen untereinander erst die volle Wirkung entfalten und die substituierten Tensidsysteme altbewährte Systeme darstellen.
- Unerwarteterweise zeigte sich zudem, dass die Zusammensetzungen bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung eine für den Fachmann in keiner Weise vorhersehbare Reinigungswirkung auf spezifische Verschmutzungen zeigen. Dies ermöglicht die Verwendung von umweltfreundlichen Mitteln, selbst bei hartnäckigen Verschmutzungen wie Proteinschmutz oder Teilchenschmutz.
- Überraschenderweise wurde festgestellt, dass die Zusammensetzungen bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung wider Erwarten eine sehr hohe Reinigungsleistung auf Proteinschmutz zeigen. Die Reinigungsleistung zur Entfernung von Proteinen erlaubt somit auch als bevorzugt Ausführungsvariante die Verwendung einer enzymfreien Ausführungsform, insbesonders bevorzugt ohne Proteasen.
- Weiterhin zeigen die Zusammensetzungen bei der Verwendung ein nicht vorhersehbar gutes Schmutztragevermögen vergleichbar mit üblicherweise verwendeten Tensidsystemen für diese Aufgabe. Das Wiederaufziehen auf gereinigte Flächen wird vermindert, was einer Vergrauung oder Verkrustung entgegengewirkt, bspw. bei der erfindungsgemässen Verwendung der Zusammensetzungen als Textilwaschmittel.
- Das hohe Dispergiervermögen der Zusammensetzungen bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung erlaubt zudem eine Stabilisierung von unlöslichen Inhaltsstoffen in der Zusammensetzung, wie bspw. Abrasiva oder Wachskörper o.ä.
- Ein weiterer Vorteil der Erfindung ist, dass anders als in üblicherweise verwendeten anionischen Tensidsystemen, wie z.B. Sodium laureth sulfate oder Sodium lauryl sulfate, die Zusammensetzung bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung unempfindlich gegen hartes Wasser ist und damit keine Verminderung des Schmutztragevermögens in Anwesenheit von Calcium- und Magnesiumionen erfolgt. Dadurch können überraschenderweise auch nichtionische Tenside mit mittelkettigen Kohlenstoffketten mit hohem Irritationspotential, wie z.B. Decyl glucosid, oder Tenside aus Fermentation (Biotenside), die für hartes Wasser üblicherweise eingesetzt werden, ausgeschlossen werden.
- Überraschenderweise wurden Synergien in den Zusammensetzungen bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung betreffend des Schmutztragevermögens bei hoher Elektrolytkonzentration oder hartem Wasser festgestellt.
- Das Schaumverhalten der Zusammensetzungen bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung entspricht trotz grundsätzlich längerer Kohlenstoffketten der Fettsäureacylreste der Tenside einem reinen Sodium laureth sulfat- Tensidsystem. Wider Erwarten kann in den Zusammensetzungen bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung ein stabiler Schaum erzielt werden, wodurch mittelketttige Alkylamidobetaine, Monoethanolamide und Diethanolamide, welche ein erhebliches Irritationspotential aufweisen, reduziert werden. Eine bevorzugt verwendete Ausführungsvariante ist daher frei von Alkylamidobetaine, wie bspw. Cocoamidopropylbetain. Eine weitere bevorzugt verwendete Ausführungsvariante ist frei von Mono- und Diethanolamiden, wie Cocamid DEA, Cocamid MEA u.a.
- Ein weiterer Vorteil ist, dass sich die Zusammensetzung bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung durch eine hohe Stabilität auszeichnet. Die Zusammensetzung wird bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung auch in einer konservierungsmittelfreien Ausführungsform offenbart.
- Gegenstand dieser Anmeldung ist die erfindungsgemässe Verwendung der Zusammensetzungen als Wasch - und Reinigungsmittel für harte oder flexible Oberflächen, sowie für Textilien, Teppiche oder Naturfasern in den Bereichen Industrie-, institutionelle, Textil- und Haushaltsreinigung.
- In einem weiteren Erfindungsgegenstand richtet sich die Erfindung auf ein Wasch- und Reinigungsverfahren umfassend
- a) die Bereitstellung einer Wasch- und Reinigungslösung umfassend ein Mittel verwendet gemäss dem ersten Erfindungsgegenstand
- b) in Kontakt bringen einer Oberfläche oder Textilien, Teppiche oder Naturfasern mit der Waschlösung gemäss (a).
- Eine bevorzugt verwendete Ausführungsvariante stellen feste Substrate, wie Tücher dar. Diese werden mit einer Zubereitung getränkt und haben den Vorteil, dass bereits die richtige Dosierung vorgegeben ist. Die Mittel weisen bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung eine hohe Kompatibiltät mit den spezifischen Inhaltsstoffen (z.B. kationischen Tensiden) auf und zeigen ein gutes Aufzieherhalten auf das Substrat. Tücher kommen insbesondere dem Konsumentenwunsch der Convenience entgegen, sie sind einfach handhabbar, direkt zu verwenden ohne zusätzliche Arbeitsschritte und können auch unterwegs, z.B. auf Reisen gut angewendet werden, auch wenn kein fliessendes Wasser zur Verfügung steht. Tücher werden aus Textilien hergestellt, welche gewebt, gestrickt, oder gewirkt sein können oder als Verbundstoff in Vlies, Papier, Watte oder Filz vorliegen, wobei Vliese meist aus Polypropylen, Polyester oder Viskose hergestellt werden. Mit Mitteln imprägnierte Substrate und Tücher können auf unterschiedliche Weisen hergestellt werden - dem Tauch-, dem Abstreif- und dem Sprühverfahren.
- Technisch unterscheiden sich die Pflanzenöle aus Ölpalmen, Babassu, Palmkernen, oder Kokosnüssen deutlich in der Fettsäurezusammensetzung von den erfindungsgemässen C-18-Pflanzenölen:
In dieser Erfindung werden folgende Pflanzenöle, - fette, -wachse oder-harze als C-18-Pflanzenöl bezeichnet:
Bevorzugt handelt es sich bei den C-18-Pflanzenölen um natürliche Triglyceride. C-18-Pflanzenöle weisen ein Gemisch an gesättigten und ungesättigten Fettsäuren auf, wobei die Fettsäureverteilung von Fettsäuren mit 18 und mehr Kohlenstoffatomen über 60 Gew.-%, besonders bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt von über 77 Gew.-% liegt und wobei der Anteil an ungesättigten Fettsäuren über 55 Gew.-%, vorzugsweise über 65 Gew.-% und besonders bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% liegt. - Bevorzugt liegt der Anteil an Fettsäuren mit 16 und weniger Kohlenstoffatomen unter 30 Gew.-%, bevorzugt unter 27 Gew.-% und besonders bevorzugt unter 17 Gew.-%.
- Bevorzugt enthalten die C-18-Pflanzenöle einen Anteil von < 0.5%, besonders bevorzugt > 0.05% Fettsäuren mit 6 Kohlenstoffatomen.
- Bevorzugt enthalten die C-18-Pflanzenöle einen Anteil von < 75 Gew-% Hydroxyfettsäuren, bevorzugt < 25 Gew.-%, besonders bevorzugt < 5 Gew.-%.
- Bevorzugt enthalten C-18-Pflanzenöle gesättigte oder ungesättigte Fettsäuren mit 20 und mehr Kohlenstoffatomen, wobei deren Gehalt bis zu 96 Gew.-% betragen kann. Bevorzugt enthalten C-18-Pflanzenöle einen Anteil von gesättigten oder ungesättigten Fettsäuren mit 20 und mehr Kohlenstoffatomen von > 0.01 Gew.-% und besonders bevorzugt > 0.05 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt > 0.1 Gew-% und äusserst bevorzugt >= 0.2 Gew.-%.
- Bevorzugt enthalten die C-18-Pflanzenöle einen Anteil von weniger als 95 Gew.-% Ölsäure, besonders bevorzugt unter 85 Gew.-% Ölsäure; Gew.-% in Definition C-18-Pflanzenöl jeweils bezogen auf den Gesamtgehalt an Fettsäuren im Pflanzenöl.
- Aus folgenden Pflanzen bzw. Pflanzenteilen, wie Samen, Kerne, Früchte, Blätter, Wurzeln und andere, im folgenden C-18-Pflanzen genannt, können C-18 Pflanzenöle gewonnen werden, welche die technischen Merkmale betreffend Fettsäurezusammensetzungen für die erfindungsgemässen Mittel erfüllen und vorzugsweise aus der Gruppe ausgewählt werden umfassend die Pflanzen: Amarant, Anis, Apfel, Aprikose, Argan, Arnika, Avocado, Baumwolle, Borretsch, Brennessel, Brokkoli, Canola, Chia, Hanf, Haselnuss, Buche, Buchsbaum, Distel, Dinkel, Erdnuss, Erdmandel, Flieder, Gartenkresse, Gerste, Granatapfel, Hafer, Hanf, Haselnuss, Heidelbeere, Holunder, Jasmin, Johannisbeere, Johanniskraut, Jojoba, Kamelie, Kamille, Kümmel, Karotte, Kirsche, Koriander, Königskerze, Krambe, Kreuzblättrige Wolfsmilch, Kreuzblütengewächse, Kürbis, Iberischer Drachenkopf, Lavendel, Leindotter, Leinsamen, Liguster, Lupine, Luzerne, Macademia, Mais, Mandel, Marula, Mirabelle, Melone, Mohn, Mongongo, Nachtkerze, Olive, Ölrettich, Ölrauke, Passionsblume, Pekannuss, Pfirsich, Pflaume, Pistazie, Preiselbeere, Purgiernuss (Jatropha), Raps, Reis, Ringelblume, Rübsen, Saflor, Salbei, Sanddorn, Schwarzkümmel, Sesam, Sesamblatt, Senf, Sonnenblume, Soja, Tabak, Walnuss, Weintraube, Weizen, Wiesenschaumkraut und Wildrose; sowie deren Kombinationen.
- Vorzugsweise ist das Öl ausgewählt aus der Gruppe: Aprikose, Avocado, Baumwolle, Brokkoli, Buche, Distel, Dinkel, Erdmandel, Gerste, Hanf, Haselnuss, Jojoba, Kirsche, Königskerze, Krambe, Kreuzblättrige Wolfsmilch, Kürbis, Iberischer Drachenkopf, Leindotter, Leinsamen, Lupine, Luzerne, Macademia, Mandel, Mais, Mohn, Nachtkerze, Olive, Ölrettich, Ölrauke, Pfirsich, Raps, Reis, Ringelblume, Rübsen, Saflor, Salbei, Sanddorn, Schwarzkümmel, Sesam, Sesamblatt, Senf, Sonnenblume, Soja, Tabak, Walnuss, Weintraube und Weizen, sowie deren Kombinationen.
- Ganz besonders bevorzugt ist das Öl ausgewählt aus der Gruppe Aprikose, Distel, Erdmandel, Hanf, Krambe, Iberischer Drachenkopf, Leindotter, Leinsamen, Lupine, Luzerne, Mais, Mandel, Olive, Ölrettich, Pfirsich, Raps, Rübsen, Sesam, Sesamblatt, Sonnenblume, Soja, Weintraube und Weizen, sowie deren Kombinationen.
- Der Begriff Öle wird in dieser Erfindung stellvertretend für Fette, Wachse und Harze verwendet.
- Unter mittelkettigen Tensiden werden im Rahmen der Erfindung Tenside mit gesättigten Alkyl- oder Acylgruppen mit Kettenlängen zwischen 8-18 Kohlenstoffatomen oder Gemische aus gesättigten Alkyl- oder Acylgruppen mit 8 bis18 Kohlenstoffatomen und ungesättigten C-18-Alkenyl- oder Acylgruppen verstanden, wie sie aus Kokosöl, Palmkernöl oder Babassuöl erhalten werden.
- Soweit nicht explizit anders angegeben, steht im Rahmen der vorliegenden Erfindung Alkyl- und Acyl- für gesättigte und ungesättigte Reste.
- Im Rahmen der vorliegenden Erfindung steht - soweit nicht anders angegeben- auf Basis von oder abgeleitet von Pflanzenölen, -fetten oder -wachsen stellvertretend für Derivate aus Fettsäuren nach chemischen Umsetzungen- gereinigt oder als Gemisch - und/oder deren synthetische Reaktionsprodukte, wie beispielsweise Additionsprodukte an die Doppelbindung, Reaktionen an der Fettsäurefunktion, wie z.B. Fettalkohole und deren Ether und/ oder Carboxyether, Amine oder Fettsäureamide, Fettsäureester, sowie Imine. Bevorzugt liegen diese Fettsäurederivate als Mischung gemäss der Fettsäureverteilung im nativen Öl vor oder wie sie bei der Umsetzung von natürlich vorkommenden Pflanzenöle oder Fetten anfallen.
- Im Rahmen der vorliegenden Erfindung stehen Fettsäuren bzw. Fettalkohole bzw. Fettsäureacyl- bzw. deren Derivate soweit nicht anders angegeben - stellvertretend für verzweigte oder unverzweigte, lineare oder substituierte, insbesondere hydroxysubstituierte, gesättigte, einfach oder mehrfach ungesättigte Carbonsäuren bzw. Alkohole bzw. deren Derivaten mit vorzugsweise 6 bis 24 Kohlenstoffatomen.
- Unter Tensid werden im Zusammenhang dieser Erfindung amphiphile organische Substanzen mit grenzflächenaktiven Eigenschaften verstanden, die sich an die Grenzfläche zwischen zwei Flüssigkeiten, wie beispielsweise Öl und Wasser adsorbieren und die Fähigkeit besitzen, die Oberflächenspannung von Wasser zu verringern. In Lösung tendieren Tenside zur Selbstaggregation und bilden Strukturen wie bspw. Mizellen, lamellare Strukturen u.a. Im Zusammenhang mit dieser Erfindung werden als Tenside Verbindungen bezeichnet, die die Fähigkeit besitzen, die Oberflächenspannung von Wasser bei 20°C und bei einer Konzentration von 0.5 Gew.-% bezogen auf die Gesamtmenge der Zubereitung auf unter 45 mN/m zu verringern.
- PEGylierte Pflanzenöle sind ethoxylierte Pflanzenöle wie definiert in "Safety Assessment of PEGylated Oils as Used in Cosmetics", International Journal of Toxicology November/December 2014, 33. Im Rahmen dieser Erfindung wird die Terminologie verwendet, welche bei kosmetischen Inhaltsstoffen Anwendung findet, welche die Veretherungs- und Veresterungsprodukte von Glyceriden und Fettsäuren mit Ethylenoxid beschreibt. Im Rahmen der Erfindung sind hier insbesondere Vertreter abgeleitet von C-18-Pflanzen bevorzugt;
- PEGylierte Fettsäureglyceride sind Mono-, Di- und/oder Triglyceride, welche mit einer spezifischen Anzahl an Alkylenglycol-Einheiten, meist Ethylenglycoleinheiten modifiziert wurden und Nebenprodukte der Reaktion enthalten können. Im Rahmen dieser Erfindung werden PEGylierte Fettsäureglyceride definiert wie in "Safety Assessment of PEGylated Alkyl Glycerides as Used in Cosmetics", Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) 2014. Zu bemerken ist, dass CIR unter "Alkyl" auch ungesättigte Fettsäuren berücksichtigt. Im Rahmen der Erfindung sind hier insbesondere Vertreter abgeleitet von C-18-Pflanzen bevorzugt;
- Im Rahmen dieser Erfindung steht soweit nicht anders vermerkt Biotensid für die erfindungsgemäss definierten Biotensid-Glycolipide aus fermentativer Herstellung.
- Im Rahmen dieser Anmeldung wird unter "Schwefeltenside" anionische oder amphotere Tenside mit einem schwefelhaltigen hydrophilen Rest verstanden wie z.B. Alkylsulfate, Alkylethersulfate, (alkoxylierte) Sulfosuccinate, (alkoxylierte) Sulfonate, (alkoxylierte) Isethionate, (alkoxylierte) Taurate, Sulfobetaine und Sultaine. Beispiele für sulfathaltige Tenside stellen Sodium Laureth Sulfate, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, Ammonium Laureth Sulfate, Ammonium Lauryl Sulfate, Sodium Myreth Sulfate, Sodium Coco Sulfate, Sodium Trideceth Sulfate oder MIPA-Laureth Sulfate dar.
- Frei von Schwefeltensiden, Phosphaten, Phosphonaten bedeutet, dass die Formulierung keine nennenswerten Mengen an Schwefeltensiden, Phosphaten, Phosphonaten aufweisen. Insbesondere ist hierunter zu verstehen, dass Schwefeltenside, Phosphate, Phosphonate jeweils in Mengen von kleiner 0.1 Gew.-%, bevorzugt von kleiner 0.01 Gew.-% bezogen auf die Gesamtformulierung, insbesondere keine nachweisbaren Mengen, enthalten sind.
- "Mindestens ein" wie hierin verwendet, bezieht sich auf 1 oder mehr, beispielsweise 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 oder mehr.
- Unter "Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel" wird im Rahmen der Erfindung ein Mittel zur Entfernung unerwünschter Verschmutzungen oder Belägen verstanden wie beispielweise Flecken, Rückstände, Verunreinigungen, Stoffwechselprodukte von biologischen Vorgängen von harten oder flexiblen Oberflächen, sowie Textilien, Teppiche oder Naturfasern in Industrie-, institutioneller, Textil- und Haushaltsreinigung. Die Mittel können durch einreiben, zudosieren, sprayen, schäumen und andere Methoden (z.B. auflegen) direkt oder über ein Hilfsmittel wie beispielsweise ein Tuch, verdünnt oder unverdünnt, auf das zu reinigende Material aufgebracht werden. Bevorzugt umfassen Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel neben dem primären Tensid zusätzlich mindestens 4 weitere Inhaltsstoffe ausgewählt aus den Gruppen: Lösungsmittel; weitere Tenside; Enthärter und Komplexbildner; Viskositätsregulatoren; pH-Stellmittel und Säuren und Basen; Gerüststoffe; Lösungsvermittler; Abrasiva; Antioxidantien; Vitamine; UV-Filter; Trübungsmittel; Antikorrosionsmittel; Konservierungsmittel; Duftstoffe; Farbstoffe; anorganische Alkali- oder Erdalkalisalze; gegebenenfalls Enyzme.
- Unter "Reinigungsleistung" oder "Waschkraft" wird im Rahmen dieser Erfindung die Entfernung von einer oder mehreren Anschmutzungen verstanden.
- Die Entfernung kann über eine Aufhellung oder Verringerung der Anschmutzung messtechnisch erfasst oder visuell beurteilt werden.
- Der HLB (hydrophile-lipophile balance) Wert ist ein Mass für die Hydrophilie, bzw. Lipophilie eines Stoffes, in der Regel eines nichtionischen Tensids. Der Wert kann theoretisch wie in einschlägiger Literatur beschrieben (z.B. nach der Griffin-Methode) oder experimentell durch den Vergleich des Löslichkeitsverhaltens von Standardzusammensetzungen mit bekanntem HLB gemessen werden.
- Stoffe, die auch als Inhaltsstoffe von kosmetischen Mitteln dienen, werden nachfolgend gegebenenfalls gemäss der International Nomenclature Cosmetic Ingredient- (INCI-) Nomenklatur bezeichnet. Die INCI-Bezeichnungen sind dem "International Cosmetic Ingredient Dictionary and Handbook, 13th Edition (2010)" zu entnehmen. Herausgeber: The Personal Care Products Council.
- Soweit nicht explizit anders angegeben, beziehen sich die angegeben Mengen in Gewichtsprozent (Gew.-%) auf die Gesamtmasse des Mittels. Dabei beziehen sich die prozentualen Mengenangaben auf Aktivgehalte.
- Ein erster Gegenstand der Erfindung richtet sich auf die Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung als Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel für Industrie-, institutionelle, Textil- und Haushaltsreinigung, bevorzugt für harte Oberflächen und Textilien, enthaltend mindestens eine Verbindung der Formel (I), bevorzugt ein Gemisch aus Verbindungen der Formel (I), und ein oder mehrere weitere Tenside (III).
- Tensid (I)
(I) R'-O(CbH2bO)o-{CH2-CH[O(CbH2bO)pR"]-CH2O}r-(CbH2bO)q-R‴
- mit b einer ganzen Zahl zwischen 2 und 4, o, p, q unabhängig voneinander Zahlen von 0 bis 75, wobei o+p+q mindestens 2 ist, r ist 0 oder 1,
- R', R" und R‴ sind jeweils unabhängig voneinander H, CH2COOM, oder RCO, wobei einer oder zwei, bevorzugt einer der Reste R', R" und R‴ CH2COOM darstellen: Wenn R' = CH2COOM dann gilt o≠0, wenn R" = CH2COOM dann gilt p≠0, wenn R‴= CH2COOM dann gilt q≠0, mit M = H, Alkali-, Erdalkali-, Ammonium-, oder lösliche Salze organischer Basen, z.B. organisches Ammoniumkation, Mono-, Di- oder Tri- bzw. Tetraalkylammonium, DEA, MEA, TEA, MIPA, oder TIPA;
- und wobei einer oder zwei der Reste R', R" und R‴ Fettsäureacylreste RCO darstellen; mit R einer gesättigten, ein- oder mehrfach ungesättigten Kohlenwasserstoffkette mit 5-23 Kohlenstoffatomen; welche aus einem C-18-Pflanzenöl abgeleitet ist;
- wobei der Anteil von 18 und mehr Kohlenstoffatomen der Fettsäureacylreste RCO in der Verbindung (I) oder in dem Gemisch von Verbindungen (I) über 60 Gew.-%, bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt von über 77 Gew.-% liegt; und der Anteil der ungesättigten Fettsäureacylresten über 55 Gew.-%, vorzugsweise über 65 Gew.-% und besonders bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% liegt, jeweils bezogen auf den Gesamtanteil an Fettsäureacylresten RCO der ein oder mehreren Verbindungen (I) im Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel;
- und wobei die Verbindung (I) vorzugsweise aus einem Gemisch unterschiedlicher Kettenlängen und Sättigungsgrade des Fettsäurerests RCO wie oben definiert besteht und vorzugsweise abgeleitet ist von C-18-Pflanzenölen aus der Gruppe umfassend die Pflanzen wie oben definiert.
- Bevorzugt liegt der Fettsäurerest RCO mit einem Anteil von 20 oder mehr Kohlenstoffatomen bevorzugt > 0.01 Gew.-%, besonders bevorzugt > 0.05 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt ≥ 0.1 Gew.-% beträgt und äusserst bevorzugt ≥ 0.2 Gew.-%. Bevorzugt liegt der der Anteil an Fettsäureresten RCO mit Fettsäuren von 16 und weniger Kohlenstoffatomen unter 30 Gew.-%, bevorzugt unter 27 Gew.-% und besonders bevorzugt unter 17 Gew.-%; bevorzugt liegt der der Anteil an Fettsäureresten RCO mit Fettsäuren von 6 und weniger Kohlenstoffatomen < 0.5%, besonders bevorzugt < 0.05%; bevorzugt liegt der der Anteil an Hydroxyfettsäureresten < 75 Gew-%, bevorzugt < 25 Gew.-%, besonders bevorzugt < 5 Gew.-%; bevorzugt kann der Anteil an Fettsäureresten RCO mit 20 und mehr Kohlenstoffatomen bis zu 96 Gew.-% betragen kann; bevorzugt liegt der der Anteil des Ölsäureacylrestes bei weniger als 95 Gew.-%, besonders bevorzugt unter 85 Gew.-%, jeweils bezogen auf den Gesamtanteil an Fettsäureresten RCO des eingesetzten Tensids (I).
- Erfindungsgemäss verwendete Tenside dieser Klasse werden bevorzugt erhalten durch die dem Fachmann bekannte Reaktion von Monochloressigsäure an einer terminalen Hydroxylgruppe eines alkoxylierten Fettsäureesters, eines alkoxylierten Alkyl Glycerids, bevorzugt eines Mono- oder Diglycerids, eines alkoxylierten Polyglycerids, oder eines alkoxylierten C-18-Pflanzenöls, oder deren Gemische und anschliessend mit einer Lauge neutralisiert.
- Bevorzugt werden die erhaltenen Produktgemische für b=2 allgemein bezeichnet als (i) oder (ii):
- Metall PEG-x Pflanzenöl Carboxylat (i)
- Metall PEG-x Pflanzenglycerid Carboxylat oder Metall Pflanzenöl Glycereth-x carboxylat (ii)
- Mit Metall = Alkalimetallkation, Erdalkalimetallkation, Ammoniumkation (i.e. Carboxylat) oder H (i.e. Carbonsäure) mit Ethoxylierungsgrad x = 2-75, bevorzugt 2-20, besonders bevorzugt 2-8.
- Geeignete Vertreter der Tenside für die Zusammensetzungen bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung umfassen, sind jedoch nicht beschränkt auf: Natrium PEG-6 Mandelöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Mandelöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Aprikosenkernöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Buxus Chinensis Oil Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-6 Aprikosenkernöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-40 Aprikosenkernöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Arganöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Avocadoöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-11 Avocadoöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Borretschsamenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Macademia Tenuifolia Öl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-6 Maisöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Maisöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Traubenkernöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Haselnussöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Leinsamenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-6 Olivenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-7 Olivenöl Carboxylat, Kalium PEG-7 Olivenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Olea Europaea Öl Carboxylat, Ammonium PEG-7 Olivenöl Carboxylat, PEG-7 Olivenöl Carbonsäure, Natrium PEG-8 Olivenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-10 Olivenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Oryza Sativa Öl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Prunus Dulcis Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Persea Gratissma Öl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Passiflora edulis seed oil Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-6 Erdnussöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-45 Crambe Absyssinica Seed oil Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-75 Wiesenschaumkrautöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Kürbiskernöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-3 Rapssamenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-20 Rapssamenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Diestelöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Schinziophyton Rautaneii Kernöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Sesamsamenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Senum Indicum Öl Carboxylat Natrium PEG-8 Sojabohnenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-20 Sojabohnenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-36 Sojabohnenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Sonnenblumenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-32 Sonnenblumenöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Süssmandelöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Wassermelonenkernöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Weizenkeimöl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-8 Zea Mais Öl Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-6 Mandelglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium Mandelöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Carboxylat Natrium PEG-20 Mandelglycerid Carboxylat, Kalium PEG-35 Mandelglycerid Carboxylat, Ammonium PEG-60 Mandelglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium Avocadoöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-11 Avocadoglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium Arganöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium Mandelöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-14 Mandelglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium Maisöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-20 Maisglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-60 Maisglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-20 Nachtkerzenglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-60 Nachtkerzenglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium Traubenkernöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium Cannabis Sativa Kernöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium Jojobaöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-16 Macademiaglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-25 Moringaglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-2 Olivenglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-6 Olivenglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-7 Olivenglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium Olivenöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-10 Olivenglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-40 Olivenglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium Pfirsichkernöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-60 Passiflora edulis seed glycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-60 Passiflora Incarnata seed glycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-40 Diestelglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium Sojaöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-35 Soja glycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-75 Soja glycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-2 Sonnenblumenglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-7 Sonnenblumenglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium Sonnenblumenöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-10 Sonnenblumenglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-13 Sonnenblumenglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-7 Rapsglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-4 Rapsglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-10 Canolaglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-5 Tsubakiateglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-10 Tsubakiateglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-20 Tsubakiateglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium PEG-60 Tsubakiateglycerid Carboxylat, Natrium Baumwollöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium Reisöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium Sesamöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat, Natrium Weizenkeimöl Glycereth-8 Carboxylat.
- In dieser Erfindung besonders bevorzugt sind die Vertreter der Tenside mit der allgemeinen Bezeichnung
- Metall Pflanzenöl PEG-n Carboxylat,
- Mit Metall = Na, K, H, Ammonium; n=ganze Zahlen zwischen 2 und 8,
- und den bevorzugten Pflanzenölen ausgewählt aus der Gruppe Distel, Erdmandel, Hanf, Krambe, Iberischer Drachenkopf, Leindotter, Leinsamen, Lupine, Luzerne, Mais, Olive, Ölrettich, Raps, Rübsen, Sesamblatt, Sonnenblume, Soja, Weintraube und Weizen, sowie deren Kombinationen.
- Bevorzugt werden die Verbindungen (I), besonders bevorzugt Poly(Oxy-1,2-Ethandiyl), .Alpha.-Carboxy-.Omega.-(Olivenölfettsäuren)Oxy-, Natriumsalz (mit 7 mol EO durchschnittlichem EO-Gehalt), erfindungsgemäss als reinigendes Tensid für Proteinschmutz eingesetzt.
- Bevorzugt werden die Verbindungen (I), besonders bevorzugt Poly(Oxy-1,2-Ethandiyl), Alpha.-Carboxy-.Omega.-(Olivenölfettsäuren)Oxy-, Natriumsalz (mit 7 mol EO durchschnittlichem EO-Gehalt), als reinigendes Tensid für ein verbessertes Schmutztragevermögen eingesetzt.
- Bevorzugt werden die Verbindungen (I), besonders bevorzugt Poly(Oxy-1,2-Ethandiyl), .Alpha.-Carboxy-.Omega.-(Olivenölfettsäuren)Oxy-, Natriumsalz (mit 7 mol EO durchschnittlichem EO-Gehalt), als Dispergierungsmittel eingesetzt. Bevorzugt werden die Verbindungen (I), besonders bevorzugt Poly(Oxy-1,2-Ethandiyl), .Alpha.-Carboxy-.Omega.-(Olivenölfettsäuren)Oxy-, Natriumsalz (mit 7 mol EO durchschnittlichem EO-Gehalt), als Stabilisator für partikuläre Inhaltsstoffe eingesetzt.
- Bevorzugt werden die Verbindungen (I), besonders bevorzugt Poly(Oxy-1,2-Ethandiyl), .Alpha.-Carboxy-.Omega.-(Olivenölfettsäuren)Oxy-, Natriumsalz (mit 7 mol EO durchschnittlichem EO-Gehalt), als Stabilisator bei hohem Elektrolytgehalt oder hartem Wasser eingesetzt.
- Bevorzugt werden die Verbindungen (I), besonders bevorzugt Poly(Oxy-1,2-Ethandiyl), .Alpha.-Carboxy-.Omega.-(Olivenölfettsäuren)Oxy-, Natriumsalz (mit 7 mol EO durchschnittlichem EO-Gehalt), zur Minderung von Augenreizungen durch Tensidsysteme eingesetzt.
- Besonders bevorzugt sind Vertreter mit einem HLB > 10.5 und <12.0.
- Ganz besonders bevorzugt ist die Zusammensetzung enthaltend die Verbindung (I) mit dem INCI Name: Natrium Olivenöl PEG-7 Carboxylat bzw. Sodium PEG-7 olive oil carboxylate, IUPC-Name Poly(Oxy-1,2-Ethandiyl), .Alpha.-Carboxy-.Omega.-(Olivenölfettsäuren)Oxy-, Natriumsalz mit 7 mol EO durchschnittlichem EO-Gehalt), HLB = 11.
- Im Sinne dieser Anmeldung liegt der Verbindung (I) eine Mischung von Fettsäurederivaten auf Basis von C18-Pflanzenölen mit unterschiedlicher Kettenlänge und Sättigungsgrad zugrunde. Die Mischung folgt bevorzugt der Fettsäureverteilung im nativen Öl oder wie sie bei der Umsetzung von natürlich vorkommenden Pflanzenöle oder Fette anfallen. Indem für die Synthese der Tensidklasse Gemische von Fettsäurederivaten verwendet werden - wie sie bei der Umsetzung von natürlich vorkommenden Pflanzenöle oder Fette anfallen - können die Tenside kostengünstig, ressourceneffizient und umweltschonend produziert werden. Zusätzliche Reinigungsverfahren, wie z.B. die Trennung der Fettsäuren, bzw. Fettsäureester durch fraktionierte Destillation oder zusätzliche Syntheseschritte, wie z.B. zum Fettalkohol, werden hier nicht benötigt. Neben den ökologischen und ökomischen Vorteilen der Verwendung von natürlichen Fettsäuregemischen, zeigen die verwendeten Tensidmischungen eine erhöhte Reinigungsleistung.
- Vorzugsweise ist die Polyglykolkette der Verbindung (I) pflanzlichen Ursprungs.
- Die Zusammensetzungen enthalten bei der Verwendung bevorzugt 0.01 bis 50 Gew.-% einer oder mehrerer Verbindungen (I), bevorzugter 0.25 bis 40 Gew-%, besonders bevorzugt 0.6 bis 20 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt 0.6 Gew.-% bis 8 Gew.-%, bezogen auf die Gesamtmasse der Zusammensetzung.
- Ein weiterer Gegenstand der Erfindung richtet sich auf die Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung umfassend ein oder mehrere zusätzliche Tenside (II), ausgewählt aus den Gruppen der Alkylethersulfate, Alkylsulfate, Acylglutamate, Acylsarcosinate, Sulfosuccinatester, bevorzugt ethoxylierte oder nicht ethoxyliert, Alkylglucoside, Amidoalkylbetaine, Alkanolamide und Amphoacetate, wobei die Tenside gesättigte Alkyl- oder Acylgruppen mit Kettenlängen zwischen 8-18 Kohlenstoffatomen, oder Gemische aus gesättigten Alkyl- oder Acylgruppen mit 8 bis 18 Kohlenstoffatomen und ungesättigten C-18-Alkenyl- oder Acylgruppen enthalten, wie sie aus Kokosöl, Palmkernöl oder Babassuöl erhalten werden;
und wobei das Gewichts-Verhältnis von (I) zu der Summe der Tenside (II) ≥ 2 : 1 ist, bevorzugt ≥ 3,5 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 5 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt 1: 0 ist. - Bevorzugte Verbindungen aus der Gruppe der Alkylethersulfate sind: Alkylethersulfate: Sodium laureth sulfate, Sodium coceth sulfate; Sodium myristyl ether sulfate, Sodium trideceth sulfate.
- Bevorzugte Verbindungen aus der Gruppe der Alkylsulfate sind: Sodium Lauryl sulfate, Sodium coco sulfate, Ammonium lauryl sulfate; Bevorzugte Verbindungen aus der Gruppe der Acylglutamate sind: Sodium cocoyl glutamate, TEA cocoyl glutamate, Sodium lauroyl glutamate; Bevorzugte Verbindungen aus der Gruppe der Acylsarcosinate sind Sodium lauroyl sarcosinate, Sodium myristoyl sarcosinate; Bevorzugte Verbindungen aus der Gruppe der Sulfosuccinatester sind bevorzugt Disodium laurylsulfosuccinate, Disodium Laureth sulfosuccinat; Bevorzugte Verbindungen aus der Gruppe der Alkylglucoside, sind Coco glucoside, Lauryl glucoside, Decyl glucoside, C10-C16 alkyl glucoside; Bevorzugte Verbindungen aus der Gruppe der Amidoalkylbetaine und Betaine sind Cocoamidopropylbetain und Coco betaine; Bevorzugte Verbindungen aus der Gruppe der Alkanolamide sind Lauramide DEA oder MEA, Cocamid DEA oder MEA; Bevorzugte Verbindungen aus der Gruppe der Amphoacetate sind Sodium Coco Amphoacetate, Sodium lauroamphoacetat; wobei "Sodium" exemplarisch steht für alle Alkali-, Erdalkali-, Ammonium-, oder organisches Ammoniumkationen.
- Hierbei gilt insbesondere:
- Bevorzugt ist das Verhältnis von (I) zu den Alkylethersulfate ≥ 3,5 : 1 ist, bevorzugt ≥ 5 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 10 : 1
- Bevorzugt ist das Verhältnis von (I) zu den Alkylsulfate ≥ 3,5 : 1 ist, bevorzugt ≥ 5 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 10 : 1.
- Bevorzugt ist das Verhältnis von (I) zu den Acylglutamate ≥ 1,5 : 1 ist, bevorzugt ≥ 3,5 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 7 : 1.
- Bevorzugt ist das Verhältnis von (I) zu den Acylsarcosinate ≥ 1 ,5 : 1 ist, bevorzugt ≥ 3 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 7 : 1.
- Bevorzugt ist das Verhältnis von (I) zu den Sulfosuccinatester ≥ 1,5 : 1 ist, bevorzugt ≥ 2,5 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 5 : 1.
- Bevorzugt ist das Verhältnis von (I) zu den Alkylglucoside ≥ 3,5 : 1 ist, bevorzugt ≥ 5 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 10 : 1.
- Bevorzugt ist das Verhältnis von (I) zu den Amidoalkylbetaine ≥ 1 : 1 ist, bevorzugt ≥ 3 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 6 : 1.
- Bevorzugt ist das Verhältnis von (I) zu den Alkanolamide ≥ 1 : 1 ist, bevorzugt ≥ 3 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 6 : 1.
- Bevorzugt ist das Verhältnis von (I) zu den Amphoacetate ≥ 3,5 : 1 ist, bevorzugt ≥ 5 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 10 : 1 .
- In den Zusammensetzungen ist es bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung gelungen, den Gehalt an mittelkettigen Tensiden bei gleichbleibender oder verbesserter Leistung zu reduzieren. In den erfindungsgemässen Verwendungen der Mischungen ist es gelungen, die Einstufung für die Augenreizung gegenüber mittelkettigen Tensidmischungen um mindestens eine Stufe zu verbessern.
- Die Mittel enthalten bei der Verwendung bevorzugt bis 25 Gew.-% eines oder mehrere Verbindungen (II), bevorzugter bis 15 Gew-%, besonders bevorzugt bis 10 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt bis 1 Gew.-%, bezogen auf die Gesamtmasse der Zusammensetzung
- Die erfindungsgemäss verwendeten Zusammensetzungen zeichnen sich durch eine hohe Dispergierwirkung aus. Die verwendete Zusammensetzung enthält keine Biotenside.
- Eine bevorzugt verwendete Ausführungsvariante enthält keine Tenside der Gruppen (II). Eine bevorzugt verwendete Ausführungsvariante enthält ein oder mehrere Tenside der Verbindung (I) sowie weitere Tenside (III) abgeleitet von C18-Pflanzenölen.
- Die Erfindung richtet sich auf die Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung zusätzlich umfassend ein oder mehrere Tenside (III) ausgewählt aus der Gruppe der Seifen (Alkalimetall- oder Ammonium-Fettsäurecarboxylate), der ethoxylierten Fettsäurealkylester, der Fettsäureamide und der Fettsäureimine, wobei die Fettsäurereste von einem C-18-Pflanzenöl abgeleitet sind.
- Hierbei ist vorzugsweise zumindest eine Seife enthalten, ausgewählt aus Alkalimetall- oder Ammoniumsalze von gesättigten oder ungesättigten Fettsäuren, hergestellt durch Verseifung von C-18-Pflanzenölen, wie oben definiert.
- Hierbei ist vorzugsweise zumindest einer derethoxylierten Fettsäurealkylester, abgeleitet von einem C18-Pflanzenöl, ausgewählt aus der Gruppe der ethoxylierten Fettsäuremethylester oder ethoxylierten Fettsäureethylester,
Hierbei ist vorzugsweise zumindest einer der Fettsäureamide, abgeleitet von einem C18-Pflanzenöl ausgewählt aus der Gruppe der N-Acylaminosäurederivate, N-Acylaspartat, N-Acylglycinat, N-Acylalaninat, N-Acylsarcosinat, N-Acylglutamat, acylierte Polypeptide, N-Acylaminosulfonsäuren, N-Acyltaurid, alkoxylierten Fettsäureamide, Polyhydroxyfettsäureamide, gegebenfalls ethoxyliert oder carboxyliert , Carbonsäureamidethersulfate, Alkanolamin-Carbonsäure-Kondensate, Amidoalkylpyrrolidone, Amidoamine, N-Alkylamidobetaine, Alkylaminopropionsäure, acylierte Diamine und Polyamine sowie deren Salze, besonders bevorzugt sind ein oder mehrere Tenside (III) ausgewählt aus den Gruppen der Fettsäureamiden (A) oder der Polyhydroxyfettsäureamiden (B). - Hierbei ist vorzugsweise zumindest einer der Fettsäureimine, abgeleitet von einem C18-Pflanzenöl ausgewählt aus der Gruppe der Imidazolcarboxylate, Alkyliminopropionsäure, Amphoacetate. Besonders bevorzugt sind ein oder mehrere Tenside (III) ausgewählt aus den Gruppen der Amphoacetate (C).
- Ein weiterer Gegenstand der Erfindung richtet sich auf die Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung umfassend ein oder mehrere Tenside (III) ausgewählt aus der Gruppe der alkoxylierten Fettsäureamide der Formel (A) folgend,
(A) R- CO-NH-(CmH2mO)n -H
- Wobei m die ganze Zahlen 2 oder 3 ist, bevorzugt 2, n Zahl im Bereich von 2-10, bevorzugt im Bereich 2-8, ganz besonders bevorzugt 2-4, mit R = gesättigte, ein- oder mehrfach ungesättigter Kohlenwasserstoffkette mit 5-23 Kohlenstoffatomen und RCO abgeleitet aus einem Fettsäuregemisch, wobei der Anteil von 18 und mehr Kohlenstoffatomen des Fettsäurerestes RCO über 60 Gew.-%, bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt von über 77 Gew.-% liegt; und wobei der Anteil an ungesättigten Fettsäureresten über 55 Gew.-%, vorzugsweise über 65 Gew.-% und besonders bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% liegt, jeweils bezogen auf den Gesamtanteil an Fettsäureresten RCO des eingesetzten Tensids (A);
- und wobei das Tensid (A) vorzugsweise aus einem Gemisch unterschiedlicher Kettenlängen und Sättigungsgrade des Fettsäurerests RCO wie oben definiert besteht und RCO vorzugsweise abgeleitet ist von einem C-18-Pflanzenöl aus der oben offenbarten Gruppe der Pflanzen.
- Besonders bevorzugt sind Fettsäureamide der Formel (A) abgeleitet von Distel, Erdmandel, Hanf, Krambe, Iberischer Drachenkopf, Leindotter, Leinsamen, Lupine, Luzerne, Mais, Olive, Ölrettich, Raps, Rübsen, Sesamblatt, Sonnenblume, Soja, Weintraube und Weizen, sowie deren Kombinationen. Besonders bevorzugt sind Fettsäureamide der Formel (A) mit einem HLB > 10.5 und <12.0. Vorzugsweise ist die Polyglykolkette der Verbindung (A) pflanzlichen Ursprungs.
- Die Zusammensetzungen enthalten bei der Verwendung bevorzugt bis 30 Gew.-% eines oder mehrerer Verbindungen (A), bevorzugter bis 10 Gew-%, besonders bevorzugt 0,5 -3 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt 0,5 Gew.-% bis 2 Gew.-%, bezogen auf die Gesamtmasse der Zusammensetzung.
- Erfindungsgemäss äusserst bevorzugt ist das ethoxylierte Fettsäureamid auf Basis Rapsöl, IUPAC Name: Amides, rape oil, N-(hydroxyethyl), ethoxylated; INCI Name: PEG-4-Rapssamenamid, oder Rübsamenamid bzw. PEG-4 rapeseed amide. Handelsname: Amidet N von Kao. Im Vergleich zu dem meist verwendeten Tensid Natrium Laureth Sulfate, weist PEG-4-Rapssamenamid ein deutlich geringeres Augenirritationspotential auf und eignet sich daher hervorragend für die erfindungsgemäss verwendeten Zusammensetzungen.
-
- Wobei R4 einen C1-C4-Alkylrest bedeutet, vorzugsweise Methyl und R eine gesättigte, ein- oder mehrfach ungesättigter Kohlenwasserstoffkette mit 5-23 Kohlenstoffatomen und RCO abgeleitet aus einem Fettsäuregemisch, wobei der Anteil von 18 und mehr Kohlenstoffatomen des Fettsäurerestes RCO über 60 Gew.-%, bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt von über 77 Gew.-% liegt; und wobei der Anteil an ungesättigten Fettsäureresten über 55 Gew.-%, vorzugsweise über 65 Gew.-% und besonders bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% liegt, jeweils bezogen auf den Gesamtanteil an Fettsäureresten RCO des eingesetzten Tensids (B);
- und wobei das Tensid (B) vorzugsweise aus einem Gemisch unterschiedlicher Kettenlängen und Sättigungsgrade des Fettsäurerests RCO wie oben definiert besteht und wobei RCO vorzugsweise abgeleitet ist von einem C-18-Pflanzenöl aus der oben offenbarten Gruppe der Pflanzen. Erfinderisch besonders bevorzugt sind Fettsäureamide der Formel (B) abgeleitet von Distel, Erdmandel, Hanf, Krambe, Iberischer Drachenkopf, Leindotter, Leinsamen, Lupine, Luzerne, Mais, Olive, Ölrettich, Raps, Rübsen, Sesamblatt, Sonnenblume, Soja, Weintraube und Weizen, sowie deren Kombinationen.
- Die Zusammensetzungen enthalten bei der Verwendung bevorzugt bis 30 Gew.-% eines oder mehrerer Verbindungen (B), bevorzugter bis 10 Gew-%, besonders bevorzugt 0,5 -5 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt 0,5 Gew.-% bis 3 Gew.-%, bezogen auf die Gesamtmasse der Zusammensetzung.
- Erfindungsgemäss äusserst bevorzugt ist das Polyhdroxy Fettsäureamid oder Glucamid gemäss Formel (B) auf Basis Sonnenblumenöl, INCI Name: Sunfloweroyl Methylglucamide.
- Im Vergleich zu dem meist verwendeten Tensid Natrium Laureth Sulfate, weist Sunfloweroyl Methylglucamide ein deutlich geringeres Augenirritationspotential auf und eignet sich daher hervorragend für die erfindungsgemässe Verwendung der Zusammensetzungen.
- Ein weiterer Gegenstand der Erfindung richtet sich auf die Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung umfassend ein oder mehrere Tenside (III) ausgewählt aus der Gruppe der Amphoacetate (C) oder Amphoglycinate, wobei das Tensid (C) vorzugsweise aus einem Gemisch unterschiedlicher Kettenlängen und Sättigungsgrade des Fettsäurerests RCO wie für Tensid (I) definiert besteht und wobei RCO vorzugsweise abgeleitet ist von einem C-18-Pflanzenöl aus der gemäss Definitionen offenbarten bevorzugten Gruppe der Pflanzen.
- Geeignete Amphoacetate umfassen, sind jedoch nicht beschränkt, auf sodium oliveamphoacetate, sodium sunflowerseedamphoacetate, sodium grapeseedamphoacetate, sodium cottonseedamphoacetate, sodium ricebranamphoacetate, sodium sesamamphoacetate, sodium sweetalmondamphoacetate, sodium peanutamphoacetate, sodium wheat germamphoacetate, und deren Mischungen.
- Erfinderisch besonders bevorzugt sind weiterhin Amphoacetate (C) abgeleitet von Distel, Erdmandel, Hanf, Krambe, Iberischer Drachenkopf, Leindotter, Leinsamen, Lupine, Luzerne, Mais, Olive, Ölrettich, Raps, Rübsen, Sesamblatt, Sonnenblume, Soja, Weintraube und Weizen, sowie deren Kombinationen.
- Die Zusammensetzungen enthalten bei der Verwendung bevorzugt bis 40 Gew.-% eines oder mehrere Verbindungen (C), bevorzugter 0,5 - 25 Gew-%, besonders bevorzugt 0,5 -10 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt 0,5 Gew.-% bis 5 Gew.-%, bezogen auf die Gesamtmasse der Zusammensetzung.
- Besonders bevorzugt werden Amphoacetate (C), abgeleitet von C-18-Pflanzenölen, in einer Konzentration ≥ 5 Gew.-%, bevorzugt ≥ 10 Gew.-%, besonders bevorzugt ≥ 20 Gew.-%, eingesetzt, bezogen auf die Gesamtmasse der Tenside in der verwendeten Zusammensetzung.
- In einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform, werden bei der Verwendung ausschliesslich Amphoacetate (C) abgeleitet von C-18-Pflanzenölen als amphotere Tenside in der Wasch- und Reinigungszusammensetzung eingesetzt.
- Ein weiterer Gegenstand der Erfindung richtet sich auf die Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung umfassend ein oder mehrere zusätzliche Tenside ausgewählt aus der Gruppe der alkoxylierten Fettsäureester (D), wobei (D) vorzugsweise aus einem Gemisch unterschiedlicher Kettenlängen und Sättigungsgrade des Fettsäurerests RCO wie oben definiert besteht und wobei RCO vorzugsweise abgeleitet ist von einem C-18-Pflanzenöl aus der oben offenbarten bevorzugten Gruppe der Pflanzen.
- Geeignete Fettsäureester umfassen, sind jedoch nicht beschränkt auf: Pflanzenöl-PEG- ester (i): PEG-6 Mandelöl, PEG-8 Mandelöl, PEG-8 Aprikosenkernöl, PEG-6 Aprikosenkernöl, PEG-40 Aprikosenkernöl, PEG-8 Avocadoöl, PEG-11 Avocadoöl, PEG-8 Borretschsamenöl, PEG-8 Macademia Tenuifolia Öl, PEG-6 Maisöl, PEG-8 Maisöl, PEG-8 Traubenkernöl, PEG-8 Haselnussöl, PEG-8 Leinsamenöl, PEG-6 Olivenöl, PEG-7 Olivenöl, PEG-7 Olivenöl, PEG-8 Olea Europaea Öl, PEG-7 Olivenöl, PEG-7 Olivenöl, PEG-8 Olivenöl, PEG-10 Olivenöl, PEG-8 Oryza Sativa Öl, PEG-8 Prunus Dulcis, PEG-8 Persea Gratissma Öl, PEG-8 Passiflora edulis seed oil, PEG-6 Erdnussöl, PEG-45 Crambe Absyssinica Seed oil, PEG-75 Wiesenschaumkrautöl, PEG-8 Kürbiskernöl, PEG-3 Rapssamenöl, PEG-20 Rapssamenöl, PEG-8 Diestelöl, PEG-8 Schinziophyton Rautaneii Kernöl, PEG-8 Sesamsamenöl, PEG-8 Senum Indicum Öl, PEG-8 Sojabohnenöl, PEG-20 Sojabohnenöl, PEG-36 Sojabohnenöl, PEG-8 Sonnenblumenöl, PEG-32 Sonnenblumenöl, PEG-8 Süssmandelöl, PEG-8 Wassermelonenkernöl, PEG-8 Weizenkeimöl, PEG-8 Zea Mais Öl; sowie PEG-Pflanzenölglyceridester (ii): PEG-6 Mandelglycerid, Mandelöl Glycereth-8 Ester, PEG-20 Mandelglycerid, PEG-35 Mandelglycerid, PEG-60 Mandelglycerid, Avocadoöl Glycereth-8 Ester, PEG-11 Avocadoglycerid, Arganöl Glycereth-8 Ester, Mandelöl Glycereth-8 Ester, PEG-14 Mandelglycerid, Maisöl Glycereth-8 Ester, PEG-20 Maisglycerid, PEG-60 Maisglycerid, PEG-20 Nachtkerzenglycerid, PEG-60 Nachtkerzenglycerid, Traubenkernöl Glycereth-8 Ester, Cannabis Sativa Kernöl Glycereth-8 Ester, Jojobaöl Glycereth-8 Ester, PEG-16 Macademiaglycerid, PEG-25 Moringaglycerid, PEG-2 Olivenglycerid, PEG-6 Olivenglycerid, PEG-7 Olivenglycerid, Olivenöl Glycereth-8 Ester, PEG-10 Olivenglycerid, PEG-40 Olivenglycerid, Pfirsichkernöl Glycereth-8 Ester, PEG-40 Distelglycerid, Sojaöl Glycereth-8 Ester, PEG-35 Soja glycerid, PEG-75 Soja glycerid Ester, PEG-2 Sonnenblumenglycerid, PEG-7 Sonnenblumenglycerid, Sonnenblumenöl Glycereth-8 Ester, PEG-10 Sonnenblumenglycerid, PEG-13 Sonnenblumenglycerid, PEG-7 Rapsglycerid, PEG-4 Rapsglycerid, PEG-10 Canolaglycerid, Baumwollöl Glycereth-8 Ester, Reisöl Glycereth-8 Ester, Sesamöl Glycereth-8 Ester, Weizenkeimöl Glycereth-8 Ester; sowie ethoxylierte Fettsäurealkylester (iii): Ethoxylierte Rapsmethylester (EO 7-15), Ethoxylierte Rapsethylester (EO 7-15), Ethoxylierte Sojamethylester (EO 7-15), Ethoxylierte Sojaethylester (EO 7-15). Vorzugsweise ist die Polyglykolkette der Verbindung (D) pflanzlichen Ursprungs.
- Die Zusammensetzungen enthalten bei der Verwendung bevorzugt bis 30 Gew.-% eines oder mehrere Verbindungen (D), bevorzugter bis 20 Gew-%, besonders bevorzugt bis 10 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt 1 Gew.-% bis 3 Gew.-%, bezogen auf die Gesamtmasse der Zusammensetzungen.
- Bevorzugt umfasst die Zusammensetzung bei der Verwendung ein oder mehrere zusätzliche Tenside ausgewählt aus der Gruppe der alkoxylierte Fettsäurester (D), wobei besonders bevorzugt das Gewichts-Verhältnis von (I) zu der Summe von C18-Pflanzenöl-PEG- estern (i), insbesondere bevorzugt zu PEG-7-Olivenölester ≥ 2 : 1 ist, bevorzugt ≥ 3,5 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 5: 1.
- Die Zusammensetzungen enthalten bei der Verwendung bevorzugt bis 5 Gew.-% eines oder mehrerer C18-Pflanzenöl-PEG-ester (i), bevorzugter bis 3 Gew-%, besonders bevorzugt bis 1 Gew.-%. In einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform der Zusammensetzungen wird bei der Verwendung kein zusätzlicher C18-Pflanzenöl-PEG- ester (i) zu der Verbindung (I) zugegeben.
- Die Zusammensetzungen enthalten bevorzugt bis 50 Gew.-% eines oder mehrere Verbindungen (III), bevorzugter bis 40 Gew-%, besonders bevorzugt 0.6 bis 20 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt 0.6 Gew.-% bis 8 Gew.-%, bezogen auf die Gesamtmasse der Zusammensetzung.
- Unter Tensid werden in diesem Zusammenhang amphiphile organische Substanzen mit grenzflächenaktiven Eigenschaften verstanden, die sich an die Grenzfläche zwischen zwei Flüssigkeiten, wie beispielsweise Öl und Wasser adsorbieren und die Fähigkeit besitzen, die Oberflächenspannung von Wasser zu verringern. In Lösung tendieren Tenside zur Selbstaggregation und bilden Strukturen wie bspw. Micellen, lamellare Strukturen u.a. Im Zusammenhang mit dieser Erfindung werden als Tenside Verbindungen bezeichnet, die die Fähigkeit besitzen, die Oberflächenspannung von Wasser bei 20°C und bei einer Konzentration von 0.5 Gew.-% bezogen auf die Gesamtmenge der Zubereitung auf unter 45 mN/m zu verringern.
- Für weitere optionale Tenside, welche vom Fachmann bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung frei mit der Zusammensetzung kombiniert werden können, wird auf die einschlägige Fachliteratur wie z.B. Richard J. Farn, Chemistry and Technology of Surfactants, Blackwell Publishing, verwiesen. Die Tenside umfassen Kohlenwasserstoffketten, abgeleitet aus Fettsäuren oder synthetischen Kohlenwasserstoffen gesättigt oder ungesättigt, substituiert oder nicht-substituiert, linear oder verzweigt mit 4-24 Kohlenstoffatomen in der Kohlenwasserstoffkette. Optionale Tenside umfassen bevorzugt weitere Tenside aus C18-Pflanzenölen, sind jedoch nicht auf diese beschränkt.
- Überraschenderweise zeigen die Zusammensetzungen bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung eine vergleichbare Reinigungsleistung zu üblichen Mitteln mit Schwefeltensiden, auch ohne deren Verwendung. Aus Umweltschutzgründen und den zunehmenden Sulfatgehalten in Trinkwasser ist eine bevorzugte Ausführungsvariante frei von allen Schwefeltensiden. Ebenso kann auf die gewässerbelastenden Phosphate und Phosphonate ohne Kompromisse an die Reinigungsleistung verzichtet werden. Eine weitere bevorzugte Ausführungsform ist bei der Verwendung phosphat- und phosphonatfrei.
- Weiterhin kann die Zusammensetzung bei der Verwendung optional kationische Tenside enthalten, beispielsweise primäre, sekundäre, tertiäre oder quartäre Alkylammoniumsalze der Formel (RI)(RII)(RIII)(RIV)N+X-, in der RI bis RVI unabhängig voneinander gleich- oder verschiedenartige Alkylreste, verzweigt und unverzweigt, gesättigt oder ungesättigt, unsubstituiert, einfach oder mehrfach substituiert, oder H, wobei X- für ein Anion steht.
- Vorzugsweise werden Tenside verwendet, deren hydrophiler Teil aus pflanzlichem Ursprung stammt, ganz besonders bevorzugt abgeleitet von Pflanzen aus Mitteleuropa, wie beispielsweise Zuckertenside oder Aminosäuretenside.
- Die Zusammensetzungen entwickeln bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung einen stabilen Schaum und machen damit das häufig eingesetzte Cocoamidopropyl Betain entbehrlich. Diese Substanz weist ein erhebliches Irritationspotential auf. Eine bevorzugte Ausführungsvariante ist daher bei Verwendung frei von Cocoamidopropyl Betain.
- Eine weitere bevorzugt verwendete Ausführungsvariante ist frei von Cocamid DEA und Cocamid MEA, welche ebenso zur Schaumstabilisierung Anwendung finden und als hautreizend bekannt sind.
- Bevorzugt beträgt die Summe der Tenside, abgeleitet von C18-Fettsäuren (I)+(III), bezogen auf die Gesamtmasse der in der Zusammensetzung vorliegenden Tenside > 50 Gew.-%, bevorzugt > 65 Gew.-%, besonders bevorzugt > 75 Gew.-%.
- In einer besonders bevorzugt verwendeten Ausführungsvariante beträgt die Summe der Tenside, abgeleitet von C-18-Fettsäuren (I)+(III)+ (IV), bezogen auf die Gesamtmasse der in der Zusammensetzung vorliegenden Tenside, 100%.
- Die Zusammensetzung kann bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung alle in Wasch- und Reinigungsmitteln üblichen Lösungsmittel enthalten. In einer bevorzugten flüssigen oder gelförmigen Ausführungsform enthält die verwendete Zusammensetzung Wasser als Lösungsmittel, wobei mehr als 5 Gew.-%, bevorzugt mehr als 15 Gew.-% und besonders bevorzugt mehr als 25 Gew.% Wasser enthält, jeweils bezogen auf die Gesamtmenge der Zusammensetzung. Besonders bevorzugte Zusammensetzungen enthalten bei der Verwendung - bezogen auf ihr Gewicht- 5 bis 98 Gew.-%, bevorzugt 10 bis 90 Gew.-%, besonders bevorzugt 25 bis 75 Gew.-% Wasser. Alternativ kann es sich bei der Verwendung um wasserarme oder wasserfreie Zusammensetzungen handeln, wobei der Gehalt an Wasser in einer bevorzugt verwendeten Ausführungsform weniger als 10 Gew.-%, und mehr bevorzugt weniger als 8 Gew.-% enthält, jeweils bezogen auf die gesamte flüssige Zusammensetzung. In einer weiteren flüssigen oder gelförmigen Ausführungsform ist die Zusammensetzung bei der Verwendung wasserfrei, wobei die Zusammensetzung ein organisches Lösungsmittel als Hauptlösungsmittel enthält. Dabei ist es bevorzugt, dass die Zusammensetzung bei der Verwendung 5 bis 98 Gew.-%, bevorzugt 10 bis 90 Gew.-%, besonders bevorzugt 25 bis 75 Gew.-% Lösungsmittel enthält.
- Hierbei ist vorzugsweise zumindest eines der Lösungsmittel ausgewählt aus der Gruppe umfassend: Aqua (Wasser), Alcohol denat. (Ethanol), Alkohole, Buteth-3, Butoxydiglycol, Butoxyethanol, Butoxyisopropanol, Butoxypropanol, n-Butyl Alcohol, t-Butyl Alcohol, Butyl-3-hydroxybutyrate, Butylene Glycol, Butyloctanol, C1-C6-Alkane, C7-C15-Alkane, Diethylene Glycol, Diethylenglycol monobutylether, Dimethoxydiglycol, Dimethyl Ether, Dimethyl 2-methylglutarat, Dipropylene Glycol, Dipropylenglycol Phenylether, Ethyllactat, 2-Ethyllactat, Ethyl levulinate glycerol ketal, Ethyl levulinate propylene glycol ketal, Ethyl levulinate ethylene glycol ketal, Ethoxydiglycol, Ethoxyethanol, Ethyl Hexanediol, Fettsäuremethylester z.B. auf Basis C18-Pflanzen, Gammalaverolacton, Glycol, Glycerin, Hexanediol, 1,2,6-Hexanetriol, Hexyl Alcohol, Hexylene Glycol, Isobutoxypropanol, Isopentyldiol, Isopropyl Alcohol (iso-Propanol), Lävulinsäure ester, 3-Methoxybutanol, Methoxydiglycol, Methoxyethanol, Methoxyisopropanol, Methoxymethylbutanol, Methoxy PEG-10, Methylal, Methyl Alcohol, Methyl-9-dodecenoate, Methyl Hexyl Ether, Methylpropanediol, 2-Methyl THF, Neopentyl Glycol, N,N-Dimethyl-9-decenamide, Polyole, PEG-4, PEG-6, PEG-7, PEG-8, PEG-9, PEG-6 Methyl Ether, Pentylene Glycol, PPG-7, PPG-2-Buteth-3, PPG-2 Butyl Ether, PPG-3 Butyl Ether, PPG-2 Methyl Ether, PPG-3 Methyl Ether, PPG-2 Propyl Ether, 1,2-Propanediol, 1,3-Propandiol, Propyl Alcohol (n-Propanol), Propylene Glycol, Propylene Glycol Butyl Ether, Propylene Glycol Propyl Ether, Terpene, z.B. Limonen, Thymol, u.a. insbesondere natürlichen Ursprungs wie Zitronenöl, Lavendelöl, Thymianöl, u.a., Tetrahydrofurfuryl Alcohol, Trimethylhexanol. Erfindungsgemäss können diese Lösungsmittel in einer dem Fachmann durchaus bekannten Art und Weise frei mit anderen Inhaltsstoffen kombiniert werden.
- In einer bevorzugt verwendeten Ausführungsform, werden Lösungsmittel aus der Gruppe Lösungsmittel, die aus pflanzlichen Rohstoffen gewonnen werden und biologisch abbaubar sind, verwendet. Besonders bevorzugt sind Lösungsmittel, die keine VOC (volatile organic compounds) enthalten.
- Eine besonders bevorzugte Ausführungsform enthält bei der Verwendung zusätzlich Fettsäurealkylester der Formel R-CO-O-R6 als Lösungsmittel wobei der Fettsäurealkylester aus einem Gemisch unterschiedlicher Kettenlängen und Sättigungsgrade des Fettsäurerests RCO wie definiert bei Tensid (A) besteht und abgeleitet ist von einem C-18 Pflanzenöl;
und wobei R6 ein linearer oder verzweigter Kohlenwasserstoff von 1-5 Kohlenstoffatomen ist, bevorzugt bestehend aus einer Methyl- oder Ethylgruppe, besonders bevorzugt Methyl. Bevorzugte Vertreter sind Rapsmethylester, Sonnenblumenmethylester, Distelmethylester oder Sojamethylester. - Bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung sind alle in Wasch-, Pflege- und Reinigungsmitteln üblichen Komplexbildner geeignet. Geeignet sind bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung beispielsweise Enthärter und Komplexbildner aus den Gruppen der Phosphate und Phosphonate, Schichtsilikate, Zeolithe, Carbonate und Polycarboxylate, Aminopolycarbonsäuren, wie Aminoessigsäuren und Polyaminoessigsäuren sowie deren Salze, Hydroxycarbonsäuren und deren Salze, Polyglycoside undgluconsäuren und deren Salze.
- Hierbei ist vorzugsweise zumindest einer der Komplexbildner ausgewählt aus der Gruppe umfassend Aminotrimethylene Phosphonsäure, Beta-Alanine Acetessigsäure, Calcium Disodium EDTA, Chitosan, Zitronensäure und dessen Salze und Hydrate, Cyclodextrin, Cyclohexanediamin Tetraessigsäure, Diammonium Citrat, Diammonium EDTA, Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic Acid, Diethylenetriamine Pentamethylene Phosphorsäure, Dikalium EDTA, Dinatrium Azacycloheptane Diphosphonat, Dinatrium EDTA, Dinatrium Pyrophosphate, EDTA, Ethylenediamine- N,N'-disuccinic acid (EDDS), Etidronsäure, Galactarsäure, β-Glucan, Gluconsäure, Glucuronsäure, Glucoheptonsäure, HEDTA, Hydroxypropyl Cyclodextrin, Methyl Cyclodextrin, Pentapotassium Triphosphat, Pentasodium Aminotrimethylene Phosphonat, Phosphonobutane tricarbonsäure (PBTC), Pentasodium Ethylenediamine Tetramethylene Phosphonat, Pentasodium Pentetate, Pentasodium Triphosphate, Pentetic Acid, (DTPA), Phytic Acid, Potassium Citrate, Potassium EDTMP, Kalium Gluconate, Kalium Polyphosphate, Kalium Trisphosphonomethylamine Oxide, Ribonsäure, Natrium Chitosan Methylene Phosphonate, Natriumcitrat, Natrium Diethylenetriamine Pentamethylene Phosphonate, Natrium Dihydroxyethylglycinate, Natrium EDTMP, Natrium Glucoheptate, Natrium Gluconate, Natrium Glycereth-1 Polyphosphate, Natrium Hexametaphosphate, Natrium Metaphosphate, Natrium Metasilicate, Natrium Phytate, Natrium Polydimethylglycinophenolsulfonate, Natrium Trimetaphosphate, TEA-EDTA, TEA Polyphosphate, Tetrahydroxyethyl Ethylenediamin, Tetrahydroxypropyl Ethylenediamin, Tetrakalium Etidronat, Tetranatrium Iminodisuccinat (IDS), Tetrakalium Pyrophosphat, Tetranatrium EDTA, Tetranatrium Etidronat, Tetranatrium Pyrophosphat, Trikalium EDTA, Trikalium Dicarboxymethyl Alaninat, Trinatrium EDTA, Trinatrium HEDTA, Trinatrium Methylglycin dieacetic acid (MGDA- Na3), Trinatrium NTA und Trinatrium Phosphate, Phytinsäure, Plfanzenextrakte wie z.B. Lupinus Albus Seed Extract, Carnosine, Bambusa Arundinacea Leaf Extract, Citrus Paradisi (Grapefruit) Peel Extract, Sambucus Nigra Extract; oder im Falle von Säuren, deren Salze.
- Diese Chelatbildner können vom Fachmann frei mit anderen hier genannten Inhaltstoffen kombiniert werden.
- In einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform enthalten die Zusammensetzungen bei der erfindungsgemässen Verwendung Komplexbildner, die biologisch abbaubar sind. Bevorzugt enthalten die Zusammensetzungen bei der erfindungsgemässen Verwendung daher keine Phosphate, keine Phosphonate, kein EDTA und keine Polycarboxylate.
- Ganz besonders bevorzugt in dieser Erfindung sind folgende Komplexbildner auf Basis erneuerbarer Rohstoffe, wie beispielsweise Beta-Alanine Diacetic acid, Cyclodextrin, Diammonium citrat, Galactarsäure, Gluconsäure, Glucoronsäure, Methylcyclodextrin, Hydroxypropyl cyclodextrin, Polyasparaginsäure, Alkali Salze von Gluconate, Natrium Carbonat, Carboxymethyl Inulin und Natrium Carboxymethyl Inulin (NaCMI), Natrium Citrat, Natrium Dihydroxyethylglycinat, Natrium Gluconat, Natrium Glucoheptonat, Natrium Iminodisuccinat, Natrium Lactat, Natrium Lignosulfate, Tetranatrium GLDA (I-glutamic acid, N,N-di (acetic acid), tetrasodium salt), Zitronensäure und deren Salze.
- Bevorzugte Zusammensetzungen enthalten bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung mindestens einen Komplexbildner in einer Gesamtmenge von 0.1-20 Gew.-%, vorzugsweise 0.2-15 Gew.-%, insbesonders bevorzugt 0.5-10 Gew.-%, bezogen auf die Gesamtmenge der Zusammensetzung.
- Die Zusammensetzungen eignen sich bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung aufgrund Ihrer hohen Dispergierfähigkeit besonders gut zur Stabilisierung von Abrasiva und Poliermitteln. Hierbei ist vorzugsweise zumindest eines der Abrasiva und Poliermittel ausgewählt aus der Gruppe umfassend Kunststoffreibemittel auf der Basis von Polyethylen oder Polyurethan, organische Polymere, mineralische Reibemittel wie Kieselsäuren z.B. Gelkieselsäuren, Hydrogelkieselsäuren und Fällungskieselsäuren, Aluminiumhydroxid, Aluminiumoxid, Magnesiumsulfat, Natriumaluminiumsilikate, Calciumcarbonat, Kaolin, Sand, Kreide, Calciumpyrophosphat, Dicalcium-phosphat- dihydrat und andere sowie Reibemittel auf pflanzlicher Basis wie Cellulosederivate, Holzmehl oder Kern- und Schalenmehle, sowie deren Gemische. Insbesondere bevorzugt sind Reibemittel auf der Basis von natürlichen Kern- und/oder Schalenmehlen, insbesondere Walnussschalen, Mandelschalen, Hasselnussschalen, Olivenkern-, Aprikosenkern- und Kirschkernmehl oder Perlen aus Wachsen (z.B. Jojobawachse). Die Konzentration der Reibemittel kann bis zu 50 Gew.-% betragen, bevorzugt 0 - 30 Gew.-%, bezogen auf die Gesamtmenge der Zusammensetzung.
- Die Zusammensetzung kann bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung alle in Wasch-, Pflege- und Reinigungsmitteln übliche Konservierungsmittel enthalten, welche vom Fachmann im Sinne dieser Anwendung frei mit anderen Inhaltsstoffen kombiniert werden können.
- Hierbei ist vorzugsweise zumindest ein Konservierungsmittel ausgewählt aus der Gruppe umfassend Alkohole, Aldehyde, antimikrobiellen Säuren bzw. deren Salze, Carbonsäureester, Säureamide, Phenole, Phenolderivate, Diphenyle, Diphenylalkane, Harnstoffderivate, Sauerstoff- und Stickstoff-Acetale sowie -Formale, Benzamidine, Isothiazole und deren Derivate wie Isothiazolinone, Phtalimidderivate, Pyridinderivate, oberflächenaktive Verbindungen, Guanidine, antimikrobielle amphoterer Verbindungen, Chinoline, 1,2-Dibrom-2,4-dicyanobutan, lodo-2-propynyl-butyl-carbamat, lod, lodophore und Peroxide. Besonders bevorzugt ist die Konservierung der Zusammensetzung bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung auf Basis von antimikrobiellen Wirkstoffen ausgewählt aus antimikrobiellen Peptiden, Ethanol, Benzylalkohol, Dehydroessigsäure und deren Salzen, Sorbinsäure und Kaliumsorbat, pflanzlichen organischen Säuren und deren Salze, Ameisensäure, Glycerin, Zitronensäure, Milchsäure, Salicylsäure, sowie deren Salze.
- Die Menge der Konservierungsmittel (eine oder mehrere Verbindungen) in den Zusammensetzungen beträgt bei der Verwendung vorzugsweise 0.001 bis 30 Gew.-%, besonders bevorzugt 0.05-20 Gew.-%, insbesonders bevorzugt 1-10 Gew.-%, bezogen auf die Gesamtmenge der Zusammensetzung. Äusserst bevorzugt ist die verwendete Ausführungsform frei von chemischen Konservierungsmittel, wie in den Ausführungsbeispielen offenbart, d.h. insbesondere ohne Parabene, ohne formaldehydhaltige Konservierungsmittel bzw. Formaldehydabspalter, ohne Isothiazole und deren Derivate, ohne halogenhaltige Verbindungen, ohne Phtalimide, ohne Benzalkoniumchlorid, ohne Benzoesäure, ohne Phenoxyethanol.
- Bevorzugt werden der Zusammensetzung bei der erfindungsgemässen Verwendung Antioxidantien zugesetzt um die ungesättigten Kohlenwasserstoffketten zu schützen. Hierbei ist vorzugsweise zumindest ein Antioxidans ausgewählt aus der Gruppe umfassend Aminosäuren (z.B. Glycin, Histidin, Tyrosin, Tryptophan) und deren Derivaten, Imidazole (z.B. Urocaninsäure) und deren Derivaten, Peptide wie D,L-Carnosin, D-Carnosin, L-Carnosin und deren Derivaten (z.B. Anserin), Carotinoide, Carotine und deren Derivate, Chlorogensäure und deren Derivate, Liponsäure und deren Derivate, Aurothioglucose, Propylthiouracil und andere Thiole (z.B. Thioredoxin, Glutathion, Cystein, Cystin, Cystamin und deren Glycosyl-, N-Acetyl-, Methyl-, Ethyl-, Propyl-, Amyl-, Butyl- und Lauryl-, Palmitoyl-, Oleyl-, [gamma]-Linoleyl-, Cholesteryl- und Glycerylester) sowie deren Salze, Dilaurylthiodipropionat, Distearylthiodipropionat, Thiodipropionsäure und deren Derivate (Ester, Ether, Peptide, Lipide, Nukleotide, Nukleoside und Salze) sowie Sulfoximinverbindungen (z.B. Buthioninsulfoximine, Homocysteinsulfoximin, Buthioninsulfone, Penta-, Hexa-, Heptathioninsulfoximin) in sehr geringen verträglichen Dosierungen, ferner (Metall)-Chelatoren (z.B. [alpha]-Hydroxyfettsäuren, Palmitinsäure, Phytinsäure, Lactoferrin), [alpha]-Hydroxysäuren (z.B. Citronensäure, Milchsäure, Apfelsäure), Numinsäure, Gallensäure, Gallenextrakte, Bilirubin, Biliverdin, EDTA, EGTA und deren Derivate, ungesättigte Fettsäuren und deren Derivate (z.B. [gamma]-Linolensäure, Linolsäure, Ölsäure), Folsäure und deren Derivate, Ubichinon und Ubichinol und deren Derivate, Vitamin C und Derivate (z.B. Ascorbylpalmitat, Mg-Ascorbylphosphat, Ascorbylacetat), Tocopherole und Derivate (z.B. Vitamin-E-acetat), Vitamin A und Derivate (Vitamin-A-palmitat) sowie Koniferylbenzoat des Benzoeharzes, Rutinsäure und deren Derivate, [alpha]-Glycosylrutin, Ferulasäure, Furfurylidenglucitol, Carnosin, Butylhydroxytoluol, Butylhydroxyanisol, Nordihydroguajakharzsäure, Nordihydroguajaretsäure, Trihydroxybutyrophenon, Harnsäure und deren Derivate, Mannose und deren Derivate, Zink und dessen Derivate (z.B. ZnO, ZnSO4) Selen und dessen Derivate (z.B. Selenmethionin), Stilbene und deren Derivate (z.B. Stilbenoxid, Trans-Stilbenoxid), Superoxid-Dismutase und die erfindungsgemäss geeigneten Derivate (Salze, Ester, Ether, Zucker, Nukleotide, Nukleoside, Peptide und Lipide) dieser genannten Stoffe.
- Bevorzugt sind bei der erfindungsgemässen Verwendung Antioxidantien, die auf Rohstoffen aus Pflanzen, bevorzugt C-18-Pflanzen beruhen, wie beispielsweise Antioxidantien aus den Gruppen der Aminosäuren, Peptide, Cartinoide, Chelatoren, Pflanzenextrakten und Hydroxysäuren, sowie Mischungen derselben.
- Die Menge der Antioxidantien (eine oder mehrere Verbindungen) in den Zusammensetzungen beträgt bei der Verwendung vorzugsweise 0.001 bis 30 Gew.-%, besonders bevorzugt 0.05-20 Gew.-%, insbesondere 1-10 Gew.-%, bezogen auf die Gesamtmenge der Zusammensetzung. Diese Antioxidatien können vom Fachmann mit anderen hier genannten Inhaltstoffen kombiniert werden.
- Optional kann die Zusammensetzung Wirkstoffe gegen Mikroorganismen wie Pilze oder Bakterien bei der Verwendung enthalten. Bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung sind als keimhemmende oder antimikrobielle Wirkstoffe einsetzbar Organohalogenverbindungen sowie -halogenide, quartäre Ammoniumverbindungen, eine Reihe von Pflanzenextrakten und Zinkverbindungen. Hierzu zählen u. a. Triclosan, Chlorhexidin und Chlorhexidingluconat, 3,4,4'-Trichlorcarbanilid, Bromchlorophen, Dichlorophen, Chlorothymol, Chloroxylenol, Hexachlorophen, Dichloro-m-xylenol, Dequaliniumchlorid, Domiphenbromid, Ammoniumphenolsulfonat, Benzalkoniumhalogenide, Benzalkoniumcetylphosphat, Benzalkoniumsaccharinate, Benzethoniumchlorid, Cetylpyridiniumchlorid, Laurylpyridiniumchlorid, Laurylisoquinoliniumbromid, Methylbenzedoniumchlorid. Desweiteren sind Phenol, Phenoxyethanol, Dinatriumdihydroxyethylsulfosuccinylundecylenat, Natriumbicarbonat, Zinklactat, Natriumphenolsulfonat und Zinkphenolsulfonat, Ketoglutarsäure, Terpenalkohole wie z. B. Farnesol, Chlorophyllin-Kupfer-Komplexe, α-Monoalkylglycerinether mit einem verzweigten oder linearen gesättigten oder ungesättigten, gegebenenfalls hydroxylierten C6 - C22-Alkylrest, besonders bevorzugt α-(2-Ethylhexyl)glycerinether, Carbonsäureester des Mono-, Di- und Triglycerins (z. B. Glycerinmonolaurat, Diglycerinmonocaprinat), Lantibiotika sowie Pflanzenextrakte (z. B. grüner Tee und Bestandteile des Lindenblütenöls) einsetzbar.
- Weitere bevorzugte Wirkstoffe sind ausgewählt aus präbiotisch wirksamen Komponenten. Dazu gehören Nadelbaumextrakte, insbesondere aus der Gruppe der Pinaceae, und Pflanzenextrakte aus der Gruppe der Sapindaceae, Araliaceae, Lamiaceae und Saxifragaceae, insbeondere Extrakte aus Picea sp., Paullinia sp., Panax sp., Lamium album oder Ribes nigrum sowie Mischungen dieser Substanzen.
- Weitere bevorzugte Wirkstoffe sind ausgewählt aus den keimhemmend wirkenden Parfümölen bzw. ätherischen Ölen.
- Die Menge keimhemmenden Stoffe in den Zusammensetzungen beträgt bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung 0,1 -10 Gew.-%, vorzugsweise 0,2 - 7 Gew.-%, insbesondere 0,3 - 5 Gew.-% und außerordentlich bevorzugt 0,4 - 1,0 Gew.-%, bezogen auf die Gesamtmenge der Zusammensetzung.
- Optional können UVA- und/oder UVB-Filter der verwendeten Zusammensetzung zugegeben werden. Die Zusammensetzung eignet sich bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung insbesondere Partikel zu stabilisieren. Vorteilhaft können daher Zusammensetzungen bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung Substanzen enthalten, die UV-Strahlung im UVA und UVB-Bereich absorbieren, wobei die Gesamtmenge der Filtersubstanzen an der gesamten Zusammensetzung vorzugsweise zwischen 0.1 Gew.-% bis 30 Gew.-% betragen kann. Bevorzugt sind handelsübliche wasser- oder öllösliche UV-Filter. Üblicherweise werden Kombinationen von UV-Filtern eingesetzt, die vom Fachmann mit anderen hier genannten Inhaltstoffen kombiniert werden können.
- Die Zusammensetzung kann bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung Bindemittel bzw. Konsistenzregler enthalten z. B. natürliche und/oder synthetische wasserlösliche Polymere wie Alginate, Carrageenate, Traganth, Stärke und Stärkeether, Celluloseether wie z. B. Carboxymethylcellulose (Na-Salz), Hydroxyethylcellulose, Methylhydroxypropylcellulose, Guar, Akaziengum, Agar-Agar, Xanthan- Gum, Succinoglycan-Gum, Johannisbrotmehl, Pectine, wasserlösliche Carboxyvinylpolymere Polyvinylalkohol, Polyvinylpyrrolidon, Polyethylenglycole. Sie werden bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung bevorzugt in Mengen von 0,01- 10 Gew.-% in den Zusammensetzungen eingesetzt, Gew.-% bezogen auf die Gesamtmenge der Zusammensetzung.
- Als Wachse kommen u. a. natürliche Wachse, wie z. B. Bienenwachs, Bürzelfett, Candelillawachs, Carnaubawachs, Ceresin, Espartograswachs, Guarumawachs, Japanwachs, Korkwachs, Lanolin (Wollwachs), Mikrowachse, Montanwachs, Ozokerit (Erdwachs), Petrolatum, Paraffinwachse, Ouricourywachs, Reiskeimölwachs, Schellackwachs, Sonnenblumenwachs, Fruchtwachse wie Orangenwachse, Zitronenwachse, Grapefruitwachse, Zuckerrohrwachs, chemisch modifizierte Wachse (Hartwachse), wie z. B. Montanesterwachse, Sasolwachse, hydrierte Jojobawachse, hydriertes Rinzinusöl sowie synthetische Wachse, wie z. B. Polyalkylenwachse und Polyethylenglycolwachse in Frage. Die Wachse können bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung in den Zusammensetzungen in Mengen von 0.2 bis 80 Gew.-%, bevorzugt Mengen von 0.2 bis 70 Gew.-% eingesetzt werden, bezogen auf die Gesamtmenge der Zusammensetzung.
- Als Perlglanzwachse kommen beispielsweise in Frage: Alkylenglycolester, speziell Ethylenglycoldistearat; Fettsäurealkanolamide, Partialglyceride, Ester von mehrwertigen, gegebenenfalls hydroxysubstituierte Carbonsäuren mit Fettalkoholen mit 6 bis 24 Kohlenstoffatomen, Fettstoffe, wie beispielsweise Fettalkohole, Fettketone, Fettaldehyde, Fettether und Fettcarbonate, die in Summe mindestens 24 Kohlenstoffatome aufweisen; Fettsäuren wie Stearinsäure, Hydroxystearinsäure oder Behensäure, Ringöffnungsprodukte von Olefinepoxiden mit 12 bis 24 Kohlenstoffatomen mit Fettalkoholen mit 12 bis 24 Kohlenstoffatomen und/oder Polyolen mit 2 bis 15 Kohlenstoffatomen und 2 bis 10 Hydroxylgruppen sowie deren Mischungen. Bevorzugt sind bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung Zusammensetzungen mit Perlglanzwachsen basierend auf C18-Pflanzen.
- Die Einsatzmenge der Perlglanzwachse kann - bezogen auf die Gesamtmenge der Zusammensetzung - bei 0.1 bis 5, vorzugsweise 0.5 bis 3 und insbesondere 1 bis 1.5 Gew.-% liegen.
- Die Zusammensetzungen bilden bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung bereits ohne weitere Hilfsmittel einen stabilen Schaum. Weiterhin geeignet ist die zusätzliche Zugabe von Saponinen, beispielsweise Saponinen aus der indischen Waschnuss (Sapindus mukorossi), Koreanischen Ginsengs (Panax ginseng), Agavengewächsen, Inka-Gurke (Cyclanthera pedata), Süssholz (Glycyrrhiza glabra), Efeu (Hedera), Schlüsselblume (Primula veris), Vogelmiere (Stellaria media), Wald-Sanickel (Sanicula europaea), Dornige Hauhechel (Ononis spinosa), Hülsenfrüchten (Leguminosae), Spinat (Spinacia), Spargel (Asparagaceae), Hafer (Avena), (Ononis spinosa), Schattenblümchen (Maianthemum bifolium), Seifenkraut (Saponaria officinalis), Walnuss (Aesculus hippocastanum), Acker-Gauchheil (Anagallis arvensis), Gelber Hohlzahn (Galeopsis segetum), Karthäuser-Nelke (Dianthus carthusianorum), Ackerschachtelhalm (Equisetum arvense) und Seifenrinde (Quillaja saponaria Molina).
- Die Menge an Saponinen beträgt üblicherweise bis zu 5 Gew.-%, vorzugsweise 0.001 bis 3 Gew.-%, insbesondere 0.01 bis 2 Gew.-%. (Gew.-% Aktivstoff bezogen auf die gesamte Zusammensetzung)
- Die Saponine können in den Zusammensetzungen bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung frei mit anderen Inhaltsstoffen kombiniert werden.
- Die Zusammensetzung ist bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung über einen breiten pH-Bereich stabil. Bevorzugt ist ein pH-Bereich zwischen 1 und 13. Der pH-Wert der Zusammensetzung kann bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung mittels üblicher pH-Regulatoren eingestellt werden, wobei je nach Anwendung unterschiedliche pH-Bereiche von sauer (pH 0-4) zu neutral (pH 5-7) bis hin zu basisch (pH 8-14) eingestellt werden. Als pH-Stellmittel dienen Säuren und/oder Alkalien. Geeignete Säuren sind insbesondere organische Säuren wie die Ameisensäure, Essigsäure, Zitronensäure, Glycolsäure, Milchsäure, Bernsteinsäure, Adipinsäure, Apfelsäure, Weinsäure und Gluconsäure, Amidosulfonsäure, Methansulfonsäure. Besonders bevorzugt sind Säuren, die aus pflanzlichen Rohstoffen gewonnen werden wie Essigsäure, Zitronensäure, Milchsäure, Apfelsäure und Weinsäure sowie die Mineralsäuren Salzsäure, Schwefelsäure und Salpetersäure bzw. deren Mischungen. Bevorzugte Basen stammen aus der Gruppe der Alkali-und Erdalkalimetallhydroxide und -carbonate sowie Natriummetasilikate. Daneben kann die verwendete Zusammensetzung Ammoniak und Alkanolamine enthalten. Im Bereich der Detergenzien sind saure Reiniger wie Bad-, Sanitär-, oder WC-Reiniger, Neutralreiniger, wie Geschirrspülmittel, sowie alkalische Reiniger wie Fett- und Ölreiniger oder Waschmittel möglich.
- Die Zusammensetzungen können bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung neben den bereits genannten Stoffen weiterhin Lösungsvermittler, sog. Hydrotropika enthalten. Hierbei sind alle üblicherweise zu diesem Zweck in Wasch- und Reinigungsmitteln verwendeten Stoffe einsetzbar.
- Gerüststoffe, welche üblicherweise in Wasch- und Reinigungsmitteln eingesetzt werden, sind geeignet. Die Gerüststoffe können vom Fachmann bei der erfindungsgemässen Verwendung frei mit anderen Inhaltsstoffen in der Zusammensetzung kombiniert werden.
- Besonders bevorzugt sind bei der erfindungsgemässen Verwendung Gerüststoffe auf Basis erneuerbarer Rohstoffe, die aus Pflanzen der gemässigten Zone gewonnen werden können, in der Zusammensetzung, wie zum Beispiel Polyaspartate, Polycarboxylate wie beispielsweise Citrate, sowie Gluconate, Succinate oder Malonate.
- Optional können der Zusammensetzung bei der erfindungsgemässen Verwendung alle in Wasch- und Reinigungsmitteln üblichen Duft- und Farbstoffe zugesetzt werden. Bevorzugte Farbstoffe und Duftstoffe, deren Auswahl dem Fachmann keinerlei Schwierigkeit bereitet, besitzen eine hohe Lagerstabilität und Unempfindlichkeit gegenüber den übrigen Inhaltsstoffen der Wasch- oder Reinigungsmittel. Die Farbstoffe weisen keine ausgeprägte Substantivität gegenüber Textilfasern oder harten Oberflächen aus und färben diese nicht an. In einer weiteren bevorzugte verwendeten Ausführungsform der Erfindung, werden weder Farb-, noch Duftstoffe zugesetzt. Die verwendeten Zusammensetzungen weisen auch ohne Zugabe von Farb-oder Duftstoffen eine zufriedenstellende Ästhetik und einen angenehmen Duft aus, um so Ausführungsformen ohne Farb- und/oder Duftstoffe zu ermöglichen, wie beispielsweise für Konsumenten mit Allergien und/oder sensibler Haut.
- Die Zusammensetzung zeigt bei der Verwendung eine so gute Reinigungsleistung, dass Enzyme entbehrlich sind. Die Zusammensetzung kann bei der Verwendung optional Enzyme enthalten, insbesondere in den verwendeten Ausführungsformen der Textil-, Spezial- und Geschirrreinigung. Die Enzyme können in den Zusammensetzungen bei der erfindungsgemässen Verwendung vom Fachmann mit allen anderen hier genannten Inhaltsstoffen kombiniert werden. Vorzugsweise werden Proteasen, Lipasen, Amylasen, Hydrolasen und/oder Cellulasen eingesetzt. Sie können der Zusammensetzung bei der erfindungsgemässen Verwendung in jeder nach dem Stand der Technik etablierten Form zugesetzt werden. Hierzu gehören bei flüssigen oder gelförmigen Zusammensetzungen insbesondere Lösungen der Enzyme, vorzugsweise hoch konzentriert, wasserarm und/oder mit Stabilisatoren versetzt. Des Weiteren können die Enzyme verkapselt angewendet werden. Um ein in einer Zusammensetzung enthaltenes Enzym bei der Verwendung vor Schädigungen wie beispielsweise Inaktivierung, Denaturierung oder Zerfall etwa durch physikalische Einflüsse, Oxidation oder proteolytische Spaltung zu schützen, können dem enzymhaltigen Mitteln Enzymstabilisatoren zugesetzt werden, die dem Fachmann wohl bekannt sind.
- Überraschenderweise wird in der verwendeten enzymfreien Ausführungsform eine hervorragende Reinigungsleistung gegenüber Proteinen festgestellt, welche mit enzymhaltigen Mitteln im Markt durchaus vergleichbar ist. Eine besonders bevorzugte Ausführungsform der Erfindung ist daher die Verwendung der Zusammensetzung ohne Proteasen, ganz besonders bevorzugt ist die Verwendung der enzymfreien Ausführungsform. Diese ist besonders vorteilhaft für Konsumenten mit Allergien und/oder sensibler Haut. Verwendungen enzymfreie Ausführungsformen bei vergleichbarer Reinigungskraft sind in den Ausführungsbeispielen offenbart.
- Die flüssige oder gelförmige Ausführungsform der Zusammensetzungen weist bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung vorzugsweise eine Viskosität von 0.4 bis 10000 mPa.s. auf. Zu diesem Zweck kann die Zusammensetzung Viskositätsregulatoren enthalten. Die Menge an Viskositätsregulator beträgt üblicherweise bis zu 1.5 Gew.-%, vorzugsweise 0.001 bis 1.0 Gew.-%, insbesondere 0.01 bis 0.5 Gew.-%; Gew-% Aktivstoff bezogen auf die gesamte Zusammensetzung. Hierbei ist vorzugsweise mindestens einer der Viskositätsregulatoren ausgewählt aus der Gruppe umfassend organische abgewandelte Naturstoffe (Carboxymethylcellulose und andere Celluloseether, Hydroxyethyl- und -propylcellulose und dergleichen, Kernmehlether), organische vollsynthetische Verdickungsmittel (Polyacryl- und Polymethacryl-Verbindungen, Vinylpolymere, Polycarbonsäuren, Polyether, Polyimine, Polyamide) und anorganische Verdickungsmittel (Polykieselsäuren, Schichtsilikate, Tonmineralien wie Montmorillonite, Zeolithe, Kieselsäuren), sowie organische natürliche Verdickungsmittel (Agar-Agar, Carrageen, Xanthan, Traganth, Gummi arabicum, Alginate, Pektine, Polyosen, Guar-Mehl, Johannisbrotbaumkernmehl, Stärke, Dextrine, Gelatine, Casein). In einer bevorzugt verwendeten Ausführungsform sind die Viskositätsregulatoren natürliche organische Verdickungsmittel aus pflanzlichen Rohstoffen - einschliesslich Algen - beispielsweise Polysaccharide wie Pektine oder Stärke. In dieser verwendeten Ausführungsform werden keinerlei organische vollsynthetischen Verdickungsmittel wie Polyacryl- und Polymethacryl-Verbindungen, Vinylpolymere, Polycarbonsäuren, Polyether, Polyimine, oder Polyamide eingesetzt. Bevorzugt sind zudem anorganische Verdickungsmittel.
- Des Weiteren bevorzugt sind biotechnologisch hergestellte Verdickungsmittel mithilfe von nicht genmodifizierten Organismen (non GMO), wie beispielsweise Xanthan gumErfindungsgemäss bevorzugt verwendeteZusammensetzungen verdickt mit Xanthan gum sind in den Ausführungsbeispielen offenbart. Für die Zusammensetzungen können bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung die Viskositätsregulatoren vom Fachmann frei mit anderen hier genannten Inhaltsstoffen kombiniert werden.
- Neben den bisher genannten Komponenten kann die Zusammensetzung bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung weitere dem Fachmann bekannte Inhaltsstoffe enthalten, welche frei mit anderen hier genannten Inhaltsstoffen kombiniert werden können.
- Füll- und Hilfsstoffe wie Adsorptionsmittel, Bittermittel, Bleichmittel, Bügelhilfsmittel, weitere Basen, weitere Säuren, Einlaufverhinderer, Filmbildner, neutrale Füllsalze, Alkali- und Erdalkalisalze wie NaCl oder MgSO4, weitere Gerüststoffe, Gleitmittel, Hydrotrope, weitere Lösungsmittel und Lösungsvermittler, Opacifier, Polymere, Puffer, Quellmittel, organische und anorganische Salze, Schauminhibitoren, Silikonöle, Co-Tenside, Viskositätsregulatoren, Wachse.
- Prozesschemikalien wie Glyzerin, Vergällungsmittel, z.B. Methylethylketon, u.a., Stabilisatoren und Verunreinigungen bzw. Nebenkomponenten aus dem Herstellungsprozess.
- Funktionelle Mittel und Aktivstoffe wie Antiredepositionsmittel, Antistatika, Bakterizide, Bleichaktivatoren, Desinfektionsmittel, Farbübertragungsinhibitoren, weitere Enzyme, Fluoreszenzmittel, Fungizide, Germizide, hydrophilierende Agenzien, Imprägniermittel, Insektizide, Knitterschutzmittel, Korrosionsinhibitoren, optische Aufheller, Oxidationsmittel und - katalysatoren, Parfümträger, Phobiermittel, probiotische Inhaltsstoffe, Schiebefestmittel , UV- Absorber, Vergrauungsinhibitoren, Wäschesteifen.
- sowie Gemische derselben.
- Ein weiterer Gegenstand der Erfindung bezieht sich auf ein Verfahren zur Reinigung und Pflege.Verfahren zur Reinigung zeichnen sich im allgemeinen dadurch aus, dass in einem oder mehreren Verfahrensschritten verschiedene reinigungsaktive Substanzen auf das Reinigungsgut aufgebracht und nach der Einwirkzeit abgewaschen werden, oder dass das Reinigungsgut in sonstiger Weise mit einem Wasch-, Pflege-oder Reinigungsmittel oder einer Lösung dieses Mittels behandelt wird.
- Das Wasch- oder Reinigungsverfahren umfassend die Verfahrensschritte
- a) Bereitstellen einer Wasch-, oder Reinigungslösung unter Verwendung der Zusammensetzung gemäss den vorhergehenden Beschreibungen
- b) in Kontakt bringen einer harten oder flexiblen Oberfläche, sowie Textilien, Teppiche oder Naturfasern mit der Waschlösung gemäss (a).
- In dem beschriebenen Verfahren werden in der verwendeten Ausführungsform des Waschmittels oder Waschzusatzes Temperaturen bis 90°C und weniger eingesetzt. Bevorzugt sind Temperaturen unter 60°C und ganz besonders bevorzugt sind Temperaturen, die zu Energiespargründen kein Aufheizen der Wassertemperatur benötigen (ca. 20°C). Diese Temperaturangaben beziehen sich auf die in den Waschschritten eingesetzten Temperaturen. Alle Sachverhalte, Gegenstände und Ausführungsformen, die für die Verwendung der Zusammensetzung beschrieben sind, sind auch auf das Wasch- und Reinigungsverfahren anwendbar und umgekehrt.
- Vorzugsweise werden die Zusammensetzungen erfindungsgemäss zur Verbesserung der Reinigungsleistung eines Waschmittels oder Reinigungsmittels zur Entfernung von Proteinschmutz verwendet. Auf Proteasen kann hierbei verzichtet werden. Bevorzugte Beispiele für diese Anwendung sind Geschirrspülmittel, Textilwaschmittel, Oberflächenreiniger, Hygienereiniger, Reiniger in Lebensmittelbereichen, Kliniken, Tierhaltung.
- Vorzugsweise werden die Zusammensetzungen erfindungsgemäss zur Verbesserung der Schmutztragekraft verwendet. Bevorzugte Produkte sind Geschirrspülmittel, Textilwaschmittel, Bodenreiniger, Industriereiniger für stark verschmutzte Bereiche, wie z.B. Bergbau, Kohle, Werkstätten, Strassenbau und andere.
- Die Zusammensetzungen werden erfindungsgemäss vorzugsweise zur Verbesserung des Dispergierungsvermögens eines Waschmittel oder Reinigungsmittels verwendet. Unlösliche Teilchen werden in der Zusammensetzung stabilisiert. Bevorzugten Beispiele sind Reiniger mit Abriebkörper, Bodenreiniger auf Wachsbasis.
- Die Zusammensetzungen werden erfindungsgemäss vorzugsweise zur Verbesserung der Stabilität der Zusammensetzung bei hohen Elektrolytgehalten verwendet. Beispiele sind Textilwaschmittel.
- Die Zusammensetzungen werden erfindungsgemäss vorzugsweise zur Verbesserung der Waschleistung bei hartem Wasser verwendet. Beispiele sind Textilwaschmittel. Komplexbildner und nichtionische Tenside können reduziert werden, Vergrauung und Verkrustungen auf Wäsche und in der Maschine werden reduziert.
- Die Zusammensetzungen werden erfindungsgemäss vorzugsweise zur Reduktion der Augenreizung durch ein Wasch- oder Reinigungsmittel verwendet. Bevorzugt besitzen diese Zusammensetzungen einen pH-Wert zwischen 5 und 7. Bevorzugte Verwendung sind Geschirrspülmittel und Neutralreiniger für Oberflächen, sowie Produkte, welche über Sprüher aufgetragen werden.
- Vorzugsweise werden die Zusammensetzungen erfindungsgemäss zur Verbesserung des Materialschutzes verwendet. Bevorzugte Produkte sind Reiniger für empfindliche Oberflächen, Industriereiniger, Reiniger für Displays.
- Vorzugsweise werden die Zusammensetzungen erfindungsgemäss zur Unterstützung der Entfernung mikrobieller Verunreinigungen eines Waschmittel oder Reinigungsmittels verwendet. Aufgrund der hohen Proteinreinigung werden Hygienereiniger in der Entfernung von Biofilmen unterstützt.
- Die Zusammensetzung kann als Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel für harte und flexible Oberflächen, sowie Textilien, Teppiche oder Naturfasern verwendet werden. Zu den Wasch- und Reinigungsmitteln zählen im Rahmen der Erfindung ferner Waschhilfsmittel, die bei der manuellen oder maschinellen Reinigung zum eigentlichen Mittel zudosiert werden. Ferner zählen zu Waschmitteln im Rahmen der Erfindung auch Vor- und Nachbehandlungsmittel, also solche Mittel die vor der eigentlichen Reinigung angewendet werden, beispielsweise zum Anlösen von hartnäckigen Verschmutzungen. Die Mittel können auf das Reinigungsgut aufgebracht werden, welches sich in Haushalt, Industrie, Gewerbe bzw. Institutionen, Hafenanlagen, sowie Industrie- und Freizeit-, sowie Sportanlagen finden. Bevorzugt wird die Zusammensetzung zur Reinigung von harten Oberflächen oder Textilien verwendet. Harte Oberflächen im Sinne dieser Anmeldung sind dabei Fenster, Spiegel, sowie weitere Glasoberflächen, Oberflächen aus Keramik, Kunststoff, Metall oder Holz, eben oder uneben, lackiert sowie unlackiert, flexible Oberflächen sind beispielsweise Kunststoffplanen, Schaumstoffe, Erde oder andere.
- Textilen und Fasern sind im Sinne der Anmeldung Stoffe, Kleidung, Polster, Teppiche, Garne, u.a.
- In einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform wird die Zusammensetzung bei saurem pH zwischen 0 und 6 verwendet, bevorzugt zwischen 1 und 4 verwendet. Typische Beispiele für die Verwendungen bei saurem pH sind WC- und Sanitärreiniger, Kalkreiniger, Reiniger für Zementschleier.
- In einer anderen bevorzugten Ausführungsform wird die Zusammensetzung bei alkalischem pH zwischen 7 und 14 verwendet, bevorzugt zwischen 8 und 12 verwendet. Typische Beispiele für die Verwendungen bei alkalischem pH sind Waschmittel, Oberflächenreiniger, Küchenreiniger, Grill- und Ofenreiniger, Felgenreiniger und andere.
- In einer weiteren bevorzugen Ausführungsform wird die Zusammensetzung bei neutralem pH zwischen 5 und 7 verwendet, z.B. wenn ein hautneutraler pH wünschenswert ist, wie beispielsweise in einem Geschirrspülmittel.
- Die Zusammensetzungen eignen sich in der Verwendung für Reinigungs- und Waschzubereitungen wie beispielsweise Handgeschirrspülmittel, Maschinengeschirrspülmittel, Geschirrspülmaschinenreiniger, Waschmaschinenreiniger, Toilettenreiniger- bzw. WC-Reiniger, Universal- bzw. Allzweckreiniger, Küchenreiniger, Bad- bzw. Sanitärreiniger, Fussbodenreiniger, Backofen- und Grillreiniger, Glas- und Fensterreiniger, Metallputzmittel, Polster- und Teppichreiniger, Vollwaschmittel, Colorwaschmittel, Feinwaschmittel, Textilhilfsmittel, Vorbehandlungsmittel, Spezialwaschmittel und - reinigungsmittel, sowie weiteren Mitteln zur industriellen & gewerblichen, bzw. institutionellen Reinigung, Mittel für die Textil- und Faserbehandlung, Mittel der Lederbehandlung, sowie weitere Zubereitungsformen.
- Im Sinne dieser Anmeldung kann die Zusammensetzung als Flüssigkeit, Lösung oder Dispersion, Emulsion, Lotion, Gel, Tunkflüssigkeit, Spray oder Schaum verwendet werden. So können sie z. B. eine Lösung, eine Emulsion (O/W), oder eine multiple Emulsion, beispielsweise vom Typ Wasser-in-ÖI-in-Wasser (W/O/W), ein Gel, eine Hydrodispersion, eine lamellare Phase, eine flüssige isotrope Lösungsphase oder eine micellare Phase, darstellen. Es kann an Pulver, Granulat oder Tabs adsorbiert werden.
- Die Mittel eignen sich hierbei sowohl zur verdünnten Anwendung, als auch zur direkten Applikation auf das zu reinigende Substrat. Es eignet sich zur direkten Applikation, als auch zur Anwendung über ein Hilfsmittel, wie z.B. ein Tuch.
- Eine bevorzugte Ausführungsvariante stellt die Verwendung der Zusammensetzung auf festen Substraten, wie Tüchern dar. Diese werden mit der Zusammensetzung bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung getränkt, besprüht, bestrichen oder über ein anderes Verfahren aufgebracht. Feste Substrate haben den Vorteil, dass in ihnen die Zubereitung bereits in der richtigen Dosierung vorgegeben ist. Dies kommt insbesondere dem Konsumentenwunsch der Convenience entgegen, sie sind einfach handhabbar, direkt zu verwenden ohne zusätzliche Arbeitsschritte und können auch unterwegs, z.B. auf Reisen gut angewendet werden, auch wenn kein Wasser zur Verfügung steht.
- Bevorzugt sind Verwendungen der Zusammensetzungen in flüssigen Ausführungsformen, besonders bevorzugt in wässrigen Darreichungsformen.
- Weitere Aspekte der vorliegenden Erfindung ergeben sich aus den nachfolgenden Beispielen sowie den beigefügten Patentansprüchen.
- In den Versuchen ist Verbindung (I) Sodium PEG-7-olive oil carboxylate, I, Referenz C12 : Sodium Laureth-5 carboxylate, Referenz Oleyl: Sodium Oleth-6 carboxylate, SLES = Sodium laureth sulfate;
- Da die Reinigungskraft der hier betrachteten Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel massgeblich durch die darin enthaltenden Tenside bestimmt wird, werden die Vergleichsversuche auf Basis der wasserbasierten Tensidsysteme ohne die weiteren Zusatzstoffe durchgeführt. Die Ergebnisse können problemlos auf die kompletten Zusammensetzungen übertragen werden.
- Exemplarisch werden die Untersuchungen für die Mittel mit Sodium laureth sulfate gezeigt.
- Das Schmutztragevermögen wird als 2%-ige Lösung gegenüber Sodium laureth sulfate und Referenzen gemessen, die
- Trendlinie für die Sedimentation in Wasser ist eingezeichnet (Diagramm 1).
- Ergebnis: Überraschenderweise zeigt Verbindung (I) das gleiche gute Schmutztragevermögen wie SLES.
- Die strukturanaloge Oleyl-Referenz (keine Mischung von Fettsäureketten) und die Referenz mit gesättigter C12-Kette (üblicherweise eingesetzte Tenside) zeigen ein deutlich schlechteres Tragevermögen. Verbindung (I) kann überraschenderweise SLES substituieren, im Gegensatz zu analogen Verbindungen von (I) auf Basis von mittelkettigen Fettsäuren oder gereinigten längerkettigen Fettsäuren.
- Bei Zugabe von CaCl2 zu der Dispersion bricht der Schaum von SLES zusammen; die Teilchen flocken aus, das Schmutztragevermögen geht verloren.Dahingegen bleiben in den Mitteln mit Verbindung (I) unerwarteterweise der Schaum erhalten und das Schmutztragevermögen bleibt intakt.
- Ergebnis: Ein erster Effekt auf die Sedimentationsgeschwindigkeit ist ab einem Verhältnis von Verb.(I) : SLES = 1:1 zu erkennen. Bei einer nur teilweisen Substition von SLES, wird das beste Schmutztragevermögen bei den Verhältnissen Verb.(I) : SLES ≥ 3,5 erzielt (Diagramm 2) .
- Das gute Schmutztragevermögen der Mischungen wird auch bei Zugabe von CaCl2 erhalten.
- Überraschenderweise zeigen die Mischungen hier ein synergistisches Verhalten (Diagramm 3) - das Schmutztragevermögen der Mischungen in den offenbarten Verhältnissen ist deutlich höher als für die Lösungen der Einzelverbindungen (I) oder SLES (Diagramm 3).
- Schaumbildung und Schaumstabilität verhalten sich in den Mitteln additiv. Damit ist ein gutes Schaumverhalten gewährleistet. In hartem Wasser bleibt der Schaum nur bei den offenbarten Mitteln stabil.
- Die Tests wurden mit 84%-igem eingetrockneten Eiweiss (Mischung aus tierischem und pflanzlichem Protein) und einer 3%-igen Tensidlösung in Wasser durchgeführt (Diagramm 4).
- Ergebnis: Die Mittel Verb (I), Verb (I): SLES ≥ 3,5 : 1, bzw. SLES ≥ 5 : 1 weisen die grösste Reinigungskraft auf die Proteinflecken auf. Analoge Ergebnisse wurden auf Baumwolle und Viskose erhalten.
- Exemplarisch wird eine repräsentative Konzentration von Tensiden in einem milden Reinigungsmittel genommen, analog für Alkylethersulfate, Alkylsulfate, Acylsarcosinate, Alkylglucoside, Amidoalkylbetaine, Alkanolamide und Amphoacetate gemäss Anspruch 2.
-
Verhältnis Verb.(I)/SLES Einstufung SLES Schwere Augenschäden (Kategorie 1) - irreversibel 1:2 Augenreizung (Kategorie 2) - reversibel 1:1 Augenreizung (Kategorie 2) - reversibel 2:1 Augenreizung (Kategorie 2) - reversibel 3,5:1 - 5:1 - Verb. (I) - - Ergebnis: Die Zusammensetzung des Tensidsystems kann die Augenreizung mindestens um eine Kennzeichnungsstufe verringern.
- Durch Substituion von mittelkettigen Tensiden durch Verbindung (I) konnten überraschenderweise deutliche Verbesserungen in folgenden Bereichen erreicht werden:
- Schmutztragevermögen
- Proteinlösekraft
- Schaumverhalten
- Verhalten gegenüber hartem Wasser
- Augenreizung
- bevorzugt in einem Verhältnis von (I) zu der Summe der Tenside (II) ≥ 2 : 1, bevorzugt ≥ 3,5 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 5 : 1.
- Verbindung (A) = Ethoxyliertes Fettsäureamid; Verbindung (B) = Polyhydroxy glucamid, Verbindung (C) = Amphoacetate, (D)= Ethoxylierter Fettsäuremethylester
- Es wird die Sedimentationsgeschwindigkeit von einer 3%-igen Tensidlösung bestimmt. Die Veränderungen bei Zugabe eines weiteren Tensids zu der reinen Lösung von Verbindung (I) und der Lösung von Verbindung (I) mit SLES (2:1) werden bestimmt (Tabelle 1).
Tabelle 1: Veränderung des Schmutztragevermögens bei Zugabe eines weiteren Tensids (III) A B C D Verb. (I) + n.d. + = Verb. (I) + SLES (2:1) + + + = + Verbesserung durch 3. Tensid
- Verschlechterung durch 3. Tensid
= 3. Tensid hat keinen Einfluss - Ergebnis: Überraschenderweise haben die Tenside A-C aus C-18-Pflanzenölen einen positiven Einfluss auf das Schmutztragevermögen. Das bereits sehr gute Schmutztragevermögen wird bei der erfindungsgemässen Verwendung durch die Zugabe eines weiteren Tensids A-D nicht beeinträchtigt, im Gegenteil die Tenside A-C aus C-18-Pflanzenölen verbessern das Schmutztragevermögen.
- Es wird die Proteinreinigungskraft auf Kacheln von einer 1,5%-igen Tensidlösung bestimmt. Die Reinigungskraft einer Probe, in der ein Teil des Tensidssystems mit einem Tensid (III) ersetzt wurde, wird verglichen mit der Reinigungskraft des Tensids bei gleicher Gesamttensidkonzentration. Die Veränderung der Reinigungskraft ist in Tabelle 2 dokumentiert.
Tabelle 2: Veränderung der Reinigungskraft bei Zugabe eines weiteren Tensids (III) A B C D Verb. (I) = n.d. = = Verb. (I) + SLES (2:1) + + = = + Verbesserung durch 3. Tensid
- Verschlechterung durch 3. Tensid
= 3. Tensid hat keinen Einfluss - Ergebnis: Überraschenderweise haben die Tenside A und B aus C-18-Pflanzenölen einen positiven Einfluss auf die Reinigungskraft. Das bereits sehr gute Proteinlösevermögen wird bei erfindungsgemässer Verwendung durch die Zugabe eines weiteren Tensids A-D nicht beeinträchtigt.
-
a) Saure Reiniger1 Referenz 2 Referenz 3 4 Verbindung (I) 1,0% 2,5% 2,5% 1,5% PEG-4 Rapssamenamid 0,5% Ethoxylierter Rapssäuremethylester 0,5% Natrium laureth sulfate 0,3% 0,2% Zitronensäure 1,9% 2,9% 2,9% 2,9% Milchsäure 0,9% Xanthan gum 0,4% 0,4% 0,4% 0,4% Ethanol Konservierungsmittel optional optional optional optional Farb-, Duftstoffe optional optional optional optional Wasser ad 100% ad 100% ad 100% ad 100%
B) Neutrale Reiniger5 6 7 8 Tensid (I) 10,0% 10,0% 10,0% 10,0% Natrium oliveoilamphoaetat 5,0% 5,0% Sunfloweroyl Methylglucamide 2,9% 2,9% Sodium laureth sulfate 0,50% 0,9% 0,9% Natriumcitrat 1,0% 1,0% 1,0% Tetranatrium Glutamate Diacetat 0,5% 0,5% Tetranatrium Iminosuccinat 0,5% Alkohol 2,0% Propylenglycol 2,0% optional Konservierungsmittel 0,001 % 0,001 % 0,001% 0,001% Milchsäure pH-Einst. pH-Einst. pH-Einst. pH-Einst. Wasser ad 100% ad 100% ad 100% ad 100%
c) Basische Reiniger9 Referenz 10 Referenz 11 12 Verbindung (I) 2,0% 2,0% 2,0% 2,0% PEG-8 Sonnenblumenöl 1,0% 1,0% Natriumsalze der Rapsfettsäuren (Seife) 0,2% Cocoamidopropylbetain 0,50% Sodium laureth sulfate 0,2% Amidet N 0,5% Olive amidopropylbetain 1,0% Natriumcarbonat 0,2% 0,2% 2,0% 1,0% Calciumcarbonat 30,0% 30,0% Konservierungsmittel 0,010% 0,010% 0,010% 0,010% Parfum 0,100% 0,1% 0,1% 0,1% Milchsäure pH-Einst. pH-Einst. pH-Einst. pH-Einst. Wasser ad 100% ad 100% ad 100% ad 100%
Claims (17)
- Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung als Wasch- und Reinigungsmitteln für harte oder flexible Oberflächen, sowie für Textilien, Teppiche oder Naturfasern in den Bereichen Industrie-, institutionelle, Textil- und Haushaltsreinigung enthaltend mindestens eine Verbindung der Formel (I)
(I) R'-O(CbH2bO)o-{CH2-CH[O(CbH2bO)pR"]-CH2O}r-(CbH2bO)q-R‴
mit b einer ganzen Zahl zwischen 2 und 4, o, p, q unabhängig voneinander ganze Zahlen von 0 bis 75, wobei o+p+q mindestens 2 ist, r ist 0 oder 1,R', R" und R‴ sind jeweils unabhängig voneinander H, CH2COOM, oder RCO, wobei einer oder zwei, bevorzugt einer der Reste R', R" und R‴ CH2COOM darstellen: Wenn R' = CH2COOM dann gilt o≠0, wenn R" = CH2COOM dann gilt p≠0, wenn R‴= CH2COOM dann gilt q≠0, mit M = H, Alkali-, Erdalkali-, Ammonium-, oder organisches Ammoniumkation, und wobei einer oder zwei der Reste R', R" und R‴ Fettsäureacylreste RCO darstellen; mit Reiner gesättigten, ein- oder mehrfach ungesättigten Kohlenwasserstoffkette mit 5-23 Kohlenstoffatomen; welche aus einem C-18-Pflanzenöl abgeleitet ist;wobei der Anteil von 18 und mehr Kohlenstoffatomen der Fettsäureacylreste RCO in der Verbindung (I) oder in dem Gemisch von Verbindungen (I) über 60 Gew.-%, bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt von über 77 Gew.-% liegt;und der Anteil der ungesättigten Fettsäureacylresten über 55 Gew.-%, vorzugsweise über 65 Gew.-% und besonders bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% liegt, jeweils bezogen auf den Gesamtanteil an Fettsäureacylresten RCO der ein oder mehreren Verbindungen (I) in der Zusammensetzung;und wobei die Verbindung (I) vorzugsweise aus einem Gemisch unterschiedlicher Kettenlängen und Sättigungsgrade des Fettsäurerestes RCO besteht;und wobei die Polyglykolkette der Verbindung (I) vorzugsweise pflanzlichen Ursprungs ist;und wobei die Zusammensetzung zusätzlich ein oder mehr Tenside (III) umfasst ausgewählt aus der Gruppe der Seifen, Fettsäureamide, Fettsäureimine und der ethoxylierten Fettsäurealkylester, wobei die Fettsäurereste jeweils von C-18-Pflanzenölen abgeleitet sind und bevorzugt als Mischung gemäss der Fettsäureverteilung im nativen Öl vorliegen oder wie sie bei der Umsetzung von natürlichen Pflanzenölen oder Fetten anfallen;und wobei die Zusammensetzung keine Biotensid-Glykolipide aus fermentativer Herstellung enthält. - Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung gemäss Anspruch 1, zusätzlich umfassend ein oder mehrere Tenside (II), ausgewählt aus den Gruppen der Alkylethersulfate, Alkylsulfate, Acylglutamate, Acylsarcosinate, Sulfosuccinatester, Alkylglucoside, Amidoalkylbetaine, Alkanolamide und Amphoacetate, wobei die Tenside gesättigte Alkyl- oder Acylgruppen mit Kettenlängen zwischen 8-18 Kohlenstoffatomen, oder Gemische aus gesättigten Alkyl- oder Acylgruppen mit 8 bis18 Kohlenstoffatomen und ungesättigten C-18-Alkenyl- oder Acylgruppen enthalten, wie sie aus Kokosöl, Palmkernöl oder Babassuöl erhalten werden;
und wobei das Gewichts-Verhältnis von (I) zu der Summe der Tenside (II) ≥ 2 : 1 ist, bevorzugt ≥ 3,5 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 5 : 1 ist und ganz besonders bevorzugt 1 : 0 . - Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorstehenden Ansprüche, umfassend ein oder mehrere Tenside ausgewählt aus der Gruppe der alkoxylierten Fettsäureamide der Formel (A)
(A) R- CO-NH-(CmH2mO)n -H
Wobei m die ganze Zahlen 2 oder 3 ist, bevorzugt 2, n Zahl im Bereich von 2-10, bevorzugt im Bereich 2-8, ganz besonders bevorzugt 2-4, mit R = gesättigte, ein- oder mehrfach ungesättigter Kohlenwasserstoffkette mit 5-23 Kohlenstoffatomen und RCO abgeleitet aus einem Fettsäuregemisch, wobei der Anteil von 18 und mehr Kohlenstoffatomen des Fettsäurerestes RCO über 60 Gew.-%, bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt von über 77 Gew.-% liegt; und wobei der Anteil an ungesättigten Fettsäureresten über 55 Gew.-%, vorzugsweise über 65 Gew.-% und besonders bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% liegt, jeweils bezogen auf den Gesamtanteil an Fettsäureresten RCO des eingesetzten Tensids (A); und wobei das Tensid (A) vorzugsweise aus einem Gemisch unterschiedlicher Kettenlängen und Sättigungsgrade des Fettsäurerests RCO besteht und abgeleitet ist von C-18-Pflanzenölen; und wobei die Polyglykolkette der Verbindung (A) vorzugsweise pflanzlichen Ursprungs ist. - Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorstehenden Ansprüche, umfassend ein oder mehrere Tenside ausgewählt aus der Gruppe der Polyhydroxy Fettsäureamide der Formel (B) folgend,Wobei R4 einen C1-C4-Alkylrest bedeutet, vorzugsweise Methyl und R eine gesättigte, ein- oder mehrfach ungesättigter Kohlenwasserstoffkette mit 5-23 Kohlenstoffatomen und RCO abgeleitet aus einem Fettsäuregemisch, wobei der Anteil von 18 und mehr Kohlenstoffatomen des Fettsäurerestes RCO über 60 Gew.-%, bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt von über 77 Gew.-% liegt; und wobei der Anteil an ungesättigten Fettsäureresten über 55 Gew.-%, vorzugsweise über 65 Gew.-% und besonders bevorzugt über 72 Gew.-% liegt, jeweils bezogen auf den Gesamtanteil an Fettsäureresten RCO des eingesetzten Tensids (B);und wobei das Tensid (B) vorzugsweise aus einem Gemisch unterschiedlicher Kettenlängen und Sättigungsgrade des Fettsäurerests RCO wie oben definiert besteht und wobei RCO vorzugsweise abgeleitet ist von C-18-Pflanzenölen.
- Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorstehenden Ansprüche, umfassend ein oder mehrere Tenside ausgewählt aus der Gruppe der Amphoacetate (C), wobei das Tensid (C) vorzugsweise aus einem Gemisch unterschiedlicher Kettenlängen und Sättigungsgrade des Fettsäurerests RCO wie oben definiert besteht und wobei RCO abgeleitet ist von C-18-Pflanzenölen.
- Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorstehenden Ansprüche, zusätzlich umfassend ein oder mehrere zusätzliche Tenside ausgewählt aus der Gruppe der alkoxylierten Fettsäureester (D), wobei (D) vorzugsweise aus einem Gemisch unterschiedlicher Kettenlängen und Sättigungsgrade des Fettsäurerests RCO wie oben definiert besteht und wobei RCO abgeleitet ist von C-18-Pflanzenölen;und wobei die Polyglykolkette der Verbindung (D) vorzugsweise pflanzlichen Ursprungs ist;und wobei die Zusammensetzung bevorzugt bis 30 Gew.-% eines oder mehrerer Verbindungen (D), bevorzugter bis 20 Gew.-% und besonders bevorzugt bis 10 Gew.-% und ganz besonders bevorzugt 1 Gew.-% bis 3 Gew.-% enthalten;und wobei bevorzugt das Gewichts-Verhältnis von (I) zu der Summe von C-18-Pflanzenöl-PEG-estern, insbesondere bevorzugt zu PEG-7-Olivenölester ≥ 2 : 1, bevorzugt ≥ 3,5 : 1 und besonders bevorzugt ≥ 5 : 1 ist;und wobei die Zusammensetzung bevorzugt bis 5 Gew.-% eines oder mehrerer C18-Pflanzenöl-PEG-ester (i), bevorzugter bis 3 Gew.-%, besonders bevorzugt bis 1 Gew.-% enthalten oder in einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform kein zusätzlicher C18-Pflanzenöl-PEG-ester (i) zu der Verbindung (I) zugegeben wird; Gew.-% bezogen auf die Gesamtmasse der Zusammensetzung.
- Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorstehenden Ansprüche, wobei die Summe der Tenside, abgeleitet von C-18-Fettsäuren (I) und (III) bezogen auf die Gesamtmasse der in der Zusammensetzung vorliegenden Tenside > 50 Gew.-%, bevorzugt > 65 Gew.-%, besonders bevorzugt > 75 Gew.-% beträgt; in einer ganz besonders bevorzugten Ausführungsvariante beträgt die Summe der Tenside abgeleitet von C-18-Fettsäuren, (I) + (III) + weiterer optionaler Tenside (IV), bezogen auf die Gesamtmasse der in der Zubereitung vorliegenden Tenside, 100 Gew.-%.
- Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche zur Verbesserung der Reinigungsleistung eines Waschmittel oder Reinigungsmittels, insbesondere zur Entfernung von Proteinschmutz, besonders bevorzugt zur Entfernung von Proteinschmutz und partikulärem Schmutz.
- Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche zur Verbesserung des Dispergierungsvermögens oder der Schmutztragekraft eines Waschmittels oder Reinigungsmittels.
- Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel neben dem primären Tensid (I) zusätzlich mindestens vier weitere Inhaltsstoffe umfasst, ausgewählt aus den Gruppen: Lösungsmittel, weitere Tenside, Enthärter und Komplexbildner, Viskositätsregulatoren, pH-Stellmittel und Säuren und Basen, Gerüststoffe, Lösungsvermittler, Abrasiva, Antioxidantien, Vitamine, UV-Filter, Trübungsmittel, Antikorrosionsmittel, Konservierungsmittel, Duftstoffe, Farbstoffe, anorganische Alkali- oder Erdalkalisalze, gegebenenfalls Enzyme.
- Verwendung der Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche zur Verbesserung der Stabilität der Zusammensetzung bei hohen Elektrolytgehalten oder zur Verbesserung der Waschleistung bei hartem Wasser und Reduktion von Vergrauung und Verkrustung auf Wäsche und in der Maschine.
- Verwendung der Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche als Wasch- oder Reinigungsmittel, insbesondere als Handgeschirrspülmittel, Maschinengeschirrspülmittel, Klarspüler, Geschirrspülmaschinenreiniger, Waschmaschinenreiniger, Toilettenreiniger-, WC-Reiniger, Universal-, Allzweckreiniger, Bodenreiniger, Scheuermilch, Küchenreiniger, Bad-, Sanitärreiniger, Fussbodenreiniger, Backofen- und Grillreiniger, Glas- und Fensterreiniger, Metallputzmittel, Polster- und Teppichreiniger, Vollwaschmittel, Colorwaschmittel, Feinwaschmittel, Textilhilfsmittel, Vorbehandlungsmittel zur Reinigung, Spezialwaschmittel und - reinigungsmittel oder zur industriellen & gewerblichen und institutionellen Reinigung, insbesondere Autoreinigungsmittel, Metallreinigungsmittel, Reinigungsmittel für den Lebensmittelbereich, Textil- und Faserbehandlung, Mittel für die Lederbehandlung.
- Verwendung der Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche in der flüssigen Ausführungsform, besonders bevorzugt in wässrigen Darreichungsformen.
- Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, wobei die Verbindung (I), besonders bevorzugt Poly(Oxy-1,2-Ethandiyl), .Alpha.-Carboxy-.Omega.-(Olivenölfettsäuren)Oxy-, Natriumsalz (mit 7 mol EO durchschnittlichem EO-Gehalt), als reinigendes Tensid für Proteinschmutz oder als reinigendes Tensid für ein verbessertes Schmutztragevermögen oder als Dispergierungsmittel oder als Stabilisator für partikuläre Inhaltsstoffe oder als Stabilisator bei hohem Elektrolytgehalt oder hartem Wasser, oder zur Minderung der Augenreizung durch Tensidsysteme, eingesetzt wird.
- Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche für einen stabilen Schaum.
- Verwendung einer Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, wobei die Zusammensetzung frei von Alkylamidobetainen, insbesondere Cocoamidopropylbetain, oder frei von Mono- und Diethanolamiden, insbesondere Cocamid DEA oder Cocamid MEA, ist.
- Wasch- und Reinigungsverfahren für harte oder flexible Oberflächen, sowie für Textilien, Teppiche oder Naturfasern in den Bereichen Industrie-, institutionelle, Textil- und Haushaltsreinigung umfassenda) die Bereitstellung einer Wasch- und Reinigungslösung unter Verwendung der Zusammensetzung gemäss einem der vorhergehenden Ansprücheb) in Kontakt bringen einer Oberfläche oder Textilien, Teppiche oder Naturfasern mit der Waschlösung gemäss a)
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH000273/2018A CH714724B1 (de) | 2018-03-06 | 2018-03-06 | Wasch- und Reinigungsmittelzusammensetzung. |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3536769A1 EP3536769A1 (de) | 2019-09-11 |
| EP3536769B1 true EP3536769B1 (de) | 2023-08-16 |
| EP3536769C0 EP3536769C0 (de) | 2023-08-16 |
Family
ID=65686660
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19020100.4A Active EP3536769B1 (de) | 2018-03-06 | 2019-03-01 | Wasch- und reinigungsmittelzusammensetzung enthaltend ein polyoxyalkylen carboxylat |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP3536769B1 (de) |
| CH (1) | CH714724B1 (de) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2025103680A1 (de) * | 2023-11-13 | 2025-05-22 | Henkel Ag & Co. Kgaa | Wasch- und reinigungsmittel mit ligninderivaten |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113004982A (zh) * | 2021-03-09 | 2021-06-22 | 深圳市洁力士化工产品有限公司 | 一种抗菌洗洁精膏及其制备方法 |
| EP4341480A4 (de) * | 2021-06-23 | 2025-06-18 | Burlington Industries LLC | Insektenresistente gewebe mit mizellaren systemen |
| CN114561253A (zh) * | 2022-03-09 | 2022-05-31 | 深圳市山口科技有限公司 | 一种工业清洗粉及其制备方法 |
| CN115368971A (zh) * | 2022-08-08 | 2022-11-22 | 南京华狮新材料有限公司 | 一种洗碗机用洗涤剂 |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10141781A1 (de) | 2001-08-25 | 2003-03-06 | Beiersdorf Ag | Olivenöl-PEG-7-Carboxylate in kosmetischen Reinigungsrezepturen |
| DE10147049A1 (de) | 2001-09-25 | 2003-04-10 | Beiersdorf Ag | Verwendung von Tensiden mit einem Quotienten aus Hämolysewert und Denaturierungsindex von größer oder gleich 1 zum Erzielen oder Erhöhen der Selektivität von Reinigungszubereitungen |
| DE102011090030B4 (de) | 2011-12-28 | 2025-11-06 | Evonik Operations Gmbh | Wässrige Haar- und Hautreinigungszusammensetzungen, enthaltend Biotenside |
| EP3070155A1 (de) * | 2015-03-18 | 2016-09-21 | Evonik Degussa GmbH | Zusammensetzung enthaltend peptidase und biotensid |
-
2018
- 2018-03-06 CH CH000273/2018A patent/CH714724B1/de unknown
-
2019
- 2019-03-01 EP EP19020100.4A patent/EP3536769B1/de active Active
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| DATABASE GNPD [online] MINTEL; 16 June 2015 (2015-06-16), ANONYMOUS: "Anti-Bacterial All-Purpose Cleansing Spray", XP055721098, retrieved from www.gnpd.com Database accession no. 3249119 * |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2025103680A1 (de) * | 2023-11-13 | 2025-05-22 | Henkel Ag & Co. Kgaa | Wasch- und reinigungsmittel mit ligninderivaten |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CH714724A2 (de) | 2019-09-13 |
| CH714724B1 (de) | 2023-05-15 |
| EP3536769A1 (de) | 2019-09-11 |
| EP3536769C0 (de) | 2023-08-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3290500B1 (de) | Wasch-, pflege- und reinigungsmittel mit polyoxyalkylen carboxylat | |
| EP3290501B1 (de) | Wasch- und reinigungsmittel mit alkoxylierten fettsäureamiden | |
| EP3536769B1 (de) | Wasch- und reinigungsmittelzusammensetzung enthaltend ein polyoxyalkylen carboxylat | |
| EP3201302B1 (de) | Biotensidhaltige formulierung | |
| EP1317522B1 (de) | Schnell trocknendes wasch- und reinigungsmittel, insbesondere handgeschirrspülmittel | |
| EP2592134B1 (de) | Nachhaltige Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel | |
| ES2825033T3 (es) | Composición limpiadora antimicrobiana | |
| DE102009001559A1 (de) | Kalklösendes Reinigungsmittel | |
| EP4361238A1 (de) | Zusammensetzungen mit glycaminen | |
| EP3744819A1 (de) | Mittel mit alkoxylierten fettsäuren | |
| WO2015120990A1 (de) | Saure reiniger für harte oberflächen | |
| CH705767A2 (de) | Milde und nachhaltige Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel. | |
| EP3536383B1 (de) | Reinigungs- und pflegezubereitungen enthaltend ein polyoxyalkylen carboxylat | |
| EP3107986A1 (de) | Wasch- oder reinigungsmittel mit verbessertem schaumverhalten unter hoher schmutzbelastung | |
| EP3116984A1 (de) | Verbesserte tensidmischung mit optimiertem ethoxylierungsgrad | |
| WO2014053365A1 (de) | Leistungsgesteigerte wasch- oder reinigungsmittel mit komplexbildnern i | |
| DE102012221021A1 (de) | Wasch- und Reinigungsmittel mit Alkylpolypentosiden | |
| DE102018131883A1 (de) | Wasch- oder Reinigungsmittel enthaltend Iminodisuccinat und/oder Iminotrisuccinat | |
| EP1775338B1 (de) | Festseifen mit verringerter Rissbildung | |
| DE102021206001A1 (de) | Verfahren zur antimikrobiellen Behandlung mittels Radiowellenstrahlung | |
| DE102017206013A1 (de) | Wasch- oder Reinigungsmittel mit verbessertem Schaumverhalten | |
| DE102023212840A1 (de) | Handgeschirrspülmittelkonzentrat | |
| EP3502223A1 (de) | Aminoxidhaltige handgeschirrspülmittel | |
| DE102016201295A1 (de) | C8-10-Alkylamidoalkylbetain als Antiknitterwirkstoff |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN PUBLISHED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20200309 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20200406 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: PERFECT IDEAS GMBH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: PREVIOUS MAIN CLASS: C11D0001740000 Ipc: C11D0001720000 Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R079 Ref document number: 502019008921 Country of ref document: DE Free format text: PREVIOUS MAIN CLASS: C11D0001740000 Ipc: C11D0001720000 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: C11D 11/00 20060101ALI20230127BHEP Ipc: C11D 1/72 20060101AFI20230127BHEP |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20230316 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502019008921 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| U01 | Request for unitary effect filed |
Effective date: 20230816 |
|
| U07 | Unitary effect registered |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG DE DK EE FI FR IT LT LU LV MT NL PT SE SI Effective date: 20230822 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231216 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230816 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231116 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231216 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230816 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230816 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230816 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230816 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230816 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230816 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230816 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230816 |
|
| U20 | Renewal fee for the european patent with unitary effect paid |
Year of fee payment: 6 Effective date: 20240325 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502019008921 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20240429 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20240627 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20240517 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230816 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230816 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20240301 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20240301 |
|
| U20 | Renewal fee for the european patent with unitary effect paid |
Year of fee payment: 7 Effective date: 20250325 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20190301 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20190301 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20190301 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: H13 Free format text: ST27 STATUS EVENT CODE: U-0-0-H10-H13 (AS PROVIDED BY THE NATIONAL OFFICE) Effective date: 20251023 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20250301 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230816 |