EP3367415B1 - Air circuit breaker having separable electrical contacts for interrupting an electrical current - Google Patents
Air circuit breaker having separable electrical contacts for interrupting an electrical current Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3367415B1 EP3367415B1 EP18157542.4A EP18157542A EP3367415B1 EP 3367415 B1 EP3367415 B1 EP 3367415B1 EP 18157542 A EP18157542 A EP 18157542A EP 3367415 B1 EP3367415 B1 EP 3367415B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- breaking
- trigger
- protuberance
- equal
- breaking device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 claims description 46
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000003351 stiffener Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000004431 polycarbonate resin Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 229920005668 polycarbonate resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000012815 thermoplastic material Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000010891 electric arc Methods 0.000 description 18
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000003570 air Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000012080 ambient air Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003365 glass fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 229920000515 polycarbonate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004417 polycarbonate Substances 0.000 description 2
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920004142 LEXAN™ Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 241001639412 Verres Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004026 adhesive bonding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000712 assembly Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000429 assembly Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008033 biological extinction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001627 detrimental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920006351 engineering plastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000010304 firing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002427 irreversible effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005405 multipole Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000008188 pellet Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035484 reaction time Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000284 resting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010998 test method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001960 triggered effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H71/00—Details of the protective switches or relays covered by groups H01H73/00 - H01H83/00
- H01H71/10—Operating or release mechanisms
- H01H71/50—Manual reset mechanisms which may be also used for manual release
- H01H71/52—Manual reset mechanisms which may be also used for manual release actuated by lever
- H01H71/526—Manual reset mechanisms which may be also used for manual release actuated by lever the lever forming a toggle linkage with a second lever, the free end of which is directly and releasably engageable with a contact structure
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H71/00—Details of the protective switches or relays covered by groups H01H73/00 - H01H83/00
- H01H71/02—Housings; Casings; Bases; Mountings
- H01H71/025—Constructional details of housings or casings not concerning the mounting or assembly of the different internal parts
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H71/00—Details of the protective switches or relays covered by groups H01H73/00 - H01H83/00
- H01H71/10—Operating or release mechanisms
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H71/00—Details of the protective switches or relays covered by groups H01H73/00 - H01H83/00
- H01H71/02—Housings; Casings; Bases; Mountings
- H01H71/025—Constructional details of housings or casings not concerning the mounting or assembly of the different internal parts
- H01H71/0257—Strength considerations
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H71/00—Details of the protective switches or relays covered by groups H01H73/00 - H01H83/00
- H01H71/10—Operating or release mechanisms
- H01H71/12—Automatic release mechanisms with or without manual release
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H73/00—Protective overload circuit-breaking switches in which excess current opens the contacts by automatic release of mechanical energy stored by previous operation of a hand reset mechanism
- H01H73/02—Details
- H01H73/18—Means for extinguishing or suppressing arc
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H9/00—Details of switching devices, not covered by groups H01H1/00 - H01H7/00
- H01H9/54—Circuit arrangements not adapted to a particular application of the switching device and for which no provision exists elsewhere
- H01H9/541—Contacts shunted by semiconductor devices
- H01H9/542—Contacts shunted by static switch means
- H01H2009/546—Contacts shunted by static switch means the static switching means being triggered by the voltage over the mechanical switch contacts
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H9/00—Details of switching devices, not covered by groups H01H1/00 - H01H7/00
- H01H9/30—Means for extinguishing or preventing arc between current-carrying parts
- H01H9/34—Stationary parts for restricting or subdividing the arc, e.g. barrier plate
- H01H9/346—Details concerning the arc formation chamber
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an apparatus for breaking an electric current with separable electrical contacts and cut in air.
- the invention relates to the field of electrical switchgear, such as low-voltage circuit breakers and high power.
- Such devices comprise an electric current cut-off device comprising separable electrical contacts.
- the member is switchable between open or closed positions to interrupt or, respectively, allow the circulation of an electric current within the device. This switching is controlled by means of a control mechanism, for example a rocking mechanism known as the "tumbler" in the English language.
- These devices also include a trigger coupled to the control mechanism and which controls the control mechanism, so as to open the cut-off device when it detects an electrical fault.
- the electrical fault is usually a short circuit or an overcurrent of the current flowing through the unit.
- the trigger is magnetic, or thermal, or electronic.
- the electrical contacts are partially separated from each other by an electromagnetic repulsion force, and are then in an unstable position. An electric arc appears between these electrical contacts.
- the trigger must therefore control the opening of the cutoff device, as soon as this electric arc appears, to completely separate the electrical contacts, in order to safely interrupt the flow of electrical current in the device and ensure galvanic isolation. This interruption must occur as soon as possible after the occurrence of the electrical fault, for example in less than 5ms, to avoid damage to the device and avoid a situation that is unsafe. Indeed, it is essential to limit the amount of energy released during the cut.
- the known devices do not give satisfaction because, in certain circumstances, the trigger has a reaction time to an electrical fault that is not short enough to react the control mechanism in the necessary time. There is therefore a risk that the cutter closes accidentally, thus preventing the interruption of the current.
- Cutting devices are known to overcome this drawback and in which an overpressure within the apparatus, resulting from the release of cut gas caused by the electric arc, is used to trigger the control mechanism before the trigger can not go into action.
- An example of such an apparatus is described in WO-2010/112420 .
- the apparatus includes a piston that is in fluid communication with an arc-breaking chamber and is mechanically coupled to the control mechanism. In this way, an abnormal increase in pressure inside the apparatus causes a displacement of the piston, which then triggers the opening of the cut-off device, faster than the trigger associated with this device .
- the invention more particularly intends to remedy, by proposing an apparatus for breaking an electric current with separable electrical contacts and cut in the air, this apparatus allowing a rapid opening of the electrical contacts in case electrical fault, while being simple to manufacture and having a satisfactory reliability.
- the increase in pressure resulting from the appearance of the electric arc causes the deformation of the side walls.
- the protrusion is rigid and integral with one of the side walls, it moves under the effect of the deformation of this side wall.
- This displacement because of the relationship of the protrusion with the trigger member, causes the displacement of the trigger member to a trigger position to move the separable electrical contacts to the open position.
- the triggering is done quickly, since the trigger chain of the control mechanism is shorter than in known devices, because of the absence of an intermediate element such as a piston.
- the apparatus also has a simplified design, because, to the extent that the protrusion is provided on the side wall, it is easy to integrate during the manufacture of the side wall.
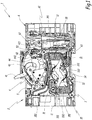
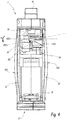
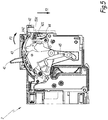
- the Figures 1 to 5 represent an apparatus for breaking an electric current, for example a circuit breaker.
- the apparatus 1 is a unipolar circuit breaker with alternating current or continuous low voltage and high intensity.
- the apparatus 1 is adapted to operate with electrical voltages of less than 1500 V DC or 1000 V AC and with electric currents of short circuit of intensity greater than or equal to 1 kA.
- the apparatus 1 may be different, for example, be a multipole circuit breaker.
- the apparatus 1 is intended to be connected to an electrical circuit for protection against electrical faults.
- electrical fault is meant here a short circuit or an overcurrent of the electric current flowing in the device.
- the apparatus 1 comprises a cut-off block 2 including a cut-off member 3, also called cut-off assembly, a control mechanism 4 and a casing 5.
- the apparatus 1 also comprises a trigger block 6, described in greater detail in FIG. what follows.
- the cut-off member 3 and the control mechanism 4 are housed inside the casing 5, in internal compartments distinct from this casing 5.
- the member 3 is switchable, reversibly and selectively, between two stable and distinct states, said open state and closed state.
- the member 3 In the closed state, the member 3 allows the circulation of an electric current within the apparatus 1, for example between connection areas of this apparatus 1.
- the member 3 prevents the circulation of an electric current in the absence of an electric arc within the apparatus 1.
- opening of the member 3 means switching the member 3 from the closed state to the open state.
- the member 3 comprises separable electrical contacts made of an electrically conductive material, such as copper. More specifically, the apparatus 1 here comprises fixed electrical contacts 31 and movable electrical contacts 32, the latter being movable relative to the fixed electrical contacts 31.
- the fixed and movable electrical contacts 31 and 31 are here provided with electrically conductive contact pads respectively denoted 331 and 332.
- the fixed and movable electrical contacts 31 and 32 are in contact with each other. Their respective contact pads 331, 332 are in direct contact, so as to allow the passage of current between these electrical contacts 31 and 32.
- the electrical contacts 32 are remote from the fixed electrical contacts 31, so that their respective contact pads 331, 332 are electrically insulated by the ambient air.
- the movable contacts 32 are formed by a single piece of electrically conductive material, which is carried by a rotary member 34 rotatably mounted relative to the housing 5.
- the fixed contacts 31 are here two in number and are arranged symmetrically with respect to the axis of rotation of the member 34.
- the member 3 also comprises arc breaking chambers 35, the role of which is to ensure the extinction of this electric arc.
- the breaking chamber 35 comprises a stack of cutting plates 351, as well as a channel 352 for evacuating the cutoff gases, which fluidly connects the breaking chamber to the outside of the casing 5.
- the chambers 35 are here two in number and are each placed at a contact zone between a fixed contact 31 and a movable contact 32.
- the control mechanism 4 makes it possible to control the switching of the member 3 between the open and closed states.
- the mechanism 4 is here mechanically coupled with the rotary member 34, so that a specific action on the mechanism 4 drives the electrical contacts 31 and 32 in displacement to switch the member 3 between the open states. and closed.
- the control mechanism 4 comprises a lever 41, also called a crankpin, which is accessible from outside the housing 5 and which is intended to be handled by an operator to switch, through the mechanism 4, the cutoff member between the open and closed positions. To the figure 1 the lever 41 is in a position corresponding to the closed state of the cut-off member 3.
- the control mechanism 4 also comprises a trigger member 42.
- the member 42 is movable between a rest position and a trigger position. When the member 42 moves from the rest position to the trigger position, it triggers the mechanism 4, which then switches the member 3 to the open state. Once the member 3 is in the open state, it remains in this open state.
- the mechanism 4 must be rearmed, for example by means of a manual action of an operator on the lever 41, to allow again the passage of the member 3 in its closed state.
- the member 42 is then returned to its rest position by the mechanism 4, for example by means of a spring 422.
- Mechanism 4 is here a rocking mechanism, also called "tumbler" in English. Such a mechanism is well known and, for example, is described in the patent application EP 0555158 A1 .
- the mechanism 4 comprises the trigger member 42, a hook 43, a lock 44 and a connecting rod 45, the latter providing the mechanical coupling between the mechanism 4 and the rotary member 34.
- the hook 43 is subject to an elastic restoring force, which tends to bring it back to a position corresponding to the open state of the member 3. This return movement is inhibited by the hooking of one end of the hook 43 on the latch 44, both that the latter is itself kept hooked to the trigger member 42 as long as it is in its rest position.
- the triggering member 42 is here mounted in rotation, between its resting and tripping positions, about an axis of rotation X42 perpendicular to the side walls of the casing 5.
- the trigger member 42 is here provided with a projecting lug 421, extending perpendicularly to the axis of rotation X42, the function of which is described in more detail in the following.
- the trigger block 6 is configured to trigger the switching of the member 3 to the open state, through the mechanism 4, when an electrical fault is detected from the current flowing through the device 1.
- the trigger block 6 comprises for this purpose a trigger 61, here of magneto-thermal type, which is adapted to monitor the electric current flowing in the trigger block and to move a striker 62 mobile block 6 when it detects the appearance of an electrical fault.
- a trigger is well known to those skilled in the art and is not described here in more detail.
- the block 6 is also provided with a connector 63 intended to be connected to the breaking block 2.
- the triggering unit 6 is attached to the breaking block 2 and the connector 63 is electrically connected to a corresponding fixed electrical contact 31 of the member 3.
- the triggering block 6 can react according to the current flowing through the electrical device 1.
- connection areas of the device 1 There are “11” and “12” of the connection areas of the device 1. These areas 11 and 12 make it possible to connect the device 1 to the electrical circuit that it must protect.
- the range 11 here corresponds to one end of one of the fixed electrical contacts 31, while the range 12 corresponds to an outer end of the connector 63.
- the trigger 61 When an electrical fault is detected by the trigger 61, the latter moves the striker 62, which then exerts a mechanical force on the trigger member 42, so as to move it to its trigger position. In response, the control mechanism is triggered and causes switching and then maintaining the breaking device 3 in the open state, so as to interrupt the flow of electric current between the areas 11 and 12.
- the casing 5 forms an outer casing of the cutoff block 2.
- the trigger block 6 is detachable from the cutoff block 2.
- the casing 5 forms an envelope of the only cutoff block 2.
- the casing 5 surrounds at least the member 3 and the mechanism 4.
- the triggering block 6 has its own case.
- the housing 5 comprises in particular side walls 51, 52 which delimit opposite side faces of the cutoff block 2.
- the lever 41 is located on a front face of the device 1.
- the lateral faces extend perpendicularly to this front face and perpendicular to the lower and upper faces of the cutoff block 2.
- the triggering unit 6 is here attached to the cutoff block 2 on a lower face of this cutoff block 2.
- the side walls 51 and 52 are deformable, reversibly, between a normal state and a deformed state.
- the side walls 51 and 52 have a substantially planar shape and extend parallel to each other.
- each wall 51, 52 has a curved shape towards the outside of the apparatus 1, as illustrated in FIG. figure 4 .
- the amplitude of the deformation of each wall 51, 52 is, for example, measured as the distance between the positions of the center of this wall between the normal and deformed states.
- the walls 51 and 52 are simultaneously either in their normal state or in their deformed state, since they surround the same member 3. However, when they are in a deformed state, they may not have a deformation strictly identical, that is to say of the same shape or the same amplitude, due in particular to the arrangement of the constituents of the apparatus 1 inside the housing 5.
- the dashed lines bearing the references 51d and 52d illustrate the position of the side walls, respectively 51 and 52, when they are in the deformed state.
- the walls 51 and 52 elastically deform from their normal state to their deformed state as the pressure inside the housing 5 increases.
- a deformation greater than or equal to 1 mm is observed when the pressure exceeds a value of 6 bars, this deformation being here measured along an axis parallel to the axis X42.
- Such an increase in pressure is caused by the appearance of the electric arc during the separation between the fixed contacts 31 and the movable contacts 32 of the member 3.
- the increase in pressure is such that the cutoff gas generated by the electric arc can not be instantly discharged into the outlet channel 352. They then spread inside the housing 5 and generate an overpressure, compared to the pressure that normally prevails in this housing 5. For example the pressure increases until it is greater than or equal to 6 bars, or even greater than or equal to 20 bars.
- the electric arc must be interrupted as soon as possible to limit this overpressure. For example, it is desirable to open the member 3 before the pressure in the housing becomes greater than or equal to 5 bars.
- the housing 5 is made from a thermoplastic material, for example by molding.
- the walls 51 and 52 are made of the same material as the housing 5.
- the walls 51 and 52 have a modulus of elasticity of between 1 GPa and 5 GPa.
- the walls 51 and 52 are resistant to impacts and in particular have an impact resistance greater than or equal to 10 kJ / m 2 .
- This impact resistance is here measured with the so-called Charpy test method as defined by the ISO 179 / 1eA standard, performed at room temperature and with a probe of dimensions 80x10x3 mm.
- the housing 5, and therefore the walls 51 and 52 are made of glass fiber reinforced polycarbonate.
- polycarbonate resin marketed under the reference LEXAN® EXL5689 by the company SABIC is used.
- polycarbonate resin sold under the reference XANTAR® XRM5010 may be used instead by MITSUBISHI ENGINEERING PLASTICS CORPORATION.
- the walls 51, 52 each have a thickness greater than or equal to 1 mm and less than or equal to 3 mm, this thickness being measured when the walls 51, 52 are in the idle state.
- the walls 51, 52 return to their state of rest when the pressure in the housing 5 becomes equal to the surrounding atmospheric pressure, without the housing 5 suffering from mechanical sequelae detrimental to its operation.
- the housing 5 is here formed by two molded half-shells, similar and complementary in shape to each other, each carrying a wall 51, 52. These two half-shells are intended to be secured to one another to ensure the integrity of the housing 5.
- the housing 5 comprises means for fixing the walls 51, 52.
- the fastening means are rivets, whose respective heads are referenced 55.
- the walls 51, 52 then comprise through holes to allow the passage of these rivets.
- the fixing means are arranged only near the edges of the walls 51, 52, so as not to hinder their deformation.
- the housing 5 also includes a window 54 which at least partially exposes the trigger member 42 outside the housing 5. In this way, the striker 62 can act mechanically on the member 42, even though the striker 62 is located outside the housing 5.
- the trigger 61 and the striker 62 can be housed inside the housing 5.
- the window 54 can be omitted.
- one of the side walls in this case here the side wall 52, further comprises, on its inner face 521, a rigid protrusion 53 which extends inwardly of the housing 5, perpendicular to this inner face 521
- the protrusion 53 is integral with the wall 52, preferably without degree of freedom in flexion.
- the inner face 521 is here the face of the lateral wall 52 which is turned towards the interior of the housing 5. This inner face 521 is opposite to the outer face of the lateral wall 52.
- the protrusion 53 Due to its attachment to the deformable side wall 52, the protrusion 53 is movable between a first position and a second position. The protrusion 53 is in the first position when the side wall 52 is in the normal state, and in the second position when the side wall 52 is in the deformed state.
- the protrusion 53 moves to its second position as the corresponding side wall 52 deforms from its normal state to its deformed state.
- the protrusion 53 is formed in one piece with the corresponding lateral wall 52.
- the protrusion 53 is integral with the wall 52. This makes it possible to further simplify the manufacture of the device 1, since the protrusion 53 is then manufactured simultaneously with the side wall 52, for example during a single molding operation.
- the protrusion 53 may be an insert separate from the wall 52 and which is fixed integrally to the wall 52.
- this fixing is performed by means of a rivet or by gluing or welding.
- X53 is the longitudinal axis along which the protrusion 53 extends when it is in its first position and X53d the direction in which the protrusion extends when it is in the second position.
- the axis X53 is here perpendicular to the walls 51 and 52 when they are in their state of rest.
- the angle between the axes X53 and X53d is greater than or equal to 8 ° when the wall 52 is deformed by an amplitude greater than or equal to 1 mm.
- the protrusion 53 is arranged relative to the trigger member 42 so that its displacement from its first position to its second position causes a displacement of the trigger member 42 from its inactive position to its trigger position. In this way, the displacement of the protrusion 53 resulting from the deformation of the walls 51, 52 causes the trigger mechanism 4 to switch the cutoff member 3 to its open state.
- the protrusion 53 is here coupled with the triggering member 42.
- the pin 421 is here placed on the path followed by the protrusion 53 between its first and second positions.
- the protrusion 53 is here disposed above the lug 421.
- the protrusion 53 when the protrusion 53 is in its first position and the member 42 is in its rest position, then the lower face of the beam 531 is in contact with the lug 421 without exerting any effort on this When it passes into its second position, the protrusion 53 presses on the lug 421, since it is situated on its trajectory, and drives the latter in rotation about the axis X42.
- the dimensions of the protrusion 53 are also chosen as a function of the force that it is necessary to apply to the lug 421 in order to move the member 42 towards its tripping position.
- the protrusion 53 is adapted to exert a force on the lug 421 of intensity greater than or equal to 5 Newton when it moves towards its second position.
- the lug 421 advantageously serves as a lever and makes it possible to reduce the force required to rotate the member 42.
- the length of the protrusion 53, the length of the lug 421 and the relative position of the lug 421 with respect to the protrusion 53, are adapted to benefit from a leverage effect, which reduces the the force required to move the trigger member 42 to its trigger position.
- the zone of contact between the protrusion 53 and the lug 421 is located at a distance from the inner face 521 which is greater than or equal to one-third of the width of the member 3, more preferably equal to half of this width.
- the contact zone is here the surface portion of the pin 421 on which the protrusion 53 presses when it moves towards its second position while the member 42 is in its rest position.
- This width is, for example, measured along the axis X53.
- this width is equal to the spacing between the side walls 51 and 52.
- the length of the protrusion 53 is preferably greater than or equal to 10 mm.
- the length of the protrusion 53 is here measured along the axis X53 when it is in its first position.
- the pin 421 is dimensioned so that the distance between said contact zone and the axis X42 is equal, for example to within 5%, to the distance between the axis X42 and the zone hooking the member 42 to the lock 44.
- the projection 53 comprises a beam 531 and a stiffener 532.
- the beam 531 and the stiffener 532 are here made of the same material.
- the beam 531 extends longitudinally along the axis X53 and has a cylindrical shape with a cross section of area greater than or equal to 5 mm 2 .
- the stiffener 532 here comprises a triangular-shaped flat wall which extends under this beam 531 and which is anchored to the inner face 521 along one of its sides and anchored to the beam 531 along another of its sides.
- the choice of the dimensions of the protrusion 53, in particular its shape and / or section, as well as the use of the stiffener 532, make it possible to increase the stiffness of the protrusion 53. This is particularly useful when the protrusion 53 is made in one piece with the side wall 52. Indeed, the protrusion is then made of the same material as the side wall 52. Now, this material is deformable, while it is precisely desired to prevent the protrusion 53 it itself does not deform when it exerts a support on the organ 42.
- the protrusion 53 thus makes it possible to trigger the control mechanism 4 during the occurrence of an electric arc between electrical contacts 31, 32, which generates a clearance of cut-off gas and therefore an overpressure in the housing 5.
- the protrusion 53 then exerts a force on the lug 421, which causes the displacement of the trigger member 42 towards its trigger position, as illustrated by the arrow F3 at the figure 5 . Because of the design of the mechanism 4, this movement of the member 42 in turn causes the switching of the member 3 to its open state, as explained above.
- the electrical contacts 31 and 32 are then kept separate, thus ensuring the stop of the flow of electric current.
- the increase in pressure which results from the appearance of the electric arc causes the deformation of the side walls 51, 52 and therefore the triggering of the mechanism 4, via the protrusion 53.
- the trigger mechanism 4 is achieved quickly, since the trigger chain is shorter than in known devices, because of the absence of an intermediate element such as a piston.
- the overpressure triggers the trigger mechanism 4 after a period of less than or equal to 1 ms.
- the trigger 61 comes into action, moving the firing pin 62, after a period of 3 ms.
- the manufacture of the device 1 is simpler and more economical. This also gives the device 1 a better robustness, insofar as the operation of the protrusion 53, because of its simplicity, is not sensitive to a possible risk of pollution by the cutoff gases.
- protrusion 53 is configured to act on the trigger member 42 triggers the mechanism 4 using the same control chain as the trigger 61. It is therefore not necessary to change the architecture mechanisms existing controls, and to increase the external volume and size of the cut-off block 2.
- the invention thus makes it possible to use the deformation of the side walls 51 and 52 caused by the overpressure due to the cutting gas, which is traditionally perceived as a harmful and undesirable effect, in order to control the triggering of the mechanism 4 quickly and reliably and with a simplified implementation.
- the figure 6 represents an electrical switching device 1 'according to the second embodiment of the invention.
- the elements of the apparatus 1 'of this embodiment which are analogous to the switchgear 1 bear the same references increased by the symbol "'" and are not described in more detail, since the description below above can be transposed to them.
- the apparatus 1 is a bipolar electric circuit breaker, adapted to operate with electric currents flowing along two distinct electric poles P1 and P2.
- the apparatus 1 here comprises a breaking block 2' and a trigger block 6 ', which play the same role, respectively, as the blocks 2 and 6 of the apparatus 1.
- Block 2 'differs in particular from block 2 in that it comprises two cut-off devices, or cut-off assemblies, each associated with one of the electric poles P1 and P2.
- the apparatus 1 'then comprises a plurality of connection pads associated with each of the poles P1 and P2.
- the block 2 ' also comprises a control mechanism similar to the mechanism 4, in particular provided with a lever 41' and a trigger member 42 'including a lug 421'.
- the control mechanism of the block 2 ' is arranged to simultaneously control the two cut-off members of the block 2' in the same state, in particular to open simultaneously the two cut-off members of the poles P1 and P2.
- the apparatus 1 ' comprises a housing similar to the housing 5 and inside which the block 2' is housed.
- This housing has deformable side walls 51 'and 52' similar to the walls 51, 52.
- the wall 52 ' carries a protrusion 53' which plays the same role as the protrusion 53.
- the protrusion 53 ' is adapted to move towards its second position when the wall 52' is deformed, under the effect of an increase in the pressure in the housing, resulting from the occurrence of an electric arc in at least one of the cut-off members of the block 2 '.
- the protrusion 53 ' exerts a force on the lug 421', which moves the member 42 'towards its release position in order to open the cut-off members of the block 2'.
- the invention is easily applicable to devices other than the apparatus 1, without the need to modify their architecture in depth.
- the distance previously defined between the contact zone and the wall 52' is here equal to the distance between the wall 52 'and the geometric plane separating one on the other, the two cut-off members of the block 2 '.
- the apparatus 1 ' also comprises a cover 500 intended to cover a front face of the apparatus 1'.
- This cover 500 is provided with lateral flanges 502 folded which are intended to cover the front edge of the side faces 51 ', 52' when the cover 500 is in configuration mounted on the apparatus 1 '.
- the dimensions of the flanges 502 are limited so as not to hinder the deformation of the walls 51 'and 52'.
Landscapes
- Switch Cases, Indication, And Locking (AREA)
- Breakers (AREA)
- Scissors And Nippers (AREA)
- Processing Of Stones Or Stones Resemblance Materials (AREA)
- Switches Operated By Changes In Physical Conditions (AREA)
- Arc-Extinguishing Devices That Are Switches (AREA)
Description
La présente invention concerne un appareil de coupure d'un courant électrique à contacts électriques séparables et à coupure dans l'air.The present invention relates to an apparatus for breaking an electric current with separable electrical contacts and cut in air.
De façon générale, l'invention concerne le domaine des appareils électriques de coupure, tels que les disjoncteurs à basse tension et à puissance élevée.In general, the invention relates to the field of electrical switchgear, such as low-voltage circuit breakers and high power.
De tels appareils comportent un organe de coupure du courant électrique comprenant des contacts électriques séparables. L'organe est commutable entre des positions ouverte ou fermé pour interrompre ou, respectivement, autoriser la circulation d'un courant électrique au sein de l'appareil. Cette commutation est commandée au moyen d'un mécanisme de commande, par exemple un mécanisme à bascule connu sous le nom de « tumbler » en langue anglaise.Such devices comprise an electric current cut-off device comprising separable electrical contacts. The member is switchable between open or closed positions to interrupt or, respectively, allow the circulation of an electric current within the device. This switching is controlled by means of a control mechanism, for example a rocking mechanism known as the "tumbler" in the English language.
Ces appareils comportent également un déclencheur couplé au mécanisme de commande et qui pilote ce mécanisme de commande, de manière à ouvrir l'organe de coupure lorsqu'il détecte un défaut électrique. Le défaut électrique est généralement un court-circuit ou une surintensité du courant qui circule dans l'appareil. Par exemple, le déclencheur est de type magnétique, ou thermique, ou électronique.These devices also include a trigger coupled to the control mechanism and which controls the control mechanism, so as to open the cut-off device when it detects an electrical fault. The electrical fault is usually a short circuit or an overcurrent of the current flowing through the unit. For example, the trigger is magnetic, or thermal, or electronic.
Typiquement, en cas de défaut électrique, les contacts électriques sont partiellement séparés l'un de l'autre par une force électromagnétique de répulsion, et se trouvent alors dans une position instable. Il apparaît alors un arc électrique entre ces contacts électriques. Le déclencheur doit donc commander l'ouverture de l'organe de coupure, dès l'apparition de cet arc électrique, pour séparer complètement les contacts électriques, afin d'interrompre de façon sûre la circulation du courant électrique dans l'appareil et assurer une isolation galvanique. Cette interruption doit intervenir le plus rapidement possible après l'apparition du défaut électrique, par exemple en moins de 5ms, afin d'éviter un endommagement de l'appareil et éviter une situation contraire à la sécurité. En effet, il est primordial de limiter la quantité d'énergie dégagée lors de la coupure.Typically, in case of electrical fault, the electrical contacts are partially separated from each other by an electromagnetic repulsion force, and are then in an unstable position. An electric arc appears between these electrical contacts. The trigger must therefore control the opening of the cutoff device, as soon as this electric arc appears, to completely separate the electrical contacts, in order to safely interrupt the flow of electrical current in the device and ensure galvanic isolation. This interruption must occur as soon as possible after the occurrence of the electrical fault, for example in less than 5ms, to avoid damage to the device and avoid a situation that is unsafe. Indeed, it is essential to limit the amount of energy released during the cut.
Les dispositifs connus ne donnent cependant pas satisfaction car, dans certaines circonstances, le déclencheur présente un temps de réaction à un défaut électrique qui n'est pas suffisamment court pour faire réagir la mécanique de commande dans le délai nécessaire. Il existe donc un risque que l'organe de coupure se referme accidentellement, empêchant ainsi l'interruption du courant.The known devices, however, do not give satisfaction because, in certain circumstances, the trigger has a reaction time to an electrical fault that is not short enough to react the control mechanism in the necessary time. There is therefore a risk that the cutter closes accidentally, thus preventing the interruption of the current.
On connaît certes des appareils de coupure visant à remédier à cet inconvénient et dans lesquels une surpression au sein de l'appareil, provenant du dégagement de gaz de coupure causé par l'arc électrique, est utilisée pour déclencher le mécanisme de commande avant que le déclencheur ne puisse entrer en action. Un exemple d'un tel appareil est décrit dans
Un exemple d'un tel appareil est décrit dans la demande de brevet
Une telle solution présente toutefois des inconvénients. D'une part, elle nécessite l'ajout d'un dispositif supplémentaire, ici d'une chaîne mécanique comprenant le piston, ce qui complique la fabrication industrielle de l'appareil et en renchérit le coût unitaire. En outre, la fiabilité n'est pas suffisante, car la communication fluidique entre la chambre de coupure et le piston est susceptible d'être détériorée du fait de la pollution due au gaz de coupure. Enfin, ces dispositifs ne sont, malgré tout, pas suffisamment rapides lorsqu'ils sont utilisés dans certaines conditions de fonctionnement requises par les gammes contemporaines de produits. En effet, les exigences actuelles conduisent à une diminution des dimensions des appareils de coupure et à une augmentation des valeurs maximales de courant électrique mis en jeu lors du fonctionnement de ces appareils. Le fonctionnement de ces dispositifs ne peut alors plus être garanti. Leur utilisation dans les appareils contemporains n'est donc pas possible en l'état.Such a solution, however, has disadvantages. On the one hand, it requires the addition of an additional device, here a mechanical chain comprising the piston, which complicates the industrial manufacture of the device and increases the unit cost. In addition, the reliability is not sufficient, because the fluid communication between the cutting chamber and the piston is likely to be deteriorated due to the pollution due to the cut gas. Finally, these devices are, despite everything, not fast enough when used in certain operating conditions required by the contemporary ranges of products. Indeed, the current requirements lead to a reduction in the size of the switchgear and to an increase in the maximum values of electric current involved during operation of these devices. The operation of these devices can no longer be guaranteed. Their use in contemporary devices is therefore not possible in the state.
C'est à ces inconvénients qu'entend plus particulièrement remédier l'invention, en proposant un appareil de coupure d'un courant électrique à contacts électriques séparables et à coupure dans l'air, cet appareil permettant une ouverture rapide des contacts électriques en cas de défaut électrique, tout en étant simple à fabriquer et présentant une fiabilité satisfaisante.It is to these drawbacks that the invention more particularly intends to remedy, by proposing an apparatus for breaking an electric current with separable electrical contacts and cut in the air, this apparatus allowing a rapid opening of the electrical contacts in case electrical fault, while being simple to manufacture and having a satisfactory reliability.
A cet effet, l'invention concerne un appareil de coupure d'un courant électrique à contacts électriques séparables et à coupure dans l'air, cet appareil comprenant :
- un ensemble de coupure commutable entre un état ouvert autorisant la circulation d'un courant électrique au sein de l'appareil et un état fermé empêchant la circulation du courant électrique ;
- un mécanisme de commande de la commutation de l'ensemble de coupure entre ses états ouvert et fermé, ce mécanisme de commande comprenant un organe de déclenchement agencé pour déclencher la commutation de l'ensemble de coupure vers l'état ouvert lorsque cet organe de déclenchement est déplacé d'une position de repos vers une position de déclenchement ;
- un boîtier à l'intérieur duquel sont logés l'ensemble de coupure et le mécanisme de commande et comprenant des parois latérales.
- les parois latérales sont déformables élastiquement, depuis un état de repos vers un état déformé, lorsque la pression qui règne à l'intérieur du boîtier augmente ;
- l'une des parois latérales comporte, sur sa face intérieure, une excroissance rigide s'étendant vers l'intérieur du boîtier perpendiculairement à cette face intérieure, de sorte que la déformation de ladite paroi latérale entraîne un déplacement de l'excroissance d'une première position vers une deuxième position ;
- l'excroissance est agencée par rapport à l'organe de déclenchement, de sorte que son déplacement vers la deuxième position entraîne le déplacement de l'organe de déclenchement de la position de repos vers la position de déclenchement.
- a switchable breaking assembly between an open state allowing the circulation of an electric current within the apparatus and a closed state preventing the flow of electric current;
- a control mechanism for switching the cutoff assembly between its open and closed states, said control mechanism comprising a switching member tripping arranged to trigger switching of the cutoff assembly to the open state when this trigger member is moved from a rest position to a trigger position;
- a housing inside which are housed the cutoff assembly and the control mechanism and comprising sidewalls.
- the side walls are elastically deformable, from a state of rest to a deformed state, when the pressure inside the housing increases;
- one of the side walls has, on its inner face, a rigid protuberance extending inwardly of the housing perpendicular to this inner face, so that the deformation of said side wall causes a displacement of the protuberance of a first position to a second position;
- the protrusion is arranged relative to the trigger member, so that its movement to the second position causes the displacement of the trigger member from the rest position to the trigger position.
Grâce à l'invention, dès l'apparition d'un arc électrique entre les contacts électriques, l'augmentation de pression qui résulte de l'apparition de l'arc électrique entraîne la déformation des parois latérales. Comme l'excroissance est rigide et solidaire avec l'une des parois latérales, elle se déplace sous l'effet de la déformation de cette paroi latérale. Ce déplacement, du fait de la relation de l'excroissance avec l'organe de déclenchement, entraîne le déplacement de l'organe de déclenchement vers une position de déclenchement pour déplacer les contacts électriques séparables vers la position ouverte. Ainsi, le déclenchement est réalisé rapidement, puisque la chaîne de déclenchement du mécanisme de commande est plus courte que dans les dispositifs connus, du fait de l'absence d'un élément intermédiaire tel qu'un piston. L'appareil présente également une conception simplifiée, car, dans la mesure où l'excroissance est ménagée sur la paroi latérale, elle est facile à intégrer lors de la fabrication de la paroi latérale. Du fait de cette simplicité de réalisation et de l'absence de dispositif supplémentaire, la fabrication de l'appareil est plus simple et plus économique. Cela confère également à l'appareil de coupure une plus grande robustesse, dans la mesure où le fonctionnement de l'excroissance, du fait de sa simplicité, n'est pas sensible à un éventuel risque de pollution par les gaz de coupure.Thanks to the invention, as soon as an electric arc appears between the electrical contacts, the increase in pressure resulting from the appearance of the electric arc causes the deformation of the side walls. As the protrusion is rigid and integral with one of the side walls, it moves under the effect of the deformation of this side wall. This displacement, because of the relationship of the protrusion with the trigger member, causes the displacement of the trigger member to a trigger position to move the separable electrical contacts to the open position. Thus, the triggering is done quickly, since the trigger chain of the control mechanism is shorter than in known devices, because of the absence of an intermediate element such as a piston. The apparatus also has a simplified design, because, to the extent that the protrusion is provided on the side wall, it is easy to integrate during the manufacture of the side wall. Due to this simplicity of implementation and the absence of additional device, the manufacture of the device is simpler and more economical. This also gives the switchgear a greater robustness, insofar as the operation of the protrusion, because of its simplicity, is not sensitive to a possible risk of pollution by the cutoff gases.
Selon des aspects avantageux mais non obligatoires de l'invention, un tel appareil de coupure peut incorporer une ou plusieurs des caractéristiques suivantes, prises isolément ou selon toute combinaison techniquement admissible :
- L'excroissance est formée d'un seul tenant avec ladite paroi latérale.
- Les parois latérales sont réalisées en une matière thermoplastique moulée.
- Les parois latérales sont réalisées en résine polycarbonate renforcée aux fibres de verre.
- Les parois latérales présentent un module d'élasticité en flexion qui est supérieur ou égal à 1 GPa, et inférieur ou égal à 5 GPa, de sorte à ce que l'amplitude de la déformation des parois latérales soit supérieure ou égale à 1mm lorsque la pression à l'intérieur du boîtier devient supérieure ou égale à 6 bars.
- L'excroissance comporte une poutre rigide s'étendant selon un axe longitudinal de l'excroissance et un raidisseur.
- L'excroissance présente une longueur supérieure ou égale à 5mm.
- Une zone de contact entre l'excroissance et l'ergot est située à une distance de la face intérieure qui est supérieure ou égale au tiers de la largeur de l'ensemble de coupure.
- L'organe de déclenchement est mobile en rotation autour d'un axe de rotation et est pourvu d'un ergot saillant s'étendant perpendiculairement à l'axe de rotation, l'ergot étant placé sur la trajectoire suivie par l'excroissance lorsqu'elle se déplace depuis sa première position vers sa deuxième position.
- L'appareil comporte un bloc déclencheur comportant un déclencheur et un percuteur mobile, le déclencheur étant configuré pour déplacer l'organe de déclenchement vers sa position de déclenchement lorsqu'il détecte un défaut électrique à partir du courant électrique qui circule au travers de l'appareil.
- The protrusion is formed integrally with said side wall.
- The side walls are made of a molded thermoplastic material.
- The side walls are made of polycarbonate resin reinforced with glass fibers.
- The side walls have a modulus of elasticity in flexion which is greater than or equal to 1 GPa, and less than or equal to 5 GPa, so that the amplitude of the deformation of the side walls is greater than or equal to 1 mm when the pressure inside the housing becomes greater than or equal to 6 bar.
- The protrusion comprises a rigid beam extending along a longitudinal axis of the protrusion and a stiffener.
- The outgrowth has a length greater than or equal to 5mm.
- A contact zone between the protuberance and the lug is located at a distance from the inner face which is greater than or equal to one third of the width of the clipping assembly.
- The trigger member is rotatable about an axis of rotation and is provided with a projecting lug extending perpendicular to the axis of rotation, the lug being placed on the path followed by the protrusion when she moves from her first position to her second position.
- The apparatus includes a trigger unit having a trigger and a movable striker, the trigger being configured to move the trigger member to its trigger position when it detects an electrical fault from the electrical current flowing through the trigger. apparatus.
L'invention sera mieux comprise et d'autres avantages de celle-ci apparaitront plus clairement à la lumière de la description qui va suivre, d'un mode de réalisation d'un appareil de coupure donné uniquement à titre d'exemple et faite en référence aux dessins annexés, dans lesquels :
- la
figure 1 représente schématiquement, selon une vue en coupe longitudinale, un appareil de coupure d'un courant électrique selon un mode de réalisation de l'invention ; - la
figure 2 est une représentation schématique, selon une vue en perspective et partiellement éclatée, de l'appareil de coupure de lafigure 1 ; - la
figure 3 est une représentation schématique, selon une vue rapprochée de la zone III de lafigure 2 , d'une portion de l'appareil de coupure de lafigure 2 ; - la
figure 4 est une représentation schématique, selon une vue du côté inférieur, de l'appareil de coupure desfigures 1 à 3 ; - la
figure 5 est une représentation schématique, selon une vue latérale, d'un mécanisme de commande de l'appareil de coupure desfigures 1 à 4 ; - la
figure 6 est une représentation schématique, selon une vue en perspective et partiellement éclatée, d'un appareil de coupure d'un courant électrique selon un autre mode de réalisation de l'invention.
- the
figure 1 shows schematically, according to a longitudinal sectional view, an apparatus for breaking an electric current according to one embodiment of the invention; - the
figure 2 is a schematic representation, in a perspective and partially exploded view, of the switchgear of thefigure 1 ; - the
figure 3 is a schematic representation, according to a close-up view of zone III of thefigure 2 , a portion of the cut-off device of thefigure 2 ; - the
figure 4 is a schematic representation, in a view of the lower side, of the cut-off apparatus ofFigures 1 to 3 ; - the
figure 5 is a schematic representation, in a side view, of a control mechanism of the cut-off apparatus ofFigures 1 to 4 ; - the
figure 6 is a schematic representation, in a perspective and partially exploded view, of an apparatus for breaking an electric current according to another embodiment of the invention.
Les
Dans cet exemple, l'appareil 1 est un disjoncteur unipolaire à courant alternatif ou continu à basse tension et à haute intensité. Par exemple, l'appareil 1 est adapté pour fonctionner avec des tensions électriques inférieures à 1500 V DC ou à 1000 V AC et avec des courants électriques de court-circuit d'intensité supérieure ou égale à 1 kA.In this example, the
En variante, l'appareil 1 peut être différent, par exemple être un disjoncteur multipolaire.Alternatively, the
L'appareil 1 est destiné à être connecté à un circuit électrique en vue d'en assurer sa protection contre des défauts électriques. Par « défaut électrique », on désigne ici un court-circuit ou une surintensité du courant électrique qui circule dans l'appareil.The
Comme illustré à la
Dans cet exemple, l'organe de coupure 3 et le mécanisme de commande 4 sont logés à l'intérieur du boîtier 5, dans des compartiments internes distincts de ce boîtier 5.In this example, the cut-
L'organe 3 est commutable, réversiblement et sélectivement, entre deux états stables et distincts, dits état ouvert et état fermé.The
Dans l'état fermé, l'organe 3 autorise la circulation d'un courant électrique au sein de l'appareil 1, par exemple entre des plages de raccordement de cet appareil 1.In the closed state, the
Dans l'état ouvert, l'organe 3 empêche la circulation d'un courant électrique en l'absence d'arc électrique au sein de l'appareil 1.In the open state, the
Par « ouverture » de l'organe 3, on désigne la commutation de l'organe 3 depuis l'état fermé vers l'état ouvert.By "opening" of the
A cet effet, l'organe 3 comporte des contacts électriques séparables réalisés en un matériau électriquement conducteur, tel que du cuivre. Plus précisément, l'appareil 1 comporte ici des contacts électriques fixes 31 et des contacts électriques mobiles 32, ces derniers étant déplaçables par rapport aux contacts électriques fixes 31.For this purpose, the
Les contacts électriques fixes 31 et mobiles 32 sont ici pourvus de pastilles de contact électriquement conductrices, respectivement notées 331 et 332.The fixed and movable
Dans l'état fermé, les contacts électriques fixes et mobiles 31 et 32 sont en contact l'un avec l'autre. Leurs pastilles de contact 331, 332 respectives sont en contact direct, de manière à autoriser le passage du courant entre ces contacts électriques 31 et 32.In the closed state, the fixed and movable
Dans l'état ouvert, les contacts électriques 32 sont à distance des contacts électriques fixes 31, de sorte que leurs pastilles de contact 331, 332 respectives soient isolées électriquement par l'air ambiant.In the open state, the
Dans cet exemple illustratif, les contacts mobiles 32 sont formés par une unique pièce en un matériau électriquement conducteur, qui est portée par un organe rotatif 34 monté en rotation par rapport au boîtier 5. Les contacts fixes 31 sont ici au nombre de deux et sont disposés symétriquement par rapport à l'axe de rotation de l'organe 34.In this illustrative example, the
Sur la
De façon connue, lorsque deux contacts électriques 31 et 32 sont partiellement séparés alors qu'un courant électrique circule au travers de l'appareil 1, par exemple sous l'effet d'une force de répulsion résultant d'un défaut électrique, il apparaît un arc électrique entre les pastilles 331 et 332 correspondantes. Cet arc électrique est le résultat d'une ionisation de l'air ambiant. Il en résulte une augmentation de la température puis de la pression, car l'arc électrique entraîne à son tour l'ionisation de constituants de l'organe 3, par exemple l'ionisation des pastilles de contact 331 et 332. L'arc électrique s'accompagne d'une brusque élévation de la température et de la pression à l'intérieur de l'organe 3.In known manner, when two
L'organe 3 comporte également des chambres de coupure 35 d'arc électrique, dont le rôle est d'assurer l'extinction de cet arc électrique.The
La chambre de coupure 35 comporte un empilement de plaques 351 de coupure, ainsi qu'un canal 352 d'évacuation des gaz de coupure, qui relie fluidiquement la chambre de coupure à l'extérieur du boîtier 5.The breaking
Les chambres 35 sont ici au nombre de deux et sont chacune placée au niveau d'une zone de contact entre un contact fixe 31 et un contact mobile 32.The
Ces chambres de coupure 35 sont bien connues et ne sont pas décrites plus en détail.These breaking chambers are well known and are not described in more detail.
En variante, d'autres configurations de l'organe 3 sont possibles, par exemple en utilisant un seul contact électrique fixe et un seul contact électrique mobile. Le nombre et la forme des chambres de coupure 35 sont alors adaptés en conséquence.Alternatively, other configurations of the
Le mécanisme de commande 4 permet de commander la commutation de l'organe 3 entre les états ouvert et fermé. A cet effet, le mécanisme 4 est ici couplé mécaniquement avec l'organe rotatif 34, de sorte à ce qu'une action spécifique sur le mécanisme 4 entraîne en déplacement les contacts électriques 31 et 32 pour commuter l'organe 3 entre les états ouvert et fermé.The control mechanism 4 makes it possible to control the switching of the
Le mécanisme de commande 4 comporte un levier 41, aussi nommé maneton, qui est accessible depuis l'extérieur du boîtier 5 et qui est destiné à être manipulé par un opérateur pour commuter, au travers du mécanisme 4, l'organe de coupure entre les positions ouverte et fermée. A la
Le mécanisme de commande 4 comporte également un organe de déclenchement 42. L'organe 42 est déplaçable entre une position de repos et une position de déclenchement. Lorsque l'organe 42 passe de la position de repos vers la position de déclenchement, il déclenche le mécanisme 4, qui commute alors l'organe 3 vers l'état ouvert. Une fois que l'organe 3 est passé dans l'état ouvert, il reste dans cet état ouvert. Le mécanisme 4 doit être réarmé, par exemple au moyen d'une action manuelle d'un opérateur sur le levier 41, pour autoriser à nouveau le passage de l'organe 3 dans son état fermé. L'organe 42 est alors ramené dans sa position de repos par le mécanisme 4, par exemple au moyen d'un ressort 422.The control mechanism 4 also comprises a
Le mécanisme 4 est ici un mécanisme à bascule, aussi nommé « tumbler » en langue anglaise. Un tel mécanisme est bien connu et, par exemple, est décrit dans la demande de brevet
Dans cet exemple, le mécanisme 4 comporte l'organe de déclenchement 42, un crochet 43, un verrou 44 et une bielle 45, celle-ci assurant le couplage mécanique entre le mécanisme 4 et l'organe rotatif 34. Le crochet 43 est soumis à une force de rappel élastique, qui tend à le ramener vers une position correspondant à l'état ouvert de l'organe 3. Ce mouvement de rappel est inhibé par l'accrochage d'une extrémité du crochet 43 sur le verrou 44, tant que ce dernier est lui-même maintenu accroché à l'organe de déclenchement 42 tant qu'il est dans sa position de repos.In this example, the mechanism 4 comprises the
Lorsque l'organe de déclenchement 42 se déplace vers sa position de déclenchement, il autorise un déplacement du crochet 43, qui autorise à son tour un déplacement de la bielle 45 vers l'état ouvert de l'organe 3.When the triggering
L'organe de déclenchement 42 est ici monté en rotation, entre ses positions de repos et de déclenchement, autour d'un axe de rotation X42 perpendiculaire à des parois latérales du boîtier 5.The triggering
En outre, l'organe de déclenchement 42 est ici pourvu d'un ergot saillant 421, s'étendant perpendiculairement à l'axe de rotation X42, dont la fonction est décrite plus en détail dans ce qui suit.In addition, the
Le bloc déclencheur 6 est configuré pour déclencher la commutation de l'organe 3 vers l'état ouvert, par l'intermédiaire du mécanisme 4, lorsqu'un défaut électrique est détecté à partir du courant qui circule au travers de l'appareil 1.The
Comme illustré à la
En pratique, dans une configuration de fonctionnement de l'appareil 1, le bloc déclencheur 6 est attaché au bloc de coupure 2 et le connecteur 63 est relié électriquement à un contact électrique fixe 31 correspondant de l'organe 3. Ainsi, le bloc déclencheur 6 peut réagir en fonction du courant qui circule au travers de l'appareil électrique 1.In practice, in an operating configuration of the
On note « 11 » et « 12 » des plages de raccordement de l'appareil 1. Ces plages 11 et 12 permettent de raccorder l'appareil 1 au circuit électrique qu'il doit protéger. La plage 11 correspond ici à une extrémité d'un des contacts électriques fixes 31, alors que la plage 12 correspond à une extrémité extérieure du connecteur 63.There are "11" and "12" of the connection areas of the
Pour faciliter la lecture de la
Lorsqu'un défaut électrique est détecté par le déclencheur 61, celui-ci entraîne en déplacement le percuteur 62, qui vient alors exercer un effort mécanique sur l'organe de déclenchement 42, de manière à le déplacer vers sa position de déclenchement. En réponse, le mécanisme de commande est déclenché et entraîne la commutation puis le maintien de l'organe de coupure 3 dans l'état ouvert, de manière à interrompre la circulation du courant électrique entre les plages 11 et 12.When an electrical fault is detected by the
Le boîtier 5 forme une enveloppe extérieure du bloc de coupure 2.The
Dans cet exemple, le bloc déclencheur 6 est détachable du bloc de coupure 2. Le boîtier 5 forme une enveloppe du seul bloc de coupure 2. Ainsi, le boîtier 5 entoure au moins l'organe 3 et le mécanisme 4. Le bloc déclencheur 6 comporte son propre boîtier.In this example, the
Le boîtier 5 comporte notamment des parois latérales 51, 52 qui délimitent des faces latérales opposées du bloc de coupure 2.The
Dans cet exemple, le levier 41 est situé sur une face avant de l'appareil 1. Les faces latérales s'étendent perpendiculairement à cette face avant et perpendiculairement à des faces inférieure et supérieure du bloc de coupure 2. Le bloc déclencheur 6 est ici attaché au bloc de coupure 2 sur une face inférieure de ce bloc de coupure 2.In this example, the
Les parois latérales 51 et 52 sont déformables, de façon réversible, entre un état normal et un état déformé.The
Dans l'état normal, les parois latérales 51 et 52 présentent une forme essentiellement plane et s'étendent parallèlement l'une avec l'autre.In the normal state, the
Dans l'état déformé, les parois latérales 51 et 52 présentent une forme bombée vers l'extérieur de l'appareil 1, comme illustré à la
En pratique, dans cet exemple, les parois 51 et 52 sont simultanément soit dans leur état normal, soit dans leur état déformé, puisqu'elles entourent le même organe 3. Toutefois, lorsqu'elles sont dans un état déformé, elles peuvent ne pas présenter une déformation rigoureusement identique, c'est-à-dire de même forme ou de même amplitude, en raison notamment de l'agencement des constituants de l'appareil 1 à l'intérieur du boîtier 5.In practice, in this example, the
Sur la
Les parois 51 et 52 se déforment, de façon élastique, depuis leur état normal vers leur état déformé, lorsque la pression à l'intérieur du boîtier 5 augmente.The
Par exemple, une déformation supérieure ou égale à 1mm est observée lorsque la pression dépasse une valeur de 6 bars, cette déformation étant ici mesurée selon un axe parallèle à l'axe X42.For example, a deformation greater than or equal to 1 mm is observed when the pressure exceeds a value of 6 bars, this deformation being here measured along an axis parallel to the axis X42.
Lorsque la pression diminue, les parois 51, 52 reviennent vers leur état normal.When the pressure decreases, the
Une telle augmentation de pression est causée par l'apparition de l'arc électrique lors de la séparation entre les contacts fixes 31 et les contacts mobiles 32 de l'organe 3. En effet, typiquement, l'augmentation de pression est telle que les gaz de coupure engendrés par l'arc électrique ne peuvent pas être instantanément évacués dans le canal de sortie 352. Ils se répandent alors à l'intérieur du boîtier 5 et engendrent une surpression, par rapport à la pression qui règne normalement dans ce boîtier 5. Par exemple, la pression augmente jusqu'à être supérieure ou égale à 6 bars, voire supérieure ou égale à 20 bars.Such an increase in pressure is caused by the appearance of the electric arc during the separation between the fixed
Pour éviter tout dommage irréversible de l'appareil 1, l'arc électrique doit être interrompu au plus vite pour limiter cette surpression. Par exemple, il est souhaitable d'ouvrir l'organe 3 avant que la pression dans le boîtier ne devienne supérieure ou égale à 5 bars.To avoid irreversible damage to the
De préférence, le boîtier 5 est réalisé à partir d'une matière thermoplastique, par exemple par moulage.Preferably, the
Les parois 51 et 52 sont réalisées dans le même matériau que le boîtier 5.The
A titre d'exemple illustratif, les parois 51 et 52 présentent un module d'élasticité compris entre 1 GPa et 5 GPa.By way of illustrative example, the
Avantageusement, les parois 51 et 52 sont résistantes aux chocs et présentent notamment une résistance aux impacts supérieure ou égale à 10 kJ/m2. Cette résistance à l'impact est ici mesurée avec la méthode dite du test de Charpy tel que défini par la norme ISO 179/1eA, réalisée à température ambiante et avec une sonde de dimensions 80x10x3 mm.Advantageously, the
De préférence, le boîtier 5, et donc les parois 51 et 52, sont réalisés en polycarbonate renforcé aux fibres de verre.Preferably, the
A titre d'exemple, on utilise la résine polycarbonate commercialisée sous la référence LEXAN® EXL5689 par la société SABIC. En variante, on peut utiliser à la place la résine polycarbonate commercialisée sous la référence XANTAR® XRM5010 par la société MITSUBISHI ENGINEERING PLASTICS CORPORATION.By way of example, the polycarbonate resin marketed under the reference LEXAN® EXL5689 by the company SABIC is used. Alternatively, the polycarbonate resin sold under the reference XANTAR® XRM5010 may be used instead by MITSUBISHI ENGINEERING PLASTICS CORPORATION.
Dans cet exemple, les parois 51, 52 présentent chacune une épaisseur supérieure ou égale à 1 mm et inférieure ou égale à 3 mm, cette épaisseur étant mesurée lorsque les parois 51, 52 sont dans l'état de repos.In this example, the
Le choix d'un tel matériau avec ces propriétés mécaniques permet de garantir une bonne tenue mécanique du boitier 5, tout en obtenant une déformation des parois 51, 52 en fonction de la pression dans le boîtier 5.The choice of such a material with these mechanical properties ensures a good mechanical strength of the
Comme la déformation est élastique, les parois 51, 52 reviennent dans leur état de repos lorsque la pression dans le boîtier 5 redevient égale à la pression atmosphérique environnante, sans que le boîtier 5 ne souffre de séquelles mécaniques préjudiciables à son fonctionnement.As the deformation is elastic, the
A titre d'exemple illustratif, le boîtier 5 est ici formé par deux demi-coques moulées, semblables et de forme complémentaire l'une avec l'autre, portant chacune une paroi 51, 52. Ces deux demi-coques sont destinées à être solidarisées l'une avec l'autre afin de garantir l'intégrité du boîtier 5. A cet effet, le boîtier 5 comporte des moyens de fixation des parois 51, 52.By way of illustrative example, the
Dans cet exemple, les moyens de fixation sont des rivets, dont les têtes respectives portent la référence 55. Les parois 51, 52 comportent alors des trous traversants pour permettre le passage de ces rivets. De préférence, les moyens de fixation sont disposés uniquement près des bords des parois 51, 52, de façon à ne pas entraver leur déformation.In this example, the fastening means are rivets, whose respective heads are referenced 55. The
Le boîtier 5 comporte également une fenêtre 54 qui expose au moins en partie l'organe de déclenchement 42 à l'extérieur du boîtier 5. De cette manière, le percuteur 62 peut agir mécaniquement sur l'organe 42, quand bien même le percuteur 62 se situe à l'extérieur du boîtier 5.The
Selon une variante, le déclencheur 61 et le percuteur 62 peuvent être logés à l'intérieur du boîtier 5. Dans ce cas, la fenêtre 54 peut être omise.Alternatively, the
Comme illustré plus en détail aux
La face intérieure 521 est ici la face de la paroi latérale 52 qui est tournée vers l'intérieur du boîtier 5. Cette face intérieure 521 est opposée à la face extérieure de la paroi latérale 52.The
Du fait de sa solidarisation à la paroi latérale 52 déformable, l'excroissance 53 est déplaçable entre une première position et une deuxième position. L'excroissance 53 est dans la première position lorsque la paroi latérale 52 est dans l'état normal, et dans la deuxième position lorsque la paroi latérale 52 est dans l'état déformé.Due to its attachment to the
De cette façon, l'excroissance 53 se déplace vers sa deuxième position au fur et à mesure que la paroi latérale 52 correspondante se déforme depuis son état normal vers son état déformé.In this way, the
De façon préférentielle, l'excroissance 53 est formée d'un seul tenant avec la paroi latérale correspondante 52. En d'autres termes, l'excroissance 53 est venue de matière avec la paroi 52. Cela permet de simplifier encore plus la fabrication de l'appareil 1, puisque l'excroissance 53 est alors fabriquée simultanément avec la paroi latérale 52, par exemple lors d'une seule et même opération de moulage.Preferably, the
En variante, toutefois, l'excroissance 53 peut être une pièce rapportée distincte de la paroi 52 et qui est fixée solidairement à la paroi 52. Par exemple, cette fixation est réalisée au moyen d'un rivet ou par collage ou par soudage.Alternatively, however, the
On note X53 l'axe longitudinal selon lequel l'excroissance 53 s'étend lorsqu'elle est dans sa première position et on note X53d la direction selon sur laquelle l'excroissance s'étend lorsqu'elle est dans la deuxième position. L'axe X53 est ici perpendiculaire aux parois 51 et 52 lorsqu'elles sont dans leur état de repos.X53 is the longitudinal axis along which the
A titre d'exemple, l'angle entre les axes X53 et X53d est supérieur ou égal à 8° lorsque la paroi 52 se déforme d'une amplitude supérieure ou égale à 1mm.By way of example, the angle between the axes X53 and X53d is greater than or equal to 8 ° when the
L'excroissance 53 est agencée par rapport à l'organe de déclenchement 42 de sorte à ce que son déplacement depuis sa première position vers sa deuxième position entraîne un déplacement de l'organe de déclenchement 42 de sa position inactive vers sa position de déclenchement. De cette manière, le déplacement de l'excroissance 53 résultant de la déformation des parois 51, 52 entraîne le déclenchement du mécanisme 4 pour commuter l'organe de coupure 3 vers son état ouvert.The
En d'autres termes, l'excroissance 53 est ici couplée avec l'organe de déclenchement 42.In other words, the
A cet effet, l'ergot 421 est ici placé sur la trajectoire suivie par l'excroissance 53 entre ses première et deuxième positions. L'excroissance 53 est ici disposée au-dessus de l'ergot 421.For this purpose, the
Par exemple, lorsque l'excroissance 53 est dans sa première position et que l'organe 42 est dans sa position de repos, alors la face inférieure de la poutre 531 est en contact avec l'ergot 421 sans toutefois exercer d'effort sur cet ergot 421. Lorsqu'elle passe dans sa deuxième position, l'excroissance 53 appuie sur l'ergot 421, puisqu'il est situé sur sa trajectoire, et entraîne ce dernier en rotation autour de l'axe X42.For example, when the
Les dimensions de l'excroissance 53, notamment sa longueur et sa position, sont aussi choisies en fonction de l'effort qu'il est nécessaire d'appliquer sur l'ergot 421 afin de déplacer l'organe 42 vers sa position de déclenchement.The dimensions of the
A titre d'exemple illustratif, l'excroissance 53 est adaptée pour exercer un effort sur l'ergot 421 d'intensité supérieure ou égale à 5 Newton lorsqu'elle se déplace vers sa deuxième position.As an illustrative example, the
L'ergot 421 sert avantageusement de levier et permet de réduire l'effort nécessaire pour mettre en rotation l'organe 42.The
De plus, la longueur de l'excroissance 53, la longueur de l'ergot 421 et la position relative de l'ergot 421 par rapport à l'excroissance 53, sont adaptées pour bénéficier d'un effet de levier, ce qui réduit l'effort nécessaire pour déplacer l'organe de déclenchement 42 vers sa position de déclenchement.In addition, the length of the
Par exemple, la zone de contact entre l'excroissance 53 et l'ergot 421 est située à une distance de la face intérieure 521 qui est supérieure ou égale au tiers de la largeur de l'organe 3, de préférence encore égale à la moitié de cette largeur. La zone de contact est ici la portion de surface de l'ergot 421 sur laquelle l'excroissance 53 appuie lorsqu'elle se déplace vers sa deuxième position alors que l'organe 42 est dans sa position de repos.For example, the zone of contact between the
Cette largeur est, par exemple, mesurée selon l'axe X53. Ici, cette largeur est égale à l'écartement entre les parois latérales 51 et 52.This width is, for example, measured along the axis X53. Here, this width is equal to the spacing between the
La longueur de l'excroissance 53 est de préférence supérieure ou égale à 10mm . La longueur de l'excroissance 53 est ici mesurée selon l'axe X53 lorsqu'elle est dans sa première position.The length of the
Dans cet exemple, de façon complémentaire, l'ergot 421 est dimensionné de sorte que la distance entre ladite zone de contact et l'axe X42 soit égale, par exemple à 5% près, à la distance entre l'axe X42 et la zone d'accrochage de l'organe 42 au verrou 44.In this example, in a complementary manner, the
Avantageusement, l'excroissance 53 comporte une poutre 531 et un raidisseur 532. La poutre 531 et le raidisseur 532 sont ici réalisés dans le même matériau.Advantageously, the
La poutre 531 s'étend longitudinalement selon l'axe X53 et présente une forme cylindrique avec une section transversale de superficie supérieure ou égale à 5mm2.The
Le raidisseur 532 comporte ici une paroi plane de forme triangulaire qui s'étend sous cette poutre 531 et qui est ancré à la face intérieure 521 le long d'un de ses côtés et ancré à la poutre 531 le long d'un autre de ses côtés.The
Le choix des dimensions de l'excroissance 53, notamment sa forme et/ou sa section, ainsi que l'emploi du raidisseur 532, permettent d'augmenter la raideur de l'excroissance 53. Cela est particulièrement utile lorsque l'excroissance 53 est réalisée d'un seul tenant avec la paroi latérale 52. En effet, l'excroissance est alors réalisée dans le même matériau que la paroi latérale 52. Or, ce matériau est déformable, alors qu'on souhaite justement éviter que l'excroissance 53 elle-même ne se déforme lorsqu'elle exerce un appui sur l'organe 42.The choice of the dimensions of the
L'excroissance 53 permet ainsi de déclencher le mécanisme de commande 4 lors de l'apparition d'un arc électrique entre des contacts électriques 31, 32, ce qui engendre un dégagement de gaz de coupure et donc une surpression dans le boîtier 5.The
Lorsque les parois latérales 51, 52 et notamment la paroi latérale 52, se déforment du fait d'une augmentation de pression dans le boîtier 5, elles passent dans leur état déformé. Du fait de cette déformation, l'excroissance 53 se déplace vers sa deuxième position. Le sens de déplacement de l'excroissance 53 est illustré par la flèche F1 sur la
L'excroissance 53 exerce alors un effort sur l'ergot 421, ce qui entraîne le déplacement de l'organe de déclenchement 42 vers sa position de déclenchement, comme illustré par la flèche F3 à la
Grâce à l'invention, dès l'apparition d'un arc électrique entre les contacts électriques, l'augmentation de pression qui résulte de l'apparition de l'arc électrique entraîne la déformation des parois latérales 51, 52 et donc le déclenchement du mécanisme 4, par l'intermédiaire de l'excroissance 53.Thanks to the invention, as soon as an electric arc appears between the electrical contacts, the increase in pressure which results from the appearance of the electric arc causes the deformation of the
Ainsi, le déclenchement du mécanisme 4 est réalisé rapidement, puisque la chaîne de déclenchement est plus courte que dans les dispositifs connus, du fait de l'absence d'un élément intermédiaire tel qu'un piston.Thus, the trigger mechanism 4 is achieved quickly, since the trigger chain is shorter than in known devices, because of the absence of an intermediate element such as a piston.
A titre d'exemple illustratif, pour un courant de coupure d'intensité supérieure ou égale à 8 kA crête, la surpression engendre le déclenchement du mécanisme 4 au bout d'une durée inférieure ou égale à 1ms. Dans les mêmes circonstances, le déclencheur 61 n'entre en action, en déplaçant le percuteur 62, qu'au bout d'une durée de 3 ms.By way of illustrative example, for a breaking current of intensity greater than or equal to 8 kA peak, the overpressure triggers the trigger mechanism 4 after a period of less than or equal to 1 ms. In the same circumstances, the
En outre, du fait de cette simplicité de réalisation et de l'absence de dispositif supplémentaire, tel qu'un piston, la fabrication de l'appareil 1 est plus simple et plus économique. Cela confère également à l'appareil 1 une meilleure robustesse, dans la mesure où le fonctionnement de l'excroissance 53, du fait de sa simplicité, n'est pas sensible à un éventuel risque de pollution par les gaz de coupure.In addition, because of this simplicity of implementation and the absence of additional device, such as a piston, the manufacture of the
Le fait que l'excroissance 53 soit configurée pour agir sur l'organe de déclenchement 42 permet de déclencher le mécanisme 4 en utilisant la même chaîne de commande que le déclencheur 61. Il n'est donc pas nécessaire de modifier l'architecture des mécanismes de commande existants, ni d'augmenter le volume extérieur et l'encombrement du bloc de coupure 2.The fact that the
L'invention permet ainsi d'utiliser la déformation des parois latérales 51 et 52 causée par la surpression due aux gaz de coupure, qui est traditionnellement perçue comme un effet néfaste et indésirable, afin de commander le déclenchement du mécanisme 4 de façon rapide et fiable et avec une implémentation simplifiée.The invention thus makes it possible to use the deformation of the
La
Plus précisément, l'appareil 1' est un disjoncteur électrique bipolaire, adapté pour fonctionner avec des courants électriques circulant selon deux pôles électriques P1 et P2 distincts.More specifically, the apparatus 1 'is a bipolar electric circuit breaker, adapted to operate with electric currents flowing along two distinct electric poles P1 and P2.
L'appareil 1' comporte ici un bloc de coupure 2' et un bloc déclencheur 6', qui jouent le même rôle, respectivement, que les blocs 2 et 6 de l'appareil 1.The apparatus 1 'here comprises a breaking block 2' and a trigger block 6 ', which play the same role, respectively, as the
Le bloc 2' diffère notamment du bloc 2 en ce qu'il comporte deux organes de coupure, ou ensembles de coupure, chacun associé à un des pôles électriques P1 et P2. L'appareil 1' comporte alors plusieurs plages de raccordement associées à chacun des pôles P1 et P2.Block 2 'differs in particular from
Le bloc 2' comporte également un mécanisme de commande analogue au mécanisme 4, notamment pourvu d'un levier 41' et d'un organe de déclenchement 42' incluant un ergot 421'. Le mécanisme de commande du bloc 2' est agencé pour commander simultanément les deux organes de coupure du bloc 2' dans un même état, notamment pour ouvrir simultanément les deux organes de coupure des pôles P1 et P2.The block 2 'also comprises a control mechanism similar to the mechanism 4, in particular provided with a lever 41' and a trigger member 42 'including a lug 421'. The control mechanism of the block 2 'is arranged to simultaneously control the two cut-off members of the block 2' in the same state, in particular to open simultaneously the two cut-off members of the poles P1 and P2.
L'appareil 1' comporte un boîtier analogue au boîtier 5 et à l'intérieur duquel est logé le bloc 2'. Ce boîtier comporte des parois latérales 51' et 52' déformables analogues aux parois 51, 52.The apparatus 1 'comprises a housing similar to the
La paroi 52' porte une excroissance 53' qui joue le même rôle que l'excroissance 53. Notamment, l'excroissance 53' est adaptée pour se déplacer vers sa deuxième position lorsque la paroi 52' se déforme, sous l'effet d'une l'augmentation de la pression dans le boîtier, résultant de l'apparition d'un arc électrique dans au moins l'un des organes de coupure du bloc 2'. En se déplaçant, l'excroissance 53' exerce un effort sur l'ergot 421', qui déplace l'organe 42' vers sa position de déclenchement afin d'ouvrir les organes de coupure du bloc 2'.The wall 52 'carries a protrusion 53' which plays the same role as the
Du fait que l'excroissance 53' est portée par la seule paroi latérale 52', l'invention est facilement applicable à des appareils autres que l'appareil 1, sans avoir besoin de modifier en profondeur leur architecture.Because the protrusion 53 'is carried by the single side wall 52', the invention is easily applicable to devices other than the
A titre d'illustration, du fait de la structure du bloc 2', la distance précédemment définie entre la zone de contact et la paroi 52' est ici égale à l'écartement entre la paroi 52' et le plan géométrique séparant l'un de l'autre les deux organes de coupure du bloc 2'.By way of illustration, because of the structure of the block 2 ', the distance previously defined between the contact zone and the wall 52' is here equal to the distance between the wall 52 'and the geometric plane separating one on the other, the two cut-off members of the block 2 '.
Dans cet exemple, l'appareil 1' comporte également un couvercle 500 destiné à recouvrir une face avant de l'appareil 1'. Ce couvercle 500 est pourvu de rebords latéraux 502 rabattus qui sont destinés à recouvrir le bord avant des faces latérales 51', 52' lorsque le couvercle 500 est en configuration montée sur l'appareil 1'. De préférence, les dimensions des rebords 502 sont limitées de façon à ne pas entraver la déformation des parois 51' et 52'.In this example, the apparatus 1 'also comprises a
Les modes de réalisation et les variantes envisagés ci-dessus peuvent être combinés entre eux pour générer de nouveaux modes de réalisation.The embodiments and alternatives contemplated above may be combined with one another to generate new embodiments.
Claims (10)
- Breaking device (1; 1') for breaking an electric current, with separable electrical contacts and air breaking, the device comprising:- a breaking assembly (3) which can be switched between an open state allowing an electric current to flow within the device and a closed state preventing the flow of the electric current;- a control mechanism (4) for controlling the switching of the breaking assembly (3) between its open and closed states, the control mechanism (4) comprising a triggering member (42; 42') arranged to trigger the switching of the breaking assembly (3) to the open state when the triggering member (42; 42') is displaced from a rest position to a triggering position;- a housing (5) inside which there are housed the breaking assembly (3) and the control mechanism (4), and which has lateral walls (51, 52; 51', 52');the breaking device (1; 1') being characterised in that:- the lateral walls (51, 52; 51', 52') are resiliently deformable, from a rest state to a deformed state, when the pressure prevailing inside the housing (5) increases;- one of the lateral walls (52; 52') has, on its inside face (521), a rigid protuberance (53; 53') extending towards the inside of the housing perpendicularly to that inside face (521), so that the deformation of said lateral wall (52; 52') causes a displacement of the protuberance (53; 53') from a first position to a second position;- the protuberance (53; 53') is arranged relative to the triggering member so that its displacement to the second position causes the displacement of the triggering member (42; 42') from the rest position to the triggering position.
- Breaking device (1; 1') according to claim 1, characterised in that the protuberance (53; 53') is formed in one piece with said lateral wall (52; 52').
- Breaking device (1; 1') according to any one of the preceding claims, characterised in that the lateral walls (51, 52; 51', 52') are made of a moulded thermoplastic material.
- Breaking device (1; 1') according to claim 3, characterised in that the lateral walls (51, 52; 51', 52') are made of glass-fibre-reinforced polycarbonate resin.
- Breaking device (1; 1') according to any one of the preceding claims, characterised in that the lateral walls (51, 52; 51', 52') have a flexural modulus of elasticity which is greater than or equal to 1 GPa and less than or equal to 5 GPa, so that the amplitude of the deformation of the lateral walls (51, 52; 51', 52') is greater than or equal to 1 mm when the pressure inside the housing becomes greater than or equal to 6 bar.
- Breaking device (1; 1') according to any one of the preceding claims, characterised in that the protuberance (53; 53') has a rigid beam (531) extending along a longitudinal axis (X53) of the protuberance (53; 53') and a stiffener (532).
- Breaking device (1; 1') according to any one of the preceding claims, characterised in that the protuberance (53; 53') has a length greater than or equal to 5 mm.
- Breaking device (1; 1') according to any one of the preceding claims, characterised in that the triggering member (42; 42') is movable in rotation about an axis of rotation (X42) and is provided with a projecting lug (421; 421') extending perpendicularly to the axis of rotation (X42), the lug (421; 421') being positioned on the trajectory followed by the protuberance (53; 53') when it moves from its first position to its second position.
- Breaking device (1; 1') according to claim 8, characterised in that a contact zone between the protuberance and the lug (421; 421') is situated at a distance from the inside face (521) which is greater than or equal to one third of the width of the breaking assembly (3).
- Breaking device (1; 1') according to any one of the preceding claims, characterised in that it has a trigger block (6) comprising a trigger (61) and a movable striker (62), the trigger (61) being configured to displace the triggering member (42; 42') to its triggering position when it detects an electrical fault on the basis of the current flowing through the device (1; 1').
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PL18157542T PL3367415T3 (en) | 2017-02-22 | 2018-02-20 | Air circuit breaker having separable electrical contacts for interrupting an electrical current |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR1751389A FR3063174B1 (en) | 2017-02-22 | 2017-02-22 | APPARATUS FOR CUTTING AN ELECTRICAL CURRENT WITH SEPARABLE ELECTRICAL CONTACTS AND CUTTING IN THE AIR |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3367415A1 EP3367415A1 (en) | 2018-08-29 |
| EP3367415B1 true EP3367415B1 (en) | 2019-12-04 |
Family
ID=59381349
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP18157542.4A Active EP3367415B1 (en) | 2017-02-22 | 2018-02-20 | Air circuit breaker having separable electrical contacts for interrupting an electrical current |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10418215B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP3367415B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP7089894B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR102549652B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN108461359B (en) |
| BR (1) | BR102018001263B1 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2770144T3 (en) |
| FR (1) | FR3063174B1 (en) |
| PL (1) | PL3367415T3 (en) |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2661776B1 (en) * | 1990-05-04 | 1996-05-10 | Merlin Gerin | INSTANT TRIGGER OF A CIRCUIT BREAKER. |
| JP3399301B2 (en) * | 1997-07-09 | 2003-04-21 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Circuit breaker |
| JPH11224584A (en) * | 1998-02-05 | 1999-08-17 | Fuji Electric Co Ltd | Fixing structure of case and cover of circuit breaker |
| US6377144B1 (en) | 1999-11-03 | 2002-04-23 | General Electric Company | Molded case circuit breaker base and mid-cover assembly |
| CN101241820B (en) * | 2008-03-07 | 2010-06-30 | 常熟开关制造有限公司(原常熟开关厂) | Single-pole modular low-voltage breaker |
| DE102009015126A1 (en) * | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-14 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Trigger for an electrical switching arrangement |
| FR2946192A1 (en) * | 2009-05-28 | 2010-12-03 | Schneider Electric Ind Sas | DEVICE FOR LIMITING THE PRESSURE INSIDE A COMPARTMENT BELONGING TO AN ELECTRICAL APPARATUS |
| CN102299032B (en) * | 2011-08-09 | 2016-04-13 | 无锡新宏泰电器科技股份有限公司 | Direct-driven gas blow tripping device of breaker |
| CN103903928B (en) * | 2014-04-16 | 2016-05-11 | 南京大全电气研究院有限公司 | A kind of breaker with heat loss through convection housing |
| FR3042640B1 (en) * | 2015-10-20 | 2019-05-31 | Schneider Electric Industries Sas | ELECTRICAL SWITCHING APPARATUS COMPRISING A SWITCHING MECHANISM AND AT LEAST ONE AUXILIARY MODULE |
-
2017
- 2017-02-22 FR FR1751389A patent/FR3063174B1/en active Active
-
2018
- 2018-01-22 BR BR102018001263-0A patent/BR102018001263B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2018-01-24 US US15/878,861 patent/US10418215B2/en active Active
- 2018-02-09 CN CN201810133151.2A patent/CN108461359B/en active Active
- 2018-02-20 ES ES18157542T patent/ES2770144T3/en active Active
- 2018-02-20 PL PL18157542T patent/PL3367415T3/en unknown
- 2018-02-20 EP EP18157542.4A patent/EP3367415B1/en active Active
- 2018-02-21 KR KR1020180020790A patent/KR102549652B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2018-02-21 JP JP2018029003A patent/JP7089894B2/en active Active
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| None * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP7089894B2 (en) | 2022-06-23 |
| EP3367415A1 (en) | 2018-08-29 |
| JP2018137226A (en) | 2018-08-30 |
| US20180240632A1 (en) | 2018-08-23 |
| KR102549652B1 (en) | 2023-06-29 |
| BR102018001263A2 (en) | 2018-10-30 |
| CN108461359B (en) | 2021-10-29 |
| PL3367415T3 (en) | 2020-06-01 |
| US10418215B2 (en) | 2019-09-17 |
| BR102018001263B1 (en) | 2023-12-26 |
| FR3063174A1 (en) | 2018-08-24 |
| KR20180097156A (en) | 2018-08-30 |
| ES2770144T3 (en) | 2020-06-30 |
| FR3063174B1 (en) | 2019-04-19 |
| CN108461359A (en) | 2018-08-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0225207B1 (en) | Cinematic transmission chain between the control mechanism and the poles of an electric circuit breaker with a moulded insulating casing | |
| FR2891661A1 (en) | Multi-pole circuit breaker provide compensating rotation moment to driving shafts so that contact force between contactors in single pole breaking unit far from switching mechanism is smaller than that of other breaking units | |
| EP1743346B1 (en) | Surge voltage protection device with arc-breaking means | |
| EP1815569B1 (en) | Overvoltage-protection device with improved disconnection | |
| EP2478544A1 (en) | Single-pole cutoff unit comprising a rotary contact bridge, cutoff device comprising such a unit, and circuit breaker comprising such a device | |
| EP2330611B1 (en) | Selective circuit-breaker | |
| EP3367415B1 (en) | Air circuit breaker having separable electrical contacts for interrupting an electrical current | |
| EP3499541B1 (en) | Electrical protection apparatus comprising a pyrotechnical actuation system | |
| EP1842269A2 (en) | Electrical installation protection device with improved interrupting capacity | |
| EP2743958B1 (en) | Electric current breaking apparatus, in particular a coupling breaker | |
| EP2894647A1 (en) | Unipolar breaking unit and switchgear comprising such a unit | |
| EP0118334B2 (en) | Current-limiting switch | |
| FR2982995A1 (en) | Electrical shut-off device i.e. multipolar contactor for direct current switching, has controller controlling each arc cutting screen to occupy rolling position for elongating electric arc when fixed and mobile contacts are in open position | |
| EP0996959B1 (en) | Circuit breaker for low voltage alternating electric installation | |
| EP1829176B1 (en) | Improved-disconnection overvoltage protection device and corresponding method | |
| FR2958447A1 (en) | Electromagnetic tripping device for double-break low voltage multi-polar type breaker, has airgap between heads and adjustable core maximum to rest position, and adjustment units adjusting airgap value along displacement axis of core | |
| EP0054499B1 (en) | Circuit breaker with neutral-line disconnection | |
| EP2743947B1 (en) | Support shaft of the movable contacts in an electric current breaking apparatus, and current breaking apparatus comprising same, in particular a coupling breaker | |
| EP3161850B1 (en) | Thermal-magnetic tripping mechanism | |
| FR2981789A1 (en) | Electrical cut-off device e.g. circuit breaker, for cutting direct current in photovoltaic electricity generation station, has actuating mechanism with reversal unit to move mobile contact bridge between contact and separating positions | |
| EP0403329A1 (en) | Circuit breaker with automatic tripping, particularly protective switch and fault-current protective switch | |
| EP3857585B1 (en) | Electric arc-extinguishing device for an electrical protection unit, and electrical protection apparatus incorporating said device | |
| EP4298653A1 (en) | Electrical device and power cut-off system comprising such a device | |
| WO2022018053A1 (en) | Electric arc extinction chamber for an electrical protection device and an electrical protection device comprising at least one such extinction chamber | |
| FR2980908A1 (en) | Unipolar shutting-off device for cutting off arc due to short-circuit, has screen comprising locking unit that cooperates directly with arm contact, where locking unit is released for allowing displacement of screen to its rest position |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN PUBLISHED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20190201 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: H01H 9/34 20060101ALN20190626BHEP Ipc: H01H 71/02 20060101AFI20190626BHEP |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20190715 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 1210440 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20191215 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602018001423 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: FRENCH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20191204 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200305 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200304 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200304 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2770144 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20200630 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200429 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200404 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602018001423 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 1210440 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20191204 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20200229 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200220 Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20200907 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200220 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200229 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20210228 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20210228 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20191204 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20240307 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20240228 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20240220 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Payment date: 20240208 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20240222 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20240226 Year of fee payment: 7 |