EP3266498B1 - System and method for facial nerve stimulation - Google Patents
System and method for facial nerve stimulation Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3266498B1 EP3266498B1 EP17181237.3A EP17181237A EP3266498B1 EP 3266498 B1 EP3266498 B1 EP 3266498B1 EP 17181237 A EP17181237 A EP 17181237A EP 3266498 B1 EP3266498 B1 EP 3266498B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- muscle
- facial
- contacts
- electrode
- nerve
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/18—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes
- A61N1/32—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents
- A61N1/36—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents for stimulation
- A61N1/3605—Implantable neurostimulators for stimulating central or peripheral nerve system
- A61N1/3606—Implantable neurostimulators for stimulating central or peripheral nerve system adapted for a particular treatment
- A61N1/36067—Movement disorders, e.g. tremor or Parkinson disease
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/24—Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals of the body or parts thereof
- A61B5/316—Modalities, i.e. specific diagnostic methods
- A61B5/389—Electromyography [EMG]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/24—Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals of the body or parts thereof
- A61B5/316—Modalities, i.e. specific diagnostic methods
- A61B5/389—Electromyography [EMG]
- A61B5/395—Details of stimulation, e.g. nerve stimulation to elicit EMG response
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/02—Details
- A61N1/04—Electrodes
- A61N1/0404—Electrodes for external use
- A61N1/0472—Structure-related aspects
- A61N1/0476—Array electrodes (including any electrode arrangement with more than one electrode for at least one of the polarities)
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/02—Details
- A61N1/04—Electrodes
- A61N1/05—Electrodes for implantation or insertion into the body, e.g. heart electrode
- A61N1/0526—Head electrodes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/02—Details
- A61N1/04—Electrodes
- A61N1/05—Electrodes for implantation or insertion into the body, e.g. heart electrode
- A61N1/0551—Spinal or peripheral nerve electrodes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/18—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes
- A61N1/32—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents
- A61N1/36—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents for stimulation
- A61N1/36003—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents for stimulation of motor muscles, e.g. for walking assistance
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/18—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes
- A61N1/32—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents
- A61N1/36—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents for stimulation
- A61N1/3605—Implantable neurostimulators for stimulating central or peripheral nerve system
- A61N1/36128—Control systems
- A61N1/36135—Control systems using physiological parameters
- A61N1/36139—Control systems using physiological parameters with automatic adjustment
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/18—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes
- A61N1/32—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents
- A61N1/36—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents for stimulation
- A61N1/3605—Implantable neurostimulators for stimulating central or peripheral nerve system
- A61N1/36128—Control systems
- A61N1/36146—Control systems specified by the stimulation parameters
- A61N1/36182—Direction of the electrical field, e.g. with sleeve around stimulating electrode
- A61N1/36185—Selection of the electrode configuration
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/02—Details
- A61N1/04—Electrodes
- A61N1/05—Electrodes for implantation or insertion into the body, e.g. heart electrode
- A61N1/0551—Spinal or peripheral nerve electrodes
- A61N1/0553—Paddle shaped electrodes, e.g. for laminotomy
Definitions
- the invention generally relates to stimulation systems and, more particularly, the invention relates to facial nerve stimulation systems and non-therapeutic facial nerve stimulation methods.
- the face is the mirror of the soul and facial expressions are an indispensable element of verbal and nonverbal human communication.
- Degenerative lesions of the facial nerve such as tumors or traumas, lead to permanent facial nerve damage which, in contrast to many other neural lesions, cannot be hidden.
- Functional rehabilitation of facial nerve paresis has remained unsatisfactory despite optimal microsurgical reconstruction of the damaged nerve parts.
- peripheral facial paresis Unilateral damage of the nerve fibers of the facial nerve or its nucleus leads to peripheral facial paresis. This is to be distinguished from supranuclear lesions along the corticonuclear tract which lead to a so-called central facial paresis.
- central facial paresis In Western Europe and the USA, the incidence of peripheral facial pareses is approx. 20-35/100,000 inhabitants. The most frequent reasons for peripheral facial paresis are idiopathic facial paresis (two thirds of the cases, no reason can be found despite extensive diagnostics), traumatic pareses following fractures of the petrous part of the temporal bone or face injuries, inflammatory paresis accompanying chronic ear infections, and destruction of the nerve by tumors.
- central facial pareses 200/1,000,000 inhabitants, as the incidence of the most frequent cause of central facial paresis, i.e., stroke which often causes facial paresis, is 250/100,000 inhabitants. Cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral inflammation and brain tumors are less frequent causes of the central form.
- facial paresis is a common disease.
- peripheral paresis shows non-degenerative paresis (neurapraxia according to Seddon) so that 80% of the cases show regeneration of the nerve under adequate therapy. 95% of cases with central facial paresis show regeneration.
- degenerative paresis asxonotmesis, neurotmesis, mixed forms according to Seddon
- persistent defects are observed after healing. The extent of persistent defects after healing depends on the degree of the neural lesion and the applied therapy. If only a small peripheral branch of the facial nerve is affected, mimic muscles only show very localized deficits.
- a complete loss of the peripheral facial nerve leads to a loss of muscle tone in the affected half of the face and the soft tissues of the face sag. Voluntary motor movement is lost, and mimic muscles can no longer be moved. The inability to close the eyelid indirectly leads to vision disorders since the eye waters and inflammation is possible. Lack of mouth movement limits speaking and eating.
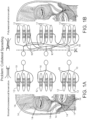
- the regenerating neurons with their sprouting axons grow accidentally into these bands of the individual nerve branches and are directed to the peripheral mimic muscles. Individual axons perish and do not reach the periphery, some accidentally reach their original target muscle, while others reach a completely different target muscle. Due to axonal collateral sprouting, the most frequently observed effect is simultaneous sprouting to several target muscles, such as shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B .
- synkinesis This leads clinically to simultaneous movement of several target muscles (a condition called synkinesis). Patients often complain about involuntary lid closure while moving the mouth, e.g., when eating. Simultaneous movement of antagonist muscles leads to the autoparalytic syndrome: muscle forces cancel each other out and no movement is observed clinically despite innervation.
- New research shows that not only collateral sprouting but also terminal sprouting (such as shown in FIGS. 2A and 2B ) of the regenerating axons directly at the neuromuscular end-plates causes uncoordinated muscle function. This explains why the patients' quality of life is significantly limited even after surgical reconstruction of the nerve.
- the patient can no longer be offered a nerve graft.
- Possible therapies include dynamic muscle grafts, free nerve-muscle transplantation, implantation of upper lid weights or static suspensions. Functional results of these secondary procedures are even less satisfactory than the above mentioned nerve grafts. These procedures may, at best, restore muscle tone, but facial expression remains very mask-like and the dynamic muscle suspensions allow reproducing only few and very mechanistic movement vectors.
- Document US-A-2003/055468 discloses the most relevant prior art.
- the system according to the invention is defined in claim 1.
- the method according to the invention is defined in claim 12 and limited to non-therapeutic stimulation methods. Embodiments (if any) in contradiction to claim 1 or 12 do not form part of the claimed invention.
- a method of stimulating facial nerves in a subject with synkinetic reinnervated muscles includes providing an electrode, having a plurality of contacts, in a parotid region of the subject's face. The method also includes stimulating each of the plurality of contacts separately, identifying one or more contacts from the plurality of contacts that cause one or more nerve branches to activate a desired facial muscle, and selecting the identified contacts to stimulate the one or more nerve branches.
- the stimulation in this method is non-therapeutic.
- the electrode may be an array electrode and/or a rod electrode.
- the facial muscle may be the orbicularis oculi muscle, the orbicularis oris muscle, the occipitofrontalis muscle, the procerus muscle, the nasalis muscle, the depressor septi nasi muscle, the corrugator supercilii muscle, the depressor supercilii muscle, the auricular muscles (anterior, superior, posterior), the depressor anguli oris muscle, the risorius muscle, the zygomaticus major muscle, the zygomaticus minor muscle, the levator labii superioris muscle, the levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle, the depressor labii inferioris muscle, the levator anguli oris muscle, the buccinator muscle, and/or the mentalis muscle.
- the electrode may be implanted within an operable distance of the one or more nerve branches, e.g., implanted below one or more nerve branches or implanted above the nerve branches between the nerve branches and the subject's skin.
- the stimulation of the one or more nerve branches may be triggered based on a sensed signal, e.g., measured using EMG sensors and/or acceleration sensors.
- the sensed signal may be recorded from a recording electrode in the parotid region of the subject's damaged side and/or healthy side of the face.
- the recording electrode may have a plurality of contacts.
- the sensed signal may be recorded from sensors placed on or under the subject's skin.
- the method may further include selecting one or more contacts to stimulate nerve branches in order to block activation of other facial muscles.
- the method may identify one or more first contacts that cause the activation of a first facial muscle and one or more second contacts that cause the activation of a second facial muscle. The method may then select the identified first and second contacts.
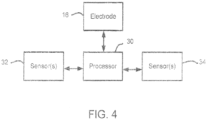
- a system for stimulating facial nerves in a subject includes an electrode having a plurality of contacts and a processor in communication with the electrode.
- the processor has program code for stimulating each of the plurality of contacts separately, for identifying one or more contacts from the plurality of contacts that cause one or more nerve branches to activate a desired facial muscle, and for selecting the identified contacts to stimulate the one or more nerve branches.
- the electrode may be an array electrode and/or a rod electrode.
- the system may further include one or more sensors in communication with the processor.
- the sensors may be configured to provide facial movement information to the processor for use with the program code for identifying one or more contacts.
- the sensors may be EMG sensors and/or acceleration sensors.
- the program code for selecting the identified contacts may continuously stimulate the one or more nerve branches to maintain or recover a damaged side of a hemiparalyzed face.
- a method of stimulating facial nerves in a subject with facial palsy includes providing an electrode, having a plurality of contacts, in a parotid region of the subject's face. The method also includes stimulating each of the plurality of contacts separately, identifying one or more contacts from the plurality of contacts that cause one or more nerve branches to activate a desired facial muscle, and selecting the identified contacts to continuously stimulate the one or more nerve branches.
- the stimulation in this method is non-therapeutic.
- the electrode may be an array electrode and/or a rod electrode.
- the electrode may be implanted within an operable distance of the one or more nerve branches, e.g., implanted below one or more nerve branches or implanted above the nerve branches between the nerve branches and the subject's skin.
- the stimulation of the one or more nerve branches may be triggered based on a sensed signal, e.g., measured using EMG sensors and/or acceleration sensors.
- the recording electrode may have a plurality of contacts.
- the sensed signal may be recorded from sensors placed on or under the subject's skin.
- the method may identify one or more first contacts that cause the activation of a first facial muscle and one or more second contacts that cause the activation of a second facial muscle. The method may then select the identified first and second contacts.
- Various embodiments of the present invention provide a neuroprosthesis for restoring or partially restoring a unilaterally paralyzed face.
- the muscle(s) of interest for rehabilitation are synkinetic (i.e., misdirected) reinnervated muscles and not denervated muscles.
- Embodiments apply electrostimulation in a prescribed manner and location in order to stimulate the appropriate facial nerves on the damaged side of a subject's face. This is accomplished by placing an electrode in the parotid region of the subject's damaged side of the face and stimulating the appropriate nerve branches in order to activate the desired facial muscles.
- the sum action potential of the activated mimic muscles may be recorded with a medical device, such as an EMG and/or acceleration sensor.
- This impulse may then be used to determine which nerves branches to subsequently stimulate in order to activate the desired mimic muscles on the damaged side of the face. This potentially allows the facial muscles of both the healthy side and the corresponding damaged side to move synchronously. Details of illustrative embodiments are discussed below.
- a muscle ⁇ e.g., "a PCA muscle”
- a PCA muscle includes a plurality of such muscles (e.g., a plurality of PCA muscles), and so forth.
- the term "about,” when referring to a value or to an amount of mass, weight, time, quantity, volume, current, concentration or percentage is meant to encompass variations of in some embodiments +/-20%, in some embodiments +/-10%, in some embodiments +/-5%, in some embodiments +/-1%, in some embodiments +/-0.5%, and in some embodiments +/-0.1 % from the specified value, as such variations are appropriate.
- subject and patient are used interchangeably herein and each term refers, preferably, to a vertebrate subject or patient.
- a representative vertebrate is warm-blooded; a representative warm-blooded vertebrate is a mammal.
- a representative mammal is a human.
- the terms “subject” and “patient” include both human and animal subjects. Thus, veterinary therapeutic uses are provided in accordance with the presently disclosed subject matter.
- the presently disclosed subject matter provides for the treatment of mammals such as humans, as well as those mammals of importance due to being endangered, such as Siberian tigers; of economic importance, such as animals raised on farms for consumption by humans; and/or animals of social importance to humans, such as animals kept as pets or in zoos.
- mammals such as humans, as well as those mammals of importance due to being endangered, such as Siberian tigers; of economic importance, such as animals raised on farms for consumption by humans; and/or animals of social importance to humans, such as animals kept as pets or in zoos.
- animals include but are not limited to: carnivores such as cats and dogs; swine, including pigs, hogs, and wild boars; ruminants and/or ungulates such as cattle, oxen, sheep, giraffes, deer, goats, bison, and camels; and horses.
- domesticated fowl e.g., poultry, such as turkeys, chickens, ducks, geese, guinea fowl, and the like, as they are also of economic importance to humans.
- livestock including, but not limited to, domesticated swine, ruminants, ungulates, horses (including race horses and show horses), poultry, and the like.
- the signal was externally amplified and the stimulation electrode stimulated.
- the stimulation electrode was placed around the neural stump of the neuromuscular transplant as a cuff electrode. Facial movements of rabbit led to contraction of the originally denervated neck muscles.
- the same technique principally enabled electrostimulation of the denervated orbicularis oculi muscle of rabbit using the signal of the same muscle of the healthy side.
- the publication does not detail recording and stimulation parameters. Also, the duration of the experiment remains unclear. Cadaver examinations showed that the same neuromuscular transplants can be used for neurotization in the human face. The experiment was repeated one last time in dog.
- Cochlear implants are the most highly developed electrostimulation implants. They stimulate at 12-24 channels (cardiac pacemakers at 1, pain pacemakers at 4-8) with up to 20,000 pulses per second (cardiac pacemakers with 1, pain pacemakers with up to 190) per channel, up to a maximum of 50,000Hz. They process incoming signals in various amplitude ranges and frequencies up to 20,000Hz (at present only cardiac pacemakers with EMG signal recording and foot-drop implants with external heel switches are approved marketed systems with sensors). Cochlear implants are meanwhile also able to measure evoked potentials in the middle ear.
- the electrodes are thinner and more flexible than cardiac pacemaker electrodes, pain, Parkinson, tremor etc., pacemaker electrodes, although they have considerably more recording and stimulation contacts. Due to the high stimulation rate, cardiac pacemaker batteries would last only about 17 days, therefore cochlear implants are still inductively coupled systems, i.e., energy and signals are transmitted through the skin to the implanted stimulator via high frequency.
- first-generation devices worked exclusively via external triggers, new devices use sensors to detect muscle or joint position or EMG signals of neighboring intact muscle for improved impulse control. These developments led to improved electrodes (reduced risk of breakage, multi-channel systems) and improved stimulation units (miniaturization, implantability).
- extraneural electrodes such as cuff electrodes, epineural and interfascicular electrodes have also been developed. These electrodes have the advantage of a more selective stimulation of the enclosed nerve at the price of more invasive implantation.
- FIGS. 1A and 1B show diagrams of the normal somatotopic organization of facial innervation and the organization after lesion of the facial nerve, respectively.
- FIG. 1A normally exactly one axon 10 projects to one end-plate on the muscle fiber 12.
- Each of the different muscle groups 14 of the face is activated by the motor neuron pool of a subnucleus of the nucleus.
- FIG. 1B despite transsection and optimal reconstruction of the facial nerve, the regenerating axons 10 may sprout collaterally at the site of the lesion.
- the axons 10 sprout purely accidentally to any muscle fibers 12. Somatotopic order is lost.
- the clinical result is synkinesis.
- FIGS. 2A and 2B show diagrams of a normal end-plate region on the muscle fiber 12 and end-plate regions activated by several axons 10 due to terminal sprouting, respectively.
- FIG. 2A normally exactly one axon 10 projects to one end-plate on the muscle fiber 12.
- terminal sprouting may occur (such as shown in FIG. 2B ) in addition to collateral sprouting.
- individual end-plates may be activated by several axons 10.
- activating a desired facial muscle may entail considerable challenges since stimulating a nerve branch on the damaged side of the subject's face may not activate the corresponding facial muscle, but an entirely different, unpredictable facial muscle or muscles.
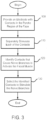
- FIG. 3 shows a process of stimulating facial nerves
- FIG. 4 shows a system for stimulating facial nerves according to embodiments of the present invention.
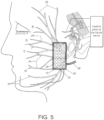
- the process begins at step 100, in which an electrode 16 is provided in the parotid region of the subject's face, such as shown in FIG. 5 .
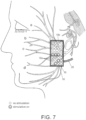
- the electrode 16 has a plurality of contacts 18, which may be configured in rows and columns (e.g., an array electrode 20 such as shown in FIGS. 5-7 ), or configured in one or more rows (e.g., one or more rod electrodes 22 such as shown in FIGS.
- the contacts 18 may be used to stimulate nerve branches 24 or to record nerve impulses or potentials from the nerve branches 24.
- the electrode 16 may have an insulating electrode pad 26 surrounding the contacts 18 and an electrode lead 28 electrically connecting the electrode 16 to a processor 30 for controlling the stimulation and/or recording of the electrode 16.
- the processor 30 may also provide signal processing capabilities to the stimulation and/or recording signal information.
- the electrode 16 is implanted in the parotid region within an operable distance of stimulating the branches 24 of the distal part of the facial nerve.
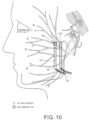
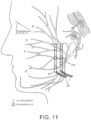
- the benefit of placing the electrode 16 in this region is that the facial nerve is already split up into separate nerve branches 24, allowing different regions (e.g., designated a, b, c, and d in FIGS. 5-7 and 9-11 ) and functions of the face to be innervated separately.
- two functions of the facial nerve may include closing the eyelids through the orbicularis oculi muscle (MOC) and pursing the lips through the orbicularis oris muscle (MOR).
- MOC orbicularis oculi muscle
- MOR pursing the lips through the orbicularis oris muscle
- facial muscles may also be innervated, such as the occipitofrontalis muscle, the procerus muscle, the nasalis muscle, the depressor septi nasi muscle, the corrugator supercilii muscle, the depressor supercilii muscle, the auricular muscles (anterior, superior, posterior), the depressor anguli oris muscle, the risorius muscle, the zygomaticus major muscle, the zygomaticus minor muscle, the levator labii superioris muscle, the levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle, the depressor labii inferioris muscle, the levator anguli oris muscle, the buccinator muscle, and/or the mentalis muscle.
- the electrode 16 may be implanted above the facial nerve between the nerve and the skin or below the facial nerve.
- the various contacts 18 may provide the stimulation or recording (or no stimulation or no recording) sequentially or simultaneously, in a prescribed manner as discussed in more detail below.
- each of the contacts 18 in the electrode 16 is stimulated separately in order to determine which nerve branches 24 activate which facial muscles.
- the movement of the various facial muscles may be measured by sensors 32 placed on the skin or implanted under the skin.
- the sensors 32 may be electromyographic (EMG) sensors, acceleration sensors, or other sensors that may effectively measure muscle movement as is well known to those skilled in the art.
- EMG electromyographic
- the sensors 32 are in communication with the processor 30 so that the contact stimulation information is correlated with the measured muscle movement information in order to determine which contact(s) 18 ultimately activated which facial muscle(s).
- the contacts 18 may be stimulated in a sequential manner (e.g., the first contact in the first row, first column, and then the second contact in the first row, second column, etc.) or in any order or pattern which would provide the desired information so long as one contact 18 is stimulated at a time.
- FIG. 6 shows one contact being stimulated (e.g., a star pattern denoting a stimulated contact 18a), while the remaining contacts are not stimulated (e.g., a plain circle denoting a contact 18b with no stimulation).
- nerve branch(es) for the eye would activate facial muscle(s) for the eye
- nerve branch(es) for the mouth would activate facial muscle(s) for the mouth
- nerve branch(es) for the eye might activate other facial muscle(s) (e.g., facial muscles for the mouth or facial muscles for the mouth and the eye).
- one or more contacts 18 are identified (in step 120) which stimulate nerve branches activating a particular facial muscle, e.g., muscle fibers responsible for closing the eye.
- one or more contacts 18 may even be used to block the other nerve branches. For example, if one contact stimulates nerve branch a + b, and another contact stimulates branch b, than a distal blocking stimulation of branch b combined with a proximal stimulation of branch a + b may selectively stimulate just branch a.
- the nerve blocking may be accomplished in a number of ways, such as nerve collision blocking, anodal blocking, high frequency blocking, etc.
- the identified contacts 18 are selected to stimulate the appropriate nerve branch(es) in order to activate a desired facial muscle.
- the processor 30 may determine which nerve branch(es) are the appropriate ones based on the measured muscle movement information.
- the processor 30 may then select and stimulate the identified contacts 18.
- one or more contacts 18a may be stimulated simultaneously in order to activate one facial muscle.
- Two or more sets of contacts 18a may also be stimulated together to activate more than one facial muscle. For example, if one or more contacts are identified to activate a first facial muscle and one or more contacts are identified to activate a second facial muscle, then the first and second set of contacts may be selected at the same time to activate both facial muscles.
- the two sets of contacts may have some contacts in common, may be completely different contacts, or be the same contacts, depending on the subject's initial assessment.
- the processor 30 may continuously stimulate the identified contacts 18 with a fixed stimulation protocol without further sensor input, e.g., trigger signals from a healthy side of the face. This continuous stimulation may allow the nerve function to maintain or recover the resting tone of a hemiparalyzed face, since the asymmetry of the face at rest is typically the most striking stigma attracting the interest of other people.
- FIGS. 8A and 8B show diagrams of two unilaterally paralyzed faces, both having a damaged right side and a healthy left side.
- FIG. 8A a system of closing the eyelids through the MOC is shown and in FIG. 8B a system of closing the eyelids through the MOC and pursing the lips through the MOR is shown.
- the facial movement on the healthy side of the face may be measured or recorded using one or more sensors 34. As shown in FIG.
- the facial movement information may, optionally, undergo amplification and/or modulation of the signal in a stimulation unit 36 (S), which may be in communication with the processor 30.
- the processor 30 may record or determine which muscles were moved on the healthy side of the face, determine which contact(s) 18 to select on the damaged side of the face in order to stimulate the appropriate nerve branches, and then select those contact(s) 18.
- the initial assessment may determine that the nerve branch(es) for the eye may actually activate the facial muscle(s) for the mouth, rather than the normal corresponding facial muscle(s) for the eye, and the nerve branch(es) for the mouth may activate the facial muscle(s) for the eye.
- the processor 30 selects the contacts 18 that stimulate the nerve branch(es) for the mouth on the damaged side, which in turn activate the facial muscle(s) for the eye.
- the movement on the healthy side typically just triggers the same corresponding muscle on the damaged side which, in this example, would have moved the mouth muscles rather than the desired eye muscles on the damaged side of the face.
- the facial movement on the damaged side of the face may alternatively be measured or recorded using one or more of the electrode contacts 18.
- the facial movement information may, optionally, undergo amplification and/or modulation of the signal in a stimulation unit 36 (S), which may be in communication with the processor 30.
- the processor 30 may record or determine which muscles should have been moved on the damaged side via recording the appropriate misdirected nerve branch signal of the face, determine which contact(s) 18 to select on the damaged side of the face in order to stimulate the appropriate misdirected nerve branch(es), and then select those contact(s) 18.
- This means contact 18a in FIG. 6 is measuring or recording information from a misdirected nerve fiber which would on the healthy side carry information for activation of a muscle innervated by nerve branch c.
- the facial movement information may, optionally, undergo amplification and/or modulation of the signal in a stimulation unit 36 (S), which may be in communication with the processor 30.
- the processor 30 may determine which muscles should have been moved on the damaged side and determine which contact(s) 18 to select on the damaged side of the face in order to stimulate the appropriate misdirected nerve branch(es), and then select those contact(s) 18a in FIG. 7 .
- the facial movement information from the healthy side of the face may be provided for more than one muscle system using additional sensors 34.
- two separate stimulation units 36 S1, S2 may, optionally, be used to amplify and/or modify the signals measured by the sensors 34.
- FIGS. 8A and 8B show one and two muscle systems, respectively, more than two muscle systems, or other muscle systems than those shown, may also be used.
- one or two stimulation units are shown, no stimulation unit or more than two stimulation units may also be used, or one stimulation unit may be used for two or more muscle systems.
- FIGS. 9-11 show a rod electrode implanted in the parotid region according to other embodiments of the present invention. As shown, two rod electrodes 22 with contacts 18 in a row may be implanted in the subject, although one rod electrode or more than two rod electrodes may also be used. The two rod electrodes are shown in a parallel orientation, but other configurations for two or more rod electrodes may be used which give good results for stimulation.
- processor 30 may be implemented as hardware, software (e.g., a computer program product), or a combination of both software and hardware.
- embodiments may be implemented as a computer program product for use with a computer system.
- Such implementation may include a series of computer instructions fixed either on a tangible medium, such as a computer readable medium (e.g., a diskette, CD-ROM, ROM, or fixed disk) or transmittable to a computer system, via a modem or other interface device, such as a communications adapter connected to a network over a medium.
- the medium may be either a tangible medium (e.g., optical or analog communications lines) or a medium implemented with wireless techniques (e.g., microwave, infrared or other transmission techniques).
- the series of computer instructions may embody all or part of the functionality previously described herein with respect to the processor.
- Those skilled in the art should appreciate that such computer instructions may be written in a number of programming languages for use with many computer architectures or operating systems.
- such instructions may be stored in any memory device, such as semiconductor, magnetic, optical or other memory devices, and may be transmitted using any communications technology, such as optical, infrared, microwave, or other transmission technologies.
- It is expected that such a computer program product may be distributed as a removable medium with accompanying printed or electronic documentation (e.g., shrink wrapped software), preloaded with a computer system (e.g., on system ROM or fixed disk), or distributed from a server or electronic bulletin board over the network (e.g., the Internet or World Wide Web).
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Physical Education & Sports Medicine (AREA)
- Orthopedic Medicine & Surgery (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Electrotherapy Devices (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10708108P | 2008-10-21 | 2008-10-21 | |
| EP09822609.5A EP2349451B1 (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2009-10-21 | System for facial nerve stimulation |
| PCT/US2009/061441 WO2010048261A1 (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2009-10-21 | System and method for facial nerve stimulation |
Related Parent Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP09822609.5A Division EP2349451B1 (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2009-10-21 | System for facial nerve stimulation |
| EP09822609.5A Division-Into EP2349451B1 (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2009-10-21 | System for facial nerve stimulation |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3266498A1 EP3266498A1 (en) | 2018-01-10 |
| EP3266498B1 true EP3266498B1 (en) | 2024-08-07 |
Family
ID=42119649
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP17181237.3A Active EP3266498B1 (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2009-10-21 | System and method for facial nerve stimulation |
| EP09822609.5A Active EP2349451B1 (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2009-10-21 | System for facial nerve stimulation |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP09822609.5A Active EP2349451B1 (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2009-10-21 | System for facial nerve stimulation |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US8792989B2 (enExample) |
| EP (2) | EP3266498B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP5687627B2 (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR101708515B1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN102202725B (enExample) |
| AU (1) | AU2009307634B2 (enExample) |
| CA (1) | CA2741086C (enExample) |
| RU (1) | RU2511082C2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2010048261A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (51)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA2741086C (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2016-11-22 | Med-El Elektromedizinische Geraete Gmbh | System and method for facial nerve stimulation |
| US9162059B1 (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2015-10-20 | Med-El Elektromedizinische Geraete Gmbh | Method for facial nerve stimulation of aging or dysfunctional muscles |
| WO2011044179A1 (en) * | 2009-10-05 | 2011-04-14 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Extracranial implantable devices, systems and methods for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders |
| WO2012082961A2 (en) | 2010-12-14 | 2012-06-21 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Extracranial implantable devices, systems and methods for the treatment of medical disorders |
| US9364674B2 (en) | 2010-11-30 | 2016-06-14 | Ian A. Cook | Pulse generator for cranial nerve stimulation |
| AU2011343763B2 (en) | 2010-12-14 | 2017-02-16 | Neurosigma, Inc. | Devices, systems and methods for the treatment of medical disorders |
| US8934992B2 (en) * | 2011-09-01 | 2015-01-13 | Inspire Medical Systems, Inc. | Nerve cuff |
| EP2790774B1 (en) * | 2011-12-14 | 2017-10-25 | MED-EL Elektromedizinische Geräte GmbH | System for eyelid stimulation |
| CA2869612A1 (en) * | 2012-04-05 | 2013-10-10 | Antonio A. F. Desalles | Subcutaneous electrodes for cranial nerve stimulation |
| US9144688B2 (en) * | 2012-11-12 | 2015-09-29 | Empi, Inc. | Systems and methods for wireless pairing and communication for electro-stimulation |
| WO2014110575A1 (en) * | 2013-01-14 | 2014-07-17 | Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary | Facial movement and expression detection and stimulation |
| US12453853B2 (en) | 2013-01-21 | 2025-10-28 | Cala Health, Inc. | Multi-modal stimulation for treating tremor |
| CN105142714B (zh) | 2013-01-21 | 2018-02-16 | 卡拉健康公司 | 用于控制震颤的设备和方法 |
| US9259576B2 (en) * | 2013-03-12 | 2016-02-16 | University Health Network | Functional electrical stimulation method, use and apparatus for mood alteration |
| WO2014176420A1 (en) * | 2013-04-24 | 2014-10-30 | Tufts University | Apparatus, systems, and methods for detecting or stimullating muscle activity |
| JP6190056B2 (ja) | 2013-06-28 | 2017-08-30 | コチ・ウニヴェルシテシKoc Universitesi | 電気刺激デバイス |
| KR101538678B1 (ko) * | 2013-11-14 | 2015-07-22 | 최승우 | 눈꺼풀의 근력 측정장치 |
| KR20150104345A (ko) * | 2014-03-05 | 2015-09-15 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 음성 합성 장치 및 음성 합성 방법 |
| KR101643367B1 (ko) * | 2014-05-29 | 2016-07-27 | 경희대학교 산학협력단 | 안면 운동 장치 |
| WO2015187712A1 (en) | 2014-06-02 | 2015-12-10 | Cala Health, Inc. | Systems and methods for peripheral nerve stimulation to treat tremor |
| US9616217B1 (en) * | 2014-09-17 | 2017-04-11 | Jay Pensler | Method of applying electrotherapy to facial muscles |
| CN104706517A (zh) * | 2015-03-31 | 2015-06-17 | 上海银狐医疗科技有限公司 | 一种一体化面瘫治疗箱 |
| US10751532B2 (en) | 2015-04-09 | 2020-08-25 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Nerve stimulation device for treating or reducing paralysis |
| US10010713B2 (en) * | 2015-04-09 | 2018-07-03 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Nerve stimulation device for treating or reducing paralysis |
| EP4342516A3 (en) | 2015-06-10 | 2024-07-10 | Cala Health, Inc. | Systems and methods for peripheral nerve stimulation to treat tremor with detachable therapy and monitoring units |
| US10603482B2 (en) | 2015-09-23 | 2020-03-31 | Cala Health, Inc. | Systems and methods for peripheral nerve stimulation in the finger or hand to treat hand tremors |
| CN108778411B (zh) | 2016-01-21 | 2022-06-03 | 卡拉健康公司 | 用来治疗与膀胱过动症相关的疾病的用于外周神经调制的系统、方法和装置 |
| CA3015079C (en) | 2016-03-09 | 2022-06-14 | Koc Universitesi | Electro-stimulation device effective in muscle location identification and therapeutic response enhancement |
| IL264116B2 (en) | 2016-07-08 | 2024-01-01 | Cala Health Inc | Systems and methods for stimulating n nerves with exactly n electrodes and improved dry electrodes |
| CN109803717B (zh) | 2016-08-25 | 2024-01-09 | 卡拉健康公司 | 通过周围神经刺激治疗心脏机能障碍的系统和方法 |
| RU2635483C1 (ru) * | 2016-08-29 | 2017-11-13 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение "Санкт-Петербургский научно-исследовательский институт уха, горла, носа и речи" Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации (ФГБУ "СПб НИИ ЛОР Минздрава России") | Способ хирургической санации инфралабиринтной-апикальной холестеатомы пирамиды височной кости |
| US11103665B2 (en) | 2016-11-09 | 2021-08-31 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Respiratory apparatus and method of operating the respiratory apparatus |
| CA3058786A1 (en) | 2017-04-03 | 2018-10-11 | Cala Health, Inc. | Systems, methods and devices for peripheral neuromodulation for treating diseases related to overactive bladder |
| US11141089B2 (en) | 2017-07-05 | 2021-10-12 | Yusuf Ozgur Cakmak | System for monitoring auditory startle response |
| US11298540B2 (en) | 2017-08-11 | 2022-04-12 | Inspire Medical Systems, Inc. | Cuff electrode |
| CN107468248A (zh) * | 2017-09-08 | 2017-12-15 | 刘冠宇 | 神经传导检测装置及检测方法 |
| EP3740274A4 (en) | 2018-01-17 | 2021-10-27 | Cala Health, Inc. | SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR TREATING INFLAMMATORY INTESTINAL DISEASE USING PERIPHERAL NERVE STIMULATION |
| EP3857342A4 (en) * | 2018-09-26 | 2021-12-01 | Facebook Technologies, LLC. | NEUROMUSCULAR CONTROL OF PHYSICAL OBJECTS IN AN ENVIRONMENT |
| JP7333900B2 (ja) * | 2018-11-07 | 2023-08-28 | 国立大学法人 岡山大学 | 電気刺激支援システム及び電気刺激支援方法 |
| CN110060758A (zh) * | 2019-04-11 | 2019-07-26 | 刘刚 | 一种面神经微创切除术在梅杰综合征中的应用系统 |
| RU2710794C1 (ru) * | 2019-04-26 | 2020-01-14 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "Альматек" | Способ тренировки спортсменов |
| RU2718574C1 (ru) * | 2019-04-26 | 2020-04-08 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "Альматек" | Способ тренировки при выполнении физических упражнений |
| RU2723287C1 (ru) * | 2019-04-26 | 2020-06-09 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "Альматек" | Способ тренировки оперативных сотрудников, работа которых сопряжена с физическими нагрузками и умением точно координировать движения членов своего тела |
| WO2020218944A1 (ru) * | 2019-04-26 | 2020-10-29 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "Альматек" | Способ тренировки при выполнении физических упражнений |
| US12251560B1 (en) | 2019-08-13 | 2025-03-18 | Cala Health, Inc. | Connection quality determination for wearable neurostimulation systems |
| US11890468B1 (en) | 2019-10-03 | 2024-02-06 | Cala Health, Inc. | Neurostimulation systems with event pattern detection and classification |
| RU2721456C1 (ru) * | 2019-10-18 | 2020-05-19 | Юлиана Владимировна Махнева | Тренажер для тренировки мышц лица (варианты) |
| KR102356607B1 (ko) * | 2019-11-29 | 2022-02-07 | (주)와이브레인 | 환자의 신경에 전기적인 자극을 가하여 신경을 조절하는 장치, 방법 및 프로그램 |
| CA3201692A1 (en) | 2020-12-08 | 2022-06-16 | Stoparkinson Healthcare Systems, Inc. | Electro-stimulation apparatus effective in auricular stimulation |
| WO2024064740A1 (en) * | 2022-09-21 | 2024-03-28 | Covidien Lp | Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation |
| CN115645744B (zh) * | 2022-11-01 | 2025-09-05 | 中国人民解放军总医院第六医学中心 | 一种电刺激控制系统 |
Family Cites Families (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3279468A (en) * | 1963-05-14 | 1966-10-18 | Vine Sidney Le | Electrotherapeutic facial mask apparatus |
| US3851651A (en) | 1972-12-22 | 1974-12-03 | P Icenbice | Facial stimulating apparatus having sequentially energized electrodes |
| FR2279376A1 (fr) * | 1974-07-26 | 1976-02-20 | Elbaz Jean | Procede de commande de la contraction d'un muscle du cote paralyse d'un visage atteint d'une paralysie faciale unilaterale et dispositifs pour la mise en oeuvre de ce procede |
| US4165750A (en) * | 1978-03-18 | 1979-08-28 | Aleev Leonid S | Bioelectrically controlled electric stimulator of human muscles |
| SU1500317A1 (ru) * | 1987-06-25 | 1989-08-15 | Научно-Исследовательский Институт Экспериментальной Медицины Амн Ссср | Способ восстановлени функций мимических мышц при нарушении анатомической целостности лицевого нерва |
| RU2008038C1 (ru) * | 1991-11-18 | 1994-02-28 | Акционерное общество закрытого типа "Сердолик" | Способ лечения парезов мимической мускулатуры при поражении периферических ветвей лицевого нерва |
| US5350414A (en) | 1991-12-10 | 1994-09-27 | Electro Science Technologies, Inc. | Local application microprocessor based nerve and muscle stimulator |
| US6233472B1 (en) * | 1995-06-06 | 2001-05-15 | Patient Comfort, L.L.C. | Electrode assembly and method for signaling a monitor |
| US5772605A (en) * | 1996-12-18 | 1998-06-30 | Medtronic, Inc. | System and method for detecting facial symmetry |
| US7403820B2 (en) * | 1998-08-05 | 2008-07-22 | Neurovista Corporation | Closed-loop feedback-driven neuromodulation |
| US6516227B1 (en) * | 1999-07-27 | 2003-02-04 | Advanced Bionics Corporation | Rechargeable spinal cord stimulator system |
| EP1372781A2 (en) | 2001-04-05 | 2004-01-02 | Med-El Elektromedizinische Geräte GmbH | Pacemaker for bilateral vocal cord autoparalysis |
| US6892098B2 (en) * | 2001-04-26 | 2005-05-10 | Biocontrol Medical Ltd. | Nerve stimulation for treating spasticity, tremor, muscle weakness, and other motor disorders |
| US20030045922A1 (en) * | 2001-08-29 | 2003-03-06 | Nancy Northrop | Skin treatment method and apparatus |
| US20030055468A1 (en) * | 2001-09-18 | 2003-03-20 | Michael Sachs | Bi-lateral cervico-facial stimulation system |
| US20070088335A1 (en) | 2001-10-24 | 2007-04-19 | Med-El Elektromedizinische Geraete Gmbh | Implantable neuro-stimulation electrode with fluid reservoir |
| JP2003339884A (ja) * | 2002-05-31 | 2003-12-02 | Fes:Kk | 顔面電気刺激装置 |
| US7769461B2 (en) * | 2003-12-19 | 2010-08-03 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Skull-mounted electrical stimulation system and method for treating patients |
| US7774068B1 (en) * | 2005-11-03 | 2010-08-10 | Lozano Andres M | System and method for treating movement disorders, including restless leg syndrome |
| WO2008028078A2 (en) | 2006-08-30 | 2008-03-06 | Med-El Elektromedizinische Geraete Gmbh | System, apparatus, and method for facilitating interface with laryngeal structures |
| US7890178B2 (en) * | 2006-12-15 | 2011-02-15 | Medtronic Xomed, Inc. | Method and apparatus for assisting deglutition |
| WO2008097407A2 (en) * | 2006-12-18 | 2008-08-14 | Trillium Precision Surgical, Inc. | Intraoperative tissue mapping and dissection systems, devices, methods, and kits |
| CA2741086C (en) | 2008-10-21 | 2016-11-22 | Med-El Elektromedizinische Geraete Gmbh | System and method for facial nerve stimulation |
-
2009
- 2009-10-21 CA CA2741086A patent/CA2741086C/en active Active
- 2009-10-21 KR KR1020117011578A patent/KR101708515B1/ko active Active
- 2009-10-21 EP EP17181237.3A patent/EP3266498B1/en active Active
- 2009-10-21 JP JP2011532345A patent/JP5687627B2/ja active Active
- 2009-10-21 EP EP09822609.5A patent/EP2349451B1/en active Active
- 2009-10-21 US US12/582,990 patent/US8792989B2/en active Active
- 2009-10-21 WO PCT/US2009/061441 patent/WO2010048261A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2009-10-21 AU AU2009307634A patent/AU2009307634B2/en active Active
- 2009-10-21 RU RU2011116044/14A patent/RU2511082C2/ru active
- 2009-10-21 CN CN200980141808.9A patent/CN102202725B/zh active Active
-
2014
- 2014-07-07 US US14/324,287 patent/US9155890B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| AU2009307634B2 (en) | 2013-02-07 |
| US9155890B2 (en) | 2015-10-13 |
| CA2741086A1 (en) | 2010-04-29 |
| CA2741086C (en) | 2016-11-22 |
| CN102202725B (zh) | 2016-06-01 |
| EP3266498A1 (en) | 2018-01-10 |
| US8792989B2 (en) | 2014-07-29 |
| EP2349451B1 (en) | 2017-08-16 |
| AU2009307634A1 (en) | 2010-04-29 |
| CN102202725A (zh) | 2011-09-28 |
| US20100114240A1 (en) | 2010-05-06 |
| EP2349451A1 (en) | 2011-08-03 |
| JP2012506262A (ja) | 2012-03-15 |
| KR20110075027A (ko) | 2011-07-05 |
| WO2010048261A1 (en) | 2010-04-29 |
| KR101708515B1 (ko) | 2017-02-20 |
| RU2011116044A (ru) | 2012-11-27 |
| RU2511082C2 (ru) | 2014-04-10 |
| US20140324121A1 (en) | 2014-10-30 |
| JP5687627B2 (ja) | 2015-03-18 |
| EP2349451A4 (en) | 2012-05-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3266498B1 (en) | System and method for facial nerve stimulation | |
| US9162059B1 (en) | Method for facial nerve stimulation of aging or dysfunctional muscles | |
| Overstreet et al. | Fascicle specific targeting for selective peripheral nerve stimulation | |
| WO2020041633A1 (en) | Non-invasive spinal cord stimulation for nerve root palsy, cauda equina syndrome, and restoration of upper extremity function | |
| US20090105786A1 (en) | Method and device for strengthening synaptic connections | |
| US8065014B2 (en) | Method for promoting selective reinnervation of denervated tissue | |
| JP2007524463A (ja) | 患者の神経機能における持続的変化を実現するための方法および装置 | |
| KR20090101901A (ko) | 말의 기도 장애 | |
| EP3934742B1 (en) | Electrical apparatus for an eye | |
| Moore et al. | The effects of chronic intracochlear electrical stimulation on inferior colliculus spatial representation in adult deafened cats | |
| King et al. | A physiological and behavioral system for hearing restoration with cochlear implants | |
| US10010713B2 (en) | Nerve stimulation device for treating or reducing paralysis | |
| US10751532B2 (en) | Nerve stimulation device for treating or reducing paralysis | |
| Clark | A hearing prosthesis for serve perceptive Deafness—Experimental studies | |
| AU2015203522B2 (en) | System and Method for Facial Nerve Stimulation | |
| AU2013205733B2 (en) | System and method for facial nerve stimulation | |
| Askari et al. | Closed loop microfabricated facial reanimation device coupling EMG-Driven facial nerve stimulation with a chronically implanted multichannel cuff electrode | |
| Shahdoost et al. | A brain-spinal interface (BSI) system-on-chip (SoC) for closed-loop cortically-controlled intraspinal microstimulation | |
| US20250135201A1 (en) | Selective neurostimulation of peripheral nerves with reduced off-target activation | |
| Jia et al. | Improved long‐term recording of nerve signal by modified intrafascicular electrodes in rabbits | |
| Jowett et al. | THE BIONIC FACE: A NOVEL NEUROPROSTHETIC DEVICE PARADIGM FOR FACIAL REANIMATION COMPRISING NEURAL BLOCKADE AND FUNCTIONAL ELECTRICAL STIMULATION | |
| NE et al. | WO03/000338A2| | |
| Wark | Expanding the applications of Utah Arrays: A neural interface for smaller nerves, the control of urination and prosthetic limbs | |
| Zimmermann | Cortical control of intraspinal microstimulation to restore motor function after paralysis | |
| Branner | Studies on the feasibility of a penetrating microelectrode array as a peripheral nerve interface |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN PUBLISHED |
|
| AC | Divisional application: reference to earlier application |
Ref document number: 2349451 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20180709 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20201027 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20231023 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20231218 |
|
| GRAJ | Information related to disapproval of communication of intention to grant by the applicant or resumption of examination proceedings by the epo deleted |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSDIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20240315 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AC | Divisional application: reference to earlier application |
Ref document number: 2349451 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602009065331 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG9D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20240807 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20241029 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20241107 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 1710285 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20240807 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20241209 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20241108 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20241029 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20241207 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20241031 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20241209 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20241107 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20241207 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20241108 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602009065331 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20241021 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20241031 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20250508 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20241031 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20241031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240807 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20241021 |