EP3103649B2 - Wärmeempfindliches aufzeichnungsmedium - Google Patents
Wärmeempfindliches aufzeichnungsmedium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3103649B2 EP3103649B2 EP15766003.6A EP15766003A EP3103649B2 EP 3103649 B2 EP3103649 B2 EP 3103649B2 EP 15766003 A EP15766003 A EP 15766003A EP 3103649 B2 EP3103649 B2 EP 3103649B2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- thermosensitive recording
- undercoat layer
- water
- recording medium
- fluorane
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L Calcium carbonate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=O VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 63
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 57
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims description 57
- 229920002451 polyvinyl alcohol Polymers 0.000 claims description 43
- 235000019422 polyvinyl alcohol Nutrition 0.000 claims description 43
- 229940088417 precipitated calcium carbonate Drugs 0.000 claims description 35
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 claims description 29
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 claims description 26
- 239000000049 pigment Substances 0.000 claims description 25
- 229920003048 styrene butadiene rubber Polymers 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 claims description 17
- 239000011163 secondary particle Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000002174 Styrene-butadiene Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000011164 primary particle Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- MTAZNLWOLGHBHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N butadiene-styrene rubber Chemical compound C=CC=C.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 MTAZNLWOLGHBHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000011115 styrene butadiene Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 103
- 229910000040 hydrogen fluoride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 57
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 56
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 55
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 50
- 239000004372 Polyvinyl alcohol Substances 0.000 description 38
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorane Chemical class F KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 30
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 26
- 239000000975 dye Substances 0.000 description 25
- 238000002845 discoloration Methods 0.000 description 18
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 16
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 16
- 239000004816 latex Substances 0.000 description 14
- 229920000126 latex Polymers 0.000 description 14
- QWQJPPOEEGYTIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-fluoro-1-phenylhydrazine Chemical compound NN(F)C1=CC=CC=C1 QWQJPPOEEGYTIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- KZTYYGOKRVBIMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N S-phenyl benzenesulfonothioate Natural products C=1C=CC=CC=1S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 KZTYYGOKRVBIMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 11
- -1 for example Chemical compound 0.000 description 11
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 10
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 10
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 9
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 239000004927 clay Substances 0.000 description 8
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 8
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 description 8
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 7
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 6
- 229920002401 polyacrylamide Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 229920000768 polyamine Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000011247 coating layer Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 5
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000011241 protective layer Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920001281 polyalkylene Polymers 0.000 description 4
- YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N salicylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1O YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000004576 sand Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920000178 Acrylic resin Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004925 Acrylic resin Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000005995 Aluminium silicate Substances 0.000 description 3
- KAKZBPTYRLMSJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butadiene Chemical group C=CC=C KAKZBPTYRLMSJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methacrylic acid Chemical compound CC(=C)C(O)=O CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229920001328 Polyvinylidene chloride Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920002125 Sokalan® Polymers 0.000 description 3
- XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Urea Natural products NC(N)=O XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- YKTSYUJCYHOUJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N [O--].[Al+3].[Al+3].[O-][Si]([O-])([O-])[O-] Chemical compound [O--].[Al+3].[Al+3].[O-][Si]([O-])([O-])[O-] YKTSYUJCYHOUJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000008186 active pharmaceutical agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K aluminium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[OH-].[OH-].[Al+3] WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 3
- 235000012211 aluminium silicate Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 3
- NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N kaolin Chemical compound O.O.O=[Al]O[Si](=O)O[Si](=O)O[Al]=O NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 150000002576 ketones Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000013508 migration Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000005012 migration Effects 0.000 description 3
- 150000002989 phenols Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000004584 polyacrylic acid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920002239 polyacrylonitrile Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920006122 polyamide resin Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920002689 polyvinyl acetate Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000011118 polyvinyl acetate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920000915 polyvinyl chloride Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004800 polyvinyl chloride Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000005033 polyvinylidene chloride Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920002050 silicone resin Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000001993 wax Substances 0.000 description 3
- LNAZSHAWQACDHT-XIYTZBAFSA-N (2r,3r,4s,5r,6s)-4,5-dimethoxy-2-(methoxymethyl)-3-[(2s,3r,4s,5r,6r)-3,4,5-trimethoxy-6-(methoxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-6-[(2r,3r,4s,5r,6r)-4,5,6-trimethoxy-2-(methoxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxyoxane Chemical compound CO[C@@H]1[C@@H](OC)[C@H](OC)[C@@H](COC)O[C@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](OC)[C@@H](OC)[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](OC)[C@H](OC)O[C@@H]2COC)OC)O[C@@H]1COC LNAZSHAWQACDHT-XIYTZBAFSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IANQTJSKSUMEQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-benzofuran Chemical compound C1=CC=C2OC=CC2=C1 IANQTJSKSUMEQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OPQSLUUXOWKRPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[4-[4-[4-(4-propan-2-yloxyphenyl)sulfonylphenoxy]butoxy]phenyl]sulfonylphenol Chemical compound C1=CC(OC(C)C)=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)C(C=C1)=CC=C1OCCCCOC1=CC=C(S(=O)(=O)C=2C=CC(O)=CC=2)C=C1 OPQSLUUXOWKRPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XQXPVVBIMDBYFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 XQXPVVBIMDBYFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920002134 Carboxymethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 2
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001856 Ethyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 2
- ZZSNKZQZMQGXPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl cellulose Chemical compound CCOCC1OC(OC)C(OCC)C(OCC)C1OC1C(O)C(O)C(OC)C(CO)O1 ZZSNKZQZMQGXPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Formaldehyde Chemical compound O=C WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N Fumaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C\C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920000663 Hydroxyethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004354 Hydroxyethyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 2
- TWRXJAOTZQYOKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L Magnesium chloride Chemical compound [Mg+2].[Cl-].[Cl-] TWRXJAOTZQYOKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 239000004368 Modified starch Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000881 Modified starch Polymers 0.000 description 2
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1 ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004793 Polystyrene Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920002396 Polyurea Polymers 0.000 description 2
- PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Styrene Chemical compound C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titan oxide Chemical compound O=[Ti]=O GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920001807 Urea-formaldehyde Polymers 0.000 description 2
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XLOMVQKBTHCTTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc monoxide Chemical compound [Zn]=O XLOMVQKBTHCTTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SMEGJBVQLJJKKX-HOTMZDKISA-N [(2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-5-acetyloxy-3,4,6-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]methyl acetate Chemical compound CC(=O)OC[C@@H]1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H](O1)O)OC(=O)C)O)O SMEGJBVQLJJKKX-HOTMZDKISA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229940081735 acetylcellulose Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000001336 alkenes Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- ROOXNKNUYICQNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N ammonium persulfate Chemical compound [NH4+].[NH4+].[O-]S(=O)(=O)OOS([O-])(=O)=O ROOXNKNUYICQNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910000019 calcium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000378 calcium silicate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052918 calcium silicate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- OYACROKNLOSFPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N calcium;dioxido(oxo)silane Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-][Si]([O-])=O OYACROKNLOSFPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001768 carboxy methyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010948 carboxy methyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000008112 carboxymethyl-cellulose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000002091 cationic group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 229920002301 cellulose acetate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920003086 cellulose ether Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003431 cross linking reagent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920001249 ethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 235000019325 ethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- NIHNNTQXNPWCJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluorene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2CC3=CC=CC=C3C2=C1 NIHNNTQXNPWCJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004088 foaming agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- LEQAOMBKQFMDFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N glyoxal Chemical compound O=CC=O LEQAOMBKQFMDFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000019447 hydroxyethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000004615 ingredient Substances 0.000 description 2
- ZLNQQNXFFQJAID-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium carbonate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[O-]C([O-])=O ZLNQQNXFFQJAID-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 239000001095 magnesium carbonate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910000021 magnesium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- HCWCAKKEBCNQJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N magnesium orthosilicate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[Mg+2].[O-][Si]([O-])([O-])[O-] HCWCAKKEBCNQJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000391 magnesium silicate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052919 magnesium silicate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 235000019792 magnesium silicate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229920000609 methyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000001923 methylcellulose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010981 methylcellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 235000019426 modified starch Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- JRZJOMJEPLMPRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N olefin Natural products CCCCCCCC=C JRZJOMJEPLMPRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001254 oxidized starch Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000013808 oxidized starch Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Al]O[Al]=O TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N papa-hydroxy-benzoic acid Natural products OC(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003208 petroleum Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920005672 polyolefin resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920002223 polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920005749 polyurethane resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000002243 precursor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229960004889 salicylic acid Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000003505 terpenes Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 235000007586 terpenes Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229920005992 thermoplastic resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N titanium oxide Inorganic materials [Ti]=O OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-butenedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=CC(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- BIQGQLXQLYTHRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2-phenylnaphthalen-1-yl) hydrogen carbonate Chemical compound C1=CC2=CC=CC=C2C(OC(=O)O)=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 BIQGQLXQLYTHRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LIZLYZVAYZQVPG-UHFFFAOYSA-N (3-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)methanol Chemical compound OCC1=CC=CC(Br)=C1F LIZLYZVAYZQVPG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JZLWSRCQCPAUDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine;urea Chemical compound NC(N)=O.NC1=NC(N)=NC(N)=N1 JZLWSRCQCPAUDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YJTKZCDBKVTVBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-Diphenylbenzene Chemical group C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC(C=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 YJTKZCDBKVTVBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LJSLYKNKVQMIJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-diethoxynaphthalene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(OCC)=CC=C(OCC)C2=C1 LJSLYKNKVQMIJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AGPLQTQFIZBOLI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-benzyl-4-phenylbenzene Chemical group C=1C=C(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=CC=1CC1=CC=CC=C1 AGPLQTQFIZBOLI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NNORAMKREOSIBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methyl-3-[(4-phenylphenyl)methoxy]benzene Chemical group CC1=CC=CC(OCC=2C=CC(=CC=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 NNORAMKREOSIBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OAGNKYSIOSDNIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methyl-3-[2-(3-methylphenoxy)ethoxy]benzene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC(OCCOC=2C=C(C)C=CC=2)=C1 OAGNKYSIOSDNIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XAAILNNJDMIMON-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2'-anilino-6'-(dibutylamino)-3'-methylspiro[2-benzofuran-3,9'-xanthene]-1-one Chemical compound C=1C(N(CCCC)CCCC)=CC=C(C2(C3=CC=CC=C3C(=O)O2)C2=C3)C=1OC2=CC(C)=C3NC1=CC=CC=C1 XAAILNNJDMIMON-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HUOKHAMXPNSWBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2'-chloro-6'-(diethylamino)-3'-methylspiro[2-benzofuran-3,9'-xanthene]-1-one Chemical compound O1C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2C21C1=CC(Cl)=C(C)C=C1OC1=CC(N(CC)CC)=CC=C21 HUOKHAMXPNSWBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LCPVQAHEFVXVKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2,4-difluorophenoxy)pyridin-3-amine Chemical compound NC1=CC=CN=C1OC1=CC=C(F)C=C1F LCPVQAHEFVXVKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JAHNSTQSQJOJLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(3-fluorophenyl)-1h-imidazole Chemical compound FC1=CC=CC(C=2NC=CN=2)=C1 JAHNSTQSQJOJLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JHOPNNNTBHXSHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)phenol Chemical group C1=CC(O)=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1O JHOPNNNTBHXSHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WQYFETFRIRDUPJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[2-hydroxy-5-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenyl]sulfanyl-4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenol Chemical compound CC(C)(C)CC(C)(C)C1=CC=C(O)C(SC=2C(=CC=C(C=2)C(C)(C)CC(C)(C)C)O)=C1 WQYFETFRIRDUPJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- APOJPPIKGSIVIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[2-hydroxy-6-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenyl]sulfanyl-3-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenol Chemical compound CC(C)(C)CC(C)(C)C1=CC=CC(O)=C1SC1=C(O)C=CC=C1C(C)(C)CC(C)(C)C APOJPPIKGSIVIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YAZSBRQTAHVVGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-aminobenzenesulfonamide Chemical class NC1=CC=CC=C1S(N)(=O)=O YAZSBRQTAHVVGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QKJAZPHKNWSXDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-bromoquinoline Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=NC(Br)=CC=C21 QKJAZPHKNWSXDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MDTCOHCLYIIHEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-hydroxy-4-[2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)ethoxy]benzoic acid Chemical compound C1=CC(OC)=CC=C1OCCOC1=CC=C(C(O)=O)C(O)=C1 MDTCOHCLYIIHEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GXSBLOWJMZJYPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-hydroxybenzoic acid;dihydrate Chemical compound O.O.OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1O GXSBLOWJMZJYPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YCMLQMDWSXFTIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylbenzenesulfonimidic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1S(N)(=O)=O YCMLQMDWSXFTIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XCSGHNKDXGYELG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-phenoxyethoxybenzene Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1OCCOC1=CC=CC=C1 XCSGHNKDXGYELG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WLTCCDHHWYAMCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-phenylmethoxynaphthalene Chemical compound C=1C=C2C=CC=CC2=CC=1OCC1=CC=CC=C1 WLTCCDHHWYAMCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WXWMNIHSZVPJOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-tert-butyl-4-(5-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-2-methylphenyl)sulfonyl-5-methylphenol Chemical compound CC1=CC(O)=C(C(C)(C)C)C=C1S(=O)(=O)C1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C=C1C WXWMNIHSZVPJOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XOUQAVYLRNOXDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-tert-butyl-5-methylphenol Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(C(C)(C)C)C(O)=C1 XOUQAVYLRNOXDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZMYXVVLVLCQKQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3',6,6'-tris(diethylamino)spiro[2-benzofuran-3,9'-fluorene]-1-one Chemical compound C12=CC=C(N(CC)CC)C=C2C2=CC(N(CC)CC)=CC=C2C21OC(=O)C1=CC(N(CC)CC)=CC=C21 ZMYXVVLVLCQKQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CONFUNYOPVYVDC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,3-bis(1-ethyl-2-methylindol-3-yl)-2-benzofuran-1-one Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(C3(C4=CC=CC=C4C(=O)O3)C3=C(C)N(C4=CC=CC=C43)CC)=C(C)N(CC)C2=C1 CONFUNYOPVYVDC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ABJAMKKUHBSXDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,3-bis(6-amino-1,4-dimethylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-yl)-2-benzofuran-1-one Chemical compound C1=CC(C)=CC(N)C1(C)C1(C2(C)C(C=C(C)C=C2)N)C2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)O1 ABJAMKKUHBSXDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PYSRRFNXTXNWCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(2-phenylethenyl)furan-2,5-dione Chemical compound O=C1OC(=O)C(C=CC=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 PYSRRFNXTXNWCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MTMKZABGIQJAEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4'-sulfonylbis[2-(prop-2-en-1-yl)phenol] Chemical compound C1=C(CC=C)C(O)=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C(CC=C)=C1 MTMKZABGIQJAEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VPWNQTHUCYMVMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4'-sulfonyldiphenol Chemical compound C1=CC(O)=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 VPWNQTHUCYMVMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VWGKEVWFBOUAND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4'-thiodiphenol Chemical compound C1=CC(O)=CC=C1SC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 VWGKEVWFBOUAND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QWBBYMMSNINPNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-3,3-bis[2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethenyl]-2-benzofuran-1-one Chemical compound C1=CC(OC)=CC=C1C(C=1C=CC(=CC=1)N(C)C)=CC1(C=C(C=2C=CC(OC)=CC=2)C=2C=CC(=CC=2)N(C)C)C(C(Br)=C(Br)C(Br)=C2Br)=C2C(=O)O1 QWBBYMMSNINPNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VJPFNMREYDOHSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-3h-2-benzofuran-1-one Chemical compound BrC1=C(Br)C(Br)=C2COC(=O)C2=C1Br VJPFNMREYDOHSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NYMQRLJHQHVCAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,5,6,7-tetrachloro-3,3-bis[2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethenyl]-2-benzofuran-1-one Chemical compound C1=CC(OC)=CC=C1C(C=1C=CC(=CC=1)N(C)C)=CC1(C=C(C=2C=CC(OC)=CC=2)C=2C=CC(=CC=2)N(C)C)C(C(Cl)=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C2Cl)=C2C(=O)O1 NYMQRLJHQHVCAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IBNFPRMKLZDANU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(4-hydroxy-3-methylphenyl)sulfanyl-2-methylphenol Chemical compound C1=C(O)C(C)=CC(SC=2C=C(C)C(O)=CC=2)=C1 IBNFPRMKLZDANU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VHLLJTHDWPAQEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-yl]phenol Chemical compound C=1C=C(O)C=CC=1C(C)(CC(C)C)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 VHLLJTHDWPAQEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NOMXFWAANLCUKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[2-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)sulfanylethoxy]ethylsulfanyl]phenol Chemical compound C1=CC(O)=CC=C1SCCOCCSC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 NOMXFWAANLCUKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QBZPUSKHVURBGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[2-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)sulfanylethoxymethoxy]ethylsulfanyl]phenol Chemical compound C1=CC(O)=CC=C1SCCOCOCCSC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 QBZPUSKHVURBGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PRMDDINQJXOMDC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[4,4-bis(5-cyclohexyl-4-hydroxy-2-methylphenyl)butan-2-yl]-2-cyclohexyl-5-methylphenol Chemical compound C=1C(C2CCCCC2)=C(O)C=C(C)C=1C(C)CC(C=1C(=CC(O)=C(C2CCCCC2)C=1)C)C(C(=CC=1O)C)=CC=1C1CCCCC1 PRMDDINQJXOMDC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PRWJPWSKLXYEPD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[4,4-bis(5-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-2-methylphenyl)butan-2-yl]-2-tert-butyl-5-methylphenol Chemical compound C=1C(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C=C(C)C=1C(C)CC(C=1C(=CC(O)=C(C=1)C(C)(C)C)C)C1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C=C1C PRWJPWSKLXYEPD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XRHGYUZYPHTUJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-chlorobenzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 XRHGYUZYPHTUJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GOUHYARYYWKXHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-formylbenzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=O)C=C1 GOUHYARYYWKXHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SHTDEQRFYNZCOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-n,6-n-diethyl-2-n-fluoro-3-methyl-2-n-phenyloctane-2,6-diamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)C(CC)CCC(C)C(C)N(F)C1=CC=CC=C1 SHTDEQRFYNZCOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AJWUMVPXWNNESR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-n,6-n-diethyl-2-n-fluoro-3-methyloctane-2,6-diamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)C(CC)CCC(C)C(C)NF AJWUMVPXWNNESR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UFPJLFNADVHTGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-[4-(2-cyclohexylethylamino)-2-methoxyphenyl]-7-(1-ethyl-2-methylindol-3-yl)furo[3,4-b]pyridin-5-one Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2N(CC)C(C)=C1C1(C2=NC=CC=C2C(=O)O1)C(C(=C1)OC)=CC=C1NCCC1CCCCC1 UFPJLFNADVHTGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RCVMSMLWRJESQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-[4-(diethylamino)-2-ethoxyphenyl]-7-(1-ethyl-2-methylindol-3-yl)furo[3,4-b]pyridin-5-one Chemical compound CCOC1=CC(N(CC)CC)=CC=C1C1(C=2C3=CC=CC=C3N(CC)C=2C)C2=NC=CC=C2C(=O)O1 RCVMSMLWRJESQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NLCOOYIZLNQIQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-[4-(diethylamino)-2-ethoxyphenyl]-7-(2-methyl-1-octylindol-3-yl)furo[3,4-b]pyridin-5-one Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2N(CCCCCCCC)C(C)=C1C1(C2=NC=CC=C2C(=O)O1)C1=CC=C(N(CC)CC)C=C1OCC NLCOOYIZLNQIQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NLHHRLWOUZZQLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acrylonitrile Chemical compound C=CC#N NLHHRLWOUZZQLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WZUKKIPWIPZMAS-UHFFFAOYSA-K Ammonium alum Chemical compound [NH4+].O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.[Al+3].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O.[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O WZUKKIPWIPZMAS-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonium chloride Substances [NH4+].[Cl-] NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MOZDKDIOPSPTBH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzyl parahydroxybenzoate Chemical compound C1=CC(O)=CC=C1C(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 MOZDKDIOPSPTBH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VOWWYDCFAISREI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bisphenol AP Chemical compound C=1C=C(O)C=CC=1C(C=1C=CC(O)=CC=1)(C)C1=CC=CC=C1 VOWWYDCFAISREI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SDDLEVPIDBLVHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bisphenol Z Chemical compound C1=CC(O)=CC=C1C1(C=2C=CC(O)=CC=2)CCCCC1 SDDLEVPIDBLVHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BTBUEUYNUDRHOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Borate Chemical compound [O-]B([O-])[O-] BTBUEUYNUDRHOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000014036 Castanea Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 241001070941 Castanea Species 0.000 description 1
- IPAJDLMMTVZVPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Crystal violet lactone Chemical compound C1=CC(N(C)C)=CC=C1C1(C=2C=CC(=CC=2)N(C)C)C2=CC=C(N(C)C)C=C2C(=O)O1 IPAJDLMMTVZVPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002085 Dialdehyde starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 1
- BRLQWZUYTZBJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Epichlorohydrin Chemical compound ClCC1CO1 BRLQWZUYTZBJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethene Chemical compound C=C VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005977 Ethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000084 Gum arabic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001612 Hydroxyethyl starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910021578 Iron(III) chloride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000877 Melamine resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000459 Nitrile rubber Polymers 0.000 description 1
- MXRIRQGCELJRSN-UHFFFAOYSA-N O.O.O.[Al] Chemical compound O.O.O.[Al] MXRIRQGCELJRSN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005062 Polybutadiene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004721 Polyphenylene oxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propanedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)CC(O)=O OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000978776 Senegalia senegal Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920000147 Styrene maleic anhydride Polymers 0.000 description 1
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000007983 Tris buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002433 Vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- MBHRHUJRKGNOKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N [(4,6-diamino-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]methanol Chemical compound NC1=NC(N)=NC(NCO)=N1 MBHRHUJRKGNOKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000205 acacia gum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010489 acacia gum Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920006243 acrylic copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000012190 activator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000001931 aliphatic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UMGDCJDMYOKAJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N aminothiocarboxamide Natural products NC(N)=S UMGDCJDMYOKAJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000019270 ammonium chloride Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910001870 ammonium persulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000002490 anilino group Chemical group [H]N(*)C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000000129 anionic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000003078 antioxidant effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- VEQOALNAAJBPNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N antipyrine Chemical class CN1C(C)=CC(=O)N1C1=CC=CC=C1 VEQOALNAAJBPNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960000892 attapulgite Drugs 0.000 description 1
- RWCCWEUUXYIKHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzophenone Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 RWCCWEUUXYIKHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000012965 benzophenone Substances 0.000 description 1
- BDDYZHKLKHFEBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoyloxymethyl benzoate Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1C(=O)OCOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 BDDYZHKLKHFEBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KZRMDZPUXBGINF-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl 4-[2-(4-phenylmethoxycarbonylphenoxy)ethoxy]benzoate Chemical compound C=1C=C(OCCOC=2C=CC(=CC=2)C(=O)OCC=2C=CC=CC=2)C=CC=1C(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 KZRMDZPUXBGINF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BPLKDVGMXNZCQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl 4-phenylmethoxybenzoate Chemical compound C=1C=C(OCC=2C=CC=CC=2)C=CC=1C(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 BPLKDVGMXNZCQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IZJIAOFBVVYSMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N bis(4-methylphenyl) carbonate Chemical compound C1=CC(C)=CC=C1OC(=O)OC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 IZJIAOFBVVYSMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QWHCTYYBLDCYIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N bis[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl] oxalate Chemical compound C1=CC(Cl)=CC=C1COC(=O)C(=O)OCC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 QWHCTYYBLDCYIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FPFZBTUMXCSRLU-UHFFFAOYSA-N bis[(4-methylphenyl)methyl] oxalate Chemical compound C1=CC(C)=CC=C1COC(=O)C(=O)OCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 FPFZBTUMXCSRLU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IISBACLAFKSPIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N bisphenol A Chemical compound C=1C=C(O)C=CC=1C(C)(C)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 IISBACLAFKSPIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N boric acid Chemical compound OB(O)O KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004327 boric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000000484 butyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- QHIWVLPBUQWDMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl prop-2-enoate;methyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate;prop-2-enoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C=C.COC(=O)C(C)=C.CCCCOC(=O)C=C QHIWVLPBUQWDMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- CJZGTCYPCWQAJB-UHFFFAOYSA-L calcium stearate Chemical compound [Ca+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O CJZGTCYPCWQAJB-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 239000008116 calcium stearate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013539 calcium stearate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000003490 calendering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004202 carbamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001732 carboxylic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000005018 casein Substances 0.000 description 1
- BECPQYXYKAMYBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N casein, tech. Chemical compound NCCCCC(C(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(CC(C)C)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(C(C)O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(COP(O)(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(N)CC1=CC=CC=C1 BECPQYXYKAMYBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000021240 caseins Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920002678 cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000001913 cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000013522 chelant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052570 clay Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920006026 co-polymeric resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000008119 colloidal silica Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004040 coloring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 125000002147 dimethylamino group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])N(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004945 emulsification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001804 emulsifying effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010419 fine particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003983 fluorenyl group Chemical class C1(=CC=CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3CC12)* 0.000 description 1
- 239000007850 fluorescent dye Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005755 formation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000001530 fumaric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940015043 glyoxal Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 1
- HSEMFIZWXHQJAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexadecanamide Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(N)=O HSEMFIZWXHQJAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940050526 hydroxyethylstarch Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000001023 inorganic pigment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920000554 ionomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- RBTARNINKXHZNM-UHFFFAOYSA-K iron trichloride Chemical compound Cl[Fe](Cl)Cl RBTARNINKXHZNM-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 230000001788 irregular Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000031700 light absorption Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000670 limiting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910001629 magnesium chloride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- VTHJTEIRLNZDEV-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium dihydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[OH-].[Mg+2] VTHJTEIRLNZDEV-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 239000000347 magnesium hydroxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001862 magnesium hydroxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229940107698 malachite green Drugs 0.000 description 1
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N maleic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C/C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011976 maleic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- WPBNNNQJVZRUHP-UHFFFAOYSA-L manganese(2+);methyl n-[[2-(methoxycarbonylcarbamothioylamino)phenyl]carbamothioyl]carbamate;n-[2-(sulfidocarbothioylamino)ethyl]carbamodithioate Chemical compound [Mn+2].[S-]C(=S)NCCNC([S-])=S.COC(=O)NC(=S)NC1=CC=CC=C1NC(=S)NC(=O)OC WPBNNNQJVZRUHP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- LVHBHZANLOWSRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N methylenebutanedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)CC(=C)C(O)=O LVHBHZANLOWSRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- VYQNWZOUAUKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N monobenzone Chemical compound C1=CC(O)=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC=C1 VYQNWZOUAUKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960000990 monobenzone Drugs 0.000 description 1
- RQAQWBFHPMSXKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(phosphonooxy)naphthalene-2-carboxamide Chemical compound OP(O)(=O)OC1=CC2=CC=CC=C2C=C1C(=O)NC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 RQAQWBFHPMSXKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FTQWRYSLUYAIRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[(octadecanoylamino)methyl]octadecanamide Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)NCNC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC FTQWRYSLUYAIRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- LYRFLYHAGKPMFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanamide Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(N)=O LYRFLYHAGKPMFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BRNPAEUKZMBRLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecyl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCOC(=O)C1=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1 BRNPAEUKZMBRLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052625 palygorskite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- QHDYIMWKSCJTIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenyl 1-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxylate Chemical compound C1=CC2=CC=CC=C2C(O)=C1C(=O)OC1=CC=CC=C1 QHDYIMWKSCJTIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KZQFPRKQBWRRHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate Chemical compound C1=CC(C)=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)OC1=CC=CC=C1 KZQFPRKQBWRRHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002985 plastic film Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006255 plastic film Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004014 plasticizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002037 poly(vinyl butyral) polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002857 polybutadiene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000570 polyether Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 description 1
- USHAGKDGDHPEEY-UHFFFAOYSA-L potassium persulfate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[O-]S(=O)(=O)OOS([O-])(=O)=O USHAGKDGDHPEEY-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 239000003755 preservative agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002335 preservative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000002572 propoxy group Chemical group [*]OC([H])([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 238000001454 recorded image Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- CHQMHPLRPQMAMX-UHFFFAOYSA-L sodium persulfate Substances [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S(=O)(=O)OOS([O-])(=O)=O CHQMHPLRPQMAMX-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 125000003003 spiro group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003457 sulfones Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000010998 test method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920002803 thermoplastic polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002562 thickening agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003585 thioureas Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052718 tin Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011135 tin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- LMYRWZFENFIFIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene-4-sulfonamide Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(N)(=O)=O)C=C1 LMYRWZFENFIFIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000003852 triazoles Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- AAAQKTZKLRYKHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N triphenylmethane Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 AAAQKTZKLRYKHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004961 triphenylmethanes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003751 zinc Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000011787 zinc oxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- XOOUIPVCVHRTMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L zinc stearate Chemical compound [Zn+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O XOOUIPVCVHRTMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- MLVWCBYTEFCFSG-UHFFFAOYSA-L zinc;dithiocyanate Chemical compound [Zn+2].[S-]C#N.[S-]C#N MLVWCBYTEFCFSG-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41M—PRINTING, DUPLICATING, MARKING, OR COPYING PROCESSES; COLOUR PRINTING
- B41M5/00—Duplicating or marking methods; Sheet materials for use therein
- B41M5/26—Thermography ; Marking by high energetic means, e.g. laser otherwise than by burning, and characterised by the material used
- B41M5/40—Thermography ; Marking by high energetic means, e.g. laser otherwise than by burning, and characterised by the material used characterised by the base backcoat, intermediate, or covering layers, e.g. for thermal transfer dye-donor or dye-receiver sheets; Heat, radiation filtering or absorbing means or layers; combined with other image registration layers or compositions; Special originals for reproduction by thermography
- B41M5/42—Intermediate, backcoat, or covering layers
- B41M5/426—Intermediate, backcoat, or covering layers characterised by inorganic compounds, e.g. metals, metal salts, metal complexes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41M—PRINTING, DUPLICATING, MARKING, OR COPYING PROCESSES; COLOUR PRINTING
- B41M2205/00—Printing methods or features related to printing methods; Location or type of the layers
- B41M2205/04—Direct thermal recording [DTR]
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41M—PRINTING, DUPLICATING, MARKING, OR COPYING PROCESSES; COLOUR PRINTING
- B41M2205/00—Printing methods or features related to printing methods; Location or type of the layers
- B41M2205/38—Intermediate layers; Layers between substrate and imaging layer
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a thermosensitive recording medium for recording image by utilizing a color formation reaction between a colorless or pale colored electron donating leuco dye (henceforth referred to as “leuco dye”) and an electron accepting color developing agent (henceforth referred to as “color developing agent”), which has an excellent heat discoloration resistance, especially an excellent heat discoloration resistance in the blank portions.
- leuco dye colorless or pale colored electron donating leuco dye
- color developing agent electron accepting color developing agent
- Thermosensitive recording media are ordinarily prepared by mixing together a colorless or pale-colored leuco dye and a color developing agent, such as a phenolic compound and the like, after grinding them into fine particles, preparing a coating solution by adding a binder, a filler, a sensitivity enhancing agent, a slipping agent and other aids to the mixture and applying the coating solution onto a substrate such as paper, synthetic paper, film, plastic and the like.
- Thermosensitive recording media are widely used as various recording media.
- thermosensitive recording media are used extensively in recording media such as facsimile devices, computer terminal printers, automatic ticket dispensers, recorders for meters, receipts at super markets and convenience stores and the like. Furthermore the use of thermosensitive recording media is expanding, such as its use for various ticket, receipts, labels, ATM of Bank, meter reading of gas and electricity, cash vouchers, such as car racing or horseracing betting.
- the storage stability of the image portion and the blank portion has been required in more severe conditions, for example, in a high temperature condition in a car in midsummer.
- the color developing agent and the leuco dye and the configuration of the protective layer have been studied (see References 1-3).
- thermosensitive recording layer which contains inorganic pigments or plastic particles (see References 4,5, etc.).
- the color developing agent and the leuco dye and the composition of the protective layer have, conventionally, been mainly studied in order to improve the heat discoloration resistance, especially the heat discoloration resistance in the blank portions of the thermosensitive recording medium, as described above (References 1-3), while the present inventors have examined the composition of the undercoat layer in the structure having an undercoat layer between the support and the thermosensitive recording layer, in order to improve the heat discoloration resistance.
- the objective of the present invention is to provide a thermosensitive recording medium having an excellent heat discoloration resistance, especially an excellent heat discoloration resistance in the blank portions.
- the inventors have discovered that the heat discoloration resistance of a thermosensitive recording medium, especially the heat discoloration resistance in the blank portions, can be improved by installing an undercoat layer between the support and the thermosensitive recording layer, incorporating a precipitated calcium carbonate as a pigment in the undercoat layer, and limiting its bulk density to a specific bulk density, in which the precipitated calcium carbonate comprises spindle-shaped primary particles aggregated radially to form secondary particles with a characteristic rosette type shape.
- the undercoat layer containing such a pigment hampers the heat transfer from the support to the thermosensitive recording layer effectively, which is considered to improve the heat discoloration resistance of the thermosensitive recording medium by reducing the heat transfer even when the thermosensitive recording medium is stored at a high temperature condition.
- the undercoat layer containing such a pigment is considered to have a specific absorbing property for the materials contained in the undercoat layer and the adjacent thermosensitive recording layer.
- the undercoat layer is considered to absorb the color developing material contained in the thermosensitive recording layer, especially the excess color developing agents that are not involved in the chemical reaction with the leuco dye (i.e. cannot participate in the color developing) after the color developing agent melts by being heated by a thermal head during printing.
- the printing (recording) run-ability i.e. prevention of head debris
- this may have an influence on the expression of binders contained in the undercoat layer.
- thermosensitive recording medium comprising (i) a support, (ii) an undercoat layer installed on the support, comprising a pigment and a binder as main components, and (iii) a thermosensitive recording layer installed on the undercoat layer, comprising a colorless or pale colored electron donating leuco dye and an electron accepting color developing agent as main components, wherein the pigment contained in the undercoat layer is a rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate comprising spindle-shaped primary particles aggregated radially to form secondary particles, and the bulk density of the rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate is 240 g/L or less, wherein the bulk density is measured according to Japanese Industrial Standard JIS-K-5101-12-1.
- thermosensitive recording medium of the present invention comprises (i) a support, (ii) an undercoat layer installed on the support, and (iii) a thermosensitive recording layer installed on the undercoat layer.
- the undercoat layer comprises a pigment and a binder as main components, wherein the pigment is a rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate comprising spindle-shaped primary particles aggregated radially to form secondary particles.
- the bulk density of the precipitated calcium carbonate is 240 g/L or less, preferably 150 - 220g/L.
- the bulk density is measured according to Japanese Industrial Standard JIS-K-5101-12-1 (a test method for pigments - Part 12: Apparent density or apparent specific volume - Section 1: standing method).
- the rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate for use in the present invention comprises spindle-shaped primary particles aggregated radially to form secondary particles.
- the "aggregated radially” is referred to those of each primary particle extending to longitudinal direction from the approximate center of the secondary particles.
- the rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate for use in the present invention is available as Albacar (R) LO (Bulk density: 210g/L), a product of Specialty Minerals Inc., and TP211BM (Bulk density: 220g/L), a product of Okutama Kogyo Co., Ltd., etc.
- Such organic hollow particles are available as SX8782 (JSR Corporation), MH5055 and MH8103K (Nippon Zeon Co., Ltd.), Ropaque (R) HP-91 (Rohm and Haas Japan Co.) and the like.
- the average particle diameter is represented by the median size d 50 , which can be measured by a laser diffraction type particle size distribution measuring apparatus.
- the median size d 50 is the diameter in which the amount of one group with larger diameter than the diameter and the amount of another group with smaller diameter than the diameter are equivalent by volume.
- the binders used in the undercoat layer include water-soluble resins and water-insoluble resins.
- the water-soluble resin polyvinyl alcohols such as completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol, partially saponified polyvinyl alcohol, carboxyl-modified polyvinyl alcohol, silanol-modified polyvinyl alcohol, cation-modified polyvinyl alcohol, terminal alkyl-modified polyvinyl alcohol and the like; cellulose ethers and derivatives thereof such as hydroxyethyl cellulose, methyl cellulose, ethyl cellulose, carboxymethyl cellulose, acetyl cellulose and the like; starches such as starch, enzyme modified starch, thermochemically modified starch, oxidized starch, esterified starch, etherified starch (for example, such as hydroxyethyl starch), cationic starch and the like; polyacrylamides such as polyacrylamide, cationic polyacrylamides, anionic polyacrylamides, amphoteric polyacrylamide
- water-insoluble resin styrene-butadiene resins, acrylic resins, polyolefin-based resins are preferable, and styrene-butadiene resins are more preferable.
- the water-insoluble resin can be used as an emulsion or a dispersed emulsion as a paste in water or other media.
- binders may be used in combination of two or more depending on the required quality.
- the binder used in the undercoat layer of the present invention it is preferable to use a water-soluble resin and a water-insoluble resin at a specific ratio.
- the weight ratio (in solid content) of water-soluble resin / water-insoluble resin is preferably 35/100 or less, more preferably from 3/100 to 30/100, further preferably from 3/100 to 20/100.
- the weight ratio of the water-soluble resin / non-water-soluble resin is larger than 35/100, the heat discoloration resistance, printing image quality, prevention of head debris tend to be lowered (see Examples below). Further, if the amount of water-soluble resin is less than 3/100, the prevention of migration (described later) is not sufficient, then the strength of the coating layer may decrease.
- Water-soluble resins such as polyvinyl alcohols are generally viscous and retain water. Therefore the water-soluble resins penetrate into the voids in the undercoat layer that contains the pigments of the present invention with a specific shape and a specific bulk density, and the water-soluble resins tend to remain there. Accordingly, the water-soluble resins may fill the voids in the undercoat layer, which will deteriorate the heat discoloration resistance, the print quality, and the prevention of head debris.
- the water-insoluble resins such as styrene-butadiene resins
- the water-insoluble resins are generally less viscous and retain less water. Therefore the water-insoluble resins may pass through the undercoat layer that contains the pigments of the present invention with a specific shape and a specific bulk density, and penetrate into the support. This problem is called as "migration".
- various aids such as a dispersion agent, plasticizer, thickeners, surfactants, activator, pH controlling agent, de-foaming agent, water retention agent, preservative, coloring dye, UV light inhibiting agent, antioxidants, water and oil repellants and the like may be added to the undercoat layer in the range that does not adversely affect the desired effects for the problems described above.
- the amounts of the pigment, the organic hollow particle and the binder used in the undercoat layer are determined according to the required performance and recording properties and are not particularly restricted.
- the amount (in solid) of the pigment in the undercoat layer is ordinarily from 50 to 95 weight parts, preferably from 70 to 90 weight parts per 100 weight parts of the total solid content of the undercoat layer.
- the amount (in solid) of the organic hollow particle in the undercoat layer is preferably from 1 to 18 weight parts, more preferably from 3 to 15 weight parts per 100 weight parts of the total solid content of the undercoat layer.
- the color developing sensitivity will increase as the amount of the organic hollow particles increases, while the printing (recording) run-ability (i.e.
- the amount (in solid) of the binder is preferably from 7 to 30 weight parts, more preferably from 10 to 25 weight parts per 100 weight parts of the total solid content of the undercoat layer.
- the method for coating the undercoat layer is not limited in particular, but any well-known conventional techniques may be used to coat on a support of suitable material, such as paper, recycled paper, plastic film, synthetic paper or the like.
- the method for coating may be appropriately selected and used among, for example, off-machine coater and on-machine coater, which is equipped with coaters such as air knife coater, rod blade coater, bent blade coater, bevel blade coater, roll coater, curtain coater and the like.
- a blade coater such as rod blade coater, bent blade coater, bevel blade coater and the like, since a coating solution can be coated with higher concentration, then undercoat solution is unlikely to penetrate into the support, and then a uniform undercoat layer can be formed.
- the coating amount of the undercoat layer is not limited in particular, but the typical dried coating amount of the undercoat layer is ordinarily in the range of from 1 to 15g/m 2 .
- thermosensitive recording layer of the thermosensitive recording medium of the present invention The various materials used in the thermosensitive recording layer of the thermosensitive recording medium of the present invention are shown below. However, a binder, a cross linking agent, a pigment etc. can be used also for other coating layer(s) in the range which does not inhibit the desired effect for the problems described above.
- thermosensitive recording material of the present invention All of the color developing agents well known in the conventional field of pressure sensitive and thermosensitive recording media may be used as the color developing agent in a thermosensitive recording material of the present invention.
- the color developing agent is not particularly restricted, activated clay, attapulgite, colloidal silica, inorganic acidic substances such as aluminum silicate and the like, 4,4'-isopropylidene diphenol, 1,1-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl) cyclohexane, 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-methylpentane, 4,4'-dihydroxydiphenyl sulfide, hydroquinone monobenzyl ether, benzyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, 4,4'-dihydroxy diphenyl sulfone, 2,4'-dihydroxy diphenyl sulfone, 4-hydroxy-4'-isopropxy diphenyl sulfone, 4-hydroxy-4'-n-propoxy diphenyl sulfone,
- thiourea compounds such as N,N'-di-m-chlorophenyl thiourea and the like, p-chlorobenzoic acid, stearyl gallate, bis [zinc 4-octyloxy carbonylamino] salicylate dihydrate, 4-[2-(p-methoxyphenoxy) ethyloxy] salicylic acid, 4-[3-(p-trisulfonyl) propyloxy] salicylic acid, aromatic carboxylic acids such as 5-[p-(2-p-methoxyphenoxyethoxy) cumyl] salicylic acid and salts of these aromatic carboxylic acids and polyvalent metals such as zinc, magnesium, aluminum, calcium, titanium, manganese, tin, nickel and the like, and, furthermore, antipirin complexes of zinc thiocyanate and complex zinc salts and the like of terephthal aldehyde acid with other aromatic carboxylic acids, for example, may be cited as the
- These color developing agents may be used individually and in mixtures of at least two.
- leuco dyes well known in the conventional field of pressure sensitive and thermosensitive recording media may be used as the electron donating leuco dye in the present invention.
- the leuco dye is not particularly restricted, triphenylmethane type compounds, fluorane type compounds, fluorene type compounds, divinyl type compounds and the like are preferred as the leuco dye.
- specific examples of the typical colorless to pale colored basic colorless leuco dye (leuco dye precursors) are shown below.
- these leuco dye precursors may be used individually and also in mixtures of at least two of them.
- sensitizers may be used as the sensitizer in the thermosensitive recording medium of the present invention.
- sensitizers aliphatic acid amides such as stearic acid amide, palmitic acid amide and the like, ethylene bis-amide, montan acid wax, polyethylene wax, 1,2-di-(3-methylphenoxy) ethane, p-benzyl biphenyl, ⁇ -benzyloxy naphthalene, 4-biphenyl-p-tolyl ether, m-terphenyl, 1,2-diphenoxyethane, dibenzyl oxalate, di(p-chlorobenzyl) oxalate, di(p-methylbenzyl) oxalate, dibenzyl terephthalate, benzyl p-benzyloxy benzoate, di-p-tolyl carbonate, phenyl- ⁇ -naphthyl carbonate, 1,4-diethoxynaphthalen
- kaolin kaolin, calcined kaolin, calcium carbonate, aluminum oxide, titanium oxide, magnesium carbonate, aluminum silicate, magnesium silicate, calcium silicate, aluminum hydroxide, silica and the like may be used. These pigments may be used in combinations depending on the required quality.
- binder used in the present invention completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol, partially saponified polyvinyl alcohol, acetoacetylated polyvinyl alcohol, carboxyl-modified polyvinyl alcohol, amide-modified polyvinyl alcohol, sulfonic acid-modified polyvinyl alcohol, butyral-modified polyvinyl alcohol, olefin-modified polyvinyl alcohol, nitrile-modified polyvinyl alcohol, pyrolidone-modified polyvinyl alcohol, silicone-modified polyvinyl alcohol, other modified polyvinyl alcohol; cellulose derivatives such as hydroxyethyl cellulose, methyl cellulose, ethyl cellulose, carboxymethyl cellulose, acetyl cellulose and the like; styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer, styrene-butadiene copolymer; casein, gum arabic, oxidized starch, etherified starch, dialdehyde
- polymeric substances may be used upon dissolving them in a solvent such as water, alcohol, ketones, esters, hydrocarbons and the like or upon emulsifying or dispersing into a paste in water or other media.
- a solvent such as water, alcohol, ketones, esters, hydrocarbons and the like
- the polymeric materials may also be used in combinations according to the qualities demanded.
- fatty acid metal salts such as zinc stearate, calcium stearate, and the like; waxes; silicone resins, and the like may be cited.
- a stabilizing agent that improves oil resistance in recorded images and the like such as 4,4'-butylidene (6-t-butyl-3-methylphenol), 2,2'-di-t-butyl-5,5'-dimethyl-4,4'-sulfonyl diphenol, 1,1,3-tris (2-methyl-4-hydroxy-5-cyclohexylphenyl) butane, 1,1,3-tris (2-methyl-4-hydroxy-5-t-butylphenyl) butane and the like may also be added in the range that does not adversely affect the desired effects for the problems described above.
- the types and amounts of the leuco dye, color developing agent, sensitizer and other various ingredients used in the thermosensitive recording medium of the present invention are determined according to the required performance and printability and are not particularly restricted. However, from 0.5 to 10 parts of the color developing agent, from 0.5 to 20 parts of the pigment, from 0.5 to 10 parts of the sensitizer, from 0.01 to 10 parts of the stabilizing agent and from 0.01 to 10 parts of the other ingredients are ordinarily used per 1 part of the leuco dye.
- the appropriate amount (in solid) of the binder in the thermosensitive recording layer is from 5 to 25 weight %.
- the leuco dye, the color developing agent and materials added when needed are finely ground into particles, several microns or smaller in size, using a grinder or a suitable emulsification device such as a ball mill, attritor, sand grinder and the like, and a coating solution is prepared by adding a binder and various additive materials depending on the objective.
- a coating solution is prepared by adding a binder and various additive materials depending on the objective.
- Water, alcohol and the like can be used as the solvent for the coating solution and the solid content of the coating solution is about from 20 to 40 weight %.
- thermosensitive recording medium of the present invention has the undercoat layer installed on the support and the thermosensitive recording layer installed on the undercoat layer
- the thermosensitive recording medium may further have other layer other than the undercoat layer and the thermosensitive recording layer appropriately.
- thermosensitive recording medium may further have a protective layer on the thermosensitive recording layer, and a back coat layer on the surface of the support opposite to the thermosensitive recording layer.
- the method for coating the coating layer other than the undercoat layer is not limited in particular, but any well-known conventional techniques may be used.
- the method for coating may be appropriately selected and used among, for example, off-machine coater and on-machine coater, which is equipped with coaters such as air knife coater, rod blade coater, bent blade coater, bevel blade coater, roll coater, curtain coater.
- the coating amount of the coating layer other than the undercoat layer is determined according to the required performance and recording suitability, but is not limited in particular.
- the dried coating amount of the thermosensitive recording layer is ordinarily in the range of from 2 to 12g/m 2
- the dried coating amount of the protective layer is preferably in the range of from 0.5 to 5.0 g/m 2 .
- thermosensitive recording medium field various technologies known in the thermosensitive recording medium field may be used as needed, for example, a flattening treatment such as super calendaring and the like can be conducted after coating individual coating layers.
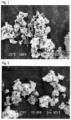
- Undercoat layer coating solution was prepared by dispersing and stirring the following formulation: Rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate (Specialty Minerals Inc., Albacar (R) LO, Bulk density: 210g/L, Figure 1 ) 100.0 parts Styrene-butadiene copolymer latex (Zeon Corporation, ST5526, solid content: 48%) 40.0 parts Aqueous solution of completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol (Kuraray Co., Ltd., PVA117, solid content: 10%) 30.0 parts Water 100.0 parts
- This undercoat layer coating solution was applied on one side of a support (i.e. groundwood free paper with a basis weight of 60g/m 2 ) by using a bent blade coater with a coating amount (in solid) of 10.0 g/m 2 , and was dried to prepare an undercoated paper.
- a support i.e. groundwood free paper with a basis weight of 60g/m 2
- a bent blade coater with a coating amount (in solid) of 10.0 g/m 2
- a color developing agent dispersion (solution A) and a leuco dye dispersion (solution B) with the following formulation were separately wet ground using sand grinders until the average particle size was about 0.5 ⁇ m.
- Color developing agent dispersion (Solution A) 4-hydroxy-4'-isopropxy diphenyl sulfone (API Corporation, NYDS) 6.0 parts Aqueous solution of completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol (Kuraray Co., Ltd., PVA117, solid content: 10%) 18.8 parts Water 11.2 parts Leuco dye dispersion (Solution B) 3-Dibutylamino-6-methyl-7-anilinofluorane (Yamamoto Chemicals Inc., ODB-2) 6.0 parts Aqueous solution of completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol (Kuraray Co., Ltd., PVA117, solid content: 10%) 4.6 parts Water 2.6 parts
- thermosensitive recording layer coating solution 1 Color developing agent dispersion (Solution A) 36.0 parts Leuco dye dispersion (Solution B) 13.2 parts Aqueous solution of completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol (Kuraray Co., Ltd., PVA117, solid content: 10%) 25.0 parts Aluminum hydroxide (Showa Denko K.K, Higilite (R) H-32, 50% dispersion) 12.0 parts
- thermosensitive recording layer coating solution 1 was applied on the undercoat layer of the above undercoated paper by using a rod blade coater with a coating amount (in solid) of 2.5 g/m 2 and was dried and super calendared so that the smoothness was 500-1,000 seconds to yield a thermosensitive recording medium.
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of changing the amount of the styrene-butadiene copolymer latex in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 40.0 parts to 45.0 parts and the amount of the aqueous solution of completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 30.0 parts to 7.0 parts.
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of changing the amount of the styrene-butadiene copolymer latex in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 40.0 parts to 44.0 parts and the amount of the aqueous solution of completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 30.0 parts to 11.0 parts.
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of changing the amount of the styrene-butadiene copolymer latex in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 40.0 parts to 39.0 parts and the amount of the aqueous solution of completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 30.0 parts to 37.0 parts.
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of changing the amount of the styrene-butadiene copolymer latex in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 40.0 parts to 36.0 parts and the amount of the aqueous solution of completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 30.0 parts to 50.0 parts.
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of changing the amount of the styrene-butadiene copolymer latex in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 40.0 parts to 35.0 parts and the amount of the aqueous solution of completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 30.0 parts to 55.0 parts.
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of changing the amount of the styrene-butadiene copolymer latex in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 40.0 parts to 23.5 parts and the amount of the aqueous solution of completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 30.0 parts to 111.0 parts.
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of changing the amount of the styrene-butadiene copolymer latex in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 40.0 parts to 15.5 parts and the amount of the aqueous solution of completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol in the undercoat layer coating solution 1 from 30.0 parts to 148.0 parts.
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of using the rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate (Okutama Kogyo Co., Ltd., TP221BM, Bulk density: 230g/L, Figure 2 ) in place of the rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate (Albacar (R) LO).
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of using the undercoat layer coating solution 2 in place of the undercoat layer coating solution 1.
- Undercoat layer coating solution 2 Rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate (Albacar (R) LO) 100.0 parts Organic hollow particles (Rohm and Haas, HP1055, Average particle diameter (d 50 ): 1.0 ⁇ m, Hollow ratio: 50%) 20.0 parts Styrene-butadiene copolymer latex (Zeon Corporation, ST5526) 40.0 parts
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of using the undercoat layer coating solution 3 in place of the undercoat layer coating solution 1.
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of using the rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate (Specialty Minerals Inc., Albacar (R) 5970, Bulk density: 250g/L) in place of the rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate (Albacar (R) LO) in the undercoat layer coating solution 1.
- the rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate Specialty Minerals Inc., Albacar (R) 5970, Bulk density: 250g/L
- Albacar (R) LO rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 10 with the exception of using the rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate (Albacar (R) 5970) in place of the rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate (Albacar (R) LO) in the undercoat layer coating solution 2.
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of using the undercoat layer coating solution 4 in place of the undercoat layer coating solution 1.
- Undercoat layer coating solution 4 Rosette type precipitated calcium carbonate (Albacar (R) 5970) 80.0 parts Calcined clay (BASF Co., Ansilex (R) 93) 20.0 parts Styrene-butadiene copolymer latex (Zeon Corporation, ST5526) 40.0 parts
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of using the undercoat layer coating solution 5 in place of the undercoat layer coating solution 1.
- Undercoat layer coating solution 5 Calcined clay (BASF Co., Ansilex (R) 93) 100.0 parts Styrene-butadiene copolymer latex (Zeon Corporation, ST5526) 40.0 parts Aqueous solution of completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol (Kuraray Co., Ltd., PVA117) 30.0 parts Water 100.0 parts
- thermosensitive recording medium was prepared in the same manner described in Example 1 with the exception of using the undercoat layer coating solution 6 in place of the undercoat layer coating solution 1.
- Undercoat layer coating solution 6 Organic hollow particles (Rohm and Haas, HP1055) 20.0 parts Styrene-butadiene copolymer latex (Zeon Corporation, ST5526) 40.0 parts Aqueous solution of completely saponified polyvinyl alcohol (Kuraray Co., Ltd., PVA117) 30.0 parts Water 100.0 parts
- thermosensitive recording media obtained were evaluated as described below.
- thermosensitive recording medium print tester Ohkura Engineering Co., Ltd. TH-PMD equipped with a thermal head by Kyocera Co.
- the density of the solid pattern was measured by using Macbeth Densitometer (RD-914, with Amber filter) to evaluate the color developing sensitivity.
- thermosensitive recording medium was treated in an environment of 80 degree C for one hour and stored in an environment of 23 degree C, 50% RH for three hours.
- the color density of non-printed portion i.e. blank portion
- Macbeth Densitometer RD-914, with Amber filter
- the heat discoloration resistance in the blank portion was evaluated on the following criteria. If the evaluation is rated as Good or Fair, no problem happens in the practical use..
- Background color value (color density of the non-printing portion after the treatment) - (color density of the non-printing portion before the treatment)
- thermosensitive recording medium was printed a solid pattern by using a thermosensitive recording medium print tester (Ohkura Engineering Co., Ltd. TH-PMD equipped with a thermal head by Kyocera Co.) at applied energy of 0.15 mJ/dot and printing speed of 50mm/sec. Then the print image quality of the solid pattern was visually evaluated on the following criteria. If the evaluation is rated as Excellent, Good or Fair, no problem happens in the practical use..
- a thermosensitive recording medium print tester Ohkura Engineering Co., Ltd. TH-PMD equipped with a thermal head by Kyocera Co.
- thermosensitive recording medium was printed a solid pattern by using a print tester (Canon Inc., HT180) at applied energy of 0.20 mJ/dot and at -10 degree C. After printing 1m long, the debris on the thermal head of the printer was visually evaluated on the following criteria. If the evaluation is rated as Excellent, Good or Fair, no problem happens in the practical use..
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Heat Sensitive Colour Forming Recording (AREA)
Claims (7)
- Ein wärmeempfindliches Aufzeichnungsmedium, umfassend(i) einen Träger,(ii) eine auf dem Träger aufgebrachte Grundierungsschicht, umfassend ein Pigment und ein Bindemittel als Hauptkomponenten, und(iii) eine auf der Grundierungsschicht aufgebrachte wärmeempfindliche Aufzeichnungsschicht, die einen farblosen oder blass gefärbten Elektronen spendenden Leukofarbstoff und ein Elektronen-aufnehmende und Farbeentwickelnde Agens als Hauptkomponenten umfasst,dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das in der Grundierungsschicht enthaltene Pigment ein ausgefälltes rosettenartiges Calciumcarbonat ist, das spindelförmige Primärteilchen umfasst, die radial zu sekundären Teilchen aggregiert sind, und dass die Schüttdichte des ausgefällten rosettenartigen Calciumcarbonats 240 g/l oder weniger ist, wobei die Schüttdichte gemäß dem japanischen Industriestandard JIS-K-5101-12-1 gemessen ist.
- Thermosensitives Aufzeichnungsmedium nach Anspruch 1, wobei die Schüttdichte des ausgefällten rosettenartigen Calciumcarbonats von 150 bis 220 g/l beträgt.
- Thermosensitives Aufzeichnungsmedium nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, wobei das in der Grundierungsschicht enthaltene Bindemittel ein wasserlösliches Harz und ein wasserunlösliches Harz umfasst und das Gewichtsverhältnis, im Feststoffgehalt, von wasserlöslichem Harz / wasserunlöslichem Harz 35/100 oder weniger ist.
- Thermosensitives Aufzeichnungsmedium nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, wobei das in der Grundierungsschicht enthaltene Bindemittel ein wasserlösliches Harz und ein wasserunlösliches Harz umfasst und das Gewichtsverhältnis, im Feststoffgehalt, von wasserlöslichem Harz / wasserunlöslichem Harz von 3/100 bis 30/100 ist.
- Thermosensitives Aufzeichnungsmedium nach einem der Ansprüche 3 oder 4, wobei das wasserlösliche Harz Polyvinylalkohol ist.
- Thermosensitives Aufzeichnungsmedium nach einem der Ansprüche 3 bis 5, wobei das wasserunlösliche Harz Styrol-Butadien-Harz ist.
- Thermosensitives Aufzeichnungsmedium nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 6, wobei die Menge des ausgefällten rosettenartigen Calciumcarbonats 70 Gew.-% oder mehr der gesamten in der Grundierungsschicht enthaltenen Pigmente beträgt.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014052924 | 2014-03-17 | ||
| PCT/JP2015/056651 WO2015141497A1 (ja) | 2014-03-17 | 2015-03-06 | 感熱記録体 |
Publications (4)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3103649A1 EP3103649A1 (de) | 2016-12-14 |
| EP3103649A4 EP3103649A4 (de) | 2017-02-22 |
| EP3103649B1 EP3103649B1 (de) | 2018-01-03 |
| EP3103649B2 true EP3103649B2 (de) | 2025-01-22 |
Family
ID=54144470
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP15766003.6A Active EP3103649B2 (de) | 2014-03-17 | 2015-03-06 | Wärmeempfindliches aufzeichnungsmedium |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP3103649B2 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP5823086B1 (de) |
| CN (1) | CN106103122B (de) |
| WO (1) | WO2015141497A1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6447246B2 (ja) * | 2015-03-04 | 2019-01-09 | 日本製紙株式会社 | 感圧複写紙 |
| JP2017056727A (ja) * | 2015-09-16 | 2017-03-23 | 日本製紙株式会社 | 感熱記録体 |
| JP2023502524A (ja) * | 2019-11-22 | 2023-01-24 | アプビオン リミテッド ライアビリティ カンパニー | 水分散性の直接感熱またはインクジェット印刷可能媒体 |
| CN114472115A (zh) * | 2020-11-11 | 2022-05-13 | 湖南鼎一致远科技发展有限公司 | 无墨打印金属广告板 |
| US12151498B2 (en) | 2020-12-10 | 2024-11-26 | Appvion, Llc | Multi-purpose phenol-free direct thermal recording media |
| US12115803B2 (en) | 2020-12-10 | 2024-10-15 | Appvion, Llc | Fade-resistant water-dispersible phenol-free direct thermal media |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05162446A (ja) † | 1991-12-11 | 1993-06-29 | Oji Paper Co Ltd | 感熱記録紙 |
| DE102008057270A1 (de) † | 2008-11-13 | 2010-05-20 | Kanzan Spezialpapiere Gmbh | Aufzeichnungsmaterial |
| EP1910281B1 (de) † | 2005-07-28 | 2013-07-03 | Basf Se | Stabile wässrige dispersionen von farbentwicklern |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5364610A (en) | 1993-06-15 | 1994-11-15 | P. H. Glatfelter Company | Process for preparation of high opacity precipitated calcium carbonate by reacting sodium carbonate with calcium hydroxide |
| DE102006032521B3 (de) | 2006-07-12 | 2008-04-03 | Papierfabrik August Koehler Ag | Wärmeempfindliches Aufzeichnungsmaterial |
| JP4907374B2 (ja) * | 2007-02-08 | 2012-03-28 | 株式会社リコー | 感熱記録材料 |
| CN101652253B (zh) * | 2007-03-29 | 2011-11-23 | 日本制纸株式会社 | 感热记录体 |
| JPWO2009066662A1 (ja) * | 2007-11-19 | 2011-04-07 | 日本製紙株式会社 | インクジェット記録用紙 |
| JP2012076230A (ja) * | 2010-09-30 | 2012-04-19 | Nippon Paper Industries Co Ltd | 感熱記録体 |
| DE102013002297A1 (de) | 2013-02-08 | 2014-08-14 | Papierfabrik August Koehler Se | Wärmeempfindliches Aufzeichnungsmaterial |
-
2015
- 2015-03-06 EP EP15766003.6A patent/EP3103649B2/de active Active
- 2015-03-06 CN CN201580012775.3A patent/CN106103122B/zh active Active
- 2015-03-06 JP JP2015536711A patent/JP5823086B1/ja active Active
- 2015-03-06 WO PCT/JP2015/056651 patent/WO2015141497A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05162446A (ja) † | 1991-12-11 | 1993-06-29 | Oji Paper Co Ltd | 感熱記録紙 |
| EP1910281B1 (de) † | 2005-07-28 | 2013-07-03 | Basf Se | Stabile wässrige dispersionen von farbentwicklern |
| DE102008057270A1 (de) † | 2008-11-13 | 2010-05-20 | Kanzan Spezialpapiere Gmbh | Aufzeichnungsmaterial |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| Datasheet "ALBACAR® 5970", Specialty Minerals, 1998 † |
| SOCAL® GEFALLTES CALCIUMCARBONAT HERSTELLUNG,EIGENSCHAFTEN, ANWENDUNGEN", SOLVAY, 2005, pages 1-54 † |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5823086B1 (ja) | 2015-11-25 |
| CN106103122B (zh) | 2019-06-14 |
| WO2015141497A1 (ja) | 2015-09-24 |
| EP3103649A4 (de) | 2017-02-22 |
| CN106103122A (zh) | 2016-11-09 |
| EP3103649B1 (de) | 2018-01-03 |
| JPWO2015141497A1 (ja) | 2017-04-06 |
| EP3103649A1 (de) | 2016-12-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2184175B1 (de) | Thermisches aufzeichnungsmedium | |
| EP4043229B1 (de) | Wärmeempfindliches aufzeichnungsmedium | |
| EP3312018B1 (de) | Wärmeaufzeichnungsmaterial | |
| JP6255889B2 (ja) | 感熱記録体 | |
| EP3103649B2 (de) | Wärmeempfindliches aufzeichnungsmedium | |
| EP3141397B1 (de) | Hitzeempfindliches aufzeichnungsmaterial | |
| EP4098454A1 (de) | Hitzeempfindliches aufzeichnungsmaterial | |
| EP3351398B1 (de) | Wärmeempfindliches aufzeichnungsmedium | |
| EP3053752B1 (de) | Wärmeempfindliches aufzeichnungsmedium | |
| EP1844947A1 (de) | Wärmeempfindliches aufzeichnungsmedium | |
| EP3919283B1 (de) | Wärmeempfindlicher aufzeichnungskörper | |
| EP4316861A1 (de) | Wärmeempfindliches aufzeichnungsmaterial | |
| JP2015123702A (ja) | 感熱記録体 | |
| JP6727082B2 (ja) | 感熱記録体 | |
| JP2008006744A (ja) | 感熱記録体 | |
| JP2017177514A (ja) | 感熱記録体 | |
| EP4501658A1 (de) | Wärmeempfindlicher aufzeichnungskörper | |
| JP2006175636A (ja) | 感熱記録体の製造方法 | |
| EP4653202A1 (de) | Wärmeempfindlicher aufzeichnungskörper | |
| JP2016028847A (ja) | 感熱記録体 | |
| JP2008006739A (ja) | 感熱記録体 | |
| JP2007253579A (ja) | 感熱記録体 | |
| JP2007307857A (ja) | 感熱記録体 | |
| JP2007253581A (ja) | 感熱記録体 | |
| JP2007253580A (ja) | 感熱記録体 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20160909 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R079 Ref document number: 602015007250 Country of ref document: DE Free format text: PREVIOUS MAIN CLASS: B41M0005280000 Ipc: B41M0005420000 |
|
| A4 | Supplementary search report drawn up and despatched |
Effective date: 20170125 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: B41M 5/42 20060101AFI20170119BHEP |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| DAV | Request for validation of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20170614 |
|
| GRAJ | Information related to disapproval of communication of intention to grant by the applicant or resumption of examination proceedings by the epo deleted |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSDIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| INTC | Intention to grant announced (deleted) | ||
| GRAR | Information related to intention to grant a patent recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR71 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20171123 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 959858 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20180115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602015007250 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 959858 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180403 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180404 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180403 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180503 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R026 Ref document number: 602015007250 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: SCHAEFER KALK GMBH & CO. KG Effective date: 20181002 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20180331 |
|
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180306 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180306 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180331 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180331 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180331 |
|
| PLBB | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition received |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS3 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20190306 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190306 Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180306 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20150306 Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| PLAB | Opposition data, opponent's data or that of the opponent's representative modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPO |
|
| R26 | Opposition filed (corrected) |
Opponent name: SCHAEFER KALK GMBH & CO. KG Effective date: 20181002 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Payment date: 20210318 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |
|
| APBM | Appeal reference recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREFNO |
|
| APBP | Date of receipt of notice of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA2O |
|
| PLAB | Opposition data, opponent's data or that of the opponent's representative modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPO |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FI Ref legal event code: MAE |
|
| R26 | Opposition filed (corrected) |
Opponent name: SCHAEFER KALK GMBH & CO. KG Effective date: 20181002 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220306 |
|
| APBQ | Date of receipt of statement of grounds of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA3O |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230522 |
|
| APBU | Appeal procedure closed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA9O |
|
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 20250122 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R102 Ref document number: 602015007250 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20250326 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20250318 Year of fee payment: 11 |