EP2662575A2 - Membrane et agencement de récipient - Google Patents
Membrane et agencement de récipient Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2662575A2 EP2662575A2 EP13165977.3A EP13165977A EP2662575A2 EP 2662575 A2 EP2662575 A2 EP 2662575A2 EP 13165977 A EP13165977 A EP 13165977A EP 2662575 A2 EP2662575 A2 EP 2662575A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- container
- membrane
- connecting element
- halves
- container halves
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 89
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 16
- 239000013013 elastic material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 11
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 9
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 6
- 229920001971 elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 4
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 3
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N nitrogen Substances N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000005060 rubber Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920002943 EPDM rubber Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 244000043261 Hevea brasiliensis Species 0.000 description 2
- 229920000459 Nitrile rubber Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011324 bead Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920005549 butyl rubber Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920003052 natural elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920001194 natural rubber Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920003048 styrene butadiene rubber Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000002174 Styrene-butadiene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001186 cumulative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000806 elastomer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001973 fluoroelastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002681 hypalon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- QJGQUHMNIGDVPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N nitrogen group Chemical group [N] QJGQUHMNIGDVPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920002725 thermoplastic elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B1/00—Installations or systems with accumulators; Supply reservoir or sump assemblies
- F15B1/02—Installations or systems with accumulators
- F15B1/04—Accumulators
- F15B1/08—Accumulators using a gas cushion; Gas charging devices; Indicators or floats therefor
- F15B1/10—Accumulators using a gas cushion; Gas charging devices; Indicators or floats therefor with flexible separating means
- F15B1/12—Accumulators using a gas cushion; Gas charging devices; Indicators or floats therefor with flexible separating means attached at their periphery
- F15B1/14—Accumulators using a gas cushion; Gas charging devices; Indicators or floats therefor with flexible separating means attached at their periphery by means of a rigid annular supporting member
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B2201/00—Accumulators
- F15B2201/20—Accumulator cushioning means
- F15B2201/205—Accumulator cushioning means using gas
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B2201/00—Accumulators
- F15B2201/30—Accumulator separating means
- F15B2201/315—Accumulator separating means having flexible separating means
- F15B2201/3151—Accumulator separating means having flexible separating means the flexible separating means being diaphragms or membranes
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B2201/00—Accumulators
- F15B2201/30—Accumulator separating means
- F15B2201/315—Accumulator separating means having flexible separating means
- F15B2201/3156—Accumulator separating means having flexible separating means characterised by their attachment
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B2201/00—Accumulators
- F15B2201/40—Constructional details of accumulators not otherwise provided for
- F15B2201/405—Housings
- F15B2201/4056—Housings characterised by the attachment of housing components
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B2201/00—Accumulators
- F15B2201/60—Assembling or methods for making accumulators
- F15B2201/605—Assembling or methods for making housings therefor
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B2201/00—Accumulators
- F15B2201/60—Assembling or methods for making accumulators
- F15B2201/61—Assembling or methods for making separating means therefor
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a membrane of a container, in particular a pressure expansion vessel, as well as a container arrangement, which is designed in particular as a pressure expansion vessel.
- Expansion tanks or surge tank of the type in question are well known in the art.
- surge tanks are designed as components in hydraulic systems that absorb the change in volume of the hydraulic fluid between minimum and maximum temperature and thus should keep the pressure largely constant.
- expansion tanks are used in heating systems and service water, cold water, solar and hydraulic circuits.
- Such reservoirs have a flexible rubber membrane, which separates the liquid and the gas storage within a vessel formed by two half-shells. Here, the membrane is clamped between the two half-shells on the outer bead and held together with a rotating steel clip.
- a disadvantage of such embodiments is that the container wall must be made massive due to the forces occurring and the structural connection of the two half-shells. Incidentally, the installation space must be kept relatively large because of the peripheral edge. Incidentally, the complex installation of such systems leads to high production costs.
- a membrane of a container in particular a pressure expansion vessel or expansion tank, wherein the membrane is formed of an elastic material, and wherein the membrane has a working area which is adapted to displace within a container, and a mounting area has, over which the membrane in the region of two joining regions of two container halves on the container can be fixed, that the container halves are connected to one another via a material connection.
- the membrane thus serves in particular for use in a membrane expansion vessel and is thus designed as a preferably flexible rubber membrane.
- the membrane advantageously consists of an elastic material or elastomer so as to shift at least in its working area within the container.
- the materials used for the membrane are NBR (nitrile-butadiene rubber), EPDM (ethylene-propylene-diene rubber), SBR (styrene-butadiene rubber), CSM (chlorosulfonated polyethylene), FKM (fluoro rubber), NR (natural rubber) , TPV (thermoplastic elastomer) or IIR (butyl rubber) in question.
- the membrane may be formed from mixtures of the aforementioned materials.
- the membrane may have a layered structure of different materials. The membrane serves to separate the liquid from a gas cushion. When heated, the nearly incompressible liquid expands, compressing the gas cushion on the other side of the membrane.
- the membrane is designed as a flat body and particularly expediently, this has a (fairly) square or round, preferably circular, planar configuration.
- the edge regions of the membrane the latter has a fastening region, by way of which the membrane can be fixed to the container in the region of two joining regions of two container halves, so that the container halves can be connected to one another via a material connection.
- the attachment region of the membrane can thus be a peripheral edge.
- the joining region of a container half generally represents the region or section of the container half, via which the container half is connected or connectable to another container half or another element.
- the fastening area is designed such that it is not clamped between the two container halves and clamped by a clamping ring, but in such a way that a cohesive connection of the two container halves is possible with each other.
- the cohesive connection of the two container halves can be effected here indirectly or directly. In an immediate cohesive connection of the container halves they are directly contacting each other, for example glued or welded. In an indirect connection of the two container halves, an intermediate element, for example a connecting element, is provided, on which the two container halves are fixed cohesively.
- the attachment region has an adhesion layer in order to fix it to at least one of the container halves or a connecting element.
- the adhesion layer may for example be formed as an adhesive layer or adhesive layer and connects the attachment region of the membrane with at least one of the container halves or a connecting element such that a gas flow or a fluid flow can not occur.
- the advantageously forming the outer periphery of the diaphragm mounting portion may therefore be determined directly or indirectly on at least one of the container halves.
- the membrane is conveniently glued to the inner peripheral surface of the container half.
- the fastening region of the membrane to a connecting element is expediently determined by way of bonding or welding. in this respect It is particularly useful when the mounting area is set adjacent to the joining area at the two container halves.
- the attachment region is non-positively and / or positively and / or materially connected to a connecting element, via which the membrane can be fixed to at least one of the container halves.
- the connection between the membrane and the connecting element can for example be made cohesively.
- the attachment region of the membrane can be glued or welded to the connecting element.
- a non-positive and / or positive connection can also be created.
- the connecting element can be vulcanized into the fastening region of the membrane.
- the engagement areas may be formed, for example, as recesses, projections or openings or the like.
- the connecting element is made of an adhesive or weldable material, preferably a metal such as steel.
- the connecting element and at least one of the container halves are made of the same material. This makes it possible to materially connect one or both container halves to the connecting element, for example via a weld.
- the membrane is connected either to the connecting element or to at least one of the container halves. So it is not necessary for the attachment of the membrane several components.
- the membrane can be explicitly attached to the connector without touching the container half (s) at the same time.
- the membrane may be secured to one of the container halves without the other container half and / or the connecting element to touch or on both container halves, without touching the connecting element.
- a plane is formed substantially centrally between the container halves, wherein the fastening region is arranged in this plane.
- the plane can also be referred to as a parting plane, since it separates the two container halves, so to speak. To form the plane, the container halves do not have to touch each other. The plane, even if the container halves are spaced apart, extends substantially midway between the container halves. Expediently, the plane is arranged substantially centrally or even offset between two joining regions of two container halves and substantially parallel (or not) between two joining regions of two container halves. If the container halves are welded on impact, the two joining regions of the container halves expediently form the plane together. More generally, the container halves form a free space between them.
- the mounting area is positioned in the region of the free space.
- a container arrangement in particular a pressure expansion vessel or membrane expansion vessel, comprising two container halves and a membrane made of an elastic material, wherein the membrane has a working area, which is designed to be displaced within the container, and wherein the membrane has a mounting area has, over which the membrane in such a range of two joining areas of the container halves is fixed to this, that the container halves are connected or connected to each other via a material connection.
- a container arrangement is thus provided in which the two container halves are not clamped together by a clamping ring, but which are connected to one another via a cohesive connection or connectable.
- the cohesive connection can in this case directly or directly, for example, by welding together the two container halves, or indirectly, for example, by welding the two container halves to a vitelagertes Element or connecting element, take place. It is understood that the further advantages and features as described with regard to the membrane according to the invention can also be used in the container arrangement according to the invention.
- the fastening region is non-positively and / or positively and / or materially connected to at least one of the container halves or a connecting element.
- the membrane can also be connected via its mounting region with two container halves.
- the fastening region in the assembled state of the container halves on the one or between the two flanges can be fixed cohesively and / or non-positively and positively. Seen radially outwards, the two container halves can then butt against one another and be glued or welded together or be connected to one another in another cohesive connection method.
- the fastening region preferably has an adhesion layer, via which it is fixed to at least one of the container halves or the connecting element. This makes it possible to fix the attachment region of the membrane cohesively to the connecting element or at least one of the container halves.
- At least one of the container halves or the connecting element has engagement regions, via which the fastening region is non-positively and positively connected to at least one of the container halves or the connecting element.
- the engagement regions may be formed, for example, as projections, recesses, recesses or openings. In this case, it is possible for the container halves or the connecting element to be vulcanized or cast into the region of attachment of the membrane in the region of the engagement regions.
- a connecting element is provided, via which the fastening region is fixed to at least one of the container halves.
- the membrane is thus not directly or directly fixed to the container or the container halves. Rather, the definition of the membrane is indirectly or indirectly via the intermediate connection element.
- the connecting element is designed as an annular body, which is fixed to the joining areas of the container halves such that the connecting element forms a part of the container wall.
- the connecting element forms part of the container outer wall and is designed for this purpose as a ring-shaped or cylindrical body.
- the connecting element is arranged on the respective inner lateral surface or outer lateral surface of the respective container half, that is, the cylinder jacket surface of the connecting element expediently contacts the cylindrical outer surface of each container half.
- the container halves are fixed to the opposite end faces of the cylindrical or annular body. In other words, in the former alternative, the connecting element and the respective container halves overlap in the longitudinal direction, whereas in the second alternative, the container halves and the connecting element do not overlap, but are connected to one another adjacent to one another.
- the connecting element is non-positively and / or positively and / or materially fixed to the joining areas of the container halves.
- the connecting element is firmly bonded to the joining areas of the respective container halves via an adhesive connection or welded connection.
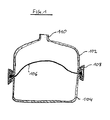
- FIG. 1 is a known from the prior art embodiment of a membrane expansion vessel shown.
- This has an upper container half 102, a lower container half 104 and a membrane 106.
- the membrane 106 divides the container formed by the upper container half 102 and lower container half 104 into two spaces.
- the membrane is clamped by a bead located at its edge by means of a clamping ring 108 between the two container halves 102, 104.
- a liquid for example water, which can enter and leave via a connection 110.
- FIG. 2 are a sectional view and a detailed sectional view of a preferred exemplary embodiment of the container assembly according to the invention shown.
- the container arrangement has a first or upper container half 2, a second or lower container half 4 and a membrane 6.
- the two container halves 2, 4 are expediently designed as closed on one side, cylindrical container.
- the diaphragm 6 divides the space formed by the container halves 2, 4 into two partial areas, namely a lower partial area, in which advantageously a gas, such as nitrogen, is provided and an upper portion, in which a liquid, such as water is present.
- the gas cushion arranged on the other membrane side is compressed upon heating due to the incompressibility of the liquid, so that due to the flexible membrane a pressure compensation between liquid and gas cushion is made possible.
- the upper container half 2 has a connection 8 in order to supply and remove the liquid to the container arrangement.
- a connecting element 10 is provided, by means of which the membrane 6 is fixed indirectly to the two container halves 2, 4.
- the membrane 6 is expediently flexible, in particular of an elastic material, for example rubber.
- the membrane 6 has a working area 12 which can shift within the container arrangement.
- the working area 12 is in particular a central region of the membrane 6.
- a fastening area 14 is provided beyond which the membrane 6 can be fixed directly or indirectly to at least one of the container halves 2, 4.
- the connecting element 10 is formed as a cylindrical body, on whose - viewed in the radial direction r - inner lateral surface in the longitudinal direction l at least partially overlapping the first container half 2 and second container half 4 is arranged.
- the first container half 2 is directly connected via a cohesive connection in the form of a weld 16 to the connecting element 10.
- the two end edges of the container halves 2, 4 do not abut each other, but are spaced apart such that a free space 18 is formed between them.
- This is an adhesion layer 20 is provided, which creates a material connection between the membrane 6 and connecting element 10.
- FIG. 3 is a further preferred, exemplary embodiment of the container assembly according to the invention shown.
- the connecting element 10 is not arranged in the longitudinal direction l overlapping with the two container halves 2, 4, but is located between the two end sides of the container halves 2, 4. In other words, contact the end faces of the container halves 2, 4, the end face of the annular connecting element 10th and are connected to each other via a weld 22 at their respective end faces cohesively.
- the connecting element 10 has engaging regions 24 in its radially inwardly directed region in order to connect the fastening region 14 of the diaphragm 6 positively and positively to the connecting element 10. Additionally or alternatively, the membrane 6 can also be connected to the connecting element 10 via an adhesion layer.
- FIG. 4 is a further preferred, exemplary embodiment of the container assembly according to the invention shown.
- the two container halves 2, 4 have at their end faces in each case one in the radial direction r inwardly projecting flange 26, which serves to fix the diaphragm 6.
- the attachment region 14 of the membrane 6 on the flange 26 facing sides may have an adhesion layer 20.
- the attachment portion 14 on the two flanges 26 facing sides each have an adhesion layer 20.
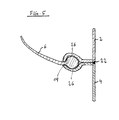
- a combination of fixing the fastening region 14 to the flange 26 via a non-positive and positive connection would be conceivable, as shown in FIG FIG. 5 is shown.
- the two flanges 26 are concavely formed at their mutually facing sides to receive a receiving space for a bead-like region or edge region of the membrane 6 therein.
- the end faces of the two container halves 2, 4 contact each other directly and are adhesively connected to one another via a bond 28.
- the cohesive connection can also be brought about by welding.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Filling Or Discharging Of Gas Storage Vessels (AREA)
- Separation Using Semi-Permeable Membranes (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102012207705.7A DE102012207705B4 (de) | 2012-05-09 | 2012-05-09 | Membrane und Behälteranordnung |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2662575A2 true EP2662575A2 (fr) | 2013-11-13 |
| EP2662575A3 EP2662575A3 (fr) | 2014-04-23 |
Family
ID=48190349
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP13165977.3A Withdrawn EP2662575A3 (fr) | 2012-05-09 | 2013-04-30 | Membrane et agencement de récipient |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2662575A3 (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE102012207705B4 (fr) |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3144176A1 (de) * | 1980-11-18 | 1982-06-24 | Greer Hydraulics, Inc., 91311 Chatsworth, Calif. | Druckgefaess, insbesondere hydrospeicher, und verfahren zu seiner herstellung |
| GB2102068A (en) * | 1981-05-11 | 1983-01-26 | Fawcett Eng Ltd | Pressure vessels |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1600605A1 (de) * | 1967-06-01 | 1970-03-19 | Erich Schueler | Hydraulischer Speicher mit Gleichdruck-Verhalten |
| DE2102969C3 (de) * | 1971-01-22 | 1978-06-15 | 2800 Bremen | Behälter mit Membrane |
| BE795495A (fr) * | 1972-03-07 | 1973-05-29 | Mercier Jacques H | Reservoir de pression |
| AU7940875A (en) * | 1975-04-01 | 1976-09-30 | Fawcett Eng Ltd | Accumulator |
| DE2707080A1 (de) * | 1977-02-18 | 1978-08-24 | Sugimura | Speichervorrichtung mit einer geschweissten kapsel und einem eingesetzten trennelement |
| DE29718588U1 (de) * | 1997-10-20 | 1998-01-15 | Böhm, Klaus, 09128 Chemnitz | Hydropneumatischer Druckspeicher |
| DE202010005994U1 (de) * | 2010-04-23 | 2010-07-15 | Winkelmann Sp. Z.O.O. | Membranausdehnungsgefäß |
-
2012
- 2012-05-09 DE DE102012207705.7A patent/DE102012207705B4/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2013
- 2013-04-30 EP EP13165977.3A patent/EP2662575A3/fr not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3144176A1 (de) * | 1980-11-18 | 1982-06-24 | Greer Hydraulics, Inc., 91311 Chatsworth, Calif. | Druckgefaess, insbesondere hydrospeicher, und verfahren zu seiner herstellung |
| GB2102068A (en) * | 1981-05-11 | 1983-01-26 | Fawcett Eng Ltd | Pressure vessels |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2662575A3 (fr) | 2014-04-23 |
| DE102012207705A1 (de) | 2013-11-14 |
| DE102012207705B4 (de) | 2017-09-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1134415B1 (fr) | Serrage de membrane avec un système de compensation d'élasticité | |
| EP0163252B1 (fr) | Raccord fileté pour tube avec joint de contact | |
| EP2430318B1 (fr) | Accumulateur hydraulique | |
| DE112010003557T5 (de) | Absperrklappe | |
| EP1735537A1 (fr) | Accumulateur hydraulique | |
| DE112014001073T5 (de) | Verbindungsstück | |
| DE10355151B4 (de) | Schwingungsdämpfer mit einem extern angeschlossenen Gehäuse | |
| DE102018203450B4 (de) | Dichtungsanordnung, Fluidregelventil mit einer solchen Dichtungsanordnung und Verwendung eines solchen Fluidregelventils | |
| EP2962017B1 (fr) | Joint plat pour raccords à brides | |
| WO2001006116A1 (fr) | Raccord et carter pour un systeme d'injection de carburant pourvu d'un accumulateur de carburant haute pression | |
| DE102013215294A1 (de) | Membrananordnung für eine Ventileinrichtung | |
| EP3311063A1 (fr) | Ensemble réservoir en deux parties pour air comprimé | |
| DE102012207705B4 (de) | Membrane und Behälteranordnung | |
| EP3334514A1 (fr) | Dispositif filtrant et élément filtrant | |
| DE102017004478B4 (de) | Dichtring, dessen Verwendung und Einrohr-Gasdruckstoßdämpfer, der den Dichtring umfasst | |
| WO2016058767A1 (fr) | Procédé de raccordement d'une plaque de séparation d'un amortisseur de vibration à un cylindre , amortisseur de vibrations et véhicule automobile | |
| EP1544530B1 (fr) | Raccord pour tuyaux flexibles | |
| WO2014114499A1 (fr) | Ensemble cylindre présentant une liaison par adhésif | |
| WO2019170735A1 (fr) | Ensemble d'étanchéité et soupape de réglage de fluide | |
| EP3499081A1 (fr) | Ressort pneumatique | |
| DE202013007855U1 (de) | Dichteinrichtung für Rohrverbindungen | |
| DE202010005994U1 (de) | Membranausdehnungsgefäß | |
| EP0058211A1 (fr) | Rondelle auto-étanche | |
| EP3198175B1 (fr) | Joint d'étanchéité servant à étanchéifier des raccords par brides | |
| WO2006072437A1 (fr) | Valve de pneu, et garniture d'etancheite moulee pour valve de pneu |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: F15B 1/14 20060101AFI20140319BHEP |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20140625 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: SEMPERIT AG HOLDING |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20151209 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 20171103 |