EP2642095B1 - Dispositif de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour moteur diesel - Google Patents
Dispositif de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour moteur diesel Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2642095B1 EP2642095B1 EP11842356.5A EP11842356A EP2642095B1 EP 2642095 B1 EP2642095 B1 EP 2642095B1 EP 11842356 A EP11842356 A EP 11842356A EP 2642095 B1 EP2642095 B1 EP 2642095B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- exhaust gas
- concentration
- tubular
- collecting
- cyclone
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Not-in-force
Links
- 239000013618 particulate matter Substances 0.000 claims description 152
- 238000001556 precipitation Methods 0.000 claims description 27
- JTJMJGYZQZDUJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N phencyclidine Chemical class C1CCCCN1C1(C=2C=CC=CC=2)CCCCC1 JTJMJGYZQZDUJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 26
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000000295 fuel oil Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 21
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 21
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 21
- 239000003570 air Substances 0.000 description 14
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 9
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sulfate Chemical compound [O-]S([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 7
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000005119 centrifugation Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000001276 controlling effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000009931 harmful effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001737 promoting effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005686 electrostatic field Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009191 jumping Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007790 scraping Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003915 air pollution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012080 ambient air Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000711 cancerogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000315 carcinogenic Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003367 polycyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000010248 power generation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010926 purge Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004071 soot Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01N—GAS-FLOW SILENCERS OR EXHAUST APPARATUS FOR MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; GAS-FLOW SILENCERS OR EXHAUST APPARATUS FOR INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
- F01N3/00—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust
- F01N3/02—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B03—SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS OR USING PNEUMATIC TABLES OR JIGS; MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C—MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C3/00—Separating dispersed particles from gases or vapour, e.g. air, by electrostatic effect
- B03C3/34—Constructional details or accessories or operation thereof
- B03C3/40—Electrode constructions
- B03C3/45—Collecting-electrodes
- B03C3/49—Collecting-electrodes tubular
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B03—SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS OR USING PNEUMATIC TABLES OR JIGS; MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C—MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C3/00—Separating dispersed particles from gases or vapour, e.g. air, by electrostatic effect
- B03C3/02—Plant or installations having external electricity supply
- B03C3/04—Plant or installations having external electricity supply dry type
- B03C3/14—Plant or installations having external electricity supply dry type characterised by the additional use of mechanical effects, e.g. gravity
- B03C3/15—Centrifugal forces
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B03—SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS OR USING PNEUMATIC TABLES OR JIGS; MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C—MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C3/00—Separating dispersed particles from gases or vapour, e.g. air, by electrostatic effect
- B03C3/34—Constructional details or accessories or operation thereof
- B03C3/36—Controlling flow of gases or vapour
- B03C3/368—Controlling flow of gases or vapour by other than static mechanical means, e.g. internal ventilator or recycler
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B03—SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS OR USING PNEUMATIC TABLES OR JIGS; MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C—MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C3/00—Separating dispersed particles from gases or vapour, e.g. air, by electrostatic effect
- B03C3/34—Constructional details or accessories or operation thereof
- B03C3/40—Electrode constructions
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B03—SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS OR USING PNEUMATIC TABLES OR JIGS; MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C—MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C3/00—Separating dispersed particles from gases or vapour, e.g. air, by electrostatic effect
- B03C3/34—Constructional details or accessories or operation thereof
- B03C3/40—Electrode constructions
- B03C3/41—Ionising-electrodes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B03—SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS OR USING PNEUMATIC TABLES OR JIGS; MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C—MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C3/00—Separating dispersed particles from gases or vapour, e.g. air, by electrostatic effect
- B03C3/34—Constructional details or accessories or operation thereof
- B03C3/86—Electrode-carrying means
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B04—CENTRIFUGAL APPARATUS OR MACHINES FOR CARRYING-OUT PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES
- B04C—APPARATUS USING FREE VORTEX FLOW, e.g. CYCLONES
- B04C5/00—Apparatus in which the axial direction of the vortex is reversed
- B04C5/02—Construction of inlets by which the vortex flow is generated, e.g. tangential admission, the fluid flow being forced to follow a downward path by spirally wound bulkheads, or with slightly downwardly-directed tangential admission
- B04C5/04—Tangential inlets
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01N—GAS-FLOW SILENCERS OR EXHAUST APPARATUS FOR MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; GAS-FLOW SILENCERS OR EXHAUST APPARATUS FOR INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
- F01N3/00—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust
- F01N3/01—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust by means of electric or electrostatic separators
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01N—GAS-FLOW SILENCERS OR EXHAUST APPARATUS FOR MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; GAS-FLOW SILENCERS OR EXHAUST APPARATUS FOR INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
- F01N3/00—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust
- F01N3/02—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust
- F01N3/021—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust by means of filters
- F01N3/023—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust by means of filters using means for regenerating the filters, e.g. by burning trapped particles
- F01N3/027—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust by means of filters using means for regenerating the filters, e.g. by burning trapped particles using electric or magnetic heating means
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01N—GAS-FLOW SILENCERS OR EXHAUST APPARATUS FOR MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; GAS-FLOW SILENCERS OR EXHAUST APPARATUS FOR INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
- F01N3/00—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust
- F01N3/02—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust
- F01N3/021—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust by means of filters
- F01N3/023—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust by means of filters using means for regenerating the filters, e.g. by burning trapped particles
- F01N3/027—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust by means of filters using means for regenerating the filters, e.g. by burning trapped particles using electric or magnetic heating means
- F01N3/0275—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust by means of filters using means for regenerating the filters, e.g. by burning trapped particles using electric or magnetic heating means using electric discharge means
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01N—GAS-FLOW SILENCERS OR EXHAUST APPARATUS FOR MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; GAS-FLOW SILENCERS OR EXHAUST APPARATUS FOR INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
- F01N3/00—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust
- F01N3/02—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust
- F01N3/037—Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous, or otherwise treating exhaust for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust by means of inertial or centrifugal separators, e.g. of cyclone type, optionally combined or associated with agglomerators
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B03—SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS OR USING PNEUMATIC TABLES OR JIGS; MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C—MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C2201/00—Details of magnetic or electrostatic separation
- B03C2201/08—Ionising electrode being a rod
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B03—SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS OR USING PNEUMATIC TABLES OR JIGS; MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C—MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C2201/00—Details of magnetic or electrostatic separation
- B03C2201/10—Ionising electrode with two or more serrated ends or sides
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B03—SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS OR USING PNEUMATIC TABLES OR JIGS; MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C—MAGNETIC OR ELECTROSTATIC SEPARATION OF SOLID MATERIALS FROM SOLID MATERIALS OR FLUIDS; SEPARATION BY HIGH-VOLTAGE ELECTRIC FIELDS
- B03C2201/00—Details of magnetic or electrostatic separation
- B03C2201/30—Details of magnetic or electrostatic separation for use in or with vehicles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B04—CENTRIFUGAL APPARATUS OR MACHINES FOR CARRYING-OUT PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES
- B04C—APPARATUS USING FREE VORTEX FLOW, e.g. CYCLONES
- B04C9/00—Combinations with other devices, e.g. fans, expansion chambers, diffusors, water locks
- B04C2009/001—Combinations with other devices, e.g. fans, expansion chambers, diffusors, water locks with means for electrostatic separation
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an exhaust gas treatment technique for large-displacement diesel engines using particularly a low-grade fuel equal to or less than fuel oil, such as for watercrafts, for power generation, or for industrial purposes, for eliminating particulate matter (called below "PM") mainly composed of carbon, or harmful gas, contained in exhaust gas of a diesel engine to purify the exhaust gas, and, in particular, relates to an exhaust gas treatment equipment using corona discharge in the large-displacement diesel engine exhausting high-temperature exhaust gas.
- PM particulate matter
- Diesel engines are widely adopted as power sources for various watercrafts, power generators, large construction machines, and further, various automobiles, but since the PM contained in exhaust gas exhausted from the diesel engines, as is well known, not only causes air pollution, but also is extremely harmful to human bodies, purification of the exhaust gas is extremely important. Therefore, many suggestions have already been made, such as improvement of combustion systems of diesel engines, adoption of various types of exhaust gas filters, or electrical treatment methods using corona discharge, and some of such suggestions have been in practical use.
- the components of the PM (particulate matter) in the exhaust gas of the diesel engine can be classified into two components: soluble organic fractions (called below “SOF”); and insoluble organic fractions (called below “ISF”), and the SOF of the two components is mainly composed of unburnt combustion components of fuel or lubricant oil, and including harmful matter such as carcinogenic polycyclic aromatics.
- the ISF is mainly composed of low electrical resistive carbon (soot) and sulfate components, and the exhaust gas is desired to have as small an amount of SOF and ISF as possible, because of the effects of the SOF and ISF on human bodies and the environment.
- the degree of the harmful effect of the PM on human bodies is problematic especially when the particulate size becomes nanometer size.
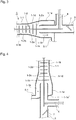
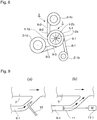
- the patent literature 1 suggests an electrical treatment method and equipment for exhaust gas of a diesel engine, the method and equipment having a system in which a discharging and charging part 22 comprising a corona discharging part 22-1 and a charging part 22-2 is so provided as to communicate with an exhaust gas passage 21, PM 28 mainly composed of carbon in exhaust gas G1 is charged with corona-discharged electrons 29, and the charged PM 28 is collected by a collection plate 23 disposed in the exhaust gas passage 21, the method and equipment having a configuration in which the length of an electrode needle 24 in the discharging and charging part 22 is short in a flowing direction of an exhaust gas stream, and the collection plate 23 is disposed so as to be perpendicular to the flowing direction of the exhaust gas stream.
- the reference numeral 25 denotes a seal gas pipe, 26 high-voltage power supply apparatus, and 27 an exhaust gas guide pipe.
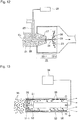
- the patent literature 4 suggests a diesel-engine exhaust gas purification equipment comprising an electrical precipitation means having a discharge electrode charging PM contained in exhaust gas of a diesel engine and a precipitation electrode collecting the charged PM, a means for detaching the PM collected and retained on the precipitation electrode from the particulate electrode, and a cyclone-system segregating and collecting means for segregating and collecting the PM detached from the precipitation electrode.
- This equipment is configured to treat the exhaust gas while causing the exhaust gas to flow laterally, and comprises an electrical precipitation part 51 for collecting the PM, and a cyclone 52 serving as a segregating and collecting part, where the electrical precipitation part 51 comprises: a precipitation electrode 54 composed of a tubular metal body 57 attached to an inner peripheral face of a tubular housing 56 and an uneven part 58 formed on an inner peripheral face of the tubular metal body; and a discharge electrode 55 composed of a main electrode 59 extending along the axial line of the precipitation electrode 54 and a group of radially-projecting electrode needles 60 disposed at predetermined intervals in a longitudinal direction of the main electrode 59, and the cyclone 52 is configured downstream from a guide vane 61 converting a gas stream 53 which has passed through the electrical precipitation part 51 into a swirling flow, and an exhaust pipe 62 for discharging gas in the cyclone and a hopper 63 collecting the PM separated by centrifugation
- the reference numeral 64 denotes a detaching mechanism detaching the PM collected and retained on the precipitation electrode 54 from the precipitation electrode, and composed of an eccentric motor 65 generating vibration due to eccentricity, for example.
- the reference numeral 66 denotes a gas-extraction pipe for returning the exhaust gas in the exhaust pipe 62 to an upper space of the hopper 63.
- the exhaust gas purification equipment thus configured has an arrangement in which the PM in the exhaust gas which has flowed into the electrical precipitation part 51 is charged by discharge between the precipitation electrode 54 and the discharge electrode 55 to be collected on the precipitation electrode 54 by coulomb force, then the collected PM flows into the guide vane 61 with the gas stream, then the PM is centrifugally separated by the cyclone 52 configured downstream from the guide vane 61, and then the centrifugally-separated PM falls down to the hopper 63 and is collected, while the purified exhaust gas is released outside via the exhaust pipe 62.
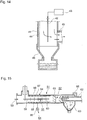
- this gas treatment equipment has a configuration in which the charging and agglomerating part 70 is disposed upstream, and the filter part 80 is disposed downstream, a gas passage wall of the charging and agglomerating part 70 is formed of tubular bodies 71, 71a, etc., a precipitation electrode, which is a low-voltage electrode, is formed of a conductive tubular body 71f disposed in the vicinity of the surface of the gas passage wall, corona electrodes are formed of wire-like high-voltage electrodes disposed inside these tubular bodies, and the tubular body of the gas passage wall is formed as a gas cooling part where natural convection and heat radiation cool gas naturally, and further a turbulence promoting means 71e for promoting disturbance of a gas stream passing in the vicinity of an inner surface of the tubular body of the gas passage wall or the conductive tubular body is provided on the surface of the tubular body or in the vicinity of the surface thereof.
- a precipitation electrode which is a low-voltage electrode
- the reference numeral 71c denotes a gas intake chamber, 71b a corona electrode, and 71d a gas outlet chamber.
- Document JP 5 222915 discloses an exhaust gas purification for an internal combustion engine that comprises two collectors of cyclone type at upstream and downstream stages in conjunction.
- the upstream collector includes a discharge electrode for corona discharge in an inner tube thereof and the downstream collector includes an air purging pipe connected to a discharge pipe of the downstream collector so as to cause cleaned gas to be blown to an insulator for supporting the discharge electrode, and thereby to prevent particulate collection ability from decreasing with decreasing applied voltage due to leak occurred between the electrode bar and the upstream collector, and accordingly to achieve prevention of decreasing purification efficiency.
- the downstream particulate separator which is a vertical collector of cyclone type where particles fall in the bottom of the collector receives from an outer tube tangentially, all of the gas flown from the upstream electric particulate agglomerator at a high velocity.
- the separator discharges the gas in a vertical discharge pipe, while the separator discharges particulate from the bottom of a tapered part to deliver the particulate to a particulate collector to burn the collected particulate at regular time intervals.
- the flow in the second collector is not controlled.
- the electrical treatment method and equipment for exhaust gas of a diesel engine described in the patent literature 1 has problems as follows: high flow resistance (pressure loss) due to the configuration in which the length of the electrode needle 24 in the discharging and charging part 22 is short in the flowing direction of the exhaust gas stream and the collection plate 23 is so disposed as to be perpendicular to the flowing direction of the exhaust gas stream, and in which the exhaust gas stream directly hits the collection plate 23; a possibility that since the collection plate 23 is thin and short in length in the flowing direction of the exhaust gas stream, the PM might pass through the collection plate 23 and the PM collection efficiency thus could not sufficiently be increased; and a worry that once the PM passes through the collection plate 23, the PM may not be charged by corona discharge or collected again, and may be exhausted as it is.
- the patent literature 1 neither discloses nor suggests the technical idea that the collection plate has a tubular shape which is long in the flowing direction of the exhaust gas stream, the electrode needle is disposed in an axial direction of the tubular collecting part, a jumping phenomenon of depositing and detaching repeatedly the PM particles flowing in the flowing direction of the exhaust gas stream is caused so that the PM is grown, this growth phenomenon causes the size of the PM in the exhaust gas stream in the vicinity of an inner face of the tubular collecting part to increase so that a cyclone can easily collect the PM, and causes the PM concentration to increase, and this exhaust gas stream having the large-size PM and the high PM concentration is selectively extracted and then the PM is collected by the cyclone.
- the exhaust gas PM collecting apparatus described in the patent literature 2 and the exhaust gas purification equipment described in the patent literature 3 have drawbacks as follows: a difficulty in setting both the discharge voltage and the collecting deflection voltage at their respective appropriate conditions due to the fact that the voltages are the same potential; a requirement that a large space must be left between the deflection electrode and the collecting electrode in order to prevent a spark from occurring therebetween; a reduction in collection efficiency due to an increase in the amount of PM passing through a collecting section without being collected due to the above requirement; and further, an inevitable increase in equipment size, which is inappropriate as a marine component that is desired to be small in size and light in weight, due to a requirement that the volume of the collecting part must be large in order to raise the collection efficiency.
- the patent literature 2 states that the collecting electrode 32 is formed as a tunnel-like electrode through which the exhaust gas passes, that a combined-electrode body composed of the needle electrodes 31 and the deflection electrodes 36 is disposed in the tunnel of the collecting electrode 32 substantially coaxially with the tunnel, and that the combined-electrode body, which is thick and long, is disposed in the tubular collecting part over substantially the entire length thereof and arranged in a grid-like pattern.
- a tubular collecting part is formed according to the following statements: "...an electrode bar 42 constituting one of the discharge electrode pair and one of the collection electrode is hung along the axis of the stationary cylindrical body 41, ...a wide gas outlet is provided in a lower side face of the stationary cylindrical body 41, and the gas outlet is fitted with a downstream exhaust pipe 45" in paragraph [0033] in Example 6; "the rotary cylindrical part 46 has the shape of an inverted truncated cone, ...a long bar (scraping part) 44 extends upward on an inner face of the rotary cylindrical part 46, and an outer edge of the bar 44 is in contact with an inner face of a wide portion of the stationary cylindrical body 41.” in paragraph [0035]; "...diesel particulates...
- the technique described in the patent literature 3 is such a technique that the collecting electrode is provided as a stationary cylindrical portion (tubular) which is long in the flowing direction of the exhaust gas stream, the electrode needle is disposed with a space in the axial direction of the tubular collecting part, the PM is deposited flowing in the flowing direction of the exhaust gas stream, and the deposited PM particles are scraped off with the bar, and such technique is a technique which is very likely to discharge some of the PM particles, which fly when the PM particles are scraped off, from the downstream exhaust pipe fitted in the wide gas outlet port provided upstream from the collection box.
- the gas treatment equipment described in the patent literature 5 is a vehicle-mounted small-sized gas treatment equipment, and is directed to a technique relating to an equipment in which the charging and agglomerating part 70 is configured to be disposed upstream, and the filter part 80 is disposed downstream, the charging and agglomerating part 70 is provided with the gas intake chamber 71c branching the exhaust gas into many streams, the gas passage wall is formed of the tubular body 71f, the tubular body 71f is exposed to ambient air and the tubular body 71f, which is the gas passage wall, is formed as a gas cooling part cooling the gas by natural heat loss due to natural convection and heat radiation, and the branched exhaust gas streams are then mixed again in the gas outlet chamber 71d.
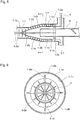
- the low-PM-concentration exhaust gas outlet pipe 3 is provided with a flow-rate control damper 7 for regulating the inflow rate and inflow velocity of the high-concentration exhaust gas to the tangential cyclone 2-1a and the discharge rate of the low-concentration exhaust gas.
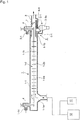
- the dashed line in FIG. 1 shows an example of a combination of a main engine 12 and an auxiliary engine 13 in a marine diesel engine.
- the modes of engine operation include parallel operation of the main engine 12 and the auxiliary engine 13 and individual operation thereof, where the load of each engine also significantly varies, and therefore the total flow rate of exhaust gas significantly varies.
- a plurality of the collecting pipes 1-1 may be provided in parallel (not shown).
- the PM in the exhaust gas flowing into the collecting pipe 1-1 from the exhaust gas inlet 1-1a is charged by discharge between the collecting wall 1-1k which is an inner wall of the collecting pipe 1-1 constituting the precipitation electrode and the discharge electrode 1-2, the charged PM particles are collected on the collecting wall 1-1k by coulomb force.
- An exhaust gas stream including PM in high concentration is created such that PM particles collected from an exhaust gas stream in the vicinity of the axial center are further deposited on the PM particles collected on the collecting wall 1-1k of the collecting pipe 1-1 and gradually grown into masses over time, and the PM masses flow while being concentrated in the vicinity of the collecting wall by repeating detachment due to the exhaust flow and reattachment to the tubular collecting wall 1-1k due to the coulomb force involved in the discharge (charge), and, as the same time, the PM in the exhaust gas flowing in the vicinity of the axial center of the collecting pipe 1-1 is gradually diluted by collecting the PM on the collecting wall 1-1k, so that the exhaust gas flows downstream as a stream having only a low PM concentration.
- the exhaust gas which has flowed into the collecting pipe 1-1 from the exhaust gas inlet 1-1a is separated into a high PM concentration of exhaust gas stream and a low PM concentration of exhaust gas stream in the course of flowing down in the tubular collecting part 1, and the high-PM-concentration exhaust gas stream flows downstream in the vicinity of the collecting wall 1-1k of the inner wall of the collecting pipe 1-1, and the low PM concentration of exhaust gas stream in the vicinity of the axial center of the collecting pipe 1-1.
- the high PM concentration of exhaust gas stream which has flowed in the vicinity of the collecting wall 1-1k of the inner wall of the collecting pipe 1-1 is introduced into the tangential cyclone 2-1a from the high-PM-concentration exhaust gas outlet portion 1-1b of the collecting pipe 1-1 via the communicating pipe 5-1 and the PM is separated by centrifugation. While, in the case of the diesel-engine exhaust gas treatment equipment shown in FIG.
- the high PM concentration of exhaust gas stream which has flowed in the vicinity of the collecting wall 1-1k of the inner wall of the collecting pipe 1-1 is introduced into the two tangential cyclones 2-1a from the high-PM-concentration exhaust gas outlet portion 1-1b of the collecting pipe 1-1 via the communicating pipes 5-1, 5-2 and the PM is separated by centrifugation.
- the low PM concentration of exhaust gas stream flowing in the vicinity of the axial center portion of the collecting pipe 1-1 is discharged outside through the low-PM-concentration exhaust gas outlet pipe 3 provided in the vicinity of the axial center portion of the collecting pipe 1-1, in both the cases of the exhaust gas treatment equipments for a diesel engine in FIGS. 1 and 2 .
- the exhaust gas streams purified by the tangential cyclones 2-1a are caused to mixed into the low PM concentration of exhaust gas stream flowing in the low-PM-concentration exhaust gas outlet pipe 3 via the discharge pipes 6-1, 6-1, and 6-2, respectively.
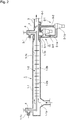
- an exhaust gas treatment equipment for a diesel engine shown as a fifth embodiment equipment in FIG. 7 is configured such that an exhaust gas intake chamber 1-1f is disposed upstream from the collecting pipe 1-1, a narrowing portion 1-1f and a radially-expanding portion 1-1h are disposed between the exhaust gas intake chamber 1-1f and the collecting pipe 1-1, the narrowing portion 1-1g and the radially-expanding portion 1-1h are also provided with the electrode needles 1-2b, and the exhaust gas inlet 1-1a to the exhaust gas intake chamber 1-1f and a seal air inlet 1-1j to a seal air intake chamber 1-1i are disposed so as to face each other.
- the cyclone collecting means is thus composed of tangential cyclones having different treatment capacities, not only does it become possible to select more appropriately each tangential cyclone according to the exhaust gas flow rate that changes according to a change in operating conditions or the engine load ratio involved in the parallel operation or individual operation of the main engine and the auxiliary engine in a marine engine, but it also becomes possible to control more appropriately the tangential velocity of exhaust gas flowing in each tangential cyclone by controlling the respective flow-rate control dampers 9-1, 9-2, 9-3 provided for the tangential cyclones in combination with the damper provided in the low-PM-concentration exhaust gas outlet pipe 3, so that a high collection efficiency can be ensured and maintained over a wide range of engine load ratios, or the like.
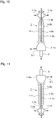
- the tubular collecting part 1 is disposed substantially vertically and upward, as shown in FIG. 11 , there is not only the advantage that it becomes easy to collect the falling PM, but also the advantage that, when SOF, sulfate, or the like, attached to the collecting wall face is liquefied, it becomes easy to collect the liquefied components because of falling down the surface of the collecting wall, and further the advantage it becomes easy to collect even heavy oxidized scales corroded by sulfate or the like detaching and falling from the surface of the wall.
- the tubular collecting part 1 is disposed substantially horizontally, there is the advantage that workability at a maintenance time of the collecting pipe, the discharge electrode, and the like becomes excellent since the tubular collecting part 1 is maintained at a horizontally substantially constant height from the floor surface of the engine room in which the engine is placed.
- the exhaust gas purification equipment for a diesel engine has a system in which the exhaust gas is purified by introducing a stream of part of the entire exhaust gas amount which has been concentrated up to a high PM concentration by condensing PM in advance into the cyclone and thereby the size of the cyclone can be reduced, and besides, when the system is such that the cyclone collecting means is composed of a plurality of tangential cyclones so that the high PM concentration of exhaust gas stream discharged through the high-PM-concentration exhaust gas outlet portion is selectively introduced into the tangential cyclones according to the flow rate of the exhaust gas, it becomes possible to select an appropriate treatment capacity and the appropriate number of the tangential cyclones in a well-balanced manner according to a significant increase or decrease in the exhaust gas flow rate (flow velocity) involved in a change in operating conditions or a fluctuation in engine load ratio caused by parallel operation or individual operation of the main engine and the auxiliary engine in a marine engine, in addition to the function effect of the
- the diesel-engine exhaust gas purification equipment according to the present invention makes a great consideration to exhaust gas purification treatment for a diesel engine for various applications, such as for watercrafts, for automobiles, or for industrial purposes, using a low-grade fuel equal to or less than fuel oil.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Processes For Solid Components From Exhaust (AREA)
- Electrostatic Separation (AREA)
- Cyclones (AREA)
Claims (9)
- Équipement de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour un moteur diesel, comprenant : un moyen de précipitation électrique ayant une électrode de décharge (1-2) pour charger la matière particulaire contenue dans les gaz d'échappement d'un moteur diesel qui utilise un carburant de qualité inférieure qui est égal ou inférieur au mazout, et une partie de collecte tubulaire (1) ayant une longueur prédéterminée et comprenant une électrode de précipitation pour collecter la matière particulaire chargée, l'électrode de décharge (1-2) étant composée d'une électrode principale (1-2a) disposée dans une direction axiale dans la partie de collecte tubulaire (1-1) et d'une pluralité d'aiguilles d'électrode (1-2b) disposées à intervalles sur l'électrode principale et faisant saillie radialement ; et un moyen de séparation et de collecte (2) d'un système cyclonique, pour séparer et collecter la matière particulaire qui s'est détachée de la partie de collecte tubulaire,
l'équipement de traitement des gaz d'échappement ayant un agencement dans lequel un tuyau de sortie des gaz d'échappement (3) pour une faible concentration de matière particulaire (PM) est disposé à proximité d'un centre axial du côté aval de la partie de collecte tubulaire et une partie de sortie des gaz d'échappement (1-1b) pour une concentration élevée de matière particulaire est disposée à proximité d'une face périphérique interne du côté aval de la partie de collecte tubulaire, un moyen de collecte à cyclone (2-1) pour collecter la matière particulaire est disposé de sorte à communiquer avec la partie de sortie des gaz d'échappement pour une concentration élevée de matière particulaire, le moyen de collecte à cyclone comprenant un cyclone tangentiel (2-1a) et un amortisseur (7) disposé dans le tuyau de sortie des gaz d'échappement (3) pour une faible concentration de matière particulaire et un moyen conçu pour réguler la vitesse des gaz d'échappement circulant dans le cyclone tangentiel (2-1a) en régulant une position d'ouverture de l'amortisseur (7). - Équipement de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour un moteur diesel selon la revendication 1, dans lequel le moyen de collecte à cyclone (2-1a) comprend une pluralité de cyclones tangentiels (2-1b, 2-1c, 2-1d) de telle sorte que la concentration élevée de matière particulaire des gaz d'échappement évacués au moyen de la partie de sortie des gaz d'échappement (1-1b) pour une concentration élevée de matière particulaire soit introduite de façon sélective dans les cyclones tangentiels selon le débit de la concentration élevée de matière particulaire des gaz d'échappement.
- Équipement de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour un moteur diesel selon la revendication 1 ou 2, dans lequel la partie de collecte tubulaire comporte une partie tubulaire s'étendant radialement ayant un diamètre augmentant petit à petit (1-1d) et une partie tubulaire à diamètre important (1-1e) communiquant avec la partie tubulaire s'étendant radialement (1-1d) au niveau d'une extrémité du côté aval de la partie de collecte tubulaire, et le tuyau de sortie des gaz d'échappement (3) pour une faible concentration de matière particulaire et la partie de sortie des gaz d'échappement (1-1b) pour une concentration élevée de matière particulaire sont disposées, de manière communiquant, à proximité d'un centre axial de la partie tubulaire à diamètre important (1-1e) et à proximité d'une face périphérique interne de la partie tubulaire à diamètre important (1-1e), respectivement.
- Équipement de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour un moteur diesel selon la revendication 3, dans lequel l'électrode de décharge (1-2a) est disposée de sorte à s'étendre jusqu'à la zone de la partie tubulaire s'étendant radialement (1-1d) ou jusqu'à la partie tubulaire à diamètre important (1-1e) communiquant avec la partie tubulaire s'étendant radialement, dans la partie de collecte tubulaire (1-1) .
- Équipement de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour un moteur diesel selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 4, dans lequel la partie de collecte tubulaire (1-1) est disposée sensiblement horizontalement.
- Équipement de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour un moteur diesel selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 4, dans lequel la partie de collecte tubulaire (1-1) est disposée sensiblement verticalement avec le côté aval vers le haut.
- Équipement de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour un moteur diesel selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 4, dans lequel la partie de collecte tubulaire (1-1) est disposée sensiblement verticalement avec le côté aval vers le bas.
- Équipement de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour un moteur diesel selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 7, dans lequel le moyen de collecte à cyclone (2-1a) comprend une pluralité de cyclones tangentiels (2-1b, 2-1c, 2-1d) ayant des capacités de traitement différentes et un amortisseur de régulation de débit (9-1, 9-2, 9-3) est disposé au niveau d'un orifice d'entrée de chaque cyclone tangentiel.
- Équipement de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour un moteur diesel selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 8, dans lequel un tuyau d'évacuation (6-2) pour contraindre les gaz purifiés qui ont traversé le cyclone tangentiel (2-1a) à se mélanger dans la faible concentration de matière particulaire des gaz d'échappement est disposé entre le cyclone tangentiel et le tuyau de sortie des gaz d'échappement (3) pour une faible concentration de matière particulaire et une buse d'air (10) est disposée, ou un ventilateur entraîné par un moteur (11) est disposé, dans le tuyau d'évacuation (6-2).
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010256160A JP5863087B2 (ja) | 2010-11-16 | 2010-11-16 | 重油以下の低質燃料を使用する大排気量ディーゼルエンジン用排ガス処理装置 |
| PCT/JP2011/067318 WO2012066825A1 (fr) | 2010-11-16 | 2011-07-28 | Dispositif de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour moteur diesel |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2642095A1 EP2642095A1 (fr) | 2013-09-25 |
| EP2642095A4 EP2642095A4 (fr) | 2014-11-05 |
| EP2642095B1 true EP2642095B1 (fr) | 2018-02-14 |
Family
ID=46083769
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP11842356.5A Not-in-force EP2642095B1 (fr) | 2010-11-16 | 2011-07-28 | Dispositif de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour moteur diesel |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2642095B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JP5863087B2 (fr) |
| KR (1) | KR101423016B1 (fr) |
| CN (1) | CN103261596B (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO2012066825A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20150113959A1 (en) * | 2012-05-29 | 2015-04-30 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Particulate matter processing apparatus |
| JP6172714B2 (ja) | 2013-05-09 | 2017-08-02 | 臼井国際産業株式会社 | 重油を使用する船舶用ディーゼルエンジンの排ガス処理装置 |
| JP6238823B2 (ja) * | 2014-04-08 | 2017-11-29 | 臼井国際産業株式会社 | 高濃度に硫黄成分を含有する低質燃料を使用する船舶用ディーゼルエンジンの排ガス処理装置 |
| CN104174489B (zh) * | 2014-08-22 | 2017-03-22 | 成都代代吉前瞻科技股份有限公司 | 一种滤除可入肺颗粒物的空气净化器 |
| FR3026660B1 (fr) * | 2014-10-01 | 2016-12-23 | Coutier Moulage Gen Ind | Dispositif de separation de gouttes d’huile dans un melange de gaz et d’huile et procede de separation mettant en œuvre un tel dispositif de separation |
| JP6646952B2 (ja) * | 2015-06-09 | 2020-02-14 | 臼井国際産業株式会社 | ディーゼルエンジン排ガス処理用電気集塵装置の放電電極 |
| DE102016200936A1 (de) * | 2016-01-22 | 2017-07-27 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Kraftfahrzeug mit Staubsammler |
| KR101814980B1 (ko) * | 2016-08-08 | 2018-01-04 | 주식회사 애니텍 | 오리피스형 입자상 물질 제거용 배기가스 전처리 장치 |
| CN106362520B (zh) * | 2016-12-02 | 2018-11-27 | 大连圣洁热处理科技发展有限公司 | 一种烟气除尘装置 |
| JP2018202297A (ja) * | 2017-05-31 | 2018-12-27 | 臼井国際産業株式会社 | ディーゼルエンジン排ガス処理用電気集塵装置の放電電極 |
| CN107262277B (zh) * | 2017-07-27 | 2023-06-27 | 西安热工研究院有限公司 | 一种氧化皮分离组件及方法 |
| FR3073430B1 (fr) * | 2017-11-14 | 2021-12-17 | Leclerc Christian Huret | Module de depoussierage electrostatique |
| KR102133870B1 (ko) * | 2018-08-20 | 2020-07-14 | 엠에이티플러스 주식회사 | 폐가스 처리 장치 |
| JP7146347B2 (ja) * | 2018-10-16 | 2022-10-04 | 臼井国際産業株式会社 | 塗装用乾燥炉の排気ガス用静電集塵装置 |
| KR102618450B1 (ko) * | 2020-12-28 | 2023-12-27 | 엘에스일렉트릭(주) | 집진 유닛을 구비한 인버터 장치 |
| JP2024510102A (ja) * | 2021-02-17 | 2024-03-06 | クマール ヴィドヤルシ,ムケシュ | 内燃ディーゼルエンジンにおいて分極された大気および分極された排気ガスを同時に充填するための装置およびその方法 |
| CN113117906B (zh) * | 2021-04-21 | 2022-01-04 | 西南石油大学 | 一种针对页岩锤磨钻屑粉尘的静电旋风复合分离装置 |
| DE102022203622B8 (de) | 2022-01-24 | 2023-06-15 | Cummins Emission Solutions Inc. | Abgasfiltrationsvorrichtung |
Family Cites Families (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US1890070A (en) * | 1931-07-14 | 1932-12-06 | Prat Daniel Corp | Dust separator control |
| US3253400A (en) * | 1961-08-07 | 1966-05-31 | Union Oil Co | Exhaust treatment apparatus and method |
| US3495401A (en) * | 1967-10-23 | 1970-02-17 | Ethyl Corp | Exhaust system |
| JPS57117711U (fr) * | 1981-01-13 | 1982-07-21 | ||
| DE3141156A1 (de) * | 1981-10-16 | 1983-04-28 | Robert Bosch Gmbh, 7000 Stuttgart | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum entfernen von festen bestandteilen und aerosolen, insbesondere von russbestandteilen aus dem abgas von brennkraftmaschinen |
| GB2215645A (en) * | 1988-03-17 | 1989-09-27 | Ford Motor Co | Separator for IC engine exhaust system |
| JPH06173637A (ja) | 1991-02-18 | 1994-06-21 | Nagao Kogyo:Kk | 車両用ディ−ゼル機関の排気ガス浄化装置 |
| JPH05222915A (ja) * | 1992-02-10 | 1993-08-31 | Nippon Soken Inc | 内燃機関の排気ガス浄化装置 |
| JPH05277313A (ja) * | 1992-03-31 | 1993-10-26 | Teikoku Piston Ring Co Ltd | 微粒子分離装置 |
| DE4319283C1 (de) * | 1993-06-10 | 1994-10-20 | Daimler Benz Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Verminderung von Partikeln in Abgasen |
| JP2698804B2 (ja) | 1995-10-24 | 1998-01-19 | 株式会社オーデン | 電気的制御によるディーゼルエンジンの排気微粒子捕集装置 |
| GB2339398B (en) * | 1998-07-10 | 2002-05-01 | Notetry Ltd | Apparatus and method for concentrating gasborne particles in a portion of a gas stream |
| JP4339049B2 (ja) * | 2003-08-29 | 2009-10-07 | 日新電機株式会社 | 排ガス処理方法及び排ガス処理装置 |
| WO2006033574A1 (fr) * | 2004-09-23 | 2006-03-30 | E-Traction Europe B.V. | Dispositif et procédé d’extraction de particules des gaz d’échappement |
| JP4529013B2 (ja) | 2004-10-01 | 2010-08-25 | いすゞ自動車株式会社 | ガス処理装置 |
| JP2006136766A (ja) * | 2004-11-10 | 2006-06-01 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | ディーゼルエンジン排ガス浄化装置 |
| EP1837489B9 (fr) | 2004-12-17 | 2012-09-12 | Usui Kokusai Sangyo Kaisha Limited | Moyen de traitement electrique pour gaz d'echappement de moteur diesel et son dispositif |
| FR2884857B1 (fr) * | 2005-04-26 | 2007-06-22 | Renault Sas | Dispositif a elements de separation par voie inertielle pour le filtrage et l'elimination de particules contenues dans des gaz d'echappement |
| JP2007187132A (ja) * | 2006-01-16 | 2007-07-26 | Toyota Motor Corp | 排ガス浄化装置 |
| JP2007255284A (ja) * | 2006-03-23 | 2007-10-04 | Nissan Diesel Motor Co Ltd | 排気浄化装置 |
-
2010
- 2010-11-16 JP JP2010256160A patent/JP5863087B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2011
- 2011-07-28 EP EP11842356.5A patent/EP2642095B1/fr not_active Not-in-force
- 2011-07-28 WO PCT/JP2011/067318 patent/WO2012066825A1/fr active Application Filing
- 2011-07-28 CN CN201180055097.0A patent/CN103261596B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2011-07-28 KR KR1020137015397A patent/KR101423016B1/ko active IP Right Grant
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| None * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2642095A4 (fr) | 2014-11-05 |
| JP5863087B2 (ja) | 2016-02-16 |
| CN103261596A (zh) | 2013-08-21 |
| KR101423016B1 (ko) | 2014-07-23 |
| WO2012066825A1 (fr) | 2012-05-24 |
| CN103261596B (zh) | 2015-12-16 |
| JP2012107556A (ja) | 2012-06-07 |
| EP2642095A1 (fr) | 2013-09-25 |
| KR20130087566A (ko) | 2013-08-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2642095B1 (fr) | Dispositif de traitement des gaz d'échappement pour moteur diesel | |
| EP2868880B1 (fr) | Dispositif de traitement de gaz d'échappement pour moteur diesel marin utilisant un carburant de qualité inférieure à celle de l'huile lourde | |
| JP6172714B2 (ja) | 重油を使用する船舶用ディーゼルエンジンの排ガス処理装置 | |
| JP2013238172A5 (fr) | ||
| EP3308863A1 (fr) | Électrode de décharge de dépoussiéreur électrostatique pour le traitement de gaz d'échappement de moteur diesel | |
| JP2014238086A5 (fr) | ||
| JP2006136766A (ja) | ディーゼルエンジン排ガス浄化装置 | |
| KR20170081703A (ko) | 데미스터, 배기 가스 재순환 시스템, 및 이를 구비한 선박용 엔진 | |
| EP3632570A1 (fr) | Électrode de décharge de dépoussiéreur électrostatique pour le traitement de gaz d'échappement de moteur diesel | |
| CN109569904B (zh) | 一种旋流-静电除雾器 | |
| PH12014000396B1 (en) | Composite dust collector | |
| RU152074U1 (ru) | Вихревой сепаратор с лопаточным аппаратом | |
| WO2017057199A1 (fr) | Dépoussiéreur électrostatique pour le traitement des gaz d'échappement d'un moteur diesel | |
| RU113489U1 (ru) | Батарейный циклон для очистки газов | |
| JPH0549972A (ja) | サイクロン分離装置 | |
| RU2318580C1 (ru) | Устройство обезвреживания токсичных компонентов газовых выбросов, содержащих дисперсные частицы | |
| RU139471U1 (ru) | Устройство циклонного разделения | |
| RU95549U1 (ru) | Электрофильтр | |
| RU117321U1 (ru) | Циклон-электрофильтр | |
| KR20230173018A (ko) | 전기 집진 장치 | |
| RU136365U1 (ru) | Электроциклон | |
| RU94877U1 (ru) | Циклон | |
| EA025229B1 (ru) | Вихревой сепаратор с лопаточным аппаратом | |
| Irzycki et al. | Improvement of axially symmetrical plasma reactor structure within a framework of particles pollution decrease in engine's exhaust | |
| JPS60187710A (ja) | 内燃機関の排ガスから固体粒子を除去する装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20130613 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| A4 | Supplementary search report drawn up and despatched |
Effective date: 20141007 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: B03C 3/40 20060101ALN20140930BHEP Ipc: B04C 9/00 20060101ALI20140930BHEP Ipc: B04C 5/04 20060101ALN20140930BHEP Ipc: B03C 3/86 20060101ALN20140930BHEP Ipc: F01N 3/027 20060101ALI20140930BHEP Ipc: B03C 3/49 20060101ALN20140930BHEP Ipc: F01N 3/01 20060101ALI20140930BHEP Ipc: B03C 3/15 20060101AFI20140930BHEP Ipc: B03C 3/36 20060101ALI20140930BHEP Ipc: B03C 3/41 20060101ALN20140930BHEP Ipc: F01N 3/02 20060101ALN20140930BHEP Ipc: F01N 3/037 20060101ALI20140930BHEP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R079 Ref document number: 602011045668 Country of ref document: DE Free format text: PREVIOUS MAIN CLASS: F01N0003020000 Ipc: B03C0003150000 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: B03C 3/41 20060101ALN20170727BHEP Ipc: F01N 3/027 20060101ALI20170727BHEP Ipc: F01N 3/01 20060101ALI20170727BHEP Ipc: B03C 3/49 20060101ALN20170727BHEP Ipc: B04C 9/00 20060101ALI20170727BHEP Ipc: B03C 3/86 20060101ALN20170727BHEP Ipc: B03C 3/15 20060101AFI20170727BHEP Ipc: B04C 5/04 20060101ALN20170727BHEP Ipc: B03C 3/36 20060101ALI20170727BHEP Ipc: F01N 3/037 20060101ALI20170727BHEP |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20170823 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602011045668 Country of ref document: DE Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 969535 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20180315 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20180214 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 969535 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20180214 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180514 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180514 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180515 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602011045668 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20181115 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20180728 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180728 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20180731 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180731 Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180728 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180731 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180731 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180731 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180728 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180728 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180214 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20110728 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180214 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180614 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Payment date: 20210721 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20210729 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 602011045668 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220728 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20230201 |