EP2329944B1 - Presse destinée à produire une force de pression pour le traitement d'une pièce - Google Patents
Presse destinée à produire une force de pression pour le traitement d'une pièce Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2329944B1 EP2329944B1 EP10014816.2A EP10014816A EP2329944B1 EP 2329944 B1 EP2329944 B1 EP 2329944B1 EP 10014816 A EP10014816 A EP 10014816A EP 2329944 B1 EP2329944 B1 EP 2329944B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- press
- ram
- linear electric
- electric motor
- linear
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 title description 2
- 238000003754 machining Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 24
- 210000003128 head Anatomy 0.000 description 8
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000010687 lubricating oil Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000005461 lubrication Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000004080 punching Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000003856 thermoforming Methods 0.000 description 3
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005802 health problem Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000010720 hydraulic oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012777 electrically insulating material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003925 fat Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013861 fat-free Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035515 penetration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002787 reinforcement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003351 stiffener Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010689 synthetic lubricating oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012549 training Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B30—PRESSES
- B30B—PRESSES IN GENERAL
- B30B1/00—Presses, using a press ram, characterised by the features of the drive therefor, pressure being transmitted directly, or through simple thrust or tension members only, to the press ram or platen
- B30B1/10—Presses, using a press ram, characterised by the features of the drive therefor, pressure being transmitted directly, or through simple thrust or tension members only, to the press ram or platen by toggle mechanism
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21J—FORGING; HAMMERING; PRESSING METAL; RIVETING; FORGE FURNACES
- B21J9/00—Forging presses
- B21J9/10—Drives for forging presses
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B26—HAND CUTTING TOOLS; CUTTING; SEVERING
- B26D—CUTTING; DETAILS COMMON TO MACHINES FOR PERFORATING, PUNCHING, CUTTING-OUT, STAMPING-OUT OR SEVERING
- B26D5/00—Arrangements for operating and controlling machines or devices for cutting, cutting-out, stamping-out, punching, perforating, or severing by means other than cutting
- B26D5/08—Means for actuating the cutting member to effect the cut
- B26D5/086—Electric, magnetic, piezoelectric, electro-magnetic means
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B26—HAND CUTTING TOOLS; CUTTING; SEVERING
- B26F—PERFORATING; PUNCHING; CUTTING-OUT; STAMPING-OUT; SEVERING BY MEANS OTHER THAN CUTTING
- B26F1/00—Perforating; Punching; Cutting-out; Stamping-out; Apparatus therefor
- B26F1/38—Cutting-out; Stamping-out
- B26F1/40—Cutting-out; Stamping-out using a press, e.g. of the ram type
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B30—PRESSES
- B30B—PRESSES IN GENERAL
- B30B1/00—Presses, using a press ram, characterised by the features of the drive therefor, pressure being transmitted directly, or through simple thrust or tension members only, to the press ram or platen
- B30B1/42—Presses, using a press ram, characterised by the features of the drive therefor, pressure being transmitted directly, or through simple thrust or tension members only, to the press ram or platen by magnetic means, e.g. electromagnetic
Definitions
- the invention relates to a press for generating a pressure force for the machining of a workpiece.
- Presses are already known in various embodiments. Such presses are used to generate a compressive force for the machining of a workpiece. They are used for example in stamping machines or in thermoforming or cutting machines. In general, presses on a press table, a press frame, a plunger and a drive for driving this plunger on.
- Examples of known presses are the so-called tryout presses or the so-called hydraulic presses.
- Eccentric presses have a drive with a rotationally driven drive shaft, wherein this rotating drive movement of the drive shaft is converted into a linear movement of the tappet. For the purpose of this conversion, eccentrics are typically used.
- a linear drive is formed by means of a spindle.
- a rotationally driven shaft such as the drive shaft of a motor, is converted by means of the spindle into a linear movement.
- the EP 1 892 084 A2 , the EP 1 892 082 A2 and the JP 2001 352747 A disclose presses according to the preamble of claim 1 with one or more linear motors for driving the plunger.
- a press which uses four linear electric motors as drives.
- These linear electric motors each have a magnetic plate and a coil plate, which are arranged laterally next to the magnetic plate and the linear driving of the magnetic plate is used.
- the longitudinal direction of these plates in the vertical direction, and the plates are positioned laterally of the working area which is formed between the press head and the press table, in such a way that on two opposite sides in each case two linear electric motors are arranged.
- Between the two each arranged on the same side linear electric motors each type of window is formed.
- a press according to claim 1 is proposed. Examples of such a press can be taken from the subclaims and the following description. According to the invention, therefore, a press is proposed for generating a pressure force for the machining of a workpiece, which has a machine table or press table, a machine frame or press frame, a tappet and a plurality of drives for driving the tappet.
- linear electric motors are provided for driving the plunger, wherein all these linear electric motors are exactly coupled to the plunger and wherein the linear electric motors are integrated into the press table and in the press head.
- the linear electric motors have a plurality of mutually offset magnetic poles and a means of these poles linearly displaceable part, such as drive axle, on.
- the magnetic poles of the linear electric motors are formed by coils extending around an axis, which are axially offset with respect to this axis.
- the linearly displaceable part extends in the direction of this axis and is linearly displaceable by means of the coils in the direction of this axis.
- a workpiece is to be understood broadly.
- a workpiece can be an isolated workpiece or, for example, also contiguous material that is separated, for example by cutting, punching or the like.
- the machining of the workpiece can also take place in various ways in the sense of the present invention.
- the processing may consist in a "deep drawing” or a “cutting” or a "punching".
- the press according to the invention may for example be part of a thermoforming machine or a punching machine or a cutting machine or another type of machine in which a pressure force for machining a workpiece is required.
- the linear electric motor is designed as a servo motor.
- the linear electric motor is designed so that its linearly displaceable part is a drive axis which projects into or is arranged in a magnetic field or a plurality of magnetic fields of the linear electric motor and can be moved axially by means of the magnetic field or fields.
- This can in particular be such that the linearly displaceable part or drive axle can be moved axially back and forth by means of the magnetic field (s).
- the drive shaft or the linearly displaceable part is therefore in particular a kind of core of the electric motor, which is axially movable.
- These magnetic fields are formed in particular by the poles.
- the coils can in particular be current-carrying or are current-flowed through to effect the corresponding magnetic poles.
- the plunger is coupled to at least one first tool or a plurality of first tools, and in particular is directly coupled.
- a first tool holder for receiving the first tool.
- the first tool holder may for example consist of a plurality of grooves, in particular T-shaped grooves.
- a second tool holder for receiving at least one second tool is provided on the press table.
- the press table in particular the upper surface or table top of the press table, one or more second tool holders for receiving a second tool.
- the second tool holder may for example consist of a plurality of grooves, in particular T-shaped grooves.
- the press table can, in particular on its upper side, be provided with one or more guide devices and / or with one or more holding devices for guiding or holding the workpiece. These can for example be detachably mounted.
- a first tool may be a stamp and a second tool may be a drawing ring or a die. Another second tool may be a hold-down.
- the force transmission path between a linear electric motor or its linearly displaceable part or its drive axis and the plunger or the first tool or the first tool holder is free of rotating parts.
- a linearly displaceable part of the linear electric motor or a drive axis of the linear electric motor - ie in particular an axis which projects into the one or more magnetic fields of the electric motor and is driven by or from this - can be coupled directly to the plunger be.
- This can for example be such that the addressed drive axle or the addressed linearly displaceable part and the mentioned plunger are connected to each other directly via a screw or the like.
- a bolt or a bolt arrangement produces such a direct connection.
- a coupling between a linearly displaceable part or a drive axis of a linear electric motor and the plunger also indirectly, for example via a toggle, done.
- a toggle lever may in particular be pivotally mounted, for example pivotally mounted on the press table or on the press frame. It should be noted that in particular it is provided that such a toggle overruns in operation a pivoting range, which is less than 360 degrees, in particular less than or equal to 270 degrees, in particular less than or equal to 180 degrees, in particular less than or equal to 150 degrees, and for example in the range of 120 degrees up to 130 degrees. Smaller angles or paths in the pivoting direction that are traveled by the toggle lever can also be provided.
- At least one linear electric motor is arranged above the press table, the press having a press head which is arranged above the press table and spaced from this press table, in particular vertically, and in which the linear electric motor is integrated. It is envisaged that (vertically) between the press table and the press head, a work area for the machining of workpieces is formed.
- the plunger is arranged above the press table.
- at least one linear electric motor is integrated in the press table. This can for example be such that the workpiece or the first and / or second tool holder is arranged between the plunger and the linear electric motor. It can be provided that the or a drive axle or one or the linearly displaceable part of the linear electric motor is located parallel to the thrust direction of the plunger. But it can also be provided that such a drive axis of the linear electric motor is located transversely, in particular perpendicular, to the thrust direction of the plunger.
- the power transmission from the linearly displaceable part or the drive axle on the plunger can be done for example by means of wedge surfaces or by means of a toggle lever.
- the plunger is provided with linear guides.
- four linear guides may be provided for the plunger.
- the plunger may be such that the height of this plunger in the direction of the impact direction of the plunger is less than the width of the plunger extending perpendicularly to this impact direction and / or the depth of the plunger extending perpendicular to this width and perpendicular to this impact direction ram.
- the plunger may for example have an outer contour that is substantially rectangular or substantially square. It may be provided that the plunger has stiffeners to prevent or at least reduce the risk that the plunger undergoes deformations under load.
- the press to prevent the breakdown of the plunger in the absence of power to the linear electric motor has a hold-brake for the linearly displaceable part or for the drive axle.
- Such a holding brake may for example be designed as a positive brake or as a frictional brake, wherein a combination of these types of brakes may be provided.
- the brake may have a positive or frictional forceps with two brake shoes, which can embrace the linearly displaceable part or the drive axle. It can also be provided that a tooth is arranged on the linearly displaceable part or on the drive axle, which cooperates with a rack for braking.
- the rack is spring-actuated in the direction of the tooth or a tooth / rack engaging position is pressed, for example, an electric motor that may be different from the at least one drive of the plunger or the linear electric motors or a drives of Tappet or this linear electric motors, against the spring force exerts a force on the rack to hold them in a disengaged position with the tooth.
- the power supply is interrupted, cracked by the intended for the holding brake electric motor, which may also be linear electric motor, exerted on the rack force from, so that the rack under the action of the spring force with the on the linearly displaceable part or . is arranged on the drive axle arranged teeth engaged and prevents axial displacement of this linearly displaceable part or this drive axle.
- such a holding brake with positive or frictional forceps and two brake shoes can also act a spring force on the brake shoes, which are held in a disengaged position by means of an electric motor provided for the holding brake in a corresponding manner, as long as the power supply is given.
- the brake shoes move to the linearly displaceable part or to the drive axle and keep them in their axial position.
- a holding brake can be designed, for example, hydraulically or mechanically. This is in particular such that, when power is removed, the hold-up brake is moved from a released position to a braking position to prevent continued movement of the linearly displaceable part or the drive shaft or the plunger.
- At least one linear electric motor which is integrated in the press table, it can be provided that on the plunger an angle element - in particular fixed - is formed or molded, via the one or the linearly displaceable part or the or a respective drive shaft with coupled to the plunger.
- a plurality of linear electric motors which are integrated in the press table, may be provided in particular that a plurality of such angles are provided.
- the drives or drive units are mounted from above and from below, so that a pushing and pulling movement is exerted on the plunger.
- the drive or electric motor or the drive units or drives can also be freely selected with regard to the number or position.
- the drives or drive units or linear electric motors can drive toggle as a power amplifier.
- a horizontal attachment can also be made possible by means of a toggle lever system, that is, in particular also horizontal arrangement of the drive axle or drive axles of the linear electric motor or electric motor.
- all linear electric motors are coupled with exactly one plunger in order to drive them.
- each of these multiple linear electric motors may be formed and / or arranged as the aforementioned a linear electric motor, provided that this does not reveal obvious contradictions.
- these several each serving as a drive for the same ram linear electric motors are different and / or arranged, in particular, is provided that different exemplary inventive designs of the linear electric motors are combined.
- the linear electric motors are in particular such that their coils envelop the respective linearly displaceable part or its respective drive axis. It can be provided that the linear electric motors are each rotationally symmetrical.
- the drive axes are magnets, in particular permanent magnets, or magnetic.
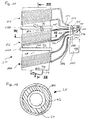
- the press 1 according to the Fig. 1 to 9 has a press table 10, a press frame 12, a machine head or press head 14 and a plunger 16.
- the machine head 14 may also be referred to as the machine upper part or press upper part.
- the press frame 12 has four columns 18 in the present embodiment.
- a plurality of drives 20 are provided, which are each here as a linear electric motor 20, and in particular designed as a servomotor linear electric motor, are formed.
- Fig. 1 how good the Fig. 1 can be removed, 14 chambers 22a, 22b, 22c and 22d are formed in this embodiment in the press upper part or press head, in each of which one of the linear electric motors 20 is arranged. In this embodiment, four linear electric motors 20 are provided, but the number may also vary.
- linear electric motors 20 are also integrated in the press table 10.
- a lateral arrangement of the linear electric motors 20 may alternatively be provided.
- the columns 18 of the press frame 20 are arranged on the four corners of an imaginary rectangular contour.
- the columns 18 are here so that they carry the press head 14.
- the linear electric motors 20 each have a designed as a drive axis 24 linearly displaceable part, the or in the operation of the linear electric motor 20 can be moved axially and can be moved axially back and forth, in particular by means of one or more magnetic fields or by means of a plurality of magnetic poles of the linear electric motor 20th
- an eye 26 is provided on the linear electric motor 20 far end of the drive shaft 24, wherein this eye 26 of the coupling with the plunger 16 is used.
- the plunger 16 has a substantially rectangular outer contour and is designed so that it ensures the best possible rigidity. In the exemplary embodiment, this is so that four plates 28, 30, 32, 34 which are essentially height-related form a kind of rectangular frame, the parallel plates 32 and 34 forming short sides and the parallel plates 28 and 30 forming long sides of a rectangle , However, the short sides 34, 32 may be longer than the distance of the plates 28 and 30, so that the plates 32, 34 project beyond the end of the plate 28 and 30 respectively.
- triangular plates 36 are formed on the respective abutting plates in the region in which each of the shorter plates 32, 34 project beyond the plates 28, 30. In the exemplary embodiment shown, this is such that three triangular plates 36 are integrally formed in each of these corner areas, one bottom, one top and one substantially in the middle being formed.
- plates 38, 40 are provided, which here connect the plates 32 and 34 and, for example - as in Fig. 9 shown - parallel to the plates 28 and 30 run. It could also be provided, for example, that the stiffening plates in the manner of a half-timber pattern within of the frame are arranged.
- a bolt extends through two plates for each of the linear electric motors 20. This is so here that two bolts 42 are respectively mounted in the plate 30 and the adjacent plate 40 and two bolts 42 are respectively mounted in the plate 28 and in the adjacent plate 40. In this state, these bolts 42 each extend through an eye 26 of a linear electric motor 20th
- the plunger 16 further includes a bottom plate 44 which Fig. 2 can be seen.
- the bottom plate 44 has a first receiving area 46 for receiving a tool, not shown.
- the receiving region 46 has a plurality of grooves 48, which are designed T-shaped in this embodiment.
- the press table 10 or the press table top on its upper side a second receiving area 50 for a second tool, which is also not shown.
- This second receiving region 50 is formed by a plurality of grooves 52, which for example likewise have a T-shaped cross-sectional profile, or has such.
- corresponding power transmission paths which are formed for example by L-shaped parts and which provide the coupling to the plunger, in the region of the press frame or between the columns of the press frame.
- the in the Fig. 1 to 9 The design shown can be, for example, part of a stamping machine or part of a cutting machine or part of a thermoforming machine.
- the invention has various advantages. So it offers a high variability, that means in particular a freely programmable ram speed in every position. Furthermore, tryout operation is possible.
- the design can be used according to a Exzenterstanzautomat or according to a hydraulic press. It is also advantageous that no more synthetic lubricating or hydraulic oils are required. Next occur no rotating bearings, so that no lubrication is required.
- the invention offers a high degree of variability, at least in its developments.
- the linear movement of the plunger 16 is realized directly by a linear movement of the drive. There is no or no conversion of a rotational to a linear movement. Thus, less energy losses occur.
- Fig. 10 shows a second embodiment of the invention in a schematic view, wherein like or corresponding parts are provided with the reference numerals, which are also in the Fig. 1 to 9 were used.
- the design according to Fig. 10 corresponds essentially to the design according to the Fig. 1 to 9 so that on the Fig. 1 to 9 subject to the following deviations also for the design according to Fig. 10 applies.
- Fig. 10 shows the arrangement of the linear electric motors.
- the drive shaft 24 is connected to an angle 60 which engages laterally in the plunger 16.
- the drive axle 24 can be connected directly to the plunger 16 without the interposition of an angle, for example laterally or from below.
- embodiments of the invention there are fewer health problems for persons than in the design according to him EP 0 943 422 A2 because the magnetic fields do not have to be that strong.
- the magnetic fields can be easily shielded.
- embodiments of the invention can be made oil and / or fat free.
- the Fig. 11 to 13 show an exemplary linear electric motor 20 which can be used in inventive designs, such as in the design as a drive for the plunger 16, in the Fig. 1 to 9 is shown, or in the design, in Fig. 10 is shown.
- Fig. 11 is a front view of the linear electric motor 20, while Fig. 12 a section along the line XII-XII Fig. 11 shows and while Fig. 13 a section along the line XIII-XIII Fig. 11 shows.
- the linear electric motor 20 has a plurality of magnetic poles 70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80, which are arranged offset axially relative to the central longitudinal axis 82 of the linear electric motor 20 to each other.
- poles 70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80 are formed by means of coils 84, 86, 88, which are also arranged axially offset with respect to the central longitudinal axis 82.
- Each of these coils 84, 86, 88 is wound on a bobbin 90, 92, 94 on its radially outer surface.
- each of the coils 84, 86, 88 are traversed by an electric current and is accordingly made of suitable, electrically conductive material, such as metal, in particular copper.
- suitable, electrically conductive material such as metal, in particular copper.
- each of the coils 84, 86, 88 is wound from a corresponding wire.
- the magnetic field forming as a result of the current flow through the respective coil 84, 86, 88 then generates in each case one plus pole and one negative pole in the interior 96, which will be discussed below.
- the magnetic poles 70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80 must or should therefore not permanently act as positive pole or negative pole, but rather can be made by energizing the respectively corresponding coil to a positive pole or negative pole. This is particularly so that, if one of these coils 84, 86, 88 is traversed by an electric current, the relevant coil 84, 86, 88 a magnetic field with its associated, previously mentioned poles 70 and 72, or 74 and 76, or 78 and 80 generated. In the above-mentioned pairwise order, these poles are assigned to the coils 84, 86 and 88.
- poles 70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80 need not be physically tangible, and thus can be formed by the magnetic field itself.
- Each of the coil supports 90, 92, 94 may also be made of electrically conductive material, such as metal, in particular copper, or of an electrically insulating material.
- a linearly displaceable part is arranged, which is also referred to as rotor or drive axle 24, and in the direction of the axis 82 by means of the coils 84, 86th , 88 is axially displaceable.
- This drive axle 24 is completely or partially designed as a permanent magnet and accordingly forms magnetic poles 100, 102 at its axial ends 104, 106.
- the drive shaft 24 may be provided with an eye 26 for coupling to the plunger 16, or be fixedly coupled to an intermediate portion 107, which in turn has the eye 26. Instead of the eye 26, however, a differently designed coupling point for the plunger 16 may be provided.
- Axial between the coils 84, 86, 88 and / or coil supports 90, 92, 94 may be provided electrical and / or magnetic insulators 108, 110, however, have radially inwardly through holes 112, so that the rotor 24 can enter or pass unhindered ,
- a control device 142 which the energization of the coils 84, 86, 88 and / or the switching positions of the switching device 140 to cause the respectively desired axial displacement of the rotor 24, and thus of the plunger 16.
- This control device 142 which may also have other control functions, such as the control of the workpiece movement by the press, controls the coils 84, 86, 88 in a defined order, so as to effect the respective desired axial displacement of the rotor 24.
- the driving takes place so that the axial displacement by the respective interaction of the poles 100, 102 of the rotor 24 with the forming poles 70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80 of the respective energized coil 84, 86, 88, comes about. It is exploited that the same magnetic poles, i. two magnetic plus poles or two magnetic minus poles, repelled and different poles, i. a positive magnetic pole and a negative magnetic pole, tighten.
- controlled energization of the various coils 84, 86, 88 by means of Control device 142 can thus be an axial movement of the drive shaft 24, and thus of the plunger 16, are effected, which can extend axially over a plurality of the coils 84, 86, 88.
- the drive shaft 24, and thus the plunger 16 can be moved axially, optionally in either one of the two opposite orientations.
- the drive shaft 24, and thus the plunger 16 with the tool mounted or held thereon can thus be reciprocated for machining the workpiece.
- This movement can also be controlled by means of the control device 142 so that it is tuned to the feed of the workpiece and its timing.
- the drive shaft 24 can be stopped and held in predetermined axial positions or in any axial position of its axial travel range.
- - depending on the desired holding position and / or number of coils 84, 86, 88 - one or more coils 84, 86, 88 are energized such that in the desired position by means of the poles 70th , 72, 74, 76, 78, 80 of the currently energized coils 84, 86, 88 an axial force equilibrium on the drive axle 24 is generated.
- power relationships can also be a damped braking movement of the drive shaft 24 are generated.
- the corresponding tuning of the current supply in the coil or coils 84, 86, 88 can be controlled by the control device 142.
- a plurality of coils 84, 86, 88 can also be supplied with current at the same time or overlapping in time.
- the respective axial position can also be determined by calculation in the control device 142 as a function of previous control characteristics.
- a rotation lock for the rotor 24 may be present, which counteracts a rotation of the rotor 24 about the axis 82. While in the Fig. 11 to 13 the bobbin carriers 90, 92, 94 are hollow cylindrical and the rotor 24 are shown cylindrically, but other cross-sectional shapes, such as, for example, triangular, quadrangular, pentagonal, hexagonal or the like may also be provided in each case.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Forests & Forestry (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Press Drives And Press Lines (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Claims (12)
- Presse destinée à produire une force de pression pour l'usinage d'une pièce comprenant :- un plateau (10) de presse,- un bâti (12) de presse,- un coulisseau (16), et- au moins un entraînement conçu sous la forme d'un moteur électrique linéaire (20) destiné à entraîner le coulisseau (16), l'au moins un moteur électrique linéaire (20) présente plusieurs pôles magnétiques (70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80) décalés les uns par rapport aux autres ainsi qu'un axe d'entraînement (24) dotés d'aimants, déplaçable linéairement au moyen desdits pôles (70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80), les pôles magnétiques (70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80) d'au moins un moteur électrique linéaire (20) formant des bobines (84, 86, 88) s'étendant autour d'un axe (82), lesdites bobines étant décalées axialement l'une par rapport selon ledit axe (82), et l'axe d'entraînement (24) déplaçable linéairement s'étendant dans le sens dudit axe (82) et étant déplacé linéairement au moyen des bobines (84, 86, 88) dans le sens dudit axe (82), la presse présentant une tête (14) de presse disposée au-dessus du plateau (10) de presse, entre le plateau (10) de presse et la tête (14) de presse étant formée une zone de travail (62) destinée à l'usinage de pièces, plusieurs moteurs électriques linéaires (20) étant destinés à entraîner le coulisseau (16) et l'ensemble desdits moteurs électriques linéaires (20) étant couplés au coulisseau (16), caractérisée en ce que le coulisseau (16) est doté de guidages linéaires et en ce que les moteurs électriques linéaires (20) sont intégrés dans le plateau (10) de presse et dans la tête (14) de presse.
- Presse selon la revendication 1, caractérisée en ce que l'axe d'entraînement (24) est symétrique en rotation.
- Presse selon l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, caractérisée en ce que le trajet de transmission de force se situe entre le moteur électrique linéaire (20) et le coulisseau (16) sans partie tournante.
- Presse selon l'une quelconques des revendications 1 à 3, caractérisée en ce que l'axe d'entraînement (24) est directement couplé au coulisseau (16).
- Presse selon l'une quelconques des revendications 1 à 3, caractérisée en ce que l'axe d'entraînement (24) est directement couplé au coulisseau (16) au moyen d'un levier à genouillère.
- Presse selon l'une quelconques des revendications précédentes, caractérisée en ce que l'axe d'entraînement (24) au moins d'un moteur électrique linéaire (20) est placé parallèlement au sens du choc du coulisseau (16).
- Presse selon l'une quelconques des revendications précédentes 1 à 5, caractérisée en ce que l'axe d'entraînement (24) au moins d'un moteur électrique linéaire (20) est placé perpendiculairement au sens du choc du coulisseau (16).
- Presse selon l'une quelconques des revendications précédentes, caractérisée en ce que quatre guidages linéaires sont prévus pour le coulisseau (16).
- Presse selon l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, caractérisée en ce que la hauteur dudit coulisseau (16) dans son sens du choc est inférieure à la largeur du coulisseau (16) s'étendant perpendiculairement audit sens du choc et/ou à la profondeur du coulisseau (16) s'étendant perpendiculairement audit sens du choc et perpendiculairement au sens de largeur associée à la largeur.
- Presse selon l'une quelconques des revendications précédentes, caractérisée en ce que sur le coulisseau (16) est disposé une première zone de réception d'outil (46) destinée à réceptionner un premier outil.
- Presse selon la revendication 10, caractérisée en ce que sur le plateau (10) de presse est disposée une seconde zone de réception d'outil (50) destinée à réceptionner un second outil.
- Presse selon l'une quelconques des revendications précédentes, caractérisée en ce que la presse (1) présente un frein à grande tenue pour l'axe d'entraînement (24) afin d'empêcher le passage du coulisseau (16) en cas de défaut d'alimentation électrique.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| SI201031294A SI2329944T1 (sl) | 2009-12-03 | 2010-11-22 | Stiskalnica za generiranje stiskalne sile za obdelovanje obdelovanca |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT19142009A AT509090B1 (de) | 2009-12-03 | 2009-12-03 | Presse zum erzeugen einer druckkraft für die bearbeitung eines werkstücks |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2329944A2 EP2329944A2 (fr) | 2011-06-08 |
| EP2329944A3 EP2329944A3 (fr) | 2013-09-18 |
| EP2329944B1 true EP2329944B1 (fr) | 2016-08-31 |
Family
ID=43502553
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP10014816.2A Active EP2329944B1 (fr) | 2009-12-03 | 2010-11-22 | Presse destinée à produire une force de pression pour le traitement d'une pièce |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2329944B1 (fr) |
| AT (1) | AT509090B1 (fr) |
| EA (1) | EA023188B1 (fr) |
| ES (1) | ES2603981T3 (fr) |
| HU (1) | HUE030662T2 (fr) |
| PL (1) | PL2329944T3 (fr) |
| SI (1) | SI2329944T1 (fr) |
| UA (1) | UA108189C2 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2749368A1 (fr) * | 2011-09-06 | 2014-07-02 | Gaindu, S.L. | Machine pour la fracture d'une bielle |
| CN102886563B (zh) * | 2012-10-19 | 2015-09-02 | 江苏高博智融科技有限公司 | 一种具有加速增力功能的液压剪板机活动刀架 |
| CN105107924B (zh) * | 2015-09-25 | 2017-04-26 | 东莞市锐祥智能卡科技有限公司 | 一种多尺寸芯片冲切设备 |
| CN108787972B (zh) * | 2018-06-15 | 2024-05-24 | 郭小红 | 智能化直驱电磁锻造锤 |
| DE102019110889B4 (de) * | 2019-04-26 | 2024-08-22 | Langenstein & Schemann Gmbh | Antriebseinheit mit Linearantrieben für eine Umformmaschine und Umformmaschine mit einer solchen Antriebseinheit |
| DE102020206223A1 (de) | 2020-05-18 | 2021-11-18 | Sms Group Gmbh | Querhaupt zur Verwendung als Ober- und/oder Unterholm in einer Presse |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2597559A (en) * | 1949-07-18 | 1952-05-20 | Bekey Andrew | Electromagnetically operated mechanism using resonance effects |
| US2951437A (en) * | 1957-03-29 | 1960-09-06 | Elemag Anstalt | Electromagnetic press |
| SU500980A1 (ru) * | 1972-06-05 | 1976-01-30 | Электромагнитный пресс | |
| SU453327A1 (ru) * | 1973-08-13 | 1974-12-15 | Привод гидравлического пресса | |
| US4056029A (en) * | 1976-04-29 | 1977-11-01 | Doherty Norman R | Electrically actuated power press |
| SU629075A1 (ru) * | 1977-01-05 | 1978-10-25 | Свердловский Завод Пластмасс | Пресс дл полимерных материалов |
| JPS5985329A (ja) * | 1982-11-09 | 1984-05-17 | Amada Co Ltd | 打ち抜きプレスの打撃装置 |
| US5357779A (en) * | 1990-09-07 | 1994-10-25 | Coors Brewing Company | Can body maker with magnetic ram bearing and redraw actuator |
| EP0943422B1 (fr) * | 1998-03-16 | 2004-05-19 | Yamada Dobby Co., Ltd. | Dispositif de commande du coulisseau dans une presse |
| JP2001352747A (ja) * | 2000-06-09 | 2001-12-21 | Aida Eng Ltd | リニアモータおよびこれを駆動源とするプレス成形装置 |
| US7000537B2 (en) * | 2001-04-26 | 2006-02-21 | Sodick Co., Ltd. | Press and machine tool |
| JP2008043991A (ja) * | 2006-08-21 | 2008-02-28 | Murata Mach Ltd | リニアモータ搭載プレス機械 |
| KR20080017229A (ko) * | 2006-08-21 | 2008-02-26 | 무라타 기카이 가부시키가이샤 | 리니어 모터 및 그것을 탑재한 공작기계 |
| JP2008043992A (ja) * | 2006-08-21 | 2008-02-28 | Murata Mach Ltd | リニアモータ搭載プレス機械 |
| JP2008043993A (ja) * | 2006-08-21 | 2008-02-28 | Murata Mach Ltd | リニアモータ搭載プレス機械 |
| JP5100073B2 (ja) * | 2006-09-28 | 2012-12-19 | 村田機械株式会社 | リニアモータ装置およびそれを搭載した工作機械 |
| JP2008086144A (ja) * | 2006-09-28 | 2008-04-10 | Murata Mach Ltd | リニアモータおよびそれを搭載した工作機械 |
-
2009
- 2009-12-03 AT AT19142009A patent/AT509090B1/de active
-
2010
- 2010-11-22 HU HUE10014816A patent/HUE030662T2/en unknown
- 2010-11-22 PL PL10014816T patent/PL2329944T3/pl unknown
- 2010-11-22 EP EP10014816.2A patent/EP2329944B1/fr active Active
- 2010-11-22 SI SI201031294A patent/SI2329944T1/sl unknown
- 2010-11-22 ES ES10014816.2T patent/ES2603981T3/es active Active
- 2010-12-02 EA EA201001743A patent/EA023188B1/ru not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2010-12-02 UA UAA201014452A patent/UA108189C2/ru unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2329944A3 (fr) | 2013-09-18 |
| UA108189C2 (uk) | 2015-04-10 |
| ES2603981T3 (es) | 2017-03-02 |
| HUE030662T2 (en) | 2017-05-29 |
| PL2329944T3 (pl) | 2017-02-28 |
| AT509090B1 (de) | 2014-03-15 |
| EA201001743A1 (ru) | 2011-06-30 |
| EA023188B1 (ru) | 2016-05-31 |
| SI2329944T1 (sl) | 2017-02-28 |
| AT509090A1 (de) | 2011-06-15 |
| EP2329944A2 (fr) | 2011-06-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2527058B1 (fr) | Machine-outil sous la forme d'une presse pour le traitement de pièces usinées, notamment de tôles | |
| EP0418779B1 (fr) | Méthode pour manufacture de pièces d'oeuvre par découpage, en particulier dans un outil à contre découpage à précision | |
| EP2329944B1 (fr) | Presse destinée à produire une force de pression pour le traitement d'une pièce | |
| DE3110221A1 (de) | Stanzpresse | |
| DE2738344A1 (de) | Werkzeugmaschine, insbesondere stanzmaschine | |
| DE3012486A1 (de) | Vorrichtung nach art einer stanze oder presse | |
| EP0121826A2 (fr) | Outil de découpage et de cintrage | |
| EP3515624A1 (fr) | Procédé, machine-outil et outil de découpage pour le découpage continu à course multiple de pièces en forme de plaque | |
| DE2741576A1 (de) | Bearbeitungsmaschine fuer draht und band, insbesondere stanz- und biegeautomat, mit mehreren werkzeugebenen | |
| DE102007030956A1 (de) | Schlittenanordnung für eine Werkzeugmaschine | |
| EP1202825A2 (fr) | Procede et dispositif pour la formation d'un coin limite sur trois cotes a partir d'un materiau en forme de plaque et a surface plane | |
| EP0739663B1 (fr) | Machine pour former des pièces | |
| DE10019788A1 (de) | Werkzeugmaschine | |
| DE19745342B4 (de) | Tischhebeeinrichtung für eine Werkzeugmaschine | |
| EP2457672B1 (fr) | Amortisseur de matrice | |
| DE202013103426U1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Erzeugung einer Bohrung in einem Werkstück oder eines Gewindes in einer Bohrung eines Werkstücks | |
| EP2114587B1 (fr) | Presse de formage présentant une fonction de coussin pneumatique intégrée au plateau coulissant | |
| EP3025803B1 (fr) | Dispositif d'entraînement pour une machine-outil et machine-outil dotée d'un tel dispositif d'entraînement | |
| DE10063154B4 (de) | Schmiedepresse mit Stellvorrichtung auf Matrizenseite | |
| EP3095534B1 (fr) | Cintreuse | |
| DE202012001836U1 (de) | Antriebseinrichtung für eine Bearbeitungsmaschine | |
| DE102013108170B3 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Erzeugung einer Bohrung in einem Werkstück oder eines Gewindes in einer Bohrung eines Werkstücks | |
| WO2011038921A1 (fr) | Procédé pour déplacer une unité de façonnage d'une machine | |
| DE102012102526A1 (de) | C-Gestell-Presse | |
| AT510052A1 (de) | Antriebseinheit für einen stanzautomat oder eine presse |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: B26D 5/08 20060101ALI20130809BHEP Ipc: B30B 1/42 20060101AFI20130809BHEP Ipc: B30B 1/10 20060101ALI20130809BHEP Ipc: B21J 7/30 20060101ALI20130809BHEP |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20140319 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20150831 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: B30B 1/42 20060101AFI20160405BHEP Ipc: B26D 5/08 20060101ALI20160405BHEP Ipc: B21J 7/30 20060101ALI20160405BHEP Ipc: B26F 1/40 20060101ALI20160405BHEP Ipc: B21J 9/10 20060101ALI20160405BHEP Ipc: B30B 1/10 20060101ALI20160405BHEP |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20160531 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502010012284 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 824630 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20161015 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20160831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20161130 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20161130 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20161201 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HU Ref legal event code: AG4A Ref document number: E030662 Country of ref document: HU |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20161130 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170102 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502010012284 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20161130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20161130 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20161130 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20170601 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20161130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20161130 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20161122 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 824630 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20161122 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20161122 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20161130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160831 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Payment date: 20211117 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Payment date: 20211116 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20221123 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20231120 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: SI Payment date: 20231109 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20231124 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20231120 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20231121 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: CZ Payment date: 20231110 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20240126 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20221122 |