EP1591024B2 - Procédé et systeme pour le suivi de données de produits dans un flux d'articles à transprter et stocker dans l'industrie du tabac - Google Patents
Procédé et systeme pour le suivi de données de produits dans un flux d'articles à transprter et stocker dans l'industrie du tabac Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1591024B2 EP1591024B2 EP05090118.0A EP05090118A EP1591024B2 EP 1591024 B2 EP1591024 B2 EP 1591024B2 EP 05090118 A EP05090118 A EP 05090118A EP 1591024 B2 EP1591024 B2 EP 1591024B2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- product
- product data
- memory
- mass flow
- transport
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Not-in-force
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A24—TOBACCO; CIGARS; CIGARETTES; SIMULATED SMOKING DEVICES; SMOKERS' REQUISITES
- A24C—MACHINES FOR MAKING CIGARS OR CIGARETTES
- A24C5/00—Making cigarettes; Making tipping materials for, or attaching filters or mouthpieces to, cigars or cigarettes
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method and a system for tracking product data, for example quality data, brand information, production machine identification, production time, in a transport storage section of the tobacco processing industry.
- the object of the invention is to provide a method and a system for tracking product data of a product mass flow in a transport storage line of the tobacco processing industry.
- the invention solves this object by a method having the features of claim 1 and by a system having the features of claim 12.
- the invention is particularly based on the virtual portioning of the product mass flow and the generation and storage of product data records that correspond to the individual product portions. By means of this subdivision, tracking according to the invention via a product portion of averaged product data is possible.
- the data memory has a memory input and a memory output, wherein the product data records are written into the memory means via the memory input and stored there in a fixed order, and the product data records written in the memory means in an order corresponding to the order of the corresponding product portions in the transport memory segment , are read out of the storage means via the output.
- the transport storage line is a system for automatically transporting and / or storing the product mass flow.
- the data storage logically maps the transport storage path. If, for example, the transport storage path comprises a pure transport path or a FIFO storage in which the product mass flow enters an entrance and exits at an exit in the same sequence, the data storage expediently comprises a corresponding FIFO data storage (first in-first out principle).
- the transport storage section comprises a bag store into which the product mass flow enters and out of which the product mass flow emerges in the reverse order
- the data store expediently comprises a corresponding FILO or LIFO data memory (first in-last out or last in-first) out principle).
- a preferred implementation of a FIFO data memory is a ring memory, each with a movable read and write pointer. Preferably, their position is moved after writing a product data record or after the emergence of a product portion of the transport path to a logically adjacent memory unit.
- the position of the read or write pointer is held in the event of an interruption of the product mass flow entering the transport path or the product mass flow exiting the transport path.
- FIFO data memory is a FIFO stack (FIFO stack).
- FIFO stack FIFO stack
- Product data sets of product mass flow entering the transport path are written to the FIFO stack and product data sets of product mass flow exiting the transport path are read from the FIFO stack.
- a preferred implementation of a FILO data memory is accordingly a FILO stack (FILO stack).
- the invention is not limited to the aforementioned implementations of FIFO or FILO data memories.
- the use of, for example, shift registers is also encompassed by the invention.
- the portioning is carried out in uniform lengths of the product mass flow in the transport direction, since this size is particularly easy to determine from the conveying speed.
- portioning are also conceivable, for example in portions with an approximately equal number of individual products, or in portions of approximately the same weight.
- the length of the product portions is adjustable to allow for adaptation to different requirements.
- the product data sets are set up to store the length of the product portion in the transport direction. This can be expedient in particular for transport storage sections with several conveyor sections of different conveying speed, since the length of the product portions varies here.
- the product data sets are preferably set up for storing a product occupancy identifier, which indicates whether the transport segment corresponding to the product data record is occupied by product. This may be useful to mark a missing or otherwise occupancy of transport sections.
- the product data tracking system preferably comprises corresponding input or output sensors.
- each sub-store may be a ring store with a read and write pointer as described above.
- Each sub-memory can for example also be designed as a FIFO or FILO stack.
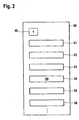
- the conveyor line 12 comprises a plurality of conveyor devices 14-17, which are drawn purely schematically as conveyor belts in the figures, but are by no means limited thereto.
- the conveyor line 12 includes, inter alia, a FIFO cigarette storage 16 with a conveyor 18 whose length is variable depending on the storage space, as in Fig. 1 indicated by dashed lines.
- the product data tracking system comprises a data processing unit 20 having a control means 21 and a storage means 22.
- the control means 21 requests production data from the cigarette production machine 10 and periodically writes respective production data sets 30a, 30b, 30c, ... into the storage means 22.
- the product mass flow 11 is virtually divided into product portions 11a, 11b, 11c, ... divided as in Fig. 1 indicated by the dotted lines.
- the control means 21 writes production data requested once per second by the cigarette production machine 10 as production data records 30a, 30b, 30c,...
- this corresponds to one virtual portioning of the product mass flow 12 in product portions 11a, 11b, 11c, ... with a certain length, in this example a portion length of 20 cm.
- the production data record expediently contains production data averaged over a storage period.
- a production record 30 includes, for example, a field 31 for storing the cigarette brand, a field 32 for storing the label of the cigarette production machine 10, a field 33 for storing production date and time, a field 34 for storing the portion length (here in cm), and fields 35, 36, ... for storing cigarette quality data, such as mean weight, mean weight standard deviation, etc.
- the designation "1" in the product occupancy label field 40 indicates that the dataset 30 is a product portion and not, for example, an empty portion due to an interruption of the product mass flow 11 corresponds.
- a writing of production data sets in the storage means 22 takes place only when entering the conveyor line 12 product.
- the input sensor 23 is provided, which sends a corresponding signal to the control means 21 when entering into the conveyor line 12 to activate the writing or, in an interruption of entering the conveyor line 12 product mass flow, by means of a corresponding signal the Write interrupt.
- the storage means 22 comprises at least one FIFO stack 26 in which the product data sets 30a, 30b, 30c,... Are stored in a fixed sequence in the form of a stack, wherein the product data sets 30a, 30b, first deposited on the stack, 30c, ... in the same order 30a, 30b, 30c, ... are read out again by ablation of the stack (FIFO principle).
- an output sensor 24 is preferably provided in order to detect product emerging from the conveying path 12.
- the control means 21 read the associated product data set from the storage means 22 and provide for further use, for example, to the packing machine 13 transmit. This happens when using a FIFO stack simply by periodically removing a product record from the stack. Due to the defined order within the stack and the FIFO principle, it is ensured that the product data records 30a, 30b, 30c,... Are correctly assigned to the product portions 11a, 11b, 11c, 11d,... Exiting the conveyor line 12, and Although regardless of the respective length of the transport path 12, for example, in the cigarette memory 16.
- the readout period is suitably adapted to the exit period of the exiting product portions 11a, 11b, 11c, 11d, ..., with the length of the exiting product portions 11a, 11b, 11c , 11d, ... is related. With a constant length of the exiting product portions 11a, 11b, 11c, 11d,... And unchanged conveying speed over the entire transport path 12, the read-out period expediently corresponds to the storage period.
- the information about entering the conveyor line 12 product may, for example, from one of the conveying section 12 upstream component, here the cigarette production machine 10 are related, if there is a product serving characterizing information.
- Figs. 3A to 3C serve to explain the storage and read operation for a ring buffer and a FIFO stack.
- Fig. 3A is shown schematically passing through a cigarette mass flow through the conveyor line 12, wherein of top to bottom consecutive times are shown.
- the vertical line “E” designates the input, the vertical line “A” the output of the conveying path 12.
- a product portion arranged above the line “E” is detected by the input sensor 23, a product portion arranged above the line "A” by the output sensor 24.
- Fig. 3B in each case the corresponding memory state of a ring memory 25 in the memory means 22 for storing the product data sets 30a, 30b, 30c, ... is shown.
- Fig. 3A in each case the corresponding memory state of a ring memory 25 in the memory means 22 for storing the product data sets 30a, 30b, 30c, ... is shown.
- the corresponding memory state of a FIFO stack 26 is shown in the storage means 22 for storing the product data sets 30a, 30b, 30c, ..., respectively.
- the memory units 25a, 25b, 25c,... Of the ring memory 25 and the memory units 26a, 26b, 26c,... Of the FIFO stack 26 respectively serve to store a product data record 30.
- the ring memory 25 has a write pointer 27 and a read pointer 28 on.
- the FIFO stack 26 has a stack input 50 and a stack output 51.
- the read pointer 28 is shifted by a memory unit.
- the product record "4" is written in the memory unit 25d indicated by the write pointer 27, the write pointer 27 is shifted by one memory unit, and the product record "2" is read from the memory unit 25b indicated by the read pointer 28 and the read pointer 28 is read by a memory unit postponed.
- the product data set "3" is read from the memory unit 25c identified by the read pointer 28 and the read pointer 28 is shifted by one memory unit.
- the output sensor 24 detects that the product mass flow 11 exiting the transport path 12 is interrupted, and therefore interrupts the reading of product data sets from the ring memory 25.
- the output sensor 24 determines that product exits the transport path 12. Therefore, the product record "4" is read from the memory unit 25d indicated by the read pointer 28, and the read pointer 28 is shifted by one memory unit.
- the transport path 12 is empty and the ring memory 25 is in a state as at time t1.
- the memory is designed as a ring memory 25, so that after a certain final memory unit, the write and read pointers 27, 28 are moved to an initial memory unit (see time t11 ).
- the stack 26 is empty at time t1.
- the stack memory 26 has a stack input 50 and a stack output 51.
- incoming product in the conveyor line 12 is detected by the input sensor 23, a corresponding product data set "1" generated by the control means 21 and placed on the stack, that is written by the stack input 50 in the stack 26.
- product entering the conveyor line 12 is detected by the input sensor 23, a corresponding product data record "2" is generated by the control means 21 and written to the stack memory 26.
- the product data set "3" corresponding to the product portion "3" is written into the stack memory 26 at the time t4.
- the input sensor 23 determines that the product mass flow 11 entering the transport path 12 is interrupted, and therefore discontinues writing product data records to the stack memory 26.
- the output sensor 24 determines that product exits the transport path 12. Therefore, it takes the product record "1" from the stack, ie it reads the product record "1" the stack output 51 of the stack 26 from.
- the product record "4" is written to the stack memory 26, and the product record "2" is read from the stack memory 26.
- the product record "3" is read from the stack memory 26.
- the output sensor 24 detects that the product mass flow 11 exiting the transport path 12 is interrupted, and therefore stops reading product data sets from the stack memory 26.
- the output sensor 24 determines that product exits the transport path 12. Therefore, the product record "4" is read from the stack memory 26.
- the transport path 12 and therefore also the stack memory 26 is empty.
- Each conveyor 14-17 of the transport path 12 may be a separate partial data memory, in particular a ring memory 25 each with write and read pointers 27, 28, or in each case a FIFO (or optionally FILO) stack memory 26, be assigned.
- a FIFO or optionally FILO stack memory 26
- Fig. 1 Let it be assumed that the conveyor 14 moves at 20 cm / s, the conveyor 15, however, at 25 cm / s and the product portions have a length L of 20 cm when entering the conveying path 12. After the transfer of the product portions from the conveyor 14 to the conveyor 15, they become longer and shallower due to the speed increase; more precisely, they have a length determined by the ratio of the conveying speeds of 25 cm.
- the length specification in box 34 of the product data set accordingly changed the ratio of the conveyor speeds and written the changed product data set in the sub-memory of the subsequent conveyor 15.
- each conveying device or each transport section is assigned its own partial data store. A single data store for the entire transport storage distance can then be sufficient.
Landscapes
- Manufacturing Of Cigar And Cigarette Tobacco (AREA)
- Wrapping Of Specific Fragile Articles (AREA)
- Arrangements For Transmission Of Measured Signals (AREA)
Claims (19)
- Procédé de suivi de données produit d'un flux massique de produits sortant d'une machine de fabrication de cigarettes (10) sous la forme d'un flux désordonné de cigarettes (11) de l'ordre de 1000 cigarettes par mètre de tronçon de transport dans une ligne de transport-stockage de l'industrie de transformation du tabac, le flux de cigarettes (11) étant transporté à l'aide d'un tronçon de transport (12) vers une machine d'emballage (13), comportant les étapes suivantes : la génération de jeux de données produit (30a, 30b, 30c, ...) qui correspondent chacun à des portions approximativement semblables (11a, 11b, 11c, ...) du flux massique de produits entrant dans la ligne de transport-stockage et à approximativement une longueur déterminée du flux massique de produits (11) dans le sens du transport, l'écriture des jeux de données produit (30a, 30b, 30c, ...) dans des unités de mémoire correspondantes (25a, 25b, 25c, ... ; 26a, 26b, 26c, ...) d'une mémoire de données (25 ; 26), et la lecture, depuis la mémoire de données (25 ; 26), des jeux de données produit correspondant au flux massique de produits sortant de la ligne de transport-stockage (12).
- Procédé de suivi de données produit selon la revendication 1, caractérisé en ce que la longueur des portions de produits (11a, 11b, 11c, ...) est réglable.
- Procédé de suivi de données produit selon la revendication 1 ou 2, caractérisé en ce que les jeux de données produit (30a, 30b, 30c, ...) présentent un champ (34) permettant de mémoriser la longueur de la portion de produit (11a, 11b, 11c, ...) dans le sens du transport.
- Procédé de suivi de données produit selon l'une des revendications 1 à 3, caractérisé en ce que les jeux de données produit (30a, 30b, 30c, ...) présentent un champ (40) permettant de mémoriser une identification d'occupation de produit.
- Procédé de suivi de données produit selon l'une des revendications 1 à 4, caractérisé en ce que les jeux de données produit (30a, 30b, 30c, ...) sont inscrits respectivement dans une unité de mémorisation (25a, 25b, 25c, ... ; 26a, 26b, 26c, ...) caractérisée par un pointeur d'écriture (27) mobile.
- Procédé de suivi de données produit selon la revendication 5, caractérisé en ce qu'après l'écriture d'un jeu de données produit (30a, 30b, 30c, ...), le pointeur d'écriture (27) est déplacé vers une unité de mémorisation logiquement voisine (25a, 25b, 25c, ... ; 26a, 26b, 26c, ...).
- Procédé de suivi de données produit selon la revendication 5 ou 6, caractérisé en ce qu'en cas d'interruption du flux massique de produits (11) entrant dans la ligne de transport-stockage (12), le pointeur d'écriture (27) est arrêté.
- Procédé de suivi de données produit selon l'une des revendications 1 à 7, caractérisé en ce que les jeux de données produit (30a, 30b, 30c, ...) sont respectivement lus depuis une unité de mémorisation (25a, 25b, 25c, ... ; 26a, 26b, 26c, ...) caractérisée par un pointeur de lecture (28) mobile.
- Procédé de suivi de données produit selon la revendication 8, caractérisé en ce qu'après la sortie d'une portion de produit (11a, 11b, 11c, ...) de la ligne de transport-stockage (12), le pointeur de lecture (28) est déplacé vers une unité de mémorisation logiquement voisine (25a, 25b, 25c, ... ; 26a, 26b, 26c, ...).
- Procédé de suivi de données produit selon la revendication 8 ou 9, caractérisé en ce qu'en cas d'interruption du flux massique de produits (11) sortant de la ligne de transport-stockage (12), le pointeur de lecture (28) est arrêté.
- Procédé de suivi de données produit selon la revendication 9, caractérisé en ce que lors de la mise en service de la ligne transport-stockage (12), le pointeur d'écriture (27) et le pointeur de lecture (28) sont placés sur la même unité de mémorisation (25a, 25b, 25c, ... ; 26a, 26b, 26c, ...).
- Système de suivi de données produit d'un flux massique de produits sortant d'une machine de fabrication de cigarettes (10) sous la forme d'un flux désordonné de cigarettes (11) de l'ordre de 1000 cigarettes par mètre de tronçon de transport dans une ligne de transport-stockage de l'industrie de transformation du tabac, le flux de cigarettes (11) étant transporté à l'aide d'un tronçon de transport (12) vers une machine d'emballage (13), comportant un moyen de mémorisation (22) qui comprend une mémoire de données (25 ; 26) pour mémoriser les données produit, un moyen de commande en écriture (21) pour commander l'écriture des données produit du flux massique de produits entrant dans la ligne de transport-stockage (12) dans la mémoire de données (25 ; 26), et un moyen de commande de lecture (21) pour commander la lecture des données produit du flux massique de produits (11) sortant de la ligne de transport-stockage (12) depuis la mémoire de données, le moyen de commande d'écriture (21) étant disposé pour générer des jeux de données produit (30a, 30b, 30c, ...) qui correspondent chacun à des portions approximativement semblables (11a, 11b, 11c, ...) du flux massique de produits (11) entrant dans la ligne de transport-stockage (12) et à approximativement une longueur déterminée du flux massique de produits (11) dans le sens du transport, et pour écrire les jeux de données produit (30a, 30b, 30c, ...) dans la mémoire de données (25 ; 26).
- Système de suivi de données produit selon la revendication 12, caractérisé en ce qu'un capteur d'entrée (23) est prévu pour détecter une portion de produit (11a, 11b, 11c, ...) entrant dans la ligne de transport-stockage (12).
- Système de suivi de données produit selon la revendication 12 ou 13, caractérisé en ce qu'un capteur de sortie (24) est prévu pour détecter une portion de produit (11a, 11b, 11c, ...) sortant de la ligne de transport-stockage (12).
- Système de suivi de données produit selon l'une des revendications 12 à 14, caractérisé en ce que la mémoire de données (25 ; 26) représente logiquement la ligne de transport-stockage (12).
- Système de suivi de données produit selon l'une des revendications 12 à 15, caractérisé en ce que la mémoire de données (25 ; 26) comprend au moins une mémoire de données FIFO.
- Système de suivi de données produit selon la revendication 16, caractérisé en ce que la mémoire de données FIFO est une mémoire tampon circulaire (25).
- Système de suivi de données produit selon la revendication 16 ou 17, caractérisé en ce que la mémoire de données FIFO est une pile FIFO (26).
- Système de suivi de données produit selon l'une des revendications 12 à 18, caractérisé en ce que la mémoire de données (25 ; 26) comporte au moins une mémoire de données FILO.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PL05090118T PL1591024T5 (pl) | 2004-04-28 | 2005-04-27 | Sposób i urządzenie do śledzenia danych o produktach w masowym strumieniu produktów w ciągu zasobników transportowych w branży przetwarzania tytoniu |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102004021440 | 2004-04-28 | ||
| DE102004021440A DE102004021440A1 (de) | 2004-04-28 | 2004-04-28 | Verfahren und System zum Verfolgen von Produktdaten eines Produktmassenstroms in einer Transportstrecke der tabakverarbeitenden Industrie |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1591024A1 EP1591024A1 (fr) | 2005-11-02 |
| EP1591024B1 EP1591024B1 (fr) | 2009-12-23 |
| EP1591024B2 true EP1591024B2 (fr) | 2018-12-12 |
Family
ID=34938441
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP05090118.0A Not-in-force EP1591024B2 (fr) | 2004-04-28 | 2005-04-27 | Procédé et systeme pour le suivi de données de produits dans un flux d'articles à transprter et stocker dans l'industrie du tabac |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7474935B2 (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP1591024B2 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JP4902135B2 (fr) |
| CN (1) | CN1695506B (fr) |
| AT (1) | ATE452547T1 (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE102004021440A1 (fr) |
| PL (1) | PL1591024T5 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006172159A (ja) * | 2004-12-16 | 2006-06-29 | Seiko Epson Corp | 電子デバイス製造システム、電子デバイスの製造方法、電子デバイス、並びに電気光学装置 |
| US8862264B2 (en) * | 2011-10-07 | 2014-10-14 | R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Company | Verification systems for filter elements of smoking articles, and associated methods |
| US20150067151A1 (en) * | 2013-09-05 | 2015-03-05 | Output Technology, Incorporated | System and method for gathering and displaying data in an item counting process |
| BR112017001012A2 (pt) * | 2016-12-12 | 2020-10-27 | Sicpa Holding Sa | sistema e método para rastrear um item de produto em uma linha de produção |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1234776A (en) † | 1967-06-21 | 1971-06-09 | Desmon Walter Molins | Improvements in conveying cigarettes |
| US3672373A (en) † | 1969-01-08 | 1972-06-27 | Hauni Werke Koerber & Co Kg | Method and means for regulating the operation of apparatus for the production and processing of cigarettes or the like |
| US4280187A (en) † | 1978-09-29 | 1981-07-21 | Hauni-Werke Korber & Co. Kg | Method and apparatus for pinpointing the causes of malfunction of machines for the manufacture and/or processing of cigarettes or the like |
| EP0602683A1 (fr) † | 1992-12-18 | 1994-06-22 | G.D Societa' Per Azioni | Procédé de fabrication de produits, notamment des produits de tabac |
| WO2000016647A1 (fr) † | 1998-09-18 | 2000-03-30 | Philip Morris Products Inc. | Machine de fabrication de cigarettes et systeme de commande correspondant |
| DE10216069A1 (de) † | 2002-04-11 | 2003-10-23 | Hauni Maschinenbau Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Einwirken auf Artikel der tabakverarbeitenden Industrie |
| WO2005049235A1 (fr) † | 2003-11-24 | 2005-06-02 | International Tobacco Machinery Poland Ltd. | Procede pour definir, reperer et eliminer la partie d'elements defectueux en forme de tige transportes par un convoyeur d'une chaine de production de l'industrie du tabac, et systeme permettant de definir, de reperer et d'eliminer la partie d'elements defectueux en forme de tige se situant sur ledit convoyeur |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2030515A1 (de) * | 1970-06-20 | 1972-01-05 | Hauni Werke Koerber & Co Kg | Verfahren und Anordnung zum Fördern von Gütern auf einer geschlossenen Förderbahn |
| US5190428A (en) * | 1986-02-25 | 1993-03-02 | Molins Machine Company, Inc. | Conveyor system for rod-like articles |
| US5764520A (en) * | 1993-05-04 | 1998-06-09 | Motorola, Inc. | Control of lots in a continuous environment |
| DE4404929C2 (de) * | 1994-02-16 | 1995-12-14 | Bat Cigarettenfab Gmbh | Anlage zum Herstellen und Verpacken von Cigaretten |
| US5555504A (en) * | 1994-06-10 | 1996-09-10 | Johnson & Johnson Vision Products, Inc. | Production line tracking and quality control system |
| US6549891B1 (en) * | 1996-03-26 | 2003-04-15 | Recovery Management Corporation | Method for managing inventory |
| US6883710B2 (en) * | 2000-10-11 | 2005-04-26 | Amerasia International Technology, Inc. | Article tracking system and method |
| US6961000B2 (en) * | 2001-07-05 | 2005-11-01 | Amerasia International Technology, Inc. | Smart tag data encoding method |
| DE10213459A1 (de) * | 2002-03-26 | 2003-10-30 | Koenig & Bauer Ag | Gütertransportsystem mit einem Schienennetz und ein Verfahren zum Betreiben dieses Gütertransportsystems |
| US7007841B2 (en) * | 2003-10-14 | 2006-03-07 | Kocott Joseph M | Systems and methods for tracking tobacco packages |
| ITBO20030628A1 (it) * | 2003-10-23 | 2005-04-24 | Gd Spa | Metodo ed unita' di controllo per un magazzino a capacita' variabile. |
| US20060180647A1 (en) * | 2005-02-11 | 2006-08-17 | Hansen Scott R | RFID applications |
-
2004
- 2004-04-28 DE DE102004021440A patent/DE102004021440A1/de not_active Ceased
-
2005
- 2005-04-27 DE DE502005008731T patent/DE502005008731D1/de active Active
- 2005-04-27 US US11/115,324 patent/US7474935B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2005-04-27 AT AT05090118T patent/ATE452547T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2005-04-27 JP JP2005128804A patent/JP4902135B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2005-04-27 PL PL05090118T patent/PL1591024T5/pl unknown
- 2005-04-27 EP EP05090118.0A patent/EP1591024B2/fr not_active Not-in-force
- 2005-04-27 CN CN2005100685921A patent/CN1695506B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1234776A (en) † | 1967-06-21 | 1971-06-09 | Desmon Walter Molins | Improvements in conveying cigarettes |
| US3672373A (en) † | 1969-01-08 | 1972-06-27 | Hauni Werke Koerber & Co Kg | Method and means for regulating the operation of apparatus for the production and processing of cigarettes or the like |
| US4280187A (en) † | 1978-09-29 | 1981-07-21 | Hauni-Werke Korber & Co. Kg | Method and apparatus for pinpointing the causes of malfunction of machines for the manufacture and/or processing of cigarettes or the like |
| EP0602683A1 (fr) † | 1992-12-18 | 1994-06-22 | G.D Societa' Per Azioni | Procédé de fabrication de produits, notamment des produits de tabac |
| WO2000016647A1 (fr) † | 1998-09-18 | 2000-03-30 | Philip Morris Products Inc. | Machine de fabrication de cigarettes et systeme de commande correspondant |
| DE10216069A1 (de) † | 2002-04-11 | 2003-10-23 | Hauni Maschinenbau Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Einwirken auf Artikel der tabakverarbeitenden Industrie |
| WO2005049235A1 (fr) † | 2003-11-24 | 2005-06-02 | International Tobacco Machinery Poland Ltd. | Procede pour definir, reperer et eliminer la partie d'elements defectueux en forme de tige transportes par un convoyeur d'une chaine de production de l'industrie du tabac, et systeme permettant de definir, de reperer et d'eliminer la partie d'elements defectueux en forme de tige se situant sur ledit convoyeur |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1591024B1 (fr) | 2009-12-23 |
| CN1695506A (zh) | 2005-11-16 |
| JP2005312452A (ja) | 2005-11-10 |
| US20050246048A1 (en) | 2005-11-03 |
| PL1591024T5 (pl) | 2019-04-30 |
| US7474935B2 (en) | 2009-01-06 |
| CN1695506B (zh) | 2010-06-23 |
| JP4902135B2 (ja) | 2012-03-21 |
| PL1591024T3 (pl) | 2010-06-30 |
| DE102004021440A1 (de) | 2005-11-24 |
| EP1591024A1 (fr) | 2005-11-02 |
| ATE452547T1 (de) | 2010-01-15 |
| DE502005008731D1 (de) | 2010-02-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1591024B2 (fr) | Procédé et systeme pour le suivi de données de produits dans un flux d'articles à transprter et stocker dans l'industrie du tabac | |
| EP2106376B1 (fr) | Piste intelligente de transport et de retenue | |
| EP1989945B1 (fr) | Transport de charges d'articles en forme de tige de l'industrie de traitement du tabac | |
| DE102005063193B4 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Gruppieren von Stückgut | |
| DE102014116578A1 (de) | Anordnung und Verfahren zum Fördern eines aus stabförmigen Artikeln der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie gebildeten Produktmassenstroms sowie Behälter zur Aufnahme und Abgabe von Portionen des Produktmassenstroms | |
| DE102013206138A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Komplettieren eines Formatsatzes von Produkten | |
| EP2181311B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de pesée dynamique de contrôle | |
| DE102014103347B4 (de) | Bedingte Verkettungsglieder für Direct-Memory-Access-Controller | |
| WO2002004330A1 (fr) | Procede et dispositif de transport d'objets a l'etat maintenu sur une voie de transport comprenant une reserve d'accumulation | |
| DE2830197C2 (fr) | ||
| EP1108650A1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour former et transférer des groupes de cigarettes dans des machines d'emballage multi-chemins | |
| EP2763923B1 (fr) | Dispositif de commande informatisé, procédé mis en oeuvre sur ordinateur pour la commande d'une installation de traitement de produits et produit-programme informatique | |
| DE102007040300A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur dynamischen Kontrollwägung | |
| EP2441717B1 (fr) | Procédé de fonctionnement d'un dispositif de transport ainsi que dispositif de transport pour la mise en oeuvre du procédé | |
| EP2088096A1 (fr) | Dispositif d'insertion automatisée pour un stock de pharmacie | |
| EP2524889A2 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif destinés au transfert de produits d'impression | |
| DE2331874B2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum rechnerischen Verbeiten von Kostenrechnungsaufzeichnungen | |
| DE102010019661A1 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Befüllen von Schragen mit stabförmigen Artikeln sowie Herstellmaschine für stabförmige Artikel mit einer solchen Vorrichtung | |
| DE19720675C2 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Zuführen von flachen Gütern zu einer Transportverpackung | |
| DE202014000234U1 (de) | Flaschenrücknahmeeinrichtung | |
| DE2224600C3 (de) | Verteilmaschine | |
| EP2818440B1 (fr) | Ligne d'assemblage pour produits plats et procédé pour équiper une ligne d'assemblage pour produits plats | |
| DE2123824A1 (de) | Steuerung für Förderanlagen mit Teilstrecken | |
| CH487054A (de) | Sortieranlage für Stückgüter | |
| DE102004039942A1 (de) | Verfahren und Anordnung zur Speicherung und Abfrage von Daten |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA HR LV MK YU |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20060426 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20070712 |
|
| TPAC | Observations filed by third parties |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNTIPA |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 502005008731 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20100204 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091223 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091223 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091223 |
|
| LTIE | Lt: invalidation of european patent or patent extension |
Effective date: 20091223 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091223 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FD4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091223 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20100423 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091223 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20100323 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20100423 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20100403 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091223 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091223 |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: INTERNATIONAL TOBACCO MACHINERY POLAND SP. Z O.O. Effective date: 20100917 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091223 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091223 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20100324 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: HAUNI MASCHINENBAU A.G. Effective date: 20100430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100430 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20101230 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091223 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100430 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100430 |
|
| PLAF | Information modified related to communication of a notice of opposition and request to file observations + time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCOBS2 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100430 |
|
| PLBB | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition received |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS3 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100427 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100427 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20100624 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091223 |
|
| APBM | Appeal reference recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREFNO |
|
| APBP | Date of receipt of notice of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA2O |
|
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |
|
| APBM | Appeal reference recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREFNO |
|
| APBP | Date of receipt of notice of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA2O |
|
| APBQ | Date of receipt of statement of grounds of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA3O |
|
| APBQ | Date of receipt of statement of grounds of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA3O |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20140422 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20150427 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150427 |
|
| RAP2 | Party data changed (patent owner data changed or rights of a patent transferred) |
Owner name: HAUNI MASCHINENBAU GMBH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 502005008731 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: HAUNI MASCHINENBAU GMBH, DE Free format text: FORMER OWNER: HAUNI MASCHINENBAU AG, 21033 HAMBURG, DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: PD Owner name: HAUNI MASCHINENBAU GMBH; DE Free format text: DETAILS ASSIGNMENT: VERANDERING VAN EIGENAAR(S), VERANDERING VAN DE JURIDISCHE ENTITEIT; FORMER OWNER NAME: HAUNI MASCHINENBAU AG Effective date: 20160928 |
|
| APBU | Appeal procedure closed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA9O |
|
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 20181212 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R102 Ref document number: 502005008731 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: FP |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Payment date: 20210322 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20210430 Year of fee payment: 17 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20210427 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20210424 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 502005008731 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20220501 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220501 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20221103 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220427 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220427 |