EP1209274A2 - Curtain coater - Google Patents
Curtain coater Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1209274A2 EP1209274A2 EP01127739A EP01127739A EP1209274A2 EP 1209274 A2 EP1209274 A2 EP 1209274A2 EP 01127739 A EP01127739 A EP 01127739A EP 01127739 A EP01127739 A EP 01127739A EP 1209274 A2 EP1209274 A2 EP 1209274A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- guide element
- curtain
- guide
- application device
- application
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C—APPARATUS FOR APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C5/00—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work
- B05C5/005—Curtain coaters
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C—APPARATUS FOR APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C5/00—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work
- B05C5/007—Slide-hopper coaters, i.e. apparatus in which the liquid or other fluent material flows freely on an inclined surface before contacting the work
- B05C5/008—Slide-hopper curtain coaters
Definitions
- the invention relates to a device for applying liquid or pasty application medium, especially aqueous pigment suspension, on a running surface, including a curtain commission, which the application medium from a dispensing nozzle as in the Moving curtain or veil due to gravity delivers the surface, whereby the surface with the direct application Surface of a material web, in particular made of paper or cardboard, and with indirect application, the surface of a transfer element, preferably a transfer roller, which is then the application medium to the Surface of the material web transfers.
- a curtain commission which the application medium from a dispensing nozzle as in the Moving curtain or veil due to gravity delivers the surface, whereby the surface with the direct application Surface of a material web, in particular made of paper or cardboard, and with indirect application, the surface of a transfer element, preferably a transfer roller, which is then the application medium to the Surface of the material web transfers.
- the application medium is applied to the substrate in the form of a Application medium curtain or curtain (for the sake of simplicity in the following only the term “order medium curtain” or only “Curtain” used), which is essentially due to gravity moved from the commissioned work to the underground. That this Curtain application work itself at a predetermined distance from Among other things, it has the advantage that it is located underground is at a lower risk of damage in the event of a web break.
- the surface tension tries the curtain a very large one based on its volume or cross-sectional area Surface or circumferential length has to contract, so its Reduce surface area. Gravity opposes this effect, who tries to stretch the curtain. It is therefore easy to see that it the more difficult it is to get one evenly across the entire working width to get thick application medium curtain, the larger this working width is.
- the coating of material webs by means of a curtain applicator, which feeds the application medium to the material medium as an application medium curtain that moves due to gravity, has long been known from the coating of photographic films, tapes and the like.
- corresponding devices for applying a liquid film to a textile material web with the aid of an application medium curtain that moves due to gravity are known from the field of the textile industry, for example from DE 33 33 592 A1 and DE 40 15 946 A1.
- the material webs in these fields of application have a considerably smaller width than is the case with modern systems for the production of paper and cardboard webs, in which material web widths of more than 10 m are required today.
- the high web speeds also put a further high load on the stability of the application medium curtain, since the application medium curtain is not only stretched due to gravity in free fall (gravity stretching), but also when it comes into contact with the ground due to the difference between the speeds of the freely falling application medium shortly before it hits the surface and the running speed of the moving surface (Contact stretching).
- No. 10024360 is a curtain applicator published in which an order fluid through two counter-rotating rollers are extracted from a reservoir, the application liquid being stretched into a thin film, and then essentially under the influence of gravity on you Surface is applied.
- the effects mentioned have a stronger influence on the quality of the application medium curtain, the smaller the flow rate of the application medium delivered by the curtain application unit per meter of working width to the substrate, ie the thinner the application medium curtain.
- a film thickness range from 2 ml / m 2 to 50 ml / m 2 , as is not uncommon in the case of a thinly applied layer ("1: 1" application) of thin layers of application medium, gravity stretching is limited by the effects mentioned above.
- the order medium curtain is most likely based on the fact that the application medium when it comes into contact with the guide element is slowed down, which stabilizes the shape of the application medium curtain.
- the falling speed more precisely the flow speed, takes of the application medium along the guide element, again.
- This stabilization of the application medium curtain according to the invention can determine the total fall height of the curtain and thus the total achievable gravity stretch compared to a conventional one free-falling application medium curtain without sacrificing the Quality of the application medium layer thus formed can be increased.
- the words “lead along the fall path” in the Connection with the present invention also mean can that the application medium curtain through the guide element from the the path corresponding to the free fall can be deflected.
- a directing element directly adjoining the dispensing nozzle Avoid the so-called "teapot effect”.
- This "teapot effect” a characteristic deformation of that emerging from the dispensing nozzle Application medium curtain occurs in practice when the Flow rate of the application medium when leaving the Dispensing nozzle falls below a limit speed, which on the one hand of the physical properties of the application medium and the other depends on the thickness of the application medium curtain. Thin curtains also tend to the To show "teapot effect”.
- Exceeds the Outflow velocity the limit mentioned above, a parabolic curve of the application medium curtain usually forms out.
- the guide element can also be used as a scraper against the ground.
- the influence of the guide element that stabilizes the application medium curtain added that this is the air boundary layer carried by the subsurface weaken and thus their adverse influence on the order result can mitigate.
- such Guide scraper localized interruptions of the application medium curtain can be prevented that are not covered with application medium Places of the underground would lead.
- the local one Introduction of air pockets between the subsurface and Application medium, which is quasi as a preliminary stage of a local tearing of the Order medium curtain can be viewed using the Guide scraper according to the invention can be avoided. Any friction heat generated by the relative movement of the scraper and underground is not a problem in practice as it is easier in Way can be dissipated by the application medium itself.
- the guide element is used as a guide scraper, there has been one inclined arrangement of this guide scraper proved to be advantageous.
- the guide element with the free fall of the curtain Direction an angle of between about 20 ° and about Include 80 °, preferably between about 45 ° and about 80 °.
- the length of guide scraper covered by application medium advantageously at most about 50 mm, preferably at most about 10 mm.
- the of the application medium curtain covered surface of the guide element to the underground has an adjacently arranged end section which is connected to a imaginary extension of the surface an angle of between about 30 ° and about 50 °.
- the guide element over the entire distance between the dispensing nozzle and Extends underground, so the benefits of extending to the dispensing nozzle immediately following guide element with one as a guide scraper used to connect the guide element.
- the guiding element must either have a compromise between found the two arrangement alternatives mentioned or that Guide element are curved, so that it is both in the area the dispensing nozzle as well as in the area of the substrate one each has advantageous inclination angle.
- a curved design of the guide element also allows over the shape of the curvature, the speed and / or the thickness of the application medium curtain to influence. It can both use of convex as well as concave curved guide elements be, with convex or concave the curvature of the application medium facing surface of the guide element is designated.
- the guide element made of metal or plastic, for example, carbon fiber or glass fiber reinforced plastic
- the application medium is in contact with the Guide scraper is braked more than it is for achieving the desired one Stabilization of the application medium curtain is actually required.
- the braking force applied by the scraper to the application medium exercises are reduced in that the guide element at least hydrophobic on its surface facing the curtain or veil is formed so that the flow rate of the Order medium is retained on the guide element.
- This hydrophobic formation of the surface of the guide element can be in can be obtained in a technically simple manner in that the Provide the surface of the guide element with a hydrophobic coating is coated, for example with a Teflonized glass fiber film. in the With regard to a favorable detachment behavior of the application medium from the guide element However, at least the end face of the guide element should be free of be hydrophobic coating.
- the application medium curtain facing away from at least one electrode By means of the the application medium can emanate from this electrode and its interaction with the surface of the guide element to achieve or ensure a uniform layer thickness of the Application medium curtain can be influenced advantageously.
- a suction box in front of the contact line of the Curtain or veil.
- This suction box can be used in addition or as an alternative to a scraper Guiding element for combating the air boundary layer carried by the subsurface be used.
- Material web is sucked into safe contact against the guide scraper, so that this effectively removes the air boundary layer from the web surface can take off.
- the suction box can be on the inlet side and / or outlet side be assigned a scraper element, which with a scraper edge on the Rests on the ground, with the scraper element on the outlet side of the Guide element can be formed. Also with regard to constructive details of the mentioned suction box is on the above two referred to German patent applications.
- the guiding element based on its The most distant underground either in or against the direction of the Can be arranged inclined underground, the guide element with the direction corresponding to the free fall of the application medium curtain in include an angle of up to about 70 ° in both orientations can. In terms of tearing off the application medium curtain In critical cases, the orientation of the guide element on the drain side preferable.
- Guide element is designed as a running surface that the fall of the Curtain or veil in one from the dispensing nozzle to the guide element leading free fall section and one from the guide element to Subdivided underground leading free fall section, and their running speed is greater than the falling speed of the Application medium at the end of the free fall section leading to the guide element.
- the order medium becomes a first gravity extension through the running surface of a subjected to the first contact stretching, after which the detachment of the application medium of the running surface serving as a guiding element second gravity or acceleration stretch and then the Contact extension through the running surface follows.
- the current guiding element forming such a guiding element Surface realized, for example, by an endless, circulating belt become.
- the peripheral speed is greater than that Falling speed of the application medium at the end of the as a guiding element serving roller leading free fall section.
- such Roll preferably made of metal at least in the area of its peripheral surface be made.
- the current one serving as the guiding element Surface for example the rotating roller, not just a relatively long one Free fall section divided into two shorter free fall sections what regarding the effects of external influences on the application medium curtain is advantageous, but it will also stretch the total distributed a variety of stretch levels, which the stress of the Application medium curtain reduced in the individual stretching stages. Thus, even a stronger overall can be achieved with the same total fall height Achieve extension of the application medium curtain.
- the running direction of the Guide surface serving it has proven to be advantageous to change the running direction of the Guide surface serving to choose such that the Section of the running surface serving as a guide element, which with the Application medium of the free fall section leading to the guide element in Contact is made, moving in the same direction as the surface.
- the Direction of rotation of the roller should preferably be chosen such that the Circumferential section of the roller, with the application medium of the roller leading free-fall section comes into contact in the same direction moves like the underground.
- a scraper element for example a Piercing scraper is provided, which lifts the application medium from it and to the free fall section leading from the guide element to the subsurface emits.
- This scraper element can, for example, against the as Guiding element serving running surface, for example the surface of the roller, be employed. If a roller is used as the guide element, it can but also from a wall section of a roller supporting the roller Roll bed be formed.
- the length of the scraper element can be in Direction of movement of the application medium measured between about 5 mm and be about 50 mm.
- any of the current surface, e.g. B. the spinning roller, free fall sections formed by additional Guiding elements can be further divided.
- additional Guiding elements such as rotating rollers, be or also permanently installed, i.e. non-moving guide elements, for example, essentially flat baffles.
- the additional guiding elements can do the free fall section in which they are arranged, again divide into two free-fall subsections.
- a guide element it is also possible for such a guide element to be attached directly the discharge nozzle of the curtain applicator connects or as Guide scraper against the surface of the running surface or the or a running surface, e.g. B. a rotating roller is employed.
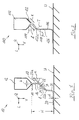
- a curtain application device is general designated 10. It comprises a curtain application 12, from the Dispensing nozzle 14 liquid or pasty application medium 16 in the form of a Order medium curtain or veil 18 is delivered.
- the Curtain 18 moves vertically due to gravity Direction V down to an underground U, which is under the Application unit 12 in the running direction L at a speed at Cardboard web from about 200 m / min and with a paper web of between about 1,000 m / min and about 3,000 m / min.
- the underground With direct application, the surface of the material web can, in particular the paper or cardboard web, but also a film or textile web, or in the case of indirect application, the surface of a transfer element, for example a transfer roller.
- the aim of the application device 10 is the application medium 16 is essentially fully metered, i.e. ideally as "1: 1" order to apply to the underground U as an order layer 20, which has a thickness d of between about 2 microns and 100 microns.
- the reduction is based on such curtain applicators 10 the thickness of the application medium curtain 18 from the width b of the dispensing nozzle 14 to the thickness d of the application layer 20 essentially to two Effects, namely the stretching of the curtain due to gravity 18 during the free fall from the dispensing nozzle 14 to Underground U and on the other hand the contact extension due to the Difference between the falling speed of the curtain 18 just before Reaching the underground U and the running speed of the underground U.
- the stretch due to gravity is not only due to physical effects (interplay between gravity and surface tension the order medium 16), but also due to external influences (for example, the curtain 18 is carried along by the Underground U, air currents and the like) set limits.
- the present invention is based on the finding that the drop height H and thus the overall achievable extension of the Order medium 16 can be increased by being in the path of the order medium 16 from the dispensing nozzle 14 to the underground U a guide element 22, for example a guide plate or a guide blade. It It has been shown that the viscous frictional force between the Application medium 16 and the guide element 22 on the application medium curtain 18 a stabilizing, i.e. especially comparative end Has an effect.
- the application medium 16 can be selected with a suitable choice Inclination angle ⁇ that the surface of the plan essentially Includes guide element 22 with the vertical V, and corresponding Choice of the surface properties of the guide element 22 at its Movement along the guide element 22 can be further accelerated. Consequently the application medium curtain 18 also experiences in the area of the guide element 22 an extension.
- Fig. 1 divides that Guide element 22 the path of the application medium 16 from the dispensing nozzle 14 to the underground U in a first free fall section 24 and a second Free fall section 26. After a first extension due to gravity in the First free-fall section 24, the application medium 14 strikes the Guide element 22, which stabilizes the curtain 18 and yet its allows further extension due to gravity. Then arrives the application medium 16 in the area of the second free-fall section 26, in which it is stretched again due to gravity before it opens the underground U hits.
- the end face 22b of the guide element 22 is designed so beveled that it with the Application medium 16 covered surface 22a of the guide element 22 a Include angle ⁇ of between about 20 ° and about 60 °.
- the angle of inclination ⁇ of the guide element 22 relative to the vertical V can have a value of up to 70 °, the guide element 22 as in FIG. 1, can be arranged on the outlet side with respect to the substrate U. can. Basically, however, an inlet-side arrangement of the Guide element 22 conceivable.
- the guide element or baffle 22 that from Metal or plastic, for example carbon or glass fiber reinforced Plastic that can be manufactured advantageously has a Thickness D of between about 0.2 mm and about 1.0 mm.
- the Total fall height H can be up to 400 mm, the distance in which the application medium 16 moves along the guide element 22, a length I of between about 1 mm and about 200 mm, preferably between about 1 mm and about 50 mm.
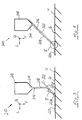
- the curtain application device 110 shown in FIG. 2 differentiates differs from the embodiment according to FIG. 1 only in that the Guide element 122 to the discharge nozzle 114 of the curtain applicator 112 is arranged immediately afterwards. Also by this execution lets the mentioned stabilization of the application medium curtain 118 achieve in the area of the guide element 122, so that in this respect to the above description of the embodiment of FIG. 1 referenced can be.
- the speed of the application medium 116 on The detaching edge 122c of the guide element 122 should ideally also be so be chosen so that the application medium 116 does not have this edge Shoots out 122c and then takes a parabolic course (dash-dotted course P), but essentially at the edge 122c directly in the essentially vertical course shown in FIG. 2 transforms.
- the guide element can also be used 222 a stabilizing the application medium curtain 218 Effect are exerted on the order medium 216 by the Curtain applicator 212 from its discharge opening 214 to the underground U is delivered. Therefore, in this regard, the above Description of the embodiment shown in FIG. 1.
- the guide element 322 is on its top 322a and its underside 322d each with a hydrophobic Provide coating 330.
- This hydrophobic coating can for example in the form of a teflon-coated glass fiber film, which are applied to the surface 322a and 322d of the guide element 322, is glued on, for example.
- Such a hydrophobic coating has due to their water and therefore also the application medium 316 repellent Properties have the advantage that on the one hand the viscous Frictional forces between the guide element 322 and the application medium 316 are reduced, so that the application medium 316 also along the Surface 322a accelerated more due to gravity and thus can be stretched, and it also has the advantage of less Danger of contamination due to adherence of application medium 316 on Guide 322.
- the guide element 322 As a result of the coating of the guide element 322 also on its underside 322d with the hydrophobic coating 330, the guide element 322, as shown in Fig. 5, float slightly so that in the area of the tip 322c of the guide scraper 322 a small, highly swirled one Forms amount 316 'of order medium 316.
- This application medium vortex 316 'prevents air from entering the Area between the underground U and the order view 320.
- the guide scraper 322 slides on this vortex 316 'with low friction what not only wear on the guide scraper 322, but also direct order also the wear occurring on the material web lowers.
- the end face 322c of the tip is not one hydrophobic film is provided. The reason for this lies on the one hand in the easier to manufacture. On the other hand, the end face 322c is even supposed to be wettable, while on the hydrophobic coating Application medium rolls off to make a smoother transition to To allow underground U.
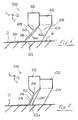
- the application device 410 according to FIG. 6 differs in terms of the construction of the curtain applicator 412 and the guide element 422 not from the embodiment described above according to FIG. 4, i.e. the guide element 422 extends continuously from the dispensing nozzle 414 to the underground U. Therefore, in this regard, the Description of the embodiment shown in FIG. 4.
- a suction box 432 is provided.
- This suction box 432 serves the to weaken air boundary layer G carried along by underground U. or vacuum, even before they even hit the ground U employed scraper 422 arrives.
- To increase the suction efficiency of the Suction device 432 has a sealing lip on the input side or Sealing blade or sealing scraper 434, which together with the guide scraper 422, the suction box 432 and the underground U an absorbent Encloses volume 436.
- the suction box 532 to assign two sealing elements 534 and 534 'specially assigned to it, one of which with respect to the running direction L of the underground U am inlet side end of the suction box 532 and the other at its discharge end is arranged.
- the application medium curtain is also on 418 underside 422d of the guide scraper 422 facing away an electrode 440 is arranged, which due to the emanating from it electric field allows the order medium 416 in the sense of a to influence additional stabilization of the application medium curtain 418.
- an electrode 440 is arranged, which due to the emanating from it electric field allows the order medium 416 in the sense of a to influence additional stabilization of the application medium curtain 418.
- a plurality of such electrodes can also be used be provided.
- the arrangement of electrodes and suction boxes furthermore to the post-published ones originating from the applicant's group German patent applications DE 100 12 256.6 and DE 100 12 347.3 referenced.
- Application medium 16 always on the top 22a of the guide element 22 moved along is to be based on the application device 510 according to FIG. 7 are also shown that it is in principle also possible that the order medium 516 or the order medium curtain 518 due to of adhesive forces between the guide element 522 and the application medium 516 also along the underside 522d of the guide element 522 can move, provided that the guide element 522 directly to the Delivery opening 514 of curtain applicator 512 connects.
- the guide element 622 or 722 of the application device 610 or 710 also convex (FIG. 8) 'or concave (Fig. 9) can be curved.
- the thickness or the speed of the Application medium curtain 618 or 718 can be influenced in a targeted manner.
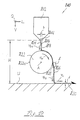
- a roller 822 is arranged, which the fall height H divided into a first free fall section 824, which is different from the Dispensing nozzle 814 until the curtain 818 hits the Roller surface 822a, and a second free-fall portion 826, which leads from the roller 822 to the underground U.
- the roller 822 rotates about its axis A running in the transverse direction Q, specifically at a speed selected such that the speed v W of the surface 822a of the roller 822 has a greater value than the falling speed v F1 of the curtain 818 in first free-fall section 824 shortly before hitting roller surface 822a (v W > v F1 ).
- the application medium 816 when it hits the roller surface 822a after gravity stretching in the free-fall section 824, experiences a contact stretching by the rotating roller 822.
- the application medium curtain 818 is stabilized by the adhesive forces between the application medium 816 and the roller surface 822a.
- scraper 828 lifts the application medium 816 from the Surface 822a of the roller 822 and transfers it to the second free-fall section 826.
- the length I of the piercing scraper 828 is between approximately 5 mm and about 50 mm.
- the diameter of the roller 822 is between 38 mm and about 500 mm. Its surface 822a is preferred trained hydrophilic.
- the curtain 818 is again stretched, which means that its falling speed v F2 shortly before it hits the surface U has a greater value than the surface speed v W of the roller 822 (v F2 > v W ) , However, this falling speed v F2 is still lower than the running speed v U of the underground U in the running direction L (v U > v F2 ).
- the application medium 816 is thus stretched again when it comes into contact with the underground U.
- the total extension of the application medium curtain 818 from the thickness b when leaving the discharge opening 814 to the layer thickness d is the The application layer 820 applied on the background U thus takes place at the Application device 810 according to FIG. 1 in four stages, namely a first Gravity stretching in the first free fall section 824, a first Contact stretching when it hits the roller surface 822a, one second gravity stretch in the second free fall section 826 and one second contact stretch when hitting the underground U.
Landscapes
- Coating Apparatus (AREA)
- Paper (AREA)
- Application Of Or Painting With Fluid Materials (AREA)
- Formation And Processing Of Food Products (AREA)
- Saccharide Compounds (AREA)
- Polysaccharides And Polysaccharide Derivatives (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft eine Vorrichtung zum Auftragen von flüssigem oder pastösem Auftragsmedium, insbesondere wässriger Pigmentsuspension, auf einen laufenden Untergrund, umfassend ein Vorhang-Auftragswerk, welches das Auftragsmedium aus einer Abgabedüse als sich im Wesentlichen schwerkraftbedingt bewegenden Vorhang oder Schleier an den Untergrund abgibt, wobei der Untergrund bei direktem Auftrag die Oberfläche einer Materialbahn, insbesondere aus Papier oder Karton, und bei indirektem Auftrag die Oberfläche eines Übertragselements, vorzugsweise einer Übertragswalze, ist, welches das Auftragsmedium dann an die Oberfläche der Materialbahn überträgt.The invention relates to a device for applying liquid or pasty application medium, especially aqueous pigment suspension, on a running surface, including a curtain commission, which the application medium from a dispensing nozzle as in the Moving curtain or veil due to gravity delivers the surface, whereby the surface with the direct application Surface of a material web, in particular made of paper or cardboard, and with indirect application, the surface of a transfer element, preferably a transfer roller, which is then the application medium to the Surface of the material web transfers.
Bei der Beschichtung von Materialbahnen unter Einsatzes eines Vorhang-Auftragswerks (in der Fachwelt auch als "Curtain Coating" bezeichnet) wird das Auftragsmedium an den Untergrund in Form eines Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs bzw. -Schleiers (der Einfachheit halber werden im Folgenden nur noch die Begriffs "Auftragsmedium-Vorhang" bzw. nur "Vorhang" verwendet) abgegeben, der sich im Wesentlichen schwerkraftbedingt vom Auftragswerk zum Untergrund bewegt. Dass das Vorhang-Auftragswerk sich dabei in einem vorbestimmten Abstand vom Untergrund befindet, hat unter anderem den Vorteil, dass es beispielsweise bei einem Bahnabriss einem geringeren Beschädigungsrisiko ausgesetzt ist. Vorhang-Auftragswerke unterscheiden sich von anderen "kontaktlosen" Auftragswerken, beispielsweise Freistrahl-Düsenauftragswerken, bei welchen die Bewegung des Auftragsmediums vom Auftragswerk zum Untergrund hauptsächlich vom Ausstoßimpuls aus der Abgabedüse des Auftragswerks herrührt, grundlegend, da die Gestalt des aus der Abgabedüse austretenden Vorhangs lediglich dem Wechselspiel zwischen der Oberflächenspannung des Auftragsmediums und der Schwerkraft ausgesetzt ist. Die Oberflächenspannung versucht dabei, den Vorhang, der bezogen auf sein Volumen bzw. seine Querschnittsfläche eine sehr große Oberfläche bzw. Umfangslänge aufweist, zusammenzuziehen, um so seine Oberfläche zu verringern. Diesem Effekt widersetzt sich die Schwerkraft, die den Vorhang zu strecken sucht. Es ist daher leicht einzusehen, dass es umso schwieriger ist, einen über die gesamte Arbeitsbreite gleichmäßig dicken Auftragsmedium-Vorhang zu erhalten, je größer diese Arbeitsbreite ist.When coating material webs using a curtain applicator (also known as "curtain coating" in the professional world) the application medium is applied to the substrate in the form of a Application medium curtain or curtain (for the sake of simplicity in the following only the term "order medium curtain" or only "Curtain" used), which is essentially due to gravity moved from the commissioned work to the underground. That this Curtain application work itself at a predetermined distance from Among other things, it has the advantage that it is located underground is at a lower risk of damage in the event of a web break. Custom curtain works differ from other "contactless" Applicators, for example free jet nozzle applicators, at which the movement of the order medium from the order work to Mainly from the ejection pulse from the discharge nozzle of the Commissioned work originates fundamentally, since the shape of the from the Dispensing nozzle emerging curtain only the interplay between the surface tension of the application medium and gravity is exposed. The surface tension tries the curtain a very large one based on its volume or cross-sectional area Surface or circumferential length has to contract, so its Reduce surface area. Gravity opposes this effect, who tries to stretch the curtain. It is therefore easy to see that it the more difficult it is to get one evenly across the entire working width to get thick application medium curtain, the larger this working width is.
Die Beschichtung von Materialbahnen mittels eines Vorhang-Auftragswerks,
das der Materialbahn das Auftragsmedium als sich im Wesentlichen
schwerkraftbedingt bewegenden Auftragsmedium-Vorhang zuführt, ist von
der Beschichtung von fotografischen Filmen, Tonbändern und dergleichen
seit langem bekannt. Weiterhin sind aus dem Bereich der Textilindustrie,
bspw. aus der DE 33 33 592 A1 und der DE 40 15 946 A1 entsprechende
Vorrichtungen zum Aufbringen eines Flüssigkeitsfilms auf eine textile
Warenbahn mit Hilfe eines sich im Wesentlichen schwerkraftbedingt
bewegenden Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs bekannt. Allerdings weisen die
Materialbahnen auf diesen Anwendungsgebieten eine erheblich geringere
Breite auf, als dies bei modernen Anlagen zur Herstellung von Papier- und
Kartonbahnen der Fall ist, bei denen heutzutage Materialbahnbreiten von
mehr als 10 m gefordert werden. Einen über diese Breite gleichmäßigen
Auftragsmedium-Vorhang bilden und stabil halten zu können, ist eine
Aufgabe, bei der es alles andere als naheliegt, sich von den
vergleichsweise einfach zu kontrollierenden, bekannten schmalen
Auftragsmedium-Vorhängen Anregungen für eine funktionstaugliche
Lösung zu erwarten. Darüber hinaus bewegen sich die Materialbahnen in
modernen Anlagen zur Herstellung von Papierbahnen mit
Geschwindigkeiten von etwa 1.000 m/min bis zu 3.000 m/min, und in
Anlagen zur Herstellung von Kartonbahnen mit Geschwindigkeiten ab etwa
200 m/min, was zumeist ein Vielfaches der Geschwindigkeit ist, mit der
sich die bekannten schmalen Materialbahnen bewegen. Die hohen Bahn-Geschwindigkeiten
stellen überdies eine weitere hohe Belastung für die
Stabilität des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs dar, da der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang
nicht nur im freien Fall schwerkraftbedingt gestreckt wird
(Schwerkraftstreckung), sondern auch beim Kontakt mit dem Untergrund
aufgrund des Unterschieds zwischen der Geschwindigkeit des frei fallenden
Auftragsmediums kurz vor dem Auftreffen auf dem Untergrund und der
Laufgeschwindigkeit des sich bewegenden Untergrunds
(Kontaktstreckung).The coating of material webs by means of a curtain applicator, which feeds the application medium to the material medium as an application medium curtain that moves due to gravity, has long been known from the coating of photographic films, tapes and the like. Furthermore, corresponding devices for applying a liquid film to a textile material web with the aid of an application medium curtain that moves due to gravity are known from the field of the textile industry, for example from DE 33 33 592 A1 and DE 40 15 946 A1. However, the material webs in these fields of application have a considerably smaller width than is the case with modern systems for the production of paper and cardboard webs, in which material web widths of more than 10 m are required today. To be able to form and keep a stable application medium curtain across this width is a task in which it is anything but obvious to expect suggestions for a functional solution from the comparatively easy to control, known narrow application medium curtains. In addition, the material webs move in modern systems for the production of paper webs with speeds of approximately 1,000 m / min up to 3,000 m / min, and in systems for the production of cardboard webs with speeds of approximately 200 m / min, which is usually a multiple of the speed with which the known narrow material webs move. The high web speeds also put a further high load on the stability of the application medium curtain, since the application medium curtain is not only stretched due to gravity in free fall (gravity stretching), but also when it comes into contact with the ground due to the difference between the speeds of the freely falling application medium shortly before it hits the surface and the running speed of the moving surface
(Contact stretching).
In "Patent Abstracts of Japan", Nr. 10024360 ist eine Vorhang-Auftragsvorrichtung veröffentlicht, bei der eine Auftragsflüssigkeit durch zwei gegenläufige Walzen aus einem Reservoir heraus extrahiert wird, wobei die Auftragsflüssigkeit zu einem dünnen Film gestreckt wird, und danach im Wesentlichen unter Einfluss der Schwerkraft auf einen Untergrund aufgetragen wird.In "Patent Abstracts of Japan", No. 10024360 is a curtain applicator published in which an order fluid through two counter-rotating rollers are extracted from a reservoir, the application liquid being stretched into a thin film, and then essentially under the influence of gravity on you Surface is applied.
Zur Erzielung eines qualitativ hochwertigen Auftragsergebnisses ist es wünschenswert, die Gesamtstreckung (= Schwerkraftstreckung x Kontaktstreckung) möglichst gleichmäßig auf die Schwerkraftstreckung und die Kontaktstreckung zu verteilen. Hierzu ist es insbesondere bei hohen Laufgeschwindigkeiten des Untergrunds erforderlich, dass der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang kurz vor dem Kontakt mit dem Untergrund eine möglichst hohe Fallgeschwindigkeit aufweist, was eine entsprechend hohe Fallhöhe bedingt. Der Fallhöhe sind jedoch physikalische Grenzen gesetzt. Bei einer zu großen Fallhöhe würde nämlich zum einen der Einfluss der Oberflächenspannung des Auftragsmediums und zum anderen der Einfluss von Luftbewegungen in der Nähe des Auftragsmediums-Vorhangs zu groß, um einen stabilen Auftragsmedium-Vorhang zuverlässig und reproduzierbar gewährleisten zu können. Die genannten Effekte erlangen einen umso stärkeren Einfluss auf die Qualität des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs, je kleiner die Durchflussmenge des vom Vorhang-Auftragswerk pro Meter Arbeitsbreite an den Untergrund abgegebenen Auftragsmediums ist, d.h. je dünner der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang ist. Insbesondere in einem Filmdickenbereich von 2 ml/m2 bis 50 ml/m2, wie sie beim fertigdosierten Auftrag ("1:1"-Auftrag) dünner Auftragsmediumschichten keine Seltenheit sind, wird die Schwerkraftstreckung durch die vorstehend genannten Effekte begrenzt.In order to achieve a high-quality order result, it is desirable to distribute the total extension (= gravity extension x contact extension) as evenly as possible between the gravity extension and the contact extension. For this purpose, it is necessary, in particular when the subsurface is running at high speeds, that the application medium curtain has the highest possible fall speed shortly before contact with the subsurface, which requires a correspondingly high fall height. However, there are physical limits to the fall height. If the drop height were too large, the influence of the surface tension of the application medium and, on the other hand, the influence of air movements in the vicinity of the application medium curtain would be too great to be able to reliably and reproducibly ensure a stable application medium curtain. The effects mentioned have a stronger influence on the quality of the application medium curtain, the smaller the flow rate of the application medium delivered by the curtain application unit per meter of working width to the substrate, ie the thinner the application medium curtain. In particular in a film thickness range from 2 ml / m 2 to 50 ml / m 2 , as is not uncommon in the case of a thinly applied layer ("1: 1" application) of thin layers of application medium, gravity stretching is limited by the effects mentioned above.
Es ist daher Aufgabe der Erfindung, eine Vorrichtung der eingangs genannten Art anzugeben, bei welcher der Einfluss der vorstehend diskutierten Effekte auf die Schwerkraftstreckung reduziert ist.It is therefore an object of the invention to provide a device at the outset Specify the type in which the influence of the above discussed effects on gravity extension is reduced.
Diese Aufgabe wird erfindungsgemäß durch eine Vorrichtung der gattungsgemäßen Art gelöst, bei welcher in dem Fallweg des Vorhangs wenigstens ein Leitelement angeordnet ist, das den Vorhang längs zumindest eines Teils des Fallwegs auf seiner gesamten Breite führt.This object is achieved by a device of the generic type Kind solved, in which at least in the fall path of the curtain a guide element is arranged, the curtain along at least one Part of the fall path leads across its entire width.
Der vorteilhafte Effekt des erfindungsgemäß eingesetzten Leitelements auf den Auftragsmedium-Vorhang beruht höchstwahrscheinlich darauf, dass das Auftragsmedium beim Kontakt mit dem Leitelement zunächst etwas abgebremst wird, was die Form des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs stabilisiert. Mit zunehmender Bewegung des Auftragsmediums längs des Leitelements nimmt dann aber die Fallgeschwindigkeit, genauer gesagt die Fließgeschwindigkeit des Auftragsmediums längs des Leitelements, wieder zu. Durch diese erfindungsgemäße Stabilisierung des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs kann die Gesamtfallhöhe des Vorhangs und somit die insgesamt erzielbare Schwerkraftstreckung verglichen mit einem herkömmlichen freifallenden Auftragsmedium-Vorhang ohne Einbußen hinsichtlich der Qualität der damit gebildeten Auftragsmediumschicht erhöht werden. Hierdurch ist es möglich, sich der durch die physikalischen Eigenschaften des Auftragsmediums limitierten Filmstreckungsgrenze, bei der sich im dosierten Film, die Gleichmäßigkeit des Strichs negativ beeinflussende Schwingungswellen bilden, stärker anzunähern als dies bislang mit einem frei fallenden Auftragsmedium-Vorhang möglich war. The advantageous effect of the guide element used according to the invention the order medium curtain is most likely based on the fact that the application medium when it comes into contact with the guide element is slowed down, which stabilizes the shape of the application medium curtain. With increasing movement of the application medium along the guide element but then the falling speed, more precisely the flow speed, takes of the application medium along the guide element, again. This stabilization of the application medium curtain according to the invention can determine the total fall height of the curtain and thus the total achievable gravity stretch compared to a conventional one free-falling application medium curtain without sacrificing the Quality of the application medium layer thus formed can be increased. This makes it possible to understand the physical properties of the order medium limited film stretch limit at which dosed film, negatively influencing the uniformity of the stroke Form vibration waves, closer to each other than previously free falling order medium curtain was possible.
Anzumerken ist in diesem Zusammenhang, dass unter einer "im Wesentlichen schwerkraftbedingten" Bewegung des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs hier verstanden wird, dass von allen, das Auftragsmedium zum Untergrund hin treibenden Kräften die Schwerkraft den größten Einfluss auf den Auftragsmedium-Vorhang ausübt. Die schwerkraftbedingte Bewegung kann aber auch von weiteren Kräften unterstützt (beispielsweise von elektrostatischen Kräften) oder in anderer Art und Weise beeinflusst werden (beispielsweise viskose Reibung bei der Bewegung längs des Leitelements).It should be noted in this context that under an "essentially gravity-related "movement of the application medium curtain here it is understood that everyone applies the application medium to the underground gravitational forces have the greatest influence on the application medium curtain exercises. The movement due to gravity can also supported by other forces (e.g. electrostatic Forces) or influenced in some other way (e.g. viscous friction when moving along the guide element).
Anzumerken ist weiterhin, dass die Worte "längs des Fallwegs führen" im Zusammenhang mit der vorliegenden Erfindung durchaus auch bedeuten können, dass der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang durch das Leitelement aus der dem freien Fall entsprechenden Bahn ausgelenkt werden kann.It should also be noted that the words "lead along the fall path" in the Connection with the present invention also mean can that the application medium curtain through the guide element from the the path corresponding to the free fall can be deflected.
Anzumerken ist ferner, dass als Materialbahnen neben Papier und Karton auch Folien oder Textilien mittels der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung mit Auftragsmedium beschichtet werden können.It should also be noted that as material webs in addition to paper and cardboard also films or textiles using the device according to the invention Application medium can be coated.
Die vorstehend beschriebenen Vorteile können insbesondere dann erzielt werden, wenn das Leitelement den Fallweg in einen von der Abgabedüse zum Leitelement führenden Freifall-Abschnitt und einem vom Leitelement zum Untergrund führenden Freifall-Abschnitt unterteilt. In diesem Fall kann der gesamte Fallweg des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs mittels eines einzigen Leitelements in drei Abschnitte unterteilt werden, nämlich zwei Freifall-Abschnitte, die durch einen den Auftragsmedium-Vorhang stabilisierenden Abschnitt längs des Leitelements voneinander getrennt sind. Selbstverständlich kann jeder der Freifall-Abschnitte durch zusätzliche Leitelemente weiter unterteilt sein.The advantages described above can then be achieved in particular be when the guide element drops into one of the dispensing nozzle Free fall section leading to the guide element and one from the guide element divided into the free fall section leading to the subsurface. In this case the entire fall of the application medium curtain using a single one Guide element can be divided into three sections, namely two free-fall sections, those that stabilize the application medium curtain Section along the guide element are separated from each other. Of course can each of the free fall sections by additional guide elements be further divided.
Aber auch dann, wenn das Leitelement den Fallweg des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs nicht in zwei Freifall-Abschnitte unterteilt, wirkt sich der stabilisierende Einfluss des Leitelements vorteilhaft auf die Qualität des Auftragsergebnisses aus, wobei mittels dieser Leitelemente dann noch weitere, das Auftragsergebnis letzten Endes vorteilhaft beeinflussende Wirkungen erzielt werden können:But also when the guide element is the fall of the application medium curtain not divided into two free fall sections, the stabilizing influence of the guide element advantageous on the quality of the Order result, with the help of these guidance elements others that ultimately have a positive impact on the order result Effects can be achieved:
So läßt sich beispielsweise gemäß einer ersten Ausführungsvariante mittels eines sich unmittelbar an die Abgabedüse anschließenden Leitelements der sogenannte "Teekannen-Effekt" vermeiden. Dieser "Teekannen-Effekt", eine charakteristische Verformung des aus der Abgabedüse austretenden Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs, tritt in der Praxis dann auf, wenn die Strömungsgeschwindigkeit des Auftragsmediums beim Verlassen der Abgabedüse eine Grenzgeschwindigkeit unterschreitet, die zum einen von den physikalischen Eigenschaften des Auftragsmediums und zum anderen von der Dicke des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs abhängt. Dünne Vorhänge neigen auch bei größerer Ausströmungsgeschwindigkeit dazu, den "Teekannen-Effekt" zu zeigen. Überschreitet die Ausströmungsgeschwindigkeitden vorstehend angesprochenen Grenzwert, so bildet sich üblicherweise ein parabolischer Verlauf des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs aus. Ideal wäre es hingegen, den Auftragsmedium-Vorhang exakt mit der Grenzgeschwindigkeit aus der Abgabedüse austreten zu lassen, da der Vorhang in diesem Fall einen nahezu perfekt vertikalen Verlauf nimmt.For example, according to a first embodiment variant of a directing element directly adjoining the dispensing nozzle Avoid the so-called "teapot effect". This "teapot effect", a characteristic deformation of that emerging from the dispensing nozzle Application medium curtain occurs in practice when the Flow rate of the application medium when leaving the Dispensing nozzle falls below a limit speed, which on the one hand of the physical properties of the application medium and the other depends on the thickness of the application medium curtain. Thin curtains also tend to the To show "teapot effect". Exceeds the Outflow velocity the limit mentioned above, a parabolic curve of the application medium curtain usually forms out. On the other hand, it would be ideal to have the application medium curtain exactly to leave the discharge nozzle at the limit speed, because in this case the curtain runs almost perfectly vertical.
Dieser Idealfall läßt sich unter Einsatz eines sich unmittelbar an die Abgabedüse anschließenden Leitelements in einfacher Weise erreichen bzw. zumindest annähern. Wie bereits vorstehend ausgeführt wurde, wird der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang durch den Einfluss des Leitelements zunächst stabilisiert und dann von der Schwerkraft, wenn auch in einem durch den Kosinus des Neigungswinkels geminderten Maße, längs des Leitelements beschleunigt. Bei entsprechender Wahl der Länge des Leitelements in Bewegungsrichtung des Vorhangs kann erreicht werden, dass der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang am Ende des Leitelements sich exakt mit der Grenzgeschwindigkeit oder einer geringfügig größeren Geschwindigkeit bewegt, so dass der "Teekannen-Effekt" sicher vermieden werden kann und der Vorhang das Leitelement nahezu in vertikaler Richtung verläßt.This ideal case can be directly addressed to the Reach discharge nozzle adjoining guide element in a simple manner or at least approximate. As already stated above, the application medium curtain initially due to the influence of the guide element stabilized and then by gravity, albeit in one by the Cosine of the angle of inclination diminished dimensions, along the guide element accelerated. With a corresponding choice of the length of the guide element in Direction of movement of the curtain can be achieved that the Application medium curtain at the end of the guide element exactly with the Limit speed or a slightly higher speed moved so that the "teapot effect" can be safely avoided and the curtain leaves the guide element almost in the vertical direction.
Um die erfindungsgemäße Auftragsvorrichtung in einfacher Weise an die physikalischen Eigenschaften verschiedener Auftragsmedien, verschiedene Vorhangdicken, und dergleichen Parameter mehr anpassen zu können, wird vorgeschlagen, dass die in Bewegungsrichtung des Vorhangs gemessene, von Auftragsmedium bedeckte Länge des Leitelements veränderbar ist. Ferner hat es sich als vorteilhaft erwiesen, wenn das Leitelement mit der dem freien Fall des Vorhangs entsprechenden Richtung einen Winkel von zwischen etwa 5° und etwa 30° einschließt. Das "Teekannen-Effekt"-freie Ablösen des Vorhangs vom Leitelement kann dadurch erleichtert werden, dass die von dem Auftragsmedium-Vorhang bedeckte Oberfläche des Leitelements mit der Stirnfläche des Leitelements einen Winkel von zwischen etwa 20° und etwa 60° einschließt. Die von Auftragsmedium bedeckte Länge des Leitelements sollte vorteilhafterweise höchstens etwa 200 mm, vorzugsweise höchstens etwa 50 mm, betragen.To the application device according to the invention in a simple manner to the physical properties of different application media, different Curtain thicknesses, and the like parameters can be adjusted more proposed that the measured in the direction of movement of the curtain, length of the guide element covered by the application medium is changeable. Furthermore, it has proven to be advantageous if the guide element with the direction corresponding to the free fall of the curtain between about 5 ° and about 30 °. The "teapot effect" -free Detaching the curtain from the guide element can be facilitated by that the surface of the guide element covered by the application medium curtain with the end face of the guide element an angle of between about 20 ° and about 60 °. The one covered by order medium The length of the guide element should advantageously be at most about 200 mm, preferably at most about 50 mm.
Gemäß einer weiteren Ausführungsvariante kann das Leitelement aber auch als Leitschaber gegen den Untergrund angestellt sein. In diesem Fall tritt zu dem den Auftragsmedium-Vorhang stabilisierenden Einfluss des Leitelements hinzu, dass dieser die vom Untergrund mitgeführte Luftgrenzschicht schwächen und somit deren nachteiligen Einfluss auf das Auftragsergebnis mindern kann. Beispielsweise können mittels eines derartigen Leitschabers lokal begrenzte Unterbrechungen des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs verhindert werden, die zu nicht mit Auftragsmedium bedeckten Stellen des Untergrunds führen würden. Aber auch die lokale Einschleppung von Lufteinschlüssen zwischen Untergrund und Auftragsmedium, die quasi als Vorstadium eines lokalen Reissens des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs angesehen werden können, können mittels des erfindungsgemäßen Leitschabers vermieden werden. Eine etwaig entstehende Reibungswärme durch die Relativbewegung von Leitschaber und Untergrund stellt in der Praxis kein Problem dar, da sie in einfacher Weise durch das Auftragsmedium selbst abgeführt werden kann.According to a further embodiment variant, the guide element can also be used as a scraper against the ground. In this case occurs the influence of the guide element that stabilizes the application medium curtain added that this is the air boundary layer carried by the subsurface weaken and thus their adverse influence on the order result can mitigate. For example, such Guide scraper localized interruptions of the application medium curtain can be prevented that are not covered with application medium Places of the underground would lead. But also the local one Introduction of air pockets between the subsurface and Application medium, which is quasi as a preliminary stage of a local tearing of the Order medium curtain can be viewed using the Guide scraper according to the invention can be avoided. Any friction heat generated by the relative movement of the scraper and underground is not a problem in practice as it is easier in Way can be dissipated by the application medium itself.
Auch im Falle des Einsatzes des Leitelements als Leitschaber hat sich eine geneigte Anordnung dieses Leitschabers als vorteilhaft erwiesen. Beispielsweise kann das Leitelement mit der dem freien Fall des Vorhangs entsprechenden Richtung einen Winkel von zwischen etwa 20° und etwa 80°, vorzugsweise zwischen etwa 45° und etwa 80°, einschließen. Die von Auftragsmedium bedeckte Länge des Leitschabers sollte vorteilhafterweise höchstens etwa 50 mm, vorzugsweise höchstens etwa 10 mm, betragen.Even when the guide element is used as a guide scraper, there has been one inclined arrangement of this guide scraper proved to be advantageous. For example can the guide element with the free fall of the curtain Direction an angle of between about 20 ° and about Include 80 °, preferably between about 45 ° and about 80 °. The length of guide scraper covered by application medium advantageously at most about 50 mm, preferably at most about 10 mm.
Um einerseits einen annähernd linienartigen Kontakt zwischen Leitschaber und Untergrund sicherstellen und andererseits einen annähernd stufenfreien Übergang des Auftragsmediums vom Leitschaber zum Untergrund ermöglichen zu können, wird ferner vorgeschlagen, dass die von dem Auftragsmedium-Vorhang bedeckte Oberfläche des Leitelements einen dem Untergrund benachbart angeordneten Endabschnitt aufweist, der mit einer gedachten Verlängerung der Oberfläche einen Winkel von zwischen etwa 30° und etwa 50° einschließt.On the one hand, an almost line-like contact between the guide scraper ensure and underground and on the other hand an almost step-free Enable the transfer of the application medium from the scraper to the surface To be able to, it is also proposed that the of the application medium curtain covered surface of the guide element to the underground has an adjacently arranged end section which is connected to a imaginary extension of the surface an angle of between about 30 ° and about 50 °.
Gemäß einer weiteren Ausführungsvariante ist es ferner möglich, dass sich das Leitelement über die gesamte Strecke zwischen Abgabedüse und Untergrund erstreckt, um so die Vorteile einer sich an die Abgabedüse unmittelbar anschließenden Leitelements mit jenen eines als Leitschaber eingesetzten Leitelements zu verbinden. Hinsichtlich des Neigungswinkels des Leitelements muss in diesem Fall entweder ein Kompromiss zwischen den beiden genannten Anordnungsalternativen gefunden oder das Leitelement gekrümmt ausgebildet werden, so dass es sowohl im Bereich der Abgabedüse als auch im Bereich des Untergrunds einen jeweils vorteilhaften Neigungswinkel aufweist. Selbstverständlich ist es aber auch möglich, zwei voneinander getrennte Leitelemente vorzusehen, von denen eines sich unmittelbar an die Abgabedüse anschließt, während das andere als Leitschaber gegen den Untergrund angestellt ist.According to a further embodiment variant, it is also possible that the guide element over the entire distance between the dispensing nozzle and Extends underground, so the benefits of extending to the dispensing nozzle immediately following guide element with one as a guide scraper used to connect the guide element. With regard to the angle of inclination In this case, the guiding element must either have a compromise between found the two arrangement alternatives mentioned or that Guide element are curved, so that it is both in the area the dispensing nozzle as well as in the area of the substrate one each has advantageous inclination angle. Of course it is too possible to provide two separate guide elements, one of which one connects directly to the dispensing nozzle while the other is employed as a scraper against the underground.
Eine gekrümmte Ausbildung des Leitelements ermöglicht es überdies, über die Form der Krümmung die Geschwindigkeit oder/und die Dicke des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs zu beeinflussen. Dabei kann sowohl an den Einsatz von konvex als auch von konkav gekrümmten Leitelementen gedacht werden, wobei mit konvex bzw. konkav die Krümmung der dem Auftragsmedium zugewandten Oberfläche des Leitelements bezeichnet ist.A curved design of the guide element also allows over the shape of the curvature, the speed and / or the thickness of the application medium curtain to influence. It can both use of convex as well as concave curved guide elements be, with convex or concave the curvature of the application medium facing surface of the guide element is designated.
Insbesondere dann, wenn das Leitelement aus Metall oder Kunststoff, beispielsweise kohlefaser- oder glasfaser-verstärkten Kunststoff, gefertigt ist, kann es vorkommen, dass das Auftragsmedium beim Kontakt mit dem Leitschaber stärker abgebremst wird, als es für die Erzielung der gewünschten Stabilisierung des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs eigentlich erforderlich ist. In diesem Fall kann die Bremskraft, die der Leitschaber auf das Auftragsmedium ausübt, dadurch gemindert werden, dass das Leitelement zumindest auf seiner dem Vorhang bzw. Schleier zugewandten Oberfläche hydrophob ausgebildet ist, so dass die Strömungsgeschwindigkeit des Auftragsmediums auf dem Leitelement erhalten bleibt.Especially when the guide element made of metal or plastic, for example, carbon fiber or glass fiber reinforced plastic , it can happen that the application medium is in contact with the Guide scraper is braked more than it is for achieving the desired one Stabilization of the application medium curtain is actually required. In this case, the braking force applied by the scraper to the application medium exercises, are reduced in that the guide element at least hydrophobic on its surface facing the curtain or veil is formed so that the flow rate of the Order medium is retained on the guide element.
Diese hydrophobe Ausbildung der Oberfläche des Leitelements kann in herstellungstechnisch einfacher Weise dadurch erhalten werden, dass die Oberfläche des Leitelements mit einer hydrophoben Beschichtung versehen ist, beispielsweise mit einer teflonisierten Glasfaserfolie beschichtet ist. Im Hinblick auf ein günstiges Ablöseverhalten des Auftragsmediums vom Leitelement sollte jedoch zumindest die Stirnfläche des Leitelements frei von hydrophober Beschichtung sein.This hydrophobic formation of the surface of the guide element can be in can be obtained in a technically simple manner in that the Provide the surface of the guide element with a hydrophobic coating is coated, for example with a Teflonized glass fiber film. in the With regard to a favorable detachment behavior of the application medium from the guide element However, at least the end face of the guide element should be free of be hydrophobic coating.
Bei der vorstehenden Diskussion wurde implizit stets davon ausgegangen, dass sich der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang auf der Oberseite des Leitelements entlangbewegt, also von der Schwerkraft an dieser Oberseite gehalten wird. Grundsätzlich ist es jedoch auch möglich, dass sich der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang auf der Unterseite des Leitelements entlangbewegt, wobei er an dieser Unterseite durch Adhäsionskräfte gehalten wird.In the discussion above, it was always implicitly assumed that that the application medium curtain is on the top of the guide element moved along, so held by gravity on this top becomes. In principle, however, it is also possible that the Moving the application medium curtain along the underside of the guide element, being held on this underside by adhesive forces.
In Weiterbildung der Erfindung kann auf der dem Auftragsmedium-Vorhang abgewandten Seite wenigstens eine Elektrode angeordnet sein. Mittels des von dieser Elektrode ausgehenden elektrischen Felds kann das Auftragsmedium und dessen Wechselwirkung mit der Oberfläche des Leitelements zur Erzielung bzw. Sicherstellung einer gleichmäßigen Schichtdicke des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs vorteilhaft beeinflusst werden. Dies ist ausführlich in den nachveröffentlichten deutschen Patentanmeldungen DE 100 12 256.6 und DE 100 12 347.3 aus dem Konzern der Anmelderin beschrieben, auf die hiermit Bezug genommen wird.In a development of the invention, the application medium curtain facing away from at least one electrode. By means of the the application medium can emanate from this electrode and its interaction with the surface of the guide element to achieve or ensure a uniform layer thickness of the Application medium curtain can be influenced advantageously. This is detailed in the post-published German patent applications DE 100 12 256.6 and DE 100 12 347.3 from the applicant's group to which reference is hereby made.
Ferner kann in Laufrichtung des Untergrunds vor der Kontaktlinie des Vorhangs bzw. Schleiers ein Saugkasten angeordnet sein. Dieser Saugkasten kann zusätzlich oder alternativ zu einem als Leitschaber eingesetzten Leitelement zur Bekämpfung der vom Untergrund mitgeführten Luftgrenzschicht eingesetzt werden. Wird im Falle des direkten Auftrags des Auftragsmediums auf eine Materialbahn ein gegen die Materialbahn angestellter Leitschaber eingesetzt, so kann mittels des Saugkastens die Materialbahn in sicheren Kontakt gegen den Leitschaber angesaugt werden, so dass dieser die Luftgrenzschicht effektiv von der Materialbahnoberfläche abheben kann. Dem Saugkasten kann zulaufseitig oder/und auslaufseitig ein Schaberelement zugeordnet sein, das mit einer Schaberkante auf dem Untergrund aufliegt, wobei das auslaufseitige Schaberelement von dem Leitelement gebildet sein kann. Auch hinsichtlich konstruktiver Details des angesprochenen Saugkastens sei auf die vorstehend genannten beiden deutschen Patentanmeldungen verwiesen.Furthermore, in front of the contact line of the Curtain or veil a suction box can be arranged. This suction box can be used in addition or as an alternative to a scraper Guiding element for combating the air boundary layer carried by the subsurface be used. In the case of a direct order from the Application medium on a material web against the material web employed scraper used, so can by means of the suction box Material web is sucked into safe contact against the guide scraper, so that this effectively removes the air boundary layer from the web surface can take off. The suction box can be on the inlet side and / or outlet side be assigned a scraper element, which with a scraper edge on the Rests on the ground, with the scraper element on the outlet side of the Guide element can be formed. Also with regard to constructive details of the mentioned suction box is on the above two referred to German patent applications.
Nachzutragen ist noch, dass das Leitelement ausgehend von seiner dem Untergrund fernsten Stelle entweder in oder entgegen der Laufrichtung des Untergrunds geneigt angeordnet sein kann, wobei das Leitelement mit der dem freien Fall des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs entsprechenden Richtung in beiden Orientierungen einen Winkel von bis zu etwa 70° einschließen kann. In hinsichtlich des Abreißens des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs kritischen Fällen ist dabei die ablaufseitige Orientierung des Leitelements vorzuziehen.It must also be added that the guiding element based on its The most distant underground either in or against the direction of the Can be arranged inclined underground, the guide element with the direction corresponding to the free fall of the application medium curtain in include an angle of up to about 70 ° in both orientations can. In terms of tearing off the application medium curtain In critical cases, the orientation of the guide element on the drain side preferable.
Eine weitere vorteilhafte Weiterbildung der Erfindung sieht vor, dass das Leitelement als laufende Oberfläche ausgebildet ist, die den Fallweg des Vorhangs bzw. Schleiers in einen von der Abgabedüse zum Leitelement führenden Freifall-Abschnitt und einem von dem Leitelement zum Untergrund führenden Freifall-Abschnitt unterteilt, und deren Laufgeschwindigkeit größer ist als die Fallgeschwindigkeit des Auftragsmediums am Ende der zu dem Leitelement führenden Freifall-Abschnitts. Durch den erfindungsgemäßen Einsatz der als Leitelement dienenden laufenden Oberfläche setzt sich die Gesamtstreckung nicht mehr nur aus einer einmaligen Schwerkraftstreckung und einer einmaligen Kontaktstreckung zusammen. Vielmehr wird das Auftragsmedium nach einer ersten Schwerkraftstreckung durch die laufende Oberfläche einer ersten Kontaktstreckung unterworfen, worauf nach dem Ablösen des Auftragsmediums von der als Leitelement dienenden laufenden Oberfläche eine zweite Schwerkraft- bzw. Beschleunigungsstreckung und anschließend die Kontaktstreckung durch den laufenden Untergrund folgt. Hierzu ist es lediglich erforderlich, dass die Laufgeschwindigkeit des Untergrunds größer ist als die Fallgeschwindigkeit des Auftragsmediums am Ende des zum Untergrund führenden Freifall-Abschnitts.Another advantageous development of the invention provides that Guide element is designed as a running surface that the fall of the Curtain or veil in one from the dispensing nozzle to the guide element leading free fall section and one from the guide element to Subdivided underground leading free fall section, and their running speed is greater than the falling speed of the Application medium at the end of the free fall section leading to the guide element. Through the use of the invention as a guide element serving running surface, the total stretch no longer settles only from a single gravity stretch and a one-off Contact extension together. Rather, the order medium becomes a first gravity extension through the running surface of a subjected to the first contact stretching, after which the detachment of the application medium of the running surface serving as a guiding element second gravity or acceleration stretch and then the Contact extension through the running surface follows. This is it only required that the running speed of the surface be greater is as the falling speed of the application medium at the end of the Leading free-fall section.
Erfindungsgemäß kann als eine solche das Leitelement bildende laufende Oberfläche beispielsweise durch ein endloses, umlaufendes Band realisiert werden. In einer weiteren, besonders bevorzugten Ausführung dieser Variante der Erfindung ist als Leitelement eine sich drehende Walze vorgesehen, deren Umfangsgeschwindigkeit größer ist als die Fallgeschwindigkeit des Auftragsmediums am Ende des zur als Leitelement dienenden Walze führenden Freifallabschnitts. Hierbei kann eine solche Walze vorzugsweise zumindest im Bereich ihrer Umfangsfläche aus Metall gefertigt sein.According to the invention, the current guiding element forming such a guiding element Surface realized, for example, by an endless, circulating belt become. In a further, particularly preferred embodiment of this A variant of the invention is a rotating roller as the guide element provided, the peripheral speed is greater than that Falling speed of the application medium at the end of the as a guiding element serving roller leading free fall section. Here, such Roll preferably made of metal at least in the area of its peripheral surface be made.
Erfindungsgemäß wird also durch die als Leitelement dienende laufende Oberfläche, bspw. die sich drehende Walze, nicht nur ein relativ langer Freifall-Abschnitt in zwei kürzere Freifall-Abschnitte unterteilt, was hinsichtlich der Auswirkungen äußerer Einflüsse auf den Auftragsmedium-Vorhang vorteilhaft ist, sondern es wird zudem die Gesamtstreckung auf eine Vielzahl von Streckungsstufen verteilt, was die Beanspruchung des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs in den einzelnen Streckungsstufen reduziert. Somit läßt sich insgesamt bei gleicher Gesamtfallhöhe sogar eine stärkere Streckung des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs erzielen.According to the invention, the current one serving as the guiding element Surface, for example the rotating roller, not just a relatively long one Free fall section divided into two shorter free fall sections what regarding the effects of external influences on the application medium curtain is advantageous, but it will also stretch the total distributed a variety of stretch levels, which the stress of the Application medium curtain reduced in the individual stretching stages. Thus, even a stronger overall can be achieved with the same total fall height Achieve extension of the application medium curtain.
Nachzutragen ist noch, dass der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang durch die Adhäsionskräfte zwischen dem Auftragsmedium und der als Leitelement dienenden laufenden Oberfläche, bspw. der Umfangsfläche der Walze, stabilisiert wird, was für seine Qualität und somit auch die Qualität des letztendlich mit Hilfe dieses Vorhangs erzielten Auftragsergebnisses günstig ist.It is still to be added that the order medium curtain through the Adhesive forces between the application medium and that as the guiding element serving running surface, e.g. the peripheral surface of the roller, is stabilized, which for its quality and thus also the quality of the ultimately, order profit achieved with the help of this curtain is.
Ferner hat es sich als vorteilhaft erwiesen, die Laufrichtung der als Leitelement dienenden Oberfläche derart zu wählen, dass sich der Abschnitt der als Leitelement dienenden laufenden Oberfläche, der mit dem Auftragsmedium des zu dem Leitelement führenden Freifall-Abschnitts in Kontakt gelangt, in der gleichen Richtung bewegt wie der Untergrund. Falls als Leitelement eine Walze eingesetzt wird, heißt dies also, dass der Drehsinn der Walze bevorzugt derart gewählt werden soll, dass sich der Umfangsabschnitt der Walze, der mit dem Auftragsmedium des zur Walze führenden Freifall-Abschnitts in Kontakt gelangt, in gleicher Richtung bewegt wie der Untergrund. Furthermore, it has proven to be advantageous to change the running direction of the Guide surface serving to choose such that the Section of the running surface serving as a guide element, which with the Application medium of the free fall section leading to the guide element in Contact is made, moving in the same direction as the surface. If a roller is used as the guide element, this means that the Direction of rotation of the roller should preferably be chosen such that the Circumferential section of the roller, with the application medium of the roller leading free-fall section comes into contact in the same direction moves like the underground.
Um das Ablösen des Auftragsmediums von der als Leitelement dienenden laufenden Oberfläche erleichtern zu können bzw. um zuverlässig sicherstellen zu können, dass sich auch nach dem Ablösen des Auftragsmediums von der als Leitelement dienenden laufenden Oberfläche ein gleichmäßiger Auftragsmedium-Vorhang bildet, wird in Weiterbildung der Erfindung vorgeschlagen, dass ein Schaberelement, beispielsweise ein Stechschaber, vorgesehen ist, der das Auftragsmedium von dieser abhebt und an den von dem Leitelement zum Untergrund führenden Freifall-Abschnitt abgibt. Dieses Schaberelement kann beispielsweise gegen die als Leitelement dienende laufende Oberfläche, bspw. die Oberfläche der Walze, angestellt sein. Falls als Leitelement eine Walze eingesetzt wird, kann es jedoch auch von einem Wandungsabschnitt eines die Walze lagernden Walzenbetts gebildet sein. Die Länge des Schaberelements kann dabei in Bewegungsrichtung des Auftragsmediums gemessen zwischen etwa 5 mm und etwa 50 mm betragen.To detach the application medium from the one serving as the guide element to facilitate running surface or to be reliable to be able to ensure that even after removing the Application medium from the running surface serving as a guiding element forms a uniform application medium curtain, is in continuing education the invention proposed that a scraper element, for example a Piercing scraper is provided, which lifts the application medium from it and to the free fall section leading from the guide element to the subsurface emits. This scraper element can, for example, against the as Guiding element serving running surface, for example the surface of the roller, be employed. If a roller is used as the guide element, it can but also from a wall section of a roller supporting the roller Roll bed be formed. The length of the scraper element can be in Direction of movement of the application medium measured between about 5 mm and be about 50 mm.
Selbstverständlich kann jeder der von der laufenden Oberfläche, z. B. der sich drehenden Walze, gebildeten Freifall-Abschnitte durch zusätzliche Leitelemente weiter unterteilt sein. Dabei können diese zusätzlichen Leitelemente weitere laufende Oberflächen, etwa sich drehende Walzen, sein oder aber auch festmontierte, d.h. sich nicht bewegende Leitelemente, beispielsweise im Wesentlichen plane Leitbleche. Die zusätzlichen Leitelemente können dabei den betreffenden Freifall-Abschnitt, in dem sie angeordnet sind, wiederum in zwei Freifall-Unterabschnitte unterteilen. Es ist jedoch auch möglich, dass sich ein derartiges Leitelement unmittelbar an die Abgabedüse des Vorhang-Auftragswerks anschließt bzw. als Leitschaber gegen die Oberfläche des laufenden Untergrunds oder der bzw. einer laufenden Oberfläche, z. B. einer sich drehenden Walze, angestellt ist.Of course, any of the current surface, e.g. B. the spinning roller, free fall sections formed by additional Guiding elements can be further divided. These can be additional Other running surfaces, such as rotating rollers, be or also permanently installed, i.e. non-moving guide elements, for example, essentially flat baffles. The additional guiding elements can do the free fall section in which they are arranged, again divide into two free-fall subsections. It However, it is also possible for such a guide element to be attached directly the discharge nozzle of the curtain applicator connects or as Guide scraper against the surface of the running surface or the or a running surface, e.g. B. a rotating roller is employed.
Die Erfindung wird im Folgenden an Ausführungsbeispielen anhand der beigefügten Zeichnung näher erläutert werden. Es stellt dar:
- Fig. 1 - 4
- schematische Seitenansichten verschiedener Varianten erfindungsgemäßer Auftragsvorrichtungen mit an unterschiedlichen Positionen zwischen dem Auftragswerk und dem Untergrund angeordneten Leitelementen;
- Fig. 5
- eine vergrößerte Ansicht des Details V gemäß Fig. 4, wobei eine geringfügige Abweichung lediglich hinsichtlich des Auftreffens des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs besteht;
- Fig. 6 und 7
- zwei mit Saugkasten ausgestatteten Varianten erfindungsgemäßer Auftragsvorrichtungen;
- Fig. 8 und 9
- zwei erfindungsgemäße Auftragsvorrichtungen mit konvexem bzw. konkavem Leitelement; und
- Fig. 10
- eine schematische Seitenansicht einer Weiterbildung einer erfindungsgemäßen Auftragsvorrichtung mit einem als Walze ausgebildeten Leitelement.
- 1-4
- schematic side views of different variants of application devices according to the invention with guide elements arranged at different positions between the application unit and the substrate;
- Fig. 5
- an enlarged view of the detail V according to FIG 4, with a slight deviation only with regard to the impact of the application medium curtain.
- 6 and 7
- two variants of application devices according to the invention equipped with a suction box;
- 8 and 9
- two application devices according to the invention with convex or concave guide element; and
- Fig. 10
- is a schematic side view of a development of an application device according to the invention with a guide element designed as a roller.
In Fig. 1 ist eine erfindungsgemäße Vorhang-Auftragsvorrichtung allgemein
mit 10 bezeichnet. Sie umfasst ein Vorhang-Auftragswerk 12, aus dessen
Abgabedüse 14 flüssiges oder pastöses Auftragsmedium 16 in Form eines
Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs bzw. -Schleiers 18 abgegeben wird. Der
Vorhang 18 bewegt sich im Wesentlichen schwerkraftbedingt in vertikaler
Richtung V nach unten zu einem Untergrund U, der sich unter dem
Auftragswerk 12 in Laufrichtung L mit einer Geschwindigkeit bei einer
Kartonbahn ab etwa 200 m/min und bei einer Papierbahn von zwischen
etwa 1.000 m/min und etwa 3.000 m/min vorbeibewegt. Der Untergrund
U kann bei direktem Auftrag die Oberfläche der Materialbahn, insbesondere
der Papier- oder Kartonbahn, aber auch einer Folien- oder Textilbahn, sein,
oder bei indirektem Auftrag die Oberfläche eines Übertragselements,
beispielsweise einer Übertragswalze. Ziel der Auftragsvorrichtung 10 ist es,
das Auftragsmedium 16 im Wesentlichen fertig dosiert, d.h. im Idealfall als
" 1:1 "-Auftrag, auf den Untergrund U aufzubringen als eine Auftragsschicht
20, die eine Dicke d von zwischen etwa 2 µm und 100 µm aufweist.In Fig. 1, a curtain application device according to the invention is general
designated 10. It comprises a
Bei derartigen Vorhang-Auftragsvorrichtungen 10 beruht die Reduzierung
der Dicke des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs 18 von der Breite b der Abgabedüse
14 auf die Dicke d der Auftragsschicht 20 im Wesentlichen auf zwei
Effekten, nämlich zum einen der schwerkraftbedingten Streckung des Vorhangs
18 während des freien Falls von der Abgabedüse 14 zum
Untergrund U und zum anderen der Kontaktstreckung aufgrund des
Unterschieds zwischen der Fallgeschwindigkeit des Vorhangs 18 kurz vor
Erreichen des Untergrunds U und der Laufgeschwindigkeit des Untergrunds
U. Dabei sind der schwerkraftbedingten Streckung nicht nur aufgrund
physikalischer Effekte (Wechselspiel zwischen Schwerkraft und Oberflächenspannung
des Auftragsmediums 16), sondern auch aufgrund
äußerer Einflüsse (beispielsweise Mitnahme des Vorhangs 18 durch den
Untegrund U, Luftströmungen und dergleichen) Grenzen gesetzt.The reduction is based on
Die vorliegende Erfindung beruht auf der Erkenntnis, dass man die Fallhöhe
H und somit die insgesamt erzielbare schwerkraftbedingte Streckung des
Auftragsmediums 16 dadurch vergrößern kann, dass man im Weg des Auftragsmediums
16 von der Abgabedüse 14 zum Untergrund U ein Leitelement
22, beispielsweise ein Leitblech oder eine Leitklinge, anordnet. Es
hat sich nämlich gezeigt, dass die viskose Reibungskraft zwischen dem
Auftragsmedium 16 und dem Leitelement 22 auf den Auftragsmedium-Vorhang
18 eine diesen stabilisierende, d.h. insbesondere vergleichmäßigende
Wirkung ausübt.The present invention is based on the finding that the drop height
H and thus the overall achievable extension of the
Gleichwohl kann das Auftragsmedium 16 bei geeigneter Wahl des
Neigungswinkels α, den die Oberfläche des im Wesentlichen planen
Leitelements 22 mit der Vertikalen V einschließt, sowie entsprechender
Wahl der Oberflächeneigenschaften des Leitelements 22 bei seiner
Bewegung längs des Leitelements 22 weiter beschleunigt werden. Somit
erfährt der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang 18 auch im Bereich des Leitelements
22 eine Streckung.Nevertheless, the
In dem in Fig. 1 dargestellten Ausführungsbeispiel unterteilt das
Leitelement 22 den Weg des Auftragsmediums 16 von der Abgabedüse 14
zum Untergrund U in einen ersten Freifall-Abschnitt 24 und einen zweiten
Freifall-Abschnitt 26. Nach einer ersten schwerkraftbedingten Streckung im
ersten Freifall-Abschnitt 24 trifft das Auftragsmedium 14 also auf das
Leitelement 22, das den Vorhang 18 stabilisiert und dennoch dessen
weitere schwerkraftbedingte Streckung ermöglicht. Anschließend gelangt
das Auftragsmedium 16 in den Bereich des zweiten Freifall-Abschnitts 26,
in welchem es nochmals schwerkraftbedingt gestreckt wird, bevor es auf
dem Untergrund U auftrifft. Um eine nachteilige Beeinflussung des
Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs 18 beim Übergang vom Leitelement 22 in den
zweiten Freifall-Abschnitt 26 verhindern zu können, ist die Stirnfläche 22b
des Leitelements 22 derart angeschrägt ausgebildet, dass sie mit der vom
Auftragsmedium 16 bedeckten Oberfläche 22a des Leitelements 22 einen
Winkel β von zwischen etwa 20° und etwa 60° einschließen.In the embodiment shown in Fig. 1 divides that
Der Neigungswinkel α des Leitelements 22 relativ zur Vertikalen V kann
einen Wert von bis zu 70° aufweisen, wobei das Leitelement 22 wie in Fig.
1 dargestellt, bezüglich des Untergrunds U ablaufseitig angeordnet sein
kann. Grundsätzlich ist jedoch auch eine zulaufseitige Anordnung des
Leitelements 22 denkbar. Das Leitelement bzw. Leitblech 22, das aus
Metall oder Kunststoff, beispielsweise kohlefaser- oder glasfaser-verstärktem
Kunststoff, gefertigt sein kann, weist vorteilhafterweise eine
Dicke D von zwischen etwa 0,2 mm und etwa 1,0 mm auf. Die
Gesamtfallhöhe H kann bis zu 400 mm betragen, wobei die Strecke, in
welcher sich das Auftragsmedium 16 längs des Leitelements 22 bewegt,
eine Länge I von zwischen etwa 1 mm und etwa 200 mm, vorzugsweise
zwischen etwa 1 mm und etwa 50 mm, aufweist.The angle of inclination α of the
Die in Fig. 2 dargestellte Vorhang-Auftragsvorrichtung 110 unterscheidet
sich von der Ausführungsform gemäß Fig. 1 lediglich dadurch, dass das
Leitelement 122 an die Abgabedüse 114 des Vorhang-Auftragswerks 112
unmittelbar anschließend angeordnet ist. Auch durch diese Ausführung läßt
sich die angesprochene Stabilisierung des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs 118
im Bereich des Leitelements 122 erzielen, so dass diesbezüglich auf die
vorstehende Beschreibung der Ausführungsform gemäß Fig. 1 verwiesen
werden kann.The
Mit der Auftragsvorrichtung 110 gemäß Fig. 2 läßt sich jedoch noch ein
weiterer Vorteil erzielen. Und zwar kann durch entsprechende Anpassung
der Länge I an die Eigenschaften des Auftragsmediums 116 und weiterer
Parameter, wie beispielsweise die Dicke und die Austrittsgeschwindigkeit
des Vorhangs 118 aus der Abgabedüse 114, erreichen, dass der Vorhang
118 sich im Anschluss an das Leitelement 122 im Bereich des zum Untergrund
U führenden Freifall-Abschnitts 126 nahezu perfekt in vertikaler
Richtung V bewegt, und nicht einen Verlauf nimmt wie er von dem sogenannten
"Teekannen-Effekt" verursacht wird (in Fig. 2 gestrichelt
angedeuteter Verlauf T). Die Geschwindigkeit des Auftragsmediums 116 an
der Ablösekante 122c des Leitelements 122 sollte idealerweise ferner so
gewählt werden, dass das Auftragsmedium 116 nicht über diese Kante
122c hinausschießt und anschließend einen parabelförmigen Verlauf nimmt
(strichpunktierter Verlauf P), sondern an der Kante 122c im Wesentlichen
unmittelbar in den in Fig. 2 dargestellten im Wesentlichen vertikalen Verlauf
übergeht.The
Dies alles kann mit der Vorhang-Auftragsvorrichtung 110 gemäß Fig. 2 in
einfacher Weise erreicht werden, da die "aktive" Länge I des Leitelements
122 und somit die Geschwindigkeit des Auftragsmediums 116 im Bereich
der Kante 122c durch einfaches mechanisches Verstellen des Leitelements
122 in Richtung des Doppelpfeils X bewerkstelligt werden kann. Es ist also
nicht erforderlich, die hydrodynamischen Parameter in dem Auftragswerk
112 zu beeinflussen, was steuerungs- bzw. regelungstechnisch mit erheblichem
Aufwand verbunden wäre.All this can be done with the
Auch bei der Auftragsvorrichtung 210 gemäß Fig. 3 kann durch das Leitelement
222 eine den Auftragsmedium-Vorhang 218 stabilisierende
Wirkung auf das Auftragsmedium 216 ausgeübt werden, das von dem
Vorhang-Auftragswerk 212 aus dessen Abgabeöffnung 214 zum Untergrund
U hin abgegeben wird. Daher kann diesbezüglich auf die vorstehende
Beschreibung der Ausführungsform gemäß Fig. 1 verwiesen werden.In the
Bei der Auftragsvorrichtung 210 gemäß Fig. 3 ist jedoch das Leitelement
222 als Leitschaber gegen die Oberfläche des Untergrunds U angestellt.
Aufgabe dieses Leitschabers ist es, die vom Untergrund U mitgeführte
Luftgrenzschicht G vom Untergrund U zu entfernen, um deren nachteiligen
Einfluss (lokales Reißen des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs 218; Lufteinschleppung
zwischen Untergrund U und Auftragsschicht 220) auf das
Auftragsergebnis zu mindern, wenn nicht gar vollständig zu eliminieren.3, however, is the
Um gleichwohl einen möglichst stufenfreien Übergang des
Auftragsmediums 216 vom Leitschaber 222 zum Untergrund U hin
sicherstellen zu können, ist die Stirnfläche 222b angeschrägt ausgebildet,
wobei sie mit der von Auftragsmedium 216 nicht benetzten Unterseite
222d des Leitschabers einen Winkel γ einschließt, dessen Wert zwischen
etwa 30° und etwa 50° beträgt.In order to achieve a smooth transition from the
Application medium 216 from the
Selbstverständlich ist es auch möglich, die Ausführungsformen gemäß Fig.
2 und 3 miteinander zu kombinieren, d.h. sowohl ein dem "Teekannen-Effekt"
vorbeugendes, sich an die Abgabeöffnung des Vorhang-Auftragswerks
unmittelbar anschließendes Leitelement als auch einen gegen den
Untergrund U angestellten Leitschaber vorzusehen. Ja, es ist sogar
denkbar, wie dies bei dem Vorhang-Auftragswerk 310 gemäß Fig. 4
dargestellt ist, diese beiden Leitelemente zu einem einzigen Leitelement
322 zu kombinieren, das sich von der Abgabeöffnung 314 des Vorhang-Auftragswerks
312 durchgehend bis zum Untergrund U erstreckt, gegen
den es als Leitschaber angestellt ist. In diesem Fall übt das Leitelement 322
über die gesamte Fallhöhe H (s. Fig. 1) die den Vorhang 318 stabilisierende
Wirkung auf das Auftragsmedium 316 aus. Ferner besteht keinerlei Gefahr
des Auftretens des "Teekannen-Effekts". Und schließlich wird auch
jeglicher nachteiliger Einfluss der Luftgrenzschicht G auf die
Auftragsschicht 320 unterdrückt.Of course, it is also possible to implement the embodiments according to FIG.
To combine 2 and 3, i.e. both the "teapot effect"
preventive, at the delivery opening of the curtain application
immediately following guide element as well as one against the
U scraper to be used underground. Yes, it is
conceivable, as is the case with the
Anhand der in Fig. 5 dargestellten Detailansicht der Spitze eines als
Leitschaber gegen den Untergrund U angestellten Leitelements 322 soll im
Folgenden eine Ausführungsvariante des erfindungsgemäßen Leitelements
näher erläutert werden. Und zwar ist das Leitelement 322 an seiner Oberseite
322a und seiner Unterseite 322d jeweils mit einer hydrophoben
Beschichtung 330 versehen. Diese hydrophobe Beschichtung kann
beispielsweise in Form einer teflonisierten Glasfaserfolie ausgebildet sein,
die auf die Oberfläche 322a und 322d des Leitelements 322 aufgebracht,
beispielsweise aufgeklebt ist. Eine derartige hydrophobe Beschichtung hat
aufgrund ihrer Wasser und somit auch das Auftragsmedium 316 abweisenden
Eigenschaften den Vorteil, dass zum einen die viskosen
Reibungskräfte zwischen dem Leitelement 322 und dem Auftragsmedium
316 reduziert sind, so dass das Auftragsmedium 316 auch längs der
Oberfläche 322a stärker schwerkraftbedingt beschleunigt und somit
gestreckt werden kann, und sie hat ferner den Vorteil einer geringeren
Verschmutzungsgefahr durch Anhaften von Auftragsmedium 316 am
Leitelement 322.Based on the detailed view of the tip of a as shown in Fig. 5
Guide scraper against the underground
In Folge der Beschichtung des Leitelements 322 auch an seiner Unterseite
322d mit der hydrophoben Beschichtung 330 kann das Leitelement 322,
wie dies in Fig. 5 dargestellt ist, geringfügig aufschwimmen, so dass sich
im Bereich der Spitze 322c des Leitschabers 322 eine geringe stark verwirbelte
Menge 316' an Auftragsmedium 316 ausbildet. Dieser Auftragsmediumwirbel
316' verhindert zum einen den Eintritt von Luft in den
Bereich zwischen dem Untergrund U und der Auftragssicht 320. Zum
anderen gleitet der Leitschaber 322 auf diesem Wirbel 316' reibungsarm
dahin, was nicht nur den Verschleiß am Leitschaber 322, sondern bei
direktem Auftrag auch den an der Materialbahn auftretenden Verschleiß
senkt. Anzumerken ist, dass die Stirnfläche 322c der Spitze nicht mit einer
hydrophoben Folie versehen ist. Der Grund hierfür liegt zum einen in der
einfacheren Herstellbarkeit. Zum anderen soll die Stirnfläche 322c sogar
benetzbar sein, während auf der hydrophoben Beschichtung das
Auftragsmedium abperlt, um einen gleichmäßigeren Übergang zum
Untergrund U zu ermöglichen.As a result of the coating of the
Die Auftragsvorrichtung 410 gemäß Fig. 6 unterscheidet sich hinsichtlich
des Aufbaus des Vorhang-Auftragswerks 412 und des Leitelements 422
nicht von der vorstehend beschriebenen Ausführungsform gemäß Fig. 4,
d.h. das Leitelement 422 erstreckt sich von der Abgabedüse 414 durchgehend
bis zum Untergrund U. Daher sei diesbezüglich auf die
Beschreibung der Ausführungsform gemäß Fig. 4 verwiesen.The
Als zusätzliche Maßnahme zur Erzielung einer qualitativ hochwertigen
Auftragsschicht 420 ist in Laufrichtung L vor dem Auftragswerk 412 ferner
ein Saugkasten 432 vorgesehen. Dieser Saugkasten 432 dient dazu, die
vom Untergrund U mitgeführte Luftgrenzschicht G bereits zu schwächen
bzw. abzusaugen, noch bevor sie überhaupt zu dem gegen den Untergrund
U angestellten Leitschaber 422 gelangt. Zur Erhöhung der Saugeffizienz der
Saugvorrichtung 432 weist diese eingangsseitig eine Dichtlippe bzw.
Dichtklinge bzw. Dichtschaber 434 auf, die zusammen mit dem Leitschaber
422, dem Saugkasten 432 und dem Untergrund U ein saugaktives
Volumen 436 umschließt. As an additional measure to achieve a high
Grundsätzlich ist es jedoch auch möglich, wie dies am Beispiel der
Auftragsvorrichtung 510 gemäß Fig. 7 dargestellt ist, dem Saugkasten 532
zwei diesem speziell zugeordnete Dichtelemente 534 und 534' zuzuordnen,
von denen das eine bezüglich der Laufrichtung L des Untergrunds U am
zulaufseitigen Ende des Saugkastens 532 und das andere an dessen
ablaufseitigem Ende angeordnet ist.In principle, however, it is also possible, as is the case with the
Bei der Ausführungsform 410 gemäß Fig. 6 ist ferner an der dem Auftragsmedium-Vorhang
418 abgewandten Unterseite 422d des Leitschabers 422
eine Elektrode 440 angeordnet, welche es aufgrund des von ihr ausgehenden
elektrischen Feldes erlaubt, das Auftragsmedium 416 im Sinne einer
zusätzlichen Stabilisierung des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs 418 zu beeinflussen.
Selbstverständlich kann auch eine Mehrzahl derartiger Elektroden
vorgesehen sein. Bezüglich der Anordnung von Elektroden und Saugkästen
sei ferner auf die aus dem Konzern der Anmelderin stammenden, nachveröffentlichten
deutsche Patentanmeldungen DE 100 12 256.6 und
DE 100 12 347.3 verwiesen.In the
Obgleich bei den vorstehend beschriebenen Ausführungsformen sich das
Auftragsmedium 16 stets auf der Oberseite 22a des Leitelements 22
entlang bewegte, soll anhand der Auftragsvorrichtung 510 gemäß Fig. 7
ferner aufgezeigt werden, dass es grundsätzlich auch möglich ist, dass sich
das Auftragsmedium 516 bzw. der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang 518 aufgrund
von Adhäsionskräften zwischen dem Leitelement 522 und dem Auftragsmedium
516 auch längs der Unterseite 522d des Leitelements 522
bewegen kann, sofern das Leitelement 522 sich unmittelbar an die
Abgabeöffnung 514 des Vorhang-Auftragswerks 512 anschließt.Although in the above-described
Anhand der Fig. 8 und 9 soll noch aufgezeigt werden, dass das Leitelement
622 bzw. 722 der Auftragsvorrichtung 610 bzw. 710 auch konvex (Fig. 8)
' oder konkav (Fig. 9) gekrümmt ausgebildet sein kann. Durch gezielte Wahl
des gekrümmten Verlaufs kann die Dicke bzw. die Geschwindigkeit des
Auftragsmedium-Vorhang 618 bzw. 718 gezielt beeinflusst werden.8 and 9 it should be shown that the
Bei der in Fig. 10 gezeigten Ausführung einer erfindungsgemäßen Vorhang-Auftrags-Vorrichtung
810 ist in dem Fallweg des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs
818 von der Abgabedüse 814 des Vorhang-Auftragswerks 812
zum Untergrund U eine Walze 822 angeordnet, welche die Fallhöhe H
unterteilt in einen ersten Freifall-Abschnitt 824, der sich von der
Abgabedüse 814 bis zum Auftreffen des Vorhangs 818 auf der
Walzenoberfläche 822a erstreckt, und einen zweiten Freifall-Abschnitt 826,
der von der Walze 822 bis zum Untergrund U führt.In the embodiment of a curtain application device according to the invention shown in FIG. 10
810 is in the fall path of the
Erfindungsgemäß dreht sich die Walze 822 um ihre in Querrichtung Q
verlaufende Achse A, und zwar mit einer Drehzahl, die derart gewählt ist,
dass die Geschwindigkeit vW der Oberfläche 822a der Walze 822 einen
größeren Wert aufweist als die Fallgeschwindigkeit vF1 des Vorhangs 818
im ersten Freifall-Abschnitt 824 kurz vor dem Auftreffen auf der
Walzenoberfläche 822a (vW > vF1). Hierdurch erfährt das Auftragsmedium
816 beim Auftreffen auf der Walzenoberfläche 822a nach der
Schwerkraftstreckung im Freifall-Abschnitt 824 eine Kontaktstreckung
durch die sich drehende Walze 822. Ferner wird der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang
818 durch die Adhäsionskräfte zwischen dem Auftragsmedium
816 und der Walzenoberfläche 822a stabilisiert. Zu diesen
Adhäsionskräften können selbstverständlich auch weitere auf das
Auftragsmedium 816 einwirkende Kräfte hinzutreten, beispielsweise
elektrostatische Kräfte, wenn im Inneren der Walze 822 eine auf einem
vorbestimmten elektrischen Potential gehaltene Elektrode angeordnet ist,
oder die Mantelfläche der Walze 822 selbst als Elektrode ausgebildet ist.According to the invention, the
Ein entgegen der Drehrichtung der Walze 822 gegen deren Oberfläche
822a angestellter Stechschaber 828 hebt das Auftragsmedium 816 von der
Oberfläche 822a der Walze 822 ab und überführt es in den zweiten Freifall-Abschnitt
826. Die Länge I des Stechschabers 828 beträgt zwischen etwa
5 mm und etwa 50 mm. Der Durchmesser der Walze 822 beträgt zwischen
38 mm und etwa 500 mm. Ihre Oberfläche 822a ist vorzugsweise
hydrophil ausgebildet.One against the direction of rotation of the
In dem zweiten Freifall-Abschnitt 826 erfährt der Vorhang 818 wiederum
eine Streckung, die dazu führt, dass seine Fallgeschwindigkeit vF2 kurz vor
Auftreffen auf dem Untergrund U einen größeren Wert aufweist als die
Oberflächengeschwindigkeit vW der Walze 822 (vF2 > vW). Diese Fallgeschwindigkeit
vF2 ist jedoch immer noch kleiner als die Laufgeschwindigkeit
vU des Untergrunds U in Laufrichtung L (vU > vF2). Somit wird das
Auftragsmedium 816 beim Kontakt mit dem Untergrund U nochmals
gestreckt.In the second free-
Die Gesamtstreckung des Auftragsmedium-Vorhangs 818 von der Dicke b
beim Verlassen der Abgabeöffnung 814 ist zur Schichtdicke d der auf den
Untergrund U aufgebrachten Auftragsschicht 820 erfolgt somit bei der
Auftragsvorrichtung 810 gemäß Fig. 1 in vier Stufen, nämlich einer ersten
Schwerkraftstreckung im ersten Freifall-Abschnitt 824, einer ersten
Kontaktstreckung beim Auftreffen auf die Walzenoberfläche 822a, einer
zweiten Schwerkraftstreckung im zweiten Freifall-Abschnitt 826 und einer
zweiten Kontaktstreckung beim Auftreffen auf den Untergrund U.The total extension of the application
Claims (39)
wobei der Untergrund (U) bei direktem Auftrag die Oberfläche einer Materialbahn, insbesondere aus Papier oder Karton, und bei indirektem Auftrag die Oberfläche eines Übertragselements, vorzugsweise einer Übertragswalze, ist, welches das Auftragsmedium dann an die Oberfläche der Materialbahn überträgt,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass in dem Fallweg des Vorhangs bzw. Schleiers.(18) wenigstens ein Leitelement (22) angeordnet ist, das den Vorhang bzw. Schleier (18) längs zumindest eines Teils des Fallwegs im Wesentlichen auf seiner gesamten Breite führt.Device (10) for applying liquid or pasty application medium (16), in particular aqueous pigment suspension, to a running surface (U), comprising a curtain application unit (12), which essentially applies the application medium from a dispensing nozzle (14) as a result of gravity emits a moving curtain or veil (18) to the underground (U),
where the substrate (U) is the surface of a material web, in particular of paper or cardboard, when directly applied and the surface of a transfer element, preferably a transfer roller, is applied indirectly, which then transfers the application medium to the surface of the material web,
characterized in that at least one guide element (22) is arranged in the fall path of the curtain or veil (18), which guides the curtain or veil (18) along at least part of the fall path essentially over its entire width.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Leitelement (22) den Fallweg in einen von der Abgabedüse (14) zum Leitelement (22) führenden Freifall-Abschnitt (24) und einem vom Leitelement (22) zum Untergrund (U) führenden Freifall-Abschnitt (26) unterteilt.Application device according to claim 1,
characterized in that the guide element (22) guides the fall into a free-fall section (24) leading from the dispensing nozzle (14) to the guide element (22) and a free-fall section (26) leading from the guide element (22) to the subsurface (U) divided.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass sich das Leitelement (122) unmittelbar an die Abgabedüse (114) anschließt. Application device according to claim 1,
characterized in that the guide element (122) directly adjoins the dispensing nozzle (114).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die in Bewegungsrichtung des Vorhangs bzw. Schleiers (118) gemessene, von Auftragsmedium (116) bedeckte Länge (I) des Leitelements (122) veränderbar ist.Application device according to claim 3,
characterized in that the length (I) of the guide element (122) measured in the direction of movement of the curtain or veil (118) and covered by application medium (116) can be changed.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Leitelement (122) mit der dem freien Fall des Vorhangs bzw. Schleiers (118) entsprechenden Richtung (V) einen Winkel (α) von zwischen etwa 5° und etwa 30° einschließt.Application device according to claim 3 or 4,
characterized in that the guide element (122) forms an angle (α) of between approximately 5 ° and approximately 30 ° with the direction (V) corresponding to the free fall of the curtain or veil (118).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die von dem Auftragsmedium-Vorhang (18; 118) bedeckte Oberfläche (22a) des Leitelements (22; 122) mit der Stirnfläche (22b) des Leitelements einen Winkel (β) von zwischen etwa 20° und etwa 60° einschließt.Application device according to one of claims 2 to 5,
characterized in that the surface (22a) of the guide element (22; 122) covered by the application medium curtain (18; 118) forms an angle (β) of between approximately 20 ° and approximately 60 ° with the end face (22b) of the guide element ,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Leitelement als Leitschaber (222; 322) gegen den Untergrund (U) angestellt ist.Application device according to one of claims 3 to 6,
characterized in that the guide element is employed as a guide scraper (222; 322) against the subsurface (U).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Leitelement (222; 322) mit der dem freien Fall des Vorhangs bzw. Schleiers (218; 318) entsprechenden Richtung (V) einen Winkel (α) von zwischen etwa 20° und etwa 80°, vorzugsweise zwischen etwa 45° und etwa 80°, einschließt.Application device according to claim 7,
characterized in that the guide element (222; 322) with the direction (V) corresponding to the free fall of the curtain or veil (218; 318) has an angle (α) of between approximately 20 ° and approximately 80 °, preferably between approximately 45 ° and about 80 °.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die von dem AuftragsmediumVorhang (218; 318) bedeckte Oberfläche des Leitelements (222; 322) einen dem Untergrund (U) benachbart angeordneten Endabschnitt (222b) aufweist, der mit einer gedachten Verlängerung der Oberfläche einen Winkel (y) von zwischen etwa 30° und etwa 50° einschließt.Application device according to claim 7 or 8,
characterized in that the surface of the guide element (222; 322) covered by the application medium curtain (218; 318) has an end section (222b) which is arranged adjacent to the substrate (U) and which, with an imaginary extension of the surface, has an angle (y) of between about 30 ° and about 50 °.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass sich das Leitelement (322) über die gesamte Strecke zwischen Abgabedüse (314) und Untergrund (U) erstreckt.Application device according to one of claims 3 to 6 and one of claims 7 to 9,
characterized in that the guide element (322) extends over the entire distance between the discharge nozzle (314) and the substrate (U).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Leitelement (322) zumindest auf seiner dem Vorhang bzw. Schleier (318) zugewandten Oberfläche (322a) hydrophob ausgebildet ist.Application device according to one of claims 1 to 10,
characterized in that the guide element (322) is designed to be hydrophobic at least on its surface (322a) facing the curtain or veil (318).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Oberfläche (322a) des Leitelements (322) mit einer hydrophoben Beschichtung (330) versehen ist, beispielsweise mit einer teflonisierten Glasfaserfolie beschichtet ist.Applicator according to claim 11,
characterized in that the surface (322a) of the guide element (322) is provided with a hydrophobic coating (330), for example coated with a teflon-coated glass fiber film.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass zumindest die Stirnfläche (322c) des Leitelements (322) frei von hydrophober Beschichtung ist.Application device according to claim 11 or 12,
characterized in that at least the end face (322c) of the guide element (322) is free of hydrophobic coating.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang (18) sich auf der Oberseite (22a) des Leitelements (22) entlangbewegt. Application device according to one of claims 1 to 13,
characterized in that the application medium curtain (18) moves along the top (22a) of the guide element (22).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang (518) sich auf der Unterseite (522d) des Leitelements (522) entlangbewegt.Application device according to one of claims 1 to 13,
characterized in that the application medium curtain (518) moves along the underside (522d) of the guide element (522).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass auf der dem Auftragsmedium-Vorhang (418) abgewandten Seite (422d) des Leitelements (422) wenigstens eine Elektrode (440) angeordnet ist.Application device according to one of claims 1 to 15,
characterized in that at least one electrode (440) is arranged on the side (422d) of the guide element (422) facing away from the application medium curtain (418).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass in Laufrichtung (L) des Untergrunds (U) vor der Kontaktlinie des Vorhangs bzw. Schleiers (418; 518) ein Saugkasten (432; 532) angeordnet ist.Application device according to one of claims 1 to 16,
characterized in that a suction box (432; 532) is arranged in the running direction (L) of the substrate (U) in front of the line of contact of the curtain or veil (418; 518).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass dem Saugkasten (432; 532) zulaufseitig oder/und auslaufseitig ein Schaberelement (434, 422; 534, 534') zugeordnet ist, das mit einer Schaberkante auf dem Untergrund (U) aufliegt.Application device according to claim 17,
characterized in that the suction box (432; 532) is assigned a scraper element (434, 422; 534, 534 ') on the inlet side and / or outlet side, which rests with a scraper edge on the substrate (U).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das auslaufseitige Schaberelement von dem Leitelement (422) gebildet ist.Applicator according to claim 18,
characterized in that the outlet-side scraper element is formed by the guide element (422).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass sich der Auftragsmedium-Vorhang (18) über eine Strecke (I) von zwischen etwa 1 mm und etwa 200 mm, vorzugsweise zwischen etwa 1 mm und etwa 50 mm, längs der Oberfläche des Leitelements (22) bewegt. Application device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that the application medium curtain (18) moves over a distance (I) of between approximately 1 mm and approximately 200 mm, preferably between approximately 1 mm and approximately 50 mm, along the surface of the guide element (22).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass sich der Untergrund (U) im Falle der Beschichtung einer Papierbahn mit einer Geschwindigkeit von zwischen etwa 1000 m/min und etwa 3000 m/min und im Falle der Beschichtung einer Kartonbahn mit einer Geschwindigkeit von zwischen etwa 200 m/min und etwa 1.000 m/min bewegt.Application device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that the substrate (U) in the case of coating a paper web at a speed of between about 1000 m / min and about 3000 m / min and in the case of coating a cardboard web at a speed of between about 200 m / min and moved about 1,000 m / min.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Auftragsmedium (16) fertigdosiert auf den Untergrund (U) aufgebracht wird.Application device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that the application medium (16) is applied in a metered manner to the substrate (U).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Abgabedüse (14) das Auftragsmedium (16) mit einer Rate von zwischen etwa 2 l/min und etwa 200 l/min je Meter Arbeitsbreite abgibt.Application device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that the dispensing nozzle (14) dispenses the application medium (16) at a rate of between approximately 2 l / min and approximately 200 l / min per meter of working width.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Länge (H) des Vorhangs (18) einen Wert von zwischen etwa 5 mm und etwa 400 mm, vorzugsweise von zwischen etwa 40 mm und etwa 200 mm aufweist.Application device according to one of the preceding claims
characterized in that the length (H) of the curtain (18) has a value of between approximately 5 mm and approximately 400 mm, preferably between approximately 40 mm and approximately 200 mm.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Leitelement (22) aus Metall oder Kunststoff, beispielsweise kohlefaser- oder glasfaser-verstärktem Kunststoff, gefertigt ist.Application device according to one of the preceding claims
characterized in that the guide element (22) is made of metal or plastic, for example carbon fiber or glass fiber reinforced plastic.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Leitelement (22) eine Dicke (D) von zwischen etwa 0,2 mm und etwa 1,0 mm aufweist. Application device according to one of the preceding claims
characterized in that the guide element (22) has a thickness (D) of between approximately 0.2 mm and approximately 1.0 mm.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Leitelement (22) ausgehend von seiner dem Untergrund (U) fernsten Stelle in oder entgegen der Laufrichtung (L) des Untergrunds (U) geneigt angeordnet sein kann,
wobei das Leitelement (22) mit der dem freien Fall des Vorhangs bzw. Schleiers (18) entsprechenden Richtung (V) in beiden Orientierungen einen Winkel (α) von bis zu etwa 70° einschließt.Application device according to one of the preceding claims
characterized in that the guide element (22) can be arranged inclined, starting from its point farthest from the subsurface (U), in or counter to the running direction (L) of the subsurface (U),
wherein the guide element (22) with the direction (V) corresponding to the free fall of the curtain or veil (18) encloses an angle (α) of up to approximately 70 ° in both orientations.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Leitelement (622; 722) konvex oder konkav gekrümmt ausgebildet ist.Application device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that the guide element (622; 722) is convex or concave.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, eine an die gekrümmte Fläche angelegte Tangente mit der dem freien Fall des Vorhangs bzw. Schleiers (618; 718) entsprechenden Richtung (V) einen Winkel (α) von bis zu etwa 70° einschließt.Application device according to claim 28,
characterized in that a tangent to the curved surface with the direction (V) corresponding to the free fall of the curtain or veil (618; 718) encloses an angle (α) of up to approximately 70 °.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Leitelement als laufende Oberfläche ausgebildet ist, die den Fallweg des Vorhangs bzw. Schleiers (818) in einen von der Abgabedüse (814) zum Leitelement führenden Freifall-Abschnitt (824) und einen von dem Leitelement zum Untergrund (U) führenden Freifall-Abschnitt (826) unterteilt, und deren Laufgeschwindigkeit größer ist als die Fallgeschwindigkeit (vF1) des Auftragsmediums (816) am Ende des zu dem Leitelement führenden Freifall-Abschnitts (824).Application device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that the guide element is designed as a running surface , which covers the fall path of the curtain or veil (818) into a free fall section (824) leading from the dispensing nozzle (814) to the guide element and one from the guide element to the substrate (U) leading free fall section (826), and the running speed of which is greater than the fall speed (v F1 ) of the application medium (816) at the end of the free fall section (824) leading to the guide element.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Leitelement als endloses, umlaufendes Band ausgebildet ist. Application device according to claim 30,
characterized in that the guide element is designed as an endless, circumferential band.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass als Leitelement eine sich drehende Walze (822) vorgesehen ist, deren Umfangsgeschwindigkeit (vW) größer ist als die Fallgeschwindigkeit (vF1) des Auftragsmediums (816) am Ende des zur Walze (822) führenden Freifall-Abschnitts (824).Application device according to claim 30,
characterized in that a rotating roller (822) is provided as the guide element, the peripheral speed (v W ) of which is greater than the falling speed (v F1 ) of the application medium (816) at the end of the free-fall section (824) leading to the roller (822) ).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Laufgeschwindigkeit (vU) des Untergrunds (U) größer ist als die Fallgeschwindigkeit (vF2) des Auftragsmediums (816) am Ende des zum Untergrund (U) führenden Freifall-Abschnitts (826).Application device according to one of claims 30 to 32,
characterized in that the running speed (v U ) of the subsurface (U) is greater than the falling speed (v F2 ) of the application medium (816) at the end of the free-fall section (826) leading to the subsurface (U).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Laufrichtung der das Leitelement bildenden laufenden Oberfläche derart gewählt ist, dass sich der Abschnitt (822a) der das Leitelement bildenden laufenden Oberfläche, der mit dem Auftragsmedium (816) des zu dem Leitelement führenden Freifall-Abschnitts (24) in Kontakt gelangt, in der gleichen Richtung bewegt, wie der Untergrund (U).Application device according to one of claims 30 to 33,
characterized in that the running direction of the running surface forming the guide element is selected such that the section (822a) of the running surface forming the guide element comes into contact with the application medium (816) of the free-fall section (24) leading to the guide element arrives, moves in the same direction as the underground (U).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass eine Schaberfläche (28), beispielsweise in Form eines Stechschabers, vorgesehen ist, die gegen die das Leitelement bildende laufende Oberfläche angestellt ist, das Auftragsmedium (16) von dieser Oberfläche abhebt und an den von dem Leitelement zum Untergrund (U) führenden Freifall-Abschnitt (26) abgibt. Application device according to one of claims 30 to 34,
characterized in that a scraper surface (28), for example in the form of a piercing scraper, is provided which is placed against the running surface forming the guide element, lifts the application medium (16) from this surface and on the surface from the guide element to the substrate (U) leading free-fall section (26).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Schaberfläche (28) in Bewegungsrichtung (L) des Auftragsmediums (16) gemessen eine Länge (I) von zwischen etwa 5 mm und etwa 50 mm aufweist.Applicator according to claim 35,
characterized in that the scraper surface (28) measured in the direction of movement (L) of the application medium (16) has a length (I) of between approximately 5 mm and approximately 50 mm.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die das Leitelement bildende laufende Oberfläche zumindest teilweise hydrophil ausgebildet ist.Applicator according to one of claims 30 to 36,
characterized in that the running surface forming the guide element is at least partially hydrophilic.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Walze (822) zumindest im Bereich ihrer Umfangsfläche (822a) aus Metall gefertigt ist.Applicator according to one of claims 32 to 37,
characterized in that the roller (822) is made of metal at least in the region of its peripheral surface (822a).
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Walze (822) einen Durchmesser von zwischen etwa 38 mm und etwa 500 mm aufweist.Application device according to one of claims 32 to 38,
characterized in that the roller (822) has a diameter of between approximately 38 mm and approximately 500 mm.
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE2000157734 DE10057734A1 (en) | 2000-11-22 | 2000-11-22 | Web curtain coating station, especially using a pigment suspension, has a guide in the free fall path of the coating to divide the path into two sections and reduce distorting effects on the laid coating at the moving substrate surface |
| DE10057732 | 2000-11-22 | ||
| DE10057734 | 2000-11-22 | ||
| DE2000157732 DE10057732A1 (en) | 2000-11-22 | 2000-11-22 | Web curtain coating station has a rotating roller in the curtain fall path, to divide the coating path into two sections to set the coating speed according to the substrate speed to prevent coating distortions |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1209274A2 true EP1209274A2 (en) | 2002-05-29 |
| EP1209274A3 EP1209274A3 (en) | 2003-06-11 |
| EP1209274B1 EP1209274B1 (en) | 2010-01-27 |
Family
ID=26007728
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP01127739A Expired - Lifetime EP1209274B1 (en) | 2000-11-22 | 2001-11-21 | Curtain coater |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1209274B1 (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE456695T1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE50115328D1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2003059528A1 (en) * | 2002-01-16 | 2003-07-24 | Metso Paper, Inc. | Method and apparatus for feeding a treating agent onto a moving surface |
| JP2006247611A (en) * | 2005-03-14 | 2006-09-21 | Voith Paper Patent Gmbh | Coating device |
| EP1767282A2 (en) * | 2005-09-22 | 2007-03-28 | Voith Patent GmbH | Coating device |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106563608A (en) * | 2016-11-04 | 2017-04-19 | 三峡大学 | Method and device for preparing anti-reflection self-cleaning film on glass |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0421466A2 (en) | 1989-10-06 | 1991-04-10 | Fuji Photo Film Co., Ltd. | Coating apparatus |
| US5277041A (en) | 1990-05-18 | 1994-01-11 | Eduard Kusters Maschinenfabrik Gmbh & Co. Kg | Drain board for a device for applying a liquid film to a web of textile material |
| JPH06262129A (en) | 1993-03-12 | 1994-09-20 | Sumitomo Metal Ind Ltd | Curtain flow coating method |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2809128A (en) * | 1953-07-14 | 1957-10-08 | Ransburg Electro Coating Corp | Electrostatic method and apparatus for atomizing and for coating |
| DE2438673A1 (en) * | 1974-08-12 | 1976-02-26 | Riggs & Lombard Inc | Fabric web scouring machine - pours liquid onto web carried on vibrated mesh suction conveyor |
| DE2631559A1 (en) * | 1976-07-14 | 1978-01-19 | Helvisol Ag | Adhesive distributor for travelling strip - has set of slope and height adjustable troughs between adhesive container and conveyor |
| DE3333592A1 (en) * | 1983-09-16 | 1985-04-18 | Brückner-Apparatebau GmbH, 6120 Erbach | Apparatus for the application of a liquid film to a length of material |
| JPH02277570A (en) * | 1989-04-19 | 1990-11-14 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | Applicator |
| DE3915844C1 (en) * | 1989-05-16 | 1990-12-06 | Eduard Kuesters Maschinenfabrik Gmbh & Co Kg, 4150 Krefeld, De | |
| JP2533812B2 (en) * | 1990-07-13 | 1996-09-11 | 富士写真フイルム株式会社 | Glass dry plate manufacturing method and apparatus |
| DE9012108U1 (en) * | 1990-08-23 | 1990-10-25 | Fa. Theodor Hymmen, 4800 Bielefeld | Pouring head of a pouring machine for pouring liquids |
| JPH1024260A (en) * | 1996-07-11 | 1998-01-27 | Nippon Steel Corp | Roller curtain coater |
| DE19903559B4 (en) * | 1998-01-30 | 2004-02-26 | Mitsubishi Paper Mills Limited | Process and apparatus for curtain coating |
-
2001
- 2001-11-21 DE DE50115328T patent/DE50115328D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-11-21 AT AT01127739T patent/ATE456695T1/en active
- 2001-11-21 EP EP01127739A patent/EP1209274B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0421466A2 (en) | 1989-10-06 | 1991-04-10 | Fuji Photo Film Co., Ltd. | Coating apparatus |
| US5277041A (en) | 1990-05-18 | 1994-01-11 | Eduard Kusters Maschinenfabrik Gmbh & Co. Kg | Drain board for a device for applying a liquid film to a web of textile material |
| JPH06262129A (en) | 1993-03-12 | 1994-09-20 | Sumitomo Metal Ind Ltd | Curtain flow coating method |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2003059528A1 (en) * | 2002-01-16 | 2003-07-24 | Metso Paper, Inc. | Method and apparatus for feeding a treating agent onto a moving surface |
| US7303634B2 (en) | 2002-01-16 | 2007-12-04 | Metso Paper, Inc. | Method and apparatus for feeding a treating agent onto a moving surface |
| JP2006247611A (en) * | 2005-03-14 | 2006-09-21 | Voith Paper Patent Gmbh | Coating device |
| EP1767282A2 (en) * | 2005-09-22 | 2007-03-28 | Voith Patent GmbH | Coating device |
| EP1767282A3 (en) * | 2005-09-22 | 2008-04-16 | Voith Patent GmbH | Coating device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1209274A3 (en) | 2003-06-11 |
| ATE456695T1 (en) | 2010-02-15 |
| DE50115328D1 (en) | 2010-03-18 |
| EP1209274B1 (en) | 2010-01-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1208917B1 (en) | Curtain coating device | |
| EP1367174B1 (en) | Application device | |
| EP0969147B1 (en) | Device and process for applying a fluid or pasty material onto a moving bed | |
| EP0930397B1 (en) | Apparatus and process for applying a liquid or pasty medium onto a moving web, in particular of paper or board | |
| DE3723149A1 (en) | DEVICE FOR APPLYING A LIQUID TO A CARRIER | |
| DE10012344A1 (en) | Continuous liquid curtain coating, for paper or card operates under specified conditions of temperature, pressure and viscosity, leaving thin wet film on surface | |
| DE10057734A1 (en) | Web curtain coating station, especially using a pigment suspension, has a guide in the free fall path of the coating to divide the path into two sections and reduce distorting effects on the laid coating at the moving substrate surface | |
| DE10232949A1 (en) | Web coating curtain applicator, for wide paper/cardboard webs moving at high speeds, has side guides with jet openings to stabilize the falling curtain coating to give a consistent edge coating application | |
| DE68919699T2 (en) | CURTAIN COATING, METHOD AND APPARATUS. | |
| EP1541765A1 (en) | Coater | |
| EP1209274B1 (en) | Curtain coater | |
| DE10012345A1 (en) | Web coating station, for paper or cardboard, comprises applicator with delivery jet, to form structured free-fall coating curtain to moving web surface, with adjustments to set relative alignments of applicator and web | |
| EP1198643B1 (en) | Application device | |
| EP1432525B1 (en) | Application device | |
| DE10057732A1 (en) | Web curtain coating station has a rotating roller in the curtain fall path, to divide the coating path into two sections to set the coating speed according to the substrate speed to prevent coating distortions | |
| DE10057731A1 (en) | Assembly discharges liquid coating to fast moving web paper descending over a roller at a defined angle | |
| EP1266093B2 (en) | Application device and process | |
| DE10358754B4 (en) | Rail conveyor | |
| DE4230276A1 (en) | Coating device for running webs, especially paper or cardboard | |
| WO2008015042A1 (en) | Application device | |
| DE102006019788A1 (en) | Curtain application unit for applying aqueous pigment suspension on moving paper-, cardboard- or fibrous material web comprises, delivery-slot nozzle, guidance element and impingement surface | |
| DE102006036448A1 (en) | applicator | |
| DE102005035317A1 (en) | Method for directly applying layers of a liquid-to-pasty medium to a paper, cardboard or other fibrous strip comprises releasing the media separately from one another from chambers and combining to form a curtain | |
| DE10125376A1 (en) | Paper or carton curtain-coating assembly has combined suction/blower unit disrupting air boundary layer over moving web | |
| DE102005036667A1 (en) | Application process |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20011121 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK RO SI |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20031222 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT DE FI SE |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: VOITH PATENT GMBH |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT DE FI SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 50115328 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20100318 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20101028 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20101112 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20101119 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Payment date: 20111114 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20111128 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 456695 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20121121 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20121121 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20121122 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20121121 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 50115328 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130601 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130601 |